

What are Definite, Indefinite Articles? Definition, Examples of English Articles
Home » The Writer’s Dictionary » What are Definite, Indefinite Articles? Definition, Examples of English Articles
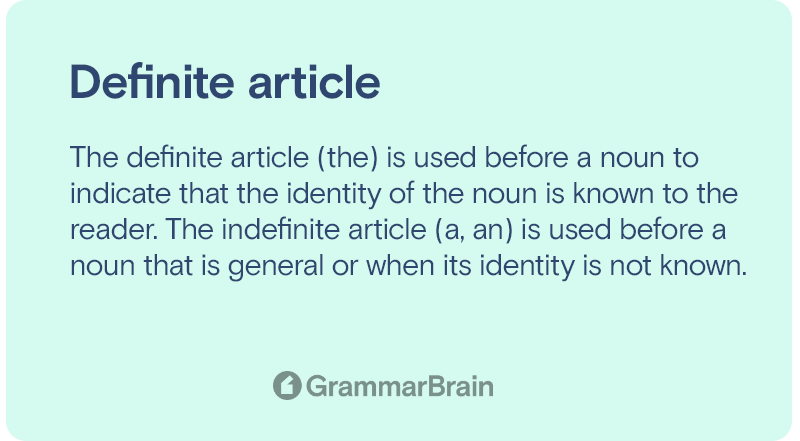
Definite and indefinite articles are parts of speech referring to the terms “the,” “a,” and “an.”
Definite articles definition: a determiner (the) that introduces specific nouns and noun phrases.
Indefinite articles definition: a determiner (a, an) that introduces nonspecific nouns and noun phrases.
What is an Article?
What is a definite article? A definite article is a part of speech that identifies a specific noun . “The” is the only definite article.
Placing “the” before a noun makes it specific. In order to say “the book,” the audience has to know to what book you are referring.
What is an indefinite article? An indefinite article is a part of speech that identifies a nonspecific noun. “A” and “an” are the only indefinite articles.
Placing “a” or “an” before a noun makes it nonspecific. To say “a book” refers to any book, not a single specific book.

- a cow (nonspecific—could be any cow)
- the cow (specific—referring to a particular cow)
- an animal (nonspecific—could be any animal)
- the animal (specific—referring to a particular animal)
Two Types of Articles: Definite and Indefinite Articles
The definite article.
The definite article is “the.” “The” refers to a particular noun that is understood. The audience is aware of the object of reference and no further identification is needed.

- the chair, the city, the manager
- the chairs, the cities, the managers
- the boxes, the towns, the women
- the food, the luggage, the electricity
The Indefinite Article
The indefinite article is “a” / “an” “A” and “an” refer to nonspecific nouns. The object of reference is not clear and further identification would be needed to know the exact object.
Indefinite Article Examples:
- a chair, a city, a manager
- plural—CANNOT BE USED
- a box, a town, a woman
- non-count—CANNOT BE USED
A vs. An: Remember A/An Depends on Sound
Which indefinite article to use (“a” or “an”), depends on the initial sound of the noun.

- A few days after Britain voted to leave the European Union, Monika Baginski was in a supermarket , chatting with a friend on the phone in her native Polish, when a man followed her down the aisle. – The New York Times
When to use An: If the initial sound of the noun when pronounced is a vowel sound, “an” is used.
- A catchy soundtrack used to be enough, but the 21st century needs an app to publicize shark activity near New England’s coasts. – The Christian Science Monitor
Exercises with Articles: Indefinite vs. Definite Articles
Select the appropriate article (a, an, the) and fill-in the blank below.
- Do you have ___ different table available?
- He was searching for ____ right word to describe the situation.
- This is ___ last time I will remind you to do your chores.
- Braxten brought ___ apricot, ___ sandwich, and ____ cookie for lunch.
- My mom demanded ____ explanation.
See answers below.
Articles and Proper Nouns

Use Articles With:
- the Smith Family, the Jones Family
- the United Kingdom, the United States, the Dominican Republic, the Philippines, the Canary Islands,
- the Rocky Mountains, the Amazon, the Atlantic Ocean
- the New York Times , the Red Cross, the Hyatt, the Capitol Building
Summary: What are Definite and Indefinite Articles in English?
Define definite article: The definition of a definite article is a determiner (the) used to identify a specific noun or noun phrase.
Define indefinite article: The definition of an indefinite article is a determiner (a, an) used to identify a nonspecific noun or noun phrase
In summary, articles can be definite or indefinite.
When to use the: Use a definite article (the) when the noun is a known entity.
When to use a, an: Use indefinite articles (a/an) when the noun is an unknown entity.
- To save this word, you'll need to log in. Log In
indefinite article
Definition of indefinite article
Did you know.
What are the definite and indefinite articles ?
The most common of all adjectives are the two (or three) articles . An article always comes before the noun it describes and before any other adjectives that also describe the noun. Articles are used to show whether or not the noun refers to a specific person or thing.
The indefinite article is a; it identifies a single, but not specific, person or thing. An is used instead of a whenever the word following it begins with a vowel sound.
Are you going to buy a house? The smile is a universal sign of pleasure. It's an honor to have been invited. I've got an uncle in Miami.
The definite article is the; it is used to refer to identified or specified people or things, both singular and plural.
Will you be painting the house this summer? He's the uncle I was telling you about. Please put the dishes away.
Articles Related to indefinite article

'A' or 'an'? What about before 'h'? An...
'A' or 'an'? What about before 'h'? An Indefinite Article Guide
When to use each, and when to say 'either one works'
Dictionary Entries Near indefinite article
indefinite integral
Cite this Entry
“Indefinite article.” Merriam-Webster.com Dictionary , Merriam-Webster, https://www.merriam-webster.com/dictionary/indefinite%20article. Accessed 3 Apr. 2024.
Subscribe to America's largest dictionary and get thousands more definitions and advanced search—ad free!

Can you solve 4 words at once?
Word of the day.
See Definitions and Examples »
Get Word of the Day daily email!
Popular in Grammar & Usage
The tangled history of 'it's' and 'its', more commonly misspelled words, why does english have so many silent letters, your vs. you're: how to use them correctly, every letter is silent, sometimes: a-z list of examples, popular in wordplay, the words of the week - mar. 29, 10 scrabble words without any vowels, 12 more bird names that sound like insults (and sometimes are), 8 uncommon words related to love, 9 superb owl words, games & quizzes.


paper-free learning
- conjunctions
- determiners
- interjections
- prepositions
- affect vs effect
- its vs it's
- your vs you're
- which vs that
- who vs whom
- who's vs whose
- averse vs adverse
- 250+ more...
- apostrophes
- quotation marks
- lots more...
- common writing errors
- FAQs by writers
- awkward plurals
- ESL vocabulary lists
- all our grammar videos
- idioms and proverbs
- Latin terms
- collective nouns for animals
- tattoo fails
- vocabulary categories
- most common verbs
- top 10 irregular verbs
- top 10 regular verbs
- top 10 spelling rules
- improve spelling
- common misspellings
- role-play scenarios
- favo(u)rite word lists
- multiple-choice test
- Tetris game
- grammar-themed memory game
- 100s more...
Indefinite Article
What is the indefinite article.
- I'm a pirate.
- I'm the pirate.
Table of Contents
More about the Indefinite Article
Why indefinite articles are important.

- The Definite Article ("the")
- The Indefinite Article ("a" and "an").
- Pass me a hammer.
- Pass me the hammer.
- I need a chair.
- I need the chair.
(Issue 1) Choosing "an" or "a."
- An MoD official and a MAFF official visited an NBC facility of a NATO country.
- I had a unique opportunity to strike an unexpected blow.
(Issue 2) Writing a job title or an office name with a lowercase letter.
- The Prime Minister said: "Being a prime minister is a lonely job... you cannot lead from the crowd." (Prime Minister Margaret Thatcher). [correct]
- Use "an" before a word that starts with a vowel sound , and use "a" before a word that starts with a consonant sound .
- When a job title (e.g., ambassador ) or an office name (e.g., finance office ) is preceded by "an" or "a" (as opposed to "the"), it should be written with a lowercase letter.

