Marketing Mix paper Essay
Introduction, coca cola company, promotion strategies, pricing methods.
Over the recent past, marketing has grown to become one of the key functional areas of business organizations. This growth has come in the wake of the realization that the traditional business practice methods are no longer relevant in the modern day business environment (Michael & Saren, 2010).
For a long time, business managers ignored the aspect of marketing and paid much emphasis on the production of goods and services. However, in the current day business world where competition is a major determinant of the adoptability of a product by the consumers, marketing has become an inevitable functional area of most organizations.
The importance of marketing comes in that the various products; both goods and services offered by an organization ought to be presented to the target consumers. More so, due to the availability of competitor products and supplementary products, marketing is necessary so as to help push the products to the consumers (Richard, 2009). Marketing therefore takes different forms and the final aim of any marketing activity is to enable the product being marketed to get adopted by the target consumers.
The success of a marketing strategy and subsequent marketing activities is judged by the increase in the amount of sales generated from the marketing activity (Marian, 2010). This essay presents and explains the four elements of marketing mix; Product, Pricing, Promotion and Place. The Coca cola Company will be analyzed in this essay.
Coca Cola Company is the world’s number one manufacturer, marketer and distributor of non-alcoholic drinks. It is a multinational giant that has headquarters in the United States of America. The company has managed to produce top brands in the beverage industry such as Fanta, Coke, and Sprite and so on. Its main objective is to maintain its global leadership in the production and distribution of the soft drinks.
This objective has largely been achieved because most of the coca cola company products are house hold brands and continue to be used by many. The challenge is however maintaining this status and in order to achieve this, the company has come up with ways in which it can effectively use the 4 Ps of marketing to ensure that its brand remains visible all over the world. The following text discusses how the different P’s of marketing have affected the Coca-cola company marketing strategy.
Product is one of the four main elements of marketing mix that concerns with the product itself. A company’s product is the sole reason for the existence of the company. This is because it is what meets the customers’ needs (Michael & Saren, 2010). There are various attributes of a product that help in marketing. These include the product lifecycle, product line and the product mix. A marketer should be able to manage the product in such a manner that its relevant to the consumers’ needs remain unaffected (Richard, 2009).
Coca-cola Company has managed to incorporate this marketing element to be able to achieve some marketing objective. One way of dealing with the product is through having a continual reinvention of the product that makes sure that the consumers continue to enjoy and derive benefits from that particular product.
The other way is by extending the product life cycle. The company has managed to continually re-invent its products over the years and this has offered a great deal of help in retaining the brand visibility among majority of consumers in the world.
The various Coca-cola Company products such as the Coke, Fanta, and Sprite have maintained their visibility among the consumers over the years. These products have been regularly associated with the young people and as such, the marketing strategy for these products revolves round the young people. This has been a successful strategy since the products have remained house hold brands among many individuals.
Promotion is the other marketing mix element that deals with a company’s act of driving the products to the consumers. This is achieved through employing marketing activities that convince the consumers to purchase the particular product (Christ, 2011). There are various available promotional strategies. The most common ones are the push-pull strategy and the message & media strategy.
The push-pull strategy deals with the manufacturer promoting the product to the retailers directly so as to ensure that they keep the goods in their stock. The message & media strategy deals with the manufacturer performing the promotional activities independent of the retailer and this is aimed at creating a demand for the product among the consumers such that the retailers will act on the demand and therefore stock the product (Richard, 2009).
Coca-cola Company has majorly employed the message & media strategy. Their products are marketed via the different media such as the televisions, bill-boards, Social media, and so on. This element of promotion has affected the company’s marketing strategy since the company majorly employs promotion as the key marketing activity for its products.
The company gains a lot from this strategy since the consumers who regularly see these promotional messages in the mass media become accustomed to the products and as such, develop loyalty on the products. The brands that have managed to achieve success through this method are Coke and Fanta.
Pricing is another element of marketing mix that deals with the setting of the product price. Price is usually the factor that determines the consumers’ willingness and ability to pay for the particular product (Christ, 2011). This is because of the fact that money is usually a scarce resource and as such, the available limited disposable income is allocated to the unlimited competing needs. Companies therefore ought to have a pricing strategy that does not exploit the consumers hence scaring them from purchasing the products.
The Coca-Cola Company effectively employs the pricing strategy and as such, it is able to gain a competitive advantage over other competitors’ such as Pepsi. The Coca-cola products are sold at relative lower prices comparing to the competitors. this has been achieved through the ability to gain on the economies of scale therefore having low products cost per unit.
The strategy that the company has used in this area is through having a suggested retail price. This prevents that consumers from being exploited by the retailers and also helps maintain the confidence the consumers have on the brand.
This marketing element has to deal with the businesses’ act of ensuring that the products are presented at a convenient location to the consumers. Place also forms a type of utility where the consumer needs the product being offered by the business to be in an accessible location or a convenient one (Marian, 2010).
This is done either through transporting the products to the areas near the consumer or carrying out production near the consumers. The boon in this is that the consumer is allowed is able to purchase the product without major logistical issues.
Coca-cola Company has been able to put this element into consideration when coming up with marketing strategy. The company has expanded its tentacles to almost all the countries of the world and as such, it is able to carry out production and subsequent distribution to the consumers at their convenience.
Companies that have moved their products closer to the consumers not only enjoy brand visibility and recognition among the consumers but they also incur fewer expenses during production. The advantage of this is that the company is able to sell at lower prices and thus attract more customers who result in growth in the revenues.
Coca-cola Company has set numerous bottling plants in many countries and this has greatly helped in achieving low production costs. This has also ensured that the consumers purchase these goods at their own convenience. The strategy involved by Coca-Cola Company in this case is referred to as exclusive distribution.
This is where the company opts to solely and exclusively carry out its own distribution process without engaging other third parties. This helps in the consumers’ appreciation of the products and also increased the brand value of the company among the various consumers.
The importance of incorporating the 4Ps of marketing in crafting the marketing strategy cannot be overemphasized. Once a company has fully articulated the requirements of the 4ps of marketing, the marketers need to incorporate the customer focus marketing approach that leads to the 4Cs of marketing mix. These are the Commodity, cost, channel, and Communication. Once all these factors are put in place, the marketing strategy can be said to be complete and as such positive results can be expected from such an approach.
Christ, P. (2011). Principles of Marketing. New York: Butterworth- Heinemann.
Marian, B. W. (2010). Essential Guide to Marketing Planning. New York: Pearson Publishers.
Michael, J. B., & Saren, M. (2010). marketing Theory. London: Sage Publishers.
Richard, H. (2009). Brilliant Marketing: What the Best Marketers Know, Do and Say (3rd Edition ed.). New York: Pearson.
- Chicago (A-D)
- Chicago (N-B)
IvyPanda. (2020, January 11). Marketing Mix paper. https://ivypanda.com/essays/marketing-mix-paper/
"Marketing Mix paper." IvyPanda , 11 Jan. 2020, ivypanda.com/essays/marketing-mix-paper/.
IvyPanda . (2020) 'Marketing Mix paper'. 11 January.
IvyPanda . 2020. "Marketing Mix paper." January 11, 2020. https://ivypanda.com/essays/marketing-mix-paper/.
1. IvyPanda . "Marketing Mix paper." January 11, 2020. https://ivypanda.com/essays/marketing-mix-paper/.
Bibliography
IvyPanda . "Marketing Mix paper." January 11, 2020. https://ivypanda.com/essays/marketing-mix-paper/.
- Guinness' and Fanta's Advertising Campaigns
- Positioning Mapping and Situation Analysis
- Coca-Cola's Strategic Partnership With Dr. Pepper Snapple Group
- The Coca-Cola Company Analysis
- Pepsi and Coke Competition
- The ‘Share a Coke’ Marketing Communications Plan
- Africa: Coke's Last Frontier
- Brand Overview: Diet Coke
- Cola Wars Continue: Coke and Pepsi in 2010
- The Website Visibility of Apparel Brands
- Palisades Promotional Assessment
- Australian Beauty Industry
- Ford Mustang Market Environment Research
- Marketing Research on Biotech Industry
- Marketing Strategy: Product Perceptual Map
- Undergraduate
- High School
- Architecture
- American History
- Asian History
- Antique Literature
- American Literature
- Asian Literature
- Classic English Literature
- World Literature
- Creative Writing
- Linguistics
- Criminal Justice
- Legal Issues
- Anthropology
- Archaeology
- Political Science
- World Affairs
- African-American Studies
- East European Studies
- Latin-American Studies
- Native-American Studies
- West European Studies
- Family and Consumer Science
- Social Issues
- Women and Gender Studies
- Social Work
- Natural Sciences
- Pharmacology
- Earth science
- Agriculture
- Agricultural Studies
- Computer Science
- IT Management
- Mathematics
- Investments
- Engineering and Technology
- Engineering
- Aeronautics
- Medicine and Health
- Alternative Medicine
- Communications and Media
- Advertising
- Communication Strategies
- Public Relations
- Educational Theories
- Teacher's Career
- Chicago/Turabian
- Company Analysis
- Education Theories
- Shakespeare
- Canadian Studies
- Food Safety
- Relation of Global Warming and Extreme Weather Condition
- Movie Review
- Admission Essay
- Annotated Bibliography
- Application Essay
- Article Critique
- Article Review
- Article Writing
- Book Review
- Business Plan
- Business Proposal
- Capstone Project
- Cover Letter
- Creative Essay
- Dissertation
- Dissertation - Abstract
- Dissertation - Conclusion
- Dissertation - Discussion
- Dissertation - Hypothesis
- Dissertation - Introduction
- Dissertation - Literature
- Dissertation - Methodology
- Dissertation - Results
- GCSE Coursework
- Grant Proposal
- Marketing Plan
- Multiple Choice Quiz
- Personal Statement
- Power Point Presentation
- Power Point Presentation With Speaker Notes
- Questionnaire
- Reaction Paper
Research Paper
- Research Proposal
- SWOT analysis
- Thesis Paper
- Online Quiz
- Literature Review
- Movie Analysis
- Statistics problem
- Math Problem
- All papers examples
- How It Works
- Money Back Policy
- Terms of Use
- Privacy Policy
- We Are Hiring

