
Want to create or adapt books like this? Learn more about how Pressbooks supports open publishing practices.
Part Three Editing / Grammar Skills

Unit 9 Verb Basics in Academic Writing
Learning Objectives
- To understand what a verb is and why it is important
- To differentiate between “Be” verbs and “Do” verbs, action verbs and non-action verbs, helping verbs and main verbs, with their various uses though multiple examples and exercises
- To be aware of the twelve verb tenses and five basic verb forms

The following ten sentences are about pets. Some verbs are bold-faced. Identify what type of verb each one is by selecting one of the two choices. After you finish one sentence, you will get instant feedback on your answer before the next sentence. If you make mistakes, you can retry all the questions or see all the answers at the end of the pre-test.
II. Definition of a Verb and Its Importance
Each sentence in English must have a verb. A verb expresses an action or shows a state of existence [1] .
Why are verbs important? There are two reasons:
- They appear in every sentence in English.
- Errors in verbs cause serious misunderstanding [2] .
In order to express ideas clearly and accurately, you need to make sure:
- You have a basic understanding of different types of verbs. This is the purpose of this unit.
- A subject and its verb must match each other. For detailed information and practice, please refer to Unit 10 Subject-Verb Agreement. ( Open Unit 10 here. )
- A verb tense and its verb form must match each other. There are detailed explanations and practice in verb tenses and forms from Unit 11 through Unit 14 in this book. (Open Unit 11 Present Tenses , Unit 12 Past Tenses , Unit 13 Future Tenses , Unit 14 Mixed Tenses here.)
For detailed explanations and practice in sentence structure and punctuation, open Unit 7 here.
Exercise 1. Highlight the verbs in the following short paragraph about pet dogs. (To highlight, you position your computer curser on the verbs and right click.)
III. “Be” Verbs and “Do” Verbs
“Be” verbs: They look different depending on the subjects and the verb tenses. The most common ones are “am, is, are, was, were”. A “Be” verb is often followed by a noun, a pronoun, an adjective, a prepositional phrase, or an expression of age.
- My neighbor’s pet is a rabbit. Her name is Bonny. (followed by nouns)
- Bonny is not mine. (a pronoun)
- Bonny’s tail is short and cute. (adjectives)
- Bonny is in a cage when my neighbor is at work. (prepositional phrases)
- Bonny was two months old when I first met her. (an age)
“Do” verbs: There are many “Do” verbs: study, get, sleep, wear, have, like, think…
Their forms also change based on the subjects and the verb tenses.
- Bonny stays indoors most days.
- My neighbor prepares special food for her.
- Sometimes I see Bonnie in my neighbor’s backyard.
- I played with her yesterday.
- I hope that I can play with her again soon.
- A “Be” verb is NEVER followed by the base form of a “Do” verb.
- Bonny is stay indoors most days. X
- Bonny stays indoors most days. √
- Most rabbits are stay in a cage. X
- Most rabbits stay in a cage. √
- I was meet my neighbor’s pet rabbit for the first time last week. X
- I met my neighbor’s pet rabbit for the first time last week. √
IV. Action and Non-Action Verbs
Action verbs: They show the action of the subject. All action verbs are “Do” verbs.
- In the U.S., many pet owners treat their pets as part of the family.
- Those pets get special food and even regular medical checkups.
- Some of them sleep in their owner’s bed.
- They receive toys and often wear festive [3] outfits [4] during holidays.
- Most pets enjoy their good lives.
Non-action verbs: They do not show actions; instead, they show emotional or mental states, five senses, possessions, and others. Non-action verbs are also called stative verbs or non-progressive verbs. “Be” verbs are non-action verbs in most cases.
- Pets love their owners.
- Pets understand how much they are loved.
- Some pets can weigh over fifty pounds.
- Most pets have animal doctors called vets.
- Pets are our good friends.
Sometimes, the same verb can be both an action verb and a non-action verb, with different meanings and grammatical structures. Discuss the difference between the underlined verbs below.
- What do you think of my kitten? It seems that she is always thinking about playing hide and seek with me. (non-action, action)
- Feel the fur of my kitten. It feels so soft. (action, non-action)
- My kitten measures twelve inches in length [5] . I measure her every month to see how much she has grown. (non-action, action)
- I see some red pots on the kitten’s skin. I am taking her to her vet. We are seeing the vet at 3 pm this afternoon. (non-action, action)
Non-action verbs can be used in different verb tenses except progressive tenses, but action verbs can be used in all tenses.
- The kitten has been napping for a long time. He looks ( is looking ) content [6] in his sleep.
- Samantha likes ( is liking ) kittens. She has ( is having ) two. Right now she is preparing their favorite snacks.
Exercise 2. The following sentences are about color-blindness [7] of dogs. Some verbs are bold-faced. Highlight if each bold-faced verb is an action verb or a non-action verb. The first one is an example. When you finish the exercise, you can retry or see all the answers. (To highlight, you position your computer curser on the verbs and right click.)

