Martin Luther King Essay for Students and Children
500+ words essay on martin luter king.
Martin Luther King Jr. was an African-American leader in the U.S. He lost his life while performing a peaceful protest for the betterment of blacks in America. His real name was Michael King Jr. He completed his studies and attained a Ph.D. After that, he joined the American Civil Right Movement. He was among one of the great men who dedicated their life for the community.


Reason for Martin Luther King to be famous
There are two reasons for someone to be famous either he is a good man or a very bad person. Martin Luther King was among the good one who dedicated his life to the community. Martin Luther King was also known as MLK Jr. He gained popularity after he became the leader and spokesperson of the Civil Rights Movement in the 1950s and 1960s.
Martin Luther King was an American activist, minister, and humanitarian. Also, he had worked for several other causes and actively participated in many protests and boycotts. He was a peaceful man that has faith in Christian beliefs and non-violence. Also, his inspiration for them was the work of Mahatma Gandhi and Nelson Mandela. For his work in the field of civil rights, the Nobel Committee awarded him the Nobel Peace Prize.
He was a great speaker that motivated the blacks to protest using non-violence. Also, he uses peaceful strategies like a boycott, protest march , and sit-ins, etc. for protests against the government.
Impact of King
King is one of the renowned leaders of the African-American who worked for the welfare of his community throughout his life. He was very famous among the community and is the strongest voice of the community. King and his fellow companies and peaceful protesters forced the government several times to bend their laws. Also, kings’ life made a seismic impact on life and thinking of the blacks. He was among one of the great leaders of the era.
Get the huge list of more than 500 Essay Topics and Ideas
Humanitarian and civil rights work
As we know that King was a civic leader . Also, he has taken part in many civil right campaigns and boycotts like the Bus Boycott, Voting Rights and the most famous March on Washington. In this march along with more than 200,000 people, he marched towards Washington for human right. Also, it’s the largest human right campaign in U.S.A. history. During the protest, he gave a speech named “I Have a Dream” which is history’s one of the renowned speeches.
Death and memorial
During his life working as a leader of the Civil Rights Movement he makes many enemies. Also, the government and plans do everything to hurt his reputation. Martin Luther King was assassinated in 1968. Every year the US celebrates his anniversary as Martin Luther King Jr. day in the US. Also, they honored kings’ memory by naming school and building after him and a Memorial at Independence Mall.
Martin Luther King was a great man who dedicated his whole life for his community. Also, he was an active leader and a great spokesperson that not only served his people but also humanity. It was due to his contribution that the African-American got their civil rights.
Essay Topics on Famous Leaders
- Mahatma Gandhi
- APJ Abdul Kalam
- Jawaharlal Nehru
- Swami Vivekananda
- Mother Teresa
- Rabindranath Tagore
- Sardar Vallabhbhai Patel
- Subhash Chandra Bose
- Abraham Lincoln
- Martin Luther King
Customize your course in 30 seconds
Which class are you in.

- Travelling Essay
- Picnic Essay
- Our Country Essay
- My Parents Essay
- Essay on Favourite Personality
- Essay on Memorable Day of My Life
- Essay on Knowledge is Power
- Essay on Gurpurab
- Essay on My Favourite Season
- Essay on Types of Sports
Leave a Reply Cancel reply
Your email address will not be published. Required fields are marked *
Download the App

- History Classics
- Your Profile
- Find History on Facebook (Opens in a new window)
- Find History on Twitter (Opens in a new window)
- Find History on YouTube (Opens in a new window)
- Find History on Instagram (Opens in a new window)
- Find History on TikTok (Opens in a new window)
- This Day In History
- History Podcasts
- History Vault
Martin Luther King Jr.
By: History.com Editors
Updated: January 25, 2024 | Original: November 9, 2009

Martin Luther King Jr. was a social activist and Baptist minister who played a key role in the American civil rights movement from the mid-1950s until his assassination in 1968. King sought equality and human rights for African Americans, the economically disadvantaged and all victims of injustice through peaceful protest. He was the driving force behind watershed events such as the Montgomery Bus Boycott and the 1963 March on Washington , which helped bring about such landmark legislation as the Civil Rights Act and the Voting Rights Act . King was awarded the Nobel Peace Prize in 1964 and is remembered each year on Martin Luther King Jr. Day , a U.S. federal holiday since 1986.
When Was Martin Luther King Born?
Martin Luther King Jr. was born on January 15, 1929, in Atlanta, Georgia , the second child of Martin Luther King Sr., a pastor, and Alberta Williams King, a former schoolteacher.
Along with his older sister Christine and younger brother Alfred Daniel Williams, he grew up in the city’s Sweet Auburn neighborhood, then home to some of the most prominent and prosperous African Americans in the country.
Did you know? The final section of Martin Luther King Jr.’s iconic “I Have a Dream” speech is believed to have been largely improvised.
A gifted student, King attended segregated public schools and at the age of 15 was admitted to Morehouse College , the alma mater of both his father and maternal grandfather, where he studied medicine and law.
Although he had not intended to follow in his father’s footsteps by joining the ministry, he changed his mind under the mentorship of Morehouse’s president, Dr. Benjamin Mays, an influential theologian and outspoken advocate for racial equality. After graduating in 1948, King entered Crozer Theological Seminary in Pennsylvania, where he earned a Bachelor of Divinity degree, won a prestigious fellowship and was elected president of his predominantly white senior class.
King then enrolled in a graduate program at Boston University, completing his coursework in 1953 and earning a doctorate in systematic theology two years later. While in Boston he met Coretta Scott, a young singer from Alabama who was studying at the New England Conservatory of Music . The couple wed in 1953 and settled in Montgomery, Alabama, where King became pastor of the Dexter Avenue Baptist Church .
The Kings had four children: Yolanda Denise King, Martin Luther King III, Dexter Scott King and Bernice Albertine King.
Montgomery Bus Boycott
The King family had been living in Montgomery for less than a year when the highly segregated city became the epicenter of the burgeoning struggle for civil rights in America, galvanized by the landmark Brown v. Board of Education decision of 1954.
On December 1, 1955, Rosa Parks , secretary of the local chapter of the National Association for the Advancement of Colored People ( NAACP ), refused to give up her seat to a white passenger on a Montgomery bus and was arrested. Activists coordinated a bus boycott that would continue for 381 days. The Montgomery Bus Boycott placed a severe economic strain on the public transit system and downtown business owners. They chose Martin Luther King Jr. as the protest’s leader and official spokesman.
By the time the Supreme Court ruled segregated seating on public buses unconstitutional in November 1956, King—heavily influenced by Mahatma Gandhi and the activist Bayard Rustin —had entered the national spotlight as an inspirational proponent of organized, nonviolent resistance.
King had also become a target for white supremacists, who firebombed his family home that January.
On September 20, 1958, Izola Ware Curry walked into a Harlem department store where King was signing books and asked, “Are you Martin Luther King?” When he replied “yes,” she stabbed him in the chest with a knife. King survived, and the attempted assassination only reinforced his dedication to nonviolence: “The experience of these last few days has deepened my faith in the relevance of the spirit of nonviolence if necessary social change is peacefully to take place.”
Southern Christian Leadership Conference
Emboldened by the success of the Montgomery Bus Boycott, in 1957 he and other civil rights activists—most of them fellow ministers—founded the Southern Christian Leadership Conference (SCLC), a group committed to achieving full equality for African Americans through nonviolent protest.
The SCLC motto was “Not one hair of one head of one person should be harmed.” King would remain at the helm of this influential organization until his death.
In his role as SCLC president, Martin Luther King Jr. traveled across the country and around the world, giving lectures on nonviolent protest and civil rights as well as meeting with religious figures, activists and political leaders.
During a month-long trip to India in 1959, he had the opportunity to meet family members and followers of Gandhi, the man he described in his autobiography as “the guiding light of our technique of nonviolent social change.” King also authored several books and articles during this time.
Letter from Birmingham Jail
In 1960 King and his family moved to Atlanta, his native city, where he joined his father as co-pastor of the Ebenezer Baptist Church . This new position did not stop King and his SCLC colleagues from becoming key players in many of the most significant civil rights battles of the 1960s.
Their philosophy of nonviolence was put to a particularly severe test during the Birmingham campaign of 1963, in which activists used a boycott, sit-ins and marches to protest segregation, unfair hiring practices and other injustices in one of America’s most racially divided cities.
Arrested for his involvement on April 12, King penned the civil rights manifesto known as the “ Letter from Birmingham Jail ,” an eloquent defense of civil disobedience addressed to a group of white clergymen who had criticized his tactics.
March on Washington
Later that year, Martin Luther King Jr. worked with a number of civil rights and religious groups to organize the March on Washington for Jobs and Freedom, a peaceful political rally designed to shed light on the injustices Black Americans continued to face across the country.
Held on August 28 and attended by some 200,000 to 300,000 participants, the event is widely regarded as a watershed moment in the history of the American civil rights movement and a factor in the passage of the Civil Rights Act of 1964 .
"I Have a Dream" Speech
The March on Washington culminated in King’s most famous address, known as the “I Have a Dream” speech, a spirited call for peace and equality that many consider a masterpiece of rhetoric.
Standing on the steps of the Lincoln Memorial —a monument to the president who a century earlier had brought down the institution of slavery in the United States—he shared his vision of a future in which “this nation will rise up and live out the true meaning of its creed: ‘We hold these truths to be self-evident, that all men are created equal.'”
The speech and march cemented King’s reputation at home and abroad; later that year he was named “Man of the Year” by TIME magazine and in 1964 became, at the time, the youngest person ever awarded the Nobel Peace Prize .
In the spring of 1965, King’s elevated profile drew international attention to the violence that erupted between white segregationists and peaceful demonstrators in Selma, Alabama, where the SCLC and Student Nonviolent Coordinating Committee (SNCC) had organized a voter registration campaign.
Captured on television, the brutal scene outraged many Americans and inspired supporters from across the country to gather in Alabama and take part in the Selma to Montgomery march led by King and supported by President Lyndon B. Johnson , who sent in federal troops to keep the peace.
That August, Congress passed the Voting Rights Act , which guaranteed the right to vote—first awarded by the 15th Amendment—to all African Americans.
Assassination of Martin Luther King Jr.
The events in Selma deepened a growing rift between Martin Luther King Jr. and young radicals who repudiated his nonviolent methods and commitment to working within the established political framework.
As more militant Black leaders such as Stokely Carmichael rose to prominence, King broadened the scope of his activism to address issues such as the Vietnam War and poverty among Americans of all races. In 1967, King and the SCLC embarked on an ambitious program known as the Poor People’s Campaign, which was to include a massive march on the capital.
On the evening of April 4, 1968, Martin Luther King was assassinated . He was fatally shot while standing on the balcony of a motel in Memphis, where King had traveled to support a sanitation workers’ strike. In the wake of his death, a wave of riots swept major cities across the country, while President Johnson declared a national day of mourning.
James Earl Ray , an escaped convict and known racist, pleaded guilty to the murder and was sentenced to 99 years in prison. He later recanted his confession and gained some unlikely advocates, including members of the King family, before his death in 1998.
After years of campaigning by activists, members of Congress and Coretta Scott King, among others, in 1983 President Ronald Reagan signed a bill creating a U.S. federal holiday in honor of King.
Observed on the third Monday of January, Martin Luther King Day was first celebrated in 1986.
Martin Luther King Jr. Quotes
While his “I Have a Dream” speech is the most well-known piece of his writing, Martin Luther King Jr. was the author of multiple books, include “Stride Toward Freedom: The Montgomery Story,” “Why We Can’t Wait,” “Strength to Love,” “Where Do We Go From Here: Chaos or Community?” and the posthumously published “Trumpet of Conscience” with a foreword by Coretta Scott King. Here are some of the most famous Martin Luther King Jr. quotes:
“Injustice anywhere is a threat to justice everywhere.”
“Darkness cannot drive out darkness; only light can do that. Hate cannot drive out hate; only love can do that.”
“The ultimate measure of a man is not where he stands in moments of comfort and convenience, but where he stands at times of challenge and controversy.”
“Freedom is never voluntarily given by the oppressor; it must be demanded by the oppressed.”
“The time is always right to do what is right.”
"True peace is not merely the absence of tension; it is the presence of justice."
“Our lives begin to end the day we become silent about things that matter.”
“Free at last, Free at last, Thank God almighty we are free at last.”
“Faith is taking the first step even when you don't see the whole staircase.”
“In the end, we will remember not the words of our enemies, but the silence of our friends.”
"I believe that unarmed truth and unconditional love will have the final word in reality. This is why right, temporarily defeated, is stronger than evil triumphant."
“I have decided to stick with love. Hate is too great a burden to bear.”
“Be a bush if you can't be a tree. If you can't be a highway, just be a trail. If you can't be a sun, be a star. For it isn't by size that you win or fail. Be the best of whatever you are.”
“Life's most persistent and urgent question is, 'What are you doing for others?’”
Photo Galleries

HISTORY Vault: Voices of Civil Rights
A look at one of the defining social movements in U.S. history, told through the personal stories of men, women and children who lived through it.

Sign up for Inside History
Get HISTORY’s most fascinating stories delivered to your inbox three times a week.
By submitting your information, you agree to receive emails from HISTORY and A+E Networks. You can opt out at any time. You must be 16 years or older and a resident of the United States.
More details : Privacy Notice | Terms of Use | Contact Us
Martin Luther King Jr.
Martin Luther King Jr. was a Baptist minister and major leader of the Civil Rights Movement. After his assassination, he was memorialized by Martin Luther King Jr. Day.

We may earn commission from links on this page, but we only recommend products we back.
In Focus: Martin Luther King Jr. Day
Days after his 1968 assassination , a campaign for a holiday in King’s honor began. U.S. Representative John Conyers Jr. of Michigan first proposed a bill on April 8, 1968, but the first vote on the legislation didn’t happen until 1979. King’s widow, Coretta Scott King , led the lobbying effort to drum up public support. Fifteen years after its introduction, the bill finally became law.
In 1983, President Ronald Reagan ’s signature created Martin Luther King Jr. Day of Service as a federal holiday. It’s celebrated annually on the third Monday in January. The only national day of service, Martin Luther King Jr. Day was first celebrated in 1986. The first time all 50 states recognized the holiday was in 2000.
See Martin Luther King Jr.’s life depicted onscreen in the 2018 documentary I Am MLK Jr. or the Oscar-winning movie Selma .
Quick Facts
Where did martin luther king jr. go to school, philosophy of nonviolence, civil rights accomplishments, "i have a dream" and other famous speeches, wife and kids, fbi surveillance, later activism, assassination, who was martin luther king jr.
Martin Luther King Jr. was a Baptist minister and civil rights activist who had a seismic impact on race relations in the United States, beginning in the mid-1950s. Among his many efforts, King headed the Southern Christian Leadership Conference (SCLC). Through his nonviolent activism and inspirational speeches , he played a pivotal role in ending legal segregation of Black Americans, as well as the creation of the Civil Rights Act of 1964 and the Voting Rights Act of 1965 . King won the Nobel Peace Prize in 1964, among several other honors. He was assassinated by James Earl Ray and died on April 4, 1968, at age 39. King continues to be remembered as one of the most influential and inspirational Black leaders in history.
FULL NAME: Martin Luther King Jr. BIRTHDAY: January 15, 1929 DIED: April 4, 1968 BIRTHPLACE: Atlanta, Georgia SPOUSE: Coretta Scott King (1953-1968) CHILDREN: Yolanda, Martin III, Dexter, and Bernice King ASTROLOGICAL SIGN: Capricorn
Martin Luther King Jr. was born as Michael Luther King Jr. in Atlanta. His birthday was January 15, 1929.

