Economics Essay Examples


Ace Your Essay With Our Economics Essay Examples
Published on: Jun 6, 2023
Last updated on: Jan 31, 2024

Share this article
Are you struggling to understand economics essays and how to write your own?
It can be challenging to grasp the complexities of economic concepts without practical examples.
But don’t worry!
We’ve got the solution you've been looking for. Explore quality examples that bridge the gap between theory and real-world applications. In addition, get insightful tips for writing economics essays.
So, if you're a student aiming for academic success, this blog is your go-to resource for mastering economics essays.
Let’s dive in and get started!
On This Page On This Page -->
What is an Economics Essay?
An economics essay is a written piece that explores economic theories, concepts, and their real-world applications. It involves analyzing economic issues, presenting arguments, and providing evidence to support ideas.
The goal of an economics essay is to demonstrate an understanding of economic principles and the ability to critically evaluate economic topics.
Why Write an Economics Essay?
Writing an economics essay serves multiple purposes:
- Demonstrate Understanding: Showcasing your comprehension of economic concepts and their practical applications.
- Develop Critical Thinking: Cultivating analytical skills to evaluate economic issues from different perspectives.
- Apply Theory to Real-World Contexts: Bridging the gap between economic theory and real-life scenarios.
- Enhance Research and Analysis Skills: Improving abilities to gather and interpret economic data.
- Prepare for Academic and Professional Pursuits: Building a foundation for success in future economics-related endeavors.

Paper Due? Why Suffer? That's our Job!
If youâre wondering, âhow do I write an economics essay?â, consulting an example essay might be a good option for you. Here are some economics essay examples:
Short Essay About Economics
A Level Economics Essay Examples
Here is an essay on economics a level structure:
Band 6 Economics Essay Examples
Here are some downloadable economics essays:
Economics essay pdf
Economics essay introduction
Economics Extended Essay Examples
In an economics extended essay, students have the opportunity to delve into a specific economic topic of interest. They are required to conduct an in-depth analysis of this topic and compile a lengthy essay.
Here are some potential economics extended essay question examples:
- How does foreign direct investment impact economic growth in developing countries?
- What are the factors influencing consumer behavior and their effects on market demand for sustainable products?
- To what extent does government intervention in the form of minimum wage policies affect employment levels and income inequality?
- What are the economic consequences of implementing a carbon tax to combat climate change?
- How does globalization influence income distribution and the wage gap in developed economies?
IB Economics Extended Essay Examples
IB Economics Extended Essay Examples
Economics Extended Essay Topic Examples
Extended Essay Research Question Examples Economics
Tips for Writing an Economics Essay
Writing an economics essay requires specific expertise and skills. So, it's important to have some tips up your sleeve to make sure your essay is of high quality:
- Start with a Clear Thesis Statement: It defines your essay's focus and argument. This statement should be concise, to the point, and present the crux of your essay.
- Conduct Research and Gather Data: Collect facts and figures from reliable sources such as academic journals, government reports, and reputable news outlets. Use this data to support your arguments and analysis and compile a literature review.
- Use Economic Theories and Models: These help you to support your arguments and provide a framework for your analysis. Make sure to clearly explain these theories and models so that the reader can follow your reasoning.
- Analyze the Micro and Macro Aspects: Consider all angles of the topic. This means examining how the issue affects individuals, businesses, and the economy as a whole.
- Use Real-World Examples: Practical examples and case studies help to illustrate your points. This can make your arguments more relatable and understandable.
- Consider the Policy Implications: Take into account the impacts of your analysis. What are the potential solutions to the problem you're examining? How might different policies affect the outcomes you're discussing?
- Use Graphs and Charts: These help to illustrate your data and analysis. These visual aids can help make your arguments more compelling and easier to understand.
- Proofread and Edit: Make sure to proofread your essay carefully for grammar and spelling errors. In economics, precision and accuracy are essential, so errors can undermine the credibility of your analysis.
These tips can help make your essay writing journey a breeze. Tailor them to your topic to make sure you end with a well-researched and accurate economics essay.
To wrap it up , writing an economics essay requires a combination of solid research, analytical thinking, and effective communication.
You can craft a compelling piece of work by taking our examples as a guide and following the tips.
However, if you are still questioning "how do I write an economics essay?", it's time to get professional help from the best essay writing service - CollegeEssay.org.
Our economics essay writing service is always ready to help students like you. Our experienced economics essay writers are dedicated to delivering high-quality, custom-written essays that are 100% plagiarism free.
Also try out our AI essay writer and get your quality economics essay now!
Barbara P (Literature)
Barbara is a highly educated and qualified author with a Ph.D. in public health from an Ivy League university. She has spent a significant amount of time working in the medical field, conducting a thorough study on a variety of health issues. Her work has been published in several major publications.
Paper Due? Why Suffer? That’s our Job!

Legal & Policies
- Privacy Policy
- Cookies Policy
- Terms of Use
- Refunds & Cancellations
- Our Writers
- Success Stories
- Our Guarantees
- Affiliate Program
- Referral Program
- AI Essay Writer
Disclaimer: All client orders are completed by our team of highly qualified human writers. The essays and papers provided by us are not to be used for submission but rather as learning models only.

Macro Economic Essays
These are a collection of essays written for my economic blogs.
Exchange Rate Essays
- Effects of a falling Dollar
- Why Dollar keeps falling
- Discuss Policies to Stop the Dollar Falling
- Does Devaluation Cause Inflation?
- Benefits and Costs of Falling Dollar
- Reasons for Falling Dollar
- The Dollar as the World’s Reserve Currency
Economic Growth Essays
- Evaluate Benefits of Economic Growth
- Essays on Recessions
- Causes of Recessions
- Problems of Recovering from a Recession
- What can Increase Long-Run Economic Growth?
- Discuss Effect of a fall in the Savings Ratio
Inflation Essays
- Discuss the Difficulties of Controlling Inflation
- Should the aim of the Government be to Attain Low Inflation?
- Explain What Can Cause a Sustained Increase in the Rate of Inflation
- Reasons for low inflation in the UK
- Inflation Explained
- Difficulties of Inflation targeting
- Hyperinflation
Unemployment Essays
- Explain what is meant by Natural Rate of Unemployment?
- Should the Main Macro Economic Aim of the Government be Full Employment?
- The True Level of Unemployment in the UK
- What explains low inflation and low unemployment in the UK?
Demand Side Policies
- Discuss effect of Expansionary demand-side policies on Balance of Payments and Environment
- Effects of a Falling Stock Market
- How do Mortgage Defaults affect and Economy?
- Discuss the effect of increased Government spending on education
- Phillips Curve – Trade-off between Inflation and Unemployment
Development Economics
- Why Growth may not benefit developing countries
- Does Aid Increase Economic Welfare?
- Problems of Free Trade for Developing Economies
Fiscal Policy
- Will US Economy benefit from Tax Cuts?
- Can Fiscal Policy solve Unemployment?
- Explain Reasons for UK Current Account Deficit
- Benefits of Globalisation for Developing and Developed Countries
Monetary Policy
- Discuss Effects of an Increase in Interest Rates
- How MPC set Interest Rates
- Benefits of High-Interest Rates (and recessions)
- Who Sets interest rates – Markets or Bank of England?
Economic History
- Economics of the 1920s
- What Caused Wall Street Crash of 1929?
- UK economy under Mrs Thatcher
- Economy of the 1970s
- Lawson Boom of the 1980s
- UK recession of 1991
- The great recession 2008-13
General Economic Essays
- The Dismal Science
- Difference Between Economists and Non Economists
- War and Recessions
- The Economics of Fear
- The Economics of Happiness
- Can UK and US avoid Recession?
- 3 Of the Worst Economic Policies
- Overvalued Housing Markets
- What Went Wrong with US Economy?
- Problem with Bailing out financial sector
- Problems of Personal Debt
- Problem of Inflation
- National Debt in the UK
- How To Survive a Recession
- Can A recession be a good thing?
Chinese Economy
- Problems of Chinese Economic Growth
- Should we worry about a strong China
- Chinese Growth and Costs of Growth
- Chinese Interest Rates and Economic Growth
Model essays

