

Narrative Writing: A Complete Guide for Teachers and Students
MASTERING THE CRAFT OF NARRATIVE WRITING
Narratives build on and encourage the development of the fundamentals of writing. They also require developing an additional skill set: the ability to tell a good yarn, and storytelling is as old as humanity.
We see and hear stories everywhere and daily, from having good gossip on the doorstep with a neighbor in the morning to the dramas that fill our screens in the evening.
Good narrative writing skills are hard-won by students even though it is an area of writing that most enjoy due to the creativity and freedom it offers.
Here we will explore some of the main elements of a good story: plot, setting, characters, conflict, climax, and resolution . And we will look too at how best we can help our students understand these elements, both in isolation and how they mesh together as a whole.

WHAT IS A NARRATIVE?

A narrative is a story that shares a sequence of events , characters, and themes. It expresses experiences, ideas, and perspectives that should aspire to engage and inspire an audience.
A narrative can spark emotion, encourage reflection, and convey meaning when done well.
Narratives are a popular genre for students and teachers as they allow the writer to share their imagination, creativity, skill, and understanding of nearly all elements of writing. We occasionally refer to a narrative as ‘creative writing’ or story writing.
The purpose of a narrative is simple, to tell the audience a story. It can be written to motivate, educate, or entertain and can be fact or fiction.
A COMPLETE UNIT ON TEACHING NARRATIVE WRITING

Teach your students to become skilled story writers with this HUGE NARRATIVE & CREATIVE STORY WRITING UNIT . Offering a COMPLETE SOLUTION to teaching students how to craft CREATIVE CHARACTERS, SUPERB SETTINGS, and PERFECT PLOTS .
Over 192 PAGES of materials, including:
TYPES OF NARRATIVE WRITING
There are many narrative writing genres and sub-genres such as these.
We have a complete guide to writing a personal narrative that differs from the traditional story-based narrative covered in this guide. It includes personal narrative writing prompts, resources, and examples and can be found here.

As we can see, narratives are an open-ended form of writing that allows you to showcase creativity in many directions. However, all narratives share a common set of features and structure known as “Story Elements”, which are briefly covered in this guide.
Don’t overlook the importance of understanding story elements and the value this adds to you as a writer who can dissect and create grand narratives. We also have an in-depth guide to understanding story elements here .
CHARACTERISTICS OF NARRATIVE WRITING
Narrative structure.
ORIENTATION (BEGINNING) Set the scene by introducing your characters, setting and time of the story. Establish your who, when and where in this part of your narrative
COMPLICATION AND EVENTS (MIDDLE) In this section activities and events involving your main characters are expanded upon. These events are written in a cohesive and fluent sequence.
RESOLUTION (ENDING) Your complication is resolved in this section. It does not have to be a happy outcome, however.
EXTRAS: Whilst orientation, complication and resolution are the agreed norms for a narrative, there are numerous examples of popular texts that did not explicitly follow this path exactly.
NARRATIVE FEATURES
LANGUAGE: Use descriptive and figurative language to paint images inside your audience’s minds as they read.
PERSPECTIVE Narratives can be written from any perspective but are most commonly written in first or third person.
DIALOGUE Narratives frequently switch from narrator to first-person dialogue. Always use speech marks when writing dialogue.
TENSE If you change tense, make it perfectly clear to your audience what is happening. Flashbacks might work well in your mind but make sure they translate to your audience.
THE PLOT MAP
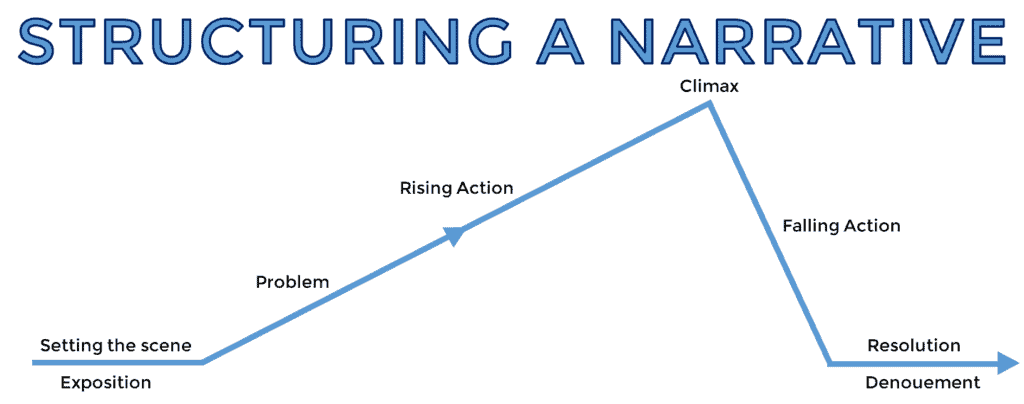
This graphic is known as a plot map, and nearly all narratives fit this structure in one way or another, whether romance novels, science fiction or otherwise.
It is a simple tool that helps you understand and organise a story’s events. Think of it as a roadmap that outlines the journey of your characters and the events that unfold. It outlines the different stops along the way, such as the introduction, rising action, climax, falling action, and resolution, that help you to see how the story builds and develops.
Using a plot map, you can see how each event fits into the larger picture and how the different parts of the story work together to create meaning. It’s a great way to visualize and analyze a story.
Be sure to refer to a plot map when planning a story, as it has all the essential elements of a great story.
THE 5 KEY STORY ELEMENTS OF A GREAT NARRATIVE (6-MINUTE TUTORIAL VIDEO)
This video we created provides an excellent overview of these elements and demonstrates them in action in stories we all know and love.

HOW TO WRITE A NARRATIVE

Now that we understand the story elements and how they come together to form stories, it’s time to start planning and writing your narrative.
In many cases, the template and guide below will provide enough details on how to craft a great story. However, if you still need assistance with the fundamentals of writing, such as sentence structure, paragraphs and using correct grammar, we have some excellent guides on those here.
USE YOUR WRITING TIME EFFECTIVELY: Maximize your narrative writing sessions by spending approximately 20 per cent of your time planning and preparing. This ensures greater productivity during your writing time and keeps you focused and on task.
Use tools such as graphic organizers to logically sequence your narrative if you are not a confident story writer. If you are working with reluctant writers, try using narrative writing prompts to get their creative juices flowing.
Spend most of your writing hour on the task at hand, don’t get too side-tracked editing during this time and leave some time for editing. When editing a narrative, examine it for these three elements.
- Spelling and grammar ( Is it readable?)
- Story structure and continuity ( Does it make sense, and does it flow? )
- Character and plot analysis. (Are your characters engaging? Does your problem/resolution work? )
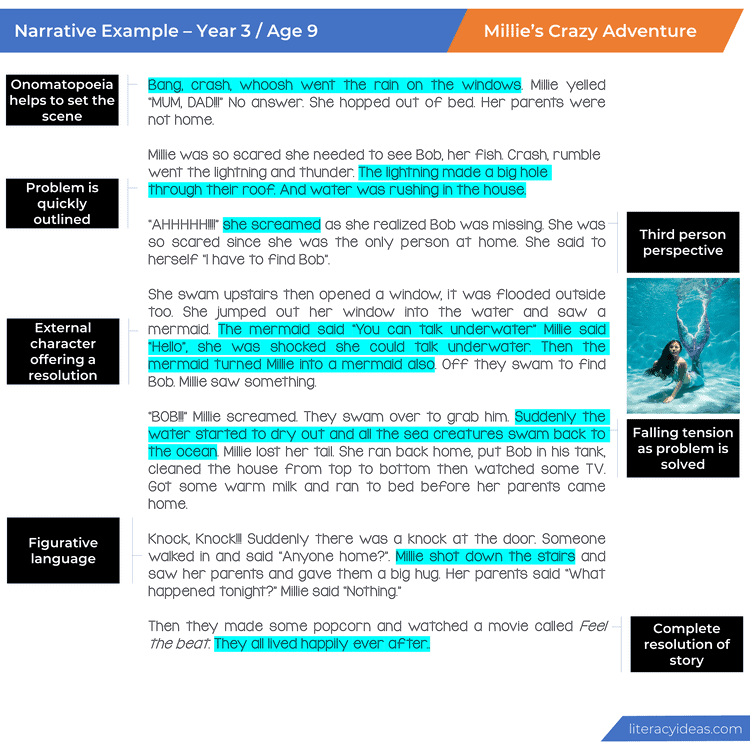
1. SETTING THE SCENE: THE WHERE AND THE WHEN

The story’s setting often answers two of the central questions in the story, namely, the where and the when. The answers to these two crucial questions will often be informed by the type of story the student is writing.
The story’s setting can be chosen to quickly orient the reader to the type of story they are reading. For example, a fictional narrative writing piece such as a horror story will often begin with a description of a haunted house on a hill or an abandoned asylum in the middle of the woods. If we start our story on a rocket ship hurtling through the cosmos on its space voyage to the Alpha Centauri star system, we can be reasonably sure that the story we are embarking on is a work of science fiction.
Such conventions are well-worn clichés true, but they can be helpful starting points for our novice novelists to make a start.
Having students choose an appropriate setting for the type of story they wish to write is an excellent exercise for our younger students. It leads naturally onto the next stage of story writing, which is creating suitable characters to populate this fictional world they have created. However, older or more advanced students may wish to play with the expectations of appropriate settings for their story. They may wish to do this for comic effect or in the interest of creating a more original story. For example, opening a story with a children’s birthday party does not usually set up the expectation of a horror story. Indeed, it may even lure the reader into a happy reverie as they remember their own happy birthday parties. This leaves them more vulnerable to the surprise element of the shocking action that lies ahead.
Once the students have chosen a setting for their story, they need to start writing. Little can be more terrifying to English students than the blank page and its bare whiteness stretching before them on the table like a merciless desert they must cross. Give them the kick-start they need by offering support through word banks or writing prompts. If the class is all writing a story based on the same theme, you may wish to compile a common word bank on the whiteboard as a prewriting activity. Write the central theme or genre in the middle of the board. Have students suggest words or phrases related to the theme and list them on the board.
You may wish to provide students with a copy of various writing prompts to get them started. While this may mean that many students’ stories will have the same beginning, they will most likely arrive at dramatically different endings via dramatically different routes.

A bargain is at the centre of the relationship between the writer and the reader. That bargain is that the reader promises to suspend their disbelief as long as the writer creates a consistent and convincing fictional reality. Creating a believable world for the fictional characters to inhabit requires the student to draw on convincing details. The best way of doing this is through writing that appeals to the senses. Have your student reflect deeply on the world that they are creating. What does it look like? Sound like? What does the food taste like there? How does it feel like to walk those imaginary streets, and what aromas beguile the nose as the main character winds their way through that conjured market?
Also, Consider the when; or the time period. Is it a future world where things are cleaner and more antiseptic? Or is it an overcrowded 16th-century London with human waste stinking up the streets? If students can create a multi-sensory installation in the reader’s mind, then they have done this part of their job well.
Popular Settings from Children’s Literature and Storytelling
- Fairytale Kingdom
- Magical Forest
- Village/town
- Underwater world
- Space/Alien planet
2. CASTING THE CHARACTERS: THE WHO
Now that your student has created a believable world, it is time to populate it with believable characters.
In short stories, these worlds mustn’t be overpopulated beyond what the student’s skill level can manage. Short stories usually only require one main character and a few secondary ones. Think of the short story more as a small-scale dramatic production in an intimate local theater than a Hollywood blockbuster on a grand scale. Too many characters will only confuse and become unwieldy with a canvas this size. Keep it simple!
Creating believable characters is often one of the most challenging aspects of narrative writing for students. Fortunately, we can do a few things to help students here. Sometimes it is helpful for students to model their characters on actual people they know. This can make things a little less daunting and taxing on the imagination. However, whether or not this is the case, writing brief background bios or descriptions of characters’ physical personality characteristics can be a beneficial prewriting activity. Students should give some in-depth consideration to the details of who their character is: How do they walk? What do they look like? Do they have any distinguishing features? A crooked nose? A limp? Bad breath? Small details such as these bring life and, therefore, believability to characters. Students can even cut pictures from magazines to put a face to their character and allow their imaginations to fill in the rest of the details.
Younger students will often dictate to the reader the nature of their characters. To improve their writing craft, students must know when to switch from story-telling mode to story-showing mode. This is particularly true when it comes to character. Encourage students to reveal their character’s personality through what they do rather than merely by lecturing the reader on the faults and virtues of the character’s personality. It might be a small relayed detail in the way they walk that reveals a core characteristic. For example, a character who walks with their head hanging low and shoulders hunched while avoiding eye contact has been revealed to be timid without the word once being mentioned. This is a much more artistic and well-crafted way of doing things and is less irritating for the reader. A character who sits down at the family dinner table immediately snatches up his fork and starts stuffing roast potatoes into his mouth before anyone else has even managed to sit down has revealed a tendency towards greed or gluttony.
Understanding Character Traits
Again, there is room here for some fun and profitable prewriting activities. Give students a list of character traits and have them describe a character doing something that reveals that trait without ever employing the word itself.
It is also essential to avoid adjective stuffing here. When looking at students’ early drafts, adjective stuffing is often apparent. To train the student out of this habit, choose an adjective and have the student rewrite the sentence to express this adjective through action rather than telling.
When writing a story, it is vital to consider the character’s traits and how they will impact the story’s events. For example, a character with a strong trait of determination may be more likely to overcome obstacles and persevere. In contrast, a character with a tendency towards laziness may struggle to achieve their goals. In short, character traits add realism, depth, and meaning to a story, making it more engaging and memorable for the reader.
Popular Character Traits in Children’s Stories
- Determination
- Imagination
- Perseverance
- Responsibility
We have an in-depth guide to creating great characters here , but most students should be fine to move on to planning their conflict and resolution.
3. NO PROBLEM? NO STORY! HOW CONFLICT DRIVES A NARRATIVE

This is often the area apprentice writers have the most difficulty with. Students must understand that without a problem or conflict, there is no story. The problem is the driving force of the action. Usually, in a short story, the problem will center around what the primary character wants to happen or, indeed, wants not to happen. It is the hurdle that must be overcome. It is in the struggle to overcome this hurdle that events happen.
Often when a student understands the need for a problem in a story, their completed work will still not be successful. This is because, often in life, problems remain unsolved. Hurdles are not always successfully overcome. Students pick up on this.
We often discuss problems with friends that will never be satisfactorily resolved one way or the other, and we accept this as a part of life. This is not usually the case with writing a story. Whether a character successfully overcomes his or her problem or is decidedly crushed in the process of trying is not as important as the fact that it will finally be resolved one way or the other.
A good practical exercise for students to get to grips with this is to provide copies of stories and have them identify the central problem or conflict in each through discussion. Familiar fables or fairy tales such as Three Little Pigs, The Boy Who Cried Wolf, Cinderella, etc., are great for this.
While it is true that stories often have more than one problem or that the hero or heroine is unsuccessful in their first attempt to solve a central problem, for beginning students and intermediate students, it is best to focus on a single problem, especially given the scope of story writing at this level. Over time students will develop their abilities to handle more complex plots and write accordingly.
Popular Conflicts found in Children’s Storytelling.
- Good vs evil
- Individual vs society
- Nature vs nurture
- Self vs others
- Man vs self
- Man vs nature
- Man vs technology
- Individual vs fate
- Self vs destiny
Conflict is the heart and soul of any good story. It’s what makes a story compelling and drives the plot forward. Without conflict, there is no story. Every great story has a struggle or a problem that needs to be solved, and that’s where conflict comes in. Conflict is what makes a story exciting and keeps the reader engaged. It creates tension and suspense and makes the reader care about the outcome.
Like in real life, conflict in a story is an opportunity for a character’s growth and transformation. It’s a chance for them to learn and evolve, making a story great. So next time stories are written in the classroom, remember that conflict is an essential ingredient, and without it, your story will lack the energy, excitement, and meaning that makes it truly memorable.
4. THE NARRATIVE CLIMAX: HOW THINGS COME TO A HEAD!

The climax of the story is the dramatic high point of the action. It is also when the struggles kicked off by the problem come to a head. The climax will ultimately decide whether the story will have a happy or tragic ending. In the climax, two opposing forces duke things out until the bitter (or sweet!) end. One force ultimately emerges triumphant. As the action builds throughout the story, suspense increases as the reader wonders which of these forces will win out. The climax is the release of this suspense.
Much of the success of the climax depends on how well the other elements of the story have been achieved. If the student has created a well-drawn and believable character that the reader can identify with and feel for, then the climax will be more powerful.
The nature of the problem is also essential as it determines what’s at stake in the climax. The problem must matter dearly to the main character if it matters at all to the reader.
Have students engage in discussions about their favorite movies and books. Have them think about the storyline and decide the most exciting parts. What was at stake at these moments? What happened in your body as you read or watched? Did you breathe faster? Or grip the cushion hard? Did your heart rate increase, or did you start to sweat? This is what a good climax does and what our students should strive to do in their stories.
The climax puts it all on the line and rolls the dice. Let the chips fall where the writer may…
Popular Climax themes in Children’s Stories
- A battle between good and evil
- The character’s bravery saves the day
- Character faces their fears and overcomes them
- The character solves a mystery or puzzle.
- The character stands up for what is right.
- Character reaches their goal or dream.
- The character learns a valuable lesson.
- The character makes a selfless sacrifice.
- The character makes a difficult decision.
- The character reunites with loved ones or finds true friendship.
5. RESOLUTION: TYING UP LOOSE ENDS
After the climactic action, a few questions will often remain unresolved for the reader, even if all the conflict has been resolved. The resolution is where those lingering questions will be answered. The resolution in a short story may only be a brief paragraph or two. But, in most cases, it will still be necessary to include an ending immediately after the climax can feel too abrupt and leave the reader feeling unfulfilled.
An easy way to explain resolution to students struggling to grasp the concept is to point to the traditional resolution of fairy tales, the “And they all lived happily ever after” ending. This weather forecast for the future allows the reader to take their leave. Have the student consider the emotions they want to leave the reader with when crafting their resolution.
While the action is usually complete by the end of the climax, it is in the resolution that if there is a twist to be found, it will appear – think of movies such as The Usual Suspects. Pulling this off convincingly usually requires considerable skill from a student writer. Still, it may well form a challenging extension exercise for those more gifted storytellers among your students.
Popular Resolutions in Children’s Stories
- Our hero achieves their goal
- The character learns a valuable lesson
- A character finds happiness or inner peace.
- The character reunites with loved ones.
- Character restores balance to the world.
- The character discovers their true identity.
- Character changes for the better.
- The character gains wisdom or understanding.
- Character makes amends with others.
- The character learns to appreciate what they have.
Once students have completed their story, they can edit for grammar, vocabulary choice, spelling, etc., but not before!
As mentioned, there is a craft to storytelling, as well as an art. When accurate grammar, perfect spelling, and immaculate sentence structures are pushed at the outset, they can cause storytelling paralysis. For this reason, it is essential that when we encourage the students to write a story, we give them license to make mechanical mistakes in their use of language that they can work on and fix later.
Good narrative writing is a very complex skill to develop and will take the student years to become competent. It challenges not only the student’s technical abilities with language but also her creative faculties. Writing frames, word banks, mind maps, and visual prompts can all give valuable support as students develop the wide-ranging and challenging skills required to produce a successful narrative writing piece. But, at the end of it all, as with any craft, practice and more practice is at the heart of the matter.
TIPS FOR WRITING A GREAT NARRATIVE
- Start your story with a clear purpose: If you can determine the theme or message you want to convey in your narrative before starting it will make the writing process so much simpler.
- Choose a compelling storyline and sell it through great characters, setting and plot: Consider a unique or interesting story that captures the reader’s attention, then build the world and characters around it.
- Develop vivid characters that are not all the same: Make your characters relatable and memorable by giving them distinct personalities and traits you can draw upon in the plot.
- Use descriptive language to hook your audience into your story: Use sensory language to paint vivid images and sequences in the reader’s mind.
- Show, don’t tell your audience: Use actions, thoughts, and dialogue to reveal character motivations and emotions through storytelling.
- Create a vivid setting that is clear to your audience before getting too far into the plot: Describe the time and place of your story to immerse the reader fully.
- Build tension: Refer to the story map earlier in this article and use conflict, obstacles, and suspense to keep the audience engaged and invested in your narrative.
- Use figurative language such as metaphors, similes, and other literary devices to add depth and meaning to your narrative.
- Edit, revise, and refine: Take the time to refine and polish your writing for clarity and impact.
- Stay true to your voice: Maintain your unique perspective and style in your writing to make it your own.
NARRATIVE WRITING EXAMPLES (Student Writing Samples)
Below are a collection of student writing samples of narratives. Click on the image to enlarge and explore them in greater detail. Please take a moment to read these creative stories in detail and the teacher and student guides which highlight some of the critical elements of narratives to consider before writing.
Please understand these student writing samples are not intended to be perfect examples for each age or grade level but a piece of writing for students and teachers to explore together to critically analyze to improve student writing skills and deepen their understanding of story writing.
We recommend reading the example either a year above or below, as well as the grade you are currently working with, to gain a broader appreciation of this text type.
NARRATIVE WRITING PROMPTS (Journal Prompts)
When students have a great journal prompt, it can help them focus on the task at hand, so be sure to view our vast collection of visual writing prompts for various text types here or use some of these.
- On a recent European trip, you find your travel group booked into the stunning and mysterious Castle Frankenfurter for a single night… As night falls, the massive castle of over one hundred rooms seems to creak and groan as a series of unexplained events begin to make you wonder who or what else is spending the evening with you. Write a narrative that tells the story of your evening.
- You are a famous adventurer who has discovered new lands; keep a travel log over a period of time in which you encounter new and exciting adventures and challenges to overcome. Ensure your travel journal tells a story and has a definite introduction, conflict and resolution.
- You create an incredible piece of technology that has the capacity to change the world. As you sit back and marvel at your innovation and the endless possibilities ahead of you, it becomes apparent there are a few problems you didn’t really consider. You might not even be able to control them. Write a narrative in which you ride the highs and lows of your world-changing creation with a clear introduction, conflict and resolution.
- As the final door shuts on the Megamall, you realise you have done it… You and your best friend have managed to sneak into the largest shopping centre in town and have the entire place to yourselves until 7 am tomorrow. There is literally everything and anything a child would dream of entertaining themselves for the next 12 hours. What amazing adventures await you? What might go wrong? And how will you get out of there scot-free?
- A stranger walks into town… Whilst appearing similar to almost all those around you, you get a sense that this person is from another time, space or dimension… Are they friends or foes? What makes you sense something very strange is going on? Suddenly they stand up and walk toward you with purpose extending their hand… It’s almost as if they were reading your mind.
NARRATIVE WRITING VIDEO TUTORIAL