Marketing Mix, Essay Example
Pages: 4
Words: 1167
Hire a Writer for Custom Essay
Use 10% Off Discount: "custom10" in 1 Click 👇
You are free to use it as an inspiration or a source for your own work.
Marketing decisions made by a company when shaping a suitable proposition for the potential customer can be organized into four major groups. These are Product, Price, Place and Promotion. The actual meaning of those four is creating the right product, selling it at the right price and in the right place, with the use of the most effective promotion possible. When being in the process of bringing some particular product to the market, the organization is supposed to make choices concerning the product that will eventually influence the effectiveness of a chosen strategy. The four P’s are a sort of parameters that are under marketer’s control. “The goal is to make decisions that center the four P’s on the customers in the target market in order to create perceived value and generate a positive response” (Net MBA Business Knowledge Center).
The term ‘Product’ refers to both tangible physical goods and services. The choices that are made concerning the product can be: brand name, design, functionality, protection, maintenance, packaging, guarantee, accessories and services. To define what the product is supposed to represent questions may be asked like: What does the consumer want from the product/service? What requirements does it satisfy? What characteristics is it supposed to have to meet customers’ requirements? How and where will the customer exercise it? What does it look like? How is it different from the one product of your competitors?
The term ‘Price’ refers to the choice of appropriate approaches to forming the actual price of the product. It is no secret that each person pays a lot of attention to the price of the product being bought. Each customer weights benefit the product is to bring versus its cost in order to make a wise decision. It is also important to mention that while all the other three aspects of marketing mix are costs, price is the only one which creates sales revenue. Investigating consumers’ attitude toward pricing is significant since it specifies how they value what they are looking for, as well as what they would like to pay for it. Naturally, company’s pricing policy depends a lot on the circumstances in which the organization is operating. The possible decisions marketer is making concerning the price are: pricing strategy (demand-, cost-, profit- or competition- based methods), suggested retail price, volume discounts and wholesale pricing, seasonal pricing, bundling, price flexibility and discrimination, etc. The questions that can be asked in order to understand the pricing element better are: What is the value of the product or service to the purchaser? Is the client price sensitive? What discounts should be proposed to customers, or to other particular segments of your market? How will your price contrast with that of your competitors?
‘Place’ element of the marketing mix is the one being concerned with a range of methods of transferring and storing goods, and then making them accessible to the consumers. Significantly, approximately a fifth of the product’s cost goes on its distribution. What value do product’s exceptional features have if it is stored badly, or if the potential customers have no way to get it? Delivering the right product to the proper place at the right time requires creation of a distribution system. Once again, the choice of convenient distribution methods depends greatly on present circumstances. When referring to ‘place’ marketer has to make decision on distribution channels and centers, transportation, warehousing, order processing, etc. Understanding of this particular element of the marketing mix can be obtained if giving answers to such questions as: Where do buyers search for your product or service? In what kind of stored do they look for the product? How can you contact the appropriate distribution channels? What do you competitors do, and how can you benefit from that?
‘Promotion’ refers to the actual process of communicating with consumers. It is concerned with presenting customers with information needed to make a decision. The fact is that, even though being sometimes extremely costly, promotion can increase the sales significantly, so that advertising and other costs are spread over a larger output. If being properly organized and successfully implemented, promotion can be extremely cost-effective. Promotion is aimed at generating the positive customers’ response and deals with decisions on promotional strategy, advertising, public relations and publicity, sales promotions, marketing communication budgeting, etc. These are the questions that can be helpful when defining this particular element of marketing mix: Where and when can one get across your marketing messages to the target market? How will you reach your audience in the most effective way possible? When is the best time to promote? Is there seasonality in the market? How do your competitors promote their product and how can it influence your promotional strategies?
Such a great profit-oriented company as Nike, which is the global sports shoe company and is the largest seller of athletic footwear in the world, does surely pay a lot of attention to the development of its marketing mix. If referring to the ‘product’ element of Nike’s company, we can talk about how Nike proposes broad choice of shoe, apparel and equipment products. The company also market head gear under the brand name Sports Specialties. Nike’s pricing is considered to be competitive to the other sport shoe sellers. The pricing is established on the basis of premium segment as target customers. Nike shoes are available all over the world in the multi-brand and the exclusive Nike stores. “Nike sells its product to about 20,000 retail accounts in the U.S. and in almost 200 countries around the world. In the international markets, Nike sells its products through independent distributors, licensees and subsidiaries” (Cuizon, 2009). Nike’s promotion is greatly concerned with finding reachable store locations. It also involves targeted advertising in the newspaper and generating strategic associations. For example, Nike cooperates with a number of famous athletes that serve as brand representatives. Nike’s brand image, name and the trademark swoosh, position the company as one of the most identifiable brands in the world.
Adidas, Nike’s biggest competitor, is also one of the most recognizable brands of nowadays. As well as the Nike Company is, Adidas is oriented to obtaining high profits. Nowadays Adidas has a reputation of a strong brand for sports apparels. The company supports its brand by continually advancing and improving products’ original features and quality to please and satisfy its customers. If referring to Adidas pricing policy, it uses the market skimming method, positioning itself as a shopping product with prices lower than that of its major competitors. Adidas sportswear can be found in specialized brand stores, sporting outlets and in the internet. Company’s major promotion objective is to become world number one sportswear company. Promotion is implemented mostly through advertising in the mass-medias and internet, and through supporting various sport events.
Cuizon, G. (2009, February 13). Audit on Nike’s Marketing Strategies: The 4Ps – Product, Price, Place and Promotion. Retrieved July 6, 2009, from http://corporate-marketing-branding.suite101.com/article.cfm/audit_on_nikes_marketing_strategies
Net MBA Business Knowledge Center. (2007). The Marketing Mix (The 4 P’s of Marketing) . Retrieved July 6, 2009, from http://www.netmba.com/marketing/mix/
Stuck with your Essay?
Get in touch with one of our experts for instant help!
Against Adolescent Pregnancy, Research Paper Example
Operations Management: Planning and Breakeven, Essay Example
Time is precious
don’t waste it!
Plagiarism-free guarantee
Privacy guarantee
Secure checkout
Money back guarantee