This page was written by Craig Shrives .
Learning Resources
more actions:
This test is printable and sendable
Help Us Improve Grammar Monster
- Do you disagree with something on this page?
- Did you spot a typo?
Find Us Quicker!
- When using a search engine (e.g., Google, Bing), you will find Grammar Monster quicker if you add #gm to your search term.
You might also like...
Share This Page

If you like Grammar Monster (or this page in particular), please link to it or share it with others. If you do, please tell us . It helps us a lot!
Create a QR Code

Use our handy widget to create a QR code for this page...or any page.
< previous lesson
next lesson >
- English Grammar
- Determiners and quantifiers
The indefinite article: 'a' and 'an'
Level: beginner
We use the indefinite article, a / an , with singular nouns when the listener/reader does not know exactly which one we are referring to:
Police are searching for a 14-year-old girl .
We also use it to show that the person or thing is one of a group :
She is a pupil at London Road School . Police have been looking for a 14-year-old girl who has been missing since Friday. Jenny Brown is a pupil at London Road School . She is 1.6 metres tall, with short, blonde hair. When she left home, she was wearing a blue jacket , a blue and white blouse , dark blue jeans and blue shoes. Anyone who has information should contact the local police on 0800 349 781.
We do not use an indefinite article with plural nouns or uncount nouns :
She was wearing blue shoes . (plural noun) She has short, blonde hair . (uncount noun)
GapFillDragAndDrop_MTU3MTE=
GapFillTyping_MTU3MTI=
GapFillTyping_MTkxMTE =
We use a before a consonant sound :
and an before a vowel sound :
Note that the choice of a or an depends on sound , not spelling .
GapFillTyping_MTU3MTM=
Hi the LearnEnglish Team, I have one question. Why in the sentence "Police are searching for a 14-year-old girl" word "police" had been used without the definite article "the"? In the next article about using "the" saying that "police" as a service must be written with "the".
Thank you for the answer Polemnn
- Log in or register to post comments
Hello polemnn,
It's a subtle difference. When we say 'Police are searching ...' it's not so much about a service as actual police officers out in the field looking for someone. We could also say 'The police' here, and this would refer to the police as a service, but for some reason we tend to think of the human police officers in such a case.
Hope this helps.
Best wishes, Kirk LearnEnglish team
Hi, Can you please clear out my confusion on use of article a/an in below sentences :
1. She is as beautiful "a" girl as you are ever likely to meet. 2. It was so forceful "a" blow 3. He was too valuable "an" asset.
I am not fully able to digest why article is needed. For example, the 3rd sentence can be modified to "He was too valuable asset" - If I am not wrong, it conveys the same meaning.
Thanks in Advance.
Regards, Abhay
Hi abhaykumar,
Actually, the article is necessary and without the article, the sentences are not grammatical. The article is needed because a singular noun needs a determiner, and an article is a type of determiner. The modifying phrases (e.g. so forceful ) are not determiners themselves, i.e. they cannot replace the article - they just modify the noun.
LearnEnglish team
Hi is there a difference when we say "The police" instead of '' Police " in this sentence "Police are searching for a 14-year-old girl.".
Hello Ahmed Hassan,
No, there's no difference.
Peter The LearnEnglish Team
Hello Teacher Peter What about these "I will study until the school starts" and "I will study until school starts". are they the same with and without the definite article before the word "school"?
The second sentence (without 'the') suggests that the speaker is a student at the school. The first sentence does not suggest this. They may be simply using a room which they will have to vacate when lessons begin, for example.
Hello Nevi,
I'm not sure what your question is here! It seems like you have a pretty good grasp of the topic as your explanation of your example is correct. If you substitute 'the' for 'a' here then you would be asking about a specific and known item, not just any item.
I want a computer = any computer is fine; it doesn't have to be a particular one
I want the computer = you know which one I want; maybe it's the only one we have, or maybe it's one we've talked about already
The LearnEnglish Team
We use 'a' with singular nouns, so it refers to one item rather than more than one. It also tells us that the speaker is not talking about a particular computer. The answer to your question, therefore, is that 'a' carries both of these meanings, not just one of them.
In 99.9% of situations people would mean that they have one brother by saying this. In a very specific (and unusual) context in which the speaker was, for example, trying to hide the fact that they have more than one brother, it could mean that the speaker has at least one (not a particular) male sibling, but that is quite unusual. As I said, in the vast majority of situations, they would say 'I have two brothers' (or however many brothers there are) instead of 'I have a brother'.
As I said, the unusual case I mentioned is extraordinarily rare, so in general you can count on this meaning that the speaker has one brother.
All the best,
Hello again Nevi,
I think you're looking for a grammatical rule here where it's really more the intention of the speaker which matters.
When a person says 'I need a telephone' they're generally not talking about the phone itself but rather the call: I need to call someone. The number of phones is not really in their mind. The only time you would say 'I need one phone' is when for some reason two or three or more would cause you problems for some reason.
Hello Ahmed Imam,
I don't think we would use either construction. You need to include an adjective of some kind:
Mr Ashraf is such an honest man (that) you can trust him. Mr Ashraf is so honest (that) you can trust him.
Alternatively, you could use a phrase like this:
Mr Ashraf is the kind of man (that) you can trust.
Both are possible. I don't think there's any difference in meaning so it's really a question of personal choice and linguistic background (idiolect and dialect).
Hi tanipetrush,
There is no article here because we are talking about spiders in general. If we were talking about a particular spider then we would use 'a spider' for first mention and 'the spider' later (or 'spiders' and 'the spiders' for more than one spider), but for general meaning we do not use any article.
Hello Dipak,
The phrase ' ...is history ' is a fixed expression. It means something is done, finished or ended. It can also mean that something or someone has been defeated.
We only use 'a history' in the context of a book: this is a great history of the Roman Empire .
I think 'Sudan' is becoming more and more common, but you can still hear 'the Sudan'. However, this is a political question as much as a language question following the secession of South Sudan in 2011.
Hi dipakrgandhi,
Good question! It's because in this sentence, US is describing the other noun, passport . US isn't the main noun in the phrase. So, the article we choose depends on the main noun, passport (not on any other nouns that describe it).
Does that make sense?
Yes! Exactly :)
Yes! You may have seen some examples like these.
- It was a most excellent meal.
- This is a most dangerous situation.
- She was a most valuable member of the team.
In those examples, the meaning is 'very' or 'extremely'. This is different to, for example, She was the most valuable member of the team , which means she was the 'number one most valuable' or the absolute best.
Using the indefinite article with most in this way is a relatively formal in style. We can only use this structure with most - we can't use it with single-word superlatives (e.g. we can't say 'It was a best meal').
About your sentence, it should be most of the time (without the before most , and with time instead of times ).
Hello knownman,
There are several possibilities here, depending on whether you are using a title or a description of a position:
Steve Walsh is Professor of Applied Linguistics and Communication
This is his title
Steve Walsh is the professor of Applied Linguistics and Communication
This is his position; there is only one such position.
Steve Walsh is a professor of Applied Linguistics and Communication
This is his position; there are several such positions; he is one of several.
As the word 'professor' is capitalised, I assume the write was using it as a title, so no article makes sense.
'Head of Department' functions in a similar way.
The second version (with 'the') is correct. Railway networks, including underground networks, usually take the definite article unless we are dealing with the name of a company:
the New York Metro the London Underground the Trans-Siberian Railway
Britsh Rail (a company) Virgin Trains (a company)
Hello emiliano_81,
Both 'met for coffee' and 'met for a coffee' are possible in this context.
When we are talking about meals we do not use an article, so we can say 'meet for breakfast', 'meet for lunch' etc. 'Meet for coffee' is similar to this.
As you say, we can also say 'a coffee' with the meaning 'a cup of coffee', and it is also correct here.
Hello Ike Kyoshi,
In 1, ' coffee ' is an uncount noun , whereas in 2 it is a count noun. The noun 'drink' is normally a count noun (as in 4). It can also be used as an uncount noun, but we don't use it sentences like 3. There is no obvious rule that explains this -- it's just the way we use the uncount noun 'drink'.
Hope this helps you make sense of it.
I don't think it's only related to the noun being countable or uncountable. For example, 'wine' is similar to coffee in that we can say 'I'll have a glass of white wine' or 'I'll have a white wine', but we wouldn't say 'Let's meet for wine' in the way that we can say 'Let's meet for coffee'.
I think the explanation is that certain activities can be used not only to represent a particular action (in this case, drinking something), but also to represent a social event. 'Meet for coffee' describes a social situation which is something of a tradition. It's similar to 'meet for lunch', I would say. As such, its use is rooted not in grammar but rather in social norms and traditions.
Hello Dipak Gandhi,
Exception is a countable noun and not an abstract concept, so we would use a plural form if we wanted to generalise. The same applies to rule :
Exceptions cannot be rules.
The rules for article use with general meaning are quite complex:
>> a + singular countable noun <<
we can use this with general meaning when we are talking about something which defines the group . For example:
An elephant is an impressive sight.
In other words, being an impressive sight is one of the characteristics of an elephant; if we saw an animal and it was not impressive then we could be fairly sure that it was not an elephant. We are talking about any elephant here - it is true of them all.
>> the + singular noun <<
we can use this with general meaning when we are talking about our image or concept of the noun . For example:
The elephant can live for over sixty years.
Here we are not talking about a real elephant, but rather the concept of 'elephant' in our heads.
>> no article + plural countable noun or uncountable noun <<
we use this to talk about what is normal or typical of a type. It may or may not be true of all individuals but it is typical of most. For example:
Swedish people are tall.
Here we are talking about the average height of Swedes, not any particular person or concept.
The distinctions are subtle but sometimes can be important. For example, we can say with general meaning:
Whales are in danger of becoming extinct.
The whale is in danger of becoming extinct.
However, we cannot say:
A whale is in danger of becoming extinct.
This is because being in danger of becoming extinct may be true but it does not define the whale.
Hello Dipak Gandhi,
Yes, that's correct. Well done!
Online courses

Group and one-to-one classes with expert teachers.