Teaching Resources
Use our resources and tools to improve your student’s writing skills through proven teaching strategies.
When teaching narrative writing, it is essential that you have a range of tools, strategies and resources at your disposal to ensure you get the most out of your writing time. You can find some examples below, which are free and paid premium resources you can use instantly without any preparation.
FREE Narrative Graphic Organizer
THE STORY TELLERS BUNDLE OF TEACHING RESOURCES

A MASSIVE COLLECTION of resources for narratives and story writing in the classroom covering all elements of crafting amazing stories. MONTHS WORTH OF WRITING LESSONS AND RESOURCES, including:
NARRATIVE WRITING CHECKLIST BUNDLE

OTHER GREAT ARTICLES ABOUT NARRATIVE WRITING

Narrative Writing for Kids: Essential Skills and Strategies

7 Great Narrative Lesson Plans Students and Teachers Love

Top 7 Narrative Writing Exercises for Students

How to Write a Scary Story
Have a language expert improve your writing
Run a free plagiarism check in 10 minutes, generate accurate citations for free.
- Knowledge Base
- How to write a narrative essay | Example & tips
How to Write a Narrative Essay | Example & Tips
Published on July 24, 2020 by Jack Caulfield . Revised on July 23, 2023.
A narrative essay tells a story. In most cases, this is a story about a personal experience you had. This type of essay , along with the descriptive essay , allows you to get personal and creative, unlike most academic writing .
Instantly correct all language mistakes in your text
Upload your document to correct all your mistakes in minutes

Table of contents
What is a narrative essay for, choosing a topic, interactive example of a narrative essay, other interesting articles, frequently asked questions about narrative essays.
When assigned a narrative essay, you might find yourself wondering: Why does my teacher want to hear this story? Topics for narrative essays can range from the important to the trivial. Usually the point is not so much the story itself, but the way you tell it.
A narrative essay is a way of testing your ability to tell a story in a clear and interesting way. You’re expected to think about where your story begins and ends, and how to convey it with eye-catching language and a satisfying pace.
These skills are quite different from those needed for formal academic writing. For instance, in a narrative essay the use of the first person (“I”) is encouraged, as is the use of figurative language, dialogue, and suspense.
Prevent plagiarism. Run a free check.
Narrative essay assignments vary widely in the amount of direction you’re given about your topic. You may be assigned quite a specific topic or choice of topics to work with.
- Write a story about your first day of school.
- Write a story about your favorite holiday destination.
You may also be given prompts that leave you a much wider choice of topic.
- Write about an experience where you learned something about yourself.
- Write about an achievement you are proud of. What did you accomplish, and how?
In these cases, you might have to think harder to decide what story you want to tell. The best kind of story for a narrative essay is one you can use to talk about a particular theme or lesson, or that takes a surprising turn somewhere along the way.
For example, a trip where everything went according to plan makes for a less interesting story than one where something unexpected happened that you then had to respond to. Choose an experience that might surprise the reader or teach them something.
Narrative essays in college applications
When applying for college , you might be asked to write a narrative essay that expresses something about your personal qualities.
For example, this application prompt from Common App requires you to respond with a narrative essay.
In this context, choose a story that is not only interesting but also expresses the qualities the prompt is looking for—here, resilience and the ability to learn from failure—and frame the story in a way that emphasizes these qualities.
An example of a short narrative essay, responding to the prompt “Write about an experience where you learned something about yourself,” is shown below.
Hover over different parts of the text to see how the structure works.
Since elementary school, I have always favored subjects like science and math over the humanities. My instinct was always to think of these subjects as more solid and serious than classes like English. If there was no right answer, I thought, why bother? But recently I had an experience that taught me my academic interests are more flexible than I had thought: I took my first philosophy class.
Before I entered the classroom, I was skeptical. I waited outside with the other students and wondered what exactly philosophy would involve—I really had no idea. I imagined something pretty abstract: long, stilted conversations pondering the meaning of life. But what I got was something quite different.
A young man in jeans, Mr. Jones—“but you can call me Rob”—was far from the white-haired, buttoned-up old man I had half-expected. And rather than pulling us into pedantic arguments about obscure philosophical points, Rob engaged us on our level. To talk free will, we looked at our own choices. To talk ethics, we looked at dilemmas we had faced ourselves. By the end of class, I’d discovered that questions with no right answer can turn out to be the most interesting ones.
The experience has taught me to look at things a little more “philosophically”—and not just because it was a philosophy class! I learned that if I let go of my preconceptions, I can actually get a lot out of subjects I was previously dismissive of. The class taught me—in more ways than one—to look at things with an open mind.
If you want to know more about AI tools , college essays , or fallacies make sure to check out some of our other articles with explanations and examples or go directly to our tools!
- Ad hominem fallacy
- Post hoc fallacy
- Appeal to authority fallacy
- False cause fallacy
- Sunk cost fallacy
College essays
- Choosing Essay Topic
- Write a College Essay
- Write a Diversity Essay
- College Essay Format & Structure
- Comparing and Contrasting in an Essay
(AI) Tools
- Grammar Checker
- Paraphrasing Tool
- Text Summarizer
- AI Detector
- Plagiarism Checker
- Citation Generator
If you’re not given much guidance on what your narrative essay should be about, consider the context and scope of the assignment. What kind of story is relevant, interesting, and possible to tell within the word count?
The best kind of story for a narrative essay is one you can use to reflect on a particular theme or lesson, or that takes a surprising turn somewhere along the way.
Don’t worry too much if your topic seems unoriginal. The point of a narrative essay is how you tell the story and the point you make with it, not the subject of the story itself.
Narrative essays are usually assigned as writing exercises at high school or in university composition classes. They may also form part of a university application.
When you are prompted to tell a story about your own life or experiences, a narrative essay is usually the right response.
The key difference is that a narrative essay is designed to tell a complete story, while a descriptive essay is meant to convey an intense description of a particular place, object, or concept.
Narrative and descriptive essays both allow you to write more personally and creatively than other kinds of essays , and similar writing skills can apply to both.
Cite this Scribbr article
If you want to cite this source, you can copy and paste the citation or click the “Cite this Scribbr article” button to automatically add the citation to our free Citation Generator.
Caulfield, J. (2023, July 23). How to Write a Narrative Essay | Example & Tips. Scribbr. Retrieved March 31, 2024, from https://www.scribbr.com/academic-essay/narrative-essay/
Is this article helpful?

Jack Caulfield
Other students also liked, how to write an expository essay, how to write a descriptive essay | example & tips, how to write your personal statement | strategies & examples, unlimited academic ai-proofreading.
✔ Document error-free in 5minutes ✔ Unlimited document corrections ✔ Specialized in correcting academic texts