Related Essay Samples & Examples
Voting as a civic responsibility, essay example.
Pages: 1
Words: 287
Utilitarianism and Its Applications, Essay Example
Words: 356
The Age-Related Changes of the Older Person, Essay Example
Pages: 2
Words: 448
The Problems ESOL Teachers Face, Essay Example
Pages: 8
Words: 2293
Should English Be the Primary Language? Essay Example
Words: 999
The Term “Social Construction of Reality”, Essay Example
Words: 371
Your Article Library
Essay on marketing mix: meaning, components and observations.
ADVERTISEMENTS:
Essay on Marketing Mix: Meaning, Components and Observations !
Essay 1 # Meaning of Marketing Mix:
Marketing mix might be defined as follows:
Marketing mix is a unique combination of the basic ingredients of marketing viz. product, price, place (channels of distribution) and promotion-designed for the best realisation of the objectives of marketing management.
(1) “Marketing mix refers to the apportionment of effort, combination, designing and integration of the various elements of marketing into a programme, of mix which will best achieve the marketing objectives of an enterprise at a given time”.
—Prof. Neil Borden of the Harvard Business School
(2) “Marketing mix is the term used to describe the combination of four inputs which constitute the core of the company’s marketing system- the product, the price structure, the promotional activities and the distribution system”.
—William J. Stanton
Marketing mix is a mix of the type that is planned to ensure that the ‘product’ does sell even amidst intensely competitive conditions; providing best satisfaction to consumers and providing, in turn, handsome profits to the enterprise- in addition to fulfillment of other objectives of marketing management.
Point of Comment:
An analogy could be drawn between the marketing mix of a manufacturer and the spices-mix of a famous ‘Chat-wala’ located at the corner of a busy street in the walled city of Delhi; who combines spices like-salt, rock salt, pepper, black pepper, spices for seasoning food (i.e. garam masala) etc. in such proportions that the chat becomes so tasty as to lead to a remarkable rapidity of turnover fetching handsome profits to the chat-wala.
The chat masala mix is so to say, the trade secret of the chat-wala- unknown to the competitors. Further, the consumers, being unable to prepare that much tasty type of a chat at their homes, are persuaded to visit that particular chat-wala for the satisfaction of their ‘tongue-needs.’
A manufacturer, in a likewise manner, must design such a marketing-mix, that despite severe business competition-consumers do prefer his product and are led to buy that product for the satisfaction of those needs of theirs- for which that particular product is designed.
Essay 2 # Components of Marketing Mix – The 4p’s Of Marketing Mix:
Though there are a large number of component parts (or factors) which may go into the making of a marketing mix; yet, authorities on marketing management agree on four basic elements of marketing mix-popularized as the 4p’s of marketing viz. the product, the price, the place (i.e. the channels of distribution) and the promotion.
In fact, each of these four elements has many variables or variations of factors, and accordingly within the marketing mix we have four sub-mixes i.e. the product-mix, the price-mix the place-mix and the promotion-mix. In other words, the marketing-mix is a fine blend of product mix, price-mix place-mix and promotion-mix.
Following is a brief account of the four sub-mixes, comprised in the marketing mix:
(1) Product-Mix:
A product is not just, a physical tangible object; it is rather a ‘bundle of services’ associated with the utilisation of that product. A person e.g. does not buy a product simply for possession sake; rather he/she expects a number of services and conveniences-to be obtained from using that product.
Some of the important factors which usually go into the designing of the product mix are decisions about:
1. The product-range
2. Design, shape, colour, size, weight of the product etc.
3. Multiple uses of the product.
4. Standardisation/grading of the product.
5. Brand name of the product.
6. Guarantees and warranties offered by the seller.
7. After sales service provided.
A unique combination of these product factors and others makes for designing the product- mix. The basic idea behind making a product mix is to produce and offer a product that makes it acceptable to the target-consumers; by providing them maximum satisfaction for their needs for the fulfillment of which, the product, in question, is intended.
(2) Price-Mix:
The price-factor is, perhaps, the most-crucial factor of the marketing mix; as the buying decisions of most of the consumers are dependent on the price of the product. For the manufacturers also, the price decision is directly reflected in the profits; which they make from selling the product.
Some of the important factors which usually go into the designing of the price-mix are decisions about:
1. Price-range
2. Profit-margin to be included in the price
3. Discounts to be offered-cash discounts and trade discounts.
4. Credit terms
5. Competitors’ prices for similar type of products.
6. Discriminating pricing aspect.
7. Resale price maintenance policy etc.
A unique combination of these price factors and others makes for designing the price-mix. The basic idea behind making a price-mix is to offer the product at a price which is affordable by the target-consumers; making the product worthwhile for purchase; in view of the utility of the product.
(3) Place-Mix:
In marketing management, the term place is used to refer to channels to distribution i.e. intermediaries which fetch products from the place of the manufacturer to the place of ultimate consumers.
The ‘place’ is an important ingredient of marketing mix; as howsoever useful the product might be and howsoever suitable its price, be; unless and until products are made available to consumers at ‘centres of convenient buying’, the busy consumers of today’s affluent societies will be most unwilling to buy those product-travelling long distances.
The important factors which usually go into the making of the place-mix are decisions about:
1. Wholesalers
2. Selling agents
3. Transportation agencies
4. Warehousing agencies
5. Company’s direct selling outlets
6. Home delivery of products.
A unique combination of these place factors and others makes for designing the place-mix. The basic idea behind making a place-mix is to make the product available at such common centres of consumption; as makes for most convenient buying-on the part of the busy consumers of today.
(4) Promotion-Mix:
Promotion refers to creation, maintenance and increase of the demand of the product-through communication of the existence and utility of the product to target consumers and general public’s.
Promotion is a very significant component part of the marketing mix; as without promotional efforts, people would never be able to appreciate the utility of the product for satisfaction of their needs; and conducting sales-transactions, would not, obviously, be possible for the marketer.
Promotion, in a sense, is a sort of best consumer-education; which educates consumers as to the availability and usefulness of various products.
Some of the factors which go into making of the promotion mix are decisions about:
1. Advertising-through various media like the press, radio, TV, films, outdoor advertising, point of purchase-advertising etc.
2. Personal selling or salesmanship through various types of salesmen
3. Sale promotion methods (i.e. methods other than advertising and salesmanship) like- coupons, reduction sales, distribution of free samples, trading stamps, bonus offers, prize- contests and a host of other devices.
A unique combination of various advertising media, various types of salesmen and attractive sales promotions devices, makes for designing the promotion-mix.
The basic idea behind making a promotion-mix is to so communicate knowledge about the existence and utility of products; that prospects appreciate the significance of the products for the satisfaction of their needs and may become ready to buy the product-so promoted.
Point of comment Synchronization of sub-mixes i.e. product-mix, price-mix place-mix and promotion-mix into a grand-plan of marketing, would result in the development of a marketing mix of type which makes
1. The product acceptable
2. The price affordable
3. The place most convenient and
4. The promotion most influencing.
The criterion for measuring the success of the marketing mix is the volume of sales of product turned over by it.
The concept of marketing mix could, we’ll be illustrated, by means of the following circular diagram:

Note: Letter ‘C’ in the inner circle of the diagram indicates the term ‘Consumer’.
Essay 3 # Observations of Marketing Mix:
Certain observations on the concept of marketing mix:
(1) Target consumer is the focal point of designing marketing-mix. In fact, consumer is the central point around which the whole circle of marketing mix is drawn.
(2) All the four P’s of marketing mix are equally important; while designing the marketing mix. If e.g. the product is good (acceptable); but the price is not affordable the product may not be a good success.
Or if the product is acceptable and its price is also affordable; but the place (i.e. Channels of distribution) is not convenient for buying on the part of consumers-the product may not sell as much as expected.
Again, if the product, price and place-all the three meet the requirements of consumers; but the promotion is not properly communicative and influencing-the product may not sell much.
Therefore, an equal amount of emphasis must be placed on each of the four major elements of marketing mix; as an over-emphasis on any one element of the mix at the cost of other elements would simply mean a failure of the entire design of marketing mix.
(3) The four P’s of marketing mix are interrelated and interdependent; because a change in any one element of marketing mix is likely to necessitate suitable changes in other related elements of it.
For example, if a change (of any type, for that matter) is proposed to be made in the product; it might also be considered fit, by marketing management, to effect a change in the price of the product or a change in the promotional techniques; and so on for changes in other elements of marketing mix.
(4) Marketing mix is not developed in a vacuum:
Besides the 4P’s of marketing mix, which are the controllable elements of it; there are certain external environmental factors which are the uncontrollable elements of marketing mix.
Any design of the marketing mix must, accordingly, be shaped in view of the implications of environmental factors, amidst which the marketing mix is to demonstrate its impact on the marketing operations of the business enterprises.
In fact, the environmental factors provide the basic framework; within which the marketing mix is to be designed . (The outer circle of the marketing mix diagram shows the significance of environmental factors; while designing the marketing mix ).
Related Articles:
- Marketing Mix: Meaning, Definition and Characteristics of Marketing Mix (with diagram)
- Elements of Marketing Mix: Product, Price, Place (Distribution) and Promotion
Comments are closed.
How to Develop a Successful Marketing Mix Strategy [+ Templates]
Updated: July 28, 2021
Published: July 02, 2020
One of the first things you're taught in your Introduction to Marketing class is that marketing can be best explained using the marketing mix – also known as the four Ps.

They are – and say 'em with me because if you took that class, you know these four words by heart:
![essay on marketing mix → Free Resource: 4 Marketing Mix Templates [Access Now]](https://no-cache.hubspot.com/cta/default/53/c79f682e-61ec-4234-80b3-0b1f3833ee30.png)
However, once you're in your first marketing internship or job, you learn that marketing entails so much more than can be simplified in a four-section marketing mix matrix.
Still, there's an undeniable benefit of marketing teams organizing their work into the marketing mix framework.
When you stray too far away from the four P's, it can be easy to lose focus on your purpose as a marketer.
Marketing truly is about teams and individuals working together to promote a product in the right place at the right price point. Efforts beyond this scope are essential, but they do all stem off of this foundation of the marketing mix.
Here, we're going to dive into what a marketing mix is and how to develop a successful marketing mix strategy for your own company.
What is a marketing mix?
The marketing mix refers to the actions a company takes to market its product(s) and/or service(s). Typically, it acts as a framework for breaking down the four key components of marketing — product, price, place, and promotion.
The marketing mix helps companies organize their marketing initiatives by task and department for more process-driven and impactful marketing campaigns.
This framework has roots dating back to the 1940s and has been evolving ever since. While some elements have been added or tweaked over the years – most notably for the modern digital age – the core elements of the marketing mix (i.e. the four P's) have remained consistent for decades.
Featured Resource: Marketing Mix Templates

