

What is automated essay scoring?
Automated essay scoring (AES) is an important application of machine learning and artificial intelligence to the field of psychometrics and assessment. In fact, it’s been around far longer than “machine learning” and “artificial intelligence” have been buzzwords in the general public! The field of psychometrics has been doing such groundbreaking work for decades.
So how does AES work, and how can you apply it?
The first and most critical thing to know is that there is not an algorithm that “reads” the student essays. Instead, you need to train an algorithm. That is, if you are a teacher and don’t want to grade your essays, you can’t just throw them in an essay scoring system. You have to actually grade the essays (or at least a large sample of them) and then use that data to fit a machine learning algorithm. Data scientists use the term train the model , which sounds complicated, but if you have ever done simple linear regression, you have experience with training models.
There are three steps for automated essay scoring:
- Establish your data set (collate student essays and grade them).
- Determine the features (predictor variables that you want to pick up on).
- Train the machine learning model.
Here’s an extremely oversimplified example:
- You have a set of 100 student essays, which you have scored on a scale of 0 to 5 points.
- The essay is on Napoleon Bonaparte, and you want students to know certain facts, so you want to give them “credit” in the model if they use words like: Corsica, Consul, Josephine, Emperor, Waterloo, Austerlitz, St. Helena. You might also add other Features such as Word Count, number of grammar errors, number of spelling errors, etc.
- You create a map of which students used each of these words, as 0/1 indicator variables. You can then fit a multiple regression with 7 predictor variables (did they use each of the 7 words) and the 5 point scale as your criterion variable. You can then use this model to predict each student’s score from just their essay text.
Obviously, this example is too simple to be of use, but the same general idea is done with massive, complex studies. The establishment of the core features (predictive variables) can be much more complex, and models are going to be much more complex than multiple regression (neural networks, random forests, support vector machines).
Here’s an example of the very start of a data matrix for features, from an actual student essay. Imagine that you also have data on the final scores, 0 to 5 points. You can see how this is then a regression situation.
How do you score the essay?
If they are on paper, then automated essay scoring won’t work unless you have an extremely good software for character recognition that converts it to a digital database of text. Most likely, you have delivered the exam as an online assessment and already have the database. If so, your platform should include functionality to manage the scoring process, including multiple custom rubrics. An example of our FastTest platform is provided below.
Some rubrics you might use:
- Supporting arguments
- Organization
- Vocabulary / word choice
How do you pick the Features?
This is one of the key research problems. In some cases, it might be something similar to the Napoleon example. Suppose you had a complex item on Accounting, where examinees review reports and spreadsheets and need to summarize a few key points. You might pull out a few key terms as features (mortgage amortization) or numbers (2.375%) and consider them to be Features. I saw a presentation at Innovations In Testing 2022 that did exactly this. Think of them as where you are giving the students “points” for using those keywords, though because you are using complex machine learning models, it is not simply giving them a single unit point. It’s contributing towards a regression-like model with a positive slope.
In other cases, you might not know. Maybe it is an item on an English test being delivered to English language learners, and you ask them to write about what country they want to visit someday. You have no idea what they will write about. But what you can do is tell the algorithm to find the words or terms that are used most often, and try to predict the scores with that. Maybe words like “jetlag” or “edification” show up in students that tend to get high scores, while words like “clubbing” or “someday” tend to be used by students with lower scores. The AI might also pick up on spelling errors. I worked as an essay scorer in grad school, and I can’t tell you how many times I saw kids use “ludacris” (name of an American rap artist) instead of “ludicrous” when trying to describe an argument. They had literally never seen the word used or spelled correctly. Maybe the AI model finds to give that a negative weight. That’s the next section!
How do you train a model?
Well, if you are familiar with data science, you know there are TONS of models, and many of them have a bunch of parameterization options. This is where more research is required. What model works the best on your particular essay, and doesn’t take 5 days to run on your data set? That’s for you to figure out. There is a trade-off between simplicity and accuracy. Complex models might be accurate but take days to run. A simpler model might take 2 hours but with a 5% drop in accuracy. It’s up to you to evaluate.
If you have experience with Python and R, you know that there are many packages which provide this analysis out of the box – it is a matter of selecting a model that works.
How well does automated essay scoring work?
Well, as psychometricians love to say, “it depends.” You need to do the model fitting research for each prompt and rubric. It will work better for some than others. The general consensus in research is that AES algorithms work as well as a second human, and therefore serve very well in that role. But you shouldn’t use them as the only score; of course, that’s impossible in many cases.
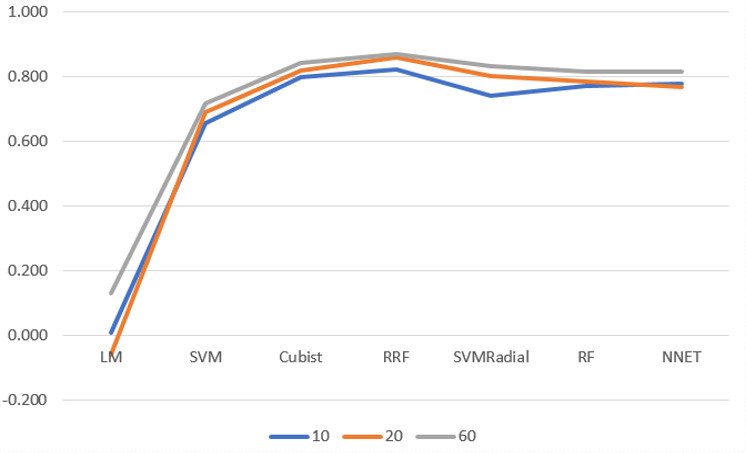
Here’s a graph from some research we did on our algorithm, showing the correlation of human to AES. The three lines are for the proportion of sample used in the training set; we saw decent results from only 10% in this case! Some of the models correlated above 0.80 with humans, even though this is a small data set. We found that the Cubist model took a fraction of the time needed by complex models like Neural Net or Random Forest; in this case it might be sufficiently powerful.
How can I implement automated essay scoring without writing code from scratch?
There are several products on the market. Some are standalone, some are integrated with a human-based essay scoring platform. ASC’s platform for automated essay scoring is SmartMarq; click here to learn more . It is currently in a standalone approach like you see below, making it extremely easy to use. It is also in the process of being integrated into our online assessment platform, alongside human scoring, to provide an efficient and easy way of obtaining a second or third rater for QA purposes.
Want to learn more? Contact us to request a demonstration .
- Latest Posts
Nathan Thompson, PhD
Latest posts by nathan thompson, phd ( see all ).
- Likert Scale Items - February 9, 2024
- Test Blueprints & Specifications - January 30, 2024
- What is a testlet? - January 17, 2024
Online Testing Solutions
Psychometrics
Subscribe to the PwC Newsletter
Join the community, add a new evaluation result row, automated essay scoring.
24 papers with code • 1 benchmarks • 1 datasets
Essay scoring: Automated Essay Scoring is the task of assigning a score to an essay, usually in the context of assessing the language ability of a language learner. The quality of an essay is affected by the following four primary dimensions: topic relevance, organization and coherence, word usage and sentence complexity, and grammar and mechanics.
Source: A Joint Model for Multimodal Document Quality Assessment
Benchmarks Add a Result
Most implemented papers, automated essay scoring based on two-stage learning.
Current state-of-art feature-engineered and end-to-end Automated Essay Score (AES) methods are proven to be unable to detect adversarial samples, e. g. the essays composed of permuted sentences and the prompt-irrelevant essays.
A Neural Approach to Automated Essay Scoring
nusnlp/nea • EMNLP 2016
SkipFlow: Incorporating Neural Coherence Features for End-to-End Automatic Text Scoring

Our new method proposes a new \textsc{SkipFlow} mechanism that models relationships between snapshots of the hidden representations of a long short-term memory (LSTM) network as it reads.
Neural Automated Essay Scoring and Coherence Modeling for Adversarially Crafted Input
Youmna-H/Coherence_AES • NAACL 2018
We demonstrate that current state-of-the-art approaches to Automated Essay Scoring (AES) are not well-suited to capturing adversarially crafted input of grammatical but incoherent sequences of sentences.
Co-Attention Based Neural Network for Source-Dependent Essay Scoring
This paper presents an investigation of using a co-attention based neural network for source-dependent essay scoring.
Language models and Automated Essay Scoring
In this paper, we present a new comparative study on automatic essay scoring (AES).
Evaluation Toolkit For Robustness Testing Of Automatic Essay Scoring Systems
midas-research/calling-out-bluff • 14 Jul 2020
This number is increasing further due to COVID-19 and the associated automation of education and testing.
Prompt Agnostic Essay Scorer: A Domain Generalization Approach to Cross-prompt Automated Essay Scoring
Cross-prompt automated essay scoring (AES) requires the system to use non target-prompt essays to award scores to a target-prompt essay.
Many Hands Make Light Work: Using Essay Traits to Automatically Score Essays
To find out which traits work best for different types of essays, we conduct ablation tests for each of the essay traits.
EXPATS: A Toolkit for Explainable Automated Text Scoring
octanove/expats • 7 Apr 2021
Automated text scoring (ATS) tasks, such as automated essay scoring and readability assessment, are important educational applications of natural language processing.
- Open supplemental data
- Reference Manager
- Simple TEXT file
People also looked at
Original research article, explainable automated essay scoring: deep learning really has pedagogical value.

