- Clean energy
- The advantages and disadvan...

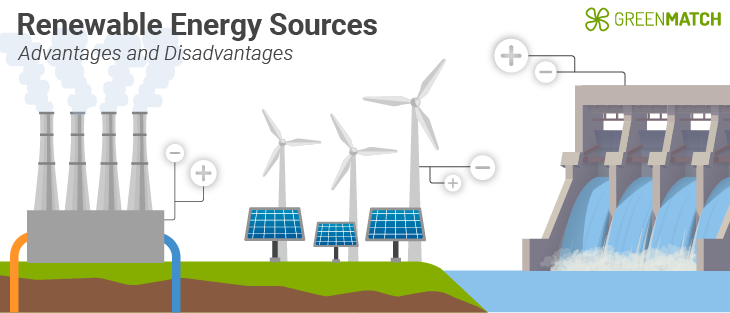
The advantages and disadvantages of renewable energy
- Share to LinkedIn
- Share to Facebook
- Kerry Thoubboron
As subject matter experts, we provide only objective information. We design every article to provide you with deeply-researched, factual, useful information so that you can make informed home electrification and financial decisions. We have:
Sourced the majority of our data from hundreds of thousands of quotes through our own marketplace.
Incorporated third-party data and information from primary sources, government agencies, educational institutions, peer-reviewed research, or well-researched nonprofit organizations.
Built our own database and rating system for solar equipment, including solar panels, inverters, and batteries.
We won't charge you anything to get quotes through our marketplace. Instead, installers and other service providers pay us a small fee to participate after we vet them for reliability and suitability. To learn more, read about how we make money and our Editorial Guidelines .
)
As we move toward a zero-carbon future, wind power, geothermal energy, solar energy, hydropower, tidal energy, hydrogen, and other renewable technologies are becoming widely popular energy sources worldwide. Countries, corporations, and individuals are adopting clean energy for several great benefits, from reduced air pollution to financial savings. In this article, we’ll dive into some of the advantages and disadvantages of renewable energy .
- 100% free to use, 100% online
- Access the lowest prices from installers near you
- Unbiased Energy Advisors ready to help
Here are some of the most important pros and cons of using clean, renewable energy:
Advantages of renewable energy
Renewable energy has multiple advantages over fossil fuels. Here are some of the top benefits of using an alternative energy source:
Renewable energy won’t run out.
Renewable energy has lower maintenance requirements.
Renewables save money.
Renewable energy has numerous environmental benefits.
Renewables lower reliance on foreign energy sources.
Renewable energy leads to cleaner water and air.
Renewable energy creates jobs.
Renewable energy can cut down on waste.
1. Renewable energy won’t run out
Renewable energy technologies use resources straight from the environment to generate power. These energy sources include sunshine, wind, tides, and biomass. Renewable resources won’t run out, which cannot be said for many types of fossil fuels – as we use fossil fuel resources, they will be increasingly difficult to obtain, likely driving up both the cost and environmental impact of extraction.
2. Maintenance requirements are lower for renewable energy
Renewable energy systems usually require less overall maintenance than generators that use traditional fuel sources. This is because generating technology like solar panels and wind turbines either have few or no moving parts and don’t rely on flammable, combustible fuel sources to operate. Fewer maintenance requirements translate to more time and money saved.
3. Renewables save money
Using renewable energy can help you save money long term. Not only will you save on maintenance costs but also on operating costs. You don't have to pay to refuel when you’re using a technology that generates power from the sun, wind, steam, or natural processes. The amount of money you will save using renewable energy can vary depending on several factors, including the technology itself. In most cases, transitioning to renewable energy means anywhere from hundreds to thousands of dollars in savings—find out how much you can save by switching to solar energy .
4. Renewable energy has numerous environmental benefits
Renewable energy generation sources lead to lower greenhouse gas emissions than traditional fuel sources like natural gas. This means a smaller carbon footprint and an overall positive impact on the natural environment . During the combustion process, fossil fuels emit high amounts of greenhouse gases, which have been proven to exacerbate climate change, which in turn causes rising global temperatures and higher frequencies of extreme weather events.
The use of fossil fuels emits greenhouse gases and other harmful pollutants that lead to respiratory and cardiac health issues . With renewable energy, you’re helping decrease these pollutants' prevalence and contributing to a healthier atmosphere.
5. Renewables lower reliance on foreign energy sources
With renewable energy technologies, you can produce energy locally. The higher the amount of our energy use is renewable, the less we’ll rely on imported energy, and the more we’ll contribute to U.S. energy independence. Renewable energy sources can help us minimize the geo-political risks associated with fossil fuels, from trade disputes to political instability to pricing wars, which are often rooted in access to oil.
6. Renewable energy leads to cleaner water and air
When you burn fossil fuels to generate electricity, it contaminates the air and water we use. For example, coal power stations release high volumes of carbon dioxide, nitrous oxide, and harmful toxins like mercury, lead, and sulfur dioxide. Health problems from ingesting these elements can be dangerous and even fatal. Investing in renewable energy is a great way to work against these risks, as renewables have a far lower negative impact on our air and water.
The use of fossil fuels emits greenhouse gases and other harmful pollutants that lead to respiratory and cardiac health issues . With renewable energy, you’re helping decrease these pollutants' prevalence and contributing to a healthier environment.
7. Renewable energy creates new jobs
While the U.S. shifts its focus to combat global warming, we’re setting ambitious carbon-reduction goals that require labor to get the job done. Today, the renewable energy sector employs three times as many people as fossil fuels in the U.S. That number is expected to rise over the next few years—and as a plus, these jobs tend to pay above average wages, making it a desirable career option and an overall economic boom.
8. Renewable energy can help solve our waste problem
Specifically, biomass energy can offer a significant benefit in this way. Biomass generators consume used organic products like vegetable oil, corn and soybean byproducts, and even algae to generate energy. Because of this, using biomass as an energy source can reduce the amount of waste that goes into landfills, which helps cut down on carbon emissions and environmental contamination.
Disadvantages of renewable energy
Renewable energy has many benefits, but it’s not always sunny when it comes to renewable energy. Here are some cons of renewable energy when compared to traditional fuel sources:
Renewable energy has high upfront costs.
Renewable energy is intermittent.
Renewables have storage capabilities.
Renewable energy sources have geographic limitations.
Renewables aren’t always 100% carbon-free.
1. Higher upfront cost
While you can save money using renewable energy, the technologies are typically more expensive upfront than traditional energy generators. To combat this, financial incentives such as tax credits and rebates are available to help alleviate your initial costs of renewable technology.
2. Intermittency
Though renewable energy resources are available around the world, many of these resources aren’t available 24/7, year-round. Some days may be windier than others, the sun doesn’t shine at night, and droughts may occur for periods. Unpredictable weather events can disrupt these technologies, and the amount of energy we can get from renewable power sources can be inconsistent. Fossil fuels are not intermittent, and power plants can be turned on or off at any time to provide an energy supply. Wondering if you should make the switch to renewables? Find out if an energy source like solar power is a good fit for you .
3. Storage capabilities
Because of the intermittency of some renewable energy sources, there’s a high need for energy storage. Storage technologies are available but can be expensive, especially for large-scale renewable energy plants. It’s worth noting that energy storage capacity is growing as the technology progresses, and batteries are becoming more affordable as time passes.
4. Geographic limitations
The United States has a diverse geography with varying climates, topographies, vegetation, etc. This creates a beautiful melting pot of landscapes but also means that some geographies are more suitable for renewable technologies than others. For example, a large property in a rural area with open space may be an excellent place for a residential wind farm or a large-scale solar farm. At the same time, a townhome in a city covered in shade from taller buildings wouldn’t be able to reap the benefits of either technology. There are other options if your property isn’t suitable for a personal renewable energy technology. If you’re interested in solar but don’t have a sunny property, you can often still benefit from renewable energy by purchasing green power or enrolling in a community solar option .
5. Not 100% carbon-free
Although solar panels and other forms of renewable energy drastically reduce carbon emissions, these resources aren’t always completely clean. The manufacturing, transportation, and installation of renewable energy, like wind turbines, can create a carbon footprint since they’re usually produced in factories powered by fossil fuels —not to mention the diesel and gasoline needed to fuel the transport trucks. As the U.S. becomes more and more electrified – from solar panels on factories to electric transport trucks – carbon emissions associated with solar will continue to decrease.
6. Supply chain constraints
Renewables must have an effective distribution network created to transfer the energy where it’s needed on a large scale. These networks need non-renewable fuels to be generated, which offsets the benefits of renewable energy for a bit until it’s paid back. Additionally, politics can play a factor in installing renewable energy if it’s not a priority among local governments.
Types of renewable energy sources
There are a few types of renewable sources we can use for energy production:
Wind energy leverages the power of wind motion to generate electricity created by the uneven heating of the Earth’s surface.
Solar power uses energy from the sun to generate electricity and heat.
Hydropower utilizes fast-moving water to spin turbines and generate electricity. This is also known as hydroelectric power or hydroelectricity.
Biomass generates electricity from organic plant matter.
Geothermal energy leverages heat from inside the earth to generate electricity.
Tidal produces electricity with special generators that leverage the surges of the ocean created during rising and falling tides. Hydrogen: utilized as fuel and electricity when separated from other elements like oxygen.
Nuclear energy , while not technically renewable, is often lumped in with the abovementioned sources. Nuclear power has the potential to provide electricity generation on a massive scale with zero emissions, making it an intriguing part of our energy future.
Renewable energy has more benefits than drawbacks
When it comes to renewable energy, the positives outweigh the negatives. Transitioning to renewables on a personal, corporate, or governmental level will help you save money and promote a cleaner, healthier environment for the future.
Installing solar panels is one of the easiest ways to go green. By signing up on the EnergySage Solar Marketplace , you can compare multiple quotes from local, pre-screened installers to see what solar costs and savings for your property. The quotes will also include estimates of the amount of carbon dioxide emissions you will offset over 20 years and what this equates to in both trees planted and gallons of gasoline burned.
Create your own clean energy with solar panels.
Enjoy the benefits of solar without rooftop panels.
Explore heat pumps, the latest in clean heating & cooling technology.
See solar prices near you.
Enter your zip code to find out what typical solar installations cost in your neighborhood.
- Our offerings
- Community solar
- Heating & cooling
- Backup power
- EV charging
- For your business
- Other energy options
- Solar calculator
- Solar rebates
- Help center
- Home solar guide
- Market intel
- Refer a friend
- Mission & values
- How it works
- Editorial guidelines
- Work with us
- Solar & HVAC installers
- Corporate partnerships
- Community programs
- Utility programs
ENERGYSAGE is a registered trademark and the EnergySage logo is a trademark of EnergySage, Inc. Other trademarks are the property of either EnergySage, Inc. or our licensors and are used with permission.
© Copyright 2009-2024 EnergySage, Inc. All rights reserved.
Learn more about our success working with the U.S. Department of Energy.
New developments in renewable energy are making headlines and inspiring hope in communities worldwide, from a remote Arctic village working to harness solar and wind power under challenging conditions to a U.S. Air Force base planning an advanced, utility-scale geothermal power system.
As much of the world grapples with mitigating the effects of climate change and global warming, innovation and advancements in renewable energy have emerged as a bright spot. Solar energy, wind energy, hydropower, geothermal energy and biomass energy generation is better for the planet than the burning of fossil fuels including oil, natural gas and coal.
But for all of the advantages of renewable energy, its development and use has disadvantages, too. Let’s take a look at both.
The multiple (and sometimes surprising) advantages of renewable energy
The advantages of renewable energy power sources are wide-ranging, and some are more obvious than others.
Inexhaustible supply
One of the main benefits of renewable energy sources like the sun, wind and water is that they will never run out. In contrast, non-renewable resources are not only finite, but cost more as their availability declines and require more extreme extraction methods with greater environmental impacts.
Carbon-free energy generation
The goal of the clean energy transition is decarbonization . Carbon dioxide emissions reached 11.2 gigatonnes (Gt) in 2022 from oil alone, whereas renewable energy generation emits little to no carbon emissions to power homes, cars and businesses.
A cleaner, healthier environment
The burning of fossil fuels, like coal, releases airborne pollutants such as nitrogen oxide and sulfur dioxide, while the mining of these resources can result in water pollution and damage animal habitats. Using renewable energy in place of fossil fuels can reduce these pollutants and help mitigate risks to human health and natural environments.
Energy independence
Renewable energy provides for stronger energy security by opening up new opportunities for domestic energy production, thereby reducing reliance on foreign-sourced energy supply. For example, since Russia’s invasion of Ukraine, European countries have sought to reduce their imports of Russian oil and gas. In 2023, domestic renewable energy production in Europe rose to account for a record 44% of the EU’s electricity mix while imports from Russia declined, helping build a more stable, resilient power grid.
Less maintenance
For certain types of renewable energy sources, the maintenance and maintenance costs of their infrastructure are minimal. Solar photovoltaic systems, for example, generally don’t have moving parts and can last 25 years or more with little maintenance. Hydroelectric power plants typically have low operating costs and require little maintenance as well, with long-lasting equipment that can remain in operation for decades.
Affordable energy
When it comes to costs, renewable energy sources once compared unfavorably to fossil fuels. But as fossil fuel prices rise renewable energy has emerged as an affordable alternative energy option. An estimated 96% of new utility-scale solar and wind power projects had lower generation costs than new coal and natural gas plants. As more renewable energy resources are integrated into power grids, businesses are also implementing energy management programs to optimize energy usage and reduce overall energy costs.
Job creation
While both clean energy and fossil fuel industries have seen job growth in recent years, growth has been markedly faster in the former. As a result, clean energy roles now account for more than half of the 67 million jobs in the global energy sector. Such growth is fueling demand for additional workers and retraining for existing fossil fuel workers to transition to the renewable energy industry.
Hurdles to a clean transition: the disadvantages to renewable energy
For all the celebrated benefits of renewable energy, the sector has some downsides as well. Understanding the disadvantages of renewable energy can help organizations better plan its deployment. Here are some of the cons of renewable energy projects today:
High upfront costs
Shifting to renewable energy technologies saves money in the long run but component costs and initial costs for set-up can be expensive. For example, small businesses can expect to pay USD 100,000 or more for commercial solar installations, depending on their energy needs. However, legislation for incentives, tax credits and various rebates can help offset these costs.
Location and landmass requirements
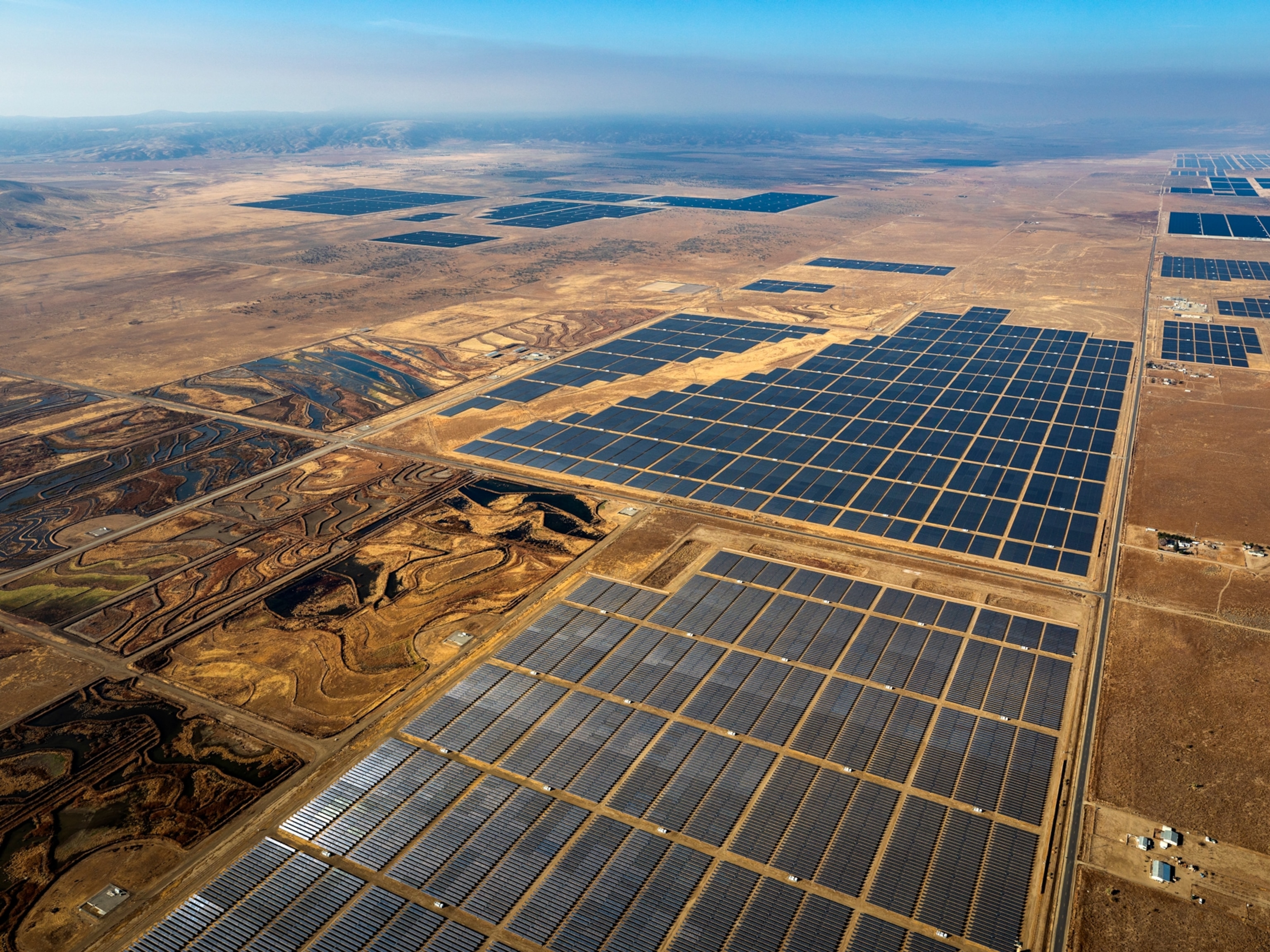
Most renewable energy power generation is location dependent—solar farms require unobstructed sunlight, hydropower requires water movement, wind farms require open spaces and traditional geothermal power requires proximity to sources of hot water. In many cases, renewable energy systems require a lot of space—more than traditional power stations. Research conducted by the ICF Climate Center found that large-scale renewable energy installations require 10 times more land than coal- and natural gas-fired power plants.
Production volatility
Renewable electricity generation is vulnerable to weather conditions: solar power is susceptible to cloudy days, hydropower to droughts and wind power to calm days. As such, guaranteeing the amount of energy produced at any given time is a challenge. To help companies adapt to this volatility, solutions like the IBM Environmental Intelligence Suite use sensors, geospatial data , advanced analytics, machine learning , artificial intelligence (AI) and weather data to generate day-ahead wind and solar forecasts .
Storage requirements
Due to the intermittent nature of renewable power, batteries are required to collect energy during peak production periods for distribution in a controlled, consistent manner during periods of low- to non-production. Energy storage systems to support utility-scale applications are costly but technology is being developed to support more affordable long-term storage.
Supply chain limitations
Supply chain hurdles are hindering the installation of renewable energy projects. According to a report by McKinsey, project developers face three main challenges : access to raw materials and rare earth metals amid a projected shortage; access to the talent and machinery necessary; and little supplier diversification for critical components. For example, in the case of polysilicon, a material used in solar panels, 79% of global capacity is concentrated in China, making the solar PV industry vulnerable to disruptions in that country.
Carbon footprint and waste
Although solar and wind power emit no harmful emissions during power generation, the manufacturing, installation and transportation of renewable energy equipment does often produce greenhouse gas emissions . Additionally, waste products are created during asset production process and disposal, with wind turbine blades and solar panels taking up space in landfills.
Optimizing renewable energy sourcing
Businesses in the renewable energy industry or interested in sourcing renewable power can proactively monitor renewable energy trends with the right tools. The IBM Environmental Intelligence Suite uses historical energy generation data, weather data and more to generate high-accuracy energy forecasts for wind and solar assets to inform key decision-making at the enterprise level.
More from Sustainability
An integrated asset management data platform.
3 min read - Part 2 of this four-part series discusses the complex tasks energy utility companies face as they shift to holistic grid asset management to manage through the energy transition. The first post of this series addressed the challenges of the energy transition with holistic grid asset management. In this part, we discuss the integrated asset management platform and data exchange that unite business disciplines in different domains in one network. The asset management ecosystem The asset management network is complex. No…
SEC climate-related disclosure rules for public companies
3 min read - On March 6, 2024, the US Securities and Exchange Commission (SEC) adopted rules to enhance and standardize climate-related disclosures by public companies and in public offerings. The commission’s adoption of the rules is two years in the making. The original proposed rules, issued in March 2022, aimed to ensure consistency in how publicly traded companies provided climate-related information to investors. These new rules join existing regulations in both the US and around the world requiring companies to make climate-related disclosures…
Exploring architectural choices: Options for running IBM TRIRIGA Application Suite on AWS with Red Hat OpenShift
5 min read - IBM® TRIRIGA® Application Suite (TAS) is a market-leading integrated workplace management system for organizations managing their facility portfolios and assets throughout their lifecycle efficiently. It helps organizations optimize their workplace experience, facility resource scheduling, facility strategic planning, lease accounting and asset disposal, and manage their transactions, capital projects, space, facility maintenance and facility sustainability. Data and AI are increasingly critical tools in how organizations are evolving their facilities management. Real-time insights infused with AI support dynamic space planning. Shared data allows…
IBM Newsletters