His parents were Michael Luther King Sr. and Alberta Williams King. The Williams and King families had roots in rural Georgia. Martin’s maternal grandfather, A.D. Williams, was a rural minister for years and then moved to Atlanta in 1893. He took over the small, struggling Ebenezer Baptist Church with around 13 members and made it into a forceful congregation. He married Jennie Celeste Parks, and they had one child who survived, Alberta.
Michael Sr. came from a family of sharecroppers in a poor farming community. He married Alberta in 1926 after an eight-year courtship. The newlyweds moved to A.D.’s home in Atlanta. Michael stepped in as pastor of Ebenezer Baptist Church upon the death of his father-in-law in 1931. He, too, became a successful minister and adopted the name Martin Luther King Sr. in honor of the German Protestant religious leader Martin Luther . In due time, Michael Jr. followed his father’s lead and adopt the name himself to become Martin Luther King Jr.
A middle child, Martin Jr. had an older sister, Willie, and a younger brother, Alfred. The King children grew up in a secure and loving environment. Martin Sr. was more the disciplinarian, while Alberta’s gentleness easily balanced out their father’s strict hand.
Although they undoubtedly tried, Martin Jr.’s parents couldn’t shield him completely from racism. His father fought against racial prejudice, not just because his race suffered, but also because he considered racism and segregation to be an affront to God’s will. He strongly discouraged any sense of class superiority in his children, which left a lasting impression on Martin Jr.
Growing up in Atlanta, King entered public school at age 5. In May 1936, he was baptized, but the event made little impression on him.
In May 1941, King was 12 years old when his grandmother Jennie died of a heart attack. The event was traumatic for the boy, more so because he was out watching a parade against his parents’ wishes when she died. Distraught at the news, young King jumped from a second-story window at the family home, allegedly attempting suicide.
King attended Booker T. Washington High School, where he was said to be a precocious student. He skipped both the ninth and eleventh grades and, at age 15, entered Morehouse College in Atlanta in 1944. He was a popular student, especially with his female classmates, but largely unmotivated, floating through his first two years.
Influenced by his experiences with racism, King began planting the seeds for a future as a social activist early in his time at Morehouse. “I was at the point where I was deeply interested in political matters and social ills,” he recalled in The Autobiography of Martin Luther King, Jr . “I could envision myself playing a part in breaking down the legal barriers to Negro rights.”
The Autobiography of Martin Luther King, Jr.

At the time, King felt that the best way to serve that purpose was as a lawyer or a doctor. Although his family was deeply involved in the church and worship, King questioned religion in general and felt uncomfortable with overly emotional displays of religious worship. This discomfort had continued through much of his adolescence, initially leading him to decide against entering the ministry, much to his father’s dismay.
But in his junior year, King took a Bible class, renewed his faith, and began to envision a career in the ministry. In the fall of his senior year, he told his father of his decision, and he was ordained at Ebenezer Baptist Church in February 1948.
Later that year, King earned a sociology degree from Morehouse College and began attended the liberal Crozer Theological Seminary in Chester, Pennsylvania. He thrived in all his studies, was elected student body president, and was valedictorian of his class in 1951. He also earned a fellowship for graduate study.
Even though King was following his father’s footsteps, he rebelled against Martin Sr.’s more conservative influence by drinking beer and playing pool while at college. He became romantically involved with a white woman and went through a difficult time before he could break off the relationship.
During his last year in seminary, King came under the guidance of Morehouse College President Benjamin E. Mays, who influenced King’s spiritual development. Mays was an outspoken advocate for racial equality and encouraged King to view Christianity as a potential force for social change.

After being accepted at several colleges for his doctoral study, King enrolled at Boston University. In 1954, while still working on his dissertation, King became pastor of the Dexter Avenue Baptist Church of Montgomery, Alabama. He completed his doctorate and earned his degree in 1955 at age 25.
Decades after King’s death, in the late 1980s, researchers at Stanford University’s King Papers Project began to note similarities between passages of King’s doctoral dissertation and those of another student’s work. A committee of scholars appointed by Boston University determined that King was guilty of plagiarism in 1991, though it also recommended against the revocation of his degree.

First exposed to the concept of nonviolent resistance while reading Henry David Thoreau ’s On Civil Disobedience at Morehouse, King later discovered a powerful exemplar of the method’s possibilities through his research into the life of Mahatma Gandhi . Fellow civil rights activist Bayard Rustin , who had also studied Gandhi’s teachings, became one of King’s associates in the 1950s and counseled him to dedicate himself to the principles of nonviolence.
As explained in his autobiography , King previously felt that the peaceful teachings of Jesus applied mainly to individual relationships, not large-scale confrontations. But he came to realize: “Love for Gandhi was a potent instrument for social and collective transformation. It was in this Gandhian emphasis on love and nonviolence that I discovered the method for social reform that I had been seeking.”
It led to the formation of King’s six principles of nonviolence :
- Nonviolence is a way of life for courageous people.
- Nonviolence seeks to win friendship and understanding.
- Nonviolence seeks to defeat injustice, not people.
- Nonviolence holds that suffering for a just cause can educate and transform.
- Nonviolence chooses love instead of hate.
- Nonviolence believes that the universe is on the side of justice.
In the years to come, King also frequently cited the “ Beloved Community ”—a world in which a shared spirit of compassion brings an end to the evils of racism, poverty, inequality, and violence—as the end goal of his activist efforts.

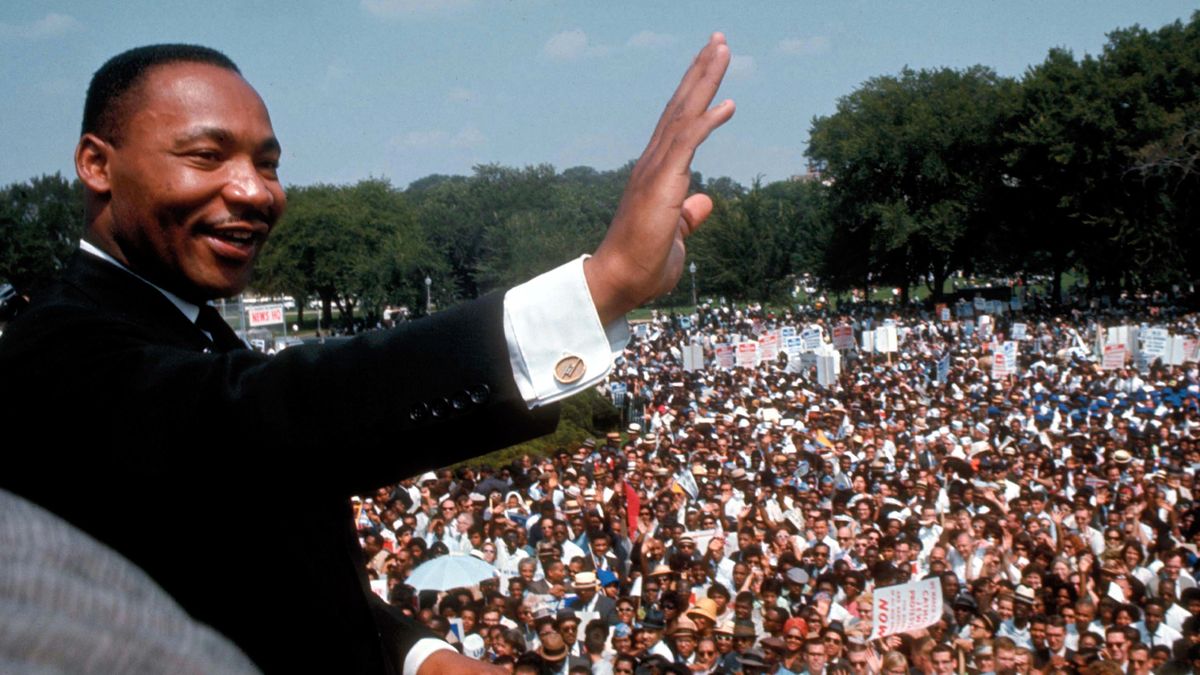
Led by his religious convictions and philosophy of nonviolence, King became one of the most prominent figures of the Civil Rights Movement . He was a founding member of the Southern Christian Leadership Conference and played key roles in several major demonstrations that transformed society. This included the Montgomery Bus Boycott that integrated Alabama’s public transit, the Greensboro Sit-In movement that desegregated lunch counters across the South, the March on Washington that led to the passage of the 1964 Civil Rights Act, and the Selma-to-Montgomery marches in Alabama that culminated in the 1965 Voting Rights Act.
King’s efforts earned him the Nobel Peace Prize in 1964 when he was 35.
Montgomery Bus Boycott
King’s first leadership role within the Civil Rights Movement was during the Montgomery Bus Boycott of 1955–1956. The 381-day protest integrated the Alabama city’s public transit in one of the largest and most successful mass movements against racial segregation in history.
The effort began on December 1, 1955, when 42-year-old Rosa Parks boarded the Cleveland Avenue bus to go home after an exhausting day at work. She sat in the first row of the “colored” section in the middle of the bus. As the bus traveled its route, all the seats in the white section filled up, then several more white passengers boarded the bus.
The bus driver noted that there were several white men standing and demanded that Parks and several other African Americans give up their seats. Three other Black passengers reluctantly gave up their places, but Parks remained seated.
The driver asked her again to give up her seat, and again she refused. Parks was arrested and booked for violating the Montgomery City Code. At her trial a week later, in a 30-minute hearing, Parks was found guilty and fined $10 and assessed $4 court fee.
The local NAACP chapter had been looking to challenge Montgomery’s segregated bus policy and had almost made 15-year-old Claudette Colvin the face of the campaign months earlier. She similarly refused to give up her bus seat to a white man on March 2, 1955, but after organizers learned Colvin was pregnant, they feared it would scandalize the deeply religious Black community and make Colvin, along with the group’s efforts, less credible in the eyes of sympathetic white people. Parks’ experience of discrimination provided another opportunity.
On the night Parks was arrested, E.D. Nixon , head of the local NAACP chapter, met with King and other local civil rights leaders to plan a Montgomery Bus Boycott. King was elected to lead the boycott because he was young, well-trained, and had solid family connections and professional standing. He was also new to the community and had few enemies, so organizers felt he would have strong credibility with the Black community.
In his first speech as the group’s president, King declared:
“We have no alternative but to protest. For many years, we have shown an amazing patience. We have sometimes given our white brothers the feeling that we liked the way we were being treated. But we come here tonight to be saved from that patience that makes us patient with anything less than freedom and justice.”
King’s skillful rhetoric put new energy into the civil rights struggle in Alabama. The Montgomery Bus Boycott began December 5, 1955, and for more than a year, the local Black community walked to work, coordinated ride sharing, and faced harassment, violence, and intimidation. Both King’s and Nixon’s homes were attacked.
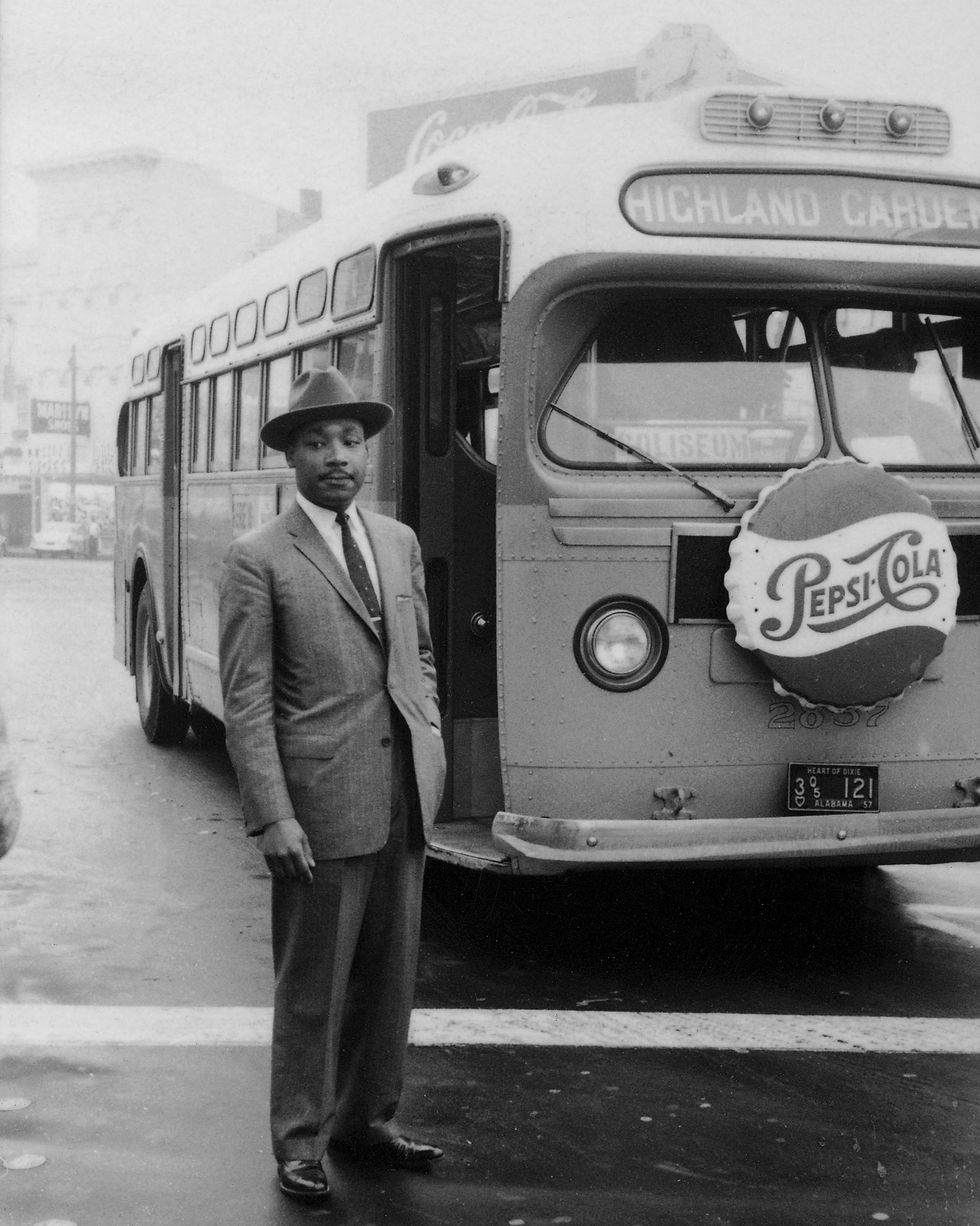
In addition to the boycott, members of the Black community took legal action against the city ordinance that outlined the segregated transit system. They argued it was unconstitutional based on the U.S. Supreme Court ’s “separate is never equal” decision in Brown v. Board of Education (1954). Several lower courts agreed, and the nation’s Supreme Court upheld the ruling in a November 13, 1956, decision that also ruled the state of Alabama’s bus segregation laws were unconstitutional.
After the legal defeats and large financial losses, the city of Montgomery lifted the law that mandated segregated public transportation. The boycott ended on December 20, 1956.
Southern Christian Leadership Conference
Flush with victory, African American civil rights leaders recognized the need for a national organization to help coordinate their efforts. In January 1957, King, Ralph Abernathy , and 60 ministers and civil rights activists founded the Southern Christian Leadership Conference to harness the moral authority and organizing power of Black churches. The SCLC helped conduct nonviolent protests to promote civil rights reform.
King’s participation in the organization gave him a base of operation throughout the South, as well as a national platform. The SCLC felt the best place to start to give African Americans a voice was to enfranchise them in the voting process. In February 1958, the SCLC sponsored more than 20 mass meetings in key southern cities to register Black voters. King met with religious and civil rights leaders and lectured all over the country on race-related issues.
Stride Toward Freedom: The Montgomery Story

