
30 Globalization Pros and Cons
Definition: Globalization refers to the increasing global interconnectedness of nations. It it not only economic integration. It also refers to cultural , technological , social , and political integration (Dincer et al., 2018). A good catch-all definition comes from Hodos (2016), who writes: “Globalization is defined as the process of becoming globally connected.”

Globalization Pros and Cons
The advantages of globalization, 1. increased economic growth.

Globalization facilitates technology, knowledge, and goods transfer, which in turn boosts economic growth (Erixon, 2018).
Through globalization, countries can now purchase the newest technologies and import the most productive machinery from other countries.
This means every country now has access to the most productive machineries, making the whole world more productive. Productivity means more output, which means more economic growth.
2. Cultural exchange and diversity
Globalization facilitates cultural exchange and diversity by increasing interactions among people from different parts of the world through trade, travel, and communication.
This exposure leads to the sharing of ideas, traditions, languages, and values across borders, enriching the cultural landscape of participating societies.
Such interactions often lead to the fusion of cuisines, music, art, and fashion, creating new, hybrid forms of cultural expression.
3. Improvement in global communication

Globalization is both caused by and a catalyst for the expansion of global technology and telecommunications. For example, the internet helps facilitate global trade, and demand for a fast and reliable global internet has stimulated its technological development.
The resulting interconnectedness allows for real-time communication across different countries, breaking down geographical and temporal barriers. The result is a more integrated world where cultural and professional exchanges occur more seamlessly.
4. Greater access to foreign investment

Globalization leads to greater access to foreign investment. With broken-down financial barriers, businesses can now source overseas investors for funds. This helps push down the cost of investment and stimulate local business (Erixon, 2018).
It’s also good for investors. They can diversify their portfolios by investing in different countries, and developing countries can benefit from foreign capital to fund growth and development projects.
This influx of foreign investment can lead to economic growth, technological advancements, and increased employment opportunities in the recipient countries.
5. Access to new markets for businesses

200 years ago, everyday small businesspeople could generally only trade with nearby communities. They had to get goods to market via horse and cart and anything perishable had to be consumed fast. There were no refigerators!
Today, with global supply chains, refrigerators, and free trade agreements, even small businesspeople have access to global markets.
Companies can therefore expand their operations and customer base beyond their domestic markets, tapping into demand in different countries (Erixon, 2018).
6. Increased migration opportunities

Globalization has opened up global labor markets. Nowadays, it takes less than 24 hours to move anywhere across the world. No more 3-month boat rides! This has allowed highly-skilled professionals to cross the world and get jobs exactly where there is market demand.
This mobility benefits migrants through better opportunities, the companies by linking them up with the best possible employees, and also contributes to the cultural and economic dynamism of the host countries (Dumont, Rayp & Willemé, 2012).
7. Reduction in prices of goods and services

Globalization leads to a reduction in prices of goods and services by allowing countries to specialize in producing goods where they have a comparative advantage, leading to more efficient production and lower costs (Mir, Hassan & Qadri, 2014).
The removal of trade barriers and the increased competition in global markets drive down prices, making products more affordable for consumers (Erixon, 2018).
Additionally, the global supply chain means consumers have access to a wider variety of goods and services from different parts of the world.
8. Increased competition leading to innovation

Globalization leads to increased competition because you’re no longer just competing with Bob down the road. Businesses are now competing with other businesses from the other side of the world (Erixon, 2018).
While at first this competition sounds bad, it tends to have positive effects. For example, it spurs innovation as companies strive to maintain their competitive edge in a global market.
The exposure to different market needs and technological advancements across borders encourages businesses to innovate and improve their products and services.
This competition not only drives technological advancement but also leads to better quality and diverse options for consumers.
9. Opportunity for developing countries to develop faster

Developing countries need foreign investment and access to foreign markets in order to grow. Globalization provides this access (Mir, Hassan & Qadri, 2014).
This exposure to global markets and capital can accelerate economic growth, create jobs, and promote infrastructure development.
Furthermore, the exchange of knowledge and best practices with developed nations can enhance the skills and capacities of the workforce in developing countries, leading to sustainable development.
10. Spread of democratic values

Some argue that globalization has led to the spread of democratic values. Arjun Appadurai calls this the “ideoscape” of globalization.
The global spread of media and the internet allows for the rapid dissemination of democratic ideals and human rights concepts.
We saw this, for example, during the Arab Spring of 2011, where activist groups multiple countries in the Arab world collaborated via social media to demand democratic reforms.
11. Global talent pool for employment

Globalization leads to a global talent pool for employment as businesses and organizations have access to a wider range of skills and expertise from around the world (Dumont, Rayp & Willemé, 2012).
Enhanced mobility and interconnectedness allow employers to recruit talent from different countries, enabling them to meet specific skill requirements more effectively.
This global workforce diversifies the workplace, fosters innovation, and enhances competitiveness by bringing together diverse perspectives and experiences.
12. Enhanced opportunities for high-skilled workers

Globalization leads to enhanced opportunities for high-skilled workers as it opens up a vast array of international job opportunities in various sectors, including technology, finance, and healthcare (Dumont, Rayp & Willemé, 2012).
These workers can leverage their specialized skills in a broader market, often finding better employment prospects, higher salaries, and advanced career development options globally.
Moreover, the exchange of expertise and knowledge across borders contributes to professional growth and the advancement of specialized fields.
13. Enhanced global cooperation and peace

Globalization could also, in an optimistic scenario, lead to enhanced global cooperation and peace. This is based on the theory that increasing economic interdependence among nations encourages diplomatic relations and collaboration rather than war (Baldwin, 2008).
The shared interests in maintaining stable trade and investment environments promote peaceful interactions and reduce the likelihood of conflicts.
Furthermore, international institutions and agreements foster a platform for dialogue and conflict resolution, contributing to global stability and peace.
14. Widening networking opportunities

Globalization leads to widening networking opportunities as it connects people from different cultures and professional backgrounds through international business, education, and social media platforms.
These connections facilitate the exchange of ideas, collaboration on projects, and the formation of global communities with shared interests and goals.
This extensive networking can lead to new business opportunities, partnerships, and innovations, benefiting individuals and organizations alike (Dumont, Rayp & Willemé, 2012).
15. Access to more goods for consumers

Globalization leads to access to more goods for consumers by breaking down trade barriers and enabling the efficient flow of products across borders (Mir, Hassan & Qadri, 2014).
Amazon Canada doesn’t have the product? No problem, try Amazon UK instead!
This results in a wider variety of goods available in the market, often at lower prices due to increased competition and economies of scale in production.
Consumers benefit from the improved quality, variety, and affordability of products, enhancing their purchasing choices and overall quality of life.
Disadvantages of Globalization
1. widening of economic disparities.

While the above positives sound good, many like Naomi Klein argue that globalization can lead to the widening of economic disparities as it often benefits developed nations and those with competitive advantages, while less developed countries may struggle to keep up.
This can result in increased wealth for certain regions and sectors, while others may experience stagnation or decline in economic growth. The result is a growing gap between the rich and the poor, both within and between countries.
2. Cultural Homogenization (Loss of local cultures)

There is an argument that globalization can lead to the loss of local cultures and identities as global brands and Western media dominate, overshadowing local traditions, languages, and practices.
We call this ‘ cultural homogenization ‘.
The spread of a homogenized global culture can dilute the uniqueness of local cultures, leading to a decrease in cultural diversity. People may adopt global trends at the expense of traditional values and customs, leading to a loss of cultural heritage.
Others dispute this claim, arguing instead that globalization leads to a process called glocalization .
3. Exploitation of labor in developing countries

Globalization can lead to the exploitation of labor in developing countries (Sharma, 2014). Multinational companies may seek to minimize costs by relocating production to regions where labor is cheaper and regulations are less stringent (e.g. opening up factories in Mexico and China instead of midwestern USA).
This can result in poor working conditions, low wages, and a lack of labor rights, exploiting the workforce in these countries. The pursuit of profit by global corporations can overshadow the need for ethical labor practices, leading to exploitation.
4. Environmental degradation

Environmentalists are often concerned that globalization is exacerbating environmental degradation. Increased industrial activity and international transportation contribute to pollution and natural resource depletion (Mir, Hassan & Qadri, 2014).
The global demand for goods encourages mass production, often without adequate environmental safeguards, leading to habitat destruction, loss of biodiversity, and climate change.
The focus on economic growth and consumerism can overshadow the need for sustainable environmental practices, exacerbating global environmental challenges.
5. Increased risk of financial contagion

Globalization leads to an increased risk of financial contagion as economies become more interconnected, meaning that financial crises can quickly spread from one country to another (Mendoza & Quadrini, 2010; Mir, Hassan & Qadri, 2014).
This interdependence is due to global investment and the intertwined nature of banking and financial markets.
A financial problem in one country can lead to investor panic and a loss of confidence, triggering a domino effect that impacts economies worldwide.
6. Over-dependence on global markets
Globalization leads to concerns that countries are over-dependent on foreign markets for essential supplies.
This dependence can make economies vulnerable when supply chains break down. When a major global shock occurs, countries heavily reliant on that market for exports or investment can experience significant economic disruptions (Mendoza & Quadrini, 2010).
For example, most nations in the world are reliant on Taiwan for computer chips. If Taiwan were suddenly invaded by China, the rest of the world won’t be able to produce sufficient computers!
7. Threat to local businesses and industries

In a globalized marketplace, local businesses face intense competition from larger multinational corporations.
These multinationals often have greater resources, technology, and access to larger markets, which can overshadow local enterprises (Burlacu, Gutu & Matei, 2018).
This intense competition can lead to the closure of local businesses, loss of traditional industries, and a decrease in domestic job opportunities.
8. Erosion of national sovereignty

National sovereignty is threatened by a globalized world. Governments may be compelled to alter their policies and regulations to attract global investment and remain competitive in the international market, locking themselves into international trade agreements that require compromise and cooperation (Burlacu, Gutu & Matei, 2018).
This can result in countries losing control over their economic, social, and environmental policies, potentially prioritizing international interests over national priorities.
9. Downward pressure on wages

Globalization can lead to downward pressure on wages as businesses seek to reduce costs by outsourcing jobs to countries where labor is cheaper (Mir, Hassan & Qadri, 2014).
This competition for lower-cost labor markets can result in wage stagnation or decreases in higher-wage countries.
Additionally, the influx of workers willing to accept lower wages can suppress wage growth even in sectors not directly exposed to international competition.
10. Spread of Political Ideologies

While earlier I noted that globalization may have sped up the spread of democracy, the opposite may occur.
While democracy may have been promoted by globalization – especially in the 20th Century – the same could happen with anti-democratic ideologies . For example, recently we have seen the spread of authoritarianism and “illiberal democracy” across the world.
11. Brain drain in developing countries

Globalization leads to brain drain in developing countries as highly educated and skilled professionals migrate to developed countries in search of better job opportunities, salaries, and living conditions (Dumont, Rayp & Willemé, 2012).
This migration of talent results in a significant loss of skilled labor for the originating countries, impacting their development and economic growth.
The departure of these key individuals can also lead to a shortage of expertise necessary for local advancement and innovation.
12. Spread of diseases across borders
Globalization leads to the spread of diseases across borders as increased international travel and trade facilitate the rapid movement of people and goods around the world.
This mobility can enable pathogens to cross geographical boundaries more easily, leading to the faster spread of infectious diseases.
Outbreaks that might have been contained within a region in the past can now quickly escalate into global health emergencies.
13. Vulnerability to global economic fluctuations

A globalized nation may be vulnerable to global economic fluctuations as economies become increasingly interconnected through trade, investment, and financial markets (Mendoza & Quadrini, 2010).
This interconnectedness means that economic issues in one country or region can have ripple effects globally, impacting economies that might not be directly related to the initial problem.
As a result, even local economies can be significantly affected by economic downturns or crises occurring in distant markets.
14. Concentration of corporate power

Some argue that globalization leads to the concentration of corporate power as large multinational corporations expand their reach and influence across multiple countries (Cowling & Tomlinson, 2005).
These corporations can dominate markets, overshadowing smaller local businesses and potentially manipulating markets to their advantage.
This concentration of power can lead to reduced competition, influence over political and economic policies, and an unequal distribution of economic benefits.
15. Potential for global monopolies and oligopolies

Similarly, globalization could lead to the potential for global monopolies and oligopolies as dominant corporations expand their reach across international borders (Burlacu, Gutu & Matei, 2018).
These entities can gain excessive market control, limiting competition and potentially leading to higher prices and fewer choices for consumers.
The global scale of these companies makes it challenging for new entrants to compete, and their influence can extend to shaping market regulations and policies in their favor.
Baldwin, R. (2008). EU institutional reform: Evidence on globalization and international cooperation. American Economic Review, 98(2), 127-132.
Burlacu, S., Gutu, C., & Matei, F. O. (2018). Globalization–pros and cons. Calitatea , 19 (S1), 122-125.
Cowling, K., & Tomlinson, P. R. (2005). Globalisation and corporate power . Contributions to Political Economy , 24 (1), 33-54.
Dincer, H., Yüksel, S., & Hacioglu, Ü. (Eds.). (2018). Strategic Design and Innovative Thinking in Business Operations: The Role of Business Culture and Risk Management . Springer International Publishing.
Dumont, M., Rayp, G., & Willemé, P. (2012). The bargaining position of low-skilled and high-skilled workers in a globalising world . Labour Economics , 19 (3), 312-319.
Erixon, F. (2018). The economic benefits of globalization for business and consumers. European Centre for International Political Economy .
Hodos, T. (Ed.). (2016). The Routledge Handbook of Archaeology and Globalization. Taylor & Francis.
Mendoza, E. G., & Quadrini, V. (2010). Financial globalization, financial crises and contagion . Journal of monetary economics , 57 (1), 24-39.
Mir, U. R., Hassan, S. M., & Qadri, M. M. (2014). Understanding globalization and its future: An analysis. Pakistan Journal of Social Sciences , 34 (2), 607-624.
Sharma, N. K. (2013). Globalization and its impact on the third world economy. Crossing the Border: International Journal of Interdisciplinary Studies , 1 (1), 21-28.

Chris Drew (PhD)
Dr. Chris Drew is the founder of the Helpful Professor. He holds a PhD in education and has published over 20 articles in scholarly journals. He is the former editor of the Journal of Learning Development in Higher Education. [Image Descriptor: Photo of Chris]
- Chris Drew (PhD) https://helpfulprofessor.com/author/chris-drew-phd/ 5 Top Tips for Succeeding at University
- Chris Drew (PhD) https://helpfulprofessor.com/author/chris-drew-phd/ 50 Durable Goods Examples
- Chris Drew (PhD) https://helpfulprofessor.com/author/chris-drew-phd/ 100 Consumer Goods Examples
- Chris Drew (PhD) https://helpfulprofessor.com/author/chris-drew-phd/ 17 Adversity Examples (And How to Overcome Them)
Leave a Comment Cancel Reply
Your email address will not be published. Required fields are marked *
- Business Essentials
- Leadership & Management
- Credential of Leadership, Impact, and Management in Business (CLIMB)
- Entrepreneurship & Innovation
- *New* Digital Transformation
- Finance & Accounting
- Business in Society
- For Organizations
- Support Portal
- Media Coverage
- Founding Donors
- Leadership Team

- Harvard Business School →
- HBS Online →
- Business Insights →
Business Insights
Harvard Business School Online's Business Insights Blog provides the career insights you need to achieve your goals and gain confidence in your business skills.
- Career Development
- Communication
- Decision-Making
- Earning Your MBA
- Negotiation
- News & Events
- Productivity
- Staff Spotlight
- Student Profiles
- Work-Life Balance
- Alternative Investments
- Business Analytics
- Business Strategy
- Business and Climate Change
- Design Thinking and Innovation
- Digital Marketing Strategy
- Disruptive Strategy
- Economics for Managers
- Entrepreneurship Essentials
- Financial Accounting
- Global Business
- Launching Tech Ventures
- Leadership Principles
- Leadership, Ethics, and Corporate Accountability
- Leading with Finance
- Management Essentials
- Negotiation Mastery
- Organizational Leadership
- Power and Influence for Positive Impact
- Strategy Execution
- Sustainable Business Strategy
- Sustainable Investing
- Winning with Digital Platforms
6 Pros and Cons of Globalization in Business to Consider

- 01 Apr 2021
Throughout history, commerce and business have been limited by certain geographic constraints. In its earliest days, trade happened between neighboring tribes and city-states. As humans domesticated the horse and other animals, the distances they could travel to trade increased. These distances increased further with the development of seafaring capabilities.
Although humans have been using ships for centuries to transport goods, cargo, people, and ideas around the world, it wasn’t until the development of the airplane that the blueprint of a “globalized economy” was laid. This was for a simple reason: You can travel greater distances faster than ever before.
The development of the internet accelerated this process even more, making it easier to communicate and collaborate with others. Today, your international co-worker, business partner, customer, or friend is only a few taps or clicks away.
Globalization has had numerous effects—both positive and negative—on business and society at large. Here’s an overview of the pros and cons of globalization in business.
Access your free e-book today.
What Is Globalization?
Globalization is the increased flow of goods, services, capital, people, and ideas across international boundaries according to the online course Global Business , taught by Harvard Business School Professor Forest Reinhardt.
“We live in an age of globalization,” Reinhardt says in Global Business . “That is, national economies are even more tightly connected with one another than ever before.”
How Globalization Affects Daily Life
Globalization has had a significant impact on various aspects of daily life.
For example, it’s changed the way consumers shop for products and services. Today, 70 percent of Americans shop online. In 2022, there were 268 million digital buyers in the US and by 2025, this number is predicted to reach 285 million.
In addition, the globalized economy has opened up new job markets by making it more feasible to hire overseas workers. This has created a wide range of career opportunities for both job seekers and employers.
The emergence of remote work post-pandemic was also made possible by globalization. According to a survey from WFH Research , only seven percent of paid workdays in the US were remote in 2019. However, this number climbed to 29 percent by January 2024.
Check out the video below to learn more about globalization, and subscribe to our YouTube channel for more explainer content!
Advantages of Globalization
1. economic growth.
It’s widely believed that one of the benefits of globalization is greater economic growth for all parties. There are several reasons why this might be the case, including:
- Access to labor: Globalization gives all nations access to a wider labor pool. Developing nations with a shortage of knowledge workers might, for example, “import” labor to kickstart industry. Wealthier nations, on the other hand, might outsource low-skill work to developing nations with a lower cost of living to reduce the cost of goods sold and pass those savings on to the customer.
- Access to jobs: This point is directly related to labor. Through globalization, developing nations often gain access to jobs in the form of work that’s been outsourced by wealthier nations. While there are potential pitfalls to this (see “Disproportionate Growth” below), this work can significantly contribute to the local economy.
- Access to resources: One of the primary reasons nations trade is to gain access to resources they otherwise wouldn’t have. Without this flow of resources across borders, many modern luxuries would be impossible to manufacture or produce. Smartphones, for example, are dependent on rare earth metals found in limited areas around the world.
- The ability for nations to “specialize”: Global and regional cooperation allow nations to heavily lean into their economic strengths, knowing they can trade products for other resources. An example is a tropical nation that specializes in exporting a certain fruit. It’s been shown that when nations specialize in the production of goods or services in which they have an advantage, trade benefits both parties.