What Is the Future of Wind Energy?
This article was reviewed by a member of Caltech's Faculty .
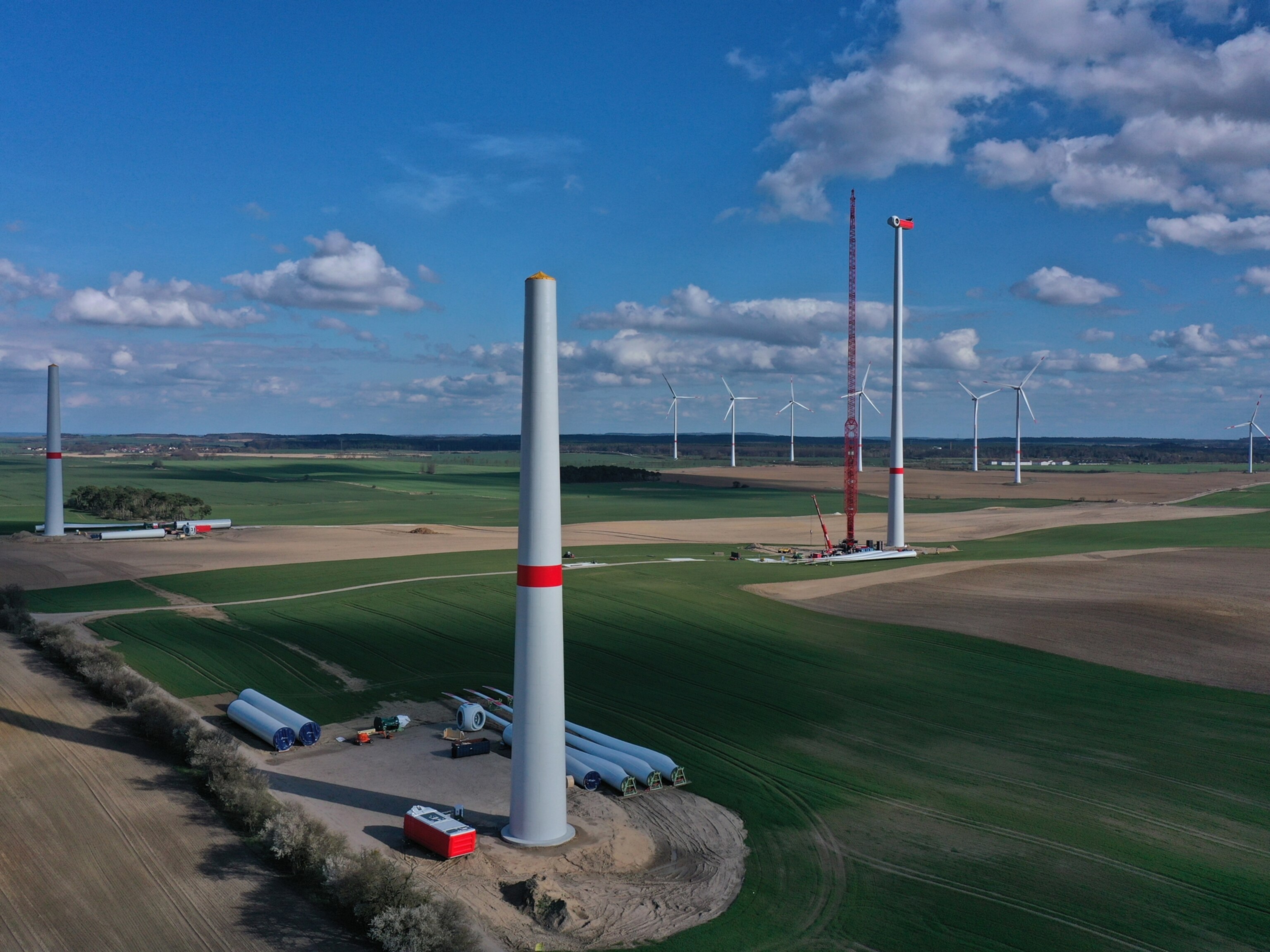
Humans have used windmills to capture the force of the wind as mechanical energy for more than 1,300 years . Unlike early windmills, however, modern wind turbines use generators and other components to convert energy from the spinning blades into a smooth flow of AC electricity.
In the video below, Resnick Sustainability Institute researcher John Dabiri discusses the future of wind energy technology.
How much of global electricity demand is met by wind energy?
Wind energy is a small but fast-growing fraction of electricity production. It accounts for 5 percent of global electricity production and 8 percent of the U.S. electricity supply.
Globally, wind energy capacity surpasses 743 gigawatts , which is more than is available from grid-connected solar energy and about half as much as hydropower can provide. Nearly three-quarters of that 651 gigawatts comes from wind farms in five countries: China, the U.S., Germany, India, and Spain. Wind energy capacity in the Americas has tripled over the past decade.
In the U.S., wind is now a dominant renewable energy source , with enough wind turbines to generate more than 100 million watts, or megawatts, of electricity, equivalent to the consumption of about 29 million average homes.
The cost of wind energy has plummeted over the past decade. In the U.S., it is cost-competitive with natural gas and solar power.
Wind energy and solar energy complement each other, because wind is often strongest after the sun has heated the ground for a time. Warm air rises from the most heated areas, leaving a void where other air can rush in, which produces horizontal wind currents . We can draw on solar energy during the earlier parts of the day and turn to wind energy in the evening and night. Wind energy has added value in areas that are too cloudy or dark for strong solar energy production, especially at higher latitudes.
How big are wind turbines and how much electricity can they generate?
Typical utility-scale land-based wind turbines are about 250 feet tall and have an average capacity of 2.55 megawatts, each producing enough electricity for hundreds of homes. While land-based wind farms may be remote, most are easy to access and connect to existing power grids.
Smaller turbines, often used in distributed systems that generate power for local use rather than for sale, average about 100 feet tall and produce between 5 and 100 kilowatts.
One type of offshore wind turbine currently in development stands 853 feet tall, four-fifths the height of the Eiffel Tower, and can produce 13 megawatts of power. Adjusted for variations in wind, that is enough to consistently power thousands of homes. While tall offshore turbines lack some of the advantages of land-based wind farms, use of them is burgeoning because they can capture the energy of powerful, reliable winds high in the air near coastlines, where most of the largest cities in the world are located.
What are some potential future wind technologies other than turbines?
Engineers are in the early stages of creating airborne wind turbines , in which the components are either floated by a gas like helium or use their own aerodynamics to stay high in the air, where wind is stronger. These systems are being considered for offshore use, where it is expensive and difficult to install conventional wind turbines on tall towers.
Trees, which can withstand gale forces and yet move in response to breezes from any direction, also are inspiring new ideas for wind energy technology. Engineers speculate about making artificial wind-harvesting trees . That would require new materials and devices that could convert energy from a tree's complex movements into the steady rotation that traditional generators need. The prize is wind energy harvested closer to the ground with smaller, less obtrusive technologies and in places with complex airflows, such as cities.
What are the challenges of using wind energy?
Extreme winds challenge turbine designers. Engineers have to create systems that will start generating energy at relatively low wind speeds and also can survive extremely strong winds. A strong gale contains 1,000 times more power than a light breeze, and engineers don't yet know how to design electrical generators or turbine blades that can efficiently capture such a broad range of input wind power. To be safe, turbines may be overbuilt to withstand winds they will not experience at many sites, driving up costs and material use. One potential solution is the use of long-term weather forecasting and AI to better predict the wind resources at individual locations and inform designs for turbines that suit those sites.
Climate change will bring more incidents of unusual weather, including potential changes in wind patterns . Wind farms may help mitigate some of the harmful effects of climate change. For example, turbines in cold regions are routinely winterized to keep working in icy weather when other systems may fail, and studies have demonstrated that offshore wind farms may reduce the damage caused by hurricanes . A more challenging situation will arise if wind patterns shift significantly. The financing for wind energy projects depends critically on the ability to predict wind resources at specific sites decades into the future. One potential way to mitigate unexpected, climate-change-related losses or gains of wind is to flexibly add and remove groups of smaller turbines, such as vertical-axis wind turbines , within existing large-scale wind farms.
Wind farms do have environmental impacts . The most well-known is harm to wildlife, including birds and bats . Studies are informing wind farm siting and management practices that minimize harm to wildlife , and Audubon, a bird conservation group, now supports well-planned wind farms. The construction and maintenance of wind farms involves energy-intensive activities such as trucking, road-building, concrete production, and steel construction. Also, while towers can be recycled, turbine blades are not easily recyclable. In hopes of developing low-to-zero-waste wind farms, scientists aim to design new reuse and disposal strategies , and recyclable plastic turbine blades. Studies show that wind energy's carbon footprint is quickly offset by the electricity it generates and is among the lowest of any energy source .
Dive Deeper

Wind Vision: A New Era for Wind Power in the United States

Caltech Energy 10 to Develop the Roadmap for 50% Reduction in Emissions by 2030

Tweaking Turbine Angles Squeezes More Power Out of Wind Farms
Accept cookies?
We use cook ies to give you the best online experience and to show personalised content and marketing. We use them to improve our website and content as well as to tailor our digital advertising on third-party platforms. You can change your preferences at any time.
Popular search terms:
- British wildlife
- Wildlife Photographer of the Year
- Explore the Museum
- Anthropocene
British Wildlife
Collections
Human evolution
What on Earth?
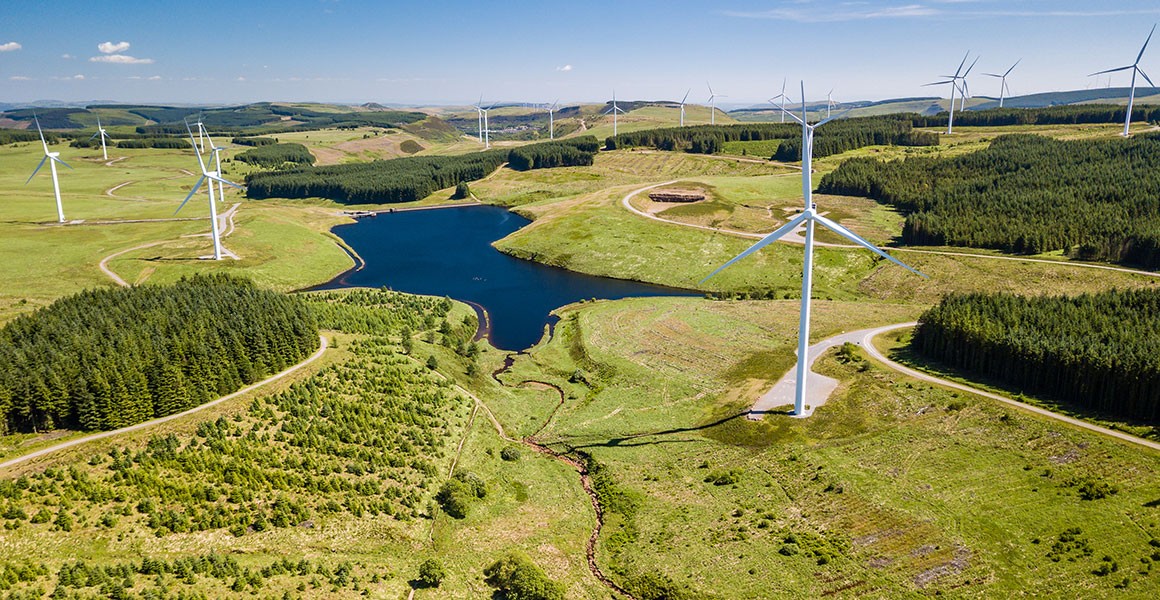