- Freelancing
- Trending Stories

Ready to express your experiences through words? Dive into our article on how to write a narrative and master engaging storytelling techniques, making your narratives impactful and memorable.
Storytelling is something people have been doing forever. It’s like sharing stories that bring us closer. From tales told by grandparents to today’s digital stories, it’s how we teach, have fun, and relate. Stories help us make sense of things, remember our past, pass on values, and share our dreams.
Not everyone is a seasoned wordsmith, and that’s perfectly fine. Whether you are a student writing an assignment, an aspiring author, or someone who wants to share their experiences effectively, this article is to help you develop the art of storytelling. In this article, we will guide you on how to write a narrative in a compelling way.
You will learn the nuances of narrative writing, the fundamental elements, and practical insights. You’ll have the tools and knowledge to craft narratives that resonate with readers, evoke emotions, and leave a lasting impact.
So, let’s embark on this literary voyage together as we explore the rich landscape of narrative writing step by step.
Table of Contents
What is a narrative?
At its core, a narrative is a method of storytelling, a way to convey events or experiences. Think of it as a structured account that unfolds in a chronological sequence. Narratives can take many forms, including books, movies, or even the tales shared by grandparents. They provide a framework for organizing a story so that it makes sense to the audience.
When you write a narrative, you’re taking your readers on a journey. It’s a guide to take them through a series of connected events, often with characters and a specific setting. It also includes a plot that unveils a problem or situation, a conflict that creates tension, and, ultimately, a resolution that ties up loose ends.
B. Key elements of a narrative
1. characters.
Characters are the heart and soul of any narrative. They are the individuals who portray your story. They guide readers through their experiences, emotions, and transformations. These characters can be real people, imaginary beings, or even symbolic representations. Their personalities, motives, and interactions add depth and humanity to your narrative.
The setting is where your story happens. It tells when and where things are going on. It helps readers see the world of your story. It can be a city, a small town, another planet, or a time in history. The setting sets the mood and affects the story.
The plot is what the story is all about. It’s the events that move the story forward. Think of it as a road map for you and your readers. A good plot keeps readers interested and eager to see what comes next.
4. Conflict
Conflict is what drives your story. It’s the problems or challenges your characters face. It’s what keeps readers interested, wondering how the characters will deal with these issues. Conflict can be things outside or inside a character.
5. Resolution
The resolution is the point where your narrative ties up loose ends and provides closure. It answers the questions posed by the conflict and often offers a sense of catharsis or fulfillment. It’s the moment when readers find out what happens to the characters they’ve come to know and care about.
Understanding these key elements and how they work together is the foundation of crafting a compelling narrative.
How to write a narrative: Choosing your narrative subject
Selecting the right subject for your narrative is crucial in crafting a compelling and engaging story. It’s the foundation upon which your entire narrative will be built, influencing the characters, plot, and overall impact of your storytelling.
- The significance of selecting the right subject
- Personal experiences:
- Fictional stories:
Observation:
Conversations:, historical events:, dreams and imagination:, a. the significance of selecting the right subject.
Selecting the right subject for your narrative is a critical step in the writing process. The subject serves as the foundation upon which your entire narrative is built. It shapes the story’s theme, tone, and the message you wish to convey.
Think of the subject as the lens through which your readers will view your narrative. It’s the aspect of your story that will resonate with them, evoke emotions, and ultimately leave a lasting impression. The significance of choosing the right subject cannot be overstated. It determines the overall impact and effectiveness of your narrative.
To select the right subject, consider your audience, your own interests, and the message you want to communicate. Whether it’s a personal experience, a work of fiction, or a historical event, ensure that the subject aligns with your purpose. It should also resonate with your intended readers.
B. Personal experiences vs. fictional stories
When embarking on your narrative journey, you face a fundamental choice: do you draw from personal experiences or create fictional stories? Each approach has its merits, and the decision largely depends on your goals and the story you wish to tell.
– Personal experiences:
Drawing from your own life experiences can infuse authenticity into your narrative. It allows you to tap into your emotions and memories, providing a rich source of material. However, it may require introspection and the willingness to delve into personal vulnerabilities.
– Fictional stories:
Creating fictional stories offers creative freedom. You can craft unique worlds, characters, and scenarios, giving you full control over the narrative. This approach often requires imaginative thinking and world-building skills.
Ultimately, the choice between personal experiences and fictional stories depends on your comfort level, the intended message, and the emotional impact you wish to achieve. Some writers blend elements of both to create narratives that resonate deeply with readers.
C. Finding inspiration for your narrative
Inspiration is the spark that ignites your narrative. It can be found in many places; often, the most compelling narratives emerge from unexpected sources. Here are some ways to uncover inspiration:
Pay close attention to the world around you. People-watching, nature, and everyday events can provide inspiration for characters, settings, and plots.
Explore a variety of books, genres, and styles. Reading can expose you to different storytelling techniques and trigger your own creativity.
Engage in conversations with people from diverse backgrounds. Listening to their experiences and perspectives can generate ideas for your narrative.
Historical events, whether well-known or obscure, can serve as a rich source of inspiration. They offer a glimpse into different time periods and the human experience.
Don’t underestimate the power of your own imagination. Dreams, daydreams, and fantasies can be fertile ground for narrative ideas.
In the quest for inspiration, keep a journal or digital note-taking tool handy to capture fleeting ideas. The more you cultivate your ability to find inspiration, the more vibrant and engaging your narratives will become.
Crafting compelling and relatable characters in a narrative
Characters are the heart of your story, the individuals your readers or audience will connect with and care about. In this section, we’ll dive into the art of creating compelling and relatable characters.
Physical attributes:
Personality:, goals and aspirations:, character traits:, motivations:, emotional depth:, realistic reactions:, universal themes:, character growth:, a. developing well-rounded characters.
Crafting characters that resonate with your readers is a cornerstone of effective storytelling. Well-rounded characters are more than mere names on a page; they come to life, eliciting emotions and driving the narrative forward. To develop such characters, consider the following aspects:
Describe their appearance in detail, but don’t stop there. Think about how their physical traits influence their actions and interactions.
Give your characters distinct personalities. Are they introverted or extroverted? Optimistic or pessimistic? Understanding their traits helps readers relate to them.
What experiences have shaped your characters? Their past can reveal their motivations and explain their behavior.
What do your characters want to achieve? Their goals drive the plot and reveal their desires.
B. Character traits, motivations, and flaws
Characters should be multifaceted, possessing both strengths and weaknesses. This complexity makes them relatable and engaging.
Identify key personality traits for each character. Are they courageous, compassionate, or cunning? These traits inform their choices and actions.
Delve into what drives your characters. Their motivations provide insight into their decisions and add depth to their development.
Imperfections make characters believable. Consider their shortcomings, whether it’s a short temper, insecurity, or a tendency to be overly trusting.
Combining positive traits, motivations, and flaws creates characters that readers can connect with on an emotional level. It allows them to see themselves in the characters’ struggles and triumphs.
C. The importance of relatable characters
Relatable characters are the bridge between the narrative and the reader. When readers can see elements of themselves in a character, they become emotionally invested in the story. To make characters relatable:
Characters should experience a range of emotions, mirroring the human experience. Show their fears, hopes, and vulnerabilities.
Characters should react to situations in a way that feels genuine. How would a real person respond to the challenges they face?
Explore themes that resonate with a broad audience, such as love, loss, ambition, or self-discovery. These themes evoke empathy.
Allow characters to evolve and learn from their experiences. Growth demonstrates their relatability and adds depth to the narrative.
In short, crafting well-rounded characters with distinct traits, motivations, and flaws is vital for a compelling narrative. Readers connect with characters who feel real and who mirror the complexities of human nature. When characters are relatable, they become the emotional anchors that keep readers engaged in your story.
Building an evocative setting for the narrative
The setting is the backdrop against which your story unfolds, and it plays a significant role in shaping the mood, atmosphere, and even the characters’ experiences. In this section, we’ll explore the art of crafting a vivid and memorable setting.
- Setting as a backdrop for the story
Visual imagery:
Auditory details:, tactile sensations, scents and smells, a. setting as a backdrop for the story.
The setting of your narrative is like the canvas upon which the story unfolds. It provides the stage, the atmosphere, and the context in which your characters and plot come to life. Just as a painter selects the perfect background to enhance their subject, choosing the right setting can significantly impact your narrative.
The setting is not merely a backdrop; it is an active participant in your story, influencing character actions, emotions, and the overall mood. It’s the difference between a story set in a bustling metropolis and one in a serene countryside. Your choice of setting sets the stage for the reader, helping them visualize and immerse themselves in the world you’ve created.
B. Creating a sense of place through description
Effective storytelling relies on the art of vivid description. When it comes to the setting, your goal is to transport the reader into the world you’ve envisioned. This involves painting a sensory-rich picture through words. Here’s how to do it:
Describe the physical elements of the setting. What does it look like? What colors dominate? Is it urban or natural, modern or historical?
Bring the setting to life with sounds. Is there the hum of traffic, the chirping of birds, or the distant roar of the ocean? These auditory cues help readers “hear” the setting.
Engage the reader’s sense of touch. Is the air humid or crisp? Is the ground soft with grass or hard with concrete? Make them feel the environment.
Don’t forget the sense of smell. Is there the aroma of freshly baked bread, the scent of blooming flowers, or the acrid smell of industry? Smells can evoke powerful memories and emotions.
– Taste: If relevant, describe the taste of the setting. It could be the saltiness of sea air or the sweetness of ripe fruit. Taste can evoke nostalgia and intimacy.
Effective description immerses the reader in your setting, making it feel tangible and real. It allows them to experience the world you’ve created with all their senses.
C. Using the setting to enhance the narrative’s mood and tone
The setting is a potent tool for shaping the mood and tone of your narrative. It can convey a sense of foreboding on a dark, stormy night or evoke tranquility in a peaceful meadow. Here’s how to harness the setting’s power:
Consider the emotional atmosphere you want to convey. Does your narrative call for suspense, romance, nostalgia, or adventure? The setting can be manipulated to evoke the desired mood.
Think about the overall feeling you want to convey. Is your story meant to be lighthearted, solemn, or thought-provoking? The setting can set the tone by reflecting the characters’ emotions and the story’s themes.
Use the setting symbolically to enhance the narrative’s depth. For example, a decaying, abandoned building can symbolize the passage of time or a character’s inner turmoil.
Explore contrasts within the setting to create tension or highlight themes. A peaceful countryside interrupted by a stark industrial complex can symbolize the clash of nature and technology.
By strategically using the setting to amplify mood and tone, you can enrich your narrative, making it resonate more deeply with readers. The setting becomes a dynamic element that enhances the emotional impact of your story, enveloping readers in an immersive world of words.
Crafting a captivating plot for your narrative
Crafting a captivating plot is the backbone of any compelling narrative. It’s the sequence of events, conflicts, and resolutions that drive your story forward, keeping your audience engaged and eager to know what happens next.
- Act 1: Setup
- Act 2: Conflict
- Act 3: Resolution
- Cliffhangers:
A. Introduction to the narrative structure
The narrative structure is the blueprint that guides your story’s development. It’s the invisible framework that ensures your narrative flows logically and captivates your audience. Think of it as the skeleton that holds the body of your story together. This structure typically consists of a beginning, middle, and end, each serving a distinct purpose:
This is where you introduce your characters, setting, and the initial situation. You set the stage, hooking your readers and giving them a reason to continue.
The middle is the heart of your story, where conflicts and obstacles arise. Tensions build, characters evolve, and the plot thickens. This is often the longest part of the narrative.
The end brings resolution. It ties up loose ends, answers questions, and provides closure. It’s the final destination your readers have been journeying toward.
B. The three-act structure: Setup, conflict, resolution
The three-act structure is a widely used framework for crafting compelling narratives. It divides your story into three distinct acts, each with its role:
– Act 1: Setup
In this initial act, you introduce your characters, setting, and the central conflict or problem. Your readers become acquainted with the world you’ve created and the characters who inhabit it. This act sets the stage, creating the foundation upon which the story will unfold.
– Act 2: Conflict
Act 2 is the meat of your narrative, where the main conflict and rising action take center stage. This is where challenges, obstacles, and complications arise, keeping readers engaged and invested in the story. Tensions escalate, character arcs develop, and the plot thickens, building towards the story’s climax.
– Act 3: Resolution
The final act provides resolution and closure. Loose ends are tied up, questions are answered, and characters’ fates are revealed. The resolution should provide a satisfying conclusion to the story, leaving your readers with a sense of fulfillment.
The three-act structure serves as a roadmap for your narrative, ensuring a balanced and engaging progression. It helps maintain the reader’s interest by providing a logical and satisfying sequence of events.
C. Incorporating tension and pacing
Tension and pacing are the engines that drive your narrative. They keep readers eagerly turning the pages, eager to discover what happens next. Here’s how to incorporate them effectively:
– Tension:
Tension arises from conflicts and challenges that hinder your characters from achieving their goals. It keeps readers engaged and invested in the story’s outcome. To create tension, introduce obstacles, uncertainties, and dilemmas that the characters must confront and overcome.
– Pacing:
Pacing refers to the rhythm and speed at which your narrative unfolds. It’s essential to balance moments of tension and action with moments of reflection and character development. Varying the pacing can create a dynamic reading experience, allowing readers to catch their breath before plunging back into the action.
– Cliffhangers:
Ending chapters or sections with suspenseful questions or unresolved conflicts can be an effective way to maintain tension and keep readers hooked.
Crafting a captivating plot requires a delicate balance of structure, tension, and pacing. When executed skillfully, your plot will propel your narrative forward, keeping readers eagerly immersed in the story’s twists and turns.
Establishing conflict for your narrative
Conflict is what propels your narrative forward, creating a sense of urgency and making the story more relatable and engaging. Here are the insights and techniques to develop compelling challenges that drive your narrative’s progression.
- Creating tension:
- Character development:
- Engaging the audience:
- Driving the plot:
- Internal conflict:
- External conflict:
- Rising action:
- Reader engagement:
- Resolution:
A. The role of conflict in storytelling
Conflict is the beating heart of storytelling. It’s the engine that propels narratives forward, captivating readers and holding their attention. In essence, conflict is the central problem or tension that characters face, and it serves several vital roles in storytelling:
– Creating tension:
Conflict introduces uncertainty and tension into the narrative. It leaves readers wondering how characters will overcome obstacles or resolve their issues.
– Character development:
Conflict forces characters to confront challenges, revealing their strengths, weaknesses, and growth throughout the story.
– Engaging the audience:
Conflict resonates with readers because it mirrors real-life struggles. It draws them into the narrative by tapping into their own experiences and emotions.
– Driving the plot:
Conflict provides the narrative with direction. It offers a clear goal or problem that characters must address, guiding the story’s progression.
B. Types of conflict: Internal and external
Conflict can manifest in various forms, but two primary categories are internal and external conflict:
– Internal conflict:
This is the battle that takes place within a character’s mind or heart. It often involves conflicting emotions, beliefs, or desires. Internal conflict adds depth to characters as they grapple with their inner demons or moral dilemmas. For example, a character torn between loyalty to family and personal ambition experiences internal conflict.
– External conflict:
External conflict arises from outside sources and can take many shapes, such as:
– Man vs. man: Character vs. character conflict, often involving opposing goals or values.
– Man vs. nature: Characters pitted against natural forces, like a survival story in the wilderness.
– Man vs. society: Characters challenge societal norms, laws, or expectations.
– Man vs. technology: Conflict stemming from technological advancements or limitations.
– Man vs. supernatural: Characters facing supernatural or paranormal elements.
Effective storytelling often combines both internal and external conflicts to create well-rounded characters and engaging narratives.
C. How conflict drives the narrative forward
Conflict is the driving force behind your narrative’s momentum. It compels readers to keep turning the pages to see how characters confront and resolve their challenges. Here’s how conflict fuels the narrative:
– Rising action:
As conflict intensifies, it leads to rising action, where tensions build, and the plot thickens. Readers become increasingly invested in the story.
Conflict pushes characters out of their comfort zones, forcing them to adapt and evolve. This evolution creates engaging character arcs that mirror real human growth.
– Reader engagement:
Conflict keeps readers engaged by creating anticipation. They want to see how characters will overcome obstacles or resolve their problems.
– Resolution:
Ultimately, conflict culminates in the story’s resolution. Whether it’s a happy ending or a tragic one, resolving the conflict provides closure and satisfaction for the reader.
Conflict is not merely an element of storytelling; it’s the lifeblood of narratives. It generates tension, shapes characters, and drives the plot forward, ensuring that your story remains compelling and memorable.
Resolving the narrative
Resolving the narrative is the critical conclusion that brings closure to your story. This part answers lingering questions and provides a sense of fulfillment for your readers or viewers. It’s the moment where loose ends are tied up, conflicts find their resolution, and the story’s overall message is conveyed.
- Emotional catharsis:
- Reflecting themes:
- Reader satisfaction:
- Plot points:
- Character arcs:
- Unanswered questions:
- Main storyline:
A. The importance of a satisfying resolution
A satisfying resolution is the culmination of your narrative, the moment when all the pieces of the storytelling puzzle fall into place. It’s the payoff that readers have been eagerly anticipating throughout the story. The resolution serves several vital functions:
– Closure:
It provides closure to the narrative, offering a sense of finality that leaves readers with a feeling of fulfillment.
– Emotional catharsis:
A well-executed resolution can elicit strong emotions from your readers, whether it’s tears of joy, sadness, or a profound sense of contentment.
– Reflecting themes:
The resolution often reflects the themes and messages you’ve woven into your narrative, offering insight or a moral lesson.
– Reader satisfaction:
A satisfying resolution is a reward for your readers’ investment in the story. It ensures they walk away with a sense of gratification.
B. Avoiding loose ends and unanswered questions
Loose ends and unanswered questions can leave readers feeling unsatisfied and frustrated. To create a strong resolution, ensure that all significant plot points, character arcs, and lingering questions are addressed:
– Plot points:
Tie up any plot threads and unresolved conflicts. Readers should have a clear understanding of how the central problem was resolved.
– Character arcs:
Ensure that each character’s journey reaches a meaningful conclusion. Characters should experience growth, change, or transformation over the course of the narrative.
– Unanswered questions:
Address any lingering questions or mysteries that were introduced earlier in the story. Leaving readers with some ambiguity can be effective, but it should feel intentional and thought-provoking, not haphazard.
C. Wrapping up character arcs and storylines
One of the most satisfying aspects of a resolution is seeing how characters’ story arcs and various storylines are wrapped up:
Characters should experience resolution to their personal conflicts and growth. This resolution should align with the changes they’ve undergone throughout the narrative.
– Main storyline:
The central storyline of your narrative should reach a satisfying conclusion, whether it’s a happy ending, a bittersweet one, or a tragic outcome. It should reflect the story’s themes and messages.
– Subplots:
If you’ve introduced subplots, ensure they are also addressed in the resolution. These can add depth and complexity to your narrative, and readers will expect to see how they play out.
Crafting a resolution that ties up all loose ends and provides emotional closure is a skill that sets exceptional storytelling apart. When readers close the book or finish the last page, they should do so with a sense of satisfaction, knowing they’ve completed a meaningful narrative journey.
Techniques for effective narrative writing
Techniques for effective narrative writing are the tools that transform your ideas and creativity into a captivating story. These techniques encompass the use of literary devices, style, and storytelling strategies that make your narrative engaging and memorable.
- Use descriptive language
- Show emotions through actions
- Dialogue and inner thoughts
- Distinctive voices
- Reveal character traits
- Advance the plot
- Show, Don’t Tell (Again)
- Action-driven exposition
- Flashbacks and backstory
A. Show, don’t tell
“Show, don’t tell” is a fundamental principle of effective storytelling. It’s the art of conveying information, emotions, and experiences through vivid and sensory-rich descriptions, allowing readers to engage with the narrative on a deeper level. Here’s how to master this technique:
– Use descriptive language:
Paint pictures with words by using descriptive language that appeals to the reader’s senses. Instead of saying, “She was sad,” you might describe her as “her eyes welled up with tears, and her voice quivered.”
– Show emotions through actions:
Instead of explicitly stating a character’s emotions, reveal them through their actions, gestures, and body language. For example, “He clenched his fists and turned away” conveys anger more effectively than simply saying, “He was angry.”
– Dialogue and inner thoughts:
Leverage dialogue and a character’s inner thoughts to reveal their feelings, motivations, and conflicts. These provide a window into the character’s mindset and add depth to their portrayal.
By showing rather than telling, you immerse readers in the narrative, allowing them to experience the story as if they were living it themselves.
B. Dialogue as a tool for character development
Dialogue is a potent tool for character development and storytelling. It’s through dialogue that characters come to life, their personalities are revealed, and their relationships are explored. To use dialogue effectively:
– Distinctive voices:
Ensure each character has a unique voice, reflecting their personality, background, and motivations. This helps readers distinguish between characters.
– Reveal character traits:
Use dialogue to unveil character traits, such as their sense of humor, beliefs, or fears. Show how they interact with others and express themselves.
– Advance the plot:
Dialogue should serve a purpose beyond just conversation. It can reveal information, drive the plot forward, or create conflict and tension.
– Subtext:
Often, what characters don’t say can be as significant as what they do say. Subtext in dialogue adds depth and intrigue, allowing readers to infer underlying emotions and conflicts.
Effective dialogue not only advances the plot but also brings characters to life, making them relatable and engaging.
C. Balancing exposition and action
Finding the right balance between exposition (the presentation of information) and action (the unfolding events) is crucial for maintaining reader engagement. Here’s how to strike that balance:
– Show, Don’t Tell (Again):
Instead of delivering information through lengthy exposition, weave it into the narrative naturally. Show details through character actions, thoughts, and dialogue.
– Timing:
Introduce exposition when it’s relevant and necessary for understanding the story. Avoid overwhelming readers with information early on; let it unfold organically.
– Action-driven exposition:
Whenever possible, incorporate exposition into scenes with action or conflict. This keeps the narrative dynamic and prevents information from feeling static.
– Flashbacks and backstory:
If backstory is essential, consider using techniques like flashbacks or character recollections to reveal it in a more engaging manner.
Striking the right balance ensures that your narrative flows smoothly and keeps readers immersed in the story without unnecessary interruptions.
These techniques are the tools of a skilled narrative writer. Mastering the art of “show, don’t tell,” using dialogue effectively, and balancing exposition and action can elevate your storytelling, making it engaging, immersive, and emotionally resonant for your readers.
Editing and revising your narrative
Editing and revising your narrative is a crucial step from a draft to a polished and compelling story. It’s where you refine your language, structure, and overall presentation to ensure your narrative is as impactful as possible.
- Clarity and coherence:
- Plot refinement:
- Language and style:
- Eliminating errors:
- Choose trusted readers:
- Specific questions:
- Open-mindedness:
- Balance of perspectives:
- Sentence structure:
- Transitions:
- Consistency:
- Word choice:
- Final proofreading:
A. The value of multiple drafts
The process of crafting a compelling narrative doesn’t end with the final sentence of your first draft. In fact, it’s only the beginning. Multiple drafts are the secret ingredient to refining your narrative and transforming it into a polished work of art. Here’s why they are invaluable:
– Clarity and coherence:
Multiple drafts allow you to revisit and refine your narrative for clarity and coherence. You can identify areas where the story might be confusing or where transitions between scenes need improvement.
With each draft, you can deepen character arcs and motivations. You can fine-tune character voices, making them more distinct and engaging.
– Plot refinement:
Subplots, pacing, and plot holes can be addressed and resolved through successive drafts. This ensures a more satisfying and well-structured narrative.
– Language and style:
You can experiment with language, style, and sentence structure to find the most effective ways to convey your story. This fine-tuning elevates the overall quality of your writing.
– Eliminating errors:
Drafts help you catch and rectify grammar, spelling, and typographical errors. These can distract readers from the story and diminish its impact.
B. Seeking feedback from others
Writing is a solitary endeavor, but feedback from others is a crucial part of the editing process. Other perspectives can uncover blind spots and provide valuable insights. Here’s how to approach seeking feedback:
– Choose trusted readers:
Select individuals whose opinions you value and who can provide constructive criticism. They may be fellow writers, friends, or editors.
– Specific questions:
Ask your readers specific questions about your narrative, such as their thoughts on character development, pacing, or the overall impact of the story.
– Open-mindedness:
Be open to feedback, even if it challenges your original vision. Constructive criticism can lead to significant improvements.
– Balance of perspectives:
Consider feedback from multiple sources to gain a well-rounded view of your narrative’s strengths and weaknesses.
C. Polishing the narrative for clarity and coherence
The final stages of editing involve polishing your narrative for maximum clarity and coherence. This is where you focus on the finer details to ensure your story flows seamlessly:
– Sentence structure:
Review sentence structure for variety and readability. Avoid overly complex sentences that may confuse readers.
– Transitions:
Smooth transitions between scenes, paragraphs, and chapters. Ensure that the narrative flows logically, guiding readers effortlessly through the story.
– Consistency:
Check for consistency in character traits, settings, and plot details. Eliminate any contradictions or discrepancies.
– Word choice:
Pay attention to word choice and diction. Select words that convey your intended meaning precisely and effectively.
– Final proofreading:
Conduct a final proofread to catch any remaining grammar, spelling, and punctuation errors. This step is essential for a polished, professional finish.
Editing and revising is where your narrative truly takes shape and shines. It’s a process that demands time, patience, and a critical eye, but the result is a narrative that is well-crafted, compelling, and ready to captivate your readers.
Now that you know how to write a narrative, it’s time to put pen to paper or fingers to the keyboard. Writing is a craft that improves with practice. Start with short stories or journal entries and gradually work up to longer narratives. Remember that every writer begins as a beginner and improves with time. Don’t be discouraged by initial challenges; embrace them as growth opportunities.
As a storyteller, you can touch hearts, spark imagination, and create lasting impressions. So, take your newfound knowledge, embrace the art of narrative writing, and embark on a journey of storytelling that will captivate and resonate with your readers and audiences.

You Might Also Like

How To End An Email To A Teacher Formally?

A Detailed Guide On What Is Informative Writing – Everything Important You Must Know

How To Write An Annotated Bibliography in APA?
No comments, leave a reply cancel reply.
Save my name, email, and website in this browser for the next time I comment.

- Scriptwriting
How to Write a Narrative Essay — A Step-by-Step Guide
N arrative essays are important papers most students have to write. But how does one write a narrative essay? Fear not, we’re going to show you how to write a narrative essay by breaking down a variety of narrative writing strategies. By the end, you’ll know why narrative essays are so important – and how to write your own.
How to Write a Narrative Essay Step by Step
Background on narrative essays.
Narrative essays are important assignments in many writing classes – but what is a narrative essay? A narrative essay is a prose-written story that’s focused on the commentary of a central theme .
Narrative essays are generally written in the first-person POV , and are usually about a topic that’s personal to the writer.
Everything in a narrative essay should take place in an established timeline, with a clear beginning, middle, and end.
In simplest terms, a narrative essay is a personal story. A narrative essay can be written in response to a prompt or as an independent exercise.
We’re going to get to tips and tricks on how to write a narrative essay in a bit, but first let’s check out a video on “story.”
How to Start a Narrative Essay • What is a Story? by Mr. Kresphus
In some regards, any story can be regarded as a personal story, but for the sake of this article, we’re going to focus on prose-written stories told in the first-person POV.
How to Start a Narrative Essay
Responding to prompts.
Many people wonder about how to start a narrative essay. Well, if you’re writing a narrative essay in response to a prompt, then chances are the person issuing the prompt is looking for a specific answer.
For example: if the prompt states “recount a time you encountered a challenge,” then chances are the person issuing the prompt wants to hear about how you overcame a challenge or learned from it.
That isn’t to say you have to respond to the prompt in one way; “overcoming” or “learning” from a challenge can be constituted in a variety of ways.
For example, you could structure your essay around overcoming a physical challenge, like an injury or disability. Or you could structure your essay around learning from failure, such as losing at a sport or performing poorly on an important exam.
Whatever it is, you must show that the challenge forced you to grow.
Maturation is an important process – and an essential aspect of narrative essays... of course, there are exceptions to the rule; lack of maturation is a prescient theme in narrative essays too; although that’s mostly reserved for experienced essay writers.
So, let’s take a look at how you might respond to a series of narrative essay prompts:
How successful are you?
This prompt begs the writer to impart humility without throwing a pity party. I would respond to this prompt by demonstrating pride in what I do while offering modesty. For example: “I have achieved success in what I set out to do – but I still have a long way to go to achieve my long-term goals.”
Who is your role model?
“My role model is [Blank] because ” is how you should start this narrative essay. The “because” is the crux of your essay. For example, I’d say “Bill Russell is my role model because he demonstrated graceful resolve in the face of bigotry and discrimination.
Do you consider yourself spiritual?
For this prompt, you should explain how you came to the conclusion of whether or not you consider yourself a spiritual person. Of course, prompt-givers will differ on how much they want you to freely express. For example: if the prompt-giver is an employee at an evangelizing organization, then they probably want to see that you’re willing to propagate the church’s agenda. Alternatively, if the prompt-giver is non-denominational, they probably want to see that you’re accepting of people from various spiritual backgrounds.
How to Write Narrative Essay
What makes a good narrative essay.
You don’t have to respond to a prompt to write a narrative essay. So, how do you write a narrative essay without a prompt? Well, that’s the thing… you can write a narrative essay about anything!
That’s a bit of a blessing and a curse though – on one hand it’s liberating to choose any topic you want; on the other, it’s difficult to narrow down a good story from an infinite breadth of possibilities.
In this next video, the team at Essay Pro explores why passion is the number one motivator for effective narrative essays.
How to Write a Narrative Essay Step by Step • Real Essay Examples by Essay Pro
So, before you write anything, ask yourself: “what am I passionate about?” Movies? Sports? Books? Games? Baking? Volunteering? Whatever it is, make sure that it’s something that demonstrates your individual growth . It doesn’t have to be anything major; take a video game for example: you could write a narrative essay about searching for a rare weapon with friends.
Success or failure, you’ll be able to demonstrate growth.
Here’s something to consider: writing a narrative essay around intertextuality. What is intertextuality ? Intertextuality is the relationship between texts, i.e., books, movies, plays, songs, games, etc. In other words, it’s anytime one text is referenced in another text.
For example, you could write a narrative essay about your favorite movie! Just make sure that it ultimately reflects back on yourself.
Narrative Writing Format
Structure of a narrative essay.
Narrative essays differ in length and structure – but there are some universal basics. The first paragraph of a narrative essay should always introduce the central theme. For example, if the narrative essay is about “a fond childhood memory,” then the first paragraph should briefly comment on the nature of the fond childhood memory.
In general, a narrative essay should have an introductory paragraph with a topic sentence (reiterating the prompt or basic idea), a brief commentary on the central theme, and a set-up for the body paragraphs.
The body paragraphs should make up the vast majority of the narrative essay. In the body paragraphs, the writer should essentially “build the story’s case.” What do I mean by “build the story’s case?”
Well, I mean that the writer should display the story’s merit; what it means, why it matters, and how it proves (or refutes) personal growth.
The narrative essay should always conclude with a dedicated paragraph. In the “conclusion paragraph,” the writer should reflect on the story.
Pro tip: conclusion paragraphs usually work best when the writer stays within the diegesis.
What is a Video Essay?
A video essay is a natural extension of a narrative essay; differentiated only by purpose and medium. In our next article, we’ll explain what a video essay is, and why it’s so important to media criticism. By the end, you’ll know where to look for video essay inspiration.
Up Next: The Art of Video Analysis →
Write and produce your scripts all in one place..
Write and collaborate on your scripts FREE . Create script breakdowns, sides, schedules, storyboards, call sheets and more.
- Pricing & Plans
- Product Updates
- Featured On
- StudioBinder Partners
- The Ultimate Guide to Call Sheets (with FREE Call Sheet Template)
- How to Break Down a Script (with FREE Script Breakdown Sheet)
- The Only Shot List Template You Need — with Free Download
- Managing Your Film Budget Cashflow & PO Log (Free Template)
- A Better Film Crew List Template Booking Sheet
- Best Storyboard Softwares (with free Storyboard Templates)
- Movie Magic Scheduling
- Gorilla Software
- Storyboard That
A visual medium requires visual methods. Master the art of visual storytelling with our FREE video series on directing and filmmaking techniques.
We’re in a golden age of TV writing and development. More and more people are flocking to the small screen to find daily entertainment. So how can you break put from the pack and get your idea onto the small screen? We’re here to help.
- Making It: From Pre-Production to Screen
- What is a Light Meter — Understanding the Photographer's Tool
- What is Metonymy — Definition, Examples & How to Use It
- What is a Short Story — The Art of Brevity in Literature
- What is an Action Hero — Best Examples & Defining Traits
- What is a Movie Spoiler — Types, Ethics & Rules Explained
- 2 Pinterest