- School of Computing and Information Systems, Faculty of Science and Technology, Athabasca University, Edmonton, AB, Canada
Automated essay scoring (AES) is a compelling topic in Learning Analytics for the primary reason that recent advances in AI find it as a good testbed to explore artificial supplementation of human creativity. However, a vast swath of research tackles AES only holistically; few have even developed AES models at the rubric level, the very first layer of explanation underlying the prediction of holistic scores. Consequently, the AES black box has remained impenetrable. Although several algorithms from Explainable Artificial Intelligence have recently been published, no research has yet investigated the role that these explanation models can play in: (a) discovering the decision-making process that drives AES, (b) fine-tuning predictive models to improve generalizability and interpretability, and (c) providing personalized, formative, and fine-grained feedback to students during the writing process. Building on previous studies where models were trained to predict both the holistic and rubric scores of essays, using the Automated Student Assessment Prize’s essay datasets, this study focuses on predicting the quality of the writing style of Grade-7 essays and exposes the decision processes that lead to these predictions. In doing so, it evaluates the impact of deep learning (multi-layer perceptron neural networks) on the performance of AES. It has been found that the effect of deep learning can be best viewed when assessing the trustworthiness of explanation models. As more hidden layers were added to the neural network, the descriptive accuracy increased by about 10%. This study shows that faster (up to three orders of magnitude) SHAP implementations are as accurate as the slower model-agnostic one. It leverages the state-of-the-art in natural language processing, applying feature selection on a pool of 1592 linguistic indices that measure aspects of text cohesion, lexical diversity, lexical sophistication, and syntactic sophistication and complexity. In addition to the list of most globally important features, this study reports (a) a list of features that are important for a specific essay (locally), (b) a range of values for each feature that contribute to higher or lower rubric scores, and (c) a model that allows to quantify the impact of the implementation of formative feedback.
Automated essay scoring (AES) is a compelling topic in Learning Analytics (LA) for the primary reason that recent advances in AI find it as a good testbed to explore artificial supplementation of human creativity. However, a vast swath of research tackles AES only holistically; only a few have even developed AES models at the rubric level, the very first layer of explanation underlying the prediction of holistic scores ( Kumar et al., 2017 ; Taghipour, 2017 ; Kumar and Boulanger, 2020 ). None has attempted to explain the whole decision process of AES, from holistic scores to rubric scores and from rubric scores to writing feature modeling. Although several algorithms from XAI (explainable artificial intelligence) ( Adadi and Berrada, 2018 ; Murdoch et al., 2019 ) have recently been published (e.g., LIME, SHAP) ( Ribeiro et al., 2016 ; Lundberg and Lee, 2017 ), no research has yet investigated the role that these explanation models (trained on top of predictive models) can play in: (a) discovering the decision-making process that drives AES, (b) fine-tuning predictive models to improve generalizability and interpretability, and (c) providing teachers and students with personalized, formative, and fine-grained feedback during the writing process.
One of the key anticipated benefits of AES is the elimination of human bias such as rater fatigue, rater’s expertise, severity/leniency, scale shrinkage, stereotyping, Halo effect, rater drift, perception difference, and inconsistency ( Taghipour, 2017 ). At its turn, AES may suffer from its own set of biases (e.g., imperfections in training data, spurious correlations, overrepresented minority groups), which has incited the research community to look for ways to make AES more transparent, accountable, fair, unbiased, and consequently trustworthy while remaining accurate. This required changing the perception that AES is merely a machine learning and feature engineering task ( Madnani et al., 2017 ; Madnani and Cahill, 2018 ). Hence, researchers have advocated that AES should be seen as a shared task requiring several methodological design decisions along the way such as curriculum alignment, construction of training corpora, reliable scoring process, and rater performance evaluation, where the goal is to build and deploy fair and unbiased scoring models to be used in large-scale assessments and classroom settings ( Rupp, 2018 ; West-Smith et al., 2018 ; Rupp et al., 2019 ). Unfortunately, although these measures are intended to design reliable and valid AES systems, they may still fail to build trust among users, keeping the AES black box impenetrable for teachers and students.
It has been previously recognized that divergence of opinion among human and machine graders has been only investigated superficially ( Reinertsen, 2018 ). So far, researchers investigated the characteristics of essays through qualitative analyses which ended up rejected by AES systems (requiring a human to score them) ( Reinertsen, 2018 ). Others strived to justify predicted scores by identifying essay segments that actually caused the predicted scores. In spite of the fact that these justifications hinted at and quantified the importance of these spatial cues, they did not provide any feedback as to how to improve those suboptimal essay segments ( Mizumoto et al., 2019 ).
Related to this study and the work of Kumar and Boulanger (2020) is Revision Assistant, a commercial AES system developed by Turnitin ( Woods et al., 2017 ; West-Smith et al., 2018 ), which in addition to predicting essays’ holistic scores provides formative, rubric-specific, and sentence-level feedback over multiple drafts of a student’s essay. The implementation of Revision Assistant moved away from the traditional approach to AES, which consists in using a limited set of features engineered by human experts representing only high-level characteristics of essays. Like this study, it rather opted for including a large number of low-level writing features, demonstrating that expert-designed features are not required to produce interpretable predictions. Revision Assistant’s performance was reported on two essay datasets, one of which was the Automated Student Assessment Prize (ASAP) 1 dataset. However, performance on the ASAP dataset was reported in terms of quadratic weighted kappa and this for holistic scores only. Models predicting rubric scores were trained only with the other dataset which was hosted on and collected through Revision Assistant itself.
In contrast to feature-based approaches like the one adopted by Revision Assistant, other AES systems are implemented using deep neural networks where features are learned during model training. For example, Taghipour (2017) in his doctoral dissertation leverages a recurrent neural network to improve accuracy in predicting holistic scores, implement rubric scoring (i.e., organization and argument strength), and distinguish between human-written and computer-generated essays. Interestingly, Taghipour compared the performance of his AES system against other AES systems using the ASAP corpora, but he did not use the ASAP corpora when it came to train rubric scoring models although ASAP provides two corpora provisioning rubric scores (#7 and #8). Finally, research was also undertaken to assess the generalizability of rubric-based models by performing experiments across various datasets. It was found that the predictive power of such rubric-based models was related to how much the underlying feature set covered a rubric’s criteria ( Rahimi et al., 2017 ).
Despite their numbers, rubrics (e.g., organization, prompt adherence, argument strength, essay length, conventions, word choices, readability, coherence, sentence fluency, style, audience, ideas) are usually investigated in isolation and not as a whole, with the exception of Revision Assistant which provides feedback at the same time on the following five rubrics: claim, development, audience, cohesion, and conventions. The literature reveals that rubric-specific automated feedback includes numerical rubric scores as well as recommendations on how to improve essay quality and correct errors ( Taghipour, 2017 ). Again, except for Revision Assistant which undertook a holistic approach to AES including holistic and rubric scoring and provision of rubric-specific feedback at the sentence level, AES has generally not been investigated as a whole or as an end-to-end product. Hence, the AES used in this study and developed by Kumar and Boulanger (2020) is unique in that it uses both deep learning (multi-layer perceptron neural network) and a huge pool of linguistic indices (1592), predicts both holistic and rubric scores, explaining holistic scores in terms of rubric scores, and reports which linguistic indices are the most important by rubric. This study, however, goes one step further and showcases how to explain the decision process behind the prediction of a rubric score for a specific essay, one of the main AES limitations identified in the literature ( Taghipour, 2017 ) that this research intends to address, at least partially.
Besides providing explanations of predictions both globally and individually, this study not only goes one step further toward the automated provision of formative feedback but also does so in alignment with the explanation model and the predictive model, allowing to better map feedback to the actual characteristics of an essay. Woods et al. (2017) succeeded in associating sentence-level expert-derived feedback with strong/weak sentences having the greatest influence on a rubric score based on the rubric, essay score, and the sentence characteristics. While Revision Assistant’s feature space consists of counts and binary occurrence indicators of word unigrams, bigrams and trigrams, character four-grams, and part-of-speech bigrams and trigrams, they are mainly textual and locational indices; by nature they are not descriptive or self-explanative. This research fills this gap by proposing feedback based on a set of linguistic indices that can encompass several sentences at a time. However, the proposed approach omits locational hints, leaving the merging of the two approaches as the next step to be addressed by the research community.
Although this paper proposes to extend the automated provision of formative feedback through an interpretable machine learning method, it rather focuses on the feasibility of automating it in the context of AES instead of evaluating the pedagogical quality (such as the informational and communicational value of feedback messages) or impact on students’ writing performance, a topic that will be kept for an upcoming study. Having an AES system that is capable of delivering real-time formative feedback sets the stage to investigate (1) when feedback is effective, (2) the types of feedback that are effective, and (3) whether there exist different kinds of behaviors in terms of seeking and using feedback ( Goldin et al., 2017 ). Finally, this paper omits describing the mapping between the AES model’s linguistic indices and a pedagogical language that is easily understandable by students and teachers, which is beyond its scope.
Methodology
This study showcases the application of the PDR framework ( Murdoch et al., 2019 ), which provides three pillars to describe interpretations in the context of the data science life cycle: P redictive accuracy, D escriptive accuracy, and R elevancy to human audience(s). It is important to note that in a broader sense both terms “explainable artificial intelligence” and “interpretable machine learning” can be used interchangeably with the following meaning ( Murdoch et al., 2019 ): “the use of machine-learning models for the extraction of relevant knowledge about domain relationships contained in data.” Here “predictive accuracy” refers to the measurement of a model’s ability to fit data; “descriptive accuracy” is the degree at which the relationships learned by a machine learning model can be objectively captured; and “relevant knowledge” implies that a particular audience gets insights into a chosen domain problem that guide its communication, actions, and discovery ( Murdoch et al., 2019 ).
In the context of this article, formative feedback that assesses students’ writing skills and prescribes remedial writing strategies is the relevant knowledge sought for, whose effectiveness on students’ writing performance will be validated in an upcoming study. However, the current study puts forward the tools and evaluates the feasibility to offer this real-time formative feedback. It also measures the predictive and descriptive accuracies of AES and explanation models, two key components to generate trustworthy interpretations ( Murdoch et al., 2019 ). Naturally, the provision of formative feedback is dependent on the speed of training and evaluating new explanation models every time a new essay is ingested by the AES system. That is why this paper investigates the potential of various SHAP implementations for speed optimization without compromising the predictive and descriptive accuracies. This article will show how the insights generated by the explanation model can serve to debug the predictive model and contribute to enhance the feature selection and/or engineering process ( Murdoch et al., 2019 ), laying the foundation for the provision of actionable and impactful pieces of knowledge to educational audiences, whose relevancy will be judged by the human stakeholders and estimated by the magnitude of resulting changes.
Figure 1 overviews all the elements and steps encompassed by the AES system in this study. The following subsections will address each facet of the overall methodology, from hyperparameter optimization to relevancy to both students and teachers.
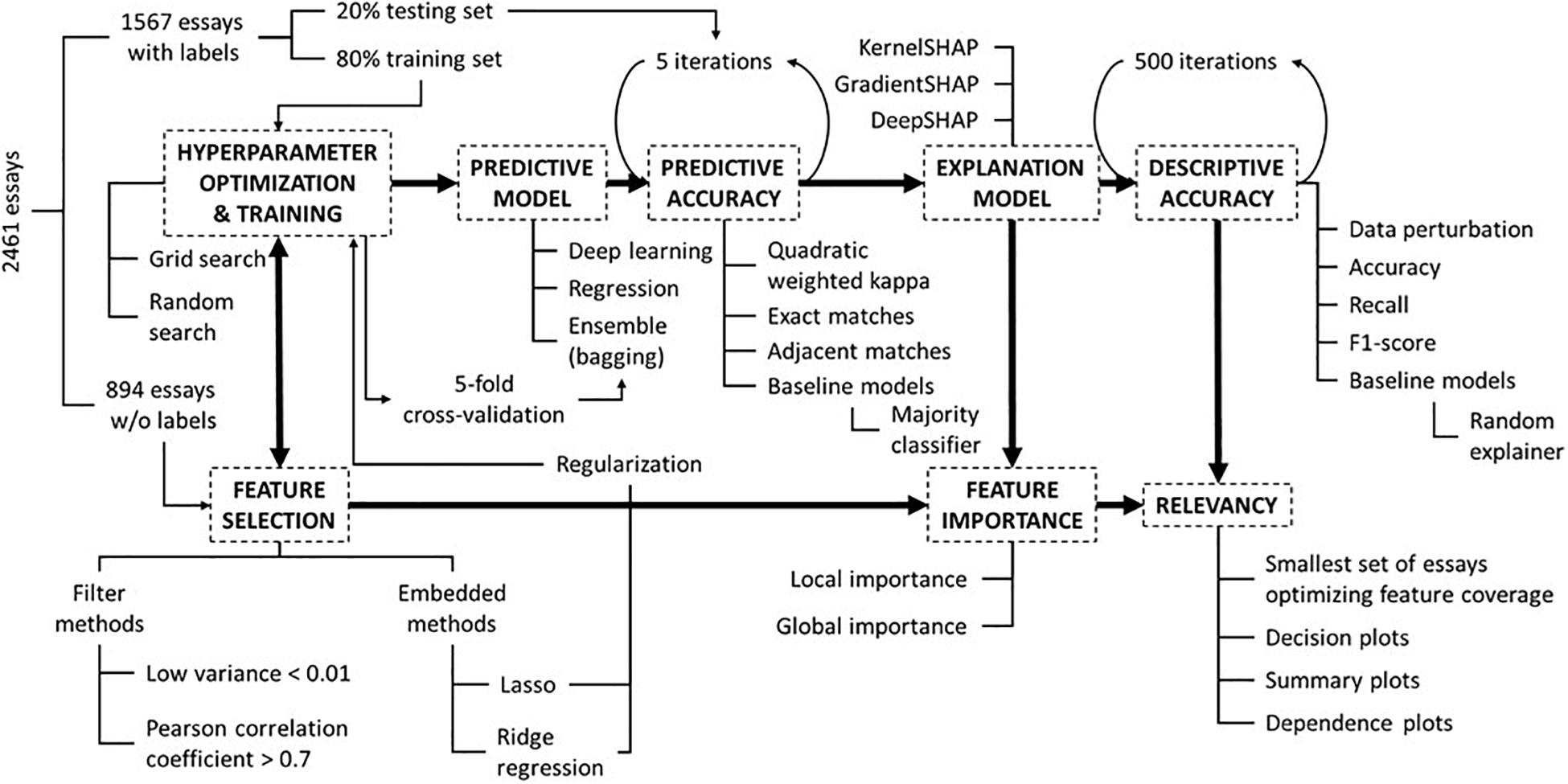
Figure 1. A flow chart exhibiting the sequence of activities to develop an end-to-end AES system and how the various elements work together to produce relevant knowledge to the intended stakeholders.
Automated Essay Scoring System, Dataset, and Feature Selection
As previously mentioned, this paper reuses the AES system developed by Kumar and Boulanger (2020) . The AES models were trained using the ASAP’s seventh essay corpus. These narrative essays were written by Grade-7 students in the setting of state-wide assessments in the United States and had an average length of 171 words. Students were asked to write a story about patience. Kumar and Boulanger’s work consisted in training a predictive model for each of the four rubrics according to which essays were graded: ideas, organization, style, and conventions. Each essay was scored by two human raters on a 0−3 scale (integer scale). Rubric scores were resolved by adding the rubric scores assigned by the two human raters, producing a resolved rubric score between 0 and 6. This paper is a continuation of Boulanger and Kumar (2018 , 2019 , 2020) and Kumar and Boulanger (2020) where the objective is to open the AES black box to explain the holistic and rubric scores that it predicts. Essentially, the holistic score ( Boulanger and Kumar, 2018 , 2019 ) is determined and justified through its four rubrics. Rubric scores, in turn, are investigated to highlight the writing features that play an important role within each rubric ( Kumar and Boulanger, 2020 ). Finally, beyond global feature importance, it is not only indispensable to identify which writing indices are important for a particular essay (local), but also to discover how they contribute to increase or decrease the predicted rubric score, and which feature values are more/less desirable ( Boulanger and Kumar, 2020 ). This paper is a continuation of these previous works by adding the following link to the AES chain: holistic score, rubric scores, feature importance, explanations, and formative feedback. The objective is to highlight the means for transparent and trustable AES while empowering learning analytics practitioners with the tools to debug these models and equip educational stakeholders with an AI companion that will semi-autonomously generate formative feedback to teachers and students. Specifically, this paper analyzes the AES reasoning underlying its assessment of the “style” rubric, which looks for command of language, including effective and compelling word choice and varied sentence structure, that clearly supports the writer’s purpose and audience.
This research’s approach to AES leverages a feature-based multi-layer perceptron (MLP) deep neural network to predict rubric scores. The AES system is fed by 1592 linguistic indices quantitatively measured by the Suite of Automatic Linguistic Analysis Tools 2 (SALAT), which assess aspects of grammar and mechanics, sentiment analysis and cognition, text cohesion, lexical diversity, lexical sophistication, and syntactic sophistication and complexity ( Kumar and Boulanger, 2020 ). The purpose of using such a huge pool of low-level writing features is to let deep learning extract the most important ones; the literature supports this practice since there is evidence that features automatically selected are not less interpretable than those engineered ( Woods et al., 2017 ). However, to facilitate this process, this study opted for a semi-automatic strategy that consisted of both filter and embedded methods. Firstly, the original ASAP’s seventh essay dataset consists of a training set of 1567 essays and a validation and testing sets of 894 essays combined. While the texts of all 2461 essays are still available to the public, only the labels (the rubric scores of two human raters) of the training set have been shared with the public. Yet, this paper reused the unlabeled 894 essays of the validation and testing sets for feature selection, a process that must be carefully carried out by avoiding being informed by essays that will train the predictive model. Secondly, feature data were normalized, and features with variances lower than 0.01 were pruned. Thirdly, the last feature of any pair of features having an absolute Pearson correlation coefficient greater than 0.7 was also pruned (the one that comes last in terms of the column ordering in the datasets). After the application of these filter methods, the number of features was reduced from 1592 to 282. Finally, the Lasso and Ridge regression regularization methods (whose combination is also called ElasticNet) were applied during the training of the rubric scoring models. Lasso is responsible for pruning further features, while Ridge regression is entrusted with eliminating multicollinearity among features.
Hyperparameter Optimization and Training
To ensure a fair evaluation of the potential of deep learning, it is of utmost importance to minimally describe this study’s exploration of the hyperparameter space, a step that is often found to be missing when reporting the outcomes of AES models’ performance ( Kumar and Boulanger, 2020 ). First, a study should list the hyperparameters it is going to investigate by testing for various values of each hyperparameter. For example, Table 1 lists all hyperparameters explored in this study. Note that L 1 and L 2 are two regularization hyperparameters contributing to feature selection. Second, each study should also report the range of values of each hyperparameter. Finally, the strategy to explore the selected hyperparameter subspace should be clearly defined. For instance, given the availability of high-performance computing resources and the time/cost of training AES models, one might favor performing a grid (a systematic testing of all combinations of hyperparameters and hyperparameter values within a subspace) or a random search (randomly selecting a hyperparameter value from a range of values per hyperparameter) or both by first applying random search to identify a good starting candidate and then grid search to test all possible combinations in the vicinity of the starting candidate’s subspace. Of particular interest to this study is the neural network itself, that is, how many hidden layers should a neural network have and how many neurons should compose each hidden layer and the neural network as a whole. These two variables are directly related to the size of the neural network, with the number of hidden layers being a defining trait of deep learning. A vast swath of literature is silent about the application of interpretable machine learning in AES and even more about measuring its descriptive accuracy, the two components of trustworthiness. Hence, this study pioneers the comprehensive assessment of deep learning impact on AES’s predictive and descriptive accuracies.
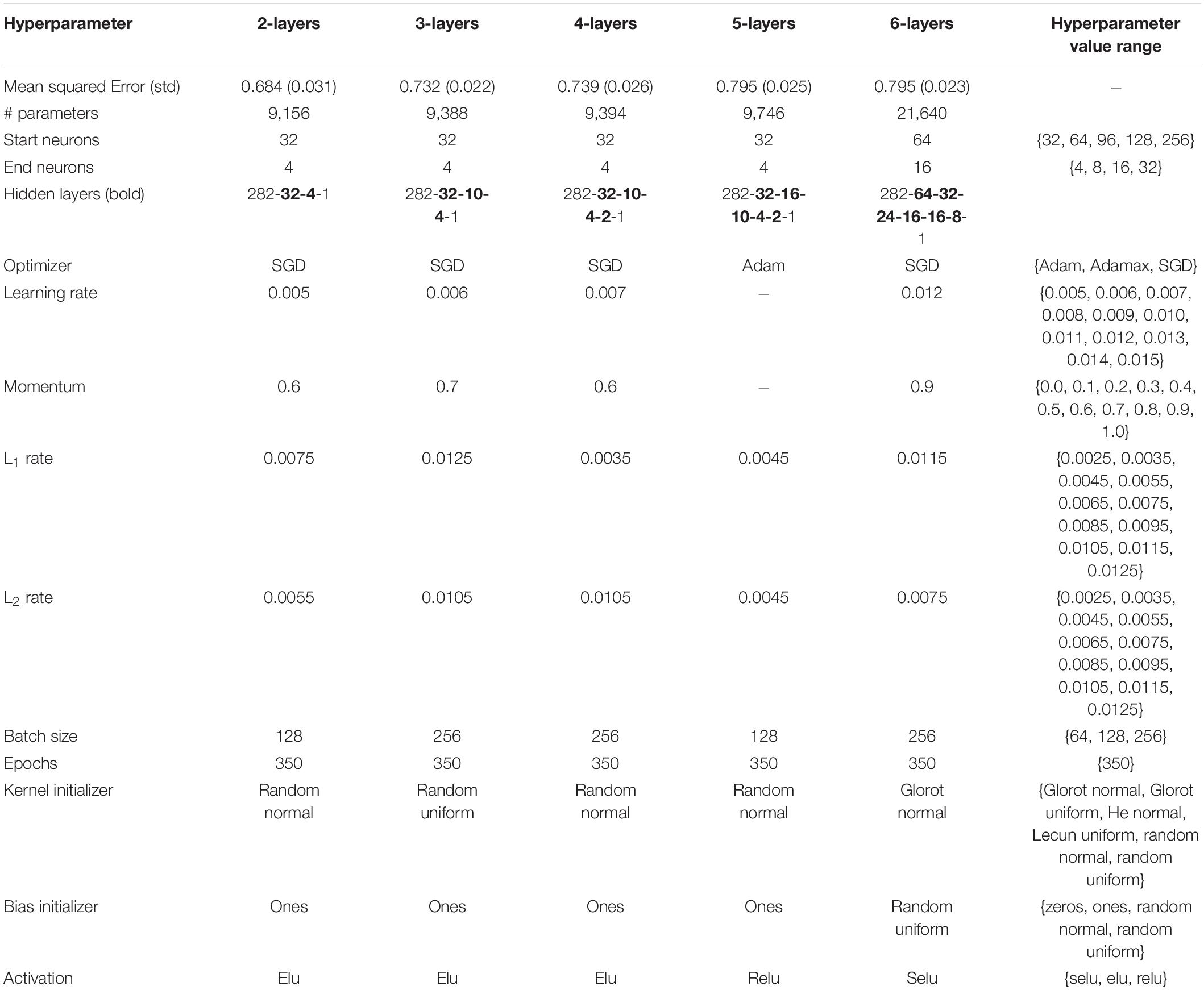
Table 1. Hyperparameter subspace investigated in this article along with best hyperparameter values per neural network architecture.
Consequently, the 1567 labeled essays were divided into a training set (80%) and a testing set (20%). No validation set was put aside; 5-fold cross-validation was rather used for hyperparameter optimization. Table 1 delineates the hyperparameter subspace from which 800 different combinations of hyperparameter values were randomly selected out of a subspace of 86,248,800 possible combinations. Since this research proposes to investigate the potential of deep learning to predict rubric scores, several architectures consisting of 2 to 6 hidden layers and ranging from 9,156 to 119,312 parameters were tested. Table 1 shows the best hyperparameter values per depth of neural networks.
Again, the essays of the testing set were never used during the training and cross-validation processes. In order to retrieve the best predictive models during training, every time the validation loss reached a record low, the model was overwritten. Training stopped when no new record low was reached during 100 epochs. Moreover, to avoid reporting the performance of overfit models, each model was trained five times using the same set of best hyperparameter values. Finally, for each resulting predictive model, a corresponding ensemble model (bagging) was also obtained out of the five models trained during cross-validation.
Predictive Models and Predictive Accuracy
Table 2 delineates the performance of predictive models trained previously by Kumar and Boulanger (2020) on the four scoring rubrics. The first row lists the agreement levels between the resolved and predicted rubric scores measured by the quadratic weighted kappa. The second row is the percentage of accurate predictions; the third row reports the percentages of predictions that are either accurate or off by 1; and the fourth row reports the percentages of predictions that are either accurate or at most off by 2. Prediction of holistic scores is done merely by adding up all rubric scores. Since the scale of rubric scores is 0−6 for every rubric, then the scale of holistic scores is 0−24.
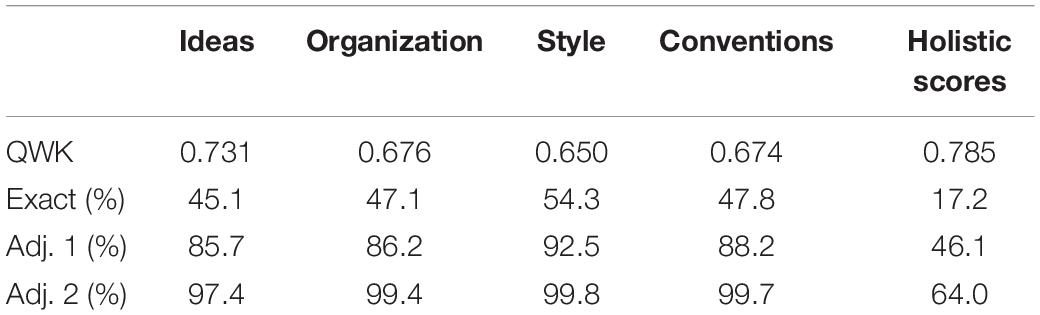
Table 2. Rubric scoring models’ performance on testing set.
While each of these rubric scoring models might suffer from its own systemic bias and hence cancel off each other’s bias by adding up the rubric scores to derive the holistic score, this study (unlike related works) intends to highlight these biases by exposing the decision making process underlying the prediction of rubric scores. Although this paper exclusively focuses on the Style rubric, the methodology put forward to analyze the local and global importance of writing indices and their context-specific contributions to predicted rubric scores is applicable to every rubric and allows to control for these biases one rubric at a time. Comparing and contrasting the role that a specific writing index plays within each rubric context deserves its own investigation, which has been partly addressed in the study led by Kumar and Boulanger (2020) . Moreover, this paper underscores the necessity to measure the predictive accuracy of rubric-based holistic scoring using additional metrics to account for these rubric-specific biases. For example, there exist several combinations of rubric scores to obtain a holistic score of 16 (e.g., 4-4-4-4 vs. 4-3-4-5 vs. 3-5-2-6). Even though the predicted holistic score might be accurate, the rubric scores could all be inaccurate. Similarity or distance metrics (e.g., Manhattan and Euclidean) should then be used to describe the authenticity of the composition of these holistic scores.
According to what Kumar and Boulanger (2020) report on the performance of several state-of-the-art AES systems trained on ASAP’s seventh essay dataset, the AES system they developed and which will be reused in this paper proved competitive while being fully and deeply interpretable, which no other AES system does. They also supply further information about the study setting, essay datasets, rubrics, features, natural language processing (NLP) tools, model training, and evaluation against human performance. Again, this paper showcases the application of explainable artificial intelligence in automated essay scoring by focusing on the decision process of the Rubric #3 (Style) scoring model. Remember that the same methodology is applicable to each rubric.
Explanation Model: SHAP
SH apley A dditive ex P lanations (SHAP) is a theoretically justified XAI framework that can provide simultaneously both local and global explanations ( Molnar, 2020 ); that is, SHAP is able to explain individual predictions taking into account the uniqueness of each prediction, while highlighting the global factors influencing the overall performance of a predictive model. SHAP is of keen interest because it unifies all algorithms of the class of additive feature attribution methods, adhering to a set of three properties that are desirable in interpretable machine learning: local accuracy, missingness, and consistency ( Lundberg and Lee, 2017 ). A key advantage of SHAP is that feature contributions are all expressed in terms of the outcome variable (e.g., rubric scores), providing a same scale to compare the importance of each feature against each other. Local accuracy refers to the fact that no matter the explanation model, the sum of all feature contributions is always equal to the prediction explained by these features. The missingness property implies that the prediction is never explained by unmeasured factors, which are always assigned a contribution of zero. However, the converse is not true; a contribution of zero does not imply an unobserved factor, it can also denote a feature irrelevant to explain the prediction. The consistency property guarantees that a more important feature will always have a greater magnitude than a less important one, no matter how many other features are included in the explanation model. SHAP proves superior to other additive attribution methods such as LIME (Local Interpretable Model-Agnostic Explanations), Shapley values, and DeepLIFT in that they never comply with all three properties, while SHAP does ( Lundberg and Lee, 2017 ). Moreover, the way SHAP assesses the importance of a feature differs from permutation importance methods (e.g., ELI5), measured as the decrease in model performance (accuracy) as a feature is perturbated, in that it is based on how much a feature contributes to every prediction.
Essentially, a SHAP explanation model (linear regression) is trained on top of a predictive model, which in this case is a complex ensemble deep learning model. Table 3 demonstrates a scale explanation model showing how SHAP values (feature contributions) work. In this example, there are five instances and five features describing each instance (in the context of this paper, an instance is an essay). Predictions are listed in the second to last column, and the base value is the mean of all predictions. The base value constitutes the reference point according to which predictions are explained; in other words, reasons are given to justify the discrepancy between the individual prediction and the mean prediction (the base value). Notice that the table does not contain the actual feature values; these are SHAP values that quantify the contribution of each feature to the predicted score. For example, the prediction of Instance 1 is 2.46, while the base value is 3.76. Adding up the feature contributions of Instance 1 to the base value produces the predicted score:
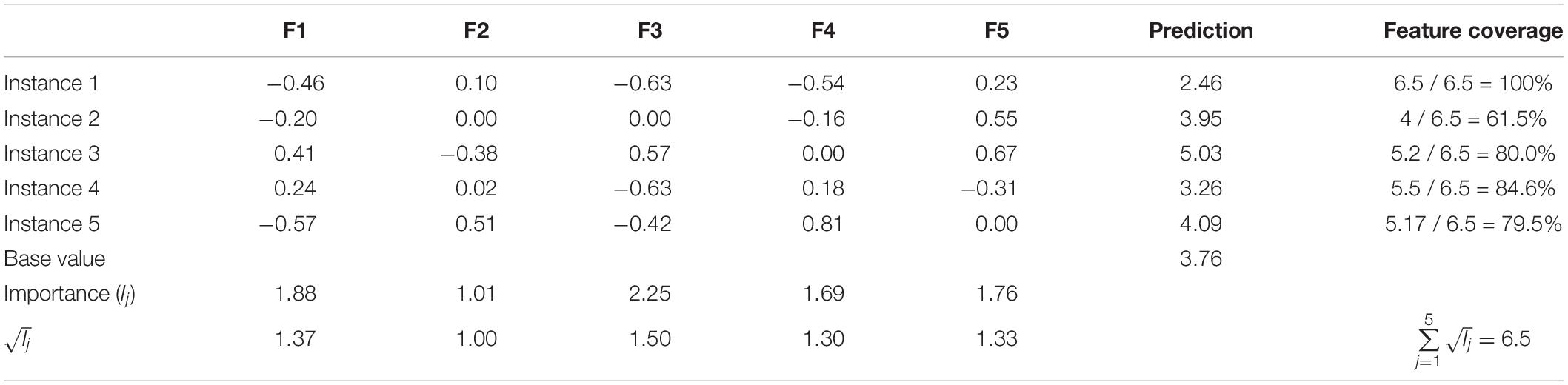
Table 3. Array of SHAP values: local and global importance of features and feature coverage per instance.
Hence, the generic equation of the explanation model ( Lundberg and Lee, 2017 ) is:
where g(x) is the prediction of an individual instance x, σ 0 is the base value, σ i is the feature contribution of feature x i , x i ∈ {0,1} denotes whether feature x i is part of the individual explanation, and j is the total number of features. Furthermore, the global importance of a feature is calculated by adding up the absolute values of its corresponding SHAP values over all instances, where n is the total number of instances and σ i ( j ) is the feature contribution for instance i ( Lundberg et al., 2018 ):
Therefore, it can be seen that Feature 3 is the most globally important feature, while Feature 2 is the least important one. Similarly, Feature 5 is Instance 3’s most important feature at the local level, while Feature 2 is the least locally important. The reader should also note that a feature shall not necessarily be assigned any contribution; some of them are just not part of the explanation such as Feature 2 and Feature 3 in Instance 2. These concepts lay the foundation for the explainable AES system presented in this paper. Just imagine that each instance (essay) will be rather summarized by 282 features and that the explanations of all the testing set’s 314 essays will be provided.
Several implementations of SHAP exist: KernelSHAP, DeepSHAP, GradientSHAP, and TreeSHAP, among others. KernelSHAP is model-agnostic and works for any type of predictive models; however, KernelSHAP is very computing-intensive which makes it undesirable for practical purposes. DeepSHAP and GradientSHAP are two implementations intended for deep learning which takes advantage of the known properties of neural networks (i.e., MLP-NN, CNN, or RNN) to accelerate up to three orders of magnitude the processing time to explain predictions ( Chen et al., 2019 ). Finally, TreeSHAP is the most powerful implementation intended for tree-based models. TreeSHAP is not only fast; it is also accurate. While the three former implementations estimate SHAP values, TreeSHAP computes them exactly. Moreover, TreeSHAP not only measures the contribution of individual features, but it also considers interactions between pairs of features and assigns them SHAP values. Since one of the goals of this paper is to assess the potential of deep learning on the performance of both predictive and explanation models, this research tested the former three implementations. TreeSHAP is recommended for future work since the interaction among features is critical information to consider. Moreover, KernelSHAP, DeepSHAP, and GradientSHAP all require access to the whole original dataset to derive the explanation of a new instance, another constraint TreeSHAP is not subject to.
Descriptive Accuracy: Trustworthiness of Explanation Models
This paper reuses and adapts the methodology introduced by Ribeiro et al. (2016) . Several explanation models will be trained, using different SHAP implementations and configurations, per deep learning predictive model (for each number of hidden layers). The rationale consists in randomly selecting and ignoring 25% of the 282 features feeding the predictive model (e.g., turning them to zero). If it causes the prediction to change beyond a specific threshold (in this study 0.10 and 0.25 were tested), then the explanation model should also reflect the magnitude of this change while ignoring the contributions of these same features. For example, the original predicted rubric score of an essay might be 5; however, when ignoring the information brought in by a subset of 70 randomly selected features (25% of 282), the prediction may turn to 4. On the other side, if the explanation model also predicts a 4 while ignoring the contributions of the same subset of features, then the explanation is considered as trustworthy. This allows to compute the precision, recall, and F1-score of each explanation model (number of true and false positives and true and false negatives). The process is repeated 500 times for every essay to determine the average precision and recall of every explanation model.
Judging Relevancy
So far, the consistency of explanations with predictions has been considered. However, consistent explanations do not imply relevant or meaningful explanations. Put another way, explanations only reflect what predictive models have learned during training. How can the black box of these explanations be opened? Looking directly at the numerical SHAP values of each explanation might seem a daunting task, but there exist tools, mainly visualizations (decision plot, summary plot, and dependence plot), that allow to make sense out of these explanations. However, before visualizing these explanations, another question needs to be addressed: which explanations or essays should be picked for further scrutiny of the AES system? Given the huge number of essays to examine and the tedious task to understand the underpinnings of a single explanation, a small subset of essays should be carefully picked that should represent concisely the state of correctness of the underlying predictive model. Again, this study applies and adapts the methodology in Ribeiro et al. (2016) . A greedy algorithm selects essays whose predictions are explained by as many features of global importance as possible to optimize feature coverage. Ribeiro et al. demonstrated in unrelated studies (i.e., sentiment analysis) that the correctness of a predictive model can be assessed with as few as four or five well-picked explanations.
For example, Table 3 reveals the global importance of five features. The square root of each feature’s global importance is also computed and considered instead to limit the influence of a small group of very influential features. The feature coverage of Instance 1 is 100% because all features are engaged in the explanation of the prediction. On the other hand, Instance 2 has a feature coverage of 61.5% because only Features 1, 4, and 5 are part of the prediction’s explanation. The feature coverage is calculated by summing the square root of each explanation’s feature’s global importance together and dividing by the sum of the square roots of all features’ global importance:
Additionally, it can be seen that Instance 4 does not have any zero-feature value although its feature coverage is only 84.6%. The algorithm was constrained to discard from the explanation any feature whose contribution (local importance) was too close to zero. In the case of Table 3 ’s example, any feature whose absolute SHAP value is less than 0.10 is ignored, hence leading to a feature coverage of:
In this paper’s study, the real threshold was 0.01. This constraint was actually a requirement for the DeepSHAP and GradientSHAP implementations because they only output non-zero SHAP values contrary to KernelSHAP which generates explanations with a fixed number of features: a non-zero SHAP value indicates that the feature is part of the explanation, while a zero value excludes the feature from the explanation. Without this parameter, all 282 features would be part of the explanation although a huge number only has a trivial (very close to zero) SHAP value. Now, a much smaller but variable subset of features makes up each explanation. This is one way in which Ribeiro et al.’s SP-LIME algorithm (SP stands for Submodular Pick) has been adapted to this study’s needs. In conclusion, notice how Instance 4 would be selected in preference to Instance 5 to explain Table 3 ’s underlying predictive model. Even though both instances have four features explaining their prediction, Instance 4’s features are more globally important than Instance 5’s features, and therefore Instance 4 has greater feature coverage than Instance 5.
Whereas Table 3 ’s example exhibits the feature coverage of one instance at a time, this study computes it for a subset of instances, where the absolute SHAP values are aggregated (summed) per candidate subset. When the sum of absolute SHAP values per feature exceeds the set threshold, the feature is then considered as covered by the selected set of instances. The objective in this study was to optimize the feature coverage while minimizing the number of essays to validate the AES model.
Research Questions
One of this article’s objectives is to assess the potential of deep learning in automated essay scoring. The literature has often claimed ( Hussein et al., 2019 ) that there are two approaches to AES, feature-based and deep learning, as though these two approaches were mutually exclusive. Yet, the literature also puts forward that feature-based AES models may be more interpretable than deep learning ones ( Amorim et al., 2018 ). This paper embraces the viewpoint that these two approaches can also be complementary by leveraging the state-of-the-art in NLP and automatic linguistic analysis and harnessing one of the richest pools of linguistic indices put forward in the research community ( Crossley et al., 2016 , 2017 , 2019 ; Kyle, 2016 ; Kyle et al., 2018 ) and applying a thorough feature selection process powered by deep learning. Moreover, the ability of deep learning of modeling complex non-linear relationships makes it particularly well-suited for AES given that the importance of a writing feature is highly dependent on its context, that is, its interactions with other writing features. Besides, this study leverages the SHAP interpretation method that is well-suited to interpret very complex models. Hence, this study elected to work with deep learning models and ensembles to test SHAP’s ability to explain these complex models. Previously, the literature has revealed the difficulty to have at the same time both accurate and interpretable models ( Ribeiro et al., 2016 ; Murdoch et al., 2019 ), where favoring one comes at the expense of the other. However, this research shows how XAI makes it now possible to produce both accurate and interpretable models in the area of AES. Since ensembles have been repeatedly shown to boost the accuracy of predictive models, they were included as part of the tested deep learning architectures to maximize generalizability and accuracy, while making these predictive models interpretable and exploring whether deep learning can even enhance their descriptive accuracy further.
This study investigates the trustworthiness of explanation models, and more specifically, those explaining deep learning predictive models. For instance, does the depth, defined as the number of hidden layers, of an MLP neural network increases the trustworthiness of its SHAP explanation model? The answer to this question will help determine whether it is possible to have very accurate AES models while having competitively interpretable/explainable models, the corner stone for the generation of formative feedback. Remember that formative feedback is defined as “any kind of information provided to students about their actual state of learning or performance in order to modify the learner’s thinking or behavior in the direction of the learning standards” and that formative feedback “conveys where the student is, what are the goals to reach, and how to reach the goals” ( Goldin et al., 2017 ). This notion contrasts with summative feedback which basically is “a justification of the assessment results” ( Hao and Tsikerdekis, 2019 ).
As pointed out in the previous section, multiple SHAP implementations are evaluated in this study. Hence, this paper showcases whether the faster DeepSHAP and GradientSHAP implementations are as reliable as the slower KernelSHAP implementation . The answer to this research question will shed light on the feasibility of providing immediate formative feedback and this multiple times throughout students’ writing processes.
This study also looks at whether a summary of the data produces as trustworthy explanations as those from the original data . This question will be of interest to AES researchers and practitioners because it could allow to significantly decrease the processing time of the computing-intensive and model-agnostic KernelSHAP implementation and test further the potential of customizable explanations.
KernelSHAP allows to specify the total number of features that will shape the explanation of a prediction; for instance, this study experiments with explanations of 16 and 32 features and observes whether there exists a statistically significant difference in the reliability of these explanation models . Knowing this will hint at whether simpler or more complex explanations are more desirable when it comes to optimize their trustworthiness. If there is no statistically significant difference, then AES practitioners are given further flexibility in the selection of SHAP implementations to find the sweet spot between complexity of explanations and speed of processing. For instance, the KernelSHAP implementation allows to customize the number of factors making up an explanation, while the faster DeepSHAP and GradientSHAP do not.
Finally, this paper highlights the means to debug and compare the performance of predictive models through their explanations. Once a model is debugged, the process can be reused to fine-tune feature selection and/or feature engineering to improve predictive models and for the generation of formative feedback to both students and teachers.
The training, validation, and testing sets consist of 1567 essays, each of which has been scored by two human raters, who assigned a score between 0 and 3 per rubric (ideas, organization, style, and conventions). In particular, this article looks at predictive and descriptive accuracy of AES models on the third rubric, style. Note that although each essay has been scored by two human raters, the literature ( Shermis, 2014 ) is not explicit about whether only two or more human raters participated in the scoring of all 1567 essays; given the huge number of essays, it is likely that more than two human raters were involved in the scoring of these essays so that the amount of noise introduced by the various raters’ biases is unknown while probably being at some degree balanced among the two groups of raters. Figure 2 shows the confusion matrices of human raters on Style Rubric. The diagonal elements (dark gray) correspond to exact matches, whereas the light gray squares indicate adjacent matches. Figure 2A delineates the number of essays per pair of ratings, and Figure 2B shows the percentages per pair of ratings. The agreement level between each pair of human raters, measured by the quadratic weighted kappa, is 0.54; the percentage of exact matches is 65.3%; the percentage of adjacent matches is 34.4%; and 0.3% of essays are neither exact nor adjacent matches. Figures 2A,B specify the distributions of 0−3 ratings per group of human raters. Figure 2C exhibits the distribution of resolved scores (a resolved score is the sum of the two human ratings). The mean is 3.99 (with a standard deviation of 1.10), and the median and mode are 4. It is important to note that the levels of predictive accuracy reported in this article are measured on the scale of resolved scores (0−6) and that larger scales tend to slightly inflate quadratic weighted kappa values, which must be taken into account when comparing against the level of agreement between human raters. Comparison of percentages of exact and adjacent matches must also be made with this scoring scale discrepancy in mind.
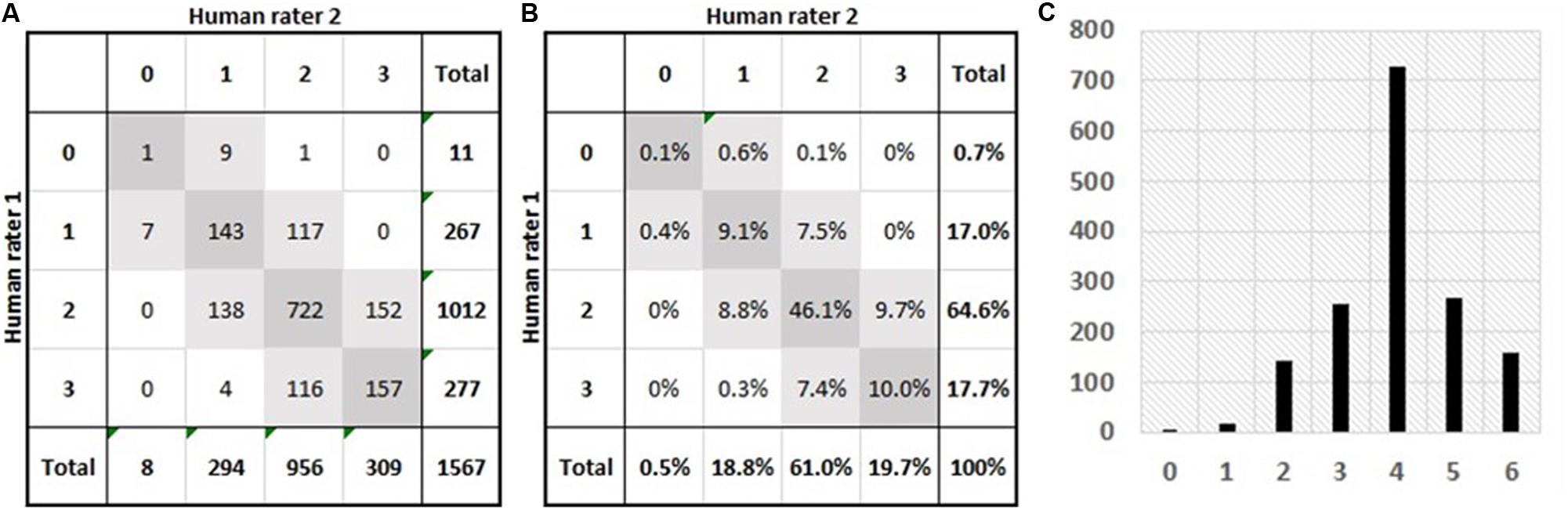
Figure 2. Summary of the essay dataset (1567 Grade-7 narrative essays) investigated in this study. (A) Number of essays per pair of human ratings; the diagonal (dark gray squares) lists the numbers of exact matches while the light-gray squares list the numbers of adjacent matches; and the bottom row and the rightmost column highlight the distributions of ratings for both groups of human raters. (B) Percentages of essays per pair of human ratings; the diagonal (dark gray squares) lists the percentages of exact matches while the light-gray squares list the percentages of adjacent matches; and the bottom row and the rightmost column highlight the distributions (frequencies) of ratings for both groups of human raters. (C) The distribution of resolved rubric scores; a resolved score is the addition of its two constituent human ratings.
Predictive Accuracy and Descriptive Accuracy
Table 4 compiles the performance outcomes of the 10 predictive models evaluated in this study. The reader should remember that the performance of each model was averaged over five iterations and that two models were trained per number of hidden layers, one non-ensemble and one ensemble. Except for the 6-layer models, there is no clear winner among other models. Even for the 6-layer models, they are superior in terms of exact matches, the primary goal for a reliable AES system, but not according to adjacent matches. Nevertheless, on average ensemble models slightly outperform non-ensemble models. Hence, these ensemble models will be retained for the next analysis step. Moreover, given that five ensemble models were trained per neural network depth, the most accurate model among the five is selected and displayed in Table 4 .
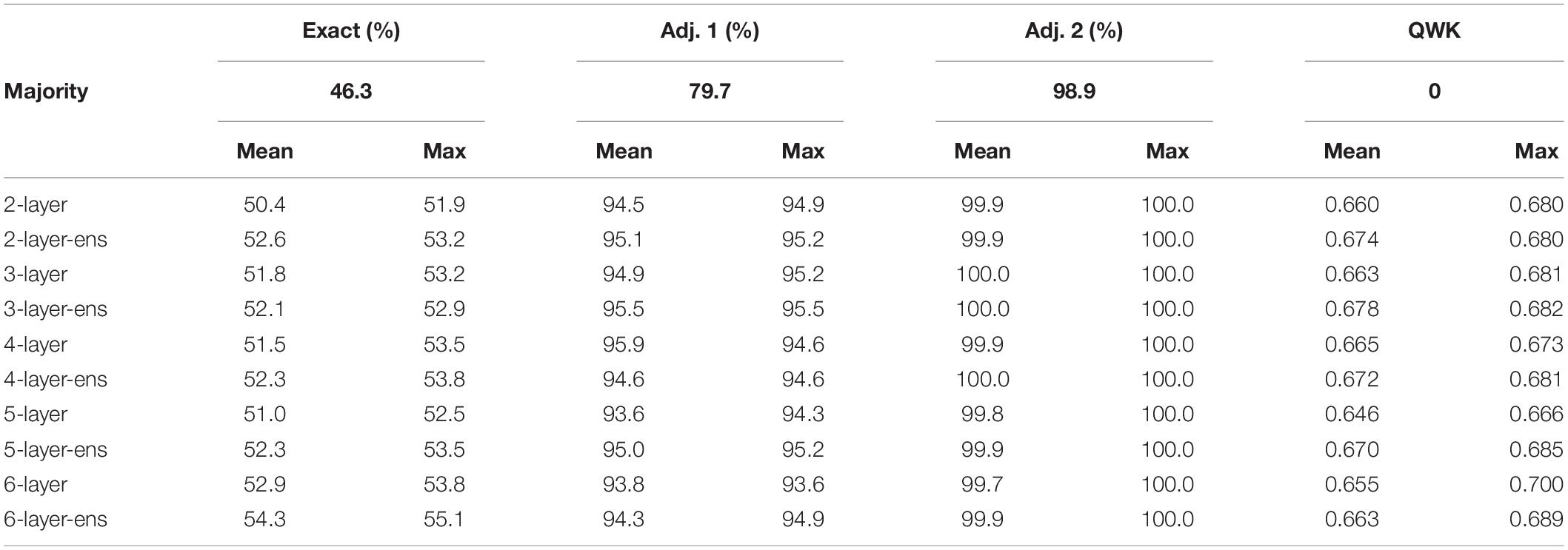
Table 4. Performance of majority classifier and average/maximal performance of trained predictive models.
Next, for each selected ensemble predictive model, several explanation models are trained per predictive model. Every predictive model is explained by the “Deep,” “Grad,” and “Random” explainers, except for the 6-layer model where it was not possible to train a “Deep” explainer apparently due to a bug in the original SHAP code caused by either a unique condition in this study’s data or neural network architecture. However, this was beyond the scope of this study to fix and investigate this issue. As it will be demonstrated, no statistically significant difference exists between the accuracy of these explainers.
The “Random” explainer serves as a baseline model for comparison purpose. Remember that to evaluate the reliability of explanation models, the concurrent impact of randomly selecting and ignoring a subset of features on the prediction and explanation of rubric scores is analyzed. If the prediction changes significantly and its corresponding explanation changes (beyond a set threshold) accordingly (a true positive) or if the prediction remains within the threshold as does the explanation (a true negative), then the explanation is deemed as trustworthy. Hence, in the case of the Random explainer, it simulates random explanations by randomly selecting 32 non-zero features from the original set of 282 features. These random explanations consist only of non-zero features because, according to SHAP’s missingness property, a feature with a zero or a missing value never gets assigned any contribution to the prediction. If at least one of these 32 features is also an element of the subset of the ignored features, then the explanation is considered as untrustworthy, no matter the size of a feature’s contribution.
As for the layer-2 model, six different explanation models are evaluated. Recall that layer-2 models generated the least mean squared error (MSE) during hyperparameter optimization (see Table 1 ). Hence, this specific type of architecture was selected to test the reliability of these various explainers. The “Kernel” explainer is the most computing-intensive and took approximately 8 h of processing. It was trained using the full distributions of feature values in the training set and shaped explanations in terms of 32 features; the “Kernel-16” and “Kernel-32” models were trained on a summary (50 k -means centroids) of the training set to accelerate the processing by about one order of magnitude (less than 1 h). Besides, the “Kernel-16” explainer derived explanations in terms of 16 features, while the “Kernel-32” explainer explained predictions through 32 features. Table 5 exhibits the descriptive accuracy of these various explanation models according to a 0.10 and 0.25 threshold; in other words, by ignoring a subset of randomly picked features, it assesses whether or not the prediction and explanation change simultaneously. Note also how each explanation model, no matter the underlying predictive model, outperforms the “Random” model.
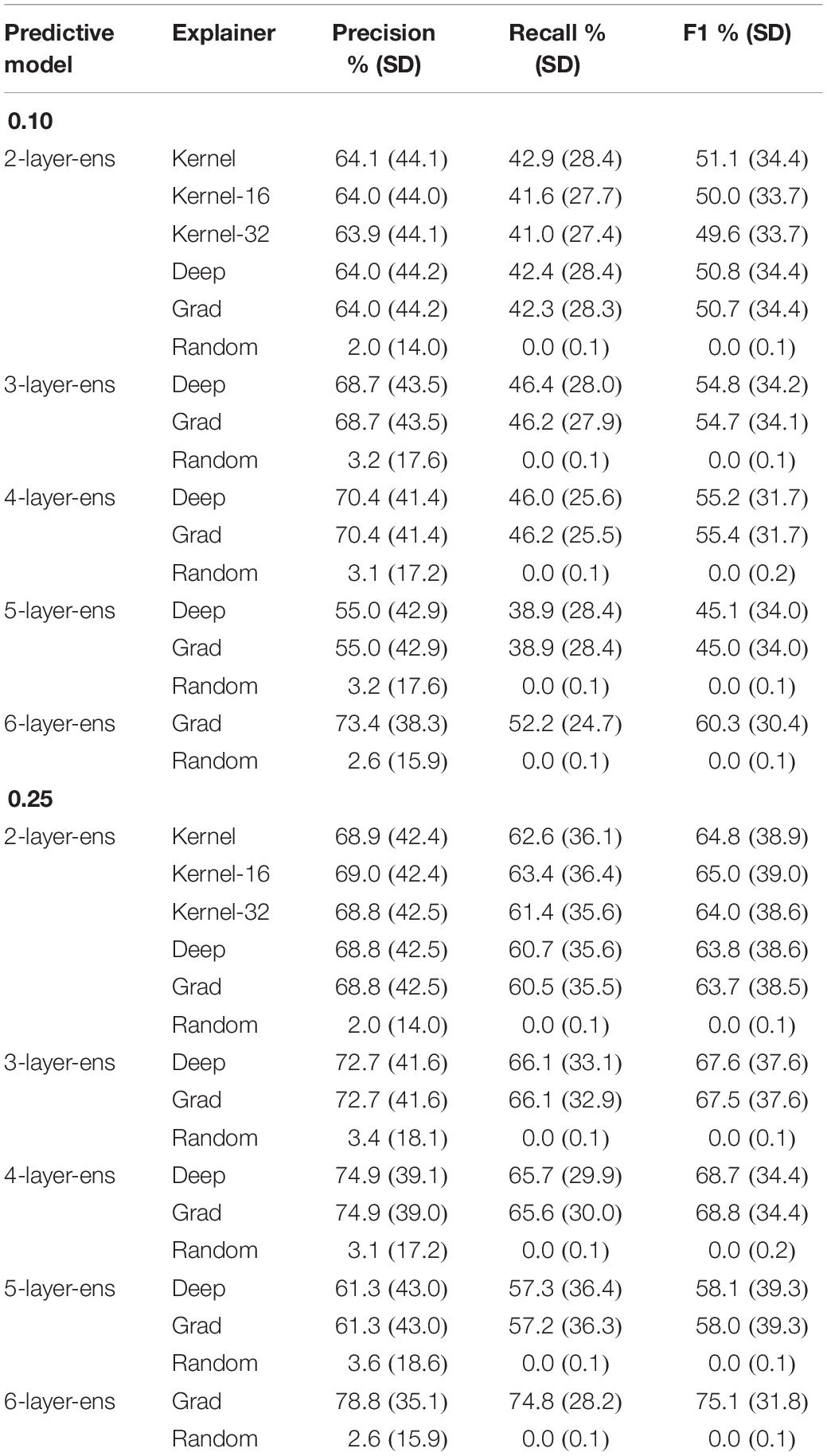
Table 5. Precision, recall, and F1 scores of the various explainers tested per type of predictive model.
The first research question addressed in this subsection asks whether there exists a statistically significant difference between the “Kernel” explainer, which generates 32-feature explanations and is trained on the whole training set, and the “Kernel-32” explainer which also generates 32-feature explanations and is trained on a summary of the training set. To determine this, an independent t-test was conducted using the precision, recall, and F1-score distributions (500 iterations) of both explainers. Table 6 reports the p -values of all the tests and for the 0.10 and 0.25 thresholds. It reveals that there is no statistically significant difference between the two explainers.
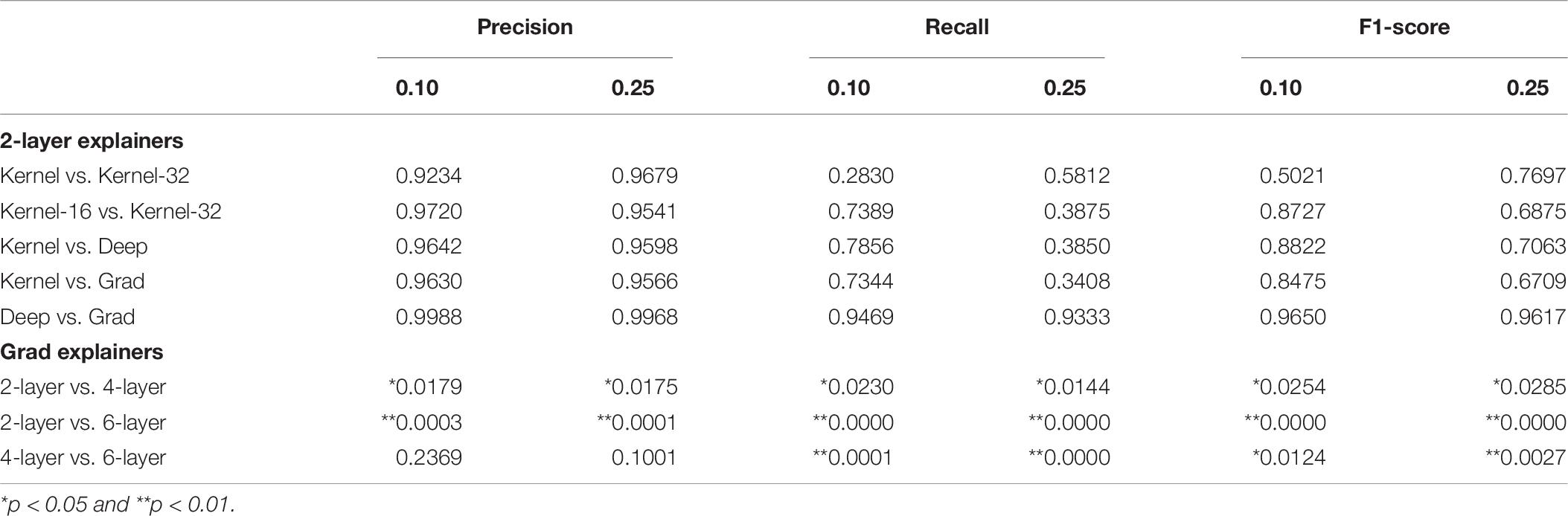
Table 6. p -values of independent t -tests comparing whether there exist statistically significant differences between the mean precisions, recalls, and F1-scores of 2-layer explainers and between those of the 2-layer’s, 4-layer’s, and 6-layer’s Gradient explainers.
The next research question tests whether there exists a difference in the trustworthiness of explainers shaping 16 or 32-feature explanations. Again t-tests were conducted to verify this. Table 6 lists the resulting p -values. Again, there is no statistically significant difference in the average precisions, recalls, and F1-scores of both explainers.
This leads to investigating whether the “Kernel,” “Deep,” and “Grad” explainers are equivalent. Table 6 exhibits the results of the t-tests conducted to verify this and reveals that none of the explainers produce a statistically significantly better performance than the other.
Armed with this evidence, it is now possible to verify whether deeper MLP neural networks produce more trustworthy explanation models. For this purpose, the performance of the “Grad” explainer for each type of predictive model will be compared against each other. The same methodology as previously applied is employed here. Table 6 , again, confirms that the explanation model of the 2-layer predictive model is statistically significantly less trustworthy than the 4-layer’s explanation model; the same can be said of the 4-layer and 6-layer models. The only exception is the difference in average precision between 2-layer and 4-layer models and between 4-layer and 6-layer models; however, there clearly exists a statistically significant difference in terms of precision (and also recall and F1-score) between 2-layer and 6-layer models.
The Best Subset of Essays to Judge AES Relevancy
Table 7 lists the four best essays optimizing feature coverage (93.9%) along with their resolved and predicted scores. Notice how two of the four essays were picked by the adapted SP-LIME algorithm with some strong disagreement between the human and the machine graders, two were picked with short and trivial text, and two were picked exhibiting perfect agreement between the human and machine graders. Interestingly, each pair of longer and shorter essays exposes both strong agreement and strong disagreement between the human and AI agents, offering an opportunity to debug the model and evaluate its ability to detect the presence or absence of more basic (e.g., very small number of words, occurrences of sentence fragments) and more advanced aspects (e.g., cohesion between adjacent sentences, variety of sentence structures) of narrative essay writing and to appropriately reward or penalize them.
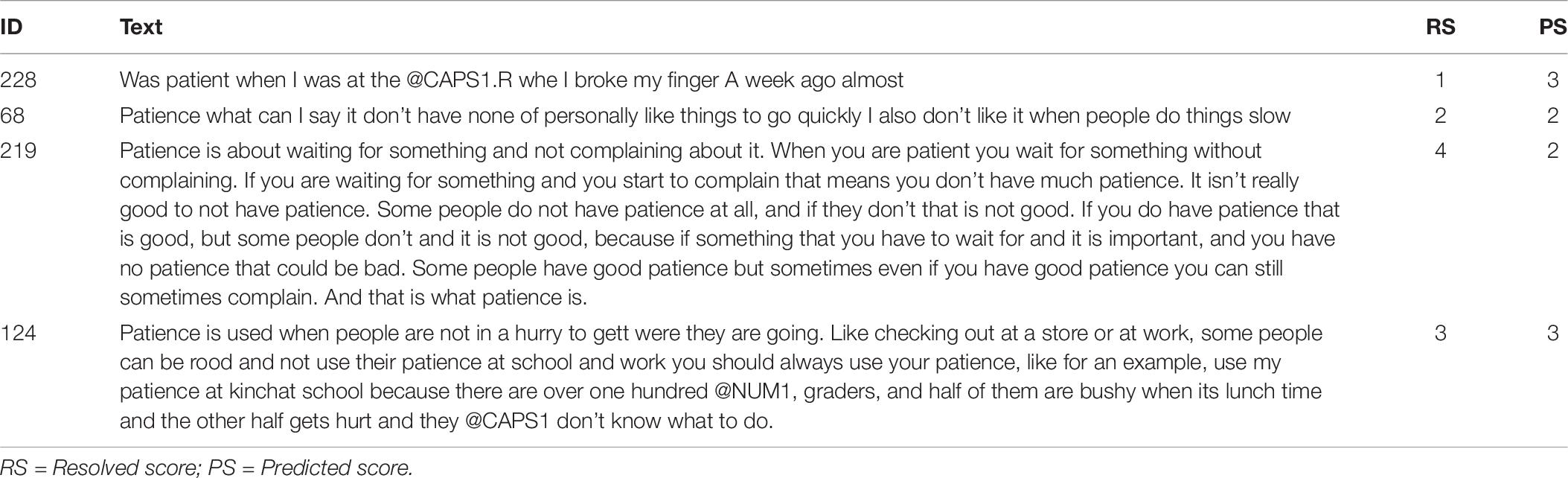
Table 7. Set of best essays to evaluate the correctness of the 6-layer ensemble AES model.
Local Explanation: The Decision Plot
The decision plot lists writing features by order of importance from top to bottom. The line segments display the contribution (SHAP value) of each feature to the predicted rubric score. Note that an actual decision plot consists of all 282 features and that only the top portion of it (20 most important features) can be displayed (see Figure 3 ). A decision plot is read from bottom to top. The line starts at the base value and ends at the predicted rubric score. Given that the “Grad” explainer is the only explainer common to all predictive models, it has been selected to derive all explanations. The decision plots in Figure 3 show the explanations of the four essays in Table 7 ; the dashed line in these plots represents the explanation of the most accurate predictive model, that is the ensemble model with 6 hidden layers which also produced the most trustworthy explanation model. The predicted rubric score of each explanation model is listed in the bottom-right legend. Explanation of the writing features follow in a next subsection.
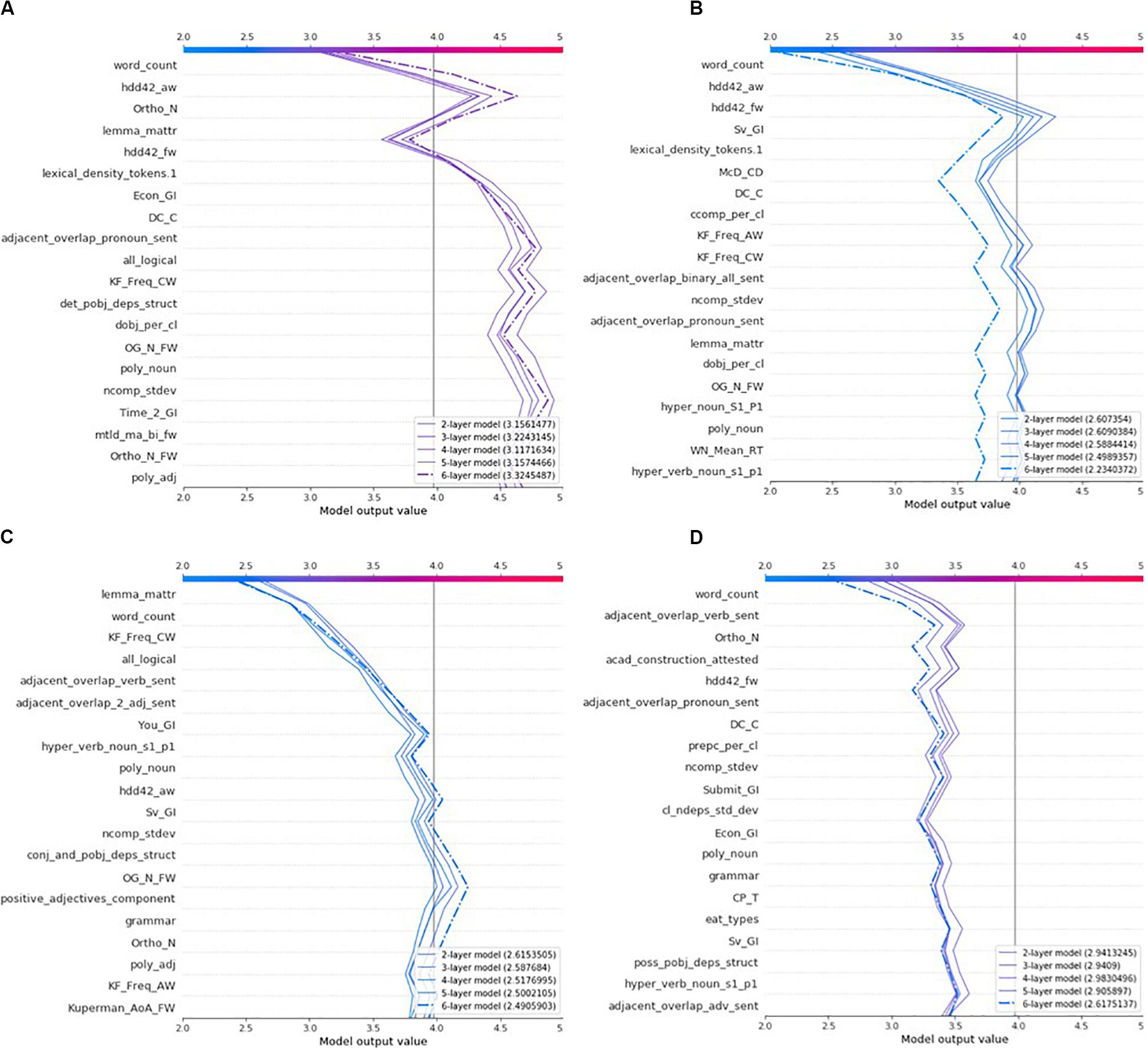
Figure 3. Comparisons of all models’ explanations of the most representative set of four essays: (A) Essay 228, (B) Essay 68, (C) Essay 219, and (D) Essay 124.
Global Explanation: The Summary Plot
It is advantageous to use SHAP to build explanation models because it provides a single framework to discover the writing features that are important to an individual essay (local) or a set of essays (global). While the decision plots list features of local importance, Figure 4 ’s summary plot ranks writing features by order of global importance (from top to bottom). All testing set’s 314 essays are represented as dots in the scatterplot of each writing feature. The position of a dot on the horizontal axis corresponds to the importance (SHAP value) of the writing feature for a specific essay and its color indicates the magnitude of the feature value in relation to the range of all 314 feature values. For example, large or small numbers of words within an essay generally contribute to increase or decrease rubric scores by up to 1.5 and 1.0, respectively. Decision plots can also be used to find the most important features for a small subset of essays; Figure 5 demonstrates the new ordering of writing indices when aggregating the feature contributions (summing the absolute values of SHAP values) of the four essays in Table 7 . Moreover, Figure 5 allows to compare the contributions of a feature to various essays. Note how the orderings in Figures 3 −5 can differ from each other, sharing many features of global importance as well as having their own unique features of local importance.
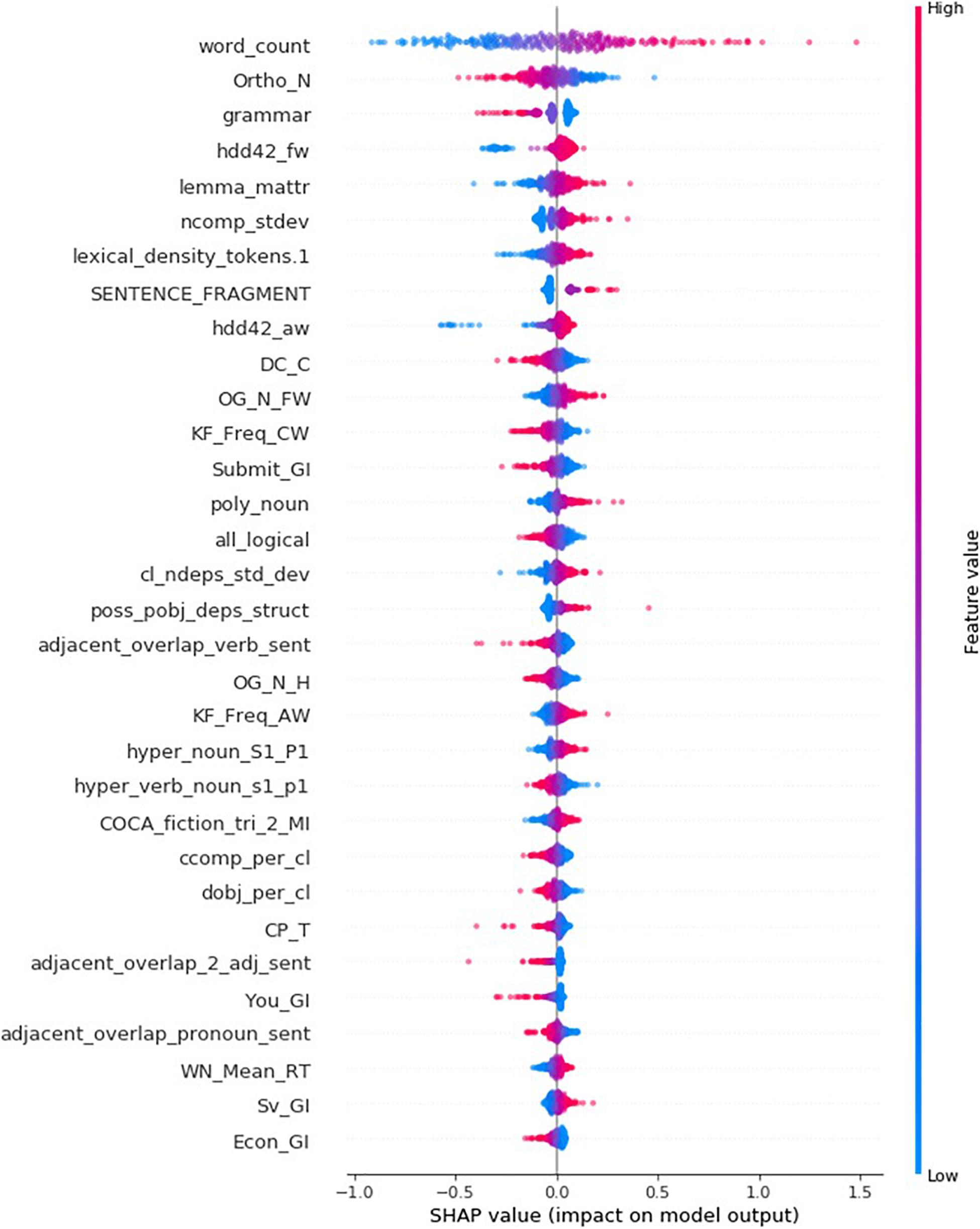
Figure 4. Summary plot listing the 32 most important features globally.