Aerial view of a wind farm at Pen y Cymoedd in south Wales, UK. Wind-generated power in the UK increased by 83% between 2015 and 2020 to provide nearly a quarter of our electricity . It's also one of the fastest-growing renewable energy technologies globally. © Richard Whitcombe/ Shutterstock
During Beta testing articles may only be saved for seven days.
Create a list of articles to read later. You will be able to access your list from any article in Discover.
You don't have any saved articles.
Renewable energy and its importance for tackling climate change
Replacing fossil fuel-reliant power stations with renewable energy sources, such as wind and solar, is a vital part of stabilising climate change and achieving net zero carbon emissions.
Professor Magda Titirici , Chair in Sustainable Energy Materials at Imperial College London, offers an introduction to renewable energy and the future of clean, green power in the UK.
What is renewable energy?
Renewable energy comes from sources that replenish naturally and continually within a human lifetime. Renewable energy is often called sustainable energy.
Major sources of renewable energy include solar, wind, hydroelectric, tidal, geothermal and biomass energy, which is derived from burning plant or animal matter and waste.
Switching our reliance on fossil fuels to renewable energy sources that produce lower or no greenhouse gas emissions is critically important in tackling the climate crisis .
Clean, green or renewable - what's the difference?
Clean energy doesn't produce any pollution once installed. Nor does green energy, which comes from natural sources such as the Sun and is produced without any major negative impacts on the environment. Renewable energy refers to sources that are constantly replenished.
While there is often overlap between these definitions and most renewable energy sources can also be considered clean and green, it's not always the case.
Nuclear energy doesn't release greenhouse gases into the atmosphere, so some people consider it to be clean - providing the radioactive waste is stored safely and doesn't escape into the environment. But the uranium energy source used in nuclear power plants isn't renewable.
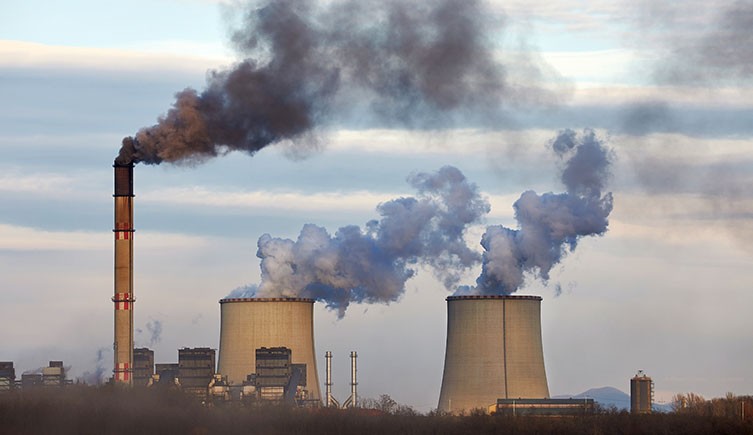

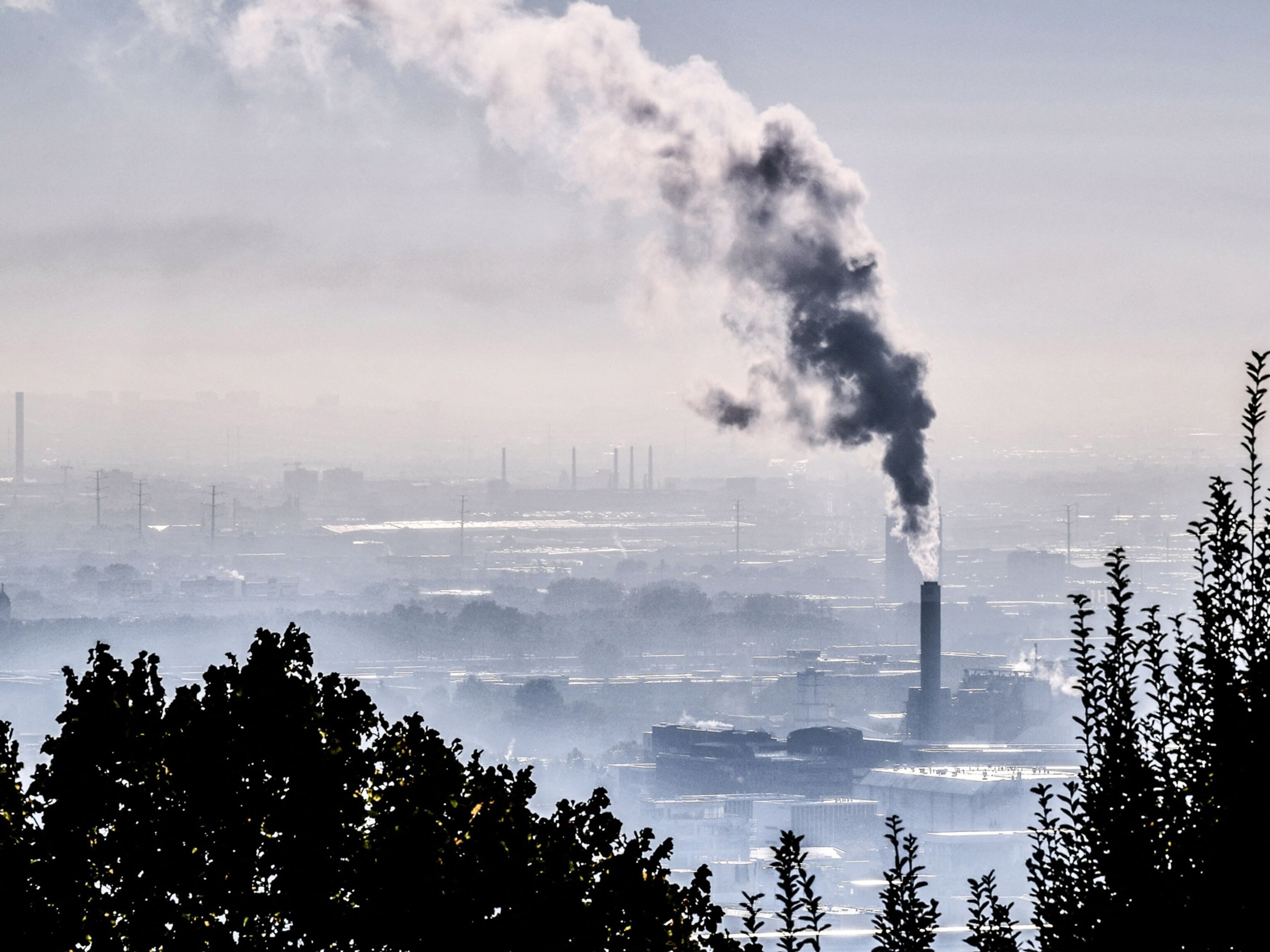
A coal power plant emitting smoke, steam and carbon dioxide. Fossil fuels such as coal are non-renewable resources. Burning fossil fuels contributes to climate change by releasing greenhouse gases into the atmosphere. © Peter Gudella/ Shutterstock
What's the difference between renewable and non-renewable energy?
Non-renewable energy comes from natural resources such as coal, oil and natural gas that take billions of years to form, which is why we call them fossil fuels. They are present in finite amounts and will run out, as we are using them far more quickly than they form.
When will fossil fuels run out?
Research based on 2015 data predicts that coal stocks will last well into the next century, but oil and natural gas reserves (stocks that we know we can extract from) will run out in the late 2060s . However, scientific models suggest that if we are to limit global warming to 2°C - the target agreed at COP26 is 1.5°C - over 80% of coal, 50% of gas and 30% of oil reserves will need to be left untouched anyway.
When we extract fossil fuels from deep within the planet and burn them, we can generate electricity quite efficiently. But the process releases a lot of carbon dioxide (CO 2 ) into the atmosphere, which contributes to the greenhouse effect, global warming and biodiversity loss .
Magda explains, 'Fossil fuels brought with them immense technological progress but using them releases CO 2 into the atmosphere, which acts like a blanket, trapping heat that would otherwise escape into space and causing global warming.'
Did you know?
The energy sector is responsible for almost three-quarters of the emissions that have caused global temperatures to warm by 1.1°C since pre-industrial times.
If we continue to use fossil fuels, the effect will only worsen.
Magda adds, 'If we want to live on this planet much longer than 2050 and keep temperature levels below the 1.5°C of warming agreed to by governments around the world, we need to make some radical changes right now. We need to move to technologies that will give us the same level and comfort of living but drastically cut our emissions and carbon footprint .'
Examples of renewable energy sources
The main types of renewable energy are wind, solar, hydroelectric, tidal, geothermal and biomass. Read on to discover the pros and cons of each of these renewable energy sources.
One of the main benefits of most renewable energy sources is that they don't release carbon dioxide or pollute the air when they are used to produce electricity or heat. Greenhouse gases are emitted during the lifetime of some of the technologies - for example, during their manufacture or construction - but overall emissions are significantly lower than for fossil fuels.
Whereas some countries lack direct access to fossil fuels and must rely on international sources, renewable energy often allows countries to supply their own energy needs, a big economic and political advantage.
Wind energy
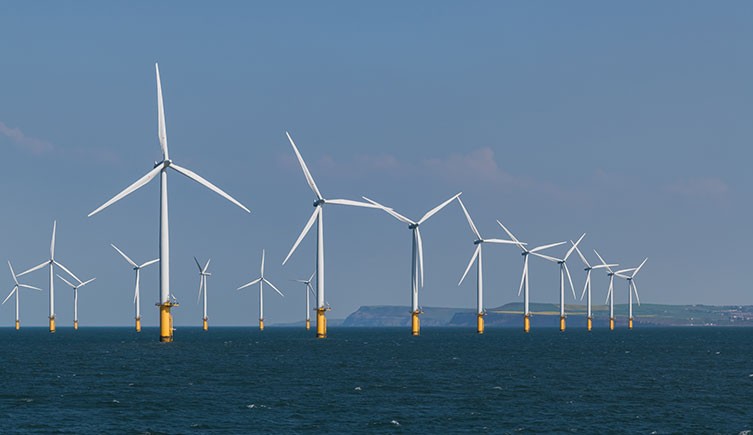

An offshore wind farm in the North Sea off the UK coast. Wind energy is an important renewable resource for the UK. According to analysis by Imperial College London's Energy Institute , offshore wind turbines offer the best-value option for meeting the UK's target of delivering carbon neutral electricity by 2035. But the UK's current target for offshore wind electricity production - up to 50 gigawatts by 2030 - will need to be significantly increased to do so. © Riekelt Hakvoort/ Shutterstock
Wind power converts wind - the movement of air - into stored power by turning turbines and converting mechanical energy into electricity. Wind farms can be built both on land and offshore. They work well wherever wind is strong and reliable.
Advantages: Wind energy is a clean, green and renewable resource and turbines can be placed on farmland with minimal disruption. It has the lowest carbon footprint of all renewable energy sources .
Disadvantages: Like any infrastructure, there is an upfront establishment cost and ongoing maintenance fees. These are even higher if wind farms are built offshore. Turbines have a reputation for being noisy and poorly sited wind farms can be dangerous to some wildlife - for instance, if they're placed in the migration paths of birds or bats.
How loud is a wind turbine?
At 300 metres from a dwelling, wind turbines have a sound pressure of 43 decibels , which is between the volume of a refrigerator and an air conditioner.
Solar energy
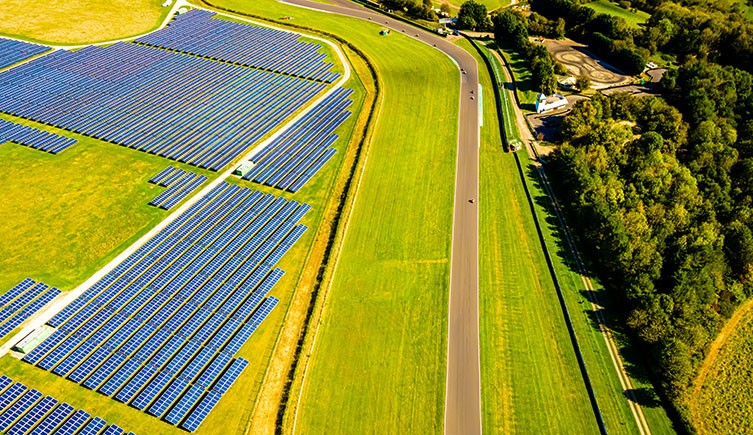

An array of solar panels in a field in Chippenham, UK. Solar energy is a renewable resource, and the Sun provides more energy than we'll ever use. If we could capture it all, an hour of sunlight would meet the world's energy needs for a year. © Alexey Fedorenko/ Shutterstock
Solar power captures energy (radiation) from the Sun and converts it into electricity, which is then fed into a power grid or stored for later use. Although places near the equator receive the most solar energy, solar panels can generate electricity anywhere that gets sunlight.
Advantages: Solar energy is renewable, clean, increasingly efficient and has low maintenance costs. Once established, it can dramatically reduce the price of generating electricity.
Disadvantages: Setting up a solar array is costly and there are expenses involved with energy storage. Solar panels can take up more land than some other types of renewable energy and performance depends on the availability of sunlight. The mining and processing of minerals needed to make the panels can pollute and damage the environment.
China is currently leading the world in solar energy production , with roughly 35% of the global market.
Hydroelectric energy
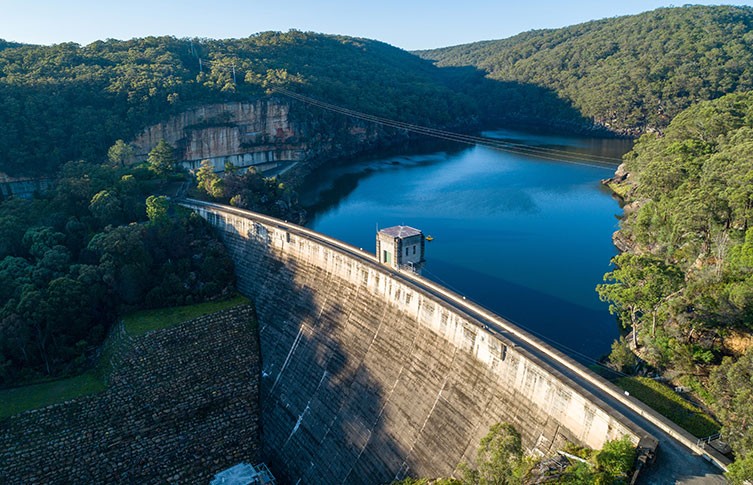

Although hydroelectric energy is renewable, it is not always considered green, as building large-scale dams can negatively impact the environment. Nepean Dam in Australia, shown here, was included in a study that showed dams are causing problems for platypuses by creating a barrier between populations. © Greg Brave/ Shutterstock
Hydroelectric power uses the flow of water, often from rivers and lakes controlled by a dam, to turn turbines and power generators, creating electricity. Hydropower works best for regions with reliable rainfall and large, natural water reservoirs.
Hydropower currently produces more electricity than all other renewable energy sources combined and provides around 17% of the world's energy.
Advantages: Hydroelectricity is dependable and renewable for as long as there is rainfall or flowing water. Reservoirs can offer additional benefits, such as providing drinking water, irrigation and recreational opportunities, including swimming or boating.
Disadvantages: Hydropower plants take up a lot of room and aren't suited to all climates. They are susceptible to drought. Creating artificial water reservoirs can harm biodiversity in natural water systems by limiting the inflow of nutrients and blocking the journey of migratory fish populations. These reservoirs can also release methane - a type of greenhouse gas - as vegetation in the flooded area decomposes. Large amounts of cement are used to construct dams. The manufacture of this material produces large amounts of carbon dioxide.
Tidal energy
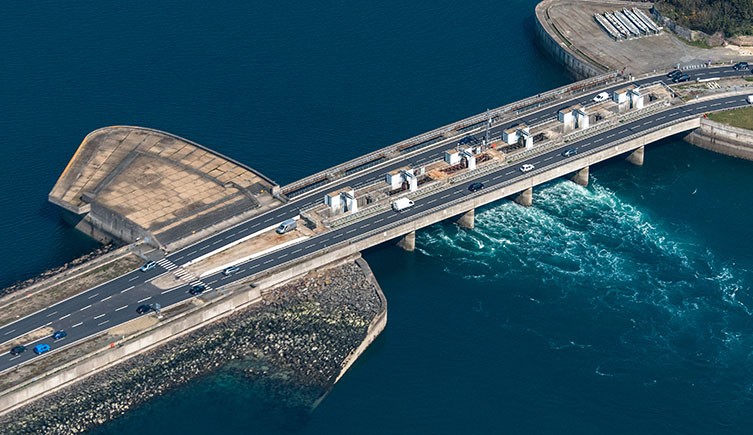