Need a way to visualize your marketing mix to share it with your employees or investors? Use these four marketing mix templates to organize your initiatives and activities by the right section. Click here to download them now .
Marketing Mix Elements
When perfected and synchronized, the core elements of a marketing mix provide a well-rounded approach to marketing strategy.
Product refers to what your business is selling – product(s), service(s), or both. The bulk of the work in this element is typically done by product marketers or managers.
Nailing the product element of the marketing mix means doing extensive research and development, understanding the need for the product, developing a product launch plan and timeline, and educating customers and employees – especially salespeople – on the product's purpose.
Price refers to the price point at which you'll sell your product(s)/service(s) to consumers. Arriving on this dollar amount requires consideration of multiple pricing strategies, analysis of similarly priced products in your market, and insights from consumers through surveys and focus groups.
Price speaks to positioning in the market, the speed at which you want to penetrate your market, and your company's revenue goals and profit margin.
In the marketing mix, place refers to where your product or service will be sold. For tangible products, this will include physical locations such as your own store, or a retailer where your product will be resold.
It can also include the other methods where your products can be purchased, like online or over the phone.
4. Promotion
Promotional activities are those that make your target market aware and excited about what you're selling.
While this does include paid initiatives like commercials and advertising, promotion also entails organic initiatives like word-of-mouth marketing, content marketing, and public relations.
Other Elements
While the marketing mix can often be simplified down to the 4 P's, the expansion of the scope of marketing in recent years has resulted in more P's added to the list.
For example, Smart Insights includes the following elements in its marketing mix definition:
- Process , or the large internal initiatives taken to support a product launch, such as including salespeople in goal setting.
- People , which can refer to your buyer, market, and target audience, or your internal team responsible for a launch.
- Partners , or who you'll be working with outside of your company, such as distributors or co-marketing partners.
Some of the other P's can include:
- Payment , or how transactions will be held and processed.
- Physical evidence, or anything tangible pertaining to your product or service, like any materials needed to complete your service or deliver your product.
- Packaging , or anything pertaining to the physicality of your product, like how it looks or how it's packaged.
These other marketing mix elements should be utilized as you see fit for your projects. However, every good marketing mix should rely on a thorough exploration of those first 4 Ps.
Marketing Mix Templates
Fill out the form to get your templates, marketing mix examples from real businesses.
Fintech companies are everywhere, but how many of them focus on organic and non-GMO agriculture?
As sustainable agriculture becomes more top of mind, brands like Mercaris help support agriculture companies looking to stay ahead in the market. Beyond delivering a service, the company identified a niche and launched a business with few direct competitors.
They offer a monthly subscription-based service that arms agricultural companies with the market intelligence needed to compete in the space. This includes detailed reports on food production, commodity prices, and market shifts.
Not long after Airbnb launched, users filed complaints of racism from their hosts and expressed reluctance to use the platform's services. The company implemented measures to appease these concerns. However, it brought attention to an important issue.
It's this uncertainty that allowed Noirbnb to enter the market. The brand tapped into people of color's desire to feel safe and welcomed in their temporary home while traveling – then, they used it as their unique selling position (USP).
The brand even plays on Airbnb's name – which is now a household one – to indicate that they offer a similar service that's been adapted to cater to travelers of color.
Warby Parker
This online retailer of prescription eyeglasses and sunglasses is known for its stylish yet affordable glasses. Warby Parker 's pricing, which starts at $95, undercuts many of its competitors, making it a popular go-to for consumers.
The brand's pricing strategy is based on public perception. In interviews, the founders revealed that originally, they were going to price their frames as low as $45. However, after considering how low prices for items like glasses can be perceived as low quality, they doubled the price to settle at a number that was still competitive.
A brand's pricing strategy can have an important role in how it's perceived in the market. So, it's important to consider what that perception is and if it's the one you want to put out there.
When Canva entered the market, it was every small business owner's dream. You could design any marketing material you wanted for FREE, what more could you ask for?
Eventually, the brand introduced premium versions of its platform. Catering to businesses ranging from small to enterprise-level, they added features like high-quality stock visuals, social media publishing tools, marketing campaign management, and large cloud storage.
Hu , short for "Get Back to Human," is a dessert company that specializes in making organic, paleo chocolate bars free of the junk ingredients we find in big-name products.
The brand has made its products available from multiple major retailers, including Walmart, Target, and Whole Foods. They also have a virtual storefront on Amazon. If stock ever runs out there, you can always purchase their products through their website.
Hu has made its product accessible through multiple channels, maximizing its earning potential while expanding its brand awareness.
The Lip Bar
Vegan beauty brand The Lip Bar leverages influencers and celebrities to promote its products and increase its brand awareness. Recently, the brand partnered with beauty influencer Raye Boyce to announce its expansion into Walmart stores and its nine latest products.
The Lip Bar places women of color at the center of its products and collaborating with a Black influencer known for her love of lipsticks is in perfect alignment with the brand's identity.
Beyond a robust social media presence, the company also has a blog on its website with content that appeals to audiences across the buyer's journey.
Avant-Garde Vegan
Some brands launch a product then promote, while others promote then launch.
Avant-Garde Vegan , an online brand created by UK-based chef Gaz Oakley, grew his business on social media – namely YouTube. Oakley gained popularity posting recipes for healthy, vegan dishes and soon became a go-to resource for new and established vegan consumers.
Eventually, Oakley released his first product, a cookbook. Now the brand sells both cookbooks as well as merchandise.
The reason why this strategy works particularly well is that it focuses on adding value instead of selling. Oakley gained his audience's trust and loyalty through consistent and quality posts on social media.
Once he introduced a product, many of his followers were ready to make a purchase. It's a long-term strategy that can have a big payoff if executed well.
How to Develop a Marketing Mix Strategy
Because the marketing mix incorporates elements from across your department – and even your company – it's imperative to establish a marketing mix strategy for each product you launch, or for your company as a whole. For a fully fleshed-out marketing mix, follow these steps.
1. Engage in market research and product development.
The success of your marketing work is first and foremost contingent on your product. Make sure it's well developed and your team can speak to its benefits and the story behind it.
Best practices in this step include:
- Engaging in market research to understand your buyers' needs.
- Speaking to your current customers to uncover their pain points and see which needs to address in your current product or service line.
- Monitoring industry trends to identify a potential demand in your market.
- Examining the competition.
- Collaborating with your product team during product development to ensure it meets your buyer personas' needs.
- Having your product tested by current customers to see how they're using the product or service and if it's actually solving for their problems.
Taking these actions ensures you're making every effort to understand and solve for your customer, providing a solid foundation for your product to launch successfully.
Featured Tool: Market Research Kit . To make your R&D more impactful, use these free market research templates so you can better understand your customers and competitors.
2. Determine your pricing model.
A lot goes into choosing a price point – so much so that we wrote an entire guide to pricing strategies .
Luckily, you'll be able to refer to much of the work done in the previous section. Thanks to your understanding of your market through research, you'll have answered most of the necessary questions in this section. You'll also need to take your costs into account so you can maximize unit sales and profit.
During this stage, make sure you do the following.
- Speak to customers (or refer to previously completed market research) to determine the ideal selling price.
- Work with the product team to ensure the product can be developed in a cost-effective manner that would ensure profitability at your target price point.
- Meet with financial experts to determine aggressive yet realistic sales forecasts to contribute to the company's bottom line.
- Collaborate with your sales team to determine discounting strategies.
- Determine how you'll adjust price and revenue forecasts when selling through resellers.
Lastly, don't forget to factor in the perceived value by the customer. Even if your product or service doesn't cost a significant amount to make, you'll be able to mark up your product more if you face little competition and provide an irreplaceable benefit to your customers.
Featured Tool: Pricing Strategy Calculator . If you need help selecting your pricing model, use this template to compare different pricing strategies and see which will yield your company the most profit and revenue based on your forecasts.
3. Choose your distribution channels.
The "place" part of the marketing mix answers where your product will be sold. Keep in mind, this can be any combination of your store, a distributor's store, or online. You'll want to address the following points before moving onto the promotion stage:
- Determine if your product will fare best in your physical location, a store of another retailer, on your website, on another company's website, or some combination of these locations.
- Think about geographic location – make sure your supply meets regional demand, and plan for whether or not what you're selling will be available in a certain city, a state, the country, or worldwide.
- Come to an agreement with retailers and resellers on margins, markups, and manufacturer suggested retail prices (MSRP).
- Figure out how many salespeople will be needed to ensure you meet your goals.
- Set goals for retail, third-party sellers, since you may be sharing shelf space or search results with a competitor or two.
4. Select your promotion tactics.
Finally, it's time to promote your product. While this is probably the element most associated with marketing, it's crucial that this element be completed last, because you need the foundation of product, price, and place before determining promotion tactics.
Think about it – shouldn't you know what you're promoting, why you're promoting it, and where it's available before actually promoting it? It's tempting to jump right to this step, but your promotion will be much better off if it's done after everything else in the marketing mix.
Once you do have that understanding, consider the following promotional channels and choose the one(s) that makes the most sense for your product, its buyers, and its price point:
- Content marketing efforts, such as blogging, content creation, and building a website.
- Public relations and working with affiliates and/or influencers.
- Social media marketing – both organic and paid – on channels such as LinkedIn, Facebook, and Instagram.
- Search engine ads on sites like Google and Bing.
- Ads to air on video streaming sites like YouTube, or on TV.
- Event marketing, including attending industry events or hosting your own event.
- Customer marketing and utilizing referrals.
- And more – There are countless promotional ideas you can use to spread the word on your product, service, or business.
Featured Tool: Marketing Plan Template . If your promotional tactics are multi-faceted enough, consider documenting your plans in this customizable template.
Every company's marketing mix is different, placing emphasis on certain factors over others.
Some businesses use their marketing mix for a single product, while others adopt a company-wide marketing mix. However, good marketing mixes should tie in all the elements without neglecting one.
All elements of the marketing mix are important, so don't be quick to overlook any of them, and find ways for different elements of the mix to overlap and share goals.
With so many activities happening to support a single initiative, it's helpful to organize everything in a single template for easy reference. Here are a few examples of marketing mix templates your marketing department can use, in addition to when they might make sense to reference.
1. Simple Marketing Mix Template
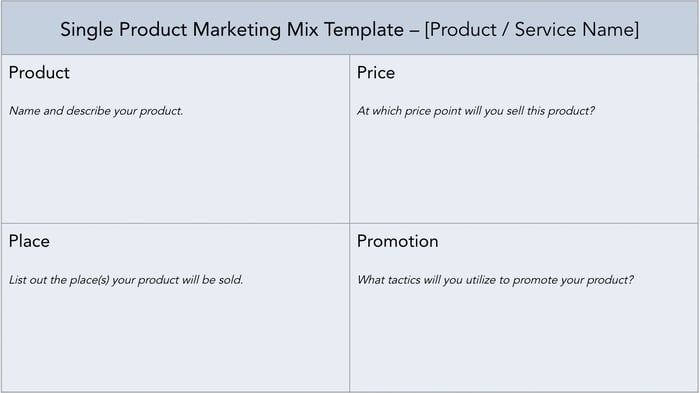
Download this Template
This template is a great starter for organizing a marketing mix. It's ideal for one product and for the marketing mix's maker to get an understanding of all the elements involved in the marketing of a product.