Figure 5. Decision plot delineating the best model’s explanations of Essays 228, 68, 219, and 124 (6-layer ensemble).
Definition of Important Writing Indices
The reader shall understand that it is beyond the scope of this paper to make a thorough description of all writing features. Nevertheless, the summary and decision plots in Figures 4 , 5 allow to identify a subset of features that should be examined in order to validate this study’s predictive model. Supplementary Table 1 combines and describes the 38 features in Figures 4 , 5 .
Dependence Plots
Although the summary plot in Figure 4 is insightful to determine whether small or large feature values are desirable, the dependence plots in Figure 6 prove essential to recommend whether a student should aim at increasing or decreasing the value of a specific writing feature. The dependence plots also reveal whether the student should directly act upon the targeted writing feature or indirectly on other features. The horizontal axis in each of the dependence plots in Figure 6 is the scale of the writing feature and the vertical axis is the scale of the writing feature’s contributions to the predicted rubric scores. Each dot in a dependence plot represents one of the testing set’s 314 essays, that is, the feature value and SHAP value belonging to the essay. The vertical dispersion of the dots on small intervals of the horizontal axis is indicative of interaction with other features ( Molnar, 2020 ). If the vertical dispersion is widespread (e.g., the [50, 100] horizontal-axis interval in the “word_count” dependence plot), then the contribution of the writing feature is most likely at some degree dependent on other writing feature(s).
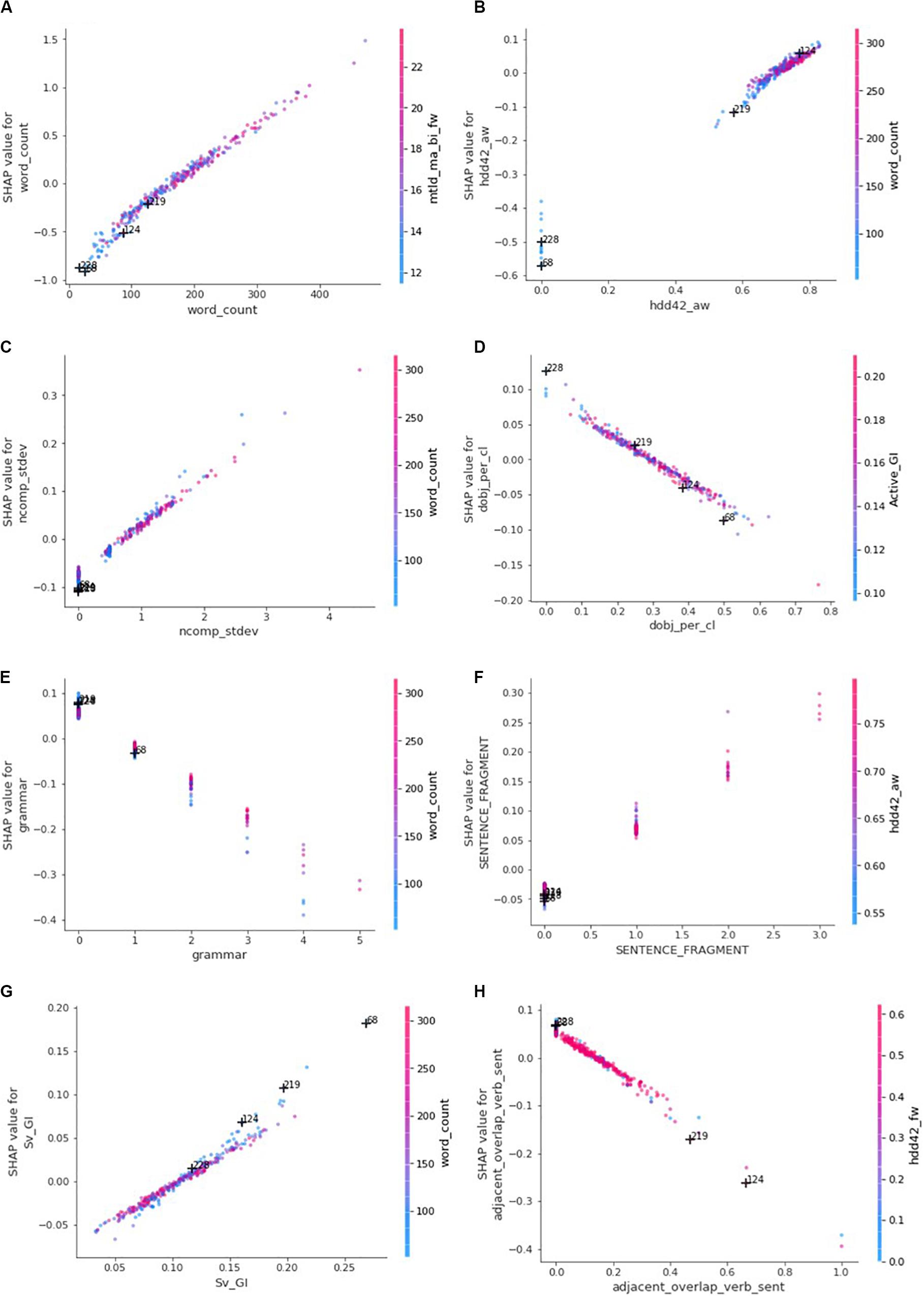
Figure 6. Dependence plots: the horizontal axes represent feature values while vertical axes represent feature contributions (SHAP values). Each dot represents one of the 314 essays of the testing set and is colored according to the value of the feature with which it interacts most strongly. (A) word_count. (B) hdd42_aw. (C) ncomp_stdev. (D) dobj_per_cl. (E) grammar. (F) SENTENCE_FRAGMENT. (G) Sv_GI. (H) adjacent_overlap_verb_sent.
The contributions of this paper can be summarized as follows: (1) it proposes a means (SHAP) to explain individual predictions of AES systems and provides flexible guidelines to build powerful predictive models using more complex algorithms such as ensembles and deep learning neural networks; (2) it applies a methodology to quantitatively assess the trustworthiness of explanation models; (3) it tests whether faster SHAP implementations impact the descriptive accuracy of explanation models, giving insight on the applicability of SHAP in real pedagogical contexts such as AES; (4) it offers a toolkit to debug AES models, highlights linguistic intricacies, and underscores the means to offer formative feedback to novice writers; and more importantly, (5) it empowers learning analytics practitioners to make AI pedagogical agents accountable to the human educator, the ultimate problem holder responsible for the decisions and actions of AI ( Abbass, 2019 ). Basically, learning analytics (which encompasses tools such as AES) is characterized as an ethics-bound, semi-autonomous, and trust-enabled human-AI fusion that recurrently measures and proactively advances knowledge boundaries in human learning.
To exemplify this, imagine an AES system that supports instructors in the detection of plagiarism, gaming behaviors, and the marking of writing activities. As previously mentioned, essays are marked according to a grid of scoring rubrics: ideas, organization, style, and conventions. While an abundance of data (e.g., the 1592 writing metrics) can be collected by the AES tool, these data might still be insufficient to automate the scoring process of certain rubrics (e.g., ideas). Nevertheless, some scoring subtasks such as assessing a student’s vocabulary, sentence fluency, and conventions might still be assigned to AI since the data types available through existing automatic linguistic analysis tools prove sufficient to reliably alleviate the human marker’s workload. Interestingly, learning analytics is key for the accountability of AI agents to the human problem holder. As the volume of writing data (through a large student population, high-frequency capture of learning episodes, and variety of big learning data) accumulate in the system, new AI agents (predictive models) may apply for the job of “automarker.” These AI agents can be quite transparent through XAI ( Arrieta et al., 2020 ) explanation models, and a human instructor may assess the suitability of an agent for the job and hire the candidate agent that comes closest to human performance. Explanations derived from these models could serve as formative feedback to the students.
The AI marker can be assigned to assess the writing activities that are similar to those previously scored by the human marker(s) from whom it learns. Dissimilar and unseen essays can be automatically assigned to the human marker for reliable scoring, and the AI agent can learn from this manual scoring. To ensure accountability, students should be allowed to appeal the AI agent’s marking to the human marker. In addition, the human marker should be empowered to monitor and validate the scoring of select writing rubrics scored by the AI marker. If the human marker does not agree with the machine scores, the writing assignments may be flagged as incorrectly scored and re-assigned to a human marker. These flagged assignments may serve to update predictive models. Moreover, among the essays that are assigned to the machine marker, a small subset can be simultaneously assigned to the human marker for continuous quality control; that is, to continue comparing whether the agreement level between human and machine markers remains within an acceptable threshold. The human marker should be at any time able to “fire” an AI marker or “hire” an AI marker from a pool of potential machine markers.
This notion of a human-AI fusion has been observed in previous AES systems where the human marker’s workload has been found to be significantly alleviated, passing from scoring several hundreds of essays to just a few dozen ( Dronen et al., 2015 ; Hellman et al., 2019 ). As the AES technology matures and as the learning analytics tools continue to penetrate the education market, this alliance of semi-autonomous human and AI agents will lead to better evidence-based/informed pedagogy ( Nelson and Campbell, 2017 ). Such a human-AI alliance can also be guided to autonomously self-regulate its own hypothesis-authoring and data-acquisition processes for purposes of measuring and advancing knowledge boundaries in human learning.
Real-Time Formative Pedagogical Feedback
This paper provides the evidence that deep learning and SHAP can be used not only to score essays automatically but also to offer explanations in real-time. More specifically, the processing time to derive the 314 explanations of the testing set’s essays has been benchmarked for several types of explainers. It was found that the faster DeepSHAP and GradientSHAP implementations, which took only a few seconds of processing, did not produce less accurate explanations than the much slower KernelSHAP. KernelSHAP took approximately 8 h of processing to derive the explanation model of a 2-layer MLP neural network predictive model and 16 h for the 6-layer predictive model.
This finding also holds for various configurations of KernelSHAP, where the number of features (16 vs. 32) shaping the explanation (where all other features are assigned zero contributions) did not produce a statistically significant difference in the reliability of the explanation models. On average, the models had a precision between 63.9 and 64.1% and a recall between 41.0 and 42.9%. This means that after perturbation of the predictive and explanation models, on average 64% of the predictions the explanation model identified as changing were accurate. On the other side, only about 42% of all predictions that changed were detected by the various 2-layer explainers. An explanation was considered as untrustworthy if the sum of its feature contributions, when added to the average prediction (base value), was not within 0.1 from the perturbated prediction. Similarly, the average precision and recall of 2-layer explainers for the 0.25-threshold were about 69% and 62%, respectively.
Impact of Deep Learning on Descriptive Accuracy of Explanations
By analyzing the performance of the various predictive models in Table 4 , no clear conclusion can be reached as to which model should be deemed as the most desirable. Despite the fact that the 6-layer models slightly outperform the other models in terms of accuracy (percentage of exact matches between the resolved [human] and predicted [machine] scores), they are not the best when it comes to the percentages of adjacent (within 1 and 2) matches. Nevertheless, if the selection of the “best” model is based on the quadratic weighted kappas, the decision remains a nebulous one to make. Moreover, ensuring that machine learning actually learned something meaningful remains paramount, especially in contexts where the performance of a majority classifier is close to the human and machine performance. For example, a majority classifier model would get 46.3% of predictions accurate ( Table 4 ), while trained predictive models at best produce accurate predictions between 51.9 and 55.1%.
Since the interpretability of a machine learning model should be prioritized over accuracy ( Ribeiro et al., 2016 ; Murdoch et al., 2019 ) for questions of transparency and trust, this paper investigated whether the impact of the depth of a MLP neural network might be more visible when assessing its interpretability, that is, the trustworthiness of its corresponding SHAP explanation model. The data in Tables 1 , 5 , 6 effectively support the hypothesis that as the depth of the neural network increases, the precision and recall of the corresponding explanation model improve. Besides, this observation is particularly interesting because the 4-layer (Grad) explainer, which has hardly more parameters than the 2-layer model, is also more accurate than the 2-layer model, suggesting that the 6-layer explainer is most likely superior to other explainers not only because of its greater number of parameters, but also because of its number of hidden layers. By increasing the number of hidden layers, it can be seen that the precision and recall of an explanation model can pass on average from approximately 64 to 73% and from 42 to 52%, respectively, for the 0.10-threshold; and for the 0.25-threshold, from 69 to 79% and from 62 to 75%, respectively.
These results imply that the descriptive accuracy of an explanation model is an evidence of effective machine learning, which may exceed the level of agreement between the human and machine graders. Moreover, given that the superiority of a trained predictive model over a majority classifier is not always obvious, the consistency of its associated explanation model demonstrates this better. Note that theoretically the SHAP explanation model of the majority classifier should assign a zero contribution to each writing feature since the average prediction of such a model is actually the most frequent rubric score given by the human raters; hence, the base value is the explanation.
An interesting fact emerges from Figure 3 , that is, all explainers (2-layer to 6-layer) are more or less similar. It appears that they do not contradict each other. More specifically, they all agree on the direction of the contributions of the most important features. In other words, they unanimously determine that a feature should increase or decrease the predicted score. However, they differ from each other on the magnitude of the feature contributions.
To conclude, this study highlights the need to train predictive models that consider the descriptive accuracy of explanations. The idea is that explanation models consider predictions to derive explanations; explanations should be considered when training predictive models. This would not only help train interpretable models the very first time but also potentially break the status quo that may exist among similar explainers to possibly produce more powerful models. In addition, this research calls for a mechanism (e.g., causal diagrams) to allow teachers to guide the training process of predictive models. Put another way, as LA practitioners debug predictive models, their insights should be encoded in a language that will be understood by the machine and that will guide the training process to avoid learning the same errors and to accelerate the training time.
Accountable AES
Now that the superiority of the 6-layer predictive and explanation models has been demonstrated, some aspects of the relevancy of explanations should be examined more deeply, knowing that having an explanation model consistent with its underlying predictive model does not guarantee relevant explanations. Table 7 discloses the set of four essays that optimize the coverage of most globally important features to evaluate the correctness of the best AES model. It is quite intriguing to note that two of the four essays are among the 16 essays that have a major disagreement (off by 2) between the resolved and predicted rubric scores (1 vs. 3 and 4 vs. 2). The AES tool clearly overrated Essay 228, while it underrated Essay 219. Naturally, these two essays offer an opportunity to understand what is wrong with the model and ultimately debug the model to improve its accuracy and interpretability.
In particular, Essay 228 raises suspicion on the positive contributions of features such as “Ortho_N,” “lemma_mattr,” “all_logical,” “det_pobj_deps_struct,” and “dobj_per_cl.” Moreover, notice how the remaining 262 less important features (not visible in the decision plot in Figure 5 ) have already inflated the rubric score beyond the base value, more than any other essay. Given the very short length and very low quality of the essay, whose meaning is seriously undermined by spelling and grammatical errors, it is of utmost importance to verify how some of these features are computed. For example, is the average number of orthographic neighbors (Ortho_N) per token computed for unmeaningful tokens such as “R” and “whe”? Similarly, are these tokens considered as types in the type-token ratio over lemmas (lemma_mattr)? Given the absence of a meaningful grammatical structure conveying a complete idea through well-articulated words, it becomes obvious that the quality of NLP (natural language processing) parsing may become a source of (measurement) bias impacting both the way some writing features are computed and the predicted rubric score. To remedy this, two solutions are proposed: (1) enhancing the dataset with the part-of-speech sequence or the structure of dependency relationships along with associated confidence levels, or (2) augmenting the essay dataset with essays enclosing various types of non-sensical content to improve the learning of these feature contributions.
Note that all four essays have a text length smaller than the average: 171 words. Notice also how the “hdd42_aw” and “hdd42_fw” play a significant role to decrease the predicted score of Essays 228 and 68. The reader should note that these metrics require a minimum of 42 tokens in order to compute a non-zero D index, a measure of lexical diversity as explained in Supplementary Table 1 . Figure 6B also shows how zero “hdd42_aw” values are heavily penalized. This is extra evidence that supports the strong role that the number of words plays in determining these rubric scores, especially for very short essays where it is one of the few observations that can be reliably recorded.
Two other issues with the best trained AES model were identified. First, in the eyes of the model, the lowest the average number of direct objects per clause (dobj_per_cl), as seen in Figure 6D , the best it is. This appears to contradict one of the requirements of the “Style” rubric, which looks for a variety of sentence structures. Remember that direct objects imply the presence of transitive verbs (action verbs) and that the balanced usage of linking verbs and action verbs as well as of transitive and intransitive verbs is key to meet the requirement of variety of sentence structures. Moreover, note that the writing feature is about counting the number of direct objects per clause, not by sentence. Only one direct object is therefore possible per clause. On the other side, a sentence may contain several clauses, which determines if the sentence is a simple, compound, or a complex sentence. This also means that a sentence may have multiple direct objects and that a high ratio of direct objects per clause is indicative of sentence complexity. Too much complexity is also undesirable. Hence, it is fair to conclude that the higher range of feature values has reasonable feature contributions (SHAP values), while the lower range does not capture well the requirements of the rubric. The dependence plot should rather display a positive peak somewhere in the middle. Notice how the poor quality of Essay 228’s single sentence prevented the proper detection of the single direct object, “broke my finger,” and the so-called absence of direct objects was one of the reasons to wrongfully improve the predicted rubric score.
The model’s second issue discussed here is the presence of sentence fragments, a type of grammatical errors. Essentially, a sentence fragment is a clause that misses one of three critical components: a subject, a verb, or a complete idea. Figure 6E shows the contribution model of grammatical errors, all types combined, while Figure 6F shows specifically the contribution model of sentence fragments. It is interesting to see how SHAP further penalizes larger numbers of grammatical errors and that it takes into account the length of the essay (red dots represent essays with larger numbers of words; blue dots represent essays with smaller numbers of words). For example, except for essays with no identified grammatical errors, longer essays are less penalized than shorter ones. This is particularly obvious when there are 2−4 grammatical errors. The model increases the predicted rubric score only when there is no grammatical error. Moreover, the model tolerates longer essays with only one grammatical error, which sounds quite reasonable. On the other side, the model finds desirable high numbers of sentence fragments, a non-trivial type of grammatical errors. Even worse, the model decreases the rubric score of essays having no sentence fragment. Although grammatical issues are beyond the scope of the “Style” rubric, the model has probably included these features because of their impact on the quality of assessment of vocabulary usage and sentence fluency. The reader should observe how the very poor quality of an essay can even prevent the detection of such fundamental grammatical errors such as in the case of Essay 228, where the AES tool did not find any grammatical error or sentence fragment. Therefore, there should be a way for AES systems to detect a minimum level of text quality before attempting to score an essay. Note that the objective of this section was not to undertake thorough debugging of the model, but rather to underscore the effectiveness of SHAP in doing so.
Formative Feedback
Once an AES model is considered reasonably valid, SHAP can be a suitable formalism to empower the machine to provide formative feedback. For instance, the explanation of Essay 124, which has been assigned a rubric score of 3 by both human and machine markers, indicates that the top two factors contributing to decreasing the predicted rubric score are: (1) the essay length being smaller than average, and (2) the average number of verb lemma types occurring at least once in the next sentence (adjacent_overlap_verb_sent). Figures 6A,H give the overall picture in which the realism of the contributions of these two features can be analyzed. More specifically, Essay 124 is one of very few essays ( Figure 6H ) that makes redundant usage of the same verbs across adjacent sentences. Moreover, the essay displays poor sentence fluency where everything is only expressed in two sentences. To understand more accurately the impact of “adjacent_overlap_verb_sent” on the prediction, a few spelling errors have been corrected and the text has been divided in four sentences instead of two. Revision 1 in Table 8 exhibits the corrections made to the original essay. The decision plot’s dashed line in Figure 3D represents the original explanation of Essay 124, while Figure 7A demonstrates the new explanation of the revised essay. It can be seen that the “adjacent_overlap_verb_sent” feature is still the second most important feature in the new explanation of Essay 124, with a feature value of 0.429, still considered as very poor according to the dependence plot in Figure 6H .

