Home / Guides / Citation Guides / MLA Format / MLA In-text Citations

MLA In-Text Citations
An in-text citation is a reference to a source that is found within the text of a paper ( Handbook 227). This tells a reader that an idea, quote, or paraphrase originated from a source. MLA in-text citations usually include the last name of the author and the location of cited information.
This guide focuses on how to create MLA in-text citations, such as citations in prose and parenthetical citations in the current MLA style, which is in its 9th edition. This style was created by the Modern Language Association . This guide reviews MLA guidelines but is not related directly to the association.
Table of Contents
Here’s a quick rundown of the contents of this guide on how to use in-text citations.
Fundamentals
- Why in-text citations are important
- Prose vs parenthetical in-text citation differences
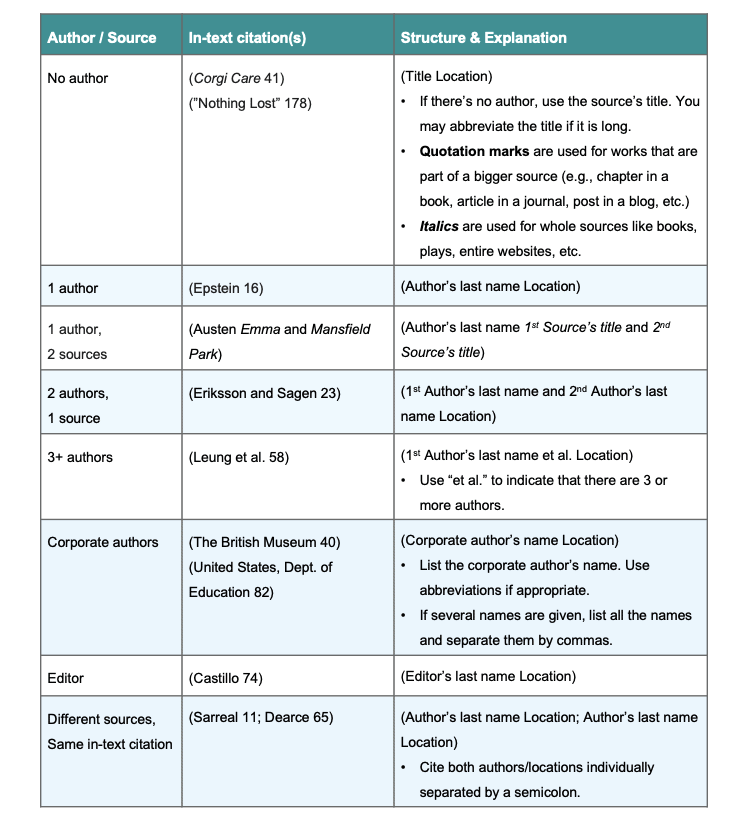
- Parenthetical citation reference chart
In-text citation examples
- In-text citation with two authors
- In-text citation with 3+ authors
- In-text citation with no authors
- In-text citation with corporate authors
- In-text citation with edited books and anthologies
- In-text citation with no page numbers and online sources
- Citing the same sources multiple times
- Citing 2+ sources in the same in-text citation
- Citing multiple works by the same author in the same in-text citation
- Abbreviating titles
- Citing religious works and scriptures
- Citing long or block quotes
Why are in-text citations important?
In-text citations
- Give full credit to sources that are quoted and paraphrased in a work/paper.
- Help the writer avoid plagiarism.
- Are a signal that the information came from another source.
- Tell the reader where the information came from.
In-text citation vs. in-prose vs. parenthetical
An in-text citation is a general citation of where presented information came from. In MLA, an in-text citation can be displayed in two different ways:
- In the prose
- As a parenthetical citation
While the two ways are similar, there are slight differences. However, for both ways, you’ll need to know how to format page numbers in MLA .
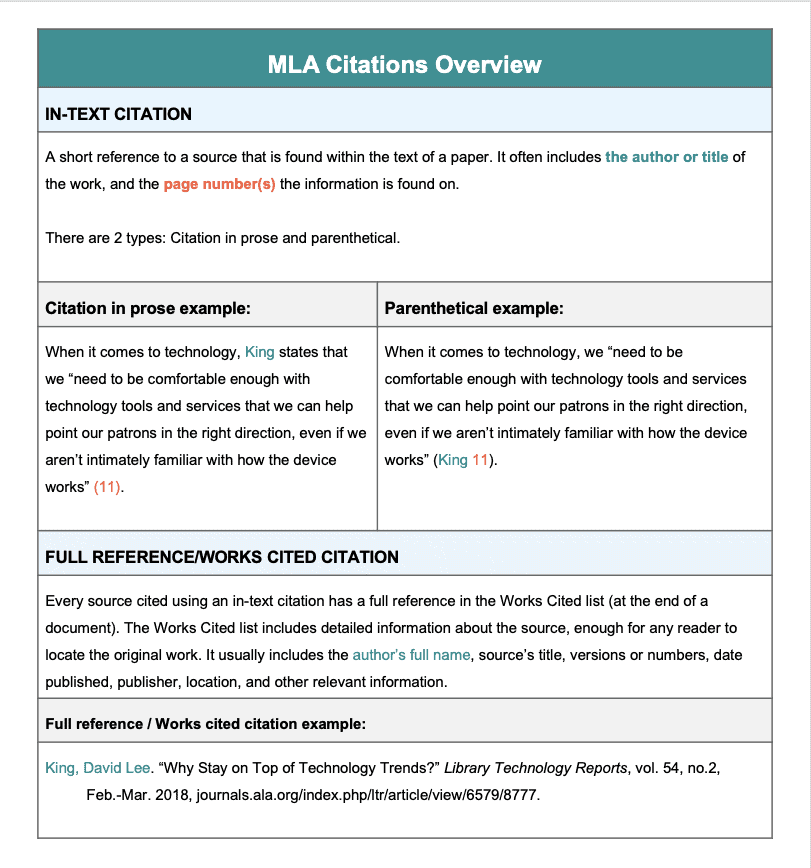
Citation in prose
An MLA citation in prose is when the author’s name is used in the text of the sentence. At the end of the sentence, in parentheses, is the page number where the information was found.
Here is an example
When it comes to technology, King states that we “need to be comfortable enough with technology tools and services that we can help point our patrons in the right direction, even if we aren’t intimately familiar with how the device works” (11).
This MLA citation in prose includes King’s name in the sentence itself, and this specific line of text was taken from page 11 of the journal it was found in.
Parenthetical citation
An MLA parenthetical citation is created when the author’s name is NOT in the sentence. Instead, the author’s name is in parentheses after the sentence, along with the page number.
Here is an MLA parenthetical citation example
When it comes to technology, we “need to be comfortable enough with technology tools and services that we can help point our patrons in the right direction, even if we aren’t intimately familiar with how the device works” (King 11).
In the above example, King’s name is not included in the sentence itself, so his name is in parentheses after the sentence, with 11 for the page number. The 11 indicates that the quote is found on page 11 in the journal.
Full reference
For every source that is cited using an in-text citation, there is a corresponding full reference. This allows readers to track down the original source.
At the end of the assignment, on the MLA works cited page , is the full reference. The full reference includes the full name of the author, the title of the article, the title of the journal, the volume and issue number, the date the journal was published, and the URL where the article was found.
Here is the full reference for King’s quote
King, David Lee. “Why Stay on Top of Technology Trends?” Library Technology Reports , vol. 54, no. 2, Feb.-Mar. 2018, ezproxy.nypl.org/login?url=//search-proquest-com.i.ezproxy.nypl.org/docview/2008817033?accountid=35635.
Readers can locate the article online via the information included above.
Citation overview
The next section of this guide focuses on how to structure an MLA in-text citation and reference in parentheses in various situations.
A narrative APA in-text citation and APA parenthetical citation are somewhat similar but have some minor differences. Check out our helpful guides, and others, on EasyBib.com!
Wondering how to handle these types of references in other styles? Check out our page on APA format , or choose from more styles .
Parenthetical Citation Reference Chart
Sources with two authors.
There are many books, journal articles, magazine articles, reports, and other source types written or created by two authors.
When a source has two authors, place both authors’ last names in the body of your work ( Handbook 232). The last names do not need to be listed in alphabetical order. Instead, follow the same order as shown on the source.
In an MLA in-text citation, separate the two last names with the word “and.” After both authors’ names, add a space and the page number where the original quote or information is found on.
Here is an example of an MLA citation in prose for a book with two authors
Gaiman and Pratchett further elaborate by sharing their creepy reminder that “just because it’s a mild night doesn’t mean that dark forces aren’t abroad. They’re abroad all of the time. They’re everywhere” (15).
Here is an example of an MLA parenthetical citation for a book with two authors
Don’t forget that “just because it’s a mild night doesn’t mean that dark forces aren’t abroad. They’re abroad all of the time. They’re everywhere” (Gaiman and Pratchett 15).
If you’re still confused, check out EasyBib.com’s MLA in-text citation generator, which allows you to create MLA in-text citations and other types of references in just a few clicks!
If it’s an APA book citation you’re looking to create, we have a helpful guide on EasyBib.com. While you’re at it, check out our APA journal guide!
Sources With Three or More Authors
There are a number of sources written or created by three or more authors. Many research studies and reports, scholarly journal articles, and government publications are developed by three or more individuals.
If you included the last names of all individuals in your MLA in-text citations or in parentheses, it would be too distracting to the reader. It may also cause the reader to lose sight of the overall message of the paper or assignment. Instead of including all last names, only include the last name of the first individual shown on the source. Follow the first author’s last name with the Latin phrase, “et al.” This Latin phrase translates to “and others.” Add the page number after et al.
Here’s an example of an MLA parenthetical citation for multiple authors
“School library programs in Croatia and Hong Kong are mainly focused on two major educational tasks. One task is enhancing students’ general literacy and developing reading habits, whereas the other task is developing students’ information literacy and research abilities” (Tam et al. 299).
The example above only includes the first listed author’s last name. All other authors are credited when “et al.” is used. If the reader wants to see the other authors’ full names, the reader can refer to the final references at the end of the assignment or to the full source.
The abbreviation et al. is used with references in parentheses, as well as in full references. To include the authors’ names in prose, you can either write each name out individually or, you can type out the meaning of et al., which is “and others.”
Here is an acceptable MLA citation in prose example for sources with more than three authors
School library programming in Croatia and Hong Kong is somewhat similar to programming in the United States. Tam, Choi, Tkalcevic, Dukic, and Zheng share that “school library programs in Croatia and Hong Kong are mainly focused on two major educational tasks. One task is enhancing students’ general literacy and developing reading habits, whereas the other task is developing students’ information literacy and research abilities” (299).
If your instructor’s examples of how to do MLA in-text citations for three or more authors looks different than the example here, your instructor may be using an older edition of this style. To discover more about previous editions, learn more here .
Need some inspiration for your research project? Trying to figure out the perfect topic? Check out our Dr. Seuss , Marilyn Monroe , and Malcolm X topic guides!
Sources Without an Author
It may seem unlikely, but there are times when an author’s name isn’t included on a source. Many digital images, films and videos, encyclopedia articles, dictionary entries, web pages, and more do not have author names listed.
If the source you’re attempting to cite does not have an author’s name listed, the MLA in-text citation or parenthetical citation should display the title. If the title is rather long, it is acceptable to shorten it in the body of your assignment. If you choose to shorten the title, make sure the first word in the full citation is also the first word used in the citation in prose or parenthetical citation. This is done to allow the reader to easily locate the full citation that corresponds with the reference in the text.
If, in the Works Cited list, the full reference has the title within quotation marks, include those quotation marks in the in-text citation or reference in parentheses. If the title is written in italics in the full reference, use italics for the title in the in-text citation or reference in parentheses as well.
Parenthetical Citations MLA Examples
The example below is from a poem found online, titled “the last time.” the poem’s author is unknown..
“From the moment you hold your baby in your arms you will never be the same. You might long for the person you were before, when you had freedom and time and nothing in particular to worry about” (“The Last Time”).
The example below is from the movie, The Englishman Who Went Up a Hill But Came Down a Mountain .
“Perhaps it would have been different if there hadn’t been a war, but this was 1917, and people were exhausted by loss. Those that were allowed to stay manned the pits, mining the coal that would fuel the ships. Twenty-four hours a day they labored” ( Englishman ).
Notice the shortened title in the above reference. This allows the reader to spend more time focusing on the content of your project, rather than the sources.
If you’re looking for an MLA in-text citation website to help you with your references, check out EasyBib Plus on EasyBib.com! EasyBib Plus can help you determine how to do in-text citations MLA and many other types of references!
Corporate Authors
Numerous government publications, research reports, and brochures state the name of the organization as the author responsible for publishing it.
When the author is a corporate entity or organization, this information is included in the MLA citation in prose or parenthetical citation.
“One project became the first to evaluate how e-prescribing standards work in certain long-term care settings and assessed the impact of e-prescribing on the workflow among prescribers, nurses, the pharmacies, and payers” (Agency for Healthcare Research and Quality 2).
If the full name of the organization or governmental agency is long in length, it is acceptable to abbreviate some words, as long as they are considered common abbreviations. These abbreviations should only be in the references with parentheses. They should not be used in citations in prose.
Here is a list of words that can be abbreviated in parentheses:
- Department = Dept.
- Government = Govt.
- Corporation = Corp.
- Incorporated = Inc.
- Company = Co.
- United States = US
Example of a shortened corporate author name in an MLA parenthetical citation
“Based on our analysis of available data provided by selected states’ departments of corrections, the most common crimes committed by inmates with serious mental illness varied from state to state” (US Govt. Accountability Office 14).
Here is how the same corporate author name would look in an MLA citation in prose
The United States Government Accountability Office states, “Based on our analysis of available data provided by selected states’ departments of corrections, the most common crimes committed by inmates with serious mental illness varied from state to state” (14).
Remember, citations in prose should not have abbreviations; other types of references can.
Looking for more information on abbreviations? Check out our page on MLA format.
Edited Books and Anthologies
Edited books and anthologies often include chapters or sections, each written by an individual author or a small group of authors. These compilations are placed together by an editor or a group of editors. There are tons of edited books and anthologies available today, ranging from ones showcasing Black history facts and literature to those focusing on notable individuals such as scientists like Albert Eintein and politicians such as Winston Churchill .
If you’re using information from an edited book or an anthology, include the chapter author’s name in your MLA citation in prose or reference in parentheses. Do not use the name(s) of the editor(s). Remember, the purpose of these references is to provide the reader with some insight as to where the information originated. If, after reading your project, the reader would like more information on the sources used, the reader can use the information provided in the full reference, at the very end of the assignment. With that in mind, since the full reference begins with the author of the individual chapter or section, that same information is what should be included in any citations in prose or references in parentheses.
Here is an example of an MLA citation in prose for a book with an editor
Weinstein further states that “one implication of this widespread adaptation of anthropological methods to historical research was the eclipse of the longstanding concern with “change over time,” and the emergence of a preference for synchronic, rather than diachronic, themes” (195).
Full reference at the end of the assignment
Weinstein, Barbara. “History Without a Cause? Grand Narratives, World History, and the Postcolonial Dilemma.” Postcolonial Studies: An Anthology , edited by Pramod K. Nayar, Wiley-Blackwell, 2015, p. 196. Wiley , www.wiley.com/en-us/Postcolonial+Studies%3A+An+Anthology-p-9781118780985.
Once you’re through with writing and citing, run your paper through our innovative plagiarism checker ! It’s the editor of your dreams and provides suggestions for improvement.
Sources Without Page Numbers and Online Sources
When a source has no page numbers, which is often the case with long web page articles, e-books, and numerous other source types, do not include any page number information in the body of the project. Do not estimate or invent your own page numbering system for the source. If there aren’t any page numbers, omit this information from the MLA in-text citation. There may, however, be paragraph numbers included in some sources. If there are distinct and clear paragraph numbers directly on the source, replace the page number with this information. Make it clear to the reader that the source is organized by paragraphs by using “par.” before the paragraph number, or use “pars.” if the information is from more than one paragraph.
Here is an example of how to create an MLA parenthetical citation for a website
“She ran through the field with the wind blowing in her hair and a song through the breeze” (Jackson par. 5).
Here’s an example of an MLA citation in prose for a website
In Brenner’s meeting notes, he further shared his motivation to actively seek out and secure self help resources when he announced, “When we looked at statistical evidence, the most commonly checked out section of the library was self-help. This proves that patrons consistently seek out help for personal issues and wish to solve them with the help of the community’s resources” (pars. 2-3).
Here’s another MLA in-text citation example for a website
Holson writes about a new mindful app, which provides listeners with the soothing sound of not only Bob Ross’ voice, but also the “soothing swish of his painter’s brush on canvas.”
In above example, the information normally found in the parentheses is omitted since there aren’t any page, parentheses, or chapter numbers on the website article.
Looking for APA citation website examples? We have what you need on EasyBib.com!
Need an in-text or parenthetical citation MLA website? Check out EasyBib Plus on EasyBib.com! Also, check out MLA Citation Website , which explains how to create references for websites.
Citing the Same Source Multiple Times
It may seem redundant to constantly include an author’s name in the body of a research project or paper. If you use an author’s work in one section of your project, and the next piece of information included is by the same individual(s), then it is not necessary to share in-text, whether in prose or in parentheses, that both items are from the same author. It is acceptable to include the last name of the author in the first use, and in the second usage, only a page number needs to be included.