V. Helping Verbs and Main Verbs
Helping verbs: They are also called auxiliary verbs . These verbs “help” the main verbs to
- show verb tense
- make a negative sentence
- ask a question
- change the meaning or tone
- change the voice (from active to passive or passive to active, not addressed in this course)
Helping verbs must work with main verbs to form complete verbs. Common helping verbs include “do, does, did, have, had, had, will”.
helping verb + main verb = complete verb
- Mohamod has always wanted to get his driver’s license. (helping verb “has” + main verb “wanted”)
- He has prepared for this driver’s test for several months. (helping verb “has” + main verb “prepared”)
- He does not want to carpool with his friend every day. (helping verb “does” + main verb “want”)
- He hopes that he will pass the road test. (helping verb “will” + main verb “pass”)
- Should he celebrate if he passes? (helping verb “should” + main verb “celebrate”)

Modals: Modals are a special type of helping verbs. They mainly show ability, possibility, obligation, advice, and many others. They are followed by the base form of the main verb.
- Every driver in the U.S. must have a driver’s license. (modal/helping verb “must” + main verb “have”)
- Should he or she buy car insurance, too? (modal/helping verb “should” + main verb “buy”)
- Maintaining a car can be expensive. (modal/helping verb “can” + main verb “be”)
- Life could become difficult without a car. (modal/helping verb “could” + main verb “become”)
For detailed explanations and examples of modals, please refer to Unit 15 Modals. ( Open Unit 15 here. )
Exercise 3. The following is a brief account of Jose and his car. Type the helping verb in each sentence in the appropriate boxe. The first sentence is an example. When you finish the entire exercise, you can retry or see all the answers.
VI. Twelve Verb Tenses
While verbs show actions or states of being, verb tenses indicate the time of those actions or states of being:
- in the past, in the present, in the future, or from past to present
- happened just once, happened repeatedly, or is still happening.
There are twelve tenses in English:
In this course, you will be focusing on using eight of the above tenses in writing: simple present, present progressive, present perfect, present perfect progressive, simple past, past progressive, past perfect, and simple future tenses. You will learn the rest of the tenses in future courses.
VII. Five Basic Verb Forms
In the above chart, the verb “study” appears in different forms – study, studies, am studying, had been studying, will be studying, and some others. These are called verb forms. Verbs have five basic forms:
Always remember that a verb tense and its verb forms must match each other. There are detailed explanations and practice in verb tenses and forms from Unit 11 through Unit 14 in this book. (Open Unit 11 Present Tenses , Unit 12 Past Tenses , Unit 13 Future Tenses , Unit 14 Mixed Tenses here.)
VIII. Unit Review Practice
Exercise 4. The following paragraph about leashing the dog is from a previous unit. Highlight “Be” for “Be verbs” and “Do” for “Do verbs”. The first one is an example. When you finish the exercise, you can retry or see all the answers. (To highlight, you position your computer curser on the verbs and right click.)

Exercise 5. The following is a story about two puppies in love. Some verbs are bold-faced. Select what the type of verb each one is. You will get instant feedback after each sentence. If you make a mistake, you may also retry or see the answer.

Exercise 6. Take a paragraph you have written in this course. Exchange it with your partner’s.
In your partner’s paragraph,
- single underline all the “Be” verbs.
- double underline all the helping verbs.
- circle all the non-action verbs.
When you finish, return the paragraph to your partner. Discuss if you agree with each other on all the verbs.
NSNT Practice

Go to The NSNT Free Writing Approach and Additional Weekly Prompts for Writing in Appendix A. ( Open Appendix A here. ) Choose two topics to write a paragraph each. You may start with the NSNT approach and then rewrite it. Pay attention to the use of verbs. Be mindful of the verbs you are using: Are they main verbs or helping verbs? Action verbs or non-action verbs? “Be” verbs or “do” verbs? You are encouraged to share your writing with your partner and help each other improve.
Vocabulary Review