Renewable tidal energy is produced by the natural rise and fall of the sea. However, tidal power plants can change the local biodiversity. This one on the River Rance in Brittany, France, not only led to the local extinction of a fish called plaice but to an increase in the number of cuttlefish, which now thrive there. © Francois BOIZOT/ Shutterstock
Tidal energy uses the continual movement of ocean tides to generate power. Turbines in the water turn a generator, creating electricity.
Advantages: Tidal energy is renewable, generates no carbon emissions and can produce a lot of energy very reliably.
Disadvantages: Offshore infrastructure is expensive to set up and maintain and there are a limited number of appropriate sites for tidal power plants around the world. They can also damage marine environments and impact local plants and animals.
Geothermal energy
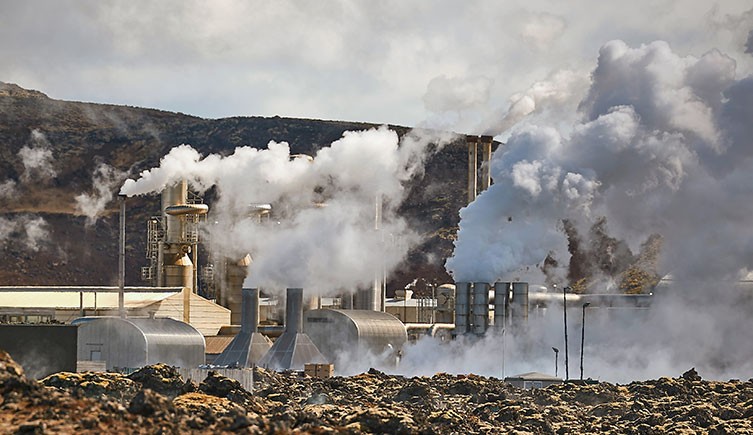

A geothermal power plant in Iceland harnesses this renewable energy source. © Peter Gudella/ Shutterstock
Geothermal power uses underground reservoirs of hot water or steam created by the heat of Earth's core to generate electricity. It works best in regions near tectonic plate boundaries .
Advantages: Geothermal energy is highly reliable and has a consistent power output. It also has a relatively small footprint on the land.
Disadvantages: Drilling geothermal wells is expensive and can affect the stability of surrounding land. It must be monitored carefully to minimise environmental impact. There is also a risk of releasing greenhouse gases trapped under Earth's surface.
Biomass energy
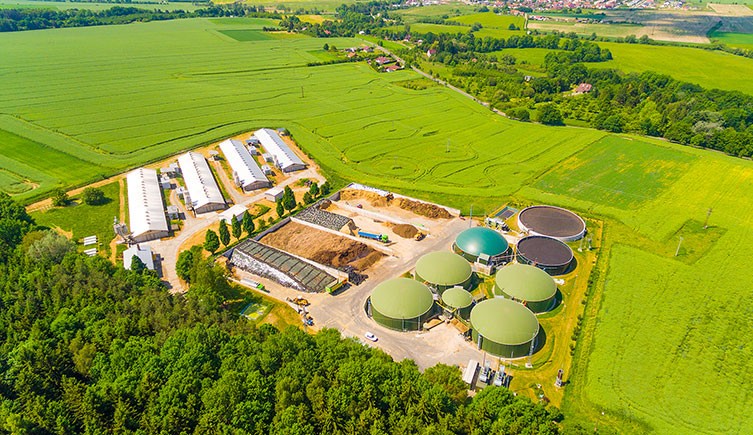

A biogas plant producing renewable energy from biomass in the Czech Republic. © Kletr/ Shutterstock
Biomass energy comes from burning plants, plant by-products or waste. Examples include ethanol (from corn or sugarcane), biodiesel (made from vegetable oils, used cooking oils and animal fats), green diesel (derived from algae, sustainable wood crops or sawdust) and biogas (derived from animal manure and other waste).
Advantages: Abundant and cheaply produced, biomass energy is a novel use of waste product and leftover crops. It creates less emissions than burning fossil fuels and having carbon capture in place can stop carbon dioxide entering the atmosphere. Biofuels are also considered relatively easy and inexpensive to implement, as they are compatible with existing agriculture and waste processing and used in existing petrol and diesel vehicles.
Disadvantages: Generating biofuels requires land and water so growing demand for them could lead to deforestation and biodiversity loss. Burning biomass emits carbon dioxide unless carbon capture is implemented.
Ethanol-powered vehicles create up to 86% less greenhouse gas emissions than petrol vehicles, and crops that are grown to produce biomass absorb carbon dioxide.
Can renewable energy replace fossil fuels in the UK?
In 2020, 42% of the UK's electricity came from renewable energy. A quarter of the UK's electricity was produced by wind power, which is the highest proportion of any G20 country and more than four times the global average. Statistics on UK energy trends reveal that from April to June 2022, nearly 39% of the UK's electricity came from renewable energy, slightly more than during the same period in 2021, but down from 45.5% between January and March 2022 when it was unusually sunny and wind speeds were high.
'There has been good news in recent years in terms of progress on renewables,' says Magda, 'but in my opinion, the UK is still lagging behind. It is not so strong yet for truly sustainable technologies. It needs storage and conversion.'
Magda believes that wind (particularly offshore), solar, green hydrogen and rapid innovation in battery storage will be key to the UK reaching net zero by 2050.
She explains, 'The UK is a really windy place, so wind is the perfect renewable energy technology. By 2035 wind and solar should provide 75-90% of total UK electricity to bring emissions down significantly.'
'It has already been shown that it's feasible to produce 90% of the UK's electricity from wind and solar combined. The tech is there and it's becoming more efficient and affordable each year.'
'Offshore wind capacity will also help produce green hydrogen, another crucial part of the UK decarbonisation path.'
What is green hydrogen?
Green hydrogen is a fuel created using renewable energy in a process known as electrolysis. When green hydrogen is burned to produce energy, it releases water.
It's predicted that the UK will need 100 terawatt-hours of green hydrogen by 2035.
What is a terawatt-hour?
A terawatt-hour is a unit of measurement that's large enough to describe the annual electricity needs of entire countries. For scale, one terawatt-hour is equivalent to burning 588,441 barrels of oil.
The future of renewable energy in the UK
Magda believes the UK is at a very critical point in its sustainable technologies journey.
'Everything will depend on what happens this year and next. We need to see radical changes, investment, subsidies and support to reach our target of net zero by 2050.'
'It would cost less than 1% of GDP to get to net zero by 2050 but the advantages would be immense: new jobs, a sustainable economy and a healthy and resilient society.'
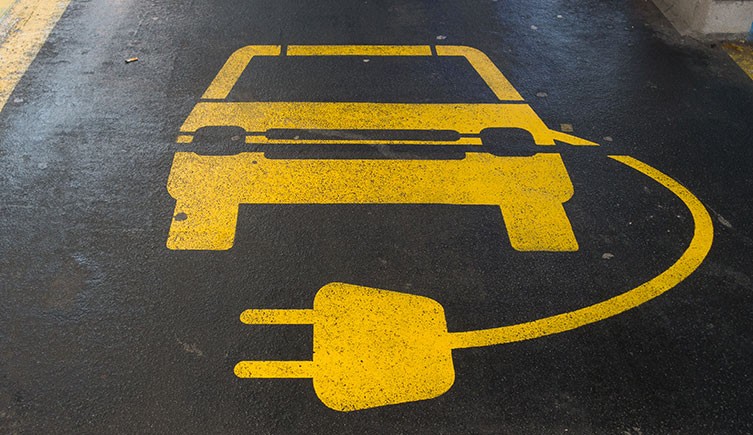

An empty electric vehicle charging point © Tony Skerl/ Shutterstock
Challenges and opportunities for renewable energy in the UK
One of the biggest challenges the UK is facing right now is battery storage and access to materials like cobalt and lithium , which are needed to produce lithium-ion batteries at scale.
Why are batteries important for renewable energy?
Batteries help make renewable energy supply reliable and portable - such as in the case of electric vehicles.
Batteries are an important part of our transition to renewable technologies, as they allow energy to be stored and released as needed. For example, solar panels generate energy during the day, and batteries make it possible to store and use that electricity at night.
Currently, just a few countries are responsible for most of the world's production of lithium.
According to Magda, the UK lacks access to the supply chain needed for Li-ion batteries. 'As a result, she adds, 'Johnson Matthey, which is a major company driving battery innovations in the UK, announced they would stop lithium battery research because they are unable to secure a path to raw materials and be competitive on the international market.'
Museum researchers are investigating whether it would be possible to develop a more sustainable, domestic supply chain by extracting lithium from UK rocks. They made a key breakthrough in 2021 when they produced battery-grade lithium chemicals from UK rocks for the first time.
According to Professor Richard Herrington, Head of Earth Sciences at the Museum, 'An increased, reliable supply of lithium is critical if we are to meet the rising demand for electric cars and provide a dependable supply of energy from renewable sources. The next generation of batteries that don't require lithium may still be three to five years away from being ready for public use.'
However, Magda is optimistic that the UK could lead in emerging battery technologies. 'I think the UK has an amazing opportunity to pioneer the next generation of batteries,' she says.
Innovative models already under development at The Faraday Institution include:
- Sodium-ion batteries, which are based on waste-derived anodes and critical metal -free cathodes, provide almost the same performance as lithium-ion batteries at half the cost.
- Lithium-sulphur batteries with 10 times the energy density of lithium-ion batteries make more efficient use of limited materials and eliminate metals from the cathode by using sulphur instead.
Magda adds, 'We need to focus on the areas where the UK has the potential to lead. The UK has such a big tradition in new materials and discoveries, we could move to completely new technologies both for batteries and hydrogen production.'
'There are a lot of challenges, but if we're investing in it, we could be future leaders and even solve one of the most difficult challenges in decarbonisation: flight.'
- Sustainability
- Biodiversity
- Climate change

Protecting our planet
We're working towards a future where both people and the planet thrive.
Hear from scientists studying human impact and change in the natural world.

How are climate change and biodiversity loss linked?
The climate crisis and biodiversity loss are closely connected but the good news is, so are the solutions.

Net zero is cheaper and greener than continuing the use of fossil fuels
Going green is no longer just the smart decision – it's also the most profitable one.

Nine ways Museum scientists are fighting the planetary emergency
Discover how we're fighting to keep nature healthy.
Lithium carbonate has been produced from UK rocks for the first time
A breakthrough in domestic production could bring down the carbon footprint of lithium-ion batteries.
Don't miss a thing
Receive email updates about our news, science, exhibitions, events, products, services and fundraising activities. We may occasionally include third-party content from our corporate partners and other museums. We will not share your personal details with these third parties. You must be over the age of 13. Privacy notice .
Follow us on social media
- ENVIRONMENT
Renewable energy, explained
Solar, wind, hydroelectric, biomass, and geothermal power can provide energy without the planet-warming effects of fossil fuels.
In any discussion about climate change , renewable energy usually tops the list of changes the world can implement to stave off the worst effects of rising temperatures. That's because renewable energy sources such as solar and wind don't emit carbon dioxide and other greenhouse gases that contribute to global warming .
Clean energy has far more to recommend it than just being "green." The growing sector creates jobs , makes electric grids more resilient, expands energy access in developing countries, and helps lower energy bills. All of those factors have contributed to a renewable energy renaissance in recent years, with wind and solar setting new records for electricity generation .
For the past 150 years or so, humans have relied heavily on coal, oil, and other fossil fuels to power everything from light bulbs to cars to factories. Fossil fuels are embedded in nearly everything we do, and as a result, the greenhouse gases released from the burning of those fuels have reached historically high levels .
As greenhouse gases trap heat in the atmosphere that would otherwise escape into space, average temperatures on the surface are rising . Global warming is one symptom of climate change, the term scientists now prefer to describe the complex shifts affecting our planet’s weather and climate systems. Climate change encompasses not only rising average temperatures but also extreme weather events, shifting wildlife populations and habitats, rising seas , and a range of other impacts .
Of course, renewables—like any source of energy—have their own trade-offs and associated debates. One of them centers on the definition of renewable energy. Strictly speaking, renewable energy is just what you might think: perpetually available, or as the U.S. Energy Information Administration puts it, " virtually inexhaustible ." But "renewable" doesn't necessarily mean sustainable, as opponents of corn-based ethanol or large hydropower dams often argue. It also doesn't encompass other low- or zero-emissions resources that have their own advocates, including energy efficiency and nuclear power.
Types of renewable energy sources
Hydropower: For centuries, people have harnessed the energy of river currents, using dams to control water flow. Hydropower is the world's biggest source of renewable energy by far, with China, Brazil, Canada, the U.S., and Russia the leading hydropower producers . While hydropower is theoretically a clean energy source replenished by rain and snow, it also has several drawbacks.
FREE BONUS ISSUE
Large dams can disrupt river ecosystems and surrounding communities , harming wildlife and displacing residents. Hydropower generation is vulnerable to silt buildup, which can compromise capacity and harm equipment. Drought can also cause problems. In the western U.S., carbon dioxide emissions over a 15-year period were 100 megatons higher than they normally would have been, according to a 2018 study , as utilities turned to coal and gas to replace hydropower lost to drought. Even hydropower at full capacity bears its own emissions problems, as decaying organic material in reservoirs releases methane.
Dams aren't the only way to use water for power: Tidal and wave energy projects around the world aim to capture the ocean's natural rhythms. Marine energy projects currently generate an estimated 500 megawatts of power —less than one percent of all renewables—but the potential is far greater. Programs like Scotland’s Saltire Prize have encouraged innovation in this area.
Wind: Harnessing the wind as a source of energy started more than 7,000 years ago . Now, electricity-generating wind turbines are proliferating around the globe, and China, the U.S., and Germany are the leading wind energy producers. From 2001 to 2017 , cumulative wind capacity around the world increased to more than 539,000 megawatts from 23,900 mw—more than 22 fold.
You May Also Like

Can energy harnessed from Earth’s interior help power the world?