Here is an example of how to cite the same source multiple times
“One of the major tests is the Project for Standardized Assessment of Information Literacy Skills. This measurement was developed over four years as a joint partnership between the Association of Research Libraries and Kent State University” (Tong and Moran 290). This exam is just one of many available to measure students’ information literacy skills. It is fee-based, so it is not free, but the results can provide stakeholders, professors, curriculum developers, and even librarians and library service team members with an understanding of students’ abilities and misconceptions. It is not surprising to read the results, which stated that “upper-level undergraduate students generally lack information literacy skills as evidenced by the results on this specific iteration of the Standardized Assessment of Information Literacy Skills test” (295).
The reader can assume that the information in the second quote is from the same article as the first quote. If, in between the two quotes, a different source is included, Tong and Moran’s names would need to be added again in the last quote.
Here is the full reference at the end of the project:
Tong, Min, and Carrie Moran. “Are Transfer Students Lagging Behind in Information Literacy?” Reference Services Review , vol. 45, no. 2, 2017, pp. 286-297. ProQuest , ezproxy.nypl.org/login?url=//search-proquest-com.i.ezproxy.nypl.org/docview/1917280148?accountid=35635.
Citing Two or More Sources in the Same In-text Citation
According to section 6.30 of the Handbook , parenthetical citations containing multiple sources in a single parenthesis should be separated by semicolons.
(Granger 5; Tsun 77) (Ruiz 212; Diego 149)
Citing Multiple Works by the Same Author in One In-text Citation
Just as you might want to cite two different sources at the same time, it can also be useful to cite different works by the same author all at once.
Section 6.30 of the Handbook specifies that “citations of different locations in a single source are separated by commas” (251).
(Maeda 59, 174-76, 24) (Kauffman 7, 234, 299)
Furthermore, if you are citing multiple works by the same author, the titles should be joined by and if there are only two. Otherwise, use commas and and .
(Murakami, Wild Sheep Chase and Norwegian Wood ) (Murakami, Wild Sheep Chase , Norwegian Wood , and “With the Beatles”)
Abbreviating Titles
When listing the titles, be aware that long titles in parenthetical citations can distract the reader and cause confusion. It will be necessary to shorten the titles appropriately for in-text citations. According to the Handbook , “shorten the title if it is longer than a noun phrase” (237). The abbreviated title should begin with the word by which the title is alphabetized.
Best practice is to give the first word the reference is listed by so the source is easily found in the works cited. Omit articles that start a title: a, an, the. When possible, use the first noun (and any adjectives before it). For more on titles and their abbreviations, head to section 6.10 of the Handbook .
- Full title : The Curious Incident of the Dog in the Night-Time
- Abbreviated: Curious
- Full title: The Disreputable History of Frankie Landau-Banks
- Abbreviated: Disreputable History
Religious Works and Scriptures
There are instances when religious works are italicized in the text of a project, and times when it is not necessary to italicize the title.
If you’re referring to the general religious text, such as the Bible, Torah, or Qur’an, it is not necessary to italicize the name of the scripture in the body of the project. If you’re referring to a specific edition of a religious text, then it is necessary to italicize it, both in text and in the full reference.
Here are some commonly used editions:
- King James Bible
- The Orthodox Jewish Bible
- American Standard Bible
- The Steinsaltz Talmud
- The Babylonian Talmud
- New International Bible
When including a reference, do not use page numbers from the scripture. Instead, use the designated chapter numbers and verse numbers.
MLA example of an in-text citation for a religious scripture
While, unacceptable in today’s society, the Bible is riddled with individuals who have two, three, and sometimes four or more spouses. One example in the King James Bible , states that an individual “had two wives, the name of the one was Hannah, and the name of the other Peninnah. Peninnah had children, but Hannah had no children” (1 Sam. 1.2)
The only religious scripture that is allowed to be in the text of a project, but not in the Works Cited list, is the Qur’an. There is only one version of the Qur’an. It is acceptable to include the name of the Qur’an in the text, along with the specific chapter and verse numbers.
If you’re attempting to create a reference for a religious work, but it’s not considered a “classic” religious book, such as a biography about Mother Teresa , or a book about Muhammed Ali’s conversion, then a reference in the text and also on the final page of the project is necessary.
If you’re creating an APA bibliography , you do not need to create a full reference for classic religious works on an APA reference page .
For another MLA in-text citation website and for more on the Bible and other source types, click here .
Long or Block Quotes
Quotes longer than four lines are called, “block quotes.” Block quotes are sometimes necessary when you’re adding a lengthy piece of information into your project. If you’d like to add a large portion of Martin Luther King ’s “I Have a Dream” speech, a lengthy amount of text from a Mark Twain book, or multiple lines from Abraham Lincoln ’s Gettysburg Address, a block quote is needed.
MLA block quotes are formatted differently than shorter quotes in the body of a project. Why? The unique formatting signals to the reader that they’re about to read a lengthy quote.
Block quotes are called block quotes because they form their own block of text. They are set apart from the body of a project with different spacing and margins.
Begin the block quote on a new line. The body of the full project should run along the one inch margin, but the block quote should be set in an inch and a half. The entire quote should be along the inch and a half margin.
If there aren’t any quotation marks in the text itself, do not include any in the block quote. This is very different than standard reference rules. In most cases, quotation marks are added around quoted material. For block quotes, since the reader can see that the quoted material sits in its own block, it is not necessary to place quotation marks around it.
Here is an MLA citation in prose example of a block quote
Despite Bruchac’s consistent difficult situations at home, basketball kept his mind busy and focused:
When I got off the late bus that afternoon, my grandparents weren’t home. The store was locked and there was a note from Grama on the house door. Doc Magovern had come to the house because Grampa was “having trouble with his blood.” Now they were off to the hospital and I “wasn’t to worry.” This had happened before. Grampa had pernicious anemia and sometimes was very sick. So, naturally, it worried the pants off me. I actually thought about taking my bike down the dreaded 9N the three miles to the Saratoga Hospital. Instead, I did as I knew they wanted. I opened the store and waited for customers. None came, though, and my eye was caught by the basketball stowed away as usual behind the door. I had to do something to take my mind off what was happening to Grampa. I took out the ball and went around the side. (13)
Notice the use of the colon prior to the start of the block quote. Do not use a colon if the block quote is part of the sentence above it.
Here is an example of the same block quote, without the use of the colon:
Despite Bruchac’s consistent difficult situations at home, it was clear that basketball kept his mind busy and focused when he states
When I get off the late bus that afternoon, my grandparents weren’t home…
If two or more paragraphs are included in your block quote, start each paragraph on a new line.
Looking for additional helpful websites? Need another MLA in-text citation website? Check out the style in the news . We also have other handy articles, guides, and posts to help you with your research needs. Here’s one on how to write an MLA annotated bibliography .
Visit our EasyBib Twitter feed to discover more citing tips, fun grammar facts, and the latest product updates.
If you’re looking for information on styling an APA citation , EasyBib.com has the guides you need!
MLA Handbook . 9th ed., Modern Language Association of America, 2021.
Published October 31, 2011. Updated July 5, 2021.
Written and edited by Michele Kirschenbaum and Elise Barbeau. Michele Kirschenbaum is a school library media specialist and the in-house librarian at EasyBib.com. Elise Barbeau is the Citation Specialist at Chegg. She has worked in digital marketing, libraries, and publishing.
MLA Formatting Guide
MLA Formatting
- Annotated Bibliography
- Bibliography
- Block Quotes
- et al Usage
- In-text Citations
- Paraphrasing
- Page Numbers
- Sample Paper
- Works Cited
- MLA 8 Updates
- MLA 9 Updates
- View MLA Guide
Citation Examples
- Book Chapter
- Journal Article
- Magazine Article
- Newspaper Article
- Website (no author)
- View all MLA Examples
How useful was this post?
Click on a star to rate it!
We are sorry that this post was not useful for you!
Let us improve this post!
Tell us how we can improve this post?
In MLA style, if multiple sources have the same author , the titles should be joined by and if there are only two. Otherwise, use commas and and .
- In-text citation: (Austen Emma and Mansfield Park )
- Structure: (Last name 1st Source’s title and 2nd Source’s title )
- In-text citation: (Leung et al. 58)
If the author is a corporate entity or organization, included the name of the corporate entity or organization in the in-text citation.
- In-text citation: (Agency for Healthcare Research and Quality 2)
Yes, there’s an option to download source citations as a Word Doc or a Google Doc. You may also copy citations from the EasyBib Citation Generator and paste them into your paper.
Yes! Whether you’d like to learn how to construct citations on your own, our Autocite tool isn’t able to gather the metadata you need, or anything in between, manual citations are always an option. Click here for directions on using creating manual citations.
An in-text citation is a shortened version of the source being referred to in the paper. As the name implies, it appears in the text of the paper. A works cited list entry, on the other hand, details the complete information of the source being cited and is listed within the works cited list at the end of the paper after the main text. The in-text citation is designed to direct the reader to the full works cited list entry. An example of an in-text citation and the corresponding works cited list entry for a journal article with one author is listed below:
In-text citation template and example:
Only the author surname (or the title of the work if there is no author) is used in in-text citations to direct the reader to the corresponding reference list entry. For citations in prose, use the first name and surname of the author for the first occurrence. In subsequent citations, use only the surname. In parenthetical citations, always use only the surname of the author. If you are directly quoting the source, the page number should also be included in the in-text citation.
Citation in prose:
First mention: Christopher Collins ….
Subsequent occurrences: Collins ….
Parenthetical:
….(Collins)
….(Collins 5)
Works cited list entry template and example:
The title of the article is in plain text and title case and is placed inside quotation marks. The title of the journal is set in italics.
Surname, F. “Title of the Article.” Journal Title , vol. #, no. #, Publication Date, page range.
Collins, Christopher. “On Posthuman Materiality: Art-Making as Rhizomatic Rehearsal.” Text and Performance Quarterly , vol. 39, no. 2, 2019, pp. 153–59.
Note that because the author’s surname (Collins) was included in the in-text citation, the reader would then be able to easily locate the works cited list entry since the entry begins with the author’s surname.
An in-text citation is a short citation that is placed next to the text being cited. The basic element needed for an in-text citation is the author’s name . The publication year is not required in in-text citations. Sometimes, page numbers or line numbers are also included, especially when text is quoted from the source being cited. In-text citations are mentioned in the text in two ways: as a citation in prose or a parenthetical citation.
Citations in prose are incorporated into the text and act as a part of the sentence. Usually, citations in prose use the author’s full name when cited the first time in the text. Thereafter, only the surname is used. Avoid including the middle initial even if it is present in the works-cited-list entry.
Parenthetical
Parenthetical citations add only the author’s surname at the end of the sentence in parentheses.
Examples of in-text citations
Here are a few tips to create in-text citations for sources with various numbers and types of authors:
Use both the first name and surname of the author if you are mentioning the author for the first time in the prose. In subsequent occurrences, use only the author’s surname. Always use only the surname of the author in parenthetical citations.
First mention: Sheele John asserts …. (7).
Subsequent occurrences: John argues …. (7).
…. (John 7).
Two authors
Use the first name and surname of both authors if you are mentioning the work for the first time in the prose. In subsequent occurrences, use only the surnames of the two authors. Always use only the authors’ surnames in parenthetical citations. Use “and” to separate the two authors in parenthetical citations.
First mention: Katie Longman and Clara Sullivan ….
Subsequent occurrences: Longman and Sullivan ….
…. ( Longman and Sullivan).
Three or more authors
For citations in prose, use the first name and surname of the first author followed by “and others” or “and colleagues.” For parenthetical citations, use only the surname of the first author followed by “et al.”
Lincy Mathew and colleagues…. or Lincy Mathew and others ….
…. (Mathew et al.).
Corporate author
For citations in prose, treat the corporate author like you would treat the author’s name. For parenthetical citations, shorten the organization name to the shortest noun phrase. For example, shorten the Modern Language Association of America to Modern Language Association.
The Literary Society of Malaysia….
…. (Literary Society).
If there is no author for the source, use the source’s title in place of the author’s name for both citations in prose and parenthetical citations.
When you add such in-text citations, italicize the text of the title. If the source title is longer than a noun phrase, use a shortened version of the title. For example, shorten the title Fantastic Beasts and Where to Find Them to Fantastic Beasts .
Knowing Body of Work explains …. (102).
….( Knowing Body 102).
MLA Citation Examples
Writing Tools
Citation Generators
Other Citation Styles
Plagiarism Checker
Upload a paper to check for plagiarism against billions of sources and get advanced writing suggestions for clarity and style.
Get Started
Citation guides
All you need to know about citations
How to do in-text citations with multiple authors in MLA
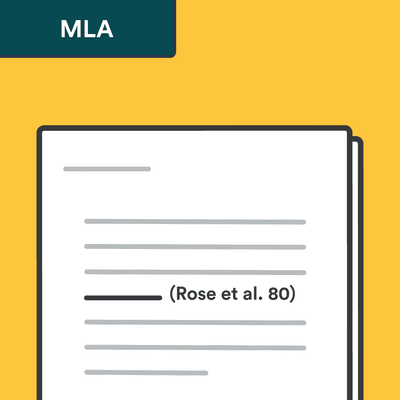
The format of MLA's in-text citations varies depending on the number of authors. In the following sections you will learn how to format in-text citations in MLA style, with one author, two authors, and multiple authors.
One Author in-text citation in MLA
To format an in-text citation of a source with one author, include the author’s last name, and the page number or page range in parentheses. For example:
- (Wollstonecraft 26)
If the author’s name is already stated in the sentence, give only the page number or page range in parenthesis at the end of the sentence, or at the next natural pause. For example:
- As Wollstonecraft stated, “I do not wish them [women] to have power over men; but over themselves.” (26).
Two authors in-text citation in MLA
To format an in-text citation of a source with two authors, include the authors' last names separated by the word and , and the page number or page range in parentheses. For example:
- (King and Straub 93-101)
If the authors' names are already stated in the sentence, give only the page number or page range in parenthesis at the end of the sentence, or at the next natural pause. For example:
- Stephen King and Peter Straub shared the same opinion (93-101).
Three or more in-text citation in MLA
To format an in-text citation of a source with three or more authors, include the first author's last name followed by et al., and the page number or page range in parentheses. For example:
- (Sumantran et al. 106-114)
- Sumantran et al. carried out a research about the future of the car (106-114).