The words here have appeared in this unit. The best way to learn them is to guess the meaning of each word from the context. Then hover your computer mouse over the number beside each word to check its meaning and part of speech. These words are also listed in the footnote area at the end of each unit.
Here, you can use the flashcards below to review these words.
- A verb shows an action or a state of being and usually comes after the subject in a sentence.
- “Be” verbs include “am, is, are, was, were” and some others.
- There are many “Do” verbs such as “swim, study, eat, drive”.
- An action verb shows the action of the subject.
- A non-action verb shows the state, condition, or possession of the subject. A non-action verb cannot be used in a progressive verb tense.
- Some verbs can be both action and non-action verbs, with a different meaning.
- A helping verb must be accompanied by a main verb in a sentence.
- There are twelve verb tenses and five basic verb forms. Each verb tense has its own verb forms. Verb tenses and verb forms must match each other in sentences.
Media Attributions
- a cat and a dog © Photo by Anusha Barwa on Unsplash
- a black dog with a yellow tennis ball in mouth © Photo by Tadeusz Lakota on Unsplash
- two people in a car © Photo by Orkun Azap on Unsplash
- two dogs on leash © Photo by Bundo Kim on Unsplash
- a dog swimming © Photo by Marcia Soligo on Unsplash
- a pen writing in a notebook © Photo by Aaron Burden on Unsplash
- a page in a dictionary © Pixabay
- existence: noun, being there, being this way ↵
- misunderstanding: noun, understand something in the wrong way ↵
- festive: adjective, joyful, about holidays or festivals ↵
- outfit: noun, clothing ↵
- length: noun, the noun form of the adjective "long" ↵
- content: adjective, happy and satisfied ↵
- color-blindness: noun, not able to see the differences in colors ↵
Building Academic Writing Skills Copyright © 2022 by Cui, Lin is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial-ShareAlike 4.0 International License , except where otherwise noted.
- Daily Crossword
- Word Puzzle
- Word Finder
- Word of the Day
- Synonym of the Day
- Word of the Year
- Language stories
- All featured
- Gender and sexuality
- All pop culture
- Grammar Coach ™
- Writing hub
- Grammar essentials
- Commonly confused
- All writing tips
- Pop culture
- Writing tips
a short literary composition on a particular theme or subject, usually in prose and generally analytic, speculative, or interpretative.
anything resembling such a composition: a picture essay.
an effort to perform or accomplish something; attempt.
Philately . a design for a proposed stamp differing in any way from the design of the stamp as issued.
Obsolete . a tentative effort; trial; assay.
to try; attempt.
to put to the test; make trial of.
Origin of essay
Other words from essay.
- es·say·er, noun
- pre·es·say, verb (used without object)
- un·es·sayed, adjective
- well-es·sayed, adjective
Words that may be confused with essay
- assay , essay
Words Nearby essay
- essay question
Dictionary.com Unabridged Based on the Random House Unabridged Dictionary, © Random House, Inc. 2024
How to use essay in a sentence
As several of my colleagues commented, the result is good enough that it could pass for an essay written by a first-year undergraduate, and even get a pretty decent grade.
GPT-3 also raises concerns about the future of essay writing in the education system.
This little essay helps focus on self-knowledge in what you’re best at, and how you should prioritize your time.
As Steven Feldstein argues in the opening essay , technonationalism plays a part in the strengthening of other autocracies too.
He’s written a collection of essays on civil engineering life titled Bridginess, and to this day he and Lauren go on “bridge dates,” where they enjoy a meal and admire the view of a nearby span.
I think a certain kind of compelling essay has a piece of that.
The current attack on the Jews,” he wrote in a 1937 essay , “targets not just this people of 15 million but mankind as such.
The impulse to interpret seems to me what makes personal essay writing compelling.
To be honest, I think a lot of good essay writing comes out of that.
Someone recently sent me an old Joan Didion essay on self-respect that appeared in Vogue.
There is more of the uplifted forefinger and the reiterated point than I should have allowed myself in an essay .
Consequently he was able to turn in a clear essay upon the subject, which, upon examination, the king found to be free from error.
It is no part of the present essay to attempt to detail the particulars of a code of social legislation.
But angels and ministers of grace defend us from ministers of religion who essay art criticism!
It is fit that the imagination, which is free to go through all things, should essay such excursions.
British Dictionary definitions for essay
a short literary composition dealing with a subject analytically or speculatively
an attempt or endeavour; effort
a test or trial
to attempt or endeavour; try
to test or try out
Collins English Dictionary - Complete & Unabridged 2012 Digital Edition © William Collins Sons & Co. Ltd. 1979, 1986 © HarperCollins Publishers 1998, 2000, 2003, 2005, 2006, 2007, 2009, 2012
Cultural definitions for essay
A short piece of writing on one subject, usually presenting the author's own views. Michel de Montaigne , Francis Bacon (see also Bacon ), and Ralph Waldo Emerson are celebrated for their essays.
The New Dictionary of Cultural Literacy, Third Edition Copyright © 2005 by Houghton Mifflin Harcourt Publishing Company. Published by Houghton Mifflin Harcourt Publishing Company. All rights reserved.
- Cambridge Dictionary +Plus
Meaning of essay in English
Your browser doesn't support HTML5 audio
- I want to finish off this essay before I go to bed .
- His essay was full of spelling errors .
- Have you given that essay in yet ?
- Have you handed in your history essay yet ?
- I'd like to discuss the first point in your essay.
- boilerplate
- composition
- dissertation
- essay question
- peer review
- go after someone
- go all out idiom
- go down swinging/fighting idiom
- go for it idiom
- go for someone
- shoot the works idiom
- smarten (someone/something) up
- smarten up your act idiom
- square the circle idiom
- step on the gas idiom
essay | Intermediate English
Examples of essay, collocations with essay.
These are words often used in combination with essay .
Click on a collocation to see more examples of it.
Translations of essay
Get a quick, free translation!

Word of the Day
a bitter pill (to swallow)
something that is very unpleasant but must be accepted

Sitting on the fence (Newspaper idioms)

Learn more with +Plus
- Recent and Recommended {{#preferredDictionaries}} {{name}} {{/preferredDictionaries}}
- Definitions Clear explanations of natural written and spoken English English Learner’s Dictionary Essential British English Essential American English
- Grammar and thesaurus Usage explanations of natural written and spoken English Grammar Thesaurus
- Pronunciation British and American pronunciations with audio English Pronunciation
- English–Chinese (Simplified) Chinese (Simplified)–English
- English–Chinese (Traditional) Chinese (Traditional)–English
- English–Dutch Dutch–English
- English–French French–English
- English–German German–English
- English–Indonesian Indonesian–English
- English–Italian Italian–English
- English–Japanese Japanese–English
- English–Norwegian Norwegian–English
- English–Polish Polish–English
- English–Portuguese Portuguese–English
- English–Spanish Spanish–English
- English–Swedish Swedish–English
- Dictionary +Plus Word Lists
- English Noun Verb
- Intermediate Noun
- Collocations
- Translations
- All translations
Add essay to one of your lists below, or create a new one.
{{message}}
Something went wrong.
There was a problem sending your report.
- Dictionaries home
- American English
- Collocations
- German-English
- Grammar home
- Practical English Usage
- Learn & Practise Grammar (Beta)
- Word Lists home
- My Word Lists
- Recent additions
- Resources home
- Text Checker
Definition of verb noun from the Oxford Advanced Learner's Dictionary
- regular/irregular verbs
- transitive/intransitive verbs
- ‘Government’ can take a singular or plural verb.
- Add an ending to make the verb agree with the subject.
- Adverbs modify verbs.
- Do you know how to conjugate the verb ‘seek’?
- In this essay he has used the same verbs over and over again.
- The subject doesn't agree with the verb.
- Transitive verbs take a direct object.
- What's the main verb of the sentence?
- intransitive
- take something
- agree with something
Take your English to the next level
The Oxford Learner’s Thesaurus explains the difference between groups of similar words. Try it for free as part of the Oxford Advanced Learner’s Dictionary app