How to Write a Perfect Narrative Essay (Step-by-Step)
By Status.net Editorial Team on October 17, 2023 — 10 minutes to read
- Understanding a Narrative Essay Part 1
- Typical Narrative Essay Structure Part 2
- Narrative Essay Template Part 3
- Step 1. How to Choose Your Narrative Essay Topic Part 4
- Step 2. Planning the Structure Part 5
- Step 3. Crafting an Intriguing Introduction Part 6
- Step 4. Weaving the Narrative Body Part 7
- Step 5. Creating a Conclusion Part 8
- Step 6. Polishing the Essay Part 9
- Step 7. Feedback and Revision Part 10
Part 1 Understanding a Narrative Essay
A narrative essay is a form of writing where you share a personal experience or tell a story to make a point or convey a lesson. Unlike other types of essays, a narrative essay aims to engage your audience by sharing your perspective and taking them on an emotional journey.
- To begin, choose a meaningful topic . Pick a story or experience that had a significant impact on your life, taught you something valuable, or made you see the world differently. You want your readers to learn from your experiences, so choose something that will resonate with others.
- Next, create an outline . Although narrative essays allow for creative storytelling, it’s still helpful to have a roadmap to guide your writing. List the main events, the characters involved, and the settings where the events took place. This will help you ensure that your essay is well-structured and easy to follow.
- When writing your narrative essay, focus on showing, not telling . This means that you should use descriptive language and vivid details to paint a picture in your reader’s mind. For example, instead of stating that it was a rainy day, describe the sound of rain hitting your window, the feeling of cold wetness around you, and the sight of puddles forming around your feet. These sensory details will make your essay more engaging and immersive.
- Another key aspect is developing your characters . Give your readers an insight into the thoughts and emotions of the people in your story. This helps them connect with the story, empathize with the characters, and understand their actions. For instance, if your essay is about a challenging hike you took with a friend, spend some time describing your friend’s personality and how the experience impacted their attitude or feelings.
- Keep the pace interesting . Vary your sentence lengths and structures, and don’t be afraid to use some stylistic devices like dialogue, flashbacks, and metaphors. This adds more depth and dimension to your story, keeping your readers engaged from beginning to end.
Part 2 Typical Narrative Essay Structure
A narrative essay typically follows a three-part structure: introduction, body, and conclusion.
- Introduction: Start with a hook to grab attention and introduce your story. Provide some background to set the stage for the main events.
- Body: Develop your story in detail. Describe scenes, characters, and emotions. Use dialogue when necessary to provide conversational elements.
- Conclusion: Sum up your story, revealing the lesson learned or the moral of the story. Leave your audience with a lasting impression.
Part 3 Narrative Essay Template
- 1. Introduction : Set the scene and introduce the main characters and setting of your story. Use descriptive language to paint a vivid picture for your reader and capture their attention.
- Body 2. Rising Action : Develop the plot by introducing a conflict or challenge that the main character must face. This could be a personal struggle, a difficult decision, or an external obstacle. 3. Climax : This is the turning point of the story, where the conflict reaches its peak and the main character must make a critical decision or take action. 4. Falling Action : Show the consequences of the main character’s decision or action, and how it affects the rest of the story. 5. Resolution : Bring the story to a satisfying conclusion by resolving the conflict and showing how the main character has grown or changed as a result of their experiences.
- 6. Reflection/Conclusion : Reflect on the events of the story and what they mean to you as the writer. This could be a lesson learned, a personal realization, or a message you want to convey to your reader.
Part 4 Step 1. How to Choose Your Narrative Essay Topic
Brainstorming ideas.
Start by jotting down any ideas that pop into your mind. Think about experiences you’ve had, stories you’ve heard, or even books and movies that have resonated with you. Write these ideas down and don’t worry too much about organization yet. It’s all about getting your thoughts on paper.
Once you have a list, review your ideas and identify common themes or connections between them. This process should help you discover potential topics for your narrative essay.
Narrowing Down the Choices
After brainstorming, you’ll likely end up with a few strong contenders for your essay topic. To decide which topic is best, consider the following:
- Relevance : Is the topic meaningful for your audience? Will they be able to connect with it on a personal level? Consider the purpose of your assignment and your audience when choosing your topic.
- Detail : Do you have enough specific details to craft a vivid story? The more detail you can recall about the event, the easier it’ll be to write a compelling narrative.
- Emotional impact : A strong narrative essay should evoke emotions in your readers. Choose a topic that has the potential to elicit some emotional response from your target audience.
After evaluating your potential topics based on these criteria, you can select the one that best fits the purpose of your narrative essay.
Part 5 Step 2. Planning the Structure
Creating an outline.
Before you start writing your narrative essay, it’s a great idea to plan out your story. Grab a piece of paper and sketch out a rough outline of the key points you want to cover. Begin with the introduction, where you’ll set the scene and introduce your characters. Then, list the major events of your story in chronological order, followed by the climax and resolution. Organizing your ideas in an outline will ensure your essay flows smoothly and makes sense to your readers.

Detailing Characters, Settings, and Events
Taking time to flesh out the characters, settings, and events in your story will make it more engaging and relatable. Think about your main character’s background, traits, and motivations. Describe their appearance, emotions, and behavior in detail. This personal touch will help your readers connect with them on a deeper level.
Also, give some thought to the setting – where does the story take place? Be sure to include sensory details that paint a vivid picture of the environment. Finally, focus on the series of events that make up your narrative. Are there any twists and turns, or surprising moments? Address these in your essay, using vivid language and engaging storytelling techniques to captivate your readers.
Writing the Narrative Essay
Part 6 step 3. crafting an intriguing introduction.
To start your narrative essay, you’ll want to hook your reader with an interesting and engaging opening. Begin with a captivating sentence or question that piques curiosity and captures attention. For example, “Did you ever think a simple bus ride could change your life forever?” This kind of opening sets the stage for a compelling, relatable story. Next, introduce your main characters and provide a bit of context to help your readers understand the setting and background of the story.
Part 7 Step 4. Weaving the Narrative Body
The body of your essay is where your story unfolds. Here’s where you’ll present a series of events, using descriptive language and vivid details.
Remember to maintain a strong focus on the central theme or main point of your narrative.
Organize your essay chronologically, guiding your reader through the timeline of events.
As you recount your experience, use a variety of sensory details, such as sounds, smells, and tastes, to immerse your reader in the moment. For instance, “The smell of freshly brewed coffee filled the room as my friends and I excitedly chattered about our upcoming adventure.”
Take advantage of dialogue to bring your characters to life and to reveal aspects of their personalities. Incorporate both internal and external conflicts, as conflict plays a crucial role in engaging your reader and enhancing the narrative’s momentum. Show the evolution of your characters and how they grow throughout the story.
Part 8 Step 5. Creating a Conclusion
Finally, to write a satisfying conclusion, reflect on the narrative’s impact and how the experience has affected you or your characters. Tie the narrative’s events together and highlight the lessons learned, providing closure for the reader.
Avoid abruptly ending your story, because that can leave the reader feeling unsatisfied. Instead, strive to create a sense of resolution and demonstrate how the events have changed the characters’ perspectives or how the story’s theme has developed.
For example, “Looking back, I realize that the bus ride not only changed my perspective on friendship, but also taught me valuable life lessons that I carry with me to this day.”
Part 9 Step 6. Polishing the Essay
Fine-tuning your language.
When writing a narrative essay, it’s key to choose words that convey the emotions and experiences you’re describing. Opt for specific, vivid language that creates a clear mental image for your reader. For instance, instead of saying “The weather was hot,” try “The sun scorched the pavement, causing the air to shimmer like a mirage.” This gives your essay a more engaging and immersive feeling.
Editing for Clarity and Concision
As you revise your essay, keep an eye out for redundancies and unnecessary words that might dilute the impact of your story. Getting to the point and using straightforward language can help your essay flow better. For example, instead of using “She was walking in a very slow manner,” you can say, “She strolled leisurely.” Eliminate filler words and phrases, keeping only the most pertinent information that moves your story forward.
Proofreading for Typos
Finally, proofread your essay carefully to catch any typos, grammatical errors, or punctuation mistakes. It’s always a good idea to have someone else read it as well, as they might catch errors you didn’t notice. Mistakes can be distracting and may undermine the credibility of your writing, so be thorough with your editing process.
Part 10 Step 7. Feedback and Revision
Gathering feedback.
After you’ve written the first draft of your narrative essay, it’s time to gather feedback from friends, family, or colleagues. Share your essay with a few trusted people who can provide insights and suggestions for improvement. Listen to their thoughts and be open to constructive criticism. You might be surprised by the different perspectives they offer, which can strengthen your essay.
Iterating on the Draft
Once you have collected feedback, it’s time to revise and refine your essay. Address any issues or concerns raised by your readers and incorporate their suggestions. Consider reorganizing your story’s structure, clarifying your descriptions, or adding more details based on the feedback you received.
As you make changes, continue to fine-tune your essay to ensure a smooth flow and a strong narrative. Don’t be afraid to cut out unnecessary elements or rework parts of your story until it’s polished and compelling.
Revision is a crucial part of the writing process, and taking the time to reflect on feedback and make improvements will help you create a more engaging and impactful narrative essay.
Frequently Asked Questions
How can i create an engaging introduction.
Craft an attention-grabbing hook with a thought-provoking question, an interesting fact, or a vivid description. Set the stage for your story by introducing the time, place, and context for the events. Creating tension or raising curiosity will make your readers eager to learn more.
What strategies help develop strong characters?
To develop strong characters, consider the following:
- Give your characters distinct traits, strengths, and weaknesses.
- Provide a backstory to explain their actions and motivations.
- Use dialogue to present their personality, emotions, and relationships.
- Show how they change or evolve throughout your story.
How can I make my story flow smoothly with transitions?
Smooth transitions between scenes or events can create a more coherent and easy-to-follow story. Consider the following tips to improve your transitions:
- Use words and phrases like “meanwhile,” “later that day,” or “afterward” to signify changes in time.
- Link scenes with a common theme or element.
- Revisit the main characters or setting to maintain continuity.
- Introduce a twist or an unexpected event that leads to the next scene.
What are some tips for choosing a great narrative essay topic?
To choose an engaging narrative essay topic, follow these tips:
- Pick a personal experience or story that holds significance for you.
- Consider a challenge or a turning point you’ve faced in your life.
- Opt for a topic that will allow you to share emotions and lessons learned.
- Think about what your audience would find relatable, intriguing, or inspiring.
How do I wrap up my narrative essay with a strong conclusion?
A compelling conclusion restates the main events and highlights any lessons learned or growth in your character. Try to end on a thought-provoking note or leave readers with some food for thought. Finally, make sure your conclusion wraps up your story neatly and reinforces its overall message.
- How to Write a Perfect Project Plan? [The Easy Guide]
- How to Write a Thoughtful Apology Letter (Inspiring Examples)
- 5 Main Change Management Models: ADKAR vs Kubler Ross vs McKinsey 7S vs Lewin's vs Kotter’s 8 Step
- How to Write a Performance Improvement Plan (PIP)
- How to Write an Effective Performance Review (Essential Steps)
- How to Write Scope of Work - 7 Necessary Steps and 6 Best Practices
- PRO Courses Guides New Tech Help Pro Expert Videos About wikiHow Pro Upgrade Sign In
- EDIT Edit this Article
- EXPLORE Tech Help Pro About Us Random Article Quizzes Request a New Article Community Dashboard This Or That Game Popular Categories Arts and Entertainment Artwork Books Movies Computers and Electronics Computers Phone Skills Technology Hacks Health Men's Health Mental Health Women's Health Relationships Dating Love Relationship Issues Hobbies and Crafts Crafts Drawing Games Education & Communication Communication Skills Personal Development Studying Personal Care and Style Fashion Hair Care Personal Hygiene Youth Personal Care School Stuff Dating All Categories Arts and Entertainment Finance and Business Home and Garden Relationship Quizzes Cars & Other Vehicles Food and Entertaining Personal Care and Style Sports and Fitness Computers and Electronics Health Pets and Animals Travel Education & Communication Hobbies and Crafts Philosophy and Religion Work World Family Life Holidays and Traditions Relationships Youth
- Browse Articles
- Learn Something New
- Quizzes Hot
- This Or That Game New
- Train Your Brain
- Explore More
- Support wikiHow
- About wikiHow
- Log in / Sign up
- Education and Communications
- English Grammar
- Writing Paragraphs
How to Write a Narrative Paragraph
Last Updated: December 5, 2023 Fact Checked
This article was co-authored by Grant Faulkner, MA . Grant Faulkner is the Executive Director of National Novel Writing Month (NaNoWriMo) and the co-founder of 100 Word Story, a literary magazine. Grant has published two books on writing and has been published in The New York Times and Writer’s Digest. He co-hosts Write-minded, a weekly podcast on writing and publishing, and has a M.A. in Creative Writing from San Francisco State University. There are 8 references cited in this article, which can be found at the bottom of the page. This article has been fact-checked, ensuring the accuracy of any cited facts and confirming the authority of its sources. This article has been viewed 317,538 times.
A narrative paragraph tells a story, either real or fictional, by introducing a topic, giving more details, and then ending with a reflection or transition to another paragraph. Being able to properly write a narrative paragraph is an essential skill for anyone who wants to write or tell stories, from authors to journalists to advertisers and beyond. Learning the essential elements (an introduction, necessary details, and a conclusion) and how to put them together concisely will enable you to craft brief but complete stories for any audience. Plus, you'll become a better, more confident writer, too!
Introducing Your Story

- You could relate something that happened to someone else, even a fictional person.

- The exception would be if you were switching between the current discussion of the story’s meaning (in present tense) and the narrative of the story’s events (past tense).

- A good first-person topic sentence might be, “I’ll never forget the time I picked out my new puppy.” If you were using third person, the same topic sentence would be written, “He would never forget the time he picked out his new puppy.”

- For the first-person example about picking out a new puppy, you might continue, “My mom drove me to the breeder, which was 45 minutes away.”

- You might say: “I was 11, so the car ride seemed like an eternity. We lived in Wisconsin at the time, and the breeder was in Chicago.”
- All background information after the topic sentence, such as other characters and where the story takes place, should be approximately 1-4 sentences long.

- While the length of your paragraph will vary based on the content, a standard 5-sentence paragraph likely will not provide enough detail to tell a complete narrative.
Providing Narrative Details

- You could say, ”When we arrived at the breeder, I felt dismayed. I didn’t see any puppies at all.”

- You might continue, ”The breeder whistled. I was relieved when the puppies bounded around a corner and into the entryway. I saw a puppy in my favorite color—white—with two black spots. ‘Mom, can we keep him?’ I asked hopefully. She paused for a minute, seeming to reconsider getting a puppy at all.”

- You could end, “Then, mom smiled. ‘Only if we can name him Oreo.’ I hugged her, and Oreo gave me a lick of approval.”
- Resolution could be as brief as 1 sentence or as many as 3.
Concluding Your Story and Proofing Your Paragraph

- Regarding the puppy story, you might say, ”It was the happiest day of my life.”
- The nature of your conclusion will depend greatly on the tone and content of your story as well as the perspective the story is told from.

- Reading your story out loud is a great way to listen for grammar problems and other spots that don’t quite flow.
- Don’t rely on spell-check, as it won’t catch everything!
Template and Example of a Narrative Paragraph

Expert Q&A

- To make your narrative paragraph engaging, bounce story ideas off a friend before you begin writing. It’s best to focus on a moment that was special and transformative for you or your narrator rather than simply relating day-to-day events. [10] X Research source Thanks Helpful 1 Not Helpful 0
- The sentence parameters outlined here are simply guidelines rather than hard rules. When needed, narrative paragraphs can run slightly shorter or longer to suit their content. Thanks Helpful 0 Not Helpful 0

You Might Also Like

- ↑ https://owl.purdue.edu/owl/general_writing/grammar/verb_tenses/verb_tense_consistency.html
- ↑ https://k12.thoughtfullearning.com/lessonplan/writing-narrative-paragraph
- ↑ http://writingcenter.unc.edu/tips-and-tools/paragraphs/paragraph-development-examples/
- ↑ https://open.lib.umn.edu/writingforsuccess/chapter/10-1-narration/
- ↑ https://opentextbc.ca/buildingblocks/chapter/narrative-paragraphs/
- ↑ https://writing.wisc.edu/Handbook/Proofreading.html
- ↑ Grant Faulkner, MA. Professional Writer. Expert Interview. 8 January 2019.
- ↑ https://opentextbc.ca/writingforsuccess/chapter/chapter-12-peer-review-and-final-revisions/
About This Article

A narrative paragraph tells a chronological story that can either be real or fictional. A good narrative starts with a strong topic sentence that draws the reader in and introduces the tale you’re going to tell. For example, you might start your paragraph with "I'll never forget the day I picked out my new puppy." Once you hook your reader, introduce any major characters involved in the tale. After you set the scene, introduce the main conflict in the story, which you'll want to resolve by the end. For instance, you might write "When we arrived at the breeder's, I was disappointed. There weren't any puppies in sight. But then I heard a whistle and saw a bunch of puppies race around the corner." Your narrative paragraph should be around 9 sentences long. For tips on how to proofread your narrative paragraph, keep reading! Did this summary help you? Yes No
- Send fan mail to authors
Reader Success Stories
Mustafa Mahmoud
May 8, 2020
Did this article help you?

Rosa Labelle
Jun 10, 2019
Sarah Simpson
Apr 18, 2020

Featured Articles

Trending Articles

Watch Articles

- Terms of Use
- Privacy Policy
- Do Not Sell or Share My Info
- Not Selling Info
wikiHow Tech Help Pro:
Level up your tech skills and stay ahead of the curve
Looking to publish? Meet your dream editor, designer and marketer on Reedsy.
Find the perfect editor for your next book
1 million authors trust the professionals on Reedsy. Come meet them.
Guides • Perfecting your Craft
Last updated on Oct 29, 2023
How to Write a Short Story in 9 Simple Steps
This post is written by UK writer Robert Grossmith. His short stories have been widely anthologized, including in The Time Out Book of London Short Stories , The Best of Best Short Stories , and The Penguin Book of First World War Stories . You can collaborate with him on your own short stories here on Reedsy .
The joy of writing short stories is, in many ways, tied to its limitations. Developing characters, conflict, and a premise within a few pages is a thrilling challenge that many writers relish — even after they've "graduated" to long-form fiction.
In this article, I’ll take you through the process of writing a short story, from idea conception to the final draft.
How to write a short story:
1. Know what a short story is versus a novel
2. pick a simple, central premise, 3. build a small but distinct cast of characters, 4. begin writing close to the end, 5. shut out your internal editor, 6. finish the first draft, 7. edit the short story, 8. share the story with beta readers, 9. submit the short story to publications.
But first, let’s talk about what makes a short story different from a novel.
The simple answer to this question, of course, is that the short story is shorter than the novel, usually coming in at between, say, 1,000-15,000 words. Any shorter and you’re into flash fiction territory. Any longer and you’re approaching novella length .
As far as other features are concerned, it’s easier to define the short story by what it lacks compared to the novel . For example, the short story usually has:
- fewer characters than a novel
- a single point of view, either first person or third person
- a single storyline without subplots
- less in the way of back story or exposition than a novel
If backstory is needed at all, it should come late in the story and be kept to a minimum.
It’s worth remembering too that some of the best short stories consist of a single dramatic episode in the form of a vignette or epiphany.