This citation style guide is based on the MLA Handbook (9 th edition).
More useful guides
- MLA Style Guide, 8th Edition: In-text Examples
- MLA In-Text Citations: The Basics
- How do I cite a source with multiple authors in MLA style (in-text)?
More great BibGuru guides
- Harvard: how to cite an online magazine article
- Chicago: how to cite a documentary
- APA: how to cite an afterword
Automatic citations in seconds
Citation generators
Alternative to.
- NoodleTools
- Getting started
From our blog
- 📚 How to write a book report
- 📝 APA Running Head
- 📑 How to study for a test
Generate accurate MLA citations for free
- Knowledge Base
Author Names in MLA | Citing One or Multiple Authors
Published on March 27, 2019 by Courtney Gahan . Revised on March 5, 2024 by Shona McCombes.
In MLA style , up to two authors are included in a citation. For sources with more than two authors, the citation is shortened with “ et al. ”
In the Works Cited list , the first author’s name is inverted (surname followed by first name). In an MLA in-text citation , only surnames are included.
The author element specifies the main creator of the source. For audiovisual sources, this may be the director, composer, or painter, for example. The author may also be an organization.
If no author at all is specified, start your citation with the source title instead.
Instantly correct all language mistakes in your text
Upload your document to correct all your mistakes in minutes