Verbs: Types of Verbs, Definition and Examples

Think of all the actions you can perform. You can walk , run , and dance . You can speak , read , and write .
All of these are verbs —words that tell us what the subject of a sentence is doing.
Verbs are one of the most important parts of speech. In fact, they’re the only word that every complete sentence needs to include.
You can build a grammatically complete sentence without any nouns or adjectives , but no matter what, you need a verb.
If you want your writing to be clear and effective, you need to understand the different types of verbs and how they work.
This article will give you a complete guide to verbs to help you improve your writing.
What Is a Verb: A Simple Explanation
A verb is a word that denotes action or a state of being.
As a part of speech in grammar, a verb is the action in the sentence. Along with a noun, the verb is a critical component of a complete sentence. Somebody (noun) does something (verb).

In grammar, the doer is the subject, and the action is the predicate (the part of the sentence containing the verb and describing the subject).
Those two elements form a complete sentence: “Jim grins .”
You may want more information in your sentence, like an object: “Jim grins at Sally .”
You may add subordinate clauses : “Jim grins at Sally when she fumbles the ball .”
However complex your sentence, the verb is the action. It tells you what the subject is doing, feeling, or being.
How to Use Verbs in Writing
You use verbs every day when you talk and write. Because verbs denote action, they move every story forward.
In writing, your verb choice delivers a punch to your prose.
Using the right verb also increases readability for your audience because you don’t need to lengthen the sentence by describing the action with extra modifiers. The verb does all the work.
Here are our three favorite tips for how to use verbs well in your writing.
Tip #1: Don’t Hide Your Verbs

Many writers unintentionally hide their verbs by turning them into nouns accompanied by a weak verb.
Take these two sentences:
- "We will decide tomorrow.”
- “We will make a decision tomorrow.”
The first sentence is shorter and more direct. In the second sentence, the strong verb decide is changed into the weaker make , which dilutes the meaning.
How can you spot hidden verbs? Look for words ending in -ment , -tion , -sion , and -ance .
Also, if you’ve used weak verbs like give , have , make , reach , and take , this could be a sign of a hidden verb.
Reading through your whole document to find weak verbs takes time. ProWritingAid automatically highlights your hidden verbs so you can change them with a single click.
Tip #2: Avoid Passive Verbs

You could say “The ball was thrown by me” or “I threw the ball,” and both sentences mean the same thing.
However, it’s normally better to convey action and grab your reader’s attention, rather than using passive verbs like is , has , and was .
Rewording your sentences to favor active verbs instead of passive verbs will strengthen your writing.
For example, you can use a verb instead of an adjective:
- Original Sentence: He is asleep under the tree.
- Improved Sentence: He sleeps under the tree.
The verb sleeps is more powerful than the passive version is asleep .
Similarly, you can use a verb instead of a noun:
- Original Sentence: She was a good writer .
- Improved Sentence: She wrote well.
Once again, the verb wrote is more powerful than the passive version was a writer , because it conveys movement and action.
Letting active verbs do the heavy lifting in your sentence will help you convey your point in a strong and concise way.
Tip #3: Choose Specific Verbs Instead of Modifying Weak Verbs

Some verbs in the English language are more descriptive and precise than others.
For example, the word whispered conveys more information than the word said , because it implies adverbs like quietly or furtively .
Similarly, the verb sprint conveys more information than move , because it tells the reader the specific type of movement being described.
There’s nothing wrong with using a generic verb like said , but if you want to provide more information, it’s almost always better to use a specific verb instead of modifying a weak verb.
Sometimes, this rule means replacing a generic verb and its adverb with a stronger, more specific verb. Consider the following example:
Original Sentence: She walked slowly up the stairs.
Improved Sentence: She trudged up the stairs.
Trudged is more concise and evocative than walked slowly .
Other times, this rule can also mean replacing a generic verb and a modifying phrase with a stronger verb.
- Original Sentence: He smiled in a mean way at the new kid in class.
- Improved Sentence: He sneered at the new kid in class.
Sneered is a more interesting way to say smiled in a mean way and will make your writing more powerful.
Keep in mind it's okay to use phrasal verbs, which are verbs that consist of multiple words, such as break down and let go .
There's a difference between using a phrasal verb and modifying a generic verb.
Choosing the right verb can help you say a lot more with fewer words.
A grammar guru, style editor, and writing mentor in one package.
Types of Verbs
There are three main types of verbs. Familiarity with verb types will help you understand when to use each type and when to avoid a verb type.
The three verb types are:
- Action verbs (which can be transitive or intransitive )
- Modal or helping verbs
- Linking verbs
Let’s take a closer look at each of these verb types and how they function in a sentence.
Action Verb: Definition & Examples
When a person or thing is doing something, that’s an action verb.
Action verbs are the best ones to use in your writing to move your story forward and create tension .
Action verbs can also clarify articles and papers by indicating direct action.
Action verbs are split into two categories: transitive verbs and intransitive verbs.
1) Transitive Verbs