Learn English in your own time, at your own pace.

One-to-one sessions focused on a personal plan.

Get the score you need with private and group classes.
Understanding the Indefinite Article (Definition, Examples, How to Use)

What is an indefinite article? Before we dive deeper into the fascinating world of indefinite articles, we need to be well-prepared with what articles mean in the world of grammar . The following article will provide a crash course on articles , explicitly focusing on the indefinite form.
What are definite articles and indefinite articles (articles)?
An article is an important device that identifies a part of a speech as a noun (or something equivalent to it). It however does not serve the purpose of describing the noun (or noun equivalent).
There are two types of articles – definite and indefinite . Among these, ‘a’ and ‘an’ fall under the indefinite category, while ‘the’ falls under the definite category.
Examples of definite and indefinite articles
The following are examples of definite and indefinite articles.
- I made a peanut butter and jelly sandwich for breakfast.
- I boiled an egg for breakfast.
- I ate the pastry on the table.
In sentence 1 , ‘a’ is the indefinite article. It identifies ‘peanut butter and jelly sandwich’ as the noun (or equivalent) without referring to any specific peanut butter and jelly sandwich.
In sentence 2 , ‘an’ is an is the indefinite article that identifies ‘egg’ as the noun (or equivalent), without referring to any specific egg.
In sentence 3 , ‘the’ is an is the definite article which identifies ‘pastry ’ as the noun (or equivalent), referring to the specific pastry on the table.
Let’s now get an in-depth idea of the indefinite articles ‘a’ and ‘an’ below.
Definition of an indefinite article
An indefinite article is instrumental in introducing a noun (or noun equivalent) without specifying it or putting it out there for the first time. It is used to refer to something non-specific or generic.

Examples of indefinite articles
The following are some examples to help you understand indefinite articles even better.
- Close a window.
Here, ‘a’ is the indefinite article that introduces a noun (window) without specifying any particular window. You can close any window in this case.
- Close the window.
Here, ‘the’ is the indefinite article that introduces a noun (window) by specifying a particular window. You have to close the particular window referred to in this case.
- I want an ice cream.
Here, ‘an’ is the indefinite article that introduces a noun (ice cream) without specifying any particular ice cream. You can provide any ice cream in this case.
- I want the ice cream.
Here, ‘the’ is the indefinite article that introduces a noun (ice cream) by specifying a particular ice cream. You have to provide the particular ice cream referred to in this case.

How does an indefinite article work?
This section will deal with the functioning of the indefinite articles ‘a’ and ‘an’. Let us discuss the two main roles that indefinite articles perform in a sentence. They are as follows:
Introducing the noun (or noun equivalent)
When a noun (or equivalent) is introduced, an indefinite article such as ‘a’ or ‘an’ is used to refer to it. After the primary introduction, the definite article ‘the’ can take over if we talk about something specific.
For example:
- I took a book from the pile. The book was on insects.
- We saw an umbrella in his hand. The umbrella was green in color.
In sentence 1 , the indefinite article ‘a’ is used to introduce the noun (book), and the definite article ‘the’ is used to provide further details about the specific book.
In sentence 2 , the indefinite article ‘an’ is used to introduce the noun (umbrella), and the definite article ‘the’ is used to provide further details about the specific umbrella.

Pointing to non-specific things
We do not always want to refer to specific objects. Sometimes, we talk about generic things whose details we either do not have or consider far too unnecessary or unimportant to provide. In such a scenario, indefinite articles come into handy.
A couple of examples will sort this out better for you, as provided below.
- My sister wants a kitten for her birthday this year. I will adopt a kitten from the local shelter instead of buying one for her.
- I added an apple to my shopping basket. The proverb that an apple a day keeps the doctor away still rings true.
How to identify an indefinite article
It is relatively easy to identify an indefinite article in a sentence. There are two indefinite articles – and an. The indefinite article ‘a’ is placed before nouns (or equivalents) starting with consonants.
The indefinite article ‘an’ is placed before nouns (or equivalents) starting with vowels .

The rules for identifying an indefinite article are as follows:
- Check that you place it before a singular count noun.
- Check that the specific identity of the noun is not known.
- A kitten was inside the basket.
- I peeled an orange.
Indefinite Article Exceptions
A and an are usually very easy to use . You have to look out whether the noun (or noun equivalent) after the article starts with a consonant or a vowel. However, there are some exceptions .
Examples of indefinite article exceptions
- I have a one-dollar note. (One starts with a consonant sound, almost like a W)
- I waited for an hour at the station. (Hour starts with a vowel sound, almost like an O)
Some other exceptions include:
- Useless, university, European, uniform (These words begin with a consonant Y sound and pair with a.)
- Honest, honor , heir, hotel (These words begin with a vowel O sound and pair with an.)
- Acronyms pair with ‘a’ or ‘an’ depending on how the words are pronounced.
Indefinite article vs. definite article
Indefinite articles deal with non-specific or generic nouns (or noun equivalents). Definite articles deal with specific nouns (or noun equivalents). A and an are indefinite articles, while the is a definite article.
- Bring me a glass of water.
- Bring me the glass of juice.
Use ‘a’ or ‘an’ for non-specific or generic nouns (or equivalents). Use ‘a’ for consonant nouns, while you can use ‘an’ for vowel nouns.
An indefinite article example is:
- I bought a doll for my niece.
- I had an avocado sandwich for lunch.
Unicorn is an exception. Since the pronunciation of a unicorn starts with a Y sound (consonant), the indefinite article used here is a.
Apply the definite article before a singular or plural noun. And indefinite before a singular noun start with a consonant (vowel sounds). Using articles with singular nouns help the reader understand who we are referring to. Use the indefinite article “a” or “an” only with a singular count noun.
Inside this article
Fact checked: Content is rigorously reviewed by a team of qualified and experienced fact checkers. Fact checkers review articles for factual accuracy, relevance, and timeliness. Learn more.

About the author
Dalia Y.: Dalia is an English Major and linguistics expert with an additional degree in Psychology. Dalia has featured articles on Forbes, Inc, Fast Company, Grammarly, and many more. She covers English, ESL, and all things grammar on GrammarBrain.
Core lessons
- Abstract Noun
- Accusative Case
- Active Sentence
- Alliteration
- Adjective Clause
- Adjective Phrase
- Adverbial Clause
- Appositive Phrase
- Body Paragraph
- Compound Adjective
- Complex Sentence
- Compound Words
- Compound Predicate
- Common Noun
- Comparative Adjective
- Comparative and Superlative
- Compound Noun
- Compound Subject
- Compound Sentence
- Copular Verb
- Collective Noun
- Colloquialism
- Conciseness
- Conditional
- Concrete Noun
- Conjunction
- Conjugation
- Conditional Sentence
- Comma Splice
- Correlative Conjunction
- Coordinating Conjunction
- Coordinate Adjective
- Cumulative Adjective
- Dative Case
- Declarative Statement
- Direct Object Pronoun
- Direct Object
- Dangling Modifier
- Demonstrative Pronoun
- Demonstrative Adjective
- Direct Characterization
- Definite Article
- Doublespeak
- Equivocation Fallacy
- Future Perfect Progressive
- Future Simple
- Future Perfect Continuous
- Future Perfect
- First Conditional
- Gerund Phrase
- Genitive Case
- Helping Verb
- Irregular Adjective
- Irregular Verb
- Imperative Sentence
- Indefinite Article
- Intransitive Verb
- Introductory Phrase
- Indefinite Pronoun
- Indirect Characterization
- Interrogative Sentence
- Intensive Pronoun
- Inanimate Object
- Indefinite Tense
- Infinitive Phrase
- Interjection
- Intensifier
- Indicative Mood
- Juxtaposition
- Linking Verb
- Misplaced Modifier
- Nominative Case
- Noun Adjective
- Object Pronoun
- Object Complement
- Order of Adjectives
- Parallelism
- Prepositional Phrase
- Past Simple Tense
- Past Continuous Tense
- Past Perfect Tense
- Past Progressive Tense
- Present Simple Tense
- Present Perfect Tense
- Personal Pronoun
- Personification
- Persuasive Writing
- Parallel Structure
- Phrasal Verb
- Predicate Adjective
- Predicate Nominative
- Phonetic Language
- Plural Noun
- Punctuation
- Punctuation Marks
- Preposition
- Preposition of Place
- Parts of Speech
- Possessive Adjective
- Possessive Determiner
- Possessive Case
- Possessive Noun
- Proper Adjective
- Proper Noun
- Present Participle
- Quotation Marks
- Relative Pronoun
- Reflexive Pronoun
- Reciprocal Pronoun
- Subordinating Conjunction
- Simple Future Tense
- Stative Verb
- Subjunctive
- Subject Complement
- Subject of a Sentence
- Sentence Variety
- Second Conditional
- Superlative Adjective
- Slash Symbol
- Topic Sentence
- Types of Nouns
- Types of Sentences
- Uncountable Noun
- Vowels and Consonants
Popular lessons

Stay awhile. Your weekly dose of grammar and English fun.