- A2 model essays
- AS model essays
- Top 10 Reasons For Studying Economics
- Inflation explained by Victor Borge
- Funny Exam Answers
- Humorous look at Subprime crisis
- PRO Courses Guides New Tech Help Pro Expert Videos About wikiHow Pro Upgrade Sign In
- EDIT Edit this Article
- EXPLORE Tech Help Pro About Us Random Article Quizzes Request a New Article Community Dashboard This Or That Game Popular Categories Arts and Entertainment Artwork Books Movies Computers and Electronics Computers Phone Skills Technology Hacks Health Men's Health Mental Health Women's Health Relationships Dating Love Relationship Issues Hobbies and Crafts Crafts Drawing Games Education & Communication Communication Skills Personal Development Studying Personal Care and Style Fashion Hair Care Personal Hygiene Youth Personal Care School Stuff Dating All Categories Arts and Entertainment Finance and Business Home and Garden Relationship Quizzes Cars & Other Vehicles Food and Entertaining Personal Care and Style Sports and Fitness Computers and Electronics Health Pets and Animals Travel Education & Communication Hobbies and Crafts Philosophy and Religion Work World Family Life Holidays and Traditions Relationships Youth
- Browse Articles
- Learn Something New
- Quizzes Hot
- This Or That Game New
- Train Your Brain
- Explore More
- Support wikiHow
- About wikiHow
- Log in / Sign up
- Education and Communications
- College University and Postgraduate
- Academic Writing
How to Write a Good Economics Essay
Last Updated: March 7, 2023 References
This article was co-authored by Emily Listmann, MA . Emily Listmann is a private tutor in San Carlos, California. She has worked as a Social Studies Teacher, Curriculum Coordinator, and an SAT Prep Teacher. She received her MA in Education from the Stanford Graduate School of Education in 2014. This article has been viewed 127,227 times.
A good economics essay requires a clear argument that is well-supported by appropriately referenced evidence. Research your topic thoroughly and then carefully plan out your essay. A good structure is essential, as is sticking closely to the main essay question. Be sure to proofread your essay and try to write in formal and precise prose.
Preparing to Write Your Essay

- For example a question such as “Discuss the macroeconomic consequences of rising house prices, alongside falling interest rates” could be divided into 2 parts: 1 part could be on the effects of rising prices, and 1 on the effects of falling interest rates.
- In this example you could begin by discussing each separately and then bringing the 2 together and analysing how they influence each other.
- Be sure to keep the question at the forefront of your mind and don’t veer off topic. [1] X Research source

- Be sure that you understand all the key terms that you are being asked about.
- Try to keep your reading focussed closely to the essay question.
- Don’t forget to look at any lecture or class notes you have made.
- 3 Come up with a thesis statement . A thesis statement is the main argument you will make in your essay. It should be 1-2 sentences long and respond to the essential question that’s being asked. The thesis will help you structure the body of your essay, and each point you make should relate back to the thesis.

- Once you have put together a list of key points, then try to add in some more detail that brings in elements from your research.
- When you come to write out your essay, you can develop a paragraph based on each point.

- All of the evidence and explanation will be in the main body of the essay.
- Order the key points in the body of your essay in such a way that they flow logically.
- If you are writing a longer essay, you can break the main body into different sections. [2] X Research source
- If you have a word limit, be sure to take this into account when you are planning.
- Allocate yourself a rough number of words per section.
- The introduction and conclusion can be just a paragraph each.
Writing the Essay

- What your essay is about.
- What material you will cover in the essay.
- What your argument is. [3] X Research source

- Having this stated clearly at the start can help you to stay focussed on the question as you work your way through the essay.
- Try writing out this one or two sentence statement and sticking it up in front of you as you write, so it’s stays at the forefront of your mind.

- Try to begin each paragraph with a sentence that outlines what the paragraph will cover.
- Look at the opening sentence of each paragraph and ask yourself if it is addressing the essay question. [5] X Research source

- Try to engage with arguments that run counter to yours, and use the evidence you have found to show the flaws.
- It might help to imagine someone reading the essay, and anticipating the objections that he might raise.
- Showing that you have thought about potential problems, and you can make an argument that overcomes them, is a hallmark of an excellent essay. [6] X Research source
- If there is conflicting evidence, discuss it openly and try to show where the weight of the evidence lies. [7] X Research source
- Don’t just ignore the evidence that runs counter to your argument.

- In the conclusion you can add a few sentences that show how your essay could be developed and taken further.
- Here you can assert why the question is important and make some tentative suggestions for further analysis.
Proofreading and Making Revisions

- As you read through it, think about how closely you stick to main overarching question.
- If you notice paragraphs that drift off into other areas, you need to be tough and cut them out.
- You have a limited number of words so it’s essential to make every one count by keeping tightly focussed on the main question.

- Think about how you use the evidence too. Do you critically engage with it, or do you merely quote it to support your point?
- A good analytical essay such discuss evidence critically at all times.
- Even if the evidence supports your argument, you need to show that you have thought about the value of this particular piece of data.
- Try to avoid making any assumptions, or writing as if something were beyond dispute. [10] X Research source

- Remember an academic essay should be written in a formal style, so avoid colloquialisms.
- Avoid contractions, such as “don’t”, or “won’t”.
- Try to avoid paragraphs that are more than ten or fifteen lines long.
- Think about how it looks on the page. [12] X Research source

- Always include a bibliography, but don’t include references to things you haven’t read or didn’t inform your argument. [13] X Research source
- Your teacher will know if you just add a load of titles into your bibliography that are not evidenced in the body of your essay.
- Always follow the bibliography format used by your department or class.
Community Q&A
You Might Also Like

- ↑ http://www.economicshelp.org/help/tips-economic-essays/
- ↑ http://www.writing.utoronto.ca/advice/planning-and-organizing/organizing
- ↑ http://carleton.ca/economics/courses/writing-preliminaries/academic-essay-writing/
- ↑ https://www.economicsnetwork.ac.uk/archive/lse_writing/page_11.htm
- ↑ http://homes.chass.utoronto.ca/~mcmillan/writing.pdf
- ↑ https://www.royalholloway.ac.uk/economics/documents/pdf/essaywriting-departmentofeconomics.pdf
About This Article

Before you begin writing your economics essay, make sure to carefully read the prompt so that you have a clear sense of the paper's purpose and scope. Once you have read the prompt, conduct research using your textbook and relevant articles. If you cannot find research materials, ask your instructor for recommendations. After your research is done, construct a 1-2 sentence thesis statement and begin outlining your main ideas so that your essay will have a clear structure. Make sure to leave time to write a draft and revise your work before it is due. If you want to learn more, like how to cite the sources you used for your essay, keep reading the article! Did this summary help you? Yes No
- Send fan mail to authors
Reader Success Stories
Twyla Kirkpatrick
Dec 8, 2020
Did this article help you?
Arshad Bhatti
Sep 10, 2017
Fungai Samantha Zuva
Jan 30, 2019
James Smith
Oct 2, 2016
Mallesh Itti
Jul 10, 2022