A transitive verb is always followed by a noun that receives the action, called the direct object.
Consider the sentence “I patted my dog’s head.”
The transitive verb is “patted,” and the noun that’s receiving this action is “my dog’s head,” which is the direct object of the action verb.
Sometimes an object can be indirect, such as when you’re expressing to whom the action is being done.
Consider the sentence “Mary gave Angelina a kiss on the cheek.”
The verb is “gave,” and the direct object was “a kiss.” To whom it happened was Angelina, the indirect object of the sentence.
Transitive verbs act on direct and indirect objects. Something or someone always gets affected by this type of verb.
2) Intransitive Verbs
When an action verb has no direct object, it’s called an intransitive verb. An adverb or adverb phrase can follow intransitive verbs, but there will not be a direct object.
Consider the sentence “Matthew runs away quickly.”
The verb is runs , and the phrase “away quickly” tells us more about the verb, but there is no object in the sentence to receive the action. Therefore, runs is an intransitive verb.
An easy way to tell the difference between a transitive and an intransitive verb is to ask the question, “Who or what is receiving the action from this verb?”
- If you can name a noun that’s on the receiving end, it’s a transitive verb.
- If you can’t name a noun, whether a direct or indirect object, then the verb is intransitive.
Either way, transitive or intransitive, active verbs lend immediacy to your sentence, drawing in the reader.
Auxiliary Verb: Definition & Examples
An auxiliary verb, also called a helping verb, modifies the action in the main verb.
Auxiliary verbs help readers to understand the main verb. They typically change the mood or tense of the main verb.
Auxiliary verbs provide hints related to the possibility of something happening (can, should, would, etc.) or time (has, did, was, etc.).
When you add auxiliary verbs to your sentence, you create verb phrases.
Auxiliary verb examples:
- Laura is (helping verb) writing (main action verb) her life story.
- Her story might (helping verb) be (main verb) embarrassing for some of her friends.
The following verbs always function as auxiliary verbs or helping verbs:
In addition, you can have auxiliary verbs comprising the forms of to be , to do , and to have .
Keep in mind that the following words can also serve as linking verbs (which we’ll discuss next):
Examples of be, do, have helping verbs in sentences:
- Juliet is changing trains at the station.
- Daniel had eaten everything on his plate.
- Every cyclist does dismount at the crossing.
Linking Verb: Definition & Examples

A linking verb connects the subject of your sentence to a noun or adjective that describes your subject. The noun or adjective is called the “subject complement.”
Here are some examples:
- My daughter is a marketing major.
- We are your new neighbors.
The most common linking verb can be found in the various forms of to be ( am , are , is , was , were , etc.). These are also called stative verbs, because they describe a state of being.
To become and to seem are always linking verbs. The following verbs, however, can sometimes be linking verbs and other times be action verbs:
- To continue
Here is an example of the difference between a linking verb and an action verb.
Linking: The seafood smelled off. (The linking verb smelled links seafood to off )
Action: I smelled the seafood before eating. (The action verb refers to the action of smelling)