Table of contents
Sources with multiple authors, sources with corporate authors, sources with no author, citing contributors other than authors, double surnames, hyphens, titles, and suffixes, pseudonyms and simplified names, foreign-language names, frequently asked questions about authors in mla.
For each source, list the authors in the order they appear in the source itself ( not in alphabetical order).
Multiple authors in the Works Cited
The first author’s name is always inverted. The last name comes first, followed by a comma, then the first name (and any middle initials, if relevant).
When there are two authors , the second author’s name is not inverted:
When there are three or more authors , only list the first author, followed by a comma and “et al.”:
Multiple authors in in-text citations
In an MLA in-text citation, you may name the author either in parentheses or in the main text.
When there are two authors , simply cite both surnames, separated by “and”.
When there are three or more authors , cite the first author’s surname followed by “et al.” if the citation appears in parentheses. If you cite in the main text, instead of “et al.”, write “and colleagues” or “and others”.
Here's why students love Scribbr's proofreading services
Discover proofreading & editing
Sometimes sources are created by corporate authors, such as institutions, government agencies, and other organizations, with no individual authors credited. In this case, simply cite the name of the organization in place of the author name.
When citing corporate authors, omit articles (the/a/an) at the start of organization names.
In this example, the publisher is separate from the organization. Sometimes, an organization is both the author and the publisher. In this situation, do not list the organization as author. Instead, start the citation with the source title , and list the organization as the publisher only.
Publications from government agencies
If you are citing a publication from a government agency, start with the name of the government and follow with the name of the agency. Always arrange the entities from largest to smallest.
Note that in the in-text citation, you should abbreviate names longer than four words.
If a source does not specify any author, begin the reference with the title of the work . In the in-text citation, if the title is longer than four words, abbreviate it to the first noun phrase, and ensure that the first word matches the first word of the Works Cited entry.
Some sources are created by many different people. If your discussion of the source focuses on the contribution of someone other than the main author (e.g. when analyzing an actor’s performance or comparing translations of a text), you may cite them in the author position with a label specifying their role (e.g. performer or translator). Don’t include this label in the in-text citation.
Citing the editor of a collection
Usually, when citing an edited collection, you should cite the author of the specific chapter or work . However, if you want to cite an entire collection or anthology, cite the editor(s) in the author position, followed by a label specifying their role. Don’t include the label in the in-text citation.
Prevent plagiarism. Run a free check.
If an author has more than one surname, include all of them in the surname position. For example, Federico Garcia Lorca would be listed in the works cited as Garcia Lorca, Federico , and in an in-text citation as ( Garcia Lorca ).
If there is a hyphen in the author’s name, keep the hyphen exactly as it appears in the source.
Do not include titles, affiliations, and degrees in source citations. For example, Sir Walter Scott would be listed as Scott, Walter .
If an author has a name with an essential suffix (one that distinguishes them from identically named members of the same family, such as “Jr.” or a roman numeral), include this at the end of the name. For example, John D. Rockefeller IV would be listed as Rockefeller, John D., IV .
When writing in MLA, it is acceptable to use pseudonyms and simplified names of famous authors. It’s usually best to list all of an author’s works under one consistent name, even if different names appear in the sources themselves.
Commonly accepted pseudonyms and simplified names include:
- Dante Alighieri → Dante
- Mary Ann Evans → George Eliot
- Samuel Clemens → Mark Twain
Names from languages that do not use the Latin alphabet, such as Chinese or Russian, may vary in spelling. If this is the case, find the most authoritative variant (i.e. the variant favored by an authoritative source, such as an academic or government publication) and apply that throughout your Works Cited list and in-text citations.
Asian languages
In Chinese, Japanese, Korean, and Vietnamese, the author name will often appear with the surname first, followed by the first name. In this case, do not include a comma between the surname and first name when creating the source reference, as the name is already inverted.
The various articles in French have different rules, which can even depend on the number of syllables in the name.
* English-language context means when the author writes in English but happens to have a French name.
For German names, von is usually considered part of the first name. However, in an English-language context, the von stays with the surname. For example, Von Trapp, Maria .
For Italian names, da , de , del , della , di and d’ are capitalized and treated as part of the surname. For example, Di Costanzo, Angelo .
For Spanish names, de is not treated as part of the surname. For example, Rueda, Lope de . However, del stays with the surname and is always capitalized. For example, Del Rio, Angel .
You may come across some Spanish authors with more than one surname. Often these authors are commonly known by one part of their surname, but you must include the entire last name—and alphabetize according to that—in your Works Cited list. For example, Garcia Lorca, Federico (commonly known as Lorca).
If a source has two authors, name both authors in your MLA in-text citation and Works Cited entry. If there are three or more authors, name only the first author, followed by et al.
If a source has no author, start the MLA Works Cited entry with the source title . Use a shortened version of the title in your MLA in-text citation .
If a source has no page numbers, you can use an alternative locator (e.g. a chapter number, or a timestamp for a video or audio source) to identify the relevant passage in your in-text citation. If the source has no numbered divisions, cite only the author’s name (or the title).
If you already named the author or title in your sentence, and there is no locator available, you don’t need a parenthetical citation:
- Rajaram argues that representations of migration are shaped by “cultural, political, and ideological interests.”
- The homepage of The Correspondent describes it as “a movement for radically different news.”
A standard MLA Works Cited entry is structured as follows:
Only include information that is available for and relevant to your source.
Cite this Scribbr article
If you want to cite this source, you can copy and paste the citation or click the “Cite this Scribbr article” button to automatically add the citation to our free Citation Generator.
Gahan, C. (2024, March 05). Author Names in MLA | Citing One or Multiple Authors. Scribbr. Retrieved April 2, 2024, from https://www.scribbr.com/mla/authors/
Is this article helpful?
Courtney Gahan
Other students also liked, how to format your mla works cited page, a complete guide to mla in-text citations, mla titles: formatting and capitalization rules, what is your plagiarism score.
In-Text Citations: An Overview
In-text citations are brief, unobtrusive references that direct readers to the works-cited-list entries for the sources you consulted and, where relevant, to the location in the source being cited.
An in-text citation begins with the shortest piece of information that directs your reader to the entry in the works-cited list. Thus, it begins with what ever comes first in the entry: the author’s name or the title (or description) of the work. The citation can appear in your prose or in parentheses.
Citation in prose Naomi Baron broke new ground on the subject. Parenthetical citation At least one researcher has broken new ground on the subject (Baron). Work cited Baron, Naomi S. “Redefining Reading: The Impact of Digital Communication Media.” PMLA , vol. 128, no. 1, Jan. 2013, pp. 193–200.
When relevant, an in-text citation also has a second component: if a specific part of a work is quoted or paraphrased and the work includes a page number, line number, time stamp, or other way to point readers to the place in the work where the information can be found, that location marker must be included in parentheses.
Parenthetical citation According to Naomi Baron, reading is “just half of literacy. The other half is writing” (194).
The author or title can also appear alongside the page number or other location marker in parentheses.
Parenthetical citation Reading is “just half of literacy. The other half is writing” (Baron 194).
All in-text references should be concise. Avoid, for instance, providing the author’s name or title of a work in both your prose and parentheses.
Citation (incorrect) According to Naomi Baron, reading is “just half of literacy. The other half is writing” (Baron 194). Citation (correct) According to Naomi Baron, reading is “just half of literacy. The other half is writing” (194).
For more on what to include in an in-text citation and how to style it, see sections 6.3–6.30 of the ninth edition of the MLA Handbook ).
55 Comments
Brandi unruh 10 april 2021 at 11:04 am.
Hello! I am a high school English teacher trying to answer a question that came up during our research unit. I can’t seem to find a definitive answer online. When using a shortened title in an in-text citation, does an ellipsis need to be included? For example, if the title was “The Problem of Poverty in America: A Historical and Cultural Analysis”, would the in-text citation be (“The Problem of Poverty in America...”) or (“The Problem of Poverty in America”)? Thank you for your time and expertise!
Your e-mail address will not be published
Laura Kiernan 12 April 2021 AT 11:04 AM
No, an ellipsis would not be used in an in-text citation. We provide extensive guidance on shortening titles in 6.10 of the new ninth edition of the MLA Handbook .
angel 10 May 2021 AT 02:05 PM
hii How to write an in text citation of an entry from encyclopedia which has an editor but no separate authors for each entry ?
William Feeler 11 May 2021 AT 01:05 PM
I see no mention of paragraph numbers for unpaginated prose or sections/lines for drama. are these practices gone?
Laura Kiernan 18 May 2021 AT 01:05 PM
This post provides a general overview of our approach to in-text citations. The complete guidelines appear in sections 6.1–6.30 of the ninth edition of the MLA Handbook .
Vonceil Park 11 May 2021 AT 01:05 PM
Dear MLA Staff, A professor at my College demands students to provide paragraph number in the in-text citation for online articles that have no page number nor paragraph number. Do we just count the paragraph number and put them in the parenthesis, for example: (para. 3)?
Laura Kiernan 18 May 2021 AT 12:05 PM
Thank you for your question. Your approach to modifying our style in accordance with your professor's instructions works, but we would suggest confirming that styling with your professor.
Arathi Babu 17 May 2021 AT 08:05 AM
How to write an in text citation of an unsigned entry from a reference work?
Laura Kiernan 08 June 2021 AT 11:06 AM
If the entry was in a print work, the in-text citation would include the entry’s title or a shortened version of the entry’s title and the page number of the quotation. If the entry was in a reference work without page numbers, the in-text citation should just contain the title or shortened title of the entry.
Sethu 17 May 2021 AT 02:05 PM
For example: Can I give an in-text citation like the following: Shakespeare, in his work Hamlet, quotes: "To be or not to be" (7).
For citing commonly studied verse works, see 6.22 in the ninth edition of the MLA Handbook .
Trinity Klein 21 May 2021 AT 11:05 AM
Can you please help with proper in-text citation placement for an embedded quotation? Does the citation come immediately after the quotation or at the very end of the sentence? For example, is this correct: He asks her to take him home “in the voice of a child afraid of the dark” which comes as a shock to Scout because he has so long held a bold and rebellious reputation (372). Or should the (372) come immediately after ...dark"...? Thank you!
For more information about the placement of a parenthetical citations, see 6.43 in the ninth edition of the MLA Handbook .
Karima 30 May 2021 AT 05:05 PM
Dear MLA staff, 1) In case i am quoting from multiple sources by the same author, am i required to introduce again the source i am quoting from in the beginning of my sentence? (Quotes are used in multiple paragraphs)
For guidance on citing multiple sources by the same author, see 6.8 in the ninth edition of the MLA Handbook .
Yves 23 June 2021 AT 06:06 PM
Hello, is there a specific rule about how to format a range of page numbers in the parenthetical citation? For example, could (Eden 44-45) be written as (Eden 44-5), or is only one example correct?
Laura Kiernan 24 September 2021 AT 02:09 PM
For information about styling number ranges, see section 2.139 of the ninth edition of the MLA Handbook .
Faliravo 11 August 2021 AT 05:08 AM
Good morning MLA team, My professor insists that I include the year of publication for in-text citations. Is it going to be okay if I insert the year between the author and the page number?
Thank you very much for your consideration.
Laura Kiernan 24 September 2021 AT 01:09 PM
Your approach to modifying our style in accordance with your professor’s instructions works, but we would suggest confirming that styling with your professor.
Pauline 14 September 2021 AT 11:09 PM
How do I cite an entire work. For example, if I want to say Toni Morrison's the "Bluest Eye" has been used as a textbook for many English literature classes, I suppose I shouldn't put any page number in the parenthetical citation. But I can't find any MLA references on this.
See section 4.14 of the ninth edition of the MLA Handbook .
myron glassenberg 04 February 2022 AT 01:02 PM
if source is the whole book, how do I cite in text and in works cited pages. e.g. freud (no page number) Freud , ( 1892) The Pleasure Principle.
Rita Rozzi 20 September 2023 AT 07:09 PM
There is no section 4.14 in the ninth edition. Do you have any updated information? Thank you.
Laura Kiernan 21 September 2023 AT 03:09 PM
Section 4.14, which is titled "Passing Mentions," can be found in chapter 4 of the ninth edition of the handbook.
Lauren McFall 13 October 2021 AT 02:10 PM
Students often refer to the same source consecutively across more than one sentence. I'm having a hard time finding information about the preferred approach according to the MLA. As a parallel, APA makes a specific recommendation - "cite the source in the first sentence in which it is relevant and do not repeat the citation in subsequent sentences as long as the source remains clear and unchanged" https://apastyle.apa.org/style-grammar-guidelines/citations/appropriate-citation
Laura Kiernan 20 October 2021 AT 04:10 PM
See 6.45 of the ninth edition of the MLA Handbook .
Ruth Schafer 01 December 2022 AT 07:12 PM
6.45 out of the MLA Handbook's ninth edition does not provide an example of how to cite a multi-sentence paraphrase when using an unpaginated source. Can you give an example of how to cite a multi-sentence paraphrase where the source does not have published page numbering?
Should I introduce the source in my prose and then again at the end of the multi-sentence paraphrase in parentheses when I have finished citing the paraphrase? Example: John Smith from Smith Architecture explains that crawl space foundations are...blah blah blah. These foundations are most commonly used in midwestern constructions where the frost line is...blah, blah, blah. Keep writing the paraphrase and then at the end of the final sentence instead of a page citation write the author's last name (Smith). This way if you switch to a different source, at least the reader knows that you have finished with the Smith source and have moved on to your own commentary or another source's information. Usually, I'd use a page citation at the end of the paraphrase, but when dealing with a source that does not have page numbering, I'm unsure what to do.
Lizzie 18 October 2021 AT 10:10 PM
If I only use textual evidence from the novel I'm examining, do I need to include the authors name with each in text citation? There are no other works cited, so it seems redundant/clutter-y to me
Kayden 29 October 2021 AT 05:10 PM
If I'm trying to cite multiple paragraphs from the same source would it be correct to say (par. 3 and 13) or should it be (par. 3, 13) and is it different if they are next to each other too like (par. 6-7) or (par. 6 and 7).
Laura Kiernan 04 November 2021 AT 11:11 AM
See sections 6.18–6.20 of the ninth edition of the MLA Handbook .
Rachel 17 November 2021 AT 01:11 PM
When citing from an online source without pagination, if you include the author's name in the introduction to the quote, do you need to include anything in parentheses like the article title?

