Purdue Online Writing Lab Purdue OWL® College of Liberal Arts

Writing Essays in Art History

Welcome to the Purdue OWL
This page is brought to you by the OWL at Purdue University. When printing this page, you must include the entire legal notice.
Copyright ©1995-2018 by The Writing Lab & The OWL at Purdue and Purdue University. All rights reserved. This material may not be published, reproduced, broadcast, rewritten, or redistributed without permission. Use of this site constitutes acceptance of our terms and conditions of fair use.
These OWL resources provide guidance on typical genres with the art history discipline that may appear in professional settings or academic assignments, including museum catalog entries, museum title cards, art history analysis, notetaking, and art history exams.
Art History Analysis – Formal Analysis and Stylistic Analysis
Typically in an art history class the main essay students will need to write for a final paper or for an exam is a formal or stylistic analysis.
A formal analysis is just what it sounds like – you need to analyze the form of the artwork. This includes the individual design elements – composition, color, line, texture, scale, contrast, etc. Questions to consider in a formal analysis is how do all these elements come together to create this work of art? Think of formal analysis in relation to literature – authors give descriptions of characters or places through the written word. How does an artist convey this same information?
Organize your information and focus on each feature before moving onto the text – it is not ideal to discuss color and jump from line to then in the conclusion discuss color again. First summarize the overall appearance of the work of art – is this a painting? Does the artist use only dark colors? Why heavy brushstrokes? etc and then discuss details of the object – this specific animal is gray, the sky is missing a moon, etc. Again, it is best to be organized and focused in your writing – if you discuss the animals and then the individuals and go back to the animals you run the risk of making your writing unorganized and hard to read. It is also ideal to discuss the focal of the piece – what is in the center? What stands out the most in the piece or takes up most of the composition?
A stylistic approach can be described as an indicator of unique characteristics that analyzes and uses the formal elements (2-D: Line, color, value, shape and 3-D all of those and mass).The point of style is to see all the commonalities in a person’s works, such as the use of paint and brush strokes in Van Gogh’s work. Style can distinguish an artist’s work from others and within their own timeline, geographical regions, etc.
Methods & Theories To Consider:
Expressionism
Instructuralism
Postmodernism
Social Art History
Biographical Approach
Poststructuralism
Museum Studies
Visual Cultural Studies
Stylistic Analysis Example:
The following is a brief stylistic analysis of two Greek statues, an example of how style has changed because of the “essence of the age.” Over the years, sculptures of women started off as being plain and fully clothed with no distinct features, to the beautiful Venus/Aphrodite figures most people recognize today. In the mid-seventh century to the early fifth, life-sized standing marble statues of young women, often elaborately dress in gaily painted garments were created known as korai. The earliest korai is a Naxian women to Artemis. The statue wears a tight-fitted, belted peplos, giving the body a very plain look. The earliest korai wore the simpler Dorian peplos, which was a heavy woolen garment. From about 530, most wear a thinner, more elaborate, and brightly painted Ionic linen and himation. A largely contrasting Greek statue to the korai is the Venus de Milo. The Venus from head to toe is six feet seven inches tall. Her hips suggest that she has had several children. Though her body shows to be heavy, she still seems to almost be weightless. Viewing the Venus de Milo, she changes from side to side. From her right side she seems almost like a pillar and her leg bears most of the weight. She seems be firmly planted into the earth, and since she is looking at the left, her big features such as her waist define her. The Venus de Milo had a band around her right bicep. She had earrings that were brutally stolen, ripping her ears away. Venus was noted for loving necklaces, so it is very possibly she would have had one. It is also possible she had a tiara and bracelets. Venus was normally defined as “golden,” so her hair would have been painted. Two statues in the same region, have throughout history, changed in their style.
Compare and Contrast Essay
Most introductory art history classes will ask students to write a compare and contrast essay about two pieces – examples include comparing and contrasting a medieval to a renaissance painting. It is always best to start with smaller comparisons between the two works of art such as the medium of the piece. Then the comparison can include attention to detail so use of color, subject matter, or iconography. Do the same for contrasting the two pieces – start small. After the foundation is set move on to the analysis and what these comparisons or contrasting material mean – ‘what is the bigger picture here?’ Consider why one artist would wish to show the same subject matter in a different way, how, when, etc are all questions to ask in the compare and contrast essay. If during an exam it would be best to quickly outline the points to make before tackling writing the essay.
Compare and Contrast Example:
Stele of Hammurabi from Susa (modern Shush, Iran), ca. 1792 – 1750 BCE, Basalt, height of stele approx. 7’ height of relief 28’
Stele, relief sculpture, Art as propaganda – Hammurabi shows that his law code is approved by the gods, depiction of land in background, Hammurabi on the same place of importance as the god, etc.
Top of this stele shows the relief image of Hammurabi receiving the law code from Shamash, god of justice, Code of Babylonian social law, only two figures shown, different area and time period, etc.
Stele of Naram-sin , Sippar Found at Susa c. 2220 - 2184 bce. Limestone, height 6'6"
Stele, relief sculpture, Example of propaganda because the ruler (like the Stele of Hammurabi) shows his power through divine authority, Naramsin is the main character due to his large size, depiction of land in background, etc.
Akkadian art, made of limestone, the stele commemorates a victory of Naramsin, multiple figures are shown specifically soldiers, different area and time period, etc.
Iconography
Regardless of what essay approach you take in class it is absolutely necessary to understand how to analyze the iconography of a work of art and to incorporate into your paper. Iconography is defined as subject matter, what the image means. For example, why do things such as a small dog in a painting in early Northern Renaissance paintings represent sexuality? Additionally, how can an individual perhaps identify these motifs that keep coming up?
The following is a list of symbols and their meaning in Marriage a la Mode by William Hogarth (1743) that is a series of six paintings that show the story of marriage in Hogarth’s eyes.
- Man has pockets turned out symbolizing he has lost money and was recently in a fight by the state of his clothes.
- Lap dog shows loyalty but sniffs at woman’s hat in the husband’s pocket showing sexual exploits.
- Black dot on husband’s neck believed to be symbol of syphilis.
- Mantel full of ugly Chinese porcelain statues symbolizing that the couple has no class.
- Butler had to go pay bills, you can tell this by the distasteful look on his face and that his pockets are stuffed with bills and papers.
- Card game just finished up, women has directions to game under foot, shows her easily cheating nature.
- Paintings of saints line a wall of the background room, isolated from the living, shows the couple’s complete disregard to faith and religion.
- The dangers of sexual excess are underscored in the Hograth by placing Cupid among ruins, foreshadowing the inevitable ruin of the marriage.
- Eventually the series (other five paintings) shows that the woman has an affair, the men duel and die, the woman hangs herself and the father takes her ring off her finger symbolizing the one thing he could salvage from the marriage.
Art History Writing Guide
I. Introduction II. Writing Assignments III. Discipline-Specific Strategies IV. Keep in Mind V. Appendix
Introduction
At the heart of every art history paper is a close visual analysis of at least one work of art. In art history you are building an argument about something visual. Depending on the assignment, this analysis may be the basis for an assignment or incorporated into a paper as support to contextualize an argument. To guide students in how to write an art history paper, the Art History Department suggests that you begin with a visual observation that leads to the development of an interpretive thesis/argument. The writing uses visual observations as evidence to support an argument about the art that is being analyzed.
Writing Assignments
You will be expected to write several different kinds of art history papers. They include:
- Close Visual Analysis Essays
- Close Visual Analysis in dialogue with scholarly essays
- Research Papers
Close Visual Analysis pieces are the most commonly written papers in an introductory art history course. You will have to look at a work of art and analyze it in its entirety. The analysis and discussion should provide a clearly articulated interpretation of the object. Your argument for this paper should be backed up with careful description and analysis of the visual evidence that led you to your conclusion.
Close Visual Analysis in dialogue with scholarly essays combines formal analysis with close textual analysis.
Research papers range from theoretic studies to critical histories. Based on library research, students are asked to synthesize analyses of the scholarship in relation to the work upon which it is based.
Discipline-Specific Strategies
As with all writing assignment, a close visual analysis is a process. The work you do before you actually start writing can be just as important as what you consider when writing up your analysis.
Conducting the analysis :
- Ask questions as you are studying the artwork. Consider, for example, how does each element of the artwork contribute to the work's overall meaning. How do you know? How do elements relate to each other? What effect is produced by their juxtaposition
- Use the criteria provided by your professor to complete your analysis. This criteria may include forms, space, composition, line, color, light, texture, physical characteristics, and expressive content.
Writing the analysis:
- Develop a strong interpretive thesis about what you think is the overall effect or meaning of the image.
- Ground your argument in direct and specific references to the work of art itself.
- Describe the image in specific terms and with the criteria that you used for the analysis. For example, a stray diagonal from the upper left corner leads the eye to...
- Create an introduction that sets the stage for your paper by briefly describing the image you are analyzing and by stating your thesis.
- Explain how the elements work together to create an overall effect. Try not to just list the elements, but rather explain how they lead to or support your analysis.
- Contextualize the image within a historical and cultural framework only when required for an assignment. Some assignments actually prefer that you do not do this. Remember not to rely on secondary sources for formal analysis. The goal is to see what in the image led to your analysis; therefore, you will not need secondary sources in this analysis. Be certain to show how each detail supports your argument.
- Include only the elements needed to explain and support your analysis. You do not need to include everything you saw since this excess information may detract from your main argument.
Keep in Mind
- An art history paper has an argument that needs to be supported with elements from the image being analyzed.
- Avoid making grand claims. For example, saying "The artist wanted..." is different from "The warm palette evokes..." The first phrasing necessitates proof of the artist's intent, as opposed to the effect of the image.
- Make sure that your paper isn't just description. You should choose details that illustrate your central ideas and further the purpose of your paper.
If you find you are still having trouble writing your art history paper, please speak to your professor, and feel free to make an appointment at the Writing Center. For further reading, see Sylvan Barnet's A Short Guide to Writing about Art , 5th edition.
Additional Site Navigation
Social media links, additional navigation links.
- Alumni Resources & Events
- Athletics & Wellness
- Campus Calendar
- Parent & Family Resources
Helpful Information
Dining hall hours, next trains to philadelphia, next trico shuttles.
Swarthmore Traditions
How to Plan Your Classes

The Swarthmore Bucket List

Search the website

ARTS - Herzberg: Writing Essays About Art
- Art History
- Current Artists and Events
- Local Art Venues
- Video and Image Resources
- Writing Essays About Art
- Citation Help
What is a Compare and Contrast Essay?
What is a compare / contrast essay.
In Art History and Appreciation, contrast / compare essays allow us to examine the features of two or more artworks.
- Comparison -- points out similarities in the two artworks
- Contrast -- points out the differences in the two artworks
Why would you want to write this type of essay?
- To inform your reader about characteristics of each art piece.
- To show a relationship between different works of art.
- To give your reader an insight into the process of artistic invention.
- Use your assignment sheet from your class to find specific characteristics that your professor wants you to compare.
How is Writing a Compare / Contrast Essay in Art History Different from Other Subjects?
You should use art vocabulary to describe your subjects..
- Find art terms in your textbook or an art glossary or dictionary
You should have an image of the works you are writing about in front of you while you are writing your essay.
- The images should be of high enough quality that you can see the small details of the works.
- You will use them when describing visual details of each art work.
Works of art are highly influenced by the culture, historical time period and movement in which they were created.
- You should gather information about these BEFORE you start writing your essay.
If you describe a characteristic of one piece of art, you must describe how the OTHER piece of art treats that characteristic.
Example: You are comparing a Greek amphora with a sculpture from the Tang Dynasty in China.

If you point out that the color palette of the amphora is limited to black, white and red, you must also write about the colors used in the horse sculpture.
Organizing Your Essay
Thesis statement.
The thesis for a comparison/contrast essay will present the subjects under consideration and indicate whether the focus will be on their similarities, on their differences, or both.
Thesis example using the amphora and horse sculpture -- Differences:
While they are both made from clay, the Greek amphora and the Tang Dynasty horse served completely different functions in their respective cultures.
Thesis example -- Similarities:
Ancient Greek and Tang Dynasty ceramics have more in common than most people realize.
Thesis example -- Both:
The Greek amphora and the Tang Dynasty horse were used in different ways in different parts of the world, but they have similarities that may not be apparent to the casual viewer.
Visualizing a Compare & Contrast Essay:
Introduction (1-2 paragraphs) .
- Creates interest in your essay
- Introduces the two art works that you will be comparing.
- States your thesis, which mentions the art works you are considering and may indicate whether the focus will be on similarities, differences, or both.
Body paragraphs
- Make and explain a point about the first subject and then about the second subject
- Example: While both superheroes fight crime, their motivation is vastly different. Superman is an idealist, who fights for justice …… while Batman is out for vengeance.
Conclusion (1-2 paragraphs)
- Provides a satisfying finish
- Leaves your reader with a strong final impression.
Downloadable Essay Guide
- How to Write a Compare and Contrast Essay in Art History Downloadable version of the description on this LibGuide.
Questions to Ask Yourself After You Have Finished Your Essay
- Are all the important points of comparison or contrast included and explained in enough detail?
- Have you addressed all points that your professor specified in your assignment?
- Do you use transitions to connect your arguments so that your essay flows into a coherent whole, rather than just a random collection of statements?
- Do your arguments support your thesis statement?
Art Terminology
- British National Gallery: Art Glossary Includes entries on artists, art movements, techniques, etc.
Lee College Writing Center
Writing Center tutors can help you with any writing assignment for any class from the time you receive the assignment instructions until you turn it in, including:
- Brainstorming ideas
- MLA / APA formats
- Grammar and paragraph unity
- Thesis statements
- Second set of eyes before turning in
Contact a tutor:
- Phone: 281-425-6534
- Email: w [email protected]
- Schedule a web appointment: https://lee.mywconline.com/
Other Compare / Contrast Writing Resources
- Southwestern University Guide for Writing About Art This easy to follow guide explains the basic of writing an art history paper.
- Purdue Online Writing Center: writing essays in art history Describes how to write an art history Compare and Contrast paper.
- Stanford University: a brief guide to writing in art history See page 24 of this document for an explanation of how to write a compare and contrast essay in art history.
- Duke University: writing about paintings Downloadable handout provides an overview of areas you should cover when you write about paintings, including a list of questions your essay should answer.
- << Previous: Video and Image Resources
- Next: Citation Help >>
- Last Updated: Jun 19, 2023 4:30 PM
- URL: https://lee.libguides.com/Arts_Herzberg

Heilbrunn Timeline of Art History
Discover the story of art and global culture through The Met collection. Funded by the Heilbrunn Foundation, New Tamarind Foundation, and Zodiac Fund.
Explore more than 1,000 essays on a wide range of topics, including artists, materials, movements, and themes.

Andean Textiles
For centuries prior to the Spanish Conquest, Andean textiles were used to express status and identity.

Artists of the Saqqakhana Movement
Inspired by Iranian popular culture, these artists celebrated the lives of the underprivileged masses.
Works of Art
Browse a selection of more than 8,000 works from the collection.

Creation of the World and the Expulsion from Paradise
Giovanni di Paolo

Untitled Film Still #21
Cindy Sherman
Chronologies
Trace the global evolution of art and culture across millennia.

Ancient Greece, 1000 B.C.–1 A.D.

China, 500–1000 A.D.

Eastern Africa, 1600–1800 A.D.
Discover connections across time and cultures through more than 150 essays and 800 works of art in this book inspired by the Timeline .

The Writing Place
Resources – how to write an art history paper, introduction to the topic.
There are many different types of assignments you might be asked to do in an art history class. The most common are a formal analysis and a stylistic analysis. Stylistic analyses often involve offering a comparison between two different works. One of the challenges of art history writing is that it requires a vocabulary to describe what you see when you look at a painting, drawing, sculpture or other media. This checklist is designed to explore questions that will help you write these types of art history papers.
Features of An Art History Analysis Paper
Features of a formal analysis paper.
This type of paper involves looking at compositional elements of an object such as color, line, medium, scale, and texture. The goal of this kind of assignment it to demonstrate how these elements work together to produce the whole art object. When writing a formal analysis, ask yourself:
- What is the first element of the work that the audience’s eye captures?
- What materials were used to create the object?
- What colors and textures did the artist employ?
- How do these function together to give the object its overall aesthetic look?
Tips on Formal Analysis
- Describe the piece as if your audience has not seen it.
- Be detailed.
- The primary focus should be on description rather than interpretation.
Features of a Stylistic / Comparative Analysis
Similar to a formal analysis, a stylistic analysis asks you to discuss a work in relation to its stylistic period (Impressionism, Fauvism, High Renaissance, etc.). These papers often involve a comparative element (such as comparing a statue from Early Antiquity to Late Antiquity). When writing a stylistic analysis, ask yourself:
- How does this work fit the style of its historical period? How does it depart from the typical style?
- What is the social and historical context of the work? When was it completed?
- Who was the artist? Who commissioned it? What does it depict?
- How is this work different from other works of the same subject matter?
- How have the conventions (formal elements) for this type of work changed over time?
Tips for Stylistic and Comparative Analysis
- In a comparison, make a list of similarities and differences between the two works. Try to establish what changes in the art world may account for the differences.
- Integrate discussions of formal elements into your stylistic analysis.
- This type of paper can involve more interpretation than a basic formal analysis.
- Focus on context and larger trends in art history.
A Quick Practice Exercise...
Practice - what is wrong with these sentences.
The key to writing a good art history paper involves relating the formal elements of a piece to its historical context. Can you spot the errors in these sentences? What would make the sentences better?
- “Courbet’s The Stone Breakers is a good painting because he uses texture.”
- “Duchamp’s work is in the Dada style while Dali’s is Surrealist.”
- “Pope Julius II commissioned the work.”
- “Gauguin uses color to draw in the viewer’s eye.”
Answers for Practice Sentences
- Better: “Courbet’s The Stone Breakers is a radical painting because the artist used a palette knife to create a rough texture on the surface.”
- Better: “The use of everyday objects in Duchamp’s work reflects the Dada style while Dali’s incorporation of absurd images into his work demonstrates a Surrealist style.”
- Better: “In 1505, Pope Julius II commissioned the sculpture for his tomb.”
- Better: “The first element a viewer notices is the bold blue of the sky in Gauguin’s painting.”
Adapted by Ann Bruton, with the help of Isaac Alpert, From:
The Writing Center at UNC Handouts ( http://writingcenter.unc.edu/handouts/art-history/ )
The Writing Center at Hamilton College ( http://www.hamilton.edu/writing/writing-resources/writing-an-art-history-paper )
Click here to return to the “Writing Place Resources” main page.

By Will Fenstermaker
June 14, 2017

There has never been a time when art critics held more power than during the second half of the twentieth century. Following the Second World War, with the relocation of the world’s artistic epicenter from Paris to New York, a different kind of war was waged in the pages of magazines across the country. As part of the larger “culture wars” of the mid-century, art critics began to take on greater influence than they’d ever held before. For a time, two critics in particular—who began as friends, and remained in the same social circles for much of their lives—set the stakes of the debates surrounding the maturation of American art that would continue for decades. The ideas about art outlined by Clement Greenberg and Harold Rosenberg are still debated today, and the extent to which they were debated in the past has shaped entire movements of the arts. Below are ten works of criticism through which one can trace the mainstreaming of Clement Greenberg’s formalist theory, and how its dismantling led us into institutional critique and conceptual art today.
The American Action Painters
Harold Rosenberg

Harold Rosenberg, a poet who came to art through his involvement with the Artist’s Union and the WPA, was introduced to Jean-Paul Sartre as the “first American existentialist.” Soon, Rosenberg became a contributor to Sartre’s publication in France, for which he first drafted his influential essay. However, when Sartre supported Soviet aggression against Korea, Rosenberg brought his essay to Elaine de Kooning , then the editor of ARTnews , who ran “The American Action Painters” in December, 1952.
RELATED: What Did Harold Rosenberg Do? An Introduction to the Champion of “Action Painting”
Rosenberg’s essay on the emerging school of American Painters omitted particular names—because they’d have been unfamiliar to its original French audience—but it was nonetheless extraordinarily influential for the burgeoning scene of post-WWII American artists. Jackson Pollock claimed to be the influence of “action painting,” despite Rosenberg’s rumored lack of respect for the artist because Pollock wasn’t particularly well-read. Influenced by Marxist theory and French existentialism, Rosenberg conceives of a painting as an “arena,” in which the artist acts upon, wrestles, or otherwise engages with the canvas, in what ultimately amounts to an expressive record of a struggle. “What was to go on the canvas,” Rosenberg wrote, “was not a picture but an event.”
Notable Quote
Weak mysticism, the “Christian Science” side of the new movement, tends … toward easy painting—never so many unearned masterpieces! Works of this sort lack the dialectical tension of a genuine act, associated with risk and will. When a tube of paint is squeezed by the Absolute, the result can only be a Success. The painter need keep himself on hand solely to collect the benefits of an endless series of strokes of luck. His gesture completes itself without arousing either an opposing movement within itself nor the desire in the artist to make the act more fully his own. Satisfied with wonders that remain safely inside the canvas, the artist accepts the permanence of the commonplace and decorates it with his own daily annihilation. The result is an apocalyptic wallpaper.
‘American-Type’ Painting
Clement Greenberg

