- PRO Courses Guides New Tech Help Pro Expert Videos About wikiHow Pro Upgrade Sign In
- EDIT Edit this Article
- EXPLORE Tech Help Pro About Us Random Article Quizzes Request a New Article Community Dashboard This Or That Game Popular Categories Arts and Entertainment Artwork Books Movies Computers and Electronics Computers Phone Skills Technology Hacks Health Men's Health Mental Health Women's Health Relationships Dating Love Relationship Issues Hobbies and Crafts Crafts Drawing Games Education & Communication Communication Skills Personal Development Studying Personal Care and Style Fashion Hair Care Personal Hygiene Youth Personal Care School Stuff Dating All Categories Arts and Entertainment Finance and Business Home and Garden Relationship Quizzes Cars & Other Vehicles Food and Entertaining Personal Care and Style Sports and Fitness Computers and Electronics Health Pets and Animals Travel Education & Communication Hobbies and Crafts Philosophy and Religion Work World Family Life Holidays and Traditions Relationships Youth
- Browse Articles
- Learn Something New
- Quizzes Hot
- This Or That Game New
- Train Your Brain
- Explore More
- Support wikiHow
- About wikiHow
- Log in / Sign up
- Education and Communications
- English Grammar
- Writing Paragraphs

How to Write a Concluding Paragraph for a Persuasive Essay
Last Updated: February 13, 2024 Fact Checked
This article was co-authored by Jake Adams . Jake Adams is an academic tutor and the owner of Simplifi EDU, a Santa Monica, California based online tutoring business offering learning resources and online tutors for academic subjects K-College, SAT & ACT prep, and college admissions applications. With over 14 years of professional tutoring experience, Jake is dedicated to providing his clients the very best online tutoring experience and access to a network of excellent undergraduate and graduate-level tutors from top colleges all over the nation. Jake holds a BS in International Business and Marketing from Pepperdine University. This article has been fact-checked, ensuring the accuracy of any cited facts and confirming the authority of its sources. This article has been viewed 184,161 times.
Giving an Overview

- If it helps, print out a copy of the body of the paper and highlight the main points to be summarized.

- For instance, "Gun laws should be changed to reflect the evolving needs of today's generations.”

- You can, however, create a call to action or end with a creative and engaging hook statement.

- Using the first sentence to restate the hypothesis in your introduction, in different wording
- Writing the next 2-3 sentence to summarize the key arguments made in your paper
- Having the last 1-2 sentences be a grand statement of conclusion, saying what your final findings are
Using Convincing Wording

- For instance, "Regular exercise reduces stress, improves your sleep, and promotes weight loss."

- For instance, instead of writing, "The traditional American Dream is not dead and gone," write, "The American Dream is not dead.”
- However, keep in mind that in some cases, more elaborate wording may be necessary to drive home your point.

Establishing the Relevance of Your Conclusion

- For example,"What will happen to small businesses as different industries continue to go digital?"

- For example, "Being environmentally responsible is a necessary step for all people, in order to save the parts of nature that we have left."

- For example, "If this competitive nature of school work were replaced with a more community-based learning approach, we might see happier, healthier children."
Community Q&A
You Might Also Like

- ↑ Jake Adams. Academic Tutor & Test Prep Specialist. Expert Interview. 20 May 2020.
- ↑ https://opentextbc.ca/writingforsuccess/chapter/chapter-10-persuasion/
- ↑ http://penandthepad.com/write-concluding-paragraph-persuasive-essay-college-1412.html
- ↑ http://examples.yourdictionary.com/parallel-structure-examples.html
- ↑ http://writingcenter.fas.harvard.edu/pages/ending-essay-conclusions
- ↑ https://owl.purdue.edu/owl/general_writing/common_writing_assignments/argument_papers/conclusions.html
About This Article

To write a concluding paragraph for your persuasive essay, you’ll need to briefly summarize your main arguments. Use the first sentence to restate your hypothesis from your introduction in different words. Then, spend 2 or 3 sentences reminding the reader of the main arguments you made throughout the essay. Use strong, simple language to emphasize your conclusion. You can also add a call to action or tell the reader what you think should happen as a result of your conclusions. For example, "If this competitive nature of school work were replaced with a more community-based learning approach, we might see happier, healthier children." For more tips from our Teaching co-author, including how to position your arguments within the bigger picture, read on! Did this summary help you? Yes No
- Send fan mail to authors
Reader Success Stories
Bella Cosgrove
Aug 5, 2019
Did this article help you?

Mahak Azeem
Jun 15, 2020

Featured Articles

Trending Articles

Watch Articles

- Terms of Use
- Privacy Policy
- Do Not Sell or Share My Info
- Not Selling Info
Get all the best how-tos!
Sign up for wikiHow's weekly email newsletter
Have a language expert improve your writing
Run a free plagiarism check in 10 minutes, generate accurate citations for free.
- Knowledge Base
- How to conclude an essay | Interactive example
How to Conclude an Essay | Interactive Example
Published on January 24, 2019 by Shona McCombes . Revised on July 23, 2023.
The conclusion is the final paragraph of your essay . A strong conclusion aims to:
- Tie together the essay’s main points
- Show why your argument matters
- Leave the reader with a strong impression
Your conclusion should give a sense of closure and completion to your argument, but also show what new questions or possibilities it has opened up.
This conclusion is taken from our annotated essay example , which discusses the history of the Braille system. Hover over each part to see why it’s effective.
Braille paved the way for dramatic cultural changes in the way blind people were treated and the opportunities available to them. Louis Braille’s innovation was to reimagine existing reading systems from a blind perspective, and the success of this invention required sighted teachers to adapt to their students’ reality instead of the other way around. In this sense, Braille helped drive broader social changes in the status of blindness. New accessibility tools provide practical advantages to those who need them, but they can also change the perspectives and attitudes of those who do not.
Instantly correct all language mistakes in your text
Upload your document to correct all your mistakes in minutes

Table of contents
Step 1: return to your thesis, step 2: review your main points, step 3: show why it matters, what shouldn’t go in the conclusion, more examples of essay conclusions, other interesting articles, frequently asked questions about writing an essay conclusion.
To begin your conclusion, signal that the essay is coming to an end by returning to your overall argument.
Don’t just repeat your thesis statement —instead, try to rephrase your argument in a way that shows how it has been developed since the introduction.
Prevent plagiarism. Run a free check.
Next, remind the reader of the main points that you used to support your argument.
Avoid simply summarizing each paragraph or repeating each point in order; try to bring your points together in a way that makes the connections between them clear. The conclusion is your final chance to show how all the paragraphs of your essay add up to a coherent whole.
To wrap up your conclusion, zoom out to a broader view of the topic and consider the implications of your argument. For example:
- Does it contribute a new understanding of your topic?
- Does it raise new questions for future study?
- Does it lead to practical suggestions or predictions?
- Can it be applied to different contexts?
- Can it be connected to a broader debate or theme?
Whatever your essay is about, the conclusion should aim to emphasize the significance of your argument, whether that’s within your academic subject or in the wider world.
Try to end with a strong, decisive sentence, leaving the reader with a lingering sense of interest in your topic.
The easiest way to improve your conclusion is to eliminate these common mistakes.
Don’t include new evidence
Any evidence or analysis that is essential to supporting your thesis statement should appear in the main body of the essay.
The conclusion might include minor pieces of new information—for example, a sentence or two discussing broader implications, or a quotation that nicely summarizes your central point. But it shouldn’t introduce any major new sources or ideas that need further explanation to understand.
Don’t use “concluding phrases”
Avoid using obvious stock phrases to tell the reader what you’re doing:
- “In conclusion…”
- “To sum up…”
These phrases aren’t forbidden, but they can make your writing sound weak. By returning to your main argument, it will quickly become clear that you are concluding the essay—you shouldn’t have to spell it out.
Don’t undermine your argument
Avoid using apologetic phrases that sound uncertain or confused:
- “This is just one approach among many.”
- “There are good arguments on both sides of this issue.”
- “There is no clear answer to this problem.”
Even if your essay has explored different points of view, your own position should be clear. There may be many possible approaches to the topic, but you want to leave the reader convinced that yours is the best one!
- Argumentative
- Literary analysis
This conclusion is taken from an argumentative essay about the internet’s impact on education. It acknowledges the opposing arguments while taking a clear, decisive position.
The internet has had a major positive impact on the world of education; occasional pitfalls aside, its value is evident in numerous applications. The future of teaching lies in the possibilities the internet opens up for communication, research, and interactivity. As the popularity of distance learning shows, students value the flexibility and accessibility offered by digital education, and educators should fully embrace these advantages. The internet’s dangers, real and imaginary, have been documented exhaustively by skeptics, but the internet is here to stay; it is time to focus seriously on its potential for good.
This conclusion is taken from a short expository essay that explains the invention of the printing press and its effects on European society. It focuses on giving a clear, concise overview of what was covered in the essay.
The invention of the printing press was important not only in terms of its immediate cultural and economic effects, but also in terms of its major impact on politics and religion across Europe. In the century following the invention of the printing press, the relatively stationary intellectual atmosphere of the Middle Ages gave way to the social upheavals of the Reformation and the Renaissance. A single technological innovation had contributed to the total reshaping of the continent.
This conclusion is taken from a literary analysis essay about Mary Shelley’s Frankenstein . It summarizes what the essay’s analysis achieved and emphasizes its originality.
By tracing the depiction of Frankenstein through the novel’s three volumes, I have demonstrated how the narrative structure shifts our perception of the character. While the Frankenstein of the first volume is depicted as having innocent intentions, the second and third volumes—first in the creature’s accusatory voice, and then in his own voice—increasingly undermine him, causing him to appear alternately ridiculous and vindictive. Far from the one-dimensional villain he is often taken to be, the character of Frankenstein is compelling because of the dynamic narrative frame in which he is placed. In this frame, Frankenstein’s narrative self-presentation responds to the images of him we see from others’ perspectives. This conclusion sheds new light on the novel, foregrounding Shelley’s unique layering of narrative perspectives and its importance for the depiction of character.
If you want to know more about AI tools , college essays , or fallacies make sure to check out some of our other articles with explanations and examples or go directly to our tools!
- Ad hominem fallacy
- Post hoc fallacy
- Appeal to authority fallacy
- False cause fallacy
- Sunk cost fallacy
College essays
- Choosing Essay Topic
- Write a College Essay
- Write a Diversity Essay
- College Essay Format & Structure
- Comparing and Contrasting in an Essay
(AI) Tools
- Grammar Checker
- Paraphrasing Tool
- Text Summarizer
- AI Detector
- Plagiarism Checker
- Citation Generator
Your essay’s conclusion should contain:
- A rephrased version of your overall thesis
- A brief review of the key points you made in the main body
- An indication of why your argument matters
The conclusion may also reflect on the broader implications of your argument, showing how your ideas could applied to other contexts or debates.
For a stronger conclusion paragraph, avoid including:
- Important evidence or analysis that wasn’t mentioned in the main body
- Generic concluding phrases (e.g. “In conclusion…”)
- Weak statements that undermine your argument (e.g. “There are good points on both sides of this issue.”)
Your conclusion should leave the reader with a strong, decisive impression of your work.
The conclusion paragraph of an essay is usually shorter than the introduction . As a rule, it shouldn’t take up more than 10–15% of the text.
Cite this Scribbr article
If you want to cite this source, you can copy and paste the citation or click the “Cite this Scribbr article” button to automatically add the citation to our free Citation Generator.
McCombes, S. (2023, July 23). How to Conclude an Essay | Interactive Example. Scribbr. Retrieved April 3, 2024, from https://www.scribbr.com/academic-essay/conclusion/
Is this article helpful?
Shona McCombes
Other students also liked, how to write an essay introduction | 4 steps & examples, how to write a thesis statement | 4 steps & examples, example of a great essay | explanations, tips & tricks, what is your plagiarism score.
Purdue Online Writing Lab Purdue OWL® College of Liberal Arts
Conclusions

Welcome to the Purdue OWL
This page is brought to you by the OWL at Purdue University. When printing this page, you must include the entire legal notice.
Copyright ©1995-2018 by The Writing Lab & The OWL at Purdue and Purdue University. All rights reserved. This material may not be published, reproduced, broadcast, rewritten, or redistributed without permission. Use of this site constitutes acceptance of our terms and conditions of fair use.
This resource outlines the generally accepted structure for introductions, body paragraphs, and conclusions in an academic argument paper. Keep in mind that this resource contains guidelines and not strict rules about organization. Your structure needs to be flexible enough to meet the requirements of your purpose and audience.
Conclusions wrap up what you have been discussing in your paper. After moving from general to specific information in the introduction and body paragraphs, your conclusion should begin pulling back into more general information that restates the main points of your argument. Conclusions may also call for action or overview future possible research. The following outline may help you conclude your paper:
In a general way,
- Restate your topic and why it is important,
- Restate your thesis/claim,
- Address opposing viewpoints and explain why readers should align with your position,
- Call for action or overview future research possibilities.
Remember that once you accomplish these tasks, unless otherwise directed by your instructor, you are finished. Done. Complete. Don't try to bring in new points or end with a whiz bang(!) conclusion or try to solve world hunger in the final sentence of your conclusion. Simplicity is best for a clear, convincing message.
The preacher's maxim is one of the most effective formulas to follow for argument papers:
Tell what you're going to tell them (introduction).
Tell them (body).
Tell them what you told them (conclusion).