GET ACCOUNTABILITY
Meet writing coaches on Reedsy
Industry insiders can help you hone your craft, finish your draft, and get published.
A short story can begin life in all sorts of ways.
It may be suggested by a simple but powerful image that imprints itself on the mind. It may derive from the contemplation of a particular character type — someone you know perhaps — that you’re keen to understand and explore. It may arise out of a memorable incident in your own life.

For example:
- Kafka began “The Metamorphosis” with the intuition that a premise in which the protagonist wakes one morning to find he’s been transformed into a giant insect would allow him to explore questions about human relationships and the human condition.
- Herman Melville’s “Bartleby the Scrivener” takes the basic idea of a lowly clerk who decides he will no longer do anything he doesn’t personally wish to do, and turns it into a multi-layered tale capable of a variety of interpretations.
When I look back on some of my own short stories, I find a similar dynamic at work: a simple originating idea slowly expands to become something more nuanced and less formulaic.
So how do you find this “first heartbeat” of your own short story? Here are several ways to do so.
Experiment with writing prompts
Eagle-eyed readers will notice that the story premises mentioned above actually have a great deal in common with writing prompts like the ones put forward each week in Reedsy’s short story competition . Try it out! These prompts are often themed in a way that’s designed to narrow the focus for the writer so that one isn’t confronted with a completely blank canvas.
Turn to the originals
Take a story or novel you admire and think about how you might rework it, changing a key element. (“Pride and Prejudice and Vampires” is perhaps an extreme product of this exercise.) It doesn’t matter that your proposed reworking will probably never amount to more than a skimpy mental reimagining — it may well throw up collateral narrative possibilities along the way.
Keep a notebook
Finally, keep a notebook in which to jot down stray observations and story ideas whenever they occur to you. Again, most of what you write will be stuff you never return to, and it may even fail to make sense when you reread it. But lurking among the dross may be that one rough diamond that makes all the rest worthwhile.
Like I mentioned earlier, short stories usually contain far fewer characters than novels. Readers also need to know far less about the characters in a short story than we do in a novel (sometimes it’s the lack of information about a particular character in a story that adds to the mystery surrounding them, making them more compelling).

Yet it remains the case that creating memorable characters should be one of your principal goals. Think of your own family, friends and colleagues. Do you ever get them confused with one another? Probably not.
Your dramatis personae should be just as easily distinguishable from one another, either through their appearance, behavior, speech patterns, or some other unique trait. If you find yourself struggling, a character profile template like the one you can download for free below is particularly helpful in this stage of writing.

FREE RESOURCE
Reedsy’s Character Profile Template
A story is only as strong as its characters. Fill this out to develop yours.
- “The Yellow Wallpaper” by Charlotte Perkins Gilman features a cast of two: the narrator and her husband. How does Gilman give her narrator uniquely identifying features?
- “The Tell-Tale Heart” by Edgar Allan Poe features a cast of three: the narrator, the old man, and the police. How does Poe use speech patterns in dialogue and within the text itself to convey important information about the narrator?
- “A Good Man Is Hard to Find” by Flannery O’Connor is perhaps an exception: its cast of characters amounts to a whopping (for a short story) nine. How does she introduce each character? In what way does she make each character, in particular The Misfit, distinct?

He’s right: avoid the preliminary exposition or extended scene-setting. Begin your story by plunging straight into the heart of the action. What most readers want from a story is drama and conflict, and this is often best achieved by beginning in media res . You have no time to waste in a short story. The first sentence of your story is crucial, and needs to grab the reader’s attention to make them want to read on.
One way to do this is to write an opening sentence that makes the reader ask questions. For example, Kingsley Amis once said, tongue-in-cheek, that in the future he would only read novels that began with the words: “A shot rang out.”
This simple sentence is actually quite telling. It introduces the stakes: there’s an immediate element of physical danger, and therefore jeopardy for someone. But it also raises questions that the reader will want answered. Who fired the shot? Who or what were they aiming at, and why? Where is this happening?
We read fiction for the most part to get answers to questions. For example, if you begin your story with a character who behaves in an unexpected way, the reader will want to know why he or she is behaving like this. What motivates their unusual behavior? Do they know that what they’re doing or saying is odd? Do they perhaps have something to hide? Can we trust this character?
As the author, you can answer these questions later (that is, answer them dramatically rather than through exposition). But since we’re speaking of the beginning of a story, at the moment it’s enough simply to deliver an opening sentence that piques the reader’s curiosity, raises questions, and keeps them reading.
“Anything goes” should be your maxim when embarking on your first draft.

FREE COURSE
How to Craft a Killer Short Story
From pacing to character development, master the elements of short fiction.
By that, I mean: kill the editor in your head and give your imagination free rein. Remember, you’re beginning with a blank page. Anything you put down will be an improvement on what’s currently there, which is nothing. And there’s a prescription for any obstacle you might encounter at this stage of writing.
- Worried that you’re overwriting? Don’t worry. It’s easier to cut material in later drafts once you’ve sketched out the whole story.
- Got stuck, but know what happens later? Leave a gap. There’s no necessity to write the story sequentially. You can always come back and fill in the gap once the rest of the story is complete.
- Have a half-developed scene that’s hard for you to get onto the page? Write it in note form for the time being. You might find that it relieves the pressure of having to write in complete sentences from the get-go.
Most of my stories were begun with no idea of their eventual destination, but merely an approximate direction of travel. To put it another way, I’m a ‘pantser’ (flying by the seat of my pants, making it up as I go along) rather than a planner. There is, of course, no right way to write your first draft. What matters is that you have a first draft on your hands at the end of the day.
It’s hard to overstate the importance of the ending of a short story : it can rescue an inferior story or ruin an otherwise superior one.
If you’re a planner, you will already know the broad outlines of the ending. If you’re a pantser like me, you won’t — though you’ll hope that a number of possible endings will have occurred to you in the course of writing and rewriting the story!
In both cases, keep in mind that what you’re after is an ending that’s true to the internal logic of the story without being obvious or predictable. What you want to avoid is an ending that evokes one of two reactions:
- “Is that it?” aka “The author has failed to resolve the questions raised by the story.”
- “WTF!” aka “This ending is simply confusing.”
Like Truman Capote said, “Good writing is rewriting.”
Once you have a first draft, the real work begins. This is when you move things around, tightening the nuts and bolts of the piece to make sure it holds together and resembles the shape it took in your mind when you first conceived it.
In most cases, this means reading through your first draft again (and again). In this stage of editing , think to yourself:
- Which narrative threads are already in place?
- Which may need to be added or developed further?
- Which need to perhaps be eliminated altogether?

All that’s left afterward is the final polish . Here’s where you interrogate every word, every sentence, to make sure it’s earned its place in the story:
- Is that really what I mean?
- Could I have said that better?
- Have I used that word correctly?
- Is that sentence too long?
- Have I removed any clichés?
Trust me: this can be the most satisfying part of the writing process. The heavy lifting is done, the walls have been painted, the furniture is in place. All you have to do now is hang a few pictures, plump the cushions and put some flowers in a vase.
Eventually, you may reach a point where you’ve reread and rewritten your story so many times that you simply can’t bear to look at it again. If this happens, put the story aside and try to forget about it.
When you do finally return to it, weeks or even months later, you’ll probably be surprised at how the intervening period has allowed you to see the story with a fresh pair of eyes. And whereas it might have felt like removing one of your own internal organs to cut such a sentence or paragraph before, now it feels like a liberation.
The story, you can see, is better as a result. It was only your bloated appendix you removed, not a vital organ.
It’s at this point that you should call on the services of beta readers if you have them. This can be a daunting prospect: what if the response is less enthusiastic than you’re hoping for? But think about it this way: if you’re expecting complete strangers to read and enjoy your story, then you shouldn’t be afraid of trying it out first on a more sympathetic audience.
This is also why I’d suggest delaying this stage of the writing process until you feel sure your story is complete. It’s one thing to ask a friend to read and comment on your new story. It’s quite another thing to return to them sometime later with, “I’ve made some changes to the story — would you mind reading it again?”

So how do you know your story’s really finished? This is a question that people have put to me. My reply tends to be: I know the story’s finished when I can’t see how to make it any better.
This is when you can finally put down your pencil (or keyboard), rest content with your work for a few days, then submit it so that people can read your work. And you can start with this directory of literary magazines once you're at this step.
The truth is, in my experience, there’s actually no such thing as a final draft. Even after you’ve submitted your story somewhere — and even if you’re lucky enough to have it accepted — there will probably be the odd word here or there that you’d like to change.
Don’t worry about this. Large-scale changes are probably out of the question at this stage, but a sympathetic editor should be willing to implement any small changes right up to the time of publication.
Join a community of over 1 million authors
Reedsy is more than just a blog. Become a member today to discover how we can help you publish a beautiful book.
Bring your short stories to life
Fuse character, story, and conflict with tools in the Reedsy Book Editor. 100% free.

1 million authors trust the professionals on Reedsy. Come meet them.
Enter your email or get started with a social account:
- Features for Creative Writers
- Features for Work
- Features for Higher Education
- Features for Teachers
- Features for Non-Native Speakers
- Learn Blog Grammar Guide Community Events FAQ
- Grammar Guide
Telling the Story of Yourself: 6 Steps to Writing Personal Narratives

Jennifer Xue

Table of Contents
Why do we write personal narratives, 6 guidelines for writing personal narrative essays, inspiring personal narratives, examples of personal narrative essays, tell your story.
First off, you might be wondering: what is a personal narrative? In short, personal narratives are stories we tell about ourselves that focus on our growth, lessons learned, and reflections on our experiences.
From stories about inspirational figures we heard as children to any essay, article, or exercise where we're asked to express opinions on a situation, thing, or individual—personal narratives are everywhere.
According to Psychology Today, personal narratives allow authors to feel and release pains, while savouring moments of strength and resilience. Such emotions provide an avenue for both authors and readers to connect while supporting healing in the process.
That all sounds great. But when it comes to putting the words down on paper, we often end up with a list of experiences and no real structure to tie them together.
In this article, we'll discuss what a personal narrative essay is further, learn the 6 steps to writing one, and look at some examples of great personal narratives.
As readers, we're fascinated by memoirs, autobiographies, and long-form personal narrative articles, as they provide a glimpse into the authors' thought processes, ideas, and feelings. But you don't have to be writing your whole life story to create a personal narrative.
You might be a student writing an admissions essay , or be trying to tell your professional story in a cover letter. Regardless of your purpose, your narrative will focus on personal growth, reflections, and lessons.
Personal narratives help us connect with other people's stories due to their easy-to-digest format and because humans are empathising creatures.
We can better understand how others feel and think when we were told stories that allow us to see the world from their perspectives. The author's "I think" and "I feel" instantaneously become ours, as the brain doesn't know whether what we read is real or imaginary.
In her best-selling book Wired for Story, Lisa Cron explains that the human brain craves tales as it's hard-wired through evolution to learn what happens next. Since the brain doesn't know whether what you are reading is actual or not, we can register the moral of the story cognitively and affectively.
In academia, a narrative essay tells a story which is experiential, anecdotal, or personal. It allows the author to creatively express their thoughts, feelings, ideas, and opinions. Its length can be anywhere from a few paragraphs to hundreds of pages.
Outside of academia, personal narratives are known as a form of journalism or non-fiction works called "narrative journalism." Even highly prestigious publications like the New York Times and Time magazine have sections dedicated to personal narratives. The New Yorke is a magazine dedicated solely to this genre.
The New York Times holds personal narrative essay contests. The winners are selected because they:
had a clear narrative arc with a conflict and a main character who changed in some way. They artfully balanced the action of the story with reflection on what it meant to the writer. They took risks, like including dialogue or playing with punctuation, sentence structure and word choice to develop a strong voice. And, perhaps most important, they focused on a specific moment or theme – a conversation, a trip to the mall, a speech tournament, a hospital visit – instead of trying to sum up the writer’s life in 600 words.
In a nutshell, a personal narrative can cover any reflective and contemplative subject with a strong voice and a unique perspective, including uncommon private values. It's written in first person and the story encompasses a specific moment in time worthy of a discussion.
Writing a personal narrative essay involves both objectivity and subjectivity. You'll need to be objective enough to recognise the importance of an event or a situation to explore and write about. On the other hand, you must be subjective enough to inject private thoughts and feelings to make your point.
With personal narratives, you are both the muse and the creator – you have control over how your story is told. However, like any other type of writing, it comes with guidelines.
1. Write Your Personal Narrative as a Story
As a story, it must include an introduction, characters, plot, setting, climax, anti-climax (if any), and conclusion. Another way to approach it is by structuring it with an introduction, body, and conclusion. The introduction should set the tone, while the body should focus on the key point(s) you want to get across. The conclusion can tell the reader what lessons you have learned from the story you've just told.
2. Give Your Personal Narrative a Clear Purpose
Your narrative essay should reflect your unique perspective on life. This is a lot harder than it sounds. You need to establish your perspective, the key things you want your reader to take away, and your tone of voice. It's a good idea to have a set purpose in mind for the narrative before you start writing.
Let's say you want to write about how you manage depression without taking any medicine. This could go in any number of ways, but isolating a purpose will help you focus your writing and choose which stories to tell. Are you advocating for a holistic approach, or do you want to describe your emotional experience for people thinking of trying it?
Having this focus will allow you to put your own unique take on what you did (and didn't do, if applicable), what changed you, and the lessons learned along the way.
3. Show, Don't Tell
It's a narration, so the narrative should show readers what happened, instead of telling them. As well as being a storyteller, the author should take part as one of the characters. Keep this in mind when writing, as the way you shape your perspective can have a big impact on how your reader sees your overarching plot. Don't slip into just explaining everything that happened because it happened to you. Show your reader with action.
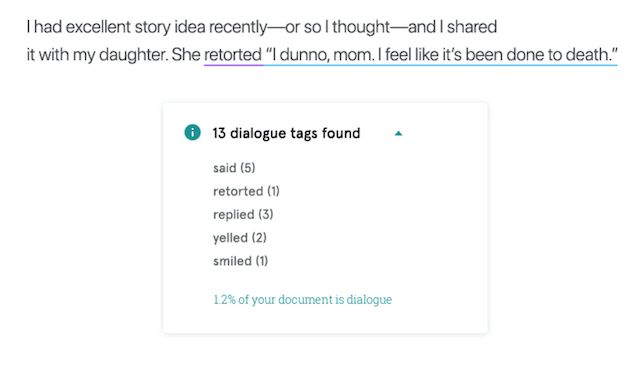
You can check for instances of telling rather than showing with ProWritingAid. For example, instead of:
"You never let me do anything!" I cried disdainfully.
"You never let me do anything!" To this day, my mother swears that the glare I levelled at her as I spat those words out could have soured milk.
Using ProWritingAid will help you find these instances in your manuscript and edit them without spending hours trawling through your work yourself.
4. Use "I," But Don't Overuse It
You, the author, take ownership of the story, so the first person pronoun "I" is used throughout. However, you shouldn't overuse it, as it'd make it sound too self-centred and redundant.
ProWritingAid can also help you here – the Style Report will tell you if you've started too many sentences with "I", and show you how to introduce more variation in your writing.
5. Pay Attention to Tenses
Tense is key to understanding. Personal narratives mostly tell the story of events that happened in the past, so many authors choose to use the past tense. This helps separate out your current, narrating voice and your past self who you are narrating. If you're writing in the present tense, make sure that you keep it consistent throughout.

6. Make Your Conclusion Satisfying
Satisfy your readers by giving them an unforgettable closing scene. The body of the narration should build up the plot to climax. This doesn't have to be something incredible or shocking, just something that helps give an interesting take on your story.
The takeaways or the lessons learned should be written without lecturing. Whenever possible, continue to show rather than tell. Don't say what you learned, narrate what you do differently now. This will help the moral of your story shine through without being too preachy.
GoodReads is a great starting point for selecting read-worthy personal narrative books. Here are five of my favourites.
Owl Moon by Jane Yolen
Jane Yolen, the author of 386 books, wrote this poetic story about a daughter and her father who went owling. Instead of learning about owls, Yolen invites readers to contemplate the meaning of gentleness and hope.
Night by Elie Wiesel
Elie Wiesel was a teenager when he and his family were sent to Auschwitz concentration camp in 1944. This Holocaust memoir has a strong message that such horrific events should never be repeated.
The Diary of a Young Girl by Anne Frank
This classic is a must-read by young and old alike. It's a remarkable diary by a 13-year-old Jewish girl who hid inside a secret annexe of an old building during the Nazi occupation of the Netherlands in 1942.
The Year of Magical Thinking by Joan Didion
This is a personal narrative written by a brave author renowned for her clarity, passion, and honesty. Didion shares how in December 2003, she lost her husband of 40 years to a massive heart attack and dealt with the acute illness of her only daughter. She speaks about grief, memories, illness, and hope.
Educated by Tara Westover
Author Tara Westover was raised by survivalist parents. She didn't go to school until 17 years of age, which later took her to Harvard and Cambridge. It's a story about the struggle for quest for knowledge and self-reinvention.
Narrative and personal narrative journalism are gaining more popularity these days. You can find distinguished personal narratives all over the web.
Curating the best of the best of personal narratives and narrative essays from all over the web. Some are award-winning articles.
Narratively
Long-form writing to celebrate humanity through storytelling. It publishes personal narrative essays written to provoke, inspire, and reflect, touching lesser-known and overlooked subjects.
Narrative Magazine
It publishes non,fiction narratives, poetry, and fiction. Among its contributors is Frank Conroy, the author of Stop-Time , a memoir that has never been out of print since 1967.
Thought Catalog
Aimed at Generation Z, it publishes personal narrative essays on self-improvement, family, friendship, romance, and others.
Personal narratives will continue to be popular as our brains are wired for stories. We love reading about others and telling stories of ourselves, as they bring satisfaction and a better understanding of the world around us.
Personal narratives make us better humans. Enjoy telling yours!

Write like a bestselling author
Love writing? ProWritingAid will help you improve the style, strength, and clarity of your stories.
Jennifer Xue is an award-winning e-book author with 2,500+ articles and 100+ e-books/reports published under her belt. She also taught 50+ college-level essay and paper writing classes. Her byline has appeared in Forbes, Fortune, Cosmopolitan, Esquire, Business.com, Business2Community, Addicted2Success, Good Men Project, and others. Her blog is JenniferXue.com. Follow her on Twitter @jenxuewrites].
Get started with ProWritingAid
Drop us a line or let's stay in touch via :
Purdue Online Writing Lab Purdue OWL® College of Liberal Arts
Narrative Essays

Welcome to the Purdue OWL
This page is brought to you by the OWL at Purdue University. When printing this page, you must include the entire legal notice.
Copyright ©1995-2018 by The Writing Lab & The OWL at Purdue and Purdue University. All rights reserved. This material may not be published, reproduced, broadcast, rewritten, or redistributed without permission. Use of this site constitutes acceptance of our terms and conditions of fair use.
The Modes of Discourse—Exposition, Description, Narration, Argumentation (EDNA)—are common paper assignments you may encounter in your writing classes. Although these genres have been criticized by some composition scholars, the Purdue OWL recognizes the widespread use of these approaches and students’ need to understand and produce them.
What is a narrative essay?
When writing a narrative essay, one might think of it as telling a story. These essays are often anecdotal, experiential, and personal—allowing students to express themselves in a creative and, quite often, moving ways.
Here are some guidelines for writing a narrative essay.
- If written as a story, the essay should include all the parts of a story.
This means that you must include an introduction, plot, characters, setting, climax, and conclusion.
- When would a narrative essay not be written as a story?
A good example of this is when an instructor asks a student to write a book report. Obviously, this would not necessarily follow the pattern of a story and would focus on providing an informative narrative for the reader.
- The essay should have a purpose.
Make a point! Think of this as the thesis of your story. If there is no point to what you are narrating, why narrate it at all?
- The essay should be written from a clear point of view.
It is quite common for narrative essays to be written from the standpoint of the author; however, this is not the sole perspective to be considered. Creativity in narrative essays oftentimes manifests itself in the form of authorial perspective.
- Use clear and concise language throughout the essay.
Much like the descriptive essay, narrative essays are effective when the language is carefully, particularly, and artfully chosen. Use specific language to evoke specific emotions and senses in the reader.
- The use of the first person pronoun ‘I’ is welcomed.
Do not abuse this guideline! Though it is welcomed it is not necessary—nor should it be overused for lack of clearer diction.
- As always, be organized!
Have a clear introduction that sets the tone for the remainder of the essay. Do not leave the reader guessing about the purpose of your narrative. Remember, you are in control of the essay, so guide it where you desire (just make sure your audience can follow your lead).