Throughout the preceding decade, Clement Greenberg, also a former poet, had established a reputation as a leftist critic through his writings with The Partisan Review —a publication run by the John Reed Club, a New York City-centered organization affiliated with the American Communist Party—and his time as an art critic with The Nation . In 1955, The Partisan Review published Greenberg’s “‘American-Type’ Painting,” in which the critic defined the now-ubiquitous term “abstract expressionism.”
RELATED: What Did Clement Greenberg Do? A Primer on the Powerful AbEx Theorist’s Key Ideas
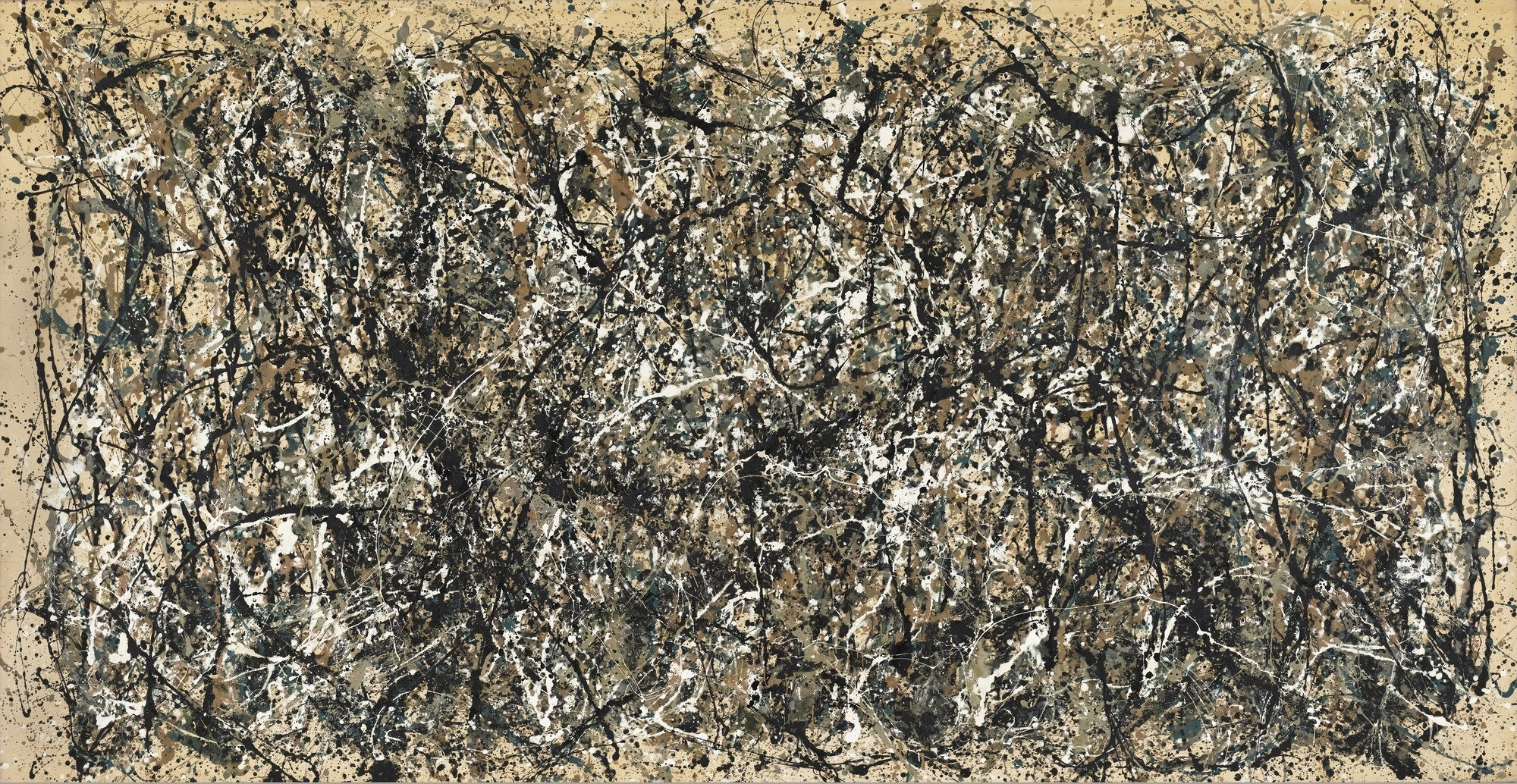
In contrast to Rosenberg’s conception of painting as a performative act, Greenberg’s theory, influenced by Clive Bell and T. S. Eliot, was essentially a formal one—in fact, it eventually evolved into what would be called “formalism.” Greenberg argued that the evolution of painting was one of historical determinacy—that ever since the Renaissance, pictures moved toward flatness, and the painted line moved away from representation. Henri Matisse and Pablo Picasso were two of the landmarks of this view. Pollock, who exhibited his drip paintings in 1951, freeing the line from figuration, was for Greenberg the pinnacle of American Modernism, the most important artist since Picasso. (Pollock’s paintings exhibited in 1954, with which he returned to semi-representational form, were regarded by Greenberg as a regression. This lead him to adopt Barnett Newman as his new poster-boy, despite the artist’s possessing vastly different ideas on the nature of painting. For one, Greenberg mostly ignored the Biblical titles of Newman’s paintings.)
Greenberg’s formalist theories were immensely influential over the subsequent decades. Artforum in particular grew into a locus for formalist discourse, which had the early effect of providing an aesthetic toolkit divorced from politic. Certain curators of the Museum of Modern Art, particularly William Rubin, Kirk Varnedoe, and to an extent Alfred Barr are credited for steering the museum in an essentially formalist direction. Some painters, such as Frank Stella , Helen Frankenthaler , and Kenneth Noland, had even been accused of illustrating Greenberg’s theories (and those of Michael Fried, a prominent Greenbergian disciple) in attempt to embody the theory, which was restrictive in its failure to account for narrative content, figuration, identity, politics, and more. In addition, Greenberg’s theories proved well-suited for a burgeoning art market, which found connoisseurship an easy sell. (As the writer Mary McCarthy said, “You can’t hang an event on your wall.”) In fact, the dominance of the term “abstract expressionism” over “action painting,” which seemed more applicable to Pollock and Willem de Kooning than any other members of the New York School, is emblematic of the influence of formalist discourse.
The justification for the term, “abstract expressionist,” lies in the fact that most of the painters covered by it took their lead from German, Russian, or Jewish expressionism in breaking away from late Cubist abstract art. But they all started from French painting, for their fundamental sense of style from it, and still maintain some sort of continuity with it. Not least of all, they got from it their most vivid notion of an ambitious, major art, and of the general direction in which it had to go in their time.
Barbara Rose

Like many critics in the 1950s and 60s, Barbara Rose had clearly staked her allegiance to one camp or the other. She was, firmly, a formalist, and along with Fried and Rosalind Krauss is largely credited with expanding the theory beyond abstract expressionist painting. By 1965, however, Rose recognized a limitation of the theory as outlined by Greenberg—that it was reductionist and only capable of account for a certain style of painting, and not much at all in other mediums.
RELATED: The Intellectual Origins Of Minimalism
In “ABC Art,” published in Art in America where Rose was a contributing editor, Rose opens up formalism to encompass sculpture, which Greenberg was largely unable to account for. The simple idea that art moves toward flatness and abstraction leads, for Rose, into Minimalism, and “ABC Art” is often considered the first landmark essay on Minimalist art. By linking the Minimalist sculptures of artists like Donald Judd to the Russian supremacist paintings of Kasimir Malevich and readymades of Duchamp, she extends the determinist history that formalism relies on into sculpture and movements beyond abstract expressionism.
I do not agree with critic Michael Fried’s view that Duchamp, at any rate, was a failed Cubist. Rather, the inevitability of a logical evolution toward a reductive art was obvious to them already. For Malevich, the poetic Slav, this realization forced a turning inward toward an inspirational mysticism, whereas for Duchamp, the rational Frenchman, it meant a fatigue so enervating that finally the wish to paint at all was killed. Both the yearnings of Malevich’s Slavic soul and the deductions of Duchamp’s rationalist mind led both men ultimately to reject and exclude from their work many of the most cherished premises of Western art in favor of an art stripped to its bare, irreducible minimum.
How I Spent My Summer Vacation
Philip Leider

Despite the rhetorical tendency to suggest the social upheaval of the '60s ended with the actual decade, 1970 remained a year of unrest. And Artforum was still the locus of formalist criticism, which was proving increasingly unable to account for art that contributed to larger cultural movements, like Civil Rights, women’s liberation, anti-war protests, and more. (Tellingly, The Partisan Review , which birthed formalism, had by then distanced itself from its communist associations and, as an editorial body, was supportive of American Interventionism in Vietnam. Greenberg was a vocal hawk.) Subtitled “Art and Politics in Nevada, Berkeley, San Francisco, and Utah,” the editor’s note to the September 1970 issue of Artforum , written by Philip Leider, ostensibly recounts a road trip undertaken with Richard Serra and Abbie Hoffman to see Michael Heizer’s Double Negative in the Nevada desert.
RELATED: A City of Art in the Desert: Behind Michael Heizer’s Monumental Visions for Nevada
However, the essay is also an account of an onsetting disillusion with formalism, which Leider found left him woefully unequipped to process the protests that had erupted surrounding an exhibition of prints by Paul Wunderlich at the Phoenix Gallery in Berkeley. Wunderlich’s depictions of nude women were shown concurrently to an exhibition of drawings sold to raise money for Vietnamese orphans. The juxtaposition of a canonical, patriarchal form of representation and liberal posturing, to which the protestors objected, showcased the limitations of a methodology that placed the aesthetic elements of a picture plane far above the actual world in which it existed. Less than a year later, Leider stepped down as editor-in-chief and Artforum began to lose its emphasis on late Modernism.
I thought the women were probably with me—if they were, I was with them. I thought the women were picketing the show because it was reactionary art. To the women, [Piet] Mondrian must be a great revolutionary artist. Abstract art broke all of those chains thirty years ago! What is a Movement gallery showing dumb stuff like this for? But if it were just a matter of reactionary art , why would the women picket it? Why not? Women care as much about art as men do—maybe more. The question is, why weren’t the men right there with them?
Why Have There Been No Great Women Artists?
Linda Nochlin

While Artforum , in its early history, had established a reputation as a generator for formalist theory, ARTnews had followed a decidedly more Rosenberg-ian course, emphasizing art as a practice for investigating the world. The January 1971 issue of the magazine was dedicated to “Women’s Liberation, Woman Artists, and Art History” and included an iconoclastic essay by Linda Nochlin titled “Why Have There Been No Great Women Artists?”
RELATED: An Introduction to Feminist Art
Nochlin notes that it’s tempting to answer the question “why have there been no great women artists?” by listing examples of those overlooked by critical and institutional organizations (a labor that Nochlin admits has great merit). However, she notes, “by attempting to answer it, they tacitly reinforce its negative implications,” namely that women are intrinsically less capable of achieving artistic merit than men. Instead, Nochlin’s essay functions as a critique of art institutions, beginning with European salons, which were structured in such a way as to deter women from rising to the highest echelons. Nochlin’s essay is considered the beginning of modern feminist art history and a textbook example of institutional critique.
There are no women equivalents for Michelangelo or Rembrandt, Delacroix or Cézanne, Picasso or Matisse, or even in very recent times, for de Kooning or Warhol, any more than there are black American equivalents for the same. If there actually were large numbers of “hidden” great women artists, or if there really should be different standards for women’s art as opposed to men’s—and one can’t have it both ways—then what are feminists fighting for? If women have in fact achieved the same status as men in the arts, then the status quo is fine as it is. But in actuality, as we all know, things as they are and as they have been, in the arts as in a hundred other areas, are stultifying, oppressive, and discouraging to all those, women among them, who did not have the good fortune to be born white, preferably middle class and above all, male. The fault lies not in our stars, our hormones, our menstrual cycles, or our empty internal spaces, but in our institutions and our education.
Doctor, Lawyer, Indian Chief
Thomas McEvilley
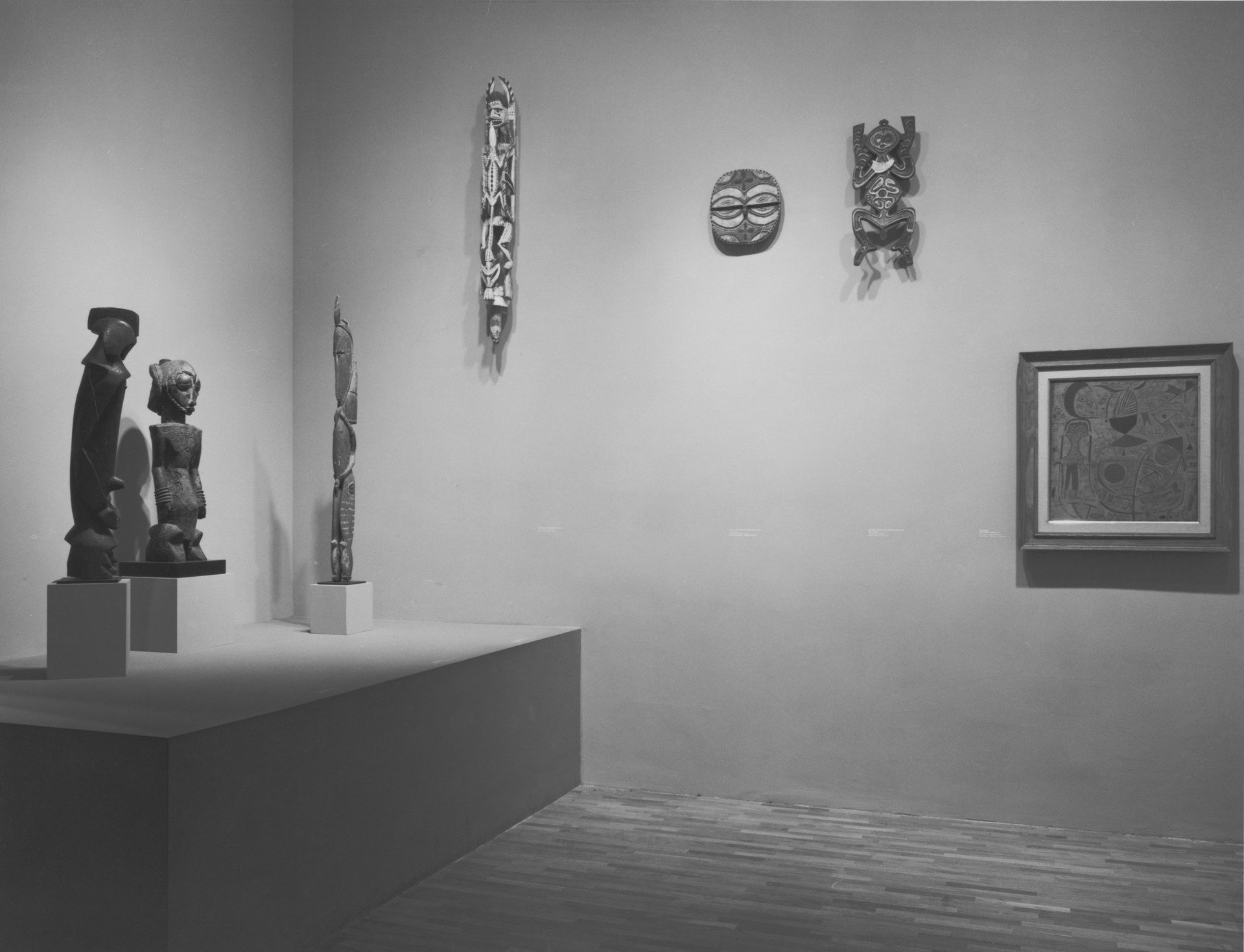

One of the many extrapolations of Nochlin’s essay is that contemporary museum institutions continue to reflect the gendered and racist biases of preceding centuries by reinforcing the supremacy of specific master artists. In a 1984 Artforum review, Thomas McEvilley, a classicist new to the world of contemporary art, made the case that the Museum of Modern Art in New York served as an exclusionary temple to certain high-minded Modernists—namely, Picasso, Matisse, and Pollock—who, in fact, took many of their innovations from native cultures.
RELATED: MoMA Curator Laura Hoptman on How to Tell a Good Painting From a “Bogus” Painting
In 1984, MoMA organized a blockbuster exhibition. Curated by William Rubin and Kirk Varnedoe, both of whom were avowed formalists, “‘Primitivism’ in 20th Century Art: Affinity of the Tribal and the Modern” collected works by European painters like Paul Gaugin and Picasso with cultural artifacts from Zaire, arctic communities, and elsewhere. McEvilley takes aim at the “the absolutist view of formalist Modernism” in which MoMA is rooted. He argues that the removal tribal artifacts from their contexts (for example, many were ritual items intended for ceremonies, not display) and placement of them, unattributed, near works by European artists, censors the cultural contributions of non-Western civilizations in deference to an idealized European genius.
The fact that the primitive “looks like” the Modern is interpreted as validating the Modern by showing that its values are universal, while at the same time projecting it—and with it MoMA—into the future as a permanent canon. A counter view is possible: that primitivism on the contrary invalidates Modernism by showing it to be derivative and subject to external causation. At one level this show undertakes precisely to coopt that question by answering it before it has really been asked, and by burying it under a mass of information.
Please Wait By the Coatroom
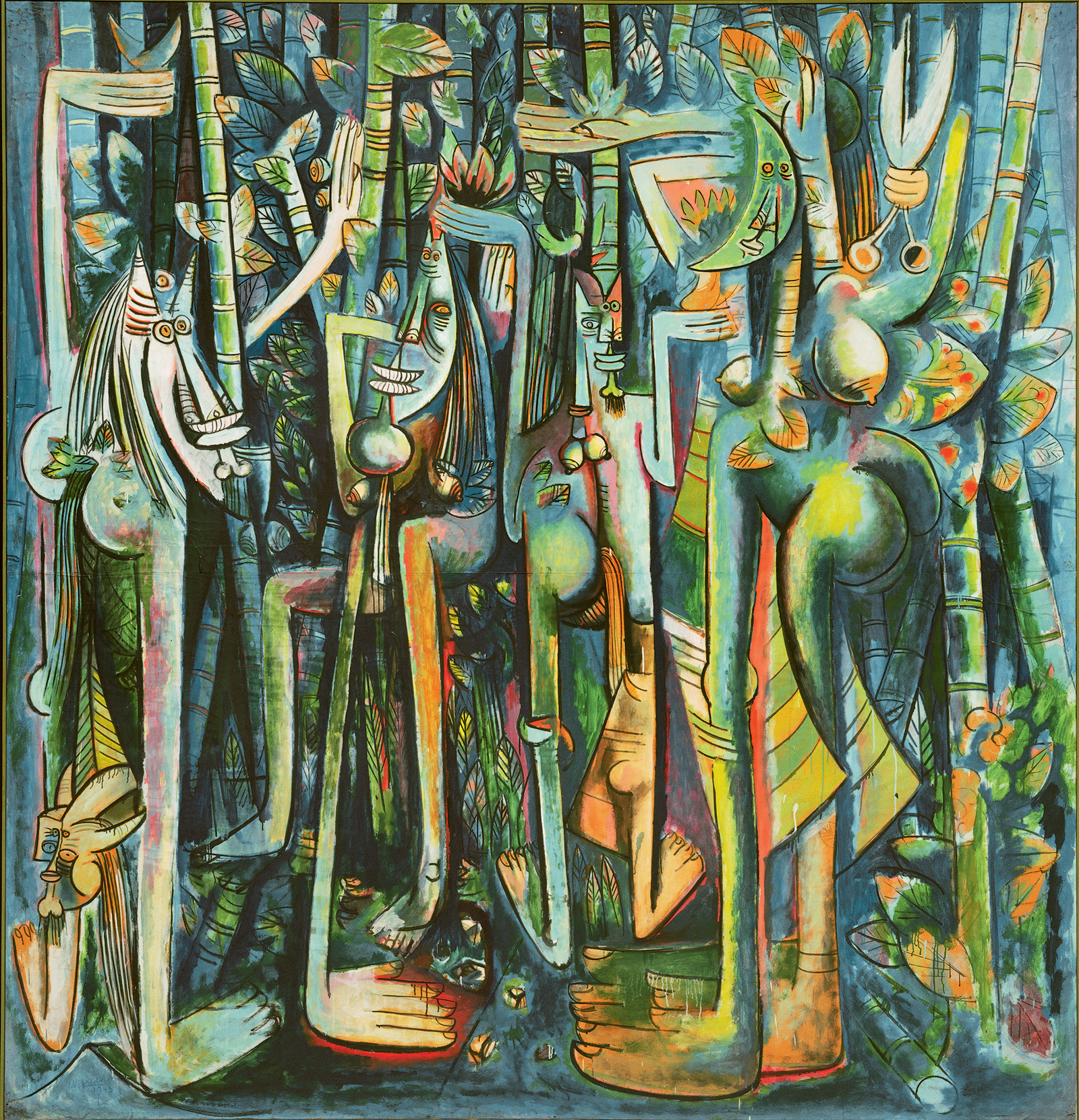

Not content to let MoMA and the last vestiges of formalism off the hook yet, John Yau wrote in 1988 an essay on Wifredo Lam, a Cuban painter who lived and worked in Paris among Picasso, Matisse, Georges Braque, and others. Noting Lam’s many influences—his Afro-Cuban mother, Chinese father, and Yoruba godmother—Yau laments the placement of Lam’s The Jungle near the coatroom in the Museum of Modern Art, as opposed to within the Modernist galleries several floors above. The painting was accompanied by a brief entry written by former curator William Rubin, who, Yau argues, adopted Greenberg’s theories because they endowed him with “a connoisseur’s lens with which one can scan all art.”
RELATED: From Cuba With Love: Artist Bill Claps on the Island’s DIY Art Scene
Here, as with with McEvilley’s essay, Yau illustrates how formalism, as adapted by museum institutions, became a (perhaps unintentional) method for reinforcing the exclusionary framework that Nochlin argued excluded women and black artists for centuries.
Rubin sees in Lam only what is in his own eyes: colorless or white artists. For Lam to have achieved the status of unique individual, he would have had to successfully adapt to the conditions of imprisonment (the aesthetic standards of a fixed tradition) Rubin and others both construct and watch over. To enter this prison, which takes the alluring form of museums, art history textbooks, galleries, and magazines, an individual must suppress his cultural differences and become a colorless ghost. The bind every hybrid American artist finds themselves in is this: should they try and deal with the constantly changing polymorphous conditions effecting identity, tradition, and reality? Or should they assimilate into the mainstream art world by focusing on approved-of aesthetic issues? Lam’s response to this bind sets an important precedent. Instead of assimilating, Lam infiltrates the syntactical rules of “the exploiters” with his own specific language. He becomes, as he says, “a Trojan horse.”
Black Culture and Postmodernism
Cornel West
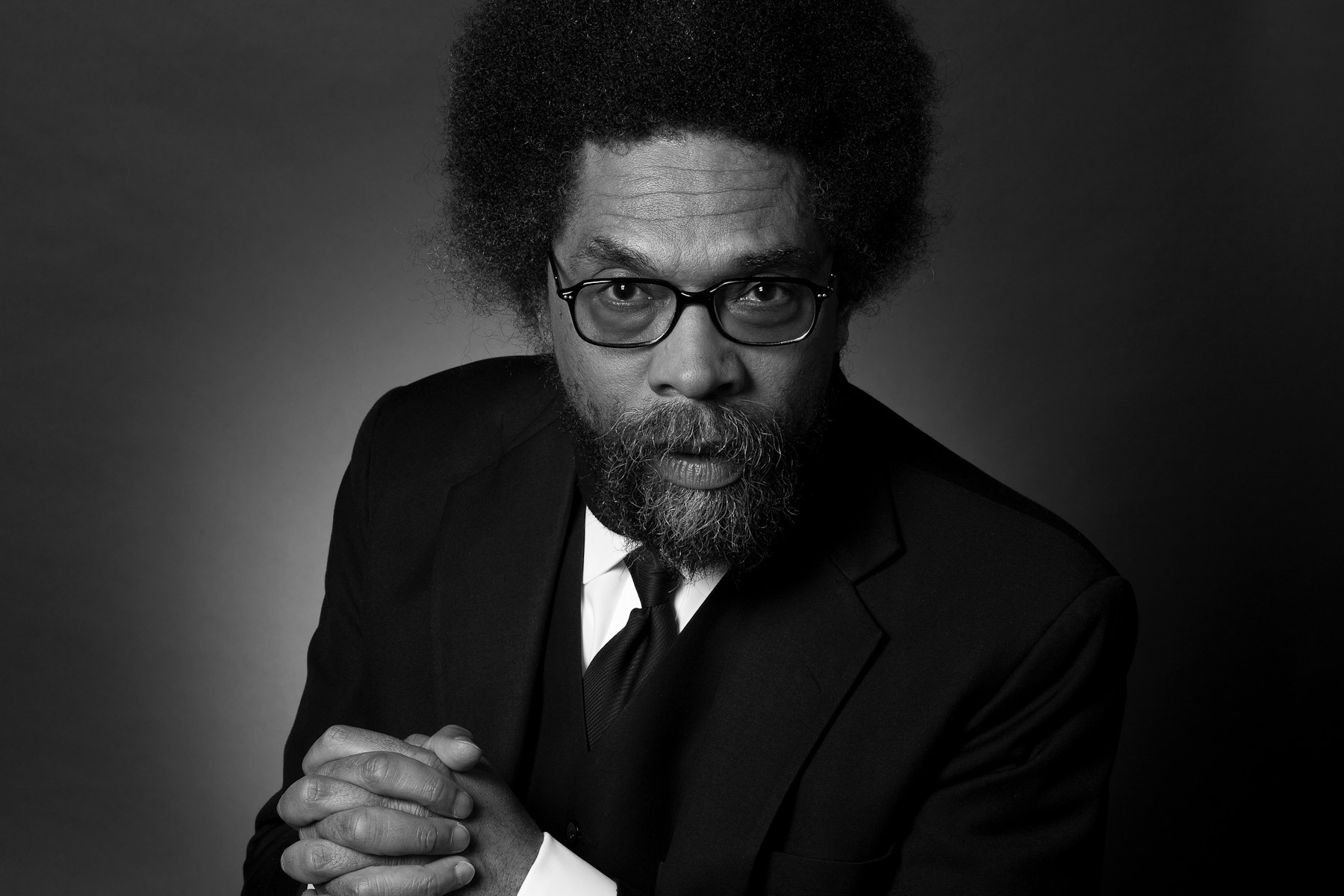