How to Write the Conclusion for a Persuasive Essay

Writing a Conclusion for a Persuasive Essay
Some high school and college students assume the body paragraphs are all that matter in an essay. However, an argument will fall flat if it does not end with a strong conclusion -- especially when your intent is to persuade. A good conclusion summarizes the points you made earlier and also makes the reader want to act in response to the paper. Occasionally, this includes the thesis statement in the conclusion paragraph, as well as new points of view for larger observations. Keeping the reader’s attention should be important to include, especially in the first sentence of the conclusion, as well as in the first paragraph, the introductory paragraph, of the essay.
The last thing you may include in a conclusion could be your main points of the essay summarized in a new way. Academic writing, especially for these essays, includes knowing what to include for the body of the paper, topic sentences, a sense of closure, restatement of main points, key points of research or insight, main arguments supported by details and context, and an effective conclusion or concluding paragraph. An essay conclusion is essential for readers to fully comprehend what you are writing your persuasive or argumentative essay about.
Describe the Stakes
According to Purdue University’s Online Writing Lab, begin with a reminder. Let the reader know what will happen if nothing is done to resolve the issue in your argument. Reuse a particular statistic or an example you used earlier. If, to get the reader interested, you started your persuasive essay on drunk driving with the story of a mother and children who were killed by a drunk driver, begin the conclusion by referring back to that family.
Summarize Your Position
Briefly restate your position. Touch on the highlights of your argument, and show how your essay resolves or addresses the issue. Waterford Union High School advises students to restate the thesis and summarize all of the main points from the body paragraphs. For example, if you're writing a persuasive essay that argues that legal consequences for drunk driving are too lenient, emphasize key evidence you introduced in the body -- such as the percent of offenders that go on to drive under the influence again.
Clincher: Call to Action
End by arming your readers with specific actions they can take based on the information you have just provided. To encourage stronger penalties for drunk driving, for example, you might ask readers to put pressure on the legislature to create change. As a final note, consider using a quote related to the topic or show how your position relates to a broader issue, according to the Harvard College Writing Center. Ending with a prediction of how the situation will improve if people follow your advice in the paper is another commonly recommended practice.
Problems to Avoid
Avoid these common pitfalls to make your conclusion stand out. The Writing Center at Harvard recommends to not begin this section or paragraph with a phrase like “in conclusion” or “to conclude." Though transitions are important in persuasive writing in general, these tend to be overused.
Make sure your final paragraph does more than just summarize your position. Remember, if you only explain why you hold a certain belief, you are not writing an argument or persuasive essay. You must cause some change in the reader to be successful with this assignment.
Related Articles

A Good Thesis Topic

How to Write an Essay About a Novel

How to Write a Good Closing Argument

How to Write a Dissertation Summary

How to Write Conclusions for Expository Papers

How to Outline a Case for Legal Studies

How to Write a Thesis Statement for "Robinson Crusoe"

The Functions of Conjunctions in English Argumentative Writing
- Purdue University Online Writing Lab: Introductions, Body Paragraphs, and Conclusions for an Argument Paper
- Harvard College Writing Center: Ending the Essay: Conclusions
<!--StartFragment-->I am a current senior studying at the University of Missouri - Columbia with a major in Journalism and a minor in Sociology. I have interests in photojournalism, documentary journalism and design fields. <!--EndFragment--><!--EndFragment--><!--EndFragment-->
- Link to facebook
- Link to linkedin
- Link to twitter
- Link to youtube
- Writing Tips
How to Write a Conclusion for an Argumentative Essay

3-minute read
- 27th October 2023
You’ve spent hours researching and writing a compelling argumentative essay – now it’s finally time to write the conclusion. The conclusion may be the most significant part of your essay because it’s your final opportunity to make a lasting impression on your reader. Intimidated? Don’t be! In this post, we’ll show you how to write a strong conclusion for an argumentative essay.
Restate the Thesis and Summarize the Key Points
Begin by reiterating your thesis statement to emphasize your main point. However, to avoid sounding repetitive, it’s best to paraphrase the thesis and not use the exact wording from the introductory paragraph. You can also briefly recap the key points you’ve made throughout your essay. You don’t need to dive into too much detail here; the conclusion should be a concise reminder of your most critical arguments and avoid unnecessary repetition or commentary. Keep in mind that the conclusion is not the place to provide information or arguments you haven’t included in the body of your essay.
Emphasize the Significance of Your Arguments
The conclusion of your essay is a good place to highlight the importance of your argument and the implications of your findings. Briefly explain why your essay topic is significant and how your perspective relates to the wider context. For example, if you’re writing on the rising cost of medicine, you can discuss how this topic relates to the broader fields of health care and pharmaceutical sales.
Briefly Address Counterarguments
If you’ve discussed counterarguments in your essay, briefly acknowledge them in the conclusion. You can simply mention that although there are opposing views, you’ve supported your argument with the evidence presented in your essay.
Find this useful?
Subscribe to our newsletter and get writing tips from our editors straight to your inbox.
Maintain a Consistent Tone
Keep the tone of your conclusion consistent with the rest of the essay. For example, if your essay has been primarily formal and academic, maintain that tone in the conclusion (e.g., avoid closing with an informal anecdote or a witty observation).
End With a Thought-Provoking Statement
End your conclusion with a thought-provoking statement or call to action . This could involve a recommendation or prediction, or you could pinpoint areas for further research or action related to the topic. For example, if your topic is the impact of technology on education, you could end your essay by recommending further research into the long-term effects of technology use on students beyond elementary school.
Ensure that your arguments take center stage by having our expert team proofread your essay. Our editors have experience with a wide variety of academic subjects and can ensure that your words make an impact. Send in your sample for free today to see for yourself!
Share this article:
Post A New Comment
Got content that needs a quick turnaround? Let us polish your work. Explore our editorial business services.
What is a content editor.
Are you interested in learning more about the role of a content editor and the...
4-minute read
The Benefits of Using an Online Proofreading Service
Proofreading is important to ensure your writing is clear and concise for your readers. Whether...
2-minute read
6 Online AI Presentation Maker Tools
Creating presentations can be time-consuming and frustrating. Trying to construct a visually appealing and informative...
What Is Market Research?
No matter your industry, conducting market research helps you keep up to date with shifting...
8 Press Release Distribution Services for Your Business
In a world where you need to stand out, press releases are key to being...
How to Get a Patent
In the United States, the US Patent and Trademarks Office issues patents. In the United...

Make sure your writing is the best it can be with our expert English proofreading and editing.
In a short paper—even a research paper—you don’t need to provide an exhaustive summary as part of your conclusion. But you do need to make some kind of transition between your final body paragraph and your concluding paragraph. This may come in the form of a few sentences of summary. Or it may come in the form of a sentence that brings your readers back to your thesis or main idea and reminds your readers where you began and how far you have traveled.
So, for example, in a paper about the relationship between ADHD and rejection sensitivity, Vanessa Roser begins by introducing readers to the fact that researchers have studied the relationship between the two conditions and then provides her explanation of that relationship. Here’s her thesis: “While socialization may indeed be an important factor in RS, I argue that individuals with ADHD may also possess a neurological predisposition to RS that is exacerbated by the differing executive and emotional regulation characteristic of ADHD.”
In her final paragraph, Roser reminds us of where she started by echoing her thesis: “This literature demonstrates that, as with many other conditions, ADHD and RS share a delicately intertwined pattern of neurological similarities that is rooted in the innate biology of an individual’s mind, a connection that cannot be explained in full by the behavioral mediation hypothesis.”
Highlight the “so what”
At the beginning of your paper, you explain to your readers what’s at stake—why they should care about the argument you’re making. In your conclusion, you can bring readers back to those stakes by reminding them why your argument is important in the first place. You can also draft a few sentences that put those stakes into a new or broader context.
In the conclusion to her paper about ADHD and RS, Roser echoes the stakes she established in her introduction—that research into connections between ADHD and RS has led to contradictory results, raising questions about the “behavioral mediation hypothesis.”
She writes, “as with many other conditions, ADHD and RS share a delicately intertwined pattern of neurological similarities that is rooted in the innate biology of an individual’s mind, a connection that cannot be explained in full by the behavioral mediation hypothesis.”
Leave your readers with the “now what”
After the “what” and the “so what,” you should leave your reader with some final thoughts. If you have written a strong introduction, your readers will know why you have been arguing what you have been arguing—and why they should care. And if you’ve made a good case for your thesis, then your readers should be in a position to see things in a new way, understand new questions, or be ready for something that they weren’t ready for before they read your paper.
In her conclusion, Roser offers two “now what” statements. First, she explains that it is important to recognize that the flawed behavioral mediation hypothesis “seems to place a degree of fault on the individual. It implies that individuals with ADHD must have elicited such frequent or intense rejection by virtue of their inadequate social skills, erasing the possibility that they may simply possess a natural sensitivity to emotion.” She then highlights the broader implications for treatment of people with ADHD, noting that recognizing the actual connection between rejection sensitivity and ADHD “has profound implications for understanding how individuals with ADHD might best be treated in educational settings, by counselors, family, peers, or even society as a whole.”
To find your own “now what” for your essay’s conclusion, try asking yourself these questions:
- What can my readers now understand, see in a new light, or grapple with that they would not have understood in the same way before reading my paper? Are we a step closer to understanding a larger phenomenon or to understanding why what was at stake is so important?
- What questions can I now raise that would not have made sense at the beginning of my paper? Questions for further research? Other ways that this topic could be approached?
- Are there other applications for my research? Could my questions be asked about different data in a different context? Could I use my methods to answer a different question?
- What action should be taken in light of this argument? What action do I predict will be taken or could lead to a solution?
- What larger context might my argument be a part of?
What to avoid in your conclusion
- a complete restatement of all that you have said in your paper.
- a substantial counterargument that you do not have space to refute; you should introduce counterarguments before your conclusion.
- an apology for what you have not said. If you need to explain the scope of your paper, you should do this sooner—but don’t apologize for what you have not discussed in your paper.
- fake transitions like “in conclusion” that are followed by sentences that aren’t actually conclusions. (“In conclusion, I have now demonstrated that my thesis is correct.”)
- picture_as_pdf Conclusions
- Features for Creative Writers
- Features for Work
- Features for Higher Education
- Features for Teachers
- Features for Non-Native Speakers
- Learn Blog Grammar Guide Community Events FAQ
- Grammar Guide
How to Write a Persuasive Essay: Tips and Tricks

Allison Bressmer

Most composition classes you’ll take will teach the art of persuasive writing. That’s a good thing.
Knowing where you stand on issues and knowing how to argue for or against something is a skill that will serve you well both inside and outside of the classroom.
Persuasion is the art of using logic to prompt audiences to change their mind or take action , and is generally seen as accomplishing that goal by appealing to emotions and feelings.
A persuasive essay is one that attempts to get a reader to agree with your perspective.

Ready for some tips on how to produce a well-written, well-rounded, well-structured persuasive essay? Just say yes. I don’t want to have to write another essay to convince you!
How Do I Write a Persuasive Essay?
What are some good topics for a persuasive essay, how do i identify an audience for my persuasive essay, how do you create an effective persuasive essay, how should i edit my persuasive essay.
Your persuasive essay needs to have the three components required of any essay: the introduction , body , and conclusion .
That is essay structure. However, there is flexibility in that structure.
There is no rule (unless the assignment has specific rules) for how many paragraphs any of those sections need.
Although the components should be proportional; the body paragraphs will comprise most of your persuasive essay.

