Perfect your citations APA, MLA, Chicago and more ...
Getting your citations right is an important but time-consuming process. Mistakes are easy to make but hard to spot.
Our AI Citation Checker and Citation Experts take this work off your hands, so you have time to focus on what really matters: the content of your paper.


Mistakes are easy to make but hard to spot
Citations can be tricky, and it’s easy to overlook mistakes. Is it (Brown et al 2020) or (Brown et al., 2020)? Don’t worry — our AI-powered scan will catch the smallest mistakes, including;
- Punctuation and capitalization errors
- Incorrect usage of “et al.”
- Missing information
- Inconsistencies between citations and references

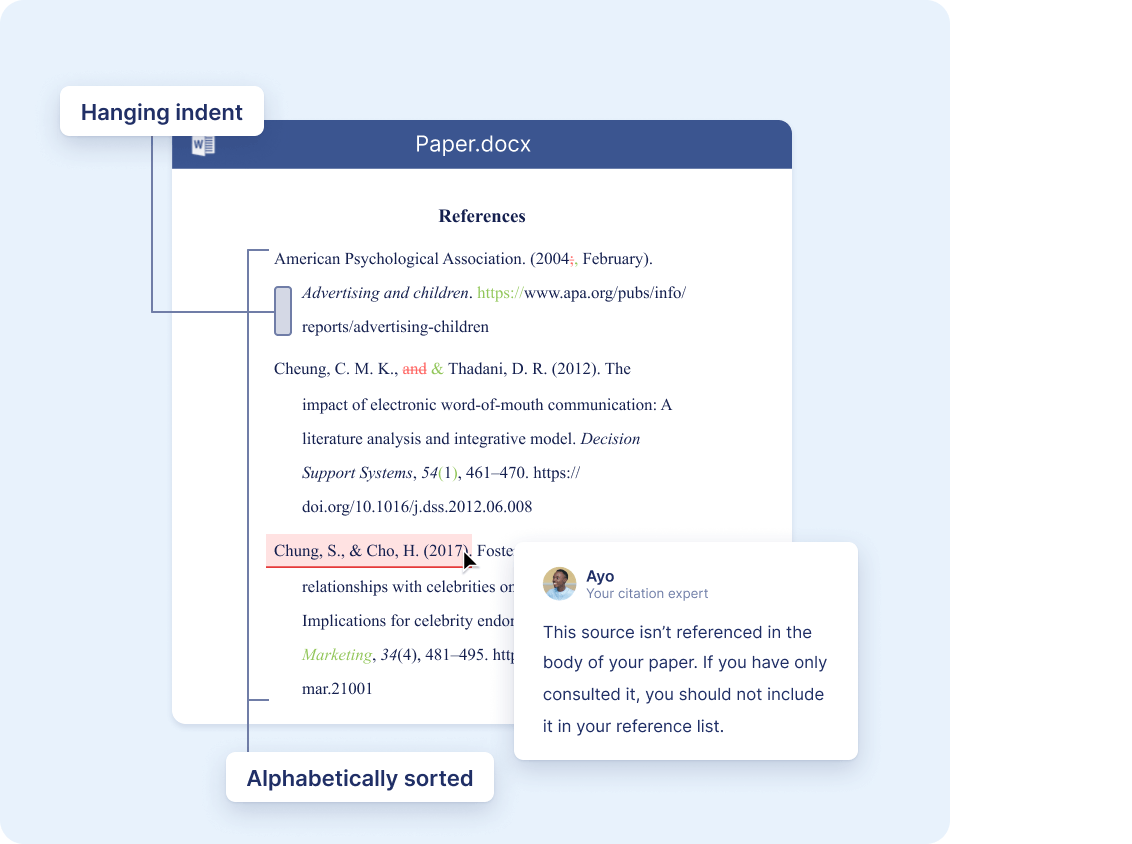
Easily detect missing references
You’re putting the final touches on your paper, but you still need to check your citations. Last-minute troubleshooting is stressful and time-consuming, just when there are other things you’d rather focus on.
The APA Citation Checker detects missing references in your document. The interactive report then allows you to fix them quickly and easily, resolving issues in seconds.
Take it to the next level: Get help from an expert
Books, webpages, articles: each source type has its own reference format. Getting the details right in APA, MLA, Chicago, Vancouver, or Harvard style is important.
Scribbr’s Citation Experts edit hundreds of references every week. They’re familiar with the latest guidelines and can handle any citation style. An expert will review every reference to ensure:
- The right information is included
- Style guide requirements are met
- Capitalization, punctuation, and formatting are spot-on
- The layout of the reference page is correct
Need help with your citations? See what’s right for you.

Use AI-powered software
Citations are checked on over 100 APA guidelines, after which you’ll receive an interactive report highlighting all errors and outlining their solutions.
APA Only • $9.95
- Powered by advanced machine learning technology
- Fix issues yourself with the help of automatically generated solutions
- Receive your citation report within a few minutes
- In-text citations and detects missing references
- Access to helpful articles and videos about citing sources
- Perfect for you if your reference list is good to go and you need to spot any leftover mistakes which you can fix yourself!
- Only available for APA 6th edition & APA 7th edition

Hire a Citation Expert
Experienced Citation Experts perfect your citations for you, with 100% accuracy in any citation style. You can sit back and relax!
All Citation Styles • $2.75 per source
- Edited by experienced Citation Experts
- Accept edits from your Citation Expert with just a click
- Get your paper back within 24 hours
- In-text citations, missing references, and formatting of your reference list
- Ask your Citation Expert any follow-up question.
- Perfect for you if you’re looking for help with your reference list and in-text citations. An expert will perfect your document before you hand it in!
- APA, MLA, Chicago, Vancouver, Harvard style, and institution-specific guidelines
Why choose Scribbr?
Authority in citing sources.
Scribbr’s citation tools and articles about citing sources help more than 2 million students every month.
Citation Guides
Becoming better at citing is simple with the help of our highly rated citation guides .
Well-trained experts
Our experts are always up to date on the latest developments, such as the new APA 7th edition guidelines.
Great customer service
Our customer support team is happy to answer any questions you may have before, during, or after using our services.
Fantastic service!!
“Excellent review of a paper that was deciding my grade. I appreciate both the edits and the feedback to increase my knowledge of correct APA formatting and accurate citations. I needed the paper returned quickly, and the team worked hard to make sure I had what I needed. I just got my grade back, A+. I would 100% use this service again, it was worth every penny!!!!!!”
Still working on your paper?
Use our handy Citation Generator for APA, MLA, Harvard and Chicago. The easiest way to generate citations and a complete reference-list for your document.
Try our Citation Generator
Ask our team
Want to contact us directly? No problem. We are always here for you.
- Email [email protected]
- Start live chat
- Call +1 (510) 822-8066
- WhatsApp +31 20 261 6040

Frequently asked questions
Reference entries are cross-checked with in-text citations to make sure there are no inconsistencies or missing entries. However, the APA Citation Checker does not check the contents or formatting of the reference entries themselves.
The APA Citation Checker can check documents in the following languages:
The APA Citation Checker currently supports APA Style 6th edition (2009) and 7th edition (2020). We are working hard to support more citation styles in the future.
Need help with a different citation style? Check out Scribbr’s Citation Editing Service .
Yes. After fixing your citations, you can upload your revised document and perform a second check free of charge. This way, you can rest assured that you haven’t introduced any new mistakes.
The APA Citation Checker is an automated tool that helps you detect and resolve issues with your in-text citations. Citation Editing is performed by human citation experts who will edit your in-text citations and reference entries.
Citation Generator
Powered by chegg.
- Select style:
- Archive material
- Chapter of an edited book
- Conference proceedings
- Dictionary entry
- Dissertation
- DVD, video, or film
- E-book or PDF
- Edited book
- Encyclopedia article
- Government publication
- Music or recording
- Online image or video
- Presentation
- Press release
- Religious text
What Is Cite This For Me's Citation Generator?
Cite This For Me’s open-access generator is an automated citation machine that turns any of your sources into citations in just a click. Using a citation generator helps students to integrate referencing into their research and writing routine; turning a time-consuming ordeal into a simple task.
A citation machine is essentially a works cited generator that accesses information from across the web, drawing the relevant information into a fully-formatted bibliography that clearly presents all of the sources that have contributed to your work.
If you don’t know how to cite correctly, or have a fast-approaching deadline, Cite This For Me’s accurate and intuitive citation machine will lend you the confidence to realise your full academic potential. In order to get a grade that reflects all your hard work, your citations must be accurate and complete. Using a citation maker to create your references not only saves you time but also ensures that you don’t lose valuable marks on your assignment.
Not sure how to format your citations, what citations are, or just want to find out more about Cite This For Me’s citation machine? This guide outlines everything you need to know to equip yourself with the know-how and confidence to research and cite a wide range of diverse sources in your work.
Why Do I Need To Cite?
Simply put, referencing is the citing of sources used in essays, articles, research, conferences etc. When another source contributes to your work, you have to give the original owner the appropriate credit. After all, you wouldn’t steal someone else’s possessions so why would you steal their ideas?
Any factual material or ideas you take from another source must be acknowledged in a reference, unless it is common knowledge (e.g. President Kennedy was killed in 1963). Failing to credit all of your sources, even when you’ve paraphrased or completely reworded the information, is plagiarism. Plagiarizing will result in disciplinary action, which can range from losing precious points on your assignment to expulsion from your university.
What’s more, attributing your research infuses credibility and authority into your work, both by supporting your own ideas and by demonstrating the breadth of your research. For many students, crediting sources can be a confusing and tedious process, but it’s a surefire way to improve the quality of your work so it’s essential to get it right. Luckily for you, using Cite This For Me’s citation machine makes creating accurate references easier than ever, leaving more time for you to excel in your studies.
In summary, the referencing process serves three main functions:
- To validate the statements and conclusions in your work by providing directions to other sound sources that support and verify them.
- To help your readers locate, read and check your sources, as well as establishing their contribution to your work.
- To give credit to the original author and hence avoid committing intellectual property theft (known as ‘plagiarism’ in academia).
How Do I Cite My Sources With The Cite This For Me's Citation Machine?
Cite This For Me’s citation generator is the most accurate citation machine available, so whether you’re not sure how to format in-text citations or are looking for a foolproof solution to automate a fully-formatted works cited list, this citation machine will solve all of your referencing needs.
Referencing your source material doesn’t just prevent you from losing valuable marks for plagiarism, it also provides all of the information to help your reader find for themselves the book, article, or other item you are citing. The accessible interface of this citation builder makes it easy for you to identify the source you have used – simply enter its unique identifier into the citation machine search bar. If this information is not available you can search for the title or author instead, and then select from the search results that appear below the citation generator.
The good news is that by using tools such as Cite This For Me, which help you work smarter, you don’t need to limit your research to sources that are traditional to cite. In fact, there are no limits to what you can reference, whether it be a YouTube video, website or a tweet.
To use the works cited generator, simply:
- Select from APA, MLA, Chicago, ASA, IEEE and AMA * styles.
- Choose the type of source you would like to cite (e.g. website, book, journal, video).
- Enter the URL , DOI , ISBN , title, or other unique source information into the citation generator to find your source.
- Click the ‘Cite’ button on the citation machine.
- Copy your new reference from the citation generator into your bibliography or works cited list.
- Repeat for each source that has contributed to your work.
*If you require another referencing style for your paper, essay or other academic work, you can select from over 7,500 styles.
Once you have created your Cite This For Me account you will be able to use the citation machine to generate multiple references and save them into a project. Use the highly-rated iOS or Android apps to create references in a flash with your smartphone camera, export your complete bibliography in one go, and much more.
What Will The Citation Machine Create For Me?
Cite This For Me’s citation maker will generate your reference in two parts; an in-text citation and a full reference to be copied straight into your work.
The citation machine will auto-generate the correct formatting for your works cited list or bibliography depending on your chosen style. For instance, if you select a parenthetical style on the citation machine it will generate an in-text citation in parentheses, along with a full reference to slot into your bibliography. Likewise, if the citation generator is set to a footnote style then it will create a fully-formatted reference for your reference page and bibliography, as well as a corresponding footnote to insert at the bottom of the page containing the relevant source.
Parenthetical referencing examples:
In-text example: A nation has been defined as an imagined community (Anderson, 2006).* Alternative format: Anderson (2006) defined a nation as an imagined community.
*The citation machine will create your references in the first style, but this should be edited if the author’s name already appears in the text.
Bibliography / Works Cited list example: Anderson, B. (2006). Imagined Communities. London: Verso.
Popular Citation Examples
- Citing archive material
- Citing artwork
- Citing an audiobook
- Citing the Bible
- Citing a blog
- Citing a book
- Citing a book chapter
- Citing a comic book
- Citing conference proceedings
- Citing a court case
- Citing a database
- Citing a dictionary entry
- Citing a dissertation
- Citing an eBook
- Citing an edited book
- Citing an email
- Citing an encyclopedia article
- Citing a government publication
- Citing an image
- Citing an interview
- Citing a journal article
- Citing legislation
- Citing a magazine
- Citing a meme
- Citing a mobile app
- Citing a movie
- Citing a newspaper
- Citing a pamphlet
- Citing a patent
- Citing a play
- Citing a podcast
- Citing a poem
- Citing a presentation
- Citing a press release
- Citing a pseudonym
- Citing a report
- Citing Shakespeare
- Citing social media
- Citing a song
- Citing software
- Citing a speech
- Citing translated book
- Citing a TV Show
- Citing a weather report
- Citing a website
- Citing Wikipedia article
- Citing a YouTube video
What Are Citation Styles?
A citation style is a set of rules that you, as an academic writer, must follow to ensure the quality and relevance of your work. There are thousands of styles that are used in different academic institutions around the world, but in the US the most common are APA, MLA and Chicago.
The style you need to use will depend on the preference of your professor, discipline or academic institution – so if you’re unsure which style you should be using, consult your department and follow their guidelines exactly, as this is what you’ll be evaluated on when it comes to grading.
Referencing isn’t just there to guard against plagiarism – presenting your research in a clear and consistent way eases the reader’s comprehension. Each style has a different set of rules for both page formatting and referencing. Be sure to adhere to formatting rules such as font type, font size and line spacing to ensure that your work is easily legible. Furthermore, if your work is published as part of an anthology or collected works, each entry will need to be presented in the same style to maintain uniformity throughout. It is important to make sure that you don’t jump from one style to another, so follow the rules carefully to ensure your reference page and bibliography are both accurate and complete.
If you need a hand with your referencing then why not try Cite This For Me’s citation builder? It’s the quickest and easiest way to reference any source, in any style. The citation generator above will create your references in MLA format style as standard, but this powerful citation machine can generate fully-formatted references in thousands of the widely used global college styles – including individual university variations of each style. So, whether your subject requires you to use the APA citation , or your professor has asked you to adopt the Chicago style citation so that your work includes numbered footnotes, we’re sure to have the style you need. Cite This For Me also offers a citation machine and helpful formatting guide for styles such as ASA , IEEE or AMA . To access all of them, simply create your free account and search for your specific style.
Popular Citation Styles
- ACS Referencing Generator
- AMA Citation Generator
- APA Citation Generator
- APSA Referencing Generator
- ASA Citation Generator
- Bluebook Citation Generator
- Chicago Style Citation Generator
- Harvard Referencing Generator
- IEEE Referencing Generator
- MHRA Referencing Generator
- MLA Citation Generator
- Nature Referencing Generator
- OSCOLA Referencing Generator
- Oxford Referencing Generator
- Turabian Citation Generator
- Vancouver Referencing Generator
How Do I Format A Works Cited List Or Bibliography?
Drawing on a wide range of sources greatly enhances the quality of your work, and reading above and beyond your recommended reading list – and then using these sources to support your own thesis – is an excellent way to impress your reader. A clearly presented works cited list or bibliography demonstrates the lengths you have gone to in researching your chosen topic.
Typically, a works cited list starts on a new page at the end of the main body of text and includes a complete list of the sources you have actually cited in your paper. This list should contain all the information needed for the reader to locate the original source of the information, quote or statistic that directly contributed to your work. On the other hand, a bibliography is a comprehensive list of all the material you may have consulted throughout your research and writing process. Both provide the necessary information for readers to retrieve and check the sources cited in your work.
Each style’s guidelines will define the terminology of ‘ works cited ’ and ‘ bibliography ’, as well as providing formatting guidelines for font, line spacing and page indentations. In addition, it will instruct you on how to order your works cited list or bibliography – this will usually be either alphabetical or chronological (meaning the order that these sources appear in your work). Before submitting your work, be sure to check that you have formatted your whole paper – including your reference page and bibliography – according to your style’s formatting guidelines.
Sounds complicated? Referencing has never been so easy; Cite This For Me’s citation machine will automatically generate fully-formatted references for your works cited page or bibliography in your chosen style. Sign in to your Cite This For Me account to save and export your bibliography straight into Microsoft Word, Evernote, EndNote and more. If that sounds like too much work.
How Do Citations Actually Work?
Although the citation generator will create your bibliography and works cited list for you in record time, it is still useful to understand how this system works behind the scenes. Understanding how a citation machine actually generates references will greatly increase the quality of your work.
As well as saving you time with its citation maker, Cite This For Me provides the learning resources to help you fully understand the citing process and the benefits of adopting great referencing standards.
The referencing process:
- Find a book, journal, website or other source that will contribute to your work.
- Save the quote, image, data or other information that you will use in your work.
- Save the source information that enables you to find it again (i.e. URL, ISBN, DOI etc.).
- Format the source information into a reference.
- Copy and paste the reference into the body of the text.
- Repeat for each source that contributes to your work.
- Export or copy and paste the fully-formatted reference into your bibliography.
Manage all your citations in one place
Create projects, add notes, cite directly from the browser and scan books’ barcodes with a mobile app.
Sign up to Cite This For Me – the ultimate citation management tool.
- Free Tools for Students
- MLA Citation Generator
Free MLA Citation Generator
Generate accurate citations in MLA format automatically, with MyBib!