That September, King survived an attempt on his life when a woman with mental illness stabbed him in the chest as he signed copies of his book Stride Toward Freedom in a New York City department store. Saved by quick medical attention, King expressed sympathy for his assailant’s condition in the aftermath .
In 1959, with the help of the American Friends Service Committee, King visited Gandhi ’s birthplace in India. The trip affected him in a profound way, increasing his commitment to America’s civil rights struggle.
Greensboro Sit-In
By 1960, King was gaining national exposure. He returned to Atlanta to become co-pastor with his father at Ebenezer Baptist Church but also continued his civil rights efforts. His next activist campaign was the student-led Greensboro Sit-In movement.
In February 1960, a group of Black students in Greensboro, North Carolina , began sitting at racially segregated lunch counters in the city’s stores. When asked to leave or sit in the “colored” section, they just remained seated, subjecting themselves to verbal and sometimes physical abuse.
The movement quickly gained traction in several other cities. That April, the SCLC held a conference at Shaw University in Raleigh, North Carolina, with local sit-in leaders. King encouraged students to continue to use nonviolent methods during their protests. Out of this meeting, the Student Nonviolent Coordinating Committee (SNCC) formed and, for a time, worked closely with the SCLC. By August 1960, the sit-ins had successfully ended segregation at lunch counters in 27 southern cities. But the movement wasn’t done yet.
On October 19, 1960, King and 75 students entered a local department store and requested lunch-counter service but were denied. When they refused to leave the counter area, King and 36 others were arrested. Realizing the incident would hurt the city’s reputation, Atlanta’s mayor negotiated a truce, and charges were eventually dropped.
Soon after, King was imprisoned for violating his probation on a traffic conviction. The news of his imprisonment entered the 1960 presidential campaign when candidate John F. Kennedy made a phone call to Martin’s wife, Coretta Scott King . Kennedy expressed his concern over the harsh treatment Martin received for the traffic ticket, and political pressure was quickly set in motion. King was soon released.
Letter from Birmingham Jail
In the spring of 1963, King organized a demonstration in downtown Birmingham, Alabama. With entire families in attendance, city police turned dogs and fire hoses on demonstrators. King was jailed, along with large numbers of his supporters.
The event drew nationwide attention. However, King was personally criticized by Black and white clergy alike for taking risks and endangering the children who attended the demonstration.
In his famous Letter from Birmingham Jail , King eloquently spelled out his theory of nonviolence: “Nonviolent direct action seeks to create such a crisis and foster such a tension that a community, which has constantly refused to negotiate, is forced to confront the issue.”
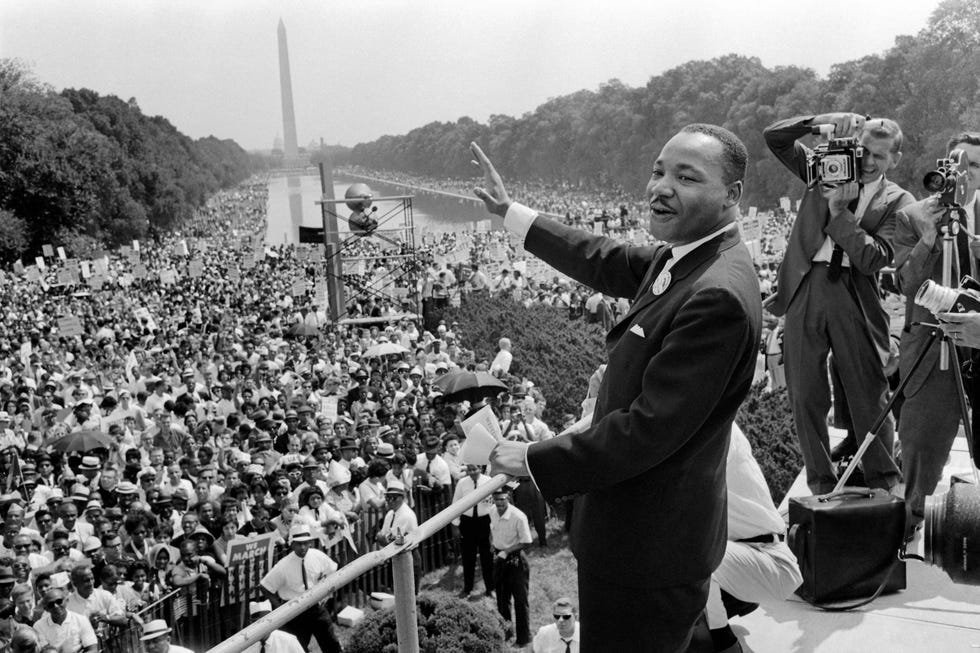
1963 March on Washington
By the end of the Birmingham campaign, King and his supporters were making plans for a massive demonstration on the nation’s capital composed of multiple organizations, all asking for peaceful change. The demonstration was the brainchild of labor leader A. Philip Randolph and King’s one-time mentor Bayard Rustin .
On August 28, 1963, the historic March on Washington for Jobs and Freedom drew an estimated 250,000 people in the shadow of the Lincoln Memorial. It remains one of the largest peaceful demonstrations in American history. During the demonstration, King delivered his famed “I Have a Dream” speech .
The rising tide of civil rights agitation that had culminated in the March on Washington produced a strong effect on public opinion. Many people in cities not experiencing racial tension began to question the nation’s Jim Crow laws and the near-century of second-class treatment of African American citizens since the end of slavery. This resulted in the passage of the Civil Rights Act of 1964 , authorizing the federal government to enforce desegregation of public accommodations and outlawing discrimination in publicly owned facilities.
Selma March
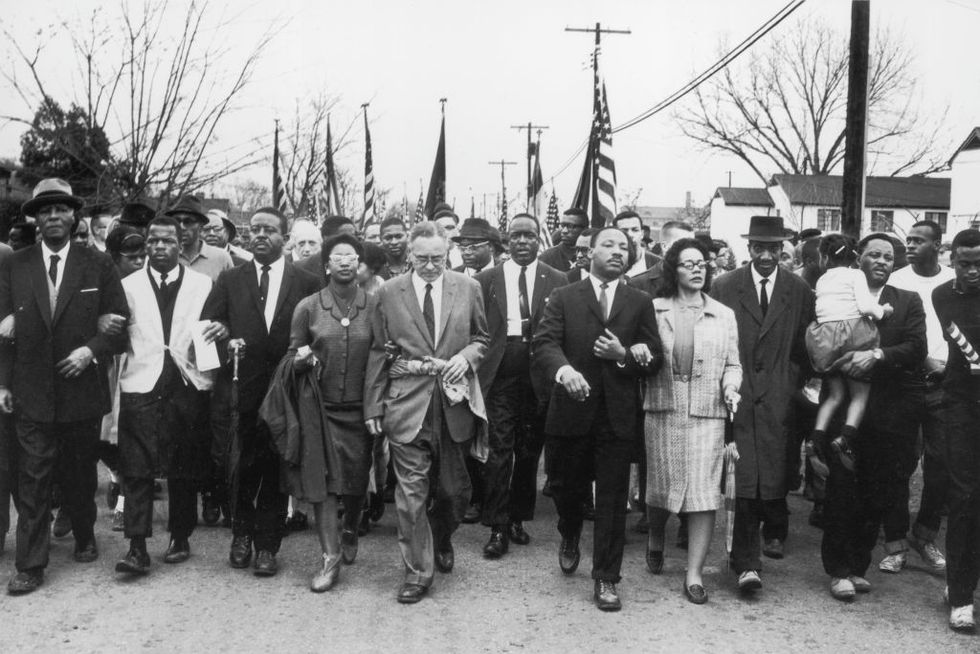

Continuing to focus on voting rights, King, the SCLC, SNCC, and local organizers planned to march peacefully from Selma, Alabama, to the state’s capital, Montgomery.
Led by John Lewis and Hosea Williams , demonstrators set out on March 7, 1965. But the Selma march quickly turned violent as police with nightsticks and tear gas met the demonstrators as they tried to cross the Edmund Pettus Bridge in Selma. The attack was televised, broadcasting the horrifying images of marchers being bloodied and severely injured to a wide audience. Of the 600 demonstrators, 58 were hospitalized in a day that became known as “ Bloody Sunday .” King, however, was spared because he was in Atlanta.
Not to be deterred, activists attempted the Selma-to-Montgomery march again. This time, King made sure he was part of it. Because a federal judge had issued a temporary restraining order on another march, a different approach was taken.
On March 9, 1965, a procession of 2,500 marchers, both Black and white, set out once again to cross the Pettus Bridge and confronted barricades and state troopers. Instead of forcing a confrontation, King led his followers to kneel in prayer, then they turned back. This became known as “Turnaround Tuesday.”
Alabama Governor George Wallace continued to try to prevent another march until President Lyndon B. Johnson pledged his support and ordered U.S. Army troops and the Alabama National Guard to protect the protestors.
On March 21, 1965, approximately 2,000 people began a march from Selma to Montgomery. On March 25, the number of marchers, which had grown to an estimated 25,000 gathered in front of the state capitol where King delivered a televised speech. Five months after the historic peaceful protest, President Johnson signed the 1965 Voting Rights Act .

Along with his “I Have a Dream” and “I’ve Been to the Mountaintop” speeches, King delivered several acclaimed addresses over the course of his life in the public eye.
“I Have A Dream” Speech
Date: august 28, 1963.
King gave his famous “I Have a Dream” speech during the 1963 March on Washington. Standing at the Lincoln Memorial, he emphasized his belief that someday all men could be brothers to the 250,000-strong crowd.
Notable Quote: “I have a dream that my four children will one day live in a nation where they will not be judged by the color of their skin but by the content of their character.”
“Give Us the Ballot” Speech
Date: may 17, 1957.
Six years before he told the world of his dream, King stood at the same Lincoln Memorial steps as the final speaker of the Prayer Pilgrimage for Freedom. Dismayed by the ongoing obstacles to registering Black voters, King urged leaders from various backgrounds—Republican and Democrat, Black and white—to work together in the name of justice.
Notable Quote: “Give us the ballot, and we will no longer have to worry the federal government about our basic rights. Give us the ballot, and we will no longer plead to the federal government for passage of an anti-lynching law... Give us the ballot, and we will transform the salient misdeeds of bloodthirsty mobs into the calculated good deeds of orderly citizens.”
Nobel Peace Prize Acceptance Speech
Date: december 10, 1964.
Speaking at the University of Oslo in Norway, King pondered why he was receiving the Nobel Prize when the battle for racial justice was far from over, before acknowledging that it was in recognition of the power of nonviolent resistance. He then compared the foot soldiers of the Civil Rights Movement to the ground crew at an airport who do the unheralded-yet-necessary work to keep planes running on schedule.
Notable Quote: “I think Alfred Nobel would know what I mean when I say that I accept this award in the spirit of a curator of some precious heirloom which he holds in trust for its true owners—all those to whom beauty is truth and truth, beauty—and in whose eyes the beauty of genuine brotherhood and peace is more precious than diamonds or silver or gold.”
“Our God is Marching On (How Long? Not Long)” Speech
Date: march 25, 1965.
At the end of the bitterly fought Selma-to-Montgomery march, King addressed a crowd of 25,000 supporters from the Alabama State Capitol. Offering a brief history lesson on the roots of segregation, King emphasized that there would be no stopping the effort to secure full voting rights, while suggesting a more expansive agenda to come with a call to march on poverty.
Notable Quote: “I come to say to you this afternoon, however difficult the moment, however frustrating the hour, it will not be long, because ‘truth crushed to earth will rise again.’ How long? Not long, because ‘no lie can live forever.’... How long? Not long, because the arc of the moral universe is long, but it bends toward justice.”
“Beyond Vietnam: A Time to Break Silence” Speech
Date: april 4, 1967.
One year before his assassination, King delivered a controversial sermon at New York City’s Riverside Church in which he condemned the Vietnam War. Explaining why his conscience had forced him to speak up, King expressed concern for the poor American soldiers pressed into conflict thousands of miles from home, while pointedly faulting the U.S. government’s role in escalating the war.
Notable Quote: “We still have a choice today: nonviolent coexistence or violent co-annihilation. We must move past indecision to action. We must find new ways to speak for peace in Vietnam and justice throughout the developing world, a world that borders on our doors. If we do not act, we shall surely be dragged down the long, dark, and shameful corridors of time reserved for those who possess power without compassion, might without morality, and strength without sight.”
“I’ve Been to the Mountaintop” Speech
Date: april 3, 1968.
The well-known orator delivered his final speech the day before he died at the Mason Temple in Memphis, Tennessee. King reflected on major moments of progress in history and his own life, in addition to encouraging the city’s striking sanitation workers.
Notable Quote: “I’ve seen the promised land. I may not get there with you. But I want you to know tonight that we, as a people, will get to the promised land.”
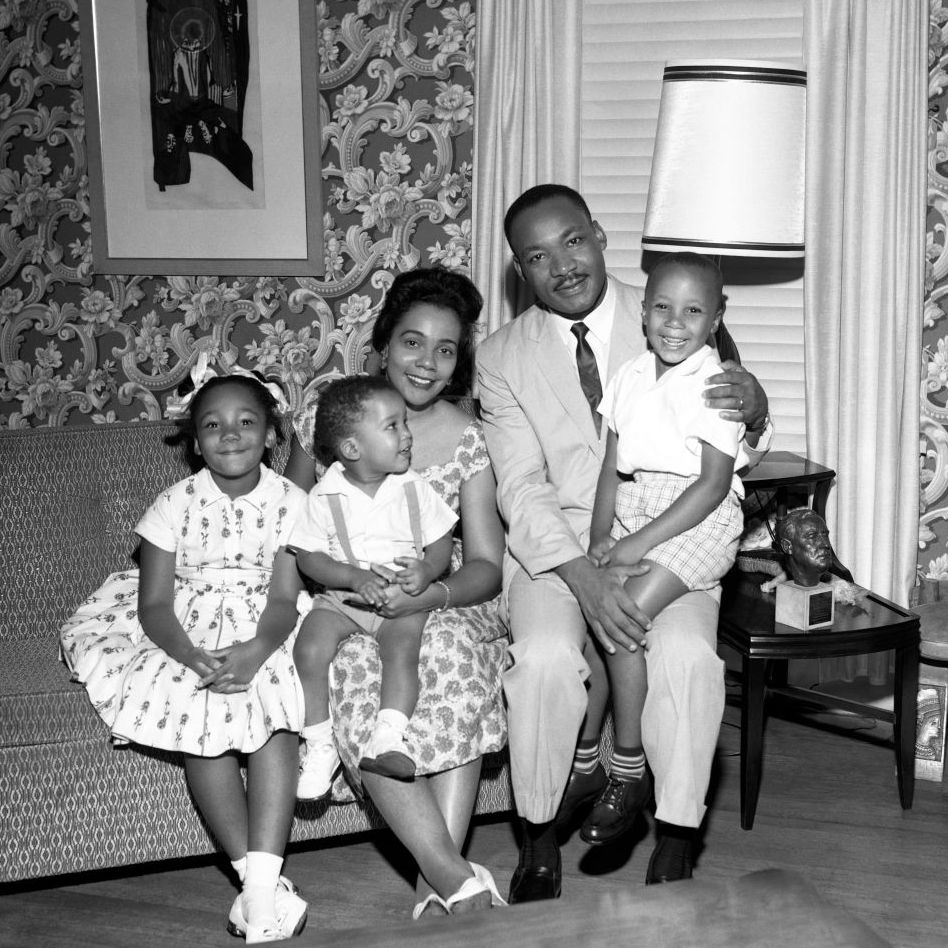
While working on his doctorate at Boston University, King met Coretta Scott , an aspiring singer and musician at the New England Conservatory school in Boston. They were married on June 18, 1953, and had four children—two daughters and two sons—over the next decade. Their oldest, Yolanda, was born in 1955, followed by sons Martin Luther King III in 1957 and Dexter in 1961. The couple welcomed Bernice King in 1963.
Although she accepted the responsibility to raise the children while King travelled the country, Coretta opened their home to organizational meetings and served as an advisor and sounding board for her husband. “I am convinced that if I had not had a wife with the fortitude, strength, and calmness of Corrie, I could not have withstood the ordeals and tensions surrounding the movement,” King wrote in his autobiography.
His lengthy absences became a way of life for their children, but Martin III remembered his father returning from the road to join the kids playing in the yard or bring them to the local YMCA for swimming. King also fostered discussions at mealtimes to make sure everyone understood the important issues he was seeking to resolve.
Leery of accumulating wealth as a high-profile figure, King insisted his family live off his salary as a pastor. However, he was known to splurge on good suits and fine dining, while contrasting his serious public image with a lively sense of humor among friends and family.
Due to his relationships with alleged Communists, King became a target of FBI surveillance and, from late 1963 until his death, a campaign to discredit the civil rights activist. While FBI wiretaps failed to produce evidence of Communist sympathies, they captured the civil rights leader’s engagement in extramarital dalliances. This led to the infamous “suicide letter” of 1964, later confirmed to be from the FBI and authorized by then-Director J. Edgar Hoover , which urged King to kill himself if he wanted to prevent news of his affairs from going public.
In 2019, historian David Garrow wrote of explosive new allegations against King following his review of recently released FBI documents. Among the discoveries was a memo suggesting that King had encouraged the rape of a parishioner in a hotel room, as well as evidence that he might have fathered a daughter with a mistress. Other historians questioned the veracity of the documentation, especially given the FBI’s known attempts to damage King’s reputation. The original surveillance tapes regarding these allegations are under judicial seal until 2027.
From late 1965 through 1967, King expanded his civil rights efforts into other larger American cities, including Chicago and Los Angeles. But he met with increasing criticism and public challenges from young Black power leaders. King’s patient, non-violent approach and appeal to white middle-class citizens alienated many Black militants who considered his methods too weak, too late, and ineffective.
To address this criticism, King began making a link between discrimination and poverty, and he began to speak out against the Vietnam War . He felt America’s involvement in Vietnam was politically untenable and the government’s conduct in the war was discriminatory to the poor. He sought to broaden his base by forming a multiracial coalition to address the economic and unemployment problems of all disadvantaged people. To that end, plans were in the works for another march on Washington to highlight the Poor People’s Campaign, a movement intended to pressure the government into improving living and working conditions for the economically disadvantaged.
By 1968, the years of demonstrations and confrontations were beginning to wear on King. He had grown tired of marches, going to jail, and living under the constant threat of death. He was becoming discouraged at the slow progress of civil rights in America and the increasing criticism from other African American leaders.
In the spring of 1968, a labor strike by Memphis, Tennessee, sanitation workers drew King to one last crusade. On April 3, 1968, he gave his final and what proved to be an eerily prophetic speech, “I’ve Been to the Mountaintop,” in which he told supporters, “Like anybody, I would like to live a long life. Longevity has its place. But I’m not concerned about that now… I’m not worried about anything. I’m not fearing any man. Mine eyes have seen the glory of the coming of the Lord.”