Laura Kiernan 22 November 2021 AT 12:11 PM
See section 6.26 of the ninth edition of the MLA Handbook .
July 25 November 2021 AT 05:11 PM
When quoting an online source (e.g. a website), do I have to indicate the fact that it's an online source in the in-text-citations as in (Name [online]) or is the author's name enough?
Thank you in advance for your answer.
Laura Kiernan 29 November 2021 AT 10:11 AM
According to MLA style, an in-text citation for an online work should not note that the work is online.
Pinkie 19 March 2022 AT 08:03 PM
If I'm writing a response paper, and I need to summarize the whole article to introduce it, then should I use in-text citation?
Laura Kiernan 25 March 2022 AT 01:03 PM
For guidance on paraphrasing, see sections 4.5–4.8 of the ninth edition of the MLA Handbook .
Kay 09 April 2022 AT 06:04 PM
Hi, am I supposed to include the DOI when one is available in the citation? If I cite the print version of a journal article that has a DOI, still include the DOI in the citation? Thank you!
Laura Kiernan 11 April 2022 AT 11:04 AM
Thank you for your questions. For guidance on including a DOI in your works-cited-list entry, see sections 5.84 and 5.93 in the ninth edition of the MLA Handbook .
Mike 16 April 2022 AT 05:04 PM
Website in-text Citation...
When I'm writing an in-text citation for a website, I'm seeing all manner of different things to include. Do I need to add the author name and year of publishing for the article?\ Do I just need the website name? I'm not really understanding what I need to add or obtain for such a citation within the text I'm writing.
I'm writing a book on my life, and I'm quoting a particular webpage to show one particular angle of an argument I'm making, and, of course, it's not common knowledge, so I want to make sure that I follow all the rules for this kind of thing, so I don't get in trouble with the author(s) of the sources I have quoted from...
Laura Kiernan 18 April 2022 AT 02:04 PM
Thank you for your questions about MLA style. For guidance on in-text citations for web pages, see section 6.26 of the ninth edition of the MLA Handbook .
Cynthia 21 May 2022 AT 10:05 PM
When you're doing an In-text citations do you put the quotations over the chapter title and then quotations over what you get from the text or do you italicize the title?
Laura Kiernan 25 May 2022 AT 03:05 PM
Thank you for your question. For guidance on how to style chapter titles, see 2.109 of the ninth edition of the MLA Handbook .
Napatsi 15 August 2022 AT 07:08 PM
I'm trying to find how to put in the in-text citation for a UN declaration article but can only find the "Resolutions of International Governing Bodies" on page 446 of the 9th edition but not how to out it in without an author.
Kim 27 September 2022 AT 12:09 PM
I'm quoting a passage from an unpublished manuscript, and it is not the only work I'm citing by the author, but the only one without a year. So using "Smith 1995, 82" is not possible. What would an in-text citation for this case look like?
Jen 17 November 2022 AT 08:11 PM
How do I cite a news cast for in-text citation like ABC News?
Samantha 04 December 2022 AT 05:12 PM
Hi, For MLA format, should a quote where you need to de-capitalize the first letter be written as "you want" or "(y)ou want". Thanks!
Laura Kiernan 07 December 2022 AT 01:12 PM
Thank you for your question. For guidance on how to indicate that you have lowercased the first letter of a quotation, see 6.56 of the ninth edition of the MLA Handbook .
Maria Albeti 07 February 2023 AT 01:02 PM
Stewart, David W. Focus groups. In: Frey, B.B. (ed.) The SAGE Encyclopedia of Educational Research, Measurement, and Evaluation, vol. 2, pp. 687–692. Thousand Oaks: Sage Publications 2018 In this case, how is the correct form to write, because the article is IN the the book?
Eros Karadzhov 15 February 2023 AT 02:02 PM
If we have a sentence that is a statement, but at the end we quote a question, which punctuation mark do we keep, the question mark or the period; maybe both? Example: (1) The author ends his poem with the following question on purpose: "Or does it explode?" (Hughes 11). (2) The author ends his poem with the following question on purpose: "Or does it explode" (Hughes 11)?
Which would be correct, or maybe both are wrong?
Thank you in advance!
Laura Kiernan 16 February 2023 AT 03:02 PM
Thank you for your question. For guidance on quotations ending in a question mark, see section 6.53 of the ninth edition of the MLA Handbook .
Anonymous 08 March 2023 AT 05:03 PM
What about online articles with no known author or multiple authors? What should the in-text citation look like?
Maria 25 March 2023 AT 04:03 PM
Please settle a dispute with my colleagues. I encourage composition students to avoid listing the title of journal articles within the essay unless it is especially relevant because it clutters their arguments. I came to this conclusion from my interpretation of this statement from MLA: "All in-text references should be concise. Avoid, for instance, providing the author’s name or title of a work in both your prose and parentheses." Could someone please provide an answer or further clarification?
Erika Suffern 30 March 2023 AT 04:03 PM
You are right to identify a principle of concision in our guidelines. That said, it is not wrong to mention a title in prose, but it should be done, as you note, when relevant–not as a de rigeur practice or for “filler.” As Eric Hayot notes in The Elements of Academic Style: Writing for the Humanities (Columbia UP, 2014), “giving the title” in prose “suggests fuller forthcoming treatment” (159). Another reason for including the title in prose might be to call attention to something about it. Many writers who do mention a title in prose fear having an incomplete citation and are tempted also to include the title in a parenthetical reference, which is unnecessary.
Jay 29 April 2023 AT 12:04 AM
How do I in-text cite a direct quote from the introduction of an ebook with no page numbers? Would I write (Author "Introduction") or just write (Author)?
Kiara 11 February 2024 AT 03:02 PM
Hello! I am a university student who is currently creating works cited entries and in-text citations for a reflection essay. How do I properly cite professor and peer comments?
Join the Conversation
We invite you to comment on this post and exchange ideas with other site visitors. Comments are moderated and subject to terms of service.
If you have a question for the MLA's editors, submit it to Ask the MLA!
University Libraries University of Nevada, Reno
- Skill Guides
- Subject Guides
MLA Citation Guide (MLA 9th Edition): In-Text Citation
- Understanding Core Elements
- Formatting Appendices and Works Cited List
- Writing an Annotated Bibliography
- Academic Honesty and Citation
In-Text Citation
- Charts, Graphs, Images, and Tables
- Class Notes and Presentations
- Encyclopedias and Dictionaries
- Generative AI
- In Digital Assignments
- Interviews and Emails
- Journal and Magazine Articles
- Newspaper Articles
- Social Media
- Special Collections
- Videos and DVDs
- When Information Is Missing
- Citation Software
In-text citations are inserted in the body of your research paper to briefly document the source of your information.
- In-text citations in MLA style follow the general format of author's last name followed by a page number enclosed in parentheses. Here is an example: "Here's a direct quote" (Smith 8).
- If the author's name is not given, use the first word (or words) of the title. Follow the same formatting that is used in the works-cited list, such as quotation marks. Here is an example: This is a paraphrase ("Trouble" 22).
- If the source does not have page numbers (for example, some online articles, websites and e-books), only include the author's name for the in-text citation. Do not estimate or make up page numbers.
- In-text citations point the reader to the works-cited list, which is located at the end of your paper, for more complete bibliographic information.
Repeated Use of Sources
If you use information from a single source more than once in succession (i.e., no other sources referred to in between), you can use a simplified in-text citation. Here is an example:
Cell biology is an area of science that focuses on the structure and function of cells (Smith 15). It revolves around the idea that the cell is a "fundamental unit of life" (17).
Note: If using this simplified in-text citation creates ambiguity regarding the source being referred to, use the full in-text citation format.
In-Text Citation Formatting and Examples
Format: (Author's Last Name Page Number)
Example: (Hunt 358)
Two Authors
Format: (Author's Last Name and Author's Last Name Page Number)
Example: (Case and Daristotle 57)
Three or More Authors
Format: (Author's Last Name et al. Page Number)
Example: (Case et al. 57)
Unknown Author
Where you would normally put the author's last name, instead use the first one, two, or three words from the title. Do not use initial articles such as "A", "An" or "The". Provide enough words to clarify which sources from your works-cited list that you are referencing.
Follow the formatting of the title. For example, if the title in the works-cited list is in italics, italicize the words from the title in the in-text citation, and if the title in the works-cited list is in quotation marks, put quotation marks around the words from the title in the in-text citation.
Format: (Title Page Number)
Examples :
( Cell Biology 12)
("Nursing" 12)
Multiple Sources
To cite more than one source when you are paraphrasing, separate the in-text citations with a semi-colon.
Format: (Author's Last Name Page Number; Author's Last Name Page Number).
(Smith 42; Bennett 71).
( It Takes Two ; Brock 43).
Note: In MLA style, the sources within the in-text citation do not need to be in alphabetical order.
Works Quoted in Another Source
Sometimes an author of a book, article or website will mention another person's work by using a quotation or paraphrased idea from that source. (This may be a secondary source.) For example, the Kirkey article you are reading includes a quotation by Smith that you would like to include in your essay. The basic rule is that in both your Works-Cited List and in-text citation you will still cite Kirkey. Kirkey will appear in your Works Cited list – NOT Smith. Add the words "qtd. in" to your in-text citation.
Examples of in-text citations:
According to a study by Smith (qtd. in Kirkey) 42% of doctors would refuse to perform legal euthanasia.
Smith (qtd. in Kirkey) states that “even if euthanasia was legal, 42% of doctors would be against this method of assisted dying” (A.10).
Example of Works Cited List citation:
Kirkey, Susan. "Euthanasia." The Montreal Gazette , 9 Feb. 2013, p. A.10. Canadian Newsstand Major Dailies.
- << Previous: Academic Honesty and Citation
- Next: How Do I Cite? >>
Lemieux Library and McGoldrick Learning Commons
Catalog search, site search.
- Seattle University
- Lemieux Library
Citing Your Sources Guide
- MLA In-Text Citations - The Basics
- Introduction to Citations
- APA In-text Citations - The Basics
- APA Reference List - The Basics
- APA Reference List - Examples
- APA Handouts
- Citing AI in APA Style
- House and Senate Reports and Documents
- Congressional Record
- Congressional Bills and Resolutions
- Federal Laws/Statutes
- Executive Documents - Presidential papers, Proclamations, and Executive Orders
- Rules/Regulations - Code of Federal Regulations (C.F.R.) and the Federal Register
- Foreign Relations of the United States
- State Legislative Documents
- State Statutes (Laws)
- Court Cases (decisions/opinions)
- Government Agencies
- MLA Works Cited List - The Basics
- MLA Works Cited - Examples
- Chicago/Turabian - The Basics
- Chicago/Turabian in-text citations
- Chicago/Turabian Bibliography - Examples
- APA Art Citations
- MLA Art Citations
- Chicago Art Citations
- ArtSTOR Citations
- AMA reference list
- Citing Business Resources This link opens in a new window
- Citation Managers
Get Research Help
Student engagement librarian.