How the historic climate bill will dramatically reduce U.S. emissions

5 environmental victories from 2021 that offer hope
Some people may object to how wind turbines look on the horizon and to how they sound, but wind energy, whose prices are declining , is proving too valuable a resource to deny. While most wind power comes from onshore turbines, offshore projects are appearing too, with the most in the U.K. and Germany. The first U.S. offshore wind farm opened in 2016 in Rhode Island, and other offshore projects are gaining momentum . Another problem with wind turbines is that they’re a danger for birds and bats, killing hundreds of thousands annually , not as many as from glass collisions and other threats like habitat loss and invasive species, but enough that engineers are working on solutions to make them safer for flying wildlife.
Solar: From home rooftops to utility-scale farms, solar power is reshaping energy markets around the world. In the decade from 2007 and 2017 the world's total installed energy capacity from photovoltaic panels increased a whopping 4,300 percent .
In addition to solar panels, which convert the sun's light to electricity, concentrating solar power (CSP) plants use mirrors to concentrate the sun's heat, deriving thermal energy instead. China, Japan, and the U.S. are leading the solar transformation, but solar still has a long way to go, accounting for around two percent of the total electricity generated in the U.S. in 2017. Solar thermal energy is also being used worldwide for hot water, heating, and cooling.
Biomass: Biomass energy includes biofuels such as ethanol and biodiesel , wood and wood waste, biogas from landfills, and municipal solid waste. Like solar power, biomass is a flexible energy source, able to fuel vehicles, heat buildings, and produce electricity. But biomass can raise thorny issues.
Critics of corn-based ethanol , for example, say it competes with the food market for corn and supports the same harmful agricultural practices that have led to toxic algae blooms and other environmental hazards. Similarly, debates have erupted over whether it's a good idea to ship wood pellets from U.S. forests over to Europe so that it can be burned for electricity. Meanwhile, scientists and companies are working on ways to more efficiently convert corn stover , wastewater sludge , and other biomass sources into energy, aiming to extract value from material that would otherwise go to waste.
Geothermal: Used for thousands of years in some countries for cooking and heating, geothermal energy is derived from the Earth’s internal heat . On a large scale, underground reservoirs of steam and hot water can be tapped through wells that can go a mile deep or more to generate electricity. On a smaller scale, some buildings have geothermal heat pumps that use temperature differences several feet below ground for heating and cooling. Unlike solar and wind energy, geothermal energy is always available, but it has side effects that need to be managed, such as the rotten egg smell that can accompany released hydrogen sulfide.
Ways to boost renewable energy
Cities, states, and federal governments around the world are instituting policies aimed at increasing renewable energy. At least 29 U.S. states have set renewable portfolio standards —policies that mandate a certain percentage of energy from renewable sources, More than 100 cities worldwide now boast at least 70 percent renewable energy, and still others are making commitments to reach 100 percent . Other policies that could encourage renewable energy growth include carbon pricing, fuel economy standards, and building efficiency standards. Corporations are making a difference too, purchasing record amounts of renewable power in 2018.
Wonder whether your state could ever be powered by 100 percent renewables? No matter where you live, scientist Mark Jacobson believes it's possible. That vision is laid out here , and while his analysis is not without critics , it punctuates a reality with which the world must now reckon. Even without climate change, fossil fuels are a finite resource, and if we want our lease on the planet to be renewed, our energy will have to be renewable.
Related Topics
- SUSTAINABILITY
- RENEWABLE ENERGY
- GEOTHERMAL ENERGY
- SOLAR POWER
- HYDROELECTRIC POWER
- CLIMATE CHANGE

Activists fear a new threat to biodiversity—renewable energy

How the Ukraine war is accelerating Germany's renewable energy transition

What’s at stake at COP26—the crucial global climate summit

We took the Great American Road Trip—in electric cars

Climate change goals and oil production are clashing in the U.S.
- History & Culture
- Environment
- Paid Content

History & Culture
- History Magazine
- Mind, Body, Wonder
- Terms of Use
- Privacy Policy
- Your US State Privacy Rights
- Children's Online Privacy Policy
- Interest-Based Ads
- About Nielsen Measurement
- Do Not Sell or Share My Personal Information
- Nat Geo Home
- Attend a Live Event
- Book a Trip
- Inspire Your Kids
- Shop Nat Geo
- Visit the D.C. Museum
- Learn About Our Impact
- Support Our Mission
- Advertise With Us
- Customer Service
- Renew Subscription
- Manage Your Subscription
- Work at Nat Geo
- Sign Up for Our Newsletters
- Contribute to Protect the Planet
Copyright © 1996-2015 National Geographic Society Copyright © 2015-2024 National Geographic Partners, LLC. All rights reserved
Solar vs wind power: The ultimate showdown

Which renewable energy is best to switch to? Image: Zbynek Burival/Unsplash
.chakra .wef-1c7l3mo{-webkit-transition:all 0.15s ease-out;transition:all 0.15s ease-out;cursor:pointer;-webkit-text-decoration:none;text-decoration:none;outline:none;color:inherit;}.chakra .wef-1c7l3mo:hover,.chakra .wef-1c7l3mo[data-hover]{-webkit-text-decoration:underline;text-decoration:underline;}.chakra .wef-1c7l3mo:focus,.chakra .wef-1c7l3mo[data-focus]{box-shadow:0 0 0 3px rgba(168,203,251,0.5);} Karsten Neumeister

.chakra .wef-9dduvl{margin-top:16px;margin-bottom:16px;line-height:1.388;font-size:1.25rem;}@media screen and (min-width:56.5rem){.chakra .wef-9dduvl{font-size:1.125rem;}} Explore and monitor how .chakra .wef-15eoq1r{margin-top:16px;margin-bottom:16px;line-height:1.388;font-size:1.25rem;color:#F7DB5E;}@media screen and (min-width:56.5rem){.chakra .wef-15eoq1r{font-size:1.125rem;}} Energy Transition is affecting economies, industries and global issues

.chakra .wef-1nk5u5d{margin-top:16px;margin-bottom:16px;line-height:1.388;color:#2846F8;font-size:1.25rem;}@media screen and (min-width:56.5rem){.chakra .wef-1nk5u5d{font-size:1.125rem;}} Get involved with our crowdsourced digital platform to deliver impact at scale
Stay up to date:, energy transition.
- Two of the most popular renewable energy sources in the US, at this moment, are solar and wind.
- But which will take the lead in 2022?
- An expert weighs up the pros and cons.
History shows that advances in renewable energy often follow crises: In the 1970s, oil embargos caused the cost of oil to quadruple, spurring efforts to reduce American dependence on fossil fuels and find alternative sources of power, including solar energy or wind power. The 2008-09 global financial crisis led to several governments linking part of their economic stimulus to investment in clean energy. The COVID-19 pandemic led to an unprecedented energy shock, and following in 2021, investment in renewable energy reached the highest levels since the Great Recession.
Following crises in Europe, Western economies are once again reminded of the importance of energy independence, and demand for renewable energy sources has gone through the roof. Two of the most popular renewable energy sources in the U.S., at this moment, are solar and wind. Will either take charge as a leader in 2022?
Thanks to the decreasing cost of solar , the technology has never been more worth it for homeowners. Its ease for residential use allows customers to reduce their carbon footprint along with their energy expenses. But humans have been using wind for thousands of years, well before the modern wind turbine ever arrived. In fact, wind power accounted for 5% more energy generation than solar did last year.
So, as we enter the era of renewable energy, will either source of power come out on top? And if you’re considering making the switch to a renewable source of energy, which is better for your needs? Let’s explore.
History of solar vs wind power
We’ll start with a little background for color. The earliest recorded evidence of wind energy being used dates to around 6000 to 5000 B.C., when the sail was invented to catch the wind and propel boats. Over the years, developments in wind power allowed humans to grind grain, pump water, and eventually, around the late 1800s, generate electricity from kinetic energy.
One could argue that solar energy has been used since 700 B.C., when mirrors were used to concentrate solar energy to make fire. But solar cells were not used to generate energy until 1839, when Edmond Becquerel, a young physicist working in France, first observed and noted the photovoltaic effect. It took more than a century to produce a practical solar panel after Becquerel’s discovery. Solar energy remained in the research-and-development phase for several decades.
Fast forward to 1973 — oil shocks caused gasoline and oil prices to spike, spreading anxiety about the United States’ energy future. U.S. leaders grew increasingly curious about alternative, domestic sources of energy that would reduce dependence on foreign oil.
Coupled with mounting pressure from environmentalists, the ‘70s saw tangible federal support for renewable energy. To encourage its development, Congress passed the 1978 Energy Tax Act to provide tax credits for homes with solar panels and fund the development of large wind turbines. Solar was not cost-effective enough to take off quite yet, but wind turbines caught some modest gains in progressive states.
Over the next few decades, the share of U.S. electricity generation from wind grew from less than 1% in 1990 to about 8.4% in 2020. Solar energy’s share of total U.S. utility-scale electricity generation grew from 0.1% in 1990 to around 2.5% in 2020.

Home solar panels
In 2022, modern solar panels are either installed on a roof or ground-mounted to convert sunlight into energy. Solar panels are made up of photovoltaic cells (or solar cells) that use the semi-conductive material silicon to create an electric current. The electricity that the panels produce is direct current (DC), and it is converted by an inverter into AC electricity, which is what we use to power our homes.
The best solar panels these days average between a power capacity of 250 to 400 watts, and the most efficient solar panels reach efficiency levels around 20%, meaning 20% of the energy that strikes the panel is converted into electricity. A typical solar array ranges anywhere from 10 to 30 solar panels (or more), with the average being around 20 to power an American household.
The average cost of a solar installation is between $20,000 to $40,000, varying with the complexity of an installation, location, and the size and energy needs of a home. This is a steep barrier to entry, and it remains one of the largest challenges to solar’s growth. However, for those able to afford the upfront cost or take out a solar financing loan, solar provides decades of energy savings and can top even $50,000 of lifetime savings in the right location.
Most homes with solar will remain grid-tied, meaning you won’t lose your connection with your local utility. However, off-grid solar can be used in small-scale applications.
Not only does residential solar help homeowners offset their electricity usage, but installations help homeowners lower their dependence on fossil fuels and public utilities, yielding a number of personal and community benefits.
Home wind turbines
Wind turbines can also be used to generate electricity. Rather than using the photovoltaic effect, the blades of wind turbines spin to turn an inner rotor. The rotor sends kinetic energy to a generator that converts it into AC electricity, similar to an inverter in a solar array. Also like solar, wind power can be grid-tied or the resulting energy can be stored in a battery.
Unlike solar panels, in the wind turbine world, bigger is better, as winds generally increase as altitudes increase.
According to the Office of Energy Efficiency and Renewable Energy, the hub height for utility-scale, land-based wind turbines has increased 59% since 1998, measuring about 295 feet in 2020 (about the same height as the Statue of Liberty). And the hub height for offshore turbines in the U.S. is projected to be even taller. Because turbines are so large, local zoning ordinances usually present challenges to residential wind installations.
This dependence on size contributes most to what differentiates wind from solar power. Wind power takes up far more space to be most effective, and as a result, most wind turbines are used on a commercial or industrial scale rather than residential. However, wind turbines harness about 50% of the energy that passes through them, compared with the 20% efficiency of the top residential solar panels. And unlike solar panels, wind turbines can produce energy at any time of day, making them very effective when implemented properly.
In closing, location is key for wind as a source of energy. Wind turbines work best in large expanses of land without trees, buildings or other obstructions. States like Texas, Oklahoma, Iowa, Kansas and Illinois are leading the nation in wind energy, and coastal states such as Virginia, Massachusetts and New Jersey have invested heavily in offshore wind power, a promising avenue for growth.
Benefits of solar panels and wind turbines for the home
Though the road has been bumpy with squeezed supply chains and inflation, the cost of renewable energy technologies is near the lowest it has ever been, eclipsing that of traditional sources like coal and natural gas. Solar and wind installations continue to grow exponentially, and technological advances and low costs have made residential clean energy sources extremely in-demand.
Generally speaking, however, wind installations are in almost every case used on a commercial or industrial scale, while solar has proved its value in the residential market. Let’s go over the biggest benefits and drawbacks of each.
Pros and cons of solar power
As mentioned, solar panel installations offer tremendous opportunities as a residential-scale energy source. Here are the main reasons why:

Pros and cons of wind power
Wind power, rather, is much more practical at the utility scale.

So which is better, solar or wind power?
Wind power currently outpaces that of solar when it comes to overall share of electricity generated. For homeowners, solar energy is a far more practical option.
What it really comes down to, however, is location. In the world of energy, there is no one-size-fits-all solution. Intelligence is a species’ ability to live harmoniously in its environment, using the energy sources most logical for that region. We would never expect solar power to outpace a source of energy like hydropower in regions like the Pacific Northwest. Just like we wouldn’t expect wind power to take off in dense urban areas like New York City.
The future of energy is a decentralized one — one where energy is generated and consumed locally. For homeowners looking to make tangible changes in their lives to work toward a more sustainable future, solar power offers a wonderful opportunity to make a difference. Wind power may not present the same opportunities for homes, but it will surely be a huge part of the collaboration of renewable energy sources in the efforts to reach a net-zero-carbon future.
Have you read?
The cost of renewable energy is declining and it's going to change everything, what's the future of renewable energy in the us, europe is beating its renewable energy targets. which countries are leading the charge, don't miss any update on this topic.
Create a free account and access your personalized content collection with our latest publications and analyses.
License and Republishing
World Economic Forum articles may be republished in accordance with the Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial-NoDerivatives 4.0 International Public License, and in accordance with our Terms of Use.
The views expressed in this article are those of the author alone and not the World Economic Forum.
The Agenda .chakra .wef-n7bacu{margin-top:16px;margin-bottom:16px;line-height:1.388;font-weight:400;} Weekly
A weekly update of the most important issues driving the global agenda
.chakra .wef-1dtnjt5{display:-webkit-box;display:-webkit-flex;display:-ms-flexbox;display:flex;-webkit-align-items:center;-webkit-box-align:center;-ms-flex-align:center;align-items:center;-webkit-flex-wrap:wrap;-ms-flex-wrap:wrap;flex-wrap:wrap;} More on Energy Transition .chakra .wef-17xejub{-webkit-flex:1;-ms-flex:1;flex:1;justify-self:stretch;-webkit-align-self:stretch;-ms-flex-item-align:stretch;align-self:stretch;} .chakra .wef-nr1rr4{display:-webkit-inline-box;display:-webkit-inline-flex;display:-ms-inline-flexbox;display:inline-flex;white-space:normal;vertical-align:middle;text-transform:uppercase;font-size:0.75rem;border-radius:0.25rem;font-weight:700;-webkit-align-items:center;-webkit-box-align:center;-ms-flex-align:center;align-items:center;line-height:1.2;-webkit-letter-spacing:1.25px;-moz-letter-spacing:1.25px;-ms-letter-spacing:1.25px;letter-spacing:1.25px;background:none;padding:0px;color:#B3B3B3;-webkit-box-decoration-break:clone;box-decoration-break:clone;-webkit-box-decoration-break:clone;}@media screen and (min-width:37.5rem){.chakra .wef-nr1rr4{font-size:0.875rem;}}@media screen and (min-width:56.5rem){.chakra .wef-nr1rr4{font-size:1rem;}} See all

Weekend Reads: Funding AI’s future, imperfect environmentalists and Jane Goodall’s lessons on hope
Linda Lacina
April 5, 2024

What to do with ageing oil and gas platforms – and why it matters
Victoria Masterson
April 2, 2024

How ‘slow steaming’ reduces emissions from shipping

A new study reveals how renewables could power Africa by 2040
Christiane Zarfl and Rebecca Peters
March 27, 2024

Geopolitics, the equitable transition, and AI: things to look out for in energy in 2024
Robin Pomeroy and Sophia Akram
March 26, 2024

Industrial electrification is a joint venture: why collaboration across sectors is key
Francisco Laverón, Randolph Brazier, Natalia Zabolotnikova and Xabier Mugarza Zorriqueta
- Advantages and Disadvantages of Renewable Energy
What Are the Advantages and Disadvantages of Renewable Energy?