Featured Articles

Trending Articles

Watch Articles

- Terms of Use
- Privacy Policy
- Do Not Sell or Share My Info
- Not Selling Info
wikiHow Tech Help Pro:
Level up your tech skills and stay ahead of the curve
Reimagining the global economy: Building back better in a post-COVID-19 world
- Download the full essay collection
Subscribe to Global Connection
November 17, 2020
The COVID-19 global pandemic has produced a human and economic crisis unlike any in recent memory. The global economy is experiencing its deepest recession since World War II, disrupting economic activity, travel, supply chains, and more. Governments have responded with lockdown measures and stimulus plans, but the extent of these actions has been unequal across countries. Within countries, the most vulnerable populations have been disproportionately affected, both in regard to job loss and the spread of the virus.
The implications of the crisis going forward are vast. Notwithstanding the recent announcement of vaccines, much is unknown about how the pandemic will spread in the short term and beyond, as well as what will be its lasting effects. What is clear, however, is that the time is ripe for change and policy reform. The hope is that decisionmakers can rise to the challenge in the medium term to tackle the COVID-19 virus and related challenges that the pandemic has exacerbated—be it the climate crisis, rising inequality, job insecurity, or international cooperation.
In this collection of 12 essays, leading scholars affiliated with the Global Economy and Development program at Brookings present new ideas that are forward-looking, policy-focused, and that will guide policies and shape debates in a post-COVID-19 world.
Sustainable Development Goals
Authors: Homi Kharas , John W. McArthur
Some have questioned whether the pandemic has put attaining the already ambitious 17 Sustainable Development Goals (SDGs) out of reach, and whether they should be scaled back and deprioritized. In this essay, Homi Kharas and John McArthur argue that the SDGs remain as relevant as ever and that the goals can in fact provide a handrail for recovery policy.
Continue reading
Leadership at the local level
Authors: Anthony F. Pipa , Max Bouchet
The pandemic has revealed the importance of good leadership at the local level. In this essay, Anthony F. Pipa and Max Bouchet explore the role that global cities can have in driving a sustainable recovery.
Multilateralism
Authors: Kemal Derviş
Given the global nature of the pandemic, there have been calls for greater international cooperation. In this essay, Kemal Derviş examines the state of multilateralism and presents lessons of caution as its future is reimagined.
Rebooting the climate agenda
Authors: Amar Bhattacharya
Shared recognition of the climate agenda is central to global cooperation. In this essay, Amar Bhattacharya explores how international action can pursue a recovery that produces sustainable, inclusive, and resilient growth.
The international monetary and financial system
Authors: Brahima Sangafowa Coulibaly , Eswar Prasad
The pandemic has exposed the weaknesses in the international financial system and the need to improve the financial safety net for emerging and developing countries. In this essay, Brahima Coulibaly and Eswar Prasad make the case for an international monetary and financial system that is fit for purpose to help countries better withstand shocks like a global pandemic.
The future of global supply chains
Authors: David Dollar
International trade has slowed, and existing trade challenges, including automation, new data flows, and the rise of protectionism, could accelerate post-COVID. In this essay, David Dollar discusses these challenges, the future of global supply chains, and the implications for international trade.
The global productivity slump
Authors: Alistair Dieppe , M. Ayhan Kose
COVID-19 could further accelerate the fall in global productivity, which has been slowing since the global financial crisis. Evidence from other recent pandemics such as SARS and Ebola show their negative impact on investment growth and productivity. In this essay, Alistair Dieppe and Ayhan Kose argue that policy approaches to boost productivity must be country-specific and well-targeted.
Dislocation of labor markets
Authors: Marcela Escobari , Eduardo Levy Yeyati
Throughout the world, the health and economic costs of the pandemic have been felt harder by less well-off populations. On the jobs front, the pandemic is affecting labor markets differently across and within advanced and developing countries as low-wage, high-contact jobs are disproportionally affected. In this essay, Marcela Escobari and Eduardo Levy Yeyati explore the future of work and policies for formalizing and broadening labor protections to bolster resiliency.
Tackling the inequality pandemic
Authors: Zia Qureshi
Technology, globalization, and weakening redistribution policies are leading to rising inequality in many countries. To tackle inequality, Zia Qureshi discusses policies to better harness technology for fostering inclusive economic growth.
The human costs of the pandemic
Authors: Carol Graham
Evidence suggests that the poor have been suffering higher emotional costs during the pandemic. In this essay, Carol Graham offers a look into well-being measurement and strategies to combat the effects of the lockdowns.
The complexity of managing COVID-19
Authors: Alaka M. Basu , Kaushik Basu , Jose Maria U. Tapia
From strict lockdowns to ensuring sufficient supplies of personal protective equipment to sending students home from school, governments around the world have enacted varying measures to respond to the virus. In this essay, Alaka M. Basu, Kaushik Basu, and Jose Maria U. Tapia examine how governments in emerging markets have managed the crisis so far, as they design governance strategies that both reduce the spread of infection and avoid prohibiting economic activity.
Global education
Authors: Emiliana Vegas , Rebecca Winthrop
COVID-19 disrupted education systems everywhere and has accelerated education inequality as seen through what service governments could provide: At one point during the pandemic, 1 in 4 low-income countries was able to provide remote education, while 9 in 10 high-income countries were able to. In this essay, Emiliana Vegas and Rebecca Winthrop present an aspirational vision for transforming education systems to better serve all children.
Global Trade Sustainable Development Goals
Global Economy and Development
The Brookings Institution, Washington DC
10:00 am - 11:30 am EDT
Kevin Dong, Mallie Prytherch, Lily McElwee, Patricia M. Kim, Jude Blanchette, Ryan Hass
March 15, 2024
March 6, 2024
Economics Essay Topics: Valuable Tips

Economics is a subject that has gained immense popularity in recent times. It deals with interesting economics topics like the production, distribution, and consumption of goods and services. Moreover, it is a social science that provides insights into how individuals, businesses, and governments make decisions that affect the overall economy. Given its importance, economics essays have become a crucial part of the curriculum for students pursuing various degrees.
Short Description
In this article, our essay writer will take you on a journey through various exciting topics in economics. We'll cover everything from big-picture concepts like macroeconomics to more focused ideas like microeconomics, international trade, and economic policy. Our goal is to help you find the perfect topic for your economics essay—one that matches your interests and demonstrates your understanding of how economics affects the real world.
🎓 What is Economics: Understanding the Importance
Before we dive into the different economics essay topics, it is crucial to understand what economics is and its importance. Economics is a social science that deals with the production, distribution, and consumption of goods and services. It is concerned with how individuals, businesses, and governments make decisions about allocating resources to satisfy their unlimited wants and needs.
Economics as a science provides a framework for analyzing society's production, distribution, and consumption of goods and services. It helps us understand how markets work and how they can be improved to increase efficiency and welfare. Moreover, economic principles have significant implications for various social issues, including poverty, inequality, environmental sustainability, and public policy. By studying economics essay topics, we can gain insights into these issues and develop policies that promote rapid economic growth and social welfare.

When it comes to economics, the range of essay topics is vast and covers various aspects of human interactions on different levels. With so many possibilities to explore, we understand the difficulty of narrowing down your options. That's why our ' write me an essay ' experts are here to offer their guidance and support. We're ready to help you select the ideal topic if you wish to learn how to write informative essay on economics.

🧩 Tips for Choosing Your Ideal Topic
Choosing a topic is the first and most crucial step in writing an economics essay. Your topic will determine the direction and scope of your essay. Here are some tips for choosing the ideal topic from our finance essay writing service :
Tip 1: Understand the relevance of economics to daily life and choose a topic with practical applications.
Recognize that economics plays a significant role in our everyday lives, as it encompasses the production, distribution, and consumption of goods and services. Therefore, when selecting a topic, ensure its societal relevance. For instance, you might consider exploring 'The Impact of Automation on Employment Rates' or 'The Role of Government Regulations in Controlling Inflation.'
Tip 2: Opt for narrow economics research topics to make them more manageable and allow for in-depth exploration.
Instead of tackling broad subjects like 'International Trade,' narrow down your focus to something like 'The Effects of Tariffs on Small Businesses in the Agriculture Sector' or 'The Relationship Between Exchange Rates and Export Performance in Developing Countries.' By delving deeper into a specific aspect, you can provide more detailed financial analysis and insights.
Tip 3: Conduct preliminary research to identify current topics, debates, and research gaps.
Before finalizing your topic, engage in preliminary research to gain an understanding of recent trends and issues in economics. Explore academic journals, news articles, and books to discover areas that warrant further exploration. For example, you might come across intriguing research gaps such as 'The Impact of Cryptocurrencies on Financial Markets' or 'The Role of Behavioral Economics in Shaping Consumer Decision-Making.'
Tip 4: Seek input from peers or professors to enhance your topic selection process.
Collaborate with your peers during brainstorming sessions to generate fresh ideas and gain different perspectives on potential topics. Additionally, seek guidance from your professor, who can offer valuable insights and feedback to refine your chosen topic. For instance, you can discuss your ideas with classmates and receive suggestions like 'The Influence of Economic Policies on Income Inequality' or receive expert advice from your professor on 'The Implications of Globalization on Developing Economies.'
And if you want expert assistance in applying theoretical concepts to practice and creating an exceptional paper, then address your request to our custom essay writing services .

🗒 Economics Essay Topics: A Comprehensive List
If you are looking for a comprehensive list of interesting economics essay topics, you have come to the right place. Here are some ideas that you can consider:

- The role of central banks in fiscal policy: You can explore the role of central banks in implementing fiscal policies, such as setting interest rates, regulating money supply, and managing inflation.
- The effects of automation on the labor market: You can explore the impact of automation on the labor market, including the displacement of workers and the emergence of new job opportunities.
- The impact of immigration on the labor market: You can explore the impact of immigration on the labor market, including the effects on wages, employment opportunities, and economic growth.
- The economics of climate change: You can explore the economic impact of climate change, including the costs of mitigation and adaptation measures, the effects on industries, and the role of governments in addressing the issue.
- The economics of healthcare: You can explore the economics of healthcare, including the costs of healthcare, the role of insurance companies, and the impact of healthcare policies on the economy.
- The role of government in the economy: You can explore the role of governments in implementing economic policies, including fiscal and monetary policies, and the impact of these policies on the economy.
- The impact of globalization on the economy: You can explore the economic implications of globalization, including the effects on industries, trade, and employment opportunities.
- The economics of poverty and inequality: You can explore the economics of poverty and inequality, including the causes and effects of poverty and inequality and the role of governments in addressing these issues.
- The economics of education: You can explore the economics of education, including the costs of education, the impact of education on economic growth, and the role of governments in promoting education.
- The role of competition in the marketplace: You can explore the role of competition in promoting economic growth, innovation, and consumer welfare.
- The economics of entrepreneurship: You can explore the economics of entrepreneurship, including the factors that promote entrepreneurship, the impact of entrepreneurship on the economy, and the role of governments in promoting entrepreneurship.
- The impact of quantitative easing on economic recovery: You can explore the consequences of large-scale asset purchases and their influence on inflation, employment rates, and overall economic stability.
- The economics of renewable energy transition: You can analyze the costs, benefits, and challenges associated with adopting renewable energy technologies and their potential effects on energy prices, employment, and environmental sustainability.
- The role of technological innovation in economic development: You can examine the impact of research and development, technological diffusion, and digitalization on productivity, job creation, and competitiveness in various sectors of the economy.
- Behavioral economics and consumer decision-making: You can examine concepts such as cognitive biases, heuristics, and framing effects and explore how these factors shape consumer behavior, market outcomes, and the effectiveness of public policies.
Ready to Advance Yourself in the Economics Field?
Get the essay that will have even experts in awe!
🧮 Macroeconomics Essay Topics
Macroeconomics is a fascinating and complex field of study that aims to understand the overall performance of an economy. It takes into account various factors such as economic growth, inflation, unemployment, and trade policies. If you are looking for some thought-provoking macroeconomics essay topics, here are a few that you might find interesting:
- The role of digital currencies (cryptocurrencies) in the global economy and their impact on monetary policy.
- The economics of aging populations: Analyzing the challenges and opportunities associated with demographic shifts.
- The impact of trade wars and protectionist policies on global economic growth and international trade.
- The economics of happiness and well-being: Investigating the relationship between economic factors and subjective measures of life satisfaction.
- The role of government spending in stimulating economic growth and addressing income inequality.
- The economics of urbanization: Examining the effects of urban growth on productivity, income distribution, and resource allocation.
- The impact of automation and artificial intelligence on employment and the future of work.
- The economics of climate change: Analyzing the economic costs and benefits of climate policies and the transition to a low-carbon economy.
- The role of financial markets in transmitting economic shocks and their implications for systemic risk and financial stability.
- The economics of inequality: Investigating the causes and consequences of income and wealth disparities within and between countries.
📉 Microeconomics Essay Topics
Microeconomics focuses on the behavior of individual consumers and businesses in the market. The principles of microeconomics are used to analyze how these entities make decisions, interact with each other, and influence the overall economy. If you're interested in exploring this field further, here are some microeconomics essay topics that you might find interesting:
- Behavioral economics and its implications for consumer decision-making.
- The impact of artificial intelligence and automation on labor economics and income inequality.
- Pricing strategies in the sharing economy: A critical analysis of platforms like Uber and Airbnb.
- The economics of addiction: Analyzing the factors influencing consumer behavior and the effects on individual welfare.
- The role of information and asymmetry in financial markets: Examining the impact on investor decision-making and market efficiency.
- Game theory and its application in strategic decision-making in business and economics.
- The economics of innovation and entrepreneurship: Studying the factors that drive technological advancements and their impact on economic growth.
- Health economics: Analyzing the relationship between healthcare expenditure, access, and health outcomes.
- The economics of education: Investigating the determinants of educational attainment and its effects on individual and societal welfare.
- The economics of discrimination: Examining the economic implications of bias based on race, gender, or other factors in labor markets and beyond.
🎏 International Economics Essay Topics
International economics deals with the economic interactions between countries, including trade, investment, and migration. Here are some international economic relations topics:
- The impact of trade liberalization on developing economies: A comparative analysis of different trade policies and their effects on economic growth and income distribution.
- The role of foreign direct investment (FDI) in promoting technological transfer and industrial development in emerging markets.
- The economics of global supply chains: Analyzing the benefits and challenges of interconnected production networks in the context of international trade.
- The implications of Brexit on the European Union and the United Kingdom: Assessing the economic consequences and potential trade arrangements.
- The role of international institutions (such as the World Trade Organization, International Monetary Fund, etc.) in governing global economic relations: Evaluating their effectiveness and relevance in modern world economics.
- The economics of currency exchange rates: Examining the factors influencing exchange rate movements and their impact on trade and investment flows.
- The rise of protectionist policies and their implications for global trade: Assessing the economic consequences and potential risks associated with trade barriers.
- The impact of international migration on labor markets and economic development: Analyzing the effects of immigration policies and the role of migrant workers in host countries.
- The economics of foreign aid: Evaluating the effectiveness of foreign aid in promoting economic development and reducing poverty in recipient countries.
- The economics of regional economic integration: Examining the benefits and challenges of regional trade agreements, such as the European Union or the Association of Southeast Asian Nations (ASEAN).
📉 Behavioral Economics Essay Topics
Behavioral economics combines psychology and economics to analyze how people make decisions. Here are some behavioral economics essay topics:
- The influence of socio-economic norms on consumer behavior and decision-making.
- The impact of framing effects on individual choices and decision-making processes.
- The role of default options in shaping consumer behavior and encouraging desirable outcomes.
- Prospect theory and its implications for understanding risk-taking behavior.
- Nudging strategies and their effectiveness in promoting positive behaviors and outcomes.
- The role of behavioral economics in understanding and addressing irrational financial decision-making.
- Behavioral economics interventions to promote sustainable and environmentally friendly behaviors.
- The psychology of pricing: How behavioral economics principles influence consumer perception of value.
- The influence of emotional factors on consumer decision-making processes.
- Behavioral biases in investment decision-making and their impact on financial markets.
🚑 Healthcare Economics Essay Topics
Healthcare economics analyzes how the healthcare system operates, including the costs and benefits of healthcare interventions. Here are some healthcare economics essay topics:
- The impact of healthcare insurance coverage on access to care and health outcomes.
- The role of economic incentives in shaping healthcare provider behavior and the quality of care.
- The economics of pharmaceutical pricing and its effects on affordability and access to medications.
- The cost-effectiveness of preventive healthcare interventions and their implications for healthcare spending.
- The economics of healthcare disparities and the role of social determinants of health in driving inequities.
- The impact of healthcare market competition on prices, quality, and innovation.
- The role of health technology assessment in informing healthcare resource allocation decisions.
- The economic evaluation of alternative healthcare delivery models, such as telemedicine and community health clinics.
- The impact of healthcare reforms and policy changes on healthcare costs and access to care.
- The economics of aging populations and the challenges of financing healthcare for the elderly.
🌎 Consumerism Essay Topics
Consumerism refers to the cultural and economic mindset that encourages the acquisition of goods and services. Here are some consumerism essay topics:
- The effects of consumerism on individual well-being and happiness.
- Consumerism and its impact on environmental sustainability and resource depletion.
- The role of advertising and marketing in shaping consumer behavior and promoting consumerism.
- Consumerism and its relationship with materialism and the pursuit of social status.
- The influence of consumerism on personal debt and financial well-being.
- Consumerism and its effects on societal values, culture, and social relationships.
- The ethical implications of consumerism and the responsibilities of consumers in a globalized world.
- The role of consumer activism in challenging and reshaping consumerism.
- Consumerism and its impact on mental health and psychological well-being.
- The future of consumerism in the digital age and the rise of e-commerce and online shopping.
📚 Economic History Topics
Economic history is a field of study that examines the historical development of economic systems, policies, and institutions, as well as the social, political, and cultural factors that have influenced economic outcomes over time. Here are the 10 interesting topics:
- The Industrial Revolution and its impact on economic development and societal transformation.
- Economic consequences of colonialism: examining the long-term effects on former colonies' economies.
- The Great Depression: causes, consequences, and policy responses.
- The role of institutions in economic development: a comparative study of different countries and regions.
- The rise and fall of economic empires: analyzing the economic power of ancient civilizations.
- The economic effects of wars and conflicts throughout history.
- The evolution of money and financial systems: from barter to digital currencies.
- The economic impact of technological advancements: case studies from different time periods.
- Economic inequality over time: trends, drivers, and consequences.
- The role of trade and globalization in shaping economic history: exploring patterns and impacts.
📊 Public Finance Research Topics
Public finance research focuses on the study of the government's role in the allocation, distribution, and management of resources within an economy. It encompasses the analysis of public revenues, expenditures, taxation policies, and the impact of government interventions on economic outcomes and social welfare. Here are 10 relevant economics papers topics:
- The impact of government spending on economic growth and development.
- The effectiveness of fiscal policy in managing economic downturns and promoting stability.
- The role of taxation in income redistribution and reducing income inequality.
- The economics of public debt and its implications for economic stability and future generations.
- The efficiency and equity implications of different tax systems (e.g., progressive, regressive, flat).
- The economic consequences of public infrastructure investment and its role in promoting economic productivity.
- The evaluation of government subsidies and incentives in promoting desired behaviors and industries.
- The economics of public-private partnerships and their effectiveness in delivering public goods and services.
- The impact of social welfare programs on labor supply, poverty reduction, and income mobility.
- The economics of environmental policy and the use of market-based instruments to address externalities.
Closing Remarks
To wrap up, economics is a subject that offers insights into how the world works. It provides a framework for analyzing complex social issues, including poverty, inequality, and public policy. Therefore, exploring economics essays topics is an excellent way of understanding the subject's relevance in the real world.
By following the tips for choosing your ideal topic and exploring the comprehensive list of economics topics for an essay, you can write an insightful and inspiring paper that contributes to the ongoing dialogue on economics.
Looking for Someone to Reduce Your College Stress?
Our expert writers can craft A+ essays when you want and how you want
Related Articles
.webp)
Home — Essay Samples — Economics — Economy
Essays on Economy
Negative effects of the cold war, economic challenges in the age of pandemics and warfare, made-to-order essay as fast as you need it.
Each essay is customized to cater to your unique preferences
+ experts online
The Oscillating Tides of The American Economy
A research on the relationship between the global economy and the environmental protection issues, the u.s. economic downfall in the early 2000’s and different types of economies, the analysis of global economic structure, let us write you an essay from scratch.
- 450+ experts on 30 subjects ready to help
- Custom essay delivered in as few as 3 hours
My Desire to Get Economical Education in Keio University
The reliance of the saudi arabian economy on oil revenues, alexander hamilton's impact on american economy, hong kong: history, economy, political system, get a personalized essay in under 3 hours.
Expert-written essays crafted with your exact needs in mind
Overview of The Economic and Social Issues Associated with Congestion in Australia
Irish financial crisis, qatar's foreign & security policy under hamad bin khalifa, how uob run and maintain its considerable influence in the banking industry, comparison between adam smith and karl marx, epr reviews of the organization of economic co-operation and development countries, the measures needed to adapt to an oil-free future, crytptocurrency ox (zrx): open protocol on decentralized exchanges, external business risks, the classification of entrepreneurial activity as the purpose or scope of activity, problem related to the national debt, the issues and methods of economics, to eradicate slums using technology in urban areas, future of small business, the context and institutional environment of africa, metro denver economic review, usa: the largest in terms of national debt, the great recession, a history of the world in a glass: the superiority of spirits, intersections of food production/distribution and broad categories of social policy in cuba, relevant topics.
- American Dream
- Macroeconomics
- Industrialization
- Human Development
- Microeconomics
- Socioeconomic Status
- Economic Growth
- Economic System
By clicking “Check Writers’ Offers”, you agree to our terms of service and privacy policy . We’ll occasionally send you promo and account related email
No need to pay just yet!
We use cookies to personalyze your web-site experience. By continuing we’ll assume you board with our cookie policy .
- Instructions Followed To The Letter
- Deadlines Met At Every Stage
- Unique And Plagiarism Free
Why I Chose to Study Economics: A Student Shares Her Story
Just before my senior year of high school, I decided on a whim that I wanted to take the AP Economics course that my high school offered. Going into it, I had next to no knowledge about any economic topic.
At the time, my older sister, who was in college, had taken an economics course and told me that she found it interesting. This was definitely a contributing factor to my decision, since my older sister and I have always shared a lot of common interests.