The world's best online resource for learning English. Understand words, phrases, slang terms, and all other variations of the English language.
- Abbreviations
- Editorial Policy
What Is the Indefinite Article? (with Examples)
Marcus Froland
March 28, 2024
Think about the small words in English that we use all the time without giving them much thought. Among these tiny giants of language, one stands out for its simplicity and complexity at the same time. We’re talking about the indefinite article . It might seem like just a drop in the vast ocean of English grammar, but it plays a crucial role in how we communicate every day.
Now, you might wonder why such a small word deserves so much attention. The answer lies in its power to transform a sentence, shaping our thoughts and how we express them. This seemingly insignificant word packs a punch stronger than its weight class suggests. But what is it about the indefinite article that makes it so special? Stick around as we peel back the layers of this linguistic enigma.
The indefinite article in English is a simple but important part of speech. It includes the words “a” and “an.” We use these articles before singular, countable nouns when the exact identity of the noun is not known to the reader or listener. The choice between “a” and “an” depends on sound. Use “a” before words that start with a consonant sound, like “a dog” or “a house.” Use “an” before words that start with a vowel sound, like “an apple” or “an hour.” Understanding how to use indefinite articles correctly helps make your English clearer and more natural.
Understanding the Basics of Indefinite Articles
Indefinite articles play a crucial role in English grammar , having the primary function of acting as markers that a word is either a noun or serves as a noun within a sentence. Unlike definite articles, they do not provide specific details about the noun. Instead, they are used more broadly to introduce the noun in a nonspecific or general sense.
“I saw a dog at the park.”
In this example, the indefinite article “a” doesn’t identify a specific dog, but merely suggests that there was a dog at the park. It is important to understand the basic definition and functions of indefinite articles to properly communicate in English.
Definition and Function in English Grammar
Let’s define indefinite articles more explicitly and explore their grammar functions in the English language . An indefinite article is a word preceding a noun (or a noun equivalent) to signal that the noun is nonspecific or being mentioned for the first time. They help provide context by hinting at the introduction of a new noun or noun-equivalent, but without specifying it directly.
The Two Types: ‘A’ and ‘An’
There are only two indefinite articles in English: “a” and “an.” The choice between them is determined by the initial sound of the following word.
- “A” is commonly placed before words that begin with consonant sounds
- “An” is correct before vowel sounds
This rule goes beyond examining the first letter of a word, relying heavily on the sound that word makes when pronounced. For example:
While these guidelines are simple and generally easy to follow, there are exceptions and special cases that you need to be aware of in order to master the use of indefinite articles. As you progress in learning and using English, continue to study these rules and techniques to support your mastery of the language’s basics.
The Proper Use of ‘A’ and ‘An’ Depending on Context
To improve your English writing skills, a solid understanding of proper article usage is essential. The indefinite articles “a” and “an” play a crucial role in grammatical context. They are not only used to introduce nouns but also refer to them nonspecifically or set up mentions for further clarification. This section focuses on how and when to use “a” or “an” based on the context.
Remember, using “a” or “an” correctly depends on the sound of the subsequent word. If the next word begins with a vowel sound, use “an.” If it begins with a consonant sound, use “a.” This guideline applies to the immediate following word, which isn’t always the main noun—it could also be an adjective or a word with a silent letter, affecting which article should be applied.
“A historical event” (correct) vs. “An historical event” (incorrect) “An honor” (correct) vs. “A honor” (incorrect)
Here are some general contexts where indefinite articles are appropriate:
- Introducing a noun for the first time: “I saw a bird in my backyard.”
- Indicating nonspecific nouns: “I would like a cup of coffee.”
- Presenting an example of something: “Such a device, like a smartphone, can help you stay connected.”
When your main noun is preceded by an adjective, the choice of “a” or “an” depends on the sound of the adjective instead of the noun:
“An impressive building” (correct) vs. “A impressive building” (incorrect) “A unique perspective” (correct) vs. “An unique perspective” (incorrect)
To choose the correct article based on context, pay close attention to the pronunciation of the next word, and follow these simple guidelines. As you become more proficient in using indefinite articles, your overall writing skills will improve, resulting in clear and effective communication.
Common Mistakes and How to Avoid Them
While navigating English grammar rules , it’s essential to know the common mistakes made with indefinite articles and how to avoid them. Two prevalent errors are misusing ‘a’ or ‘an’ with plural nouns and uncountable nouns. We’ll explore both in detail and provide guidance on preventing these mistakes.
Misusing ‘A’ and ‘An’ with Plural Nouns
One common mistake is using indefinite articles with plural nouns, which is grammatically incorrect. When dealing with plurals, either use “the” or no article, depending on the sentence context. For example:
- Incorrect: She brought me a books.
- Correct: She brought me books (with no article).
- Correct: She brought me the books (with a definite article).
Pro tip: Pay attention to sentence context when dealing with plural nouns to decide whether an article is necessary or not.
Indefinite Articles with Uncountable Nouns
Another common misstep is using indefinite articles before uncountable nouns. Regardless of their singular form, uncountable nouns (like “milk” or “electricity”) do not pair with “a” or “an.” Here are some examples:
- Incorrect: She poured me a milk into the cup.
- Correct: She poured milk into the cup (with no article).
- Correct: She poured the milk into the cup (with a definite article).
Remember, practice makes perfect, and consistently applying these guidelines will enhance your writing and help you prevent indefinite article misusage . By being mindful of plural nouns grammar rules and proper article usage with uncountable nouns, you’ll be well on your way to avoiding grammar mistakes and improving your English skills.
Indefinite Articles with Adjectives and Noun Equivalents
Indefinite articles play a crucial role in English grammar , especially when it comes to interacting with adjectives and noun equivalents. Let’s dive deep into how the correct application of indefinite articles with adjectives and noun equivalents can significantly enhance your grammar skills.
Adjectives and Articles
Adjectives that precede nouns in a sentence can impact the usage of “a” or “an.” The sound of the adjective, rather than the noun, determines the appropriate article. For example:
- An impressive statue
- A significant event
Notice that in both cases, the article choice depends on the adjective’s initial sound, not the noun. This rule is essential to remember when dealing with adjectives and indefinite article application .
Noun equivalents are phrases or clauses acting as nouns within a sentence. Indefinite articles with noun equivalents follow the general pronunciation rules of indefinite article usage. Consider the following examples:
Gathering information is crucial for any project. A thorough investigation can make a noticeable difference in the outcome. She believes that an understanding of different cultures is vital for global harmony.
As with adjectives, the sound of the phrase that acts as the noun equivalent, rather than the noun itself, determines the usage of “a” or “an.”
Being mindful of indefinite article application rules and exceptions will enhance your writing and communication skills, making it easier for your audience to understand and connect with your message. Practice makes perfect, so keep working on implementing the correct indefinite articles with adjectives and noun equivalents to master English grammar .
Navigating Tricky Exceptions and Pronunciation Rules
When it comes to using indefinite articles, some pronunciation exceptions can be challenging and confusing. The primary factor to focus on when choosing between “a” and “an” is the sound that comes after the article. Understanding consonant vs. vowel sounds and knowing when to apply the correct article is essential in English grammar.
Consonant Sounds vs. Vowel Sounds
While it might seem simple enough to use “a” before consonants and “an” before vowels, there are instances where the sound doesn’t match the starting letter of a word. In some cases, words have an initial vowel sound but start with a consonant letter, such as “honor” or “hour.” These words take “an” as their article.
It was an honor to meet the President. We arrived an hour ago.
On the other hand, some words start with a vowel letter but have a consonant sound when pronounced, such as “university” or “European.” These words require “a” as their article.
I went to a university in the United States. She enjoyed a European vacation last summer.
Special Cases: Acronyms and Silent Letters
Another area where pronunciation exceptions might be tricky is with acronyms and words with silent letters. For acronyms, you should listen carefully to the pronunciation before choosing the article. For example:
- A NASA scientist
- An FBI agent
Silent letters also complicate things when it comes to determining the appropriate article. For instance, the word “hour” has a silent ‘h’ and requires “an” as its article. Conversely, the word “historical” has a pronounced ‘h’, making “a” the correct article.
I spent an hour reading a book. It was a historical event that shaped our nation.
As you can see, understanding and navigating the pronunciation exceptions and rules can be challenging. However, by focusing on the consonant vs. vowel sounds and paying close attention to acronyms and silent letters, you’ll be able to master the correct usage of indefinite articles in your writing.
Expanding Your Use of Indefinite Articles in Writing
Improving your writing skills goes beyond mastering vocabulary and sentence structure; it also involves the proper and varied use of indefinite articles. As you become more familiar with writing with articles , you will notice that your writing becomes clearer, and your ideas are more effectively communicated. To expand your indefinite article techniques , practice is key, as well as keeping an eye on the various grammatical details mentioned in this article.
One important aspect to focus on is the sound of words, rather than the written letters. This will help you determine whether “a” or “an” should be used before a noun or an adjective. Additionally, accurately introducing nouns for the first time is essential in making your writing coherent. Always use real examples and brands for better authenticity and credibility in your writing.
Remember to correctly apply indefinite articles when working with adjectives, acronyms, and silent letters. This attention to detail will contribute to polished and grammatically sound writing. As you pay more attention to these rules and exceptions, you will notice a significant improvement in your grammar skills and increase the overall quality of your writing.
Share this:
Two minute english.
English Made Simple: Two-Minute Lessons for Busy Learners
Copyright © 2024 • TwoMinEnglish.com
- Cambridge Dictionary +Plus