The opening up of cultural discourse did not mean that it immediately made room for voices of all dimensions. Cornel West notes as much in his 1989 essay “Black Culture and Postmodernism,” in which he argues that postmodernism, much like Modernism before it, remains primarily ahistorical, which makes it difficult for “oppressed peoples to exercise their opposition to hierarchies of power.” West’s position is that the proliferation of theory and criticism that accompanied the rise of postmodernism provided mechanisms by which black culture could “be conversant with and, to a degree, participants in the debate.” Without their voices, postmodernism would remain yet another exclusionary movements.
RELATED: Kerry James Marshall on Painting Blackness as a Noun Vs. Verb
As the consumption cycle of advanced multinational corporate capitalism was sped up in order to sustain the production of luxury goods, cultural production became more and more mass-commodity production. The stress here is not simply on the new and fashionable but also on the exotic and primitive. Black cultural products have historically served as a major source for European and Euro-American exotic interests—interests that issue from a healthy critique of the mechanistic, puritanical, utilitarian, and productivity aspects of modern life.
Minimalism and the Rhetoric of Power
Anna C. Chave

In recent years, formalist analysis has been deployed as a single tool within a more varied approach to art. Its methodology—that of analyzing a picture as an isolated phenomena—remains prevalent, and has its uses. Yet, many of the works and movements that rose to prominence under formalist critics and curators, in no small part because of their institutional acceptance, have since become part of the rearguard rather than the vanguard.
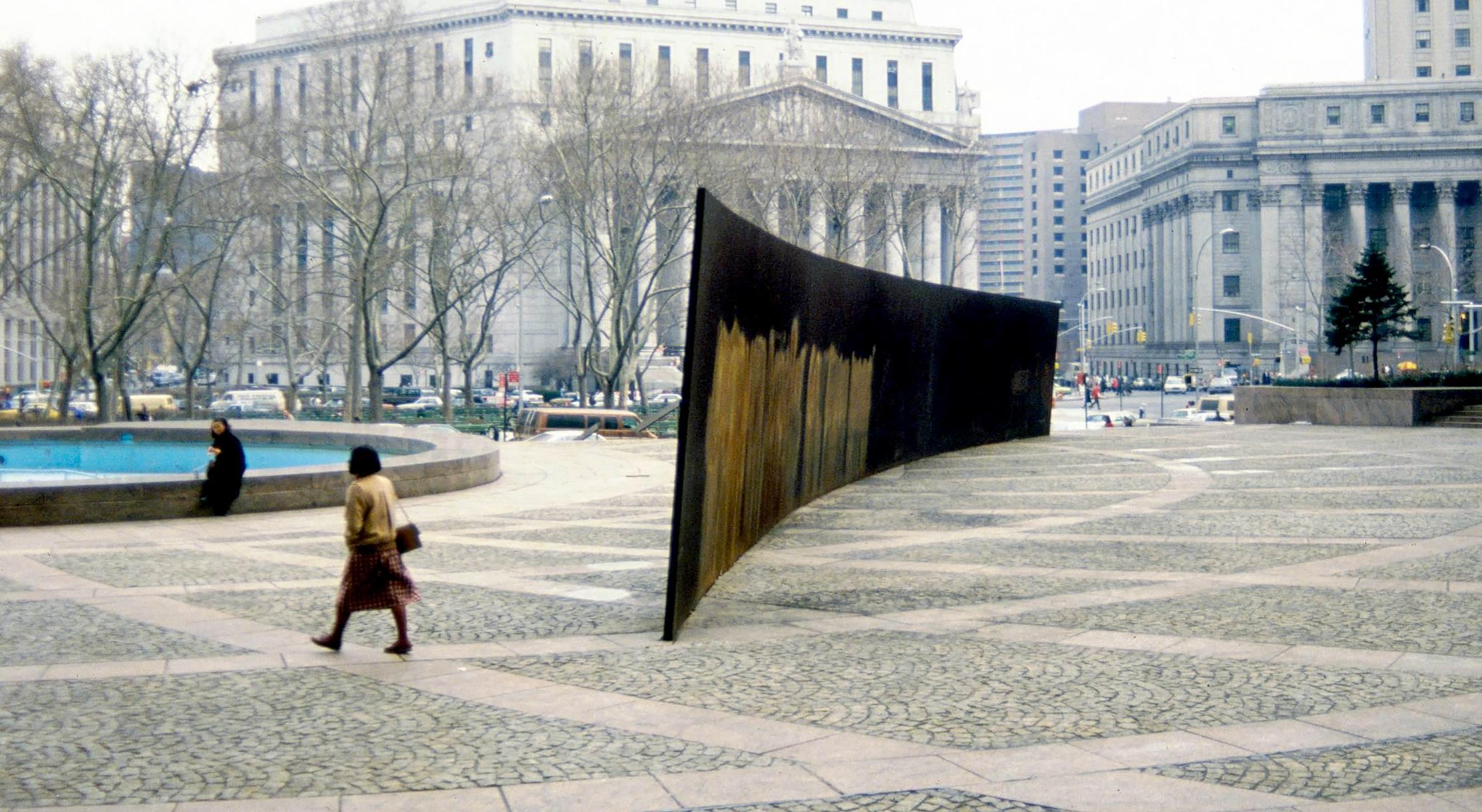
In a 1990 essay for Arts Magazine , Anna Chave analyzes how Minimalist sculpture possesses a “domineering, sometimes brutal rhetoric” that was aligned with “both the American military in Vietnam, and the police at home in the streets and on university campuses across the country.” In particular, Chave is concerned with the way Minimalist sculptures define themselves through a process of negation. Of particular relevance to Chave’s argument are the massive steel sculptures by Minimalist artist Richard Serra.
Tilted Arc was installed in Federal Plaza in lower Manhattan in 1981. Chave describes the work as a “mammoth, perilously tilted steel arc [that] formed a divisive barrier too tall to see over, and a protracted trip to walk around.” She writes, “it is more often the case with Serra that his work doesn’t simply exemplify aggression or domination, but acts it out.” Tilted Arc was so controversial upon its erecting that the General Services Administration, which commissioned the work, held hearings in response to petitions demanding the work be removed. Worth quoting at length, Chave writes:
A predictable defense of Serra’s work was mounted by critics, curators, dealers, collectors, and some fellow artists…. The principle arguments mustered on Serra’s behalf were old ones concerning the nature and function of the avant-garde…. What Rubin and Serra’s other supporters declined to ask is whether the sculptor really is, in the most meaningful sense of the term, an avant-garde artist. Being avant-garde implies being ahead of, outside, or against the dominant culture; proffering a vision that implicitly stands (at least when it is conceived) as a critique of entrenched forms and structures…. But Serra’s work is securely embedded within the system: when the brouhaha over Arc was at its height, he was enjoying a retrospective at the Museum of Modern Art…. [The defense’s] arguments locate Serra not with the vanguard but with the standing army or “status quo.” … More thoughtful, sensible, and eloquent testimony at the hearing came instead from some of the uncouth:
My name is Danny Katz and I work in this building as a clerk. My friend Vito told me this morning that I am a philistine. Despite that I am getting up to speak…. I don’t think this issue should be elevated into a dispute between the forces of ignorance and art, or art versus government. I really blame government less because it has long ago outgrown its human dimension. But from the artists I expected a lot more. I didn’t expect to hear them rely on the tired and dangerous reasoning that the government has made a deal, so let the rabble live with the steel because it’s a deal. That kind of mentality leads to wars. We had a deal with Vietnam. I didn’t expect to hear the arrogant position that art justifies interference with the simple joys of human activity in a plaza. It’s not a great plaza by international standards, but it is a small refuge and place of revival for people who ride to work in steel containers, work in sealed rooms, and breathe recirculated air all day. Is the purpose of art in public places to seal off a route of escape, to stress the absence of joy and hope? I can’t believe this was the artistic intention, yet to my sadness this for me has become the dominant effect of the work, and it’s all the fault of its position and location. I can accept anything in art, but I can’t accept physical assault and complete destruction of pathetic human activity. No work of art created with a contempt for ordinary humanity and without respect for the common element of human experience can be great. It will always lack dimension.
The terms Katz associated with Serra’s project include arrogance and contempt, assault, and destruction; he saw the Minimalist idiom, in other words, as continuous with the master discourse of our imperious and violent technocracy.
The End of Art
Arthur Danto
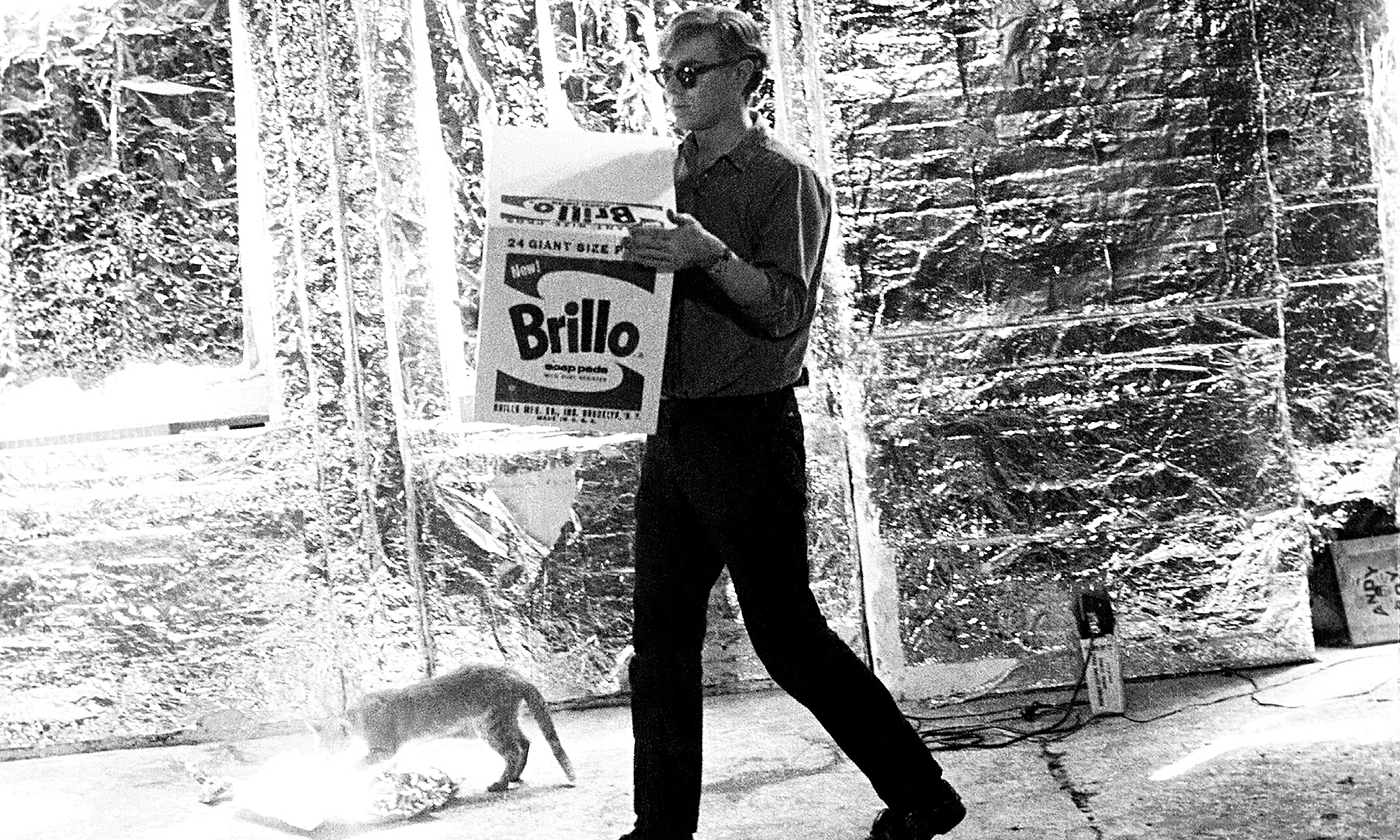

Like Greenberg, Arthur Danto was an art critic for The Nation . However, Danto was overtly critical of Greenberg’s ideology and the influence he wielded over Modern and contemporary art. Nor was he a follower of Harold Rosenberg, though they shared influences, among them the phenomenologist Maurice Merleau-Ponty. Danto’s chief contribution to contemporary art was his advancing of Pop Artists, particularly Andy Warhol and Roy Lichtenstein .
In “The End of Art” Danto argues that society at large determines and accepts art, which no longer progresses linearly, categorized by movements. Instead, viewers each possess a theory or two, which they use to interpret works, and art institutions are largely tasked with developing, testing, and modifying various interpretive methods. In this way, art differs little from philosophy. After decades of infighting regarding the proper way to interpret works of art, Danto essentially sanctioned each approach and the institutions that gave rise to them. He came to call this “pluralism.”
RELATED: What Was the Pictures Generation?
Similarly, in “Painting, Politics, and Post-Historical Art,” Danto makes the case for an armistice between formalism and the various theories that arose in opposition, noting that postmodern critics like Douglas Crimp in the 1980s, who positioned themselves against formalism, nonetheless adopted the same constrictive air, minus the revolutionary beginnings.
Modernist critical practice was out of phase with what was happening in the art world itself in the late 60s and through the 1970s. It remained the basis for most critical practice, especially on the part of the curatoriat, and the art-history professoriat as well, to the degree that it descended to criticism. It became the language of the museum panel, the catalog essay, the article in the art periodical. It was a daunting paradigm, and it was the counterpart in discourse to the “broadening of taste” which reduced art of all cultures and times to its formalist skeleton, and thus, as I phrased it, transformed every museum into a Museum of Modern Art, whatever that museum’s contents. It was the stable of the docent’s gallery talk and the art appreciation course—and it was replaced, not totally but massively, by the postmodernist discourse that was imported from Paris in the late 70s, in the texts of Michel Foucault, Jacques Derrida, Jean Baudrillard, Jean-François Lyotard, and Jacques Lacan, and of the French feminists Hélène Cixous and Luce Irigaray. That is the discourse [Douglas] Crimp internalizes, and it came to be lingua artspeak everywhere. Like modernist discourse, it applied to everything, so that there was room for deconstructive and “archeological” discussion of art of every period.
Editor’s Note: This list was drawn in part from a 2014 seminar taught by Debra Bricker Balken in the MFA program in Art Writing at the School of Visual Arts titled Critical Strategies: Late Modernism/Postmodernism. Additional sources can be found here , here , here (paywall), and here . Also relevant are reviews of the 2008 exhibition at the Jewish Museum, “Action/Abstraction: Pollock, de Kooning, and American Art, 1940–1976,” notably those by Roberta Smith , Peter Schjeldahl , and Martha Schwendener .

Related Articles
Know your critics.
Current Shows
Receive our award winning emails & enjoy 10% off your first purchase, thanks for signing up for our newsletter., that email has already been subscribed..
Now, personalize your account so you can discover more art you'll love.
a treasure trove of fine art from the world's most renowned artists, galleries, museums and cultural institutions. We offer exclusive works you can't find anywhere else.
through exclusive content featuring art news, collecting guides, and interviews with artists, dealers, collectors, curators and influencers.
authentic artworks from across the globe. Collecting with us means you're helping to sustain creative culture and supporting organizations that are making the world a better place.
with our art advisors for buying advice or to help you find the art that's perfect for you. We have the resources to find works that suit your needs.

INSIDER ACCESS TO THE WORLD'S BEST ART
Artspace offers you authentic, exclusive works from world-renowned artists, galleries, museums and cultural institutions. Collecting with us helps support creative culture while bringing you art news, interviews and access to global art resources.
COLLECT FROM 300+ GALLERIES & MUSEUMS
Sign in for personalized experiences, exclusive access to new works, special offers, invitations and features.
Collect the world's best
Sign up to view price and receive personalized experiences exclusive access to new works, special offers, invitations and features.
Thank you for signing up
Tailor your art, news & information to your preferences.
THANK YOU FOR SIGNING-UP TO ARTSPACE
Welcome to the world's premier online marketplace for fine art.
Enjoy 10% on your next purchase by using coupon code WELCOME10 at checkout.
THANK YOU FOR RETURNING TO ARTSPACE
The world's premier online marketplace for fine art.
Enjoy 10% on your next purchase by using coupon code PHAIDON10 at checkout.
Forgot your password?
Please enter your email below and we will send you a new password.
We've emailed you a new password. Sign In
Interested in Firstname Lastname?
To follow this artist and get updates on new work & exclusives, you must be signed into your Artspace account. Don't have one? Create one now.
You are now following first name last name
Interested in saving this work.
To save this work to your personal gallery and to access other features like this, you must be signed into your Artspace account.
prompt placeholder
The 10 Essays That Changed Art Criticism Forever
Share this article
Use this form to share great articles with your friends.
Enter your email
Enter your friend's email
Your message was sent
Thank you for sharing with your friends.
- Share on Facebook
- Share on Twitter
- Share on Pinterest
Your email has been submitted and a 10% off discount code sent to you. Next, personalize your Artspace experience by creating an account.
Please select the statement that best describes you:
- I am an existing collector.
- I am a new and aspiring collector.
Types of art that interest you
Select all that interest you:, partners you'd like to follow, enter or select all partners that interest you:.
Your preferences have been saved to your account. Update them at any time in your Preference Center
How it Works
How bidding works.
To place a bid, enter the maximum amount you are willing to pay for the work. Artspace will accept a bid at the next increment, and save any excess amount as a maximum bid. If you are outbid, we will continue bid on your behalf up to your maximum bid.
Bid Increments
Bidding increments increase at the following intervals:
- Below $400: $50
- Between $400 and $699: $100
- Between $700 and $1,499: $200
- Between $1,500 and $2,499: $300
- Between $2,500 and $4,999: $500
- Between $5,000 and $9,999: $1,000
- Between $10,000 and $19,999: $2,000
- Between $20,000 and $29,999: $3,000
- Between $30,000 and $49,999: $4,000
- Between $50,000 and $99,999: $5,000
- Above $100,000: $10,000
You will receive an email confirmation of your bid and when you are outbid.
If you are the winning bidder, you will be contacted 48 hours after of the close of the auction.
Maximum Bidding
Every bid submitted is treated as a maximum bid. You should always bid the maximum you are willing to spend for a work, though this does not necessarily mean you will pay that price. As the auction unfolds, we will increase your bid by increments to ensure you remain the highest bidder. If the winning amount is less than your maximum bid, you will pay the current increment. If your maximum bid no longer exceeds the current bid, you will receive an outbid notification email, and have the option to bid again.
In the case of multiple bidders placing the same maximum bid, the first person to place the maximum amount takes precedence as the highest bid until another bidder exceeds the maximum amount.
Buyer's Premium & Additional Charges
For Artspace Auctions winning bidders are charged a 15% Buyer's Premium on top of the hammer price. For Artspace Benefit Auctions, Buyer's Premiums are not applied. If they are, this will be clearly noted. Purchases made from all auctions, including benefit auctions, are subject to sales tax.
Winning bidders will be contacted within 48 hours to arrange shipping and to provide final price including commission, shipping, and taxes and duties when applicable. Promotion codes cannot be applied to auction works.
Auction Pre-Registration
Credit Card Validation
In order to secure a bid, please enter your credit card details below. We will not charge your card but only use it to validate your bid. We only need to validate your card once. You will be notified that you are the winning bidder before your card is charged, and you will have the option to change your payment method at that time.

Create an Artspace account
All our frames are manufactured in the USA, using eco-friendly & sustainably sourced engineered hardwood for durability and a uniform finish that is free of defects. Frames are available in Black or White Satin and Honey Pecan.
- White Satin
- Honey Pecan
- Black Satin
All prints are hinged to a conservation quality, acid-free and lignin-free Alpha Cellulose matboard, using an acid-free linen tape. The mat's surface paper is fade and bleed resistant and is attached to a conservation quality foam-core mounting board that will keep the work safe from deterioration over time. Artworks with a deckled or decorative edges will be floated on the matboard, with acrylic spacers to separate the art from the glazing. All mounting is fully reversible, without any potential damage to the art.
Acrylic Glazing
All of our frames come with picture quality .090 mm plexiglass, which blocks 66% of UV to prevent color fading from exposure to light, keeping your art protected for years to come. It is now considered the industry standard for artists, museums and galleries throughout the world.
For images up to 30" x 40"
- 1 1/4” wide, 3/4” deep, with a 2 1/2” wide mat.
- We generally leave 1/4” - 1/2” of paper showing around the image, to accommodate signatures and for visual appeal.
For sheet sizes larger than 30” x 40”
- Please contact an Artspace advisor for a custom quote.
Artists you'd like to follow
Enter or select all artists that interest you:.

Introduction to Art 30,000 years of human creativity

The history of art is a vast story of human creativity, a record of our passions and struggles from before written history through today. Obelisk is a free, online art history textbook, sharing the wild, tragic and inspiring stories of artists and their work from 30,000 BCE through Modern Art. Obelisk is designed for discovery, a cross-linked web of artworks, biographies and writings, a choose-your-own-adventure where every path leads you to something new and interesting.
Meet the artists , discover artwork , or explore the timeline . But if you'd like to learn more about how to look at and understand art, the next few pages describe the visual language of art, the ways we can understand it, and why art is important. So dig in!