While standing on a balcony outside his room at the Lorraine Motel in Memphis, Tennessee, Martin Luther King Jr. was killed by a sniper’s bullet on April 4, 1968. King died at age 39. The shocking assassination sparked riots and demonstrations in more than 100 cities across the country.
The shooter was James Earl Ray , a malcontent drifter and former convict. He initially escaped authorities but was apprehended after a two-month international manhunt. In 1969, Ray pleaded guilty to assassinating King and was sentenced to 99 years in prison.
The identity of King’s assassin has been the source of some controversy. Ray recanted his confession shortly after he was sentenced, and King’s son Dexter publicly defended Ray’s innocence after meeting with the convicted gunman in 1997. Another complicating factor is the 1993 confession of tavern owner Loyd Jowers, who said he contracted a different hit man to kill King. In June 2000, the U.S. Justice Department released a report that dismissed the alternative theories of King’s death. Ray died in prison on April 23, 1998.
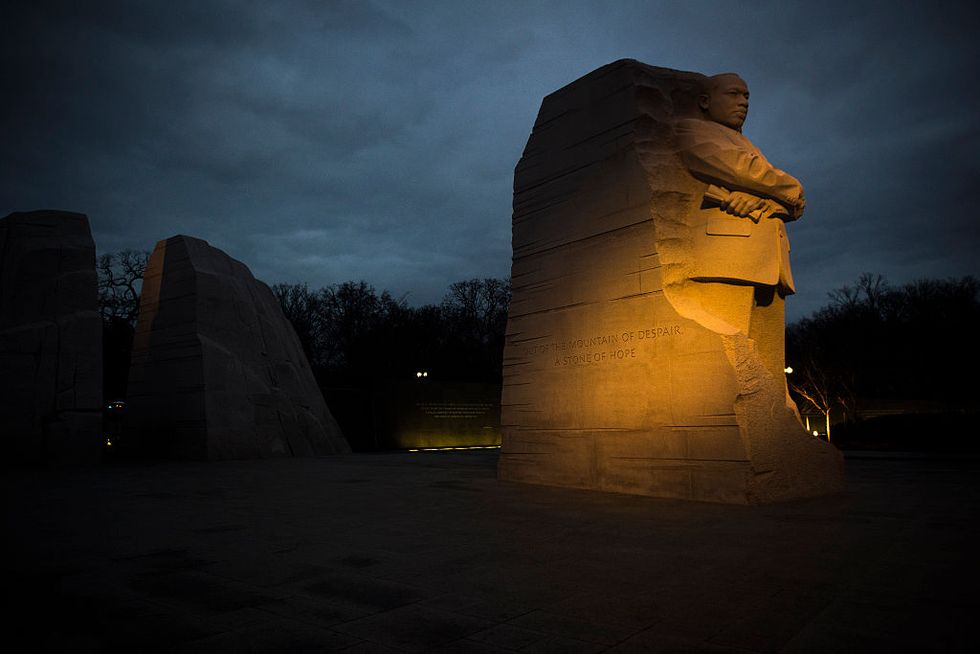

King’s life had a seismic impact on race relations in the United States. Years after his death, he is the most widely known Black leader of his era.
His life and work have been honored with a national holiday, schools and public buildings named after him, and a memorial on Independence Mall in Washington, D.C.
Over the years, extensive archival studies have led to a more balanced and comprehensive assessment of his life, portraying him as a complex figure: flawed, fallible, and limited in his control over the mass movements with which he was associated, yet a visionary leader who was deeply committed to achieving social justice through nonviolent means.
- But we come here tonight to be saved from that patience that makes us patient with anything less than freedom and justice.
- There comes a time when the cup of endurance runs over and men are no longer willing to be plunged into an abyss of injustice where they experience the bleakness of corroding despair.
- Any law that uplifts human personality is just. Any law that degrades human personality is unjust.
- The whirlwinds of revolt will continue to shake the foundations of our nation until the bright day of justice emerges.
- Let us not seek to satisfy our thirst for freedom by drinking from the cup of bitterness and hatred.
- Darkness cannot drive out darkness: only light can do that. Hate cannot drive out hate: only love can do that.
- The ultimate measure of a man is not where he stands in moments of comfort and convenience, but where he stands at times of challenge and controversy. The true neighbor will risk his position, his prestige, and even his life for the welfare of others.
- We must all learn to live together as brothers, or we will all perish together as fools.
- Forgiveness is not an occasional act; it is a permanent attitude.
- I have a dream that my four children will one day live in a nation where they will not be judged by the color of their skin but by the content of their character.
- The function of education, therefore, is to teach one to think intensively and to think critically. But education which stops with efficiency may prove the greatest menace to society. The most dangerous criminal may be the man gifted with reason but with no morals.
- I’ve seen the promised land. I may not get there with you. But I want you to know tonight that we, as a people, will get to the promised land.
- Power at its best is love implementing the demands of justice. Justice at its best is love correcting everything that stands against love.
- A man who won’t die for something is not fit to live.
- At the center of non-violence stands the principle of love.
- Right, temporarily defeated, is stronger than evil triumphant.
- In the end, we will remember not the words of our enemies, but the silence of our friends.
- Injustice anywhere is a threat to justice everywhere.
- Our lives begin to end the day we become silent about things that matter.
Fact Check: We strive for accuracy and fairness. If you see something that doesn’t look right, contact us !
The Biography.com staff is a team of people-obsessed and news-hungry editors with decades of collective experience. We have worked as daily newspaper reporters, major national magazine editors, and as editors-in-chief of regional media publications. Among our ranks are book authors and award-winning journalists. Our staff also works with freelance writers, researchers, and other contributors to produce the smart, compelling profiles and articles you see on our site. To meet the team, visit our About Us page: https://www.biography.com/about/a43602329/about-us
Civil Rights Activists

30 Civil Rights Leaders of the Past and Present

Benjamin Banneker

Marcus Garvey

Madam C.J. Walker

Maya Angelou

17 Inspiring Martin Luther King Quotes

Bayard Rustin

Colin Kaepernick

W.E.B. Du Bois and Booker T. Washington’s Clash
- African American Heroes
Hero for All: Martin Luther King, Jr.
Civil Rights leader Dr. Martin Luther King, Jr., never backed down in his stand against racism. Learn more about the life of this courageous hero who inspired millions of people to right a historical wrong.
A hero is born
Dr. Martin Luther King, Jr., was born in Atlanta, Georgia , in 1929. At the time in that part of the country, segregation—or the separation of races in places like schools, buses, and restaurants—was the law. He experienced racial predjudice from the time he was very young, which inspired him to dedicate his life to achieving equality and justice for Americans of all colors. King believed that peaceful refusal to obey unjust law was the best way to bring about social change.
Marching Forward
King and his wife, Coretta Scott King, lead demonstrators on the fourth day of a historic five-day march in 1965. Starting in Selma, Alabama , where local African Americans had been campaigning for the right to vote, King led thousands of nonviolent demonstrators 54 miles to the state capitol of Montgomery.
Brave sacrifices
King was arrested several times during his lifetime. In 1960, he joined Black college students in a sit-in at a segregated lunch counter. Presidential candidate John F. Kennedy interceded to have King released from jail, an action that is credited with helping Kennedy win the presidency.
speaking out
King inspires a large crowd with one of his many speeches. Raised in a family of preachers, he's considered one of the greatest speakers in U.S. history.