Why Are Verbs Important?
Verbs are action words that engage your reader and help them picture what's happening in your writing.
Choosing the right verb can elicit an emotional response, whether you're writing academic essays or narrative fiction .
Verbs in Academic Writing
Academic writing tends to stick to more formal writing styles than fiction writing, but you still want to keep your reader’s interest and communicate your points clearly.
Whether you’re a student writing essays for class, or a professional researcher trying to publish a paper, using strong action verbs will improve your academic writing.
Look for weak verbs in your writing and try to replace them with precise and dynamic verbs.
Consider the following examples of verb choices in academic writing.
- Original Sentence: “A recent psychological study makes it clear that children are more likely to respond to positive reinforcement than negative reinforcement.”
Improved Sentence: “A recent psychological study demonstrates that children are more likely to respond to positive reinforcement than negative reinforcement.”
Original Sentence: “This result is an example of how a single night of sleep loss can have long-term impacts on the brain.”
Improved Sentence: “This result illustrates how a single night of sleep loss can have long-term impacts on the brain.”
Original Sentence: “Her findings are in agreement with the conclusions I’ve presented in this paper.”
- Improved Sentence: “Her findings support the conclusions I’ve presented in this paper.”
If you are new to thinking about verb use, here’s a list of 100 strong English verbs you can use to improve your essays, papers, and articles:
- Contemplate
- Corroborate
- Demonstrate
- Hypothesize
- Misconstrue
- Substantiate
Verbs in Fiction Writing
Fiction writers use verbs with exactitude to prompt reader engagement, thereby sparking emotions and a desire to keep reading.
Dull verbs make for lackluster reading. Finding the right verb for your character’s action brings your story to life.
You might have heard the classic writing advice “Show, don’t tell.” Using strong verbs is a great way to show the reader what’s happening clearly and concisely.
Consider the following examples of verb choice in fiction writing.
- Original Sentence: “Her long skirt was blown outward as she fell through the air.”
- Improved Sentence: “Her long skirt ballooned outward as she fell through the air.”
- Original Sentence: “The sound of his father’s last words was still running through his mind.”
- Improved Sentence: “The sound of his father’s last words reverberated through his mind.”
- Original Sentence: “The man in the black hat walked into the room.”
- Improved Sentence: “The man in the black hat charged into the room.”
If you want a good starting point for stronger verbs to use, here’s a list of 100 strong verbs in English that you can use for fiction writing:
- Reverberate
Using ProWritingAid to Strengthen Your Verbs
It’s easy to skip over weak verbs in your writing when you’re self-editing.
But, taking time to focus directly on your verbs helps ensure you’re always using the best word for your sentence.
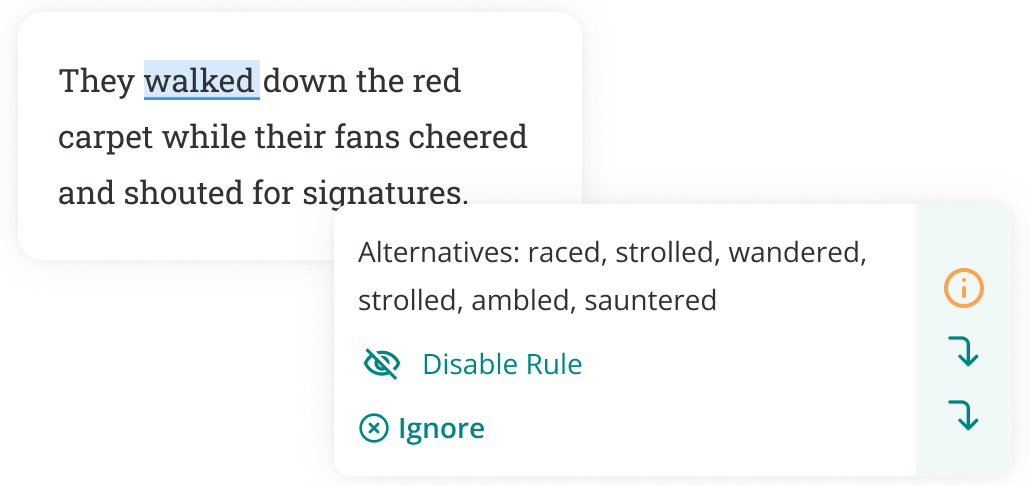
ProWritingAid’s Thesaurus Report highlights all the verbs in your writing so you can get an overview of the strength and specificity of your word choices throughout your document.
Hover over a verb to see synonyms and click to replace weak verbs in your text with more powerful alternatives.
Conclusion on Verbs
There you have it: our complete guide to verbs.
Here’s a quick recap of everything we’ve discussed.
Increase the power of your writing by following these three tips:
- Don’t hide your verbs
- Avoid passive verbs
- Choose specific verbs instead of modifying weak verbs
Action verbs (such as run, jump, and dance)
Modal or helping verbs (such as can, was, and has)
Linking verbs (such as to look, to feel, and to taste)
Whether you’re writing fiction or non-fiction, specific verbs spark emotions in your readers and keep them engrossed in your writing.
We hope this article helps you choose strong verbs to create powerful, professional prose.
Take your writing to the next level:

20 Editing Tips From Professional Writers
Whether you are writing a novel, essay, article, or email, good writing is an essential part of communicating your ideas., this guide contains the 20 most important writing tips and techniques from a wide range of professional writers., common questions about verbs: types of verbs, definition and examples, can i use a gerund after "allows", which version of the verb should be used with "every", what verb form should you use after "consider" and "imagine" infinitive or gerund, do you need to include "started to" in a sentence, should you use "going to" or "will", why should you not overuse words like "believe" and "think", why is "do + verb" not a great construct, what is a split infinitive and when should you avoid using one, why should you not overuse "knew", why should you not overuse "feel", why should you not overuse "could", why shouldn't i write "start to" or "begin to", what are modal verbs how do you use them, why should i use "went" instead of "decided to go", when can you omit "in order" in a sentence, what is correct subject–verb agreement, do we need "manage to" in a sentence, "was/were able to" vs "could", "(am/are/is/was/were) not going to" vs "will not", "indicate" vs "show", what form of verb should be used after "been" or "was", should i use "conduct an interrogation of" or "interrogate" in my work, "participate" vs "take part", when should you use "choose/decide" before an infinitive, should i use "demonstrate" or "show" in my work, subject–verb agreement, what form of verb should you use after modal verbs, what forms should you use after "have", incorrect verb form, watch out for hidden verbs in your writing—set them free (video available), obtain vs get, learn more about grammar:, your personal writing coach.
Drop us a line or let's stay in touch via :

Definition of 'essay'

Video: pronunciation of essay

essay in British English
Essay in american english, examples of 'essay' in a sentence essay, cobuild collocations essay, trends of essay.
View usage for: All Years Last 10 years Last 50 years Last 100 years Last 300 years
Browse alphabetically essay
- essay competition
- essay contest
- essay discusses
- All ENGLISH words that begin with 'E'
Related terms of essay
- essay topic
- photo essay
- short essay
- View more related words
Quick word challenge
Quiz Review
Score: 0 / 5