- What Exactly Is Renewable Energy?
Renewable energy is any form available in the natural environment and can be replenished repeatedly. For example, solar energy is naturally available, and we can’t run out of it by consuming it.
On the contrary, as w e burn fossil fuels like oil and coal , their resources constantly decrease. Scientists have estimated that the remaining oil resources might last around 190 years . This estimation is up to 230 years for natural gas resources.
Unfortunately, renewable energy supplies less than 16% of the total energy we consume worldwide. However, this share constantly increases , especially in advanced countries with supportive policies. For instance, the UK has planned to increase its renewable capacity from 47.16 GW in 2019 to 86.21 GW by 2026 .
- 7 Types of Renewable Energy Sources
- Advantages of Renewable Energy
- Disadvantages of Renewable Energy
- Why Is Renewable Energy Important?
Fortunately, renewable energy is available in various forms depending on the location and the season . For example, some areas have gale-force winds, but the sunlight is not enough because of cloudy weather.
Having a distributed network of different forms of energy can ensure that we have sustainable and clean energy . Here are 7 types of alternative energy sources available out there:
Solar Energy
Solar energy is the only type of renewable energy you can easily harness at home . You need to buy either solar water heaters or solar panels to use solar energy and reduce your energy bills. There are different types of PV panels and you can choose the best one for your home according to the price, efficiency, and other criteria.
Wind Energy
To utilize gale-force winds, we need to build large turbines in windy areas. Wind farms can help rural and remote areas to have green electricity. For example, offshore and onshore wind in the UK is generating around 24.2% of the UK’s electricity .
Hydroelectric
Hydroelectric power is similar to wind energy technology except for the working liquid, water instead of air . Building large dams and using turbines might be expensive, but it will produce a great amount of electricity.
Geothermal Energy
Geothermal energy is another clean and renewable energy that can be regarded as a sustainable power source. It is the heat within the planet Earth that can be harnessed in some areas.
Biomass energy is the heat we can derive from organic waste by burning it . It’s regarded as a renewable energy source because we always regenerate organic materials, mostly plants.
Tidal Energy
Tidal or ocean energy is the hydropower energy we can get from tides . This energy is sometimes sorted under the category of hydropower, not in a separate one.
Hydrogen is the most abundant element available on our planet, two-thirds of which is water. This element can be used as a zero-carbon fuel if we separate it.
First, looking at the advantages of using renewable energy sources instead of burning fossil fuels is good. Here are several important benefits of using renewable energy:
1. Renewable Energy Sources Will Not Run Out
As it comes from the name, a renewable energy source is sustainable, meaning it will not run out soon. For example, the sun is expected to shine every morning for at least 4.5 – 5.5 billion years to come, so we can consider it a renewable energy source. This might be the most important difference between renewables and fossil fuels.
2. Renewable Energy Is Reliable
Despite fossil fuels, which are always subject to disputes and wars between countries, we can easily and peacefully gain control of renewable energy sources. In other words, trade laws, political instabilities, territorial claims, and market turmoil cannot impact the use of renewable energy sources.
Although renewable energy sources are not distributed equally, with a smart and widespread energy network, they can be used as reliable means of supplying energy.
3. Renewable Energy Is Environmentally Friendly
Renewable energy sources are natural ways of energy generation and, therefore, can be considered clean. Although renewable energy technologies can cause some emissions, overall, minimum carbon and GHG will be emitted to the environment.
When you compare them with fossil fuels, the difference is significant. Therefore, catastrophic environmental issues like global warming, climate change, and low air quality can be omitted if we go for renewable energy .
4. Renewable Energy Can Increase Public Health
We’ll have healthier air and soil by reducing greenhouse emissions and other polluting substances. This will improve public health, and people will have happier lives. Additionally, having a healthier population will cause a significant reduction in the health budget people and governments should set aside each year.
Scientists have tried to improve fossil fuel technologies to make them less polluting without reducing their efficiency. However, renewable energy technologies are still way healthier than traditional technologies.
5. Renewable Technologies Create Lots of Jobs
Besides the environmental impact of using renewable technologies, they can benefit the economy. This is especially important in some unprivileged regions. This new and stable job market has recently emerged and can empower people in poor areas .
With a concerted effort and prudent investment, renewable jobs can reduce poverty all over the globe. Also, it can prevent people from emigrating from the countryside to urban areas. Governments can offer them a fair share of the energy generated by renewable electricity on their farms. In advanced countries such as the UK, numerous renewable jobs have already been created due to governmental grants.
6. Renewable Technologies Require Less Maintenance Cost
If you compare renewable energy technologies with fossil fuel power stations, you see fewer moving or combusting parts. Solar energy systems don’t need rotating parts although you can see turbines in wind farms or hydropower stations. This makes renewable energy technologies more durable; therefore, you will spend less on maintenance and repair. Overall, the operational cost of renewable energy stations is significantly less than traditional power stations.
7. Renewable Energy Can Reduce Turmoil in Energy Prices
If you usually follow the news, you must have heard of daily ups and downs in oil prices. Renewable energy can greatly help in this regard, reducing this turmoil and stabilising the global energy market. Because using renewable energy only demands an initial investment and doesn’t require any fuel, as for instance with an air source heat pump .
On the contrary, using traditional technologies demands a significant budget for fossil fuel prices, which are subject to ever-existing inflations . When countries reduce their reliance on fossil fuels, the prices in this market will change more smoothly.
8. Renewable Energy Can Increase Countries’ Economic Independence
Countries with no fossil fuel resources can reduce their energy dependence with a distributed network of renewable energy technologies. In fact, local people can generate electricity using renewable technologies and help governments reduce oil imports. This will decrease the risk of an energy crisis and benefit the countries’ sustainable development.
9. Leftovers Can Be Used in Renewable Technologies
Landfills are among the major crises in the world. It’s good to know that some sorts of renewable energy technologies can use leftovers and reduce the amount of waste materials that are piled in landfills.
Biomass energy, for instance, biomass boilers , has this beneficial aspect that can consume used organic products as fuel . This is a promising way to kill two birds with a single stone. First, the size of landfills should be reduced, and second, energy should be generated without paying for fossil fuels.
Now, it’s time to look at some disadvantages of renewable energy that make it difficult.
1. Renewable Energy Is Not Available Round the Clock
Renewable energy sources are natural forces that are strongly dependent on the weather conditions. Therefore, when you have bad weather conditions , renewable energy technologies such as solar cells will be of less use.
For example, when it rains, your PV panels can’t generate electricity, so you have to get back to traditional power sources. This uncertainty is the most important drawback of relying on renewable technologies.
2. The Efficiency of Renewable Technologies Is Low
Each type of energy requires a specific technology so that we can convert it into electricity. The efficiency of energy conversion devices is very important when prioritizing energy sources. Unfortunately, the efficiency of renewable technologies is not that high compared with traditional energy conversion devices.
For example, solar panel efficiency , that are available in the market, is between 15% and 20% . On the other hand, traditional technologies that use coal or natural gas can reach efficiency levels of up to 40% and 60%, respectively.
3. The Initial Cost of Renewable Energy Is High
Considering the energy we can get from renewable technologies, their initial cost is high and sometimes unaffordable. Renewable energy devices’ manufacturing and installation processes, like PV panels, are relatively expensive. Also heat pump costs can be quite high for some households. Governments are setting aside considerable budgets , such as solar panel grants and heat pump grants , to help these technologies grow.
4. Renewable Energy Sites Require A Lot of Space
To harness nature’s energies, we need a lot of space . This will cause many problems for renewable energy sites. Compared with traditional power stations, we must use more land to establish renewable energy farms.
5. Renewable Energy Devices Need Recycling
Generating electricity from renewable energy sources produces way lower levels of pollution. However, renewable devices are subject to some concerns because manufacturing them and their disposal process might emit pollution.
For example, solar cells will fail to perform well after a while, so we need to throw them away. However, these devices might be toxic, so we need to think of a recycling process for them.
Why is Renewable Energy Important?
We’re now facing unprecedented heatwaves, polluted air, and unbelievable health issues caused by fossil fuels. In Addition to this issue, fossil fuels are about to run out if we continue to burn them uncontrollably.
Renewable energy sources are our best chance to stop the current trend and make the world a better place to live. Therefore, governments are considering using renewable energy sources to generate electric power. As a result, renewable energy is increasingly used to gen erate electricity in all countries .
For example, the share of renewable energy in global electricity generation increased to 29% in 2020 . This is a success compared with a 27% share in electricity generation in 2019.
Some advanced countries, such as the UK, have aimed for 100% renewable cities by 2050. Around 43% of the UK’s electricity is generated by renewables. Despite many obstacles towards 100% renewable energy, there are promising advantages to using renewable technologies.
Overall, the advantages of using renewable energy sources outweigh the disadvantages. Although the initial cost of establishing a network of renewable technologies might be higher, the expenses will be offset over time. Considering the lateral influencers of using renewable energy, postponing shifting toward 100% renewable is not a wise course of action.

Hossein Karami Lakeh is an engineer interested in different aspects of energy, especially renewable energy technologies. He holds a master’s degree in mechanical engineering, focusing on thermo-photovoltaic systems. He has written several articles for valid ISI journals, international conferences, and high-authority websites to share his ideas on how to make the world a better place to live.

Renewable Energy – Pros and Cons
According to the International Energy Agency (IEA), Renewable electricity is growing at a faster rate in India than any other major economy, with new capacity additions on track to double by 2026.

Table of Contents
Context: According to the International Energy Agency (IEA), Renewable electricity is growing at a faster rate in India than any other major economy, with new capacity additions on track to double by 2026.
About Renewable Energy
- Renewable energy refers to energy sources that are naturally replenished and have a significantly lower impact on the environment compared to fossil fuels.
- The most popular renewable energy sources currently are: Solar energy, Wind energy, Hydro energy, Tidal energy, Geothermal energy, Biomass energy.
- When it comes to nuclear energy , the energy produced by nuclear power plants is considered renewable, but the fuel required for nuclear reactions is not renewable. Additionally, nuclear energy production does not release greenhouse gases, making it a low-carbon energy source.
India’s Renewable Energy Landscape
- As of May 2023, India’s installed renewable energy (RE) capacity, including nuclear power, stands at 197 GW, which accounts for 43% of the total installed energy capacity.
- India stands 4th globally in Renewable Energy Installed Capacity , 4th in Wind Power capacity & 4th in Solar Power capacity (as per REN21 Renewables 2022 Global Status Report).
- Reach 500 GW Non-fossil energy capacity by 2030.
- 50 per cent of its energy requirements from renewable energy by 2030.
- Reduction of total projected carbon emissions by one billion tonnes from now to 2030.
- Reduction of the carbon intensity of the economy by 45 per cent by 2030, over 2005 levels.
- Achieving the target of net zero emissions by 2070.
Pros and Cons of Renewable Energies & India’s Potential and Efforts
Sharing is caring!

Leave a comment
Your email address will not be published. Required fields are marked *
Save my name, email, and website in this browser for the next time I comment.

- UPSC Online Coaching
- UPSC Exam 2024
- UPSC Syllabus 2024
- UPSC Prelims Syllabus 2024
- UPSC Mains Syllabus 2024
- UPSC Exam Pattern 2024
- UPSC Age Limit 2024
- UPSC Calendar 2024
- UPSC Syllabus in Hindi
- UPSC Full Form

Recent Posts
- UPPSC Exam 2024
- UPPSC Calendar
- UPPSC Syllabus 2024
- UPPSC Exam Pattern 2024
- UPPSC Application Form 2024
- UPPSC Eligibility Criteria 2024
- UPPSC Admit card 2024
- UPPSC Salary And Posts
- UPPSC Cut Off
- UPPSC Previous Year Paper
BPSC Exam 2024
- BPSC 70th Notification
- BPSC 69th Exam Analysis
- BPSC Admit Card
- BPSC Syllabus
- BPSC Exam Pattern
- BPSC Cut Off
- BPSC Question Papers
IB ACIO Exam
- IB ACIO Salary
- IB ACIO Syllabus
CSIR SO ASO Exam
- CSIR SO ASO Exam 2024
- CSIR SO ASO Result 2024
- CSIR SO ASO Exam Date
- CSIR SO ASO Question Paper
- CSIR SO ASO Answer key 2024
- CSIR SO ASO Exam Date 2024
- CSIR SO ASO Syllabus 2024
Study Material Categories
- Daily The Hindu Analysis
- Daily Practice Quiz for Prelims
- Daily Answer Writing
- Daily Current Affairs
- Indian Polity
- Environment and Ecology
- Art and Culture
- General Knowledge
- Biographies