2. Company Marketing Mix Template
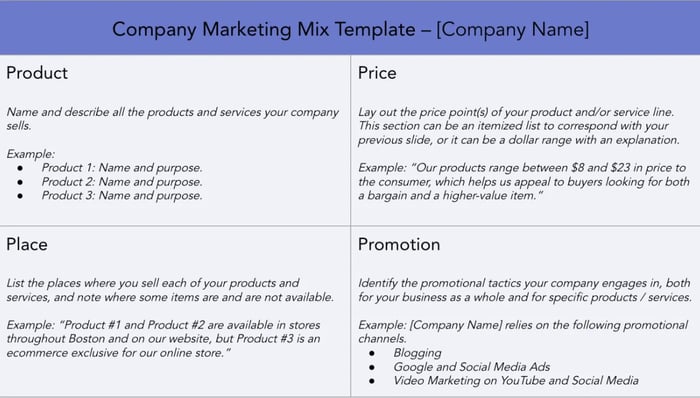
For a marketing mix that applies company-wide, this template is a perfect fit. You can outline the initiatives that apply to most or all of the products and/or services in your suite.
3. Structured Marketing Mix Template
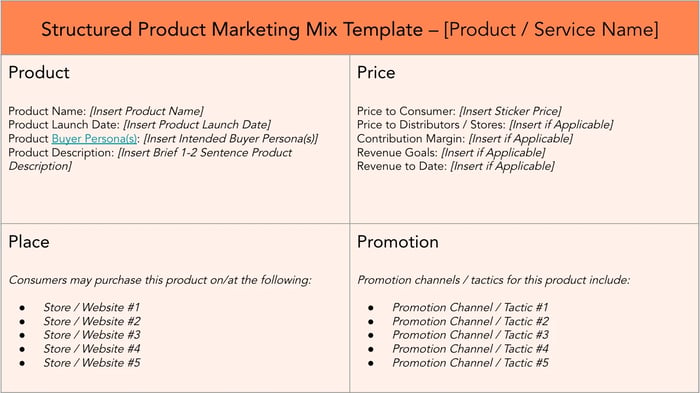
For when you need to get right to the point with a more organized, actionable visualization, use this structured, bulleted template for quick reference and clarification.
4. Production Marketing Mix Template
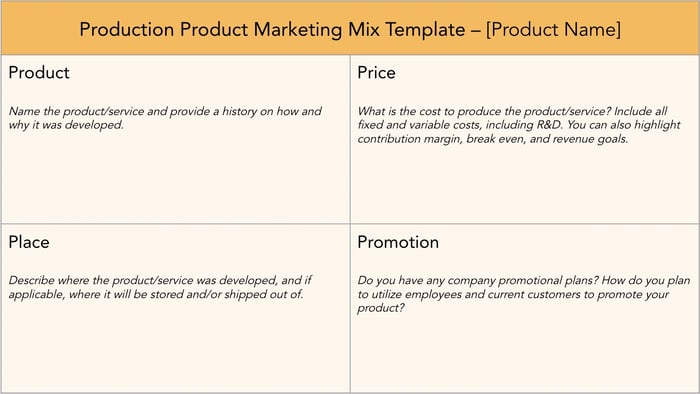
Finally, a production marketing mix template is best utilized for internal reference. This template answers questions on the go-to-market efforts for products and services that you're selling.
Mix It All Together
Whether you're a student just learning to understand everything that marketing entails or a CMO hoping to clearly convey the work that your team is doing to your fellow employees, the marketing mix framework is an essential tool to help you get the job done.
Don't forget – if you need to organize your marketing initiatives into a central location, try using HubSpot's Marketing Mix Templates to document your activities in one place.

Don't forget to share this post!
Related articles.

Marketing Agencies We Admired in 2023
![essay on marketing mix Marketing Budget: How Much Should Your Team Spend in 2024? [By Industry]](https://blog.hubspot.com/hubfs/how%20to%20spend%20your%20marketing%20budget_featured.webp)
Marketing Budget: How Much Should Your Team Spend in 2024? [By Industry]

12 Best Free (& Private) Email Accounts & Service Providers for 2024
![essay on marketing mix How to Delete Your Instagram [Easy Guide]](https://blog.hubspot.com/hubfs/delete-instagram.png)
How to Delete Your Instagram [Easy Guide]

The Best Free Business Budget Templates
![essay on marketing mix Millennials vs. Gen Z: Why Marketers Need to Know the Difference [New Data]](https://blog.hubspot.com/hubfs/millenials%20vs%20gen%20z%20what%20marketers%20need%20to%20know%20when%20trying%20to%20reach%20each%20generation.jpg)
Millennials vs. Gen Z: Why Marketers Need to Know the Difference [New Data]
![essay on marketing mix How Marketing Leaders are Navigating Recession [New Data]](https://blog.hubspot.com/hubfs/how%20marketing%20leaders%20are%20navigating%20recession.webp)
How Marketing Leaders are Navigating Recession [New Data]

The 11 Best Ways to Send Large Files
![essay on marketing mix 3 Ways Marketers are Already Navigating Potential Recession [Data]](https://blog.hubspot.com/hubfs/how-marketers-are-navigating-recession.jpg)
3 Ways Marketers are Already Navigating Potential Recession [Data]
![essay on marketing mix How to Edit a PDF [Easy Guide]](https://blog.hubspot.com/hubfs/280_How-to-Edit-PDF.png)
How to Edit a PDF [Easy Guide]
Organize your product, price, place, and promotion initiatives in a simple, single template.
Marketing software that helps you drive revenue, save time and resources, and measure and optimize your investments — all on one easy-to-use platform
[email protected] Visit FAQs
Terms - Privacy Business.co.za 2021 Webhosting by Domains.co.za
What Is a Marketing Mix And Why Is It Important?

Content Agency
@ contentagency
Whether you’re a marketing manager or small business owner, chances are you’ve heard the term marketing mix before. For those reading this who have not come across the term, a marketing mix is the set of marketing tools, mediums and perspectives which a business utilises to sell its products or services to its target market.
Marketing Mix In A Nutshell.
Businesses have always used various marketing tools to promote and sell their products and services, but the term “marketing mix” was coined in the mid 20th century. One of the term’s first uses was during an address delivered back in 1953 to the American Marketing Association, by Harvard professor Neil Bordon, who outlined how marketers develop and implement successful marketing plans.
By accurately identifying and arranging the elements of a marketing mix, business owners can make profitable marketing decisions at every level of their business. These decisions can help businesses:
Develop their strengths and limit their weaknesses.
Become more competitive and adaptable in their markets.
Improve profitable collaboration between departments and partners.
Since the 50s, the key elements of the marketing mix have underdone many transformations as a result of emerging technologies and other changes to what is considered to be best practices.
The Four Ps of a Marketing Mix:
Since the 60s, the marketing mix has been associated with the “Four Ps”, namely price, product, promotion and place:
Price. Refers to the cost of purchasing a product. A price depends on a consumer’s perceived value of a product, and it can drastically affect your marketing strategies. Of course, a lower price makes products more accessible to more customers, while a higher rate appeals to customers seeking exclusivity or high-end products. In terms of both, the price has to be greater than the production costs for your business to make a profit.
Product. Refers to what is being sold. Marketers need to consider the life cycle of their products to address and difficulties which might arise once it’s in the hands of their consumers. For instance, the first generation iPod had battery life issues which were only discovered after a specific time, and Apple had to work towards developing methods to address this issue.
Promotion. Promotion refers to the advertising, direct marketing and sales promotion of your products and services. Television ads, web ads, catalogues, trade fairs, billboard advertising and even ads on branded vehicles (cabs, buses, trains and even Ubers) are all forms of promotion. Furthermore, this category also includes PR (public relations), i.e. the distribution of press releases or ongoing relationships with the media. Promotion encompasses that which is communicated, whom it is delivered to, how your audience is reached and how frequently the promotion happens.
Place. Refers to any physical location which a customer can use, access, or buy a product or service. Places include distribution centres, transport, warehousing, inventory decisions and franchises.
The Seven Ps of the Marketing Mix.
Often, in marketing strategies, the four Ps are expanded to include the seven Ps. In addition to the four Ps, the seven Ps include physical evidence, people and process:
Physical evidence. This refers to anything tangible related to your product or the physical environment in which service occurs. Physical evidence includes product packaging, delivery receipts, signage, as well as the layout of a physical store.
People. Refers to your employees, including those who interact directly with your customers (salespeople, customer service and delivery people) as well as staff recruitment and training. This “P” also includes how efficiently employees perform at work, their appearance (for instance, if they have uniforms), and how customers feel about the experience with them.
Process. Lastly, process refers to any aspect within your business which affects how a product or service is carried out by employees and delivered to clients. Examples include the order in which employees are required to carry out tasks, the number of queries your sales team receives, where customers are directed for help and how performance is tracked and measured. Furthermore, it also covers which elements of the process are standardised and which have room for customisation on a per-customer basis.
What is a Digital Marketing Mix?
In a nutshell, a digital marketing mix is how businesses achieve their marketing goals through the use of digital tools. As more business is conducted online every day, digital marketing tools are becoming vastly more important to all types of businesses, as opposed to only those which are tech-orientated.
A digital marketing mix employs the same basic principles of the traditional marketing mix, however, these elements are adapted to align with how the Internet influences emerging technologies and consumer behaviours.
The Four Cs of a Marketing Mix.
In the early 90s, the four Ps were updated to four Cs, to place less focus on the business and more on the customer. The four Cs refer to the consumer, cost, convenience, and communication. In certain instances, the four Cs might be more applicable to a digital marketing mix and than the four Ps.
Consumer. This refers to the wants and needs of the consumer. Using this model, the business should put its focus on solving problems for consumers as opposed to creating products. The model requires adequate research into consumer behaviour and needs as well as interacting with potential costumes to determine their wants.
Cost. This refers to the total cost of acquiring a product or service, which goes beyond just the price tag. The cost includes the time it takes to conduct research into a product before making a purchase. Moreover, it might also cover the cost in trade-offs which consumers need to make, for instance, forgoing another purchase, or the cost of guilt which they may experience when buying or not buying a product or service.
Convenience. Refers to how easy or difficult it is for customers to find and purchase a product or service. The advent of Internet marketing and buying has made this “C” notably important with regards to customer decisions as opposed to physical places.
Communication. This “C” refers to the dialogue, which depends as much on the seller as it does the consumer. It includes advertising, marketing and media appearances. However, in the digital realm, it also includes emails, brand ambassadors or influencers, blogging, websites, sponsored product placement and of course, a business’s social media channels.
How To Define Your Marketing Mix.
In order to secure early sales and develop a solid customer base, a business owner needs to identify its marketing mix. The first step in this process is identifying and defining your target customer.
Once you’ve determined who your customer is, you’ll begin to understand their relationship with your business.
What problem does your target customer have?
What is preventing them from solving that problem?
How do your products or services address their needs or challenges?
How do your target customers feel about your competition and you?
What is your target customer’s motivation to make a purchase?
Following this, you need to identify your sales and growth goals, as well as your marketing budget. Then, select a marketing tactic or tactics which will help you reach your target audience and achieve your goals.
For instance, if you require 25 leads to sell one product, and you desire to sell 1,000 products per month, then you’ll need 25,000 fresh leads. You’re aware that your target customer reads and trusts two different websites, one which has 25,000 visitors a month and one with a million per month. The website which only has 25,000 per month is more cost-effective to advertise on, but of course, it’s highly unlikely that all 25,000 visitors will become new leads. Thus, the website boasting a million visitors is of better use to your ad budget, even if it costs more to advertise there.
By carefully working through the elements of your business’s marketing mix, you’ll have the power to develop strategies which effectively reach consumers, secure sales and grow your business more efficiently.
If you require any marketing assistance, please visit the Barrk Marketing page to access their contact and service information.
- communicate
- small business
- digital marketing
Discuss this article
ℹ You can select the account to comment from with the dropdown arrow on the left, and you can easily mention businesses using their @businesshandle in order to let them know about this article.