When writers set down the facts of their lives into a compelling story , they’re writing a narrative essay. Personal narrative essays explore the events of the writer’s own life, and by crafting a nonfiction piece that resonates as storytelling, the essayist can uncover deeper truths in the world.
Narrative essays weave the author’s factual lived experiences into a compelling story.
So, what is a narrative essay? Whether you’re writing for college applications or literary journals , this article separates fact from fiction. We’ll look at how to write a narrative essay through a step-by-step process, including a look at narrative essay topics and outlines. We’ll also analyze some successful narrative essay examples.
Learn how to tell your story, your way. Let’s dive into this exciting genre!
What is a Narrative Essay?
The narrative essay is a branch of creative nonfiction . Also known as a personal essay, writers of this genre are tasked with telling honest stories about their lived experiences and, as a result, arriving at certain realizations about life.
Think of personal narrative essays as nonfiction short stories . While the essay and the short story rely on different writing techniques, they arrive at similar outcomes: a powerful story with an idea, theme , or moral that the reader can interpret for themselves.
Now, if you haven’t written a narrative essay before, you might associate the word “essay” with high school English class. Remember those tedious 5-paragraph essays we had to write, on the topic of some book we barely read, about subject matter that didn’t interest us?
Don’t worry—that’s not the kind of essay we’re talking about. The word essay comes from the French essayer , which means “to try.” That’s exactly what writing a narrative essay is: an attempt at organizing the real world into language—a journey of making meaning from the chaos of life.
Narrative essays work to surface meaning from lived experience.
Narrative Essay Example
A great narrative essay example is the piece “Flow” by Mary Oliver, which you can read for free in Google Books .
The essay dwells on, as Mary Oliver puts it, the fact that “we live in paradise.” At once both an ode to nature and an urge to love it fiercely, Oliver explores our place in the endless beauty of the world.
Throughout the essay, Oliver weaves in her thoughts about the world, from nature’s noble beauty to the question “What is the life I should live?” Yet these thoughts, however profound, are not the bulk of the essay. Rather, she arrives at these thoughts via anecdotes and observations: the migration of whales, the strings of fish at high tide, the inventive rescue of a spiny fish from the waterless shore, etc.
What is most profound about this essay, and perhaps most amusing, is that it ends with Oliver’s questions about how to live life. And yet, the stories she tells show us exactly how to live life: with care for the world; with admiration; with tenderness towards all of life and its superb, mysterious, seemingly-random beauty.
Such is the power of the narrative essay. By examining the random facts of our lives, we can come to great conclusions.
What do most essays have in common? Let’s look at the fundamentals of the essay, before diving into more narrative essay examples.
Narrative Essay Definition: 5 Fundamentals
The personal narrative essay has a lot of room for experimentation. We’ll dive into those opportunities in a bit, but no matter the form, most essays share these five fundamentals.
- Personal experience
- Meaning from chaos
- The use of literary devices
Let’s explore these fundamentals in depth.
All narrative essays have a thesis statement. However, this isn’t the formulaic thesis statement you had to write in school: you don’t need to map out your argument with painstaking specificity, you need merely to tell the reader what you’re writing about.
Take the aforementioned essay by Mary Oliver. Her thesis is this: “How can we not know that, already, we live in paradise?”
It’s a simple yet provocative statement. By posing her thesis as a question, she challenges us to consider why we might not treat this earth as paradise. She then delves into her own understanding of this paradise, providing relevant stories and insights as to how the earth should be treated.
Now, be careful with abstract statements like this. Mary Oliver is a master of language, so she’s capable of creating a thesis statement out of an abstract idea and building a beautiful essay. But concrete theses are also welcome: you should compel the reader forward with the central argument of your work, without confusing them or leading them astray.
You should compel the reader forward with the central argument of your work, without confusing them or leading them astray
2. Personal Experience
The personal narrative essay is, shockingly, about personal experience. But how do writers distill their experiences into meaningful stories?
There are a few techniques writers have at their disposal. Perhaps the most common of these techniques is called braiding . Rather than focusing on one continuous story, the writer can “braid” different stories, weaving in and out of different narratives and finding common threads between them. Often, the subject matter of the essay will require more than one anecdote as evidence, and braiding helps the author uphold their thesis while showing instead of telling .
Another important consideration is how you tell your story . Essayists should consider the same techniques that fiction writers use. Give ample consideration to your essay’s setting , word choice , point of view , and dramatic structure . The narrative essay is, after all, a narrative, so tell your story how it deserves to be told.
3. Meaning from Chaos
Life, I think we can agree, is chaotic. While we can trace the events of our lives through cause and effect, A leads to B leads to C, the truth is that so much of our lives are shaped through circumstances beyond our control.
The narrative essay is a way to reclaim some of that control. By distilling the facts of our lives into meaningful narratives, we can uncover deeper truths that we didn’t realize existed.
By distilling the facts of our lives into meaningful narratives, we can uncover deeper truths that we didn’t realize existed.
Consider the essay “ Only Daughter ” by Sandra Cisneros. It’s a brief read, but it covers a lot of different events: a lonesome childhood, countless moves, university education, and the trials and tribulations of a successful writing career.
Coupled with Cisneros’ musings on culture and gender roles, there’s a lot of life to distill in these three pages. Yet Cisneros does so masterfully. By organizing these life events around her thesis statement of being an only daughter, Cisneros finds meaning in the many disparate events she describes.
As you go about writing a narrative essay, you will eventually encounter moments of insight . Insight describes those “aha!” moments in the work—places in which you come to deeper realizations about your life, the lives of others, and the world at large.
Now, insight doesn’t need to be some massive, culture-transforming realization. Many moments of insight are found in small interactions and quiet moments.
For example, In the above essay by Sandra Cisneros, her moments of insight come from connecting her upbringing to her struggle as an only daughter. While her childhood was often lonely and disappointing, she realizes in hindsight that she’s lucky for that upbringing: it helped nurture her spirit as a writer, and it helped her pursue a career in writing. These moments of gratitude work as insight, allowing her to appreciate what once seemed like a burden.
When we reach the end of the essay, and Cisneros describes how she felt when her father read one of her stories, we see what this gratitude is building towards: love and acceptance for the life she chose.
5. Literary Devices
The personal narrative essay, as well as all forms of creative writing, uses its fair share of literary devices . These devices don’t need to be complex: you don’t need a sprawling extended metaphor or an intricate set of juxtapositions to make your essay compelling.
However, the occasional symbol or metaphor will certainly aid your story. In Mary Oliver’s essay “Flow,” the author uses literary devices to describe the magnificence of the ocean, calling it a “cauldron of changing greens and blues” and “the great palace of the earth.” These descriptions reinforce the deep beauty of the earth.
In Sandra Cisneros’ essay “Only Daughter,” the author employs different symbols to represent her father’s masculinity and sense of gender roles. At one point, she lists the few things he reads—sports journals, slasher magazines, and picture paperbacks, often depicting scenes of violence against women. These symbols represent the divide between her father’s gendered thinking and her own literary instincts.
More Narrative Essay Examples
Let’s take a look at a few more narrative essay examples. We’ll dissect each essay based on the five fundamentals listed above.
Narrative Essay Example: “Letting Go” by David Sedaris
Read “Letting Go” here in The New Yorker .
Sedaris’ essay dwells on the culture of cigarette smoking—how it starts, the world it builds, and the difficulties in quitting. Let’s analyze how this narrative essay example uses the five fundamentals of essay writing.
- Thesis: There isn’t an explicitly defined thesis, which is common for essays that are meant to be humorous or entertaining. However, this sentence is a plausible thesis statement: “It wasn’t the smoke but the smell of it that bothered me. In later years, I didn’t care so much, but at the time I found it depressing: the scent of neglect.”
- Personal Experience: Sedaris moves between many different anecdotes about smoking, from his family’s addiction to cigarettes to his own dependence. We learn about his moving around for cheaper smokes, his family’s struggle to quit, and the last cigarette he smoked in the Charles de Gaulle airport.
- Meaning from Chaos: Sedaris ties many disparate events together. We learn about his childhood and his smoking years, but these are interwoven with anecdotes about his family and friends. What emerges is a narrative about the allure of smoking.
- Insight: Two parts of this essay are especially poignant. One, when Sedaris describes his mother’s realization that smoking isn’t sophisticated, and soon quits her habit entirely. Two, when Sedaris is given the diseased lung of a chain smoker, and instead of thinking about his own lungs, he’s simply surprised at how heavy the lung is.
- Literary Devices: Throughout the essay, Sedaris demonstrates how the cigarette symbolizes neglect: neglect of one’s body, one’s space, and one’s self-presentation.
Narrative Essay Example: “My Mother’s Tongue” by Zavi Kang Engles
Read “My Mother’s Tongue” here in The Rumpus .
Engles’ essay examines the dysphoria of growing up between two vastly different cultures and languages. By asserting the close bond between Korean language and culture, Engles explores the absurdities of growing up as a child of Korean immigrants. Let’s analyze how this narrative essay example uses the five fundamentals of essay writing.
- Thesis: Engles’ essay often comes back to her relationship with the Korean language, especially as it relates to other Korean speakers. This relationship is best highlighted when she writes “I glowed with [my mother’s] love, basked in the warm security of what I thought was a language between us. Perhaps this is why strangers asked for our photos, in an attempt to capture a secret world between two people.”This “secret world” forms the crux of her essay, charting not only how Korean-Americans might exist in relation to one another, but also how Engles’ language is strongly tied to her identity and homeland.
- Personal Experience: Engles writes about her childhood attachment to both English and Korean, her adolescent fallout with the Korean language, her experiences as “not American enough” in the United States and “not Korean enough” in Korea, and her experiences mourning in a Korean hospital.
- Meaning from Chaos: In addition to the above events, Engles ties in research about language and identity (also known as code switching ). Through language and identity, the essay charts the two different cultures that the author stands between, highlighting the dissonance between Western individualism and an Eastern sense of belonging.
- Insight: There are many examples of insight throughout this essay as the author explores how out of place she feels, torn between two countries. An especially poignant example comes from Engles’ experience in a Korean hospital, where she writes “I didn’t know how to mourn in this country.”
- Literary Devices: The essay frequently juxtaposes the languages and cultures of Korea and the United States. Additionally, the English language comes to symbolize Western individualism, while the Korean language comes to symbolize Eastern collectivism.
Narrative Essay Example: 3 Rules for Middle-Age Happiness by Deborah Copaken
Read “3 Rules for Middle-Age Happiness” here in The Atlantic .
Copaken’s essay explores her relationship to Nora Ephron, the screenwriter for When Harry Met Sally . Let’s analyze how this narrative essay example uses the five fundamentals of essay writing.
- Thesis: This essay hands us the thesis statement in its subtitle: “Gather friends and feed them, laugh in the face of calamity, and cut out all the things—people, jobs, body parts—that no longer serve you.”
- Personal Experience: Copaken weaves two different threads through this essay. One thread is her personal life, including a failing marriage, medical issues, and her attempts at building a happy family. The other is Copaken’s personal relationship to Ephron, whose advice coincides with many of the essay’s insights.
- Meaning from Chaos: This essay organizes its events chronologically. However, the main sense of organization is found in the title: many of the essayist’s problems can be perceived as middle-aged crises (family trouble, divorce, death of loved ones), but the solutions to those crises are simpler than one might realize.
- Insight: In writing this essay, Copaken explores her relationship to Ephron, as well as Copaken’s own relationship to her children. She ties these experiences together at the end, when she writes “The transmission of woes is a one-way street, from child to mother. A good mother doesn’t burden her children with her pain. She waits until it becomes so heavy, it either breaks her or kills her, whichever comes first.”
- Literary Devices: The literary devices in this article explore the author’s relationship to womanhood. She wonders if having a hysterectomy will make her “like less of a woman.” Also important is the fact that, when the author has her hysterectomy, her daughter has her first period. Copaken uses this to symbolize the passing of womanhood from mother to daughter, which helps bring her to the above insight.
How to Write a Narrative Essay in 5 Steps
No matter the length or subject matter, writing a narrative essay is as easy as these five steps.
1. Generating Narrative Essay Ideas
If you’re not sure what to write about, you’ll want to generate some narrative essay ideas. One way to do this is to look for writing prompts online: Reedsy adds new prompts to their site every week, and we also post writing prompts every Wednesday to our Facebook group .
Taking a step back, it helps to simply think about formative moments in your life. You might a great idea from answering one of these questions:
- When did something alter my worldview, personal philosophy, or political beliefs?
- Who has given me great advice, or helped me lead a better life?
- What moment of adversity did I overcome and grow stronger from?
- What is something that I believe to be very important, that I want other people to value as well?
- What life event of mine do I not yet fully understand?
- What is something I am constantly striving for?
- What is something I’ve taken for granted, but am now grateful for?
Finally, you might be interested in the advice at our article How to Come Up with Story Ideas . The article focuses on fiction writers, but essayists can certainly benefit from these tips as well.
2. Drafting a Narrative Essay Outline
Once you have an idea, you’ll want to flesh it out in a narrative essay outline.
Your outline can be as simple or as complex as you’d like, and it all depends on how long you intend your essay to be. A simple outline can include the following:
- Introduction—usually a relevant anecdote that excites or entices the reader.
- Event 1: What story will I use to uphold my argument?
- Analysis 1: How does this event serve as evidence for my thesis?
- Conclusion: How can I tie these events together? What do they reaffirm about my thesis? And what advice can I then impart on the reader, if any?
One thing that’s missing from this outline is insight. That’s because insight is often unplanned: you realize it as you write it, and the best insight comes naturally to the writer. However, if you already know the insight you plan on sharing, it will fit best within the analysis for your essay, and/or in the essay’s conclusion.
Insight is often unplanned: you realize it as you write it, and the best insight comes naturally to the writer.
Another thing that’s missing from this is research. If you plan on intertwining your essay with research (which many essayists should do!), consider adding that research as its own bullet point under each heading.
For a different, more fiction-oriented approach to outlining, check out our article How to Write a Story Outline .
3. Starting with a Story
Now, let’s tackle the hardest question: how to start a narrative essay?
Most narrative essays begin with a relevant story. You want to draw the reader in right away, offering something that surprises or interests them. And, since the essay is about you and your lived experiences, it makes sense to start your essay with a relevant anecdote.
Think about a story that’s relevant to your thesis, and experiment with ways to tell this story. You can start with a surprising bit of dialogue , an unusual situation you found yourself in, or a beautiful setting. You can also lead your essay with research or advice, but be sure to tie that in with an anecdote quickly, or else your reader might not know where your essay is going.
For examples of this, take a look at any of the narrative essay examples we’ve used in this article.
Theoretically, your thesis statement can go anywhere in the essay. You may have noticed in the previous examples that the thesis statement isn’t always explicit or immediate: sometimes it shows up towards the center of the essay, and sometimes it’s more implied than stated directly.
You can experiment with the placement of your thesis, but if you place your thesis later in the essay, make sure that everything before the thesis is intriguing to the reader. If the reader feels like the essay is directionless or boring, they won’t have a reason to reach your thesis, nor will they understand the argument you’re making.
4. Getting to the Core Truth
With an introduction and a thesis underway, continue writing about your experiences, arguments, and research. Be sure to follow the structure you’ve sketched in your outline, but feel free to deviate from this outline if something more natural occurs to you.
Along the way, you will end up explaining why your experiences matter to the reader. Here is where you can start generating insight. Insight can take the form of many things, but the focus is always to reach a core truth.
Insight might take the following forms:
- Realizations from connecting the different events in your life.
- Advice based on your lived mistakes and experiences.
- Moments where you change your ideas or personal philosophy.
- Richer understandings about life, love, a higher power, the universe, etc.
5. Relentless Editing
With a first draft of your narrative essay written, you can make your essay sparkle in the editing process.
Remember, a first draft doesn’t have to be perfect, it just needs to exist.
Remember, a first draft doesn’t have to be perfect, it just needs to exist. Here are some things to focus on in the editing process:
- Clarity: Does every argument make sense? Do my ideas flow logically? Are my stories clear and easy to follow?
- Structure: Does the procession of ideas make sense? Does everything uphold my thesis? Do my arguments benefit from the way they’re laid out in this essay?
- Style: Do the words flow when I read them? Do I have a good mix of long and short sentences? Have I omitted any needless words ?
- Literary Devices: Do I use devices like similes, metaphors, symbols, or juxtaposition? Do these devices help illustrate my ideas?
- Mechanics: Is every word spelled properly? Do I use the right punctuation? If I’m submitting this essay somewhere, does it follow the formatting guidelines?
Your essay can undergo any number of revisions before it’s ready. Above all, make sure that your narrative essay is easy to follow, every word you use matters, and that you come to a deeper understanding about your own life.
Above all, make sure that your narrative essay is easy to follow, every word you use matters, and that you come to a deeper understanding about your own life.
Next Steps for Narrative Essayists
When you have a completed essay, what’s next? You might be interested in submitting to some literary journals . Here’s 24 literary journals you can submit to—we hope you find a great home for your writing!
If you’re looking for additional feedback on your work, feel free to join our Facebook group . You can also take a look at our upcoming nonfiction courses , where you’ll learn the fundamentals of essay writing and make your story even more compelling.
Writing a narrative essay isn’t easy, but you’ll find that the practice can be very rewarding. You’ll learn about your lived experiences, come to deeper conclusions about your personal philosophies, and perhaps even challenge the way you approach life. So find some paper, choose a topic, and get writing—the world is waiting for your story!
Sean Glatch
Thanks for a superbly efficient and informative article…
We’re glad it was helpful, Mary!
Very helpful,, Thanks!!!
Leave a Comment Cancel Reply
Save my name, email, and website in this browser for the next time I comment.

- Testimonials
How to Write a Novel: A Step-by-Step Guide
- by Andrea Feccomandi
- March 24, 2024
Starting to write a novel is like beginning a big adventure.
It takes bravery , strength , and a bit of audacity . It’s not just about writing words down but creating a story that touches people’s hearts and minds .
Think of this guide as your map, helping you through the complex journey of writing a novel.
How can someone with no experience write a book?
Imagine a world birthed from the recesses of your imagination, characters who feel like old friends, and a story that echoes the very essence of human experience. This is the power of a novel. But how does one begin this creative endeavor?
You should start by understanding that novel writing is an intricate art form , a balance between disciplined structure and unbridled creativity. It’s a marathon, not a sprint, and like any long journey, it starts with a single step.
You need not be intimidated by the scope of the task ahead. Instead, embrace it with a spirit of exploration and the willingness to learn as you go .
Remember, every novelist was once a beginner . The literary giants whose works we revere once stood exactly where you stand now – at the beginning of an untold story.
Take comfort in the knowledge that the path you’re about to tread has been walked by many before you, and each of them started with a blank page .
You can always edit a bad page. You can’t edit a blank page. Jodi Picoult
How to write a novel for beginners: tips for writers with no prior experience
So, you’re at the threshold, ready to write your first novel. Here are some tips that can help you in this incredible journey.
- Immerse yourself in the genre you wish to write . Read widely and critically, absorbing the nuances of pacing, character development , and plot construction. This will fuel your imagination and give you a firm grasp of what makes a novel successful within your chosen genre.
- Brainstorm . Let your ideas flow without censorship. Craft the seed of your story – a premise that excites you and holds the promise of a flourishing narrative. This seed will grow into the heart of your novel, the central theme that will guide your writing journey.
- Embrace your unique voice . You have a story within you that no one else can tell. Trust in your perspective and allow it to inform your writing. Your inexperience can be a strength , lending a distinctive flavor to your narrative that seasoned writers might struggle to capture.
- Educate yourself on the craft . There are countless resources available – from books on writing to online courses and writing groups – that can provide guidance and support. Learning the basics of narrative structure , character development, and dialogue can significantly elevate the quality of your manuscript.
- Set realistic goals and a consistent writing schedule . Writing a novel requires discipline. Determine an achievable daily word count, and commit to writing regularly. This routine will help transform writing from a mere aspiration into a vital part of your daily life.
- Be patient with yourself . Writing a novel is a process of growth and discovery. Allow yourself the freedom to make mistakes and learn from them. Each word you write is a step forward in your journey as an author, and with perseverance, you will reach your destination.
- Celebrate each milestone . Take a moment to acknowledge the progress you’ve made from the first word you wrote to the final edit. You’ve transformed a flicker of thought into a world others can explore and enjoy. That, in itself, is an extraordinary feat.
- Take care of yourself . Writing a novel can be mentally and emotionally taxing. Ensure you’re getting enough rest, eating well, and engaging in activities that rejuvenate your spirit. A healthy writer is a productive writer.
Get it down. Take chances. It may be bad, but it’s the only way you can do anything really good. William Faulkner
How to write a novel step-by-step
Diving into the detailed process of novel writing can seem overwhelming, but breaking it down into manageable steps can demystify the process and provide a clear roadmap to follow.
#1 Ideation and conceptualization
Your novel starts with an idea, a spark of inspiration. This can come from anywhere – a dream, an overheard conversation, a personal experience. Nurture this idea, expand upon it, and consider the different ways it could unfold into a story.