2. Increased Global Cooperation
For a globalized economy to exist, nations must be willing to put their differences aside and work together. Therefore, increased globalization has been linked to a reduction—though not an elimination—of conflict.
“Of course, as long as there have been nations, they've been connected with each other through the exchange of lethal force—through war and conquest—and this threat has never gone away,” Reinhardt says in Global Business . “The conventional wisdom has been that the increased intensity of these other flows—goods, services, capital, people, and so on—have reduced the probability that the world's nations will fall back into the catastrophe of war.”

3. Increased Cross-Border Investment
According to the course Global Business , globalization has led to an increase in cross-border investment. At the macroeconomic level, this international investment has been shown to enhance welfare on both sides of the equation.
The country that’s the source of the capital benefits because it can often earn a higher return abroad than domestically. The country that receives the inflow of capital benefits because that capital contributes to investment and, therefore, to productivity. Foreign investment also often comes with, or in the form of, technology, know-how, or access to distribution channels that can help the recipient nation.
Disadvantages of Globalization
1. increased competition.
When viewed as a whole, global free trade is beneficial to the entire system. Individual companies, organizations, and workers can be disadvantaged, however, by global competition. This is similar to how these parties might be disadvantaged by domestic competition: The pool has simply widened.
With this in mind, some firms, industries, and citizens may elect governments to pursue protectionist policies designed to buffer domestic firms or workers from foreign competition. Protectionism often takes the form of tariffs, quotas, or non-tariff barriers, such as quality or sanitation requirements that make it more difficult for a competing nation or business to justify doing business in the country. These efforts can often be detrimental to the overall economic performance of both parties.
“Although we live in an age of globalization, we also seem to be living in an age of anti-globalization,” Reinhardt says in Global Business . “Dissatisfaction with the results of freer trade, concern about foreign investment, and polarized views about immigration all seem to be playing important roles in rich-country politics in the United States and Europe. The threats in Western democracy to the post-war globalist consensus have never been stronger.”
2. Disproportionate Growth
Another issue of globalization is that it can introduce disproportionate growth both between and within nations. These effects must be carefully managed economically and morally.
Within countries, globalization often has the effect of increasing immigration. Macroeconomically, immigration increases gross domestic product (GDP), which can be an economic boon to the recipient nation. Immigration may, however, reduce GDP per capita in the short run if immigrants’ income is lower than the average income of those already living in the country.
Additionally, as with competition, immigration can benefit the country as a whole while imposing costs on people who may want their government to restrict immigration to protect them from those costs. These sentiments are often tied to and motivated—at least in part—by racism and xenophobia.
“Meanwhile, outside the rich world, hundreds of millions of people remain mired in poverty,” Reinhardt says in Global Business. “We don't seem to be able to agree about whether this is because of too much globalization or not enough.”
3. Environmental Concerns
Increased globalization has been linked to various environmental challenges, many of which are serious, including:
- Deforestation and loss of biodiversity caused by economic specialization and infrastructure development
- Greenhouse gas emissions and other forms of pollution caused by increased transportation of goods
- The introduction of potentially invasive species into new environments
While such issues are governed by existing or proposed laws and regulations, businesses have made climate change concerns and sustainability a priority by, for example, embracing the tenets of the triple bottom line and the idea of corporate social responsibility .

Managing the Risks of Globalization
The world is never going to abandon globalization. While it’s true that individual countries and regions put policies and practices in place that limit globalization, such as tariffs, it’s here to stay. The good news is that businesses and professionals willing to prepare for globalization’s challenges by developing strong social impact skills have the potential to benefit immensely.
Whether you’re a business owner, member of executive leadership, or an employee, understanding the impacts of globalization and how to identify its opportunities and risks can help you become more effective in your role and drive value for your organization.
Taking a course like Global Business is one path toward developing international business skills and gaining an understanding of the macroeconomic, political , and social conditions that continue to impact globalization.
Are you interested in breaking into a global market? Sharpen your knowledge of the international business world with Global Business , one of our online business in society courses . If you aren't sure which course is the right fit, download our free course flowchart .
This post was updated on February 26, 2024. It was originally published on April 15, 2021.

About the Author
An economist explains the pros and cons of globalization

Piling up: Global trade has increased, but has it been a positive or negative force? Image: REUTERS/Tyrone Siu
.chakra .wef-1c7l3mo{-webkit-transition:all 0.15s ease-out;transition:all 0.15s ease-out;cursor:pointer;-webkit-text-decoration:none;text-decoration:none;outline:none;color:inherit;}.chakra .wef-1c7l3mo:hover,.chakra .wef-1c7l3mo[data-hover]{-webkit-text-decoration:underline;text-decoration:underline;}.chakra .wef-1c7l3mo:focus,.chakra .wef-1c7l3mo[data-focus]{box-shadow:0 0 0 3px rgba(168,203,251,0.5);} Gita Gopinath
Ceri parker.

.chakra .wef-9dduvl{margin-top:16px;margin-bottom:16px;line-height:1.388;font-size:1.25rem;}@media screen and (min-width:56.5rem){.chakra .wef-9dduvl{font-size:1.125rem;}} Explore and monitor how .chakra .wef-15eoq1r{margin-top:16px;margin-bottom:16px;line-height:1.388;font-size:1.25rem;color:#F7DB5E;}@media screen and (min-width:56.5rem){.chakra .wef-15eoq1r{font-size:1.125rem;}} Global Governance is affecting economies, industries and global issues

.chakra .wef-1nk5u5d{margin-top:16px;margin-bottom:16px;line-height:1.388;color:#2846F8;font-size:1.25rem;}@media screen and (min-width:56.5rem){.chakra .wef-1nk5u5d{font-size:1.125rem;}} Get involved with our crowdsourced digital platform to deliver impact at scale
Stay up to date:, global governance.
Every industrial revolution has driven a wave of globalization. The first wave was driven by innovations such as the steam engine and the industrial weaving machine; the second by the assembly line, the car and the plane; and the third by the digital revolution.

As we enter the fourth wave of globalization, driven by the digital revolution, there is renewed debate over whether it is a beneficial force: powering economic growth, and allowing the spread of ideas to improve people’s lives; or whether it erodes communities, and widens the gap between the elites and the rest of the world.

Globalization results in increased trade and lower prices. It heightens competition within domestic product, capital, and labour markets, as well as among countries adopting different trade and investment strategies.
But how do these impacts net out? What are the positive and negative effects of globalization? The below is an edited transcript of a conversation with Gita Gopinath, Chief Economist of the International Monetary Fund (IMF).
Overall, what are the advantages of globalization?
The advantages of globalization are actually much like the advantages of technological improvement. They have very similar effects: they raise output in countries, raise productivity, create more jobs, raise wages, and lower prices of products in the world economy.
What might be the advantages of globalization that someone would feel in their day-to-day life?
I think something that's not sufficiently appreciated about, for instance, international trade is that it reduces the prices of goods that they consume. So if you look at day-to-day things that you purchase, in terms of washing machines, or cars, or even clothing, because of international trade we've had a decline in prices of these goods, so they have become far more affordable for a lot of people in the world.
How have the benefits played out in advanced economies versus poorer ones over the last three decades?
Both advanced economies and developing economies have benefited overall in terms of having higher productivity, more job creation, and higher wages. As we've always known, and this is true again with technology, there are always some winners and losers. So there are communities and there are workers who lose out when there is more trade integration. That is what we're seeing right now in terms of discontent with international trade.
Who have been the biggest losers?
The biggest losers from international trade are always those whose skills have a cheaper competitor in a different market. So, in the case of the US, it's been those who work in the manufacturing sector because jobs in the manufacturing sector have been outsourced to countries where labour is far cheaper.
On the other hand, in developing countries, more capital-intensive goods get imported more cheaply from the outside. So if you're a manufacturer of a capital-intensive good in a developing country you tend to lose because of that competition.
This is how it is with international trade: production goes to wherever it is most efficient to produce. So, when people in any country are exposed to this kind of competition, some win and some lose.

Is it possible as an economist to come up with a verdict? Has this wave of globalized trade been a net positive or a net negative?
If you say, I'm going to look at it from a measure of overall effect on a country's income, on its purchasing power, on the prices that its people pay, overall I think the evidence that we have all points to it being a net positive.
Now, if you frame the question as, has international trade been good for the manufacturing worker in the US? Then the answer to that would be “not fully”; it's been very costly in terms of jobs and wages for them.

How optimistic are you that this next wave of globalization offers a better future?
I would make a couple of points. First, the previous waves of globalization have been quite successful in lifting a large number of people out of poverty and so we should appreciate that.
The second thing is that any form of globalization will generate winners and losers. So even if you have the perfect, most optimal international trade agreements, there will always be those who lose out because of competition, in the exact same way that people lose out whenever there's a new technology being developed.
And so if we want to make sure that the next wave of globalization is even more successful, it has to be complemented with good, sound domestic policies that help those who are getting left out.
How optimistic are you that the trade war between the US and China will be swiftly resolved?
It's absolutely essential that it be resolved, and it gets resolved in a way that's long lasting. The world economy has lived with the uncertainty about trade tensions for a while now and if there is any solution and there is a sense that the solution is only transitory and something can again get triggered in the future, I think that's very costly.
I'd say I'm mildly optimistic because I think leaders in the world are recognizing that these trade tensions are having a negative effect on their economies and so it would make sense to sit down and resolve it.
Don't miss any update on this topic
Create a free account and access your personalized content collection with our latest publications and analyses.
License and Republishing
World Economic Forum articles may be republished in accordance with the Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial-NoDerivatives 4.0 International Public License, and in accordance with our Terms of Use.
The views expressed in this article are those of the author alone and not the World Economic Forum.
Related topics:
The agenda .chakra .wef-n7bacu{margin-top:16px;margin-bottom:16px;line-height:1.388;font-weight:400;} weekly.
A weekly update of the most important issues driving the global agenda
.chakra .wef-1dtnjt5{display:-webkit-box;display:-webkit-flex;display:-ms-flexbox;display:flex;-webkit-align-items:center;-webkit-box-align:center;-ms-flex-align:center;align-items:center;-webkit-flex-wrap:wrap;-ms-flex-wrap:wrap;flex-wrap:wrap;} More on Global Governance .chakra .wef-17xejub{-webkit-flex:1;-ms-flex:1;flex:1;justify-self:stretch;-webkit-align-self:stretch;-ms-flex-item-align:stretch;align-self:stretch;} .chakra .wef-nr1rr4{display:-webkit-inline-box;display:-webkit-inline-flex;display:-ms-inline-flexbox;display:inline-flex;white-space:normal;vertical-align:middle;text-transform:uppercase;font-size:0.75rem;border-radius:0.25rem;font-weight:700;-webkit-align-items:center;-webkit-box-align:center;-ms-flex-align:center;align-items:center;line-height:1.2;-webkit-letter-spacing:1.25px;-moz-letter-spacing:1.25px;-ms-letter-spacing:1.25px;letter-spacing:1.25px;background:none;padding:0px;color:#B3B3B3;-webkit-box-decoration-break:clone;box-decoration-break:clone;-webkit-box-decoration-break:clone;}@media screen and (min-width:37.5rem){.chakra .wef-nr1rr4{font-size:0.875rem;}}@media screen and (min-width:56.5rem){.chakra .wef-nr1rr4{font-size:1rem;}} See all

This is why the number of refugees could double in the next decade, according to the head of UNHCR
Liam Coleman
March 7, 2024

AI: Will governance catch up with the tech in 2024?
David Elliott
March 1, 2024

The World Economic Forum: A Swiss success story
Selina Hänni and Micol Lucchi
January 17, 2024

Workers' rights are vital to revitalizing democracy. Here's why
Luc Triangle
January 15, 2024

How to thrive when uncertainty becomes the new norm for governance
January 11, 2024

How to build business resilience in an era of risk turbulence
Carolina Klint
January 10, 2024

19 Advantages and Disadvantages of Globalization
Globalization refers to several different concepts all rolled into one package. It may refer to the ease in which businesses conduct operations in different countries other than their own. Some look at this subject as a way to create a world without national borders. There are concepts of communication, information access, and technology development to consider when looking at this subject matter too.
Even though the geographic size of our planet remains consistent, how we interact with each other is changing by the minute. Despite more than 200 countries independently working for their best interests, we all come together in ways to make the world a better place. If you have access to a computer or mobile device with data or an ISP, then you can communicate with anyone else in the world with the same setup.
We are closer than ever before. That closeness also means that groups of people are further apart than ever before. Neighborhoods form around common interests or political perspectives more than our common humanity. Travel restrictions dictate where some people can go, and others cannot.
As the advantages and disadvantages of globalization show, even though progress occurs, we are also taking steps backward.
List of the Advantages of Globalization
1. Globalization allows us to pool all our resources together. One of the best examples of globalization within our lifetime is the construction of the International Space Station. The cost to construct the ISS was $150 billion. Compared to the Mir station at $4.2 billion, the price tag is astronomical. When the first component for the ISS was launched in 1998, five different programs came together to join in ownership, cost, and operations. The United States, Russia, Canada, Europe, and Japan are all involved in the financing and continued operations of the program.
When nations work together to fund common goals, then more money becomes useful for needs other than national defense. Imagine what we could do if the $1 trillion spent annually on warfare and defense could be used for the global greater good?
2. Globalization would also reduce labor exploitation issues. When borders become less restrictive around the world, people tend to move to locations where their best opportunities exist. Under the current structure of our planet, impoverished nations with a lower standard of living offer wages that the developed world would find abysmal. Someone in Bangladesh making clothes for 10 hours per day earns less in a month than some workers in the U.S. earn before lunch.
By focusing on globalization, we could reduce child labor issues. Human trafficking concerns would be limited because of more border freedom. People could live, work, or go where they please with fewer restrictions, making it easier to chase their dreams.
3. Globalization reduces the prospects of tyranny. As the world moved slowly toward globalization in the 20th century, the nations realized that having a concentrated power with one administration reduced the likelihood of tyranny in pockets around the globe. Although there have still be issues with government oppression, including the chemical attacks on populace centers in Syria, the number of incidents is slowly declining.
When we’re able to move toward a global-centric society instead of a nation-centric one, these issues will continue to decline over time.
4. Globalization improves communication access. The Trump Administration announced new travel restrictions in September 2017 to focus on 8 countries: North Korea, Chad, Libya, Iran, Syria, Somalia, Yemen, and Venezuela. “Making America Safe is my number one priority,” President Trump tweeted when announcing this decision. “We will not admit those into our country we cannot safely vet.”
Under a globalization perspective, people would have their risks associated by a central perspective instead. It would be like the United Nations vetting immigrants instead of the individual country. By reducing border restrictions, we improve communication access because we’re no longer restricting the movements and actions of people on a per-nation basis.
5. Globalization would remove tax havens for wealthy individuals and businesses. Tax havens are defined as either a country or independent area where taxation levies are at low rates. They offer foreign businesses and individuals an opportunity to keep their profits in local institutions with little or no liability. These havens share little, if any, information about these finances with other tax authorities.
Globalization reduces this issue because it eliminates the administrative structures in place which allow the wealthy to hide their funds from being taxed. That would mean these businesses and people would be treated as an average citizen is today. Greater transparency here would lead to better funding of social programs, which could reduce poverty and food insecurity over time.
6. Globalization would help the developing world progress faster. Most of the world today is not developed. Outside of about 40 countries which have gone through their own version of the Industrial Revolution, the rest of the population still struggles as a primarily agricultural society. By reducing border restrictions, creating common payment formats, and opening product access by reducing export barriers, more people could improve their way of life. Higher incomes often lead to lower maternal and infant mortality rates too, which means we’d be saving lives with this effort.
7. Globalization would reduce currency manipulation problems. There are three primary currencies traded in the world today: the Dollar, the Euro, and the Pound Sterling. When a nation offers access to a weaker currency, those with stronger currencies buy and sell more often with them. It offers better value than spending at home. Globalization would reduce the efforts made to build weakness or strength into these currencies to influence local markets. We’d be working toward a society where economic growth occurs on a global scale instead of in only local economies.
8. Globalization encourages free trade. Borders create restrictions to the free flow of goods and services. One example of this issue is a duty and taxes paid on imported goods originating in the U.S. when purchased in Canada. These taxes apply on luxury items and other items of high value. The HST in Canada may be collected at a rate of 13%. Canadians use shipping service receptacles at locations like Point Roberts, WA to get around this tax simply because the laws haven’t globalized like our access to goods.
There are currently over 1,500 different restrictions in place with the global import/export market right now.
9. Globalization could create more employment opportunities. With fewer barriers to the import/export market, the cost of producing goods or offering services would decline without affecting the profit margins of companies. Consumers would benefit from the lower prices, consume more, and create additional job opportunities around the world. By creating an environment where free trade encouragement readily exists, more innovation, creativity, and engagement would occur at every level of society.
List of the Disadvantages of Globalization
1. Globalization may encourage more offshoring instead of less. With fewer restrictions in place at the national level, some businesses may use offshoring to their advantage. Even if they kept jobs local, the threat of sending jobs to a different, cheaper region overseas could be used to justify lower wages at home. The end result of an effort to remove borders would be an increase in wages in the developing world, but a decrease in developed countries. Many households could see their standard of living go down if consumable price decreases don’t occur simultaneously.
2. Globalization benefits the wealthy more than the poor. Value-added taxes above 25% exist in some nations. Tariffs above 70% exist for some products. Unless borders are completely removed, the advantages of globalization are challenging to achieve. The people who have the power to dictate policy would reap the most significant rewards. Those with money to invest would see their bank accounts continue to rise. At the same time, households living paycheck-to-paycheck would struggle to access what they require, suppressing their ability to pursue a better job.
3. Globalization would encourage disease transfer. The outcome of the Columbian Exchange was profound at the time. Over 90% of some population centers died because of their exposure to smallpox, chickenpox, and other diseases that the Europeans were somewhat immune to at the time. The Europeans brought back syphilis and other diseases as well. If global travel restricts eased, then issues with malaria and tropical disease could spread to portions of the world where exposures are minimal. Tuberculosis, certain influenza strains, and other communicable disease could produce outbreaks at epidemic levels.
4. Globalization could reduce social safety net programs. Most nations today offer those in extreme poverty access to safety net programs for basic supplies. Even in the United States, programs like WIC and SNAP offer food and care access to those who cannot afford it on their own for whatever reason. When we reduce or eliminate borders, there would be a likely shift in social programs to benefit those earning less than $2 per day while ignoring the needs of those at home. Households living in poverty in the U.S. or United Kingdom fit into a different definition when compared to global poverty.
5. Globalization would create a new system of politics. We’ve already received a sneak peek of what a global society would be like from a political perspective. The individuals and organizations who spend the most to lobby politicians would receive the best chance of having their needs met first. We’ve seen billions spent in U.S. elections lately to influence legislation and policy to become favorable toward specific outcomes. This issue would translate to a global economy, where only the richest and most influential would influence laws which would impact everyone.
6. Globalization would not prevent resource consumption. The goal of globalization is to equalize patterns of consumption for populations around the world. Even though there would be movement toward doing so, there is no getting around the fact that the wealthiest nations will still consume the most resources. The 20 richest countries in the world today consume almost 90% of the planet’s resources each year. The United States constitutes 5% of the global population right now, but it consumes 24% of the world’s energy as a country.
When you look at the per capita consumption rates of energy globally, one American consumes as much energy as 31 people in India. If you go to a developing nation, it takes 370 Ethiopians to use the same amount of energy that a single U.S. citizen uses to meet their needs.
7. Globalization would make it easier for people to cheat. The statistics of consumption (especially food) show us already that those who are in power take the majority of resources away from the general population. Americans eat almost 200 billion more calories per day as a nation than they require, which means 80 million people are hungry needlessly because of these consumption habits. About 200,000 tons of edible food is disposed of daily in the United States. By the age of 75, the average person in the U.S. creates 52 tons of garbage.
Globalization would likely centralize distribution of necessary resources. With only a few controlling access to the many, the chance to negatively impact populations on a large scale become greater when borders are reduced.
8. Globalization doesn’t fix a lack of skills. The future of employment involves programming, robotics, and artificial intelligence. Workers who adapt to automation with their skillset are the most likely to find employment in the coming generations. Jobs which require repetitive functions will be the first to go away, which are the employment opportunities often found in the developing world. With no meaningful skills to a globalized economy, there could be a higher unemployment rate if border restrictions reduce because only those in the developed world would be trained for the new economy.
Unless new vocational development opportunities implement with the globalization structures, the boundaries between the developed and developing world will likely continue to exist.
9. Globalization changes how humans would identify themselves. Humans are global citizens in some ways already. We all share the same planet, after all, so we are united with that common ground. If we lose borders, however, we also lose a piece of our culture, ethnicity, or family heritage. People identify themselves based on their history, so being Irish in a global world would have less impact than it does today. We already seen how this works when Texas came into the U.S. after being an independent nation. Some Texans label themselves as such first, but many see themselves as an American before being a Texan.
10. Globalization would negatively impact the environment. We’ve already seen what free trade does to the environment. Greenhouse gas emissions rose in 2018 despite efforts to curtail them. Micro-plastics invaded our oceans, creating negative impacts on marine life. The waters of our planet are slowly acidifying, creating economic and health impacts every day. Over 200,000 Americans die each year because of pollution exposure. If caps are taken off of what is not permitted through globalization, then this issue will continue growing worse.
The advantages and disadvantages of globalization show us that a world free to move and communicate offers numerous opportunities to pursue. It also shows us a planet where fewer opportunities may exist for workers and families who are employed in low-skill positions. We have many challenges to face in the coming years as the world continues to become a smaller place. That’s why we must continually look at these issues to ensure everyone has a fair chance to find success.
- Skip to primary navigation
- Skip to main content
- Skip to primary sidebar
- Skip to footer