Kaitlyn Hoevelmann took an economics class in high school and never looked back. Now, she enjoys putting her double major in economics and journalism to work at the St. Louis Fed. Learn about our diverse career and internship opportunities.
I felt drawn to the subject, and I was lucky that my school had the resources to offer the class.
Economics immediately became my favorite subject after that. I looked forward to class every day and joined Future Business Leaders of America (FBLA) to compete in the economics category. First, I had to take a test for the district level, and the people with the top scores would be sent to the state competition.
I had to take the test only a few months into the semester—we spent all of that time studying macroeconomics, and the test covered both macroeconomics and microeconomics, so I spent hours outside of school reading books and taking practice tests to try and learn as much as I could in a condensed amount of time.
I attribute the beginning of my persistent interest in economics to these moments spent learning on my own late at night or between homework assignments. I ended up placing in the district competition and qualifying for state, where I took another test and placed in the top 10.
I decided sometime during the school year that I wanted to major in economics in college. When I was admitted into the University of Missouri’s (Mizzou) journalism school, I decided to double major in economics and journalism. Since then, I have had a great deal of fun taking different economics courses in school, and I have had many brilliant economics professors to look up to and learn from.
I also have enjoyed my position as a peer learning assistant for an introductory economics course at Mizzou designed for journalism students. In this position, I have held office hours for students to come to me for help, graded assignments and hosted review sessions.
I find the subject complex and challenging, and it is my personal mission to understand as much as I can and constantly learn more. It feels like each question and topic I face is a puzzle that needs to be solved, and I enjoy putting the pieces together.
Another experience that led me to study economics—and to the St. Louis Fed in particular—is when I went there on a field trip with my AP Economics class. We visited the Economy Museum and heard from an economist.
Based on the beautiful lobby, the friendly atmosphere and the great work that is done here, I knew the first step in my career would be getting accepted into the summer internship program at the Fed . I reached this goal in 2019, the summer after my sophomore year at Mizzou.
I’d like to someday dedicate my career to making economics more understandable and accessible to people, since it’s incredibly important in everyday life to understand the economy and the way it works.
More to Explore
Editor’s note: Kaitlyn has written about a range of economics topics. Check out her work:
- What’s a Countercyclical Capital Buffer?
- The Economic Costs of the Opioid Epidemic
- How Payday Loans Work
Plus, listen to our Women in Economics podcast to hear real stories about prominent professionals making their marks in the field of economics.

Kaitlyn Hoevelmann was a Public Affairs writer at the St. Louis Fed.
Related Topics
This blog explains everyday economics, consumer topics and the Fed. It also spotlights the people and programs that make the St. Louis Fed central to America’s economy. Views expressed are not necessarily those of the St. Louis Fed or Federal Reserve System.
Media questions
All other blog-related questions

The U.S. Economy Essay
The U.S. economy faces many challenges given the fact that it is recovering from a financial crisis. Virtually every sector of the economy was affected by the 2009 financial crisis. Economic growth slowed down while unemployment rates increased. It is important to note that these conditions have not changed much.
High rates of unemployment are still being reported in the U.S. During the financial crisis, the American economy shrunk and approximately 9 million jobs were lost. The unemployment rates have been alarming especially from 2009. The unemployment rate was 5% in 2008 but rose during the financial crisis to 10%. Though they have declined to around 7.8% as of 2012, much has to be done because the number of people unemployed is still high (Lewis, 2013).
It is paramount to note that despite the recovery that is being recorded in various sectors of the American economy, the figures are still very low compared to the drop that took place. On the same note, there are still the unpaid, and almost certainly impossible to pay, house mortgages which caused the 2009 financial crisis.
Similarly, the euro crisis is likely to spill over to other parts of the world and America’s financial system is at risk. On the same note, there is reduction in spending due to the cut in government expenditure which is slowing down economic growth. All these factors are raising eye brows among economists because they form a perfect recipe for another economic crisis (Krugman, 2012).
In conditions like the one America is in right now, choice of policy is quite vital to boost the economy. It has been stated that the economy is recovering but not as expected. In order to strengthen economic growth and job creation, private spending should be improved through increasing disposable income. To achieve this, expansionary monetary policy is essential.
The FOMC had reduced interest rates during the financial crisis to improve the public’s access to money. Maintaining the interest rates low will go a long way in ensuring ease access of credit and thus boost spending. On the same note, the FOMC can also buy more treasury bills to increase the amount of money in circulation (Lewis, 2013).
On the other hand, public spending will also be crucial in increasing aggregate consumption. Though the federal government has proposed tax cuts to increase disposable income as well as private spending, government expenditure is still low.
The policy that was implemented to reduce federal, state and local government spending is still in force (Lewis, 2013). To help the situation, the government needs to implement an expansionary fiscal policy that will not only encourage tax cuts, but also increased government spending at all levels.
Krugman, P. (2012). The Conscience of a Liberal. The New York Times . Web.
Lewis, P. (2013). Family and Business Tax Cut Certainty Act of 2012 . Munchen: GRIN Verlag.
- Chicago (A-D)
- Chicago (N-B)
IvyPanda. (2023, December 21). The U.S. Economy. https://ivypanda.com/essays/the-u-s-economy/
"The U.S. Economy." IvyPanda , 21 Dec. 2023, ivypanda.com/essays/the-u-s-economy/.
IvyPanda . (2023) 'The U.S. Economy'. 21 December.
IvyPanda . 2023. "The U.S. Economy." December 21, 2023. https://ivypanda.com/essays/the-u-s-economy/.
1. IvyPanda . "The U.S. Economy." December 21, 2023. https://ivypanda.com/essays/the-u-s-economy/.
Bibliography
IvyPanda . "The U.S. Economy." December 21, 2023. https://ivypanda.com/essays/the-u-s-economy/.
- Federal Open Market Committee (FOMC) Meeting
- Recommendation for Policy Action that should be undertaken at the next Federal Open Market Committee ("FOMC") meeting
- Non-Verbal Communication: Observation Paper
- The Federal Reserve and the Inflation Problem
- The US Monetary Policy: Federal Reserve
- The Recovery of the US Economy After the Pandemic
- Unpaid Internships and Labor Policies
- Mortgage Rates and Expansionary Economy Balance
- Japanese expansionary fiscal policy
- Unpaid Internships: Pros and Cons
- Scholars on the Effects of Capitalism
- Essay on the American Dream: Positive and Negative Aspects
- Effects of China’s Economic Growth on Sub-Saharan Africa
- Competing Theories of Economic Development
- Economic Analysis of Germany
Essay on Indian Economy
India’s economy is described as huge, complex and growing. It is one of the most exciting and emerging markets in the world. Since 1951, India has grown as a planned economy. The first few plans focused on growth with the strengthening of the manufacturing sector, emphasising heavy industries to form the backbone of the economy. Other principal areas of planning were agriculture and social development. During the post-independence period and the period of the “Five-year plans”, efforts were focused on identifying the needs of the economy. Further, the economic reforms in the early 90s opened a new chapter in India’s economic history. It gave India an opportunity to shake off the shackles of its past and emerge on the world stage as a progressive nation. This essay on the Indian Economy will help students know about the Indian economy in detail.
Students can go through the list of CBSE Essays on different topics. It will help them to improve their writing skills and also increase their scores on the English exam. Moreover, they can participate in different essay writing competitions which are conducted at the school level.
500+ Words Essay on the Indian Economy
India is on the high road to economic growth. Since 2020, the world economy has declined due to the COVID-19 pandemic. Repeated waves of infection, supply-chain disruptions and inflation have created challenging times. Faced with these challenges, the Government of India has taken immediate action so that it has the least impact on the Indian economy.
The Indian economy has been staging a sustained recovery since the second half of 2020-21. However, the second wave of the pandemic in April-June 2021 was more severe from a health perspective. The national lockdown has affected small businesses, common people and everyone in India. Due to this, the Indian economy has gone down. But now, it is slowly rising up and taking its form.
Role of Agriculture in the Indian Economy
Agriculture is one of the most important sectors of the Indian economy. It supplies food and raw materials in the country. At the time of independence, more than 70% of India’s population depended on agriculture to earn a livelihood. Accordingly, the share of agriculture in the national product/income was as high as 56.6% in 1950-51. However, with the development of industries and the service sector, the percentage of the population depending on agriculture, as well as the share of agriculture in the national product, has come down. Agriculture is the source of food supply. Agriculture is also a major source of foreign exchange earnings through export. The share of agriculture in India’s export in the year 2011-12 was 12.3%. The major items of export include tea, sugar, tobacco, spices, cotton, rice, fruits and vegetables, etc.
Role of Industry in India’s Economy
Industry is the secondary sector of the economy and is another important area of economic activity. After independence, the Government of India emphasised the role of industrialisation in the country’s economic development in the long run. Initially, the public sector contributed the maximum to economic growth. In the early 1990s, it was found that the public sector undertakings were not performing up to expectations. So, in 1991, the Indian Government decided to encourage the role of the private sector in industrial development. This step was taken to strengthen the process of industrialisation in India.
The progress of the Indian economy after independence was impressive indeed. India became self-sufficient in food production due to the green revolution, and industries became far more diversified. However, we still have to go a long way to become a 5 trillion economy by 2025. But, with government effort and the right policymakers, it can be achieved.
Students must have found this essay on the Indian Economy useful for improving their essay-writing skills. They can get the study material and the latest update on CBSE/ICSE/State Board/Competitive Exams at BYJU’S.
Leave a Comment Cancel reply
Your Mobile number and Email id will not be published. Required fields are marked *
Request OTP on Voice Call
Post My Comment
- Share Share
Register with BYJU'S & Download Free PDFs
Register with byju's & watch live videos.