Table 8. Revisions of Essay 124: improvement of sentence splitting, correction of some spelling errors, and elimination of redundant usage of same verbs (bold for emphasis in Essay 124’s original version; corrections in bold for Revisions 1 and 2).
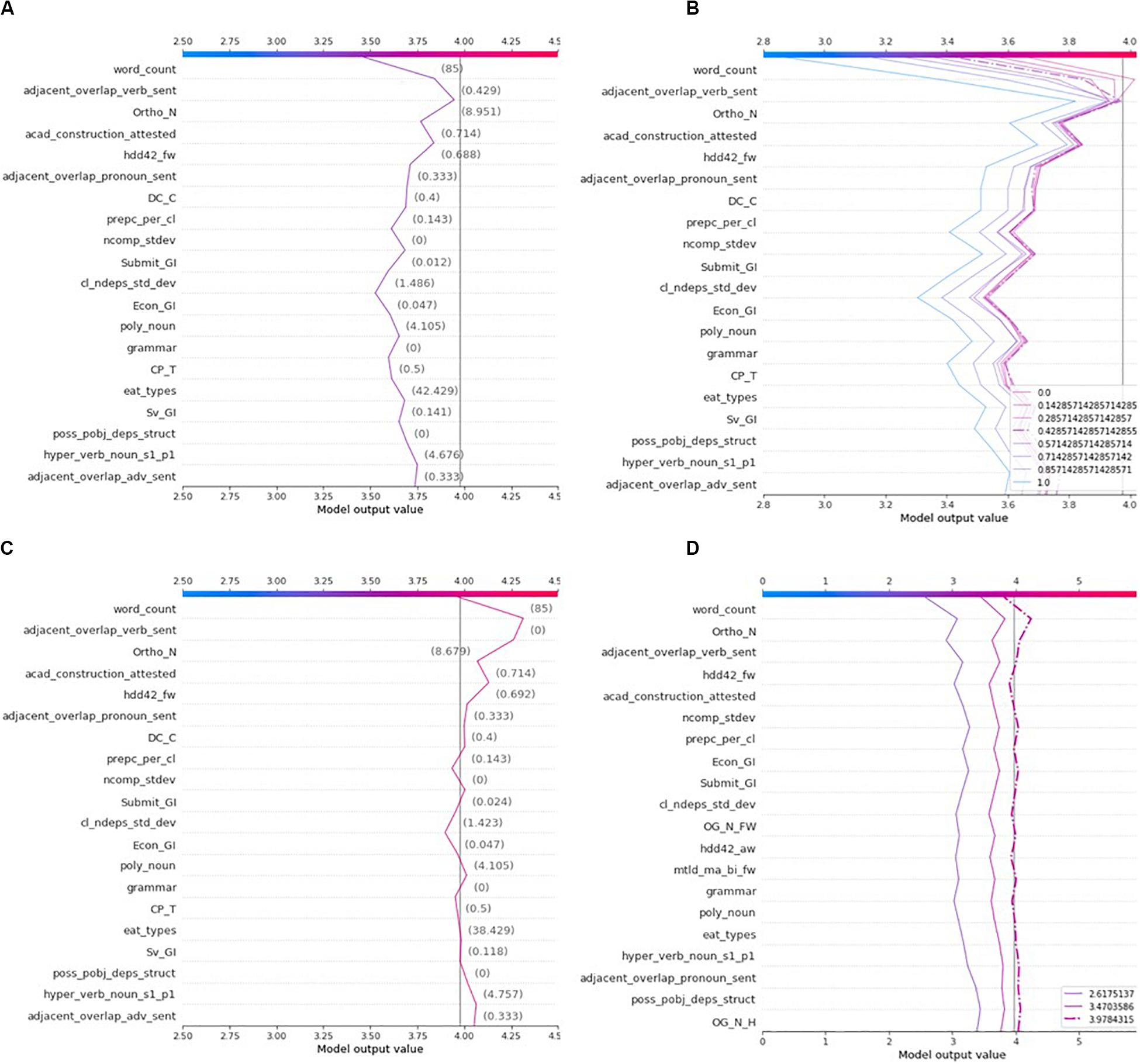
Figure 7. Explanations of the various versions of Essay 124 and evaluation of feature effect for a range of feature values. (A) Explanation of Essay 124’s first revision. (B) Forecasting the effect of changing the ‘adjacent_overlap_verb_sent’ feature on the rubric score. (C) Explanation of Essay 124’s second revision. (D) Comparison of the explanations of all Essay 124’s versions.
To show how SHAP could be leveraged to offer remedial formative feedback, the revised version of Essay 124 will be explained again for eight different values of “adjacent_overlap_verb_sent” (0, 0.143, 0.286, 0.429, 0.571, 0.714, 0.857, 1.0), while keeping the values of all other features constant. The set of these eight essays are explained by a newly trained SHAP explainer (Gradient), producing new SHAP values for each feature and each “revised” essay. Notice how the new model, called the feedback model, allows to foresee by how much a novice writer can hope to improve his/her score according to the “Style” rubric. If the student employs different verbs at every sentence, the feedback model estimates that the rubric score could be improved from 3.47 up to 3.65 ( Figure 7B ). Notice that the dashed line represents Revision 1, while other lines simulate one of the seven other altered essays. Moreover, it is important to note how changing the value of a single feature may influence the contributions that other features may have on the predicted score. Again, all explanations look similar in terms of direction, but certain features differ in terms of the magnitude of their contributions. However, the reader should observe how the targeted feature varies not only in terms of magnitude, but also of direction, allowing the student to ponder the relevancy of executing the recommended writing strategy.
Thus, upon receiving this feedback, assume that a student sets the goal to improve the effectiveness of his/her verb choice by eliminating any redundant verb, producing Revision 2 in Table 8 . The student submits his essay again to the AES system, which finally gives a new rubric score of 3.98, a significant improvement from the previous 3.47, allowing the student to get a 4 instead of a 3. Figure 7C exhibits the decision plot of Revision 2. To better observe how the various revisions of the student’s essay changed over time, their respective explanations have been plotted in the same decision plot ( Figure 7D ). Notice this time that the ordering of the features has changed to list the features of common importance to all of the essay’s versions. The feature ordering in Figures 7A−C complies with the same ordering as in Figure 3D , the decision plot of the original essay. These figures underscore the importance of tracking the interaction between the various features so that the model understands well the impact that changing one feature has on the others. TreeSHAP, an implementation for tree-based models, offers this capability and its potential on improving the quality of feedback provided to novice writers will be tested in a future version of this AES system.
This paper serves as a proof of concept of the applicability of XAI techniques in automated essay scoring, providing learning analytics practitioners and educators with a methodology on how to “hire” AI markers and make them accountable to their human counterparts. In addition to debug predictive models, SHAP explanation models can serve as some formalism of a broader learning analytics platform, where aspects of prescriptive analytics (provision of remedial formative feedback) can be added on top of the more pervasive predictive analytics.
However, the main weakness of the approach put forward in this paper consists in omitting many types of spatio-temporal data. In other words, it ignores precious information inherent to the writing process, which may prove essential to guess the intent of the student, especially in contexts of poor sentence structures and high grammatical inaccuracy. Hence, this paper calls for adapting current NLP technologies to educational purposes, where the quality of writing may be suboptimal, which is contrary to many utopian scenarios where NLP is used for content analysis, opinion mining, topic modeling, or fact extraction trained on corpora of high-quality texts. By capturing the writing process preceding a submission of an essay to an AES tool, other kinds of explanation models can also be trained to offer feedback not only from a linguistic perspective but also from a behavioral one (e.g., composing vs. revising); that is, the AES system could inform novice writers about suboptimal and optimal writing strategies (e.g., planning a revision phase after bursts of writing).
In addition, associating sections of text with suboptimal writing features, those whose contributions lower the predicted score, would be much more informative. This spatial information would not only allow to point out what is wrong and but also where it is wrong, answering more efficiently the question why an essay is wrong. This problem could be simply approached through a multiple-inputs and mixed-data feature-based (MLP) neural network architecture fed by both linguistic indices and textual data ( n -grams), where the SHAP explanation model would assign feature contributions to both types of features and any potential interaction between them. A more complex approach could address the problem through special types of recurrent neural networks such as Ordered-Neurons LSTMs (long short-term memory), which are well adapted to the parsing of natural language, and where the natural sequence of text is not only captured but also its hierarchy of constituents ( Shen et al., 2018 ). After all, this paper highlights the fact that the potential of deep learning can reach beyond the training of powerful predictive models and be better visible in the higher trustworthiness of explanation models. This paper also calls for optimizing the training of predictive models by considering the descriptive accuracy of explanations and the human expert’s qualitative knowledge (e.g., indicating the direction of feature contributions) during the training process.
Data Availability Statement
The datasets and code of this study can be found in these Open Science Framework’s online repositories: https://osf.io/fxvru/ .
Author Contributions
VK architected the concept of an ethics-bound, semi-autonomous, and trust-enabled human-AI fusion that measures and advances knowledge boundaries in human learning, which essentially defines the key traits of learning analytics. DB was responsible for its implementation in the area of explainable automated essay scoring and for the training and validation of the predictive and explanation models. Together they offer an XAI-based proof of concept of a prescriptive model that can offer real-time formative remedial feedback to novice writers. Both authors contributed to the article and approved its publication.
Research reported in this article was supported by the Academic Research Fund (ARF) publication grant of Athabasca University under award number (24087).
Conflict of Interest
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Supplementary Material
The Supplementary Material for this article can be found online at: https://www.frontiersin.org/articles/10.3389/feduc.2020.572367/full#supplementary-material
- ^ https://www.kaggle.com/c/asap-aes
- ^ https://www.linguisticanalysistools.org/
Abbass, H. A. (2019). Social integration of artificial intelligence: functions, automation allocation logic and human-autonomy trust. Cogn. Comput. 11, 159–171. doi: 10.1007/s12559-018-9619-0
CrossRef Full Text | Google Scholar
Adadi, A., and Berrada, M. (2018). Peeking inside the black-box: a survey on explainable artificial intelligence (XAI). IEEE Access 6, 52138–52160. doi: 10.1109/ACCESS.2018.2870052
Amorim, E., Cançado, M., and Veloso, A. (2018). “Automated essay scoring in the presence of biased ratings,” in Proceedings of the 2018 Conference of the North American Chapter of the Association for Computational Linguistics: Human Language Technologies , New Orleans, LA, 229–237.
Google Scholar
Arrieta, A. B., Díaz-Rodríguez, N., Ser, J., Del Bennetot, A., Tabik, S., Barbado, A., et al. (2020). Explainable Artificial Intelligence (XAI): concepts, taxonomies, opportunities and challenges toward responsible AI. Inform. Fusion 58, 82–115. doi: 10.1016/j.inffus.2019.12.012
Balota, D. A., Yap, M. J., Hutchison, K. A., Cortese, M. J., Kessler, B., Loftis, B., et al. (2007). The English lexicon project. Behav. Res. Methods 39, 445–459. doi: 10.3758/BF03193014
PubMed Abstract | CrossRef Full Text | Google Scholar
Boulanger, D., and Kumar, V. (2018). “Deep learning in automated essay scoring,” in Proceedings of the International Conference of Intelligent Tutoring Systems , eds R. Nkambou, R. Azevedo, and J. Vassileva (Cham: Springer International Publishing), 294–299. doi: 10.1007/978-3-319-91464-0_30
Boulanger, D., and Kumar, V. (2019). “Shedding light on the automated essay scoring process,” in Proceedings of the International Conference on Educational Data Mining , 512–515.
Boulanger, D., and Kumar, V. (2020). “SHAPed automated essay scoring: explaining writing features’ contributions to English writing organization,” in Intelligent Tutoring Systems , eds V. Kumar and C. Troussas (Cham: Springer International Publishing), 68–78. doi: 10.1007/978-3-030-49663-0_10
Chen, H., Lundberg, S., and Lee, S.-I. (2019). Explaining models by propagating Shapley values of local components. arXiv [Preprint]. Available online at: https://arxiv.org/abs/1911.11888 (accessed September 22, 2020).
Crossley, S. A., Bradfield, F., and Bustamante, A. (2019). Using human judgments to examine the validity of automated grammar, syntax, and mechanical errors in writing. J. Writ. Res. 11, 251–270. doi: 10.17239/jowr-2019.11.02.01
Crossley, S. A., Kyle, K., and McNamara, D. S. (2016). The tool for the automatic analysis of text cohesion (TAACO): automatic assessment of local, global, and text cohesion. Behav. Res. Methods 48, 1227–1237. doi: 10.3758/s13428-015-0651-7
Crossley, S. A., Kyle, K., and McNamara, D. S. (2017). Sentiment analysis and social cognition engine (SEANCE): an automatic tool for sentiment, social cognition, and social-order analysis. Behav. Res. Methods 49, 803–821. doi: 10.3758/s13428-016-0743-z
Dronen, N., Foltz, P. W., and Habermehl, K. (2015). “Effective sampling for large-scale automated writing evaluation systems,” in Proceedings of the Second (2015) ACM Conference on Learning @ Scale , 3–10.
Goldin, I., Narciss, S., Foltz, P., and Bauer, M. (2017). New directions in formative feedback in interactive learning environments. Int. J. Artif. Intellig. Educ. 27, 385–392. doi: 10.1007/s40593-016-0135-7
Hao, Q., and Tsikerdekis, M. (2019). “How automated feedback is delivered matters: formative feedback and knowledge transfer,” in Proceedings of the 2019 IEEE Frontiers in Education Conference (FIE) , Covington, KY, 1–6.
Hellman, S., Rosenstein, M., Gorman, A., Murray, W., Becker, L., Baikadi, A., et al. (2019). “Scaling up writing in the curriculum: batch mode active learning for automated essay scoring,” in Proceedings of the Sixth (2019) ACM Conference on Learning @ Scale , (New York, NY: Association for Computing Machinery).
Hussein, M. A., Hassan, H., and Nassef, M. (2019). Automated language essay scoring systems: a literature review. PeerJ Comput. Sci. 5:e208. doi: 10.7717/peerj-cs.208
Kumar, V., and Boulanger, D. (2020). Automated essay scoring and the deep learning black box: how are rubric scores determined? Int. J. Artif. Intellig. Educ. doi: 10.1007/s40593-020-00211-5
Kumar, V., Fraser, S. N., and Boulanger, D. (2017). Discovering the predictive power of five baseline writing competences. J. Writ. Anal. 1, 176–226.
Kyle, K. (2016). Measuring Syntactic Development In L2 Writing: Fine Grained Indices Of Syntactic Complexity And Usage-Based Indices Of Syntactic Sophistication. Dissertation, Georgia State University, Atlanta, GA.
Kyle, K., Crossley, S., and Berger, C. (2018). The tool for the automatic analysis of lexical sophistication (TAALES): version 2.0. Behav. Res. Methods 50, 1030–1046. doi: 10.3758/s13428-017-0924-4
Lundberg, S. M., Erion, G. G., and Lee, S.-I. (2018). Consistent individualized feature attribution for tree ensembles. arXiv [Preprint]. Available online at: https://arxiv.org/abs/1802.03888 (accessed September 22, 2020).
Lundberg, S. M., and Lee, S.-I. (2017). “A unified approach to interpreting model predictions,” in Advances in Neural Information Processing Systems , eds I. Guyon, U. V. Luxburg, S. Bengio, H. Wallach, R. Fergus, S. Vishwanathan, et al. (Red Hook, NY: Curran Associates, Inc), 4765–4774.
Madnani, N., and Cahill, A. (2018). “Automated scoring: beyond natural language processing,” in Proceedings of the 27th International Conference on Computational Linguistics , (Santa Fe: Association for Computational Linguistics), 1099–1109.
Madnani, N., Loukina, A., von Davier, A., Burstein, J., and Cahill, A. (2017). “Building better open-source tools to support fairness in automated scoring,” in Proceedings of the First (ACL) Workshop on Ethics in Natural Language Processing , (Valencia: Association for Computational Linguistics), 41–52.
McCarthy, P. M., and Jarvis, S. (2010). MTLD, vocd-D, and HD-D: a validation study of sophisticated approaches to lexical diversity assessment. Behav. Res. Methods 42, 381–392. doi: 10.3758/brm.42.2.381
Mizumoto, T., Ouchi, H., Isobe, Y., Reisert, P., Nagata, R., Sekine, S., et al. (2019). “Analytic score prediction and justification identification in automated short answer scoring,” in Proceedings of the Fourteenth Workshop on Innovative Use of NLP for Building Educational Applications , Florence, 316–325.
Molnar, C. (2020). Interpretable Machine Learning . Abu Dhabi: Lulu
Murdoch, W. J., Singh, C., Kumbier, K., Abbasi-Asl, R., and Yu, B. (2019). Definitions, methods, and applications in interpretable machine learning. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U.S.A. 116, 22071–22080. doi: 10.1073/pnas.1900654116
Nelson, J., and Campbell, C. (2017). Evidence-informed practice in education: meanings and applications. Educ. Res. 59, 127–135. doi: 10.1080/00131881.2017.1314115
Rahimi, Z., Litman, D., Correnti, R., Wang, E., and Matsumura, L. C. (2017). Assessing students’ use of evidence and organization in response-to-text writing: using natural language processing for rubric-based automated scoring. Int. J. Artif. Intellig. Educ. 27, 694–728. doi: 10.1007/s40593-017-0143-2
Reinertsen, N. (2018). Why can’t it mark this one? A qualitative analysis of student writing rejected by an automated essay scoring system. English Austral. 53:52.
Ribeiro, M. T., Singh, S., and Guestrin, C. (2016). “Why should i trust you?”: explaining the predictions of any classifier. CoRR, abs/1602.0. arXiv [Preprint]. Available online at: http://arxiv.org/abs/1602.04938 (accessed September 22, 2020).
Rupp, A. A. (2018). Designing, evaluating, and deploying automated scoring systems with validity in mind: methodological design decisions. Appl. Meas. Educ. 31, 191–214. doi: 10.1080/08957347.2018.1464448
Rupp, A. A., Casabianca, J. M., Krüger, M., Keller, S., and Köller, O. (2019). Automated essay scoring at scale: a case study in Switzerland and Germany. ETS Res. Rep. Ser. 2019, 1–23. doi: 10.1002/ets2.12249
Shen, Y., Tan, S., Sordoni, A., and Courville, A. C. (2018). Ordered Neurons: Integrating Tree Structures into Recurrent Neural Networks. CoRR, abs/1810.0. arXiv [Preprint]. Available online at: http://arxiv.org/abs/1810.09536 (accessed September 22, 2020).
Shermis, M. D. (2014). State-of-the-art automated essay scoring: competition, results, and future directions from a United States demonstration. Assess. Writ. 20, 53–76. doi: 10.1016/j.asw.2013.04.001
Taghipour, K. (2017). Robust Trait-Specific Essay Scoring using Neural Networks and Density Estimators. Dissertation, National University of Singapore, Singapore.
West-Smith, P., Butler, S., and Mayfield, E. (2018). “Trustworthy automated essay scoring without explicit construct validity,” in Proceedings of the 2018 AAAI Spring Symposium Series , (New York, NY: ACM).
Woods, B., Adamson, D., Miel, S., and Mayfield, E. (2017). “Formative essay feedback using predictive scoring models,” in Proceedings of the 23rd ACM SIGKDD International Conference on Knowledge Discovery and Data Mining , (New York, NY: ACM), 2071–2080.
Keywords : explainable artificial intelligence, SHAP, automated essay scoring, deep learning, trust, learning analytics, feedback, rubric
Citation: Kumar V and Boulanger D (2020) Explainable Automated Essay Scoring: Deep Learning Really Has Pedagogical Value. Front. Educ. 5:572367. doi: 10.3389/feduc.2020.572367
Received: 14 June 2020; Accepted: 09 September 2020; Published: 06 October 2020.
Reviewed by:
Copyright © 2020 Kumar and Boulanger. This is an open-access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License (CC BY) . The use, distribution or reproduction in other forums is permitted, provided the original author(s) and the copyright owner(s) are credited and that the original publication in this journal is cited, in accordance with accepted academic practice. No use, distribution or reproduction is permitted which does not comply with these terms.
*Correspondence: David Boulanger, [email protected]
This article is part of the Research Topic
Learning Analytics for Supporting Individualization: Data-informed Adaptation of Learning
e-rater ® Scoring Engine
Evaluates students’ writing proficiency with automatic scoring and feedback
Selection an option below to learn more.
How the e-rater engine uses AI technology
ETS is a global leader in educational assessment, measurement and learning science. Our AI technology, such as the e-rater ® scoring engine, informs decisions and creates opportunities for learners around the world.
The e-rater engine automatically:
- assess and nurtures key writing skills
- scores essays and provides feedback on writing using a model built on the theory of writing to assess both analytical and independent writing skills
About the e-rater Engine
This ETS capability identifies features related to writing proficiency.
How It Works
See how the e-rater engine provides scoring and writing feedback.
Custom Applications
Use standard prompts or develop your own custom model with ETS’s expertise.
Use in Criterion ® Service
Learn how the e-rater engine is used in the Criterion ® Service.
FEATURED RESEARCH
E-rater as a Quality Control on Human Scores
See All Research (PDF)

Ready to begin? Contact us to learn how the e-rater service can enhance your existing program.

- Skip to Main Content.
- Skip to Main Navigation.
- Skip to Main Footer.