😕 What is an MLA Citation Generator?
An MLA citation generator is a software tool designed to automatically create academic citations in the Modern Language Association (MLA) citation format. The generator will take information such as document titles, author, and URLs as in input, and output fully formatted citations that can be inserted into the Works Cited page of an MLA-compliant academic paper.
The citations on a Works Cited page show the external sources that were used to write the main body of the academic paper, either directly as references and quotes, or indirectly as ideas.
👩🎓 Who uses an MLA Citation Generator?
MLA style is most often used by middle school and high school students in preparation for transition to college and further education. Ironically, MLA style is not actually used all that often beyond middle and high school, with APA (American Psychological Association) style being the favored style at colleges across the country.
It is also important at this level to learn why it's critical to cite sources, not just how to cite them.
🙌 Why should I use a Citation Generator?
Writing citations manually is time consuming and error prone. Automating this process with a citation generator is easy, straightforward, and gives accurate results. It's also easier to keep citations organized and in the correct order.
The Works Cited page contributes to the overall grade of a paper, so it is important to produce accurately formatted citations that follow the guidelines in the official MLA Handbook .
⚙️ How do I use MyBib's MLA Citation Generator?
It's super easy to create MLA style citations with our MLA Citation Generator. Scroll back up to the generator at the top of the page and select the type of source you're citing. Books, journal articles, and webpages are all examples of the types of sources our generator can cite automatically. Then either search for the source, or enter the details manually in the citation form.
The generator will produce a formatted MLA citation that can be copied and pasted directly into your document, or saved to MyBib as part of your overall Works Cited page (which can be downloaded fully later!).
MyBib supports the following for MLA style:

Daniel is a qualified librarian, former teacher, and citation expert. He has been contributing to MyBib since 2018.
- Plagiarism and grammar
- Citation guides
Citation Generator
- powered by chegg.
Keep all of your citations in one safe place
Create an account to save all of your citations
Check your paper before your teacher does!
Avoid plagiarism — quickly check for missing citations and check for writing mistakes., free bibme apa format guide & generator.
Welcome to a comprehensive guide on citing sources and formatting papers in the American Psychological Association style. Below are reference and in-text citation examples, directions on formatting your paper, and background information on the style.
What is APA?
APA stands for the American Psychological Association , which is an organization that focuses on psychology. They are responsible for creating this specific citation style. They are not associated with this guide, but all of the information here provides guidance to using their style and follows the Publication Manual of the American Psychological Association.
What is APA Citing?
APA style is used by many scholars and researchers in the behavioral and social sciences, not just psychology. There are other citation formats and styles such as MLA and Chicago citation style , but this one is most popular in the fields of science.
Following the same standard format for citations allows readers to understand the types of sources used in a project and also understand their components.
The information in this guide follows the 7th edition of the Publication Manual of the American Psychological Association . It outlines proper ways to organize and structure a research paper, explains grammar guidelines, and how to properly cite sources. This webpage was created solely by BibMe to help students and researchers focus on how to create APA citations.
The 7th edition of the Publication Manual was released in 2020. We address differences between the 6th and 7th editions at the end of this guide.
For more information, please consult the official Publication Manual .
We cite sources for many reasons. One reason is to give credit to the authors of the work you used to help you with your own research. When you use another person's information to help you with your project, it is important to acknowledge that individual or group. This is one way to prevent plagiarism. Another reason why we create citations is to provide a standard way for others to understand and possibly explore the sources we used. To learn more about citations, check out this page on crediting work . Also, read up on how to be careful of plagiarism .
What Does it Look Like?
There are two types of citations:
- In-text/Parenthetical citations: Those that are found in the body of a project are called in-text/parenthetical citations. They're added into a project when a direct quote or paraphrase has been added into your work. These citations only include the name(s) of the author(s), date, and page number(s), if applicable.
- References: Those that are found on the final part of a project are called references. They're are found in the reference list (sometimes called APA works cited by some teachers), which is at the end of the assignment. It includes the full information of all sources used in a project. These types of references show the author's name, date published, title, publisher, URL, and other key pieces of information.
Depending on the types of sources used for your project, the structure for each citation may look different. There is a certain format or structure for books, a different one for journal articles, a different one for websites, and so on. Scroll down to find the appropriate APA format structure for your sources.
Even though the structure varies across different sources, see below for a full explanation of in-text citations and reference citations.
Still wondering, "What is APA format?" To learn more about APA referencing, including access to the American Psychological Association\'s blog, formatting questions, & referencing explanations, click on this link for further reading on the style . To learn more about using the BibMe service (BibMe.com) to help build APA citation website references, see the section below titled, "Using the BibMe Online Writing Center to Create Citations for your Reference List or APA Bibliography."
Citing Basics
In-text citations overview.
When using a direct quote or paraphrasing information from a source, include an in-text or parenthetical citation into the body of your project, immediately following it.
An APA in-text citation may look similar to this:
Author's Last name (Year) states that "direct quote" or paraphrase (page number).
Parenthetical citations look like this:
"Direct quote" or paraphrase (Author's Last name, Year, Page number).
These types of APA citations always have the author and the date together.
Only direct quotes need a page number. For paraphrased information, it isn't necessary, but helpful for the reader.
See the section below titled, "In-Text or Parenthetical Citations," for a full explanation and instructions.
Full References Overview
Each source used in your project is listed as a full citation on the APA reference page, which is usually the last part of a project.
The structure for each citation is based on the type of source used. Scroll down to see APA format examples of some common source formats.
Most print and offline citations include the following pieces of information, commonly in this order:
Author's Last name, First initial. Middle initial. (Date published). Title of source . Publisher.
Most online citations include the following pieces of information, commonly in this order:
Author's Last name, First Initial. Middle initial. (Date published). Title of source . URL
To see how to format each section, scroll down to the appropriate areas of this guide. There is a section on authors, one on publication dates, another on titles, publishers, and on online information.
To determine the exact APA citation format for your full citations, scroll down to the section titled, "Common Examples."
For a detailed explanation on formatting your reference list, scroll down to the section titled, "Your Reference List."
Here's a quick snapshot of the basics:
All in-text citations included throughout the paper should have a corresponding full reference at the end of the project.
Full references go on their own page at the end of a project. Title the page "References"
References are listed in alphabetical order by the first word in the reference (usually the author's last name, sometimes the title).
- If the reference begins with the words A , An , or The , ignore them and alphabetize the reference by the word following it.
If you're looking for an easy way to create your references and citations, use BibMe's free APA citation machine, which automatically formats your sources quickly and easily.
Citation Components
How to structure authors.
Authors are displayed in reverse order: Last name, First initial. Middle initial. End this information with a period.
APA format example:
Kirschenbaum, M. A.
In an APA citation, include all authors shown on a source. If using the BibMe APA citation builder, click "Add another contributor" to add additional author names. Our free citation creator will format the authors in the order in which you add them.
Multiple authors, same last name:
If your reference list has multiple authors with the same last name and initials, include their first name in brackets.
Brooks, G. [Geraldine]. (2005). March . Viking.
Brooks, G. [Gwendolyn]. (1949). Annie Allen . Harper & Brothers.
When no author is listed, exclude the author information and start the citation with the title followed by the year in parentheses.
When citing an entire edited book in APA format, place the names of editors in the author position and follow it with Ed. or Eds. in parentheses. See below for examples of citing edited books in their entirety and also APA citation format for chapters in edited books.
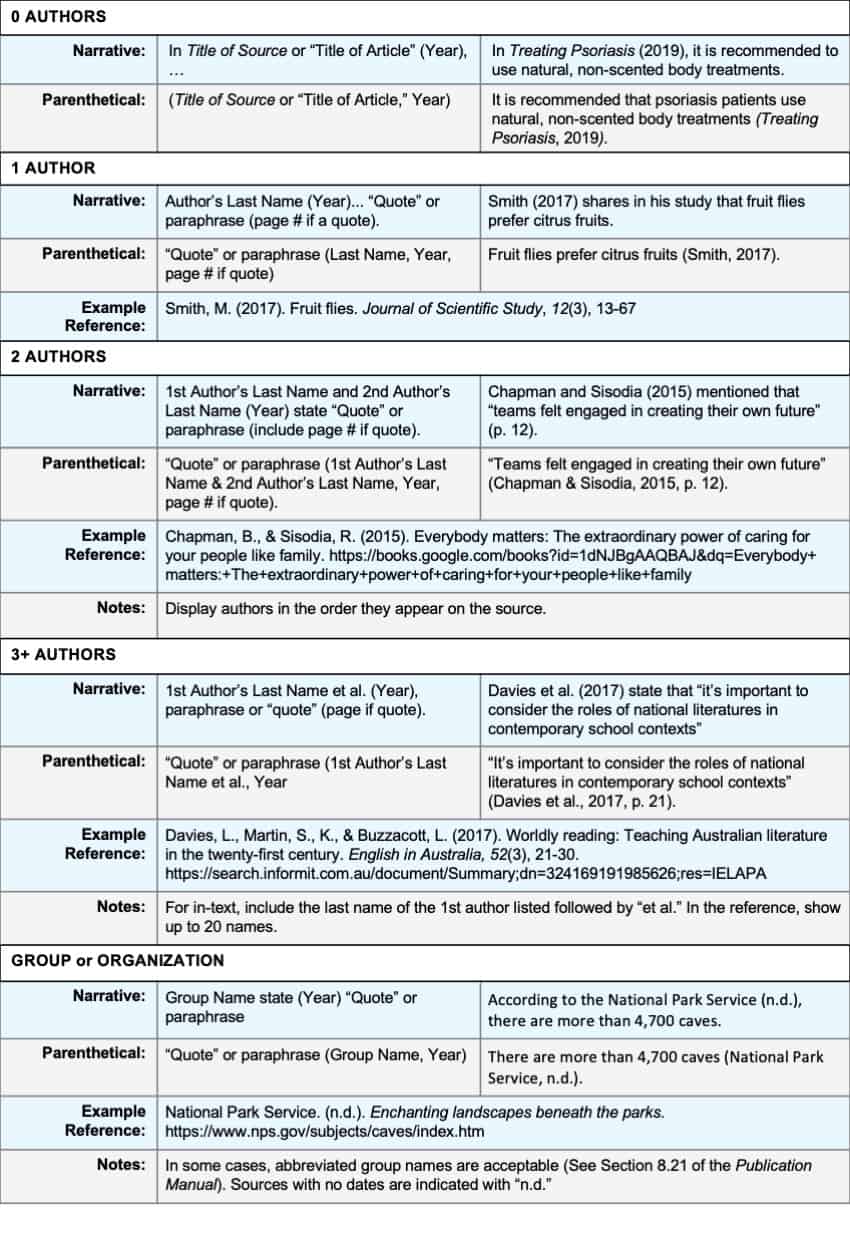
Comparison chart:
Use this handy chart to determine how to format author names in citations and references.
How to Structure Publication Dates
General structure is:
- Year, Month Day
- Example: 1998, March 22
Place the date that the source was published in parentheses after the name of the author. In APA format for periodicals, include the month and day as well. If no date is available, place n.d. in parentheses, which stands for no date. For more details, see Section 9.14 of the Publication Manual .
How to Structure the Title
For book titles: Only capitalize the first letter of the first word in the title and the same for the subtitle. Capitalize the first letter for any proper nouns as well. Place this information in italics. End it with a period.
Gone with the wind.
For articles and chapter titles: Only capitalize the first letter of the first word in the title and the same for the subtitle. Capitalize the first letter for any proper nouns as well. Do not italicize the title or place it in quotation marks. End it with a period.
The correlation between school libraries and test scores: A complete overview.
For web pages on websites: Same as above. The web page title is italicized.
Simmons, B. (2015, January 9). The tale of two Flaccos . Grantland. http://grantland.com/the-triangle/the-tale-of-two-flaccos/
For magazine, journal, and newspaper titles: Each important word should start with a capital letter.
The Boston Globe
If you believe that it will help the reader to understand the type of source, such as a brochure, lecture notes, or an audio podcast, place a description in brackets directly after the title. Only capitalize the first letter.
New World Punx. (2014, February 15). A state of trance 650 [Audio file]. https://soundcloud.com/newworldpunx/asot650utrecht
How to Structure Publication Information
Publisher Location
In previous editions of the publication manual, books and sources that were not periodicals indicated the city and state of publication. However, in the 7th edition, the location of publication is no longer given except “for works associated with specific locations, such as conference presentations” (p. 297).
For conference presentations, give the city, state/province/territory, and country. If in the US, abbreviate the state name using the two-letter abbreviation. Place a colon after the location.
- Philadelphia, PA:
- Rotterdam, Netherlands:
Periodical Volume and Number
For journals, magazines, newspapers, and other periodicals, place the volume number after the title. Italicize this information. Place the issue number in parentheses and do not italicize it. Afterwards, include page numbers.
Journal of Education for Library and Information Science, 57 (1), 79-82.
If you're citing a newspaper article, include p. or pp. before the page numbers.
How to Structure the Publisher
The names of publishers are not necessary to include for newspapers, magazines, journals, and other periodicals.
For books and other sources: It is not necessary to type out the name of the publisher exactly as it is shown on the source. Use a brief, but understandable form of the publisher's name. Exclude the terms publishers, company, and incorporated. Include Books and Press if it is part of the publisher's name. End this information with a period (See Section 9.29 in the Publication manual for more details).
Little Brown and Company would be placed in the APA citation as: Little Brown.
Oxford University Press would be placed in the citation as: Oxford University Press.
How to Structure Online Sources
For sources found online:
- include the URL at the end of the citation
- do not place a period after the URL
If you're citing a periodical article found online, there might be a DOI number attached to it. This stands for Direct Object Identifier. A DOI, or digital object identifier, is a unique string of numbers and letters assigned by a registration agency. The DOI is used to identify and provide a permanent link to its location on the Internet. The DOI is assigned when an article is published and made electronically. If your article does indeed have a DOI number, use this instead of the URL as the DOI number is static and never changes. If the source you're citing has a DOI number, after the publication information add a period and then http://dx.doi.org/10.xxxx/xxxxxx. The x's indicate where you should put the DOI number. Do not place a period after the DOI number. See sections 9.35-36 in the Publication manual for more details.
If you're using the automatic BibMe APA reference generator, you will see an area to type in the DOI number.
Lobo, F. (2017, February 23). Sony just launched the world's fastest SD card. http://mashable.com/2017/02/23/sony-sf-g-fastest-sd-card/?utm_cid=mash-prod-nav-sub-st#ErZKV8blqOqO
Chadwell, F.A., Fisher, D.M. (2016). Creating open textbooks: A unique partnership between Oregon State University libraries and press and Open Oregon State. Open Praxis, 8 (2), 123-130. http://dx.doi.org/10.5944/openpraxis.8.2.290
Looking for more help and clarification? Check out this great resource !
Citations and Examples
Citations for print books.
Author's Last name, First name initial. Middle name initial. (Year published). Title of book . Publisher.
Finney, J. (1970). Time and again . Simon and Schuster.
Looking for an APA formatter? Don't forget that the BibMe APA citation generator creates citations quickly and easily.
Notes: When creating an APA book citation, keep these in mind:
- Capitalize the first letter of the first word of the title and any subtitles, as well as the first letter of any proper nouns.
- The full title of the book, including any subtitles, should be stated and italicized.
Citations for Edited Books
Most edited books state on the cover or title page that they are edited by an author or multiple authors. The format is the same as a print book, except the editor's name is in the author's position. Include a parentheses afterwards with the abbreviation (Ed.) for an edited book by one author or (Eds.) for an edited book with two or more authors.
Editor, F. M. (Ed.). (Year published). Title of edited book . Publisher.
Gupta, R. (Ed.). (2003). Remote sensing geology . Springer-Verlag.
Citations for Chapters in Edited Books
Some edited books contain chapters written by various authors. Use the format below to cite an author's individual chapter in an edited book.
Chapter author's Last name, F. M. (Year published). Title of chapter. In F. M. Last name of Editor (Ed.), Title of book (p. x or pp. x-x). Publisher.
Notice that for APA style, the title of the chapter is not italicized, while the title of the book is. In addition, the chapter author's name is reversed at the beginning of the reference, but the editor's name is written in standard order.
Longacre, W. A., & Ayres, J. E. (1968). Archeological lessons from an Apache wickiup. In S. R. Binford & L. R. Binford (Eds.), Archeology in cultural systems (pp. 151-160). https://books.google.com/books?id=vROM3JrrRa0C&lpg=PP1&dq=archeology&pg=PR9#v=onepage&q=archeology&f=false
In the above example, Longacre and Ayers are the authors of the individual chapter and Binford & Binford are the editors of the entire book.
Citing an E-book from an E-reader
E-book is short for "electronic book." It is a digital version of a book that can be read on a computer, e-reader (Kindle, Nook, etc.), or other electronic devices. Include the DOI or URL if one exists for the e-book.
Author's Last name, F. M. (Year published). Title of work . https://doi.org/10.xxxx/xxxxxx or URL
https://doi.org/10.xxxx/xxxxxx is used when a source has a DOI number. If the e-book you're citing has a DOI number, use it in the APA citation. DOIs are preferred over URLs.
How to cite in APA (an e-book example):
Eggers, D. (2008). The circle . https://www.amazon.com
Citing an E-book Found in a Database and Online
Use this format when citing an e-book that is either found on a website, or found on a subscription database. APA formatting for this is very similar to the structure of a print book. The only difference? Instead of the publisher information, include the DOI number or URL.
Author's Last name, F. M. (Year published). Title of work . https://doi.org/10.xxxx/xxxxxx OR URL
When citing an online book or e-book, keep in mind:
- A DOI (digital object identifier) is an assigned number that helps link content to its location on the Internet. It is therefore important, if one is provided, to use it when creating a citation. In place of the x's in the DOI format, place the 10 digit DOI number.
- Notice that for e-books, publication information is excluded from the citation.
Sayre, R. K., Devercelli, A. E., Neuman, M. J., & Wodon, Q. (2015). Investment in early childhood development: Review of the world bank's recent experience . https://doi.org/10.1596/978-1-4648-0403-8
Citations for Chapters in E-books
Need to cite a chapter in an e-book? No problem! Citing a chapter in an e-book is very similar to citing a chapter in a print book. Instead of including the publisher information, include a DOI number (if one is displayed) or the URL.
Chapter author's Last name, F. M. (Year published). Title of chapter. In F. M. Last name of Editor (Ed.), Title of book (p. x or pp. x-x). https://doi.org/10.xxxx/xxxxxx or URL
Epstein W. M. (1999). The ineffectiveness of psychotherapy. In C. Feltham (Ed.), Controversies in psychotherapy and counselling (pp. 65-73). https://doi.org/10.4135/9781446217801.n8
Citations for Websites
How to cite a web page on a website in APA:
Author's Last name, F. M. (Year, Month Day published). Title of article or page . Site Name. URL
APA website citation example:
Citing a web page with a group author:
Group Name. (Year, Month Date published). Title of wep page . Saite Name included if different from Group Name. URL
Centers for Disease Control and Prevention. (2020, February 3). Be prepared to stay safe and healthy in winter . https://www.cdc.gov/features/winterweather/index.html
National Park Service. (n.d.). Enchanting landscapes beneath the parks . https://www.nps.gov/subjects/caves/index.htm
Note: "n.d." stands for "no date" and is used when there is no publication date.
The above follows Section 10.16 of the Publication manual.
Still wondering how to cite a website in APA? Check out BibMe.com! It's quick, simple, and free! Our APA citation machine also builds references for many other styles as well!
Citations for Journal Articles Found in Print
Today, most journal articles are found online, but you may be lucky enough to score a copy of a print version for your research project. If so, use the structure below for your reference:
Author's Last name, F. M. (Year published). Article title. Periodical Title, Volume (Issue), pp.-pp.
Notice that the article's title is only capitalized at the beginning. If there are any proper nouns or subtitles, capitalize the first letter for those words as well. The journal article's title and the volume number are both italicized. In addition, the title of the journal is in title case form (all important words are capitalized).
Nevin, A. (1990). The changing of teacher education special education. Teacher Education and Special Education: The Journal of the Teacher Education Division of the Council for Exceptional Children,13 (3-4), 147-148.
Citations for Journal Articles Found Online
Databases are a popular place to find high quality journal articles. These references are formatted the same way as the print versions, except the DOI or URL is included at the end. If the article has a corresponding DOI number, use it instead of the URL. No URL? Use the homepage of the journal's website for the URL. See Section 10.1 in the Publication manual for additional examples.
Author's Last name, F. M. (Year published). Title of article. Title of Journal, volume number (issue number), page range. https://doi.org/10.xxxx/xxxxxx OR URL
Spreer, P., & Rauschnabel, P. A. (2016). Selling with technology: Understanding the resistance to mobile sales assistant use in retailing. Journal of Personal Selling & Sales Management, 36 (3), 240-263. https://doi.org/10.1080/08853134.2016.1208100
Notes: When creating your online journal article citation, keep in mind:
- This citation style does NOT require you to include the date of access/retrieval date or database information for electronic sources.
- Use the URL of the journal homepage if there is no DOI assigned and the reference was retrieved online. * If the journal article has a DOI number assigned to it, include that number in the citation instead of a URL.
- Don't forget, our free BibMe APA generator is simple to use! Check out BibMe Plus while you're at it! If you have a noun , conjunction , or preposition out of place, we'll flag it and offer suggestions for quick writing fixes!
Citations for a Newspaper Article in Print
Similar to journal articles, most individuals use online newspaper articles for research projects. However, if you're able to get your hands on a print version, use this structure for your reference:
Author's Last name, F. M. (Year, Month Day of Publication). Article title. Newspaper Title, pp. xx-xx.
Rosenberg, G. (1997, March 31). Electronic discovery proves an effective legal weapon. The New York Times, p. D5.
Notes: When creating your newspaper citation, keep in mind:
- Begin page numbers with p. (for a single page) or pp. (for multiple pages).
- Even if the article appears on non-consecutive pages, include all page numbers, and use a comma to separate them. Example: pp. C2, C5, C7-C9.
- Include the full date of publication, not just the year like in most references.
Citations for Newspapers found Online
Use this structure when referencing a newspaper article found on a website or database:
Author's Last name, F. M. (Year, Month Day of Publication). Title of article. Title of Newspaper. URL of newspaper's homepage
Rosenberg, G. (1997, March 31). Electronic discovery proves an effective legal weapon. The New York Times. http://www.nytimes.com
Notes: When citing a newspaper, keep in mind:
- If the article was found on the newspaper's website, include the URL for the newspaper's homepage. For databases, include whatever URL is provided.
- Multiple lines: If the URL runs onto a second line, only break URL before punctuation (except for http://).
- This style does NOT require you to include the date of access for electronic sources. If you discovered a newspaper article via an online database, the database's information is NOT required for the citation either. If you're using the BibMe APA formatter, we make it easy for you by only including what you need in your references!
Citations for Magazines
Citing a magazine article in print:
Author's Last name, F. M. (Year, Month of publication). Article title. Magazine Title, Volume (Issue), page range.
APA format citation:
Tumulty, K. (2006, April). Should they stay or should they go? Time, 167 (15), 3-40.
Notes: When citing a magazine, keep in mind:
- You can find the volume number with the other publication information of the magazine.
- You can typically find page numbers at the bottom corners of a magazine article.
- If you cannot locate an issue number, simply don't include it in the citation.
Citing a magazine article found online:
Author's Last name, F. M. (Year, Month of publication). Article title. Magazine Title, Volume (Issue). URL
Tumulty, K. (2006, April). Should they stay or should they go? Time, 167 (15). http://content.time.com/time/magazine/article/0,9171,1179361,00.html
Notes: When creating an online magazine citation, keep in mind:
*The volume and issue number aren't always on the same page as the article. Check out the other parts of the website before leaving it out of the citation.
Citations for Blogs
Blogs are found on websites and display continuously updated content and posts by a single author, group, or company. A blog shows news updates, ideas, information, and many other types of entries. Similar to journal entries, a blog begins with the date the information was added followed by the content.
If you’re wondering how to cite a blog entry, look no further! Citing a blog is very similar to citing a website.
Citing a blog post:
Last name of Author, First initial. Middle initial. (Year, Month Day blog post was published). Title of blog post. Title of Blog . URL
Gonzalez, J. (2019, February 3). Let’s give our teaching language a makeover. Cult of Pedagogy. https://www.cultofpedagogy.com/language-makeover/
Notice that the blog title only has a capital letter at the beginning. If there are any proper nouns in the title, capitalize the first letter for those as well.
Cite a blog post in the text of the paper:
(Author’s last name, Year)
Author’s last name (Year)
Citations for Research Reports
A research, or technical report, is a piece of work that provides insight into research done by an individual researcher, a group of researchers, or a company or organization.
Citing a research report in print:
Author’s Last Name, F. M. or Organization. (Year published). Title of research report (Report No.). Publisher.
Note: If the publisher is the same as the author, use the name as the the “Author” and don't list the publisher.
Michigan Venture Capital Association. (2018). Annual research report .
Citing an online research report:
Author’s Last Name, F. M. or Organization. (Year published). Title of research report (Report No.). URL
Newson, S. E. & Berthinussen, A. (2019). Improving our understanding of the distribution and status of bats within the Ryevitalise Landscape Partnership Scheme area (BTO Research Report No. 716). https://www.bto.org/sites/default/files/publications/bto rr 716 final website.pdf
Citations for Films
Producer's Last name, F. M. (Producer), & Director's Last name, F. M. (Director). (Release Year). Title of motion picture [Motion picture]. Studio.
Bender, L. (Producer), & Tarantino, Q. (Director). (1994). Pulp fiction [Film]. Miramax.
Citations for Online Films & Videos:
Person who posted the video's Last name, F. M. [User name]. (Year, Month Day of posting). Title of video [Video]. Publishing site. URL
If the name of the individual who posted the YouTube video is not available, begin the citation with the user name and do not place this information in brackets.
Smith, R. [Rick Smith] (2013, September 20). Favre to Moss! [Video]. YouTube. https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=gOP_L6hBjn8
Note: If you're discussing a certain part of the film or video in the body of your project, include a timestamp in the in-text or parenthetical citation. (Pulp Fiction, 1994, 1:15:30). The time stamp is Hours:Minutes:Seconds.
Citations for Images
Citing an image found in a print publication (such as a book or magazine) or museum:
Creator's Last name, F. M. (Year of Publication). Title of image [Format]. Publisher/Museum.
Including the format helps the reader understand and visualize the type of image that is being referenced. It can be [Photograph], [Painting], or another medium.
Roege, W. J. (1938). St. Patrick's Cathedral, Fifth Avenue from 50th St to 51st Street [Photograph]. New York Historical Society.
Citing an image retrieved online:
Similar to citing an image in print, when citing an image found online, place the medium, or format, in the brackets. Capitalize the first letter.
Photographer, F. (Year of Publication). Title of photograph [Photograph]. Publisher. URL
Ferraro, A. (2014). Liberty enlightening the world [Digital image]. Flickr. https://www.flickr.com/photos/afer92/14278571753/in/set-72157644617030616
Citations for TV/Radio Broadcasts
Writer's Last name, F. M. (Writer), & Director's Last name, F. M. (Director). (Year of Airing). Episode title [TV series episode]. In F. M. Executive Producer's Last name (Executive Producer), TV series name . Channel.
Kand, K. (Writer), & Fryman, P. (Director). (2006). Slap bet [TV series episode]. In C. Bays (Executive Producer), How I met your mother. CBS.
TV/Radio Broadcasts found online:
Writer, F. M. (Writer), & Director, F. M. (Director). (Year of Airing). Episode title [Television series episode]. In F. M. Executive Producer's Last name (Executive Producer), TV series name . URL
Kand, K. (Writer), & Fryman, P. (Director). (2006). Slap bet [Television series episode]. In C. Bays (Executive Producer), How I met your mother. https://www.hulu.com/watch/1134858#i0,p30,d0
Note: When citing a TV show or episode, keep in mind:
- IMDB is a great resource for finding the information needed for your citation (Director, Writer, Executive Producer, etc.) * This information can also be found in the opening and closing credits of the show.
Type what you find into the BibMe APA formatter. We'll do the work for you and structure your references properly!
Citations for Songs
To cite in APA a song from an album listened to online, use the following structure:
Songwriter's Last name, F. M. (Copyright year). Title of song [Song recorded by F. M. Last name]. On Album title . Publisher. URL
- If the song is done by a band or group, include the band or group's name instead of an individual's name.
- Only include the "Recorded by F. M. Last name" portion if it's a different individual than the writer.
- The format can be CD, Online song, mp3, or any other simple description to allow the reader to understand the format.
Swift, T. (2008). Love Story [Song]. On Fearless . Big Machine Records.
If you're using the BibMe APA citation generator to build your references, choose "Music/Audio" from the source options.
Citations for Interviews
A personal interview should NOT be included in a reference list. They are not considered recoverable data (they cannot be found by a researcher). You should reference personal interviews as citations in the body of the project instead.
(J. Doe, personal communication, December 12, 2004)
Citations for Encyclopedia and Dictionary Entries
Encyclopedia/Dictionary in print:
Author's Last name, F. M. (Publication Year). Entry title. In F. M. Last name of Editor (Ed.), Title of encyclopedia or dictionary (pp. xx-xx). Publisher.
Kammen, C., & Wilson, A. H. (2012). Monuments. Encyclopedia of local history . (pp. 363-364). AltaMira Press.
Encyclopedia/Dictionary online with author(s) :
Author’s Last name, F. M. (Publication Year or n.d.). Entry title. In F. M. Last name of Editor (Ed.), Title of encyclopedia or dictionary . Publisher. Retrieved date, from URL
Encyclopedia/Dictionary online with group author:
Publisher or group name (Publication Year or n.d.). Entry title. In Title of encyclopedia or dictionary . Retrieved date, from URL
Merriam-Webster. (n.d.). Taciturn. In Merriam-Webster.com dictionary . Retrieved February 10, 2020, from https://www.merriam-webster.com/dictionary/taciturn
If an entry looks like it goes through many updates, use “n.d.” as the publication date and show the date you retrieved it. If using an archived version, no retrieval date is needed.
How to Reference a Lecture
This style of reference would be used if you were citing a set of notes from a lecture (e.g., PowerPoint or Google slides provided by your instructor).
Citing online lecture notes or presentation slides:
Author's Last name, F. M. (Publication year). Name or title of lecture [Lectures notes or PowerPoint slides]. URL
Saito, T. (2012). Technology and me: A personal timeline of educational technology [PowerPoint slides]. http://www.slideshare.net/Bclari25/educational-technology-ppt
Tip: If you want to cite information from your own personal notes from a lecture, this is considered personal communication. The notes may not be available online for others outside of the class to access. Refer to it only in the body of your essay or project. You can follow the style guide for personal communication available in the Interview section.
Citing Social Media
Social media is everywhere, even in research projects. Many influencers post thoughts, inspirational quotes, and intriguing stories in their profiles.
If you need to cite a post from a social media platform, use this structure:
Last name, F. M. or Group Name who posted the content [@Username]. (Year, Month Day posted). First 20 words of the post [Format]. Social Media Site Name. URL
A retrieval date (date you saw the page) is needed for profile pages since the contents are likely to change over time (e.g., Instagram profile, Facebook page etc.). The structure for that is:
Last name, F. M. or Group Name who posted the content [@Username]. (n.d.). Tweets or Home [Format]. Social Media Site Name. Retrieved from month day, year, URL
Some things to keep in mind:
- If the name of the individual or group is unknown, begin the citation with the handle and remove the brackets.
- If the post only includes an image or video without any text, instead of including the first 40 words of the post provide a description of the post and place it in brackets: [video of a NASA rocket leaving the atmosphere].
- The format, in brackets, can be [Tweet], [Facebook status update], [Facebook page], [Instagram photo], [Instagram video], or for a Reddit post, use [Online forum comment].
Citing a Tweet from Twitter:
BibMe [@BibMe]. (2020, January 22). How to cite primary sources ow.ly/fUb950vG3N5 [Tweet]. Twitter. https://twitter.com/bibme/status/1219976780746043392
Citing a Twitter profile:
BibMe [@BibMe] (n.d.). Tweets [Twitter profile]. Twitter. Retrieved February 18, 2020, from https://twitter.com/BibMe
Citing a Facebook post:
DeGeneres, E. (2018, December 21). Holiday party goals [Facebook status update]. Facebook. https://www.facebook.com/ellentv/photos/a.182755292239/10157188088077240/?type=3&theater
Citing a Facebook page:
Smithsonian’s National Zoo and Conservation Biology Institute. (n.d.) Home [Facebook page]. Facebook. Retrieved July 22, 2019, from https://www.facebook.com/nationalzoo
Citing an Instagram post:
Lipa, D. [@dualipa]. (2018, December 2). A lil Hollywood glam brunch! Thank you @variety for by Breakthrough Artist of the Year award and thank you for [Instagram photo]. Instagram. https://www.instagram.com/p/Bq33SC2BAsr/?utm_source=ig_web_copy_link
Since this citation style is commonly used in science-related disciplines, it makes sense that many students and scholars include tables in their projects.
It's a good idea to include a table in your project when:
- There is a good amount of quantitative information
- A table would promote understanding
Do not write out the information from the table in the text of your paper. Including the same information in two spots is repetitive. Either type out the quantitative information in your paper or use a table.
If you choose to include a table, make sure to:
- Refer to it in the text and provide a brief overview or snapshot of its contents.
- Refer to the table in the text using numbers. For example, "Table 3 shows the countries with the highest amount of spending per pupil."
- Every table should be numbered. The table mentioned closest to the beginning of the paper should be Table 1. The next table referred to in the paper is Table 2.
- If you're submitting your project for publication in a journal or elsewhere, place all of your tables, in number order, at the end of your project, after the reference list. If you're submitting your project for a class, most professors prefer tables to be situated close to mentions in text. Ask your teacher or professor which one they prefer.
- Each table needs a title. The title of the table should match the content displayed in it. Create a name for your table that is easy to understand. Italicize the title and capitalize the first letter of all major key words.
- Capitalize the first letter of every important word.
- Your table can either be single or double spaced. Keep the spacing in tables consistent throughout your project.
- A general note provides an overview of any information related to the table as well as an explanation of any abbreviations or unique characters. If you reproduced any portion of the table, include that information in the general note as well. Begin your general note with "Note." in italics and ending with period.
- A specific note explains information in a row, column, or individual cell. Place a tiny letter in the top right corner of the area to specify, and include information regarding it in the note below.
- A probability note displays the number of possibilities in the table. Use an asterisk symbol in the table, and show the probability in the notes.
Sample Table:
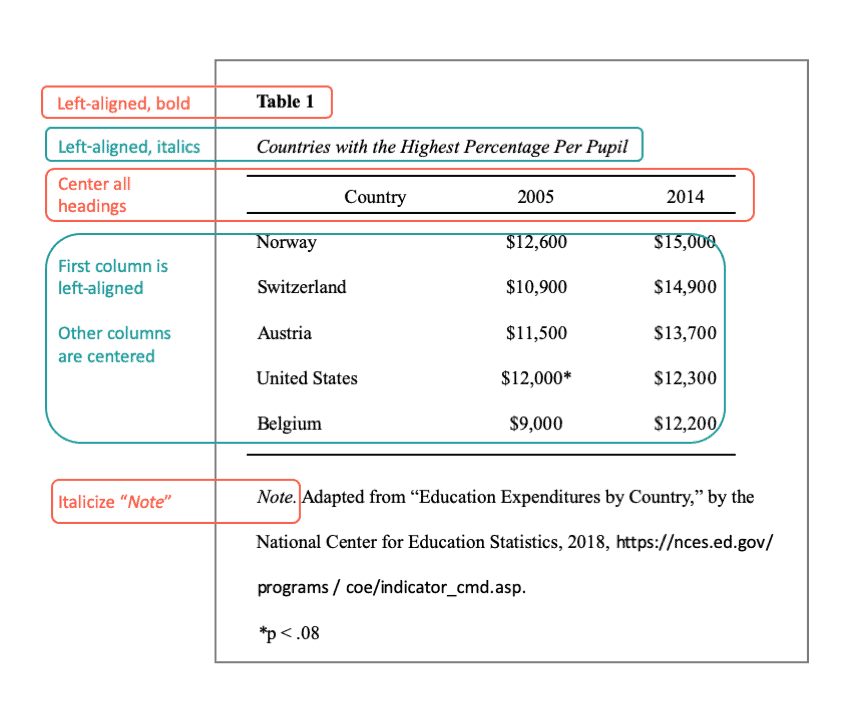
Prior to adding your table into your paper, use this handy checklist to confirm you have all of the requirements:
__ Is it necessary to include the table?
__ Are only horizontal lines included?
__ Did you include a simple, straightforward title? Is it in italics?
__ Did you use either single spaces or double spaces? APA paper format requires you to keep your tables consistent across your project.
__ Are column headings included?
__ Are notes included below the table to provide understanding? Are the notes in the proper order? Start with general notes, then include specific notes, and end with probability notes.
__ Did you refer to the table in the written portion of your paper?
Still have questions? See Chapter 7 of the Publication manual .