How Do I Start a Persuasive Essay?
As with any essay introduction, this paragraph is where you grab your audience’s attention, provide context for the topic of discussion, and present your thesis statement.
TIP 1: Some writers find it easier to write their introductions last. As long as you have your working thesis, this is a perfectly acceptable approach. From that thesis, you can plan your body paragraphs and then go back and write your introduction.
TIP 2: Avoid “announcing” your thesis. Don’t include statements like this:
- “In my essay I will show why extinct animals should (not) be regenerated.”
- “The purpose of my essay is to argue that extinct animals should (not) be regenerated.”
Announcements take away from the originality, authority, and sophistication of your writing.
Instead, write a convincing thesis statement that answers the question "so what?" Why is the topic important, what do you think about it, and why do you think that? Be specific.
How Many Paragraphs Should a Persuasive Essay Have?
This body of your persuasive essay is the section in which you develop the arguments that support your thesis. Consider these questions as you plan this section of your essay:
- What arguments support your thesis?
- What is the best order for your arguments?
- What evidence do you have?
- Will you address the opposing argument to your own?
- How can you conclude convincingly?

TIP: Brainstorm and do your research before you decide which arguments you’ll focus on in your discussion. Make a list of possibilities and go with the ones that are strongest, that you can discuss with the most confidence, and that help you balance your rhetorical triangle .
What Should I Put in the Conclusion of a Persuasive Essay?
The conclusion is your “mic-drop” moment. Think about how you can leave your audience with a strong final comment.
And while a conclusion often re-emphasizes the main points of a discussion, it shouldn’t simply repeat them.
TIP 1: Be careful not to introduce a new argument in the conclusion—there’s no time to develop it now that you’ve reached the end of your discussion!
TIP 2 : As with your thesis, avoid announcing your conclusion. Don’t start your conclusion with “in conclusion” or “to conclude” or “to end my essay” type statements. Your audience should be able to see that you are bringing the discussion to a close without those overused, less sophisticated signals.

If your instructor has assigned you a topic, then you’ve already got your issue; you’ll just have to determine where you stand on the issue. Where you stand on your topic is your position on that topic.
Your position will ultimately become the thesis of your persuasive essay: the statement the rest of the essay argues for and supports, intending to convince your audience to consider your point of view.
If you have to choose your own topic, use these guidelines to help you make your selection:
- Choose an issue you truly care about
- Choose an issue that is actually debatable
Simple “tastes” (likes and dislikes) can’t really be argued. No matter how many ways someone tries to convince me that milk chocolate rules, I just won’t agree.
It’s dark chocolate or nothing as far as my tastes are concerned.
Similarly, you can’t convince a person to “like” one film more than another in an essay.
You could argue that one movie has superior qualities than another: cinematography, acting, directing, etc. but you can’t convince a person that the film really appeals to them.

Once you’ve selected your issue, determine your position just as you would for an assigned topic. That position will ultimately become your thesis.
Until you’ve finalized your work, consider your thesis a “working thesis.”
This means that your statement represents your position, but you might change its phrasing or structure for that final version.
When you’re writing an essay for a class, it can seem strange to identify an audience—isn’t the audience the instructor?
Your instructor will read and evaluate your essay, and may be part of your greater audience, but you shouldn’t just write for your teacher.
Think about who your intended audience is.
For an argument essay, think of your audience as the people who disagree with you—the people who need convincing.
That population could be quite broad, for example, if you’re arguing a political issue, or narrow, if you’re trying to convince your parents to extend your curfew.
Once you’ve got a sense of your audience, it’s time to consult with Aristotle. Aristotle’s teaching on persuasion has shaped communication since about 330 BC. Apparently, it works.

Aristotle taught that in order to convince an audience of something, the communicator needs to balance the three elements of the rhetorical triangle to achieve the best results.
Those three elements are ethos , logos , and pathos .
Ethos relates to credibility and trustworthiness. How can you, as the writer, demonstrate your credibility as a source of information to your audience?
How will you show them you are worthy of their trust?

- You show you’ve done your research: you understand the issue, both sides
- You show respect for the opposing side: if you disrespect your audience, they won’t respect you or your ideas
Logos relates to logic. How will you convince your audience that your arguments and ideas are reasonable?

You provide facts or other supporting evidence to support your claims.
That evidence may take the form of studies or expert input or reasonable examples or a combination of all of those things, depending on the specific requirements of your assignment.
Remember: if you use someone else’s ideas or words in your essay, you need to give them credit.
ProWritingAid's Plagiarism Checker checks your work against over a billion web-pages, published works, and academic papers so you can be sure of its originality.
Find out more about ProWritingAid’s Plagiarism checks.
Pathos relates to emotion. Audiences are people and people are emotional beings. We respond to emotional prompts. How will you engage your audience with your arguments on an emotional level?

- You make strategic word choices : words have denotations (dictionary meanings) and also connotations, or emotional values. Use words whose connotations will help prompt the feelings you want your audience to experience.
- You use emotionally engaging examples to support your claims or make a point, prompting your audience to be moved by your discussion.
Be mindful as you lean into elements of the triangle. Too much pathos and your audience might end up feeling manipulated, roll their eyes and move on.
An “all logos” approach will leave your essay dry and without a sense of voice; it will probably bore your audience rather than make them care.
Once you’ve got your essay planned, start writing! Don’t worry about perfection, just get your ideas out of your head and off your list and into a rough essay format.
After you’ve written your draft, evaluate your work. What works and what doesn’t? For help with evaluating and revising your work, check out this ProWritingAid post on manuscript revision .
After you’ve evaluated your draft, revise it. Repeat that process as many times as you need to make your work the best it can be.
When you’re satisfied with the content and structure of the essay, take it through the editing process .
Grammatical or sentence-level errors can distract your audience or even detract from the ethos—the authority—of your work.
You don’t have to edit alone! ProWritingAid’s Realtime Report will find errors and make suggestions for improvements.
You can even use it on emails to your professors:
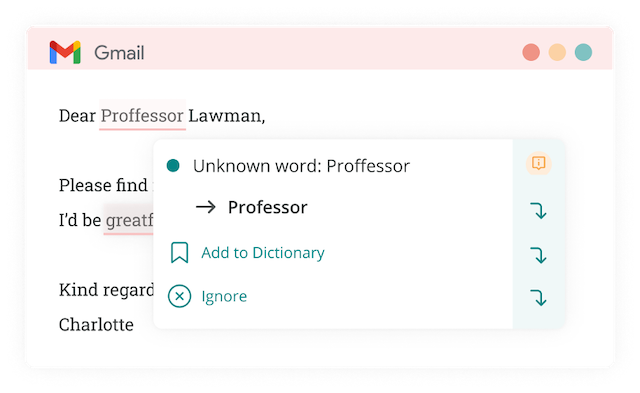
Try ProWritingAid with a free account.
How Can I Improve My Persuasion Skills?
You can develop your powers of persuasion every day just by observing what’s around you.
- How is that advertisement working to convince you to buy a product?
- How is a political candidate arguing for you to vote for them?
- How do you “argue” with friends about what to do over the weekend, or convince your boss to give you a raise?
- How are your parents working to convince you to follow a certain academic or career path?
As you observe these arguments in action, evaluate them. Why are they effective or why do they fail?
How could an argument be strengthened with more (or less) emphasis on ethos, logos, and pathos?
Every argument is an opportunity to learn! Observe them, evaluate them, and use them to perfect your own powers of persuasion.
Be confident about grammar
Check every email, essay, or story for grammar mistakes. Fix them before you press send.
Allison Bressmer is a professor of freshman composition and critical reading at a community college and a freelance writer. If she isn’t writing or teaching, you’ll likely find her reading a book or listening to a podcast while happily sipping a semi-sweet iced tea or happy-houring with friends. She lives in New York with her family. Connect at linkedin.com/in/allisonbressmer.
Get started with ProWritingAid
Drop us a line or let's stay in touch via :

- Search for:
Persuasive Essay (Conclusions)
Watch this for insights into how to conclude Persuasive Essays in Higher English (and why action until the end matters)
search thinkfour.
There’s nothing better than a good adventure story, is there?
One of my favourite adventure stories, really the one that started it all, is the Scottish classic The Thirty-Nine Steps by John Buchan. The story has it all: murder, car chases, violence, code-breaking, submarines, spies.
But, however thrilling The Thirty-Nine Steps definitely is, I always found the ending really disappointing. It seemed to be such an anticlimax, after all the thrills of the previous chapters. In fact, in three of the film adaptations of the book, the ending was completely changed by the directors because it just wasn’t exciting enough.
So, what about the conclusion to your persuasive essay? By this point, you have put in a lot of work and it would be a shame to throw this away with an ineffective and flat conclusion. How do you make sure that you carry on with the same engaging and effective writing all the way to the very end?
Hmm.. let's find out.
This is Think Four.
The conclusion is often the most overlooked part of a persuasive essay. Some people view it as a nice add on, but nothing more than that. On the contrary, your conclusion is the sign off to your essay and a clear and effective one will leave the reader with a great lasting impression. It is key to get this right. There are lots of different ways to conclude an essay, but I’ve found that three simple steps will help to ensure you end your essay clearly and with flair.
Your first step in your conclusion should be to restate your argument. Remind the reader what the whole point your essay is. You don’t need to write “In conclusion…”; in fact, I prefer not to as it can come across as a little clunky. Just a short and simple sentence that lays out your argument will do just fine.
Your second step is to briefly summarise the points that you have already made in the main body of your essay. If you’ve ever seen a courtroom drama, this is your closing statement; you are simply reminding the jury (or in this case, the reader) of the brilliant points that you have already made. You do not need to go into much detail about each of these points, you already did that, and, so, a sentence on each will be fine.
A common mistake that I have seen in writing persuasive essays is arguing a new point in the conclusion; you definitely need to avoid this, as it will break up the flow of your summarising, and you certainly won’t have enough room in your conclusion to explore the point fully. Just recap what you’ve said in a fresh and concise manner, and that will do the job nicely.
The final step in your conclusion is perhaps the most difficult to describe. I call it finishing with a flourish. Just as with your introduction you had to impress the reader with an engaging and well written hook, you should try to leave them with a creative and lasting impression of your writing skills. There are lots of different ways to do this. Some people like to finish off by directly addressing the reader and challenging them to consider or act on the points you have made. Some people like to finish with some emotive language.
Some people like to finish with a powerful rhetorical question. My personal favourite is to refer back to your hook in your introduction, whether it was an anecdote, quotation, or shocking statistic. This reminds the reader of your earlier engaging writing and also shows that you have created a sophisticated essay that can feed into itself and is a whole and coherent argument.
But, to be honest, it is up to you how you choose to flourish. You can use one of these suggestions or come up with your own. The crucial thing to remember is that you must finish in a powerful way that will have the reader thinking about your essay even after they have put it away.
Writing a persuasive essay really is one of the most satisfying and exciting tasks you can do in Higher English. I really believe that. You have a chance to genuinely challenge the way someone thinks and, maybe, even change their mind.
So, it is important that you finish with an effective and lasting conclusion. It may seem like a difficult task but, really, it’s very achievable. What’s more, it won’t take Thirty-Nine Steps, it will only take three.
This was thinkfour, thanks for watching.

© 2024 thinkfour. all rights reserved by thinkfour
- Business Management
- Mathematics
- Modern Studies
Privacy Overview
- AI Content Shield
- AI KW Research
- AI Assistant
- SEO Optimizer
- AI KW Clustering
- Customer reviews
- The NLO Revolution
- Press Center
- Help Center
- Content Resources
- Facebook Group

Writing a Conclusion for Persuasive Essays!
Table of Contents
Conclusions bring everything you have been discussing in your paper to a close.
In the introduction and body paragraphs, you transitioned from general to specific information. In your conclusion, you should start to transition back to more general information that restates the key points of your argument.
Conclusions may also suggest the following steps or summarize potential future research. In conclusion, you should reiterate your topic, the reasons it is significant, and your thesis or claim. They then discuss opposing points of view and justify why readers should support your position.
Finally, they make recommendations for future research or make a call to action. In today’s guide, we’ll look how to write a conclusion for a persuasive essay . Feels exciting? Well then, keep reading until the end!
What Is a Persuasive Essay?