Basic Composition Techniques
A few easy tips
The Elements of Art
Eight tools, infinite expression
The Value of Art
Why should we care about art?
By continuing to browse Obelisk you agree to our Cookie Policy

- University of Texas Libraries
Art and Art History
- How to Write About Art
- Overview Resources
- Find Art & Art History Books
- Find Art and Art History Articles
- Find Images
- Color Resources
- Collecting & Provenance This link opens in a new window
- Art Collections at UT
- Foundry @ FAL Information
- Professional Art Organizations
Write and Cite
- Cite Sources UT Austin Guide Learn more about what citations are and how to manage them. Includes information about citation tools like Noodle Tools and Zotero.
- UT Austin University Writing Center A resource for help with your writing. The Writing Center includes one on one consultations as well as classes.
- OWL Purdue - Chicago Style The OWL Purdue is a great resource for writing and citation help. Chicago Style is the preferred citation format for art history. The OWL also includes citation help for other styles include APA and MLA.
Writing Aids and Publication Manuals
Write about Art
- Last Updated: Oct 20, 2023 7:31 AM
- URL: https://guides.lib.utexas.edu/art

History of Art Essay Examples and Topics
Descriptive essay on art appreciation, two of shakespeare’s sonnets (18 and 55) analysis, italian and northern european renaissance comparison.
- Words: 1310
From Modernism to Postmodernism
Works of art.
- Words: 1256
Art and Literature Between the Two World Wars
Hatoum’s “light sentence” and the 20th-century art.
- Words: 2184
Difference Between Art and Useful Objects
Impressionism history.
- Words: 1707
The Colonial Trade and Slave Entrepreneurship
- Words: 1843
History of Art and Design
- Words: 1272
The Renaissance in Italy
Ancient greek vs. roman sculpture in the late classical period.
- Words: 1513
Effects of Globalization in the Contemporary Japanese Art
- Words: 1800
Introduction to Art, Renaissance and Baroque Art
How has technology influenced the creation of art, the classical period of greek art, definition of expressionism, art in “who the fuck is jackson pollock” documentary, italian and dutch renaissance art comparison, masaccio’s “holy trinity” and da vinci’s “last supper”, art, its definition, perception and functions.
- Words: 1127
Censorship and the Arts in the United States
- Words: 1411
Modern and Postmodern Art Scene in Malaysia
- Words: 8389
The Importance of Analysis of an Artwork’s Context
The national centre for popular music in sheffield.
- Words: 1692
Christian Influence on Roman Art
- Words: 2224
Impacts and Key Concepts of Impressionism
- Words: 1546
Color History and Spirituality
- Words: 2809
Deriving Meanings in the Works of Art
Analysis of “the tempest” picture by giorgione, the body in contemporary art.
- Words: 1212
Art and Freedom. History and Relationship
- Words: 2060
Illustrations After the American Civil War
Curator: definition and examples, the power of art.
- Words: 2503
Reformation and Development of the Arts
The influence of hokusai’s ukiyo-e on western art and impressionism, medicine buddha: the role of thangka art in tibetan buddhism.
- Words: 2282
History of Asian Exhibition: Analysis
Early, high, and german renaissance, good art can be ugly: applying aristotle’s aesthetics, the romantic era and relationships with nature.
- Words: 1105
Representation of People in Egyptian vs. Aegean Art
Visual research on the art nouveau style.
- Words: 2465
Expressionist Movement Art and Schoenberg Music
Non-western cultures’ commodification, the enigmatic animal images of prehistoric art, modern asian art exhibition in museum, high renaissance and baroque styles compared, the renaissance period and sandro botticelli, ancient works in the modern world: black panther origin, the return to the past in art analysis, the renaissance: donatello’s vs. michelangelo’s statue of david, the intersection of art and law, intricacies of the gupta empire’s religious art.
- Words: 1178
Religion in 16th- and 17th-Century European Art
- Words: 1161
What Can Art Be and What Is Its Purpose?
Analysis of hyperrealist and conceptual art, artworks from multiple cultures sharing one theme, patronage and the mechanical arts in the renaissance period, the man of sorrows engravings: analysis, the art of the paleolithic period, american art deco and mid-century modern designs.
- Words: 1182
Primitivism and the Avant-Garde
The search for truth: early photography, realism, and impressionism, the late baroque style in music, henri matisse’s art and life: analysis, pantheon and parthenon historical monuments.
- Words: 1213
Art, Its Functions and Purposes
Pteranodon heads pictures as museum objects, characteristics that qualify a piece as art, collections management policies.
- Words: 1950
The Technical and Artistic History of Porcelain
- Words: 1450
The Importance of Art in the Pandemic Times
Analytic views of art and art works, the best and worst examples of visual arts, how art, theater, and disney communicate history, michelangelo’s sculpture and webber’s music analysis, a change in art style after world war ii, expressionism in germany and austria, the art of ancient greece: the marble head of athena, late bronze age iib egyptian-style objects, researching and analysis of ecology in art.
- Words: 1135
The Louvre: John the Baptist Restoration
Workplace improvement recommendations with the help of art.
- Words: 1656
Neo-Classicism, Romanticism, and Rococo
The concept of modern art development, the art of mesoamerica, the extraordinary art of the dark ages documentary, heaven & hell in art of the renaissance, art: standard of ur, nefertiti bust and nok head, the nasrid palace and the court of lions, analysis of the art of return: lamassu, contemporary islamic art overview, late antique art overview, bergen dice and the sistine chapel ceiling, art history: the prehistoric aegean, ancient greece.
- Words: 1987
Understanding the Concept of ”Beauty” by Plato
Happiness in arts: happiness through virtue, first century capernaum: franciscans, home, inc. in boston: home, inc.’s role and impact.
- Words: 1011
History of Visual Communication
Living with art: from modern to postmodern, an analysis of pop art: origins, styles and legacies.
- Words: 4747
The History of Body Art
- Words: 1170
Time Capsule Assignment: Baroque & Renaissance
- Words: 1239
Leonardo Da Vinci and Galileo Galilei: Art and Science
Works of literature, painting, and music united by the idea of arabesque.
- Words: 2945
Music, Cosmology and Architecture in the Renaissance
- Words: 3122
Jarzombek’s Analysis of Architectural History and Historiography
- Words: 1478
Architecture. The Fate of the Palais Stoclet
Restrictions in art and literature, art tendencies in europe and the persian empire.
- Words: 1448
Art History: Art and Medicine of the Ancient Egypt
Ceramic vessel from nazca culture analysis.
- Words: 1376
“Salt Shaker” by Stuart Davis and Modern Art
From america to france, and vice versa, aegean art: the minoan stone vase, the stylistic differences between reliefs from the greek and roman periods.

The world of ancient Egypt
Few civilizations have enjoyed the longevity and global cultural reach of ancient Egypt. Their distinct visual expressions, writing system, and imposing monuments are instantly recognizable by viewers all around the world even today—put simply, their branding was on point.
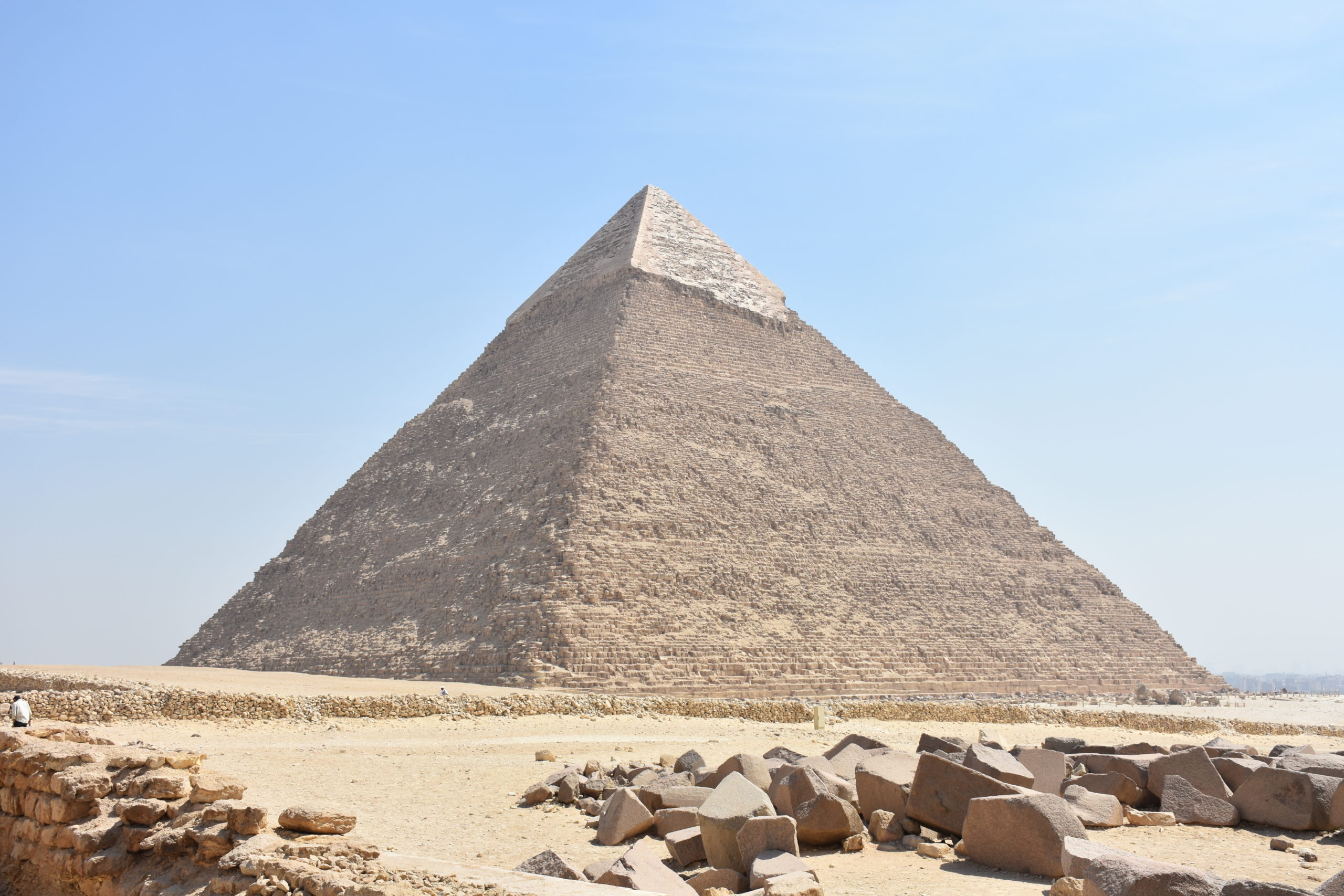

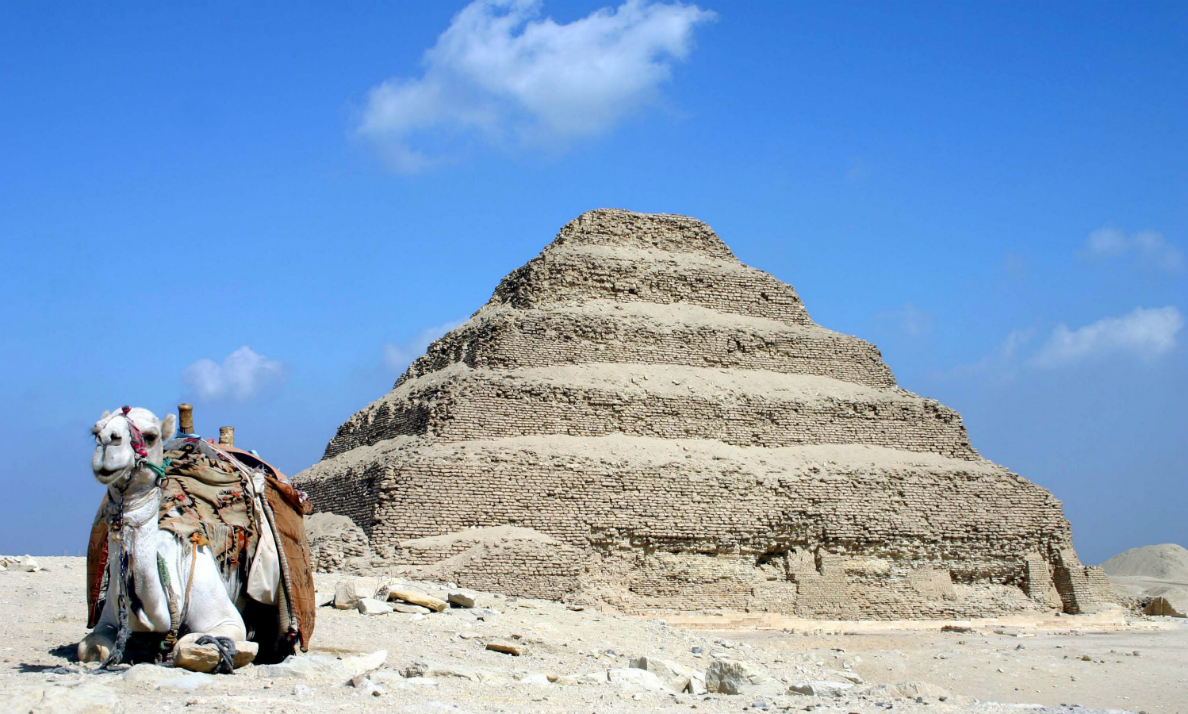
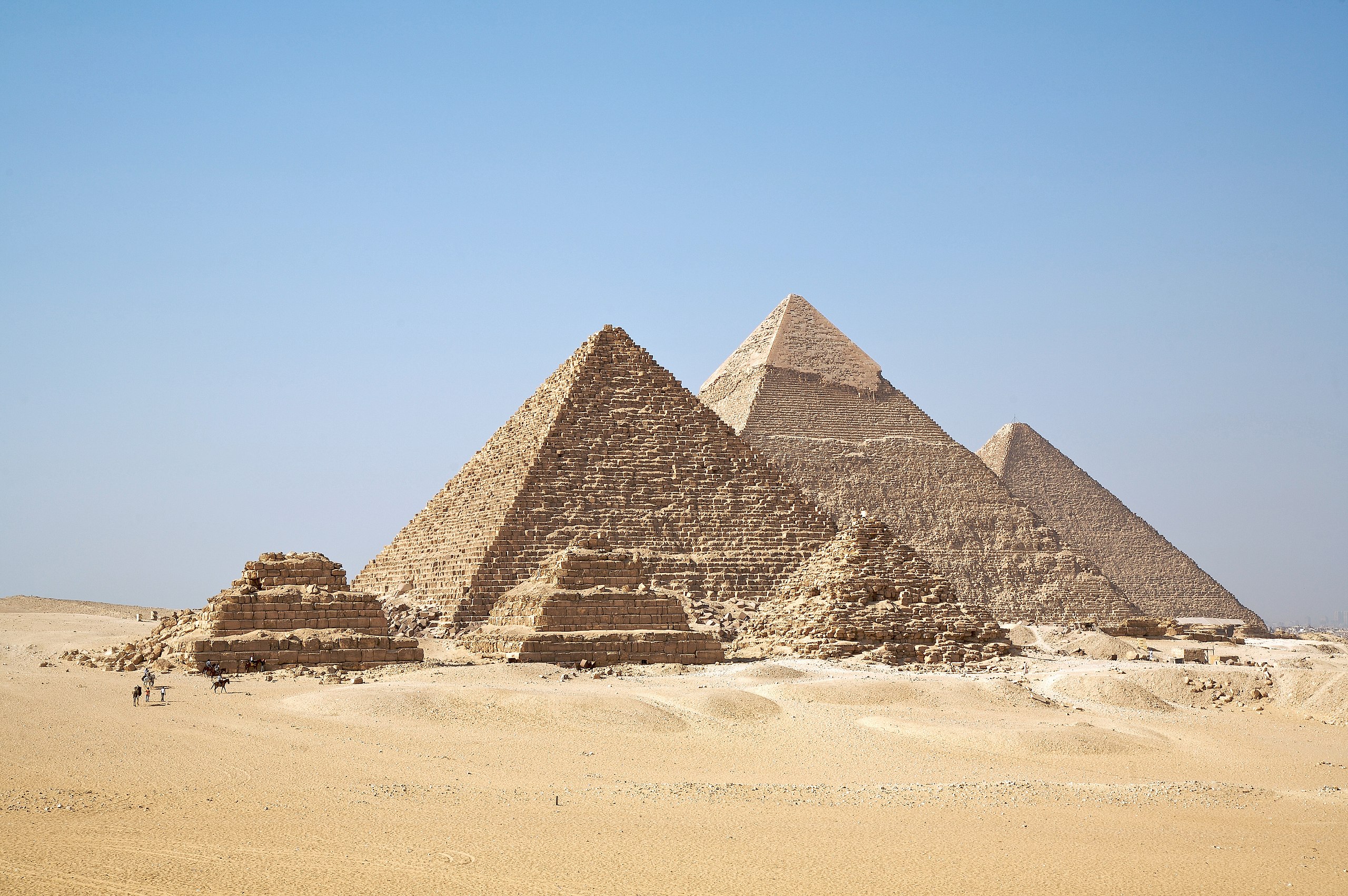
Pyramid of Khafre, Egypt (photo: MusikAnimal, CC BY-SA 3.0)
Despite portraying significant stability over a vast period of time, their civilization was not as static as it may appear at first glance, particularly if viewed through our modern eyes and cultural perspectives . Instead, the culture was dynamic even as it revolved around a stable core of imagery and concepts. The ancient Egyptians adjusted to new experiences, constantly adding to their complex beliefs about the divine and terrestrial realms, and how they interact. This flexibility, wrapped around a base of consistency, was part of the reason ancient Egypt survived for millennia and continues to fascinate.
Read an introductory essay about ancient Egypt

Ancient Egypt: an introduction
/ 1 Completed
The Natural World of Egypt
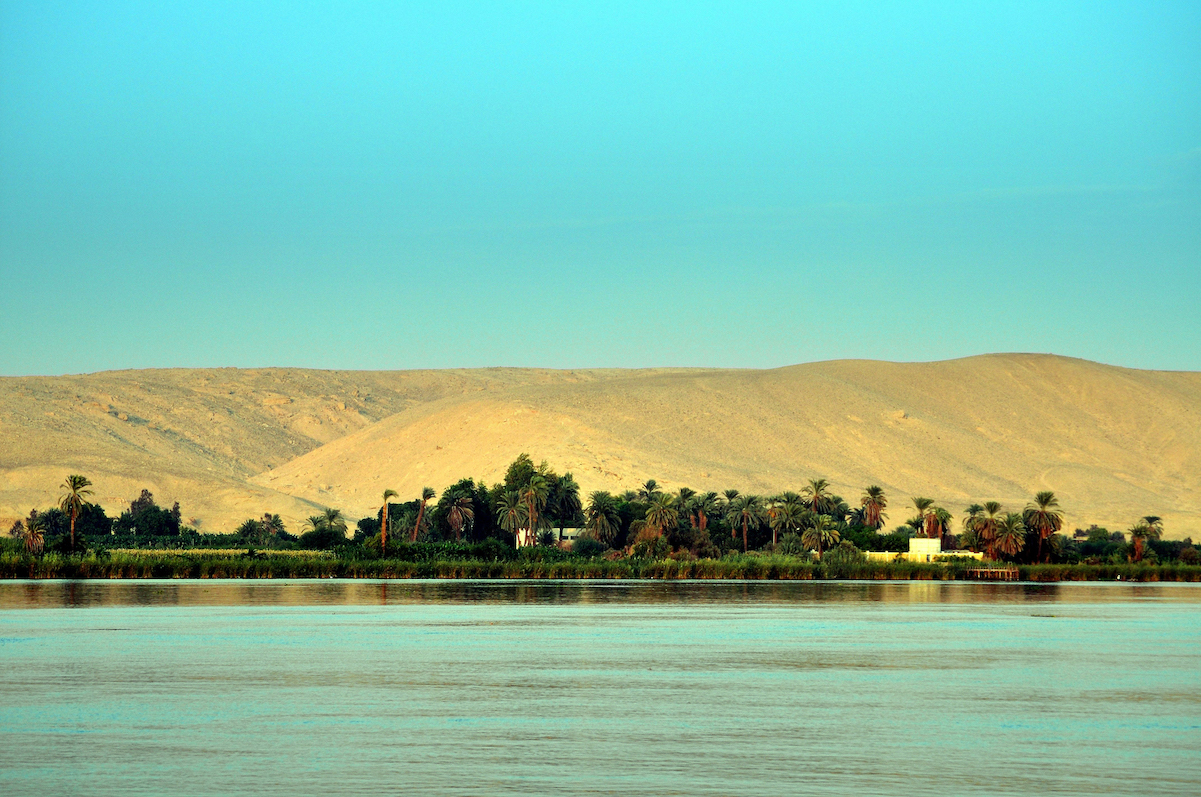

View of the Nile River, Egypt (photo: Badics, CC BY-SA 3.0)
With the blazing sun above, flanked by vast seas of shifting sand, and fed by the life-giving Nile River (which hid frightening creatures beneath its dark waters), the natural world of Egypt was inherently beautiful but also potentially deadly. Outside the lush river valley, there was little protection from the ever-dominant sun, whose intensity was both feared and revered. The deserts were home not only to many dangerous creatures, but the sands themselves were also unpredictable and constantly shifting. The clear night skies dazzled with millions of stars, some of which seemed to move of their own accord while others rose and fell at trackable intervals. The Nile, with its annual floods, brought fertility and renewal to the land, but could also overflow and wreak havoc on the villages that lined its banks. Careful observers of their environment, the Egyptians perceived divine forces in these phenomena and many of their deities, such as the powerful sun god Ra, were connected with elements from the natural world.

Hieroglyphs, detail from the White Chapel, Karnak (photo: Dr. Amy Calvert)
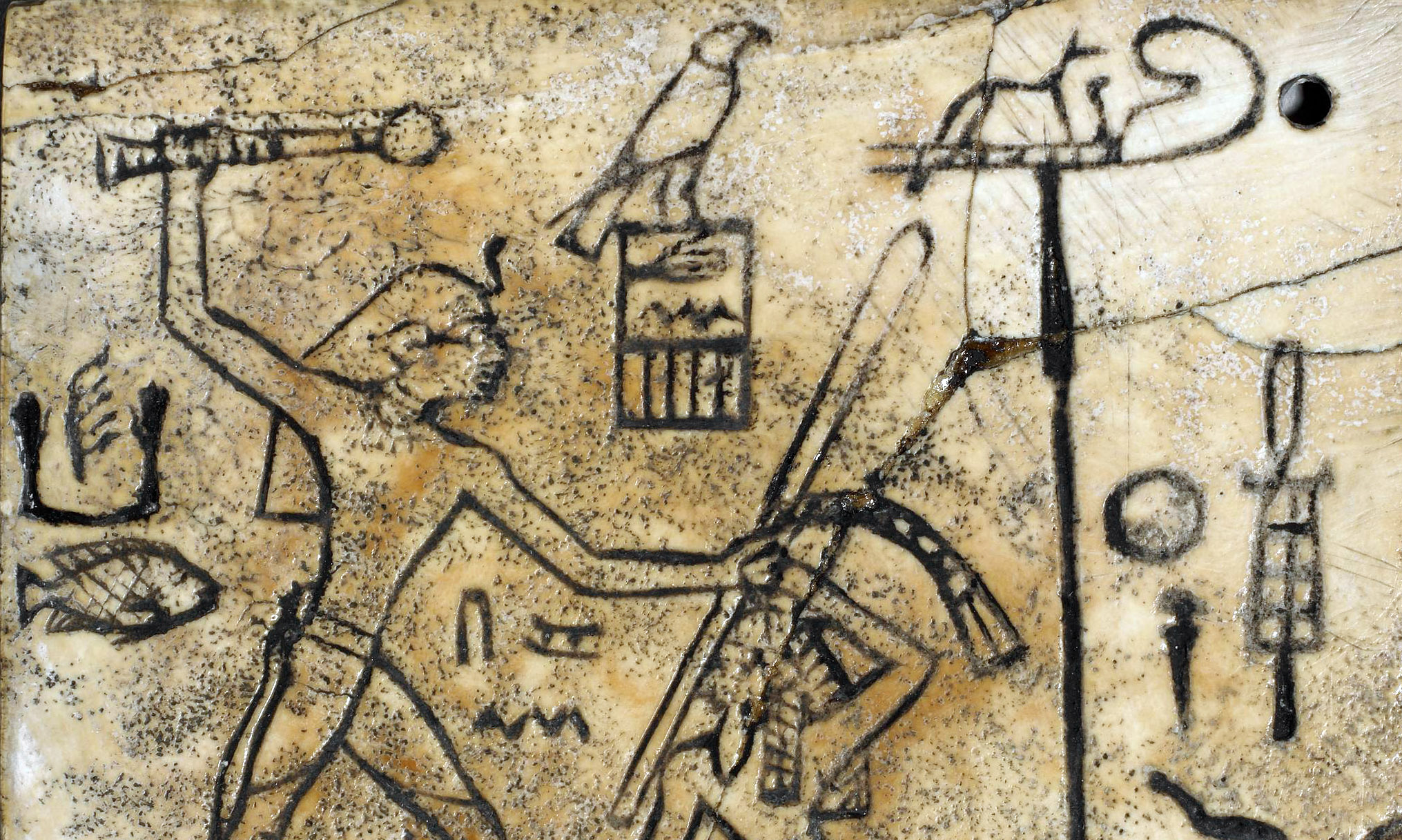
The perception of divine powers existing in the natural world was particularly true in connection with the animals that inhabited the region. There was an array of creatures that the Egyptians would have observed or interacted with on a regular basis and they feature heavily in the culture. One of the most distinctive visual attributes of Egyptian imagery is the myriad deities that were portrayed in hybrid form, with a human body and animal head. In addition, a wide range of birds, fishes, mammals, reptiles, and other creatures appear prominently in the hieroglyphic script —there are dozens of different birds alone.
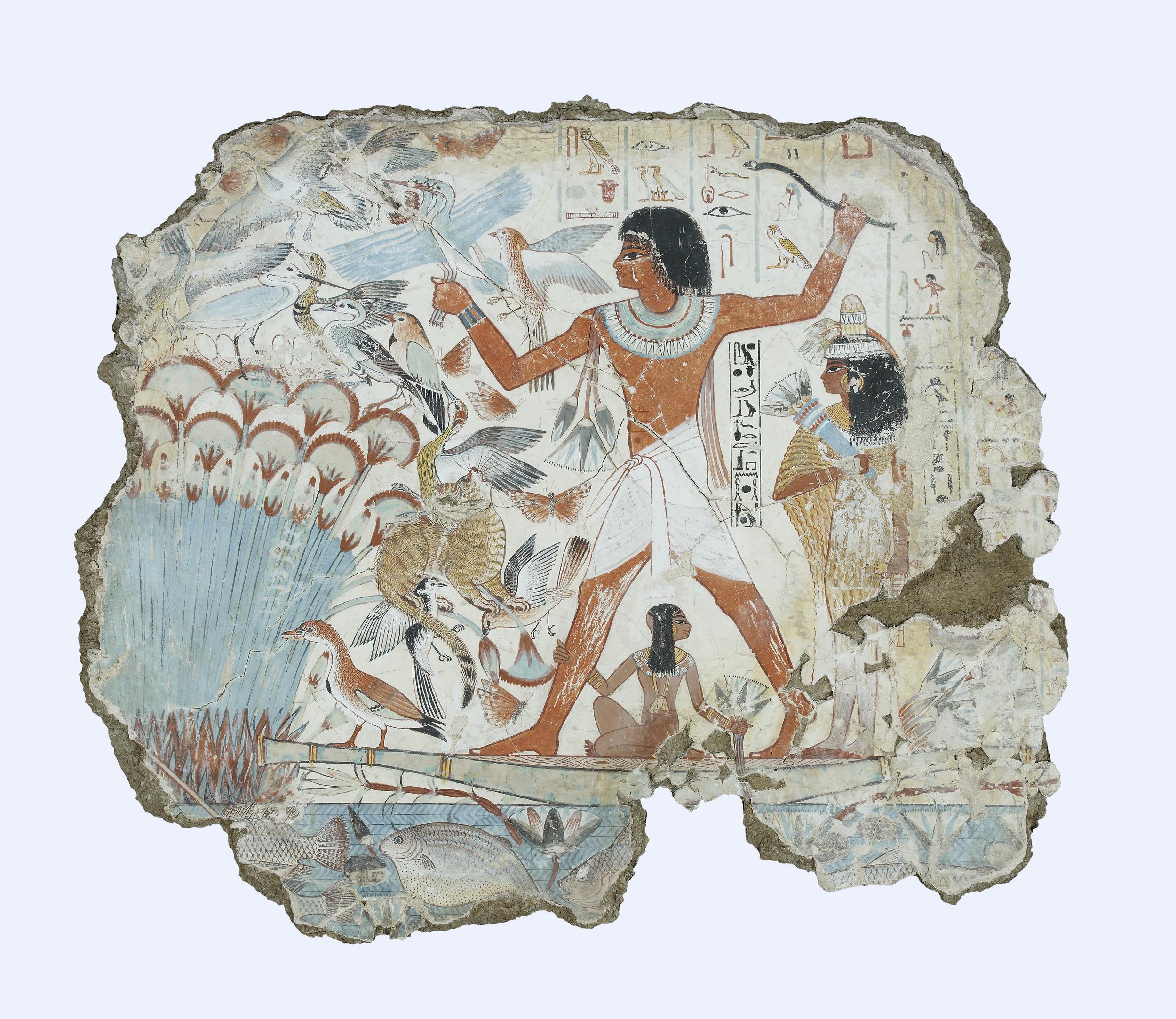