MLA In-text Citations - The Basics
In MLA, referring to the works of others within text of your paper is done using parenthetical citations . This means placing relevant source information in parentheses whenever a sentence uses a quotation or paraphrase. Usually, the simplest way is to put all of the source information in parentheses at the end of the sentence (i.e., just before the period). However, as seen below, there are situations where it makes sense to put the parenthetical elsewhere in the sentence, or even to leave information out.
General Guidelines
- upon the source medium (e.g. print, web, DVD)
- upon the source’s entry on the Works Cited page.
- Any source information that you provide in-text must correspond to the source information on the Works Cited page. More specifically, whatever signal word or phrase you provide to your readers in the text must be the first thing that appears on the left-hand margin of the corresponding entry on the Works Cited page. This is so your reader can connect your in-text citation to the right line in your Works cited page.
- Be sure to check the full selection of examples for in-text citations below, they vary slightly depending on the type of source you are citing.
MLA in-text citations
MLA format follows the author-page method of in-text citation. This means that the author's last name and the page number(s) from which the quotation or paraphrase is taken must appear in the text, and a complete reference should appear on your Works Cited page. The author's name may appear either in the sentence itself or in parentheses following the quotation or paraphrase, but the page number(s) should always appear in the parentheses, not in the text of your sentence. For example:
- Wordsworth stated that Romantic poetry was marked by a "spontaneous overflow of powerful feelings" (263).
- Romantic poetry is characterized by the "spontaneous overflow of powerful feelings" (Wordsworth 263).
- Wordsworth extensively explored the role of emotion in the creative process (263).
Both citations in the examples above, (263) and (Wordsworth 263), tell readers that the information in the sentence can be located on page 263 of a work by an author named Wordsworth. If readers want more information about this source, they can turn to the Works Cited page, where, under the name of Wordsworth, they would find the following information:
- Wordsworth, William. Lyrical Ballads . Oxford UP, 1967.
While the above is the general rule, there are some variations depending on the source of the quote or paraphrase. Here are a few examples, but please review the MLA Manual of Style for more detailed and specific information about in-text citations.
In-text citations by type
- Print Sources - Known author
- Print Sources - Corporate author
- Print Sources - No known author
- Classic works with multiple editions
- Works in an anthology
- Multiple authors
- Multiple works by same author
- Multivolume works
- Web sources
For print sources like books, magazines, scholarly journal articles, and newspapers, provide a signal word or phrase (usually the author’s last name) and a page number. If you provide the signal word/phrase in the sentence, you do not need to include it in the parenthetical citation.
- Human beings have been described by Kenneth Burke as "symbol-using animals" (3).
- Human beings have been described as "symbol-using animals" (Burke 3).
These examples must correspond to an entry that begins with Burke, which will be the first thing that appears on the left-hand margin of an entry on the Works Cited page:
- Burke, Kenneth. Language as Symbolic Action: Essays on Life, Literature, and Method . University of California Press, 1966.
When a source has a corporate author, it is acceptable to use the name of the corporation followed by the page number for the in-text citation. You should also use abbreviations (e.g., nat'l for national) where appropriate, so as to avoid interrupting the flow of reading with overly long parenthetical citations.
- Climate change is now "an important factor in developing new engineering systems" (EPA 321).
- The EPA has stated in a recent study, Climate change is now " an important factor in developing new engineering systems" (321).
When a source has no known author, use a shortened title of the work instead of an author name, following these guidelines.
- Place the title in quotation marks if it's a short work (such as an article), or italicize it if it's a longer work (e.g. plays, books, television shows, entire Web sites) and provide a page number if it is available.
Titles that are longer than a standard noun phrase should be shortened into a noun phrase by excluding articles. For example, To the Lighthouse would be shortened to just Lighthouse .
If the title cannot be easily shortened into a noun phrase, the title should be cut after the first clause, phrase, or punctuation:
- The world needs to act to reverse climate change, because it "is here, and it’s causing a wide range of impacts that will affect virtually every human on Earth in increasingly severe ways. . . ." ("Climate Impacts").
In this example, since the reader does not know the author of the article, an abbreviated title appears in the parenthetical citation, and the full title of the article appears first at the left-hand margin of its respective entry on the Works Cited page. Thus, the writer includes the title in quotation marks as the signal phrase in the parenthetical citation in order to lead the reader directly to the source on the Works Cited page. The Works Cited entry appears as follows:
- "Climate Impacts." Union of Concerned Scientists . 2022. www.ucsusa.org/climate/impacts. Accessed 24 Mar. 2022.
If the title of the work begins with a quotation mark, such as a title that refers to another work, that quote or quoted title can be used as the shortened title. The single quotation marks must be included in the parenthetical, rather than the double quotation.
Page numbers are always required, but additional information can help literary scholars, who may have a different edition of a classic work, like Marx and Engels's The Communist Manifesto .
In these cases, give the page number from your edition (making sure the edition is listed in your Works Cited page, of course) followed by a semicolon, and then the appropriate abbreviations for volume (vol.), book (bk.), part (pt.), chapter (ch.), section (sec.), or paragraph (par.). For example:
- Marx and Engels described human history as marked by class struggles (79; ch. 1).
When you cite a work that appears inside a larger source (for instance, an article in a periodical or an essay in a collection), cite the author of the internal source (i.e., the article or essay). For example, to cite Albert Einstein's article "A Brief Outline of the Theory of Relativity," which was published in Nature in 1921, you might write something like this:
- Relativity's theoretical foundations can be traced to earlier work by Faraday and Maxwell (Einstein 782).
For a source with two authors, list the authors’ last names in the text or in the parenthetical citation:
- Best and Marcus argue that one should read a text for what it says on its surface, rather than looking for some hidden meaning (9).
- The authors claim that surface reading looks at what is “evident, perceptible, apprehensible in texts” (Best and Marcus 9).
For a source with three or more authors, list only the first author’s last name, and replace the additional names with et al (which means "and others")
- According to Franck et al., “Current agricultural policies in the U.S. are contributing to the poor health of Americans” (327).
- The authors claim that one cause of obesity in the United States is government-funded farm subsidies (Franck et al. 327).
If you cite more than one work by an author, include a shortened title for the particular work from which you are quoting to distinguish it from the others. Put short titles of books in italics and short titles of articles in quotation marks.
Citing two articles by the same author:
- Lightenor has argued that computers are not useful tools for small children ("Too Soon" 38), though he has acknowledged elsewhere that early exposure to computer games does lead to better small motor skill development in a child's second and third year ("Hand-Eye Development" 17).
Citing two books by the same author:
- Murray states that writing is "a process" that "varies with our thinking style" ( Write to Learn 6). Additionally, Murray argues that the purpose of writing is to "carry ideas and information from the mind of one person into the mind of another" ( A Writer Teaches Writing 3).
**Additionally, if the author's name is not mentioned in the sentence, format your citation with the author's name followed by a comma, followed by a shortened title of the work, and, when appropriate, the page number(s):
- Visual studies, because it is such a new discipline, may be "too easy" (Elkins, "Visual Studies" 63).
If you cite from different volumes of a multivolume work, always include the volume number followed by a colon. Put a space after the colon, then provide the page number(s). (If you only cite from one volume, provide only the page number in parentheses.)
- . . . as Quintilian wrote in Institutio Oratoria (1: 14-17).
In your first parenthetical citation referencing the bible, you want to make clear which bible you're using (and underline or italicize the title), as each version varies in its translation, followed by book (do not italicize or underline), chapter, and verse. For example:
- Ezekiel saw "what seemed to be four living creatures," each with faces of a man, a lion, an ox, and an eagle ( New Jerusalem Bible , Ezek. 1.5-10).
If future references are to the same edition of the bible you’re using, list only the book, chapter, and verse in the parenthetical citation:
- John of Patmos echoes this passage when describing his vision (Rev. 4.6-8).
For electronic and Internet sources, follow the following guidelines:
- Include in the text the first item that appears in the Work Cited entry that corresponds to the citation (e.g. author name, article name, website name, film name).
- Do not provide paragraph numbers or page numbers based on your Web browser’s print preview function.
- Unless you must list the Web site name in the signal phrase in order to get the reader to the appropriate entry, do not include URLs in-text. Only provide partial URLs such as when the name of the site includes, for example, a domain name, like CNN.com or Forbes.com, as opposed to writing out http://www.cnn.com or http://www.forbes.com.
- One online film critic stated that Fitzcarraldo "has become notorious for its near-failure and many obstacles" (Taylor, “Fitzcarraldo”)
- << Previous: MLA - 9th ed.
- Next: MLA Works Cited List - The Basics >>
- Last Updated: Jan 5, 2024 3:46 PM
- URL: https://library.seattleu.edu/guides/citation
Penn State University Libraries
Mla quick citation guide 8th edition.
- In-text Citation
- Citing Web Pages and Social Media
- Citing Articles
- Citing Books
- Other formats
- MLA Style Quiz
Using In-text Citation
Include an in-text citation when you refer to, summarize, paraphrase, or quote from another source. For every in-text citation in your paper, there must be a corresponding entry in your reference list.
MLA in-text citation style uses the author's last name and the page number from which the quotation or paraphrase is taken, for example: (Smith 163). If the source does not use page numbers, do not include a number in the parenthetical citation: (Smith).
Example paragraph with in-text citation
A few researchers in the linguistics field have developed training programs designed to improve native speakers' ability to understand accented speech (Derwing et al. 246; Thomas 15). Their training techniques are based on the research described above indicating that comprehension improves with exposure to non-native speech. Derwing and others conducted their training with students preparing to be social workers, but note that other professionals who work with non-native speakers could benefit from a similar program (258).
Works Cited List
Derwing, Tracey M., et al. "Teaching Native Speakers to Listen to Foreign-accented Speech." Journal of Multilingual and Multicultural Development, vol. 23, no. 4, 2002, pp. 245-259.
Thomas, Holly K. Training Strategies for Improving Listeners' Comprehension of Foreign-accented Speech. University of Colorado, Boulder, 2004.
Citing Web Pages In Text
Cite web pages in text as you would any other source, using the author if known. If the author is not known, use the title as the in-text citation.
Your in-text citation should lead your reader to the corresponding entry in the reference list. Below are examples of using in-text citation with web pages.
Entire website with author: In-text citation Parents play an important role in helping children learn techniques for coping with bullying (Kraizer).
Works cited entry Kraizer, Sherryll. Safe Child. Coalition for Children, 2011, www.safechild.org.
Web page with no author: In-text citation The term Nittany Lion was coined by Penn State football player Joe Mason in 1904 ("All Things Nittany").
Works cited entry "All Things Nittany." About Penn State. Penn State University, 2006, www.psu.edu/ur/about/nittanymascot.html.
General Guidelines
In MLA style the author's name can be included either in the narrative text of your paper, or in parentheses following the reference to the source.
Author's name part of narrative:
Gass and Varonis found that the most important element in comprehending non-native speech is familiarity with the topic (163).
Author's name in parentheses:
One study found that the most important element in comprehending non-native speech is familiarity with the topic (Gass and Varonis 163).
Group as author: (American Psychological Association 123)
Multiple works: (separate each work with semi-colons)
Research shows that listening to a particular accent improves comprehension of accented speech in general (Gass and Varonis 143; Thomas 24).
Direct quote:
One study found that “the listener's familiarity with the topic of discourse greatly facilitates the interpretation of the entire message” (Gass and Varonis 85).
Gass and Varonis found that “the listener’s familiarity with the topic of discourse greatly facilitates the interpretation of the entire message” (85).
Note: For quotations that are more than four lines of prose or three lines of verse, display quotations as an indented block of text (one inch from left margin) and omit quotation marks. Place your parenthetical citation at the end of the block of text, after the final punctuation mark.
In addition to awareness-raising, practicing listening to accented speech has been shown to improve listening comprehension. This article recommends developing listening training programs for library faculty and staff, based on research from the linguistics and language teaching fields. Even brief exposure to accented speech can help listeners improve their comprehension, thereby improving the level of service to international patrons. (O'Malley 19)
Works by Multiple Authors
When citing works by multiple authors, always spell out the word "and." When a source has three or more authors, only the first one shown in the source is normally given followed by et al.
One author: (Field 399)
Works Cited entry: Field, John. "Intelligibility and the Listener: The Role of Lexical Stress." TESOL Quarterly , vol. 39, no. 3, 2005, pp. 399-423.
Two authors: (Gass and Varonis 67)
Works Cited entry: Gass, Susan, and Evangeline M. Varonis. "The Effect of Familiarity on the Comprehensibility of Nonnative Speech." Language Learning , vol. 34, no. 1, 1984, pp. 65-89.
Three or more authors: (Munro et al. 70)
Works Cited entry: Munro, Murray J., et al. "Salient Accents, Covert Attitudes: Consciousness-raising for Pre-service Second Language Teachers." Prospect , vol. 21, no. 1, 2006, pp. 67-79.
- << Previous: Overview
- Next: Citing Web Pages and Social Media >>
- Last Updated: Feb 14, 2024 8:46 AM
- URL: https://guides.libraries.psu.edu/mlacitationeighth

- Introduction
- Formatting Your Paper
- In-Text Citations
- Films, Movies & Videos
- Multiple Authors
- Social Media
- Video and Audio
- Avoiding Plagiarism
- Get Help Now
MLA 9th Edition Citation Guide Multiple Authors
Source with two authors.
Works Cited Page Format:
First Author's Last Name, First Name, and Second Author's First Name, Last Name. Format the remainder according to resource type.
Champaneri, Dushyant D., and Naren K. Patel. “Photo Selective Shade Net: An Effective Tool to Reduce the Impact of Global Warming and Pesticide Residues in Vegetable Production: A Review.” Agricultural Reviews , vol. 43, no. 2, 2022, pp. 135-44. EBSCOhost , https://doi.org/10.18805/ag.R-2363.
In-text Citation Example:
...(Champaneria and Patel 137).
Three or More Authors
Author's Last Name, Author's First Name, et al. Format the remainder according to resource type.
Lin, Eugenia, et al. “Imposter Syndrome Among Surgeons Is Associated With Intolerance of Uncertainty and Lower Confidence in Problem Solving.” Clinical Orthopaedics & Related Research , vol. 481, no. 4, 2023, pp. 664–71. EBSCOhost , https://doi.org/10.1097/CORR.0000000000002390.
...(Lin et al. 665).
- << Previous: Films, Movies & Videos
- Next: Social Media >>
- Last Updated: Mar 6, 2024 3:47 PM
- URL: https://library.csp.edu/mla

- Find Resources
Library and Academic Support Services Concordia University, St. Paul 1282 Concordia Aveneu Saint Paul, MN 55104
- 651-641-823
- [email protected]
- Report a problem
Connect with us
© Concordia University, St. Paul

MLA Citation Guide (9th Edition): In-Text Citation
- What Kind of Source Is This?
- Advertisements
- Books, eBooks & Pamphlets
- Book Reviews
- Class Handouts, Presentations, and Readings
- Encyclopedias & Dictionaries
- Government Documents
- Images, Artwork, Charts, Graphs & Tables
- Interviews and Emails (Personal Communications)
- Journal Articles
- Magazine Articles
- Newspaper Articles
- Primary Sources
- Religious Texts
- Social Media
- Videos & DVDs
- In-Text Citation
Works Quoted in Another Source
- No Author, No Date etc.
- Works Cited List & Sample Paper
- Annotated Bibliography
- Powerpoint Presentations
On This Page
About in-text citations, no known author, quoting directly, paraphrasing, no page numbers, repeated use of sources, in-text citation for more than one source, long quotations, quoting and paraphrasing: what's the difference, signal phrases, avoiding plagiarism when using sources.
T here are two ways to integrate others' research into your assignment: you can paraphrase or you can quote.
Paraphrasing is used to show that you understand what the author wrote. You must restate the meaning of the passage, expressing the ideas in your own words and voice, and not just change a few words here and there. Make sure to also include an in-text citation.
Quoting is copying the wording from someone else's work, keeping it exactly as it was originally written. When quoting, place quotation marks (" ") around the selected passage to show where the quote begins and where it ends. Make sure to include an in-text citation.
If you refer to the author's name in a sentence you do not have to include the name again as part of your in-text citation. Instead include the page number (if there is one) at the end of the quotation or paraphrased section.
Hunt explains that mother-infant attachment has been a leading topic of developmental research since John Bowlby found that "children raised in institutions were deficient in emotional and personality development" (358).
In MLA, in-text citations are inserted in the body of your research paper to briefly document the source of your information. Brief in-text citations point the reader to more complete information in the Works Cited list at the end of the paper.
When a source has no known author, use the first one, two, or three words from the title instead of the author's last name. Don't count initial articles like "A", "An" or "The". You should provide enough words to make it clear which work you're referring to from your Works Cited list.
If the title in the Works Cited list is in italics, italicize the words from the title in the in-text citation.
( Cell Biology 12)
If the title in the Works Cited list is in quotation marks, put quotation marks around the words from the title in the in-text citation.
("Nursing" 12)
When you quote directly from a source, enclose the quoted section in quotation marks. Add an in-text citation at the end of the quote with the author name and page number, like this:
"Here's a direct quote" (Smith 8).
"Here's a direct quote" ("Trouble" 22).
Note: The period goes outside the brackets, at the end of your in-text citation.
Mother-infant attachment has been a leading topic of developmental research since John Bowlby found that "children raised in institutions were deficient in emotional and personality development" (Hunt 358).
When you write information or ideas from a source in your own words, cite the source by adding an in-text citation at the end of the paraphrased portion, like this:
This is a paraphrase (Smith 8).
This is a paraphrase ("Trouble" 22).
Mother-infant attachment became a leading topic of developmental research following the publication of John Bowlby's studies (Hunt 65).
Note: If the paraphrased information/idea summarizes several pages, include all of the page numbers.
Mother-infant attachment became a leading topic of developmental research following the publication of John Bowlby's studies (Hunt 50, 55, 65-71).
When you quote from electronic sources that do not provide page numbers (like webpages), cite the author name only. If there is no author, cite the first word or words from the title only.
"Three phases of the separation response: protest, despair, and detachment" (Garelli).
"Nutrition is a critical part of health and development" ("Nutrition").
Sources that are paraphrased or quoted in other sources are called indirect sources. MLA recommends you take information from the original source whenever possible.
If you must cite information from an indirect source, mention the author of the original source in the body of your text and place the name of the author of the source you actually consulted in your in-text citation. Begin your in-text citation with 'qtd. in.'
Kumashiro notes that lesbian and bisexual women of colour are often excluded from both queer communities and communities of colour (qtd. in Dua 188).
(You are reading an article by Dua that cites information from Kumashiro (the original source))
Note: In your Works Cited list, you only include a citation for the source you consulted, NOT the original source.
In the above example, your Works Cited list would include a citation for Dua's article, and NOT Kumashiro's.
If you're using information from a single source more than once in a row (with no other sources referred to in between), you can use a simplified in-text citation. The first time you use information from the source, use a full in-text citation. The second time, you only need to give the page number.
Cell biology is an area of science that focuses on the structure and function of cells (Smith 15). It revolves around the idea that the cell is a "fundamental unit of life" (17). Many important scientists have contributed to the evolution of cell biology. Mattias Jakob Schleiden and Theodor Schwann, for example, were scientists who formulated cell theory in 1838 (20).
Note: If using this simplified in-text citation creates ambiguity regarding the source being referred to, use the full in-text citation format.
If you would like to cite more than one source within the same in-text citation, simply record the in-text citations as normal and separate them with a semi-colon.
(Smith 42; Bennett 71).
( It Takes Two ; Brock 43).
Note: The sources within the in-text citation do not need to be in alphabetical order for MLA style.
What Is a Long Quotation?
If your quotation is longer than four lines, it is a considered a long quotation. This can also be referred to as a block quotation.
Rules for Long Quotations
There are 4 rules that apply to long quotations that are different from regular quotations:
- Place a colon at the end of the line that you write to introduce your long quotation.
- Indent the long quotation 0.5 inches from the rest of the text, so it looks like a block of text.
- Do not put quotation marks around the quotation.
- Place the period at the end of the quotation before your in-text citation instead of after , as with regular quotations.
Example of a Long Quotation
Vivian Gornick describes the process of maturing as a reader as a reckoning with human limitations:
Suddenly, literature, politics, and analysis came together, and I began to think more inclusively about the emotional
imprisonment of mind and spirit to which all human beings are heir. In the course of analytic time, it became apparent
that—with or without the burden of social justice—the effort required to attain any semblance of inner freedom was
extraordinary. Great literature, I then realized, is a record not of the achievement, but of the effort.
With this insight as my guiding light, I began to interpret the lives and work of women and men alike who had
spent their years making literature. (x-xi)
- << Previous: Websites
- Next: Works Quoted in Another Source >>
- Last Updated: Jan 5, 2024 1:52 PM
- URL: https://columbiacollege-ca.libguides.com/MLA9