Counselling

Essay on Economy
Students are often asked to write an essay on Economy in their schools and colleges. And if you’re also looking for the same, we have created 100-word, 250-word, and 500-word essays on the topic.
Let’s take a look…
100 Words Essay on Economy
Understanding economy.
An economy is a system where people make, trade, and use things that have value. It includes everything that people and businesses do to earn money and make goods and services. These goods and services are what people need or want and can be physical things or tasks done for others.
Types of Economies
There are three main types of economies: traditional, command, and market. Traditional economies are based on customs and beliefs. Command economies are controlled by the government. In market economies, businesses and consumers decide what’s made and sold.
Role of Money
Money plays a big role in the economy. It’s used to buy and sell goods and services. Money makes trade easier by replacing the need for barter. In a barter system, people exchange goods or services directly, which can be difficult.
Supply and Demand
Supply and demand is a key part of the economy. Supply is how much of something is available. Demand is how much people want it. If supply is high and demand is low, prices fall. If demand is high and supply is low, prices rise.
The Importance of Economy
The economy is important because it helps us decide how to use resources to meet people’s needs and wants. It also helps us understand how countries, businesses, and individuals can work to become better off.
Also check:
- Paragraph on Economy
250 Words Essay on Economy
What is economy.
An economy is like a big machine that controls how a country uses or produces its resources. These resources can be things like money, land, or workers. The economy decides how these things are divided between people.
There are four main types of economies: traditional, command, market, and mixed. A traditional economy is based on old ways of doing things. A command economy is controlled by the government. A market economy is controlled by the people who buy and sell things. A mixed economy is a combination of the other three types.
How Economies Work
In an economy, people trade things. This can be goods (like cars or food) or services (like teaching or cleaning). People can trade these things for money. This is called buying and selling. When lots of people want to buy the same thing, the price of that thing goes up. When not many people want to buy something, the price goes down. This is called supply and demand.
Why Economies are Important
Economies are important because they help us decide who gets what. They also help us make sure that resources are used in the best way. For example, if there is only a little bit of something, the economy can help decide who should get it.
In conclusion, an economy is a system that helps a country manage its resources. It decides who gets what and how much things cost. Understanding the economy can help us make better choices about how to use our resources.
500 Words Essay on Economy
The economy is like a big machine that helps a country or place work smoothly. It includes all the activities we do to earn money and the things we buy with that money. So, when we talk about the economy, we talk about how people make, buy, sell, and use goods and services.
Types of Economy
There are four main types of economy. These are traditional, market, command, and mixed economies.
In a traditional economy, people do things based on habits and customs. They usually do the same job their parents and grandparents did. They trade goods and services without using money.
In a market economy, businesses and consumers decide what to produce and buy. They make these choices based on what they think is best for them. This type of economy is also called a ‘free market.’
In a command economy, the government makes all the decisions about what to produce, how to produce it, and who gets it. This is also known as a ‘planned economy.’
A mixed economy is a mix of market and command economies. The government makes some decisions, but businesses and consumers also have a say.
Why is Economy important?
The economy is important because it helps us understand how a country or place is doing. If the economy is doing well, people have jobs, businesses are making money, and the country is growing. But if the economy is doing poorly, people might lose their jobs, businesses might close, and the country might not grow.
The economy also helps us see how fair or unfair things are. For example, if some people have a lot of money and others have very little, the economy might not be fair.
How does the Economy work?
The economy works through a cycle of ups and downs. When the economy is up, businesses are doing well, and people have jobs. This is called a boom. But sometimes, the economy can go down. This is called a recession. During a recession, businesses might close, and people might lose their jobs.
To keep the economy stable, the government can do things like changing how much money is in the economy or changing interest rates. This is called economic policy.
So, the economy is a big part of our lives. It affects what jobs we can have, what we can buy, and how our country is doing. By understanding the economy, we can make better decisions and help make our country a better place.
That’s it! I hope the essay helped you.
If you’re looking for more, here are essays on other interesting topics:
- Essay on Economics Importance In Daily Life
- Essay on Economics And Society
- Essay on Economics And Economists
Apart from these, you can look at all the essays by clicking here .
Happy studying!
Leave a Reply Cancel reply
Your email address will not be published. Required fields are marked *
Save my name, email, and website in this browser for the next time I comment.
- Share full article
Advertisement
Supported by
Guest Essay
I’m an Economist. Don’t Worry. Be Happy.