INSPIRING OTHERS
King waves to supporters from the steps of the Lincoln Memorial in Washington, D.C. during the March on Washington . There, he delivered the "I Have a Dream" speech, which boosted public support for civil rights.
making history
President Lyndon B. Johnson shakes King's hand at the signing of the landmark 1964 Civil Rights Act, which outlawed racial segregation in publicly owned facilities.
FAMILY LIFE
King his wife, Coretta Scott King, sit with three of their four children in their Atlanta, Georgia, home in 1963. His wife shared the same commitment to ending the racist system they had both grown up under.
A win for peace
King receives the Nobel Prize for Peace from Gunnar Jahn, president of the Nobel Prize Committee, in Oslo, Norway , on December 10, 1964.
Remembering a hero
A crowd of mourners follows the casket of King through the streets of Atlanta, Georgia, after his assassination in April 4, 1968. King was shot by James Earl Ray on the balcony of the Lorraine Motel. Americans honor the civil rights activist on the third Monday of January each year, Martin Luther King Day.
Learn more at National Geographic.
PHOTOGRAPHS BY: COURTESY THE LIBRARY OF CONGRESS; BEN MARTIN, TIME LIFE PICTURES / GETTY IMAGES; HORACE CORT; JULIAN WASSER, TIME LIFE PICTURES / GETTY IMAGES; AFP, GETTY IMAGES; HULTON ARCHIVE / GETTY IMAGES; COURTESY ASSOCIATED PRESS; COURTESY KEYSTONE / GETTY IMAGES; COURTESY HULTON ARCHIVE / GETTY IMAGES
Explore more
African american pioneers of science, black history month, 1963 march on washington.
- Terms of Use
- Privacy Policy
- Your California Privacy Rights
- Children's Online Privacy Policy
- Interest-Based Ads
- About Nielsen Measurement
- Do Not Sell My Info
- National Geographic
- National Geographic Education
- Shop Nat Geo
- Customer Service
- Manage Your Subscription
Copyright © 1996-2015 National Geographic Society Copyright © 2015-2024 National Geographic Partners, LLC. All rights reserved
Three Essays on Religion
Author: King, Martin Luther, Jr.
Date: September 1, 1948 to May 31, 1951 ?
Location: Chester, Pa. ?
Genre: Essay
Topic: Martin Luther King, Jr. - Education
In the following three essays, King wrestles with the role of religion in modern society. In the first assignment, he calls science and religion “different though converging truths” that both “spring from the same seeds of vital human needs.” King emphasizes an awareness of God’s presence in the second document, noting that religion’s purpose “is not to perpetuate a dogma or a theology; but to produce living witnesses and testimonies to the power of God in human experience.” In the final handwritten essay King acknowledges the life-affirming nature of Christianity, observing that its adherents have consistently “looked forward for a time to come when the law of love becomes the law of life.”
"Science and Religion"
There is widespread belief in the minds of many that there is a conflict between science and religion. But there is no fundamental issue between the two. While the conflict has been waged long and furiously, it has been on issues utterly unrelated either to religion or to science. The conflict has been largely one of trespassing, and as soon as religion and science discover their legitimate spheres the conflict ceases.
Religion, of course, has been very slow and loath to surrender its claim to sovereignty in all departments of human life; and science overjoyed with recent victories, has been quick to lay claim to a similar sovereignty. Hence the conflict.
But there was never a conflict between religion and science as such. There cannot be. Their respective worlds are different. Their methods are dissimilar and their immediate objectives are not the same. The method of science is observation, that of religion contemplation. Science investigates. Religion interprets. One seeks causes, the other ends. Science thinks in terms of history, religion in terms of teleology. One is a survey, the other an outlook.
The conflict was always between superstition disguised as religion and materialism disguised as science, between pseudo-science and pseudo-religion.
Religion and science are two hemispheres of human thought. They are different though converging truths. Both science and religion spring from the same seeds of vital human needs.
Science is the response to the human need of knowledge and power. Religion is the response to the human need for hope and certitude. One is an outreaching for mastery, the other for perfection. Both are man-made, and like man himself, are hedged about with limitations. Neither science nor religion, by itself, is sufficient for man. Science is not civilization. Science is organized knowledge; but civilization which is the art of noble and progressive communal living requires much more than knowledge. It needs beauty which is art, and faith and moral aspiration which are religion. It needs artistic and spiritual values along with the intellectual.
Man cannot live by facts alone. What we know is little enough. What we are likely to know will always be little in comparison with what there is to know. But man has a wish-life which must build inverted pyramids upon the apexes of known facts. This is not logical. It is, however, psychological.
Science and religion are not rivals. It is only when one attempts to be the oracle at the others shrine that confusion arises. Whan the scientist from his laboratory, on the basis of alleged scientific knowledge presumes to issue pronouncements on God, on the origin and destiny of life, and on man's place in the scheme of things he is [ passing? ] out worthless checks. When the religionist delivers ultimatums to the scientist on the basis of certain cosomologies embedded in the sacred text then he is a sorry spectacle indeed.
When religion, however, on the strength of its own postulates, speaks to men of God and the moral order of the universe, when it utters its prophetic burden of justice and love and holiness and peace, then its voice is the voice of the eternal spiritual truth, irrefutable and invincible.,
"The Purpose of Religion"
What is the purpose of religion? 1 Is it to perpetuate an idea about God? Is it totally dependent upon revelation? What part does psychological experience play? Is religion synonymous with theology?
Harry Emerson Fosdick says that the most hopeful thing about any system of theology is that it will not last. 2 This statement will shock some. But is the purpose of religion the perpetuation of theological ideas? Religion is not validated by ideas, but by experience.
This automatically raises the question of salvation. Is the basis for salvation in creeds and dogmas or in experience. Catholics would have us believe the former. For them, the church, its creeds, its popes and bishops have recited the essence of religion and that is all there is to it. On the other hand we say that each soul must make its own reconciliation to God; that no creed can take the place of that personal experience. This was expressed by Paul Tillich when he said, “There is natural religion which belongs to man by nature. But there is also a revealed religion which man receives from a supernatural reality.” 3 Relevant religion therefore, comes through revelation from God, on the one hand; and through repentance and acceptance of salvation on the other hand. 4 Dogma as an agent in salvation has no essential place.
This is the secret of our religion. This is what makes the saints move on in spite of problems and perplexities of life that they must face. This religion of experience by which man is aware of God seeking him and saving him helps him to see the hands of God moving through history.
Religion has to be interpreted for each age; stated in terms that that age can understand. But the essential purpose of religion remains the same. It is not to perpetuate a dogma or theology; but to produce living witnesses and testimonies to the power of God in human experience.
[ signed ] M. L. King Jr. 5
"The Philosophy of Life Undergirding Christianity and the Christian Ministry"
Basically Christianity is a value philosophy. It insists that there are eternal values of intrinsic, self-evidencing validity and worth, embracing the true and the beautiful and consummated in the Good. This value content is embodied in the life of Christ. So that Christian philosophy is first and foremost Christocentric. It begins and ends with the assumption that Christ is the revelation of God. 6
We might ask what are some of the specific values that Christianity seeks to conserve? First Christianity speaks of the value of the world. In its conception of the world, it is not negative; it stands over against the asceticisms, world denials, and world flights, for example, of the religions of India, and is world-affirming, life affirming, life creating. Gautama bids us flee from the world, but Jesus would have us use it, because God has made it for our sustenance, our discipline, and our happiness. 7 So that the Christian view of the world can be summed up by saying that it is a place in which God is fitting men and women for the Kingdom of God.
Christianity also insists on the value of persons. All human personality is supremely worthful. This is something of what Schweitzer has called “reverence for life.” 8 Hunan being must always be used as ends; never as means. I realize that there have been times that Christianity has short at this point. There have been periods in Christians history that persons have been dealt with as if they were means rather than ends. But Christianity at its highest and best has always insisted that persons are intrinsically valuable. And so it is the job of the Christian to love every man because God love love. We must not love men merely because of their social or economic position or because of their cultural contribution, but we are to love them because God they are of value to God.
Christianity is also concerned about the value of life itself. Christianity is concerned about the good life for every child, man, and woman and child. This concern for the good life and the value of life is no where better expressed than in the words of Jesus in the gospel of John: “I came that you might have life and that you might have it more abundantly.” 9 This emphasis has run throughout the Christian tradition. Christianity has always had a concern for the elimination of disease and pestilence. This is seen in the great interest that it has taken in the hospital movement.
Christianity is concerned about increasing value. The whole concept of the kingdom of God on earth expressing a concern for increasing value. We need not go into a dicussion of the nature and meaning of the Kingdom of God, only to say that Christians throughout the ages have held tenaciouly to this concept. They have looked forward for a time to come when the law of love becomes the law of life.
In the light of all that we have said about Christianity as a value philosophy, where does the ministry come into the picture? 10
1. King may have also considered the purpose of religion in a Morehouse paper that is no longer extant, as he began a third Morehouse paper, “Last week we attempted to discuss the purpose of religion” (King, “The Purpose of Education,” September 1946-February 1947, in Papers 1:122).
2. “Harry Emerson Fosdick” in American Spiritual Autobiographies: Fifteen Self-Portraits, ed. Louis Finkelstein (New York: Harper & Brothers, 1948), p. 114: “The theology of any generation cannot be understood, apart from the conditioning social matrix in which it is formulated. All systems of theology are as transient as the cultures they are patterned from.”
3. King further developed this theme in his dissertation: “[Tillich] finds a basis for God's transcendence in the conception of God as abyss. There is a basic inconsistency in Tillich's thought at this point. On the one hand he speaks as a religious naturalist making God wholly immanent in nature. On the other hand he speaks as an extreme supernaturalist making God almost comparable to the Barthian ‘wholly other’” (King, “A Comparison of the Conceptions of God in the Thinking of Paul Tillich and Henry Nelson Wieman,” 15 April 1955, in Papers 2:535).
4. Commas were added after the words “religion” and “salvation.”
5. King folded this assignment lengthwise and signed his name on the verso of the last page.
6. King also penned a brief outline with this title (King, “The Philosophy of Life Undergirding Christianity and the Christian Ministry,” Outline, September 1948-May 1951). In the outline, King included the reference “see Enc. Of Religion p. 162.” This entry in An Encyclopedia of Religion, ed. Vergilius Ferm (New York: Philosophical Library, 1946) contains a definition of Christianity as “Christo-centric” and as consisting “of eternal values of intrinsic, self-evidencing validity and worth, embracing the true and the beautiful and consummated in the Good.” King kept this book in his personal library.
7. Siddhartha Gautama (ca. 563-ca. 483 BCE) was the historical Buddha.
8. For an example of Schweitzer's use of the phrase “reverence for life,” see Albert Schweitzer, “The Ethics of Reverence for Life,” Christendom 1 (1936): 225-239.
9. John 10:10.
10. In his outline for this paper, King elaborated: “The Ministry provides leadership in helping men to recognize and accept the eternal values in the Xty religion. a. The necessity of a call b. The necessity for disinterested love c. The [ necessity ] for moral uprightness” (King, “Philosophy of Life,” Outline, September 1948-May 1951).
Source: CSKC-INP, Coretta Scott King Collection, In Private Hands, Sermon file.
© Copyright Information
Cross Cultural Solidarity

MLK: Speeches, Sermons, Essays, & Interviews
Below are King’s most essential speeches, sermons, and short writings, with links to audio and video when available. When dates are uncertain, a likely range of when a work was composed or performed is given. See also this collection of articles by MLK scholars about nearly every conceivable dimension of King’s life and thought, and this resource on books by and about King.
November, 1954: Transformed Nonconformist.
December 5, 1955: Address to the first mass meeting of the Montgomery bus boycott. Audio .
1956: The Violence of Desperate Men .
April 1956: Our Struggle.
March 18, 1956: When Peace Becomes Obnoxious.
May 7, 1956: The Death of Evil upon the Seashore .
November 1956: Paul’s Letter to American Christians . Audio.
January 1, 1957: Facing the Challenge of a New Age , Address Delivered at NAACP Emancipation Day Rally.
February 6, 1957: Nonviolence and Racial Justice.
April 7, 1957: The Birth of a New Nation . (On King’s travels to Ghana.) Audio .
May 17, 1957: Give Us the Ballot . Audio.
September 2, 1957: “A Look to the Future,” Address Delivered at Highlander Folk School’s Twenty-fifth Anniversary Meeting.
November, 1957: Loving Your Enemies . Audio.
March 9, 1959: Farewell Statement for All India Radio. Audio.
March 22, 1959: Palm Sunday Sermon on Mohandas K. Gandhi.
July 1959: My Trip to the Land of Gandhi.
October 1959: The Social Organization of Nonviolence . (A response to Robert Williams call for Black people to take up arms.)
April, 1960: Pilgrimage to Nonviolence.
March 1961: The Man Who Was a Fool .
1961: Interview on BBC’s “Face to Face.” Video.
September 1962: Can A Christian Be a Communist?
July 1962 – March 1963: Shattered Dreams .
July 1962 – March 1963: Love In Action .
July 1962 – March 31, 1963: A Tough Mind and a Tender Heart .
July 1962 – March 1963: On Being a Good Neighbor.
July 1962 – March 1963: Our God is Able .
July 1962 – March 1963: Antidotes for Fear .
July 1962 – March 1963: The Answer to a Perplexing Question .
June, 1963: A Knock at Midnight . Audio .
June 23, 1963: Great March to Freedom Rally, Detroit. Audio .
August 28, 1963: I Have a Dream . Video . Audio .
September 18, 1963: Eulogy for the Martyred Children . (Funeral service for the children killed in the Birmingham bombing.) Audio.
December 10, 1964: Acceptance Address for the Nobel Peace Prize . Video.
January, 1965: MLK Playboy interview . (The interviewer is Alex Hayley.)
March 25, 1965: Address at the Conclusion of the Selma to Montgomery March . Audio.
March 28, 1965: Interview on Meet the Press , immediately following the Selma to Montgomery March. Video.
June, 1965: The Bravest Man I Ever Met .
July 4, 1965: The American Dream . Audio (different version.)
May 31, 1966: “Buddhists and Martyrs of the Civil Rights Movement”: Joint statement by Martin Luther King, Jr., and Thich Nhat Hanh, International Committee of Conscience on Vietnam.
June 5, 1966: Guidelines for a Constructive Church . Audio.
January 25, 1967: Letter from Dr. Martin Luther King, Jr. nominating Thich Nhat Hanh for the Nobel Peace Prize in 1967 .
April 4, 1967: Beyond Vietnam . Audio.
April 9, 1967: The Three Dimensions of a Complete Life. Audio.
April 14, 1967: The Other America. Video.
August 27, 1967: Why Jesus Called a Man a Fool. Audio.
August 16, 1967: “Where Do We Go From Here?,” Address Delivered at the Eleventh Annual SCLC Convention . Audio.
September 1, 1967: The Role of the Behavioral Scientist in the Civil Rights Movement .
October 26, 1967: What is Your Life’s Blueprint? Video. (No text version available.)
November/December 1967: The Impasse in Race Relations. Audio . (No text version available.)
November/December 1967: Conscience and the War in Vietnam. Audio. (No text version available.)
November/December 1967: Youth and Social Action. Audio. (No text version available.)
November/December 1967: Nonviolence and Social Change . Audio.
December 24, 1967: A Christmas Sermon on Peace (text incomplete.) Audio .
1967: Racism and the World House.
1967: King interviewed on NBC. Video.
1967: King interviewed on the Merv Griffin Show. Video ( Part 1 on civil rights, part two on Vietnam and Communism.)
February 4, 1968: The Drum Major Instinct. Audio.
February 23, 1968: Honoring Dr. Du Bois .
March 3, 1968: Unfulfilled Dreams . Audio (incomplete.)
March 18, 1968: All Labor Has Dignity.
March 31, 1968: Remaining Awake Through a Great Revolution . Audio.
April 3, 1968 (the day before King’s assassination): “ I’ve Been to the Mountaintop .” Audio .
Martin Luther King, Jr.

- Occupation: Civil Rights Leader
- Born: January 15, 1929 in Atlanta, GA
- Died: April 4, 1968 in Memphis, TN
- Best known for: Advancing the Civil Rights Movement and his "I Have a Dream" speech

- King was the youngest person to be awarded the Nobel Peace Prize in 1964.
- Martin Luther King, Jr. Day is a national holiday.
- At the Atlanta premier of the movie Gone with the Wind , Martin sang with his church choir.
- There are over 730 streets in the United States named after Martin Luther King, Jr.
- One of his main influences was Mohandas Gandhi who taught people to protest in a non-violent manner.
- He was awarded the Congressional Gold Medal and the Presidential Medal of Freedom.
- The name on his original birth certificate is Michael King. This was a mistake, however. He was supposed to be named after his father who was named for Martin Luther, the leader of the Christian reformation movement.
- He is often referred to by his initials MLK.
- Listen to a recorded reading of this page:
- Civil Rights Timeline
- African-American Civil Rights Timeline
- Magna Carta
- Bill of Rights
- Emancipation Proclamation
- Glossary and Terms
- Civil Rights
5 Things Written by Martin Luther King Jr. That Everyone Should Read, According to an Expert