MLA Style Guide: 8th Edition: Multiple Authors
- Works Cited examples
- Direct Quote
- Block Quote
- Paraphrase/Summary
- Indirect Quote
Multiple Authors
- In-Text Exceptions
- Personal Communications
- MLA Handbook/Other Resources
- NoodleTools
IN-TEXT CITATIONS FOR A...
See examples below to learn about how multiple authors for one work are handled in MLA parenthetical citations.
Include author's last name and the page number (no comma before the page number) in parentheses:
(Austen 75)
Two Authors
Include last name of both authors connected by the word ‘and’, followed by the page number (no comma before the page number) in parentheses.
(Johnson and Tuite 110)
Three or more Authors
Include the first author’s last name followed by ‘et al.’ and the page number (no comma before the page number) in parentheses.
(Richard et al. 25)
- << Previous: Indirect Quote
- Next: No Author >>
- Last Updated: Jan 5, 2023 1:44 PM
- URL: https://research.wou.edu/mla
MLA Citation Style, 9th Edition
- MLA Style, 9th Edition
- In-text citations
- Books - Multiple Authors
- Books - with editors, translators, etc.
- Book - Essay, Short Story, Poem, etc
- Books - later editions
- Articles - Multiple Authors
- Articles - from scholarly journals
- Articles - from newspapers
- Articles - from magazines
- YouTube Video
- Television Shows
- Images from the Web
- Works Cited: Websites
- Works Cited: Social Media / Informal Communication
- Works Cited: Conference Proceeding/Paper
- Don't See an Example for Your Source?!
- Report an Error / Question
Two Authors
When a work has two authors, include them in the order they appear on the work, and invert the first author's name but write out the second author's name normally.
Works Cited Format (2 authors, scholarly journal):
In-Text Citation Examples:
Author within the text, direct quote:
Authors not in the text, direct quote:
Three or More Authors
Invert the first author's name add a comma and "et al."
Works Cited Format (3 or more authors, scholarly journal):
In-text Citation Examples:
Authors within the text, direct quote:
- << Previous: Works Cited: Articles in Periodicals
- Next: Articles - from scholarly journals >>
- Last Updated: Mar 12, 2024 12:00 PM
- URL: https://libguides.uwf.edu/mla9
- PRO Courses Guides New Tech Help Pro Expert Videos About wikiHow Pro Upgrade Sign In
- EDIT Edit this Article
- EXPLORE Tech Help Pro About Us Random Article Quizzes Request a New Article Community Dashboard This Or That Game Popular Categories Arts and Entertainment Artwork Books Movies Computers and Electronics Computers Phone Skills Technology Hacks Health Men's Health Mental Health Women's Health Relationships Dating Love Relationship Issues Hobbies and Crafts Crafts Drawing Games Education & Communication Communication Skills Personal Development Studying Personal Care and Style Fashion Hair Care Personal Hygiene Youth Personal Care School Stuff Dating All Categories Arts and Entertainment Finance and Business Home and Garden Relationship Quizzes Cars & Other Vehicles Food and Entertaining Personal Care and Style Sports and Fitness Computers and Electronics Health Pets and Animals Travel Education & Communication Hobbies and Crafts Philosophy and Religion Work World Family Life Holidays and Traditions Relationships Youth
- Browse Articles
- Learn Something New
- Quizzes Hot
- This Or That Game New
- Train Your Brain
- Explore More
- Support wikiHow
- About wikiHow
- Log in / Sign up
- Education and Communications
- College University and Postgraduate
- Academic Writing
- MLA Style Manual
How to Cite Multiple Authors in MLA
Last Updated: January 7, 2024 Fact Checked
This article was reviewed by Gerald Posner and by wikiHow staff writer, Jennifer Mueller, JD . Gerald Posner is an Author & Journalist based in Miami, Florida. With over 35 years of experience, he specializes in investigative journalism, nonfiction books, and editorials. He holds a law degree from UC College of the Law, San Francisco, and a BA in Political Science from the University of California-Berkeley. He’s the author of thirteen books, including several New York Times bestsellers, the winner of the Florida Book Award for General Nonfiction, and has been a finalist for the Pulitzer Prize in History. He was also shortlisted for the Best Business Book of 2020 by the Society for Advancing Business Editing and Writing. This article has been fact-checked, ensuring the accuracy of any cited facts and confirming the authority of its sources. This article has been viewed 42,947 times.
If you're writing a research paper in the humanities or liberal arts, you may be formatting your citations using the Modern Language Association (MLA) style. This style requires a full citation to sources used in a "Works Cited" page at the end of your paper, as well as parenthetical in-text citations whenever a source is paraphrased or quoted directly. Your format will vary depending on whether you're citing a work with 2 authors or a work with 3 or more authors. [1] X Trustworthy Source Purdue Online Writing Lab Trusted resource for writing and citation guidelines Go to source
Works Cited Entry

- For example, if you used a book as a source that was written by Harry Potter and Luna Lovegood, your Works Cited entry would start "Potter, Harry."
Tip: Use the author's names in the order they appear on the title page. This is the order that the authors have agreed to, and whose name is listed first is important.

- To continue the previous example, you would write the names of the two authors as "Potter, Harry and Luna Lovegood."

- For example, suppose you were using a book as a source that was written by Severus Snape, Minerva McGonagall, and Horace Slughorn. Your Works Cited entry would start "Snape, Severus et al." [5] X Research source
In-Text Citation

- For example, you might write "The class intended to teach students how to defend themselves against the dark arts, however, was ineffective (Potter and Lovegood 47)." [7] X Research source

- For example, you might write "Hogwarts professors were deeply disturbed that Voldemort appeared to have infiltrated the school (Snape et al. 92)." [9] X Research source

- For example, you might write "Potter and Lovegood described the Defense Against the Dark Arts class as worthless when it came to teaching them anything they could use to protect themselves from a wizard as powerful as Voldemort (47).
Tip: If the work has 3 or more authors, don't forget to add the abbreviation "et al." after the first author's name, even in the text of your paper.
Expert Q&A
You might also like.

- ↑ https://owl.purdue.edu/owl/research_and_citation/mla_style/mla_formatting_and_style_guide/mla_in_text_citations_the_basics.html
- ↑ https://research.wou.edu/mla/mla-multipleauthors
- ↑ https://libguides.uwf.edu/c.php?g=840082&p=6013572
- ↑ http://libanswers.snhu.edu/faq/102973
- ↑ https://irsc.libguides.com/mla/intextexamples
About This Article

- Send fan mail to authors
Did this article help you?

Featured Articles

Trending Articles

Watch Articles

- Terms of Use
- Privacy Policy
- Do Not Sell or Share My Info
- Not Selling Info
wikiHow Tech Help Pro:
Level up your tech skills and stay ahead of the curve
MLA 9 Citation Style: Two Authors
- Textbook With One Author
- Textbook With Two Authors
- Textbook With Three or More Authors
- Textbook as an Anthology or Edited Book
- Textbook Work Within an Anthology or Edited Book
- Textbook Two or More from an Anthology or Edited Book
- Textbook with One Author (Mobile)
- Textbook with Two Authors (Mobile)
- Textbook with Three or More Authors (Mobile)
- Textbook as an Anthology or Edited Book (Mobile)
- Textbook Work Within an Anthology or Edited Book (Mobile)
- Textbook Two or More from an Anthology or Edited Book (Mobile)
- Two Authors
- Three or More Authors
- Anthology or Edited Book
- Work in an Anthology or Edited Book
- Two or More Selections from the Same Anthology or Edited Book
- Journal Article (Print)
- Journal Article (Online)
- Newspaper Articles (Print)
- Newspaper Articles (Online)
- Database Article with One Author
- Database Article with Two Authors
- Database Article with More Than Three Authors
- Database Previously Published Scholarly Article (Blooms, MasterPlots, Literary Reference Center)
- Online Government Publication
- Website with an Author’s/Contributor’s Name
- Website with No Author’s/Contributor’s Name
- Web Page with Author
- Web Page with No Author’s/Contributor’s Name
- Art – From a Book
- Art – From a Web Page
- Picture/Photo Online -- General
- Motion Picture -- DVD
- Motion Picture -- Streaming
- Video -- Online (YouTube, etc.)
- An Interview You Conducted
- Lecture Notes, PowerPoints, or Handouts from Class
- In-Text Citations
- Works Cited Page
- Popular vs. Scholarly Sources
- Direct Quotes, Paraphrasing, Summarizing
MLA Citation -- Book with Two Authors
Works Cited Format
Last name of first author, First name of first author, and First and Last name of second author. Title of Book .
Edition (if any), Publisher, Date.
In-Text Citation Format
(Author’s Last Name p. # * )
* Please note, the in-text citation should be just the number itself and should not include the p., as in the example below.
Works Cited Example
Kennedy, David M., and Lizabeth Cohen. The American Pageant . 16 th ed., Cengage Learning, 2016.
In-Text Citation Example
(Kennedy and Cohen 59)
MLA In-Text Citations
When writing an MLA paper using citations, you use two types of citations:
- in-text (or parenthetical) citation
- Works Cited citation.
These citations are directly linked. Any in-text citation should reflect a citation in your Works Cited page at the end of your MLA paper.
The in-text citation is a brief reference to your source which then leads your reader to your Works Cited page for the full citation.
A Word About Punctuation
The punctuation in your citations does matter. Make sure you pay attention to where the periods and commas are in the examples.
- << Previous: One Author
- Next: Three or More Authors >>
- Last Updated: Mar 7, 2024 10:33 AM
- URL: https://warren.libguides.com/MLA9
Warren County Community College Haytaian & Maier Library 475 Route 57 West Washington, New Jersey 07882 Text: 908-652-4445 [email protected]