Home Essay Examples Marketing Marketing Plan
Marketing Plan and Marketing Mix
- Category Marketing
- Topic Marketing Plan

Introduction
Understanding a business thoroughly requires deep concentration on its marketing plan. A marketing plan is a significant part of the business plan which lists actions regarding marketing strategy and how a business will build credibility among customers and increase their profit by fulfilling sales target (Pulido Polo, 2018). A marketing plan gives an overview of the market with related ancillary factors like its objectives, various strategies and the overall landscape of the business. In a nutshell, how a business deals with its overall future plan and acquiring them
In the previous report, a PEST analysis for Hollister on the perspective of China has been shown. In this report, a marketing plan regarding Hollister’s expansion will be described to better understand the market and what strategies Hollister needs to take for achieving the goals.
Our writers can write you a new plagiarism-free essay on any topic
Hollister’s marketing strategy for China
Target market.
As aforementioned, Hollister focuses on teens. So, the target customer has aged 13-25 years old teenager, popularly known as Generation Z, born after the year 1995, young and trendy, connected with updated technology. So, in China Hollister will target teenagers from high school, who are interested in moulding quality and fashion together. China’s huge population is an advantage for Hollister to expand the market.
Positioning
The first thing that will be noticed in case of Hollister is their store designing, giving a pinch of beach feeling, it is similar for every store of Hollister anywhere in the world. This unique design can attract customers especially teenagers as they are prone to innovative things. Hollister maintains a balance between price and quality, it also offers the differentiated product in colours and contents with a cosy shopping experience than its competitors (Saxena, 2010).
Marketing Mix
Marketing mix includes strategies Hollister will implement for their Product, price, place, promotion. What type of product they will launch, in which places, how they will set the price and which ways they will promote the products and below figure shows the constituents of the marketing mix:
Product Strategy:
For the teens of China, Hollister will come up with high quality, comfortable, theme-based products of various styles & colours. In the case of product strategy, Hollister can use a glaze of celebrities. That means by celebrity advertising, where popular celebrities of China will be shown using Hollister’s product. This direct marketing will help to attract customers easily. Hollister also provides related information regarding products to build customer credibility. But to build a strong customer relationship in China Hollister needs to spread brand awareness.
Pricing Strategy:
In China Hollister can use a value-based pricing strategy which refers to a value perceived by the customers. In the case of Hollister, quality & comfort is the top-notch area for perceiving value for 60% customers. Hollister can use two types of Value-based pricing, they are high-low pricing that is setting the price in the scale of demand. Another strategy is value-added pricing which refers unique features which competitors lack to deliver and charging a price for that quintessential feature (Hiebing, Cooper and Wehrenberg, 2011). Besides price skimming strategy can add a value to maintain brand image than Hollister’s competitor like GAP and American Eagle. It will also support the product quality. Besides introducing seasonal & quantity discounts on occasions like the new year, Mid-autumn festival of China can attract more customer for Hollister. Selecting this strategy will benefit Hollister for being the new market entrant, it will earn brand value and different perspective from its competitors, also to fulfil sales target within a short time.
Placing strategy:
For placing Hollister can use their Physical stores and web-based online store. In the case of stores, Hollister can set up their stores in vast shopping malls where gatherings will be in huge amount. In this way, Hollister can reach the customers. To implement this strategy Hollister can use Vertical Marketing Strategy (VMS). Hollister can use VMS because it will help to minimize delay time and make distributing more efficient (Gök and Hacioglu, 2010). Also, through VMS Hollister can lower the cost of distribution which will increase the good impression of customers. Besides Hollister is popularly known for their stylish coastal atmosphere store, it will also add value towards Hollister’s placing decisions.
Promotional strategy:
Hollister’s maintain top-notch Public Relation strategy to attract the customer. As Hollister focuses on teens of China. China is already technologically updated. So, to capture China’s market Hollister will use social media to build image & publicity of the brand. Besides special events like opening a new store can increase customer gatherings. Another strategy is sales promotion, giving small discounts on a specific amount of purchase, coupon, free sampling of first products etc. Sales promotion is appropriate for letting people know about the product. Advertising is another prominent promotional tool, be it in billboard or newspaper or Electronic media. Brand’s logo and tagline also work as a persuasive promotional strategy. Apart from these advertising via celebrities or direct marketing like mail, newsletter etc. Promotional strategy is vastly used for one simple purpose, reaching target customer in the simplest way.
Through an implementation plan deviation of Product, price, promotion, the distribution can be measured. In terms of Product: the cost of manufacturing, shipment and launching cost will be calculated. In the case of distribution, the cost training and developing sales representatives & employees will be monitored as well as the cost of launching new stores (Saxena, 2010). In promotion: the cost of social marketing and other advertising and events will be covered. Last but not the least Pricing will include target costing and related pricing of selection. An implementation plan is necessary for balancing between the planning and control.
Aforementioned components of product mix are given below:
- Product High quality, Comfortable, occasion-based product. Attract customer, building customer loyalty.
- Price High low pricing, Value-added pricing. To fulfil the sales target within the short time period
- Place Physical store, Online To increase the direct involvement of customers
- Promotion Direct marketing, Advertising To reach customer easily
Setting strategy is easy but implementing them is crucial. So, after setting all these strategies, Hollister can concentrate on the implementation plan. It can be done on monthly basis. Modern business is shaping every day, every now and then in various ways. To keep balance and grab new market having a good marketing plan is essential for every business as it provides an outline for the future plans. On this report, a marketing plan has been described for Hollister on the perspective of China to expand the business. How it can arrange its product line, what pricing strategy to increase profit and place & promotion strategy to reach the customer easily.
- Corporate.abercrombie.com. (2018). [online] Available at: http://corporate.abercrombie.com/our-company/our-brands/hollister [Accessed 13 Dec. 2018].
- Gök, O. and Hacioglu, G. (2010). The organizational roles of marketing and marketing managers. Marketing Intelligence & Planning, 28(3), pp.291-309.
- Hiebing, R., Cooper, S. and Wehrenberg, S. (2011). Successful Marketing Plan. Blacklick: McGraw-Hill Publishing.
- Hitt, M., Ireland, R. and Hoskisson, R. (2017). Strategic management. Boston, MA: Cengage Learning.
- Palmer, A. (2014). Principles of services marketing. London: McGraw-Hill.
- Pulido Polo, M. (2018). Acts or events? A perspective from the marketing mix. IROCAMM-International Review Of Communication And Marketing Mix, (1), pp.56-66.
- Rozelle, S. and Zhang, L. (2016). Introduction: China’s Rural Economy And Human Captial. China & World Economy, 24(3), pp.1-2.
- Saxena, R. (2010). Marketing management. New Delhi: Tata McGraw Hill.
We have 98 writers available online to start working on your essay just NOW!
Related Topics
Related essays.
By clicking "Send essay" you agree to our Terms of service and Privacy statement . We will occasionally send you account related emails.
By clicking "Receive essay" you agree to our Terms of service and Privacy statement . We will occasionally send you account related emails.
We can edit this one and make it plagiarism-free in no time
We use cookies to give you the best experience possible. By continuing we’ll assume you board with our cookie policy .