An argumentative essay, also referred to as a persuasive essay, calls for the student to research a subject and support their position.
The three sections of a college-level persuasive essay are typically an introduction with a thesis or argument, body paragraphs with supporting evidence and counterarguments, and a conclusion with a restatement of the thesis or argument. The conclusion of a persuasive essay is crucial because it leaves the reader with one final impression of the author.
In order to persuade readers to adopt a particular point of view, a persuasive essay combines logical justification with emotional appeal. You can use both academic writing and creative writing in persuasive essays.
They frequently start with a query, to which the author devotes the entire essay to make a case for or against. A strong claim will be made in a personal essay and supported by evidence from data, research, and personal experience. The author will frequently examine competing viewpoints and counterarguments in an effort to refute them.
How to Write a Conclusion for a Persuasive Essay?
Without going into too much detail in the body paragraphs, the conclusion should provide a summary of the points made and the supporting evidence used. You should rephrase the first paragraph’s thesis statement to reflect the significance or importance of the points made in the body of the paragraph. The standard length for a conclusion in an academic essay is one well-developed paragraph with at least five sentences.
The conclusion paragraph shouldn’t include any new arguments or supporting data. However, a writer may decide to demonstrate the interrelationships between his theories and research to give his argument new life. By posing inquiries at the end, he can achieve this. For instance, if he made an argument in favor of gun control, he could use questions to connect the premise and argument by reminding the audience of the supporting evidence: It should be evident that gun violence is a problem in our nation. Is it appropriate to put off dealing with the increasing death toll any longer?
In a variety of course formats, college students write persuasive essays, and their conclusion should be relevant to the topic. For instance, a student writing a political science paper might ask the reader to sign a petition or join a support group in order to convince them that stricter gun laws are necessary. The student can inspire his audience to learn more by suggesting additional reading or research materials in a science or social science course where further research is frequently required.
More Tips to Conclude
The main goal of your paper’s concluding paragraph is to restate both the paper’s argument and the ways in which you presented its supporting evidence in the paper’s body. Contrary to popular belief, your conclusion shouldn’t be a carbon copy of your introduction. The conclusion connects the dots in your paper’s argument and demonstrates the direction it has taken. A compelling conclusion persuades the reader to continue reading your essay. The introduction of new information is one of this paragraph’s most crucial functions.
Despite the fact that an effective persuasive essay must follow the organization and structure outlined in this handout, remember that writing is a fluid process. You don’t have to follow any rigid guidelines when writing. It’s not necessary to report the introduction before any other paragraphs just because it’s the first one in your essay. Consider writing as the exploration of ideas, and let this spirit of inquiry direct you as you compose your essay.
Final Words
The most important thing you need to work on in your conclusion is to make it brief. But it doesn’t mean it should not restate the important ideas in your writing again.
We hope you’ve enjoyed our guide on writing a conclusion for a persuasive essay . If you have any more questions on this topic, feel free to write to us!

Abir Ghenaiet
Abir is a data analyst and researcher. Among her interests are artificial intelligence, machine learning, and natural language processing. As a humanitarian and educator, she actively supports women in tech and promotes diversity.
Explore All Blog Post Conclusion Articles
A guide to writing a conclusion for a speech.
A quality speech or presentation is comparable to a quality play, film, or song. It begins by grabbing the listener’s…
- Blog Post Conclusion
The Ideal Length Of a Conclusion Paragraph
You have spent a lot of time writing your essay by the time you reach the final paragraph, so your…
Conclusions bring everything you have been discussing in your paper to a close. In the introduction and body paragraphs, you…
Clear Guide to Introduction & Conclusion Paragraphs Examples
The introduction and conclusion play a major role in academic essays. Writing these paragraphs typically requires much of your focus.…
Effective Guide to Write a Discussion & Conclusion
How to write a discussion and conclusion section of a paper? This is often one of the most confusing aspects,…
Importance of Good Conclusion Paragraph for a Research Paper
Writing a good conclusion paragraph for a research paper can sometimes be challenging. Writers often find it difficult to draft…
- How to Cite
- Language & Lit
- Rhyme & Rhythm
- The Rewrite
- Search Glass
How to Write a Concluding Paragraph for a Persuasive Essay in College
A persuasive essay, also known as an argumentative essay, is one that requires a student to investigate a topic and argue a viewpoint. College-level persuasive essays generally have three sections that include an introduction in which a thesis or argument is presented, body paragraphs in which arguments and counterarguments are presented, and a conclusion in which the argument is reiterated. The conclusion is an important aspect of a persuasive essay as it is the last impression a writer makes on the reader.
What to Include
The conclusion should include a brief overview of what was argued and what evidence was presented without including too many specifics from the body paragraphs. The thesis statement from the first paragraph should be restated, but reworded, and reflect the significance or importance of what was argued. A conclusion in an academic essay typically only needs to be one well-developed paragraph of at least five sentences.
New Meaning
No new evidence or arguments should be presented in the conclusion paragraph. However, a writer may choose to give his argument new meaning by showing how his ideas and research work together. He can do this by asking questions in the conclusion. For example, if he argued in support of nationalized health care he could ask questions that bring the premise and argument together, by reminding the readers of the evidence presented: Isn't it clear that healthcare is a problem in our country? Should we wait any longer to deal with the escalating costs and lack of access?
Challenge the Reader
College students write persuasive essays in many different types of classes, and their conclusion should reflect the subject matter. For example, if a student writes a political science paper trying to persuade his reader that tougher gun laws are important, he can ask the reader to sign a petition or join a support group. In a science or social science class, where further investigation is often warranted, the student can challenge his reader to study the topic further by suggesting additional reading or research materials.
Future Outlook
Another way to end a persuasive research paper is by asking the reader to look to the future, either real or imagined. For example, a persuasive paper may argue that schools need to do more about bullying. The writer could create a mental picture of a school where all students are treated with respect and appreciated for their differences. This would leave the reader with a lasting impression of what a school without bullies could look like, persuading the reader to agree with the essay's main arguments.
- Purdue Online Writing Lab: Argumentative Essays
- St. Cloud State University: Strategies for Writing a Conclusion
- Hamilton College Writing Center: Persuasive Essays, the Basics
- University of Toronto: Introductions and Conclusions
How to Write a Persuasive Essay (This Convinced My Professor!)
.png)
Table of contents

Meredith Sell
You can make your essay more persuasive by getting straight to the point.
In fact, that's exactly what we did here, and that's just the first tip of this guide. Throughout this guide, we share the steps needed to prove an argument and create a persuasive essay.
This AI tool helps you improve your essay > This AI tool helps you improve your essay >

Key takeaways: - Proven process to make any argument persuasive - 5-step process to structure arguments - How to use AI to formulate and optimize your essay
Why is being persuasive so difficult?
"Write an essay that persuades the reader of your opinion on a topic of your choice."
You might be staring at an assignment description just like this 👆from your professor. Your computer is open to a blank document, the cursor blinking impatiently. Do I even have opinions?
The persuasive essay can be one of the most intimidating academic papers to write: not only do you need to identify a narrow topic and research it, but you also have to come up with a position on that topic that you can back up with research while simultaneously addressing different viewpoints.
That’s a big ask. And let’s be real: most opinion pieces in major news publications don’t fulfill these requirements.
The upside? By researching and writing your own opinion, you can learn how to better formulate not only an argument but the actual positions you decide to hold.
Here, we break down exactly how to write a persuasive essay. We’ll start by taking a step that’s key for every piece of writing—defining the terms.
What Is a Persuasive Essay?
A persuasive essay is exactly what it sounds like: an essay that persuades . Over the course of several paragraphs or pages, you’ll use researched facts and logic to convince the reader of your opinion on a particular topic and discredit opposing opinions.
While you’ll spend some time explaining the topic or issue in question, most of your essay will flesh out your viewpoint and the evidence that supports it.
The 5 Must-Have Steps of a Persuasive Essay
If you’re intimidated by the idea of writing an argument, use this list to break your process into manageable chunks. Tackle researching and writing one element at a time, and then revise your essay so that it flows smoothly and coherently with every component in the optimal place.
1. A topic or issue to argue
This is probably the hardest step. You need to identify a topic or issue that is narrow enough to cover in the length of your piece—and is also arguable from more than one position. Your topic must call for an opinion , and not be a simple fact .
It might be helpful to walk through this process:
- Identify a random topic
- Ask a question about the topic that involves a value claim or analysis to answer
- Answer the question
That answer is your opinion.
Let’s consider some examples, from silly to serious:
Topic: Dolphins and mermaids
Question: In a mythical match, who would win: a dolphin or a mermaid?
Answer/Opinion: The mermaid would win in a match against a dolphin.
Topic: Autumn
Question: Which has a better fall: New England or Colorado?
Answer/Opinion: Fall is better in New England than Colorado.
Topic: Electric transportation options
Question: Would it be better for an urban dweller to buy an electric bike or an electric car?
Answer/Opinion: An electric bike is a better investment than an electric car.
Your turn: Walk through the three-step process described above to identify your topic and your tentative opinion. You may want to start by brainstorming a list of topics you find interesting and then going use the three-step process to find the opinion that would make the best essay topic.
2. An unequivocal thesis statement
If you walked through our three-step process above, you already have some semblance of a thesis—but don’t get attached too soon!
A solid essay thesis is best developed through the research process. You shouldn’t land on an opinion before you know the facts. So press pause. Take a step back. And dive into your research.
You’ll want to learn:
- The basic facts of your topic. How long does fall last in New England vs. Colorado? What trees do they have? What colors do those trees turn?
- The facts specifically relevant to your question. Is there any science on how the varying colors of fall influence human brains and moods?
- What experts or other noteworthy and valid sources say about the question you’re considering. Has a well-known arborist waxed eloquent on the beauty of New England falls?
As you learn the different viewpoints people have on your topic, pay attention to the strengths and weaknesses of existing arguments. Is anyone arguing the perspective you’re leaning toward? Do you find their arguments convincing? What do you find unsatisfying about the various arguments?
Allow the research process to change your mind and/or refine your thinking on the topic. Your opinion may change entirely or become more specific based on what you learn.
Once you’ve done enough research to feel confident in your understanding of the topic and your opinion on it, craft your thesis.
Your thesis statement should be clear and concise. It should directly state your viewpoint on the topic, as well as the basic case for your thesis.
Thesis 1: In a mythical match, the mermaid would overcome the dolphin due to one distinct advantage: her ability to breathe underwater.
Thesis 2: The full spectrum of color displayed on New England hillsides is just one reason why fall in the northeast is better than in Colorado.
Thesis 3: In addition to not adding to vehicle traffic, electric bikes are a better investment than electric cars because they’re cheaper and require less energy to accomplish the same function of getting the rider from point A to point B.
Your turn: Dive into the research process with a radar up for the arguments your sources are making about your topic. What are the most convincing cases? Should you stick with your initial opinion or change it up? Write your fleshed-out thesis statement.
3. Evidence to back up your thesis
This is a typical place for everyone from undergrads to politicians to get stuck, but the good news is, if you developed your thesis from research, you already have a good bit of evidence to make your case.
Go back through your research notes and compile a list of every …
… or other piece of information that supports your thesis.
This info can come from research studies you found in scholarly journals, government publications, news sources, encyclopedias, or other credible sources (as long as they fit your professor’s standards).
As you put this list together, watch for any gaps or weak points. Are you missing information on how electric cars versus electric bicycles charge or how long their batteries last? Did you verify that dolphins are, in fact, mammals and can’t breathe underwater like totally-real-and-not-at-all-fake 😉mermaids can? Track down that information.
Next, organize your list. Group the entries so that similar or closely related information is together, and as you do that, start thinking through how to articulate the individual arguments to support your case.
Depending on the length of your essay, each argument may get only a paragraph or two of space. As you think through those specific arguments, consider what order to put them in. You’ll probably want to start with the simplest argument and work up to more complicated ones so that the arguments can build on each other.
Your turn: Organize your evidence and write a rough draft of your arguments. Play around with the order to find the most compelling way to argue your case.
4. Rebuttals to disprove opposing theses
You can’t just present the evidence to support your case and totally ignore other viewpoints. To persuade your readers, you’ll need to address any opposing ideas they may hold about your topic.
You probably found some holes in the opposing views during your research process. Now’s your chance to expose those holes.
Take some time (and space) to: describe the opposing views and show why those views don’t hold up. You can accomplish this using both logic and facts.
Is a perspective based on a faulty assumption or misconception of the truth? Shoot it down by providing the facts that disprove the opinion.
Is another opinion drawn from bad or unsound reasoning? Show how that argument falls apart.
Some cases may truly be only a matter of opinion, but you still need to articulate why you don’t find the opposing perspective convincing.
Yes, a dolphin might be stronger than a mermaid, but as a mammal, the dolphin must continually return to the surface for air. A mermaid can breathe both underwater and above water, which gives her a distinct advantage in this mythical battle.
While the Rocky Mountain views are stunning, their limited colors—yellow from aspen trees and green from various evergreens—leaves the autumn-lover less than thrilled. The rich reds and oranges and yellows of the New England fall are more satisfying and awe-inspiring.
But what about longer trips that go beyond the city center into the suburbs and beyond? An electric bike wouldn’t be great for those excursions. Wouldn’t an electric car be the better choice then?
Certainly, an electric car would be better in these cases than a gas-powered car, but if most of a person’s trips are in their hyper-local area, the electric bicycle is a more environmentally friendly option for those day-to-day outings. That person could then participate in a carshare or use public transit, a ride-sharing app, or even a gas-powered car for longer trips—and still use less energy overall than if they drove an electric car for hyper-local and longer area trips.
Your turn: Organize your rebuttal research and write a draft of each one.
5. A convincing conclusion
You have your arguments and rebuttals. You’ve proven your thesis is rock-solid. Now all you have to do is sum up your overall case and give your final word on the subject.
Don’t repeat everything you’ve already said. Instead, your conclusion should logically draw from the arguments you’ve made to show how they coherently prove your thesis. You’re pulling everything together and zooming back out with a better understanding of the what and why of your thesis.
A dolphin may never encounter a mermaid in the wild, but if it were to happen, we know how we’d place our bets. Long hair and fish tail, for the win.
For those of us who relish 50-degree days, sharp air, and the vibrant colors of fall, New England offers a season that’s cozier, longer-lasting, and more aesthetically pleasing than “colorful” Colorado. A leaf-peeper’s paradise.
When most of your trips from day to day are within five miles, the more energy-efficient—and yes, cost-efficient—choice is undoubtedly the electric bike. So strap on your helmet, fire up your pedals, and two-wheel away to your next destination with full confidence that you made the right decision for your wallet and the environment.
3 Quick Tips for Writing a Strong Argument
Once you have a draft to work with, use these tips to refine your argument and make sure you’re not losing readers for avoidable reasons.
1. Choose your words thoughtfully.
If you want to win people over to your side, don’t write in a way that shuts your opponents down. Avoid making abrasive or offensive statements. Instead, use a measured, reasonable tone. Appeal to shared values, and let your facts and logic do the hard work of changing people’s minds.
Choose words with AI