By Justin Wolfers
Dr. Wolfers is a professor of economics and public policy at the University of Michigan and a host of the “Think Like an Economist” podcast.
I, too, know that flash of resentment when grocery store prices feel as if they don’t make sense. I hate the fact that a small treat feels less like an earned indulgence and more like financial folly. And I’m concerned about my kids now that house prices look like telephone numbers.
But I breathe through it. And I remind myself of the useful perspective that my training as an economist should bring. Sometimes it helps, so I want to share it with you.
Simple economic logic suggests that neither your well-being nor mine depends on the absolute magnitude of the numbers on a price sticker.
To see this, imagine falling asleep and waking up years later to discover that every price tag has an extra zero on it. A gumball costs $2.50 instead of a quarter; the dollar store is the $10 store; and a coffee is $50. The $10 bill in your wallet is now $100; and your bank statement has transformed $800 of savings into $8,000.
Importantly, the price that matters most to you — your hourly pay rate — is also 10 times as high.
What has actually changed in this new world of inflated price tags? The world has a lot more zeros in it, but nothing has really changed.
That’s because the currency that really matters is how many hours you have to work to afford your groceries, a small treat or a home, and none of these real trade-offs have changed.
This fairy tale — with some poetic license — is roughly the story of our recent inflation. The pandemic-fueled inflationary impulse didn’t add an extra zero to every price tag, but it did something similar.
The same inflationary forces that pushed these prices higher have also pushed wages to be 22 percent higher than on the eve of the pandemic. Official statistics show that the stuff that a typical American buys now costs 20 percent more over the same period. Some prices rose a little more, some a little less, but they all roughly rose in parallel.
It follows that the typical worker can now afford 2 percent more stuff. That doesn’t sound like a lot, but it’s a faster rate of improvement than the average rate of real wage growth over the past few decades .
Of course, those are population averages, and they may not reflect your reality. Some folks really are struggling. But in my experience, many folks feel that they’re falling behind, even when a careful analysis of the numbers suggests they’re not.
That’s because real people — and yes, even professional economists — tend to process the parallel rise of prices and wages in quite different ways. In brief, researchers have found that we tend to internalize the gains caused by inflation and externalize the losses. Those different processes yield different emotional responses.
Let’s start with higher prices. Sticker shock hurts. Even as someone who closely studies the inflation statistics, I’m still often surprised by higher prices. They feel unfair. They undermine my spending power, and my sense of control and order.
But in reality, higher prices are only the first act of the inflationary play. It’s a play that economists have seen before. In episode after episode, surges in prices have led to — or been preceded by — a proportional surge in wages.
Even though wages tend to rise hand in hand with prices, we tell ourselves a different story, in which the wage increases we get have nothing to do with price increases that cause them.
I know that when I ripped open my annual review letter and learned that I had gotten a larger raise than normal, it felt good. For a moment, I believed that my boss had really seen me and finally valued my contribution.
But then my economist brain took over, and slowly it sunk in that my raise wasn’t a reward for hard work, but rather a cost-of-living adjustment.
Internalizing the gain and externalizing the cost of inflation protects you from this deflating realization. But it also distorts your sense of reality.
The reason so many Americans feel that inflation is stealing their purchasing power is that they give themselves unearned credit for the offsetting wage increases that actually restore it.
Those who remember the Great Inflation of the ’60s, ’70s and early ’80s have lived through many cycles of prices rising and wages following. They understand the deal: Inflation makes life more difficult for a bit, but you’re only ever one cost-of-living adjustment away from catching up.
But younger folks — anyone under 60 — never experienced sustained inflation rates greater than 5 percent in their adult lives. And I think this explains why they’re so angry about today’s inflation.
They haven’t seen this play before, and so they don’t know that when Act I involves higher prices, Act II usually sees wages rising to catch up. If you didn’t know there was an Act II coming, you might leave the theater at intermission thinking you just saw a show about big corporations exploiting a pandemic to take your slice of the economic pie.
By this telling, decades of low inflation have left several generations ill equipped to deal with its return.
While older Americans understand that the pain of inflation is transitory, younger folks aren’t so sure. Inflation is a lot scarier when you fear that today’s price rises will permanently undermine your ability to make ends meet.
Perhaps this explains why the recent moderate burst of inflation has created seemingly more anxiety than previous inflationary episodes.
More generally, being an economist makes me an optimist. Social media is awash with (false) claims that we’re in a “ silent depression ,” and those who want to make America great again are certain it was once so much better.
But in reality, our economy this year is larger, more productive and will yield higher average incomes than in any prior year on record in American history. And because the United States is the world’s richest major economy, we can now say that we are almost certainly part of the richest large society in its richest year in the history of humanity.
The income of the average American will double approximately every 39 years. And so when my kids are my age, average income will be roughly double what it is today. Far from being fearful for my kids, I’m envious of the extraordinary riches their generation will enjoy.
Psychologists describe anxiety disorders as occurring when the panic you feel is out of proportion to the danger you face. By this definition, we’re in the midst of a macroeconomic anxiety attack.
And so the advice I give as an economist mirrors what I would give were I your therapist: Breathe through that anxiety, and remember that this, too, shall pass.
Justin Wolfers is a professor of economics and public policy at the University of Michigan and a host of the “Think Like an Economist” podcast.
The Times is committed to publishing a diversity of letters to the editor. We’d like to hear what you think about this or any of our articles. Here are some tips . And here’s our email: [email protected] .
Follow the New York Times Opinion section on Facebook , Instagram , TikTok , WhatsApp , X and Threads .
Essay on Inflation: Types, Causes and Effects
Essay on Inflation!
Essay on the Meaning of Inflation:
Inflation and unemployment are the two most talked-about words in the contemporary society. These two are the big problems that plague all the economies. Almost everyone is sure that he knows what inflation exactly is, but it remains a source of great deal of confusion because it is difficult to define it unambiguously.
Inflation is often defined in terms of its supposed causes. Inflation exists when money supply exceeds available goods and services. Or inflation is attributed to budget deficit financing. A deficit budget may be financed by additional money creation. But the situation of monetary expansion or budget deficit may not cause price level to rise. Hence the difficulty of defining ‘inflation’ .
Inflation may be defined as ‘a sustained upward trend in the general level of prices’ and not the price of only one or two goods. G. Ackley defined inflation as ‘a persistent and appreciable rise in the general level or average of prices’ . In other words, inflation is a state of rising price level, but not rise in the price level. It is not high prices but rising prices that constitute inflation.
ADVERTISEMENTS:
It is an increase in the overall price level. A small rise in prices or a sudden rise in prices is not inflation since these may reflect the short term workings of the market. It is to be pointed out here that inflation is a state of disequilibrium when there occurs a sustained rise in price level.
It is inflation if the prices of most goods go up. However, it is difficult to detect whether there is an upward trend in prices and whether this trend is sustained. That is why inflation is difficult to define in an unambiguous sense.
Let’s measure inflation rate. Suppose, in December 2007, the consumer price index was 193.6 and, in December 2008 it was 223.8. Thus the inflation rate during the last one year was 223.8 – 193.6/193.6 × 100 = 15.6%.
As inflation is a state of rising prices, deflation may be defined as a state of falling prices but not fall in prices. Deflation is, thus, the opposite of inflation, i.e., rise in the value or purchasing power of money. Disinflation is a slowing down of the rate of inflation.
Essay on the Types of Inflation :
As the nature of inflation is not uniform in an economy for all the time, it is wise to distinguish between different types of inflation. Such analysis is useful to study the distributional and other effects of inflation as well as to recommend anti-inflationary policies.
Inflation may be caused by a variety of factors. Its intensity or pace may be different at different times. It may also be classified in accordance with the reactions of the government toward inflation.
Thus, one may observe different types of inflation in the contemporary society:
(a) According to Causes:
i. Currency Inflation:
This type of inflation is caused by the printing of currency notes.
ii. Credit Inflation:
Being profit-making institutions, commercial banks sanction more loans and advances to the public than what the economy needs. Such credit expansion leads to a rise in price level.
iii. Deficit-Induced Inflation:
The budget of the government reflects a deficit when expenditure exceeds revenue. To meet this gap, the government may ask the central bank to print additional money. Since pumping of additional money is required to meet the budget deficit, any price rise may be called deficit-induced inflation.
iv. Demand-Pull Inflation:
An increase in aggregate demand over the available output leads to a rise in the price level. Such inflation is called demand-pull inflation (henceforth DPI). But why does aggregate demand rise? Classical economists attribute this rise in aggregate demand to money supply.
If the supply of money in an economy exceeds the available goods and services, DPI appears. It has been described by Coulborn as a situation of “too much money chasing too few goods” .
Note that, in this region, price level begins to rise. Ultimately, the economy reaches full employment situation, i.e., Range 3, where output does not rise but price level is pulled upward. This is demand-pull inflation. The essence of this type of inflation is “too much spending chasing too few goods.”
v. Cost-Push Inflation:
Inflation in an economy may arise from the overall increase in the cost of production. This type of inflation is known as cost-push inflation (henceforth CPI). Cost of production may rise due to increase in the price of raw materials, wages, etc. Often trade unions are blamed for wage rise since wage rate is not market-determined. Higher wage means higher cost of production.
Prices of commodities are thereby increased. A wage-price spiral comes into operation. But, at the same time, firms are to be blamed also for the price rise since they simply raise prices to expand their profit margins. Thus we have two important variants of CPI: wage-push inflation and profit-push inflation. Anyway, CPI stems from the leftward shift of the aggregate supply curve.