IMPORTANT EXAMS

- Terms & Conditions
- Return & Refund Policy
- Privacy Policy
Towards Sustainable Energy: A Systematic Review of Renewable Energy Sources, Technologies, and Public Opinions
Ieee account.
- Change Username/Password
- Update Address
Purchase Details
- Payment Options
- Order History
- View Purchased Documents
Profile Information
- Communications Preferences
- Profession and Education
- Technical Interests
- US & Canada: +1 800 678 4333
- Worldwide: +1 732 981 0060
- Contact & Support
- About IEEE Xplore
- Accessibility
- Terms of Use
- Nondiscrimination Policy
- Privacy & Opting Out of Cookies
A not-for-profit organization, IEEE is the world's largest technical professional organization dedicated to advancing technology for the benefit of humanity. © Copyright 2024 IEEE - All rights reserved. Use of this web site signifies your agreement to the terms and conditions.
Solar Energy
Solar energy is created by nuclear fusion that takes place in the sun. It is necessary for life on Earth, and can be harvested for human uses such as electricity.
Earth Science, Engineering, Physics
Loading ...
Solar energy is any type of energy generated by the sun . Solar energy is created by nuclear fusion that takes place in the sun. Fusion occurs when protons of hydrogen atoms violently collide in the sun’s core and fuse to create a helium atom. This process, known as a PP (proton-proton) chain reaction, emits an enormous amount of energy. In its core, the sun fuses about 620 million metric tons of hydrogen every second. The PP chain reaction occurs in other stars that are about the size of our sun, and provides them with continuous energy and heat. The temperature for these stars is around 4 million degrees on the Kelvin scale (about 4 million degrees Celsius, 7 million degrees Fahrenheit). In stars that are about 1.3 times bigger than the sun, the CNO cycle drives the creation of energy. The CNO cycle also converts hydrogen to helium, but relies on carbon, nitrogen, and oxygen (C, N, and O) to do so. Currently , less than two percent of the sun’s energy is created by the CNO cycle. Nuclear fusion by the PP chain reaction or CNO cycle releases tremendous amounts of energy in the form of waves and particles. Solar energy is constantly flowing away from the sun and throughout the solar system . Solar energy warms Earth, causes wind and weather , and sustains plant and animal life. The energy, heat, and light from the sun flow away in the form of electromagnetic radiation (EMR). The electromagnetic spectrum exists as waves of different frequencies and wavelengths. The frequency of a wave represents how many times the wave repeats itself in a certain unit of time. Waves with very short wavelengths repeat themselves several times in a given unit of time, so they are high-frequency. In contrast, low-frequency waves have much longer wavelengths. The vast majority of electromagnetic waves are invisible to us. The most high-frequency waves emitted by the sun are gamma rays, X-rays, and ultraviolet radiation (UV rays). The most harmful UV rays are almost completely absorbed by Earth’s atmosphere . Less potent UV rays travel through the atmosphere, and can cause sunburn. The sun also emits infrared radiation , whose waves are much lower-frequency. Most heat from the sun arrives as infrared energy. Sandwiched between infrared and UV is the visible spectrum, which contains all the colors we see on Earth. The color red has the longest wavelengths (closest to infrared), and violet (closest to UV) the shortest. Natural Solar Energy Greenhouse Effect The infrared, visible, and UV waves that reach Earth take part in a process of warming the planet and making life possible—the so-called “greenhouse effect.” About 30 percent of the solar energy that reaches Earth is reflected back into space. The rest is absorbed into Earth’s atmosphere. The radiation warms Earth’s surface, and the surface radiates some of the energy back out in the form of infrared waves. As they rise through the atmosphere, they are intercepted by greenhouse gases , such as water vapor and carbon dioxide.
Greenhouse gases trap the heat that reflects back up into the atmosphere. In this way, they act like the glass walls of a greenhouse. This greenhouse effect keeps Earth warm enough to sustain life. Photosynthesis Almost all life on Earth relies on solar energy for food, either directly or indirectly. Producers rely directly on solar energy. They absorb sunlight and convert it into nutrients through a process called photosynthesis. Producers, also called autotrophs , include plants, algae, bacteria, and fungi. Autotrophs are the foundation of the food web . Consumers rely on producers for nutrients. Herbivores, carnivores, omnivores, and detritivores rely on solar energy indirectly. Herbivores eat plants and other producers. Carnivores and omnivores eat both producers and herbivores. Detritivores decompose plant and animal matter by consuming it. Fossil Fuels Photosynthesis is also responsible for all of the fossil fuels on Earth. Scientists estimate that about three billion years ago, the first autotrophs evolved in aquatic settings. Sunlight allowed plant life to thrive and evolve. After the autotrophs died, they decomposed and shifted deeper into the Earth, sometimes thousands of meters. This process continued for millions of years. Under intense pressure and high temperatures, these remains became what we know as fossil fuels. Microorganisms became petroleum, natural gas, and coal. People have developed processes for extracting these fossil fuels and using them for energy. However, fossil fuels are a nonrenewable resource . They take millions of years to form. Harnessing Solar Energy Solar energy is a renewable resource , and many technologies can harvest it directly for use in homes, businesses, schools, and hospitals. Some solar energy technologies include photovoltaic cells and panels, concentrated solar energy , and solar architecture . There are different ways of capturing solar radiation and converting it into usable energy. The methods use either active solar energy or passive solar energy . Active solar technologies use electrical or mechanical devices to actively convert solar energy into another form of energy, most often heat or electricity. Passive solar technologies do not use any external devices. Instead, they take advantage of the local climate to heat structures during the winter, and reflect heat during the summer. Photovoltaics Photovoltaics is a form of active solar technology that was discovered in 1839 by 19-year-old French physicist Alexandre-Edmond Becquerel. Becquerel discovered that when he placed silver-chloride in an acidic solution and exposed it to sunlight, the platinum electrodes attached to it generated an electric current. This process of generating electricity directly from solar radiation is called the photovoltaic effect, or photovoltaics.
Today, photovoltaics is probably the most familiar way to harness solar energy. Photovoltaic arrays usually involve solar panels , a collection of dozens or even hundreds of solar cells. Each solar cell contains a semiconductor , usually made of silicon. When the semiconductor absorbs sunlight, it knocks electrons loose. An electrical field directs these loose electrons into an electric current, flowing in one direction. Metal contacts at the top and bottom of a solar cell direct that current to an external object. The external object can be as small as a solar-powered calculator or as large as a power station. Photovoltaics was first widely used on spacecraft. Many satellites , including the International Space Station (ISS), feature wide, reflective “wings” of solar panels. The ISS has two solar array wings (SAWs), each using about 33,000 solar cells. These photovoltaic cells supply all electricity to the ISS, allowing astronauts to operate the station, safely live in space for months at a time, and conduct scientific and engineering experiments. Photovoltaic power stations have been built all over the world. The largest stations are in the United States, India, and China. These power stations emit hundreds of megawatts of electricity, used to supply homes, businesses, schools, and hospitals. Photovoltaic technology can also be installed on a smaller scale. Solar panels and cells can be fixed to the roofs or exterior walls of buildings, supplying electricity for the structure. They can be placed along roads to light highways. Solar cells are small enough to power even smaller devices, such as calculators, parking meters, trash compactors, and water pumps. Concentrated Solar Energy Another type of active solar technology is concentrated solar energy or concentrated solar power (CSP). CSP technology uses lenses and mirrors to focus (concentrate) sunlight from a large area into a much smaller area. This intense area of radiation heats a fluid, which in turn generates electricity or fuels another process. Solar furnaces are an example of concentrated solar power. There are many different types of solar furnaces, including solar power towers , parabolic troughs, and Fresnel reflectors. They use the same general method to capture and convert energy. Solar power towers use heliostats , flat mirrors that turn to follow the sun’s arc through the sky. The mirrors are arranged around a central “collector tower,” and reflect sunlight into a concentrated ray of light that shines on a focal point on the tower. In previous designs of solar power towers, the concentrated sunlight heated a container of water, which produced steam that powered a turbine . More recently, some solar power towers use liquid sodium, which has a higher heat capacity and retains heat for a longer period of time. This means that the fluid not only reaches temperatures of 773 to 1,273K (500° to 1,000° C or 932° to 1,832° F), but it can continue to boil water and generate power even when the sun is not shining. Parabolic troughs and Fresnel reflectors also use CSP, but their mirrors are shaped differently. Parabolic mirrors are curved, with a shape similar to a saddle. Fresnel reflectors use flat, thin strips of mirror to capture sunlight and direct it onto a tube of liquid. Fresnel reflectors have more surface area than parabolic troughs and can concentrate the sun’s energy to about 30 times its normal intensity. Concentrated solar power plants were first developed in the 1980s. The largest facility in the world is a series of plants in Mojave Desert in the U.S. state of California. This Solar Energy Generating System (SEGS) generates more than 650 gigawatt-hours of electricity every year. Other large and effective plants have been developed in Spain and India.
Concentrated solar power can also be used on a smaller scale. It can generate heat for solar cookers , for instance. People in villages all over the world use solar cookers to boil water for sanitation and to cook food. Solar cookers provide many advantages over wood-burning stoves: They are not a fire hazard, do not produce smoke, do not require fuel, and reduce habitat loss in forests where trees would be harvested for fuel. Solar cookers also allow villagers to pursue time for education, business, health, or family during time that was previously used for gathering firewood. Solar cookers are used in areas as diverse as Chad, Israel, India, and Peru. Solar Architecture Throughout the course of a day, solar energy is part of the process of thermal convection , or the movement of heat from a warmer space to a cooler one. When the sun rises, it begins to warm objects and material on Earth. Throughout the day, these materials absorb heat from solar radiation. At night, when the sun sets and the atmosphere has cooled, the materials release their heat back into the atmosphere. Passive solar energy techniques take advantage of this natural heating and cooling process. Homes and other buildings use passive solar energy to distribute heat efficiently and inexpensively. Calculating a building’s “ thermal mass ” is an example of this. A building’s thermal mass is the bulk of material heated throughout the day. Examples of a building’s thermal mass are wood, metal, concrete, clay, stone, or mud. At night, the thermal mass releases its heat back into the room. Effective ventilation systems—hallways, windows, and air ducts—distribute the warmed air and maintain a moderate, consistent indoor temperature. Passive solar technology is often involved in the design of a building. For example, in the planning stage of construction, the engineer or architect may align the building with the sun’s daily path to receive desirable amounts of sunlight. This method takes into account the latitude , altitude , and typical cloud cover of a specific area. In addition, buildings can be constructed or retrofitted to have thermal insulation, thermal mass, or extra shading. Other examples of passive solar architecture are cool roofs, radiant barriers , and green roofs . Cool roofs are painted white, and reflect the sun’s radiation instead of absorbing it. The white surface reduces the amount of heat that reaches the interior of the building, which in turn reduces the amount of energy that is needed to cool the building. Radiant barriers work similarly to cool roofs. They provide insulation with highly reflective materials, such as aluminum foil. The foil reflects, instead of absorbs, heat, and can reduce cooling costs up to 10 percent. In addition to roofs and attics, radiant barriers may also be installed beneath floors. Green roofs are roofs that are completely covered with vegetation . They require soil and irrigation to support the plants, and a waterproof layer beneath. Green roofs not only reduce the amount of heat that is absorbed or lost, but also provide vegetation. Through photosynthesis, the plants on green roofs absorb carbon dioxide and emit oxygen. They filter pollutants out of rainwater and air, and offset some of the effects of energy use in that space. Green roofs have been a tradition in Scandinavia for centuries, and have recently become popular in Australia, Western Europe, Canada, and the United States. For example, the Ford Motor Company covered 42,000 square meters (450,000 square feet) of its assembly plant roofs in Dearborn, Michigan, with vegetation. In addition to reducing greenhouse gas emissions, the roofs reduce stormwater runoff by absorbing several centimeters of rainfall.
Green roofs and cool roofs can also counteract the “ urban heat island ” effect. In busy cities, the temperature can be consistently higher than the surrounding areas. Many factors contribute to this: Cities are constructed of materials such as asphalt and concrete that absorb heat; tall buildings block wind and its cooling effects; and high amounts of waste heat is generated by industry, traffic, and high populations. Using the available space on the roof to plant trees, or reflecting heat with white roofs, can partially alleviate local temperature increases in urban areas. Solar Energy and People Since sunlight only shines for about half of the day in most parts of the world, solar energy technologies have to include methods of storing the energy during dark hours. Thermal mass systems use paraffin wax or various forms of salt to store the energy in the form of heat. Photovoltaic systems can send excess electricity to the local power grid , or store the energy in rechargeable batteries. There are many pros and cons to using solar energy. Advantages A major advantage to using solar energy is that it is a renewable resource. We will have a steady, limitless supply of sunlight for another five billion years. In one hour, Earth’s atmosphere receives enough sunlight to power the electricity needs of every human being on Earth for a year. Solar energy is clean. After the solar technology equipment is constructed and put in place, solar energy does not need fuel to work. It also does not emit greenhouse gases or toxic materials. Using solar energy can drastically reduce the impact we have on the environment. There are locations where solar energy is practical . Homes and buildings in areas with high amounts of sunlight and low cloud cover have the opportunity to harness the sun’s abundant energy. Solar cookers provide an excellent alternative to cooking with wood-fired stoves—on which two billion people still rely. Solar cookers provide a cleaner and safer way to sanitize water and cook food. Solar energy complements other renewable sources of energy, such as wind or hydroelectric energy . Homes or businesses that install successful solar panels can actually produce excess electricity. These homeowners or businessowners can sell energy back to the electric provider, reducing or even eliminating power bills. Disadvantages The main deterrent to using solar energy is the required equipment. Solar technology equipment is expensive. Purchasing and installing the equipment can cost tens of thousands of dollars for individual homes. Although the government often offers reduced taxes to people and businesses using solar energy, and the technology can eliminate electricity bills, the initial cost is too steep for many to consider. Solar energy equipment is also heavy. In order to retrofit or install solar panels on the roof of a building, the roof must be strong, large, and oriented toward the sun’s path. Both active and passive solar technology depend on factors that are out of our control, such as climate and cloud cover. Local areas must be studied to determine whether or not solar power would be effective in that area. Sunlight must be abundant and consistent for solar energy to be an efficient choice. In most places on Earth, sunlight’s variability makes it difficult to implement as the only source of energy.
Agua Caliente The Agua Caliente Solar Project, in Yuma, Arizona, United States, is the world's largest array of photovoltaic panels. Agua Caliente has more than five million photovoltaic modules, and generates more than 600 gigawatt-hours of electricity.
Green Chicago Millennium Park in Chicago, Illinois, United States, has one of the most expansive green roofs in the world almost 100,000 square meters (more than a million square feet). Vegetation at ground level covers 24.5 acres of an underground parking garage, and includes gardens, picnic areas, and an outdoor concert facility.
Solar Decathlon The Solar Decathlon is a biannual international event presented by the U.S. Department of Energy. Teams compete to design, build, and operate the most attractive, effective, and energy-efficient solar-powered house.
Media Credits
The audio, illustrations, photos, and videos are credited beneath the media asset, except for promotional images, which generally link to another page that contains the media credit. The Rights Holder for media is the person or group credited.
Illustrator
Last updated.
April 3, 2024
User Permissions
For information on user permissions, please read our Terms of Service. If you have questions about how to cite anything on our website in your project or classroom presentation, please contact your teacher. They will best know the preferred format. When you reach out to them, you will need the page title, URL, and the date you accessed the resource.
If a media asset is downloadable, a download button appears in the corner of the media viewer. If no button appears, you cannot download or save the media.
Text on this page is printable and can be used according to our Terms of Service .
Interactives
Any interactives on this page can only be played while you are visiting our website. You cannot download interactives.
Related Resources

- Wind Energy Technologies Office
- Wind Energy Career Map
- Key Activities in Wind Energy
- WETO Budget
- WETO Organization & Contacts
- Atmosphere to Electrons
- Distributed Wind
- Environmental Impacts & Siting
- Next-Generation Wind Technology
- Demonstration
- Floating Offshore Wind Shot
- Market Acceleration
- R&D Consortium
- Renewable Systems Integration
- Resource Assessment & Characterization
- Testing & Certification
- Drivetrains
- Infrastructure & Logistics
- Wind Turbine Radar Interference
- Wind Turbine Sustainability
- Workforce Development & Education
- History of Wind Energy
- How Distributed Wind Works
- How Wind Turbines Work
- WINDExchange
- Small Wind Systems FAQs
- WETO Peer Reviews
- Wind Energy FAQs
- Wind Energy Market Reports
- Wind Energy Projects Map
- Related Opportunities
- Wind Energy Technologies Office Updates
- Wind R&D Newsletter
Wind energy offers many advantages, which explains why it's one of the fastest-growing energy sources in the world. To further expand wind energy’s capabilities and community benefits, researchers are working to address technical and socio-economic challenges in support of a decarbonized electricity future.
Learn more about ongoing research to take advantage of these benefits and tackle wind energy challenges.
Advantages of Wind Power
- Wind power creates good-paying jobs. There are over 125,000 people working in the U.S. wind industry across all 50 states, and that number continues to grow. According to the U.S. Bureau of Labor Statistics , wind turbine service technicians are the fastest growing U.S. job of the decade. Offering career opportunities ranging from blade fabricator to asset manager, the wind industry has the potential to support hundreds of thousands of more jobs by 2050.
- Wind power is a domestic resource that enables U.S. economic growth. In 2022, wind turbines operating in all 50 states generated more than 10% of the net total of the country’s energy . That same year, investments in new wind projects added $20 billion to the U.S. economy.
- Wind power is a clean and renewable energy source. Wind turbines harness energy from the wind using mechanical power to spin a generator and create electricity. Not only is wind an abundant and inexhaustible resource, but it also provides electricity without burning any fuel or polluting the air. Wind energy in the United States helps avoid 336 million metric tons of carbon dioxide emissions annually —equivalent to the emissions from 73 million cars.
- Wind power benefits local communities. Wind projects deliver an estimated $2 billion in state and local tax payments and land-lease payments each year. Communities that develop wind energy can use the extra revenue to put towards school budgets, reduce the tax burden on homeowners, and address local infrastructure projects.
- Wind power is cost-effective. Land-based, utility-scale wind turbines provide one of the lowest-priced energy sources available today. Furthermore, wind energy’s cost competitiveness continues to improve with advances in the science and technology of wind energy.
- Wind turbines work in different settings. Wind energy generation fits well in agricultural and multi-use working landscapes. Wind energy is easily integrated in rural or remote areas, such as farms and ranches or coastal and island communities, where high-quality wind resources are often found.
Challenges of Wind Power
- Wind power must compete with other low-cost energy sources. When comparing the cost of energy associated with new power plants , wind and solar projects are now more economically competitive than gas, geothermal, coal, or nuclear facilities. However, wind projects may not be cost-competitive in some locations that are not windy enough. Next-generation technology , manufacturing improvements , and a better understanding of wind plant physics can help bring costs down even more.
- Ideal wind sites are often in remote locations. Installation challenges must be overcome to bring electricity from wind farms to urban areas, where it is needed to meet demand. Upgrading the nation’s transmission network to connect areas with abundant wind resources to population centers could significantly reduce the costs of expanding land-based wind energy. In addition, offshore wind energy transmission and grid interconnection capabilities are improving.
- Turbines produce noise and alter visual aesthetics. Wind farms have different impacts on the environment compared to conventional power plants, but similar concerns exist over both the noise produced by the turbine blades and the visual impacts on the landscape .
- Wind plants can impact local wildlife. Although wind projects rank lower than other energy developments in terms of wildlife impacts, research is still needed to minimize wind-wildlife interactions . Advancements in technologies, properly siting wind plants, and ongoing environmental research are working to reduce the impact of wind turbines on wildlife.