The Impact Investor | ESG Investing Blog
Investing for financial return is only part of the equation.
18 Important Pros and Cons of Globalization
Updated on October 10, 2023
Our posts may contain links from our affiliate partners. This supports helps support the site as we donate 10% of all profits to sustainability organizations that align with our values. However, this does not influence our opinions or ratings. Please read our Terms and Conditions for more information.
Globalization refers to the open exchange of goods, services, information, and culture between different countries. While nations have been engaging in trade agreements for centuries, the Industrial Revolution ushered in an unprecedented shift toward a global economy.
Mankind’s rapid technological advances have since resulted in global partnerships on a previously unimaginable scale. As international markets continue to expand, it’s important to understand the benefits of globalization, as well as the unique challenges it presents.
Let’s take a closer look at what you need to know to survive in an increasingly global marketplace.
Table of Contents
Examples of Globalization in Action
The benefits of globalization, 1. access to a wider customer base, 2. economies of scale, 3. cost savings through outsourcing, 4. increased capital flow and risk sharing, 5. encourages global competition, 6. access to a global workforce, 7. information sharing, 8. cultural sharing, 9. encourages international cooperation, the challenges of globalization, 10. worker exploitation, 11. effects of outsourcing on the local economy, 12. expanding globally can be expensive, 13. compliance challenges, 14. environmental impact, 15. monopolization of foreign markets, 16. international dependence, 17. the drawbacks of sanctions and tariffs, 18. loss of cultural identity.

The odds are that you’re probably sitting within a few feet of a product that was made in another country. From cell phones and computers to clothing and consumer staples, most of us use products every day that are manufactured in foreign markets .
A thorough inventory of all the items in the average home or business would likely reveal an astounding number of products from all over the world. On the economic front, globalization is all about the expansion of fair trade across national borders.
But the benefits of globalization don’t begin and end with economic growth. As the world becomes more interconnected, more people are enjoying easier access to the cultures of other countries.
These days, most Americans don’t have to look far for an Indian restaurant, just as a trip to KFC has become a quirky Christmas tradition in Japan. People all over the world use Chinese apps like TikTok or power products with semiconductors manufactured in Taiwan.
Phones now allow us to speak to someone on the other side of the planet or to learn new languages on free apps like Duolingo. The benefits of globalization can also be seen through international organizations such as the United Nations , the World Trade Organization (WTO), and the World Bank.
Many businesses are becoming multinational corporations with various headquarters in different countries. There’s no argument that global expansion is playing an increasingly fundamental role in national economies and cultures.
Many business leaders find that understanding these ever-evolving changes is a vital part of forming a thoughtful and responsive strategy for staying relevant in the modern world.
Much like every other major movement in history, globalization comes with its own unique set of pros and cons. Before we get into the potential drawbacks and challenges of globalization, let’s take a moment to focus on some of the benefits its producing on a global scale.
From a business standpoint, one of the most obvious benefits of globalization is access to customers all over the world. Long gone are the days when businesses were limited to selling goods or services to people from their own local or national geographic areas.
Whether through eCommerce or multinational corporations, sellers now have a 1 in 8 billion chance of developing a product that someone in the world is interested in buying. Customers can also benefit from the arrangement by enjoying a wider range of product offerings.
A global business also enjoys the opportunity to take advantage of specific market niches. Even if a product doesn’t take off in one country, it might prove to be a huge success in another.
See Related: Best Emerging Markets ESG Funds
Global businesses often enjoy the economies of scale that come with a larger customer base. Simply put, economies of scale are factors that can allow a business to grow more efficiently.
The more customers a business has, the more products it’s like to manufacture at a time. As production numbers increase, manufacturing costs often decrease.
For example; you know how you can save money at stores like Costco by buying in bulk, right? It turns out businesses enjoy similar savings through bulk manufacturing.
In the end, this can be a win-win situation for everyone. When a company is able to cut its own costs, it can pass these economic benefits to customers in the form of lower prices.

Admittedly, outsourcing can be a double-edged sword, but it does have its upsides. The ability to produce products overseas can often save companies a great deal of money.
By outsourcing production to developing nations, the company is able to cut costs and pass savings along to customers. This can result in lower prices that allow people who live in developing markets to enjoy products that contribute to a higher standard of living.
Outsourcing also brings jobs to developing economies , which helps narrow the international income gap. These benefits also often translate to developed countries by lowering the cost of living, as well as inflation rates. According to a study by Grand View Research, the global outsourcing market could be worth over 405 billion by 2027.
See Related: How to Save Money When You Are Broke
Joining the global marketplace has led to increased capital flow for many developing nations. This has been particularly evident in developing countries that have only recently joined the global marketplace.
“China and India benefited enormously, leading to the largest reductions in poverty the world has ever seen,” says Project Syndicate. As the IMF puts it; “Capital flows are a boon to the region in a variety of ways. They can serve as a source of financing for countries and contribute to job creation for a fast-growing population.”
But in addition to the economic benefits of globalization in developing countries, increased cross-border capital flow can increase international risk sharing. This can help lead to the stabilization of international exchange rates.
Back in the old days, many people’s options for buying certain products were fairly slim. Imagine, for instance, that you lived in a village where only one merchant sold shoes.
Unless you were a really great DIY cobbler, you probably wouldn’t have been in a position to complain about the merchant’s prices or workmanship. But if a new merchant moved into town that sold better shoes at a cheaper price, things would drastically change overnight.
Today, the global markets offer a huge range of choices for every product under the sun. Global companies now operate with the understanding that unique product benefits are essential for gaining a competitive advantage.

While the COVID-19 pandemic was a health disaster of epic proportions, it also had far-reaching effects on the workforce. Data researchers at Ladders say that not only is remote work here to stay but that “25% of all professional jobs in North America will be remote” by 2023. In fact, 100% of the team at The Impact Investor are remote workers, and that’s not going to change!
Ladders CEO Marc Cenedella points to this surge in remote work opportunities as the biggest American societal shift since World War II. As a result, global employers are discovering access to a much wider talent pool.
Many positions are no longer bound by geographic location, leaving employers free to build a globally diversified workforce. Consequently, many employees now enjoy remote opportunities in multiple countries or states.
The rise of remote work may also help address another recent issue among Western economies. Despite decades of increased labor mobility in the early 20th century, Americans have become increasingly resistant to relocation since the 1980s.
See Related: Best Paying Jobs in Energy

The ability to share ideas, innovations, and advancements at lightning speed is arguably one of the most notable benefits of globalization. Throughout most of history, there was no guarantee that news of a major medical breakthrough or technological advance would ever reach all the countries in the world.
Many countries that did get word of new discoveries had to wait years, or even decades, depending on their proximity. Now, scientists and medical researchers can share entire studies with foreign countries all over the world by simply uploading them to the internet.
See Related: Best Globalization Jobs & Careers

Global trade has also led to the ability to enjoy the benefits of different cultures, no matter where you happen to live. It’s now common in many countries to ask what someone would like to eat based on the country the food originated in.
From Italian and Mexican food to Thai and Chinese cuisine, much of the world now enjoys a wealth of different options. The same can be said for celebrations and holidays.
Día de Los Muertos, Kwanzaa, and Hanukkah are often celebrated right alongside European traditions such as Christmas and Easter. International expansion has created an opportunity to learn more about the cultures and philosophies of other countries firsthand.
And how are we all sharing these examples of culture? We’re all speaking English, and with that language, comes centuries worth of culture, history and experiences.

One of the other potential benefits of globalization is simply that no one wants to go to war with a strong trade partner. “Countries cooperate if they perceive it to be in their best interests, both economically and politically,” explains the IMF.
As the world becomes more interdependent, nations are naturally beginning to depend on other countries as both import and export partners. The world saw the other side of this coin in early 2022 with the Russian invasion of Ukraine.
Given that Ukraine was not a member of NATO, many sympathetic countries were hesitant to send military troops to join the armed conflict. Instead, they were able to lend support by imposing harsh trade bans and sanctions on Russia without risking more lives, as well as sending humanitarian and military aid.
Consequently, Ukraine currently enjoys greater international relations, even with nations it historically has beef with (e.g. Poland). Conversely, Russia is seeing itself further isolated on the global stage, even finding it difficult to garner support from its regular allies in the BRICS nations.
Unfortunately, not all globalization benefits come without obstacles. International expansion can be difficult for global businesses at best and harmful for developing countries at worst.
Let’s take a closer look at some of the most common challenges of globalization. Simple awareness of the risks of moving into new markets can go a long way toward avoiding common mistakes.

One of the most common challenges of globalization that businesses face is ensuring that outsourcing production doesn’t come at the cost of workers’ rights. One of the reasons that overseas production can be so cheap is that some developing countries have yet to create legislation to protect employees.
The Bureau of International Labor Affairs (ILAB) maintains a list of products that are commonly produced using child or forced labor. Many American brands have fallen into the trap of outsourcing manufacturing to sweatshops and other unethical companies in foreign markets.
It’s essential for businesses that plan to outsource to a developing country to remain up to date on ever-changing labor laws and working conditions. Fashion Revolution has several great resources for retailers who are considering hiring global employees.
See Related: Best Socially Responsible Investing Jobs: What is the Best Career?
Another common global expansion obstacle is that outsourcing labor may cost local workers their jobs. A study from the Economic Policy Institute found that outsourcing labor-intensive jobs contributed to the widening of the wealth gap in industrialized countries like the United States.
While non-college-educated workers are now having a harder time finding work, college-educated professionals are finding their skills even more in demand. The increase in cheaper imports from new markets is also producing more foreign competition for US manufacturing companies.
One of the most famous studies on the topic is called “The China Syndrome: Local Labor Market Effects of Import Competition in the United States.” The report was able to link an increase in Chinese imports between 1999-2007 to a 25% decline in US manufacturing jobs.
Additionally, some multinational companies have found ways to avoid paying taxes in the United States by exploiting tax loopholes in new markets. While this may be great for business, it ultimately has a negative effect on the US economy, all while increasing the national trade deficit.
According to Velocity Global, substantial upfront capital is often required to expand into a new market overseas. The company advises that setting up a foreign entity can cost anywhere from $15,000- $20,000 and can require $200,000 each year to maintain.
International recruiting can also be a major challenge when it comes to expanding into multiple markets. Companies that wish to send members of their own teams to oversee operations in other countries may also have to contend with immigration issues.
Recruitment experts can be incredibly helpful when it comes to overcoming language and cultural barriers.
Legal compliance is among the most common challenges of globalization that many businesses face when moving into new countries. Establishing a legal presence often involves setting up a Global PEO and understanding how to maintain a compliant overseas presence.
Navigating new legal systems, registering with the appropriate tax authorities, and complying with local regulations can be a mammoth administrative task. To make matters worse, there can be severe financial or legal consequences for failing to comply with employment law in new countries.
For this reason, it’s always advised to seek legal counsel when establishing a local presence abroad.