Dr. Vincent Ng Develops AI Essay Grading Program

For professors struggling to cope with stacks of papers to grade, new software — developed by a UT Dallas researcher and powered by artificial intelligence — may offer a long-term solution.
Dr. Vincent Ng , a computer science professor who works with UT Dallas Human Language Technology Research Institute , is developing an automated grading system for longform essays. Ng said the goal of the technology is to remove the need for human graders altogether.
“Essay grading is one of the very important applications of natural language processing,” Ng said. “For one, it has a lot of commercial value. Grading essays requires an enormous amount of human labor, and these are hours that can be spent elsewhere in the classroom.”
The software, he said, will read blocks of text and parse certain pieces of information. The parsing occurs on multiple levels. Lower levels might deal with spelling and grammar. Higher levels would evaluate coherence and overall organization, and even higher, the overall persuasiveness of an essay.
The Human Language Technology Research Institute consists of eight separate laboratories, each headed by a faculty member. The labs focus on different aspects of natural speech, including essay grading.
Luba Ketsler, a UT Dallas economics professor, has a total of 449 students in her classes, in addition to a handful of research students. She said in her field it can be difficult to assess knowledge using only scantrons.
“I do have tests that are multiple choice, because I do have to control my workload somehow,” Ketsler said. “But I also want them to get some detail, some data.”
For Ketsler, that means written quizzes, regular writing assignments and three major research papers, each with a minimum of seven pages.
“That adds up quickly,” she said.
Ketsler, who has been at UT Dallas for 11 years, said she’s witnessed a lot of growth, changing the way she has to approach teaching, including reducing the number of written assignments as her class sizes grew.
“The bigger the class size, the more disparity you’re going to see between each student’s knowledge,” she said.
Ketsler said more diverse classrooms can make for interesting discussions but creates a demand for grading that takes each student’s background into account. The objectivity of grading software powered by artificial intelligence is a big draw for Ketsler, who said she doesn’t like to rely on teaching assistants to grade everything.
“I don’t let the TAs grade the research papers. I let them do a lot of the technical work, like inputting grades and marking quizzes, because I want to stay consistent with the actual grading,” she said. “Everyone grades a little subjectively.”
Biology junior Sania Zeito, who recently transferred to UT Dallas, said she felt there was a lack of objectivity when it came to grading standards at her previous university in Dubai.
“I sometimes felt like there was injustice, like maybe the grade depended on the mood of the grader,” Zeito said. “A robot would put a standard on the grading system.”
Artificial intelligence systems are modeled on the human brain. Ng said it is necessary to teach AI software how to grade by feeding it examples — in this case, essays graded by other humans. Feeding examples, however, can propagate error. If the data set contains biased grading, then AI incorporates the bias, too.
“You’re only as good as your data set,” Ng said.
Automated essay grading software has been employed at other institutions, such as Harvard University and the Massachusetts Institute of Technology, to grade student submissions in open-access online courses, which often have enrollments in the thousands.
While there aren’t any classes at UT Dallas making use of the software yet, students might have had essays graded by computers well before they enrolled at UT Dallas, as standardized exams such as the GRE and the TOEFL are scored by Criterion, an essay-grading software. Increasingly, the written portions of these standardized tests are making use of Criterion in preparation for an expected transition to fully automated grading.
Criminology freshman Giovanna Gonzalez said she is optimistic about the prospect of an automated grading system.
“It’s going to save a lot of time and money,” she said. “We’d also be able to get our grades faster.”
Gonzalez said she is concerned, however, that using automated grading software might mean that professors won’t have a complete picture of a student’s understanding of a concept.
“It would be better for the professors, maybe,” she said. “But I am not sure if it would be better for me as a student.”
Ng said the technology is still years away from grading higher-level assignments such as those in Ketsler’s classes, giving professors time to adjust.
“Professors will always find new ways to connect with their students as technology evolves,” Ng said.
Source | UT Dallas Mercury News | Megan Zerez
ABOUT THE UT DALLAS COMPUTER SCIENCE DEPARTMENT
The UT Dallas Computer Science program is one of the largest Computer Science departments in the United States with over 2,800 bachelors-degree students, more than 1,000 master’s students, 190 Ph.D. students, 52 tenure-track faculty members, and 41 full-time senior lecturers, as of Fall 2018. With The University of Texas at Dallas’ unique history of starting as a graduate institution first, the CS Department is built on a legacy of valuing innovative research and providing advanced training for software engineers and computer scientists.
How the AI-Driven PEG Scoring Algorithm Can Improve Student Writing
The Project Essay Grade (PEG) automated scoring algorithm is one of the many significant outcomes of artificial intelligence in education. In a recent blog post , ERB President Tom Rochon explained how educators can use AI to improve student writing.
Now we want to take a deeper dive into the PEG scoring algorithm that drives ERB Writing Practice, our online program that evaluates student essays and delivers instant, actionable feedback.
What Is the PEG Scoring Algorithm?
The Project Essay Grade® (PEG®) software is an automated essay scoring solution that builds upon Dr. Ellis Batten Page’s research in computational linguistics spanning over 40 years. PEG analyzes written prose, measures writing characteristics like fluency and grammar, and models the decision-making process of expert readers, ultimately producing accurate and reliable scores. The effectiveness of PEG has been validated in more independent studies than any other essay scoring solution available.
The PEG algorithm has been trained using a vast database of expertly written and graded essays as a reference point for scoring written work. It provides feedback and scores based on the six traits of effective writing: the development of ideas, organization, style, word choice, sentence fluency, and conventions.
The PEG Algorithm: Igniting Better Essays
In a national study, PEG emerged as the most accurate among the top three automated scoring algorithms. Students who received PEG feedback alongside traditional writing instruction demonstrated a 22% stronger improvement in their writing skills compared with those who did not. The study examined the work of 800 middle school students who participated in a PEG Writing intervention program over two months.
This AI-powered platform offers real-time, actionable feedback that helps students revise and refine their work effectively. It goes beyond serving as a mere proofreading tool; it is a personalized learning aid. PEG helps students understand their writing patterns, identify common errors, and learn how to avoid them in the future. In addition to resulting in higher-quality essays, PEG also nurtures a deeper grasp of the writing process, supporting students in becoming more confident and skilled writers.

Using PEG not only elevated the quality of student essays but also fostered a proactive approach to learning. Students became more engaged in their work, displaying a greater willingness to revise and refine their essays based on the algorithm’s feedback.
The Benefits of PEG in Writing Instruction
PEG opens up new possibilities for more personalized online learning, allowing students to learn at their own pace and in their preferred manner, whether in the classroom or at home. The PEG algorithm also provides teachers with detailed analytics to monitor student progress, identify areas for improvement, and tailor their teaching strategies accordingly.
However, it’s important to understand that AI tools like the PEG algorithm are not meant to replace traditional teaching methods but rather, to complement them. They provide an avenue to personalize and enhance the learning experience, empowering students to reach their full potential.
The PEG algorithm offers several advantages to educators, including:
- Eliminating bias, ensuring an objective assessment of student work
- Providing immediate feedback, enabling students to address areas needing improvement promptly
- Efficiently handling large volumes of essays, making it a valuable tool for teachers with numerous students
Automated scoring also supports parents and families in improving their students’ writing skills remotely as a supplement to classroom instruction. AI-driven feedback allows students to work independently and on demand, even personalizing instruction and giving prompts that align with students’ strengths and areas of improvement.

ERB Writing Practice and the Power of the PEG Algorithm
ERB Writing Practice exemplifies the power of the PEG scoring algorithm. Harnessing the PEG scoring algorithm to provide students with immediate feedback, ERB Writing Practice enables them to continue practicing and improving their writing skills.

Designed for students in grades 3-12, the online program helps students enhance their writing skills through practice, feedback, and guided support by offering a vast library of more than 500 prompts and lessons. By automating the feedback process, educators can gain more data to help inform student growth, save time in providing feedback, and provide students with unlimited opportunities to boost their writing skills.
Summer Discount on ERB Writing Practice
Keep learners engaged this summer and boost their writing skills with reduced pricing on ERB Writing Practice, designed for students entering grades 3-12. Learn more, or order now as an ERB member school.
Related Reading

Navigating the Middle East Conflict and Assessing Mission Success
As with any challenge to the value and integrity of schools, this is an opportunity to reaffirm our core commitments as educators. Teaching about the Middle East is part of the educational mission of schools […] read more

Spring Cleaning: Taking the Time to Reflect on the School Year
Spring is an ideal part of the year to sequester some good thinking time in order to reflect on what has worked well during the past year, along with what could have gone better. Be unsparing. Take notes. Then set it aside for at least the first half of the summer. […] read more

Making Sense of Your Assessment Data: How ERB Supports Schools
In addition to assessments and measures of student well-being and social-emotional skills, we offer a range of resources and services to help educators and families extract actionable insights from assessment data. […] read more

Spring 2024 CTP Norms Updates: What to Expect This Reporting Cycle
Comprehensive Testing Program (CTP) norms are updated annually for each reporting cycle (fall and spring). These “rolling norms,” as they are often called, are calculated after gathering three years of data, and in the fourth year, deleting the earliest year and adding data from the most recent administration. […] read more
- Next »
Are you an ERB member?
Update your email preferences to receive news and updates from ERB.
Not an ERB member? Join our global community today!
Are you an erb member, not an erb member join our global community today.
Essay-Grading Software Seen as Time-Saving Tool
- Share article
Jeff Pence knows the best way for his 7th grade English students to improve their writing is to do more of it. But with 140 students, it would take him at least two weeks to grade a batch of their essays.
So the Canton, Ga., middle school teacher uses an online, automated essay-scoring program that allows students to get feedback on their writing before handing in their work.
“It doesn’t tell them what to do, but it points out where issues may exist,” said Mr. Pence, who says the a Pearson WriteToLearn program engages the students almost like a game.
With the technology, he has been able to assign an essay a week and individualize instruction efficiently. “I feel it’s pretty accurate,” Mr. Pence said. “Is it perfect? No. But when I reach that 67th essay, I’m not real accurate, either. As a team, we are pretty good.”
With the push for students to become better writers and meet the new Common Core State Standards, teachers are eager for new tools to help out. Pearson, which is based in London and New York City, is one of several companies upgrading its technology in this space, also known as artificial intelligence, AI, or machine-reading. New assessments to test deeper learning and move beyond multiple-choice answers are also fueling the demand for software to help automate the scoring of open-ended questions.
Critics contend the software doesn’t do much more than count words and therefore can’t replace human readers , so researchers are working hard to improve the software algorithms and counter the naysayers.
While the technology has been developed primarily by companies in proprietary settings, there has been a new focus on improving it through open-source platforms. New players in the market, such as the startup venture LightSide and edX , the nonprofit enterprise started by Harvard University and the Massachusetts Institute of Technology, are openly sharing their research. Last year, the William and Flora Hewlett Foundation sponsored an open-source competition to spur innovation in automated writing assessments that attracted commercial vendors and teams of scientists from around the world. (The Hewlett Foundation supports coverage of “deeper learning” issues in Education Week .)
“We are seeing a lot of collaboration among competitors and individuals,” said Michelle Barrett, the director of research systems and analysis for CTB/McGraw-Hill, which produces the Writing Roadmap for use in grades 3-12. “This unprecedented collaboration is encouraging a lot of discussion and transparency.”
Mark D. Shermis, an education professor at the University of Akron, in Ohio, who supervised the Hewlett contest, said the meeting of top public and commercial researchers, along with input from a variety of fields, could help boost performance of the technology. The recommendation from the Hewlett trials is that the automated software be used as a “second reader” to monitor the human readers’ performance or provide additional information about writing, Mr. Shermis said.
“The technology can’t do everything, and nobody is claiming it can,” he said. “But it is a technology that has a promising future.”
‘Hot Topic’
The first automated essay-scoring systems go back to the early 1970s, but there wasn’t much progress made until the 1990s with the advent of the Internet and the ability to store data on hard-disk drives, Mr. Shermis said. More recently, improvements have been made in the technology’s ability to evaluate language, grammar, mechanics, and style; detect plagiarism; and provide quantitative and qualitative feedback.
The computer programs assign grades to writing samples, sometimes on a scale of 1 to 6, in a variety of areas, from word choice to organization. The products give feedback to help students improve their writing. Others can grade short answers for content. To save time and money, the technology can be used in various ways on formative exercises or summative tests.
The Educational Testing Service first used its e-rater automated-scoring engine for a high-stakes exam in 1999 for the Graduate Management Admission Test, or GMAT, according to David Williamson, a senior research director for assessment innovation for the Princeton, N.J.-based company. It also uses the technology in its Criterion Online Writing Evaluation Service for grades 4-12.
Over the years, the capabilities changed substantially, evolving from simple rule-based coding to more sophisticated software systems. And statistical techniques from computational linguists, natural language processing, and machine learning have helped develop better ways of identifying certain patterns in writing.
But challenges remain in coming up with a universal definition of good writing, and in training a computer to understand nuances such as “voice.”
In time, with larger sets of data, more experts can identify nuanced aspects of writing and improve the technology, said Mr. Williamson, who is encouraged by the new era of openness about the research.
“It’s a hot topic,” he said. “There are a lot of researchers and academia and industry looking into this, and that’s a good thing.”
High-Stakes Testing
In addition to using the technology to improve writing in the classroom, West Virginia employs automated software for its statewide annual reading language arts assessments for grades 3-11. The state has worked with CTB/McGraw-Hill to customize its product and train the engine, using thousands of papers it has collected, to score the students’ writing based on a specific prompt.
“We are confident the scoring is very accurate,” said Sandra Foster, the lead coordinator of assessment and accountability in the West Virginia education office, who acknowledged facing skepticism initially from teachers. But many were won over, she said, after a comparability study showed that the accuracy of a trained teacher and the scoring engine performed better than two trained teachers. Training involved a few hours in how to assess the writing rubric. Plus, writing scores have gone up since implementing the technology.
Automated essay scoring is also used on the ACT Compass exams for community college placement, the new Pearson General Educational Development tests for a high school equivalency diploma, and other summative tests. But it has not yet been embraced by the College Board for the SAT or the rival ACT college-entrance exams.
The two consortia delivering the new assessments under the Common Core State Standards are reviewing machine-grading but have not committed to it.
Jeffrey Nellhaus, the director of policy, research, and design for the Partnership for Assessment of Readiness for College and Careers, or PARCC, wants to know if the technology will be a good fit with its assessment, and the consortium will be conducting a study based on writing from its first field test to see how the scoring engine performs.
Likewise, Tony Alpert, the chief operating officer for the Smarter Balanced Assessment Consortium, said his consortium will evaluate the technology carefully.
Open-Source Options
With his new company LightSide, in Pittsburgh, owner Elijah Mayfield said his data-driven approach to automated writing assessment sets itself apart from other products on the market.
“What we are trying to do is build a system that instead of correcting errors, finds the strongest and weakest sections of the writing and where to improve,” he said. “It is acting more as a revisionist than a textbook.”
The new software, which is available on an open-source platform, is being piloted this spring in districts in Pennsylvania and New York.
In higher education, edX has just introduced automated software to grade open-response questions for use by teachers and professors through its free online courses. “One of the challenges in the past was that the code and algorithms were not public. They were seen as black magic,” said company President Anant Argawal, noting the technology is in an experimental stage. “With edX, we put the code into open source where you can see how it is done to help us improve it.”
Still, critics of essay-grading software, such as Les Perelman, want academic researchers to have broader access to vendors’ products to evaluate their merit. Now retired, the former director of the MIT Writing Across the Curriculum program has studied some of the devices and was able to get a high score from one with an essay of gibberish.
“My main concern is that it doesn’t work,” he said. While the technology has some limited use with grading short answers for content, it relies too much on counting words and reading an essay requires a deeper level of analysis best done by a human, contended Mr. Perelman.
“The real danger of this is that it can really dumb down education,” he said. “It will make teachers teach students to write long, meaningless sentences and not care that much about actual content.”
Sign Up for EdWeek Update
Edweek top school jobs.

Sign Up & Sign In


- school Campus Bookshelves
- menu_book Bookshelves
- perm_media Learning Objects
- login Login
- how_to_reg Request Instructor Account
- hub Instructor Commons
- Download Page (PDF)
- Download Full Book (PDF)
- Periodic Table
- Physics Constants
- Scientific Calculator
- Reference & Cite
- Tools expand_more
- Readability
selected template will load here
This action is not available.

2: Robo-Grader- Artificial Intelligence As An Automated Essay Grading System, The Backstory
- Last updated
- Save as PDF
- Page ID 127126
The idea of Automated Essay Graders (AEG or Robo-graders) has been around since the early 1960’s. A former English teacher, Ellis B. Page, began working on the idea of helping students improve their writing by getting quick feedback on their essays with the help of computers. In December of 1964, at the University of Connecticut, Project Essay Grade (PEG®) was born ( Page, 1967 ). At that time, 272 trial essays were written by students grades 8-12 in an “American High School” and each was judged by at least 4 independent teachers. A hypothesis was generated surrounding the variables, also referred to as features, that might influence the teachers’ judgement. The essays were manually entered into an IBM 7040 computer by clerical staff using keypunch cards. The process was time consuming and labor intensive due to the limitations of computers at that time, but the results were impressive.
Page believed that writing could be broken down into what he called a “trin” and a “prox”. The Trin was a variable that measured the intrinsic interest to the human judge, for example, word choice. The Trin was not directly measurable by the computer strategies of the 1960’s. The Prox was an approximation or correlation to the Trin, for example, the proportion of “uncommon words” used by a student (Page, 1967 ). Thirty variables were identified as criterion for Project Essay Grade (PEG®). Page found that “the overall accuracy of this beginning strategy was startling. The proxes achieved a multiple-correlation of .71 for the first set of essays analyzed, and by chance, achieved the identical coefficient for the second set.” ( Page, 1967 ) While the results were impressive, the technology of the time was too cumbersome for practical applications, and computers were not readily accessible to most people. Page’s ideas may have seemed outlandish at the time, but it could be argued that they were prophetic. His work with AEG came years before students would have computers to write essays with.
Page continued to work on PEG for the next 30 years and his research consistently showed high correlations between Automated Essay Graders (AEG) and human graders. One study, ( Page, 1994 ) analyzed 2 sets of essays: one group of 495 essays in 1989, and another group of 599 in 1990. The students involved in the analysis were high school seniors participating in the National Assessment of Educational Progress who were responding to a question about recreational opportunities and whether a city should spend money fixing up old railroad tracks or convert an old warehouse to a new use. Using 20 variables, PEG reached 87% accuracy compared with targeted human judges.
In May of 2005, Ellis B. Page passed away at the age of 81. Two years earlier, he sold Project Essay Grade (PEG®) to a company called Measurement Incorporated. PEG® is currently being used by the State of Utah as the sole essay grader on the state summative writing assessment. According to Measurement Incorporated’s website ( www.measurementinc.com ) 3 more States are considering adapting the program. PEG® is currently being used in 1,000 schools and 3,000 public libraries as a formative assessment tool. Ellis B. Page could be considered the forefather of Automated Essay Graders.
What changed since Ellis B. Page began his Project Essay Grade in 1964? Personal computers and the Internet! The onset of personal computers in the 1990’s changed the face of possibility for Automated Essay Graders. With electronic keyboards in the hands of students and the Internet to provide a universal platform to submit text for evaluation, ( Shermis, Mzumara, Olson, & Harrington, 2001 ), a new industry, testing, was born.
In 1997, Intelligent Essay Assessor® (IEA® ) was introduced as another type of automated essay grading system developed by Thomas Landauer and Peter Foltz. In 1989, the system was originally patented for indexing documents for information retrieval. The indexing programming was subsequently applied to automated essay grading. Intellectual property rights became a factor in the marketplace of automated essay grading. The Intelligent Essay Assessor® program was designed to use what’s known as Latent Semantic Analysis (LAS), which determines similarity of words and passages by analyzing bodies of text. Developers using LAS create code that estimates how close the vocabulary of the essay writer is to the targeted vocabulary set ( Landauer, Foltz, & Laham, 1998) . Like most automated essay grading systems, documents are indexed for information retrieval regarding features, such as proportion of errors in grammar, proportion of word usage errors, proportion of style components, number of discourse elements, average length of sentences, similarity in vocabulary to top scoring essays, average word length, and total number of words. Typically, these features are clustered into sets. The sets may include content, word variety, grammar, text complexity, and sentence variety. In addition to measuring observable components in writing, the IEA® system uses an approach that involves specification of vocabulary. Word variety refers to word complexity and word uniqueness. Text complexity is similar to determining the reading level of the text. As with Project Essay Grader® , IEA® has reported high correlations with human scored essays (Landauer, Foltz, & Laham 1998 ). IEA® has become the automated grading system used by Pearson VUE. In 2011, Pearson VUE and the American Council on Education (ACE) partnered and launched GED® Testing Services (GEDTS) which provides students with a high school equivalency (HSE) program.
Around the same time period as IEA® was being developed, Educational Testing Services (ETS®), was developing the Electronic Essay Rater knows as e-rater® . This system uses a “Hybrid Feature Identification Technique” ( Burstein et al, 1998 ) that includes syntactic structure analysis, rhetorical structure analysis, and topical analysis to score essay responses via automated essay reading. The e-rater® system is used to score the GRE® General Test for admission to Graduate, Business, and Law school programs. ETS also provides testing for HiSET®, and TOEFL®. The e-rater® measurement system counts discount words (words that help text flow by showing time, cause and effect, contrast, qualifications etc.), the number of complement, subordinate, infinite, and relative clauses, as well as the occurrence of modal verbs (would, could, etc.) to calculate ratios of syntactic features per sentence and per essay. The structural analysis uses 60 different variables/features similar to the proxes used in Project Essay Grader® to create the essay score ( Ruder & Gagne, 2001).
The e-rater® was the initial AEG used by the GMAT® (Graduate Management Assessment Test) when the test added an essay component to the testing format in 1999. In January 2006, ACT, Inc. became responsible for development and scoring of the written portion of the GMAT®test. At that point, ACT, Inc. partnered with Vantage Learning and a new automatic essay grading system was introduced, IntelliMetric™, for use with the Analytic Writing Assessment. Vantage Learning’s corporate policy treats IntelliMetric™ as an intellectual property asset. Many of the details regarding this automated essay grader remain trade secrets ( Rudner, Garcia, & Welch, 2005 ). However, the general concepts behind the AEG system used in IntelliMetric™ have been described by Shermis and Burstein in their book, Handbook of Automated Essay Evaluation (2013) . According to their research, the IntelliMetric™ model selects from 500 component features (proxes) and clusters them into 5 sets: content, word variety, grammar, text complexity, and sentence variety.
One thing is true across all the major automated essay grading systems: due to the proprietary nature of the artificial intelligence surrounding the exact algorithms used to create these automated essay grading systems, the exact weighting of the system’s features, or exactly how the clusters and what features are in them are created, cannot be known. It’s important for test examinees to find out which automated essay grading system is being used by the company administering the test to be taken because that is the “audience” for the essay that is to be graded. Essays have traditionally been thought of as school-related assignments, something to use for college admission or a scholarship application, but the nature of the workplace is changing and automated essay graders are also used to determine the writing skills of future employees. Automated essay graders are impacting more than just academics.
It’s important to remember that AEGs can’t read for understanding when evaluating text. That is beyond the capabilities of artificial intelligence currently. For example, an automated essay reader could not “understand” the following joke:
Did you hear about the Mathematician who is afraid of negative numbers?
He’ll stop at nothing to avoid them.
Or the following play on words:
No matter how much you push the envelope, it will still be stationary.
Artificial intelligence (AI) cannot make inferences or judge cleverness of word choice. Artificial intelligence would not understand that I feel like I have been chasing squirrels, herding cats, and falling down rabbit holes in the process tracking down the information used in this book.
Artificial intelligence cannot understand polysemy and so does not understand whether the word mine is being used as a pronoun, or an explosive device, if it is referring to a large hole in the ground from which ore is produced, or part of the name of the 2009 Kentucky Derby winner, Mine That Bird. It can count how many times the word shows up in a text. Understanding what automated essay graders can “read”, and how they “read” is important for helping test examinees learn to think like their audience and write for that audience. But if the details behind the “thought process” of automated essay graders is proprietary, what can be found out about how an AEG thinks? Research can be found that provides general details about the major AEG systems currently in use, and like a puzzle, things become clearer as more pieces are added to the picture.
In early 2012, The William and Flora Hewlett Foundation sponsored a competition geared towards data scientists and machine learning specialists called the Automated Student Assessment Prize (ASAP) . The goal of this competition was to “…help solve an important social issue. We need fast, effective and affordable solutions for automated grading of student written essays” ( www.kaggle.com ). The competition had 2,500 entries and 250 participants who made up 150 teams. The competitors were provided with essays that had been scored by human readers and that varied in length and skill level of the writers. The competition sought to find a winner who could come closest to the results of the human scorers. “Software scoring programs do not independently assess the merits of an essay; instead they predict, very accurately, how a person would have scored the essay” ( www.gettingsmart.com ). In May of 2012, a winning team was announced, but no information was provided as to the algorithms behind the winning software. That was proprietary information. However, by the Autumn of 2012, students involved in studying artificial intelligence at universities in the US began producing “final projects” for their classes that tried to duplicate the results of the ASAP competition. The students used the same sample sets of essays used in the competition. Their studies provided many more details into the process of developing automated essay graders.
Automated Scoring of Writing
- Open Access
- First Online: 15 September 2023
Cite this chapter
You have full access to this open access chapter