Meaning of indefinite article in English
Your browser doesn't support HTML5 audio
- If you ask for 'a ham sandwich ', you're using the indefinite article 'a' before the noun .
- Don't forget that, before any word beginning with a vowel , the indefinite article would be 'an', for example 'an interesting book '.
- abstract noun
- adjectivally
- common noun
- concrete noun
- conjunction
- countable noun
- definite article
- part of speech
- relative pronoun
indefinite article | Intermediate English
Examples of indefinite article, translations of indefinite article.
Get a quick, free translation!

Word of the Day
cloak-and-dagger
used to describe an exciting story involving secrets and mystery, often about spies, or something that makes you think of this

Shoots, blooms and blossom: talking about plants

Learn more with +Plus
- Recent and Recommended {{#preferredDictionaries}} {{name}} {{/preferredDictionaries}}
- Definitions Clear explanations of natural written and spoken English English Learner’s Dictionary Essential British English Essential American English
- Grammar and thesaurus Usage explanations of natural written and spoken English Grammar Thesaurus
- Pronunciation British and American pronunciations with audio English Pronunciation
- English–Chinese (Simplified) Chinese (Simplified)–English
- English–Chinese (Traditional) Chinese (Traditional)–English
- English–Dutch Dutch–English
- English–French French–English
- English–German German–English
- English–Indonesian Indonesian–English
- English–Italian Italian–English
- English–Japanese Japanese–English
- English–Norwegian Norwegian–English
- English–Polish Polish–English
- English–Portuguese Portuguese–English
- English–Spanish Spanish–English
- English–Swedish Swedish–English
- Dictionary +Plus Word Lists
- English Noun
- Intermediate Noun
- Translations
- All translations
Add indefinite article to one of your lists below, or create a new one.
{{message}}
Something went wrong.
There was a problem sending your report.
We use cookies and similar technologies to improve your website experience and help us understand how you use our website. By continuing to use this website, you consent to the usage of cookies. Learn more about our Privacy Statement and Cookie Policy .
- Our Mission
- Code of Conduct
- The Consultants
- Hours and Locations
- Apply to Become a Consultant
- Make an Appointment
- Face-to-Face Appointments
- Zoom Appointments
- Written Feedback Appointments
- Support for Writers with Disabilities
- Policies and Restrictions
- Upcoming Workshops
- Class Workshops
- Meet the Consultants
- Writing Guides and Tools
- Schedule an appointment! Login or Register
- Graduate Students
- ESOL Students
- Definite and Indefinite Articles
To decide if an article is needed before a noun or which one to choose, ask yourself the following question:
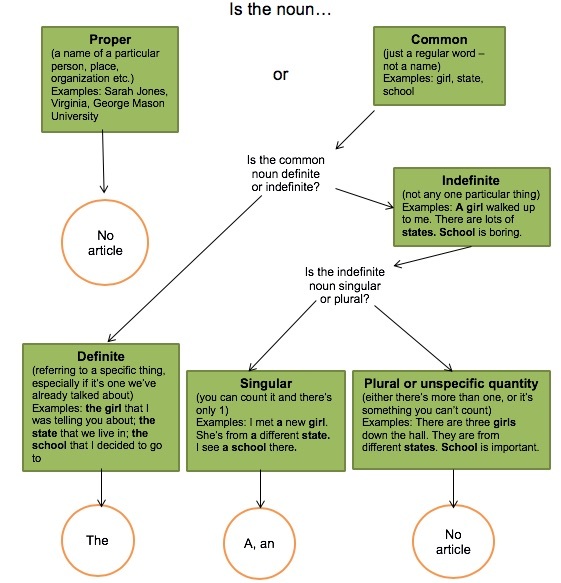
Articles in Academic Writing
The flowchart with questions can be complemented with the classification below, in which more nuanced explanations of articles are provided. This fairly non-traditional classification comes from Caplan, N. (2015). Grammar Choices for Graduate and Professional Writers. University of Michigan Press.
Articles determine or specify whether a noun is general or specific in its references. The questions we ask to determine if the noun is general or specific are: is it all things (generic reference), one of many things (indefinite reference), or this one thing (definite reference)? Below is the detailed explanation of the three types of references.
Generic Reference
Nouns that describe a class, not an individual person or thing, have generic reference; the meaning of the noun is all of it/them . Generic reference can often be seen in general statements used to introduce, define, or summarize ideas.
Indefinite Reference
Indefinite reference is appropriate when the reader and/or the writer do not both know the specific identity of the noun. This might be because:
- it is not important ( use a computer = use any computer)
- not known to the writer ( a further study is needed )
- new to the reader ( we used a new technique = the writer knows exactly which technique, but the reader does not).
The basic meaning of a noun with indefinite reference is one/some of many .
It is important to mention that there is really difficult to identify the difference with generic reference and indefinite reference with plural and non-count nouns; however, it is not necessary since they have the same grammatical rules.
Definite Reference
A definite reference is used when the reader and writer both know or can easily find the exact meaning of the noun. Academic writers use definite reference extensively to connect ideas within and between sentences and to establish sheared knowledge with readers. All common nouns (count and non-count, singular and plural) use the for definite reference. A noun is definite if:
Read this passage and fill in the blanks with either a , an , the , or no article.
Much has been learned about _____ brain in ____last 150 years. _____ brain, most complicated organ of ______ body, contains _____ ten billion nerve cells and is divided into ____ two cerebral hemispheres, one on _____right and one on ______left. Interestingly, ____ left hemisphere controls _____ movements on ______right side of ______body, while _____ right hemisphere controls_____ movements on _____ left.
______ researchers also know that______ specific abilities and behaviors are localized; in ____other words, they are controlled by ______specific areas of _____ brain. _____language, it seems, is highly localized in ______ left hemisphere. In_____1860s, Dr. Paul Broca discovered that _____damage to _____front left part of _____brain resulted in_____telegraphic speech similar to that of young children. Soon thereafter, Karl Wernicke found that _____ damage to _____ back left part of_____ brain resulted in ______speech with_____ little semantic meaning. These two regions in______brain are now referred to as _____Broca’s area and Wernicke’s area.
Although there is some debate surrounding _____ specialization of the brain, researchers generally agree that _____ speech is controlled by _____left side. There is no debate that in_______ great majority of cases, ______ injuries to ______ left side nearly always have ______impact on ____speech.
Exercise adapted from Swales, J. M., & Feak, C. B. (2004). Academic writing for graduate students: Essential tasks and skills. Ann Arbor, Michigan: University of Michigan Press.
Last updated 7/16/2018
Grammar & Style
- Converting Fragments to Full Sentences
- Active and Passive Voice
- Choosing Between Infinitive and Gerund: “To do” or “doing”?
- Choosing the Correct Word Form
- Combining Clauses to Avoid Comma Splices, Run-ons, and Fragments
- Commas, Semicolons, and Colons
- Count vs. Noncount Nouns
- Improving Cohesion: The "Known/New Contract"
- Modal Verbs
- Parallel Structure
- Prepositions
- Proper Nouns
- Reducing Informality in Academic Writing
- Run-on Sentences
- Same Form, but Different Functions: Various Meanings of Verb+ing and Verb+ed
- Subject-Verb Agreement
- The Three Common Tenses Used in Academic Writing
- Using Reduced Relative Clauses to Write Concisely
- Verb Tenses
- Word Order in Statements with Embedded Questions