You can use AI to turn your general point into a readable argument. Then, you can paraphrase each sentence and choose between competing arguments generated by the AI, until your argument is well-articulated and concise.
2. Prioritize accuracy (and avoid fallacies).
Make sure the facts you use are actually factual. You don’t want to build your argument on false or disproven information. Use the most recent, respected research. Make sure you don’t misconstrue study findings. And when you’re building your case, avoid logical fallacies that undercut your argument.
A few common fallacies to watch out for:
- Strawman: Misrepresenting or oversimplifying an opposing argument to make it easier to refute.
- Appeal to ignorance: Arguing that a certain claim must be true because it hasn’t been proven false.
- Bandwagon: Assumes that if a group of people, experts, etc., agree with a claim, it must be true.
- Hasty generalization: Using a few examples, rather than substantial evidence, to make a sweeping claim.
- Appeal to authority: Overly relying on opinions of people who have authority of some kind.
The strongest arguments rely on trustworthy information and sound logic.
Research and add citations with AI

We recently wrote a three part piece on researching using AI, so be sure to check it out . Going through an organized process of researching and noting your sources correctly will make sure your written text is more accurate.
3. Persuasive essay structure

If you’re building a house, you start with the foundation and go from there. It’s the same with an argument. You want to build from the ground up: provide necessary background information, then your thesis. Then, start with the simplest part of your argument and build up in terms of complexity and the aspect of your thesis that the argument is tackling.
A consistent, internal logic will make it easier for the reader to follow your argument. Plus, you’ll avoid confusing your reader and you won’t be unnecessarily redundant.
The essay structure usually includes the following parts:
- Intro - Hook, Background information, Thesis statement
- Topic sentence #1 , with supporting facts or stats
- Concluding sentence
- Topic sentence #2 , with supporting facts or stats
- Concluding sentence Topic sentence #3 , with supporting facts or stats
- Conclusion - Thesis and main points restated, call to action, thought provoking ending
Are You Ready to Write?
Persuasive essays are a great way to hone your research, writing, and critical thinking skills. Approach this assignment well, and you’ll learn how to form opinions based on information (not just ideas) and make arguments that—if they don’t change minds—at least win readers’ respect.
Share This Article:

What’s a Double Negative? + How To Fix It

The Official Wordtune Guide

An Expert Guide to Writing Effective Compound Sentences (+ Examples)
Looking for fresh content, thank you your submission has been received.
- Buy Custom Assignment
- Custom College Papers
- Buy Dissertation
- Buy Research Papers
- Buy Custom Term Papers
- Cheap Custom Term Papers
- Custom Courseworks
- Custom Thesis Papers
- Custom Expository Essays
- Custom Plagiarism Check
- Cheap Custom Essay
- Custom Argumentative Essays
- Custom Case Study
- Custom Annotated Bibliography
- Custom Book Report
- How It Works
- +1 (888) 398 0091
- Essay Samples
- Essay Topics
- Research Topics
- Uncategorized
- Writing Tips
How to Write a Conclusion for an Argumentative Essay
October 24, 2023
The Role of a Conclusion in an Argumentative Essay
The role of a conclusion in an argumentative essay is crucial in effectively wrapping up the discussion and leaving a lasting impression on the reader. Unlike other parts of the essay, the conclusion serves a distinct purpose beyond summarizing the main points. Its primary objective is to reiterate the central argument and present a compelling case for its validity.
To write a powerful conclusion for an argumentative essay, it is important to avoid mere repetition of the thesis statement or a simple rundown of the key arguments. Instead, the conclusion should provide a broader perspective by emphasizing the significance of the topic, highlighting its relevance in a larger context. Additionally, it is essential to address counterarguments or opposing viewpoints and offer a thoughtful response.
By weaving together the main ideas and evidence presented throughout the essay, the conclusion should be able to leave a lasting impact on the reader, reinforcing the credibility and strength of the argument put forth. It serves as a final opportunity to persuade the audience to accept your viewpoint or consider your recommendations. When you write an argumentative conclusion it requires precision and care, ensuring that it seamlessly aligns with the content of the essay while leaving a lasting impression on the reader.
Components of a Strong Argumentative Conclusion
A strong argumentative essay conclusion is comprised of several key components that work together to create a powerful ending to the essay. Here are some of the most important components to keep in mind when crafting a conclusion for an argumentative essay:
- Thesis restatement: The conclusion should begin by restating the thesis statement that was introduced in the introduction. This reminds the reader of the main argument and what was being discussed.
- Summary of main points: While it is important to avoid repetition, a summary of the main points discussed in the essay can be helpful in reinforcing the overall argument.
- Addressing counterarguments: In an argumentative essay, it is important to address any opposing viewpoints that were presented in the essay, while explaining why your argument is still valid.
- Final thought: The conclusion should end with a final thought about the topic that leaves the reader with something to think about. This can be a call-to-action, a recommendation, or even a question.
- Closing statement: A strong closing statement can help tie all of the components of the conclusion together and leave a lasting impression on the reader.
By including these key components in an argumentative essay conclusion, writers can create a powerful ending that reinforces the strength of their argument and leaves a lasting impression on the reader.
Step-by-step Conclusion Writing Guide
Writing a conclusion for an argumentative essay can be both challenging and rewarding. It is an opportunity to leave a lasting impression on the reader, persuading them of the strength of your argument and leaving them with something to think about. Here is a step-by-step guide to writing a conclusion for an argumentative essay:
- Restate your thesis – Begin writing your conclusion by reiterating your thesis statement, reminding the reader of the main point you were arguing.
- Summarize your main points – Summarize the main points you made throughout your essay. Do it in a way that does not simply repeat what you have already written but instead provides a concise but effective recap.
- Address opposing views – Acknowledge any counterarguments or opposing views presented throughout your essay by reviewing and disputing them. This demonstrates that you have considered multiple sides and have a clear understanding of the issue.
- Broaden your perspective – Broaden your perspective by providing context or additional insights on the topic. This can be done by relating your argument to a larger issue or by providing a thought-provoking example.
- Provide solutions or recommendations – Provide solutions or recommendations that the reader can consider. This can include actionable steps or invitations to think critically about the issue at hand. This makes your essay more actionable and practical.
- Use a closing statement – End your conclusion with a closing statement that leaves a lasting impression on the reader. Choose your last words carefully and keep in mind that this statement must effectively encapsulate and emphasize your argument.
- Revise your essay – After completing your conclusion, it’s time to revise your entire essay to ensure that it flows well, is concise, and avoids any grammatical errors. This step is vital for giving your essay a polished finish.
In conclusion, writing a strong conclusion for an argumentative essay requires a clear and concise summary of your main points along with effectively addressing counterarguments, and broadening your perspective. By following the above-mentioned step-by-step guide, you can craft a powerful and memorable conclusion that leaves a lasting impression on your reader. Remember, writing a conclusion is never just summarizing your arguments. It is a chance to leave a strong, final impression on your reader while restating your thesis and summarizing your arguments with clarity and effectively engaging them with your unique perspective.
Techniques to Avoid in a Conclusion Writing
In order to write a strong conclusion for an argumentative essay, it is important to steer clear of certain techniques that can undermine its effectiveness. Here are a few techniques to avoid:
- Introducing new information: Your conclusion should not introduce any new arguments or evidence that have not been discussed in the body paragraphs of your essay. Adding new information at this stage can confuse the reader and weaken the impact of your argument.
- Restating the thesis without elaboration: While it is essential to restate your thesis in the conclusion, avoid simply regurgitating it without providing further elaboration. Instead, offer a concise summary of your main points and demonstrate how they support your thesis.
- Using weak or speculative language: Avoid using phrases like “I think” or “I believe” in your conclusion. These phrases weaken the confidence and authority of your argument. Instead, use assertive and evidence-based language to strengthen your position.
- Dismissing counterarguments without addressing them: It is important to acknowledge and address counterarguments in an argumentative essay. Dismissing them without providing a clear rebuttal can make your conclusion appear dismissive or incomplete. Take the time to address opposing viewpoints and explain why your argument is still valid.
- Rushing the conclusion: A conclusion should not feel rushed or abrupt. It should provide a sense of closure and a final thought for the reader to ponder. Avoid ending your essay abruptly without providing a clear, well-crafted closing statement.
By avoiding these techniques, you can ensure that you write a conclusion for an argumentative essay that is strong, persuasive, and leaves a lasting impact on the reader. It should effectively tie together your main points, address counterarguments, and provide a thought-provoking closing statement.
Tips to Write an Effective Conclusion
Writing an effective conclusion for an argumentative essay is crucial as it can greatly impact the overall success of your essay. Here are a few tips to help you with your conclusion writing:
- Summarize your main points: Recap the key arguments you made throughout your essay in a concise and clear manner. This reaffirms your main points and reminds the reader of the strength of your argument.
- Address counterarguments: Take the opportunity in your conclusion to address any counterarguments or opposing viewpoints presented in your essay. Refute them with evidence and logic, showcasing the thoroughness of your research.
- Broaden the perspective: Expand the viewpoint in your conclusion by providing broader context or bringing in relevant examples. This helps your reader see the bigger picture and understand the wider implications of your argument.
- Provide a call to action or recommendation: End your conclusion with a call to action or recommendation that urges the reader to take further action or consider the implications of your argument. This adds a sense of importance and motivates your audience to think critically about the issue discussed.
- Use impactful language: Choose powerful words and phrases that leave a lasting impression on the reader. Capture their attention and evoke an emotional response, emphasizing the significance of your argument.
By employing these tips, you can ensure that your conclusion is a strong and memorable ending to your argumentative essay. Well-crafted conclusions are essential in leaving a lasting impact on your reader and reinforcing the strength of your position.
Argumentative Essay Conclusion Writing Example
In conclusion, it is evident that stricter gun control measures are necessary to reduce the alarming rate of gun violence in our society. The arguments presented in this essay clearly demonstrate that easy access to firearms not only leads to increased crime rates but also escalates the severity of incidents. By implementing comprehensive background checks, banning assault weapons, and implementing stricter licensing requirements, we can significantly curtail gun violence and create a safer environment for all.
Despite opposition from pro-gun lobbyists, the overwhelming evidence supports the need for stricter gun control regulations. Numerous studies have shown a direct correlation between lax gun laws and higher rates of gun-related deaths and injuries. Ignoring these findings and failing to take action would be a disservice to the well-being and safety of our communities.
It is imperative that lawmakers and citizens alike recognize the urgency of this issue. By prioritizing public safety over individual gun ownership rights, we bring ourselves closer to a society where families can feel secure and innocent lives are protected. It is time to take a stand against gun violence and implement the necessary measures to create a safer future for all. Together, we can make a difference and save countless lives.
Sociology Research Topics Ideas
Importance of Computer in Nursing Practice Essay
History Research Paper Topics For Students
By clicking “Continue”, you agree to our terms of service and privacy policy. We’ll occasionally send you promo and account related emails.
Latest Articles
Navigating the complexities of a Document-Based Question (DBQ) essay can be daunting, especially given its unique blend of historical analysis...
An introduction speech stands as your first opportunity to connect with an audience, setting the tone for the message you...
Embarking on the journey to write a rough draft for an essay is not just a task but a pivotal...
I want to feel as happy, as your customers do, so I'd better order now
We use cookies on our website to give you the most relevant experience by remembering your preferences and repeat visits. By clicking “Accept All”, you consent to the use of ALL the cookies. However, you may visit "Cookie Settings" to provide a controlled consent.