T he words written about Martin Luther King Jr. during his too-short life and in the decades since his assassination on April 4, 1968, would be impossible to count. King himself left a deep archive of writings, speeches and sermons, too. His spoken orations in particular are a powerful reminder of why he was destined to become part of the pantheon of American icons.
Step Into History: Learn how to experience the 1963 March on Washington in virtual reality
“One has to remember that King above all was a preacher,” says Carolyn Calloway-Thomas, chair of African American and African Diaspora Studies at the Indiana University Bloomington and an editor of Dr. Martin Luther King, Jr. and the Sermonic Power of Public Discourse.
While she notes that he was so prolific that it’s near impossible to choose, Calloway-Thomas spoke to TIME about the pieces of King’s work that everyone should know about. They are:
“The Death of Evil upon the Seashore” (May 17, 1956)
“The death of the Egyptians upon the seashore is a glaring symbol of the ultimate doom of evil in its struggle with good.”
This sermon was delivered to a massive crowd at the Cathedral of St. John the Divine in New York on the occasion of the two-year anniversary of the Supreme Court’s Brown v. Board of Education ruling against school segregation, at an early moment in this phase of the civil rights movement, with the Montgomery bus boycott still ongoing. To Calloway-Thomas, the sermon is noteworthy for the optimistic vision it presented at such a moment. “He had to help African-American people imagine themselves,” she says. “I think the Death of Evil upon the Seashore is that speech.”
It wasn’t the first time King preached on these ideas, and in fact the link he draws between the Biblical exodus and the story of African-American progress toward freedom and equality was an old one, but those present noted that his delivery that day was particularly moving. “He taps into that reservoir, that myth of the Hebrew children in bondage,” Calloway-Thomas says, “and he elevates it and makes it more publicly known.”
Read the full speech here
Letter from a Birmingham Jail (April 16, 1963)
“Injustice anywhere is a threat to justice everywhere. We are caught in an inescapable network of mutuality, tied in a single garment of destiny. Whatever affects one directly, affects all indirectly.”
Yes, this is a letter, not a speech or sermon — but Calloway-Thomas says it’s worth including on such a list anyway. After all, the circumstances that created this letter are inherently linked to the fact that he couldn’t deliver a speech in person. At the time, King found himself jailed in Alabama after ignoring an injunction against protests in Birmingham. During that time, a group of clergymen wrote an open letter urging him away from protests. He wanted to respond but, from the jail, his only option if he wanted to answer quickly was to write it down. “Ideas have moments and if those moments aren’t used, you lose that rhetorical moment and it no longer has the force it had,” Calloway-Thomas says.
So, in a format she likens to a spoken call and response, he answers the questions that were posed to him about his methods. While also explaining that he’s on strong biblical footing, he provides the public with a way to understand the work he’s doing. His rhetorical skills are also on display as he uses a story about his 6-year-old daughter’s early perceptions of racism and segregation to underline that the matter is not theoretical. In the years since, this letter has become one of 20th century American history’s most famous documents.
Read the full letter here
“I Have a Dream…” (Aug. 28, 1963)
“I have a dream that my four little children will one day live in a nation where they will not be judged by the color of their skin but by the content of their character.”
The speech that remains Martin Luther King Jr.’s most famous oration — one of the most famous orations in American history, if not world history — is that well-known for a good reason, Calloway-Thomas says. This was the moment when the world as a whole really saw King, and the moment was carefully orchestrated, framed by the Lincoln Memorial. “Think about how dazzling that was!” she says. “Think about the robust visuals and the lovely words echoing from Dr. King. It was an elixir that was made to circulate.”
But, she says, the power of his voice and the impact of the image can sometimes overwhelm the full message of the speech. “Dr. King had some pretty radical statements in that speech,” Calloway-Thomas adds. “Most people gloss over the part in that speech where King says that if we overlook the urgency of now there’ll be a rude awakening. I’ve never seen a student go to that section of the speech; people go right to ‘I have a dream’ and they don’t notice the threat.”
“A Time to Break Silence” (April 4, 1967)
“We still have a choice today: nonviolent coexistence or violent coannihilation. We must move past indecision to action. We must find new ways to speak for peace in Vietnam and justice throughout the developing world, a world that borders on our doors.”
In this speech, King publicly answers his conscience, as Calloway-Thomas puts it, on the matter of the Vietnam War. With an undercurrent of “anguish” about the fact that he feels he must speak, and must criticize the choices of Lyndon Johnson, who had often been an ally , he entered the arena of opposition to the war.
“This is an unsettling moment. People paid attention, but that meant there was backlash,” she says. President Johnson and many others felt that he ought to stay focused on domestic civil-rights issues and leave the foreign policy to them, but in this speech he makes clear why those two topics cannot truly be separated. That idea, Calloway-Thomas says, parallels the experience of earlier fighters for justice, such as Frederick Douglass, who got to the world stage with one kind of story — their personal freedom narratives, in that case — and shocked some of their allies when they showed that their thinking was far more expansive.
“I’ve Been to the Mountaintop” (April 3, 1968)
“I may not get there with you. But I want you to know tonight, that we, as a people, will get to the Promised Land.”
Start with the date on this one: that’s April 3, 1968, the night before King was assassinated. In this speech, which summons King’s primary background as a preacher, he returns to the story of Moses. Rather than speaking on the joy of the Exodus, though, he turns to the end of Moses’ life, and his death just outside the Promised Land to which he had delivered his people. King casts himself as another leader who may not be there for the end of the journey. “He used Christian values and Democratic traditions to bring people together, so it’s not surprising that he goes to this idea,” Calloway-Thomas says. “What’s significant here is when it occurred. It was almost apocalyptic. Because it occurred at that time it has lingering significance and carries with it an abundance of pathos.”
Of course, as Calloway-Thomas says, we can imagine a scenario in which King gave this speech and then lived. The emotional resonance of his words might be lessened without the seemingly prescient layer of fate, but the story would be there all the same. “Here’s a man talking about longevity, here’s a man talking about god’s Will, here’s a man talking about going up to the mountaintop and looking skyward toward heaven and looking over into the Promised Land,” she says. “It’s a gorgeous story.”
More Must-Reads From TIME
- Jane Fonda Champions Climate Action for Every Generation
- Passengers Are Flying up to 30 Hours to See Four Minutes of the Eclipse
- Biden’s Campaign Is In Trouble. Will the Turnaround Plan Work?
- Essay: The Complicated Dread of Early Spring
- Why Walking Isn’t Enough When It Comes to Exercise
- The Financial Influencers Women Actually Want to Listen To
- The Best TV Shows to Watch on Peacock
- Want Weekly Recs on What to Watch, Read, and More? Sign Up for Worth Your Time
Write to Lily Rothman at [email protected]
You May Also Like
- Martin Luther King, Jr.
- King's Writings
- Research Databases
Primary Sources
- Civil Rights Movement Guide This link opens in a new window
- African American Studies Guide This link opens in a new window
- Online King Records Access (Stanford)
- Smithsonian - Dr. Martin Luther King Jr.
- FBI Records: The Vault - Martin Luther King, Jr.
- JFK Presidential Library - Martin Luther King, Jr.
- Letter From a Birmingham Jail, April 16, 1963
- "I Have a Dream," August 28, 1963
- Official Program for the March on Washington, August 28, 1963
- "Who Speaks for the Negro?," March 18, 1964
- "Beyond Vietnam," April 4, 1967
- “I’ve Been to the Mountaintop,” April 3, 1968
- Black Freedom Struggle Primary Source Collection (ProQuest) This link opens in a new window In this website, the editors present primary source documents from several of the time periods in American History when the river of the Black Freedom Struggle ran more powerfully, while not losing sight of the fierce, often violent opposition that Black people have faced on the road to freedom.
- African American Newspapers (NewsBank) This link opens in a new window Over 270 African American newspapers published between 1827 and 1998.
- New York Times Historical, 1851-2019 (ProQuest) This link opens in a new window This historical newspaper provides genealogists, researchers and scholars with online, easily-searchable first-hand accounts and unparalleled coverage of the politics, society and events of the time.
- << Previous: Research Databases
- Next: Multimedia >>
- Last Updated: Jan 18, 2024 8:44 AM
- URL: https://libguides.uwf.edu/mlk
Essay on Martin Luther King’s I Have a Dream Speech
I have a dream: essay introduction, martin luther king’s speech: essay conclusion, reference list.
One of the finest explanations of American’s dream is the powerful speech of Martin Luther King, Jr. He delivered the speech at the Lincoln Memorial on August 28, 1963, in Washington D.C. The speech is mainly centered on racial equality and stoppage of discrimination.
At that time, racial segregation ruled in almost all places: be it schools, neighborhoods and even in social places. With violence and riots so often, it was a disturbing moment for America although the U.S government was doing nothing to change the situation. Through the speech, Dr. King was educating inspiring and informing both the civil supporters and the unborn generation in the world to reach out to their dreams and giving his audience hope for a better future.
Up to the time when he was delivering the speech, African Americans were still under slavery from the white people as indicated in the below excerpt.
One hundred years later, the life of the Negro is still sadly crippled by the manacles of segregation and the chains of discrimination…….One hundred years later, the Negro is still languishing in the corners of American society and finds himself an exile in his own land (Luther, 1963, para. 2).
The speech depicts the idea that someone can actually be anything that he dreams of becoming. Dr. King suggested that America is a land full of opportunities and that Americans should maximize on them. Before transforming the world, he saw the need to begin in America. Dr. King began the speech with a rhetoric phrase, ’Now is the time’, a tool that he used throughout speech. In the sixth paragraph of his speech, he used the phrase six times.
He was echoing to his audience to get hold of the moment. More so he used the phrase, ‘I have a dream eight times. By so doing he was echoing future hope for the people that will make them forget about all the slavery sufferings and injustices that they had faced while under slavery.
This is a sign of hope for the future too. He brought in the idea of slavery to suggest that it is still operational in today’s world. By using the word ‘slave-owners’, Dr. King was referring to the white, however to calm any tension between the black and the white people, he re-unites them by saying, “… will be able to sit down together at a table of brotherhood” (Luther, 1963, para.12).
I have a dream that one day this nation will rise up and live out the true meaning of its creed: “We hold these truths to be self-evident: that all men are created equal.” I have a dream that one day on the red hills of Georgia the sons of former slaves and the sons of former slave-owners ………, a desert state, sweltering with the heat of injustice and oppression, will be transformed into an oasis of freedom and justice…. I have a dream today (Luther, 1963, para.12).
The dream in the above context symbolizes the aspirations that Dr. King had of America setting the stage for the rest of the world. He also says that ‘this nation will rise up’ meaning that he had fathomed a revolution time when the Americans will be accepted as right persons in the States (Luther, 1963, para.12).
There was an established racial discrimination that is why he sent such a strong message to the white. More importantly is the fact that his words were advocating for peace hence providing the vision that anyone would buy it. There above discussion hence shows that Martin Luther King, Jr was really, an effective public speaker.
Luther, M. (1963). I have a dream. Web.
- Chicago (A-D)
- Chicago (N-B)
IvyPanda. (2023, October 29). Essay on Martin Luther King’s I Have a Dream Speech. https://ivypanda.com/essays/martin-luther-kings-speech-i-have-a-dream/
"Essay on Martin Luther King’s I Have a Dream Speech." IvyPanda , 29 Oct. 2023, ivypanda.com/essays/martin-luther-kings-speech-i-have-a-dream/.
IvyPanda . (2023) 'Essay on Martin Luther King’s I Have a Dream Speech'. 29 October.
IvyPanda . 2023. "Essay on Martin Luther King’s I Have a Dream Speech." October 29, 2023. https://ivypanda.com/essays/martin-luther-kings-speech-i-have-a-dream/.
1. IvyPanda . "Essay on Martin Luther King’s I Have a Dream Speech." October 29, 2023. https://ivypanda.com/essays/martin-luther-kings-speech-i-have-a-dream/.
Bibliography
IvyPanda . "Essay on Martin Luther King’s I Have a Dream Speech." October 29, 2023. https://ivypanda.com/essays/martin-luther-kings-speech-i-have-a-dream/.
- Interviewing Methods: Types and Features
- History: Slavery in Southern States
- Analysis of “I Have a Dream “, by Martin Luther King, Jr.
- "I Have a Dream" Speech by Martin Luther King Jr
- Dr. Martin Luther King, Jr. National Memorial Foundation
- Speech Evaluation: Martin Luther King, Jr.
- Paul Laurence Dunbar’s “We Wear the Mask” Poem
- Martin Luther King Jr’s “I Have a Dream” Speech Critique
- Harriet A. Jacobs, Incidents in the Life of a Slave Girl
- Leadership Lessons From Martin Luther King Jr.
- Skeptical and Layman Competence
- Speech Analysis: Ronald Reagan vs. Barack Obama
- The Psychology of Images
- Dogs Playing Poker
- The Art of Conversation: Rhetorical Devices
Read our research on: Abortion | International Conflict | Election 2024
Regions & Countries
How public attitudes toward martin luther king jr. have changed since the 1960s.

About eight-in-ten American adults (81%) say civil rights leader Martin Luther King Jr. has had a positive impact on the United States, according to a Pew Research Center report that comes ahead of the 60th anniversary of the March on Washington for Jobs and Freedom . This majority includes nearly half of Americans (47%) who say King’s impact has been very positive. Just 3% say his impact on the country has been negative.
Sixty years after Martin Luther King Jr. gave his “I Have a Dream” speech at the March on Washington, Pew Research Center conducted this analysis to determine how views of King have changed over time in the United States.
This analysis uses data from a 2023 Center survey as well as data from Gallup surveys conducted in May 1963, August 1964, May 1965, August 1966, May 1969 and August 2011. The Center survey polled 5,073 U.S. adults from April 10 to April 16, 2023. Everyone who took part is a member of the Center’s American Trends Panel (ATP), an online survey panel that is recruited through national, random sampling of residential addresses. Address-based sampling ensures that nearly all U.S. adults have a chance of selection. The survey is weighted to be representative of the U.S. adult population by gender, race, ethnicity, partisan affiliation, education and other categories. Read more about the ATP’s methodology .
Here are the Pew Research Center survey questions used for this analysis , along with responses, and the survey methodology .
However, views of King haven’t always been so positive.
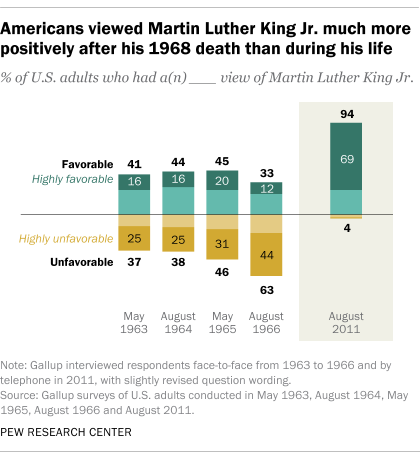
In May 1963, only about four-in-ten Americans (41%) had a favorable opinion of King, according to a Gallup survey . That included just 16% who viewed him highly favorably, rating him +4 or +5 on a scale of -5 (most unfavorable) to +5 (most favorable). The survey was conducted shortly after King’s Birmingham Campaign , which led the Alabama city to remove signs enforcing segregation of restrooms and drinking fountains and to desegregate lunch counters.
King’s favorable ratings remained about the same in Gallup surveys conducted in 1964 and 1965. But by August 1966, only a third of Americans had a favorable view of the civil rights leader. More than six-in-ten (63%) viewed him unfavorably, including 44% who viewed him highly unfavorably.
Gallup’s survey questions about King between 1963 and 1966 coincided with his civil rights work in a variety of areas:
- In August 1963, King delivered the “I Have a Dream” speech during the March on Washington.
- In June 1964, he demanded equal treatment at a segregated Florida restaurant, an act that led to his arrest.
- In December 1964, he received the Nobel Peace Prize and pledged the full financial award to civil rights efforts.
- In March 1965, he led a civil rights march from Selma, Alabama, to the state capital of Montgomery.
- In June 1966, he completed fellow civil rights leader James Meredith’s March Against Fear after Meredith was wounded by a White gunman.
- In August 1966, he was hit by a rock while marching through an all-White neighborhood in Chicago as part of the Chicago Freedom Movement. The movement sought to expand civil rights work to northern U.S. cities.
King was assassinated in April 1968 in Memphis, Tennessee. Gallup did not ask Americans to rate King again until August 2011, when the Martin Luther King Jr. Memorial was officially dedicated in Washington, D.C. By then, views of King had changed dramatically, as 94% of Americans had a favorable opinion of him. Americans were also broadly supportive of the memorial: 91% approved of it and 70% were at least somewhat interested in visiting it, according to the Gallup survey.
Racial differences in views of King
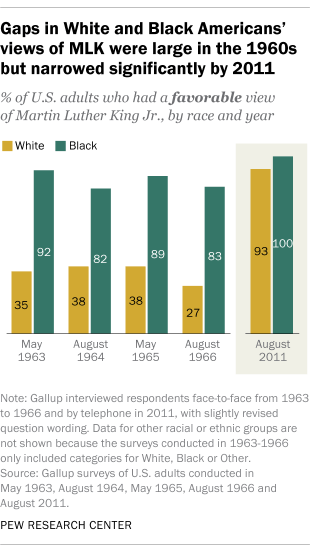
Throughout the mid-1960s, Black Americans had much more favorable views of King than White Americans did. In the May 1963 Gallup survey, for example, 92% of Black Americans but only 35% of White Americans had a favorable opinion of the civil rights leader.
As more White Americans learned who King was over the next three years, a higher share of them viewed him unfavorably. Around four-in-ten White adults (41%) had an unfavorable view of King in May 1963 – a figure that rose to 69% by August 1966.
In 1969, Gallup asked Black adults in the U.S. whether they thought King’s beliefs about nonviolence had gained or lost support since his assassination a year earlier. About half of Black Americans (52%) said they thought King’s beliefs had lost support, while 30% said his beliefs had gained support.
By 2011, White Americans’ attitudes toward King had become much more positive. Fully 100% of Black adults and 93% of White adults had a favorable opinion of him, and majorities of both Black and White Americans (96% and 65%, respectively) had highly favorable views of him.
Views of racial equality after King
More than 40 years after King’s assassination, Americans were still divided on whether his dream of racial equality had been realized. In the 2011 Gallup survey, 51% of Americans said King’s dream had been realized, while 49% said it had not.
Pew Research Center’s new report, which uses survey data from April 2023, finds that Americans are similarly divided today about whether the U.S. has made progress on racial equality over the last 60 years.
About half of U.S. adults (52%) say that the country has made a great deal or a fair amount of progress, while 33% say it has made some progress and 15% say it has not made much or any progress. But Black Americans are more pessimistic: Just 30% say the U.S. has made a great deal or a fair amount of progress, compared with 58% of White adults. And 32% of Black adults say the country has made little or no progress, compared with 11% of White adults.
Note: Here are the Pew Research Center survey questions used for this analysis , along with responses, and the survey methodology .
Sign up for our weekly newsletter
Fresh data delivered Saturday mornings
Striking findings from 2021
Public sees black people, women, gays and lesbians gaining influence in biden era, economy and covid-19 top the public’s policy agenda for 2021, 20 striking findings from 2020, our favorite pew research center data visualizations of 2019, most popular.
About Pew Research Center Pew Research Center is a nonpartisan fact tank that informs the public about the issues, attitudes and trends shaping the world. It conducts public opinion polling, demographic research, media content analysis and other empirical social science research. Pew Research Center does not take policy positions. It is a subsidiary of The Pew Charitable Trusts .
Home — Essay Samples — History — Civil Rights Movement — Martin Luther King Jr Thesis Statement
Martin Luther King Jr Thesis Statement
- Categories: Civil Rights Movement Social Justice
About this sample