The Writing Center
4400 University Drive, 2G8 Fairfax, VA 22030
- Johnson Center, Room 227E
- +1-703-993-1200
- [email protected]
Quick Links
- Register with us
© Copyright 2024 George Mason University . All Rights Reserved. Privacy Statement | Accessibility
If you're seeing this message, it means we're having trouble loading external resources on our website.
If you're behind a web filter, please make sure that the domains *.kastatic.org and *.kasandbox.org are unblocked.
To log in and use all the features of Khan Academy, please enable JavaScript in your browser.
Course: Grammar > Unit 4
- Introduction to adjectives
- Meet the adjective
- Introduction to articles
- Meet the article
Definite and indefinite articles
- The indefinite article
- Choosing between definite and indefinite articles
- Link to facebook
- Link to linkedin
- Link to twitter
- Link to youtube
- Writing Tips
What Are Articles? A Simple Grammar Guide

- 6-minute read
- 25th January 2023
English grammar can be tricky for many learners.
Let’s say you have this sentence: “I need to buy ___ envelope for my wife’s birthday card.” What word do you think should go in the blank? If you chose an , you’re right! But why is an the correct word? Why can’t we use the , a , or just leave it blank?
If you ask these questions often, then this post is for you! We’ll provide a simple guide to the wonderful world of articles in English . We’ll talk about article usage and the differences between definite and indefinite articles.
What Are Articles?
Maybe you already know what articles are, and “yay!” if you do. Articles are words that are used before nouns to define them as specific or unspecific. Let’s look at the following examples:
By using the article the , we’ve shown that it was one specific long day and that one specific cup of tea tasted good.
We use a in this example to make a general statement, implying that any cup of tea would taste good after any long day.
There are two types of articles in English: definite (the) and indefinite (a/an). We’ll go over them in the following paragraphs.
Definite Article (The)
A definite article limits the meaning of a noun to one particular thing.
For example, your friend could ask, “Are you going to the beer festival this weekend?” The definite article tells you that your friend is referring to a specific beer festival that both of you know about.
We can use the definite article with singular, plural , or countable nouns . Here are some examples of using the definite article in context:
Indefinite Article (A/An)
The two indefinite articles are a and an . The a is used when it precedes a word that begins with a consonant , while an precedes a word that begins with a vowel . Indefinite articles indicate that a noun refers to a general idea.
For example, you might ask a friend, “Should I bring a gift to the party?”
In this case, you’re not asking about a specific type of gift.
Your friend answers, “It’s up to you. I’m going to bring an apple strudel.” Your friend is not referring to a specific apple strudel. Indefinite articles only appear with singular nouns. Here are a few examples:
There are a few exceptions to using a or an . For example, you wouldn’t be able to use a with a word that begins with a silent “h” . Let’s take the word honest . Although it begins with a consonant, the “h” is silent when pronounced. Therefore, we use an instead of a . Another example would be united. The “u” is pronounced yoo , so we’d use a instead of an. Consider these examples:
This is also true with acronyms and initialisms . When you use an acronym as a noun, no article is needed.
However, you often need an article before an initialism when using it as either a noun or a modifier.
Article Usage
It’s important to use articles correctly to improve your writing and speaking skills. You should know the rules regarding articles with grammar points, such as adjectives and pronouns. Moreover, there are some specific instances where articles aren’t needed, such as proper nouns, generalizations, and certain phrases.
Articles Before an Adjective
An article sometimes modifies a noun, which has also been modified by an adjective. If the article is indefinite, you would need to choose a or an based on the first letter of the word that follows it. Let’s consider these examples:
Find this useful?
Subscribe to our newsletter and get writing tips from our editors straight to your inbox.
Indefinite Articles With Uncountable Nouns
You should never use indefinite articles with uncountable nouns. You should use words, such as some, to modify these nouns. Here’s an example:
Articles With Pronouns
As a rule, articles shouldn’t be used with possessive pronouns (his, her, my, our, its, and their). Let’s study these examples:
The and my shouldn’t be used together, as they both modify the same noun. Instead, you should use one or the other depending on the intended meaning.
Rules and Exceptions
You should be aware of some specific rules and exceptions when using articles. It’s important to practice and become familiar with article usage to improve your grammar skills.
Nouns Without Articles
In some cases, articles are not used before certain nouns. The article is implied but not actually present. This implied article is often called a “zero article”. It’s omitted before nouns that refer to abstract ideas. Consider this example:
Many languages and nationalities are also not preceded by articles. Examples include:
Additionally, sports and academics don’t require articles. Here’s an example:
Types of nouns that don’t require an article are:
● Singular proper nouns (Eiffel Tower, Cairo)
● Certain generic nouns (school, work)
● Certain phrases (at home, in bed, on TV)
● Plural nouns representing a group (dogs, cats, books)
It’s important to note that the usage of articles in English grammar might not be the same as in other languages. Therefore, getting the hang of it may require practice and attention. If you’d like some practice with English articles, try this cool exercise . For visual learners, we recommend this video using definite and indefinite articles . It even touches on zero articles!
Article FAQ
1. can you give some examples of proper nouns that don’t require an article.
You don’t need an article for singular proper nouns. The names of cities, countries, towns, and street names exemplify this rule. The only exception with countries is The Gambia (a country in Western Africa).
2. What are the rules for using articles with countries, languages, and nationalities?
Articles aren’t used with many languages and nationalities. For example, a country with a single or merged name (except The Gambia) doesn’t require articles, while plural names (The Philippines, The Bahamas) do.
3. How can I check if I am using articles correctly in my writing?
As you write, ask yourself if the noun is countable or uncountable. Is the noun specific or unspecific? It’s also a good idea to read the passage aloud with the articles to verify that they are correct. For more grammar guidance, check out our Common ESL Writing Errors guide.
Of course, proofreading your writing can help with verifying correct article usage in English. If you’re currently working on a piece of writing, our team of experts at Proofed can ensure the correct usage of articles. They can also ensure correct spelling, punctuation, and grammar. Consider submitting a 500-word document for free today!
Share this article:
Post A New Comment
Got content that needs a quick turnaround? Let us polish your work. Explore our editorial business services.
4-minute read
The Benefits of Using an Online Proofreading Service
Proofreading is important to ensure your writing is clear and concise for your readers. Whether...
2-minute read
6 Online AI Presentation Maker Tools
Creating presentations can be time-consuming and frustrating. Trying to construct a visually appealing and informative...
What Is Market Research?
No matter your industry, conducting market research helps you keep up to date with shifting...
8 Press Release Distribution Services for Your Business
In a world where you need to stand out, press releases are key to being...
3-minute read
How to Get a Patent
In the United States, the US Patent and Trademarks Office issues patents. In the United...
The 5 Best Ecommerce Website Design Tools
A visually appealing and user-friendly website is essential for success in today’s competitive ecommerce landscape....

Make sure your writing is the best it can be with our expert English proofreading and editing.
Indefinite Article: What It Is and How To Use It
Do you know what an indefinite article is? This article will provide you with all of the information you need on indefinite articles, including its definition, usage, example sentences, and more!
Your writing, at its best
Compose bold, clear, mistake-free, writing with Grammarly's AI-powered writing assistant
What is an example of an indefinite article?
An indefinite article can be used in many different contexts in the English language. Trying to use a word or literary technique in a sentence is one of the best ways to memorize what it is, but you can also try making flashcards or quizzes that test your knowledge. Try using this term of the day in a sentence today! Below are a couple of examples of indefinite articles that can help get you started incorporating this tool into your everyday use. Take a look at these indefinite article examples from Your Dictionary and see if you can identify the indefinite article. You probably already use indefinite articles in your life every day, but you may not even realize that you are doing it. Being cognizant of the grammar you are using is a great way to get a better grasp on the English language.
- I need an umbrella; it’s reading.
- A criteria for riding the rollercoaster is being taller than 4.5 feet.
- Bette is a great cook,
- The Netherlands is a great country.
- My dentist says I need a tooth pulled.
- In the United States, a person can marry whomever they like.
- I learned about demonstratives, prepositions, adjectives, partitive articles, and other topics in an English class once.
- I saw an Elephant when I went to the zoo .
- We read a book that was written in Old English.
- We visited the territories and ate an ice cream.
- The mayor made a general statement where no specific people were mentioned.
What are other grammar terms?
See how many you know from this list from OED :
- possessive pronoun
- determiner
- possessive
- conditional
- pleonasm | pleonastic
- third-person
- past participle
- non-referential
- instrumental
- attributive
- prepositional phrase
- phrasal verb
- construction
- participial adjective
- collocation | collocate
- indirect passive
- construed (const., constr.)
- part of speech
- copular verb | copula
- double object
- agree | agreement
- passive infinitive
- personal pronoun
- superlative
- present tense
- auxiliary verb | auxiliary
- comparative
- quasi –
- past tense
- absolute (absol.)
- modify | modifier
- count noun
- intransitive
- indefinite
- first person
- appositive
- cognate object
- imperative (imper.)
- nominal relative | nominal relative clause
- unmarked genitive
- indirect object
- demonstrative
- prepositional object
- participle | past participle | present participle
- modal verb | modal auxiliary verb | modal auxiliary
- similative
- direct speech
- bare infinitive
- infinitive
- combining form (comb. form)
- premodify | premodifier
- object | direct object | indirect object
- preposition (prep.)
- noun phrase
- indicative
- verbal noun
- interjection
- intensifier
- impersonal (impers.)
- compound | compounding
- proper noun | proper name
- postmodify | postmodifier
- adverb (adv.)
- interrogative
- possessive adjective
- subjunctive
- parenthetical | parenthetically
- subordinate clause
- nominative
- phrase (phr.)
- second person
- declarative
- that-clause
- direct object
- apposition
- sentence adverb |sentence adverbial
- conjunction (conj.)
- special use
- main clause
- direct question
- indirect question
- parasynthetic
- indirect speech
- progressive
- pronoun (pron.)
- apodosis and protasis
- subjective
- anticipatory
- to-infinitive
- cataphoric
- present participle
- antecedent
- complementary
- transitive
- predicative
- inflection | inflected | inflectional
- adverbial | adverbially
- complement
- accusative
- non-finite
- combination
- ellipsis | elliptical
- agent noun
- collective noun
- common noun
- periphrasis | periphrastic
- prepositional passive
- definite article
Overall, the indefinite article is a or an.
- Glossary of grammatical terms | OED
- Indefinite Article | Word Sense
- A vs. An: Basic Rules and Exceptions | Your Dictionary
- Beginners’ Italian: food and drink: 5 The indefinite article in Italian – OpenLearn | Open University – L195_1
Kevin Miller is a growth marketer with an extensive background in Search Engine Optimization, paid acquisition and email marketing. He is also an online editor and writer based out of Los Angeles, CA. He studied at Georgetown University, worked at Google and became infatuated with English Grammar and for years has been diving into the language, demystifying the do's and don'ts for all who share the same passion! He can be found online here.
Recent Posts