How to write a Conclusion
What is a Conclusion?

Before we learn how to write a conclusion, we need to determine what a conclusion is.
A conclusion is the final sentences or paragraph in a piece of writing that signifies the end of a text, event or process.
We can find conclusions everywhere, from narratives, letters and reports to persuasive essays and speeches.
Conclusions perform many functions, which we will examine throughout this article. Fundamentally, they wrap everything up and finish a piece of writing or a presentation.
Unfortunately, conclusions are often the most challenging section of a paper to write. They are the final words of the writer on the topic and, as a result, play a crucial part in the lasting impression the writing leaves on the reader.
For this reason, our students must take time to understand clearly the functions of a conclusion and how they work. Time spent mastering the art of conclusion writing will be time well spent.
A COMPLETE UNIT ON HOW TO WRITE A CONCLUSION

Teach your students to write POWERFUL CONCLUSIONS that put a bow on a great piece of writing. All too often, students struggle to conclude their writing. Stumbling, repeating themselves, or missing the opportunity to make a lasting impression.
This COMPLETE UNIT OF WORK will take your students from zero to hero over FIVE STRATEGIC LESSONS covered.
What is the Purpose of a Concluding Paragraph

Unfortunately, there is no one-size-fits-all formula we can teach our students that they can use to write any conclusion. Conclusions perform several functions, varying widely from paper to paper. Some of these functions include:
- Restates a paper’s thesis and explains why it’s important
- Synthesizes the essay’s arguments
- It opens up new questions
- Addresses limitations
- Makes a call to action.
Not all conclusions will perform each of these functions. How our students approach writing their conclusions will depend on several factors, including:
- The conventions of the writing genre
- The intended audience and their motivations
- The formality or informality of the paper
- The tone of the writing.
Now, let’s look at each of the functions of a conclusion one by one, along with a practice activity for each to give our students some hands-on practice.
1. A Concluding Paragraph Restates the Thesis and Explains Why
One of the most common errors in writing a conclusion is to use it to simply restate the thesis. Though this is widely taught, it isn’t enough.
The student should also explain why the argument made in their thesis is important. This involves considering the more widespread impact of the thesis and its supporting arguments.
The conclusion should inform the reader why the thesis matters by answering questions similar to the following:
- What are the wider societal implications of the thesis?
- Does the thesis challenge a widely accepted idea or belief?
- Does the thesis have significance for how things could be done in the future?
To write a conclusion in this vein, it is helpful for students to compose similar type questions relevant to their thesis, which they can then set out to answer.
These questions will vary widely according to the subject being written about and the genre being written in. Still, regardless, the conclusion should highlight the thesis’s significance to the wider world. This will bring context to the writing as a whole.
Example: In conclusion, this paper has argued that increasing access to education is essential for reducing poverty and promoting economic development. We have presented evidence from various studies showing the positive correlation between education and income and the role of education in fostering other developmental goals, such as improved health and reduced inequality. Restating the thesis, we can say that access to education is a fundamental human right and should be prioritized as a key development strategy to reduce poverty and promote sustainable economic growth. The evidence presented in this paper supports this argument, making a case for the importance of increasing access to education for the well-being of individuals and societies.
2. A CONCLUSION SYNTHESIZES THE PAPER’S ARGUMENTS
This is another very common function performed by the conclusion. While each body paragraph in the paper may correspond to a single specific argument in support of the central thesis, in the conclusion, the various strands of supporting arguments are woven into a coherent whole.
The conclusion is not the place to introduce new arguments or to simply list the arguments made in the body paragraphs. Instead, it provides a final opportunity for your students to drive home their main arguments one last time and make connections between them to reveal a coherent whole.
Often, a conclusion will combine functions of functions 1 and 2 by restating the thesis, synthesizing the arguments, and explaining the wider significance of the thesis.
When considering how to write a conclusion for an argumentative essay, remember to synthesize it.
Example: In conclusion, this paper has presented a thorough examination of the current state of renewable energy sources and their potential to combat climate change. Through an analysis of the economic and technical feasibility of various renewable energy options, we have shown that renewable energy is a viable and necessary solution to reducing carbon emissions. Additionally, we have highlighted the importance of government policies and investment in research and development to accelerate the adoption of renewable energy. Overall, this paper argues that renewable energy is a crucial step in the fight against climate change and must be prioritized to secure a sustainable future.
3. A CONCLUSION CAN OPEN UP NEW QUESTIONS
We often think of conclusions as drawing things to a close. But there’s another way of looking at things. Often, through the process of making various arguments in a piece of writing, new questions will emerge naturally.
This method is commonly encountered when exploring how to write a conclusion for a thesis.
This often occurs when the central thesis is set in a broader context. We can think of the progression of an essay as moving from a thesis statement through evermore specific arguments that support that initial thesis statement.
To open up new questions in the conclusion, the student should move from the specific to the more general, generating further possible lines of inquiry on the topic as they go. The effect of this type of conclusion is to spark the reader’s curiosity and further interest in the subject.
Example: In conclusion, our research has provided an in-depth examination of the effects of climate change on biodiversity. Our findings indicate that climate change is having a significant impact on the distribution and abundance of species. However, our research has also revealed that there are still many unanswered questions about the mechanisms driving these changes. For example, more research is needed to understand the role of different species interactions and the effects of climate change on specific ecosystem functions. We hope our research will serve as a foundation for further studies and inspire other researchers to continue investigating the complex relationship between climate change and biodiversity.
4. A CONCLUSION PARAGRAPH ADDRESSES THE LIMITATIONS
This method is often used in academic or scientific writing when considering how to write a conclusion for a report. In it, the student writer directly explores the weaknesses of their arguments.
It’s perhaps the bravest type of conclusion there is! Students need to be careful not to destroy their own thesis in the process. A sentence mentioning the limitation, quickly followed by a sentence or two addressing the problem, should be enough.
When done well, this strategy strengthens the impact of a paper by dealing head-on with potential criticisms and making strong counter-arguments in the process.
Example: In conclusion, our research provides valuable insights into the relationship between environmental factors and academic performance. However, it is important to note that our study has limitations. Firstly, the sample size was relatively small, and our results may not be generalizable to a larger population. Additionally, our study only considered one specific type of environmental factor and did not take into account other factors that may impact academic performance. Despite these limitations, our research provides a starting point for future studies in this area.
5. A CONCLUSION CAN OFFER A CALL TO ACTION

In a call-to-action type conclusion, the writer compels the reader to take a desired action or perform a particular task. This type of conclusion aims to persuade the reader or listener to do something.
Call-to-action conclusions work in various genres, including presentations, speeches, advertisements, and persuasive essays .
There are various techniques students can use to inspire action in their conclusions, such as appeals to emotions, the use of strong imperatives, or appeals to the reader’s or the listener’s self-interest.
Example: In conclusion, our research highlights the importance of access to clean drinking water in developing countries. Our findings show that a lack of access to clean water can lead to serious health issues and negatively impact the economy. However, it is not enough to simply acknowledge this problem – action must be taken. We call on governments, non-profit organizations, and individuals to take action by investing in infrastructure and providing education on sanitation and hygiene. Together, we can work towards providing access to clean water for all, and, ultimately, improve the quality of life for people living in developing countries.
Tips for Writing a Strong Conclusion
As young writers, crafting a solid conclusion for your essay is essential to communicate your ideas effectively. A well-written conclusion can help to summarize your main points, provide closure to your argument, and leave a lasting impression on your reader. Here are ten tips for writing a strong conclusion to an essay for high school students:
- Restate the main idea of your essay. A good conclusion should summarize the main points of your essay and reiterate the main idea or thesis statement.
- Provide closure to your argument. Your conclusion should provide a sense of closure to your argument and tie up any loose ends.
- Emphasize the importance of your topic. Your conclusion should also emphasize the importance of the topic you have discussed and why it matters to your reader.
- Offer a call to action. Encourage your reader to take action or think more deeply about the issues you have discussed in your essay.
- Avoid introducing new information. Your conclusion should be a summary of your main points, not a place to introduce new information or ideas.
- Keep it simple. Avoid using complex phrases or convoluted language in your conclusion.
- Use a strong concluding sentence. Your last sentence should be a powerful statement that leaves a lasting impression on your reader.
- Avoid summarizing every point. You don’t have to summarize every point you made in the essay; pick the main and most important ones.
- Reflect on your essay’s meaning. Take a step back and reflect on the overall meaning of your essay and the message you want to convey to your reader.
- Revise and proofread . Revise and proofread your conclusion carefully to ensure it is clear, concise, and error-free.
By following these tips, you can write a strong conclusion that effectively communicates your ideas and leaves a lasting impression on your reader.
What shouldn’t a conclusion do?
So far, we’ve discussed some conclusion writing strategies by discussing things a good conclusion should do. Now, it’s time to look at some things a conclusion shouldn’t do.
The following list contains some of the most common mistakes students must avoid making in their conclusions. This list can help students troubleshoot their conclusions when they get stuck or run into problems.
1. Uses a Vague Thesis Statement
If the student struggles to make a powerful impact in their conclusion, it may be because their thesis statement is too vague.
If this is the case, they messed up long ago.
The first time the reader sees the thesis statement should be in the introduction. Because all arguments stem from that statement, a comprehensive rewrite of the entire paper will most likely be needed.
2. Opens with a Clichéd Phrase
When students begin to learn to write conclusions, they often learn some stock phrases to help kickstart their writing. Phrases such as ‘in conclusion’ or ‘to conclude’ can be useful as prompts to get students quickly into the meat of their writing. However, overuse of such stock phrases can leave the writing feeling mechanical.
Ultimately, we want more for our students. If one of the purposes of a conclusion is to make a powerful impact on the reader, we must encourage our students to be creative and bold in their writing.
3. Doubts the Thesis
In the first part of this article, we briefly discussed the idea of addressing the limitations of the thesis and supporting arguments. This can be an effective strategy for students, but it can also be risky. The student needs to ensure they don’t undermine their stance.
When students use this strategy, ensure they understand that addressing limitations is not the same thing as apologizing for the position held. A good conclusion is impossible without the writer actually concluding something; conclusions should end with a strong statement.
4. Contains Irrelevancies
Students must ensure that every piece of information in their essay or article is relevant to the topic and thesis.
One of the most common mistakes students make is failing to ‘kill their babies’. That is, they go off on a tangent in their writing but are reluctant to remove the offending sentences in the editing process.
Often this happens because the student doesn’t want to throw out something they spent time writing, even if it’s utterly irrelevant to the topic they’re writing about.
At other times, students fail to be merciless in their editing because they’re waffling to reach an assigned word count.
In this case, it’s important to remind students that to the seasoned eye of a teacher or examiner, any puff and padding in their writing is obvious.
5. Fails to Address the Why?
As an article or a paper draws to a close, it’s essential that the reader feels the time they spent reading was time well invested. To achieve this, the student must answer the why? question satisfactorily. Students should make sure their readers leave their writing feeling like they have learned something of value, are inspired to take action or have new questions to research and answer.
Drawing the Curtains on Our Work on Conclusions
We’ve covered a lot of ground in our article on conclusions. We’ve looked at strategies and techniques our students can use to hone their conclusion-writing skills.