- Stephanie Link ORCID: orcid.org/0000-0002-5586-1495 8 &
- Svetlana Koltovskaia 9
3985 Accesses
For decades, automated essay scoring (AES) has operated behind the scenes of major standardized writing assessments to provide summative scores of students’ writing proficiency (Dikli in J Technol Learn Assess 5(1), 2006). Today, AES systems are increasingly used in low-stakes assessment contexts and as a component of instructional tools in writing classrooms. Despite substantial debate regarding their use, including concerns about writing construct representation (Condon in Assess Writ 18:100–108, 2013; Deane in Assess Writ 18:7–24, 2013), AES has attracted the attention of school administrators, educators, testing companies, and researchers and is now commonly used in an attempt to reduce human efforts and improve consistency issues in assessing writing (Ramesh and Sanampudi in Artif Intell Rev 55:2495–2527, 2021). This chapter introduces the affordances and constraints of AES for writing assessment, surveys research on AES effectiveness in classroom practice, and emphasizes implications for writing theory and practice.
- Automated essay scoring
- Summative assessment
You have full access to this open access chapter, Download chapter PDF
Automated essay scoring (AES) is used internationally to rapidly assess writing and provide summative holistic scores and score descriptors for formal and informal assessments. The ease of using AES for response to writing is especially attractive for large-scale essay evaluation, providing also a low-cost supplement to human scoring and feedback provision. Additionally, intended benefits of AES include the elimination of human bias, such as rater fatigue, expertise, severity/leniency, inconsistency, and Halo effect. While AES developers also commonly suggest that their engines perform as reliably as human scorers (e.g., Burstein & Chodorow, 2010 ; Riordan et al., 2017 ; Rudner et al., 2006 ), AES is not free of critique. Automated scoring is frequently under scrutiny for use with university-level composition students in the United States (Condon, 2013 ) and second language writers (Crusan, 2010 ), with some writing practitioners discouraging its replacement of adequate literacy education because of its inability to evaluate meaning from a humanistic, socially-situated perspective (Deane, 2013 ; NCTE, 2013 ). AES also suffers from biases, such as imperfections in the quality and representation of training data to develop the systems and inform feedback generation. These biases question the fairness of AES (Loukina et al., 2019 ), especially if scores are modeled based on data that does not adequately represent a user population—a particular concern for use of AES with minoritized populations.
Despite reservations, the utility of AES in writing practices has increased significantly in recent years (Ramesh & Sanampudi, 2021 ), partially due to its integration into classroom-based tools (see Cotos, “ Automated Feedback on Writing ” for a review of automated writing evaluation). Thus, the affordances of AES for language testing are now readily available to writing practitioners and researchers, and the time is ripe for better understanding its potential impact on the pedagogical approaches to writing studies by first better understanding the history that drives AES development.
Dating back to the 1960s, AES started with the advent of Project Essay Grade (Page, 1966 ). Since then, automated scoring has advanced into leading technologies, including e-rater by the Educational Testing Service (ETS) (Attali & Burstein, 2006 ), Intelligent Essay Assessor (IEA) by Knowledge Analysis Technologies (Landauer et al., 2003 ), Intellimetric by Vantage Learning (Elliot, 2003 ), and a large number of prospective newcomers (e.g., Nguyen & Dery, 2016 ; Riordan et al., 2017 ). These AES engines are used for tests like the Test of English as a Foreign Language (TOEFL iBT), Graduate Management Admissions Test (GMAT), and the Pearson Test of English (PTE). In such tests, AES researchers not only found the scores reliable, but some argued that they also allowed for reproducibility, tractability, consistency, objectivity, item specification, granularity, and efficiency (William et al., 1999 ), characteristics that human raters can lack (Williamson et al., 2012 ).
The immediate AES response to writing is without much question a salient feature of automated scoring for testing contexts. However, research on classroom-based implementation has suggested that instructors can utilize the AES feedback to flag students’ writing that requires teachers’ special attention (Li et al., 2014 ), highlighting its potential for constructing individual development plans or conducting analysis of students’ writing needs. AES also provides constant, individualized feedback to lighten instructors’ feedback load (Kellogg et al., 2010 ), enhance student autonomy (Wang et al., 2013 ), and stimulate editing and revision (Li et al., 2014 ).
2 Core Idea of the Technology
Automated essay scoring involves automatic assessment of a students’ written work, usually in response to a writing prompt. This assessment generally includes (1) a holistic score of students’ performance, knowledge, and/or skill and (2) a score descriptor on how the student can improve the text. For example, e-rater by ETS ( 2013 ) scores essays on a scale from 0 to 6. A score of 6 may include the following feedback:
Score of 6: Excellent
Looks at the topic from a number of angles and responds to all aspects.
Responds thoughtfully and insightfully to the issues in the topic.
Develops with a superior structure and apt reasons or examples.
Uses sentence styles and language that have impact and energy.
Demonstrates that you know the mechanics of correct sentence structure.
AES engine developers over the years have undertaken a core goal of making the assessment of writing accurate, unbiased, and fair (Madnani & Cahill, 2018 ). The differences in score generation, however, are stark given the variation in philosophical foundations, intended purposes, extraction of features for scoring writing, and criteria used to test the systems (Yang et al., 2002 ). To this end, it is important to understand the prescribed use of automated systems so that they are not implemented inappropriately. For instance, if a system is meant to measure students’ writing proficiency, the system should not be used to assess students’ aptitude. Thus, scoring models for developing AES engines are valuable and effective in distinct ways and for their specific purposes.
Because each engine may be designed to assess different levels, genres, and/or skills of writing, developers utilize different natural language processing (NLP) techniques for establishing construct validity, or the extent to which an AES scoring engine measures what it intends to measure—a common concern for AES critics (Condon, 2013 ; Perelman, 2014 , 2020 ). NLP helps computers understand human input (text and speech) by starting with human and/or computer analysis of textual features so that a computer can process the textual input and offer reliable output (e.g., a holistic score and score descriptor) on new text. These features may include statistical features (e.g., essay length, word co-occurrences also known as n-grams), style-based features (e.g., sentence structure, grammar, part-of-speech), and content-based features (e.g., cohesion, semantics, prompt relevance) (see Ramesh & Sanampudi, 2021 , for an overview of features). Construct validity should thus be interpreted in relation to feature extraction of a given AES system to adequately appreciate (or challenge) the capabilities that system offers writing studies.
In addition to a focus on a variety of textual features, AES developers have utilized varied machine learning (ML) techniques to establish construct validity and efficient score modeling. Machine learning is a category of artificial intelligence (AI) that helps computers recognize patterns in data and continuously learn from the data to make accurate holistic score predictions and adjustments without further programming (IBM, 2020 ). Early AES research utilized standard multiple regression analysis to predict holistic scores based on a set of rater-defined textual features. This approach was utilized in the early 1960s for developing Project Essay Grade by Page ( 1966 ), but it has been criticized for its bias in favor of longer texts (Hearst, 2000 ) and its ignorance towards content and domain knowledge (Ramesh & Sanampudi, 2021 ).
In subsequent years, classification models, such as the bag of words approach (BOW), were common (e.g., Chen et al., 2010 ; Leacock & Chodorow, 2003 ). BOW models extract features in writing using NLP by counting the occurrences and co-occurrences of words within and across texts. Texts with multiple shared word strings are classified into similar holistic score categories (e.g., low, medium, high) (Chen et al., 2010 ; Zhang et al., 2010 ). E-rater by ETS is a good example of this approach. The aforementioned approaches are human-labor intensive. Latent semantic analysis (LSA) is advantageous in this regard; it is also strong in evaluating semantics. In LSA, the semantic representation of a text is compared to the semantic representation of other similarly scored responses. This analysis is done by training the computer on specific corpora that mimics a given writing prompt. Landauer et al. ( 2003 ) used LSA in Intelligent Essay Grade.
Advances in NLP and progress in ML have motivated AES researchers to move away from statistical regression-based modeling and classification approaches to advanced models involving neural network approaches (Dong et al., 2017 ; Kumar & Boulanger, 2020 ; Riordan et al., 2017 ). To develop these AES models, data undergoes a process of supervised learning, where the computer is provided with labeled data that enables it to produce a score as a human would. The supervised learning process often starts with a training set—a large corpus of representative, unbiased writing that is typically human- or auto-coded for specific linguistic features with each text receiving a holistic score. Models are then generated to teach a computer to identify and extract these features and provide a holistic score that correlates with the human rating. The models are evaluated on a testing set that the computer has never seen previously. Accuracy of algorithms is then evaluated by using testing set scores and human scores to determine human–computer consistency and reliability. Common evaluations are quadrated weighted kappa, Mean Absolute Error, and Pearson Correlation Coefficient.
Once accuracy results meet an industry standard (Powers et al., 2015 ), which varies across disciplines (Weigle, 2013 ), the algorithms are made public through user-friendly interfaces for testing contexts (i.e., to provide summative feedback, formal assessments to assess students’ performance or proficiency) and direct classroom use (i.e., informal assessments to improve students’ learning). For the classroom, teachers should be active in evaluating the feedback to determine whether it is reasonably accurate in assessing a learning goal, does not lead students away from the goal, and encourages students to engage in different ways with their text and/or the course content. Effective evaluation of AES should start with an awareness of AES affordances that can impact writing practice and then continue with the training of students in the utility of these affordances.
3 Functional Specifications
The overall functionality of AES for classroom use is to provide summative assessment of writing quality. AES accomplishes this through two key affordances: a holistic score and score descriptor.
Holistic score: The summative score provides an overall, generic assessment of writing quality. For example, Grammarly provides a holistic score or “performance” score out of 100%. The score represents the quality of writing (as determined by features, such as word count, readability statistics, vocabulary usage). If a student receives a score below 60–70%, this means that it could be understood by a reader who has a 9th grade education. For the text to be readable by 80% of English speakers, Grammarly suggests getting at least 60–70%.
Score descriptor: The holistic score is typically accompanied by a descriptor that indicates what the score represents. This characterization of the score meaning can be used to interpret the feedback, evaluate the feedback, and make decisions regarding editing and revising.
That is, these key affordances can be utilized to complete several main activities.
Interpreting feedback : Once students receive the holistic score along with the descriptor, they should interpret the score. Information provided for adequate score interpretation varies across AES systems, so students may need help in interpreting the meaning of this feedback.
Evaluating feedback : After interpreting the score and the descriptor, students need to think critically about how the feedback applies to their writing. That is, students need to determine whether the computer feedback is an adequate representation of their writing weaknesses. Evaluating feedback thus entails noticing the gap or problem found in one’s own writing and becoming consciously aware of how the feedback might be used to increase the quality of writing through self-editing (Ferris, 2011 ).
Making a decision about action : Once students evaluate their writing based on a given score and descriptor, they then need to decide whether to address the issues highlighted in the descriptor or seek additional feedback. Making and executing a revision plan can ensure that the student is being critical towards the feedback rather than accepting it outright.
Revising/editing : The student then revises the paper and resubmits it to the system to see if the score improves—an indicator of higher quality writing. If needed, the student can repeat the above actions or move on to editing of surface-level writing concerns.
4 Research on AES
AES research can be categorized along two lines: system-centric research that evaluates the system itself and user-centric research that evaluates use/impact of a system on learning. From a system-centric perspective, various studies have been conducted to validate AES-system-generated scores for the testing context. The majority have focused on reliability, or the extent to which results can be considered consistent or stable (Brown, 2005 ). They often evaluate reliability based on agreement between human and computer scoring (e.g., Burstein & Chodorow, 1999 ; Elliot, 2003 ; Streeter et al., 2011 ). (See Table 1 for a summary of reliability statistics from three major AES developers.)
The process of establishing validity should not start and stop with inter-coder reliability; however, automated scoring presents some distinctive validity challenges, such as “the potential to under- or misrepresent the construct of interest, vulnerability to cheating, impact on examinee behavior, and score users’ interpretation and use of scores” (Williamson et al., 2012 , p. 3). Thus, some researchers have also demonstrated reliability by using alternative measures, such as the association with independent measures (Attali et al., 2010 ) and the generalizability of scores (Attali et al., 2010 ). Others have gone a step further and suggested a unified approach to AES validation (Weigle, 2013 , Williamson et al., 2012 ). In general, results reveal promising developments in AES with modest correlations between AES and external criteria, such as independent proficiency assessments (Attali et al., 2010 ; Powers et al., 2015 , suggesting that automated scores can relate in a similar manner to select assessment criteria and that both have the potential to reflect similar constructs, although results across AES systems can vary, and not all data are readily available to the public.
While much research has focused on reliability of AES, little is known about the quality of holistic scores in testing or classroom contexts as well as teachers’ and students’ use and perceptions of automatically generated scores. In a testing context, James ( 2006 ) compared the IntelliMetric scores of the ACCUPLACER OnLine WritePlacer Plus test to the scores of “untrained” faculty raters. Results revealed a relatively high level of correspondence between the two. In a similar study with a group of developmental writing students in a two-year college in South Texas, Wang and Brown ( 2007 ) found that ACCUPLACER’s overall holistic mean score showed significant difference between IntelliMetric and human raters, indicating that IntelliMetric tends to assign higher scores than human raters do. Li et al. ( 2014 ) investigated the correlation between Criterion’s numeric scores with the English as a second language instructors’ numeric grades and analytic ratings for classroom-based assessment. The results showed low to moderate positive correlations between Criterion’s scores and instructors’ scores and analytic ratings. Taken together, these studies suggest limited continuity of findings on AES reliability across tools.
Results of multiple studies demonstrate varied uses for holistic scores and varied teachers’ and students’ perceptions toward the scores. For example, Li et al. ( 2014 ) found that Criterion’s holistic scores in the English as a second language classroom were used in three ways. First, instructors used the scores as a forewarning. That is, the scores alerted instructors to problematic writing. Second, the scores were used as a pre-submission benchmark. That is, the students were required to obtain a certain score before submitting a final draft to their teacher. Finally, Criterion's scores were utilized as an assessment tool—scores were part of course grading. Similar findings were reported in Chen and Cheng’s ( 2008 ) study that focused on EFL Tawainese teachers’ and students’ use and perception of My Access! While one teacher used My Access! as a pre-submission benchmark, the other used it for both formative and summative assessment, heavily relying on the scores to assessing writing performance. The third teacher did not make My Access! a requirement and asked the students to use it if they needed to.
In terms of teachers’ perceptions of holistic scores, holistic scores seem to be motivators for promoting student revision (Li et al. 2014 ; Scharber et al., 2008 ) although a few teachers in Maeng ( 2010 ) commented that the score caused some stress albeit was still helpful for facilitating the feedback process (i.e., for providing sample writing and revising). Teachers also tend to have mixed confidence in holistic scores (Chen & Cheng, 2008 ; Li et al, 2014 ). For example, in Li et al.’s ( 2014 ) study, English as a second language instructors had high trust in Criterion’s low holistic scores as the essays Criterion scored low were, in fact, poor essays. However, instructors possessed low levels of trust when Criterion assigned high scores to writing as instructors judged such writing lower.
Students also tend to have low trust in holistic scores (Chen & Cheng, 2008 ; Scharber et al., 2008 ). For example, Chen and Cheng ( 2008 ) found that EFL Taiwanese students’ low level of trust in holistic scores was influenced by teachers’ low level of trust in the scores as well as discrepancies in teachers’ scores and holistic scores of My Access! that students noticed. Similar findings were reported in Scharber et al.’s ( 2008 ) study that focused on Educational Theory into Practice Software’s (ETIPS) automated scorer implemented in a post-baccalaureate program at a large public Midwestern US university. The students in their study experienced negative emotions due to discrepancies in teachers’ and ETIPS’ holistic scores. ETIPS scores were one point lower than teachers’ scores. Additionally, the students found holistic scores with the short descriptor insufficient in guiding them as to how to actually improve their essays.
5 Implications of This Technology for Writing Theory and Practice
The rapid advancement of NLP and ML approaches to automated scoring lends well to theoretical contributions that help to (re-)define traditional notions of how learning takes place and the phenomena that underscores language development. Social- and cognitive-based theories to writing studies can be expanded with the integration of AES technology by offering new, socially-situated learning opportunities in online environments that can impact how students respond to feedback. These digitally-rich learning opportunities can thus significantly impact the writing process, offering a new mode of feedback that can be meaningful, constant, timely, and manageable while addressing individual learner needs. From a traditional pen-and-paper approach, these benefits are known to contribute significantly to writing accuracy (Hartshorn et al., 2010 ), and so the addition of rapid technology has the potential to add new knowledge to writing development research.
AES research can also contribute to practice. Due to its instantaneous nature, AES holistic scores could be used for placement purposes (e.g., by using ACCUPLACER) at schools, colleges, and universities. However, relying on the AES holistic score alone may not be adequate. Therefore, just like in large-scale tests, it is important that students’ writing is double-rated to enhance reliability, with a third rater used if there is a discrepancy in AES holistic score and a human rater’s score. Similarly, AES holistic scores could be used for diagnostic assessment. Diagnostic assessment is given prior to or at the start of the semester/course to get information about students’ language proficiency as well as their strengths and weaknesses in writing. Finally, AES scoring could be used for summative classroom assessment. For example, teachers could use AES scores as a pre-submission benchmark and require students to revise their essays until they get a predetermined score, or teachers could use the AES score for partial (rather than sole) assessment of goal attainment (Li et al., 2014 ; Weigle, 2013 ). Overall, in order to avoid pitfalls such as students focusing too intensively on obtaining high scores without actually improving their writing skills, teachers and students need to be trained or seek training on the different merits and demerits of a selected AES scoring system.
6 Concluding Remarks
While traditional approaches to written corrective feedback are still leading writing studies research, the ever-changing digitalization of the writing process shines light on new opportunities for enhancing the nature of feedback provision. The evolution of AI will undoubtedly expand the affordances of AES so that writing in digital spaces can be supplemented by computer-based feedback that is increasingly accurate and reliable. For now, these technologies are only foregrounding what can come from technological advancements, and in the meantime, it is the task of researchers and practitioners to cast a critical eye while also remaining open to the potential for AES technologies to promote autonomous, lifelong learning and writing development.
7 Tool List
List of well-known Automated Essay Scoring (AES) Tools
Attali, Y., Bridgeman, B., & Trapani, C. (2010). Performance of a generic approach in automated essay scoring. Journal of Technology , Learning, and Assessment, 10 (3). http://www.jtla.org
Attali, Y., & Burstein, J. (2006). Automated essay scoring with e-rater V.2. Journal of Technology, Learning, and Assessment, 4 (3), 1–30.
Google Scholar
Brown, J. D. (2005). Testing in language programs. A comprehensive guide to English language assessment . McGraw Hill.
Burstein, J., & Chodorow, M. (1999). Automated essay scoring for nonnative English speakers . Proceedings of the ACL99 Workshop on Computer-Mediated Language Assessment and Evaluation of Natural Language Processing. http://www.ets.org/Media/Research/pdf/erater_acl99rev.pdf
Burstein, J., & Chodorow, M. (2010). Progress and new directions in technology for automated essay evaluation. In R. Kaplan (Ed.), The Oxford handbook of applied linguistics (2nd ed., pp. 487–497). Oxford University Press.
Chen, C., & Cheng, W. (2008). Beyond the design of automated writing evaluation: Pedagogical practices and perceived learning effectiveness in EFL writing classes. Language Learning & Technology, 12 (2), 94–112.
Chen, Y. Y., Liu, C. L., Chang, T. H., & Lee, C. H. (2010). An unsupervised automated essay scoring system. IEEE Intelligent Systems, 25 (5), 61–67. https://doi.org/10.1109/MIS.2010.3
Article Google Scholar
Condon, W. (2013). Large-scale assessment, locally-developed measures, and automated scoring of essays: Fishing for red herrings? Assessing Writing, 18 , 100–108. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.asw.2012.11.001
Crusan, D. (2010). Assessment in the second language writing classroom . University of Michigan Press.
Book Google Scholar
Deane, P. (2013). On the relation between automated essay scoring and modern views of the writing construct. Assessing Writing, 18 , 7–24.
Dexter, S. (2007). Educational theory into practice software. In D. Gibson, C. Aldrich, & M. Prensky (Eds.), Games and simulations in online learning: Research and development frameworks (pp. 223–238). IGI Global. https://doi.org/10.4018/978-1-59904-304-3.ch011
Dikli, S. (2006). An overview of automated scoring of essays. The Journal of Technology, Learning and Assessment, 5 (1). https://ejournals.bc.edu/index.php/jtla/article/view/1640
Dong, F., Zhang, Y., & Yang, J. (2017). Attention-based recurrent convolutional neural network for automatic essay scoring . Proceedings of the 21st Conference on Computational Natural Language Learning (CoNLL 2017). https://aclanthology.org/K17-1017.pdf
Elliot, S. (2003). IntelliMetric: From here to validity. In M. D. Shermis & J. C. Burstein (Eds.), Automatic essay scoring: A cross-disciplinary perspective (pp. 71–86). Lawrence Erlbaum Associates.
ETS. (2013). Criterion scoring guide . Retrieved September 27, 2013, from http://www.ets.org/Media/Products/Criterion/topics/co-1s.htm
Ferris, D. R. (2011). Treatment of errors in second language student writing (2nd ed.). The University of Michigan Press.
Hartshorn, K. J., Evans, N. W., Merrill, P. F., Sudweeks, R. R., Strong-Krause, D., & Anderson, N. J. (2010). Effects of dynamic corrective feedback on ESL writing accuracy. TESOL Quarterly, 44 , 84–109.
Hearst, M. (2000). The debate on automated essay grading. IEEE Intelligent Systems and their Applications, 15 (5), 22–37. https://doi.org/10.1109/5254.889104
IBM. (2020). Machine learning . IBM Cloud Education. https://www.ibm.com/cloud/learn/machine-learning
James, C. (2006). Validating a computerized scoring system for assessing writing and placing students in composition courses. Assessing Writing, 11 (3), 167–178.
Kellogg, R., Whiteford, A., & Quinlan, T. (2010). Does automated feedback help students learn to write? Journal of Educational Computing Research, 42 , 173–196.
Kumar, V., & Boulanger, D. (2020). Explainable automated essay scoring: Deep learning really has pedagogical value. Frontiers in Education (Lausanne) , 5 . https://doi.org/10.3389/feduc.2020.572367
Landauer, T. K., Laham, D., & Foltz, P. (2003). Automatic essay assessment. Assessment in Education, 10 (3), 295–308.
Leacock, C., & Chodorow, M. (2003). C-rater: Automated scoring of short-answer questions. Computers and the Humanities, 37 , 389–405.
Li, Z., Link, S., Ma, H., Yang, H., & Hegelheimer, V. (2014). The role of automated writing evaluation holistic scores in the ESL classroom. System, 44 , 66–78. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.system.2014.02.007
Loukina, A., et al. (2019). The many dimensions of algorithmic fairness in educational applications . BEA@ACL.
Madnani, N., & Cahill, A. (2018). Automated scoring: Beyond natural language processing . COLING.
Maeng, U. (2010). The effect and teachers’ perception of using an automated essay scoring system in L2 writing. English Language and Linguistics, 16 (1), 247–275.
NCTE. (2013, April 20). NCTE position statement on machine scoring . National Council of Teachers of English. https://ncte.org/statement/machine_scoring/
Nguyen, H., & Dery, L. (2016). Neural networks for automated essay grading (pp. 1–11). CS224d Stanford Reports.
Page, E. B. (1966). The imminence of grading essays by computer. Phi Delta Kappan, 48 , 238–243.
Perelman, L. (2014). When “the state of the art” is counting words. Assessing Writing, 21 , 104–111.
Perelman, L. (2020). The BABEL generator and E-rater: 21st century writing constructs and automated essay scoring (AES). Journal of Writing Assessment, 13 (1).
Powers, D. E., Escoffery, D. S., & Duchnowski, M. P. (2015). Validating automated essay scoring: A (modest) refinement of the “gold standard.” Applied Measurement in Education, 28 (2), 130–142. https://doi.org/10.1080/08957347.2014.1002920
Ramesh, D., & Sanampudi, S. K. (2021). An automated essay scoring systems: A systematic literature review. The Artificial Intelligence Review, 55 (3), 2495–2527. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10462-021-10068-2
Riordan, B., Horbach, A., Cahill, A., Zesch, T., & Lee, C. M. (2017). Investigating neural architectures for short answer scoring . Proceedings of the 12th Workshop on Innovative Use of NLP for Building Educational Applications. https://aclanthology.org/W17-5017.pdf
Rudner, L., Garcia, V., & Welch, C. (2006). An evaluation of IntelliMetricTM essay scoring system. Journal of Technology, Learning, and Assessment, 4 (4). http://escholarship.bc.edu/ojs/index.php/jtla/article/view/1651/1493
Scharber, C., Dexter, S., & Riedel, E. (2008). Students’ experiences with an automated essay scorer. Journal of Technology, Learning and Assessment, 7 (1), 1–45. https://ejournals.bc.edu/index.php/jtla/article/view/1628
Streeter, L., Bernstein, J., Foltz, P., & DeLand, D. (2011). Pearson’s automated scoring of writing, speaking, and mathematics . White Paper. http://images.pearsonassessments.com/images/tmrs/PearsonsAutomatedScoringofWritingSpeakingandMathematics.pdf
Wang, J., & Brown, M. S. (2007). Automated essay scoring versus human scoring: A comparative study. Journal of Technology, Learning, and Assessment, 6 (2). http://www.jtla.org
Wang, Y., Shang, H., & Briody, P. (2013). Exploring the impact of using automated writing evaluation in English as a foreign language university students’ writing. Computer Assisted Language Learning, 26 (3), 1–24.
Weigle, S. C. (2013). English as a second language writing and automated essay evaluation. In M. D. Shermis & J. C. Burstein (Eds.), Handbook of automated essay evaluation: Current applications and new directions (pp. 36–54). Routledge.
William, D. M., Bejar, I. I., & Hone, A. S. (1999). ’Mental model’ comparison of automated and human scoring. Journal of Educational Measurement, 35 (2), 158–184.
Williamson, D., Xi, X., & Breyer, F. J. (2012). A framework for evaluation and use of automated scoring. Educational Measurement: Issues and Practice, 31 (1), 2–13.
Yang, Y., Buckendahl, C. W., Juszkiewicz, P. J., & Bhola, D. S. (2002). A review of strategies for validating computer-automated scoring. Applied Measurement in Education, 15 (4), 391–412. https://doi.org/10.1207/S15324818AME1504_04
Zhang, Y., Jin, R., & Zhou, Z. H. (2010). Understanding bag-of-words model: A statistical framework. International Journal of Machine Learning and Cybernetics, 1 , 43–52.
Download references
Author information
Authors and affiliations.
Oklahoma State University, 205 Morrill Hall, Stillwater, OK, 74078, USA
Stephanie Link
Department of Languages and Literature, Northeastern State University, Tahlequah, OK, 74464, USA
Svetlana Koltovskaia
You can also search for this author in PubMed Google Scholar
Corresponding author
Correspondence to Stephanie Link .
Editor information
Editors and affiliations.
School of Applied Linguistics, Zurich University of Applied Sciences, Winterthur, Switzerland
School of Management and Law, Center for Innovative Teaching and Learning, Zurich University of Applied Sciences, Winterthur, Switzerland
Christian Rapp
North Carolina State University, Raleigh, NC, USA
Chris M. Anson
TECFA, Faculty of Psychology and Educational Sciences, University of Geneva, Geneva, Switzerland
Kalliopi Benetos
English Department, Iowa State University, Ames, IA, USA
Elena Cotos
School of Education, Trinity College Dublin, Dublin, Ireland
TD School, University of Technology Sydney, Sydney, NSW, Australia
Antonette Shibani
Rights and permissions
Open Access This chapter is licensed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License ( http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/ ), which permits use, sharing, adaptation, distribution and reproduction in any medium or format, as long as you give appropriate credit to the original author(s) and the source, provide a link to the Creative Commons license and indicate if changes were made.
The images or other third party material in this chapter are included in the chapter's Creative Commons license, unless indicated otherwise in a credit line to the material. If material is not included in the chapter's Creative Commons license and your intended use is not permitted by statutory regulation or exceeds the permitted use, you will need to obtain permission directly from the copyright holder.
Reprints and permissions
Copyright information
© 2023 The Author(s)
About this chapter
Link, S., Koltovskaia, S. (2023). Automated Scoring of Writing. In: Kruse, O., et al. Digital Writing Technologies in Higher Education . Springer, Cham. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-031-36033-6_21
Download citation
DOI : https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-031-36033-6_21
Published : 15 September 2023
Publisher Name : Springer, Cham
Print ISBN : 978-3-031-36032-9
Online ISBN : 978-3-031-36033-6
eBook Packages : Education Education (R0)
Share this chapter
Anyone you share the following link with will be able to read this content:
Sorry, a shareable link is not currently available for this article.
Provided by the Springer Nature SharedIt content-sharing initiative
- Publish with us
Policies and ethics
- Find a journal
- Track your research
An official website of the United States government
The .gov means it’s official. Federal government websites often end in .gov or .mil. Before sharing sensitive information, make sure you’re on a federal government site.
The site is secure. The https:// ensures that you are connecting to the official website and that any information you provide is encrypted and transmitted securely.
- Publications
- Account settings
Preview improvements coming to the PMC website in October 2024. Learn More or Try it out now .
- Advanced Search
- Journal List
- Springer Nature - PMC COVID-19 Collection

An automated essay scoring systems: a systematic literature review
Dadi ramesh.
1 School of Computer Science and Artificial Intelligence, SR University, Warangal, TS India
2 Research Scholar, JNTU, Hyderabad, India
Suresh Kumar Sanampudi
3 Department of Information Technology, JNTUH College of Engineering, Nachupally, Kondagattu, Jagtial, TS India
Associated Data
Assessment in the Education system plays a significant role in judging student performance. The present evaluation system is through human assessment. As the number of teachers' student ratio is gradually increasing, the manual evaluation process becomes complicated. The drawback of manual evaluation is that it is time-consuming, lacks reliability, and many more. This connection online examination system evolved as an alternative tool for pen and paper-based methods. Present Computer-based evaluation system works only for multiple-choice questions, but there is no proper evaluation system for grading essays and short answers. Many researchers are working on automated essay grading and short answer scoring for the last few decades, but assessing an essay by considering all parameters like the relevance of the content to the prompt, development of ideas, Cohesion, and Coherence is a big challenge till now. Few researchers focused on Content-based evaluation, while many of them addressed style-based assessment. This paper provides a systematic literature review on automated essay scoring systems. We studied the Artificial Intelligence and Machine Learning techniques used to evaluate automatic essay scoring and analyzed the limitations of the current studies and research trends. We observed that the essay evaluation is not done based on the relevance of the content and coherence.
Supplementary Information
The online version contains supplementary material available at 10.1007/s10462-021-10068-2.
Introduction
Due to COVID 19 outbreak, an online educational system has become inevitable. In the present scenario, almost all the educational institutions ranging from schools to colleges adapt the online education system. The assessment plays a significant role in measuring the learning ability of the student. Most automated evaluation is available for multiple-choice questions, but assessing short and essay answers remain a challenge. The education system is changing its shift to online-mode, like conducting computer-based exams and automatic evaluation. It is a crucial application related to the education domain, which uses natural language processing (NLP) and Machine Learning techniques. The evaluation of essays is impossible with simple programming languages and simple techniques like pattern matching and language processing. Here the problem is for a single question, we will get more responses from students with a different explanation. So, we need to evaluate all the answers concerning the question.
Automated essay scoring (AES) is a computer-based assessment system that automatically scores or grades the student responses by considering appropriate features. The AES research started in 1966 with the Project Essay Grader (PEG) by Ajay et al. ( 1973 ). PEG evaluates the writing characteristics such as grammar, diction, construction, etc., to grade the essay. A modified version of the PEG by Shermis et al. ( 2001 ) was released, which focuses on grammar checking with a correlation between human evaluators and the system. Foltz et al. ( 1999 ) introduced an Intelligent Essay Assessor (IEA) by evaluating content using latent semantic analysis to produce an overall score. Powers et al. ( 2002 ) proposed E-rater and Intellimetric by Rudner et al. ( 2006 ) and Bayesian Essay Test Scoring System (BESTY) by Rudner and Liang ( 2002 ), these systems use natural language processing (NLP) techniques that focus on style and content to obtain the score of an essay. The vast majority of the essay scoring systems in the 1990s followed traditional approaches like pattern matching and a statistical-based approach. Since the last decade, the essay grading systems started using regression-based and natural language processing techniques. AES systems like Dong et al. ( 2017 ) and others developed from 2014 used deep learning techniques, inducing syntactic and semantic features resulting in better results than earlier systems.
Ohio, Utah, and most US states are using AES systems in school education, like Utah compose tool, Ohio standardized test (an updated version of PEG), evaluating millions of student's responses every year. These systems work for both formative, summative assessments and give feedback to students on the essay. Utah provided basic essay evaluation rubrics (six characteristics of essay writing): Development of ideas, organization, style, word choice, sentence fluency, conventions. Educational Testing Service (ETS) has been conducting significant research on AES for more than a decade and designed an algorithm to evaluate essays on different domains and providing an opportunity for test-takers to improve their writing skills. In addition, they are current research content-based evaluation.
The evaluation of essay and short answer scoring should consider the relevance of the content to the prompt, development of ideas, Cohesion, Coherence, and domain knowledge. Proper assessment of the parameters mentioned above defines the accuracy of the evaluation system. But all these parameters cannot play an equal role in essay scoring and short answer scoring. In a short answer evaluation, domain knowledge is required, like the meaning of "cell" in physics and biology is different. And while evaluating essays, the implementation of ideas with respect to prompt is required. The system should also assess the completeness of the responses and provide feedback.
Several studies examined AES systems, from the initial to the latest AES systems. In which the following studies on AES systems are Blood ( 2011 ) provided a literature review from PEG 1984–2010. Which has covered only generalized parts of AES systems like ethical aspects, the performance of the systems. Still, they have not covered the implementation part, and it’s not a comparative study and has not discussed the actual challenges of AES systems.
Burrows et al. ( 2015 ) Reviewed AES systems on six dimensions like dataset, NLP techniques, model building, grading models, evaluation, and effectiveness of the model. They have not covered feature extraction techniques and challenges in features extractions. Covered only Machine Learning models but not in detail. This system not covered the comparative analysis of AES systems like feature extraction, model building, and level of relevance, cohesion, and coherence not covered in this review.
Ke et al. ( 2019 ) provided a state of the art of AES system but covered very few papers and not listed all challenges, and no comparative study of the AES model. On the other hand, Hussein et al. in ( 2019 ) studied two categories of AES systems, four papers from handcrafted features for AES systems, and four papers from the neural networks approach, discussed few challenges, and did not cover feature extraction techniques, the performance of AES models in detail.
Klebanov et al. ( 2020 ). Reviewed 50 years of AES systems, listed and categorized all essential features that need to be extracted from essays. But not provided a comparative analysis of all work and not discussed the challenges.
This paper aims to provide a systematic literature review (SLR) on automated essay grading systems. An SLR is an Evidence-based systematic review to summarize the existing research. It critically evaluates and integrates all relevant studies' findings and addresses the research domain's specific research questions. Our research methodology uses guidelines given by Kitchenham et al. ( 2009 ) for conducting the review process; provide a well-defined approach to identify gaps in current research and to suggest further investigation.
We addressed our research method, research questions, and the selection process in Sect. 2 , and the results of the research questions have discussed in Sect. 3 . And the synthesis of all the research questions addressed in Sect. 4 . Conclusion and possible future work discussed in Sect. 5 .
Research method
We framed the research questions with PICOC criteria.
Population (P) Student essays and answers evaluation systems.
Intervention (I) evaluation techniques, data sets, features extraction methods.
Comparison (C) Comparison of various approaches and results.
Outcomes (O) Estimate the accuracy of AES systems,
Context (C) NA.
Research questions
To collect and provide research evidence from the available studies in the domain of automated essay grading, we framed the following research questions (RQ):
RQ1 what are the datasets available for research on automated essay grading?
The answer to the question can provide a list of the available datasets, their domain, and access to the datasets. It also provides a number of essays and corresponding prompts.
RQ2 what are the features extracted for the assessment of essays?
The answer to the question can provide an insight into various features so far extracted, and the libraries used to extract those features.
RQ3, which are the evaluation metrics available for measuring the accuracy of algorithms?
The answer will provide different evaluation metrics for accurate measurement of each Machine Learning approach and commonly used measurement technique.
RQ4 What are the Machine Learning techniques used for automatic essay grading, and how are they implemented?
It can provide insights into various Machine Learning techniques like regression models, classification models, and neural networks for implementing essay grading systems. The response to the question can give us different assessment approaches for automated essay grading systems.
RQ5 What are the challenges/limitations in the current research?
The answer to the question provides limitations of existing research approaches like cohesion, coherence, completeness, and feedback.
Search process
We conducted an automated search on well-known computer science repositories like ACL, ACM, IEEE Explore, Springer, and Science Direct for an SLR. We referred to papers published from 2010 to 2020 as much of the work during these years focused on advanced technologies like deep learning and natural language processing for automated essay grading systems. Also, the availability of free data sets like Kaggle (2012), Cambridge Learner Corpus-First Certificate in English exam (CLC-FCE) by Yannakoudakis et al. ( 2011 ) led to research this domain.
Search Strings : We used search strings like “Automated essay grading” OR “Automated essay scoring” OR “short answer scoring systems” OR “essay scoring systems” OR “automatic essay evaluation” and searched on metadata.
Selection criteria
After collecting all relevant documents from the repositories, we prepared selection criteria for inclusion and exclusion of documents. With the inclusion and exclusion criteria, it becomes more feasible for the research to be accurate and specific.
Inclusion criteria 1 Our approach is to work with datasets comprise of essays written in English. We excluded the essays written in other languages.
Inclusion criteria 2 We included the papers implemented on the AI approach and excluded the traditional methods for the review.
Inclusion criteria 3 The study is on essay scoring systems, so we exclusively included the research carried out on only text data sets rather than other datasets like image or speech.
Exclusion criteria We removed the papers in the form of review papers, survey papers, and state of the art papers.
Quality assessment
In addition to the inclusion and exclusion criteria, we assessed each paper by quality assessment questions to ensure the article's quality. We included the documents that have clearly explained the approach they used, the result analysis and validation.
The quality checklist questions are framed based on the guidelines from Kitchenham et al. ( 2009 ). Each quality assessment question was graded as either 1 or 0. The final score of the study range from 0 to 3. A cut off score for excluding a study from the review is 2 points. Since the papers scored 2 or 3 points are included in the final evaluation. We framed the following quality assessment questions for the final study.
Quality Assessment 1: Internal validity.
Quality Assessment 2: External validity.
Quality Assessment 3: Bias.
The two reviewers review each paper to select the final list of documents. We used the Quadratic Weighted Kappa score to measure the final agreement between the two reviewers. The average resulted from the kappa score is 0.6942, a substantial agreement between the reviewers. The result of evolution criteria shown in Table Table1. 1 . After Quality Assessment, the final list of papers for review is shown in Table Table2. 2 . The complete selection process is shown in Fig. Fig.1. 1 . The total number of selected papers in year wise as shown in Fig. Fig.2. 2 .
Quality assessment analysis
Final list of papers