ESSAY SAUCE
FOR STUDENTS : ALL THE INGREDIENTS OF A GOOD ESSAY
Essay: marketing mix
Essay details and download:.
- Subject area(s): Marketing essays
- Reading time: 5 minutes
- Price: Free download
- Published: 16 June 2012*
- File format: Text
- Words: 1,446 (approx)
- Number of pages: 6 (approx)
Text preview of this essay:
This page of the essay has 1,446 words. Download the full version above.
marketing mix
The term marketing mix refers to the marketing activities used to create, communicate and deliver value to the customer (Kotler, Keller, Brady, Goodman, & Hansen, 2009, p. 866). The four main marketing mix variables, referred to as the 4Ps of marketing are: product, price, place, and promotion. Each element of the marketing mix will be discussed in relation to the Philips product eBLOCK.
Product is the first element in the marketing mix. A product can be broadly defined as “anything that can be offered to a market to satisfy a want or need and consist of a set of attributes, including physical goods, services, experiences, events, persons, places, properties, organizations, information and ideas” (Kotler, Keller, Brady, Goodman, & Hansen, 2009, p. 867). Therefore a product can be tangible or intangible or a combination of both. A tangible product being one which can actually be touched while an intangible product cannot, for example a service. Our product named eBLOCK is a tangible product which also has intangible attributes such as repair and replacement services. eBLOCK can be further classified as a durable good. Durable goods are product offerings that have a longer use lifetime (Kotler, Keller, Brady, Goodman, & Hansen, 2009, p. 508). Another way to categorize eBLOCK is as a consumer good as it is a final good purchased by the consumer for personal use.
The eBLOCK is a product which combines existing technologies and products and combines them into one multifunctional device. Phillips therefore makes use of a market breakthrough strategy to bring the eBLOCK to the potential market, as shown by Figure 1.1. The customer need fulfillment is high because the eBLOCK improves the quality of education.
Figure 1.1 Types of Product innovations
Customer Need Fulfillment LOW HIGH Newness of Technology LOW Incremental Innovation Market Breakthroug HIGH Technological Breakthrough Radical Innovation
Phillips can use of the market breakthrough strategy to bring the eBLOCK to the market. The eBLOCK is a product which uses nearly no new technologies
A product can be divided into five customer-perceived (CPV) benefit levels. The product levels are core benefit, basic product, expected product, augmented product, and potential product. The five product levels are depicted below. Each level adds more customer-perceived value resulting in the final market offering.
The elementary level is called the core benefit. The core benefit is the benefit the costumer actually buys. The core benefit of the eBLOCK is that it provides a comfortable learning environment which is easy to use.
The second level is the basic product. The most basic “eBLOCK” allows students to make notes, make calculations, view presentations and documents, and construct and view their agenda. eBLOCK also includes Bluetooth and an USB input which allows the easy transfer of PowerPoint presentations or notes before lectures. Additional applications and expansion of the eBLOCK is possible at a cost or by buying a different model.
The third level of the CPV hierarchy is the expected product. This level is “a set of attributes and conditions buyers normally expect when they purchase this product (Kotler, Keller, Brady, Goodman, & Hansen, 2009, p. 506).” Students can expect a handy, easy to use, comprehensive learning product.
Next is the fourth level, augmented product. The augmented product of the “eBLOCK” is that it comes with repair and replacement services. If the product malfunctions or breaks one can bring it in for repairs or replacements.
The final product level is the potential product, which consists of all the potential transformations that a product or offering might go through in the future. Innovation, development, and modernization of the “eBLOCK” will continue as long as the product is in use. Furthermore, one can expand the basic “eBLOCK” with more advance and or new applications in the future. Also software updates will follow.
Another important attribute of the eBLOCK is that it is an eco-friendly product. No more wasting paper, ink, nor time, the eBLOCK has it all. Buying and using the eBLOCK is a simple way to begin making a positive impact. In the long run this green product will not only save trees, but also fill your wallet and ultimately can to some extent improve the overall quality of life.
The prototype of the eBLOCK is shown below. The different images show diverse layouts of how the functions of the product will look. It also has a short description of what is being shown.
The eBLOCK is a multifunctional product which allows customers to view PowerPoint Slides while writing notes on the other side of the screen.
written down on either square paper or plain paper. This also allows the customer to draw graphs in their notes when necessary.
Another feature of the eBLOCK is that it can be bought in diverse colors to suit the different tastes of customers.
Phillips should introduce a sub site for “eBLOCK”. This subside should include an introduction to the product, further specifications, a web shop and so forth. The product should also be available at all universities and HBO colleges in the Netherlands either through the school itself or through student associations. These different types of supply spots make it easy for students to acquire an eBLOCK.
Once, Phillips decides to expand to different models of the eBLOCK, it needs to look for different distribution point. These distribution points can be found throughout its own distribution channel. Phillips needs to do so as it at this moment will also have a new focus group.
The selling price of the eBLOCK will be at 150 euro’s for the most basic version. The price for the expanded version will lie much higher at approximately 250 euro’s which includes a higher profit margin.
Phillips should adjust the basic price to accommodate different target consumer. Price discrimination occurs when a company sells a product or service at two or more prices that do not reflect a proportional difference in costs (Kotler, Keller, Brady, Goodman, & Hansen, 2009, p. 601).
Phillips can make use of second-degree price discrimination when selling “eBLOCK” to universities and HBO colleges or to student associations. In, second-degree price discrimination, the seller charges less to buyers who buy a larger volume (Kotler, Keller, Brady, Goodman, & Hansen, 2009, p. 601). Selling at a lower price to these organizations allows them to pass on the price advantage to the students, who normally do not have a great deal of spendable income left to spend.
Product-form pricing is an example of third-degree price discrimination. In third- degree price discrimination, the seller charges different amounts to different classes of buyers (Kotler, Keller, Brady, Goodman, & Hansen, 2009, p. 601). Of course, different prices go along with different models. However, Phillips can use product-form pricing to increase its profit margin. Phillips can ask a higher price for an “eBLOCK” with new features as this product will probably attract different consumers. The price will lie higher than the cost incurred in adding new features, as previously explained. Nonetheless, these presumed wealthier consumers are more willing and able to buy the eBLOCK given the higher prices.
Phillips can also give student discounts by means of logging onto a site such as SURFsport.nl. This is a web shop where students and employees of universities and HBO colleges can get official software and other ICT-products at a very low price. Students can make use of this simple ordering system as it allows them to get a discount and home delivery. This will also makes the university, HBO College or student associations pass on their price advantage to students. If they don’t, students will not buy them at these organizations and thus they will be left with extra eBLOCK’s.
Advertising is defined as any paid form of non-personal presentation and promotion of ideas, goods or services by an identified sponsor (Kotler, Keller, Brady, Goodman, & Hansen, 2009, p. 861). Phillips can advertise the eBLOCK through posters, flyers and over the web. The university, HBO collages and student organizations also have to promote the product further after the eBLOCK has taken them into inventory. When new students apply to these organizations, they can be informed about the eBLOCK and asked if they opt to buy one.
Phillips can organize an information day for all the universities and HBO colleges to introduce them to their new product. A certain amount of students can subscribe to test the eBLOCK for a period of time. This will allow students to get to know the product and its functions, and word of mouth advertising could take place.
Once Phillips expands into a more developed version of the eBLOCK, it also has to take into consideration that it needs to use different promotional tools to reach its target group. To reach the potential professional users it can make use of business-promotion tools such as presenting the product at conventions and trade shows.
...(download the rest of the essay above)
About this essay:
If you use part of this page in your own work, you need to provide a citation, as follows:
Essay Sauce, marketing mix . Available from:<https://www.essaysauce.com/marketing-essays/marketing-mix/> [Accessed 06-04-24].
These Marketing essays have been submitted to us by students in order to help you with your studies.
* This essay may have been previously published on Essay.uk.com at an earlier date.
Essay Categories:
- Accounting essays
- Architecture essays
- Business essays
- Computer science essays
- Criminology essays
- Economics essays
- Education essays
- Engineering essays
- English language essays
- Environmental studies essays
- Essay examples
- Finance essays
- Geography essays
- Health essays
- History essays
- Hospitality and tourism essays
- Human rights essays
- Information technology essays
- International relations
- Leadership essays
- Linguistics essays
- Literature essays
- Management essays
- Marketing essays
- Mathematics essays
- Media essays
- Medicine essays
- Military essays
- Miscellaneous essays
- Music Essays
- Nursing essays
- Philosophy essays
- Photography and arts essays
- Politics essays
- Project management essays
- Psychology essays
- Religious studies and theology essays
- Sample essays
- Science essays
- Social work essays
- Sociology essays
- Sports essays
- Types of essay
- Zoology essays
7Ps of the Marketing Mix
A marketing strategy is a company’s battle plan in the struggle of market competition. However, its task is in effect to outline the way the company plans to act in the market, which is made in a general way. To realize the marketing strategy, a company develops a marketing mix, which is a set of marketing tools used to influence the demand for the product (Kotler et al 2008, p.49). The first formula of the marketing mix included four elements, so-called 4Ps, which were: Product, Price, Place, and Promotion. Gradually the notion of the marketing mix has been extended to 7Ps by adding such elements as Processes, Physical Evidence, ad People (Schneider & Bowen 1998, p. 213).
Product is a service produced by the company; it can be tangible or intangible, produced on a large scale or individually. Each product has its life cycle, which includes the stages of development, introduction, growth, maturity, and decline (Kurtz, MacKenzie & Snow 2009, p.341). Each of the stages requires specific marketing decisions. Another important point is a product’s competitive advantage, which also defines the product’s marketing: it helps to expand the company’s market segment and to increase the price.
Price is not simply the cost of the product for the buyer; it is a point of communication between the producer and the customer. Price defines the product’s position in the market, informing the client about its quality and originality. Depending on a good’s parameters and the life cycle stage, different pricing strategies can be used (Bangs 2002, p. 72): premium pricing (high quality or unique products), penetration pricing (lowering the price when entering the market), economy pricing, and price skimming (the product is new or has a strong competitive advantage). There are also some alternative approaches, such as psychological pricing ($99 instead of $100), optional product pricing (setting price for the additional services), etc (Armstrong et al 2009, p. 328).
The element of Place outlines the approach of the product’s distribution and includes the distribution chain which delivers the product from the manufacturer to the customer (Kotler et al 2008, p. 50). The product can be sold directly to the customer or the dealer; the shop can be physical or virtual. The place is defined according to the peculiarities of the product sold.
Promotion is a set of tools that help to communicate to the client, which is to attract his attention, provide information about the product, and stimulate the decision to buy. The company can use such tools as direct selling, personal selling, public relations, advertising, sponsorship, etc. As a rule, they are used in complex (p.51).
Schneider and Bowen emphasize the meaning of the last 3Ps: these factors help to overgrow the marketing of products and services and embrace marketing of the whole organization with its attributes, such as people, tangibles, etc. (1998, p. 213).
The component of People includes the company’s staff with its skills and knowledge. The staff which has appropriate interpersonal skills and attitude to the work, as well as the professional competence, creates an additional competitive advantage, becoming a face of the company.
Processes also make the company competitive, increasing the customers’ loyalty. They include efficient service delivery which meets the needs and requirements of the clients, for ex., preparing a burger the way a client wants (Strydom 2005, p. 196).
Physical Evidence implies taking care of the services’ performance which influences the judgments about the company. Providing a clean environment of the restaurant or comfortable accommodation for the college students, as well as the website and brochures about the company’s service or a logo at the ticket, are examples of this element (Strydom 2004, p. 197).
Some attempts to extend 7Ps to 9Ps take place (Dacko 2008, p. 335); however, the additional elements are disputable: for example, Packaging can be considered a separate element or be included in the category of the Product, and Professionalism can be combined with People.
- Armstrong, G et al 2009, Marketing: an introduction. Harlow, England, Financial Times Prentice Hall.
- Bangs, DH 2002, The market planning guide: creating a plan to successfully market your business, product, or service. Chicago, Dearborn Trade Pub.
- Dacko, SG 2008, The advanced dictionary of marketing: putting theory to use. Oxford; New York, Oxford University Press.
- Kotler, P et al 2008, Principles of marketing. Upper Saddle River, N.J., Pearson Prentice Hall.
- Kurtz, DL, MacKenzie, HF & Snow, K 2009, Contemporary marketing. Toronto, Nelson Education.
- Schneider, B & Bowen, DE 1998, Winning the service game. Boston, Mass., Harvard Business School Press.
- Strydom, J 2004, Introduction to marketing. Lansdowne, Cape Town, S.A., Juta.
Cite this paper
- Chicago (N-B)
- Chicago (A-D)
StudyCorgi. (2021, November 26). 7Ps of the Marketing Mix. https://studycorgi.com/7ps-of-the-marketing-mix/
"7Ps of the Marketing Mix." StudyCorgi , 26 Nov. 2021, studycorgi.com/7ps-of-the-marketing-mix/.
StudyCorgi . (2021) '7Ps of the Marketing Mix'. 26 November.
1. StudyCorgi . "7Ps of the Marketing Mix." November 26, 2021. https://studycorgi.com/7ps-of-the-marketing-mix/.
Bibliography
StudyCorgi . "7Ps of the Marketing Mix." November 26, 2021. https://studycorgi.com/7ps-of-the-marketing-mix/.
StudyCorgi . 2021. "7Ps of the Marketing Mix." November 26, 2021. https://studycorgi.com/7ps-of-the-marketing-mix/.
This paper, “7Ps of the Marketing Mix”, was written and voluntary submitted to our free essay database by a straight-A student. Please ensure you properly reference the paper if you're using it to write your assignment.
Before publication, the StudyCorgi editorial team proofread and checked the paper to make sure it meets the highest standards in terms of grammar, punctuation, style, fact accuracy, copyright issues, and inclusive language. Last updated: November 26, 2021 .
If you are the author of this paper and no longer wish to have it published on StudyCorgi, request the removal . Please use the “ Donate your paper ” form to submit an essay.