Globalization has major advantages when it comes to promoting free trade and raising the gross domestic product of developing countries. But it has also come at an unfortunate cost to the environment.
According to the World Wide Fund for Nature (WWF), since 1970, the world has seen a 69% decline in the wildlife population. Additionally, the increased transport of goods is burning fossil fuels at an alarming rate.
The ITF estimates that “CO2 emissions from transport will increase by 16% to 2050 even if today’s commitments to decarbonize transport are fully implemented.” Fortunately, more major companies are beginning to make more significant commitments to sustainability.
See Related: How Does Ethical Responsibility Play a Role in Environmental Sustainability?
Monopolization is not a new phenomenon, especially in developed countries. Plenty of towns have witnessed the devastating effects that even one large chain store can have on small local businesses .
One of the challenges of globalization is ensuring that this doesn’t happen on an international scale. While industrialized nations may be able to help improve conditions in developing countries, it’s vital to ensure that each business operates in a way that doesn’t end up making a foreign economy worse.
The Russian invasion of Ukraine has proven to be a prime example of one of the challenges of globalization. Obviously, the most tragic effects of Russia’s unprovoked attack are the loss of lives and property in Ukraine.
But the citizens of many countries have been surprised by the massive ripple effects that the conflict has created throughout the global economy. While enhanced international relations are one of the goals of globalization , Russia’s barbaric actions have shown how quickly the system can unravel when even one country doesn’t cooperate.
Unfortunately, Russia is one of the largest oil and gas producers in the world and many nations are reliant on this oil and gas. Gas prices were already on the rise as the world attempted to recover from the economic fallout of COVID-19.
But news of Russia’s invasion sent the price of a barrel of crude oil skyrocketing from $76 in January 2022 to over $110 in early March 2022. The global disruption in oil supply has resulted in everything from massively inflated gas prices to shipping problems all over the world.
Additionally, Russia and Ukraine are collectively responsible for roughly a third of all wheat production in the world. For many countries, the sudden disruption in this supply has become evident in the form of rising food prices.
Over 30 countries imposed sanctions on Russian goods in response to the country’s unprovoked attack on Ukraine in 2022. But when an individual country attempts to use sanctions or tariffs to force another country into compliance, the results can be much harder to predict.
When Donald Trump ran for president in 2016, he vowed to reform America’s roughly $346 billion trade deficit with China. In simple terms, the idea was that America imports far more Chinese goods than it exports to the Chinese market.
In 2017, Trump and Chinese President Xi Jinping agreed on a deal that was intended to help fix the problem, but it quickly fizzled out. Trump responded by imposing a series of tariffs (import taxes) on Chinese goods between 2018 and 2019.
The idea was to either force the Chinese government back to the table or convince manufacturers to bring jobs back to America. But, for the most part, Trump’s tactics backfired, even as the deficit continued to widen. Shocker, I know.
As the Washington Post reported, “U.S. economic growth slowed, business investment froze, and companies didn’t hire as many people. Across the nation, a lot of farmers went bankrupt, and the manufacturing and freight transportation sectors have hit lows not seen since the last recession. Trump’s actions amounted to one of the largest tax increases in years.”
See Related: Philanthropic Investors vs Impact Investors: What’s the Difference?
On some levels, the spread of different cultures throughout the world is one of the benefits of globalization. On the flip side of the coin is the danger of cultural homogenization.
The concept refers to the idea that the more interconnected the world becomes, the harder it will be to preserve cultural diversity. Sociologists worry that the spread of Western capitalist culture through social media and popular entertainment will begin to replace the unique ideas and viewpoints of other cultures throughout the world.
History features plenty of tragic examples of cultural imperialism, such as the effects of European colonization on African, Far East Asian, and Native American cultures. While the spread of Western media may not be quite so blatant, some fear it will come to a similar end.
Only time will tell if the world has learned the importance of cultural preservation from the lessons of the past.
Related Resources
- Best Community Investments to Leave a Positive Impact
- How to Invest in Community [Step-by-Step Guide]
- What Are Community Development Financial Institutions (CDFIs)?
Kyle Kroeger, esteemed Purdue University alum and accomplished finance professional, brings a decade of invaluable experience from diverse finance roles in both small and large firms. An astute investor himself, Kyle adeptly navigates the spheres of corporate and client-side finance, always guiding with a principal investor’s sharp acumen.
Hailing from a lineage of industrious Midwestern entrepreneurs and creatives, his business instincts are deeply ingrained. This background fuels his entrepreneurial spirit and underpins his commitment to responsible investment. As the Founder and Owner of The Impact Investor, Kyle fervently advocates for increased awareness of ethically invested funds, empowering individuals to make judicious investment decisions.
Striving to marry financial prudence with positive societal impact, Kyle imparts practical strategies for saving and investing, underlined by a robust ethos of conscientious capitalism. His ambition transcends personal gain, aiming instead to spark transformative global change through the power of responsible investment.
When not immersed in the world of finance, he’s continually captivated by the cultural richness of new cities, relishing the opportunity to learn from diverse societies. This passion for travel is eloquently documented on his site, ViaTravelers.com, where you can delve into his unique experiences via his author profile.
- Search Search Please fill out this field.
What Is Globalization?
Understanding globalization, the history of globalization.
- Globalization FAQs
The Bottom Line
- Macroeconomics
Globalization in Business With History and Pros and Cons
:max_bytes(150000):strip_icc():format(webp)/jason_mugshot__jason_fernando-5bfc261946e0fb00260a1cea.jpg)
Globalization refers to the spread of the flow of financial products, goods, technology, information, and jobs across national borders and cultures. In economic terms, it describes an interdependence of nations around the globe fostered through free trade .
Key Takeaways
- Globalization is the spread of products, technology, information, and jobs across nations.
- Corporations in developed nations can gain a competitive edge through globalization.
- Developing countries also benefit through globalization as they tend to be more cost-effective and therefore attract jobs.
- The benefits of globalization have been questioned as the positive effects are not necessarily distributed equally.
- One clear result of globalization is that an economic downturn in one country can create a domino effect through its trade partners.
Alex Dos Diaz / Investopedia
Corporations gain a competitive advantage on multiple fronts through globalization. They can reduce operating costs by manufacturing abroad, buy raw materials more cheaply because of the reduction or removal of tariffs , and most of all, they gain access to millions of new consumers.
Globalization is a social, cultural, political, and legal phenomenon.
- Socially, it leads to greater interaction among various populations.
- Culturally, globalization represents the exchange of ideas, values, and artistic expression among cultures.
- Globalization also represents a trend toward the development of a single world culture.
- Politically, globalization has shifted attention to intergovernmental organizations like the United Nations (UN) and the World Trade Organization (WTO).
- Legally, globalization has altered how international law is created and enforced.
On one hand, globalization has created new jobs and economic growth through the cross-border flow of goods, capital, and labor. On the other hand, this growth and job creation are not distributed evenly across industries or countries.
Specific industries in certain countries, such as textile manufacturing in the U.S. or corn farming in Mexico, have suffered severe disruption or outright collapse as a result of increased international competition.
Globalization's motives are idealistic, as well as opportunistic, but the development of a global free market has benefited large corporations based in the Western world. Its impact remains mixed for workers, cultures, and small businesses around the globe, in both developed and emerging nations .
Globalization is not a new concept. Traders traveled vast distances in ancient times to buy commodities that were rare and expensive for sale in their homelands. The Industrial Revolution brought advances in transportation and communication in the 19th century that eased trade across borders.
The think tank Peterson Institute for International Economics (PIIE) states globalization stalled after World War I, and nations moved toward protectionism as they launched import taxes to more closely guard their industries in the aftermath of the conflict. This trend continued through the Great Depression and World War II until the U.S. took on an instrumental role in reviving international trade .
Globalization has sped up at an unprecedented pace, with public policy changes and communications technology innovations cited as the two main driving factors.
One of the critical steps in the path to globalization came with the North American Free Trade Agreement (NAFTA), signed in 1993. One of NAFTA's many effects was to give American auto manufacturers the incentive to relocate a portion of their manufacturing to Mexico where they could save on the costs of labor. NAFTA was replaced in 2020 by the United States-Mexico-Canada Agreement (USMC) .
Governments worldwide have integrated a free market economic system through fiscal policies and trade agreements in the 20th century. The core of most trade agreements is the removal or reduction of tariffs.
This evolution of economic systems has increased industrialization and financial opportunities in many nations. Governments now focus on removing barriers to trade and promoting international commerce.
Pros and Cons of Globalization
A larger market for goods and services
Cheaper consumer prices
Outsourcing can benefit both domestic firms and foreign labor
Increased standard of living
Concentrates wealth in richer countries
Some poorer countries can be left behind
Poorer countries can be exploited of their labor and physical & intellectual resources
Cultures and the products consumed around the world can become homogenized
Proponents of globalization believe it allows developing countries to catch up to industrialized nations through increased manufacturing, diversification, economic expansion, and improvements in standards of living .
Outsourcing by companies brings jobs and technology to developing countries, which helps them to grow their economies. Trade initiatives increase cross-border trading by removing supply-side and trade-related constraints.
Globalization has advanced social justice on an international scale as well, and advocates report that it has focused attention on human rights worldwide that might have otherwise been ignored on a large scale.
One clear result of globalization is that an economic downturn in one country can create a domino effect through its trade partners. For example, the 2008 financial crisis had a severe impact on Portugal, Ireland, Italy, Greece, and Spain. All these countries were members of the European Union , which had to step in to bail out debt-laden nations, which were thereafter known by the acronym PIIGS .
Globalization detractors argue that it has created a concentration of wealth and power in the hands of a small corporate elite that can gobble up smaller competitors around the globe.
Globalization has become a polarizing issue in the U.S. with the disappearance of entire industries to new locations abroad. It's seen as a major factor in the economic squeeze on the middle class .
For better and worse, globalization has also increased homogenization. Starbucks, Nike, and Gap dominate commercial space in many nations. The sheer size and reach of the U.S. have made the cultural exchange among nations largely a one-sided affair.
What Is Globalization and Why Is it Important?
In essence, globalization is about the world becoming increasingly interconnected . Countries today are more connected than ever before, due to factors such as air travel, containerized sea shipping, international trade agreements and legal treaties, and the Internet. In the world of business, globalization is associated with trends such as outsourcing, free trade, and international supply chains. Globalization is important as it increases the size of the global market, and allows more and different goods to be produced and sold for cheaper prices.
Globalization is also important because it is one of the most powerful forces affecting the modern world, so much so that it can be difficult to make sense of the world without understanding globalization. For example, many of the largest and most successful corporations in the world are in effect truly multinational organizations, with offices and supply chains stretched right across the world. These companies would not be able to exist if not for the complex network of trade routes, international legal agreements, and telecommunications infrastructure that were made possible through globalization. Important political developments, such as the ongoing trade conflict between the United States and China, are also directly related to globalization.
Is Globalization Good or Bad?
It depends. Proponents of globalization will point to the dramatic decline in poverty throughout the world for more than two decades after around year 2000, which many economists attribute in part to increased trade and investment between nations. Similarly, they will argue that globalization has allowed products and services such as cellphones, airplanes, and information technology to be spread far more widely throughout the world. On the other hand, critics of globalization will point to the negative impact it has had on specific nations’ industries, which might face increased competition from international firms. Globalization can also have negative environmental impacts due to economic development, industrialization, and international travel.
How Does Globalization Impact Society?
Globalization has had a large impact on societies around the world, leading to massive migrations from rural to industrial or urban areas, leading to the rapid growth of cities and trade hubs. While this has led to an overall increase in incomes and a higher standard of living in general, it has also led to problems of urbanization including crime, domestic violence, homelessness, and poverty. Concepts of national identity, culture, and consumption patterns also change as goods from around the world become increasingly available and at low prices. The competitiveness of global capitalism may also lead to more individualistic ideals that contradict the cultural orientations of certain, more collectivist societies.
What Is an Example of Globalization?
A simple example of globalization would be a car manufactured in the U.S. that sources parts from China, Japan, South Korea, Sri Lanka, and South Africa. The car is then exported to Europe, where it is sold to a driver who fills the car's gas tank with gasoline refined from Saudi oil.
Globalization refers to the ongoing trend of increased interconnectivity across the globe, as enabled by advancements in transportation and information technology, among others. Globalization is economically facilitated by free trade agreements, which permit barrier-free imports and exports across borders. While globalization brings many advantages—including lower prices and higher standards of living—it also has drawbacks, including wealth concentration and cultural homogenization.
Peterson Institute for International Economics. " What Is Globalization? "
Congressional Research Service. " The North American Free Trade Agreement ," Page 1.
Congressional Research Service. " The North American Free Trade Agreement ." Pages 16-17.
Office of the United States Trade Representative. " United States-Mexico-Canada Agreement ."
FasterCapital. “ Financial Bailout: PIIGS and Financial Bailouts: Lessons From the Crisis .”
Macrotrends. “ World Poverty Rate 1981-2024 .”
:max_bytes(150000):strip_icc():format(webp)/wall_street_179681980-5bfc2b9746e0fb0083c07d29.jpg)
- Terms of Service
- Editorial Policy
- Privacy Policy
- Your Privacy Choices

Home | About Us Contact Us | Privacy Policy

10+ Pros and Cons of Globalization
Globalization has been a buzzword for several decades now, and it refers to the process of increased interconnectedness and interdependence among countries, businesses, and people worldwide.
The term globalization encompasses various aspects, including economic, political, cultural, and social integration. While globalization has brought about numerous benefits, such as increased trade, improved communication, and cultural exchange, it has also faced criticism for its negative impacts, such as job loss, environmental degradation, and cultural homogenization.
In this article, we will explore the pros and cons of globalization, to help you gain a better understanding of this complex phenomenon.
Pros of Globalization
Globalization, a phenomenon that has reshaped our world over the past several decades, continues to spark lively debates about its impact on societies, economies, and cultures.
We will explore numerous benefits that globalization brings, highlighting how it fosters cultural exchange opportunities, promotes economic growth, and improves global cooperation.

1. Economic Growth Benefits
Embracing globalization can lead to significant economic growth benefits, providing opportunities for increased trade and investment across borders. By expanding markets beyond domestic boundaries, businesses can access a larger customer base, leading to higher sales and profits. This increased trade can also result in the creation of new jobs and industries, stimulating economic growth.
Globalization allows for the flow of capital across borders, enabling companies to invest in new markets and technologies. Access to a wider range of products and services from around the world can lead to greater efficiency and innovation in various sectors.
2. Cultural Exchange Opportunities
Experience diverse cultures firsthand through the cultural exchange opportunities facilitated by globalization.
By opening up borders and creating interconnectedness, globalization allows for the sharing of traditions, languages, arts, and customs between people from different parts of the world.
This can lead to a greater appreciation and understanding of various cultural backgrounds, fostering tolerance and respect.
Through travel, international events, and digital communication, individuals have the chance to immerse themselves in new ways of life, broadening their perspectives and breaking down stereotypes.
These cultural exchanges not only enrich personal experiences but also contribute to a more interconnected and harmonious global community.
Embrace the opportunity to learn from others and celebrate the diversity that globalization brings.
3. Increased Job Creation
By fostering global connections and promoting cross-border collaborations, globalization significantly contributes to the creation of job opportunities worldwide. Companies expanding internationally require a diverse workforce, leading to more employment opportunities in various sectors.
As businesses grow and establish operations in different countries, they often hire local talent, stimulating job creation within those regions. Globalization also fuels the demand for specialized roles such as language translators, international marketing experts, and supply chain managers.
The outsourcing of certain tasks to countries with lower labor costs can create new jobs in those economies. Overall, the interconnected nature of the global economy under globalization has been instrumental in generating employment opportunities on a global scale, benefiting individuals and economies alike.
4. Access to Diverse Products
Diverse products from around the world are easily accessible due to the benefits of globalization. Thanks to the interconnectedness of global markets, you now have the opportunity to enjoy a wide range of goods and services that were once unavailable in your local area.
Whether it’s trying out unique foods, purchasing traditional crafts, or accessing the latest technological gadgets, globalization has made it possible for you to explore and experience products from different cultures and regions. This access not only broadens your choices but also promotes cultural exchange and understanding.
Embracing diverse products can enrich your life, introducing you to new tastes, styles, and innovations that you may not have encountered otherwise.
5. Technological Advancements Facilitation
With globalization, technological advancements are facilitated, enhancing connectivity and efficiency across borders. The ease of sharing information and ideas globally has revolutionized communication. Through platforms like video conferencing and instant messaging, businesses can collaborate seamlessly across continents, leading to increased productivity and innovation.
Advancements in transportation technology have made it quicker and more cost-effective to transport goods worldwide. This hasn’t only expanded market opportunities for businesses but has also allowed consumers access to a wider range of products from different parts of the world.
Technological advancements in automation and artificial intelligence have streamlined processes, making production more efficient and cost-effective. Overall, the facilitation of technological advancements through globalization has led to significant benefits for businesses and consumers alike.
6. Improved Global Cooperation
Facilitating improved global cooperation, globalization fosters enhanced collaboration among nations, leading to various benefits for economies and societies worldwide. By promoting trade agreements, international organizations, and diplomatic relations, globalization helps countries work together to address global challenges such as poverty, climate change, and health crises.
Enhanced global cooperation also encourages the sharing of knowledge, resources, and technologies, allowing for more efficient problem-solving and innovation on a global scale. Through partnerships and alliances formed across borders, countries can combine their strengths and expertise to achieve common goals, resulting in mutual growth and development.
Ultimately, improved global cooperation facilitated by globalization paves the way for a more interconnected and prosperous world for all nations involved.
7. Enhanced Communication Channels
Utilizing advanced technology and interconnected networks, globalization enhances communication channels, revolutionizing the way individuals and businesses interact on a global scale.
Through the internet, social media, and instant messaging, people can now communicate effortlessly across borders in real time. This increased connectivity has paved the way for collaborations, partnerships, and knowledge-sharing opportunities that were previously unimaginable.
Businesses can now conduct meetings virtually, negotiate deals internationally, and reach a broader audience with ease. Individuals can connect with friends and family worldwide, fostering cultural exchange and understanding.
Enhanced communication channels have also facilitated rapid responses during crises, enabled remote work possibilities, and promoted global awareness of important issues. Embracing these advancements can lead to a more interconnected and informed global community.
Cons of Globalization
While globalization has brought about several benefits, it also has its downsides. We will explore the cons of globalization and how it affects different aspects of our lives.
From threats to national sovereignty to environmental degradation, we will delve into the cons of globalization. So, let’s take a closer look at the dark side of globalization and what we can do to mitigate its negative effects.

1. Job Outsourcing Impact
Outsourcing jobs to other countries has significantly impacted local employment opportunities, leading to concerns about job security and economic stability. Companies often choose to outsource jobs to countries with lower labor costs, which can result in layoffs and reduced job prospects in your community.
This practice not only affects individual workers but can also weaken the overall economy by decreasing consumer spending power and tax revenues. Job outsourcing can lead to a skills gap in certain industries as jobs are moved overseas, potentially hindering future growth and innovation locally.
As a result, the trend of outsourcing jobs is a major downside of globalization that continues to raise worries about the long-term sustainability of employment and economic development in your area.
2. Cultural Homogenization Concerns
Globalization poses a significant concern for many as it leads to cultural homogenization, potentially erasing unique traditions and identities. As different cultures interact more closely, there’s a risk of losing diversity and distinctiveness.
With the spread of Western values and consumerism, local traditions and languages may be overshadowed, impacting the cultural heritage of various societies. The dominance of global media and entertainment can further perpetuate a standardized culture, diluting the richness of individual customs.
This trend not only diminishes the authenticity of traditions but also contributes to a sense of cultural loss and disconnection among communities. Preserving cultural diversity in the face of globalization remains a pressing challenge to maintain the world’s cultural richness.
3. Environmental Degradation Risks
The increase in worldwide trade and production has led to heightened risks of environmental degradation. As companies expand globally to cut costs and increase profits, they often overlook environmental concerns. This can result in deforestation, pollution, habitat destruction, and the depletion of natural resources. Globalization encourages industries to prioritize economic growth over sustainable practices, leading to negative impacts on the environment.
The transportation of goods across long distances also contributes to greenhouse gas emissions and air pollution. Weaker environmental regulations in some countries where production is outsourced can further exacerbate these issues. It’s crucial for companies and governments to prioritize environmental protection measures to mitigate the detrimental effects of globalization on the planet.
4. Widening Wealth Disparities
Amidst the push for global economic integration, wealth disparities are widening at an alarming rate. While globalization has led to economic growth in many regions, it has also exacerbated income inequality.
Multinational corporations often exploit cheap labor in developing countries, leading to significant wage gaps between workers in different parts of the world. The concentration of wealth in the hands of a few powerful entities has left many individuals and small businesses struggling to compete in the global market.
As a result, the rich are getting richer, while the poor are finding it increasingly challenging to break the cycle of poverty. Addressing these widening wealth disparities is crucial to ensuring a more equitable and sustainable global economy.
5. Loss of Local Industries
As wealth disparities widen due to global economic integration, local industries are facing a significant threat of loss. Small businesses that once thrived in your community are struggling to compete with larger corporations that can produce goods at lower costs overseas.
This shift towards outsourcing and offshoring has led to the closure of many local factories and workshops, resulting in job losses and economic instability in your area. The unique craftsmanship and expertise that were once the pride of your town are gradually disappearing as cheaper mass-produced items flood the market.
While globalization has brought access to a wider range of products, it has come at the expense of local businesses and the cultural heritage they represent.
6. Exploitation of Labor
With global economic integration, labor exploitation has become a pressing issue, affecting workers worldwide. Companies often seek cheaper labor in developing countries, where they can pay lower wages and offer fewer protections to workers. This can lead to poor working conditions, long hours, and inadequate pay for employees who may have limited alternative job options.
Some corporations take advantage of lax labor laws in certain regions to maximize profits at the expense of fair treatment for their workers. Exploitative practices such as child labor, forced labor, and unsafe working environments are unfortunately common in industries where globalization has created a race to the bottom in terms of labor standards.
It’s crucial to address these issues and ensure that workers are treated ethically and fairly in a globalized economy.
7. Threat to National Sovereignty
Globalization poses a significant threat to national sovereignty as countries find themselves increasingly interconnected economically and politically, raising concerns about the erosion of independent decision-making power.
The rise of global trade agreements and multinational corporations can limit a country’s ability to enact policies that may contradict international agreements or offend powerful global players. Organizations like the World Trade Organization and the International Monetary Fund can impose conditions on countries seeking financial assistance, further undermining their sovereignty.
As nations become more intertwined through globalization, their autonomy to govern as they see fit becomes compromised, potentially leading to conflicts between national interests and global pressures. It’s crucial for countries to navigate these complexities carefully to protect their sovereignty in a globalized world.
Conclusion on Pros and Cons of Globalization
In conclusion, globalization has its benefits such as increased economic growth and cultural exchange.
However, it also comes with drawbacks like widening income inequality and loss of cultural identity.
It’s important to weigh these pros and cons carefully to ensure that globalization is implemented in a way that maximizes the benefits for all while minimizing the negative consequences.
Relevant Resources:
- 10+ Pros and Cons of Coffee
- 10+ Pros and Cons Of Debt Settlement
- 10+ Pros and Cons of Capital Punishment
- 10+ Pros and Cons of Veneers
- 10+ Pros and Cons of Unions

Ahmad Ali (Author)
Ahmad Ali has been a technology enthusiast and writer for the past 5 years having vast knowledge of technology.