Now, it’s up to us as teachers to create opportunities for our students to perfect their understanding and ability to use these strategies and techniques in their writing.
While the ideas above will go a long way to ensuring your students are capable of composing well-written conclusions, with time and practice, they’ll develop their own style and approach to the conclusion conundrum – and surely there can be no more fitting conclusion than that!
Conclusion Writing Teaching Strategies and Activities

Practice Activity: Connect to the Wider World : To practice this, provide the students with a copy of a well-written essay suited to their level but with the concluding paragraph snipped out. Challenge the students to first identify the thesis statement, it should be in the essay’s introduction, and then to write a conclusion that connects that thesis to the wider world by explaining why it matters.
Practice Activity: Write the Conclusion First : Sometimes, it’s helpful for students to think of the conclusion as the destination their writing is headed for. The next time your students have completed an outline for an essay , instruct them to write the conclusion first. In it, they should explore the reasons for their thesis and its wider significance and synthesize their arguments. This gives the students a clear focus for the preceding introduction and body paragraphs and gives their writing a clear direction to work towards.
Practice Activity: Shift Perspective : For many students, writing this style of conclusion will require a shift in their understanding of the purpose of a conclusion. One good way to begin to shift that perspective is to encourage students to rewrite conclusions they’ve written previously in old essays. For example, they might shift the focus of a conclusion from a local significance to global significance or from historical significance to contemporary significance.
Practice Activity: Poke the Weak Points
Students take a conclusion they have written already, such as one written for a previous activity. Then, set the students the task of rewriting the conclusion to address any limitations of the supporting arguments. To do this, students need to ask themselves:
- What aspects of my arguments are open to contradiction?
- How can I address those contradictions?
Practice Activity: Blog It! : Blogs often use calls to action in the conclusions of their informational articles. Set your students the task of identifying several blogs on subjects that interest them. Students may benefit from doing this activity in groups.
Once they’ve identified some suitable websites, instruct the students to look at the conclusion of some of the articles.
- Can they identify any calls to action there?
- How do the writers introduce their calls to action?
- What techniques does the writer use to motivate the reader?
Challenge students to identify as many different motivational techniques and strategies as possible and then make a list that they can then share with the class.
When students have become good at identifying calls to action and the various motivational techniques and strategies, they can then write a blog article on a subject that interests them, making sure to include a call to action in their conclusion.
A COMPLETE TEACHING UNIT ON PERSUASIVE WRITING SKILLS
Teach your students to produce writing that PERSUADES and INFLUENCES thinking with this HUGE writing guide bundle covering: ⭐ Persuasive Texts / Essays ⭐ Expository Essays⭐ Argumentative Essays⭐ Discussions.
A complete 140 PAGE unit of work on persuasive texts for teachers and students. No preparation is required.
CONCLUSION WRITING VIDEO TUTORIAL

ARTICLES RELATED TO CONCLUSION WRITING

How to Start an Essay with Strong Hooks and Leads

Top 5 Essay Writing Tips

How to write a perfect 5 Paragraph Essay

The Writing Process
17 Essay Conclusion Examples (Copy and Paste)

Essay conclusions are not just extra filler. They are important because they tie together your arguments, then give you the chance to forcefully drive your point home.
I created the 5 Cs conclusion method to help you write essay conclusions:

I’ve previously produced the video below on how to write a conclusion that goes over the above image.
The video follows the 5 C’s method ( you can read about it in this post ), which doesn’t perfectly match each of the below copy-and-paste conclusion examples, but the principles are similar, and can help you to write your own strong conclusion:
💡 New! Try this AI Prompt to Generate a Sample 5Cs Conclusion This is my essay: [INSERT ESSAY WITHOUT THE CONCLUSION]. I want you to write a conclusion for this essay. In the first sentence of the conclusion, return to a statement I made in the introduction. In the second sentence, reiterate the thesis statement I have used. In the third sentence, clarify how my final position is relevant to the Essay Question, which is [ESSAY QUESTION]. In the fourth sentence, explain who should be interested in my findings. In the fifth sentence, end by noting in one final, engaging sentence why this topic is of such importance.
Remember: The prompt can help you generate samples but you can’t submit AI text for assessment. Make sure you write your conclusion in your own words.
Essay Conclusion Examples
Below is a range of copy-and-paste essay conclusions with gaps for you to fill-in your topic and key arguments. Browse through for one you like (there are 17 for argumentative, expository, compare and contrast, and critical essays). Once you’ve found one you like, copy it and add-in the key points to make it your own.
1. Argumentative Essay Conclusions
The arguments presented in this essay demonstrate the significant importance of _____________. While there are some strong counterarguments, such as ____________, it remains clear that the benefits/merits of _____________ far outweigh the potential downsides. The evidence presented throughout the essay strongly support _____________. In the coming years, _____________ will be increasingly important. Therefore, continual advocacy for the position presented in this essay will be necessary, especially due to its significant implications for _____________.
Version 1 Filled-In
The arguments presented in this essay demonstrate the significant importance of fighting climate change. While there are some strong counterarguments, such as the claim that it is too late to stop catastrophic change, it remains clear that the merits of taking drastic action far outweigh the potential downsides. The evidence presented throughout the essay strongly support the claim that we can at least mitigate the worst effects. In the coming years, intergovernmental worldwide agreements will be increasingly important. Therefore, continual advocacy for the position presented in this essay will be necessary, especially due to its significant implications for humankind.

As this essay has shown, it is clear that the debate surrounding _____________ is multifaceted and highly complex. While there are strong arguments opposing the position that _____________, there remains overwhelming evidence to support the claim that _____________. A careful analysis of the empirical evidence suggests that _____________ not only leads to ____________, but it may also be a necessity for _____________. Moving forward, _____________ should be a priority for all stakeholders involved, as it promises a better future for _____________. The focus should now shift towards how best to integrate _____________ more effectively into society.
Version 2 Filled-In
As this essay has shown, it is clear that the debate surrounding climate change is multifaceted and highly complex. While there are strong arguments opposing the position that we should fight climate change, there remains overwhelming evidence to support the claim that action can mitigate the worst effects. A careful analysis of the empirical evidence suggests that strong action not only leads to better economic outcomes in the long term, but it may also be a necessity for preventing climate-related deaths. Moving forward, carbon emission mitigation should be a priority for all stakeholders involved, as it promises a better future for all. The focus should now shift towards how best to integrate smart climate policies more effectively into society.
Based upon the preponderance of evidence, it is evident that _____________ holds the potential to significantly alter/improve _____________. The counterarguments, while noteworthy, fail to diminish the compelling case for _____________. Following an examination of both sides of the argument, it has become clear that _____________ presents the most effective solution/approach to _____________. Consequently, it is imperative that society acknowledge the value of _____________ for developing a better _____________. Failing to address this topic could lead to negative outcomes, including _____________.
Version 3 Filled-In
Based upon the preponderance of evidence, it is evident that addressing climate change holds the potential to significantly improve the future of society. The counterarguments, while noteworthy, fail to diminish the compelling case for immediate climate action. Following an examination of both sides of the argument, it has become clear that widespread and urgent social action presents the most effective solution to this pressing problem. Consequently, it is imperative that society acknowledge the value of taking immediate action for developing a better environment for future generations. Failing to address this topic could lead to negative outcomes, including more extreme climate events and greater economic externalities.
See Also: Examples of Counterarguments
On the balance of evidence, there is an overwhelming case for _____________. While the counterarguments offer valid points that are worth examining, they do not outweigh or overcome the argument that _____________. An evaluation of both perspectives on this topic concludes that _____________ is the most sufficient option for _____________. The implications of embracing _____________ do not only have immediate benefits, but they also pave the way for a more _____________. Therefore, the solution of _____________ should be actively pursued by _____________.
Version 4 Filled-In
On the balance of evidence, there is an overwhelming case for immediate tax-based action to mitigate the effects of climate change. While the counterarguments offer valid points that are worth examining, they do not outweigh or overcome the argument that action is urgently necessary. An evaluation of both perspectives on this topic concludes that taking societal-wide action is the most sufficient option for achieving the best results. The implications of embracing a society-wide approach like a carbon tax do not only have immediate benefits, but they also pave the way for a more healthy future. Therefore, the solution of a carbon tax or equivalent policy should be actively pursued by governments.
2. Expository Essay Conclusions
Overall, it is evident that _____________ plays a crucial role in _____________. The analysis presented in this essay demonstrates the clear impact of _____________ on _____________. By understanding the key facts about _____________, practitioners/society are better equipped to navigate _____________. Moving forward, further exploration of _____________ will yield additional insights and information about _____________. As such, _____________ should remain a focal point for further discussions and studies on _____________.
Overall, it is evident that social media plays a crucial role in harming teenagers’ mental health. The analysis presented in this essay demonstrates the clear impact of social media on young people. By understanding the key facts about the ways social media cause young people to experience body dysmorphia, teachers and parents are better equipped to help young people navigate online spaces. Moving forward, further exploration of the ways social media cause harm will yield additional insights and information about how it can be more sufficiently regulated. As such, the effects of social media on youth should remain a focal point for further discussions and studies on youth mental health.
To conclude, this essay has explored the multi-faceted aspects of _____________. Through a careful examination of _____________, this essay has illuminated its significant influence on _____________. This understanding allows society to appreciate the idea that _____________. As research continues to emerge, the importance of _____________ will only continue to grow. Therefore, an understanding of _____________ is not merely desirable, but imperative for _____________.
To conclude, this essay has explored the multi-faceted aspects of globalization. Through a careful examination of globalization, this essay has illuminated its significant influence on the economy, cultures, and society. This understanding allows society to appreciate the idea that globalization has both positive and negative effects. As research continues to emerge, the importance of studying globalization will only continue to grow. Therefore, an understanding of globalization’s effects is not merely desirable, but imperative for judging whether it is good or bad.
Reflecting on the discussion, it is clear that _____________ serves a pivotal role in _____________. By delving into the intricacies of _____________, we have gained valuable insights into its impact and significance. This knowledge will undoubtedly serve as a guiding principle in _____________. Moving forward, it is paramount to remain open to further explorations and studies on _____________. In this way, our understanding and appreciation of _____________ can only deepen and expand.
Reflecting on the discussion, it is clear that mass media serves a pivotal role in shaping public opinion. By delving into the intricacies of mass media, we have gained valuable insights into its impact and significance. This knowledge will undoubtedly serve as a guiding principle in shaping the media landscape. Moving forward, it is paramount to remain open to further explorations and studies on how mass media impacts society. In this way, our understanding and appreciation of mass media’s impacts can only deepen and expand.
In conclusion, this essay has shed light on the importance of _____________ in the context of _____________. The evidence and analysis provided underscore the profound effect _____________ has on _____________. The knowledge gained from exploring _____________ will undoubtedly contribute to more informed and effective decisions in _____________. As we continue to progress, the significance of understanding _____________ will remain paramount. Hence, we should strive to deepen our knowledge of _____________ to better navigate and influence _____________.
In conclusion, this essay has shed light on the importance of bedside manner in the context of nursing. The evidence and analysis provided underscore the profound effect compassionate bedside manner has on patient outcome. The knowledge gained from exploring nurses’ bedside manner will undoubtedly contribute to more informed and effective decisions in nursing practice. As we continue to progress, the significance of understanding nurses’ bedside manner will remain paramount. Hence, we should strive to deepen our knowledge of this topic to better navigate and influence patient outcomes.
See More: How to Write an Expository Essay
3. Compare and Contrast Essay Conclusion
While both _____________ and _____________ have similarities such as _____________, they also have some very important differences in areas like _____________. Through this comparative analysis, a broader understanding of _____________ and _____________ has been attained. The choice between the two will largely depend on _____________. For example, as highlighted in the essay, ____________. Despite their differences, both _____________ and _____________ have value in different situations.
While both macrosociology and microsociology have similarities such as their foci on how society is structured, they also have some very important differences in areas like their differing approaches to research methodologies. Through this comparative analysis, a broader understanding of macrosociology and microsociology has been attained. The choice between the two will largely depend on the researcher’s perspective on how society works. For example, as highlighted in the essay, microsociology is much more concerned with individuals’ experiences while macrosociology is more concerned with social structures. Despite their differences, both macrosociology and microsociology have value in different situations.
It is clear that _____________ and _____________, while seeming to be different, have shared characteristics in _____________. On the other hand, their contrasts in _____________ shed light on their unique features. The analysis provides a more nuanced comprehension of these subjects. In choosing between the two, consideration should be given to _____________. Despite their disparities, it’s crucial to acknowledge the importance of both when it comes to _____________.
It is clear that behaviorism and consructivism, while seeming to be different, have shared characteristics in their foci on knowledge acquisition over time. On the other hand, their contrasts in ideas about the role of experience in learning shed light on their unique features. The analysis provides a more nuanced comprehension of these subjects. In choosing between the two, consideration should be given to which approach works best in which situation. Despite their disparities, it’s crucial to acknowledge the importance of both when it comes to student education.
Reflecting on the points discussed, it’s evident that _____________ and _____________ share similarities such as _____________, while also demonstrating unique differences, particularly in _____________. The preference for one over the other would typically depend on factors such as _____________. Yet, regardless of their distinctions, both _____________ and _____________ play integral roles in their respective areas, significantly contributing to _____________.
Reflecting on the points discussed, it’s evident that red and orange share similarities such as the fact they are both ‘hot colors’, while also demonstrating unique differences, particularly in their social meaning (red meaning danger and orange warmth). The preference for one over the other would typically depend on factors such as personal taste. Yet, regardless of their distinctions, both red and orange play integral roles in their respective areas, significantly contributing to color theory.
Ultimately, the comparison and contrast of _____________ and _____________ have revealed intriguing similarities and notable differences. Differences such as _____________ give deeper insights into their unique and shared qualities. When it comes to choosing between them, _____________ will likely be a deciding factor. Despite these differences, it is important to remember that both _____________ and _____________ hold significant value within the context of _____________, and each contributes to _____________ in its own unique way.
Ultimately, the comparison and contrast of driving and flying have revealed intriguing similarities and notable differences. Differences such as their differing speed to destination give deeper insights into their unique and shared qualities. When it comes to choosing between them, urgency to arrive at the destination will likely be a deciding factor. Despite these differences, it is important to remember that both driving and flying hold significant value within the context of air transit, and each contributes to facilitating movement in its own unique way.
See Here for More Compare and Contrast Essay Examples
4. Critical Essay Conclusion
In conclusion, the analysis of _____________ has unveiled critical aspects related to _____________. While there are strengths in _____________, its limitations are equally telling. This critique provides a more informed perspective on _____________, revealing that there is much more beneath the surface. Moving forward, the understanding of _____________ should evolve, considering both its merits and flaws.
In conclusion, the analysis of flow theory has unveiled critical aspects related to motivation and focus. While there are strengths in achieving a flow state, its limitations are equally telling. This critique provides a more informed perspective on how humans achieve motivation, revealing that there is much more beneath the surface. Moving forward, the understanding of flow theory of motivation should evolve, considering both its merits and flaws.
To conclude, this critical examination of _____________ sheds light on its multi-dimensional nature. While _____________ presents notable advantages, it is not without its drawbacks. This in-depth critique offers a comprehensive understanding of _____________. Therefore, future engagements with _____________ should involve a balanced consideration of its strengths and weaknesses.
To conclude, this critical examination of postmodern art sheds light on its multi-dimensional nature. While postmodernism presents notable advantages, it is not without its drawbacks. This in-depth critique offers a comprehensive understanding of how it has contributed to the arts over the past 50 years. Therefore, future engagements with postmodern art should involve a balanced consideration of its strengths and weaknesses.
Upon reflection, the critique of _____________ uncovers profound insights into its underlying intricacies. Despite its positive aspects such as ________, it’s impossible to overlook its shortcomings. This analysis provides a nuanced understanding of _____________, highlighting the necessity for a balanced approach in future interactions. Indeed, both the strengths and weaknesses of _____________ should be taken into account when considering ____________.
Upon reflection, the critique of marxism uncovers profound insights into its underlying intricacies. Despite its positive aspects such as its ability to critique exploitation of labor, it’s impossible to overlook its shortcomings. This analysis provides a nuanced understanding of marxism’s harmful effects when used as an economic theory, highlighting the necessity for a balanced approach in future interactions. Indeed, both the strengths and weaknesses of marxism should be taken into account when considering the use of its ideas in real life.
Ultimately, this critique of _____________ offers a detailed look into its advantages and disadvantages. The strengths of _____________ such as __________ are significant, yet its limitations such as _________ are not insignificant. This balanced analysis not only offers a deeper understanding of _____________ but also underscores the importance of critical evaluation. Hence, it’s crucial that future discussions around _____________ continue to embrace this balanced approach.
Ultimately, this critique of artificial intelligence offers a detailed look into its advantages and disadvantages. The strengths of artificial intelligence, such as its ability to improve productivity are significant, yet its limitations such as the possibility of mass job losses are not insignificant. This balanced analysis not only offers a deeper understanding of artificial intelligence but also underscores the importance of critical evaluation. Hence, it’s crucial that future discussions around the regulation of artificial intelligence continue to embrace this balanced approach.
This article promised 17 essay conclusions, and this one you are reading now is the twenty-first. This last conclusion demonstrates that the very best essay conclusions are written uniquely, from scratch, in order to perfectly cater the conclusion to the topic. A good conclusion will tie together all the key points you made in your essay and forcefully drive home the importance or relevance of your argument, thesis statement, or simply your topic so the reader is left with one strong final point to ponder.