- [email protected]
- Shapiro Library
- SNHU Library Frequently Asked Questions
FAQ: How do I cite a source with multiple authors in MLA Style (in-text)?
- 7 Academic Integrity & Plagiarism
- 60 Academic Support, Writing Help, & Presentation Help
- 27 Access/Remote Access
- 7 Accessibility
- 9 Building/Facilities
- 7 Career/Job Information
- 26 Catalog/Print Books
- 26 Circulation
- 128 Citing Sources
- 14 Copyright
- 310 Databases
- 24 Directions/Location
- 18 Faculty Resources/Needs
- 7 Hours/Contacts
- 2 Innovation Lab & Makerspace/3D Printing
- 25 Interlibrary Loan
- 43 IT/Computer/Printing Support
- 3 Library Instruction
- 37 Library Technology Help
- 6 Multimedia
- 17 Online Programs
- 19 Periodicals
- 25 Policies
- 8 RefWorks/Citation Managers
- 4 Research Guides (LibGuides)
- 217 Research Help
- 23 University Services
Last Updated: Jun 22, 2023 Views: 348299
MLA Style requires an in-text citation to indicate the sources that were consulted and used in your work. The in-text citation must correspond with the entry on the Works Cited page,
MLA in-text citations follow the Author-Page style, meaning the author's last name and the page number(s) of the quotation or paraphrase must appear in the text. Page numbers always appear in the parentheses, not in the text of your sentence.
General Format
Parenthetical Citation
(Author page#)
Citation in Prose
Author stated that ... (page#).
For Example
(Ramugondo 189)
Ramugondo stated that ....... (189).
Two Authors
(Leon and Andrews 250-258)
Javier F. Leon and Ronald Andrews argue that ....... (250-258).
Three or More Authors
(Zhang et al. 11)
Zhang and colleagues concluded from their experiments that ....... (11).
More Information
- MLA Guide (Shapiro Library)
Further Help
This information is intended to be a guideline, not expert advice. Please be sure to speak to your professor about the appropriate way to cite sources in your class assignments and projects.
Campus Students
To access Academic Support, visit your Brightspace course and select “Tutoring and Mentoring” from the Academic Support pulldown menu.
Online Students
To access help with citations and more, visit the Academic Support via modules in Brightspace:
- Academic Support Overview: Getting Help with your Schoolwork This link opens in a new window
- Share on Facebook
Was this helpful? Yes 14 No 35
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs) are a self-serve option for users to search and find answers to their questions.
Use the search box above to type your question to search for an answer or browse existing FAQs by group, topic, etc.
Tell Me More
Link to Question Form
More assistance.
Submit a Question
Related FAQs
Purdue Online Writing Lab Purdue OWL® College of Liberal Arts
In-Text Citations: Author/Authors

Welcome to the Purdue OWL
This page is brought to you by the OWL at Purdue University. When printing this page, you must include the entire legal notice.
Copyright ©1995-2018 by The Writing Lab & The OWL at Purdue and Purdue University. All rights reserved. This material may not be published, reproduced, broadcast, rewritten, or redistributed without permission. Use of this site constitutes acceptance of our terms and conditions of fair use.
Though the APA's author-date system for citations is fairly straightforward, author categories can vary significantly from the standard "one author, one source" configuration. There are also additional rules for citing authors of indirect sources, electronic sources, and sources without page numbers.
A Work by One Author
The APA manual recommends the use of the author-date citation structure for in-text citation references. This structure requires that any in-text citation (i.e., within the body of the text) be accompanied by a corresponding reference list entry. In the in-text citation provide the surname of the author but do not include suffixes such as "Jr.".
Citing Non-Standard Author Categories
A work by two authors.
Name both authors in the signal phrase or in parentheses each time you cite the work. Use the word "and" between the authors' names within the text and use the ampersand in parentheses.
A Work by Three or More Authors
List only the first author’s name followed by “et al.” in every citation, even the first, unless doing so would create ambiguity between different sources.
In et al. , et should not be followed by a period. Only "al" should be followed by a period.
If you’re citing multiple works with similar groups of authors, and the shortened “et al” citation form of each source would be the same, you’ll need to avoid ambiguity by writing out more names. If you cited works with these authors:
They would be cited in-text as follows to avoid ambiguity:
Since et al. is plural, it should always be a substitute for more than one name. In the case that et al. would stand in for just one author, write the author’s name instead.
Unknown Author
If the work does not have an author, cite the source by its title in the signal phrase or use the first word or two in the parentheses. Titles of books and reports are italicized; titles of articles, chapters, and web pages are in quotation marks. APA style calls for capitalizing important words in titles when they are written in the text (but not when they are written in reference lists).
Note : In the rare case that "Anonymous" is used for the author, treat it as the author's name (Anonymous, 2001). In the reference list, use the name Anonymous as the author.
Organization as an Author
If the author is an organization or a government agency, mention the organization in the signal phrase or in the parenthetical citation the first time you cite the source, just as you would an individual person.
If the organization has a well-known abbreviation, you may include the abbreviation in brackets the first time the source is cited and then use only the abbreviation in later citations. However, if you cite work from multiple organizations whose abbreviations are the same, do not use abbreviations (to avoid ambiguity).
Two or More Works in the Same Parentheses
When your parenthetical citation includes two or more works, order them the same way they appear in the reference list (viz., alphabetically), separated by a semi-colon.
If you cite multiple works by the same author in the same parenthetical citation, give the author’s name only once and follow with dates. No date citations go first, then years, then in-press citations.
Authors with the Same Last Name
To prevent confusion, use first initials with the last names.
Two or More Works by the Same Author in the Same Year
If you have two sources by the same author in the same year, use lower-case letters (a, b, c) with the year to order the entries in the reference list. Use the lower-case letters with the year in the in-text citation.
Introductions, Prefaces, Forewords, and Afterwords
When citing an Introduction, Preface, Foreword, or Afterword in-text, cite the appropriate author and year as usual.
Personal Communication
For interviews, letters, e-mails, and other person-to-person communication, cite the communicator's name, the fact that it was personal communication, and the date of the communication. Do not include personal communication in the reference list.
If using a footnote to reference personal communication, handle citations the same way.
Traditional Knowledge of Indigenous Peoples
When citing information you learned from a conversation with an Indigenous person who was not your research participant, use a variation of the personal communication citation above. Include the person’s full name, nation or Indigenous group, location, and any other relevant details before the “personal communication, date” part of the citation.
Citing Indirect Sources
Generally, writers should endeavor to read primary sources (original sources) and cite those rather than secondary sources (works that report on original sources). Sometimes, however, this is impossible. If you use a source that was cited in another source, name the original source in your signal phrase. List the secondary source in your reference list and include the secondary source in the parentheses. If you know the year of the original source, include it in the citation.
Electronic Sources
If possible, cite an electronic document the same as any other document by using the author-date style.
Unknown Author and Unknown Date
If no author or date is given, use the title in your signal phrase or the first word or two of the title in the parentheses and use the abbreviation "n.d." (for "no date").
Sources Without Page Numbers
When an electronic source lacks page numbers, you should try to include information that will help readers find the passage being cited. Use the heading or section name, an abbreviated heading or section name, a paragraph number (para. 1), or a combination of these.
Note: Never use the page numbers of webpages you print out; different computers print webpages with different pagination. Do not use Kindle location numbers; instead, use the page number (available in many Kindle books) or the method above.
Other Sources
The APA Publication Manual describes how to cite many different kinds of authors and content creators. However, you may occasionally encounter a source or author category that the manual does not describe, making the best way to proceed unclear.
In these cases, it's typically acceptable to apply the general principles of APA citation to the new kind of source in a way that's consistent and sensible. A good way to do this is to simply use the standard APA directions for a type of source that resembles the source you want to cite. For example, a sensible way to cite a virtual reality program would be to mimic the APA's guidelines for computer software.
You may also want to investigate whether a third-party organization has provided directions for how to cite this kind of source.

IMAGES
VIDEO
COMMENTS
In-text citations: Author-page style. MLA format follows the author-page method of in-text citation. This means that the author's last name and the page number (s) from which the quotation or paraphrase is taken must appear in the text, and a complete reference should appear on your Works Cited page. The author's name may appear either in the ...
Revised on March 5, 2024. An MLA in-text citation provides the author's last name and a page number in parentheses. If a source has two authors, name both. If a source has more than two authors, name only the first author, followed by " et al. ". If the part you're citing spans multiple pages, include the full page range.
If a source has no author, start the MLA Works Cited entry with the source title.Use a shortened version of the title in your MLA in-text citation.. If a source has no page numbers, you can use an alternative locator (e.g. a chapter number, or a timestamp for a video or audio source) to identify the relevant passage in your in-text citation. If the source has no numbered divisions, cite only ...
3.4. ( 141) An in-text citation is a reference to a source that is found within the text of a paper ( Handbook 227). This tells a reader that an idea, quote, or paraphrase originated from a source. MLA in-text citations usually include the last name of the author and the location of cited information. This guide focuses on how to create MLA in ...
Three or more in-text citation in MLA. To format an in-text citation of a source with three or more authors, include the first author's last name followed by et al., and the page number or page range in parentheses. For example: If the authors' names are already stated in the sentence, give only the page number or page range in parenthesis at ...
When there are two authors, simply cite both surnames, separated by "and". When there are three or more authors, cite the first author's surname followed by "et al." if the citation appears in parentheses. If you cite in the main text, instead of "et al.", write "and colleagues" or "and others". Number of authors.
In-Text Citations: An Overview. by Modern Language Association. In-text citations are brief, unobtrusive references that direct readers to the works-cited-list entries for the sources you consulted and, where relevant, to the location in the source being cited. An in-text citation begins with the shortest piece of information that directs ...
Multiple Sources. To cite more than one source when you are paraphrasing, separate the in-text citations with a semi-colon. Format: (Author's Last Name Page Number; Author's Last Name Page Number). Examples: (Smith 42; Bennett 71). (It Takes Two; Brock 43). Note: In MLA style, the sources within the in-text citation do not need to be in ...
MLA in-text citations. MLA format follows the author-page method of in-text citation. This means that the author's last name and the page number(s) from which the quotation or paraphrase is taken must appear in the text, and a complete reference should appear on your Works Cited page. ... Citing two books by the same author: Murray states that ...
MLA in-text citation style uses the author's last name and the page number from which the quotation or paraphrase is taken, for example: (Smith 163). If the source does not use page numbers, do not include a number in the parenthetical citation: (Smith). Example paragraph with in-text citation. A few researchers in the linguistics field have ...
Three or More Authors. Author's Last Name, Author's First Name, et al. Format the remainder according to resource type. Lin, Eugenia, et al. "Imposter Syndrome Among Surgeons Is Associated With Intolerance of Uncertainty and Lower Confidence in Problem Solving.". Clinical Orthopaedics & Related Research, vol. 481, no. 4, 2023, pp. 664-71.
In MLA, in-text citations are inserted in the body of your research paper to briefly document the source of your information. Brief in-text citations point the reader to more complete information in the works cited list at the end of the paper. In-text citations include the last name of the author followed by a page number enclosed in ...
In MLA, in-text citations are inserted in the body of your research paper to briefly document the source of your information. Brief in-text citations point the reader to more complete information in the Works Cited list at the end of the paper. Number of Authors/Editors. Format of In-Text Citation. One.
Multiple Authors. See examples below to learn about how multiple authors for one work are handled in MLA parenthetical citations. One Author. Include author's last name and the page number (no comma before the page number) in parentheses: (Austen 75) Two Authors. Include last name of both authors connected by the word 'and', followed by the ...
Do not use an ampersand (&)! Multiple authors: MLA contains special space-saving rules for sources with many authors. As of the 9th edition of the MLA Handbook, for all in-text citations with more than 2 authors, utilize "et al." after the first listed author to conserve space. Please note, "et al." is an abbreviation of the Latin et ...
This guide will assist you in formatting your in-text and Works Cited citations in MLA, 9th Edition, format. ... MLA Style, 9th Edition; In-text citations; Works Cited: Books. Books - Multiple Authors ; ... When a work has two authors, include them in the order they appear on the work, and invert the first author's name but write out the second ...
To cite a book with multiple authors in MLA style, the core elements required are the names of authors, title of the book, year of publication, and name of the publisher. A citation with three or more authors lists the author content with et al. or "and others.". The table below shows how the in-text citation and the works-cited entry are ...
This guide will assist you in formatting your in-text and Works Cited citations in MLA, 9th Edition, format. ... MLA Style, 9th Edition; In-text citations; Works Cited: Books. Books - Multiple Authors ; ... When a work has two authors, include them in the order they appear on the work, and invert the first author's name but write out the second ...
2. Provide the second author's name in first name-last name format. After the first author's name, type the word "and" followed by the second author's name. Reverse the order from the first author, typing their first name followed by their last name. Place a period at the end of the second author's name.
When writing an MLA paper using citations, you use two types of citations: in-text (or parenthetical) citation ; Works Cited citation. These citations are directly linked. Any in-text citation should reflect a citation in your Works Cited page at the end of your MLA paper. The in-text citation is a brief reference to your source which then ...
MLA Style requires an in-text citation to indicate the sources that were consulted and used in your work. The in-text citation must correspond with the entry on the Works Cited page, MLA in-text citations follow the Author-Page style, meaning the author's last name and the page number(s) of the quotation or paraphrase must appear in the text.
Formatting: There are two main ways to cite parenthetically: providing all information at the end of the idea (in-text citation) or incorporating the author's name into the sentence (narrative). Type 1: In parentheses, put the author's last name(s) and the page number(s) on which the cited information appears. The period goes after the ...
Note: In the rare case that "Anonymous" is used for the author, treat it as the author's name (Anonymous, 2001).In the reference list, use the name Anonymous as the author. Organization as an Author. If the author is an organization or a government agency, mention the organization in the signal phrase or in the parenthetical citation the first time you cite the source, just as you would an ...