Nebamun fowling in the marshes, Tomb-chapel of Nebamun, c. 1350 B.C.E., 18th Dynasty, paint on plaster, 83 x 98 cm, Thebes (© Trustees of the British Museum)
The Nile was packed with numerous types of fish, which were recorded in great detail in fishing scenes that became a fixture in non-royal tombs. Most relief and painting throughout Egypt’s history was created for divine or mortuary settings and they were primarily intended to be functional. Many tomb scenes included the life-giving Nile and all it’s abundance with the goal of making that bounty available for the deceased in the afterlife. In addition to the array of fish, the river also teemed with far more dangerous animals, like crocodiles and hippopotami. Protective spells and magical gestures were used from early on to aid the Egyptians in avoiding those watery perils as they went about their daily lives.
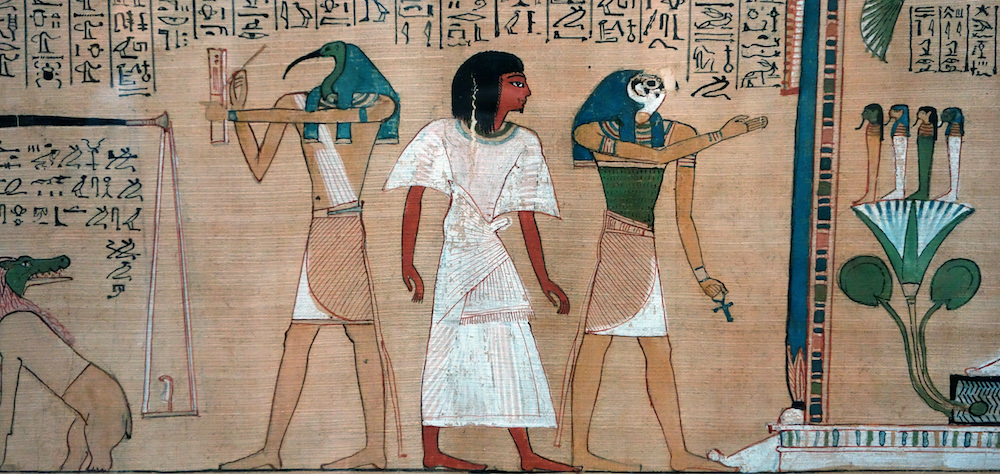

Hunefer (center) flanked by two deities: the ibis-headed Thoth (left) and the falcon-headed Horus (right), from Hunefer’s Judgement in the presence of Osiris, Book of the Dead of Hunefer, 19th Dynasty, New Kingdom, c. 1275 B.C.E., papyrus, Thebes, Egypt (British Museum)
The desert, likewise, was full of potentially dangerous creatures. Lions, leopards, jackals, cobras, and scorpions were all revered for their attributes and feared for their ferocity. Soaring above were birds of prey, like falcons who were sharp-eyed hunters, and massive vultures that consumed decaying flesh and fed it to their young. Scarab beetles also seemingly brought new life from decay and the sacred ibis with their curved beaks found sustenance hidden in the muddy banks of the Nile. All of these creatures (and many others) became closely associated with different deities very early in Egyptian history. The Egyptians did not worship animals; instead, certain animals were revered because it was believed that they were related to particular gods and thus served as earthly manifestations of those deities.
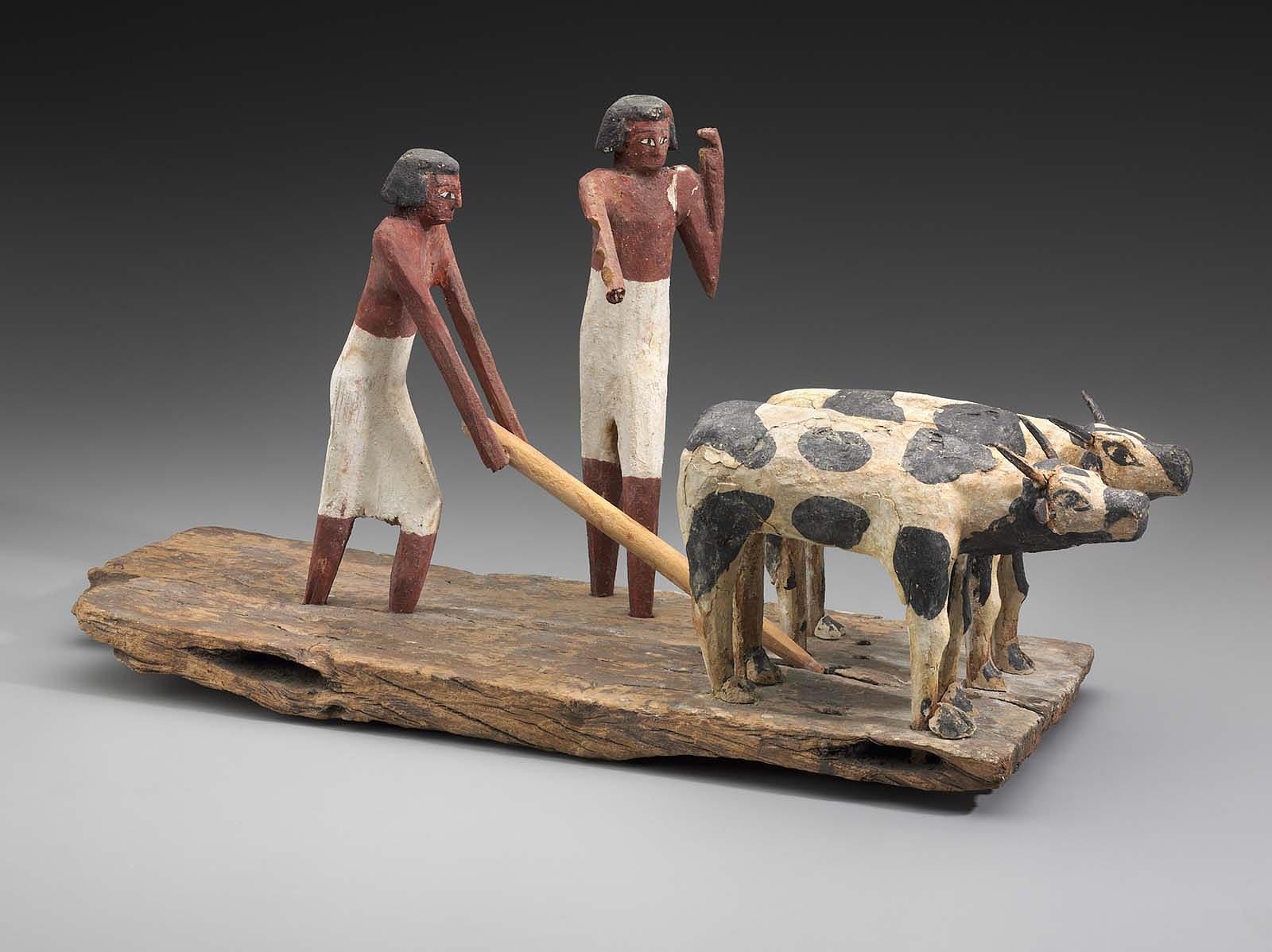

Model scene of workers ploughing a field, Middle Kingdom, late Dynasty 11, 2010–1961 B.C.E., wood, 54 cm (MFA Boston)
Even domesticated animals, such as cows, bulls, rams, and geese, became associated with deities and were viewed as vitally important. Cattle were probably the first animals to be domesticated in Egypt and domesticated cattle, donkeys, and rams appear along with wild animals on Predynastic and Early Dynastic votive objects , showing massive herds that were controlled by early rulers, demonstrating their wealth and prestige. Pastoral scenes of animal husbandry appear in numerous private tomb chapels and wooden models, providing detailed evidence of their daily practices. Herdsmen appear caring for their animals in depictions that include milking, calving, protecting the cattle as they cross the river, feeding, herding, and many other aspects of their day-to-day care.
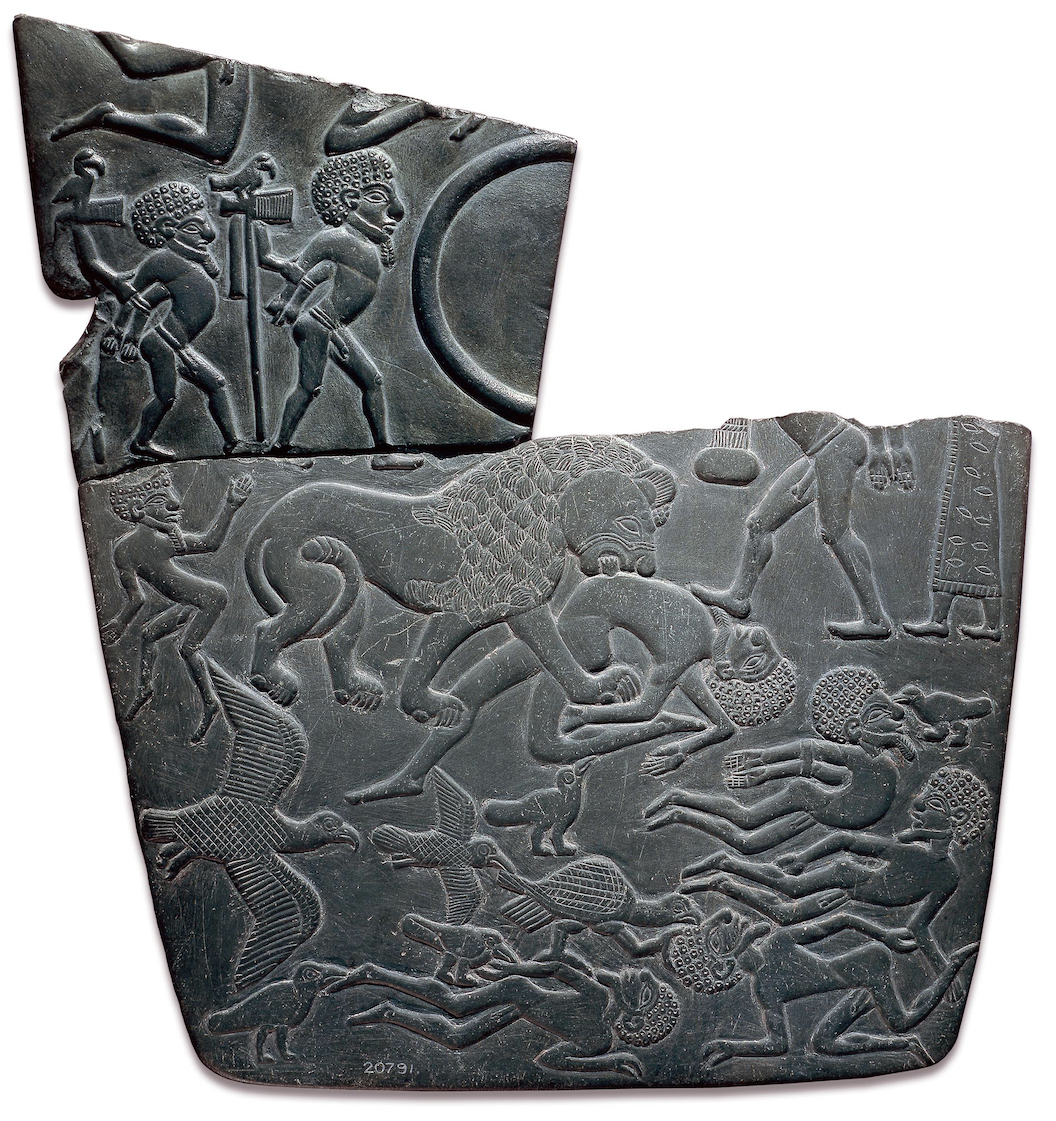

The Battlefield Palette , c. 3100 B.C.E., mudstone, found at el-Amarna, Egypt, 19.6 x 32.8 cm (© Trustees of the British Museum)
Already in the Predynastic period the king was linked with the virile wild bull, an association that continues throughout Egyptian history—one of the primary items of royal regalia was a bull tail, which appears on a huge number of pharaonic images. An early connection between the king and lions is also apparent. One scene on a Predynastic ceremonial palette ( The Battlefield Palette), shows the triumphant king as a massive lion devouring his defeated foes. First Dynasty kings appear to have kept lion cubs as pets.
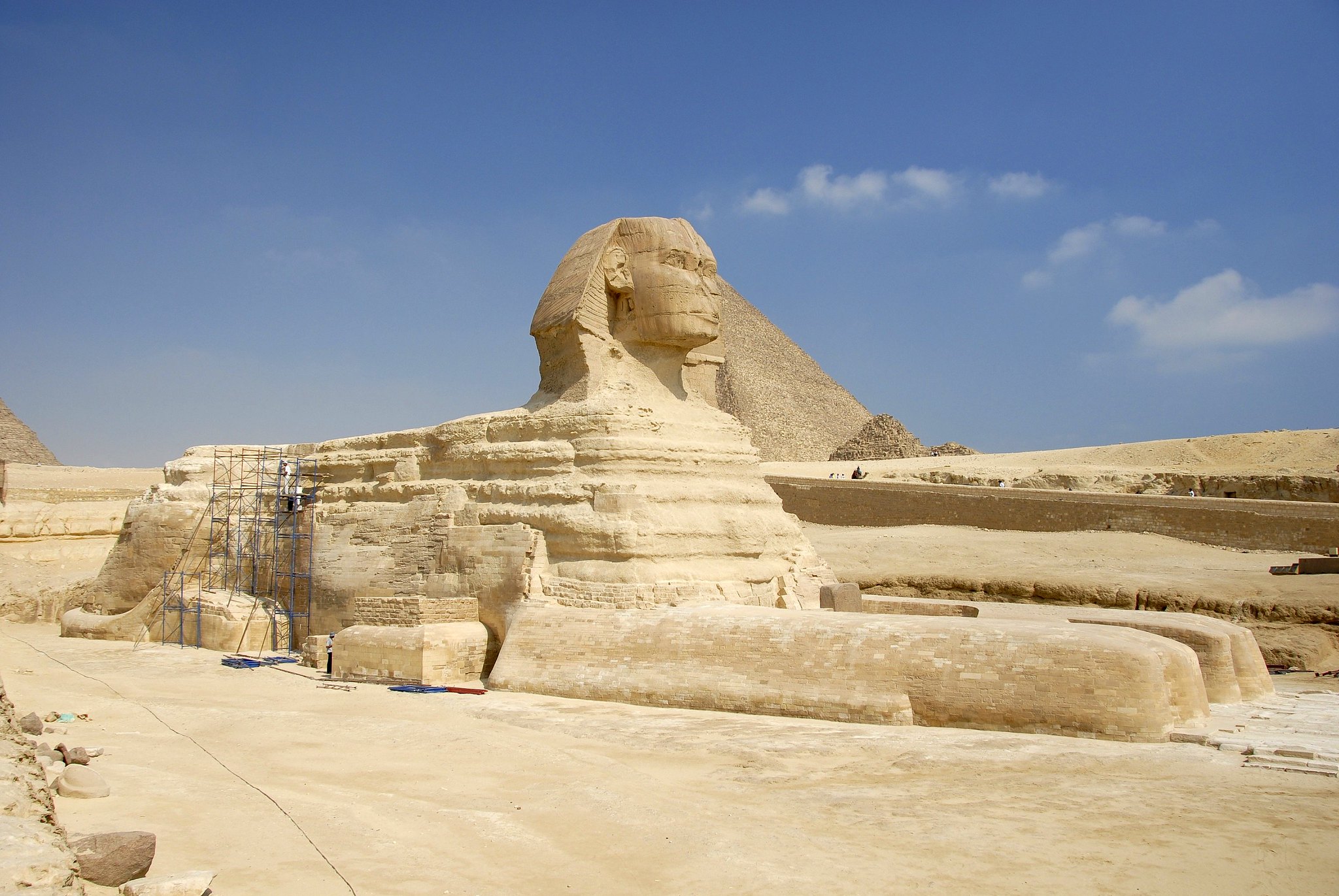

The Great Sphinx (photo: superblinkymac, CC BY-NC-ND 2.0)
In addition, lions (among other animals) were associated with the burials of some early rulers. One of the most iconic images from ancient Egypt is the massive Great Sphinx at Giza, which was sculpted from the living rock of the plateau. This fused form, with the body of a lion and the head of the king, became a common visual expression of royal power.
Historical Setting
While many of the religious and cultural characteristics of ancient Egypt were evident from very early on and continued all the way through the Roman era (contributing to overall cultural stability), sweeping conceptual developments and adoptions of external elements are also evident. Throughout ancient Egypt’s long history, periods of unified control were interspersed with moments of instability where parts of the country were controlled by different authorities. These repeated waves of political and cultural development create a decidedly complex history that spans thousands of years.
Read essays to understand the historical setting and basic characteristics of each era

Ancient Egyptian chronology and historical framework: an introduction
Predynastic and Early Dynastic: an introduction

Old Kingdom and First Intermediate Period: an introduction

Middle Kingdom and Second Intermediate Period: an introduction

New Kingdom and Third Intermediate Period: an introduction

Late Period and the Ptolemaic and Roman Periods: an introduction
/ 6 Completed
Social Organization
Conceptually, the Egyptian state was an absolute monarchy where the office of pharaoh itself was considered divine. The pharaoh (king) was viewed as the earthly manifestation of the god Horus, and was responsible as the supreme commander for making all decisions affecting the nation. In reality, the king stood at the head of a hierarchical administrative structure with layers of civil officials that oversaw various systems and were responsible to the king for their success.
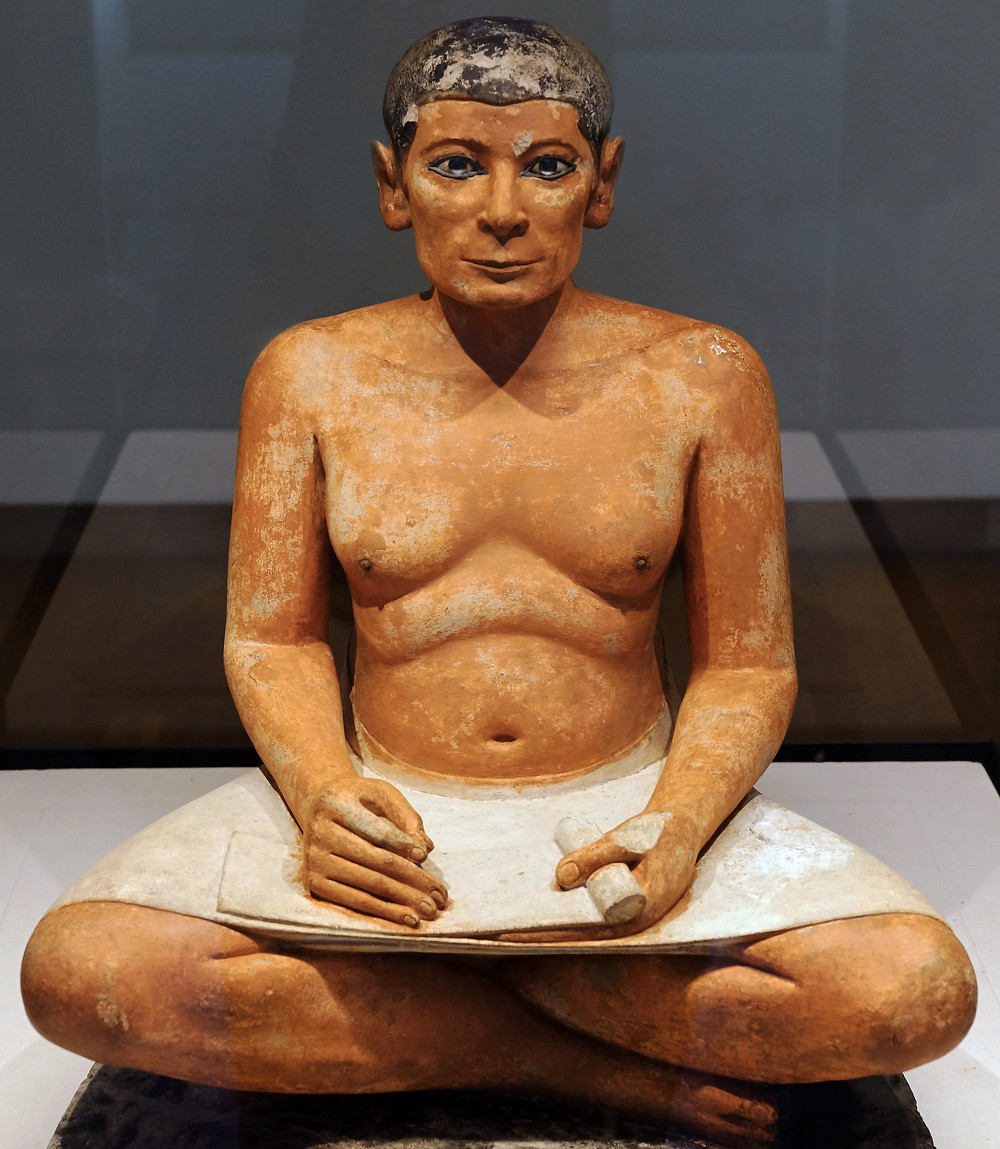