Selection process

Year wise publications
What are the datasets available for research on automated essay grading?
To work with problem statement especially in Machine Learning and deep learning domain, we require considerable amount of data to train the models. To answer this question, we listed all the data sets used for training and testing for automated essay grading systems. The Cambridge Learner Corpus-First Certificate in English exam (CLC-FCE) Yannakoudakis et al. ( 2011 ) developed corpora that contain 1244 essays and ten prompts. This corpus evaluates whether a student can write the relevant English sentences without any grammatical and spelling mistakes. This type of corpus helps to test the models built for GRE and TOFEL type of exams. It gives scores between 1 and 40.
Bailey and Meurers ( 2008 ), Created a dataset (CREE reading comprehension) for language learners and automated short answer scoring systems. The corpus consists of 566 responses from intermediate students. Mohler and Mihalcea ( 2009 ). Created a dataset for the computer science domain consists of 630 responses for data structure assignment questions. The scores are range from 0 to 5 given by two human raters.
Dzikovska et al. ( 2012 ) created a Student Response Analysis (SRA) corpus. It consists of two sub-groups: the BEETLE corpus consists of 56 questions and approximately 3000 responses from students in the electrical and electronics domain. The second one is the SCIENTSBANK(SemEval-2013) (Dzikovska et al. 2013a ; b ) corpus consists of 10,000 responses on 197 prompts on various science domains. The student responses ladled with "correct, partially correct incomplete, Contradictory, Irrelevant, Non-domain."
In the Kaggle (2012) competition, released total 3 types of corpuses on an Automated Student Assessment Prize (ASAP1) (“ https://www.kaggle.com/c/asap-sas/ ” ) essays and short answers. It has nearly 17,450 essays, out of which it provides up to 3000 essays for each prompt. It has eight prompts that test 7th to 10th grade US students. It gives scores between the [0–3] and [0–60] range. The limitations of these corpora are: (1) it has a different score range for other prompts. (2) It uses statistical features such as named entities extraction and lexical features of words to evaluate essays. ASAP + + is one more dataset from Kaggle. It is with six prompts, and each prompt has more than 1000 responses total of 10,696 from 8th-grade students. Another corpus contains ten prompts from science, English domains and a total of 17,207 responses. Two human graders evaluated all these responses.
Correnti et al. ( 2013 ) created a Response-to-Text Assessment (RTA) dataset used to check student writing skills in all directions like style, mechanism, and organization. 4–8 grade students give the responses to RTA. Basu et al. ( 2013 ) created a power grading dataset with 700 responses for ten different prompts from US immigration exams. It contains all short answers for assessment.
The TOEFL11 corpus Blanchard et al. ( 2013 ) contains 1100 essays evenly distributed over eight prompts. It is used to test the English language skills of a candidate attending the TOFEL exam. It scores the language proficiency of a candidate as low, medium, and high.
International Corpus of Learner English (ICLE) Granger et al. ( 2009 ) built a corpus of 3663 essays covering different dimensions. It has 12 prompts with 1003 essays that test the organizational skill of essay writing, and13 prompts, each with 830 essays that examine the thesis clarity and prompt adherence.
Argument Annotated Essays (AAE) Stab and Gurevych ( 2014 ) developed a corpus that contains 102 essays with 101 prompts taken from the essayforum2 site. It tests the persuasive nature of the student essay. The SCIENTSBANK corpus used by Sakaguchi et al. ( 2015 ) available in git-hub, containing 9804 answers to 197 questions in 15 science domains. Table Table3 3 illustrates all datasets related to AES systems.
ALL types Datasets used in Automatic scoring systems
Features play a major role in the neural network and other supervised Machine Learning approaches. The automatic essay grading systems scores student essays based on different types of features, which play a prominent role in training the models. Based on their syntax and semantics and they are categorized into three groups. 1. statistical-based features Contreras et al. ( 2018 ); Kumar et al. ( 2019 ); Mathias and Bhattacharyya ( 2018a ; b ) 2. Style-based (Syntax) features Cummins et al. ( 2016 ); Darwish and Mohamed ( 2020 ); Ke et al. ( 2019 ). 3. Content-based features Dong et al. ( 2017 ). A good set of features appropriate models evolved better AES systems. The vast majority of the researchers are using regression models if features are statistical-based. For Neural Networks models, researches are using both style-based and content-based features. The following table shows the list of various features used in existing AES Systems. Table Table4 4 represents all set of features used for essay grading.
Types of features
We studied all the feature extracting NLP libraries as shown in Fig. Fig.3. that 3 . that are used in the papers. The NLTK is an NLP tool used to retrieve statistical features like POS, word count, sentence count, etc. With NLTK, we can miss the essay's semantic features. To find semantic features Word2Vec Mikolov et al. ( 2013 ), GloVe Jeffrey Pennington et al. ( 2014 ) is the most used libraries to retrieve the semantic text from the essays. And in some systems, they directly trained the model with word embeddings to find the score. From Fig. Fig.4 4 as observed that non-content-based feature extraction is higher than content-based.

Usages of tools

Number of papers on content based features
RQ3 which are the evaluation metrics available for measuring the accuracy of algorithms?
The majority of the AES systems are using three evaluation metrics. They are (1) quadrated weighted kappa (QWK) (2) Mean Absolute Error (MAE) (3) Pearson Correlation Coefficient (PCC) Shehab et al. ( 2016 ). The quadratic weighted kappa will find agreement between human evaluation score and system evaluation score and produces value ranging from 0 to 1. And the Mean Absolute Error is the actual difference between human-rated score to system-generated score. The mean square error (MSE) measures the average squares of the errors, i.e., the average squared difference between the human-rated and the system-generated scores. MSE will always give positive numbers only. Pearson's Correlation Coefficient (PCC) finds the correlation coefficient between two variables. It will provide three values (0, 1, − 1). "0" represents human-rated and system scores that are not related. "1" represents an increase in the two scores. "− 1" illustrates a negative relationship between the two scores.
RQ4 what are the Machine Learning techniques being used for automatic essay grading, and how are they implemented?
After scrutinizing all documents, we categorize the techniques used in automated essay grading systems into four baskets. 1. Regression techniques. 2. Classification model. 3. Neural networks. 4. Ontology-based approach.
All the existing AES systems developed in the last ten years employ supervised learning techniques. Researchers using supervised methods viewed the AES system as either regression or classification task. The goal of the regression task is to predict the score of an essay. The classification task is to classify the essays belonging to (low, medium, or highly) relevant to the question's topic. Since the last three years, most AES systems developed made use of the concept of the neural network.
Regression based models
Mohler and Mihalcea ( 2009 ). proposed text-to-text semantic similarity to assign a score to the student essays. There are two text similarity measures like Knowledge-based measures, corpus-based measures. There eight knowledge-based tests with all eight models. They found the similarity. The shortest path similarity determines based on the length, which shortest path between two contexts. Leacock & Chodorow find the similarity based on the shortest path's length between two concepts using node-counting. The Lesk similarity finds the overlap between the corresponding definitions, and Wu & Palmer algorithm finds similarities based on the depth of two given concepts in the wordnet taxonomy. Resnik, Lin, Jiang&Conrath, Hirst& St-Onge find the similarity based on different parameters like the concept, probability, normalization factor, lexical chains. In corpus-based likeness, there LSA BNC, LSA Wikipedia, and ESA Wikipedia, latent semantic analysis is trained on Wikipedia and has excellent domain knowledge. Among all similarity scores, correlation scores LSA Wikipedia scoring accuracy is more. But these similarity measure algorithms are not using NLP concepts. These models are before 2010 and basic concept models to continue the research automated essay grading with updated algorithms on neural networks with content-based features.
Adamson et al. ( 2014 ) proposed an automatic essay grading system which is a statistical-based approach in this they retrieved features like POS, Character count, Word count, Sentence count, Miss spelled words, n-gram representation of words to prepare essay vector. They formed a matrix with these all vectors in that they applied LSA to give a score to each essay. It is a statistical approach that doesn’t consider the semantics of the essay. The accuracy they got when compared to the human rater score with the system is 0.532.
Cummins et al. ( 2016 ). Proposed Timed Aggregate Perceptron vector model to give ranking to all the essays, and later they converted the rank algorithm to predict the score of the essay. The model trained with features like Word unigrams, bigrams, POS, Essay length, grammatical relation, Max word length, sentence length. It is multi-task learning, gives ranking to the essays, and predicts the score for the essay. The performance evaluated through QWK is 0.69, a substantial agreement between the human rater and the system.
Sultan et al. ( 2016 ). Proposed a Ridge regression model to find short answer scoring with Question Demoting. Question Demoting is the new concept included in the essay's final assessment to eliminate duplicate words from the essay. The extracted features are Text Similarity, which is the similarity between the student response and reference answer. Question Demoting is the number of repeats in a student response. With inverse document frequency, they assigned term weight. The sentence length Ratio is the number of words in the student response, is another feature. With these features, the Ridge regression model was used, and the accuracy they got 0.887.
Contreras et al. ( 2018 ). Proposed Ontology based on text mining in this model has given a score for essays in phases. In phase-I, they generated ontologies with ontoGen and SVM to find the concept and similarity in the essay. In phase II from ontologies, they retrieved features like essay length, word counts, correctness, vocabulary, and types of word used, domain information. After retrieving statistical data, they used a linear regression model to find the score of the essay. The accuracy score is the average of 0.5.
Darwish and Mohamed ( 2020 ) proposed the fusion of fuzzy Ontology with LSA. They retrieve two types of features, like syntax features and semantic features. In syntax features, they found Lexical Analysis with tokens, and they construct a parse tree. If the parse tree is broken, the essay is inconsistent—a separate grade assigned to the essay concerning syntax features. The semantic features are like similarity analysis, Spatial Data Analysis. Similarity analysis is to find duplicate sentences—Spatial Data Analysis for finding Euclid distance between the center and part. Later they combine syntax features and morphological features score for the final score. The accuracy they achieved with the multiple linear regression model is 0.77, mostly on statistical features.
Süzen Neslihan et al. ( 2020 ) proposed a text mining approach for short answer grading. First, their comparing model answers with student response by calculating the distance between two sentences. By comparing the model answer with student response, they find the essay's completeness and provide feedback. In this approach, model vocabulary plays a vital role in grading, and with this model vocabulary, the grade will be assigned to the student's response and provides feedback. The correlation between the student answer to model answer is 0.81.
Classification based Models
Persing and Ng ( 2013 ) used a support vector machine to score the essay. The features extracted are OS, N-gram, and semantic text to train the model and identified the keywords from the essay to give the final score.
Sakaguchi et al. ( 2015 ) proposed two methods: response-based and reference-based. In response-based scoring, the extracted features are response length, n-gram model, and syntactic elements to train the support vector regression model. In reference-based scoring, features such as sentence similarity using word2vec is used to find the cosine similarity of the sentences that is the final score of the response. First, the scores were discovered individually and later combined two features to find a final score. This system gave a remarkable increase in performance by combining the scores.
Mathias and Bhattacharyya ( 2018a ; b ) Proposed Automated Essay Grading Dataset with Essay Attribute Scores. The first concept features selection depends on the essay type. So the common attributes are Content, Organization, Word Choice, Sentence Fluency, Conventions. In this system, each attribute is scored individually, with the strength of each attribute identified. The model they used is a random forest classifier to assign scores to individual attributes. The accuracy they got with QWK is 0.74 for prompt 1 of the ASAS dataset ( https://www.kaggle.com/c/asap-sas/ ).
Ke et al. ( 2019 ) used a support vector machine to find the response score. In this method, features like Agreeability, Specificity, Clarity, Relevance to prompt, Conciseness, Eloquence, Confidence, Direction of development, Justification of opinion, and Justification of importance. First, the individual parameter score obtained was later combined with all scores to give a final response score. The features are used in the neural network to find whether the sentence is relevant to the topic or not.
Salim et al. ( 2019 ) proposed an XGBoost Machine Learning classifier to assess the essays. The algorithm trained on features like word count, POS, parse tree depth, and coherence in the articles with sentence similarity percentage; cohesion and coherence are considered for training. And they implemented K-fold cross-validation for a result the average accuracy after specific validations is 68.12.
Neural network models
Shehab et al. ( 2016 ) proposed a neural network method that used learning vector quantization to train human scored essays. After training, the network can provide a score to the ungraded essays. First, we should process the essay to remove Spell checking and then perform preprocessing steps like Document Tokenization, stop word removal, Stemming, and submit it to the neural network. Finally, the model will provide feedback on the essay, whether it is relevant to the topic. And the correlation coefficient between human rater and system score is 0.7665.
Kopparapu and De ( 2016 ) proposed the Automatic Ranking of Essays using Structural and Semantic Features. This approach constructed a super essay with all the responses. Next, ranking for a student essay is done based on the super-essay. The structural and semantic features derived helps to obtain the scores. In a paragraph, 15 Structural features like an average number of sentences, the average length of sentences, and the count of words, nouns, verbs, adjectives, etc., are used to obtain a syntactic score. A similarity score is used as semantic features to calculate the overall score.
Dong and Zhang ( 2016 ) proposed a hierarchical CNN model. The model builds two layers with word embedding to represents the words as the first layer. The second layer is a word convolution layer with max-pooling to find word vectors. The next layer is a sentence-level convolution layer with max-pooling to find the sentence's content and synonyms. A fully connected dense layer produces an output score for an essay. The accuracy with the hierarchical CNN model resulted in an average QWK of 0.754.
Taghipour and Ng ( 2016 ) proposed a first neural approach for essay scoring build in which convolution and recurrent neural network concepts help in scoring an essay. The network uses a lookup table with the one-hot representation of the word vector of an essay. The final efficiency of the network model with LSTM resulted in an average QWK of 0.708.
Dong et al. ( 2017 ). Proposed an Attention-based scoring system with CNN + LSTM to score an essay. For CNN, the input parameters were character embedding and word embedding, and it has attention pooling layers and used NLTK to obtain word and character embedding. The output gives a sentence vector, which provides sentence weight. After CNN, it will have an LSTM layer with an attention pooling layer, and this final layer results in the final score of the responses. The average QWK score is 0.764.
Riordan et al. ( 2017 ) proposed a neural network with CNN and LSTM layers. Word embedding, given as input to a neural network. An LSTM network layer will retrieve the window features and delivers them to the aggregation layer. The aggregation layer is a superficial layer that takes a correct window of words and gives successive layers to predict the answer's sore. The accuracy of the neural network resulted in a QWK of 0.90.
Zhao et al. ( 2017 ) proposed a new concept called Memory-Augmented Neural network with four layers, input representation layer, memory addressing layer, memory reading layer, and output layer. An input layer represents all essays in a vector form based on essay length. After converting the word vector, the memory addressing layer takes a sample of the essay and weighs all the terms. The memory reading layer takes the input from memory addressing segment and finds the content to finalize the score. Finally, the output layer will provide the final score of the essay. The accuracy of essay scores is 0.78, which is far better than the LSTM neural network.
Mathias and Bhattacharyya ( 2018a ; b ) proposed deep learning networks using LSTM with the CNN layer and GloVe pre-trained word embeddings. For this, they retrieved features like Sentence count essays, word count per sentence, Number of OOVs in the sentence, Language model score, and the text's perplexity. The network predicted the goodness scores of each essay. The higher the goodness scores, means higher the rank and vice versa.
Nguyen and Dery ( 2016 ). Proposed Neural Networks for Automated Essay Grading. In this method, a single layer bi-directional LSTM accepting word vector as input. Glove vectors used in this method resulted in an accuracy of 90%.
Ruseti et al. ( 2018 ) proposed a recurrent neural network that is capable of memorizing the text and generate a summary of an essay. The Bi-GRU network with the max-pooling layer molded on the word embedding of each document. It will provide scoring to the essay by comparing it with a summary of the essay from another Bi-GRU network. The result obtained an accuracy of 0.55.
Wang et al. ( 2018a ; b ) proposed an automatic scoring system with the bi-LSTM recurrent neural network model and retrieved the features using the word2vec technique. This method generated word embeddings from the essay words using the skip-gram model. And later, word embedding is used to train the neural network to find the final score. The softmax layer in LSTM obtains the importance of each word. This method used a QWK score of 0.83%.
Dasgupta et al. ( 2018 ) proposed a technique for essay scoring with augmenting textual qualitative Features. It extracted three types of linguistic, cognitive, and psychological features associated with a text document. The linguistic features are Part of Speech (POS), Universal Dependency relations, Structural Well-formedness, Lexical Diversity, Sentence Cohesion, Causality, and Informativeness of the text. The psychological features derived from the Linguistic Information and Word Count (LIWC) tool. They implemented a convolution recurrent neural network that takes input as word embedding and sentence vector, retrieved from the GloVe word vector. And the second layer is the Convolution Layer to find local features. The next layer is the recurrent neural network (LSTM) to find corresponding of the text. The accuracy of this method resulted in an average QWK of 0.764.
Liang et al. ( 2018 ) proposed a symmetrical neural network AES model with Bi-LSTM. They are extracting features from sample essays and student essays and preparing an embedding layer as input. The embedding layer output is transfer to the convolution layer from that LSTM will be trained. Hear the LSRM model has self-features extraction layer, which will find the essay's coherence. The average QWK score of SBLSTMA is 0.801.
Liu et al. ( 2019 ) proposed two-stage learning. In the first stage, they are assigning a score based on semantic data from the essay. The second stage scoring is based on some handcrafted features like grammar correction, essay length, number of sentences, etc. The average score of the two stages is 0.709.
Pedro Uria Rodriguez et al. ( 2019 ) proposed a sequence-to-sequence learning model for automatic essay scoring. They used BERT (Bidirectional Encoder Representations from Transformers), which extracts the semantics from a sentence from both directions. And XLnet sequence to sequence learning model to extract features like the next sentence in an essay. With this pre-trained model, they attained coherence from the essay to give the final score. The average QWK score of the model is 75.5.
Xia et al. ( 2019 ) proposed a two-layer Bi-directional LSTM neural network for the scoring of essays. The features extracted with word2vec to train the LSTM and accuracy of the model in an average of QWK is 0.870.
Kumar et al. ( 2019 ) Proposed an AutoSAS for short answer scoring. It used pre-trained Word2Vec and Doc2Vec models trained on Google News corpus and Wikipedia dump, respectively, to retrieve the features. First, they tagged every word POS and they found weighted words from the response. It also found prompt overlap to observe how the answer is relevant to the topic, and they defined lexical overlaps like noun overlap, argument overlap, and content overlap. This method used some statistical features like word frequency, difficulty, diversity, number of unique words in each response, type-token ratio, statistics of the sentence, word length, and logical operator-based features. This method uses a random forest model to train the dataset. The data set has sample responses with their associated score. The model will retrieve the features from both responses like graded and ungraded short answers with questions. The accuracy of AutoSAS with QWK is 0.78. It will work on any topics like Science, Arts, Biology, and English.
Jiaqi Lun et al. ( 2020 ) proposed an automatic short answer scoring with BERT. In this with a reference answer comparing student responses and assigning scores. The data augmentation is done with a neural network and with one correct answer from the dataset classifying reaming responses as correct or incorrect.
Zhu and Sun ( 2020 ) proposed a multimodal Machine Learning approach for automated essay scoring. First, they count the grammar score with the spaCy library and numerical count as the number of words and sentences with the same library. With this input, they trained a single and Bi LSTM neural network for finding the final score. For the LSTM model, they prepared sentence vectors with GloVe and word embedding with NLTK. Bi-LSTM will check each sentence in both directions to find semantic from the essay. The average QWK score with multiple models is 0.70.
Ontology based approach
Mohler et al. ( 2011 ) proposed a graph-based method to find semantic similarity in short answer scoring. For the ranking of answers, they used the support vector regression model. The bag of words is the main feature extracted in the system.
Ramachandran et al. ( 2015 ) also proposed a graph-based approach to find lexical based semantics. Identified phrase patterns and text patterns are the features to train a random forest regression model to score the essays. The accuracy of the model in a QWK is 0.78.
Zupanc et al. ( 2017 ) proposed sentence similarity networks to find the essay's score. Ajetunmobi and Daramola ( 2017 ) recommended an ontology-based information extraction approach and domain-based ontology to find the score.
Speech response scoring
Automatic scoring is in two ways one is text-based scoring, other is speech-based scoring. This paper discussed text-based scoring and its challenges, and now we cover speech scoring and common points between text and speech-based scoring. Evanini and Wang ( 2013 ), Worked on speech scoring of non-native school students, extracted features with speech ratter, and trained a linear regression model, concluding that accuracy varies based on voice pitching. Loukina et al. ( 2015 ) worked on feature selection from speech data and trained SVM. Malinin et al. ( 2016 ) used neural network models to train the data. Loukina et al. ( 2017 ). Proposed speech and text-based automatic scoring. Extracted text-based features, speech-based features and trained a deep neural network for speech-based scoring. They extracted 33 types of features based on acoustic signals. Malinin et al. ( 2017 ). Wu Xixin et al. ( 2020 ) Worked on deep neural networks for spoken language assessment. Incorporated different types of models and tested them. Ramanarayanan et al. ( 2017 ) worked on feature extraction methods and extracted punctuation, fluency, and stress and trained different Machine Learning models for scoring. Knill et al. ( 2018 ). Worked on Automatic speech recognizer and its errors how its impacts the speech assessment.
The state of the art
This section provides an overview of the existing AES systems with a comparative study w. r. t models, features applied, datasets, and evaluation metrics used for building the automated essay grading systems. We divided all 62 papers into two sets of the first set of review papers in Table Table5 5 with a comparative study of the AES systems.
State of the art
Comparison of all approaches
In our study, we divided major AES approaches into three categories. Regression models, classification models, and neural network models. The regression models failed to find cohesion and coherence from the essay because it trained on BoW(Bag of Words) features. In processing data from input to output, the regression models are less complicated than neural networks. There are unable to find many intricate patterns from the essay and unable to find sentence connectivity. If we train the model with BoW features in the neural network approach, the model never considers the essay's coherence and coherence.
First, to train a Machine Learning algorithm with essays, all the essays are converted to vector form. We can form a vector with BoW and Word2vec, TF-IDF. The BoW and Word2vec vector representation of essays represented in Table Table6. 6 . The vector representation of BoW with TF-IDF is not incorporating the essays semantic, and it’s just statistical learning from a given vector. Word2vec vector comprises semantic of essay in a unidirectional way.
Vector representation of essays
In BoW, the vector contains the frequency of word occurrences in the essay. The vector represents 1 and more based on the happenings of words in the essay and 0 for not present. So, in BoW, the vector does not maintain the relationship with adjacent words; it’s just for single words. In word2vec, the vector represents the relationship between words with other words and sentences prompt in multiple dimensional ways. But word2vec prepares vectors in a unidirectional way, not in a bidirectional way; word2vec fails to find semantic vectors when a word has two meanings, and the meaning depends on adjacent words. Table Table7 7 represents a comparison of Machine Learning models and features extracting methods.
Comparison of models
In AES, cohesion and coherence will check the content of the essay concerning the essay prompt these can be extracted from essay in the vector from. Two more parameters are there to access an essay is completeness and feedback. Completeness will check whether student’s response is sufficient or not though the student wrote correctly. Table Table8 8 represents all four parameters comparison for essay grading. Table Table9 9 illustrates comparison of all approaches based on various features like grammar, spelling, organization of essay, relevance.
Comparison of all models with respect to cohesion, coherence, completeness, feedback
comparison of all approaches on various features
What are the challenges/limitations in the current research?
From our study and results discussed in the previous sections, many researchers worked on automated essay scoring systems with numerous techniques. We have statistical methods, classification methods, and neural network approaches to evaluate the essay automatically. The main goal of the automated essay grading system is to reduce human effort and improve consistency.
The vast majority of essay scoring systems are dealing with the efficiency of the algorithm. But there are many challenges in automated essay grading systems. One should assess the essay by following parameters like the relevance of the content to the prompt, development of ideas, Cohesion, Coherence, and domain knowledge.
No model works on the relevance of content, which means whether student response or explanation is relevant to the given prompt or not if it is relevant to how much it is appropriate, and there is no discussion about the cohesion and coherence of the essays. All researches concentrated on extracting the features using some NLP libraries, trained their models, and testing the results. But there is no explanation in the essay evaluation system about consistency and completeness, But Palma and Atkinson ( 2018 ) explained coherence-based essay evaluation. And Zupanc and Bosnic ( 2014 ) also used the word coherence to evaluate essays. And they found consistency with latent semantic analysis (LSA) for finding coherence from essays, but the dictionary meaning of coherence is "The quality of being logical and consistent."
Another limitation is there is no domain knowledge-based evaluation of essays using Machine Learning models. For example, the meaning of a cell is different from biology to physics. Many Machine Learning models extract features with WordVec and GloVec; these NLP libraries cannot convert the words into vectors when they have two or more meanings.
Other challenges that influence the Automated Essay Scoring Systems.
All these approaches worked to improve the QWK score of their models. But QWK will not assess the model in terms of features extraction and constructed irrelevant answers. The QWK is not evaluating models whether the model is correctly assessing the answer or not. There are many challenges concerning students' responses to the Automatic scoring system. Like in evaluating approach, no model has examined how to evaluate the constructed irrelevant and adversarial answers. Especially the black box type of approaches like deep learning models provides more options to the students to bluff the automated scoring systems.
The Machine Learning models that work on statistical features are very vulnerable. Based on Powers et al. ( 2001 ) and Bejar Isaac et al. ( 2014 ), the E-rater was failed on Constructed Irrelevant Responses Strategy (CIRS). From the study of Bejar et al. ( 2013 ), Higgins and Heilman ( 2014 ), observed that when student response contain irrelevant content or shell language concurring to prompt will influence the final score of essays in an automated scoring system.
In deep learning approaches, most of the models automatically read the essay's features, and some methods work on word-based embedding and other character-based embedding features. From the study of Riordan Brain et al. ( 2019 ), The character-based embedding systems do not prioritize spelling correction. However, it is influencing the final score of the essay. From the study of Horbach and Zesch ( 2019 ), Various factors are influencing AES systems. For example, there are data set size, prompt type, answer length, training set, and human scorers for content-based scoring.
Ding et al. ( 2020 ) reviewed that the automated scoring system is vulnerable when a student response contains more words from prompt, like prompt vocabulary repeated in the response. Parekh et al. ( 2020 ) and Kumar et al. ( 2020 ) tested various neural network models of AES by iteratively adding important words, deleting unimportant words, shuffle the words, and repeating sentences in an essay and found that no change in the final score of essays. These neural network models failed to recognize common sense in adversaries' essays and give more options for the students to bluff the automated systems.
Other than NLP and ML techniques for AES. From Wresch ( 1993 ) to Madnani and Cahill ( 2018 ). discussed the complexity of AES systems, standards need to be followed. Like assessment rubrics to test subject knowledge, irrelevant responses, and ethical aspects of an algorithm like measuring the fairness of student response.
Fairness is an essential factor for automated systems. For example, in AES, fairness can be measure in an agreement between human score to machine score. Besides this, From Loukina et al. ( 2019 ), the fairness standards include overall score accuracy, overall score differences, and condition score differences between human and system scores. In addition, scoring different responses in the prospect of constructive relevant and irrelevant will improve fairness.
Madnani et al. ( 2017a ; b ). Discussed the fairness of AES systems for constructed responses and presented RMS open-source tool for detecting biases in the models. With this, one can change fairness standards according to their analysis of fairness.
From Berzak et al.'s ( 2018 ) approach, behavior factors are a significant challenge in automated scoring systems. That helps to find language proficiency, word characteristics (essential words from the text), predict the critical patterns from the text, find related sentences in an essay, and give a more accurate score.
Rupp ( 2018 ), has discussed the designing, evaluating, and deployment methodologies for AES systems. They provided notable characteristics of AES systems for deployment. They are like model performance, evaluation metrics for a model, threshold values, dynamically updated models, and framework.
First, we should check the model performance on different datasets and parameters for operational deployment. Selecting Evaluation metrics for AES models are like QWK, correlation coefficient, or sometimes both. Kelley and Preacher ( 2012 ) have discussed three categories of threshold values: marginal, borderline, and acceptable. The values can be varied based on data size, model performance, type of model (single scoring, multiple scoring models). Once a model is deployed and evaluates millions of responses every time for optimal responses, we need a dynamically updated model based on prompt and data. Finally, framework designing of AES model, hear a framework contains prompts where test-takers can write the responses. One can design two frameworks: a single scoring model for a single methodology and multiple scoring models for multiple concepts. When we deploy multiple scoring models, each prompt could be trained separately, or we can provide generalized models for all prompts with this accuracy may vary, and it is challenging.
Our Systematic literature review on the automated essay grading system first collected 542 papers with selected keywords from various databases. After inclusion and exclusion criteria, we left with 139 articles; on these selected papers, we applied Quality assessment criteria with two reviewers, and finally, we selected 62 writings for final review.
Our observations on automated essay grading systems from 2010 to 2020 are as followed:
- The implementation techniques of automated essay grading systems are classified into four buckets; there are 1. regression models 2. Classification models 3. Neural networks 4. Ontology-based methodology, but using neural networks, the researchers are more accurate than other techniques, and all the methods state of the art provided in Table Table3 3 .
- The majority of the regression and classification models on essay scoring used statistical features to find the final score. It means the systems or models trained on such parameters as word count, sentence count, etc. though the parameters extracted from the essay, the algorithm are not directly training on essays. The algorithms trained on some numbers obtained from the essay and hear if numbers matched the composition will get a good score; otherwise, the rating is less. In these models, the evaluation process is entirely on numbers, irrespective of the essay. So, there is a lot of chance to miss the coherence, relevance of the essay if we train our algorithm on statistical parameters.
- In the neural network approach, the models trained on Bag of Words (BoW) features. The BoW feature is missing the relationship between a word to word and the semantic meaning of the sentence. E.g., Sentence 1: John killed bob. Sentence 2: bob killed John. In these two sentences, the BoW is "John," "killed," "bob."
- In the Word2Vec library, if we are prepared a word vector from an essay in a unidirectional way, the vector will have a dependency with other words and finds the semantic relationship with other words. But if a word has two or more meanings like "Bank loan" and "River Bank," hear bank has two implications, and its adjacent words decide the sentence meaning; in this case, Word2Vec is not finding the real meaning of the word from the sentence.
- The features extracted from essays in the essay scoring system are classified into 3 type's features like statistical features, style-based features, and content-based features, which are explained in RQ2 and Table Table3. 3 . But statistical features, are playing a significant role in some systems and negligible in some systems. In Shehab et al. ( 2016 ); Cummins et al. ( 2016 ). Dong et al. ( 2017 ). Dong and Zhang ( 2016 ). Mathias and Bhattacharyya ( 2018a ; b ) Systems the assessment is entirely on statistical and style-based features they have not retrieved any content-based features. And in other systems that extract content from the essays, the role of statistical features is for only preprocessing essays but not included in the final grading.
- In AES systems, coherence is the main feature to be considered while evaluating essays. The actual meaning of coherence is to stick together. That is the logical connection of sentences (local level coherence) and paragraphs (global level coherence) in a story. Without coherence, all sentences in a paragraph are independent and meaningless. In an Essay, coherence is a significant feature that is explaining everything in a flow and its meaning. It is a powerful feature in AES system to find the semantics of essay. With coherence, one can assess whether all sentences are connected in a flow and all paragraphs are related to justify the prompt. Retrieving the coherence level from an essay is a critical task for all researchers in AES systems.
- In automatic essay grading systems, the assessment of essays concerning content is critical. That will give the actual score for the student. Most of the researches used statistical features like sentence length, word count, number of sentences, etc. But according to collected results, 32% of the systems used content-based features for the essay scoring. Example papers which are on content-based assessment are Taghipour and Ng ( 2016 ); Persing and Ng ( 2013 ); Wang et al. ( 2018a , 2018b ); Zhao et al. ( 2017 ); Kopparapu and De ( 2016 ), Kumar et al. ( 2019 ); Mathias and Bhattacharyya ( 2018a ; b ); Mohler and Mihalcea ( 2009 ) are used content and statistical-based features. The results are shown in Fig. Fig.3. 3 . And mainly the content-based features extracted with word2vec NLP library, but word2vec is capable of capturing the context of a word in a document, semantic and syntactic similarity, relation with other terms, but word2vec is capable of capturing the context word in a uni-direction either left or right. If a word has multiple meanings, there is a chance of missing the context in the essay. After analyzing all the papers, we found that content-based assessment is a qualitative assessment of essays.
- On the other hand, Horbach and Zesch ( 2019 ); Riordan Brain et al. ( 2019 ); Ding et al. ( 2020 ); Kumar et al. ( 2020 ) proved that neural network models are vulnerable when a student response contains constructed irrelevant, adversarial answers. And a student can easily bluff an automated scoring system by submitting different responses like repeating sentences and repeating prompt words in an essay. From Loukina et al. ( 2019 ), and Madnani et al. ( 2017b ). The fairness of an algorithm is an essential factor to be considered in AES systems.
- While talking about speech assessment, the data set contains audios of duration up to one minute. Feature extraction techniques are entirely different from text assessment, and accuracy varies based on speaking fluency, pitching, male to female voice and boy to adult voice. But the training algorithms are the same for text and speech assessment.
- Once an AES system evaluates essays and short answers accurately in all directions, there is a massive demand for automated systems in the educational and related world. Now AES systems are deployed in GRE, TOEFL exams; other than these, we can deploy AES systems in massive open online courses like Coursera(“ https://coursera.org/learn//machine-learning//exam ”), NPTEL ( https://swayam.gov.in/explorer ), etc. still they are assessing student performance with multiple-choice questions. In another perspective, AES systems can be deployed in information retrieval systems like Quora, stack overflow, etc., to check whether the retrieved response is appropriate to the question or not and can give ranking to the retrieved answers.
Conclusion and future work
As per our Systematic literature review, we studied 62 papers. There exist significant challenges for researchers in implementing automated essay grading systems. Several researchers are working rigorously on building a robust AES system despite its difficulty in solving this problem. All evaluating methods are not evaluated based on coherence, relevance, completeness, feedback, and knowledge-based. And 90% of essay grading systems are used Kaggle ASAP (2012) dataset, which has general essays from students and not required any domain knowledge, so there is a need for domain-specific essay datasets to train and test. Feature extraction is with NLTK, WordVec, and GloVec NLP libraries; these libraries have many limitations while converting a sentence into vector form. Apart from feature extraction and training Machine Learning models, no system is accessing the essay's completeness. No system provides feedback to the student response and not retrieving coherence vectors from the essay—another perspective the constructive irrelevant and adversarial student responses still questioning AES systems.
Our proposed research work will go on the content-based assessment of essays with domain knowledge and find a score for the essays with internal and external consistency. And we will create a new dataset concerning one domain. And another area in which we can improve is the feature extraction techniques.
This study includes only four digital databases for study selection may miss some functional studies on the topic. However, we hope that we covered most of the significant studies as we manually collected some papers published in useful journals.
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Not Applicable.
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Contributor Information
Dadi Ramesh, Email: moc.liamg@44hsemaridad .
Suresh Kumar Sanampudi, Email: ni.ca.hutnj@idupmanashserus .
- Adamson, A., Lamb, A., & December, R. M. (2014). Automated Essay Grading.
- Ajay HB, Tillett PI, Page EB (1973) Analysis of essays by computer (AEC-II) (No. 8-0102). Washington, DC: U.S. Department of Health, Education, and Welfare, Office of Education, National Center for Educational Research and Development
- Ajetunmobi SA, Daramola O (2017) Ontology-based information extraction for subject-focussed automatic essay evaluation. In: 2017 International Conference on Computing Networking and Informatics (ICCNI) p 1–6. IEEE
- Alva-Manchego F, et al. (2019) EASSE: Easier Automatic Sentence Simplification Evaluation.” ArXiv abs/1908.04567 (2019): n. pag
- Bailey S, Meurers D (2008) Diagnosing meaning errors in short answers to reading comprehension questions. In: Proceedings of the Third Workshop on Innovative Use of NLP for Building Educational Applications (Columbus), p 107–115
- Basu S, Jacobs C, Vanderwende L. Powergrading: a clustering approach to amplify human effort for short answer grading. Trans Assoc Comput Linguist (TACL) 2013; 1 :391–402. doi: 10.1162/tacl_a_00236. [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Bejar, I. I., Flor, M., Futagi, Y., & Ramineni, C. (2014). On the vulnerability of automated scoring to construct-irrelevant response strategies (CIRS): An illustration. Assessing Writing, 22, 48-59.
- Bejar I, et al. (2013) Length of Textual Response as a Construct-Irrelevant Response Strategy: The Case of Shell Language. Research Report. ETS RR-13-07.” ETS Research Report Series (2013): n. pag
- Berzak Y, et al. (2018) “Assessing Language Proficiency from Eye Movements in Reading.” ArXiv abs/1804.07329 (2018): n. pag
- Blanchard D, Tetreault J, Higgins D, Cahill A, Chodorow M (2013) TOEFL11: A corpus of non-native English. ETS Research Report Series, 2013(2):i–15, 2013
- Blood, I. (2011). Automated essay scoring: a literature review. Studies in Applied Linguistics and TESOL, 11(2).
- Burrows S, Gurevych I, Stein B. The eras and trends of automatic short answer grading. Int J Artif Intell Educ. 2015; 25 :60–117. doi: 10.1007/s40593-014-0026-8. [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Cader, A. (2020, July). The Potential for the Use of Deep Neural Networks in e-Learning Student Evaluation with New Data Augmentation Method. In International Conference on Artificial Intelligence in Education (pp. 37–42). Springer, Cham.
- Cai C (2019) Automatic essay scoring with recurrent neural network. In: Proceedings of the 3rd International Conference on High Performance Compilation, Computing and Communications (2019): n. pag.
- Chen M, Li X (2018) "Relevance-Based Automated Essay Scoring via Hierarchical Recurrent Model. In: 2018 International Conference on Asian Language Processing (IALP), Bandung, Indonesia, 2018, p 378–383, doi: 10.1109/IALP.2018.8629256
- Chen Z, Zhou Y (2019) "Research on Automatic Essay Scoring of Composition Based on CNN and OR. In: 2019 2nd International Conference on Artificial Intelligence and Big Data (ICAIBD), Chengdu, China, p 13–18, doi: 10.1109/ICAIBD.2019.8837007
- Contreras JO, Hilles SM, Abubakar ZB (2018) Automated essay scoring with ontology based on text mining and NLTK tools. In: 2018 International Conference on Smart Computing and Electronic Enterprise (ICSCEE), 1-6
- Correnti R, Matsumura LC, Hamilton L, Wang E. Assessing students’ skills at writing analytically in response to texts. Elem Sch J. 2013; 114 (2):142–177. doi: 10.1086/671936. [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Cummins, R., Zhang, M., & Briscoe, E. (2016, August). Constrained multi-task learning for automated essay scoring. Association for Computational Linguistics.
- Darwish SM, Mohamed SK (2020) Automated essay evaluation based on fusion of fuzzy ontology and latent semantic analysis. In: Hassanien A, Azar A, Gaber T, Bhatnagar RF, Tolba M (eds) The International Conference on Advanced Machine Learning Technologies and Applications
- Dasgupta T, Naskar A, Dey L, Saha R (2018) Augmenting textual qualitative features in deep convolution recurrent neural network for automatic essay scoring. In: Proceedings of the 5th Workshop on Natural Language Processing Techniques for Educational Applications p 93–102
- Ding Y, et al. (2020) "Don’t take “nswvtnvakgxpm” for an answer–The surprising vulnerability of automatic content scoring systems to adversarial input." In: Proceedings of the 28th International Conference on Computational Linguistics
- Dong F, Zhang Y (2016) Automatic features for essay scoring–an empirical study. In: Proceedings of the 2016 Conference on Empirical Methods in Natural Language Processing p 1072–1077
- Dong F, Zhang Y, Yang J (2017) Attention-based recurrent convolutional neural network for automatic essay scoring. In: Proceedings of the 21st Conference on Computational Natural Language Learning (CoNLL 2017) p 153–162
- Dzikovska M, Nielsen R, Brew C, Leacock C, Gi ampiccolo D, Bentivogli L, Clark P, Dagan I, Dang HT (2013a) Semeval-2013 task 7: The joint student response analysis and 8th recognizing textual entailment challenge
- Dzikovska MO, Nielsen R, Brew C, Leacock C, Giampiccolo D, Bentivogli L, Clark P, Dagan I, Trang Dang H (2013b) SemEval-2013 Task 7: The Joint Student Response Analysis and 8th Recognizing Textual Entailment Challenge. *SEM 2013: The First Joint Conference on Lexical and Computational Semantics
- Educational Testing Service (2008) CriterionSM online writing evaluation service. Retrieved from http://www.ets.org/s/criterion/pdf/9286_CriterionBrochure.pdf .
- Evanini, K., & Wang, X. (2013, August). Automated speech scoring for non-native middle school students with multiple task types. In INTERSPEECH (pp. 2435–2439).
- Foltz PW, Laham D, Landauer TK (1999) The Intelligent Essay Assessor: Applications to Educational Technology. Interactive Multimedia Electronic Journal of Computer-Enhanced Learning, 1, 2, http://imej.wfu.edu/articles/1999/2/04/ index.asp
- Granger, S., Dagneaux, E., Meunier, F., & Paquot, M. (Eds.). (2009). International corpus of learner English. Louvain-la-Neuve: Presses universitaires de Louvain.
- Higgins D, Heilman M. Managing what we can measure: quantifying the susceptibility of automated scoring systems to gaming behavior” Educ Meas Issues Pract. 2014; 33 :36–46. doi: 10.1111/emip.12036. [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Horbach A, Zesch T. The influence of variance in learner answers on automatic content scoring. Front Educ. 2019; 4 :28. doi: 10.3389/feduc.2019.00028. [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- https://www.coursera.org/learn/machine-learning/exam/7pytE/linear-regression-with-multiple-variables/attempt
- Hussein, M. A., Hassan, H., & Nassef, M. (2019). Automated language essay scoring systems: A literature review. PeerJ Computer Science, 5, e208. [ PMC free article ] [ PubMed ]
- Ke Z, Ng V (2019) “Automated essay scoring: a survey of the state of the art.” IJCAI
- Ke, Z., Inamdar, H., Lin, H., & Ng, V. (2019, July). Give me more feedback II: Annotating thesis strength and related attributes in student essays. In Proceedings of the 57th Annual Meeting of the Association for Computational Linguistics (pp. 3994-4004).
- Kelley K, Preacher KJ. On effect size. Psychol Methods. 2012; 17 (2):137–152. doi: 10.1037/a0028086. [ PubMed ] [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Kitchenham B, Brereton OP, Budgen D, Turner M, Bailey J, Linkman S. Systematic literature reviews in software engineering–a systematic literature review. Inf Softw Technol. 2009; 51 (1):7–15. doi: 10.1016/j.infsof.2008.09.009. [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Klebanov, B. B., & Madnani, N. (2020, July). Automated evaluation of writing–50 years and counting. In Proceedings of the 58th Annual Meeting of the Association for Computational Linguistics (pp. 7796–7810).
- Knill K, Gales M, Kyriakopoulos K, et al. (4 more authors) (2018) Impact of ASR performance on free speaking language assessment. In: Interspeech 2018.02–06 Sep 2018, Hyderabad, India. International Speech Communication Association (ISCA)
- Kopparapu SK, De A (2016) Automatic ranking of essays using structural and semantic features. In: 2016 International Conference on Advances in Computing, Communications and Informatics (ICACCI), p 519–523
- Kumar, Y., Aggarwal, S., Mahata, D., Shah, R. R., Kumaraguru, P., & Zimmermann, R. (2019, July). Get it scored using autosas—an automated system for scoring short answers. In Proceedings of the AAAI Conference on Artificial Intelligence (Vol. 33, No. 01, pp. 9662–9669).
- Kumar Y, et al. (2020) “Calling out bluff: attacking the robustness of automatic scoring systems with simple adversarial testing.” ArXiv abs/2007.06796
- Li X, Chen M, Nie J, Liu Z, Feng Z, Cai Y (2018) Coherence-Based Automated Essay Scoring Using Self-attention. In: Sun M, Liu T, Wang X, Liu Z, Liu Y (eds) Chinese Computational Linguistics and Natural Language Processing Based on Naturally Annotated Big Data. CCL 2018, NLP-NABD 2018. Lecture Notes in Computer Science, vol 11221. Springer, Cham. 10.1007/978-3-030-01716-3_32
- Liang G, On B, Jeong D, Kim H, Choi G. Automated essay scoring: a siamese bidirectional LSTM neural network architecture. Symmetry. 2018; 10 :682. doi: 10.3390/sym10120682. [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Liua, H., Yeb, Y., & Wu, M. (2018, April). Ensemble Learning on Scoring Student Essay. In 2018 International Conference on Management and Education, Humanities and Social Sciences (MEHSS 2018). Atlantis Press.
- Liu J, Xu Y, Zhao L (2019) Automated Essay Scoring based on Two-Stage Learning. ArXiv, abs/1901.07744
- Loukina A, et al. (2015) Feature selection for automated speech scoring.” BEA@NAACL-HLT
- Loukina A, et al. (2017) “Speech- and Text-driven Features for Automated Scoring of English-Speaking Tasks.” SCNLP@EMNLP 2017
- Loukina A, et al. (2019) The many dimensions of algorithmic fairness in educational applications. BEA@ACL
- Lun J, Zhu J, Tang Y, Yang M (2020) Multiple data augmentation strategies for improving performance on automatic short answer scoring. In: Proceedings of the AAAI Conference on Artificial Intelligence, 34(09): 13389-13396
- Madnani, N., & Cahill, A. (2018, August). Automated scoring: Beyond natural language processing. In Proceedings of the 27th International Conference on Computational Linguistics (pp. 1099–1109).
- Madnani N, et al. (2017b) “Building better open-source tools to support fairness in automated scoring.” EthNLP@EACL
- Malinin A, et al. (2016) “Off-topic response detection for spontaneous spoken english assessment.” ACL
- Malinin A, et al. (2017) “Incorporating uncertainty into deep learning for spoken language assessment.” ACL
- Mathias S, Bhattacharyya P (2018a) Thank “Goodness”! A Way to Measure Style in Student Essays. In: Proceedings of the 5th Workshop on Natural Language Processing Techniques for Educational Applications p 35–41
- Mathias S, Bhattacharyya P (2018b) ASAP++: Enriching the ASAP automated essay grading dataset with essay attribute scores. In: Proceedings of the Eleventh International Conference on Language Resources and Evaluation (LREC 2018).
- Mikolov T, et al. (2013) “Efficient Estimation of Word Representations in Vector Space.” ICLR
- Mohler M, Mihalcea R (2009) Text-to-text semantic similarity for automatic short answer grading. In: Proceedings of the 12th Conference of the European Chapter of the ACL (EACL 2009) p 567–575
- Mohler M, Bunescu R, Mihalcea R (2011) Learning to grade short answer questions using semantic similarity measures and dependency graph alignments. In: Proceedings of the 49th annual meeting of the association for computational linguistics: Human language technologies p 752–762
- Muangkammuen P, Fukumoto F (2020) Multi-task Learning for Automated Essay Scoring with Sentiment Analysis. In: Proceedings of the 1st Conference of the Asia-Pacific Chapter of the Association for Computational Linguistics and the 10th International Joint Conference on Natural Language Processing: Student Research Workshop p 116–123
- Nguyen, H., & Dery, L. (2016). Neural networks for automated essay grading. CS224d Stanford Reports, 1–11.
- Palma D, Atkinson J. Coherence-based automatic essay assessment. IEEE Intell Syst. 2018; 33 (5):26–36. doi: 10.1109/MIS.2018.2877278. [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Parekh S, et al (2020) My Teacher Thinks the World Is Flat! Interpreting Automatic Essay Scoring Mechanism.” ArXiv abs/2012.13872 (2020): n. pag
- Pennington, J., Socher, R., & Manning, C. D. (2014, October). Glove: Global vectors for word representation. In Proceedings of the 2014 conference on empirical methods in natural language processing (EMNLP) (pp. 1532–1543).
- Persing I, Ng V (2013) Modeling thesis clarity in student essays. In:Proceedings of the 51st Annual Meeting of the Association for Computational Linguistics (Volume 1: Long Papers) p 260–269
- Powers DE, Burstein JC, Chodorow M, Fowles ME, Kukich K. Stumping E-Rater: challenging the validity of automated essay scoring. ETS Res Rep Ser. 2001; 2001 (1):i–44. [ Google Scholar ]
- Powers DE, Burstein JC, Chodorow M, Fowles ME, Kukich K. Stumping e-rater: challenging the validity of automated essay scoring. Comput Hum Behav. 2002; 18 (2):103–134. doi: 10.1016/S0747-5632(01)00052-8. [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Ramachandran L, Cheng J, Foltz P (2015) Identifying patterns for short answer scoring using graph-based lexico-semantic text matching. In: Proceedings of the Tenth Workshop on Innovative Use of NLP for Building Educational Applications p 97–106
- Ramanarayanan V, et al. (2017) “Human and Automated Scoring of Fluency, Pronunciation and Intonation During Human-Machine Spoken Dialog Interactions.” INTERSPEECH
- Riordan B, Horbach A, Cahill A, Zesch T, Lee C (2017) Investigating neural architectures for short answer scoring. In: Proceedings of the 12th Workshop on Innovative Use of NLP for Building Educational Applications p 159–168
- Riordan B, Flor M, Pugh R (2019) "How to account for misspellings: Quantifying the benefit of character representations in neural content scoring models."In: Proceedings of the Fourteenth Workshop on Innovative Use of NLP for Building Educational Applications
- Rodriguez P, Jafari A, Ormerod CM (2019) Language models and Automated Essay Scoring. ArXiv, abs/1909.09482
- Rudner, L. M., & Liang, T. (2002). Automated essay scoring using Bayes' theorem. The Journal of Technology, Learning and Assessment, 1(2).
- Rudner, L. M., Garcia, V., & Welch, C. (2006). An evaluation of IntelliMetric™ essay scoring system. The Journal of Technology, Learning and Assessment, 4(4).
- Rupp A. Designing, evaluating, and deploying automated scoring systems with validity in mind: methodological design decisions. Appl Meas Educ. 2018; 31 :191–214. doi: 10.1080/08957347.2018.1464448. [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Ruseti S, Dascalu M, Johnson AM, McNamara DS, Balyan R, McCarthy KS, Trausan-Matu S (2018) Scoring summaries using recurrent neural networks. In: International Conference on Intelligent Tutoring Systems p 191–201. Springer, Cham
- Sakaguchi K, Heilman M, Madnani N (2015) Effective feature integration for automated short answer scoring. In: Proceedings of the 2015 conference of the North American Chapter of the association for computational linguistics: Human language technologies p 1049–1054
- Salim, Y., Stevanus, V., Barlian, E., Sari, A. C., & Suhartono, D. (2019, December). Automated English Digital Essay Grader Using Machine Learning. In 2019 IEEE International Conference on Engineering, Technology and Education (TALE) (pp. 1–6). IEEE.
- Shehab A, Elhoseny M, Hassanien AE (2016) A hybrid scheme for Automated Essay Grading based on LVQ and NLP techniques. In: 12th International Computer Engineering Conference (ICENCO), Cairo, 2016, p 65-70
- Shermis MD, Mzumara HR, Olson J, Harrington S. On-line grading of student essays: PEG goes on the World Wide Web. Assess Eval High Educ. 2001; 26 (3):247–259. doi: 10.1080/02602930120052404. [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Stab C, Gurevych I (2014) Identifying argumentative discourse structures in persuasive essays. In: Proceedings of the 2014 Conference on Empirical Methods in Natural Language Processing (EMNLP) p 46–56
- Sultan MA, Salazar C, Sumner T (2016) Fast and easy short answer grading with high accuracy. In: Proceedings of the 2016 Conference of the North American Chapter of the Association for Computational Linguistics: Human Language Technologies p 1070–1075
- Süzen, N., Gorban, A. N., Levesley, J., & Mirkes, E. M. (2020). Automatic short answer grading and feedback using text mining methods. Procedia Computer Science, 169, 726–743.
- Taghipour K, Ng HT (2016) A neural approach to automated essay scoring. In: Proceedings of the 2016 conference on empirical methods in natural language processing p 1882–1891
- Tashu TM (2020) "Off-Topic Essay Detection Using C-BGRU Siamese. In: 2020 IEEE 14th International Conference on Semantic Computing (ICSC), San Diego, CA, USA, p 221–225, doi: 10.1109/ICSC.2020.00046
- Tashu TM, Horváth T (2019) A layered approach to automatic essay evaluation using word-embedding. In: McLaren B, Reilly R, Zvacek S, Uhomoibhi J (eds) Computer Supported Education. CSEDU 2018. Communications in Computer and Information Science, vol 1022. Springer, Cham
- Tashu TM, Horváth T (2020) Semantic-Based Feedback Recommendation for Automatic Essay Evaluation. In: Bi Y, Bhatia R, Kapoor S (eds) Intelligent Systems and Applications. IntelliSys 2019. Advances in Intelligent Systems and Computing, vol 1038. Springer, Cham
- Uto M, Okano M (2020) Robust Neural Automated Essay Scoring Using Item Response Theory. In: Bittencourt I, Cukurova M, Muldner K, Luckin R, Millán E (eds) Artificial Intelligence in Education. AIED 2020. Lecture Notes in Computer Science, vol 12163. Springer, Cham
- Wang Z, Liu J, Dong R (2018a) Intelligent Auto-grading System. In: 2018 5th IEEE International Conference on Cloud Computing and Intelligence Systems (CCIS) p 430–435. IEEE.
- Wang Y, et al. (2018b) “Automatic Essay Scoring Incorporating Rating Schema via Reinforcement Learning.” EMNLP
- Zhu W, Sun Y (2020) Automated essay scoring system using multi-model Machine Learning, david c. wyld et al. (eds): mlnlp, bdiot, itccma, csity, dtmn, aifz, sigpro
- Wresch W. The Imminence of Grading Essays by Computer-25 Years Later. Comput Compos. 1993; 10 :45–58. doi: 10.1016/S8755-4615(05)80058-1. [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Wu, X., Knill, K., Gales, M., & Malinin, A. (2020). Ensemble approaches for uncertainty in spoken language assessment.
- Xia L, Liu J, Zhang Z (2019) Automatic Essay Scoring Model Based on Two-Layer Bi-directional Long-Short Term Memory Network. In: Proceedings of the 2019 3rd International Conference on Computer Science and Artificial Intelligence p 133–137
- Yannakoudakis H, Briscoe T, Medlock B (2011) A new dataset and method for automatically grading ESOL texts. In: Proceedings of the 49th annual meeting of the association for computational linguistics: human language technologies p 180–189
- Zhao S, Zhang Y, Xiong X, Botelho A, Heffernan N (2017) A memory-augmented neural model for automated grading. In: Proceedings of the Fourth (2017) ACM Conference on Learning@ Scale p 189–192
- Zupanc K, Bosnic Z (2014) Automated essay evaluation augmented with semantic coherence measures. In: 2014 IEEE International Conference on Data Mining p 1133–1138. IEEE.
- Zupanc K, Savić M, Bosnić Z, Ivanović M (2017) Evaluating coherence of essays using sentence-similarity networks. In: Proceedings of the 18th International Conference on Computer Systems and Technologies p 65–72
- Dzikovska, M. O., Nielsen, R., & Brew, C. (2012, June). Towards effective tutorial feedback for explanation questions: A dataset and baselines. In Proceedings of the 2012 Conference of the North American Chapter of the Association for Computational Linguistics: Human Language Technologies (pp. 200-210).
- Kumar, N., & Dey, L. (2013, November). Automatic Quality Assessment of documents with application to essay grading. In 2013 12th Mexican International Conference on Artificial Intelligence (pp. 216–222). IEEE.
- Wu, S. H., & Shih, W. F. (2018, July). A short answer grading system in chinese by support vector approach. In Proceedings of the 5th Workshop on Natural Language Processing Techniques for Educational Applications (pp. 125-129).
- Agung Putri Ratna, A., Lalita Luhurkinanti, D., Ibrahim I., Husna D., Dewi Purnamasari P. (2018). Automatic Essay Grading System for Japanese Language Examination Using Winnowing Algorithm, 2018 International Seminar on Application for Technology of Information and Communication, 2018, pp. 565–569. 10.1109/ISEMANTIC.2018.8549789.
- Sharma A., & Jayagopi D. B. (2018). Automated Grading of Handwritten Essays 2018 16th International Conference on Frontiers in Handwriting Recognition (ICFHR), 2018, pp 279–284. 10.1109/ICFHR-2018.2018.00056