IDE Meaning: Here’s What It Means and How To Use It

KGB Meaning: Here’s What It Means and How To Use It

Faith Meaning: Here’s What It Means and How To Use It

Spirit Meaning: Here’s What It Means and How To Use It
When to Use Definite vs. Indefinite Articles
A rticles are a unique type of adjective that, while short, communicate some important information about a noun.
An article refers to a noun (a person, place, or thing) and specifies its definiteness. This is a formal way of saying that the article lets everyone know whether the noun is specific or unique to the sentence or not.
Not all languages have indefinite and definite articles. English has just one definite article: the , which refers to a specific noun. The indefinite articles a or an refer to nouns more generally.
What is an indefinite article ?
Indefinite articles refer to non-specific nouns. You might say, “I need a pen,” or “ I want an orange.” In both cases, you aren’t referring to a specific pen or orange. The indefinite articles communicate the fact that you’d accept any pen or orange .
Here are a few more examples:
- Let’s go to a bookstore.
- We need a plumber.
- That’s her drawing of an elephant.
In these examples, it does not matter which bookstore is visited or which plumber is called. (At least check some recommendations, please!) Someone has drawn a picture of an elephant—any elephant, not the specific elephant at the local zoo.
The above examples also demonstrate when to use a versus an . If the word following the article begins with a consonant sound, you should use a . If it begins with a vowel sound, you should use an . So if you added the word large to describe the orange you want, the sentence would become I want a large orange . The same goes for the elephant:
- That’s her drawing of a pink elephant. (They do exist!)
If you’re wondering, an originated before 950 from the Old English word for one , ?n . A is a variant of an .
What is a definite article ?
The definite article the , on the other hand, refers to a specific noun. If you were to say, “I want the orange” instead of “ an orange,” you’d be talking about one specific orange. If you requested “ the pencil” instead of “ a pencil,” you’d be asking for one particular pencil.
- The neighbor’s dog barked at me.
- I lent my brother the book when I finished reading it.
- I don’t want to go to the party.
In all these examples, the article accompanies a specific item that is being discussed. In some cases, the noun has already been named and discussed. For example:
“Did you finish reading The Poet X ?” “Yes, I lent my brother the book when I finished reading it.”
Like a and an , the has roots in Old English and dates before 900.
What if the noun is plural?
A and an only work with singular nouns because they only refer to one item. Plural, non-specific nouns don’t use articles. So if you want more than one orange but don’t care which ones, I want an orange becomes I want oranges .
The works with both singular and plural nouns. If you want a specific orange or specific oranges, you could say, “I want the orange,” or “I want the oranges.”
For example:
- I dropped the blocks and they clattered to the floor.
- I dropped a block.
- We planted trees in the yard.
- We planted a tree in the yard.
What about mass nouns?
Mass nouns are any nouns that can’t be counted. This makes them neither singular nor plural. Liquids are a great example of mass nouns. You’d still use the article the for specific mass nouns, but for non-specific ones, you wouldn’t use an article at all.
- The water is on the floor.
- Water is on the floor.
Both are are correct. The first refers to specific water, while the second doesn’t.
There’s one exception that allows you to use a or an before a mass noun. This occurs when a specific noun is implied in the context of the sentence. A scenario where this might happen would be at a restaurant. Instead of saying “I’ll have a glass of orange juice,” you’d say, “I’ll have an orange juice.” Orange juice is a mass noun, but in this context it’s implied that you’re referring to a glass of orange juice .
So go ahead and talk about the nouns in your life, in general or specifically. The English language is here to support you!
Tired of embarrassing typos? Let Grammar Coach™ do the heavy lifting, and fix your writing for free! Start now!