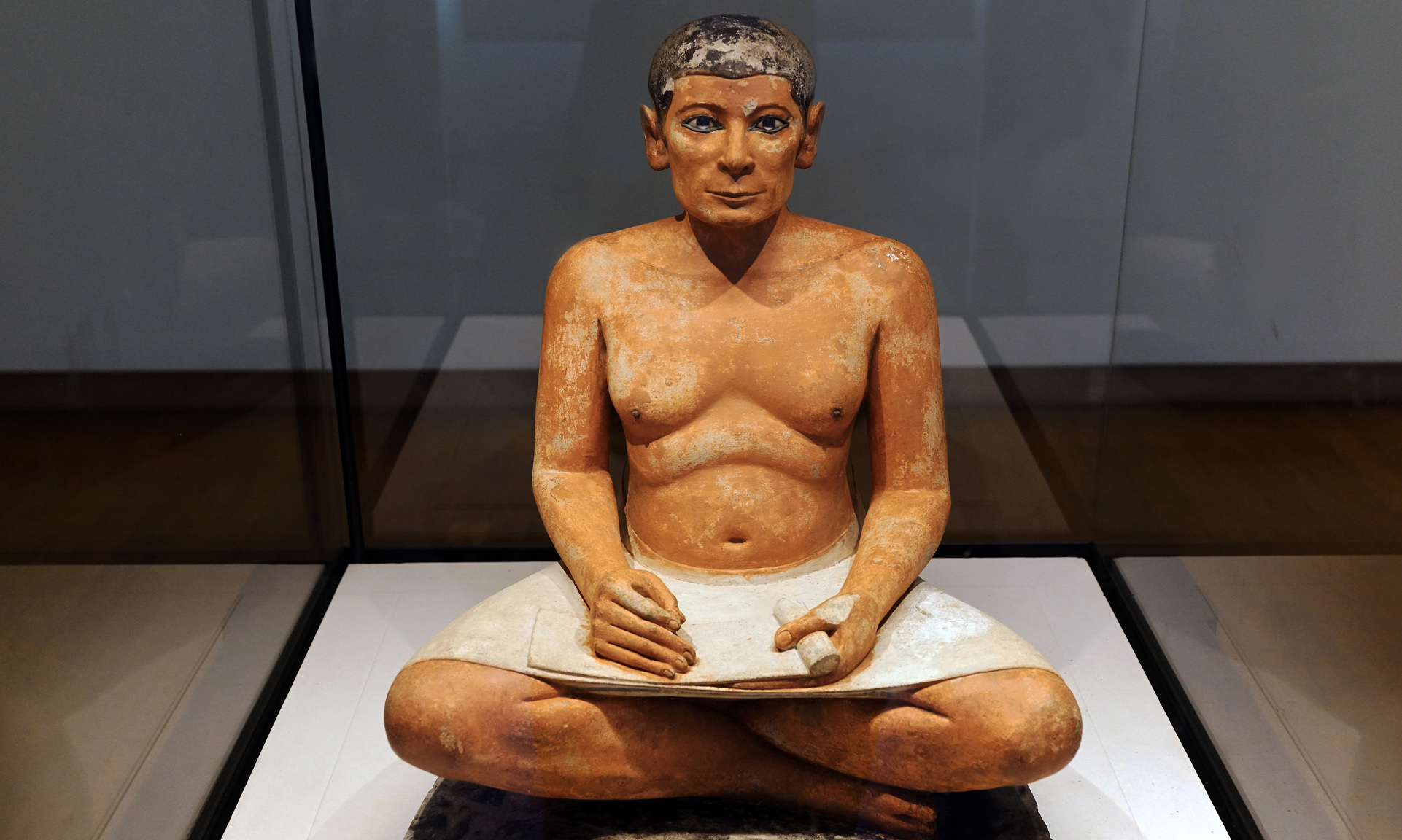
Seated Scribe , c. 2500 B.C.E., c. 4th Dynasty, Old Kingdom, painted limestone with rock crystal, magnesite, and copper/arsenic inlay for the eyes and wood for the nipples, found in Saqqara (photo: Steven Zucker, CC BY-NC-SA 2.0)
Most Egyptians followed the careers of their fathers and were taught by apprenticeship. Only the children of the higher classes, destined to become officials, were taught in schools and learned to read and write. Money in the modern sense did not exist in Egypt until the mid-fourth century B.C.E., so wages were usually paid in grain that could then be exchanged for copper or silver. Agriculture was the basis of the Egyptian economy and the foundation of the state, and produce was delivered to central storehouses to be administered and distributed.
Read essays about the various social strata in Egyptian society

Egyptian Social Organization: The Pharaoh

Egyptian Social Organization: Administrative officials, priests, ranks of the military, and the general population
/ 2 Completed
Art and Function
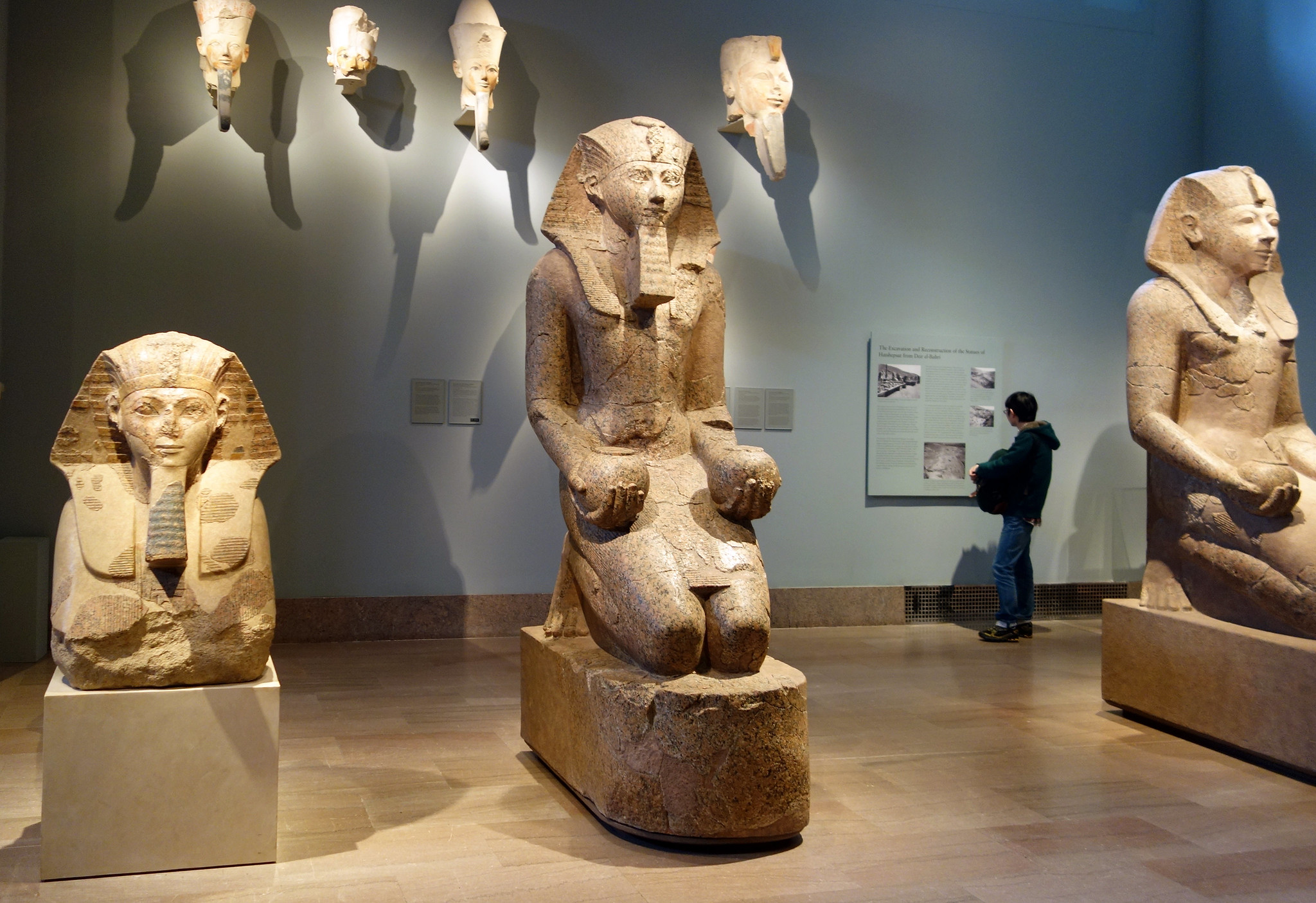

Large Kneeling Statue of Hatshepsut , c. 1479–1458 B.C.E., Dynasty 18, New Kingdom (Deir el-Bahri, Upper Egypt), granite, 261.5 x 80 x 137 cm (The Metropolitan Museum of Art)
Egyptian art is sometimes viewed as static and abstract when compared with the more naturalistic depictions of other cultures (ancient Greece for example). Much of Egyptian imagery—especially royal imagery—was governed by decorum (a sense of what was appropriate), and remained extraordinarily consistent throughout its long history. This is why their art may appear unchanging—and this was intentional. For the ancient Egyptians, consistency was a virtue and an expression of political stability, divine balance, and clear evidence of ma’at and the correctness of their culture. The Egyptians even had a tendency, especially after periods of disunion, towards archaism where the artistic style would revert to that of the earlier Old Kingdom which was perceived as a “golden age.”
Read essays about art and function

Ancient Egyptian art: an introduction its function and basic characteristics

Materials and techniques in ancient Egyptian art: an introduction
Consistency and balance

The canon of proportions grid is clearly visible in the lower, unfinished register of the Stela of Userwer, and the use of hieratic scale (where the most important figures are largest) is evident the second register that shows Userwer, his wife and his parents seated and at a larger scale than the figures offering before them. Detail of the stela of the sculptor Userwer, 12th dynasty, limestone, from Egypt, 52 x 48 cm wide (© Trustees of the British Museum)
Consistency in representation was closely related to a fundamental belief that depictions had an impact beyond the image itself. This belief led to an active resistance to changes in codified depictions. Even the way that figures were planned and laid out by the artists was codified. During the Old Kingdom, the Egyptians developed a grid system, referred to as the canon of proportions, for creating systematic figures with the same proportions. Grid lines aligned with the top of the head, top of the shoulder, waist, hips, knees, and bottom of the foot (among other body joints).
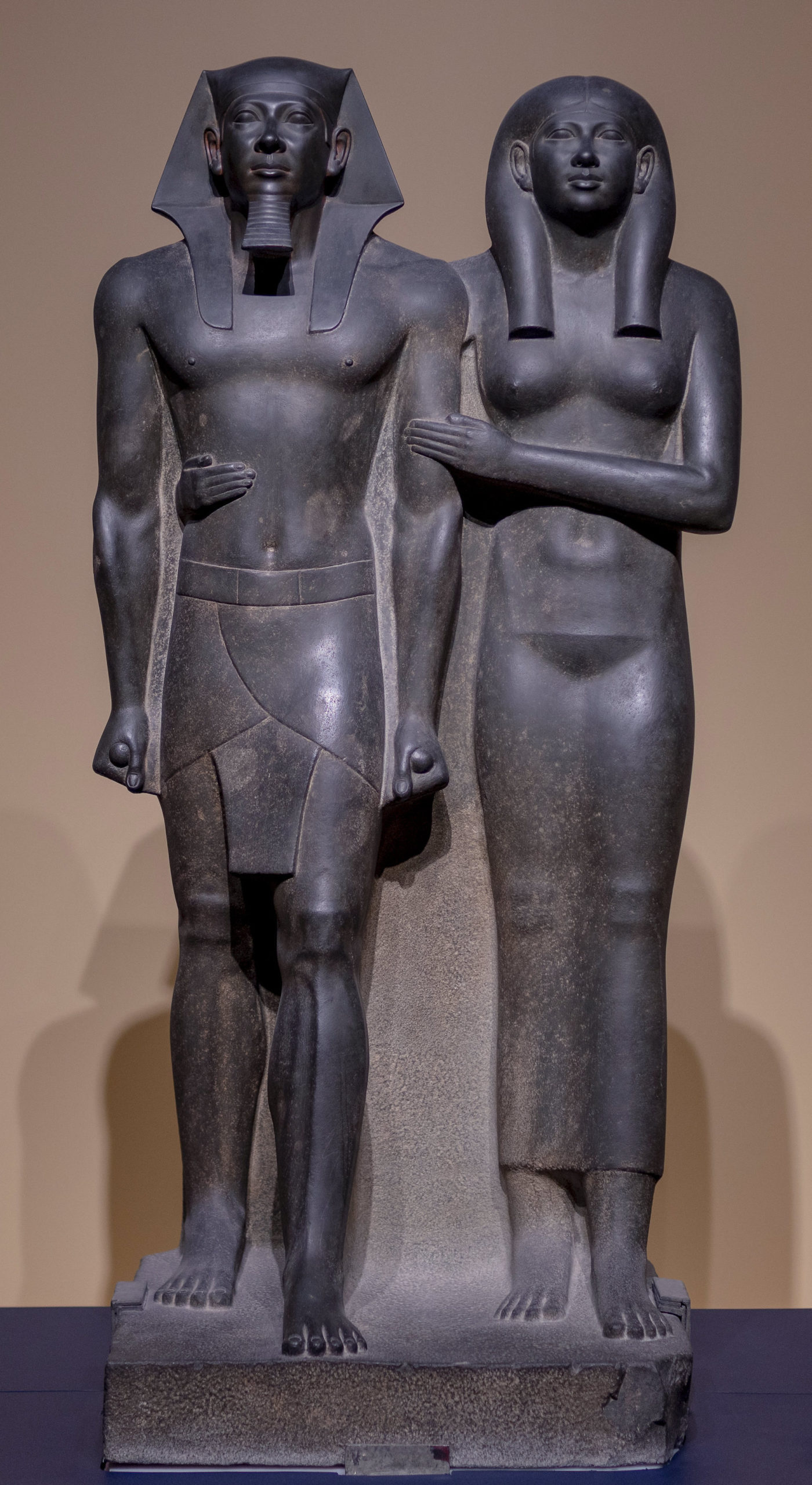

King Menkaura (Mycerinus) and Queen, 2490–2472 B.C.E., Old Kingdom, Dynasty 4, greywacke, Menkaura Valley Temple, Giza, Egypt, 142.2 x 57.1 x 55.2 cm, 676.8 kg (Museum of Fine Arts, Boston; photo: Steven Zucker, CC BY-NC-SA 2.0)
The grid aided the artist in ensuring that the proportions of their figures were correct, but those proportions shifted over time. For example, although 18 squares was the standard used for much of Egypt’s history, in the Amarna period 20 squares were used, resulting in figures with more elongated proportions.

Thutmose, Model Bust of Queen Nefertiti , c. 1340 BCE, limestone and plaster, New Kingdom, 18th dynasty, Amarna Period (Egyptian Museum and Papyrus Collection/Neues Museum, Berlin)
Below are several examples of Egyptian art that demonstrate their primary stylistic characteristics. These include:
- the use of hierarchical scale
- the use of registers
- use of the canon of proportions (described above)
- a preference for balance
- the integration of perspectives.
Read essays and watch videos about consistency and balance

Stela of the sculptor Userwer: The lower part is still covered with the grid used for ensuring that the proportions of the figures were correct.
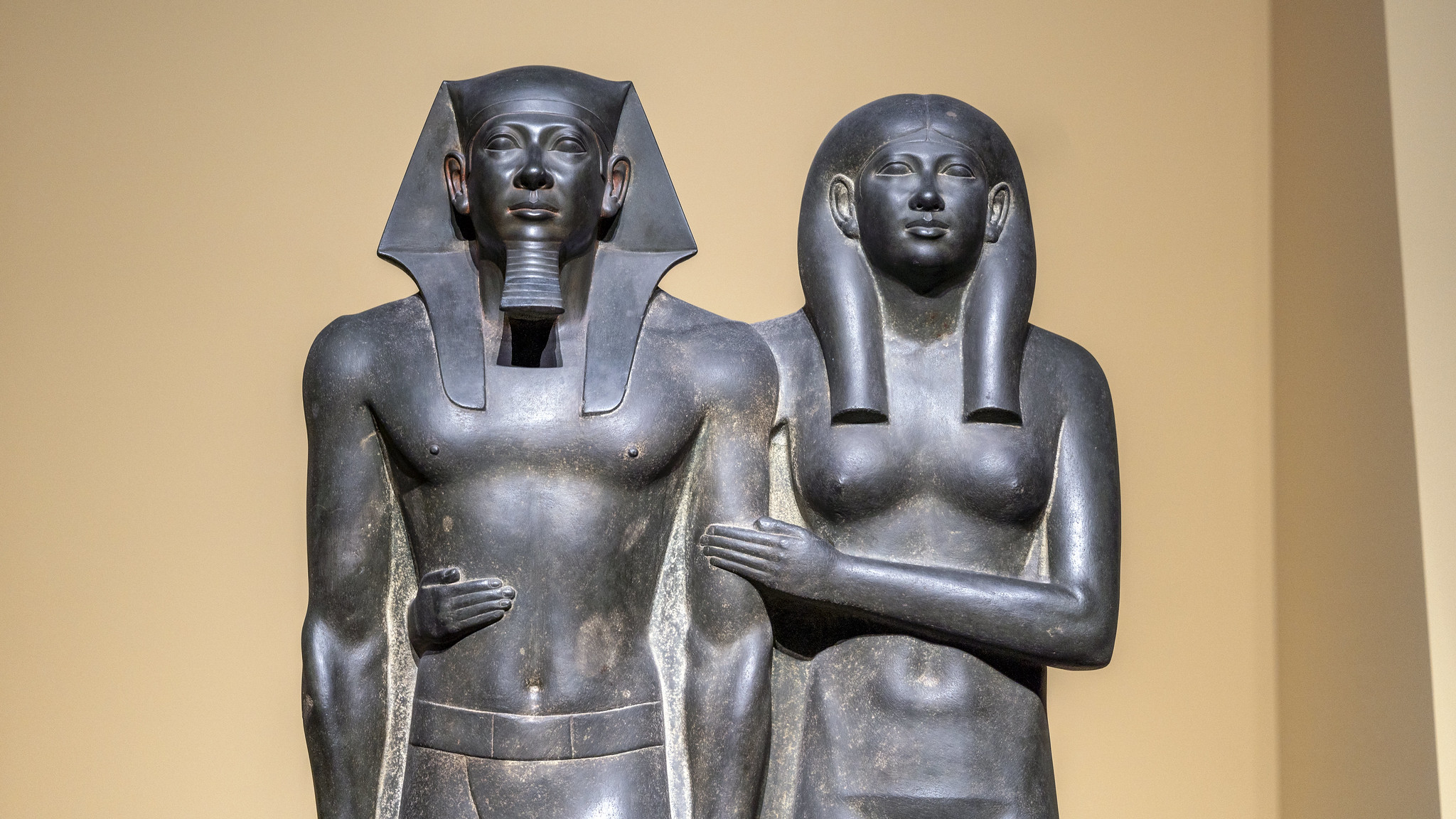

King Menkaure (Mycerinus) and queen: They both look beyond the present and into timeless eternity, their otherworldly visage displaying no human emotion whatsoever.

Thutmose, Model Bust of Queen Nefertiti : This stunning bust exemplifies a change in style.
The Seated Scribe: This painted statue differs from the ideal statues of pharaohs.
/ 4 Completed
Creative details

Nude figure of the Seal Bearer Tjetji, 2321 B.C.E.–2184 B.C.E. (6th Dynasty), from Akhmim, Upper Egypt, wood, obsidian, limestone, and copper, 75 cm high (© Trustees of the British Museum)
Although much Egyptian art is formal, many surviving examples of highly expressive depictions full of creative details prove that the ancient Egyptian artists were fully capable of naturalistic representations. Note, for example, the sensitive modeling of the musculature and close attention paid to realistic physical detail evident in a wood statue of a high official (the Seal Bearer Tjetji) from a Late Old Kingdom tomb. These very unusual and enigmatic statuettes of nude high officials, which are depicted in a standard pose of striding forward with left leg advanced and holding a long staff, were often painted and had eyes of inlaid stone set in copper.
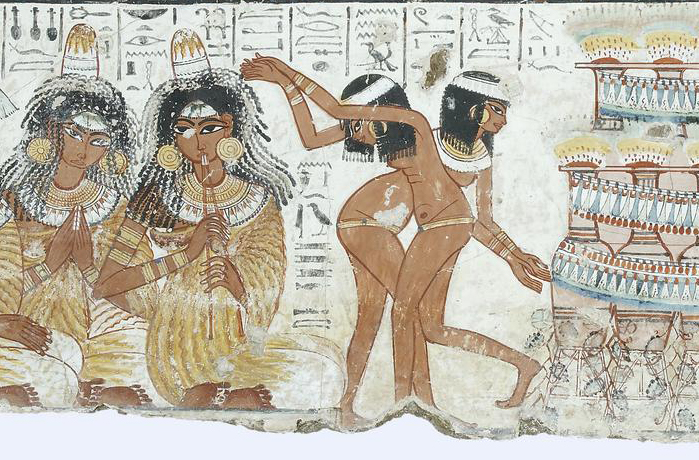

Musicians and dancers (detail), A feast for Nebamun, Tomb-chapel of Nebamun, c. 1350 B.C.E., 18th Dynasty, paint on plaster, whole fragment: 88 x 119 cm, Thebes © Trustees of the British Museum
Nebamun’s tomb, with its spectacular paintings, includes several examples that demonstrate a careful observation of the natural world—especially notable in the energetic hunting cat and the sinuous dancing of the entertainers at the banquet. A marvelous wooden head of Queen Tiye presents a woman of strong personality with details that hint at her formidable character.