#2 Research and development
Once your idea has taken root, it’s time to research. Whether it’s historical accuracy, scientific plausibility, or cultural richness, your novel will benefit from depth and authenticity. During this phase, you’ll also develop your characters, setting , and plot , fleshing out the world you’re about to create.
#3 Outlining
With research and development complete, construct your outline. Detail the major plot points and consider the journey each character will undergo. This outline will act as your navigational chart through the turbulent seas of novel writing.
#4 First draft
Now, begin your first draft. Write with abandon, allowing your story to flow. Don’t worry about perfection; focus on getting your story down on paper. This draft is for your eyes only, a place where you can tell your story honestly and without fear.
#5 Revision and editing
After completing your first draft, step away from your manuscript for a while. Returning with fresh eyes, you’ll be better equipped to revise and edit. This is a painstaking but crucial step where you refine your narrative , enhance your prose, and tighten your plot.
#6 Feedback
Once you’ve polished your novel, seek feedback from trusted beta readers or a professional editor. Their insights will be invaluable in identifying areas for improvement and ensuring your story resonates with readers.
#7 Final edits
Incorporate the feedback you’ve received and make the final edits to your manuscript. This is the stage where your novel truly starts to shine, as you fine-tune language, dialogue, and pacing.
#8 Preparation for publication
With your manuscript complete, research your publishing options. Whether you choose traditional publishing or the indie route, prepare your submission materials or take the steps necessary for self-publishing.
#9 Marketing and promotion
As publication approaches, begin to market your novel. Create an author platform, connect with readers, and build anticipation for your book’s release. Your novel’s journey doesn’t end with publication; it’s just the beginning of sharing your story with the world.
How to write a novel: common errors to avoid
Overcomplicating the plot.
One of the pitfalls many new writers encounter is creating a too convoluted plot. While complexity can add depth to a story, too many twists and subplots can confuse readers and detract from the main narrative.
Ensure your plot is engaging but not so intricate that it becomes difficult to follow. Each plot point should propel your characters toward their goals and contribute to the overall story arc.
Neglecting Character Development
Characters are the heart of your novel. Avoid the mistake of underdeveloping your protagonists or making them one-dimensional.
Your characters should grow and change throughout the story , facing challenges that test their beliefs and push them to evolve. Readers connect with characters that are flawed, relatable, and dynamic, so invest time in crafting their journeys.

Ignoring the Revision Process
The revision process is where your novel truly comes into its own, yet it’s often underestimated by beginners. Don’t rush to publish your first draft . Take the time to rework your manuscript, focusing on strengthening your prose, deepening your characters, and tightening your plot.
Seek feedback from beta readers or writing groups, and be open to constructive criticism. Revising is a crucial step in polishing your novel to its full potential.
How to write a novel: bibisco writing software can help aspiring writers
Novel writing software can be an invaluable tool in organizing and crafting your narrative. Many options are available to suit your needs, from word-processing programs to specialized writing applications.
bibisco writer software is particularly suitable for aspiring writers among the various writing programs. Here’s how bibisco’s features designed for writers can help you.
Organization
bibisco helps writers organize their thoughts, characters, and plotlines. It provides templates and tools for structuring the novel, including sections for characters, scenes, locations, and chapters.

Character Development
bibisco assists in developing well-rounded characters by prompting you to define their characters’ traits, motivations, and relationships. This helps ensure consistency and depth in character portrayal throughout the novel.
Plot Planning
bibisco offers features to help writers outline their plot, including tools for creating timelines, mind maps, and plot arcs. This can be especially helpful for first-time novelists struggling with structuring their narrative.

Writing Process Support
bibisco provides a distraction-free writing environment that allows you to focus solely on your work. It also tracks progress and word count, providing motivation and accountability throughout the writing process.
Exporting and Publishing
Once the novel is complete, bibisco allows writers to export their work into various formats, including PDF, eBook, or Word documents, making it easy to share with others or submit to publishers.
Overall, bibisco can be a valuable tool for aspiring writers embarking on their first novel-writing journey by providing organization, structure, and support throughout the entire writing process.
Conclusion: how to write a novel
The journey of writing a novel is a marathon, not a sprint. It’s a voyage that tests your resolve, challenges your creativity, and ultimately transforms you as a writer. As you embark on this quest, remember that every word you write is a step closer to achieving your dream . Embrace the highs and lows, the twists and turns, and the discoveries you’ll make about yourself along the way.
Your novel is your legacy, a testament to your dedication and passion for storytelling. It’s a gift to the world , a chance to touch the hearts and minds of readers who will journey through your pages. So take a deep breath, muster your courage, and begin. The blank page awaits your story, and only you can tell it.
As you move forward, bear in mind that while the path to writing a novel is filled with challenges, it’s also lined with the support of fellow writers, invaluable resources, and the unyielding power of your imagination. Write bravely, revise wisely, and never lose sight of the magic that sparked your desire to create.
Remember, the world needs your story, and it’s time for you to share it . Take the first step today, and let the adventure of novel writing unfold.
Social Share
- bibisco tips and tricks
- character archetypes
- character development
- narrative perspectives
- narrative techniques
- novel writing software
- story structures
- storytelling
Download bibisco!
Elevate your storytelling with bibisco!
Grab the best novel writing software for authors and dive into a world of creative writing.
Start your story today!
Leave a Reply Cancel reply
Your email address will not be published. Required fields are marked *
Related Post
What is irony in writing and how to effectively use it.

- March 27, 2024
Pathetic Fallacy | Definition and Examples in Narrative

- March 20, 2024
10 Tips for Writing a Compelling Story

- March 17, 2024

Microsoft 365 Life Hacks > Writing > Four tips for writing a memoir
Four tips for writing a memoir
Everyone possesses a life story that’s worth sharing. Life’s experiences, from joys to sorrows, loves, and loves lost, collectively shape us, and connect us through shared human experiences. Because of this connection, memoirs can palpably resonate with readers. The key differentiator between your memoir being a best-seller or relegated to the bargain bin, aside from personal fame and popularity, lies in the quality of your writing. Tell your story in a way that truly resonates with your audience by applying these four invaluable tips for writing a memoir.

What is a memoir?
A memoir is a narrative that highlights a specific moment in an author’s life. Often mistaken for an autobiography, memoirs tend to offer a more intimate perspective. Authors unpack a vulnerable and impactful moment that profoundly influenced them in a way that forges a connection with their readers. These authentic, real-life experiences are shaped by the author’s emotional response to an event, emphasizing personal interpretation and how it affected them rather than serving as a historical account.
Tips for writing a memoir
If you’ve decided to write a memoir, it’s important to remember that you’re not giving an account of your entire life. Instead, narrow your lens and focus on a few specific moments that influenced you, as opposed to an entire autobiography. Now that you understand the essence of a memoir, let’s explore some essential tips to enhance your writing:
Select a snapshot of your life
1. tell the truth.
Above all, your audience must trust you. While a memoir allows you to infuse your feelings and interpretations into events, it must remain grounded in fact, not fiction. Present the events as they occurred truthfully. The essence of a memoir lies in delving deeply into how an event transformed you, so maintain honesty with both yourself and your readers as you write.
2. Make your memoir a narrative with rich characters
Breathing life into well-developed and relatable characters is what truly brings a story to life, whether it’s a poem , short story, or memoir. When referencing people in your life, delve into their character by considering their motivations, their connection to you, and other pertinent factors as you recount your story. This approach allows readers to establish a personal connection with these individuals, making your narrative more engaging and emotionally resonant.

Get the most out of your documents with Word
Elevate your writing and collaborate with others - anywhere, anytime
3. Consider joining a memoir writing group
Give thought to becoming a part of a memoir writing group or workshop. Fellow writers can serve as excellent editors, offering valuable feedback and support. Additionally, such a group can provide you with accountability, enabling you to track your progress while gaining fresh perspectives on your writing.
4. Avoid cliches and stereotypes
To connect with your audience, it’s important to keep your story feeling fresh by steering clear of clichéd phrases and stereotypes in your memoir. Find your unique voice and embrace its originality using colloquialisms , tone , and delivery, allowing your writing to stand out without relying on tropes.
Memoirs possess the inherent power to weave compelling narratives. Effective memoirs, devoid of clichés and stereotypes, can immerse audience members in genuine experiences. Use these tips to dig deep into your personal experiences and deliver truthful, impactful narratives to your audience. For more techniques to captivate readers with accounts of your personal experiences, learn more writing tips .
Get started with Microsoft 365
It’s the Office you know, plus the tools to help you work better together, so you can get more done—anytime, anywhere.
Topics in this article
More articles like this one.

What is independent publishing?
Avoid the hassle of shopping your book around to publishing houses. Publish your book independently and understand the benefits it provides for your as an author.

What are literary tropes?
Engage your audience with literary tropes. Learn about different types of literary tropes, like metaphors and oxymorons, to elevate your writing.

What are genre tropes?
Your favorite genres are filled with unifying tropes that can define them or are meant to be subverted.

What is literary fiction?
Define literary fiction and learn what sets it apart from genre fiction.

Everything you need to achieve more in less time
Get powerful productivity and security apps with Microsoft 365

Explore Other Categories

Cambridge B2 First (FCE): How to Write a Story

B2 First story writing in a nutshell
- Mandatory task: no
- Word count: 140-190
- Main characteristics: engaging, interesting, well-structured
- Register: depending on the story
- Structure: beginning, main part, ending
- Language: adjectives/adverbs, past verb forms, direct speech, time expressions
A day to forget – a day to remember Jerry read the email and decided to go to the shopping centre immediately. He hadn’t slept well at all and was feeling quite nervous that morning and he didn’t want to let his grandma’s wish to buy some milk ruin his day. He dragged himself into his old and dirty car and set off in the direction of Central Mall. Not even ten minutes later, he had a flat tire so he spent the next hour putting on the spare before he was able to continue his dreadful journey. At the shopping centre, he walked absent-mindedly into a family and their son fell on his knee. “I’m sorry,” was the only thing he could say, but the boy’s little sister replied, “This is a gift for you,” and gave him a little piece of paper. Jerry simply stuffed it in his jacket pocket and walked off as quickly as he could. Back at home, he just wanted to go to bed, when he dropped the girl’s paper on the floor. Jerry couldn’t believe his eyes. It was a scratch card with a win of €50,000! “Not such a bad day after all,” Jerry thought with a smile and he poured himself a steaming cup of coffee.
Introduction
A story is usually written for an English language magazine or website for teenagers. The main purpose is to engage the interest of the reader. Effective answers have a clear storyline which links coherently to the first sentence, successfully uses the prompts provided and demonstrates a sound grasp of narrative tenses. from: Cambridge English B2 First for Schools Handbook for Teachers
Stories are part of the second task in the B2 First Writing exam and they are exclusive to B2 First for Schools. In this variant of the test, there are no report tasks but instead, candidates have the choice between articles , reviews , emails/letters and the topic of this article – stories.
Feel free to check out my other posts on the different B2 First writing tasks by clicking on any of the links below.
Stories might be the most underestimated task in the whole writing exam as they are only part of B2 First for Schools.
They are discussed fairly little in preparation classes even with teenagers who are more likely to run into this type of text in their test. I think that stories are fun to write because they are probably the most open task type in terms of creativity. On the other hand, this level of freedom can also pose a challenge for many so story tasks can be time-consuming and difficult.
What a typical story task looks like
As with all the other task types, stories can be broken down in the same fashion every time you want to write one.
You should analyse the task carefully in order to collect as much information as you can. This way, the writing process itself is smooth sailing from start to finish.

At first sight, this could be like any other task for an article or a review, but we need to look a little bit more closely to see what is unique about stories.
As always, you should go through task analysis step by step and ask yourself a few specific questions that will help you get all the information you need.
- What is the topic of my story?
- What exactly do I have to include in the story?
- Who is going to read my story?
The first question is fairly straightforward and can always be found by looking at the sentence given in the task.

In our example, the story needs to be about someone named Jerry you received an email and decided to go to the local shopping centre. All we get is a name a a little bit of a kickstart to the plot, but that’s it.
Every story task looks similar so always focus on the given sentence to find out more about the topic.
The second question is more specific and goes into more detail. Again, let’s see what we can extract from our example task.
The very first thing we have to include is the sentence about Jerry and the email. There is always a sentence which must be used as the very first sentence of your story. Don’t forget or change the sentence. Start your story with it as it is.
There are, however, two more ideas that you always have to write into your story. In this case, we must include a request and a present. The role these things play in your story is entirely up to you, but they should play a central role and be important parts of the plot.
The third and final question looks at the reader of the story. Remember that you never write for the examiner or your teacher but always for someone specified in the task.

Here, we write for the readers of an international magazine for teenagers, which means that teenagers from different countries are going to read your story.
As B2 First for Schools is designed to cater to people in that age group so we are writing for peers. Therefore, we can use rather informal language, but as you will see later on, register is not the most important aspect of a story compared to, for example a letter of application where a formal style is one of the key features. Stories already include so much useful language that choosing the correct register is secondary.
Remember, every story task looks similar and you can go to the same places in each task to find key pieces of information that you can use to set yourself up for success . Simply ask yourself the three questions described in this part and you shouldn’t have a problem with task analysis.
Get Your Free B2 First Writing Cheat Sheet Now!
Just leave your name and email address below.
Please check your email inbox and spam folder for your free PDF.
How to organise a story in B2 First for Schools
When we try to put our story in a well-organised structure, we can simply look at every story ever written in the history of humankind and we will find that 99% of them look like this:
This pattern can be further broken down by splitting the main part into two or even three paragraphs, but we’ll get to that in a second. First, keep the above structure in mind for the future.
At the beginning of a story, we are usually introduced to the main character(s) and learn a little bit about the background of the plot. We might also find out about how the main character(s) feel right before the action starts.
The main part includes the main actions and parts of the plot. Here, the story progresses the furthest, but we normally don’t come to a conclusion yet.
The ending does what the name suggests. It brings the plot to a conclusion and ends the story in an appropriate and satisfying way. You don’t want to keep your readers guessing too much because there won’t be a sequel. You are not writing The Avengers Part 87 but a standalone story.
Now, however, let’s go back and see how we can apply all of the above to our specific task.
Luckily, the first sentence is already there for you, but we obviously need to be a little bit more creative. Think about how Jerry might have felt in this situation and what might have happened in the lead up to him reading the email.
I usually like to introduce the two topic points in the main part of the story, but they could already appear in the beginning. Again, this is completely up to you, which makes stories exciting and stressful to write at the same time.
Either way, in order to fill the main part of your story with life, try to come up with ideas of what could have happened on Jerry’s way to the shopping centre and when he was there.
Finally, we need to bring everything together in a good ending. You can try to end the story in an unexpected or funny way, but it is definitely more important to come to a meaningful and logical ending at all.
I find it quite often with my own students that they simply cut off the plot at the end of the main part, which leaves the reader not fully informed. So, make the reader (and examiner) happy and give your story the ending it deserves.
Always make a plan for your story
If I could give my students just one piece of advice for the writing exam in B2 First, I would tell them to always make a plan before starting to write.
It only takes a few minutes, but can save you a lot more towards the end on the test when you are in time trouble and don’t know what to do.
A plan helps you stay on task and all you have to do is follow it and fill the page with life.
My plan for our example looks like this:
- Beginning: nervous; hadn’t slept well; request in the email –> buy milk for grandma
- Main paragraph 1: flat tyre; had to change it; wasted time
- Main paragraph 2: at the shopping centre; accident with family; little girl gave him piece of paper
- Ending: piece of paper was scratchcard; won €50,000
Just from my plan, you can already guess what the story will look like even though I didn’t add a lot of information. Making the plan took me three minutes, but I only need to connect the dots now and get started.
The different parts of a story in B2 First
In this part, I’m going to take you deep down the rabbit hole. We are going to go through the different parts of a great story with the help of our example task.
You will learn more about good content as well as useful language in each part.
As I mentioned earlier, the beginning of a story fulfills two tasks. It introduces the reader to the main character(s) and sets the scene. We can include previous events and background information so we can started.
One of the main criteria in a story is the correct use of narrative verb forms . These are different past verb forms, each of which has a distinct function in a story. We want to use past simple for the main events, past continuous for background actions and past perfect simple and continuous for things that happened before the main events.
Sounds complicated, but with some practice you’ll get better at it. If the names of these verb forms don’t ring a bell at all, you should definitely look into them as they are not only important in the writing test but also in Reading & Use of English and Speaking .
In addition to this particular grammar point, we want to make the beginning interesting from the get-go using some engaging adjectives/adverbs and other helpful expressions.
A day to forget – a day to remember Jerry read the email and decided to go to the shopping centre immediately. He hadn’t slept well at all and was feeling quite nervous that morning and he didn’t want to let his grandma’s wish to buy some milk ruin his day .
I gave my story a nice title. Every good story has a title so yours should have one as well, but don’t worry too much. It can be short and doesn’t have to be anything amazing. Just make sure that you include it.
I also used a mix of verb forms ( blue ) to show the main events, background actions and things that had happened before the main storyline.
On top of that, I included a few adjectives and adverbs which help make the story come to life ( red ).
Keep these things in mind when you start your story and you will be off to a good start.
The main part of a story is what the name says: the most important part which includes the majority of information.
Here we find most of the main events and the plot progresses between the beginning and ending.
Your focus in this part should lie on a logical order of events while keeping the reader engaged and interested.
We achieve this, once again, by using the correct verb forms (mostly past simple as we are in the middle of the main events) as well as other stylistic features, some of which we’ve discussed earlier and others that you can see in the example paragraphs below.
He dragged himself into his old and dirty car and set off in the direction of Central Mall. Not even ten minutes later , he had a flat tire so he spent the next hour putting on the spare before he was able to continue his dreadful journey. At the shopping centre , he walked absent-mindedly into a family and their son fell on his knee. “I’m sorry,” was the only thing he could say, but the boy’s little sister replied , “This is a gift for you,” with a smile and gave him a crumpled piece of paper. Jerry simply stuffed it in his jacket pocket and stormed off as quickly as he could .
We’ve got quite a lot to unpack here.
First and foremost, if you take a step back and read the paragraphs without paying attention to all the colourful stuff, you will see that there is a logical and chronological progression. Jerry leaves his house, has a flat tyre, makes it to the shopping mall and runs into the family. The girls gives him the paper and he leaves.
I guess this all makes sense, but I still used certain expressions of place and time ( orange ) that support this idea that there is a sequence of events. Little remarks like ‘before’ or ‘next’ can make it so much easier for the reader to follow the story so make sure you use them.
Another feature that we haven’t discussed yet is direct speech ( green ). By using direct speech we can bring the characters to life and the reader can identify with them more easily.
Finally, I continued with good and engaging past verb forms ( blue ) as well as adjectives/adverbs ( red ) which bring colour to the things and people you describe.
The very last part of every amazing story is a great ending. Here, we tie everything together and bring the events to a conclusion.
It is your decision if you want to give your story a happy ending or not, but make sure that it ends in some way. Don’t just stop after the main part and leave your reader with questions. Send them off with a smile on their face or tears in their eyes.
Back at home , he just wanted to go to bed, when he dropped the girl’s paper on the floor. Jerry couldn’t believe his eyes . It was a scratch card with a win of €50,000 ! “Not such a bad day after all,” Jerry thought with a smile and he poured himself a steaming cup of coffee.
I tried to bring a little surprise to the ending of my story and turn Jerry’s terrible day into a good one.
You can find the different stylistic features I used in different colours again. Past verb forms are blue , direct speech green , expressions of place and time orange and other interesting language and punctuation red .
Don’t stop being awesome towards the end of your story. Stay consistent and use good language throughout the whole text. That’s what the examiners want to see and that’s you you will give them if you follow the tips in this article.
Useful language for stories in B2 First
In the last part, I showed you some of the main ideas to improve your story writing. Using these language features can give you an edge over other candidates and impress your examiner. Always remember that an examiner checks dozens of texts per day and it is important to stand out with your pieces of writing.
So, below I’ve listed the different types of useful language with a few examples in each category. Obviously, this is not a complete list, but you can add expressions and adjust them to your needs.
How your B2 First story is marked
The process of marking candidates’ writing tasks in B2 First is an involved and quite complicated process. There are different criteria the examiners have to look at and even for teachers, it can be almost overwhelming to work their way through all the information.
I wrote an article on the topic that I hope will help students and teachers alike to better understand the marking process and to use it in order to improve their writing and/or teaching skills and insight.
Simply click here to find out more.
Time to become a storyteller
In this article, I’ve shared with you everything I know about how to write an excellent story in B2 First for Schools.
Take my advice and start practising. If you have any questions or problems, feel free to leave a comment and I will reply as quickly as I can.
Lots of love,
Teacher Phill 🙂
Similar Posts

Cambridge B2 First (FCE): Reading & Use of English Part 7
Reading & Use of English Part 7 If you are looking for the best information you can get about Reading…
The 25 most common mistakes in the FCE exam (and how you can avoid them)
Offence wins games, but defence wins championships The FCE exam is one of the most important language exams in the…

Cambridge B2 First (FCE): Speaking Part 3
Introduction The FCE Speaking paper is one of the more interesting exams compared to others like IELTS. In the FCE…

Cambridge B2 First (FCE): The 10 Best Books to Study for the Exam
My Top 10 books to prepare for B2 First Choosing the perfect book to prepare for Cambridge B2 First is…

Reading Skills – 7 Great Tips To Improve
Table of Contents Do You Have Problems With Your Reading Skills? If you’ve come to this article, I guess that…

Cambridge B2 First (FCE): How to Write an Essay
Essay writing is easier than you think The very first reaction I usually get when I want to practise essay…
I am in fact glad to read this weblog posts which consists of lots of useful facts, thanks for providing such data.
Thanks a lot! Best explanatatory article I’ve read about writing a story. I’ll definitely check your other guides. Love the coloring and comments to each part!
Thank you so much!!! This is excellent…easily explained…everything included A must to have when teaching…FCE!!
Comments are closed.