Words: 698 |
Published: Mar 13, 2024
Words: 698 | Pages: 2 | 4 min read

Cite this Essay
Let us write you an essay from scratch
- 450+ experts on 30 subjects ready to help
- Custom essay delivered in as few as 3 hours
Get high-quality help

Verified writer
- Expert in: History Sociology

+ 120 experts online
By clicking “Check Writers’ Offers”, you agree to our terms of service and privacy policy . We’ll occasionally send you promo and account related email
No need to pay just yet!
Related Essays
2 pages / 1077 words
3 pages / 1293 words
5 pages / 2122 words
2 pages / 961 words
Remember! This is just a sample.
You can get your custom paper by one of our expert writers.
121 writers online
Still can’t find what you need?
Browse our vast selection of original essay samples, each expertly formatted and styled
Related Essays on Civil Rights Movement
The use of allusion in literature and rhetoric has long been recognized as a powerful tool for conveying complex ideas and invoking shared cultural references. In Martin Luther King Jr.'s "Letter from Birmingham Jail," allusion [...]
The historical and literary processes of the second half of the 20th century demonstrate the merging of the civil rights movement with the left-wing literary movement, driven by critical sentiments and a deep desire for social [...]
The philosophies of Martin Luther King and Malcolm X have been pivotal in shaping the civil rights movement in the United States. Both leaders advocated for the rights and equality of African Americans, but their approaches were [...]
In 1963, Dr. Martin Luther King, Jr. and a group of African-Americans embarked on a mission to challenge the segregation laws in the South. Their plan was to march into downtown Birmingham, Alabama and express their disapproval [...]
Malcolm X, born Malcolm Little, was a prominent African American activist and leader during the civil rights movement of the 1950s and 1960s. His powerful oratory skills and unwavering commitment to the empowerment of Black [...]
Martin Luther King Jr. was a prominent leader in the American civil rights movement, known for his powerful speeches and unwavering dedication to nonviolent protest. He possessed a unique set of characteristics that set him [...]
Related Topics
By clicking “Send”, you agree to our Terms of service and Privacy statement . We will occasionally send you account related emails.
Where do you want us to send this sample?
By clicking “Continue”, you agree to our terms of service and privacy policy.
Be careful. This essay is not unique
This essay was donated by a student and is likely to have been used and submitted before
Download this Sample
Free samples may contain mistakes and not unique parts
Sorry, we could not paraphrase this essay. Our professional writers can rewrite it and get you a unique paper.
Please check your inbox.
We can write you a custom essay that will follow your exact instructions and meet the deadlines. Let's fix your grades together!
Get Your Personalized Essay in 3 Hours or Less!
We use cookies to personalyze your web-site experience. By continuing we’ll assume you board with our cookie policy .
- Instructions Followed To The Letter
- Deadlines Met At Every Stage
- Unique And Plagiarism Free
Martin Luther King Jr. didn't live long enough to see how we've dismantled his legacy
What would james baldwin, martin luther king jr. and their fellow warriors think of america today.
By 1968, Martin Luther King Jr. was flailing.
King hadn’t had a major victory in years, and his popularity had plummeted. As he neared death, almost 75% of Americans disapproved of him , labeling him a race-baiting troublemaker. Painfully for him, even a majority of Black people didn’t support him.
Those closest to King wondered how he could go on as he tumbled into depression.
The immediate past provided no encouragement in 1968. Medgar Evers had been shot to death on his driveway in Jackson, Mississippi, in June 1963. King’s simultaneous rival and comrade Malcolm X was murdered just over a year and a half later in New York.
The Black Power movement had been born a few years earlier, and its leaders were already targeted, persecuted and, at times, marked for death.
King’s 13 years on the front lines of America’s Civil Rights War ended when he was murdered in Memphis, Tennessee, on April 4, 1968. He was only 39 years old .
What followed his death was a string of events that served to dismantle his legacy and allow anti-Blackness in America to flourish.
Martin Luther King Jr. became another abandoned Black leader
Like W.E.B. Du Bois , Paul Robeson and others, King had been abandoned by many leaders of the NAACP and other Black legacy organizations.
He was still hounded by the U.S. government as FBI Director J. Edgar Hoover and COINTELPRO continued efforts to destroy Black leaders and resistance to racial inequality.
He was struggling to hold together his own coalition of lieutenants like Ralph Abernathy, Jesse Jackson, Andrew Young, Hosea Williams and others, who all quickly went their separate ways after King’s death.
What are states legislating against DEI afraid of? The truth about our racist history.
Du Bois, one Black America’s greatest intellectuals, had given up seven years earlier. He wrote to his friend Grace Goens in September 1961: “I just cannot take any more of this country’s treatment. ... Chin up, and fight on, but realize that American Negroes can’t win.”
Du Bois left for Ghana the next month and never returned. He died the day before the 1963 March on Washington , a mere two months after Evers.
MLK did not live to see us misuse his words
King did not live to see racist anti-Black politicians and pundits misuse his words arguing people should “not be judged by the color of their skin but the content of their character” to oppose Black progress.
He did not live to see the Civil Rights Act of 1964 for which he fought for so fiercely weaponized by the U.S. Supreme Court and attorneys general like Kentucky’s Russell Coleman to justify the legal destruction of affirmative action and diversity initiatives, and set the fight for racial equality back decades.
King did not live to see the Voting Rights Act of 1965, of which he was so proud, gutted and rendered little more than a “ dead letter ” by the Shelby County v. Holder ruling in 2013. Since then, racial voting disparities in America have increased exponentially.
King was a brave man born out of the Black radical tradition
King did not live to see cowardly Black free-riders (not Freedom Riders) who will not open their mouths in defense of their people benefit from his sacrifice and suffering.
He did not live long enough to see the Ward Connerlys, Clarence Thomases , Candace Owens and Daniel Camerons of the world.
MLK was my friend. How can I be excited for the future when lessons from past are ignored?
He didn’t live to see Sen. Tim Scott , R-S.C., skinning, grinning and genuflecting before Donald Trump as he bastardized the words of Fannie Lou Hamer .
He did not live long enough to see a Black man running for governor of North Carolina proudly proclaim that Black people owe America reparations .
Nor did King live long enough to see a Black president or the unrelenting white backlash that has followed him.
What would King think of America today?
The searing truth-telling writer James Baldwin didn’t see most of it, either. He outlived King by two decades, eventually dying in 1987 during the racial onslaught of the Reagan era. He was only 63 .
For those decades, Baldwin was the one left behind. He lived long enough to bear witness to the grief, pain and white retribution that followed his friends’ murders.
What Baldwin saw was neither pretty nor encouraging. He damningly reflects on America in Raoul Peck’s Oscar-nominated documentary " I am not your Negro ": “I’m terrified at the moral apathy – the death of the heart which is happening in my country. These people have deluded themselves for so long that they really don’t think I’m human. I base this on their conduct, not on what they say. And this means that they have become, in themselves, moral monsters .”
Current political and social anti-Blackness has grown more and more brazen in America and, unfortunately, there are no Kings or Baldwins left to fight it. What would Baldwin, King and their fellow warriors think of America today?
Ricky L. Jones, the Baldwin-King Scholar-in-Residence at the Christina Lee Brown Envirome Institute , is a professor of Pan-African Studies at the University of Louisville. His column appears biweekly in the Louisville Courier Journal, where this piece originally published .
- International
- Schools directory
- Resources Jobs Schools directory News Search

Martin Luther King Jr Biography Reading Comprehension Passage Printable Worksheet PDF
Subject: English
Age range: 10 - 16
Resource type: Worksheet/Activity
Last updated
21 March 2024
- Share through email
- Share through twitter
- Share through linkedin
- Share through facebook
- Share through pinterest

This reading comprehension passage about Martin Luther King Jr is designed with your students in mind, ensuring a delightful and educational experience.
What makes this resource a must-have for teachers and their students?
Engaging Content: This easy-to-understand passage is designed to spark curiosity and foster a love for reading.
Test Knowledge: Multiple question types are provided to encourage critical thinking and ensure a deep understanding of the passage.
Answer Key: Easily assess student progress.
What is all included in this:
Reading Passage with colorful picture
10 descriptive questions
5 True/False questions
5 short answer questions
Thank you for choosing to inspire and empower your students!
Your FREE worksheets are waiting… visit PrintableBazaar now!
Summary of passage
Martin Luther King Jr. was born in Atlanta, Georgia on January 15, 1929 and grew up during a time of racial inequality. He believed in equal treatment for all individuals, regardless of their appearance. As he got older, he became a minister and used his voice to advocate for those who couldn’t speak up for themselves. In 1955, he led the Montgomery Bus Boycott, a peaceful protest that successfully changed unfair laws. Martin’s leadership and belief in peaceful protests inspired many people. He faced challenges and opposition, but never gave up. On April 4, 1968, he was assassinated, but his legacy lives on. Today, Martin Luther King Jr. Day is celebrated to honor his courage and dream of a better world for all.
Tes paid licence How can I reuse this?
Your rating is required to reflect your happiness.
It's good to leave some feedback.
Something went wrong, please try again later.
This resource hasn't been reviewed yet
To ensure quality for our reviews, only customers who have purchased this resource can review it
Report this resource to let us know if it violates our terms and conditions. Our customer service team will review your report and will be in touch.
Not quite what you were looking for? Search by keyword to find the right resource:
- Skip to main content
- Keyboard shortcuts for audio player
Fractures in the Grand Alliance between Black and Jewish Americans

Devan Schwartz

Civil rights activist Martin Luther King Jr marching from Selma to Montgomery, Alabama alongside Rabbi Abraham Joshua Heschel. William Lovelace/Daily Express/Hulton Archive/Getty Images hide caption
Civil rights activist Martin Luther King Jr marching from Selma to Montgomery, Alabama alongside Rabbi Abraham Joshua Heschel.
Close your eyes and you might be able to conjure the iconic image of Rabbi Abraham Joshua Heschel, with a white bushy beard, as he marches alongside Reverend Dr. Martin Luther King, Jr. It's 1965 and they're at the front of the delegation from Selma to Mongtomery, Alabama. Everyone wears big Hawaiian leis – given as a symbol of support and solidarity by Reverend Abraham Akaka.
Scholars say this moment enshrines the so-called Grand Alliance, in which Black and Jewish leaders worked together in support of civil rights and voting rights.
After marching that day, Heschel said, "I felt my legs were praying."
And from the steps of the capitol in Montgomery, King said, "The end we seek is a society at peace with itself, a society that can live with its conscience. And that will be a day not of the white man, not of the black man. That will be the day of man as man."
Just a few months later, President Lyndon B. Johnson signed the Voting Rights Act of 1965 .
So was this a major moment in the ongoing partnership between Black and Jewish leaders — or simply the high-water mark in a relationship that has long since receded?
"Today's Black Jewish relationship is encased in amber from the civil rights era, and I don't think it's properly understood," Jacques Berlinerblau, Professor of Jewish Civilization at Georgetown University, told NPR's Morning Edition . "And until we properly understand it, we might not be able to make sense of current political developments."
Berlinerblau has long studied the relationship between these two communities. He co-authored the book Blacks and Jews: an Invitation to Dialogue with Terrence Johnson, Professor of African American Religious Studies at Harvard Divinity School.

Civil rights demonstrators pass by federal guards as they make their way from Selma to Montgomery in 1965, on the third leg of their famous march. AFP via Getty Images hide caption
Civil rights demonstrators pass by federal guards as they make their way from Selma to Montgomery in 1965, on the third leg of their famous march.
In speaking with NPR, Johnson defined the Grand Alliance as a group of elite African-American leaders working across racial religious lines to advocate for the masses in terms of voting rights and desegregation. And this sort of leadership went on to work with Jewish leaders with the founding of the NAACP in 1909 and the Urban League a year later."
"In some respects," Johnson continued, "those organizations represented the dream team of black and Jewish leaders, mostly men, unfortunately, but leaders nonetheless, who wanted to in many ways address the lingering problems of racial inequality and religious discrimination."
Johnson and Berlinerblau's book originated from a Georgetown University course they taught for years, engaging students in dialogue about the myriad ways that Black and Jewish Americans related to one another.
"It's an historic alliance because both groups have been demonized by what they can't control–a narrative of otherness," Johnson said. "And remember who was considered human in this country: Anglo-Americans. Jews were corrupted because of their blood and blacks were inferior because we didn't have a soul. And those fundamental issues are what we are haunted by now–what we hear with Black Lives Matter protests and related outcries around anti-Black racism and anti-Semitism."
And this relationship still looms large in the imagination of contemporary movement leaders. "There's no alliance more historic, nor more important, than the alliance between Black Americans and Jewish Americans," said Marc Morial, the president of the National Urban League in 2020.
A TROUBLED GRAND ALLIANCE: THEN & NOW
In a recent NY Times piece , Morial said the Grand Alliance is "being tested" by the Israel-Hamas war, with each group holding diverging views.
Recently, a group of more than 1,000 Black pastors issued a demand that the Biden Administration push Israel to curb its military campaign. In a pressure campaign, the Black pastors say the support of their parishioners, key to Biden's reelection , could be on the line. And with Jewish Americans and Black Americans providing two key constituencies for Biden's reelection bid, this could be a tough needle to thread.
Reverend Leah Daughtry leads the House of the Lord Churches, a network of churches throughout the U.S. She was also CEO of the 2008 and 2016 Democratic National Convention committees. She recently told NPR that "we as faith leaders have to be concerned about the moral toll of this war and what our authority is. And what our responsibility is in ensuring that all people are safe, are able to live their lives in freedom and security, and that all children are able to grow and to live a thriving life."
Going even further, the African Methodist Episcopal Church, a well-known Black institution, recently called for the U.S. to "immediately withdraw all funding and other support from Israel." It goes on to allege that "the United States is supporting this mass genocide."
The Israel-Hamas War clearly represents a pivotal moment — but Johnson and Berlinerblau say diverging interests and perspectives have tested the Grand Alliance from the very beginning.
"The Grand Alliance was more fraught on the ground than is commonly understood," Berlinerblau said. "And it was probably a lot more wobbly than we would generally assume."
For example, their book examines persistent accusations made by some African Americans against Jewish Americans for their alleged involvement in the transatlantic slave trade. They cite historian Seymour Drescher, a noted expert on slavery and anti-slavery movements. In his essay entitled "Jews and New Christians in the Atlantic Slave Trade," Drescher found that "at no point along the continuum of the slave trade were Jews numerous enough, rich enough and powerful enough to affect significantly the structure and flow of the slave trade or to diminish the suffering of its African victims."
Nonetheless, such claims continue to resonate and reverberate, canonized by Nation of Islam leader Louis Farrakhan in his 1991 book The Secret Relationship between Blacks and Jews .
"Indeed, the Nation of Islam's worldview has pervaded Blacks and Jews for decades," Johnson and Berlinerblau write.
In fact, distrust between Black Americans and Jewish Americans created a sizable rift just a few years after Rabbi Abraham Joshua Heschel and Reverend Dr. Martin Luther King Jr. marched together for racial equality and civil rights.
According to Terrence Johnson, the shockwaves of 1967 can be felt even today.
That's the year of the Six-Day War between Israel and a coalition of Arab States. Many Black leaders began embracing the Palestinian and Arab cause, especially with Israel expanding its ties to the Apartheid government of South Africa.
Subsequent conflicts included the purging of white and Jewish members from the Student Nonviolent Coordinating Committee after the 1967 Arab-Israeli War; a teacher strike in New York City and the Crown Heights Riots in Brooklyn, both pitt ing Black and Jewish residents against one another–as well as ongoing disputes over affirmative action.