Portrait Head of Queen Tiye with a Crown of Two Feathers , c. 1355 B.C.E., Amarna Period, Dynasty 18, New Kingdom, Egypt, yew wood, lapis lazuli, silver, gold, faience, 22.5 cm high (Egyptian Museum and Papyrus Collection at the Neues Museum, Berlin)
Read essays about creative details
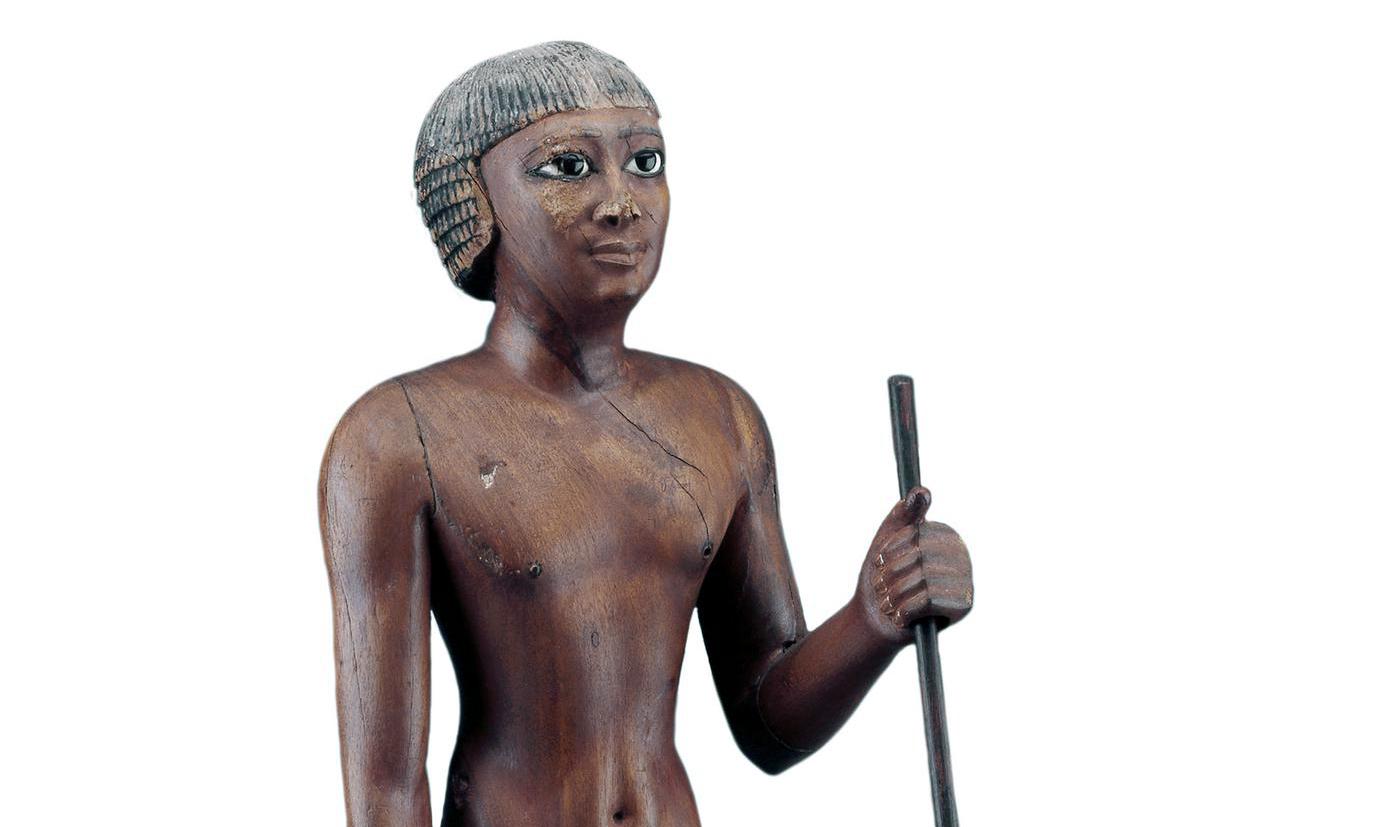

Wooden tomb statue of Tjeti: T he sculptor of this example has carefully modeled the muscles on the torso and legs, and paid close attention to the detail of the face.
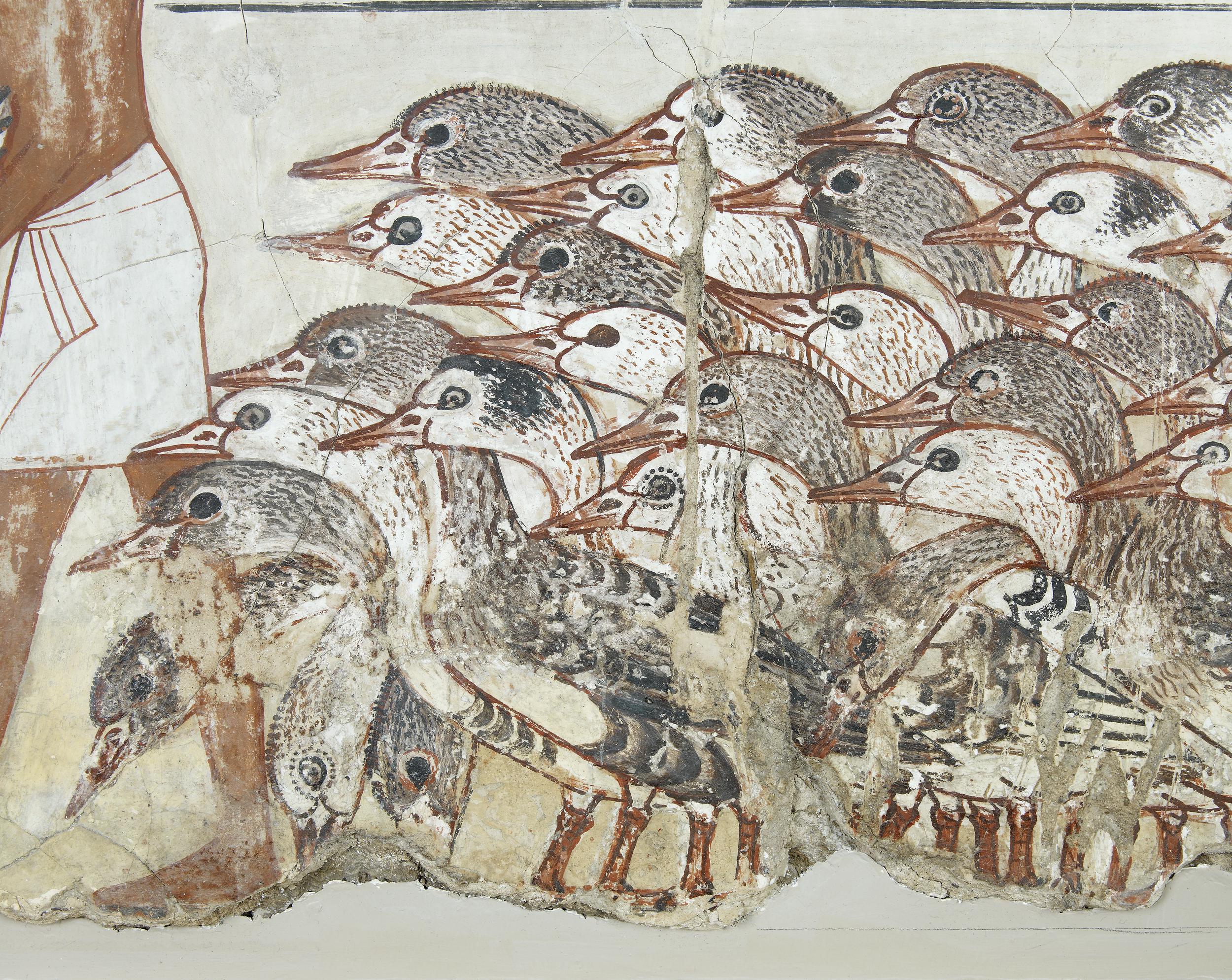

Paintings from the Tomb-chapel of Nebamun: He is shown hunting birds from a small boat in the marshes of the Nile with his wife Hatshepsut and their young daughter.
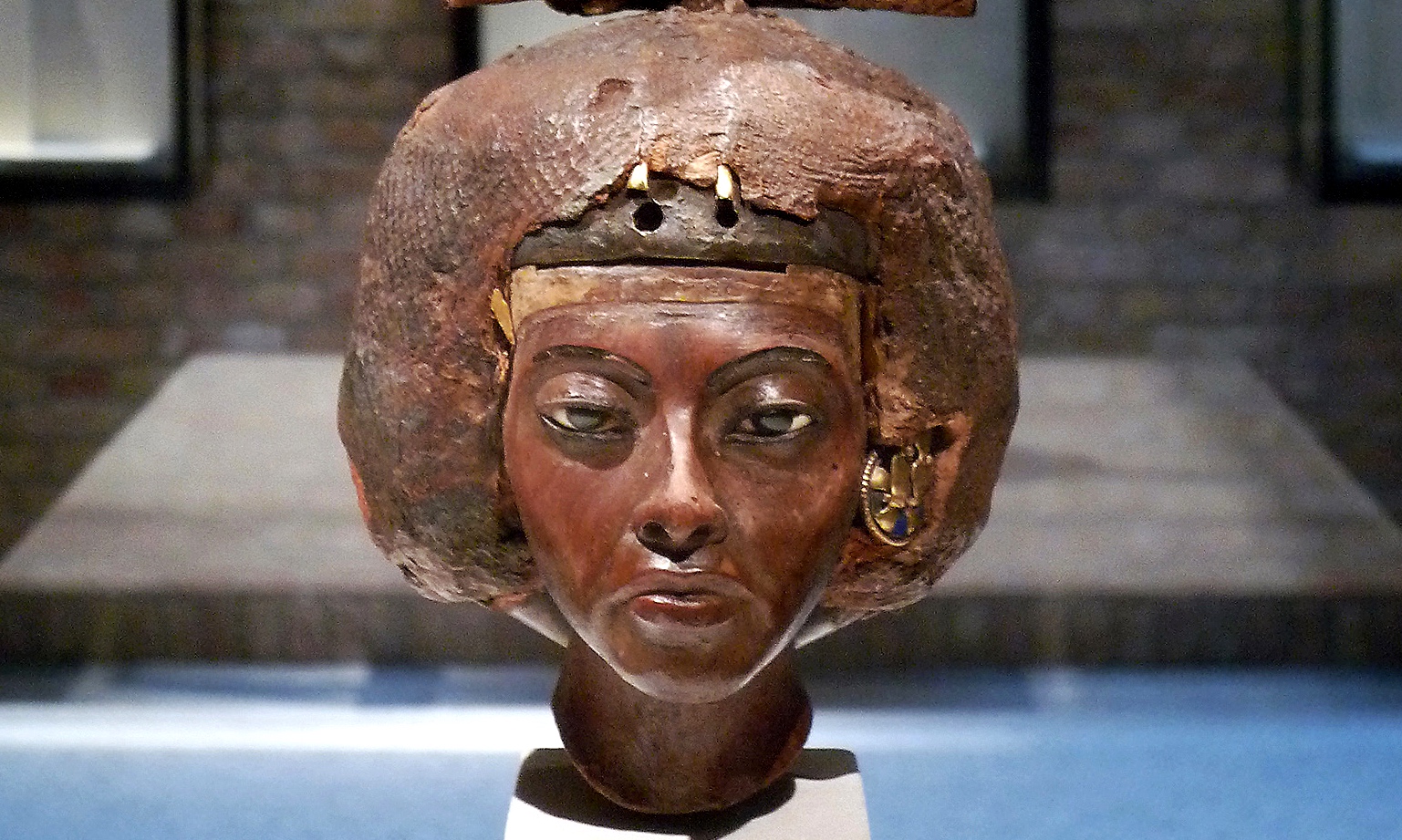

Portrait Head of Queen Tiye: She was a powerful figure, but her royal life was complicated, as demonstrated through this changing statue.
/ 3 Completed
Metalworking Traditions
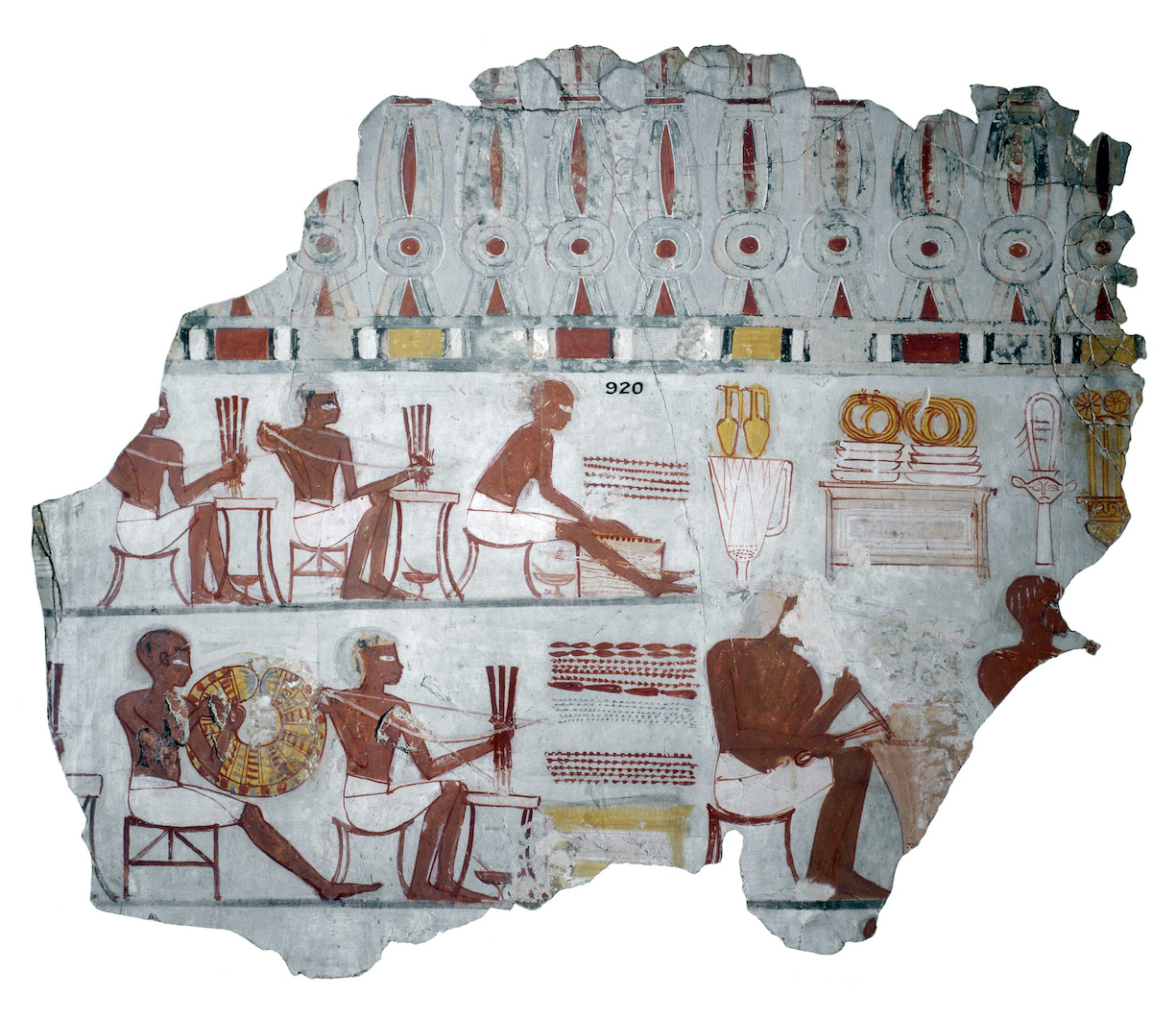

Scene showing the manufacture of valuable items, such as jewelry. Wall-painting, probably from the tomb of Sobekhotep, Thebes, c. 1400 B.C.E., New Kingdom, reign of Thutmose IV, painted stucco, 60 x 58.5 (© Trustees of the British Museum)
Egyptian artisans were highly skilled metalworkers from early times; although few metal sculptures have survived, those that are preserved show an incredible level of technical achievement. As with other types of craft, like woodworking, preserved images of artisans in their workshops found in private tombs provide information about the processes of production For instance, we can see a group of jewelers at work in a painting from the tomb of Sebekhotep.

Pectoral and Necklace of Sithathoryunet with the Name of Senwosret II, Middle Kingdom, Dynasty 12, reign of Senwosret II, c. 1887–1878 B.C.E., Egypt, Fayum Entrance Area, el-Lahun (Illahun, Kahun; Ptolemais Hormos), Tomb of Sithathoryunet (BSA Tomb 8), EES 1914, Gold, carnelian, feldspar, garnet, turquoise, lapis lazuli
The most beautifully crafted pieces of jewelry display elegant designs, incredible intricacy, and astonishingly precise stone-cutting and inlay, reaching a level that modern jewelers would be hard-pressed to achieve. The jewelry of a Middle Kingdom princess, found in her tomb at el-Lahun in the Fayum region is one spectacular example.

Statuette of Thutmose IV, 1400–1390 B.C.E., 19th Dynasty, ancient Egypt, bronze, silver, calcite, 14.7 x 6.4 cm (© Trustees of the British Museum)
The metal statues that survive demonstrate a high level of skill in both sheet working/metal forming and casting in copper and bronze. This marvelous hollow-cast bronze statuette of a kneeling Thutmosis IV, presenting an offering of wine, provides a peek into the abilities of Egypt’s craftsmen. Note that the arms were created separately and joined to the body on tenons and the eyes were originally inlaid.
Read essays and watch a video about metalworking traditions

Paintings from the tomb of Sebekhotep: Images show jewelers at work.
Pectoral and necklace of Sithathoryunet: Fashioned delicately in gold, carnelian, feldspar, garnet, turquoise, and lapis lazuli.

Bronze statuette of Thutmose IV: Very few metal statues survive that date from before the Late Period, though the Egyptians did have the technology to make large copper statues as early as the Old Kingdom.
This brief glimpse at the world of ancient Egypt is just a springboard for gaining an understanding of this compelling and complex culture.
A final note
The wonder of the internet is the astonishing access to information; one of the big problems with the internet is that anyone, regardless of knowledge or training, can post whatever they like and that information is presented at the same level as content put out by the experienced and trained. Information about ancient Egypt should always come from a well-vetted source, as there is a great deal of misinformation. The culture is astonishing enough on its own. Egypt remains highly influential across different areas of culture and vast swaths of time and space—Egyptian glass beads have been excavated in Viking tombs and revivals of Egyptian style still happen on an almost cyclical basis, even millenia later. We are surrounded by Egyptian imagery and concepts even if we don’t realize it; those emojis we use with such abandon are decidedly hieroglyphic. The more we know about what came before, the better we can grasp everything that has happened since. Only by understanding the past can we really envision the possibilities of the present and plan for the future.
Key questions to guide your reading
How did the annual flooding of the nile help form the egyptian view of the world, how might the regular behavior of certain animals—like falcons, vultures, snakes, and scarab beetles— suggest "heavenly wisdom" to the careful observer, how would you want to be depicted for eternity what identifying symbols would you want to include, terms to know and use.
canon of proportions
hierarchical scale
Need teaching images? Here is a Google Slideshow with many of the primary images in this chapter
Read a chapter about Ancient Egyptian religious life and afterlife
Collaborators
Dr. Amy Calvert
Dr. Beth Harris
Dr. Steven Zucker
The British Museum
The Metropolitan Museum of Art
Your donations help make art history free and accessible to everyone!
We've begun to update our look on video and essay pages!
Smarthistory's video and essay pages look a little different but still work the same way. We're in the process of updating our look in small ways to make Smarthistory's content easy to read and accessible on all devices. You can now also collapse the sidebar for focused watching and reading, then open it back up to navigate. We'll be making more improvements to the site over the next few months!
Arts & Culture | April 4, 2024
The Long History of Art Inspired by Solar Eclipses
For centuries, curious artists have been trying to make sense of the celestial event
:focal(1218x690:1219x691)/https://tf-cmsv2-smithsonianmag-media.s3.amazonaws.com/filer_public/6b/1c/6b1cfcc8-f8af-4174-bb06-ed982d24b719/viewfinder_still_1_cmyk_copy.jpg)
Elissaveta M. Brandon
Contributing Writer
Drivers in Dallas earlier this year may have noticed a curious trio of billboards on the side of Highway 67. Instead of advertising for the nearest brisket or “the world’s most refreshing beer,” the signs depicted a black disc ringed by a nebulous, fiery red circle.
The billboards were actually works of art. They were part of a five-billboard series called View Finder , in which American video artist Brian Fridge portrays a solar eclipse. To create his images, Fridge used a desktop lamp for the sun, an opaque disc for the moon, and a little motor pulling the disc on a string for the gravitational pull that steers the moon around the sun.
/https://tf-cmsv2-smithsonianmag-media.s3.amazonaws.com/filer_public/85/09/8509b054-51c0-4728-8c8e-116d904b830e/5_billboard_no5of5_image-2.jpg)
Fridge is one of many artists looking in the shadow of the moon for inspiration, ahead of the solar eclipse set to cross the United States on April 8 . At the Dallas Art Fair, Ashley Zelinskie will unveil an eerie sculpture depicting a bitumen-black moon cloaking a tentacled sun, plus a hologram of a floating black moon. Meanwhile, in New York City, Angela Lane , who has been creating postcard-sized oil paintings depicting eclipses, twin suns and other celestial phenomena for almost a decade, will present another exhibition of such paintings at the gallery Anat Ebgi later this year. And at her solo show at Hollis Taggart, Rachel MacFarlane will display The Event , a fantastical depiction of hurricane-battered Prince Edward Island in Canada that is coupled with an abstract depiction of a solar eclipse to imbue the landscape with a sense of foreboding. MacFarlane is also planning to view the upcoming eclipse, then rebuild the scene from memory back in her New York City studio.
/https://tf-cmsv2-smithsonianmag-media.s3.amazonaws.com/filer_public/a3/41/a3418602-747c-427e-97af-dfa541b518bb/rachel_macfarlane_-_htg19358_-_4000.jpg)
That the solar eclipse has become a favorite muse for artists isn’t all that surprising considering the theatrical allure of the phenomenon. What is remarkable is just how long artists have tried to make sense of the celestial event, and just how much their interpretations have evolved with our own understanding of eclipses.
“I think it brings us, in a visceral, time-limited way, in touch with these cosmic-scale things that really pull us out of ourselves and our own, little, tiny world and bring us into some kind of interface with the infinite,” says Karl Kusserow , a curator of American art at the Princeton University Art Museum who contributed to a 2017 exhibition about eclipses called “ Transient Effects .” “Eclipses have been happening for billions of years, and they engage us, in a very fundamental way, with that ineffable hugeness of the world beyond our daily routines.”
/https://tf-cmsv2-smithsonianmag-media.s3.amazonaws.com/filer_public/7f/e7/7fe705ec-c849-4462-a4c2-3ea96cb5a7d6/banner_eclipse-merch_1000x500_mag.jpg)
As it happens, the cyclical occurrence of a total solar eclipse (which, contrary to popular belief, isn’t all that rare and happens every 18 months or so somewhere in the world) makes this extraordinary phenomenon an ideal platform to explore the changing ways that humans perceive the world around them. These perceptions vary based on geography and culture, but also on time.
The solar eclipse hasn’t always been the entertaining tourist magnet it promises to be on April 8, when the path of totality will extend from Mexico, across the United States from Texas to Maine, and into Canada. People didn’t flock to rooftop viewing parties. They didn’t travel thousands of miles to watch the sky go dark. To ancient civilizations, an eclipse was seen as a dark omen that often signified the wrath of their gods. It wasn’t exhilarating; it was unsettling.

This might explain why, according to some experts, the solar eclipse wasn’t depicted much in the early days. In many ancient cultures, the sun was seen as a deity and a source of life that helped the crops grow every season. By the same token, the absence of a sun was fraught with danger—so why turn it into art?
“To make an illustration was not as easy as just picking up a ballpoint pen,” says Kusserow. “If you’re carving in stone, you’re going to focus on things that are not the worst of all times.”
Early depictions of the solar eclipse are few and far in between, but they do exist. In Norse mythology , the eclipse takes the form of two wolves—Skoll and Hati—chasing the sun and the moon. The story goes that if one of the wolves caught the sun, and a solar eclipse occurred, it would bring about the end of the world. And in Chinese mythology , the eclipse has often been depicted as a dragon devouring the sun.
/https://tf-cmsv2-smithsonianmag-media.s3.amazonaws.com/filer_public/f5/23/f523fa03-b997-45a9-9699-fca0bc0e50ea/lane_eclipse_after_image_2021_al1011.jpg)
In Western art, one of the most recurring representations of the eclipse has been in Christian art. But as the director of London’s Science Museum, Ian Blatchford, thoroughly outlines in a 2016 article in a Royal Society journal , there, too, the eclipse is more of a symbol than a literal depiction.
For example, the crucifixion was believed to have taken place during a total solar eclipse, so the Salerno Ivories from the 11th or 12th century show the dying Christ flanked by the sun and the moon, hinting to a verse from the Bible stating that “darkness fell over the whole land … because the sun was obscured.” In the Echternach Gospels , which illustrate the moment of Christ’s death on the cross, the sun and the moon take the form of human figures shrouding their faces in grief.
/https://tf-cmsv2-smithsonianmag-media.s3.amazonaws.com/filer_public/9b/3b/9b3b4e3b-696f-4351-8103-fc3e52fe8fd6/isaac-and-rebecca-spied-upon-by-abimelech-1519.jpg)
Depictions of eclipses became more and more realistic during the Renaissance, a period known for its convergence of art and science. Around 1518, Raphael and his workshop created a striking fresco titled Isaac and Rebecca Spied Upon by Abimelech . Located in a loggia at the Vatican Palace, the fresco features a detailed version of a solar eclipse, including the sun’s fiery streamers. Some experts believe that Raphael used the eclipse as a complex metaphor for Isaac and Rebecca’s stealthy deception and lovemaking, which occurred during totality.
In more recent years, various artists have explored celestial themes with increasing detail—from Etienne Trouvelot’s captivating astronomical drawings (1878) to Roy Lichtenstein’s cosmic pop art (1975). But the most important among them remains the early 20th-century painter Howard Russell Butler, whose eclipse paintings stand out both for their artistic and scientific merit.
Butler is most famous for his portraits of Andrew Carnegie, but he studied physics and law before turning to art. When the painter was 62 years old, he was invited to join a U.S. Naval Observatory expedition to Oregon, where he chronicled the 1918 solar eclipse. “I generally asked for ten sittings of two hours each,” he later wrote of that expedition. “But all the time they would allow me on this occasion was 112 1/10 seconds.”
/https://tf-cmsv2-smithsonianmag-media.s3.amazonaws.com/filer_public/e7/00/e7002b95-fdb7-4d69-8cff-0a97c5fbae20/pp357.jpg)
Butler would go on to paint three different eclipse paintings after observing the phenomenon in 1918, 1923 and 1925. By that time, photographers had attempted to document the eclipses with varying levels of success . But where photographers had struggled to capture the nuances and fiery hues of the sun’s corona, Butler succeeded by taking meticulous shorthand notes during the eclipses, then filling in the gaps later, a bit like a paint by numbers kit. (By some accounts, Butler had mastered this technique while painting 13 portraits of Carnegie, who reportedly could not sit still for long.)
Today, capturing a solar eclipse is no longer a herculean effort. Almost anyone with a digital camera, a solar lens filter and the patience to read explainers online can get a decent photo of it. The event has been documented in all its evanescent glory, and from every single angle. Yet, artists continue to be enthralled by it.
/https://tf-cmsv2-smithsonianmag-media.s3.amazonaws.com/filer_public/61/90/619075a4-7c73-41df-9bc5-e006454ea55b/eclipse3.jpg)
For visual artist Zelinskie, to make art that is inspired by science means to grapple with existential questions like “Why are we here?” and “What’s out there?” “We’ve been asking these questions since we were able to think, so to be answering these questions as an artist is basic human curiosity,” she says.
A little over two years ago, Zelinskie partnered with NASA scientists to produce a range of artworks, like a pair of marble gloves modeled after retired NASA astronaut Mike Massimino’s hands. This year, she’s unveiling Eclipse , a 3D-printed sculpture that doubles as a pinhole viewer, plus a hologram of the event. “[The solar eclipse] is something you have to see for yourself. You can’t describe it to somebody,” she says. “That’s why I chose to make a hologram of it. People see the hologram I’m making and take photos of it, but it doesn’t look right; you can’t tell that it’s 3D, and that’s the perfect medium.”
“It’s something you have to physically be there for,” she adds.