Rehmat Ullah (Content Reviewer)
Rehmat Ullah is a software engineer and CEO of Softhat IT Solutions. He is an expert technologist, entrepreneur, and educationist.

Leave a Comment Cancel Reply
Your email address will not be published. Required fields are marked *
Save my name, email, and website in this browser for the next time I comment.
Pros and Cons of Globalization

Some praise globalization for opening borders and connecting cultures and politics. Others blame it for disrupting local economies and eliminating jobs. The fact is that globalization has been around since ancient times, and it is fully integrated into different aspects of modern life. As a consumer, your clothing, foods and electronic gadgets are often produced by multinational companies located around the world. And as an investor, a financial advisor could help you diversify your portfolio with emerging market funds and other foreign investments.
What Is Globalization?
Globalization is defined as a process that moves businesses, organizations, workers, technology, products, ideas and information beyond national borders and cultures. Supporters say that this is making countries more interdependent on free trade. But critics maintain that it is also concentrating wealth in the corporate elite, disrupting industries and making local economies more vulnerable.
This process has roots in ancient civilizations that traded for valuable commodities that were unavailable in their homelands. But today, you can also see how large corporations similarly thrive as multinational businesses with offices and supply chains stretching around the globe.
In the recent economy, trade agreements have become the cornerstones of globalization, creating and expanding networks for trade and infrastructure. This is the case with NAFTA, which was renegotiated by the Trump administration in 2020 as the United States-Mexico-Canada Agreement (USMCA) . Initially, NAFTA incentivized U.S. businesses to relocate partially to take advantage of low-cost labor in Mexico. However, the USMCA has added protections for U.S. workers against this type of competition.
Globalization has also come under scrutiny with President Joe Biden’s recent $2.3 trillion infrastructure and jobs plan . Many large multinational companies like Amazon were singled out by Biden for taking advantage of tax loopholes to avoid paying federal income taxes . The President said that he would raise corporate taxes and eliminate these loopholes and foreign tax credits to fund his plan.
While governments focus on removing national barriers to promote global trade, they are also working on protecting local economies that could easily get disrupted. Let’s break down the advantages and disadvantages of globalization.
Advantages of Globalization
Globalization can provide greater access to goods to countries all around the world. It also provides some economic benefits that financially benefit people that otherwise wouldn’t have enough opportunity where they live. Here are the four largest advantages to globalization:
1. Globalization Broadens Access to Goods and Services
It’s hard to argue with the point that globalization makes more goods and services available to more people, often at lower prices. If you have disposable income and you’re buying a product that comes from abroad, you’re benefiting from globalization to some extent. Business owners also benefit by having access to a bigger market for their goods and services.
2. Globalization Can Lift People Out of Poverty
The argument that globalization has lifted people in developing countries out of poverty is somewhat controversial because opinions differ as to the quantity – and quality – of the jobs created by globalization. But the general wisdom is that globalization has increased job opportunities in capital-scarce, labor-rich countries, i.e. developing countries.
3. Globalization Increases Cultural Awareness
Globalization’s defenders say it has increased cross-cultural understanding and sharing. A globalized society boosts the rate at which people are exposed to the culture, attitudes and values of people in other countries. That exposure can inspire artists, strengthen ties between nations and dampen xenophobia.
4. Information and Technology Spread More Easily With Globalization
Art and culture aren’t the only things that spread more easily in a globalized society. The same goes for information and technology. For example, see the rise of mobile banking in Kenya or the practice of micro-lending. Civil society groups can look to other countries for inspiration and good ideas can spread more easily.
Drawbacks of Globalization
Globalization may benefit many but it also has some large drawbacks to consider. From negatively impacting some economies to benefiting only the largest corporations, it isn’t a perfect solution. Here are the four largest drawbacks of globalization:
1. Workers Can Lose Jobs to Countries With Low-Cost Labor
This first argument against globalization is the one that surfaces most frequently in U.S. political discussions about NAFTA and other trade deals. When the U.S. competes with less-developed countries, its big advantage is its access to capital, whereas less-developed countries’ big advantage is their cheap labor.
Generally speaking, globalization increases the returns to capital in rich countries like the U.S. and decreases the returns to labor in those same countries. That’s a fancy way of saying that low-skill jobs in the U.S. can disappear as a result of globalization (though technology plays a big role in this change, too). The result may be a decrease in the inequality between countries but an increase in the inequality within countries.
2. Globalization Hasn’t Protected Labor, Environmental or Human Rights
In theory, globalization can be an opportunity to spread values and practices like environmentalism and labor rights throughout the world. In practice, that spread has been slow and imperfect. For example, rather than exporting the labor protections that a company might have to abide by in the U.S., it might follow lower standards in another country where labor is not protected.
Some argue that globalization has caused a “race to the bottom” in which companies actively seek the countries with the weakest labor and environmental protections and the lowest wages. And while globalization has increased the flow of goods, services and capital, there are still plenty of tax havens, meaning that much of the value added by globalization is not captured and redistributed by governments.
3. Globalization Can Contribute to Cultural Homogeneity
Globalization might lead to more cultural homogeneity as people’s preferences converge and products cannot compete with cheaper multinational ones. If everyone wears jeans, learns English and watches Hollywood movies we may lose precious cultural practices and languages. Some critics of globalization worry that it’s creating a mainstream monoculture while driving other diverse cultures underground.
4. Globalization Empowers Multinational Corporations
Another criticism leveled at globalization is that it has empowered multinational corporations at the expense of governments and citizens. This reduces state sovereignty and citizens’ ability to hold their leaders accountable for conditions in their countries. It’s another reason that labor and environmental protections are harder to enforce than many critics of globalization would like. Multinational corporations may also lobby for favorable provisions in trade agreements (this was an argument invoked against the TPP ).
Bottom Line
Supporters and opponents of globalization generally agree that the phenomenon has come with great benefits and several negative impacts. Supporters argue that the benefits outweigh the drawbacks, while critics want to either improve the conditions of global trade or, in some cases, roll back globalization. Regardless, globalization is here to stay in many industries and countries so it’s important to understand how it could impact you and your company.
Tips to Grow Your Business
- Whether you’re looking to raise money for a future business or create a financial plan to reach your current business goals, a financial advisor can help you make smart money decisions. SmartAsset’s free tool matches you with up to three financial advisors who serve your area, and you can interview your advisor matches at no cost to decide which one is right for you. If you’re ready to find an advisor who can help you achieve your financial goals , get started now .
- If you’re starting up a business, you might want to consider the benefits of setting up an S Corp or an LLC . Make sure you compare the key differences to pick the best option for your needs.
- Whether you are self-employed or have an employer, you should consider opening an IRA to save money for your retirement needs. Read more about IRA contribution deadlines and income limits .
Photo credit: ©iStock.com/Rawpixel Ltd, ©iStock.com/_marqs, ©iStock.com/Rawpixel Ltd
- AI Translation
- AI quality assurance
- Collaborative translation
- Localization workflow management
- Localization process automation
- Translation quality assurance
- In-context editing
- Translation services
- Real-time support translation
- Lokalise apps
- For developers
- For product managers
- For localization managers
- For translators
- For designers
- For marketers
- For customer service
- For enterprise
- Developer Hub
- API reference
- Flutter SDK
- Android SDK
- File-formats
- Build an app
- Developer tools
- Case studies
- Product updates
- Documentation
- Try it free
- Localization
- Inside Lokalise
Globalization: the pros and cons, & the future of an interconnected (or disconnected) world
Global trade in online services and goods is booming, despite globalization being under fire in many nations .
Brexit, COVID-19, Trump’s trade war with China, and the war in Ukraine, have left many wondering if we’re entering a phase of deglobalization – a world destined to become less connected, with countries looking inwards instead of outwards.
Some welcome this movement, citing vulnerabilities of global supply chains exposed during the pandemic and the Russia-Ukraine conflict. Others believe the positive outcomes of globalization far outweigh the negatives. And those on the bench believe globalization should be redefined.
To help you understand why there’s so much debate over globalization, we’ll go over both the positives and negatives later on in this article. First, let’s go over the definition of globalization.
What is globalization?
Globalization describes how the world’s cultures and economies are connected and dependent on each other. Through trade agreements between countries, globalization allows businesses to buy and sell across borders with lower tariffs and no or fewer limits on imports and exports. Overall, the goal of governments in favor of globalization is to make it easier to do business worldwide.
Did you know? The opposite of globalization is protectionism, which restricts international trade and forces companies and consumers to buy home-grown goods and services.
Fun fact about glocalization
Nope, not a typo! Glocalization should not be mistaken for globalization. It’s a combination of globalization and localization . While globalization is the process of expanding business operations on a worldwide scale, localization is the process of adapting products, services, and marketing to meet the specific needs of local markets.
When you merge the two, you get glocalization. The concept represents a global and local approach with companies maintaining a global brand identity that’s more universally accepted, while also adapting products or services to suit local markets.
What are the advantages of globalization?
International trade is a key driver of globalization, and so we often focus on the trade benefits of globalization. But globalization also brings with it social, political, legal, and cultural benefits. Let’s go over some of these below.
Expansion into other markets
Great ideas and products are no longer confined to local markets. Businesses can expand freely to new regions, offering their products and services to a larger audience. They can also set up operations in regions where the cost of production and employment is lower, allowing them to lower manufacturing and labor costs and be more competitive.
Globalization not only benefits companies, but also customers who have access to a larger variety of products, leading to more choices, better quality (because companies need to compete), and more affordable products.
The language gap gets smaller
With more and more companies going global, the language gap is getting smaller. Companies are communicating with customers in their native language to better connect with them and create fairer and more personal experiences.
Twenty years ago, there was no way of knowing which brand was doing the best job at going global from a website perspective , as global researcher John Yunker, explains it. Communicating in other languages wasn’t something that everyone was doing back then, and so there was no blueprint to follow. This is why John created the Web Globalization Report Card (below) to measure who was doing the best job at going global.
The W eb Globalization Report Card scores global websites based on:
- Internationalization (i18n) – the flexibility of global website architecture
- Localization – the level that content has been adapted for local audiences
- Global navigation – can the user find their locale or localized site?
- Global reach – how many languages are available?
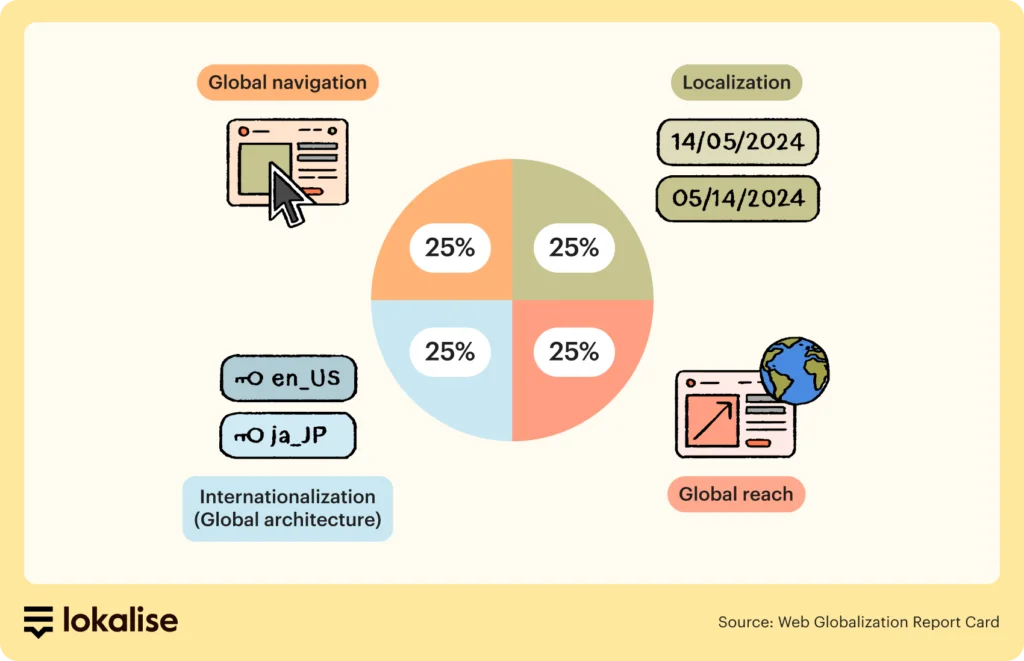
During John’s research, Google emerged as the best global website. It was the most multilingual website on the internet with 67 languages, and has become a benchmark for the rest of the world.
I n 2024, the two most linguistically fluent websites on the internet are not-for-profit organizations: The Jehovah’s Witnesses (over 1000 languages!) and Wikipedia (339 languages).
Going global? Learn how to successfully translate your website
Access to a diverse pool of talent
More and more companies operate remotely and hire globally. The big benefit is that they can tap into a vast pool of talent, bringing diverse perspectives and skills to the table. Some countries are making it even easier for so-called digital nomads to work remotely by offering temporary visas, which is reshaping local economies and becoming yet another symbol of globalization.
Transfer of technology and knowledge-sharing
Opening up borders can lead to greater innovation, breakthroughs, and growth. Though most of us want to leave COVID-19 well behind us, we need only look at the response from countries who came together to create the first vaccines in less than a year. Vaccines normally take around 5 to 10 years to create , but the deadliness, rapid spread, and disruptiveness of COVID-19 led to a new global approach to vaccine development, manufacturing, and distribution.
Access to new cultures
Globalization has made it easier to explore, learn, and be inspired by new cultures. Without the freedom to work abroad, travel across borders, and do business internationally, we wouldn’t be exposed to new ideas, products, and services. Our choices would be limited to what’s available in the countries we live in. Imagine not having access to music, food, and movies from other parts of the world!
What are the disadvantages of globalization?
Globalization doesn’t have all the answers. Where the scales tip in favor of economic growth and technological advancements, they weigh heavily with concerns over economic inequality and environmental issues. Let’s go over some of these downsides in more detail.
Cultural homogenization
Dominant cultures from other countries often influence local culture, leading to a more uniform global culture. This raises concerns about losing unique local identities, traditions, brands, languages, and cultures as locals adapt to global markets.
Financial crises and inequality
While globalization has been shown to decrease poverty overall, it’s often at the expense of local businesses and populations. Lower-priced foreign competition has led to job losses in developed nations, especially in domestic manufacturing, and exploitative labor practices in the developing world.
Globalization can also widen the inequality gap, with the rich becoming richer and the poor becoming poorer. Let’s take the modern-day example of globalization as an example: digital nomadism. This phenomenon has been blamed for rising house prices in some countries. Digital nomads are drawn to countries where living costs are low, allowing them to afford better lifestyles and save more. But this in turn sees prices in the region soar, and prices locals out of property, food, and more.
Environmental toll
Environmental degradation is common in countries where regulations are more relaxed. Projects like the construction of hydropower dams and deforestation in the name of globalization have caused environmental harm and habitat destruction. Meanwhile, global integration has led to a decrease in biodiversity and the spread of invasive species, impacting agriculture, wildlife, and ecosystems worldwide.
Supply chain vulnerabilities
Stretched supply chains make the world more susceptible to disruptions. Highlighted by the pandemic, US and China trade disputes, and more recently Russia’s war against Ukraine. The latter caused global disruptions to natural gas supplies and saw a spike in energy prices, while the ongoing spat between China and the US continues to see sanctions on exports and imports from both sides, which is disrupting global supply chains for companies.
Disruptions are not just man-made, however. Natural disasters can also be huge disruptors. Taiwan, for example, the largest manufacturer of semiconductors for large tech firms like Apple , is prone to typhoons and earthquakes.
Examples of globalization
Now that you understand the positives and negatives of globalization, let’s take a look at some examples of how globalization can show up in many different ways.
Brand and product globalization
Brands that sell their products and services in multiple countries often influence cultures and even economies on a global scale. Companies like, Coca-Cola, Nike, and McDonald’s have become ubiquitous symbols of American culture worldwide. Car companies, like Toyota – the world’s largest motor vehicle manufacturer – creates jobs and spur technological growth. Barbie, the most iconic toy doll, has influenced popular culture around the world. She’s inspired fashion, beauty standards, career choices, and trends.
These are examples of globalized brands that have universal appeal. Their brand, messaging, and products need to be consistent across markets and localized to make sure they resonate with consumers in individual markets.
Fun fact: you won’t find a McDonald’s in Iceland, where locals boycotted the hamburger chain in favor of their local burger joint.
Website globalization
As the number of brands going global continues to rise, we’ll continue to see an increase in website globalization – websites that are designed for a wider spectrum of markets . The average number of languages supported by global brands in 2024 is 34 . But there’s still a language gap.
The Website Globalization Report Card revealed that to communicate with over 90% of internet users, websites will need to support 50 or more languages. To make it easier to adapt websites for different markets, developers will need to internationalize their product’s code base. Think of internationalization as the globalization of digital products . You need to lay the foundations so your website is global-ready.
Cultural globalization
The economic interdependence of countries leads to cultural exports and exchange. Hollywood movies are a classic example, of bringing American culture to international audiences. Another more recent example is K-pop, a music genre popular in South Korea in the 90s, which has become a global cultural phenomenon.
Digital globalization
The internet is arguably the most significant technological example of digital globalization. That includes digital content and platforms, like websites, apps, and social media. It allows for real-time communication and access to information, regardless of geographical location.
Platforms like Facebook and Twitter have created virtual communities, where people from across the globe can connect, share, and unite people to support causes and movements. It brings people together more than ever and breaks down barriers of communication.
The future of globalization : finding the right balance
Right now, many people are on the fence about globalization.
The good news is that nations and corporations are reexamining their globalization strategies rather than reversing or ramping up their efforts. They’re finding new ways to adapt to the changing geopolitical landscape, including:
- Diversifying their manufacturing bases – a strategic move to strengthen supply chains. Some companies are even turning to locally sourced and manufactured solutions to help reduce environmental impact and support local economies.
- There’s talk about a Global Currency Reset , a theory investigating a new global currency
- Shifting from manufacturing to services, which play an increasingly important role in globalization
- Looking at sustainable supply chains with the need and demand for greener alternatives.
It seems more likely that globalization will evolve than reverse. By 2030, China and India are predicted to overtake the US as the world’s biggest economy, which will see a significant shift in the global economic landscape.
One thing is certain: recent and ongoing debates around globalization have highlighted how important it is to find the right balance of globalization for different regions.