IMAGES
VIDEO
COMMENTS
The success of a marketing strategy and subsequent marketing activities is judged by the increase in the amount of sales generated from the marketing activity (Marian, 2010). This essay presents and explains the four elements of marketing mix; Product, Pricing, Promotion and Place. The Coca cola Company will be analyzed in this essay.
Marketing Mix, Essay Example. HIRE A WRITER! You are free to use it as an inspiration or a source for your own work. Marketing decisions made by a company when shaping a suitable proposition for the potential customer can be organized into four major groups. These are Product, Price, Place and Promotion. The actual meaning of those four is ...
The marketing mix is a powerful paradigm that has been popular and dominant in marketing literature and practice since 1950s. It takes into account the different forces from the environment which drive the marketers to produce diverse mixes in devising marketing strategies.
Essay 1 # Meaning of Marketing Mix: Marketing mix might be defined as follows: Marketing mix is a unique combination of the basic ingredients of marketing viz. product, price, place (channels of distribution) and promotion-designed for the best realisation of the objectives of marketing management. (1) "Marketing mix refers to the ...
termed, the marketing mix, to wit; product, place, price, and promotion (365 Careers, 2017). measure of performance in each element. Colloquially, product, the first "P" or marketing r efers ...
Marketing Mix and Kindle Fire The Marketing Mix and Amazon's Kindle Fire The marketing mix is an important tool used by organizations and individuals as part of an effective marketing strategy. "Every marketing strategy is composed of the same four components: price, product, place, and promotion" (Colbert, Nantel, Bilodeau, & ich, 2001, pp. 19).
When perfected and synchronized, the core elements of a marketing mix provide a well-rounded approach to marketing strategy. 1. Product. Product refers to what your business is selling - product (s), service (s), or both. The bulk of the work in this element is typically done by product marketers or managers.
Introduction To Marketing Mix Marketing Essay. Marketing Mix is one of the most fundamental concepts in marketing management. For gaining clients and for revenue promotion, every business owner has to concentrate on four primary and three prolonged elements/components. The primary components of selling mix include product, pricing, distributive ...
The Marketing Mix Essay. Setting the right marketing mix for the product or service means that it including all of the important bases in marketing strategy. The marketing mix is generally established as the use and requirement of the 4P's which is describing the strategic position of a product in the marketplace.
Since the 50s, the key elements of the marketing mix have underdone many transformations as a result of emerging technologies and other changes to what is considered to be best practices. The Four Ps of a Marketing Mix: Since the 60s, the marketing mix has been associated with the "Four Ps", namely price, product, promotion and place: Price.
Marketing Mix The "Marketing Mix" is a term used to describe the combination of tactics used by a business to achieve its objectives by marketing its products or services effectively to the customer. It is also known as the 4 P's Product, Price, Promotion, and Place. The marketing mix is also known as the '7 P's', when you add people, process ...
A marketing plan is a significant part of the business plan which lists actions regarding marketing strategy and how a business will build credibility among customers and increase their profit by fulfilling sales target (Pulido Polo, 2018). A marketing plan gives an overview of the market with related ancillary factors like its objectives ...
In other words, marketing mix is a set of marketing tools through which the company seeks a way to influence the demand for goods or services; also it is a set of actions (strategies) that form the demand for certain goods at a specified price at a certain place with the use of certain promotion. Marketing Mix in Details.
The term marketing mix refers to the marketing activities used to create, communicate and deliver value to the customer (Kotler, Keller, Brady, Goodman, & Hansen, 2009, p. 866). The four main marketing mix variables, referred to as the 4Ps of marketing are: product, price, place, and promotion. Each element of the marketing mix will be discussed in relation to the Philips product eBLOCK.
the most important elements to increase the customer satisfaction (95.4%) and (93%) respectively. The promotion of product has a very good level to increase sells in the company (80.6% - 85%). The ...
The first formula of the marketing mix included four elements, so-called 4Ps, which were: Product, Price, Place, and Promotion. Gradually the notion of the marketing mix has been extended to 7Ps by adding such elements as Processes, Physical Evidence, ad People (Schneider & Bowen 1998, p. 213). Product is a service produced by the company; it ...
Decent Essays. 1065 Words. 5 Pages. Open Document. The marketing mix is primarily made up of four variables, and they are product, place, price, and promotion. These variables are often referred to as the four P's. Many sources often describe the marketing mix as a recipe used in developing a viable marketing strategy, with each ingredient ...
8. Disney Marketing Mix Example. Disney, one of the animation industry's leaders, boasts various characters like Mickey Mouse, Snow White, Cinderella, etc., that have made the company dear to the hearts of millions worldwide. Source.
Marketing mix is simply placing he right product in the right place for the right customer at the right price. There is no universal definition of what is right, it is instead a relative concept and depends on the nature of the product and organisation's skills and resources. Marketers must have a detailed idea of the business plan in order ...
According to the data analysis, the results show that all of marketing mix elements (product, price, place, and promotion) have a significant impact on achieving competitive advantage in the case of Al Buraimi's SMEs (p value for all marketing mix elements is less than α = .05). The most effective element when it comes to achieving ...
Good marketing mix can create value to customers and produce revenue to the organization. The growth of an organization is depends on the revenue earned. Increment of revenue earned represents success level of the organization. Thus, good marketing can let the customers to retain with the products and let them spend their money on the products ...
The marketing mix comprises of four key elements i.e., product, place, price, promotion. These elements are utilized to satisfy the target market and potential customers. These principles help the business to achieve its predefined goals. These principles are controlled and manipulated to meet the demands of end user or target customer.