Search the United Nations
- What Is Climate Change
- Myth Busters
- Renewable Energy
- Finance & Justice
- Initiatives
- Sustainable Development Goals
- Paris Agreement
- Climate Ambition Summit 2023
- Climate Conferences
- Press Material
- Communications Tips

Renewable energy – powering a safer future
Energy is at the heart of the climate challenge – and key to the solution.
A large chunk of the greenhouse gases that blanket the Earth and trap the sun’s heat are generated through energy production, by burning fossil fuels to generate electricity and heat.
Fossil fuels, such as coal, oil and gas, are by far the largest contributor to global climate change , accounting for over 75 percent of global greenhouse gas emissions and nearly 90 percent of all carbon dioxide emissions.
The science is clear: to avoid the worst impacts of climate change, emissions need to be reduced by almost half by 2030 and reach net-zero by 2050.
To achieve this, we need to end our reliance on fossil fuels and invest in alternative sources of energy that are clean, accessible, affordable, sustainable, and reliable.
Renewable energy sources – which are available in abundance all around us, provided by the sun, wind, water, waste, and heat from the Earth – are replenished by nature and emit little to no greenhouse gases or pollutants into the air.
Fossil fuels still account for more than 80 percent of global energy production , but cleaner sources of energy are gaining ground. About 29 percent of electricity currently comes from renewable sources.
Here are five reasons why accelerating the transition to clean energy is the pathway to a healthy, livable planet today and for generations to come.
1. Renewable energy sources are all around us
About 80 percent of the global population lives in countries that are net-importers of fossil fuels -- that’s about 6 billion people who are dependent on fossil fuels from other countries, which makes them vulnerable to geopolitical shocks and crises.
In contrast, renewable energy sources are available in all countries, and their potential is yet to be fully harnessed. The International Renewable Energy Agency (IRENA) estimates that 90 percent of the world’s electricity can and should come from renewable energy by 2050.
Renewables offer a way out of import dependency, allowing countries to diversify their economies and protect them from the unpredictable price swings of fossil fuels, while driving inclusive economic growth, new jobs, and poverty alleviation.
2. Renewable energy is cheaper
Renewable energy actually is the cheapest power option in most parts of the world today. Prices for renewable energy technologies are dropping rapidly. The cost of electricity from solar power fell by 85 percent between 2010 and 2020. Costs of onshore and offshore wind energy fell by 56 percent and 48 percent respectively.
Falling prices make renewable energy more attractive all around – including to low- and middle-income countries, where most of the additional demand for new electricity will come from. With falling costs, there is a real opportunity for much of the new power supply over the coming years to be provided by low-carbon sources.
Cheap electricity from renewable sources could provide 65 percent of the world’s total electricity supply by 2030. It could decarbonize 90 percent of the power sector by 2050, massively cutting carbon emissions and helping to mitigate climate change.
Although solar and wind power costs are expected to remain higher in 2022 and 2023 then pre-pandemic levels due to general elevated commodity and freight prices, their competitiveness actually improves due to much sharper increases in gas and coal prices, says the International Energy Agency (IEA).
3. Renewable energy is healthier
According to the World Health Organization (WHO), about 99 percent of people in the world breathe air that exceeds air quality limits and threatens their health, and more than 13 million deaths around the world each year are due to avoidable environmental causes, including air pollution.
The unhealthy levels of fine particulate matter and nitrogen dioxide originate mainly from the burning of fossil fuels. In 2018, air pollution from fossil fuels caused $2.9 trillion in health and economic costs , about $8 billion a day.
Switching to clean sources of energy, such as wind and solar, thus helps address not only climate change but also air pollution and health.
4. Renewable energy creates jobs
Every dollar of investment in renewables creates three times more jobs than in the fossil fuel industry. The IEA estimates that the transition towards net-zero emissions will lead to an overall increase in energy sector jobs : while about 5 million jobs in fossil fuel production could be lost by 2030, an estimated 14 million new jobs would be created in clean energy, resulting in a net gain of 9 million jobs.
In addition, energy-related industries would require a further 16 million workers, for instance to take on new roles in manufacturing of electric vehicles and hyper-efficient appliances or in innovative technologies such as hydrogen. This means that a total of more than 30 million jobs could be created in clean energy, efficiency, and low-emissions technologies by 2030.
Ensuring a just transition , placing the needs and rights of people at the heart of the energy transition, will be paramount to make sure no one is left behind.
5. Renewable energy makes economic sense
About $7 trillion was spent on subsidizing the fossil fuel industry in 2022, including through explicit subsidies, tax breaks, and health and environmental damages that were not priced into the cost of fossil fuels.
In comparison, about $4 trillion a year needs to be invested in renewable energy until 2030 – including investments in technology and infrastructure – to allow us to reach net-zero emissions by 2050.
The upfront cost can be daunting for many countries with limited resources, and many will need financial and technical support to make the transition. But investments in renewable energy will pay off. The reduction of pollution and climate impacts alone could save the world up to $4.2 trillion per year by 2030.
Moreover, efficient, reliable renewable technologies can create a system less prone to market shocks and improve resilience and energy security by diversifying power supply options.
Learn more about how many communities and countries are realizing the economic, societal, and environmental benefits of renewable energy.
Will developing countries benefit from the renewables boom? Learn more here .

What is renewable energy?
Derived from natural resources that are abundant and continuously replenished, renewable energy is key to a safer, cleaner, and sustainable world. Explore common sources of renewable energy here.

Why invest in renewable energy?
Learn more about the differences between fossil fuels and renewables, the benefits of renewable energy, and how we can act now.

Five ways to jump-start the renewable energy transition now
UN Secretary-General outlines five critical actions the world needs to prioritize now to speed up the global shift to renewable energy.

What is net zero? Why is it important? Our net-zero page explains why we need steep emissions cuts now and what efforts are underway.
- What is climate change?
Our climate 101 offers a quick take on the how and why of climate change. Read more.

How will the world foot the bill? We explain the issues and the value of financing climate action.

Climate issues
Learn more about how climate change impacts are felt across different sectors and ecosystems.
It’s time to stop burning our planet, and start investing in the abundant renewable energy all around us." ANTÓNIO GUTERRES , United Nations Secretary-General

Facts and figures
- Causes and effects
- Myth busters
Cutting emissions
- Explaining net zero
- High-level expert group on net zero
- Checklists for credibility of net-zero pledges
- Greenwashing
- What you can do
Clean energy
- Renewable energy – key to a safer future
- What is renewable energy
- Five ways to speed up the energy transition
- Why invest in renewable energy
- Clean energy stories
- A just transition
Adapting to climate change
- Climate adaptation
- Early warnings for all
- Youth voices
Financing climate action
- Finance and justice
- Loss and damage
- $100 billion commitment
- Why finance climate action
- Biodiversity
- Human Security
International cooperation
- What are Nationally Determined Contributions
- Acceleration Agenda
- Climate Ambition Summit
- Climate conferences (COPs)
- Youth Advisory Group
- Action initiatives
- Secretary-General’s speeches
- Press material
- Fact sheets
- Communications tips
Generation of electricity Pros and cons of renewable energy resources
Electricity can be generated using a turbine to drive a generator before distribution. Renewable and non-renewable energy sources have pros and cons in terms of cost, reliability and pollution.
Part of Physics Electricity
Pros and cons of renewable energy resources
Advantages of non-renewable energy resources.
Most renewable energy resources are clean, because they do not produce any pollution and cheap because their energy supplies do not have any cost.
Hydroelectric power stations, as well as tidal and wave generators, are very reliable, and both hydroelectric power stations and tidal generators produce large amounts of electricity.
Disadvantages of renewable energy resources
At the present time, most renewable energy generators are expensive to set up. Also, sources such as wind turbines and solar cells rely heavily on the weather. If it is not a windy day, wind turbines will not turn. And if it is not sunny, solar cells will not produce much electricity.
More guides on this topic
- Electrical power
- Electromagnetism
- Charge and current
- Series and parallel circuits
- Applications of series and parallel circuits
- Classroom Videos
Related links
- BBC Science
- BBC News: Science
- SQA National 4 Physics
- Physics.org
- The Physics Classroom
- Physics Central
The Federal Register
The daily journal of the united states government, request access.
Due to aggressive automated scraping of FederalRegister.gov and eCFR.gov, programmatic access to these sites is limited to access to our extensive developer APIs.
If you are human user receiving this message, we can add your IP address to a set of IPs that can access FederalRegister.gov & eCFR.gov; complete the CAPTCHA (bot test) below and click "Request Access". This process will be necessary for each IP address you wish to access the site from, requests are valid for approximately one quarter (three months) after which the process may need to be repeated.
An official website of the United States government.
If you want to request a wider IP range, first request access for your current IP, and then use the "Site Feedback" button found in the lower left-hand side to make the request.

Renewable Energy – Pros and Cons
According to the International Energy Agency (IEA), Renewable electricity is growing at a faster rate in India than any other major economy, with new capacity additions on track to double by 2026.

Table of Contents
Context: According to the International Energy Agency (IEA), Renewable electricity is growing at a faster rate in India than any other major economy, with new capacity additions on track to double by 2026.
About Renewable Energy
- Renewable energy refers to energy sources that are naturally replenished and have a significantly lower impact on the environment compared to fossil fuels.
- The most popular renewable energy sources currently are: Solar energy, Wind energy, Hydro energy, Tidal energy, Geothermal energy, Biomass energy.
- When it comes to nuclear energy , the energy produced by nuclear power plants is considered renewable, but the fuel required for nuclear reactions is not renewable. Additionally, nuclear energy production does not release greenhouse gases, making it a low-carbon energy source.
India’s Renewable Energy Landscape
- As of May 2023, India’s installed renewable energy (RE) capacity, including nuclear power, stands at 197 GW, which accounts for 43% of the total installed energy capacity.
- India stands 4th globally in Renewable Energy Installed Capacity , 4th in Wind Power capacity & 4th in Solar Power capacity (as per REN21 Renewables 2022 Global Status Report).
- Reach 500 GW Non-fossil energy capacity by 2030.
- 50 per cent of its energy requirements from renewable energy by 2030.
- Reduction of total projected carbon emissions by one billion tonnes from now to 2030.
- Reduction of the carbon intensity of the economy by 45 per cent by 2030, over 2005 levels.
- Achieving the target of net zero emissions by 2070.
Pros and Cons of Renewable Energies & India’s Potential and Efforts
Sharing is caring!
Download your free content now!

To download , General Studies PDF, please fill the form.
Please fill valid Name, Phone and Email.
Congratulations!

We have received your details!
We'll share General Studies Study Material on your E-mail Id.
We have already received your details!

Incorrect details? Fill the form again here
General Studies PDF
Download Now
- Best Current Affairs
- Current Affairs Daily
- Daily Current Affairs
- Daily Current Affairs for UPSC
Leave a comment
Your email address will not be published. Required fields are marked *
Save my name, email, and website in this browser for the next time I comment.
Trending Events
- BPSC 69th Admit Card 2023
- BPSC 67th Mains Result

- UPSC Online Coaching
- UPSC Notification 2023
- UPSC Syllabus 2023
- UPSC EPFO Notification 2023
- UPSC Prelims Syllabus
- UPSC Mains Syllabus
- UPSC Exam Pattern
- UPSC Age Limit 2023
- UPSC Calendar 2023
- UPSC Syllabus in Hindi
- UPSC Admit Card 2023
- UPSC Full Form

Recent Posts
Nda exam 2023.
- NDA Notification 2023
- NDA Form 2023
- NDA Syllabus 2023
- NDA Age Limit 2023
- NDA Admit Card 2023
- NDA Selection Process 2023
- NDA Previous Year Question Papers
- NDA Cut Off
- NDA 2 Result
CDS Exam 2023
- CDS Notification 2023
- CDS Syllabus
- CDS Age Limit
- CDS Eligibility
- CDS Exam Pattern
- CDS Previous Year Question Papers
- CDS SSB Interview
- CDS Admit Card
IMPORTANT EXAMS

- Terms & Conditions
- Return & Refund Policy
- Privacy Policy

IMAGES
VIDEO
COMMENTS
4. Renewable energy has numerous environmental benefits. Renewable energy generation sources lead to lower greenhouse gas emissions than traditional fuel sources like natural gas. This means a smaller carbon footprint and an overall positive impact on the natural environment.
Holistic asset management for utility network companies . 3 min read - Addressing challenges of the energy transition with grid asset management The energy transition is gearing up to full speed as renewable energy sources replace fossil-based systems of energy production. The grid itself must green to operate within the environmental, social and governance (ESG) objectives and become carbon ...
2. 100% Renewable Energy. 100% renewable energy is a goal shared by at least 160 American citites, 10 counties, and eight states as of Sep. 16, 2020, according to the Sierra Club. As a policy, 100% renewable energy means not using fossil fuel energy or nuclear energy, with a goal for implementation generally between 2035 and 2050.
In contrast, renewable energy sources accounted for nearly 20 percent of global energy consumption at the beginning of the 21st century, largely from traditional uses of biomass such as wood for heating and cooking.By 2015 about 16 percent of the world's total electricity came from large hydroelectric power plants, whereas other types of renewable energy (such as solar, wind, and geothermal ...
The wind, the sun, and Earth are sources of renewable energy . These energy sources naturally renew, or replenish themselves. Wind, sunlight, and the planet have energy that transforms in ways we can see and feel. We can see and feel evidence of the transfer of energy from the sun to Earth in the sunlight shining on the ground and the warmth we ...
Studies show that wind energy's carbon footprint is quickly offset by the electricity it generates and is among the lowest of any energy source. Learn the facts about renewable power produced by wind, and hear Caltech engineer John Dabiri discuss the pros and cons and the future of wind energy.
Background Info. Vocabulary. In any discussion about climate change, renewable energy usually tops the list of changes the world can implement to stave off the worst effects of rising temperatures. That's because renewable energy sources, such as solar and wind, don't emit carbon dioxide and other greenhouse gases that contribute to global warming.
The main types of renewable energy are wind, solar, hydroelectric, tidal, geothermal and biomass. Read on to discover the pros and cons of each of these renewable energy sources. One of the main benefits of most renewable energy sources is that they don't release carbon dioxide or pollute the air when they are used to produce electricity or heat.
Hydropower is the world's biggest source of renewable energy by far, with China, Brazil, Canada, the U.S., and Russia the leading hydropower producers. While hydropower is theoretically a clean ...
History shows that advances in renewable energy often follow crises: In the 1970s, oil embargos caused the cost of oil to quadruple, spurring efforts to reduce American dependence on fossil fuels and find alternative sources of power, including solar energy or wind power. The 2008-09 global financial crisis led to several governments linking part of their economic stimulus to investment in ...
Advantages and Disadvantages to the Use of Renewable Energy. Hydroelectric power is a very clean method of producing renewable energy since "it does not produce any greenhouse gases and is the cleanest of all the renewable energy sources" (National Geographic 2015, par. 4). Hydroelectric power uses the power of water to create electricity.
Using more renewable energy can lower the prices of and demand for natural gas and coal by increasing competition and diversifying our energy supplies. And an increased reliance on renewable energy can help protect consumers when fossil fuel prices spike. Explainer. Renewables face major obstacles.
8. Renewable Energy Can Increase Countries' Economic Independence. Countries with no fossil fuel resources can reduce their energy dependence with a distributed network of renewable energy technologies. In fact, local people can generate electricity using renewable technologies and help governments reduce oil imports.
Pros and Cons of Renewable Energies & India's Potential and Efforts. Solar Energy. Pros: Renewable and low carbon: Inexhaustible source of energy and is environment friendly. Cost-savings: Once installed, solar panels offer long-term cost savings, especially as the cost of solar panels continues to decline.
Argumentative Essay On Renewable Energy. The United States has used fossil fuels for electricity generation ever since the Industrial Revolution, which occurred nearly 250 years ago. It should not, therefore, be a surprise that in the recent past few years, new sources of generating clean and affordable energy have been found.
The use of renewable energy resources, such as solar, wind, and biomass will not diminish their availability. Sunlight being a constant source of energy is used to meet the ever-increasing energy need. This review discusses the world's energy needs, renewable energy technologies for domestic use, and highlights public opinions on renewable energy. A systematic review of the literature was ...
There are many pros and cons to using solar energy. Advantages A major advantage to using solar energy is that it is a renewable resource. We will have a steady, limitless supply of sunlight for another five billion years. In one hour, Earth's atmosphere receives enough sunlight to power the electricity needs of every human being on Earth for ...
Wind energy in the United States helps avoid 336 million metric tons of carbon dioxide emissions annually. (link is external) —equivalent to the emissions from 73 million cars. Wind power benefits local communities. Wind projects deliver an estimated $2 billion. (link is external) in state and local tax payments and land-lease payments each year.
Renewable energy is energy derived from natural sources that are replenished at a higher rate than they are consumed. Sunlight and wind, for example, are such sources that are constantly ...
Renewable energy actually is the cheapest power option in most parts of the world today. Prices for renewable energy technologies are dropping rapidly. The cost of electricity from solar power ...
Renewable energy will have a steady value as time progresses. For example, solar installation prices decreased by up to 70% from 2010 to 2017. (SEIA, 2017). The inevitable transition from carbon-based energy to renewable energy will provide far more benefits for the people than anything else.
National 4; Generation of electricity Pros and cons of renewable energy resources. Electricity can be generated using a turbine to drive a generator before distribution. Renewable and non ...
1023 Words5 Pages. The U.S. Energy Policy: What? Energy Efficiency: Encourages efficient energy use. Renewable Energy: Promotes the development and use of renewable energy sources. Oil and Gas: Addresses matters related to oil and gas production. Coal: Covers aspects related to coal energy. Tribal Lands: Considers energy matters concerning ...
Office of Energy Efficiency and Renewable Energy, Department of Energy. ... DOE further requested feedback on the pros and cons of potentially revising the test conditions in appendix M1. Id. AHRI pointed out that the concept of SPE07 is interesting from a research perspective but not suitable for regulatory purposes. ... BC Hydro strongly ...
Pros and Cons of Renewable Energies & India's Potential and Efforts. Solar Energy. Pros: Renewable and low carbon: Inexhaustible source of energy and is environment friendly. Cost-savings: Once installed, solar panels offer long-term cost savings, especially as the cost of solar panels continues to decline.