In-Text and Parenthetical Citations
What is an in-text citation or parenthetical citation.
The purpose of in-text and parenthetical citations is to give the reader a brief idea as to where you found your information, while they're in the middle of reading or viewing your project. You may include direct quotes in the body of your project, which are word-for-word quotes from another source. Or, you may include a piece of information that you paraphrased in your own words. These are called parenthetical citations. Both direct quotes and paraphrased information include a citation next to it. You also need to include the full citation for the source in the reference list, which is usually the last item in a project.
In-Text Citations for Direct Quotes
In-text and parenthetical citations are found immediately following any direct quotes or paraphrases. They should include the page number or section information to help the reader locate the quote themselves.
Buck needed to adjust rather quickly upon his arrival in Canada. He stated, "no lazy, sun-kissed life was this, with nothing to do but loaf and be bored. Here was neither peace, nor rest, nor a moment's safety" (London, 1903, p. 25).
Paraphrased Information
When taking an idea from another source and placing it in your own words (a paraphrase), it is not necessary to include the page number, but you can add it if the source is large and you want to direct readers right to the information.
At the time, papyrus was used to create paper, but it was only grown and available in mass quantities in Egypt. This posed a problem for the Greeks and Romans, but they managed to have it exported to their civilizations. Papyrus thus remained the material of choice for paper creation (Casson, 2001).
How to Format In-Text and Parenthetical Citations
An in-text citation in APA displays the author's name directly in the sentence, or text, of the paper. Always place the year directly after the author's name. Authors and dates stick together like peanut butter and jelly! If you're citing a direct quote, place the page number at the end of the quote.
Parenthetical citations display the author's name and year in parentheses after a quote or paraphrase. If you're citing a direct quote, include the page number as well. If you're paraphrasing, it is up to you whether or not you'd like to include a page number.
Example of various ways to cite in the body of a project:
Smith (2014) states that, "the Museum Effect is concerned with how individuals look at a work of art, but only in the context of looking at that work along with a number of other works" (p. 82). "The Museum Effect is concerned with how individuals look at a work of art, but only in the context of looking at that work along with a number of other works" (Smith, 2014, p. 82).
If your source has two authors, always include both names in each in-text or parenthetical citation.
Example: (Franks & Beans, 2019)
If your source has three or more authors, only include the first author's name and follow it with et al.
Example: (Gilley et al., 2015)
If your source was written by a company, organization, government agency, or other type of group, include the group's name in full in the first in text or parenthetical citation. In any APA citations following it, it is acceptable to shorten the group name to something that is simple and understandable.
1st citation:
(American Eagle Outfitters /[AEO/], 2017)
2nd and subsequent citations:
(AEO, 2017)
Still wondering how to in-text cite in APA? How about citing parenthetically? Check out this page to learn more about parenthetical citations. Also, BibMe writing tools can help create your in-text and parenthetical citations quickly and easily. Towards the end of creating a full reference citation, you'll see the option to create a citation for the body of your project (in-text) in the APA format generator.
Need help with your writing? Give the BibMe Plus paper checker a whirl! Upload your paper or copy and paste it into the text box on the page. We'll run it through our innovative technology and let you know if there is an adjective , verb , or pronoun out of place, plus much, much more!
Your Reference List
The listing of all sources used in your project are found in the reference list, which is the last page or part of a project. Included in this reference list are all of the sources you quoted or paraphrased in the body of your paper. This means that every reference found in the reference list should have a matching in-text or parenthetical citation in your project. Where there is one, there has to be the other. Here are general guidelines:
- Your reference page in APA should be titled "References"
- Place the title in the center of the page and bold it.
- It is not necessary to include personal communications in the reference list, such as personal emails or letters. These specific sources only need in-text citations, which are found in the body of your project.
- All references are listed in alphabetical order by the author's last name.
- The entire page should be double spaced.
- Use a hanging indent for all citations. The first line of each citation needs to be flush against the left margin. Any additional lines are indented in a half inch.
- If you have two sources by the same author, place them in order by the year of publication.
- Refer to the section titled, "How to Structure the Title," for rules regarding capitalization of source titles.
Thompson, H. S. (1971). Fear and loathing in Las Vegas: A savage journey to the heart of the American dream . Random House.
Thompson, H. S. (1998). The rum diary . Simon & Schuster.
If there are multiple sources with the same author AND same publication date, place them in alphabetical order by the title.
Dr. Seuss. (1958). The cat in the hat comes back . Random House.
Dr. Seuss. (1958). Yertle the turtle . Random House.
If a source does not have an author, place the source in alphabetical order by the first main word of the title.
Need help creating the citations in your APA reference list? BibMe.com helps you generate citations! Begin by entering a keyword, URL, title, or other identifying information. Try it out!
Sample Reference List:

Here's more information with sample papers and tutorials. Further information acan be found in Chapter 9 of the Publication manual .
How to Format Your Paper in APA:
Need to create APA format papers? Follow these guidelines:
In an APA style paper, the font used throughout your document should be in Times New Roman, 12 point font size. The entire document should be double spaced, even between titles and APA headings. Margins should be 1 inch around the entire document and indent every new paragraph using the tab button on your keyboard. See Chapter 2 of the Publication manual for more details on paper formatting.
Place the pages in the following order:
- Title page (Page 1)
- Abstract page (page 2)
- Text or body of research paper (start on page 3)
- Reference list
- Page for tables (if necessary)
- Page for figures (if necessary)
- Appendices page (if necessary)
Page numbers: The title page counts as page 1. Number subsequent pages using Arabic numbers (1, 2, 3, 4...).
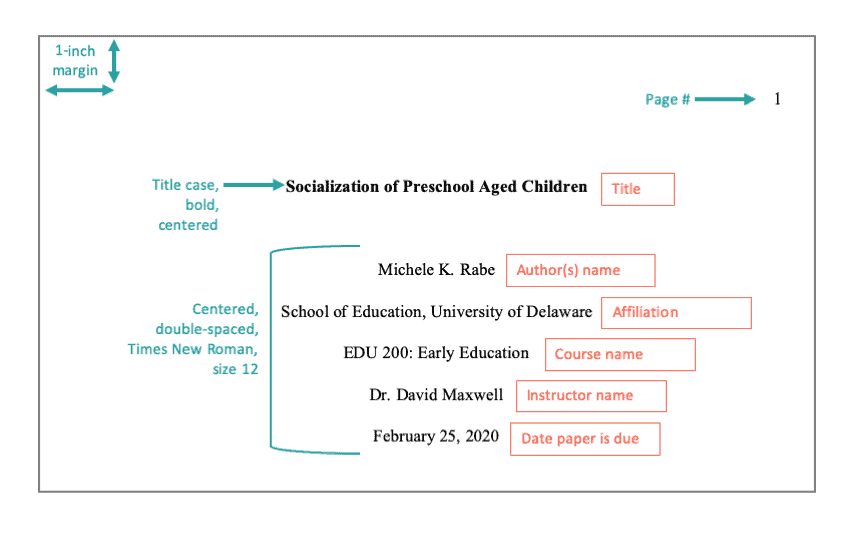
Title Page in APA
Your title page should grace the front cover of your paper. It's sometimes called an APA cover page. Included on this page are seven items:
- Page number
- Title of paper
- Name of authors
- Affiliation; name of your school or institution
- Course name
- Instructor's name
- Date paper is due
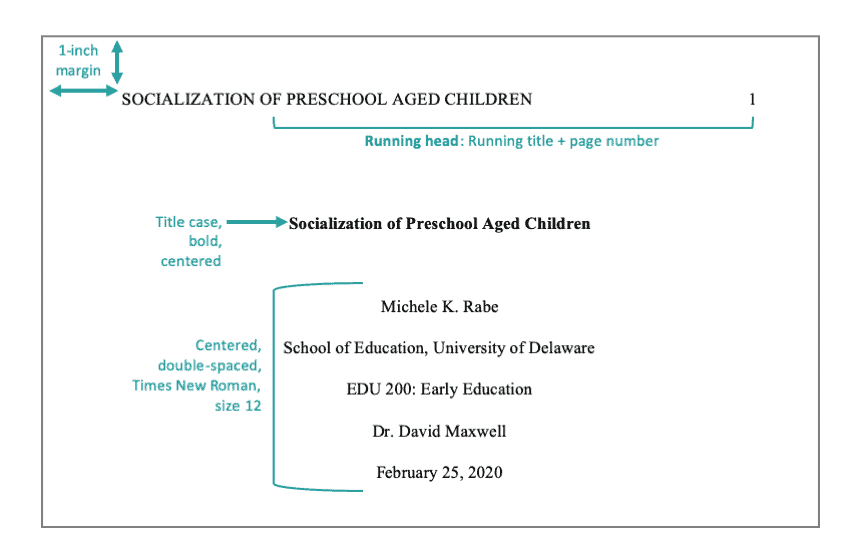
What is a running head?
The running head shows the title of your paper. It is only required for professional papers (e.g., dissertations, journal submissions, etc.).
Student papers do not need a running head (but do need the page number).
If you use one, place the running head in the top left corner of your project and place it in capital letters. Use your word processor's "header" option. It will automatically place your running head in the appropriate position, against the left margin.
Across from the running head, against the right margin, include the page number. The APA title page is 1.
Title page example:
- QUALITY LIBRARY PROGRAMS
Microsoft Word, Google Docs, and many other word processing programs allow you to set up page numbers and a repeated running head. Use these tools to make this addition easier for you!
Need help determining the title of your paper? Keep it simple and straight to the point. Exclude unnecessary terms such as "An Analysis of...." or "A Study of..." If your paper ends up being digitized and added to your school's research collection or a research database, a simple and effective title will help researchers locate it. It is recommended to keep it under 12 words and avoid abbreviations.
Order | Element | Format & Notes --- | --- | --- 0 | All elements, except page number | Centered, double-spaced lines 1 | Page number | Place “1” in the upper right corner of the page. Professional papers only: Include a running head. 2 | Title of paper | 3-4 lines from the top of the page; bolded, and title case 3 | Name of author(s) | Two double-spaced lines under the title. No font formatting (no bold italics, underline). Exclude any titles (such as Dr. or Ms.) and degrees (such as PhD). List all contributors; if there is more than one include the word “and” between the second to last and last names. 4 | Affiliation (school, department, etc.) | No font formatting. Usually includes the name of your department and university. 5 | Course name | No font formatting. Write the course name and number on your class materials: ENG 102, JPN301. 6 | Instructor | No font formatting. Show their name as they prefer, including titles and degrees. 7 | Date paper is due | Month Day, Year. Example: February 14, 2020
Example Title Page - Student Paper:
Example Title Page - Professional Paper:
If you're looking for an APA sample paper, check out the other resources found on BibMe.com.
Levels of Headings:
There are a lot of rules to follow when it comes to styling the header and title page, but there are even more rules when it comes to styling the various headings and sections in your research paper.
There are five sizes and styles, and they follow a top down approach.
In most cases, science-related papers and case studies have three sections: Method, Results, and Discussion. These three sections are considered “Level 1” and are aligned in the center of the page and in bold. Additional sections of the paper are styled as follows:
Overview of Levels
Level | Formatting --- | --- 1 | Center and bold. Use title case. 2 | Against the left margin and in bold. Use title case. Begin the next sentence on the next line, indented half an inch from the left margin. 3 | Against the left margin in bold and italics. Use title case. Begin your next sentence on the next line, and indented half an inch from the left margin. 4 | Indented half an inch from the left. Is in bold. Use title case. Begin your next sentence on the same line and immediately following the heading. 5 | Indented half an inch from the left. Is in bold and italics. Use title case. Begin your next sentence on the same line and immediately following the heading.
We’ve included a visual below to help you make sense of the five headings. Keep in mind, you do not need to have all five headings in your paper. You may only use the top two or three. It depends on the types of sections your paper includes.