Ways To Say
Synonym of the day
Indefinite Articles: A and An | Definition, Useful Rules & Usage
Indefinite Article in English! An article is a word that modifies or describes the noun. It is used before the noun to show whether it refers to something specific or not.
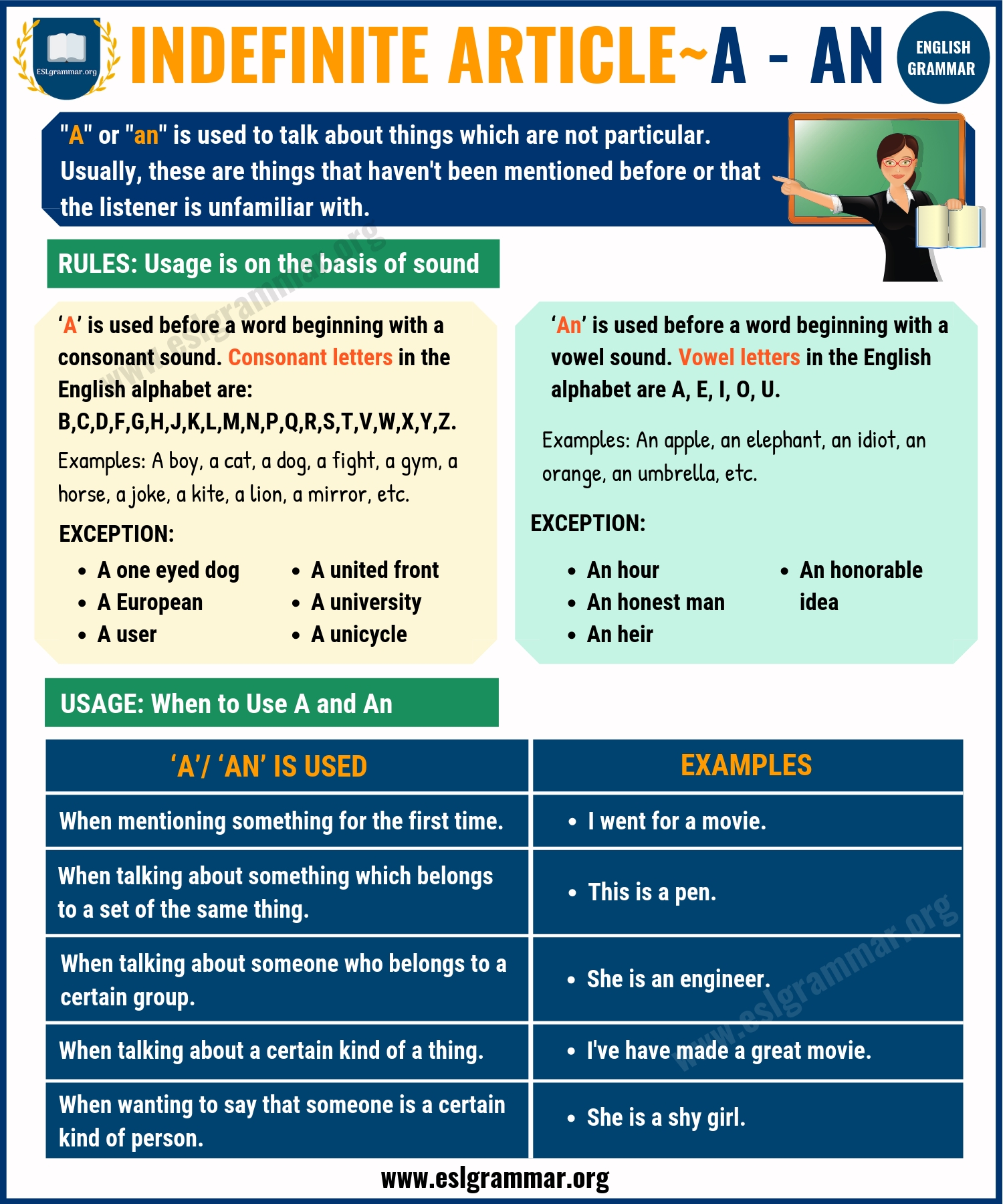
Indefinite Article – Definition
“A” or “An” is used to talk about things which are not particular. Usually, these are things that haven’t been mentioned before or that the listener is unfamiliar with.
Indefinite Article – Rules
Indefinite articles ‘a/an’ are used as follows:
‘A’ is used before a word beginning with a consonant sound . Consonant letters in the English alphabet are B,C,D,F,G,H,J,K,L,M,N,P,Q,R,S,T,V,W,X,Y,Z.
- For example: A boy, a cat, a dog, a fight, a gym, a horse, a joke, a kite, a lion, a mirror, a noise, a pin, a quilt, etc.
‘An’ is used before a word beginning with a vowel sound . Vowel letters in the English alphabet are A, E, I, O, U.
- For example: An apple, an elephant, an idiot, an orange, an umbrella, etc.
Note here that the usage is on the basis of sound and not only the letter the word starts with.
For example:
“An hour” “An honest man” “A one eyed dog”
Do these seem wrong to you?
They’re not and the reason is that the ‘usage is on the basis of sound’. The words ‘hour’ and ‘honest’ both begin with a vowel sound, as the consonant ‘h’ is not pronounced. Similarly, the word ‘one’ begins with the consonant sound of ‘w’ and hence is written as ‘a one eyed dog’, not ‘an one eyed dog’.
Also, remember that we use “a” and “an” only before a singular noun. We can’t use “a” and “an” before a plural noun.
A book – correct A books – incorrect An egg – correct An eggs – incorrect
Tips to remember the differences in a nutshell
# a + singular noun beginning with a consonant: a bag; a pen, etc.
# an + singular noun beginning with a vowel: an egg; an orphan, etc.
# a + singular noun beginning with a consonant sound: a user(sounds like ‘yoo-zer,’ i.e., gives a ‘y’ sound, so ‘a’ is used); a university; a European, etc.
# an + nouns starting with silent “h”: an hour; an honest man, etc.
These rules also apply in Acronyms.
- He is a DU ( Delhi University ) student.
- He is an IIT (Indian Institute of Technology) graduate.
The rule also applies when acronyms start with consonant letters but have vowel sounds.
- She is an MBA (Master of Business Administration).
When/If the noun is modified by an adjective, the choice between “a” and “an” depends on the initial sound of the adjective that immediately follows the article.
- a beautiful umbrella
- an unusual situation
- a European country (pronounced as ‘yer-o-pi-an,’ i.e., sounds like consonant ‘y’)
A/An is used to indicate membership in a group.
- I am a journalist. (I am a member of a large group of professionals known as journalists.)
- She is an Indian . (She is a member of the people from India, known as Indians.)
- A table to remember when or when not to use Articles
Indefinite Article – Usage
Related posts:.

I’ve have made needs to be corrected, please.
Can we use a before a person’s name who is not known peersonally? Like in this sentence: Do you know a Saleem Qureshi? Thanks
- Dictionaries home
- American English
- Collocations
- German-English
- Grammar home
- Practical English Usage
- Learn & Practise Grammar (Beta)
- Word Lists home
- My Word Lists
- Recent additions
- Resources home
- Text Checker
Definition of indefinite article noun from the Oxford Advanced Learner's Dictionary
indefinite article
Want to learn more?
Find out which words work together and produce more natural-sounding English with the Oxford Collocations Dictionary app. Try it for free as part of the Oxford Advanced Learner’s Dictionary app.


IMAGES
VIDEO
COMMENTS
An indefinite article is a part of speech that identifies a nonspecific noun. "A" and "an" are the only indefinite articles. Placing "a" or "an" before a noun makes it nonspecific. To say "a book" refers to any book, not a single specific book. The examples below will further outline the difference. a cow (nonspecific ...
The meaning of INDEFINITE ARTICLE is the word a or an used in English to refer to a person or thing that is not identified or specified; also : a word that has a similar use in another language. How to use indefinite article in a sentence.
Indefinite articles refer to a noun without specifying it. Learn how to use indefinite articles in a sentence with these examples and best practices.
The indefinite article is the word "a" or "an." It is used before a noun to define it as something non-specific (e.g., something generic or something mentioned for the first time). For example: I'm a pirate. (This means an unspecified pirate, i.e., not one previously discussed.)
Level: beginner. We use the indefinite article, a/an, with singular nouns when the listener/reader does not know exactly which one we are referring to: Police are searching for a 14-year-old girl. We also use it to show that the person or thing is one of a group: She is a pupil at London Road School. Police have been looking for a 14-year-old ...
The two indefinite articles are a and an. A is used before a singular noun that begins with a consonant sound or letter. An is the article used before a singular noun starting with a vowel sound. Here, I made some examples to better explain: An apple a day keeps the doctor away. A kiss will remove the pain.
Definition of an indefinite article. An indefinite article is instrumental in introducing a noun (or noun equivalent) without specifying it or putting it out there for the first time. It is used to refer to something non-specific or generic. Definite vs. indefinite article.
INDEFINITE ARTICLE definition: 1. the grammatical name for the words "a" and "an" in English or words in other languages that have…. Learn more.
The indefinite article in English is a simple but important part of speech. It includes the words "a" and "an.". We use these articles before singular, countable nouns when the exact identity of the noun is not known to the reader or listener. The choice between "a" and "an" depends on sound. Use "a" before words that start ...
INDEFINITE ARTICLE meaning: 1. the grammatical name for the words "a" and "an" in English or words in other languages that have…. Learn more.
Indefinite Reference. Indefinite reference is appropriate when the reader and/or the writer do not both know the specific identity of the noun. This might be because: it is not important ( use a computer = use any computer) not known to the writer ( a further study is needed) new to the reader ( we used a new technique = the writer knows ...
Transcript. Definite and indefinite articles are words that modify nouns in English. The word "the" is the definite article, which means it specifies a particular noun or a group of nouns. It can be used for singular or plural nouns. The words "a" or "an" are indefinite articles, which means they do not specify which noun they refer to. Questions.
An indefinite article is simply the word "a" or "an" used before a noun. It denotes the class to which a noun belongs but does not make the noun particular. Examples. Ted went to a store this afternoon. Ted saw an octopus at the aquarium. As you can see, an indefinite article tells us about something that isn't specific.
Indefinite article + Adverb + Adjective. The same rule comes in handy when we need to use the indefinite article that comes before an adverb followed by adjective before a noun. But in such a case, choose the indefinite article based on the first sound of the adverb, not the adjective or noun.
Articles are words that are used before nouns to define them as specific or unspecific. Let's look at the following examples: After the long day, the cup of tea tasted really good. By using the article the, we've shown that it was one specific long day and that one specific cup of tea tasted good. After a long day, a cup of tea tastes ...
Just because articles are small in size, doesn't mean they're small in importance. Learn what articles are and why they're crucial to your sentences here.
Britannica Dictionary definition of INDEFINITE ARTICLE. [count] : the word a or an used in English to refer to a person or thing that is not identified or specified. In "I gave a book to the boy" the word "a" is an indefinite article and the word "the" is a definite article. also : a word that has a similar use in another language.
What is an indefinite article? According to Your Dictionary, the indefinite articles and a and an. As opposed to other languages like French and Spanish that use masculine and feminine articles, English uses the specificity of the vowel sound or consonant sound in the pronunciation of the following word to decide on which article to use.
An indefinite article is an article that marks an indefinite noun phrase. Indefinite articles are those such as English "some" or "a", which do not refer to a specific identifiable entity. Indefinites are commonly used to introduce a new discourse referent which can be referred back to in subsequent discussion:
"A," "an," and "the" are all articles in the English language. Learn more about definite vs. indefinite articles and when to use them.
Indefinite Article in English! An article is a word that modifies or describes the noun. It is used before the noun to show whether it refers to something. ... Indefinite Article - Definition "A" or "An" is used to talk about things which are not particular. Usually, these are things that haven't been mentioned before or that the ...
Definition of indefinite article noun in Oxford Advanced Learner's Dictionary. Meaning, pronunciation, picture, example sentences, grammar, usage notes, synonyms and more.