Talk to one of our localization specialists
Book a call with one of our localization specialists and get a tailored consultation that can guide you on your localization path.
Related posts
Introducing lokalise ai: your personal localization assistant, how revolut maintains and launches new languages at scale with lokalise, how localization accelerates growth at three industry-leading tech companies, ukraine: a letter from our co-founders, carbon-neutral localization from lokalise, $50m – how we’ll invest it, using the same ios and android keys in multiplatform localization projects, learn something new every two weeks.
Get the latest in localization delivered straight to your inbox.

5 reasons why multi-language customer service is important
When you’re a business owner, nothing comes close to the disappointment and sometimes even rage of customers who are interested in purchasing your product or service, but are met with…
“The world is shifting to Asia”: discussing the APAC region with Yuka Nakasone
We have become used to thinking that the West dominates the global economy. It’s imprinted in our collective perception of the world. But the tides are turning. With the growing…
3 steps to building better market expansion strategies
Nowadays, companies can do international expansion faster than ever before. But many companies underestimate how hard it is to break into a new market. There’s quite a lot that goes…
14 Key Advantages and Disadvantages of Globalization
Globalization carries the weight of several different definitions based on the subject matter under discussion. It can refer to the growing presence of multinational companies, the preference of some individuals to reduce border restrictions, or even the communication tools that people use to collaborate with one another.
How we access data is changing rapidly in today’s world. Sometimes these changes occur by the minute. As populations shift and weather patterns change, globalization can even be the emphasis that we have when working with one another to create a better world for everyone.
There are many ways that we can benefit from a society that is growing closer together. It can improve our standard of living, give us access to new technologies, and help us to learn about other cultures with greater ease.
Several disadvantages are possible because of globalization as well. Even though we can still identify as being human, we lose some of the personal definitions that are sometimes core components of our existence.
These globalization pros and cons show us that even though our world is closer than ever before, it could be said that we are also further away than ever in our history.
List of the Pros of Globalization
1. Globalization helps the world to focus on progress. There are roughly 40 countries in the world today which have the “developed” status attached to them. That means there are 150+ nations that are still in various stages of development. Although there are many differences to consider when comparing these designations, it is poverty that stands out the most.
Over 3 billion people live on less than $2.50 per day, with at least 80% of the world living on less than $10 each day. The poorest 40% of the world’s population accounts for just 5% of global income. UNICEF estimates that over 22,000 children die every day because of the direct impact of poverty. Making an effort to create a smaller world could help to raise these living standards.
2. It would stabilize global currencies to create an equal playing field. You might be surprised to know that the British pound isn’t the most valuable currency in the world. The Kuwait dinar actually trades at roughly $3.30, making it the top choice. The Bahraini dinar trades at $2.65. The top four countries are all located in the Middle East and have that value because of their natural resources. The British pound sterling ranks fifth.
Anyone living in a country that makes it into the top 10 (or the eurozone) can reasonably manage their costs without worrying about making ends meet. The value of the currency in developing countries is much less stable. Globalization would either phase these low-value options out of existence or bring up their value some to match with the rest of the world. That would help to create a better, more equal playing field for everyone.
3. We can use our resources as one planet instead of one nation with globalization. The United Nations estimates that it would cost about $30 billion per year to solve the problem of world hunger. That’s about 5% of what the United States currently spends on defense. Although we would not completely eliminate war in a society that is global, we would be able to reduce our spending in some areas to create positive impacts in others. Many of the social issues that we face today could be stopped immediately if the trillions that are spend on border defense and resource protection were redirected into other areas.
4. Globalization could reduce human trafficking and labor exploitation. When there are fewer restrictions on travel, imports, and exports, then there are more opportunities for people to find moments of success. Although the wealthy nations might see a decline through this process, those who live in poverty would see massive increases in their standard of living. This advantage could also raise employee wages, reduce concerns with human trafficking, and limit youth labor and slavery that are still problems in some areas of the world.
The uncomfortable fact about wealth is this: it is cheaper for companies in the developed world to outsource jobs to cheaper labor markets than to hire local workers. Globalization would work to equalize wages, which would create positive impacts for everyone over a long-term evaluation period.
5. It could prevent governments from creating repressive legislation. As the world has moved closer toward a globalization environment, it has become a place that is more peaceful overall. Although there are still conflicts being waged around the world, the rate of battle deaths has been decreasing steadily for the past 50 years. It is currently lower today than at any time since the 15th century. The second half of the 20th century was extraordinarily peaceful for Europe, with fewer conflicts occurring than at any other time in the past 500 years.
Although there are risks to consider with a globalization environment where one government could crack down on everyone simultaneously, the trend for humanity has been a preference for peace when there are fewer restrictions in place.
6. We can communicate better because of globalization. Because of the Internet, it is easier to communicate with other people all over the world today than ever before. We can speak with people immediately even if they are in a time zone that is 12 hours away. This structure has created new business opportunities that were only dreamed about in generations before. It is one of the reasons why some countries are experiencing self-employment rates that are topping 40%. People can find meaningful employment that pays better as long as they have access to online resources in some way.
7. Globalization would create more opportunities for trade. If we create a world that offers fewer borders or obstacles to trade, then everyone will have more access to the unique goods and services that are available in various regions of the globe. There would be fewer taxes and tariffs involved in the movement of products. That could make it potentially cheaper to purchase some items. Although it may reduce some initial revenues for governments, it could also stimulate the economy because there are more opportunities to purchase items. There are currently over 1,500 different obstacles to importing or exporting goods in the world today. Imagine would might happen if they were to vanish one day?
List of the Cons of Globalization
1. Globalization can leave some cultures behind. The process of globalization requires countries, cultures, and communities to set aside what their definition of “normal” happens to be for something that promises to be better. The fact is that there will be cultures and countries that must sacrifice something to create more equality for others. Although people who would benefit from this action would not see it as a disadvantage, those asked to make the most significant changes could find it to be a problematic issue.
It isn’t the wealthiest countries who are solely affected by this problem either. The developing world could get left behind if they decide to isolate instead of integrate as the world moves toward a closer culture.
2. It could create adverse impacts for the global environment. The cultures that have already gone through the industrial revolution have created the issues with greenhouse gas emissions that 90+% of scientists around the world believe are a significant contributor to the processes of global warming. As our levels of trade increase globally, the amount of pollution we generate grows as well. With over 150 countries potentially needing an upgrade to their infrastructure, the environment would be set to take a significant hit to its health because of globalization.
The World Health Organization already estimates that 7 million people die prematurely each year because of pollution. That figure could triple if we continue to globalize in a way that promotes industrial equality.
3. Each culture could be asked to change how they define themselves. National borders are not the only boundaries that humans set for themselves as they go about the business of daily life. We also set limits on our cultural identity, ethnicity, and family environment. When we move toward a society that focuses on globalization first, then these points of emphasis hold less importance. They would still be present because individuals always define themselves in some way because of their history, but it would also be an element that slowly disappears.
The examples of this disadvantage are numerous in the world today. Texans consider themselves Americans first despite the fact that they were once an independent nation. People who live in the city-states of Italy are called Italians instead of what their culture prefers by the outside world. San Marino has one of the oldest democracies in the world, the lowest unemployment rate in Europe, and no national debt – and arguably no global identity.
4. Globalization would temporarily reduce high-paying jobs. There would be a surge of employment in the places of the world where the cost of living is lower. Even as this process works to raise wages around the globe, the workers who are already in high-salary positions could find their jobs threatened by a push to offshore jobs as a way to grow the world’s economy. Even if employment opportunities remained for domestic workers, the threat of outsourcing could be used as a negotiating tool to drive wages downward in the developed world. Some households would be forced to have their standard of living go down to help others see their own begin to rise. That outcome could end up creating more harm for the economy than good because there would be less spending power available.
5. There is also the chance that globalization would only help the wealthy. The people who have the power today are the ones who will drive the emphasis for globalization to become a reality. They are the individuals who will create policies, legislation, and frameworks that will bring the world closer together. There is one trait that most people who are in power share with each other: they wish to maintain it at any cost.
The natural mechanisms of globalization are to rise the living standards of the poor by redistributing some of the wealth earned by the rich. That process could be manipulated by those in charge to benefit only their nations or communities instead. This issue could even make it more challenging to find meaningful employment.
6. It could create health issues for human populations. Imagine a world anyone can travel at any time to whatever location they choose. The lack of borders would certainly promote a level of freedom in our world that we have arguably never seen before in history. It could also create problems with disease transfers that could impact an entire society. It only took one person visiting from overseas with an active measles infection to cause an outbreak in Washington State and Oregon in the unvaccinated population. History shows us that when people come to new environments, they can give and receive diseases rapidly. Globalization would make it a lot easier for regional illnesses to become global epidemics unless there are controls put in place.
7. Globalization could reduce the availability of social protection programs. When we talk about a reduction in borders, then there is a natural reduction in the potential for social safety net programs that would exist as well. Many of these supportive services are available in the developed world as a way to subsidize families so that they can get back on their feet. They do not always exist in the developing world where income levels may be less than $100 per month for workers. If we move toward a place of equality, then there are two options: provide more benefits to the developing world or cut those that are in the developed countries. Which option do you think would win out?
These globalization pros and cons give us hope because it pictures a world where we can all live in peace, striving toward goals that are mutually beneficial to everyone. There will always be conflict and issues with resource management that we must consider as the world continues to grow closer together. Even if we never eliminate borders entirely, the freedom that we experience with this process will always be tempered with risk unless we are proactive about controlling the adverse potential outcomes.

On The Site

The Pros and Cons of Globalization
November 14, 2016 | yalepress | Current Affairs , Philosophy
Peter Singer—
Consider two aspects of globalization: first, the ability of people living in Afghanistan, Iraq, or Yemen to bring sudden death and terror to New York, London, Madrid, Paris, and Sydney; and second, the emission of greenhouse gases from power stations, vehicles, and even cattle. The former leaves unforgettable images that are watched on television screens all over the world; the other causes changes to the climate of our planet in ways that can be detected only by scientific instruments. Yet both are indications of the way in which we are now one world, and the more subtle changes to which our vehicle exhausts contribute are already killing far more people than the highly visible deeds of terrorists.
Over the decades since the 1980s, as scientists piled up the evidence that continuing greenhouse gas emissions will imperil hundreds of millions, perhaps billions, of lives, state leaders struggled to agree on a plan for making sufficient cuts in those to prevent world emissions to prevent a serious risk of climate becoming catastrophic, although such a plan would clearly be in the interests of the world as a whole. As we shall see later in this book, even the agreement reached in Paris in 2015 does not do enough.
The lack of the necessary global perspective was never better illustrated than by George W. Bush. As president of the United States, the country that has, by its emissions over the past century, done more than any other to make climate change a problem, he said, “We will not do anything that harms our economy, because first things first are the people who live in America.”
That remark was not an aberration but an expression of an ethical view that too many political leaders take for granted. His father, the first President George Bush, had said much the same thing at the 1992 Earth Summit in Rio de Janeiro. When representatives of developing countries asked the president to put on the agenda the over-consumption of resources by the developed countries, especially the United States, George H. W. Bush said, “The American lifestyle is not up for negotiation.” It was not negotiable, apparently, even if maintaining this lifestyle will lead to the deaths of millions of people subject to increasingly unpredictable weather and the loss of land used by tens of millions more people because of rising ocean levels and local flooding.
But it is not only the two Bush administrations that put the interests of Americans first. In the early 1990s, in the context of the debate over whether to intervene in Bosnia to stop Serb “ethnic cleansing” operations directed against Bosnian Muslims, Colin Powell, then chairman of the Joint Chiefs of Staff under President Bill Clinton, quoted with approval Otto von Bismarck’s remark that all the Balkans were not worth the bones of a single one of his soldiers. Bismarck, however, was not thinking of intervening in the Balkans to stop crimes against humanity. As chancellor of Imperial Germany, he assumed that his country followed its national interest. To use his remark as an argument against humanitarian intervention was to return to nineteenth century power politics, ignoring both the bloody wars that style of politics brought about in the first half of the twentieth century and the efforts in the second half of the twentieth century to find a better foundation for peace and the prevention of crimes against humanity.
In Kosovo, though the Clinton administration’s policy of giving absolute priority to American lives did not prevent intervention to defend the Kosovars, it led to the restriction of intervention to aerial bombardment. Th is strategy was a total success: NATO forces suffered not a single casualty in combat. Approximately 300 Kosovar, 209 Serb, and three Chinese civilians were killed. President Barack Obama used a similar “air power only” strategy against the Islamic State, or ISIS, after 2014, when it was threatening to overrun Iraq. Again, this strategy avoids American casualties, but, as Ivan Eland pointed out, “If the U.S. uses only air power, ISIS will eventually hide in the cities and the U.S. will be faced with causing a lot of civilian casualties to get the group out or kill its fighters.”
Observing the American reliance on air-power to protect the people of Kosovo, Timothy Garton Ash wrote, “It is a perverted moral code that will allow a million innocent civilians of another race to be made destitute because you are not prepared to risk the life of a single professional soldier of your own.” Th is does not mean that putting “boots on the ground” is always a good thing to do: the American invasion of Iraq in 2003 brought about the regional chaos in which ISIS has thrived. It also, according to an estimate by researchers at Johns Hopkins University, caused 654,000 more Iraqi deaths than would have been expected under prewar conditions. Nevertheless, Ash’s comment raises a fundamental ethical issue: to what extent should political leaders see their role as limited to promoting the interests of their citizens, and to what extent should they be concerned with the welfare of people everywhere?
As Ash suggests, there is a strong ethical case for saying that it is wrong for leaders to give absolute priority to the interests of their own citizens. The value of the life of an innocent human being does not vary according to nationality. But, it might be said, the abstract ethical idea that all humans are entitled to equal consideration cannot govern the duties of a political leader. Just as parents are expected to provide for the interests of their children rather than for the interests of strangers, so too anyone accepting the office of president of the United States takes on a specific role that makes it his or her duty to protect and further the interests of Americans. Other countries have their leaders, with similar roles in respect of the interests of their fellow citizens. Th ere is no world government, and as long as that situation prevails, we must have sovereign states, and the leaders of those states must give preference to the interests of their citizens. Otherwise, unless electors were suddenly to turn into altruists of a kind never before seen on a large scale, democracy could not function. American voters would not elect a president who gave no more weight to their interests than he or she gave to the interests of Iraqis or Afghans. Our leaders feel they must give some degree of priority to the interests of their own citizens, and they are, so this argument runs, right to do so.
From One World Now by Peter Singer . Reproduced by permission.
Peter Singer has been called the world’s most influential philosopher. His Animal Liberation is widely credited with launching the animal rights movement. Singer is professor of bioethics at Princeton University and laureate professor at the University of Melbourne. He lives in New York City.
Further reading:

Recent Posts

- Ep. 133 – The Search for a Forgotten Architect
- Making the World at Home
- Helen Ziska: The Unknown Artist Who Kept the March of Progress Image Alive
- Navigating A Saltier Future
- Finding Hope Among the Fragments
- Marcus Aurelius and How to Cope with Anxiety
Sign up for updates on new releases and special offers
Newsletter signup, shipping location.
Our website offers shipping to the United States and Canada only. For customers in other countries:
Mexico and South America: Contact TriLiteral to place your order. All Others: Visit our Yale University Press London website to place your order.
Shipping Updated
Learn more about Schreiben lernen, 2nd Edition, available now.