Using the BibMe Online Writing Center to Create Citations for your Reference List or Bibliography
Looking to cite your sources quickly and easily? BibMe can help you generate your citations; simply enter a title, ISBN, URL, or other identifying information.
Click to see more styles , and if you'd like to cite your sources in MLA format , check out the BibMe MLA page. Other citation styles are available as well.
Not only will BibMe help you create your references quickly and painlessly, we'll also scan your paper with an innovative plagiarism checker . BibMe writing tools even helps to check your grammar, too! Improper usage of adverb ? Missing an interjection ? Determiner out of place? BibMe writing tools will highlight any areas of concern and offer suggestions to improve your writing. Try it out now!
Background Information and History of APA:
The American Psychological Association was founded in 1892 at Clark University in Worcester, Massachusetts. APA style format was developed in 1929 by scholars from a number of different scientific fields and backgrounds. Their overall goal was to develop a standard way to document scientific writing and research.
Since its inception, the Style Manual has been updated numerous times and it is now in its 7th edition (2020). The previous 6th edition was released in 2009. In 2012, APA published an addition to their 6th edition manual, which was a guide for creating an APA style citation for any type of electronic resource.
Today, there are close to 118,000 members. There is an annual convention, numerous databases, and journal publications. Some of their more popular resources include the database, PsycINFO, and the publications, Journal of Applied Psychology and Health Psychology .
Changes Between the 6th and 7th Editions
Below is a selection of notable citing differences between the two editions.
For journal articles with a DOI number , include the DOI as a URL.
6th edition example:
Lee, C.-H., & Mackinnon, R. (2019). Voltage sensor movements during Hyperpolarization in the HCN Channel. Cell Studies . doi: 10.1016/j.cell.2019.11.006
7th edition example:
Lee, C.-H., & Mackinnon, R. (2019). Voltage sensor movements during Hyperpolarization in the HCN Channel. Cell Studies . https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cell.2019.11.006
For ebooks , you no longer need to identify the format.
Murakami, H. (2014). Kafka on the shore [Kindle].
Murakami, H. (2014). Kafka on the shore .
Full book references no longer need to show where the publisher is located.
Murakami, H. (2014). Kafka on the shore . London: Vintage Publishing.
Murakami, H. (2014). Kafka on the shore . Vintage Publishing.
In-text citations for sources with more than 3 authors can use the notation “et al.” for brevity.
(first author’s name et al., year published)
(Anaydike, Braga, Talfah, Gonzalez, 1980)
(Anaydike et al., 1980)
When including a website URL , do not include the words “Retrieved from” before the URL cited.
Elan, P. (2019, December 6). 'A reflection of inner life': show explores history of the hoodie. The Guardian . Retrieved from https://www.theguardian.com/fashion/2019/dec/06/a-reflection-of-inner-life-show-explores-history-of-the-hoodie
Elan, P. (2019, December 6). 'A reflection of inner life': show explores history of the hoodie. The Guardian . https://www.theguardian.com/fashion/2019/dec/06/a-reflection-of-inner-life-show-explores-history-of-the-hoodie
The citing format for tables and figures are now the same. For both, indicate a table number and name at the top, and a note at the bottom.
Here are a few important paper formatting changes: * Running head is only required for professional (not student) papers * Only a single space should be placed after punctuation. * The new style version endorses the use of the singular “they” as an option for a gender neutral pronoun. * The 7th edition promotes the use of “they” as a singular, gender-neutral pronoun. * In addition to the paper title, author name, and institutional affiliation, a cover page for a student paper should also have the course, instructor name, and due date
American Psychological Association. (2020). Publication manual of the American Psychological Association (7th ed.). https://doi.org/101037/0000165-000
Updated March 10, 2020
Edited and written by Elise Barbeau and Michele Kirschenbaum. Elise is a citation expert and has her master’s degree in public history/library science. She has experience in digital marketing, libraries, and publishing. Michele is a certified library media specialist who loves citations and teaching. She’s been writing about citing sources since 2014.
- Citation Guides
- Chicago Style
- Terms of Use
- Global Privacy Policy
- Cookie Notice
- DO NOT SELL MY INFO
- Plagiarism and grammar
- Citation guides
MLA Citation Generator
Keep all of your citations in one safe place
Create an account to save all of your citations
Don't let plagiarism errors spoil your paper
The complete guide to mla & citations, what you’ll find in this guide.
This page provides an in-depth overview of MLA format. It includes information related to MLA citations, plagiarism, proper formatting for in-text and regular citations, and examples of citations for many different types of sources.
Looking for APA? Check out the Citation Machine’s guide on APA format . We also have resources for Chicago citation style as well.
How to be a responsible researcher or scholar
Putting together a research project involves searching for information, disseminating and analyzing information, collecting information, and repurposing information. Being a responsible researcher requires keeping track of the sources that were used to help develop your research project, sharing the information you borrowed in an ethical way, and giving credit to the authors of the sources you used. Doing all of these things prevents plagiarism.
What is Plagiarism?
Plagiarism is the act of using others’ information without giving credit or acknowledging them. There are many examples of plagiarism. Completely copying another individual’s work without providing credit to the original author is a very blatant example of plagiarism. Plagiarism also occurs when another individual’s idea or concept is passed off as your own. Changing or modifying quotes, text, or any work of another individual is also plagiarism. Believe it or not, you can even plagiarize yourself! Reusing a project or paper from another class or time and saying that it’s new is plagiarism. One way to prevent plagiarism is to add citations in your project where appropriate.
What is a Citation?
A citation shows the reader of your project where you found your information. Citations are included in the body of a project when you add a quote to your project. Citations are also included in the body when you’re paraphrasing another individual’s information. These citations in the body of a research paper are called in-text citations. They are found directly next to the information that was borrowed and are very brief to avoid causing distraction while reading a project. These brief citations include the last name of the author and a page number. Scroll down for an in-depth explanation and examples of MLA in-text citations.
In-text citations provide us with a brief idea as to where you found your information, though they usually don't include the title and other components. Look on the last page of a research project to find complete citations.
Complete citations are found on what MLA calls a works-cited list, which is sometimes called an MLA bibliography. All sources that were used to develop a research project are found on the works-cited list. Complete citations are also created for any quotes or paraphrased information used in the text. Complete citations include the author’s name, the title, publisher, year published, page numbers, URLs, and a few other pieces of information.
Looking to create your citations in just a few clicks? Need an MLA format website or book citation? Visit Citation Machine.net! Our Citation Machine MLA generator, which is an MLA citation website, will create all of your citations in just a few clicks. Click here to see more styles .
Why Does it Matter?
Citing your sources is an extremely important component of your research project. It shows that you’re a responsible researcher and that you located appropriate and reputable sources that support your thesis or claim. In addition, if your work ends up being posted online or in print, there is a chance that others will use your research project in their own work!
Scroll down to find directions on how to create citations.
How the Modern Language Association Helps You Become a Responsible Researcher
What is mla format.
The Modern Language Association is an organization that was created to develop guidelines on everything language and literature related. They have guidelines on proper grammar usage and research paper layouts. In addition, they have English and foreign language committees, numerous books and journal publications, and an annual conference. They are not connected with this guide, but the information here reflects the association’s rules for formatting papers and citations.
What are citations?
The Modern Language Association is responsible for creating standards and guidelines on how to properly cite sources to prevent plagiarism. Their style is most often used when writing papers and citing sources in the liberal arts and humanities fields. “Liberal arts” is a broad term used to describe a range of subjects including the humanities, formal sciences such as mathematics and statistics, natural sciences such as biology and astronomy, and social sciences such as geography, economics, history, and others. The humanities focuses specifically on subjects related to languages, art, philosophy, religion, music, theater, literature, and ethics.
Believe it or not, there are thousands of other types of citation styles. While this citation style is most often used for the liberal arts and humanities fields, many other subjects, professors, and schools prefer citations and papers to be styled in MLA format.
What’s the difference between a bibliography and a works-cited list?
Great question. The two terms cause a lot of confusion and are consistently misused not only by students but educators as well! Let’s start with what the two words mean.
A bibliography displays the sources the writer used to gain background knowledge on the topic and also research it in-depth. Before starting a research project, you might read up on the topic in websites, books, and other sources. You might even dive a bit deeper to find more information elsewhere. All of these sources you used to help you learn about the topic would go in an MLA format bibliography. You might even include other sources that relate to the topic.
A works-cited list displays all of the sources that were mentioned in the writing of the actual paper or project. If a quote was taken from a source and placed into a research paper, then the full citation goes on the works-cited list.
Both the works-cited list and bibliography go at the end of a paper. Most teachers do not expect students to hand in both a bibliography AND a works-cited list. Teachers generally expect to see a works-cited list, but sometimes erroneously call it a bibliography. If you’re not sure what your teacher expects, a page in MLA bibliography format, a works-cited list, or both, ask for guidance.
Why do we use this MLA style?
These specific guidelines and standards for creating citations were developed for numerous reasons. When scholars and researchers in literature, language, and numerous other fields all cite their sources in the same manner, it makes it easier for readers to look at a citation and understand the different components of a source. By looking at an MLA citation, we can see who the author is, the title of the source, when it was published, and other identifiable pieces of information.
Imagine how difficult it would be to understand the various components of a source if we didn’t all follow the same guidelines! Not only would it make it difficult to understand the source that was used, but it would also make it difficult for readers to locate it themselves. This streamlined process aides us in understanding a researcher’s sources.
How is the new version different than previous versions?
This citation style has changed dramatically over the past couple of years. The MLA Handbook is currently in its 9th edition.
The new version expands upon standards previously set in the 8th edition of the MLA Handbook, including the core elements. The structure of citations remains the same, but some formatting guidance and terminology have changed.
- DOI numbers are now formatted as https://doi.org/xx.xxxx/xxx.xxxx.xxxx
- Seasons in publishing daters are lowercased: spring 2020
- The term “optional elements” is now “supplemental elements”
- “Narrative in-text citations” are called “citations in prose”
In addition, new information was added on the following:
- Hundreds of works-cited-list entries
- MLA formatting for papers
- Punctuation, spelling, and other mechanics of prose
- Chapter on inclusive language
- Notes (bibliographic and content)
For more information on MLA 9, click here .
A Deeper Look at Citations
What do they look like.
There are two types of citations. The first is a full, or complete, citation. These are found at the end of research projects. These citations are usually listed in alphabetical order by the author’s last names and include all of the information necessary for readers to be able to locate the source themselves.
Full citations are generally placed in this MLA citation format:
%%Last name of the author, First name of the author. “Source’s Title.” Container’s Title, roles and names of any other individuals who helped contribute to the source, the version of the source, any numbers associated with the source, the name of the publisher, the date the source was published, the location where individuals can find the source themselves (usually a DOI, URL, or page range).
There are times when additional information is added into the full citation.
Not sure how to transfer the information from your source into your citation? Confused about the term, “containers”? See below for information and complete explanations of each citation component.
The second type of citation, called an “in-text citation,” is included in the main part, or body, of a project when a researcher uses a quote or paraphrases information from another source. See the next section to find out how to create in-text citations.
What are in-text citations?
As stated above, in-text citations are included in the main part of a project when using a quote or paraphrasing a piece of information from another source. We include these types of citations in the body of a project for readers to quickly gain an idea as to where we found the information.
These in-text citations are found directly next to the quote or paraphrased information. They contain a small tidbit of the information found in the regular MLA citation. The regular, or complete, citation is located at the end of a project, on the works-cited list.
Here’s what a typical in-text citation looks like:
In the book The Joy Luck Club, the mother uses a vast amount of Chinese wisdom to explain the world and people’s temperaments. She states, “Each person is made of five elements…. Too much fire and you have a bad temper...too little wood and you bent too quickly...too much water and you flowed in too many directions” (Tan 31).
This specific in text citation, (Tan 31), is called an MLA parenthetical citation because the author’s name is in parentheses. It’s included so the reader sees that we are quoting something from page 31 in Tan’s book. The complete, regular citation isn’t included in the main part of the project because it would be too distracting for the reader. We want the reader to focus on our work and research, not get caught up on our sources.
Here’s another way to cite in the text:
In Tan’s novel The Joy Luck Club, the mother uses a vast amount of Chinese wisdom to explain the world and people’s temperaments. She states, “Each person is made of five elements... Too much fire and you have a bad temper... too little wood and you bent too quickly... too much water and you flowed in too many directions" (31).
If the reader would like to see the source’s full information, and possibly locate the source themselves, they can refer to the last part of the project to find the regular citation.
The regular citation, at the end of the project looks like this:
%%Tan, Amy. The Joy Luck Club. Penguin, 1989, p. 31.
Notice that the first word in the full citation (Tan) matches the “Tan” used in the body of the project. It’s important to have the first word of the full citation match the term used in the text. Why? It allows readers to easily find the full citation on the works-cited list.
If your direct quote or paraphrase comes from a source that does not have page numbers, it is acceptable to place a line number (use line or lines), paragraph number (use the abbreviation par. or pars.), sections (sec. or secs.), or chapters (ch. or chs.). Only use these other terms if they are actually labeled on the source. If it specifically says on the source, “Section 1,” for example, then it is acceptable to use “sec. 1” in the in-text citation.
If there are no numbers to help readers locate the exact point in the source, only include the author’s last name.
To determine how to create in-text citations for more than one author, no authors, or corporate authors, refer to the “Authors” section below.
More about quotations and how to cite a quote:
- Use quotes from outside sources to help illustrate and expand on your own points. The majority of your paper should be your own writing and ideas.
- Include the quote exactly as you found it. It is okay to use only certain words or phrases from the quote, but keep the words (spelling and capitalization) and punctuation the same.
- It is acceptable to break up a direct quote with your own writing.
Example from a movie:
Dorothy stated, "Toto," then looked up and took in her surroundings, "I’ve a feeling we’re not in Kansas anymore" ( Wizard of Oz ).
- The entire paper should be double-spaced, including quotes.
- If the quote is longer than four lines, it is necessary to make a block quote. Block quotes show the reader that they are about to read a lengthy amount of text from another source.
- Start the quote on the next line, half an inch from the left margin.
- Do not use any indents at the beginning of the block quote.
- Only use quotation marks if there are quotation marks present in the source.
- If there is more than one paragraph in the block quote, indent the beginning of the paragraphs after the first one an additional half an inch from the left margin.
- Add your in-text citation after the final period of the block quote. Do not add an additional period after the parenthetical citation.
While his parents sat there in surprise, Colton went onto say:
“Cause I could see you,” Colon said matter-of-factly. “I went up and out of my body and I was looking down and I could see the doctor working on my body. And I saw you and Mommy. You were in a little room by yourself, praying; and Mommy was in a different room, and she was praying and talking on the phone.” (Burpo xxi)
How to create a paraphrase:
As stated above, the majority of your paper should be your own writing and ideas. It’s acceptable to include quotes, but they shouldn’t crowd your paper. If you’re finding that you’re using too many quotes in your paper, consider adding paraphrases. When you reiterate a piece of information from an outside source in your own words, you create a paraphrase.
Here’s an example:
Readers discover in the very first sentence of Peter Pan that he doesn’t grow up (Barrie 1).
What paraphrases are:
- Recycled information in the paper writer’s own words and writing style.
- They’re still references! Include an in-text citation next to the paraphrased information.
What paraphrases are not:
- A copy and pasted sentence with a few words substituted for synonyms.
Confused about whether footnotes and endnotes should be used?
Footnotes and endnotes are completely acceptable to use in this style. Use a footnote or endnote if:
- Adding additional information will help the reader understand the content. This is called a content note .
- You need to cite numerous sources in one small section of your writing. Instead of clogging up a small paragraph with in-text citations (which could cause confusion for the reader), include a footnote or endnote. This is called a bibliographic note .
Keep in mind that whether you choose to include in-text citations or footnotes/endnotes, you need to also include a full reference on the MLA format works-cited list.
Content note example:
Even Maurice Sendak’s work (the mastermind behind Where the Wild Things Are and numerous other popular children’s picture books) can be found on the banned books list. It seems as though nobody is granted immunity. 1
- In the Night Kitchen ’s main character is nude on numerous pages. Problematic for most is not the nudity of the behind, but the frontal nudity.
Work Cited:
%%Sendak, Maurice. In The Night Kitchen. Harper Collins, 1996.
Bibliographic note example:
Dahl had a difficult childhood. Both his father and sister passed away when he was a toddler. He was then sent away by his mother to boarding school (de Castella). 1
- Numerous books, such as Matilda, James and the Giant Peach, and The BFG, all feature characters with absent or difficult parents.
MLA Works Cited:
Include 4 full citations for: de Castella’s article, Matilda, James and the Giant Peach, and The BFG .
Don’t forget to create full, or regular citations, and place them at the end of your project.
If you need help with in-text and parenthetical citations, CitationMachine.net can help. Our MLA citation generator is simple and easy to use!
Common Knowledge: What Is It and How Will It Affect My Writing?
Footnotes, endnotes, references, proper structuring. We know it’s a lot. Thankfully, you don’t have to include a reference for EVERY piece of information you add to your paper. You can forget about including a reference when you share a piece of common knowledge.
Common knowledge is information that most people know. For example, these are a few facts that are considered common knowledge:
- The Statue of Liberty is located in New York City
- Tokyo is the capital of Japan
- Romeo and Juliet is a play written by William Shakespeare
- English is the language most people speak in England
- An elephant is an animal
We could go on and on. When you include common knowledge in your paper, omit a reference. One less thing to worry about, right?
Before you start adding tons of common knowledge occurrences to your paper to ease the burden of creating references, we need to stop you right there. Remember, the goal of a research paper is to develop new information or knowledge. You’re expected to seek out information from outside sources and analyze and distribute the information from those sources to form new ideas. Using only common knowledge facts in your writing involves absolutely zero research. It’s okay to include some common knowledge facts here and there, but do not make it the core of your paper.
If you’re unsure if the fact you’re including is common knowledge or not, it doesn’t hurt to include a reference. There is no such thing as being overly responsible when it comes to writing and citing.
Wikipedia - Yay or Nay?
If you’re wondering whether it’s okay to use Wikipedia in your project, the answer is, it depends.
If Wikipedia is your go-to source for quick information on a topic, you’re not alone. Chances are, it’s one of the first websites to appear on your results page. It’s used by tons of people, it’s easily accessible, and it contains millions of concise articles. So, you’re probably wondering, “What’s the problem?”
The issue with Wikipedia is that it’s a user-generated site, meaning information is constantly added and modified by registered users. Who these users are and their expertise is somewhat of a mystery. The truth is anyone can register on the site and make changes to articles.
Knowing this makes some cringe, especially educators and librarians, since the validity of the information is questionable. However, some people argue that because Wikipedia is a user-generated site, the community of registered users serve as “watchdogs,” ensuring that information is valid. In addition, references are included at the bottom of each article and serve as proof of credibility. Furthermore, Wikipedia lets readers know when there’s a problem with an article. Warnings such as “this article needs clarification,” or “this article needs references to prove its validity” are shared with the reader, thus promoting transparency.
If you choose to reference a Wikipedia article in your research project, and your teacher or professor says it’s okay, then you must reference it in your project. You would treat it just as you would with any other web source.
However, you may want to instead consider locating the original source of the information. This should be fairly easy to do thanks to the references at the bottom of each article.
Specific Components of a Citation
This section explains each individual component of the citation, with examples for each section for full citations and in-text citations.
Name of the author
The author’s name is usually the first item listed in the MLA citation. Author names start with the last name, then a comma is added, and then the author’s first name (and middle name if applicable) is at the end. A period closes this information.
Here are two examples of how an author’s name can be listed in a full citation:
Twain, Mark.
Poe, Edgar Allan.
For in-text:
(Author’s Last name page number) or Author’s Last name... (page).
Wondering how to format the author’s name when there are two authors working jointly on a source? When there are two authors that work together on a source, the author names are placed in the order in which they appear on the source. Place their names in this format:
Author 1’s Last Name, First name, and Author 2’s First Name Last Name.
Here are two examples of how to cite two authors:
Clifton, Mark, and Frank Riley.
Paxton, Roberta J., and Michael Jacob Fox.
(Author 1’s Last name and Author 2’s Last name page number) or Author 1’s Last name and Author 2’s Last name... (page).
There are many times when three or more authors work together on a source. This often happens with journal articles, edited books, and textbooks.
To cite a source with three or more authors, place the information in this format:
Author 1’s Last name, First name, et al.
As you can see, only include the first author’s name. The other authors are accounted for by using “et al.” In Latin, et al. is translated to “and others.” If using the Citation Machine citation generator, this abbreviation is automatically added for you.
Here’s an example of a citation for three or more authors:
%%Warner, Ralph, et al. How to Buy a House in California. Edited by Alayna Schroeder, 12th ed., Nolo, 2009.
(Author 1’s Last name et al. page number)
Is there no author listed on your source? If so, exclude the author’s information from the citation and begin the citation with the title of the source.
For in-text: Use the title of the source in parentheses. Place the title in italics if the source stands alone. Books and films stand alone. If it’s part of a larger whole, such as a chapter in an edited book or an article on a website, place the title in quotation marks without italics.
( Back to the Future )
(“Citing And Writing”)
Other in-text structures:
Authors with the same last name in your paper? MLA essay format requires the use of first initials in-text in this scenario.
Ex: (J. Silver 45)
Are you citing more than one source by the same author? For example, two books by Ernest Hemingway? Include the title in-text.
Example: (Hemingway, For Whom The Bell Tolls 12).
Are you citing a film or song? Include a timestamp in the format of hours:minutes:seconds. ( Back to the Future 00:23:86)
Was the source found on social media, such as a tweet, Reddit, or Instagram post? If this is the case, in an MLA format paper, you are allowed to start the citation with the author’s handle, username, or screen name.
Here is an example of how to cite a tweet:
%%@CarlaHayden. “I’m so honored to talk about digital access at @UMBCHumanities. We want to share the @libraryofcongress collection.” Twitter , 13 Apr. 2017, 6:04 p.m., twitter.com/LibnOfCongress/status/852643691802091521.
While most citations begin with the name of the author, they do not necessarily have to. Quite often, sources are compiled by editors. Or, your source may be done by a performer or composer. If your project focuses on someone other than the author, it is acceptable to place that person’s name first in the citation. If you’re using the MLA works cited generator at Citation Machine.net, you can choose the individual’s role from a drop-down box.
For example, let’s say that in your research project, you focus on Leonardo DiCaprio’s performances as an actor. You’re quoting a line from the movie Titanic in your project, and you’re creating a complete citation for it in the works-cited list.
It is acceptable to show the reader that you’re focusing on Leonardo DiCaprio’s work by citing it like this in the MLA works-cited list:
%%DiCaprio, Leonardo, performer. Titanic . Directed by James Cameron. Paramount, 1997.
Notice that when citing an individual other than the author, place the individual’s role after their name. In this case, Leonardo DiCaprio is the performer.
This is often done with edited books, too. Place the editor’s name first (in reverse order), add a comma, and then add the word editor.
If you’re still confused about how to place the authors together in a citation, the tools at CitationMachine.net can help! Our website is easy to use and will create your citations in just a few clicks!
Titles and containers
The titles are written as they are found on the source and in title form, meaning the important words start with a capital.
Here’s an example of a properly written title:
Practical Digital Libraries: Books, Bytes, and Bucks.
Wondering whether to place your title in italics or quotation marks? It depends on whether the source sits by itself or not. If the source stands alone, meaning that it is an independent source, place the title in italics. If the title is part of a larger whole, place the title of the source in quotation marks and the source it is from in italics.
When citing full books, movies, websites, or albums in their entirety, these titles are written in italics.
However, when citing part of a source, such as an article on a website, a chapter in a book, a song on an album, or an article in a scholarly journal, the part is written with quotation marks and then the titles of the sources that they are found in are written in italics.
Here are some examples to help you understand how to format titles and their containers.
To cite Pink Floyd’s entire album, The Wall , cite it as:
%%Pink Floyd. The Wall. Columbia, 1979.
To cite one of the songs on Pink Floyd’s album in MLA formatting, cite it as:
%%Pink Floyd. “Another Brick in the Wall (Part I).” The Wall, Columbia, 1979, track 3.
To cite a fairy tale book in its entirety, cite it as:
%%Colfer, Chris. The Land of Stories. Little Brown, 2016.
To cite a specific story or chapter in the book, cite it as:
%%Colfer, Chris. “Little Red Riding Hood.” The Land of Stories, Little Brown, 2016, pp. 58-65.
More about containers
From the section above, you can see that titles can stand alone, or they can sit in a container. Many times, sources can sit in more than one container. Wondering how? When citing an article in a scholarly journal, the first container is the journal. The second container? It’s the database that the scholarly journal is found in. It is important to account for all containers, so readers are able to locate the exact source themselves.
When citing a television episode, the first container is the name of the show and the second container is the name of the service that it could be streaming on, such as Netflix .
If your source sits in more than one container, the information about the second container is found at the end of the citation.
Use the following format to cite your source with multiple containers :
%%Last name of the author, First name of the author. “Source’s Title.” Container’s Title, roles and names of any other individuals who helped contribute to the source, the version of the source, any numbers associated with the source, the name of the publisher, the date the source was published, the location where individuals can find the source themselves (usually a URL or page range). Title of Second Container, roles and names of any other contributors, the version of the second container, any numbers associated with the second container, the name of the second container’s publisher, the date the second container was published, location.
If the source has more than two containers, add on another full section at the end for each container.
Not all of the fields in the citation format above need to be included in your citation. In fact, many of these fields will most likely be omitted from your citations. Only include the elements that will help your readers locate the source themselves.
Here is an example of a citation for a scholarly journal article found in a database. This source has two containers: the journal itself is one container, and the site it sits on is the other.
%%Zanetti, Francois. “Curing with Machine: Medical Electricity in Eighteenth-Century Paris.” Technology and Culture, vol. 54, no. 3, July 2013, pp. 503-530. Project Muse, muse.jhu.edu/article/520280.
If you’re still confused about containers, the Citation Machine MLA cite generator can help! MLA citing is easier when using the tools at CitationMachine.net.
Other contributors
Many sources have people besides the author who contribute to the source. If your research project focuses on an additional individual besides the author, or you feel as though including other contributors will help the reader locate the source themselves, include their names in the citation.
To include another individual in the citation, after the title, place the role of the individual, the word “by,” and then their name in standard order.
If the name of the contributor comes after a period, capitalize the first letter in the role of the individual. If it comes after a comma, the first letter in the role of the individual is lowercased.
Here’s an example of a citation for a children’s book with the name of the illustrator included:
%%Rubin, Adam. Dragons Love Tacos. Illustrated by Daniel Salmieri, Penguin, 2012.
The names of editors, directors, performers, translators, illustrators, and narrators can often be found in this part of the citation.
If the source that you’re citing states that it is a specific version or edition, this information is placed in the “versions” section of the citation.
When including a numbered edition, do not type out the number, use the numeral. Also, abbreviate the word “edition” to “ed.”
Here is an example of a citation with a specific edition:
%%Koger, Gregory. “Filibustering and Parties in the Modern State.” Congress Reconsidered, edited by Lawrence C. Dodd and Bruce I. Oppenheimer, 10th ed., CQ Press, 2013, pp. 221-236. Google Books, books.google.com/books?id=b7gkLlSEeqwC&lpg=PP1&dq=10th%20edition&pg=PR6#v=onepage&q=10th%20edition&f=false.
Many sources have numbers associated with them. If you see a number different than the date, page numbers, or editions, include this information in the “numbers” section of the citation. For MLA citing, this includes volume and/or issue numbers (use the abbreviations vol. and no.), episode numbers, track numbers, or any other numbers that will help readers identify the specific source that you used. Do not include ISBN (International Standard Book Numbers) in the citation.
It is important to include the name of the publisher (the organization that created or published the source), so that readers can locate the exact source themselves.
Include publishers for all sources except periodicals. Also, for websites, exclude this information when the name of the publisher matches the name of the website. Furthermore, the name of the publisher is often excluded from the citation for second containers, since the publisher of the second container is not necessarily responsible for the creation or production of the source’s content.
Publication dates
Publication dates are extremely important to include in citations. They allow the reader to understand when sources were published. They are also used when readers are attempting to locate the source themselves.
Dates can be written in MLA in one of two ways. Researchers can write dates as:
Day Mo. Year
Mo. Day, Year
Whichever format you decide to use, use the same format for all of your citations. If using the Citation Machine citation generator, the date will be formatted in the same way for each citation.
While it isn’t necessary to include the full date for all source citations, use the amount of information that makes the most sense to help your readers understand and locate the source themselves.
Wondering what to do when your source has more than one date? Use the date that is most applicable to your research.
The location generally refers to the place where the readers can find the source. This includes page ranges, URLs, DOI numbers, track numbers, disc numbers, or even cities and towns.
You can usually leave out http:// or https:// from URLs unless you want to hyperlink them. For DOIs, use http:// or https:// before the DOI: https://doi.org/xx.xxxx/xxx.xxxx.xxxx .
For page numbers, when citing a source found on only one page, use p.
Example: p. 6.
When citing a source that has a page range, use pp. and then add the page numbers.
Example: pp. 24-38.
Since the location is the final piece of the citation, place a period at the end. When it comes to URLs, many students wonder if the links in citations should be live or not. If the paper is being shared electronically with a teacher and other readers, it may be helpful to include live links. If you’re not sure whether to include live links or not, ask your teacher or professor for guidance.
Looking for an online tool to do the work for you? Citation Machine citing tools could help! Our site is simple (and fun!) to use.
Need some more help? There is further good information here .
Common Citation Examples
ALL sources use this format:
%%Last name of the author, First name of the author. “Source’s Title.” Container’s Title, roles and names of any other individuals who helped contribute to the source, the version of the source, any numbers associated with the source, the name of the publisher, the date the source was published, the location where individuals can find the source themselves (usually a URL or page range). *Title of Second Container, roles and names of any other contributors, the version of the second container, any numbers associated with the second container, the name of the second container’s publisher, the date the second container was published, location.
*If the source does not have a second container, omit this last part of the citation.
Remember, the Citation Machine MLA formatter can help you save time and energy when creating your citations. Check out our MLA Citation Machine pages to learn more.
- Journal Articles
How to Format a Paper
When it comes to formatting your paper or essay for academic purposes, there are specific MLA paper format guidelines to follow.
- Use paper that is 8½-by-11 inch in size. This is the standard size for copier and printer paper.
- Use high quality paper.
- Your research paper or essay should have a one-inch margin on the top, bottom, left, and right sides of the paper.
- While most word processors automatically format your paper to have one-inch margins, you can check or modify the margins of your paper by going to the “Page setup” section of your word processor.
Which font is acceptable to use?
- Use an easily readable font, specifically one that allows readers to see the difference between regular and italicized letters.
- Times New Roman, Arial, and Helvetica are recommended options.
- Use 12-point size font.
Should I double-space the paper, including citations?
- Double-space the entire paper.
- There should be a double space between each piece of information in the heading.
- Place a double space between the heading and the title.
- Place a double space between the title and the beginning of the essay.
- The works-cited list should be double-spaced as well. All citations are double-spaced.
Justification & Punctuation
- Text should be left-justified, meaning that the text is aligned, or flush, against the left margin.
- Indents signal to the reader that a new concept or idea is about to begin.
- Use the “tab” button on your keyboard to create an indent.
- Add one space after all punctuation marks.
Heading & Title
- Include a proper heading and title
- The heading should include the following, on separate lines, starting one inch from the top and left margins:
- Your full name
- Your teacher or professor’s name
- The course number
- Dates in the heading and the body of your essay should be consistent. Use the same format, either Day Month Year or Month Day, Year throughout the entire paper
- Examples: 27 July 2017 or July 27, 2017
- The title should be underneath the heading, centered in the middle of the page, without bold, underlined, italicized, or all capital letters.
Page numbers
- Number all pages, including the very first page and the works-cited list.
- Place page numbers in the top right corner, half an inch from the top margin and one inch from the right margin.
- Include your last name to the left of the page number. Example: Jacobson 4
Here’s an example to provide you with a visual:

If you need help with sentence structure or grammar, check out our paper checker. The paper checker will help to check every noun , verb , and adjective . If there are words that are misspelled or out of place, the paper checker will suggest edits and provide recommendations.
- If a citation flows onto the second line, indent it in half an inch from the left margin (called a “hanging indent”).
- For more information on the works-cited list, refer to “How to Make a Works Cited Page,” which is found below.
How to Create a Title Page
According to the Modern Language Association’s official guidelines for formatting a research paper, it is unnecessary to create or include an individual title page, or MLA cover page, at the beginning of a research project. Instead, follow the directions above, under “Heading & Title,” to create a proper heading. This heading is featured at the top of the first page of the research paper or research assignment.
If your instructor or professor does in fact require or ask for an MLA title page, follow the directions that you are given. They should provide you with the information needed to create a separate, individual title page. If they do not provide you with instructions, and you are left to create it at your own discretion, use the header information above to help you develop your research paper title page. You may want to include other information, such as the name of your school or university.
How to Make a Works Cited Page
The MLA Works Cited page is generally found at the end of a research paper or project. It contains a list of all the citations of sources used for the research project. Follow these directions to format the works-cited list to match the Modern Language Association’s guidelines.
- The “Works Cited” page has its own page at the end of a research project.
- Include the same running head as the rest of the project (Your last name and then the page number). The “Works Cited” page has the final page number for the project.
- Name the page “Works Cited,” unless your list only includes one citation. In that case, title it in MLA “Work Cited.”
- The title of the page (either “Works Cited” or “Work Cited”) is placed one inch from the top of the page, centered in the middle of the document.
- Double space the entire document, even between the title of the page and the first citation.
- Citations are listed in alphabetical order by the first word in the citation (usually the last name of the author or the first word in the title if the citation does not include the author’s name. Ignore “A,” “An,” and “The” if the title begins with these words.)
- If there are multiple citations by the same author, place them in chronological order by the date published.
- Also, instead of writing the author’s name twice in both citations, use three hyphens.
%%Angelou, Maya. I Know Why the Caged Bird Sings. Random House, 2009.
%%---. Gather Together in My Name. Random House, 1974.
- All citations begin flush against the left margin. If the citation is long and rolls onto a second or third line, indent the lines below the first line half an inch from the left margin. This is called a “hanging indent.” The purpose of a hanging indent is to make the citations easier to read. If you’re using our MLA citation machine, we’ll format each of your references with a hanging indent for you.
%%Wai-Chung, Ho. “Political Influences on Curriculum Content and Musical Meaning: Hong Kong Secondary Music Education, 1949-1997.” Journal of Historical Research in Music Education, vol. 22, no. 1, 1 Oct. 2000, pp. 5-25. Periodicals Index Online, search-proquest-com.i.ezproxy.nypl.org/pio/docview/1297849364/citation/6B70D633F50C4EA0PQ/78?accountid=35635.
- MLA “Works Cited” pages can be longer than one page. Use as many pages as necessary. If you have only one source to cite, do not place the one citation below the text of your paper. In MLA, a “Work Cited” page is still created for that individual citation.
Here’s a sample paper to give you an idea of what an MLA paper could look like. Included at the end is an MLA “Works Cited” page example.

Looking to add a relevant image, figure, table, or musical score to your paper? Here’s the easy way to do it, while following guidelines set forth by the Modern Language Association:
- Place the image, figure, table, or music close to where it’s mentioned in the text.
- Provide source information and any additional notes directly below the image, figure, table, or music.
For tables:
- Label the table as “Table” followed by an arabic numeral such as “1.” Table 1 is the table closest to the beginning of the paper. The next table mentioned in the text would be Table 2, and so on.
- Create a title for the table and place it below the label. Capitalize all important words.
- The label (Table 1) and the title should be flush against the left margin.
- Double-space everything.
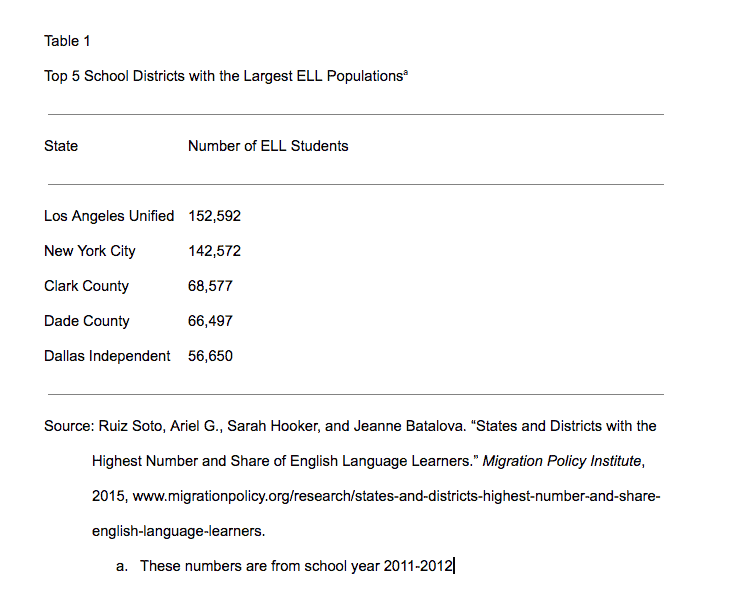
- A figure can be a map, photograph, painting, pie chart, or any other type of image.
- Create a label and place it below the figure. The figure first mentioned in the text of the project is either “Figure 1” or “Fig 1.” Though figures are usually abbreviated to “Fig.” Choose one style and use it consistently. The next mentioned figure is “Figure 2” or “Fig. 2.”, and so on.
- Place a caption next to the label. If all of the source information is included in the caption, there isn’t a need to replicate that information in the works-cited list.
MLA Final Checklist
Think you’re through? We know this guide covered a LOT of information, so before you hand in that assignment, here’s a checklist to help you determine if you have everything you need:
_ Are both in-text and full citations included in the project? Remember, for every piece of outside information included in the text, there should be a corresponding in-text citation next to it. Include the full citation at the end, on the “Works Cited” page.
_ Are all citations, both in-text and full, properly formatted in MLA style? If you’re unsure, try out our citation generator!
_ Is your paper double-spaced in its entirety with one inch margins?
_ Do you have a running header on each page? (Your last name followed by the page number)
_ Did you use a font that is easy to read?
_ Are all citations on the MLA format works-cited list in alphabetical order?
Our plagiarism checker scans for any accidental instances of plagiarism. It scans for grammar and spelling errors, too. If you have an adverb , preposition , or conjunction that needs a slight adjustment, we may be able to suggest an edit.
Common Ways Students Accidentally Plagiarize
We spoke a bit about plagiarism at the beginning of this guide. Since you’re a responsible researcher, we’re sure you didn’t purposely plagiarize any portions of your paper. Did you know students and scholars sometimes accidentally plagiarize? Unfortunately, it happens more often than you probably realize. Luckily, there are ways to prevent accidental plagiarism and even some online tools to help!
Here are some common ways students accidentally plagiarize in their research papers and assignments:
1. Poor Paraphrasing
In the “How to create a paraphrase” section towards the top of this page, we share that paraphrases are “recycled information, in the paper writer’s own words and writing style.” If you attempt to paraphrase a few lines of text and it ends up looking and sounding too close to the original author’s words, it’s a poor paraphrase and considered plagiarism.
2. Incorrect Citations
If you cite something incorrectly, even if it’s done accidentally, it’s plagiarism. Any incorrect information in a reference, such as the wrong author name or the incorrect title, results in plagiarism.
3. Forgetting to include quotation marks
When you include a quote in your paper, you must place quotation marks around it. Failing to do so results in plagiarism.
If you’re worried about accidental plagiarism, try our Citation Machine Plus essay tool. It scans for grammar, but it also checks for any instances of accidental plagiarism. It’s simple and user-friendly, making it a great choice for stress-free paper editing and publishing.
Updated June 15, 2021
Written and edited by Michele Kirschenbaum and Wendy Ikemoto. Michele Kirschenbaum has been an awesome school librarian since 2006 and is an expert in citing sources. Wendy Ikemoto has a master’s degree in library and information science and has been working for Citation Machine since 2012.
- Citation Machine® Plus
- Citation Guides
- Chicago Style
- Harvard Referencing
- Terms of Use
- Global Privacy Policy
- Cookie Notice
- DO NOT SELL MY INFO
Free plagiarism checker by EasyBib
Check for plagiarism, grammar errors, and more.
- Expert Check
Check for accidental plagiarism
Avoid unintentional plagiarism. Check your work against billions of sources to ensure complete originality.

Find and fix grammar errors
Turn in your best work. Our smart proofreader catches even the smallest writing mistakes so you don't have to.

Get expert writing help
Improve the quality of your paper. Receive feedback on your main idea, writing mechanics, structure, conclusion, and more.
What students are saying about us

"Caught comma errors that I actually struggle with even after proofreading myself."
- Natasha J.

"I find the suggestions to be extremely helpful especially as they can instantly take you to that section in your paper for you to fix any and all issues related to the grammar or spelling error(s)."
- Catherine R.

Check for unintentional plagiarism
Easily check your paper for missing citations and accidental plagiarism with the EasyBib plagiarism checker. The EasyBib plagiarism checker:
- Scans your paper against billions of sources.
- Identifies text that may be flagged for plagiarism.
- Provides you with a plagiarism score.
You can submit your paper at any hour of the day and quickly receive a plagiarism report.
What is the EasyBib plagiarism checker?
Most basic plagiarism checkers review your work and calculate a percentage, meaning how much of your writing is indicative of original work. But, the EasyBib plagiarism checker goes way beyond a simple percentage. Any text that could be categorized as potential plagiarism is highlighted, allowing you time to review each warning and determine how to adjust it or how to cite it correctly.
You’ll even see the sources against which your writing is compared and the actual word for word breakdown. If you determine that a warning is unnecessary, you can waive the plagiarism check suggestion.
Plagiarism is unethical because it doesn’t credit those who created the original work; it violates intellectual property and serves to benefit the perpetrator. It is a severe enough academic offense, that many faculty members use their own plagiarism checking tool for their students’ work. With the EasyBib Plagiarism checker, you can stay one step ahead of your professors and catch citation mistakes and accidental plagiarism before you submit your work for grading.