Many scholars say the partnership between Georgia Senators Jon Ossoff and Raphael Warnock hearkens back to the Grand Alliance of the 1960s. Win McNamee/Getty Inages hide caption
Many scholars say the partnership between Georgia Senators Jon Ossoff and Raphael Warnock hearkens back to the Grand Alliance of the 1960s.
With ups and downs between the Black and Jewish communities over the years, and many misconceptions, Johnson and Berlinerblau say they wanted to emphasize discussion and mutual understanding in their teaching and writing.
They set out to co-write their book in part to update the 1995 text by Cornel West and Rabbi Michael Lerner called Jews and Blacks: A dialogue on Race, Religion, and Culture in America.
While assembling their own book, they both saw the rising support for Palestinian rights via the Black Lives Matter movement. They also witnessed a partnership hearkening back to the Grand Alliance — the 2020 victories of Georgia Senators Rafael Warnock and Jon Ossof which demonstrated a partnership between prominent Black and Jewish leaders.
Johnson and Berlinerblau write that this could be seen as "another turning point in the Black-Jewish civil rights coalition." But since they, along with other authors , argue that the Grand Alliance of the 1960s is romanticized and oversimplified, they instead call for new ways to seek mutual understanding and collaboration.
BRIDGING THE BLACK-JEWISH DIVIDE: ART & COLLABORATION
Many scholars and movement leaders find inspiration in the indelible artistic and cultural ties between the Black and Jewish communities.
"So one reason to hope that the relationship finds a new footing or moves forward in some dynamic way," Berlinerblau told NPR, "is the sheer awesome political, artistic, cultural intelligence of these two communities working in concert."
He cites such artistic examples as: Cannonball Adderley's jazz cover of "Fiddler on the Roof," Grace Paley's short story "Zagrowsky Tells," Anna Deavere Smith's performance piece "Fires in the Mirror," Spike Lee's BlacKkKlansman , and the Safdie brothers' film, Uncut Gems .
Johnson adds that a shared Old Testament notion of Zion appears frequently in hip hop music, epitomized by Lauryn Hill's song, "To Zion."
This famous Hebrew Bible story involving Moses leading the Israelites from bondage toward freedom shows the Harvard Divinity School professor a possible path forward for reunifying the Black and Jewish communities.
"Exodus and Zion keep recurring in hip hop, so there's something about the use of these stories that are so powerful and so beyond life that captures imagination and it becomes an entry point," Johnson told NPR.

The Selma-to-Montgomery March for voting rights in 1965 featured Black leaders such as Martin Luther King Jr., joined by allies including Rabbi Abraham Joshua Heschel. AFP via Getty Images hide caption
The Selma-to-Montgomery March for voting rights in 1965 featured Black leaders such as Martin Luther King Jr., joined by allies including Rabbi Abraham Joshua Heschel.
"I was thinking of Abraham Heschel, who described this idea in 1963 of the Exodus is ongoing. And he said it was easier for the children of Israelites to cross the Red Sea than for a Black or Negro to cross the line at a university in the U.S.," Johnson said. "And there's something about this story that allows us to kind of peek into history and then figure out what's missing and whose voices are not there, even though they're very visible...and my sense is that the narratives will in some ways revive a moment that's much bigger than what we can imagine."
Berlinerblau and Johnson say that cultural and legal forces such as redlining and gentrification created physical distance between the Black and Jewish communities that were once more proximate.
"It doesn't mean they loved one another all the time," Berlinerblau said. "But they had a very, very organic, almost daily relationship with one another. And what Terence and I are increasingly seeing is that proximity, that physical proximity between African-Americans and Jewish Americans is kind of missing."
Some organizations doing this work of reconnection include: Rekindle, the Black/Jewish Justice Alliance, the Black Jewish Entertainment Alliance, and the Black and Jewish Leaders of Tomorrow. In many cases, art continues to reemerge as the bridge.
"The (Jewish) Federation in Baltimore recently had a yearlong exhibition around trauma in black and Jewish communities and used art as a way to invite people in to have these conversations," Johnson added. "So I think there are a lot of things happening on the ground. The issue becomes how did that get translated into a kind of political vocabulary that we can actually see structural change?"
Besides organizations and politicians with shared intentions, Johnson and Berlinerblau argue that reimagining Black-Jewish relations could best be accomplished by those who identify as both Black and Jewish.
Certainly, we can think of prominent celebrities such as Drake, Rashida Jones, Daveed Diggs, and Tiffany Haddish. But that's just the tip of the iceberg. In their book, the authors mention famous converts such as Sammy Davis Jr. and Nell Carter.
"We were extremely intrigued by the position of Afro Jews, Jews of color in the United States, of which we believe there may be more than half a million, if not more than that, in the country," Berlinerblau said. "But perhaps one way forward is to let this community, which physically or theologically or spiritually embodies a lot from both communities, maybe to let them lead...and to tell us where we all might move forward together."
Leah Donnella, who is Black and Jewish, is senior editor of NPR's Code Switch. And in a recent conversation, she reflected on her own upbringing. "My parents were very intentional about talking about those identities as being intertwined and related–and they did that very much through the lens of justice," Donnella said. "Fighting for justice has always been a tradition for both Black communities and Jewish communities. That's a lot of how both of my parents understood their faiths and their identities."
Outside of her own home, Donnella witnessed a major contrast. "Black people and Jewish people were not in the same spaces. There was not a lot of that overlap," Donnella said. "So that feeling of this identity being very integrated and very cohesive was not the demographic reality in the outside world."

Autumn Rowe, a songwriter and Executive Committee Member of the Black Jewish Entertainment Alliance, bridges the two backgrounds the organization seeks to unite. Black Jewish Entertainment Alliance hide caption
Autumn Rowe, a songwriter and Executive Committee Member of the Black Jewish Entertainment Alliance, bridges the two backgrounds the organization seeks to unite.
While spending time in Jewish spaces, Donnella finds herself being asked to speak on behalf of Black people. And with inflamed passions on all sides since the October 7th attacks by Hamas, and the subsequent Israel-Hamas War, she says the divides aren't necessarily deepening; they're revealing what was already there.
"I think none of the reactions that different communities are having are that surprising to me," Donnella said. "But I think it's easy to feel surprised about some of the different reactions and takes if you are not interacting with a really diverse community of different people, both racially, demographically, and just on the political spectrum."
In terms of the legacy of the Grand Alliance, and the snapshots of Heschel and King, Donnella said it's not about connecting via racial or religious identity–but about shared beliefs, and how they're being pursued.
"For me, it comes back to that childhood thing of justice," Donnella said. "A lot of it is very central to the Jewish identity I was raised with, to be focused on the idea of Tikkun Olam, healing the world. And that's also really central to Black American identity."
But in terms of putting values into action, Donnella said the details are paramount. "It obviously gets tricky when you get really real about what justice means to you," she told NPR. "What does justice look like for everyone? And how do I help make that happen? And then you go from there–and then I think the connections happen organically, because people are after the same thing."
- Jewish communities
- music and activism
- Civil Rights Movement
- Black History

COMMENTS
500+ Words Essay on Martin Luter King. Martin Luther King Jr. was an African-American leader in the U.S. He lost his life while performing a peaceful protest for the betterment of blacks in America. His real name was Michael King Jr. He completed his studies and attained a Ph.D.
Martin Luther King, Jr. (born January 15, 1929, Atlanta, Georgia, U.S.—died April 4, 1968, Memphis, Tennessee) was a Baptist minister and social activist who led the civil rights movement in the United States from the mid-1950s until his death by assassination in 1968.
Stephen F. Somerstein/Getty Images. Martin Luther King Jr. was a social activist and Baptist minister who played a key role in the American civil rights movement from the mid-1950s until his ...
This year's Martin Luther King Jr. Day, on January 15, coincides with the late civil rights leader 's birthday. Had he lived, King would be turning 95 years old. Days after his 1968 ...
Martin Luther King Jr. Biographical . M artin Luther King, Jr., (January 15, 1929-April 4, 1968) was born Michael Luther King, Jr., but later had his name changed to Martin. His grandfather began the family's long tenure as pastors of the Ebenezer Baptist Church in Atlanta, serving from 1914 to 1931; his father has served from then until the present, and from 1960 until his death Martin ...
Martin Luther King, Jr., (born Jan. 15, 1929, Atlanta, Ga., U.S.—died April 4, 1968, Memphis, Tenn.), U.S. civil rights leader. The son and grandson of Baptist preachers, King became an adherent of nonviolence while in college. Ordained a Baptist minister himself in 1954, he became pastor of a church in Montgomery, Ala.; the following year he received a doctorate from Boston University.
Introduction. Martin Luther King, Jr., made history, but he was also transformed by his deep family roots in the African-American Baptist church, his formative experiences in his hometown of Atlanta, his theological studies, his varied models of religious and political leadership, and his extensive network of contacts in the peace and social ...
A hero is born. Dr. Martin Luther King, Jr., was born in Atlanta, Georgia, in 1929. At the time in that part of the country, segregation—or the separation of races in places like schools, buses, and restaurants—was the law. He experienced racial predjudice from the time he was very young, which inspired him to dedicate his life to achieving ...
Author: King, Martin Luther, Jr. (Crozer Theological Seminary) Date: November 29, 1949 to February 15, 1950? Location: Chester, Pa.? Genre: Essay Topic: Martin Luther King, Jr. - Education Details. This paper, written at the beginning of the second term of Davis's course Christian Theology for Today, indicates King's estrangement from the conservative Baptist theology he learned as a child.
Martin Luther King, Jr., Day was established as an annual observance in the United States in 1983. The King holiday campaign overcame forceful opposition, with critics citing FBI surveillance files suggesting that King was an adulterous radical influenced by communists. Although the release of these files during the 1970s under the Freedom of ...
The Institute cannot give permission to use or reproduce any of the writings, statements, or images of Martin Luther King, Jr. Please contact Intellectual Properties Management (IPM), the exclusive licensor of the Estate of Martin Luther King, Jr., Inc. at [email protected] or 404 526-8968. Screenshots are considered by the King Estate a ...
January 25, 1967: Letter from Dr. Martin Luther King, Jr. nominating Thich Nhat Hanh for the Nobel Peace Prize in 1967. April 4, 1967: Beyond Vietnam. Audio. April 9, 1967: The Three Dimensions of a Complete Life. Audio. April 14, 1967: The Other America. Video. August 27, 1967: Why Jesus Called a Man a Fool. Audio.
Martin Luther King Jr. (born Michael King Jr.; January 15, 1929 - April 4, 1968) was an American Christian minister, activist, and political philosopher who was one of the most prominent leaders in the civil rights movement from 1955 until his assassination in 1968. A black church leader and a son of early civil rights activist and minister Martin Luther King Sr., King advanced civil rights ...
Occupation: Civil Rights Leader Born: January 15, 1929 in Atlanta, GA Died: April 4, 1968 in Memphis, TN Best known for: Advancing the Civil Rights Movement and his "I Have a Dream" speech Biography: Martin Luther King, Jr. was a civil rights activist in the 1950s and 1960s. He led non-violent protests to fight for the rights of all people including African Americans.
7 minute read. Dr. Martin Luther King addresses some 2,000 people on the eve of his death—April 3, 1968—giving the speech "I've been to the mountaintop." Bettmann/Getty Images. T he words ...
Long Essay on Martin Luther King 500 Words in English. Long Essay on Martin Luther King is usually given to classes 7, 8, 9, and 10. Introduction. Martin Luther King Jr. in one of his letters from Birmingham prison said that through painful experience alone we can know that freedom is not something that is freely given.
Hook Examples for Essay about Martin Luther King Jr. A Beacon of Hope: In a turbulent era marked by racial strife and inequality, one man's voice resonated above the clamor, offering hope, inspiration, and the promise of a brighter future. Martin Luther King Jr., a name etched into the annals of history, stood as a symbol of unwavering dedication to civil rights and justice.
Martin Luther King, Jr. 1929-1968. American orator and essayist. The following entry provides an overview of King's career. King was the leader of the civil rights movement in the United States ...
The Papers of Martin Luther King, Jr. (Vols. 1-6) by Clayborne Carson, Ralph E. Luker, and Penny A. Russell, Eds. Call Number: E185.97.K5 A2 1992. Publication Date: 1992. More than two decades since his death, Martin Luther King, Jr.'s ideas - his call for racial equality, his faith in the ultimate triumph of justice, and his insistence on the ...
I Have a Dream: Essay Introduction. One of the finest explanations of American's dream is the powerful speech of Martin Luther King, Jr. He delivered the speech at the Lincoln Memorial on August 28, 1963, in Washington D.C. The speech is mainly centered on racial equality and stoppage of discrimination. We will write a custom essay on your topic.
We are providing students with essay samples on a long essay of 500 words and a short essay of 150 words on the topic on Martin Luther King Jr. Long Essay on Martin Luther King Jr Essay Essay 500 Words in English. Long Essay on Martin Luther King Jr Essay Essay is usually given to classes 7, 8, 9, and 10.
The "Stone of Hope" statue is seen at the Martin Luther King Jr. Memorial in Washington, D.C. (Mandel Ngan/AFP via Getty Images) About eight-in-ten American adults (81%) say civil rights leader Martin Luther King Jr. has had a positive impact on the United States, according to a Pew Research Center report that comes ahead of the 60th anniversary of the March on Washington for Jobs and Freedom.
This essay will explore the life and work of Martin Luther King Jr., examining his contributions to the civil rights movement and the lasting impact of his legacy. Through an analysis of his speeches, writings, and actions, this essay will argue that Martin Luther King Jr. was not only a champion of civil rights, but also a visionary leader ...
By 1968, Martin Luther King Jr. was flailing. King hadn't had a major victory in years, and his popularity had plummeted. As he neared death, almost 75% of Americans disapproved of him ...
In 1968, Martin Luther King Jr. was giving a speech in Memphis, Tennessee, called "I've been to the mountain top," in front of a huge crowd, when an escaped convict, named James Earl Ray shot him. The speech was for striking African-American garbage men. He died on April 4, 1968. The assassin was convicted and sentenced to only nine years in ...
His advocacy, leadership, and dedication to justice changed American society and continue to motivate future generations. Martin Luther King Jr. was an American Baptist minister and civil rights leader who became the most visible spokesperson and leader in the civil rights movement from 1955 until his assassination in 1968.
5 short answer questions. answer key. Thank you for choosing to inspire and empower your students! Your FREE worksheets are waiting… visit PrintableBazaar now! Summary of passage. Martin Luther King Jr. was born in Atlanta, Georgia on January 15, 1929 and grew up during a time of racial inequality.
He was reaching out to the people who did not experience the same pain, struggle, and heartbreak people of color experienced. Martin Luther King's words were powerful. Martin Luther King's way of responding to oppression was his route of peaceful resistance. King talked about the oppressed people and their ways of dealing with their oppression.
Martin Luther King Jr. was a revolutionary civil rights leader during the 1950s and 1960s. He protested and fought for the equality that African Americans did not have in the United States. Eloquent, powerful speeches were at the forefront of his leadership, and "I Have a Dream" models that perfectly.
In fact, distrust between Black Americans and Jewish Americans created a sizable rift just a few years after Rabbi Abraham Joshua Heschel and Reverend Dr. Martin Luther King Jr. marched together ...