For her sculpture Eclipse , Zelinskie tried to convey the eerie feeling that washes over during a solar eclipse. “The birds freak out, the crickets come out, the animals think it’s nighttime, there’s a weird lighting situation,” she says. Zelinskie fashioned her moon using data from NASA’s Lunar Reconnaissance Orbiter, which has been mapping the lunar surface for 15 years. She then sheathed the sphere in a dark black patina, and she 3D-printed flares to represent the corona.
The resulting sculpture is somewhat sinister, which goes back full circle to the dawn of eclipse art. “Every culture has eclipse artwork, but it’s always, ‘God is punishing us,’” says Zelinskie. “I didn’t find one instance of, ‘Yay, an eclipse.’ I guess this is how humanity is interpreting it, so I’m staying true to that doom and gloom.”
Meanwhile, video artist Fridge has long been fascinated with light, matter and the passing of time, but his View Finder series marks the first time that he has made eclipse-inspired artwork. Fridge is known for his abstract images and films depicting natural processes that he records in his home—like seeded clouds he created in his own freezer or, in this case, desktop lamps that stand in for the sun. “I never really leave the house, and I don’t record anything outside in nature,” he told me on a recent video call from his house, which is also his studio. “I find things on the domestic scale, then try to imbue some kind of meaning to it.”
To make View Finder , Fridge used a little device that plugs into an iPhone to pick up the heat signature of any given object and create what is known as thermographic imaging. He created a six-minute film retracing the evolution of his makeshift eclipse, captured stills from various stages of an eclipse, then blew them up to fit the size of five billboards in and around Dallas.
The result was convincing enough that when the film, also titled View Finder , premiered at Dallas Contemporary on March 10, Fridge felt the need to clarify this wasn’t footage from “the actual thing” as some viewers had assumed. It was an artistic interpretation, an illusion that was intentionally created with the constraints of household objects. “I like the meaning that could come from something that’s this limited, and you feel those limits,” he says, referring to the highly realistic renderings one can achieve with a computer or artificial intelligence today.
With View Finder , Fridge says he wanted to explore different ways in which humans see things. You can don a pair of safety glasses and look up at the solar eclipse, or you can drive past a billboard on the side of a highway and find meaning in a still image.
“Hopefully that would do what art does,” he says, “which, to me, is to contribute to a sense of curiosity and wonder, and hopefully more complex and diverse ways of seeing the world.”
Get the latest Travel & Culture stories in your inbox.
/https://tf-cmsv2-smithsonianmag-media.s3.amazonaws.com/accounts/headshot/Elissaveta_M._Brandon.jpeg)
Elissaveta M. Brandon | | READ MORE
Elissaveta M. Brandon is a Brooklyn-based freelance writer whose work has appeared in Curbed , Metropolis , Architectural Digest and more. She writes about architecture, cities and the life in between.

From inspiring music to vibrant paintings, Latino art has influenced American society through a range of creative art forms.
Latino Musicians
Many music legends are part of the Latino community. Latin music has had a long presence in the United States and has brought many unique sounds and styles that are widely popular, like salsa and reggaeton. From rock to hip hop, Latino musicians have transcended boundaries and often showcase traditional Latin rhythms and sounds in their music. Latino musicians who have left a mark on pop culture include:

Explore the Smithsonian collections to learn more about groundbreaking Latino musicians.
Latino Art and Artists
Latino art embraces a captivating and diverse range of styles, including the creation of colorful paintings and murals, vibrant glass, and unique pottery. This dynamic group of artists often blends ancestral traditions with contemporary artistic styles to craft pieces that share their stories and spotlight issues important to their communities. Some of the Latina and Latino artists who have helped to expand the art scene in the United States with work that resonates across cultures include:
Judith “Judy” Baca
As someone who experienced the Chicano Movement, an era of Mexican American civil rights activism, Judy Baca knows how art can be a tool to empower communities. Through murals, monuments, paintings, sculptures, and more, Baca shares the stories of people who have contributed to U.S. history yet are often excluded from its retellings.

Antonio Sotomayor
Known primarily for his imaginative murals and paintings, Bolivian-born artist Antonio Sotomayor was a great contributor to growing the popularity of Latino Art in the United States.

The de la Torre Brothers
Mixed Media artists and brothers Einar and Jamex de la Torre collaborate to develop pieces that feature a blend of cultural influences. In their childhood, the brothers moved with their family from Mexico to the United States, and their work often draws from their resulting multifaceted views of the world. The brothers work in a variety of mediums, including blown glass, cast resin and lenticular prints.
Ana Mendieta
A Cuban-American performance artist, Ana Mendieta created a range of artistic works that drew from her experience of exile and displacement. She used photography, film, video, drawing, and more to craft groundbreaking and transformational pieces.

Rafael López
Through his illustrations, López brings vibrant and diverse characters to children’s books. In 2022 he created portraits for the Smithsonian National Museum of the American Latino and taught workshops as the first Guest Artist of the Smithsonian Postal Museum . His light installation hangs in our gallery's General Motors Learning Lounge .

Roberto Lugo
Putting a modern twist on classic styles, Roberto Lugo crafts ceramics that feature themes of poverty, inequality, and racial injustice.

Get to know more about the diverse Latino artists who have pushed the boundaries of artistic expression.
Latino Actors

- Undergraduate Admission
- Graduate Admission
- Tuition & Financial Aid
- Communications
- Health Sciences and Human Performance
- Humanities and Sciences
- Music, Theatre, and Dance
- IC Resources
- Office of the President
- Ithaca College at a Glance
- Awards and Accolades
- Five-Year Strategic Plan
- Public Health
- Directories
- Course Catalog
- Undergraduate
The Department of Art, Art History, & Architecture Visiting Artist Series Presents Sydney Maubert Wednesday, April 10, 2024 @5:30PM
Handwerker gallery.
SYDNEY MAUBERT is an architect, artist, muralist, scholar, and teacher. She is the founder and director of Studio Maubert, an architectural, artistic, and scholarly practice exploring Black, Latin, Indigenous, and Fem modes of cultural and spatial production. Studio Maubert is Maubert’s interdisciplinary architectural, artistic, and scholarly practice researching questions at the intersection of architecture, geography, and policy — including urban morphologies and racialized habitation patterns in Miami and New York, and their intertwined legacies with colonialism and genocide. Her work is largely animated by Black studies, decolonial studies, fugitive practice, history, and cultural geography.
She holds post-professional and professional degrees in architecture from Yale (2022) and the University of Miami (2020), with double minors in writing and art. A recipient of Cornell’s Strauch Fellowship, she teaches and researches (Fall 2022–ongoing) questions surrounding housing, race, geography, and unruliness. She worked as an intern at Bernheimer Architecture (2021–22) and Trelles Cabarrocas (2018, 2019) and has received several awards including the Yale Moulton Andros Award (2022) and the University of Miami Alpha Rho Chi Award (2020).

QUEEN OF THE SWAMP, An Examination of Caribbean and Southern Architecture
Individuals with disabilities requiring accommodations should contact Doreen Brown at [email protected] or 607-274-3330. We ask that requests for accommodations be made as soon as possible.

Why Taiwan Was So Prepared for a Powerful Earthquake
Decades of learning from disasters, tightening building codes and increasing public awareness may have helped its people better weather strong quakes.
Search-and-rescue teams recover a body from a leaning building in Hualien, Taiwan. Thanks to improvements in building codes after past earthquakes, many structures withstood Wednesday’s quake. Credit...
Supported by
- Share full article
By Chris Buckley , Meaghan Tobin and Siyi Zhao
Photographs by Lam Yik Fei
Chris Buckley reported from the city of Hualien, Meaghan Tobin from Taipei, in Taiwan.
- April 4, 2024
When the largest earthquake in Taiwan in half a century struck off its east coast, the buildings in the closest city, Hualien, swayed and rocked. As more than 300 aftershocks rocked the island over the next 24 hours to Thursday morning, the buildings shook again and again.
But for the most part, they stood.
Even the two buildings that suffered the most damage remained largely intact, allowing residents to climb to safety out the windows of upper stories. One of them, the rounded, red brick Uranus Building, which leaned precariously after its first floors collapsed, was mostly drawing curious onlookers.
The building is a reminder of how much Taiwan has prepared for disasters like the magnitude-7.4 earthquake that jolted the island on Wednesday. Perhaps because of improvements in building codes, greater public awareness and highly trained search-and-rescue operations — and, likely, a dose of good luck — the casualty figures were relatively low. By Thursday, 10 people had died and more than 1,000 others were injured. Several dozen were missing.
“Similar level earthquakes in other societies have killed far more people,” said Daniel Aldrich , a director of the Global Resilience Institute at Northeastern University. Of Taiwan, he added: “And most of these deaths, it seems, have come from rock slides and boulders, rather than building collapses.”
Across the island, rail traffic had resumed by Thursday, including trains to Hualien. Workers who had been stuck in a rock quarry were lifted out by helicopter. Roads were slowly being repaired. Hundreds of people were stranded at a hotel near a national park because of a blocked road, but they were visited by rescuers and medics.

On Thursday in Hualien city, the area around the Uranus Building was sealed off, while construction workers tried to prevent the leaning structure from toppling completely. First they placed three-legged concrete blocks that resembled giant Lego pieces in front of the building, and then they piled dirt and rocks on top of those blocks with excavators.
“We came to see for ourselves how serious it was, why it has tilted,” said Chang Mei-chu, 66, a retiree who rode a scooter with her husband Lai Yung-chi, 72, to the building on Thursday. Mr. Lai said he was a retired builder who used to install power and water pipes in buildings, and so he knew about building standards. The couple’s apartment, near Hualien’s train station, had not been badly damaged, he said.
“I wasn’t worried about our building, because I know they paid attention to earthquake resistance when building it. I watched them pour the cement to make sure,” Mr. Lai said. “There have been improvements. After each earthquake, they raise the standards some more.”
It was possible to walk for city blocks without seeing clear signs of the powerful earthquake. Many buildings remained intact, some of them old and weather-worn; others modern, multistory concrete-and-glass structures. Shops were open, selling coffee, ice cream and betel nuts. Next to the Uranus Building, a popular night market with food stalls offering fried seafood, dumplings and sweets was up and running by Thursday evening.
Earthquakes are unavoidable in Taiwan, which sits on multiple active faults. Decades of work learning from other disasters, implementing strict building codes and increasing public awareness have gone into helping its people weather frequent strong quakes.
Not far from the Uranus Building, for example, officials had inspected a building with cracked pillars and concluded that it was dangerous to stay in. Residents were given 15 minutes to dash inside and retrieve as many belongings as they could. Some ran out with computers, while others threw bags of clothes out of windows onto the street, which was also still littered with broken glass and cement fragments from the quake.
One of its residents, Chen Ching-ming, a preacher at a church next door, said he thought the building might be torn down. He was able to salvage a TV and some bedding, which now sat on the sidewalk, and was preparing to go back in for more. “I’ll lose a lot of valuable things — a fridge, a microwave, a washing machine,” he said. “All gone.”
Requirements for earthquake resistance have been built into Taiwan’s building codes since 1974. In the decades since, the writers of Taiwan’s building code also applied lessons learned from other major earthquakes around the world, including in Mexico and Los Angeles, to strengthen Taiwan’s code.
After more than 2,400 people were killed and at least 10,000 others injured during the Chi-Chi quake of 1999, thousands of buildings built before the quake were reviewed and reinforced. After another strong quake in 2018 in Hualien, the government ordered a new round of building inspections. Since then, multiple updates to the building code have been released.
“We have retrofitted more than 10,000 school buildings in the last 20 years,” said Chung-Che Chou, the director general of the National Center for Research on Earthquake Engineering in Taipei.
The government had also helped reinforce private apartment buildings over the past six years by adding new steel braces and increasing column and beam sizes, Dr. Chou said. Not far from the buildings that partially collapsed in Hualien, some of the older buildings that had been retrofitted in this way survived Wednesday’s quake, he said.
The result of all this is that even Taiwan’s tallest skyscrapers can withstand regular seismic jolts. The capital city’s most iconic building, Taipei 101, once the tallest building in the world, was engineered to stand through typhoon winds and frequent quakes. Still, some experts say that more needs to be done to either strengthen or demolish structures that don’t meet standards, and such calls have grown louder in the wake of the latest earthquake.
Taiwan has another major reason to protect its infrastructure: It is home to the majority of production for the Taiwan Semiconductor Manufacturing Company, the world’s largest maker of advanced computer chips. The supply chain for electronics from smartphones to cars to fighter jets rests on the output of TSMC’s factories, which make these chips in facilities that cost billions of dollars to build.
The 1999 quake also prompted TSMC to take extra steps to insulate its factories from earthquake damage. The company made major structural adjustments and adopted new technologies like early warning systems. When another large quake struck the southern city of Kaohsiung in February 2016, TSMC’s two nearby factories survived without structural damage.
Taiwan has made strides in its response to disasters, experts say. In the first 24 hours after the quake, rescuers freed hundreds of people who were trapped in cars in between rockfalls on the highway and stranded on mountain ledges in rock quarries.
“After years of hard work on capacity building, the overall performance of the island has improved significantly,” said Bruce Wong, an emergency management consultant in Hong Kong. Taiwan’s rescue teams have come to specialize in complex efforts, he said, and it has also been able to tap the skills of trained volunteers.

Taiwan’s resilience also stems from a strong civil society that is involved in public preparedness for disasters.
Ou Chi-hu, a member of a group of Taiwanese military veterans, was helping distribute water and other supplies at a school that was serving as a shelter for displaced residents in Hualien. He said that people had learned from the 1999 earthquake how to be more prepared.
“They know to shelter in a corner of the room or somewhere else safer,” he said. Many residents also keep a bag of essentials next to their beds, and own fire extinguishers, he added.
Around him, a dozen or so other charities and groups were offering residents food, money, counseling and childcare. The Tzu Chi Foundation, a large Taiwanese Buddhist charity, provided tents for families to use inside the school hall so they could have more privacy. Huang Yu-chi, a disaster relief manager with the foundation, said nonprofits had learned from earlier disasters.
“Now we’re more systematic and have a better idea of disaster prevention,” Mr. Huang said.
Mike Ives contributed reporting from Seoul.
Chris Buckley , the chief China correspondent for The Times, reports on China and Taiwan from Taipei, focused on politics, social change and security and military issues. More about Chris Buckley
Meaghan Tobin is a technology correspondent for The Times based in Taipei, covering business and tech stories in Asia with a focus on China. More about Meaghan Tobin
Siyi Zhao is a reporter and researcher who covers news in mainland China for The Times in Seoul. More about Siyi Zhao
Advertisement

IMAGES
VIDEO
COMMENTS
Art History Analysis - Formal Analysis and Stylistic Analysis . Typically in an art history class the main essay students will need to write for a final paper or for an exam is a formal or stylistic analysis. A formal analysis is just what it sounds like - you need to analyze the form of the artwork. This includes the individual design ...
New Essays. The Feathered Serpent Pyramid and Ciudadela of Teotihuacan (ca. 150-250 CE) Teotihuacan (ca. 100 BCE-800 CE) Stone Masks and Figurines from Northwest Argentina (500 BCE-650 CE) Maria Monaci Gallenga (1880-1944) Ann Lowe (ca. 1898-1981)
In art history, however, you will be asked to gather your evidence from close observations of objects or images. Beyond painting, photography, and sculpture, you may be asked to write about posters, illustrations, coins, and other materials. Even though art historians study a wide range of materials, there are a few prevalent assignments that ...
Art history essays play a pivotal role in art history studies, serving as a key medium through which students engage with and contribute to the field. These essays provide a platform for critical analysis, contextual understanding, and the exploration of artistic movements and themes. This article delves into the significance of art history ...
pier writing experience will be a better essay remains to be seen—but it is a reasonable expectation. If this happens, we might also get happier teachers. Though not intended specifically as an introduction to writing art history, this book is written from the perspective of an art historian. This is in part a limitation of the au-
Remember - essays take time. It will take at least two weeks for you to do the following steps to write your final draft: There are several excellent books available which can help you with writing essays including: Anne D'Alleva, How to Write Art History, London, Laurence King, 2010. STEP 1: CHOOSING AND ANALYSING A QUESTION:
Writing Assignments. You will be expected to write several different kinds of art history papers. They include: Close Visual Analysis Essays. Close Visual Analysis in dialogue with scholarly essays. Research Papers. Close Visual Analysispieces are the most commonly written papers in an introductory art history course.
Guide for Writing in Art History. Art history courses cultivate critically analyze images, objects, and architectural spaces as well as academic discourse, scholarship, and historical sources. Art history is a humanistic discipline that brings together research to explore historical contexts while engaging in ways of looking at, describing, and ...
Works of art are highly influenced by the culture, historical time period and movement in which they were created. You should gather information about these BEFORE you start writing your essay. If you describe a characteristic of one piece of art, you must describe how the OTHER piece of art treats that characteristic.
Although art historians vary in their approaches to art, there are a few common approaches that form the backbone of the field. The following handout describes these approaches briefly and lets you know what you might need to do to tackle a paper assignment in this field. Just remember: there is more than one way of doing art history.
Heilbrunn Timeline of Art History Discover the story of art and global culture through The Met collection. Funded by the Heilbrunn Foundation, New Tamarind Foundation, and Zodiac Fund. Essays Explore more than 1,000 essays on a wide range of topics, including artists, materials, movements, and themes. Read more essays ...
The most common are a formal analysis and a stylistic analysis. Stylistic analyses often involve offering a comparison between two different works. One of the challenges of art history writing is that it requires a vocabulary to describe what you see when you look at a painting, drawing, sculpture or other media. This checklist is designed to ...
Art History and Anthropology: Modern Encounters, 1870-1970 2023 ... The Art of Remembering: Essays on African American Art and History 2024 The Art of Resistance: Painting by Candlelight in Mao's China 2017 The Art of Sculpture 1956 The Art of Solidarity: Visual and Performative Politics in Cold War Latin America ...
Art History The transition from the Baroque to the Rococo style in sculpture and painting was attended by a concurrent shift in European power relations, as the cultural and political hegemony of the Roman Catholic Church gave way to secular institutions of power. Comparing a work produced during the height of either style demonstrates this shift implicitly, because the Rococo style contains a ...
Instead, Nochlin's essay functions as a critique of art institutions, beginning with European salons, which were structured in such a way as to deter women from rising to the highest echelons. Nochlin's essay is considered the beginning of modern feminist art history and a textbook example of institutional critique. Notable Quote
Art History 201: Art and Revolution 1750-1850. Grade: A. History painting was regarded as the highest genre in the hierarchy of arts. It showcased narrative works on a monumental scale and sought to encourage an intellectual and didactic comprehension. The late eighteenth century and early nineteenth century was a time of immense social ...
A comprehensive guide will help you understand how to approach visual analysis assignments. In art history essays, you will be required to write about a wide range of materials, from illustrations to images. You will also be expected to collect your evidence by observing objects. On the other hand, if you are determined to master this skill by ...
Art through History Essay. Exclusively available on IvyPanda. Updated: Dec 28th, 2023. During the 19 th century, conflict between the ancient and modern art emerged. As a matter of fact, the century witnessed the beginning of radical changes in the field of art (Galenson 'painting outside the Lines' 45).
So to understand the value of art, let's look at how art has been valued through history and consider how it is valuable today. The value of creating. At its most basic level, the act of creating is rewarding in itself. Children draw for the joy of it before they can speak, and creating pictures, sculptures and writing is both a valuable ...
Introduction to Art30,000 years of human creativity. The history of art is a vast story of human creativity, a record of our passions and struggles from before written history through today. Obelisk is a free, online art history textbook, sharing the wild, tragic and inspiring stories of artists and their work from 30,000 BCE through Modern Art.
Like its predecessor, this new edition consists of essays that cover a wide variety of "loaded" terms in the history of art, from sign to meaning, ritual to commodity. Each essay explains and comments on a single term, discussing the issues the term raises and putting the term into practice as an interpretive framework for a specific work of art.
One of the significant differences between Egyptian and Aegean representations of humans in art, whether in cave paintings, drawings, or sculptures, is the ideational positioning of the person in the work of art. Pages: 2. Words: 808. We will write a custom essay specifically for you. for only 11.00 9.35/page.
Throughout ancient Egypt's long history, periods of unified control were interspersed with moments of instability where parts of the country were controlled by different authorities. These repeated waves of political and cultural development create a decidedly complex history that spans thousands of years.
In the latter years of World War II, the New York art scene started coalescing around a group of artists including Jackson Pollock and Willem de Kooning, visionaries who would develop a daring new ...
Howard Russell Butler (1856-1934; born New York City, NY; died Princeton, NJ), Solar Eclipse, 1918. Oil on canvas, 82.3 x 123 cm. Princeton University, gift of H. Russell Butler Jr. Butler would ...
See how Latino Art and artists have shaped American culture through sound, painting, and a range of other creative art forms. ... monuments, paintings, sculptures, and more, Baca shares the stories of people who have contributed to U.S. history yet are often excluded from its retellings. Click to view more fullsize image of L2-0000645-D2-2022. ...
Her work is largely animated by Black studies, decolonial studies, fugitive practice, history, and cultural geography.She holds post-professional and professional degrees in architecture from Yale (2022) and the University of Miami (2020), with double minors in writing and art.
In 16th and 17th century Britain, for example, women's alopecia was sometimes interpreted as retribution for sins, including adultery. Some historical art, however, depicts a more neutral, or ...
April 4, 2024. Leer en español. When the largest earthquake in Taiwan in half a century struck off its east coast, the buildings in the closest city, Hualien, swayed and rocked. As more than 300 ...