18 Huge Globalization Pros and Cons
Thanks to several centuries of technological process improvements, advances in cooperation throughout the international community, and improvements to communication infrastructures, our planet is more connected today than ever before. The rise of globalization has helped companies to become bigger than they were during the early days of the Industrial Revolution. It has also caused a growing interdependence in the developed world that links our economies, populations, and cultures.
The international agreements that have led to our current state of globalization were formed during the early 1990s after the Cold War between the United States and the Soviet Union dissipated. Now there are more trade opportunities and investment flows in the world’s most advanced economies that are beneficial, complex, and sometimes politically charged.
Before we can examine the pros and cons of globalization, we must understand the relative costs and benefits that exist which could help or hurt the average consumer. Americans are especially vulnerable to this process because they rely on global production, imports, and export opportunities to maintain a living wage. Without this coordination, the U.S. economy would not exist as it does.
List of the Pros of Globalization
1. Globalization brings the advanced economies of the world together. Globalization provides an opportunity for the most significant economies and countries in the world today to work together to accomplish big things. Whether we are building space stations that orbit our planet, sending missions to the moon, or developing ways to counter hunger that every family can afford, this process frequently tries to make the world become a better place. The price on these massive efforts are often too high for one country to manage by itself. Through the spirit of cooperation, humanity can use its strength of diversity to tackle any problem.
Did you know that more than $1 trillion is spent each year by the nations of the world to defend themselves against attack? The United Nations estimates that it would take just $30 billion per year to solve the infrastructure problems that encourage hunger. Imagine what else we could do with those funds.
2. It stabilizes the politics of the world. Even though there is a wave of populism and elitism growing around the world in 2019, the processes of globalization still encourage more cooperation than isolation. Economies do not grow as efficiently when they are isolated from one another as they do when they work together. That means there is always a certain level of import-export opportunities that are available because there is no other way to maintain the quality of life.
The best example of this advantage right now is to compare the growth of South Korea compared to what North Korea experiences. The isolation of the north creates fewer opportunities to develop, which means only the elite are able to find success.
3. Globalization gives more power to the people. Before we had tools like the Internet available to us that provide access to e-commerce platforms, governments worked to consolidate power into a small group of people or a single individual because it was the best way to negotiate on a nation-to-nation basis. That worked fine if there were structures in place to protect the general population, but it also caused significant harm to many communities – especially people of Jewish descent.
By moving toward a greater spirit of cooperation with open communication, there is less of a need to consolidate ruling powers. We can use systems of checks and balances to ensure that the power stays with the people, reducing the problems that come when someone holds absolute power.
4. It improves the flow of cash around the world. When countries maintain their borders more than they focus on the spirit of globalization, then money is the next highest priority after power. That led to the creation of tax havens in certain countries where businesses and wealthy individuals could avoid their payment responsibilities to their local government. That is no longer possible when nations begin working together under a specific set of rules, reducing cross-border differences that help one state over another.
Even with the effort to globalize today, Gabriel Zucman of the University of California-Berkeley estimates that about $8.7 trillion is currently stuck in tax havens around the world. That means the world governments are losing $170 billion in tax revenues, with over $30 billion per year owed to the United States.
5. Globalization reduces the issues of currency manipulation. When the Eurozone was created to support the progress of the European Union and build a cooperative market, one of the reasons behind this effort was to reduce the influence of currency manipulation in the import-export market. Instead of competing with one another for the cheapest prices, sometimes even devaluing the value of the economy to create a better contract, working together creates mutually beneficial results because all of the governments can take advantage of an economy of scale.
That means consumers can receive more value for their wages with a consistent expectation of worth. Although political changes, like those that occurred in Venezuela, can counter this unique benefit of globalization, it does give individuals and organizations more confidence in what to expect with each transaction.
6. It creates more consistency with our communication networks. There will always be differences of opinion when you look at the bulk of humanity. We all have unique experiences, perspectives, and opinions that guide us toward what we think the best path forward should be. Some of these conversations are passionate, but our access to communication tools keeps us all focused on words during a disagreement instead of taking an alternative action.
When we have access to transparent tools that allow us all to see each side of a conversation, it is much easier to find some common ground. Globalization provides us with more consistency in our communications access because more of us can share how we think and feel in any given situation. With more voices, there is a higher level of diversity. That structure eventually brings us to a position of strength.
7. It encourages the advanced economies of the world to develop even faster. About 75% of the world is still classified as being in “developing” status. The remainder of the countries are in an advanced stage with their economy. Thanks to the efforts at globalization, these upper-level economies can continue pressing forward toward growth, working with each other to meet the mature needs of these markets while helping developing nations continue toward their own advanced status.
A reduction in border restrictions helps to reduce tariffs, create common payment methods, improve agricultural production, and create open markets. There would be more opportunities to establish a new way of life for struggling families, which reduces poverty and food insecurity. This work even improves medical care access.
8. Globalization allows for more free trade opportunities. When we focus on the national borders that exist in our world, then we create restrictions on the free access to goods or services. Duties and tariffs, even when they exist between allies, limit the number of import opportunities which exist. Even if excessive fees apply to luxury goods only, it creates more of a black market that encourages consumers to avoid the regulations that prevent them from accessing what they want at an affordable price.
There are more than 1,500 different restrictions in place right now that impact global trade. An additional 1,800 tariffs are in place as well. Globalization allows us to spend our resources on what we need instead of trying to enforce specific rules that we create for ourselves.
9. It creates more employment opportunities for the average person. Over the next generation, the number of freelancers and self-employed individuals is expected to increase to over 50% of the overall labor force. About one-third of workers are already earning an income outside of the traditional employment contract. When we reduce restrictions to access for these entrepreneurs, then it adds another level of value to the overall economy.
Although there could be skill-based shortages in some industries that occur because of globalization, especially with offshoring issues that may occur, this advantage makes it possible for anyone with a good idea, a special talent, or a useful skill to build a life for themselves.
List of the Cons of Globalization
1. The process of globalization reduces the need for labor exploitation. Human trafficking is a significant problem in the developing world, but it is an issue that impacts consumers in advanced economies as well. The easiest way to keep prices low for consumers in the United States, Canada, Europe, and Japan is to exploit the differences in the standard of living that exist between the developing and developed world. Because labor is the most significant expense that the average customer pays, a globalized company can take advantage of lower minimum wages to produce items for sale.
The federal minimum wage for the United States in 2019 is $7.25 per hour. If you were to provide the same labor in Sierra Leone, then it would be just $0.03 per hour. When you multiply that expense by thousands of workers, globalization encourages a transition of employment from advanced economies to developing ones.
2. Globalization creates more offshoring from the advanced economies. The advanced economies of the world have the highest labor costs, highest manufacturing costs, and the highest distribution costs unless there are specific government interventions that prevent them from increasing. China is one example of such an economy that keeps costs low by reducing free-market opportunities for consumers.
The threat of offshoring is a threat that enforces specific employment behaviors in the advanced economies that reduce wages and benefits. If we were to reduce borders and improve living conditions around the world, the developing world would see a rise in their standard of living. In the advanced economies, there would be the risk of reducing the financial strength of the average household.
3. It can impact the environment in negative ways. Pollution is one of the most common causes of death in the world today. Globalization still encourages the advanced economies of the world to exploit the raw materials in developing nations because this structure transfers a small amount of wealth from one to the other. Since there are usually fewer environmental restrictions in this type of transaction, there can be long-term issues of contamination to manage.
Even the advanced economies on our planet struggle with pollution. Over 200,000 Americans die each year as a direct result of this problem. Millions more perish throughout the undeveloped world. Unless more regulations can control this process, globalization is rarely an eco-friendly process.
4. Globalization would change the definition of humanity. The structure of humanity creates unique identifications that help us to figure out who we are. It is a process that goes back to the very beginning of our recorded history. We identify ourselves based on our family history, where we live, and what we do. When we focus on globalization, then our world becomes a smaller place where there are fewer cultures and ethnicities.
We already see this problem occur when families immigrate from one country to another. Even households that move across a border like one between the U.S. and Canada can experience unique changes that cause a reduction in the emphasis of their culture. All of us being human is arguably a good thing, but it also changes the approach we take to culture.
5. It does not create more access to skill. Although there are more job opportunities in the developing world because of globalization, it does not change the fact that an advanced economy requires individual workers with a specific skill set that may not be immediately available. Additional educational opportunities can reduce the influence of this disadvantage, but there could be a gap for more than a generation until this infrastructure can be put into place.
An example of this problem involves the developing technologies of artificial intelligence. Although anyone can learn coding, engineering, and design, the advanced economies of the world have more access to these learning tools. You’ll find more opportunities in this field in Europe or the U.S. compared to countries like Sierra Leone or the DRC. That means the wealthy still have more chances to find more money while the poor struggle to find a path out of poverty.
6. Globalization would centralize distribution networks. Even with an emphasis on infrastructure building in the developing world, we are still several decades away from having some countries match what Europe, North America, or Oceania can provide to consumers already. That means an effort to go borderless must use centralized distribution networks to ensure product access is available to everyone.
The only problem with this structure is that it creates more inefficiencies. We are already losing hundreds of thousands of tons of food every day because of waste that is built into the domestic systems. This issue would only get worse if there are more people to serve using the same processes that we currently use.
7. It would not change problems with over-consumption. The issue with the advanced economies of our world today is that they consume a vast majority if the world’s resources. The 20 wealthiest countries on our planet use 90% of what is available for consumption every day. Americans consume over 200 billion more calories per day more than is necessary for healthy living. One-quarter of the energy our planet produces is used by the United States, even though only 5% of the population lives in that country.
Unless there are structures in place to equalize this consumption issues, globalization won’t fix this disadvantage. One could even argue that the world will never come together unless people learn to share equal access. Since there are advanced economies which want to keep their status, asking them to sacrifice to help others may not provide the outcome we expect.
8. Globalization would create new political systems to navigate. When the European Union decided to come closer together in the spirit of cooperation, their treaty created a parliament that works to govern over all member nations. That structure doesn’t eliminate local governing structures, but it does require everyone to follow specific rules if they wish to continue with their participation. The EU leadership can dictate specific quotas and metrics to follow to continue receiving the benefits of this cooperative relationship as well.
Globalization would require a shift in our thinking that takes us away from nationalism. It would mean Americans would need to make the United Nations their top priority instead of their local elections for their overall governing needs. That shift is something which some cultures may be unable to accept.
9. It would reduce the availability of welfare programs and social safety nets. The advanced economies of the world provide a series of welfare programs that work to help poor families in their economy to have resource availability. Food stamps, cash stipends, housing allowances, and similar benefits would no longer be as available because the resources would shift toward those in the world who have even less. Someone in the United States receiving a standard welfare package still qualifies as being in the top 1% of global income earners.
This disadvantage would also shift how local economies in the developed world would balance their expenses. With fewer government benefits coming through local stores, there is a strong chance that a recession would occur that would be equal to or greater than what the world experienced in 2007.
Verdict on the Pros and Cons of Globalization
Globalization gives us all an opportunity to live, work, and communicate in ways that bring all of us closer together. This structure gives everyone an opportunity to create a world for themselves where any dream becomes possible. It can improve the safety of the workplace, encourage innovation, and give us more access to the goods and services that we need. It is a process that provides more competition than what border enforcement creates.
When we reduce the restrictions that are in place between nations, then we can also create more security issues that require more intelligence and communication to solve. Individuals with ill intent can move with greater freedom in a globalized world.
That’s why the pros and cons of globalization are critical to review. It can put us on a path toward economic freedom, but this structure can also encourage the rich to get wealthier at the expense of the poor.

Examining Some of the Pros and Cons of Globalization
By Matthew Mausner and Yonatan Neril
Our world has become much “smaller” and more interconnected in just the last generation. The rise and acceleration of globalization has ushered in vast increases in global migration, trade and communication—including negative effects on our environment and cultures.
To put the broad topic of globalization in context, we will consider some of the pros and cons, as well as perspectives about human rights, values, and interfaith sustainability that may help you decide for yourself how you feel about globalization.
A Brief History of Globalization
Since the Cold War ended in 1991, the world has become intertwined in terms of shared commerce, international shipping and airplane travel, and a worldwide communication web, together called “globalization.”
This is qualitatively different from previous eras when the world also “shrank” in significant ways, like the 1500s when different countries in Europe spread a lifestyle, religion, conquest and diseases to the Americas, and American foods, tobacco, gold and silver were transported from the Americas to Europeans, Asians, and Africans.
Since 1980, global trade increased tenfold to about $20 trillion per year, yet in comparison the world population has less than doubled .
Today, the immediacy and enormity of the internet, the scale of giant cargo ships—many loaded with 20,000 large containers—carrying factory goods from China to Europe and the US—and many other factors make us more aware than ever of our interconnectedness on one small shared planet.

Pros and Cons of Globalization
Some of the ‘pros’ are so good that we perhaps take them for granted.
For example, since 1991, a tremendous increase in economic growth has raised material standards of living for the world’s poor. With the spread of information, goods and services, billions of people moved from Third World poverty into the world middle class, in places like China, India, and much of South America and sub-Saharan Africa. Some of the world’s worst diseases are now near eradication.
Clean water, basic infrastructure and sanitation are available to a majority of people in the world. Education, literacy and health care have spread. Trade and travel to almost every corner of the earth is safer. Due to expanded international trade , the foods people eat have become much more diverse.
What are the detriments of globalization?
We have seen free trade lead to unfair trade agreements, that let corporations from developed countries exploit resources in poorer regions without regard to local environmental impact. These multinational corporations promote materialism and ever-increasing demand.
Based on “economies of scale,” many products a country buys end up being created in other countries, at a cheaper cost than domestically produced goods. But the cost of “cheaper” production may ignore things like the dignity of workers and the depletion of natural resources in the producing countries.
Cultural diversity and biodiversity are both being swamped by our global civilization. At least 43% of the estimated 6,000 languages spoken in the world are endangered, according to UNESCO.
The variety of life on earth is suffering perhaps irreparably, especially in the shrinking tropical forests and acidifying coral reefs that contain the lion’s share of the different species on earth.
Human pollution in all of its impacts, including plastic in the oceans , carbon in the atmosphere, toxic chemicals in the soils, and even nuclear waste, may render our ecosystems inhospitable to life as we know it far more quickly than we understand.
These disadvantages of globalization just might be overtaking the pros, and if the benefits of globalization are not sustainable, they will disappear, leaving only the negative impacts.
Without globalization, do nature and human society look different?
One can argue that the pros of globalization still outweigh the cons. A vivid example of the contradiction: next to North Korea, one of earth’s most isolated, nonglobalized societies, is one of the most vibrant and biodiverse ecological preserves on earth.
The Demilitarized Zone (DMZ) border with South Korea, a “frozen” relic of the Korean War 70 years ago, has become a green oasis, a stopping point for countless bird migrations, and one of the few places on the planet that humans mostly leave untouched.
Yet the context for that preservation has been North Korea cutting itself off from the world, creating a deeply impoverished society with frequent famines and starvation.
Can globalization bring more good than bad?
There are some arguments that global prosperity itself is the engine to bring more good than bad. Many of the worst environmental impacts, from strip mining to overfishing, result from people making economic decisions driven by scarcity, desperation, or ruthless profit-seeking.
When people are less pressed by survival needs to make the most extreme short-term decisions—and when they and their enterprises are more intertwined in a global system that incentivizes not just economic growth but sustainability—globalization makes our long term survival more feasible.
Natural Capitalism and Globalization
A globalization driven by what Pawl Hawken, Amory Lovins and Hunter Lovins called ‘Natural Capitalism ‘ will relate differently to nature than the global economy led by multinational corporations that has taken place in the past 30 years.
Natural Capitalism critiques “Industrial Capitalism”, saying that the traditional system of capitalism does not “value or appreciate ‘natural capital’– the natural resources and living systems, as well as the social and cultural systems that are the basis of human capital.”
By not valuing them, industrial capitalism extracts and degrades them.
Isn’t globalization unstoppable?
Whether we say globalization is a net positive or negative, the question is no longer whether globalization will continue, but how.
Larger developing economies like China’s have shifted from protectionist to embracing free trade. China has also invested hundreds of billions of dollars in other countries as part of its Belt and Road Initiative. In 2020, for the first time, the majority of Chinese energy investment in this Initiative went to renewable energy projects.
Can trade and investment be inspired, guided, and led in environmentally sustainable directions? Will holistic and faith-based values have enough influence, to ensure we hold to a path of healthy and livable sustainability, instead of destruction?
Faith Wisdom and Globalization
In the book Spiritual Perspectives on Globalization , Ira Rifkin writes, “On an individual level, globalization is about the promotion of consumer values that feed on the perception that happiness is rooted in material progress, that choice equals the highest freedom, and that being well connected is more important than being deeply connected.”
Religious traditions hold and have potential to offer profound wisdom to make globalization more ecologically sustainable . Some clergy, like Rabbi Micha Odenheimer, have written faith-based perspectives on globalization based on his work in countries like Burundi and Nepal.
Most clergy do not yet teach and preach about sustainability, or receive training on how to do so as part of their religious training. To actively help steer us onto a more sustainable path, people of faith can ask their clergy to engage in teaching on how a globalized humanity can live sustainably.
Since 2010, The Interfaith Center for Sustainable Development (ICSD) has organized over twelve conferences on religion and ecology , specifically engaging clergy and the institutions that train emerging clergy. ICSD’s Faith Inspired Renewable Energy Project works in Africa to deploy commercial-scale solar fields on church lands.
While the overwhelming majority (86%) of the world’s people identify to some degree as religious, the values of religion have not yet been sufficiently integrated into our rapidly changing patterns of technology and international trade. Therefore religion is one of our biggest untapped resources for positive change.
* Featured image source