Chris Drew (PhD)
Dr. Chris Drew is the founder of the Helpful Professor. He holds a PhD in education and has published over 20 articles in scholarly journals. He is the former editor of the Journal of Learning Development in Higher Education. [Image Descriptor: Photo of Chris]
- Chris Drew (PhD) https://helpfulprofessor.com/author/chris-drew-phd/ 5 Top Tips for Succeeding at University
- Chris Drew (PhD) https://helpfulprofessor.com/author/chris-drew-phd/ 50 Durable Goods Examples
- Chris Drew (PhD) https://helpfulprofessor.com/author/chris-drew-phd/ 100 Consumer Goods Examples
- Chris Drew (PhD) https://helpfulprofessor.com/author/chris-drew-phd/ 30 Globalization Pros and Cons
Leave a Comment Cancel Reply
Your email address will not be published. Required fields are marked *

IMAGES
VIDEO
COMMENTS
2. Summarize your main arguments. Your concluding paragraph should repeat the main points that you made within your paper in different words. Briefly summarize the key arguments that make up the body of your essay in a clear and concise manner. Make sure to include important keywords from each point in your conclusion.
When writing a conclusion for a persuasive essay, it is important to avoid introducing new information. The purpose of the conclusion is to summarize and reinforce the main arguments presented throughout the essay, rather than introduce new evidence or ideas. Including new information can confuse or distract the reader, weakening the overall ...
Step 1: Return to your thesis. To begin your conclusion, signal that the essay is coming to an end by returning to your overall argument. Don't just repeat your thesis statement —instead, try to rephrase your argument in a way that shows how it has been developed since the introduction. Example: Returning to the thesis.
Finally, some advice on how not to end an essay: Don't simply summarize your essay. A brief summary of your argument may be useful, especially if your essay is long--more than ten pages or so. But shorter essays tend not to require a restatement of your main ideas. Avoid phrases like "in conclusion," "to conclude," "in summary," and "to sum up ...
Conclusions. Conclusions wrap up what you have been discussing in your paper. After moving from general to specific information in the introduction and body paragraphs, your conclusion should begin pulling back into more general information that restates the main points of your argument. Conclusions may also call for action or overview future ...
According to Purdue University's Online Writing Lab, begin with a reminder. Let the reader know what will happen if nothing is done to resolve the issue in your argument. Reuse a particular statistic or an example you used earlier. If, to get the reader interested, you started your persuasive essay on drunk driving with the story of a mother ...
Emphasize the Significance of Your Arguments. The conclusion of your essay is a good place to highlight the importance of your argument and the implications of your findings. Briefly explain why your essay topic is significant and how your perspective relates to the wider context. For example, if you're writing on the rising cost of medicine ...
Highlight the "so what". At the beginning of your paper, you explain to your readers what's at stake—why they should care about the argument you're making. In your conclusion, you can bring readers back to those stakes by reminding them why your argument is important in the first place. You can also draft a few sentences that put ...
TIP 1: Be careful not to introduce a new argument in the conclusion—there's no time to develop it now that you've reached the end of your discussion! TIP 2: As with your thesis, avoid announcing your conclusion. Don't start your conclusion with "in conclusion" or "to conclude" or "to end my essay" type statements.
In this video, you'll learn how to write a strong essay conclusion paragraph that ties together the essay's main points, shows why your argument matters, and...
The persuasive essay conclusion should be brief so that the readers do not feel the repetitiveness of information. It should be at least 3-5 to five sentences long. The first sentence should restate the hypothesis. The next 2-3 sentences should provide the summary of the key points.
This is Think Four. The conclusion is often the most overlooked part of a persuasive essay. Some people view it as a nice add on, but nothing more than that. On the contrary, your conclusion is the sign off to your essay and a clear and effective one will leave the reader with a great lasting impression. It is key to get this right.
The conclusion connects the dots in your paper's argument and demonstrates the direction it has taken. A compelling conclusion persuades the reader to continue reading your essay. The introduction of new information is one of this paragraph's most crucial functions. Despite the fact that an effective persuasive essay must follow the ...
A persuasive essay, also known as an argumentative essay, is one that requires a student to investigate a topic and argue a viewpoint. College-level persuasive essays generally have three sections that include an introduction in which a thesis or argument is presented, body paragraphs in which arguments and counterarguments are presented, and a conclusion in which the argument is reiterated.
The 5 Must-Have Steps of a Persuasive Essay. If you're intimidated by the idea of writing an argument, use this list to break your process into manageable chunks. Tackle researching and writing one element at a time, and then revise your essay so that it flows smoothly and coherently with every component in the optimal place. 1.
Writing an effective conclusion for an argumentative essay is crucial as it can greatly impact the overall success of your essay. Here are a few tips to help you with your conclusion writing: Summarize your main points: Recap the key arguments you made throughout your essay in a concise and clear manner. This reaffirms your main points and ...
Restate the main idea of your essay. A good conclusion should summarize the main points of your essay and reiterate the main idea or thesis statement. Provide closure to your argument. Your conclusion should provide a sense of closure to your argument and tie up any loose ends. Emphasize the importance of your topic.
Essay Conclusion Examples. Below is a range of copy-and-paste essay conclusions with gaps for you to fill-in your topic and key arguments. Browse through for one you like (there are 17 for argumentative, expository, compare and contrast, and critical essays). Once you've found one you like, copy it and add-in the key points to make it your own.
1. Restate the thesis. An effective conclusion brings the reader back to the main point, reminding the reader of the purpose of the essay. However, avoid repeating the thesis verbatim. Paraphrase your argument slightly while still preserving the primary point. 2. Reiterate supporting points.
2 Steps to Write a Persuasive Essay. 2.1 Prepare for Writing Your Persuasive Essay. 2.2 Conduct Advanced Academic Research. 2.3 Outline Your Essay. 2.4 How to Write a Persuasive Essay: Introduction. 2.5 Write the Body of the Essay. 2.6 Make a Solid Conclusion. 2.7 Edit and Proofread Your Essay.
How to Write a Persuasive Essay: The Main Components. 1. Introduction: Capturing Attention and Stating the Thesis. The introduction serves as the gateway to your persuasive essay. Begin by grabbing the reader's attention with a compelling hook—an anecdote, a surprising fact, or a thought-provoking question.
Second, follow these steps on how to write an argumentative essay: Brainstorm: research, free-write, and read samples to choose a debatable topic. Prepare: organize thoughts, craft a thesis, decide on arguments and evidence. Draft: outline an essay, start with an engaging introduction, delve into arguments, and conclude like a boss.