University of Bridgeport News

The Art of Narrative Healing — Dean Amy Nawrocki’s Journey to Inspiring Student Success
“memory is a thing; remembering is an action, ongoing. we pause and reflect, let scenes take shape, then relive them.”, amy nawrocki, the comet’s tail.
As with many roles in higher education, the exact duties of a dean remain a mystery to most students. Indeed, the scope of a dean’s duties aren’t easy to summarize in a single sentence. From advising students and faculty to community outreach and curricula development, a dean’s work is never over.
Being an author first and foremost at heart, it seems fitting that Amy Nawrocki uses an analogy to describe the function of her role as Dean of Science and Society. “A dean helps ensure that everything happening in their college fits into the big picture of the University as a whole — making sure everything aligns with our mission,” she describes. “It’s kind of like a tree spreading everything through its roots to help nourish the tree as a whole entity. That’s how I think of it, and how it’s been for me.”

While some see the role of a dean as one of oversight, Amy takes a more holistic approach — rooted not in overseeing others but in advising and guiding them. “As a leader, I support initiatives from students and faculty — basically providing whatever they need. I help professors grow their programs, but it’s also about helping students find their way through their undergraduate or graduate programs.”
Although her professional course has charted a linear path — from English professor to department chair and coordinator — Amy never accepted roles with the intent to climb a career ladder. Reflecting on her appointment as Dean, Amy remarks that the opportunity was unexpected. “I wouldn’t have called my previous roles stepping stones. Quite frankly, I never saw myself in this role, but when the opportunity presented itself to me, I had a lot of support and encouragement. I started in August 2023 at the end of the summer semester. A lot of what I did over the summer involved transitioning. I had the benefit of working with former CSS Dean Dr. Kitty Engelmann as Associate Dean.”
It began with writing
Our most formative experiences often encompass the unplanned. Still, it may come as a surprise to learn that Amy Nawrocki never specifically sought a career in higher education.
Her road to the classroom didn’t begin with a decision to teach — instead, the first spark was lit by her passion for the written word. “Freshman and sophomore year of high school, I began gravitating to literature,” Nawrocki reflects. “Sometimes, it was about academic success. Other times, it was about finding solace in literature, which led me to explore creative writing.”

Embarking on her first year at Sarah Lawrence College, poetry was the path Nawrocki pursued. “For a first-year seminar, we had to take a core class,” she recounts. “You put down your top three choices. I don’t know if I put literature or fiction-writing, but I ended up in a poetry-writing class.”
Although poetry may not have been her first choice, Nawrocki found it was the perfect fit. “My sensibilities as a writer are more suited to poetry than prose fiction,” she shares. “I just found a home in poetry. In addition to writing poetry, I studied its form and theory.”
An odyssey interrupted
Nawrocki’s college career began unfolding like that of many first-year students. While she experienced the familiar growing pains of adjusting to higher education, the start of her time at Sarah Lawrence was also teeming with enthusiasm, creativity, and curiosity.
Yet in the summer following her first year, Amy’s journey was jolted from its tracks when she contracted encephalitis. Marked by inflammation of the brain, encephalitis is an elusive infection. Often difficult to diagnose, the consequences can be catastrophic. Affecting the brain and body, the symptoms of this life-threatening illness range from seizures and speech difficulties to paralysis and memory loss.
At only nineteen years old, Amy began experiencing these symptoms. Following a swift hospitalization, medical specialists were mystified. Debating the nature of her condition, some even cast doubts as to whether her symptoms were purely psychological.
After determining the infection in her brain was caused by a virus, Nawrocki’s physicians and family made a difficult decision. Placing Nawrocki into a medically induced coma, the doctors facilitated a high-risk healing process which, against all odds, rid her of the symptoms threatening her life.
Regaining rhythm
For Amy, the most traumatic elements of this experience did not entail medical tubes or white coats. Instead, it was the loss of her memories. From the time Amy began experiencing symptoms to her subsequent recovery, over half a year had passed without her recalling what occurred.
In the wake of her recovery, Amy needed to relearn the essential skills many take for granted — including writing. But at that time, continuing her work as a poet was not a priority. “I don’t remember being goal-oriented or conscious of my motivations, but that’s also part of recovery. You don’t necessarily think about it. You just do it.”
“It is not false modesty which detaches me now from the notion of a heroic return from unconsciousness. I want to be the girl who rebelliously poked her tongue out and stuck her middle finger up at doctors who only saw surfaces. But I can remember her, and without that, I have no agency to see what I did as miraculous. I want the music of spheres, but all I have is spacedust.”
-amy nawrocki, the comet’s tail.
Recounting what she can of the recovery process, Amy attests the path was uncertain and unsteady. Even as her memory reawakened, whether she would return to Sarah Lawrence remained indefinite. “At the time, my plans had to change because I couldn’t go back, reinvent my life, or just step back into the life I had lived,” she shares candidly. “The goal was always to return to college. That didn’t change, but it was difficult recognizing that may not be possible due to what had happened.”
Yet with steady footing and a strong will, Amy continued progressing toward her goals. “When I began taking classes again, the first step was Western Connecticut State University because it was easier for me to live at home when I started,” she recalls. “Then, I went back to Sarah Lawrence, easing into it as a part-time student.”
Amy proudly completed her undergraduate degree in poetry in 1996. Reclaiming her voice as a learner and poet was a return to the essential self — laying stones for the next steps of Amy’s journey.
Whether you plan to pursue graduate school, dive into the field, or are uncertain of your post-college goals, University of Bridgeport has your back. With resources ranging from tutoring and counseling to career development and internship opportunities , UB will help you navigate your next steps. Learn about beginning your UB journey today!
An unexpected arc.
After completing her first degree, Amy surveyed the options at her feet — her affinity for poetry acting as a compass as she crafted the path ahead. Mindfully making her next move, she balanced the aspirational with the practical. “I didn’t ever tell myself I’d be a professional poet because I knew that wasn’t something I could realistically make a living doing.”
Wanting to remain immersed in art and literature, Amy decided to pursue her Master of Fine Arts (MFA) in creative writing. When she made this choice, she didn’t realize it would lead her to answer a second, unexpected calling — teaching and inspiring students. “When I went for my MFA at the University of Arkansas, I had a graduate assistantship. It was basically teaching composition in exchange for tuition. That made me see teaching as my career path.”
In many ways, this decision sculpted a full circle, curved by irony and serendipity alike. “My mom was a first and second-grade teacher, and my dad taught special education and later became a middle school guidance counselor. I never consciously said I would be an educator just because both my parents were. It came about through my gravitation towards art, and it was very organic.”
Breaking in her teaching shoes
As Amy began her assistantship, she found herself in the shoes of an instructor for the first time. As it so happens, those shoes were leather Steve Madden knockoffs.
Before beginning to teach, Amy gained some background in pedagogical theory. “I think there was a two-week boot camp where they showed us strategies for teaching composition and rhetoric,” she recollects. “One of the pedagogical concepts we discussed was the lead-up to teaching, like building rapport with students. I don’t know if it was suggested to me, but I got the idea of doing attendance and getting to know the students by having them fill out index cards.”
While this idea seemed simple in execution, Amy’s first day of teaching didn’t go according to plan. “The first day of class was a Tuesday. University of Arkansas has a huge campus, and the bookstore where I had to pick up the index cards was far from the building where I was teaching my class,” she explains. “I went to the bookstore, and the line was out the door. My class started at 11:00. It was already 10:45, but I was committed to getting these index cards. I had to decide to stay in line and pay for my cards or leave. I stayed in line.”

Amused in hindsight, Amy recounts the panicked realization that she would be late for her first class. “I don’t remember the exact timeline, but I knew I was going to be late,” she relates. “I was panicked and flustered. I was wearing pretty new shoes. I started running, thinking I didn’t want to be as late as possible on my first day. The shoes were killing me — and Arkansas in August is hot. So, I took them off and kept running.”
Upon reaching her destination, the stress and panic of Amy’s cross-campus relay caught up with her. “I walked into class, telling the students I was sorry for being late. I was crying. I took a few minutes to compose myself, and then we started going over the syllabus.”
As Amy concluded and dismissed her class, her trying morning took a turn for the triumphant. “A group of three or four students walked up to me and said, ‘We just wanted to say it’s our first day, too.’”
That moment of solidarity would come to define Amy’s approach to teaching. “That was the first teaching experience I had that truly struck me,” she says. “It gave me the sense that we were all in it together.”
The Comet’s Tail
Amy may not still slip her Steve Maddens on, but she’s used them well at University of Bridgeport. “When I was teaching writing classes, I usually put the shoes on my desk as a first-day prompt. I put a bunch of other items on the desk, too, so students can brainstorm and free-write.”
Beyond serving as a writing exercise, Amy uses the shoes as a jumping off point — telling anxious undergraduates the story of her own nerve-wracking first day. “The takeaway was to be open-minded and pivot. And to wear comfortable shoes,” she laughs.
This isn’t the only part of Amy’s journey she’s connected back to the classroom. In 2018, she gained a sense of closure on a traumatic chapter of her own life — penning and publishing The Comet’s Tail , which she began using as a resource for reading and writing in her classes.

A memoir of her year-long road recovering from encephalitis, the story wasn’t easy to tell — especially considering memoir writing typically hinges on memory. Given Amy can’t recall the majority of what occurred, the process of piecing together her narrative was complex — often echoing the work of a detective discerning clues to understand the intricacies of a story. “I was writing it after 25 years, which is a long time, right? The process of writing it was kind of like a research paper. I didn’t know much of what happened, so I had to get medical records and go through and sort all these materials.”
“For a long time, I put that half-year away. Mapped in invisible ink, the secret short cut to present tense does not show up, even in the ultraviolet light of memory. Drafts and redrafts skip over the recovery roadblocks of embarrassment and easy silence. I didn’t like talking about it anyway. When life goes on, the old script folds faultlessly, slipped into a box in the closet, easily moved across state lines, untraceable in the memory palace.”
Performing a research project about oneself can seem surreal. But at the same time, Amy found the experience offered an enlightening change in perspective. “When I was coming out of the coma, I didn’t know what my personality was. I had to find myself and fit back into this world where things were frustrating, and I didn’t understand why. But looking back, I got a sense of what the doctors must have been going through.”
Amy continues, “The situation was difficult for everyone involved. I felt a lot of compassion and empathy for my father and siblings, my aunts and uncles, and the friends who always supported me. I could talk to some of them, and I did, but I was finally able to turn the lens out from myself and see how it affected them. I began understanding what it meant to go through that situation from their perspectives.”
Bringing her story to UB
In teaching The Comet’s Tail to UB undergraduates , Amy finds it to be a vehicle not only for teaching genre theory but for inspiring her students to craft their memoirs.
These exercises don’t just serve English majors, either. From Amy’s firsthand experience, having students of all backgrounds write their memoirs is an enriching experience. “Some students study Psychology, Human Services, or a health science, and this can help shape their understanding of that,” she offers. “It helps provide a holistic education.”
Understanding the nature of the topic at hand, Amy takes a delicate approach. “When I’ve taught The Comet’s Tail in classes, I’m very sensitive to the fact that what happened to me occurred at the end of my freshmen year, and many of my students are reading it during that period in their own lives.”
Although the topic is a delicate matter, Amy’s teaching helps students understand the healing offered by putting pain into words — aiding them in becoming more effective writers. “Usually, I introduce it as a memoir or medical narrative. I talk about the structure and use it to explain the narrative point of view. We also talk about autobiographical writing and sequence in creative writing.”
She continues, “Then when I assign a narrative project in that context, they share a lot themselves. I hope it encourages them in their own writing. I give them parameters because not everyone has had that kind of medical experience, so I’ve had a lot of students write about family members or aspects of their own mental health that have affected their lives.”
Unwritten resolution
Perhaps the biggest challenge of being appointed Dean of the College of Science and Society has been striking a new balance between art and academia. In the midst of a busy schedule, Amy attests that writing requires you to take advantage of the time you have. “When you have the energy to do a few lines, you can progress from there,” she offers. “Commit to three lines. Commit to five lines, or commit to 100 words.”
Amy still finds opportunities to use poetry writing as a method of self-restoring expression. “As part of my practice has been finding ways to experiment with form and structure to shape my free writing or my scribbles, I call them. I have notebooks all over the place, but as a poet, the goal is to shape the chaos of my mind into something that is art.”

As Dean, Amy also finds herself stepping back from the classroom. “I haven’t taught yet since becoming dean, but I’m contemplating teaching next fall. That’s one thing I don’t want to lose, and I’m hoping to continue.”
Regardless, Amy still has words of wisdom to offer UB students. “Be mindful of what’s going on in your head and lead by example,” she advises. “If you’re stressed or overwhelmed, pause to assess things before you react. Give yourself the time and space to manage emotions, frustrations, and stress. Make sure you manage your responsibilities in a way that still allows you to be healthy and happy.”
To explore Amy’s poetry and other literary works, visit her online at https://amynawrocki.org/
At UB, #UBelong. See yourself at UB — learn more about becoming a Purple Knight today!

IMAGES
VIDEO
COMMENTS
A narrative can spark emotion, encourage reflection, and convey meaning when done well. Narratives are a popular genre for students and teachers as they allow the writer to share their imagination, creativity, skill, and understanding of nearly all elements of writing. We occasionally refer to a narrative as 'creative writing' or story writing.
Vivid details are essential to crafting a narrative, so practicing descriptive writing is time well spent. You may also be able to work a description of a coffee cup, chirping bird, or passerby into your narrative. 4. Choose a theme or message for your narrative. A narrative needs a point.
Interactive example of a narrative essay. An example of a short narrative essay, responding to the prompt "Write about an experience where you learned something about yourself," is shown below. Hover over different parts of the text to see how the structure works. Narrative essay example.
A narrative structure is the order in which a story's events are presented. It is the framework from which a writer can hang individual scenes and plot points with the aim of maximizing tension, interest, excitement, or mystery. Traditionally, most stories start at the chronological beginning ("once upon a time") and finish at the end ("and ...
5. Resolution. How to write a narrative: Choosing your narrative subject. A. The significance of selecting the right subject. B. Personal experiences vs. fictional stories. - Personal experiences: - Fictional stories: C. Finding inspiration for your narrative.
Others work in pieces they arrange later, while others work from sentence to sentence. Whether you're writing a novel, novella, short story, or flash fiction, don't be afraid to try out different voices, and styles. Experiment with different story writing techniques, story ideas, and story structures. Keep what works for you and discard the ...
A narrative essay is a prose-written story that's focused on the commentary of a central theme. Narrative essays are generally written in the first-person POV, and are usually about a topic that's personal to the writer. Everything in a narrative essay should take place in an established timeline, with a clear beginning, middle, and end.
An Introduction to narratives. Part 1 in our series 'Planning & Writing a Narrative'. This video explains the basic structure of narratives and identifies th...
The individual elements of different narrative techniques can be broken down into six distinct categories: Character. Perspective. Plot. Setting. Style. Theme. Each of these plays an important role in developing a story — taking the writer's message and presenting it to their audience in a deliberate way.
A narrative essay is a form of writing where you share a personal experience or tell a story to make a point or convey a lesson. Unlike other types of essays, a narrative essay aims to engage your audience by sharing your perspective and taking them on an emotional journey. To begin, choose a meaningful topic. Pick a story or experience that ...
1. End the story with a conclusion that reflects on the event. Use your conclusion to give an opinion regarding the story. It might give insight into how the event affects the narrator (perhaps you) in the present day or how it affected choices the narrator made since that event. Typically this is 1-2 sentences long.
Know what a short story is versus a novel. 2. Pick a simple, central premise. 3. Build a small but distinct cast of characters. 4. Begin writing close to the end. 5. Shut out your internal editor.
However, like any other type of writing, it comes with guidelines. 1. Write Your Personal Narrative as a Story. As a story, it must include an introduction, characters, plot, setting, climax, anti-climax (if any), and conclusion. Another way to approach it is by structuring it with an introduction, body, and conclusion.
Narrative writing can take many different forms, such as novels, short stories, poems, plays, and even some forms of non-fiction. No matter what form it takes, the common thread is that it tells a ...
In your story, start writing scenes around conflict, and make sure each paragraph and piece of dialogue relates, in some way, to your protagonist's unmet desires. 4. Write Your First Draft. The scenes you build around conflict will eventually be stitched into a complete story.
His work is one of the best narrative essay examples of the 19th century. "My life is not an apology, but a life. It is for itself and not for a spectacle. I much prefer that it should be of a lower strain, so it be genuine and equal, than that it should be glittering and unsteady.". "Notes of a Native Son" by James Baldwin.
When writing a narrative essay, one might think of it as telling a story. These essays are often anecdotal, experiential, and personal—allowing students to express themselves in a creative and, quite often, moving ways. Here are some guidelines for writing a narrative essay. If written as a story, the essay should include all the parts of a ...
1. Generating Narrative Essay Ideas. If you're not sure what to write about, you'll want to generate some narrative essay ideas. One way to do this is to look for writing prompts online: Reedsy adds new prompts to their site every week, and we also post writing prompts every Wednesday to our Facebook group.
Whether you're writing a personal narrative, a fictional story, or a historical account, there are certain elements and strategies that can help you craft a well-written and impactful narrative. The first step in writing a narrative is to choose a topic or theme that you want to explore. This could be a personal experience, an idea or concept ...
Let your ideas flow without censorship. Craft the seed of your story - a premise that excites you and holds the promise of a flourishing narrative. This seed will grow into the heart of your novel, the central theme that will guide your writing journey. Embrace your unique voice. You have a story within you that no one else can tell.
The essence of a memoir lies in delving deeply into how an event transformed you, so maintain honesty with both yourself and your readers as you write. 2. Make your memoir a narrative with rich characters. Breathing life into well-developed and relatable characters is what truly brings a story to life, whether it's a poem, short story, or ...
Beginning: nervous; hadn't slept well; request in the email -> buy milk for grandma. Main paragraph 1: flat tyre; had to change it; wasted time. Main paragraph 2: at the shopping centre; accident with family; little girl gave him piece of paper. Ending: piece of paper was scratchcard; won €50,000.
A memoir of her year-long road recovering from encephalitis, the story wasn't easy to tell — especially considering memoir writing typically hinges on memory. Given Amy can't recall the majority of what occurred, the process of piecing together her narrative was complex — often echoing the work of a detective discerning clues to ...