Leave a Reply Cancel reply
Your email address will not be published. Required fields are marked *
Save my name, email, and website in this browser for the next time I comment.
- UPSC History Notes
- UPSC Geography Notes
- UPSC Polity Notes
- UPSC Ethics Notes
- UPSC Economics Notes
- UPSC Science and Technology Notes
- UPSC Govt. Schemes Notes
- UPSC eligibility-criteria
- UPSC Syllabus
- UPSC Exam Pattern
- UPSC Admit Card
- UPSC Optional Subject
- UPSC Prelims Syllabus
- UPSC Main Exam Pattern
- UPSC prelims-2024-exam-pattern
- Social Entrepreneurship in India
- Special Economic Zone (SEZ)
- Social Media Accountability
- Government Securities Acquisition Program (G-SAP)
- Eastern Economic Forum
- Twin Balance Sheet Problem
- Public Provident Fund
- National Family Health Survey-5
- Monoculture Plantation
- What Is Gross National Income (GNI)? Definition and Examples
- Top 10 Most Traded Currencies In The World 2024
- Achievement of Ayushman Bharat
- RBI - Digital Payments Index
- Feminization Of Agriculture
- Role of Supermarkets in the Supply Chain Management
- Industrial Corridors in India
- Educated Unemployed - A Peculiar Problem of India
- Unified Payments Interface (UPI) and its Challenges
- What Is a Good Credit Score?
Pros and Cons of Globalization
Pros and Cons of Globalization: Globalization is a system of interaction between countries throughout the world aimed at developing the global economy. Globalization refers to the worldwide interconnectedness of economies and societies. Advances in communication, transportation, and infrastructure enable technological, economic, political, and cultural exchanges, resulting in globalization.
Since the 1980s, when computer technology initially made it easier and faster to do international business, the phrase has been used with this meaning. The key aspects of this integration are international trade and cross-border investment flows. As a result, globalization is an amalgamation of interaction and integration among distinct groups of people, organizations, and governments from other countries.
In this article, we will provide the advantages and disadvantages of Globalization in detail along with the impact of globalization on specific sectors like technology, economy, and culture.
Table of Content
What is Globalization?
Advantages / pros of globalization, disadvantages / cons of globalization, impact of globalization on various sectors.
Globalization refers to the increasing interdependence of countries, economies, cultures, and societies across the world. It is a complex phenomenon that involves the exchange of goods, services, information, technology, and ideas on a global scale.
Globalization is based on the comparative advantage hypothesis, which holds that countries that are good at producing a particular good are better off selling it to less efficient countries. In turn, the latter country can export the items it produces cost-effectively to the former, which may be lacking in the same. The basic concept is that not all countries are capable of manufacturing all types of goods, hence trading with one another is beneficial. Furthermore, due to wage disparities and the diverse ways that different countries are endowed with different resources, countries stand to benefit from trading with one another.
1. Globalization brings the world’s advanced economies closer
Globalization allows the world’s most powerful economies and governments to collaborate to achieve great things. This process frequently strives to make the world a better place, whether we are creating space stations that circle our globe, sending missions to the moon, or inventing affordable solutions to combat famine. The cost of these vast initiatives is frequently too high for a single country to bear alone. Humanity can use its diversity to solve any challenge if it works together in a cooperative spirit.
2. It helps to keep the world’s politics in check
Even if populism and elitism are on the rise around the world in 2021, globalization processes still foster more cooperation than isolation. When economies are isolated from one another, they do not grow as efficiently as when they collaborate. That is to say, there will always be some amount of import-export opportunities since there is no other way to sustain the standard of living.
3. People gain increased power as a result of globalization
Governments strove to centralize power into a small group of individuals or a single individual before we had tools like the Internet to enable access to e-commerce platforms because it was the best method to bargain on a nation-to-nation basis. That worked perfectly if there were structures in place to safeguard the broader public, but it also harmed many groups, particularly those of Jewish ancestry. There is less of a need to solidify dominating powers if we move toward a larger attitude of cooperation and open communication. We may employ checks and balances systems to ensure that power remains in the hands of the people, reducing the problems that arise when one person has absolute control.
4. Globalization opens up more opportunities for free trade
When we concentrate on the national borders that exist in our world, we limit unrestricted access to goods and services. Even when they exist between allies, duties, and tariffs limit the number of import opportunities available. Even if the high fees are solely applied to luxury goods, it encourages buyers to evade the rules that prevent them from getting what they want at a reasonable price. Currently, there are more than 1,500 different trade barriers in existence that have an impact on global trade. Globalization helps us to focus our energies on what we require rather than enforcing standards that we have devised for ourselves.
5. Currency manipulation is less of an issue as a result of globalization
One of the objectives for the Eurozone’s creation was to limit the power of currency manipulation in the import-export market to assist the European Union’s progress and build a cooperative market. Rather than fighting for the lowest pricing, and sometimes even depreciating the economy to achieve a better contract, working together produces mutually beneficial results because all governments may benefit from economies of scale.
6. Globalization facilitates the spread of information and technology
In a worldwide society, art and culture aren’t the only things that spread more easily, Information and technology are in the same boat. Consider the emergence of mobile banking in Kenya or the practice of microlending as examples. Civil society organizations can draw inspiration from other countries, and successful ideas can spread more quickly.
7. Earnings fluctuate
Wages for many workers in the originating nations have declined as more corporations take advantage of international outsourcing options. Companies in poor countries can offer their services at a considerably lower cost than those in countries with higher living standards. Thus, it created an impact on workers of the larger countries. When operating in less developed countries, businesses can take advantage of the opportunities provided by globalization by paying cheaper salaries and having reduced overheads. Other savings can be gained in countries with lower taxes, less red tape, and lower business costs.
1. Globalization Has the Potential to Promote Cultural Homogeneity
As people’s preferences converge and products can’t compete with cheaper multinational ones, globalization may lead to increasing cultural homogeneity. Near future, we may lose valuable cultural customs. Some critics of globalization believe due to this goods are becoming homogeneous and people will use the same kind of things from cars to food habits. Homogenization is something that is imposed on people by market forces and it treats people as a product. Due to this, the global tendency could not eliminate cultural diversity, and thus, it creates a popular monoculture.
2. Multinational Corporations Gain Power as a Result of Globalization
Globalization has also been criticized for empowering transnational businesses at the expense of governments and populations. This erodes state sovereignty and people’s ability to hold their leaders accountable for the state of their countries. Multinational firms may also use trade agreements to press for advantageous clauses.
3. Unbalanced Development
Globalization can result in unequal growth across and within countries. Economically and morally, these consequences must be properly managed. Globalization frequently has the consequence of boosting immigration within countries. In terms of macroeconomics, immigration boosts gross domestic product (GDP), which can be beneficial to the recipient country. However, if immigrants’ income is lower than the average income of people already in the country, immigration may cut GDP per capita in the near term. Furthermore, immigration, like competition, can benefit the country as a whole while imposing costs on people who may want their government to limit immigration to shield them from those costs.
4. Globalization has failed to protect workers, the environment, or human rights
Globalization has the potential to spread principles and practices like environmentalism and labor rights all over the world. In practice, though, the expansion has been slow and uneven. Instead of exporting labor regulations that a firm may be required to follow in the United States, it may choose to follow weaker standards in another country where labor is not protected. Some say that globalization has resulted in a “race to the bottom,” in which businesses actively seek out countries with the weakest labor and environmental safeguards, as well as the lowest pay. While globalization has enhanced the flow of products, services, and capital, there are still many tax havens, implying that governments are not capturing and redistributing much of the wealth gained by globalization.
5. Low-cost labor marketplaces are exploited
Globalization enables firms to expand employment and economic prospects in underdeveloped countries, where labor costs are frequently lower. However, these countries’ total economic growth may be modest or stagnant.
6. Cause of employment loss
Globalization creates more employment, but it redistributes them by shifting production from high-cost countries to low-cost countries. When a result of globalization, high-cost countries often lose jobs as production moves outside.
7. Concerns about the environment
Globalization has been related to several environmental issues, many of which are serious, such as:
- Economic specialization and infrastructure development have resulted in deforestation and ecological loss.
- Higher movement of commodities results in increased greenhouse gas emissions and other forms of pollution.
- Invasion of new environments by potentially invasive species
- While existing or prospective rules and regulations manage such issues, businesses have prioritized environmental concerns and sustainability.
The impact of globalization in specific sectors like technology, economy, and culture, environment etc. is given in detail below:

- Economic Sector: Globalization has led to a surge in international trade by removing barriers such as trade restrictions. This has facilitated the exchange of goods and services across borders. Companies can now invest in other countries more easily, leading to increased FDI. This brings capital, technology, and expertise to different regions.
- Technological Sector: Globalization has enabled the rapid flow of information and technology across borders. Advances in communication and the internet have connected people globally. Collaboration and competition on a global scale have accelerated technological innovation. Companies from different countries contribute to technological advancements.
- Cultural Sector: Globalization has facilitated the exchange of cultural ideas, values, and traditions. People around the world have greater access to diverse cultural influences through media, entertainment, and the arts. There are concerns about the loss of cultural diversity and the dominance of a few global cultures, leading to cultural homogenization in some areas.
- Environmental Sector: Globalization has contributed to environmental challenges such as climate change, deforestation, and pollution. Transboundary environmental problems require international cooperation for effective solutions. Globalization has led to the development of international agreements and standards to address environmental issues. Collaboration is necessary to enforce and comply with these regulations.
- Health Sector: The interconnectedness of countries has facilitated the spread of diseases globally. Pandemics like COVID-19 highlight the need for international cooperation in healthcare. Globalization has improved access to medicines and medical technologies, but it also poses challenges related to affordability and equity in healthcare.
- Social Sector: Globalization has facilitated the rise of global social movements advocating for human rights, environmental protection, and social justice. While globalization has contributed to economic growth, it has also been associated with increased income inequality within and between countries.
Related Articles: Impact of Globalization on India Effects of Globalisation on Indian Society Globalisation and the Indian Economy : CBSE Class 10 Advantages of Globalisation in India
Conclusion – Pros and Cons of Globalization
Financial markets, such as capital markets, money and credit markets, and insurance markets, as well as commodity markets, such as oil, coffee, tin, and gold markets, and product markets, are examples of markets where globalization is particularly prevalent. Globalization is a term that refers to the process of integrating national and regional economies, civilizations, and cultures via a worldwide network of trade, communication, immigration, and transportation. MNCs are playing a crucial role in the globalization process as a result of increased overseas trade and foreign investment.
India has reaped significant benefits from the (Liberalization, Privatization, and Globalization) LPG framework, with its GDP increasing by 9.7% in 2007-2008. India’s market capitalization is in fourth place. Despite globalization, agricultural production has remained stagnant. Agriculture accounts for 17% of total GDP. The United States has been the largest country for less than a century, with huge movements from the U.S. Since then, India and China have become two Asian nations. According to economic specialists and global research, India and China would be the driving forces in the twenty-first century. India, which is currently the world’s fourth greatest acquirer of power, will overtake Japan and become the world’s third-largest economy in ten years. Finally, the globalization transition affects our daily lives. Globalization has both beneficial and negative consequences on India’s development.
FAQs on Pros and Cons of Globalization
Please login to comment....
- How to Delete Whatsapp Business Account?
- Discord vs Zoom: Select The Efficienct One for Virtual Meetings?
- Otter AI vs Dragon Speech Recognition: Which is the best AI Transcription Tool?
- Google Messages To Let You Send Multiple Photos
- 30 OOPs Interview Questions and Answers (2024)
Improve your Coding Skills with Practice
What kind of Experience do you want to share?
- Bahasa Indonesia
- Español (España)
- Español (América Latina)
- Francais (Canada)
- View by list
- View by logo
AGM Factory
Alchemy Software Development
Astoria Software
Digital Reef
Lassostudios
LMK Clinical Research
Lylo Media Group
Propulse Video
Scheune München
Skilltelligence
Sterling Technology
Sublime Subtitling & Translation
TransPerfect Legal
Translations.com
TransPerfect Connect
TransPerfect Digital
TransPerfect Medical Device Solutions
Trial Interactive
Subtitling vs. Dubbing: Navigating the Pros and Cons in Media Localization

In today’s world, we are more globally interconnected than ever before. The demand for international content has skyrocketed, prompting the need for effective media localization. Among the key considerations in this process are the methods of translation, or how your audience will digest your media content, and whether subtitling, dubbing, or both are necessary. Both techniques aim to break language barriers, but each comes with its own set of pros and cons. Let’s explore the intricacies of subtitling and dubbing, delving into the advantages and disadvantages of each to help you make an informed decision for your media localization strategy.
Subtitling: Pros and Cons
1. Preservation of Original Voice and Intention:
Subtitling maintains the authenticity of the original audio by preserving the original voices of the actors. This helps in conveying the nuances of emotions, tone, and cultural aspects as intended by the filmmakers or content creators.
2. Cost-Effectiveness:
Subtitling is generally more budget-friendly compared to dubbing as the process just involves translating the script and syncing it with the original audio. At times, transcreation is needed (adapting vocabulary to a specific region or country), but with subtitles, adaptations can be swapped faster than dubbing, which requires re-recording voices.
3. Accessibility:
Subtitles can allow viewers from around the world to experience a piece of content through translated text. They can also be formatted to provide descriptions of other sounds in addition to translated dialog for the deaf and hard of hearing.
1. Multitasking for Viewers:
Subtitles require viewers to read while watching, which can be challenging for some audiences and certain types of content. This can result in missed visual elements or nuances in the performances as viewers split their attention between reading and watching.
2. Barriers to Understanding
While subtitles break the language barrier to a certain extent, they may still pose a challenge for those who struggle with reading or have visual impairments, limiting accessibility for a broader audience. There are specific types of subtitles or captions that can help enhance accessibility for viewers.
3. Space Constraints:
Subtitles often have limited space on the screen, making it challenging to convey longer sentences or complex dialogue effectively. This can lead to condensed translations that may not fully capture the original meaning.
Dubbing: Pros and Cons
1. Seamless Viewing Experience:
Dubbing provides a seamless viewing experience as viewers can focus solely on the visuals without the distraction of reading subtitles. This is especially beneficial for action-packed scenes where reading may cause a disconnect.
2. Enhanced Accessibility:
Dubbing caters to a broader audience, including those who may struggle with reading or have visual impairments. Delivering content in a viewer's spoken native language eliminates barriers to understanding more effectively.
3. Cultural Adaptation and Tone:
Dubbing allows for cultural adaptation by incorporating regional accents, colloquialisms, and references, enhancing the relatability of the content for diverse audiences around the world.
1. Loss of Original Voice:
Dubbing involves replacing the original voices with those of local actors. This can lead to a loss of the original voice performances and, at times, alter the emotional impact intended by the filmmakers. For example, a large portion of Tom Cruise’s films have had the same voice actors since the eighties to keep consistency, but not all talents may be available for each project.
2. Synchronization Challenges:
Achieving perfect synchronization between the dubbed voices and the lip movements of the actors can be a complex task. Poor synchronization and bad translation can result in a disjointed viewing experience, as we’ve seen with popular foreign series in the past few years.
3. Higher Production Costs:
Depending on the technology available, dubbing can require additional resources, such as hiring voice actors, sound engineers, and translators. Technology such as cloud-based recording management tools can help reduce the overall cost significantly but still outweighs the cost of subtitling.
In the ongoing debate between subtitling and dubbing, there is no one-size-fits-all solution. The choice between the two depends on various factors, including the target audience, budget constraints, and the desired level of authenticity. Subtitling maintains the original voice and intention but may pose challenges for some viewers, while dubbing offers a seamless experience at a higher cost and the potential loss of the original voice performances.
Ultimately, the key is to strike a balance that aligns with the goals of media localization and the preferences of the target audience. As the global appetite for diverse content continues to grow, the evolution of subtitling and dubbing techniques will likely play a crucial role in bridging linguistic gaps and fostering cross-cultural understanding in the realm of entertainment.
TransPerfect Media’s teams are experts in advising per project on which tools are best for your content, the target audience, and cultural and technological factors. Learn more about our range of services and technologies to provide your next project with the global presence it deserves—with expert quality and competitive pricing. Learn more by emailing [email protected] or visiting www.transperfect.com/media .


IMAGES
VIDEO
COMMENTS
The Advantages of Globalization. 1. Increased Economic Growth. Globalization facilitates technology, knowledge, and goods transfer, which in turn boosts economic growth (Erixon, 2018). Through globalization, countries can now purchase the newest technologies and import the most productive machinery from other countries.
Globalization is the increased flow of goods, services, capital, people, and ideas across international boundaries according to the online course Global Business, taught by Harvard Business School Professor Forest Reinhardt. "We live in an age of globalization," Reinhardt says in Global Business. "That is, national economies are even more ...
Globalization with free trade increases competition as well, which means innovation must be part of the equation. Consumers benefit from that innovation with lower pricing, which means more products can be purchased, and that can stimulate further growth. 3. It eliminates currency manipulation.
The advantages of globalization are actually much like the advantages of technological improvement. They have very similar effects: they raise output in countries, raise productivity, create more jobs, raise wages, and lower prices of products in the world economy. What might be the advantages of globalization that someone would feel in their ...
Cons of globalization include: Unequal economic growth. While globalization tends to increase economic growth for many countries, the growth isn't equal—richer countries often benefit more than developing countries. Lack of local businesses. The policies permitting globalization tend to advantage companies that have the resources and ...
22 Pros and Cons of Globalization. John Spacey, May 20, 2021. Globalization is the process whereby nations become increasingly interconnected. This includes elements such as cooperation, trade, infrastructure, communication, knowledge transfer, culture, education, travel and migration whereby nations move from being isolated to a state of high ...
List of the Advantages of Globalization. 1. Globalization allows us to pool all our resources together. One of the best examples of globalization within our lifetime is the construction of the International Space Station. The cost to construct the ISS was $150 billion. Compared to the Mir station at $4.2 billion, the price tag is astronomical.
globalization, integration of the world's economies, politics, and cultures.German-born American economist Theodore Levitt has been credited with having coined the term globalization in a 1983 article titled "The Globalization of Markets." The phenomenon is widely considered to have begun in the 19th century following the advent of the Industrial Revolution, but some scholars date it ...
Before we get into the potential drawbacks and challenges of globalization, let's take a moment to focus on some of the benefits its producing on a global scale. 1. Access to a Wider Customer Base. From a business standpoint, one of the most obvious benefits of globalization is access to customers all over the world.
Globalization refers to the tendency of international trade, investments, information technology and outsourced manufacturing to weave the economies of diverse countries together. In business and ...
Improved Global Cooperation. 6. Exploitation of Labor. 7. Enhanced Communication Channels. 7. Threat to National Sovereignty. Conclusion on Pros and Cons of Globalization. The term globalization encompasses various aspects, including economic, political, cultural, and social integration.
The Pros of Globalization. A number of positive aspects of globalization include: Building up the economic and social structures of struggling countries and economies through free trade; Creation of world power and less and less compartmentalized power sectors; Learning about and sharing of new and interesting cultures with one another
3. Globalization Increases Cultural Awareness. Globalization's defenders say it has increased cross-cultural understanding and sharing. A globalized society boosts the rate at which people are exposed to the culture, attitudes and values of people in other countries.
12. Most people see speedy travel, mass communications and quick dissemination of information through the Internet as benefits of globalization. True. 13. Labor can move from country to country to ...
Global trade in online services and goods is booming, despite globalization being under fire in many nations. Brexit, COVID-19, Trump's trade war with China, and the war in Ukraine, have left many wondering if we're entering a phase of deglobalization - a world destined to become less connected, with countries looking inwards instead of outwards.
List of the Pros of Globalization. 1. Globalization helps the world to focus on progress. ... These globalization pros and cons give us hope because it pictures a world where we can all live in peace, striving toward goals that are mutually beneficial to everyone. There will always be conflict and issues with resource management that we must ...
Peter Singer has been called the world's most influential philosopher.His Animal Liberation is widely credited with launching the animal rights movement.Singer is professor of bioethics at Princeton University and laureate professor at the University of Melbourne. He lives in New York City.
List of the Cons of Globalization 1. The process of globalization reduces the need for labor exploitation. Human trafficking is a significant problem in the developing world, but it is an issue that impacts consumers in advanced economies as well. ... Verdict on the Pros and Cons of Globalization Globalization gives us all an opportunity to ...
This article will explore the pros and cons of globalization, providing readers with valuable insights to make informed decisions. The Pros of Globalization 1. Economic Growth and Prosperity.
Pros and Cons of Globalization. Some of the 'pros' are so good that we perhaps take them for granted. For example, since 1991, a tremendous increase in economic growth has raised material standards of living for the world's poor.With the spread of information, goods and services, billions of people moved from Third World poverty into the world middle class, in places like China, India ...
glocalization. cultural globalization, phenomenon by which the experience of everyday life, as influenced by the diffusion of commodities and ideas, reflects a standardization of cultural expressions around the world. Propelled by the efficiency or appeal of wireless communications, electronic commerce, popular culture, and international travel ...
Pros and Cons of Globalization: Globalization is a system of interaction between countries throughout the world aimed at developing the global economy. Globalization refers to the worldwide interconnectedness of economies and societies. Advances in communication, transportation, and infrastructure enable technological, economic, political, and cultural exchanges, resulting in globalization.
Pros: 1. Preservation of Original Voice and Intention: Subtitling maintains the authenticity of the original audio by preserving the original voices of the actors. This helps in conveying the nuances of emotions, tone, and cultural aspects as intended by the filmmakers or content creators. 2.
New York CNN —. Listing your home in the spring used to be a no-brainer. But a major real estate shakeup is complicating the equation. That shakeup is coming from a $418 million settlement the ...
The U.S. Department of Energy reports a tankless water heater is 24% to 34% more energy-efficient than storage tank water heaters—as long as you use around 41 gallons per day. However, even if ...