Wordle Helper

Scrabble Tools

- More from M-W
- To save this word, you'll need to log in. Log In
Definition of verb
(Entry 1 of 2)
Definition of verb (Entry 2 of 2)
transitive verb
Did you know?
What is a verb ?
Verbs are words that show an action ( sing ), occurrence ( develop ), or state of being ( exist ). Almost every sentence requires a verb. The basic form of a verb is known as its infinitive . The forms call , love , break , and go are all infinitives.
Almost all verbs have two other important forms called participles . Participles are forms that are used to create several verb tenses (forms that are used to show when an action happened); they can also be used as adjectives . The present participle always ends in -ing : calling , loving , breaking , going . (There is also a kind of noun, called a gerund , that is identical in form to the present participle form of a verb.) The past participle usually ends in -ed , but many past participles have irregular endings: called , loved , broken , gone .
The verb's past tense usually has the same -ed form as the past participle. For many verbs, however, the past tense is irregular. An irregular past tense is not always identical to an irregular past participle: called , loved , broke , went .
The two main kinds of verbs, transitive verbs and intransitive verbs , are discussed at the entries for transitive and intransitive .
Examples of verb in a Sentence
These examples are programmatically compiled from various online sources to illustrate current usage of the word 'verb.' Any opinions expressed in the examples do not represent those of Merriam-Webster or its editors. Send us feedback about these examples.
Word History
Middle English verbe , borrowed from Anglo-French, borrowed from Latin verbum "word, verb" — more at word entry 1
14th century, in the meaning defined above
1928, in the meaning defined above
Phrases Containing verb
- action verb
- helping verb
- modal auxiliary verb
- phrasal verb
- linking verb
- auxiliary verb
Articles Related to verb

Words Added to the Scrabble Dictionary
More words for Scrabble

What is a Verb?

8 Grammar Terms You Used to Know, But...
8 Grammar Terms You Used to Know, But Forgot
Plus yodeling

When Body Parts Are Also Verbs
Head, shoulders, metaphors, and toes
Dictionary Entries Near verb
veratrylidene
Cite this Entry
“Verb.” Merriam-Webster.com Dictionary , Merriam-Webster, https://www.merriam-webster.com/dictionary/verb. Accessed 31 Mar. 2024.
Kids Definition
Kids definition of verb, more from merriam-webster on verb.
Nglish: Translation of verb for Spanish Speakers
Britannica English: Translation of verb for Arabic Speakers
Britannica.com: Encyclopedia article about verb
Subscribe to America's largest dictionary and get thousands more definitions and advanced search—ad free!

Can you solve 4 words at once?
Word of the day.
See Definitions and Examples »
Get Word of the Day daily email!
Popular in Grammar & Usage
The tangled history of 'it's' and 'its', more commonly misspelled words, commonly misspelled words, how to use em dashes (—), en dashes (–) , and hyphens (-), absent letters that are heard anyway, popular in wordplay, the words of the week - mar. 29, 9 superb owl words, 'gaslighting,' 'woke,' 'democracy,' and other top lookups, 10 words for lesser-known games and sports, your favorite band is in the dictionary, games & quizzes.

- Share full article
Advertisement
Supported by
Word of the day
Word of the Day: jeer
This word has appeared in five articles on NYTimes.com in the past year. Can you use it in a sentence?

By The Learning Network
jeer \ dʒɪər \ verb and noun
verb: laugh at with contempt and derision noun: the act of scoffing, taunting, or mocking
Listen to the pronunciation.
The word jeer has appeared in five articles on NYTimes.com in the past year, including on Sept. 5 in The New York Times Magazine Letter of Recommendation “ Why I Love Doing Homework (Even If My Kids Hate It) ” by Saul Austerlitz:
My kids call me the homework villain. Every school-day afternoon, my two sons — the older is entering sixth grade, the younger second grade — return home and gather snacks before beginning the day’s homework tussle. They are tired and ready to play video games or to watch incomprehensible YouTube videos about video games. I ignore all complaints, offer up my trademark cackle and direct them to the index cards on our fridge listing the day’s homework: reading, math, writing and even — when I am feeling particularly villainous — Hebrew reading. … I don’t love being the bad guy my kids jeer when I remind them that it is homework time once again. But I am thankful to be granted the opportunity to walk alongside them as they commit to the work of learning. I enjoy seeing them overcome the initial impulse that if something doesn’t come easily, it isn’t worth doing …
Daily Word Challenge
Can you correctly use the word jeer in a sentence?
Based on the definition and example provided, write a sentence using today’s Word of the Day and share it as a comment on this article. It is most important that your sentence makes sense and demonstrates that you understand the word’s definition, but we also encourage you to be creative and have fun.
If you want a better idea of how jeer can be used in a sentence, read these usage examples on Vocabulary.com . You can also visit this guide to learn how to use IPA symbols to show how different words are pronounced.
If you enjoy this daily challenge, try our vocabulary quizzes .
Students ages 13 and older in the United States and the United Kingdom, and 16 and older elsewhere, can comment. All comments are moderated by the Learning Network staff.
The Word of the Day is provided by Vocabulary.com . Learn more and see usage examples across a range of subjects in the Vocabulary.com Dictionary . See every Word of the Day in this column .