Why use a plagiarism checker?
Imagine – it’s finals week and the final research paper of the semester is due in two days. You, being quite familiar with this high-stakes situation, hit the books, and pull together a ten-page, last-minute masterpiece using articles and materials from dozens of different sources.
However, in those late, coffee-fueled hours, are you fully confident that you correctly cited all the different sources you used? Are you sure you didn’t accidentally forget any? Are you confident that your teacher’s plagiarism tool will give your paper a 0% plagiarism score?
That’s where the EasyBib plagiarism checker comes in to save the day. One quick check can help you address all the above questions and put your mind at ease.
What exactly is plagiarism?
Plagiarism has a number of possible definitions; it involves more than just copying someone else’s work. Improper citing, patchworking, and paraphrasing could all lead to plagiarism in one of your college assignments. Below are some common examples of accidental plagiarism that commonly occur.
Quoting or paraphrasing without citations
Not including in-text citations is another common type of accidental plagiarism. Quoting is taking verbatim text from a source. Paraphrasing is when you’re using another source to take the same idea but put it in your own words. In both cases, it’s important to always cite where those ideas are coming from. The EasyBib plagiarism checker can help alert you to when you need to accurately cite the sources you used.
Patchwork plagiarism
When writing a paper, you’re often sifting through multiple sources and tabs from different search engines. It’s easy to accidentally string together pieces of sentences and phrases into your own paragraphs. You may change a few words here and there, but it’s similar to the original text. Even though it’s accidental, it is still considered plagiarism. It’s important to clearly state when you’re using someone else’s words and work.
Improper citations
Depending on the class, professor, subject, or teacher, there are multiple correct citation styles and preferences. Some examples of common style guides that are followed for citations include MLA, APA, and Chicago style. When citing resources, it’s important to cite them accurately. Incorrect citations could make it impossible for a reader to track down a source and it’s considered plagiarism. There are EasyBib citation tools to help you do this.
Don’t fall victim to plagiarism pitfalls. Most of the time, you don’t even mean to commit plagiarism; rather, you’ve read so many sources from different search engines that it gets difficult to determine an original thought or well-stated fact versus someone else’s work. Or worse, you assume a statement is common knowledge, when in fact, it should be attributed to another author.
When in doubt, cite your source!
Time for a quick plagiarism quiz!
Which of the following requires a citation?
- A chart or graph from another source
- A paraphrase of an original source
- Several sources’ ideas summarized into your own paragraph
- A direct quote
- All of the above
If you guessed option E than you’d be correct. Correct punctuation and citation of another individual’s ideas, quotes, and graphics are a pillar of good academic writing.
What if you copy your own previous writing?
Resubmitting your own original work for another class’s assignment is a form of self-plagiarism, so don’t cut corners in your writing. Draft an original piece for each class or ask your professor if you can incorporate your previous research.
What features are available with the EasyBib plagiarism checker?
Along with providing warnings and sources for possible plagiarism, the EasyBib plagiarism checker works alongside the other EasyBib tools, including a grammar checker and a spell checker . You’ll receive personalized feedback on your thesis and writing structure too!
The plagiarism checker compares your writing sample with billions of available sources online so that it detects plagiarism at every level. You’ll be notified of which phrases are too similar to current research and literature, prompting a possible rewrite or additional citation. You’ll also get feedback on your paper’s inconsistencies, such as changes in text, formatting, or style. These small details could suggest possible plagiarism within your assignment.
And speaking of citations, there are also EasyBib citation tools available. They help you quickly build your bibliography and avoid accidental plagiarism. Make sure you know which citation format your professor prefers!
Great! How do I start?
Simply copy and paste or upload your essay into the checker at the top of this page. You’ll receive the first five grammar suggestions for free! To try the plagiarism checker for free, start your EasyBib Plus three-day free trial.* If you love the product and decide to opt for premium services, you’ll have access to unlimited writing suggestions and personalized feedback.
The EasyBib plagiarism checker is conveniently available 24 hours a day and seven days a week. You can cancel anytime. Check your paper for free today!.
*See Terms and Conditions
Visit www.easybib.com for more information on helpful EasyBib writing and citing tools.
For informational guides and on writing and citing, visit the EasyBib guides homepage .
Purdue Online Writing Lab Purdue OWL® College of Liberal Arts
In-Text Citations: The Basics

Welcome to the Purdue OWL
This page is brought to you by the OWL at Purdue University. When printing this page, you must include the entire legal notice.
Copyright ©1995-2018 by The Writing Lab & The OWL at Purdue and Purdue University. All rights reserved. This material may not be published, reproduced, broadcast, rewritten, or redistributed without permission. Use of this site constitutes acceptance of our terms and conditions of fair use.
Note: This page reflects the latest version of the APA Publication Manual (i.e., APA 7), which released in October 2019. The equivalent resource for the older APA 6 style can be found here .
Reference citations in text are covered on pages 261-268 of the Publication Manual. What follows are some general guidelines for referring to the works of others in your essay.
Note: On pages 117-118, the Publication Manual suggests that authors of research papers should use the past tense or present perfect tense for signal phrases that occur in the literature review and procedure descriptions (for example, Jones (1998) found or Jones (1998) has found ...). Contexts other than traditionally-structured research writing may permit the simple present tense (for example, Jones (1998) finds ).
APA Citation Basics
When using APA format, follow the author-date method of in-text citation. This means that the author's last name and the year of publication for the source should appear in the text, like, for example, (Jones, 1998). One complete reference for each source should appear in the reference list at the end of the paper.
If you are referring to an idea from another work but NOT directly quoting the material, or making reference to an entire book, article or other work, you only have to make reference to the author and year of publication and not the page number in your in-text reference.
On the other hand, if you are directly quoting or borrowing from another work, you should include the page number at the end of the parenthetical citation. Use the abbreviation “p.” (for one page) or “pp.” (for multiple pages) before listing the page number(s). Use an en dash for page ranges. For example, you might write (Jones, 1998, p. 199) or (Jones, 1998, pp. 199–201). This information is reiterated below.
Regardless of how they are referenced, all sources that are cited in the text must appear in the reference list at the end of the paper.
In-text citation capitalization, quotes, and italics/underlining
- Always capitalize proper nouns, including author names and initials: D. Jones.
- If you refer to the title of a source within your paper, capitalize all words that are four letters long or greater within the title of a source: Permanence and Change . Exceptions apply to short words that are verbs, nouns, pronouns, adjectives, and adverbs: Writing New Media , There Is Nothing Left to Lose .
( Note: in your References list, only the first word of a title will be capitalized: Writing new media .)
- When capitalizing titles, capitalize both words in a hyphenated compound word: Natural-Born Cyborgs .
- Capitalize the first word after a dash or colon: "Defining Film Rhetoric: The Case of Hitchcock's Vertigo ."
- If the title of the work is italicized in your reference list, italicize it and use title case capitalization in the text: The Closing of the American Mind ; The Wizard of Oz ; Friends .
- If the title of the work is not italicized in your reference list, use double quotation marks and title case capitalization (even though the reference list uses sentence case): "Multimedia Narration: Constructing Possible Worlds;" "The One Where Chandler Can't Cry."
Short quotations
If you are directly quoting from a work, you will need to include the author, year of publication, and page number for the reference (preceded by "p." for a single page and “pp.” for a span of multiple pages, with the page numbers separated by an en dash).
You can introduce the quotation with a signal phrase that includes the author's last name followed by the date of publication in parentheses.
If you do not include the author’s name in the text of the sentence, place the author's last name, the year of publication, and the page number in parentheses after the quotation.
Long quotations
Place direct quotations that are 40 words or longer in a free-standing block of typewritten lines and omit quotation marks. Start the quotation on a new line, indented 1/2 inch from the left margin, i.e., in the same place you would begin a new paragraph. Type the entire quotation on the new margin, and indent the first line of any subsequent paragraph within the quotation 1/2 inch from the new margin. Maintain double-spacing throughout, but do not add an extra blank line before or after it. The parenthetical citation should come after the closing punctuation mark.
Because block quotation formatting is difficult for us to replicate in the OWL's content management system, we have simply provided a screenshot of a generic example below.

Formatting example for block quotations in APA 7 style.
Quotations from sources without pages
Direct quotations from sources that do not contain pages should not reference a page number. Instead, you may reference another logical identifying element: a paragraph, a chapter number, a section number, a table number, or something else. Older works (like religious texts) can also incorporate special location identifiers like verse numbers. In short: pick a substitute for page numbers that makes sense for your source.
Summary or paraphrase
If you are paraphrasing an idea from another work, you only have to make reference to the author and year of publication in your in-text reference and may omit the page numbers. APA guidelines, however, do encourage including a page range for a summary or paraphrase when it will help the reader find the information in a longer work.
Help | Advanced Search
Computer Science > Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition
Title: mm1: methods, analysis & insights from multimodal llm pre-training.
Abstract: In this work, we discuss building performant Multimodal Large Language Models (MLLMs). In particular, we study the importance of various architecture components and data choices. Through careful and comprehensive ablations of the image encoder, the vision language connector, and various pre-training data choices, we identified several crucial design lessons. For example, we demonstrate that for large-scale multimodal pre-training using a careful mix of image-caption, interleaved image-text, and text-only data is crucial for achieving state-of-the-art (SOTA) few-shot results across multiple benchmarks, compared to other published pre-training results. Further, we show that the image encoder together with image resolution and the image token count has substantial impact, while the vision-language connector design is of comparatively negligible importance. By scaling up the presented recipe, we build MM1, a family of multimodal models up to 30B parameters, including both dense models and mixture-of-experts (MoE) variants, that are SOTA in pre-training metrics and achieve competitive performance after supervised fine-tuning on a range of established multimodal benchmarks. Thanks to large-scale pre-training, MM1 enjoys appealing properties such as enhanced in-context learning, and multi-image reasoning, enabling few-shot chain-of-thought prompting.
Submission history
Access paper:.
- Download PDF
- Other Formats
References & Citations
- Google Scholar
- Semantic Scholar
BibTeX formatted citation
Bibliographic and Citation Tools
Code, data and media associated with this article, recommenders and search tools.
- Institution
arXivLabs: experimental projects with community collaborators
arXivLabs is a framework that allows collaborators to develop and share new arXiv features directly on our website.
Both individuals and organizations that work with arXivLabs have embraced and accepted our values of openness, community, excellence, and user data privacy. arXiv is committed to these values and only works with partners that adhere to them.
Have an idea for a project that will add value for arXiv's community? Learn more about arXivLabs .

IMAGES
VIDEO
COMMENTS
The APA Citation Checker detects missing references in your document. The interactive report then allows you to fix them quickly and easily, resolving issues in seconds. ... I appreciate both the edits and the feedback to increase my knowledge of correct APA formatting and accurate citations. I needed the paper returned quickly, and the team ...
Citation Machine® helps students and professionals properly credit the information that they use. Cite sources in APA, MLA, Chicago, Turabian, and Harvard for free. ... Check your paper for grammar and plagiarism. Catch plagiarism and grammar mistakes with our paper checker.
Scan your paper the way your teacher would to catch unintentional plagiarism. Then, easily add the right citation. Give your paper an in-depth check. Receive feedback within 24 hours from writing experts on your paper's main idea, structure, conclusion, and more. Don't give up sweet paper points for small mistakes.
Enter the URL, DOI, ISBN, title, or other unique source information into the citation generator to find your source. Click the 'Cite' button on the citation machine. Copy your new reference from the citation generator into your bibliography or works cited list. Repeat for each source that has contributed to your work.
Don't forget to check out our APA citation maker while you're at it! Running heads. In older editions of APA, running heads were required for all papers. Since the 7th edition, that's changed. Student paper: No running head; Professional paper: Include a running head; ... toss your entire paper into the Citation Machine Plus plagiarism ...
MyBib is a free bibliography and citation generator that makes accurate citations for you to copy straight into your academic assignments and papers. If you're a student, academic, or teacher, and you're tired of the other bibliography and citation tools out there, then you're going to love MyBib. MyBib creates accurate citations automatically ...
Give your paper an in-depth check. Receive feedback within 24 hours from writing experts on your paper's main idea, structure, conclusion, and more. ... Our easy to read guides come complete with examples and step-by-step instructions to format your full and in-text citations, paper, and works cited in MLA style. There's even information on ...
Catch plagiarism and grammar mistakes with our paper checker. Paste paper. ... No matter what citation style you're using (APA, MLA, Chicago, etc.) we'll help you create the right bibliography. Get started. Check for unintentional plagiarism. Scan your paper the way your teacher would to catch unintentional plagiarism. Then, easily add the ...
Powered by AI, this citation checker reduces the time consumed in finding citations so that you are left to focus on refining the contents of your research paper.The tool can easily spot missing punctuations, incorrect use of et al., and inconsistencies between citations and references, if any.
Generate APA style citations quickly and accurately with our FREE APA citation generator. Enter a website URL, book ISBN, or search with keywords, and we do the rest! ... then download the formatted list and append it to the end of your paper. Done! MyBib supports the following for APA style: ⚙️ Styles: APA 6 & APA 7: 📚 Sources: Websites ...
Scroll back up to the generator at the top of the page and select the type of source you're citing. Books, journal articles, and webpages are all examples of the types of sources our generator can cite automatically. Then either search for the source, or enter the details manually in the citation form. The generator will produce a formatted MLA ...
Welcome to a comprehensive guide on citing sources and formatting papers in the American Psychological Association style. Below are reference and in-text citation examples, directions on formatting your paper, and background information on the style. ... To learn more about citations, check out this page on crediting work. Also, read up on how ...
Very simply, Recite checks that your in text citations match the reference list at the end of your work. First, Recite checks that the authors and dates in the body of your work match up with the references at the end. Then Recite tells you where it finds errors. Recite also checks for a growing list of stylistic errors related to referencing.
Thankfully, the EasyBib Plus plagiarism tool provides all-in-one support to cover all your bases. Our premium essay checker is convenient, easy to use, and includes access to a grammar and spell checker, plus a plagiarism checker. With a single scan, you'll receive personalized feedback to help identify potentially missing citations and help ...
The paper checker will help to check every noun, verb, and adjective. If there are words that are misspelled or out of place, the paper checker will suggest edits and provide recommendations. MLA Works Cited: The works-cited list should be on its own page at the end of the paper.s. If a citation flows onto the second line, indent it in half an ...
Easily check your paper for missing citations and accidental plagiarism with the EasyBib plagiarism checker. The EasyBib plagiarism checker: Scans your paper against billions of sources. Identifies text that may be flagged for plagiarism. Provides you with a plagiarism score. You can submit your paper at any hour of the day and quickly receive ...
When using APA format, follow the author-date method of in-text citation. This means that the author's last name and the year of publication for the source should appear in the text, like, for example, (Jones, 1998). One complete reference for each source should appear in the reference list at the end of the paper.
A technique that might be helpful when you are writing an APA Style paper is to envision one person in your intended audience reading your paper. For example, imagine your instructor reading your paper. If you are writing a paper for a particular journal, imagine a reader of that journal reading your paper.
In this work, we discuss building performant Multimodal Large Language Models (MLLMs). In particular, we study the importance of various architecture components and data choices. Through careful and comprehensive ablations of the image encoder, the vision language connector, and various pre-training data choices, we identified several crucial design lessons. For example, we demonstrate that ...
Metrics and citations Abstract In this article, we discuss and reflect on the essential components of our concurrent session presentation at the American College of Lifestyle Medicine (ACLM) annual conference LM2023, "Implementing Lifestyle Medicine Competencies in Didactic and Clinical Settings for Allied Health Professionals."