IMAGES
VIDEO
COMMENTS
Project Essay Grade by Measurement Incorporated (MI), is a great automated grading software that uses AI technology to read, understand, process and give you results. By the use of the advanced statistical techniques found in this software, PEG can analyze written prose, make calculations based on more than 300 measurements (fluency, diction ...
Nathan Thompson, PhD. Artificial Intelligence, Education. Automated essay scoring (AES) is an important application of machine learning and artificial intelligence to the field of psychometrics and assessment. In fact, it's been around far longer than "machine learning" and "artificial intelligence" have been buzzwords in the general ...
Automated essay scoring (AES) is the use of specialized computer programs to assign grades to essays written in an educational setting.It is a form of educational assessment and an application of natural language processing.Its objective is to classify a large set of textual entities into a small number of discrete categories, corresponding to the possible grades, for example, the numbers 1 to 6.
The e-rater automated scoring engine uses AI technology and Natural Language Processing (NLP) to evaluate the writing proficiency of student essays by providing automatic scoring and feedback. The engine provides descriptive feedback on the writer's grammar, mechanics, word use and complexity, style, organization and more.
Essay scoring: **Automated Essay Scoring** is the task of assigning a score to an essay, usually in the context of assessing the language ability of a language learner. The quality of an essay is affected by the following four primary dimensions: topic relevance, organization and coherence, word usage and sentence complexity, and grammar and mechanics.
The purpose of this project is to implement and train machine learning algorithms to automatically assess and grade essay responses. These grades from the automatic grading system should match the human grades consistently. Currently, automated grading is used instead of second graders in some high-stakes applications, and as the only grading ...
Automated essay scoring (AES) is a compelling topic in Learning Analytics for the primary reason that recent advances in AI find it as a good testbed to explore artificial supplementation of human creativity. However, a vast swath of research tackles AES only holistically; few have even developed AES models at the rubric level, the very first layer of explanation underlying the prediction of ...
ETS is a global leader in educational assessment, measurement and learning science. Our AI technology, such as the e-rater ® scoring engine, informs decisions and creates opportunities for learners around the world. The e-rater engine automatically: assess and nurtures key writing skills. scores essays and provides feedback on writing using a ...
Automated essay grading software has been employed at other institutions, such as Harvard University and the Massachusetts Institute of Technology, to grade student submissions in open-access online courses, which often have enrollments in the thousands.
1) Automated Essay Scoring programs predict how humans would score an essay. 2) They require a "training set" of essays scored by human raters, a sample of the full set of essays to be scored ...
The foundational concept of automated scoring is that good writing can be predicted. PEG and other systems require training essays that have human scores, and these systems use such essays to create scoring (or prediction) models. The models typically include 30-40 features, or variables, within a set of essays that predict human ratings.
In writing assessment, automated writing evaluation (AWE) systems, also referred to as Automated Essay Evaluation, Automated Essay Scoring (Hockly, 2018; Warschauer & Ware, 2006) are developed based on interdisciplinary research and technological advances such as natural language processing, computer sciences, and latent semantic analysis that enable "the process of evaluating and scoring ...
The Project Essay Grade (PEG) automated scoring algorithm is one of the many significant outcomes of artificial intelligence in education. In a recent blog post, ERB President Tom Rochon explained how educators can use AI to improve student writing.. Now we want to take a deeper dive into the PEG scoring algorithm that drives ERB Writing Practice, our online program that evaluates student ...
The computer programs assign grades to writing samples, sometimes on a scale of 1 to 6, in a variety of areas, from word choice to organization. ... Automated essay scoring is also used on the ACT ...
The Intelligent Essay Assessor® program was designed to use what's known as Latent Semantic Analysis ... 1998). Like most automated essay grading systems, documents are indexed for information retrieval regarding features, such as proportion of errors in grammar, proportion of word usage errors, proportion of style components, number of ...
Automated essay scoring involves automatic assessment of a students' written work, usually in response to a writing prompt. This assessment generally includes (1) a holistic score of students' performance, knowledge, and/or skill and (2) a score descriptor on how the student can improve the text. For example, e-rater by ETS () scores essays ...
EssayGrader is a tool powered by AI that provides accurate and helpful feedback based on the same rubrics used by the grading teacher. Its features include speedy grading, comprehensive feedback, estimated grades, focused feedback, organized essays, show, don't tell, and personalized approach. The tool offers an easy-to-use guide for better ...
programs in evaluating student essays, Page developed an automated essay-grading sys-tem called Project Essay Grader. He started with a set of student essays that teachers had already graded. He then experimented with a variety of automatically extractable textual features and applied multiple linear regres-sion to determine an optimal ...
Automated essay scoring (AES) applies ML algorithms to automatically evaluate essays. While AES has been widely used in standardized high-stakes testing programs, such as the Test of English as a Foreign Language (TOEFL) and the Graduate Record Examination (GRE), its use has also grown in K-12 educational contexts (Jang, Citation 2014 ).
Automated essay scoring (AES) is a computer-based assessment system that automatically scores or grades the student responses by considering appropriate features. The AES research started in 1966 with the Project Essay Grader (PEG) by Ajay et al. . PEG evaluates the writing characteristics such as grammar, diction, construction, etc., to grade ...
Automated Essay Scoring (AES) Automated Essay Scoring (AES) refers to the use of technology to evaluate and score written essays. The process of AES involves using computer programs to analyze and score written work based on predefined criteria such as linguistic correctness, lexical richness, coherence, syntax, and semantic relevance.
Automated Essay Grading. Alex Adamson, Andrew Lamb, Ralph Ma. Published 2014. Computer Science, Education. TLDR. This work trained different models using word features, per-essay statistics, and metrics of similarity and coherence between essays and documents to make predictions that closely match those made by human graders. Expand.
The director of the Natural Language Processing group at Educational Testing Service, Kukich, provides an insider's view of the history of the field of automated essay grading and describes how ETS is currently using computer programs to supplement human judges in the grading process. We look at a controversy: the use of computers for automated and semiautomated grading of exams. K. Kukich ...