IMAGES
VIDEO
COMMENTS
The meaning of ESSAY is an analytic or interpretative literary composition usually dealing with its subject from a limited or personal point of view. How to use essay in a sentence. Synonym Discussion of Essay.
Verbs can indicate (physical or mental) actions, occurrences, and states of being. Examples: Verbs in a sentence. Jeffrey builds a house. Anita is thinking about horses. True love exists. Every sentence must have at least one verb. At the most basic level, a sentence can consist solely of a single verb in the imperative form (e.g., "Run.").
essay something to try to do something Word Origin late 15th cent. (as a verb in the sense 'test the quality of'): alteration of assay , by association with Old French essayer , based on late Latin exagium 'weighing', from the base of exigere 'ascertain, weigh'; the noun (late 16th cent.) is from Old French essai 'trial'.
Exercise 1. Highlight the verbs in the following short paragraph about pet dogs. (To highlight, you position your computer curser on the verbs and right click.) III. "Be" Verbs and "Do" Verbs. "Be" verbs: They look different depending on the subjects and the verb tenses. The most common ones are "am, is, are, was, were".
Action Verbs - These verbs express actions (walk, eat, give), or possession (own, have, etc.). Action verbs are of two types: . Transitive Verbs - These always use direct objects, meaning the noun receives the action of a verb.; Intransitive Verbs - These never use direct or indirect objects.; Linking Verbs - These verbs do not show action. Rather, they link a subject to a noun or an ...
Examples of Power Verbs. The following are examples of power verbs that are useful in academic writing, both for supporting an argument and for allowing you to vary the language you use. Power Verbs for Analysis: appraise, define, diagnose, examine, explore, identify, interpret, investigate, observe.
Essay definition: . See examples of ESSAY used in a sentence.
ESSAY definition: 1. a short piece of writing on a particular subject, especially one done by students as part of the…. Learn more.
ESSAY meaning: 1. a short piece of writing on a particular subject, especially one done by students as part of the…. Learn more.
A verb is a word that indicates a physical action (e.g., 'drive'), a mental action (e.g., 'think') or a state of being (e.g., 'exist'). Every sentence contains a verb. Verbs are almost always used along with a noun or pronoun to describe what the noun or pronoun is doing.
A verb is a word that indicates a physical action (e.g., "drive"), a mental action (e.g., "think"), or a state of being (e.g., "exist"). Every sentence contains a verb. Verbs are almost always used along with a noun or pronoun to describe what the noun or pronoun is doing.
Definition of verb noun in Oxford Advanced Learner's Dictionary. Meaning, pronunciation, picture, example sentences, grammar, usage notes, synonyms and more. ... In this essay he has used the same verbs over and over again. The subject doesn't agree with the verb. Transitive verbs take a direct object.
Linking Verb: Definition & Examples. A linking verb connects the subject of your sentence to a noun or adjective that describes your subject. The noun or adjective is called the "subject complement." ... Choosing the right verb can elicit an emotional response, whether you're writing academic essays or narrative fiction. Verbs in Academic ...
noun (ˈɛseɪ , for senses 2, 3 also ɛˈseɪ ) 1. a short literary composition dealing with a subject analytically or speculatively. 2. an attempt or endeavour; effort. 3. a test or trial. verb (ɛˈseɪ ) (transitive) 4.
Definition of essay in English: cite. essay noun . Pronunciation: /ˈɛseɪ/ 1 a short piece of writing on a particular subject. Example sentences ... late 15th century (as a verb in the sense 'test the quality of'): alteration of assay, by association with Old French ...
Britannica Dictionary definition of ESSAY. [+ object] formal. : to try to do, perform, or deal with (something) He at first essayed [= tried, attempted] a career as a writer. There is no hint as to which of the approaches essayed in this book will prove most useful. — sometimes followed by to + verb. He essayed [= tried, attempted] to restore ...
Active Verbs Note of Caution: Only use the verbs you're familiar with unless you take the time to examine the definition in the dictionary. This is NOT a list of synonyms. Each word has specific usage patterns that are unique to its meaning. Literary Essay Report or Persuasive Essay that refers to an expert's opinion or research studies
A composition that is usually short and has a literary theme is called an essay. You should probably start writing your essay on "To Kill a Mockingbird" sometime before the bus ride to school the day it is due. ... As a verb, to essay is to make an attempt. If you essay to run for student council, you might lose to the girl who promises more ...
You might also know that essay can be a verb, with its most common meaning being "to try, attempt, or undertake":. A very close approach to the evil of Idi Amin is essayed in Giles Foden's 1998 novel The Last King of Scotland, whose narrator is the Scottish personal physician to the dictator. — Norman Rush, The New York Review of Books, 7 Oct. 2004 The principal accidents she remembers ...
verb: [noun] a word that characteristically is the grammatical center of a predicate and expresses an act, occurrence, or mode of being, that in various languages is inflected for agreement with the subject, for tense, for voice, for mood, or for aspect, and that typically has rather full descriptive meaning and characterizing quality but is ...
Active Verbs Note of Caution: Only use the verbs you're familiar with unless you take the time to examine the definition in the dictionary. This is NOT a list of synonyms. Each word has specific usage patterns that are unique to its meaning. Literary Essay Report or Persuasive Essay that refers to an expert's opinion or research studies
Differentiates. Definition: to show or find the difference between things that are compared. Example: Smith differentiates between the two theories in paragraph 4 of the second part of the study. Diminishes. Definition: to reduce or be reduced in s i ze or importance. Example: The new findings do not diminish the findings of previous research; rather, it builds on it to present a more ...
The term "artificial general intelligence" (AGI) has become ubiquitous in current discourse around AI. OpenAI states that its mission is "to ensure that artificial general intelligence benefits all of humanity." DeepMind's company vision statement notes that "artificial general intelligence…has the potential to drive one of the greatest transformations in history."
jeer \ dʒɪər \ verb and noun. verb: laugh at with contempt and derision noun: the act of scoffing, taunting, or mocking