The price level thus determined is OP 1 . As aggregate demand curve shifts to AD 2 , price level rises to OP 2 . Thus, an increase in aggregate demand at the full employment stage leads to an increase in price level only, rather than the level of output. However, how much price level will rise following an increase in aggregate demand depends on the slope of the AS curve.
Causes of Demand-Pull Inflation :
DPI originates in the monetary sector. Monetarists’ argument that “only money matters” is based on the assumption that at or near full employment, excessive money supply will increase aggregate demand and will thus cause inflation.
An increase in nominal money supply shifts aggregate demand curve rightward. This enables people to hold excess cash balances. Spending of excess cash balances by them causes price level to rise. Price level will continue to rise until aggregate demand equals aggregate supply.
Keynesians argue that inflation originates in the non-monetary sector or the real sector. Aggregate demand may rise if there is an increase in consumption expenditure following a tax cut. There may be an autonomous increase in business investment or government expenditure. Governmental expenditure is inflationary if the needed money is procured by the government by printing additional money.
In brief, an increase in aggregate demand i.e., increase in (C + I + G + X – M) causes price level to rise. However, aggregate demand may rise following an increase in money supply generated by the printing of additional money (classical argument) which drives prices upward. Thus, money plays a vital role. That is why Milton Friedman believes that inflation is always and everywhere a monetary phenomenon.
There are other reasons that may push aggregate demand and, hence, price level upwards. For instance, growth of population stimulates aggregate demand. Higher export earnings increase the purchasing power of the exporting countries.
Additional purchasing power means additional aggregate demand. Purchasing power and, hence, aggregate demand, may also go up if government repays public debt. Again, there is a tendency on the part of the holders of black money to spend on conspicuous consumption goods. Such tendency fuels inflationary fire. Thus, DPI is caused by a variety of factors.
Cost-Push Inflation Theory :
In addition to aggregate demand, aggregate supply also generates inflationary process. As inflation is caused by a leftward shift of the aggregate supply, we call it CPI. CPI is usually associated with the non-monetary factors. CPI arises due to the increase in cost of production. Cost of production may rise due to a rise in the cost of raw materials or increase in wages.
Such increases in costs are passed on to consumers by firms by raising the prices of the products. Rising wages lead to rising costs. Rising costs lead to rising prices. And rising prices, again, prompt trade unions to demand higher wages. Thus, an inflationary wage-price spiral starts.
This causes aggregate supply curve to shift leftward. This can be demonstrated graphically (Fig. 11.4) where AS 1 is the initial aggregate supply curve. Below the full employment stage this AS curve is positive sloping and at full employment stage it becomes perfectly inelastic. Intersection point (E 1 ) of AD 1 and AS 1 curves determines the price level.
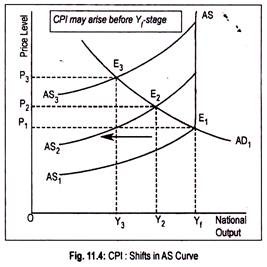
Now, there is a leftward shift of aggregate supply curve to AS 2 . With no change in aggregate demand, this causes price level to rise to OP 2 and output to fall to OY 2 .
With the reduction in output, employment in the economy declines or unemployment rises. Further shift in the AS curve to AS 2 results in higher price level (OP 3 ) and a lower volume of aggregate output (OY 3 ). Thus, CPI may arise even below the full employment (Y f ) stage.
Causes of CPI :
It is the cost factors that pull the prices upward. One of the important causes of price rise is the rise in price of raw materials. For instance, by an administrative order the government may hike the price of petrol or diesel or freight rate. Firms buy these inputs now at a higher price. This leads to an upward pressure on cost of production.
Not only this, CPI is often imported from outside the economy. Increase in the price of petrol by OPEC compels the government to increase the price of petrol and diesel. These two important raw materials are needed by every sector, especially the transport sector. As a result, transport costs go up resulting in higher general price level.
Again, CPI may be induced by wage-push inflation or profit-push inflation. Trade unions demand higher money wages as a compensation against inflationary price rise. If increase in money wages exceeds labour productivity, aggregate supply will shift upward and leftward. Firms often exercise power by pushing up prices independently of consumer demand to expand their profit margins.
Fiscal policy changes, such as an increase in tax rates leads to an upward pressure in cost of production. For instance, an overall increase in excise tax of mass consumption goods is definitely inflationary. That is why government is then accused of causing inflation.
Finally, production setbacks may result in decreases in output. Natural disaster, exhaustion of natural resources, work stoppages, electric power cuts, etc., may cause aggregate output to decline.
In the midst of this output reduction, artificial scarcity of any goods by traders and hoarders just simply ignite the situation.
Inefficiency, corruption, mismanagement of the economy may also be the other reasons. Thus, inflation is caused by the interplay of various factors. A particular factor cannot be held responsible for inflationary price rise.
Essay on the Effects of Inflation :
People’s desires are inconsistent. When they act as buyers they want prices of goods and services to remain stable but as sellers they expect the prices of goods and services should go up. Such a happy outcome may arise for some individuals; “but, when this happens, others will be getting the worst of both worlds.” Since inflation reduces purchasing power it is bad.
The old people are in the habit of recalling the days when the price of say, meat per kilogram cost just 10 rupees. Today it is Rs. 250 per kilogram. This is true for all other commodities. When they enjoyed a better living standard. Imagine today, how worse we are! But meanwhile, wages and salaries of people have risen to a great height, compared to the ‘good old days’. This goes unusually untold.
When price level goes up, there is both a gainer and a loser. To evaluate the consequence of inflation, one must identify the nature of inflation which may be anticipated and unanticipated. If inflation is anticipated, people can adjust with the new situation and costs of inflation to the society will be smaller.
In reality, people cannot predict accurately future events or people often make mistakes in predicting the course of inflation. In other words, inflation may be unanticipated when people fail to adjust completely. This creates various problems.
One can study the effects of unanticipated inflation under two broad headings:
(i) Effect on distribution of income and wealth
(ii) Effect on economic growth.
(a) Effects of Inflation on Income and Wealth Distribution :
During inflation, usually people experience rise in incomes. But some people gain during inflation at the expense of others. Some individuals gain because their money incomes rise more rapidly than the prices and some lose because prices rise more rapidly than their incomes during inflation. Thus, it redistributes income and wealth.
Though no conclusive evidence can be cited, it can be asserted that following categories of people are affected by inflation differently:
i. Creditors and Debtors:
Borrowers gain and lenders lose during inflation because debts are fixed in rupee terms. When debts are repaid their real value declines by the price level increase and, hence, creditors lose. An individual may be interested in buying a house by taking a loan of Rs. 7 lakh from an institution for 7 years.
The borrower now welcomes inflation since he will have to pay less in real terms than when it was borrowed. Lender, in the process, loses since the rate of interest payable remains unaltered as per agreement. Because of inflation, the borrower is given ‘dear’ rupees, but pays back ‘cheap’ rupees.
However, if in an inflation-ridden economy creditors chronically loose, it is wise not to advance loans or to shut down business. Never does it happen. Rather, the loan- giving institution makes adequate safeguard against the erosion of real value.
ii. Bond and Debenture-Holders:
In an economy, there are some people who live on interest income—they suffer most.
Bondholders earn fixed interest income:
These people suffer a reduction in real income when prices rise. In other words, the value of one’s savings decline if the interest rate falls short of inflation rate. Similarly, beneficiaries from life insurance programmes are also hit badly by inflation since real value of savings deteriorate.
iii. Investors:
People who put their money in shares during inflation are expected to gain since the possibility of earning business profit brightens. Higher profit induces owners of firms to distribute profit among investors or shareholders.
iv. Salaried People and Wage-Earners:
Anyone earning a fixed income is damaged by inflation. Sometimes, unionized worker succeeds in raising wage rates of white-collar workers as a compensation against price rise. But wage rate changes with a long time lag. In other words, wage rate increases always lag behind price increases.
Naturally, inflation results in a reduction in real purchasing power of fixed income earners. On the other hand, people earning flexible incomes may gain during inflation. The nominal incomes of such people outstrip the general price rise. As a result, real incomes of this income group increase.
v. Profit-Earners, Speculators and Black Marketeers:
It is argued that profit-earners gain from inflation. Profit tends to rise during inflation. Seeing inflation, businessmen raise the prices of their products. This results in a bigger profit. Profit margin, however, may not be high when the rate of inflation climbs to a high level.
However, speculators dealing in business in essential commodities usually stand to gain by inflation. Black marketeers are also benefited by inflation.
Thus, there occurs a redistribution of income and wealth. It is said that rich becomes richer and poor becomes poorer during inflation. However, no such hard and fast generalizations can be made. It is clear that someone wins and someone loses from inflation.
These effects of inflation may persist if inflation is unanticipated. However, the redistributive burdens of inflation on income and wealth are most likely to be minimal if inflation is anticipated by the people.
With anticipated inflation, people can build up their strategies to cope with inflation. If the annual rate of inflation in an economy is anticipated correctly people will try to protect them against losses resulting from inflation.
Workers will demand 10 p.c. wage increase if inflation is expected to rise by 10 p.c. Similarly, a percentage of inflation premium will be demanded by creditors from debtors. Business firms will also fix prices of their products in accordance with the anticipated price rise. Now if the entire society “learns to live with inflation” , the redistributive effect of inflation will be minimal.
However, it is difficult to anticipate properly every episode of inflation. Further, even if it is anticipated it cannot be perfect. In addition, adjustment with the new expected inflationary conditions may not be possible for all categories of people. Thus, adverse redistributive effects are likely to occur.
Finally, anticipated inflation may also be costly to the society. If people’s expectation regarding future price rise become stronger they will hold less liquid money. Mere holding of cash balances during inflation is unwise since its real value declines. That is why people use their money balances in buying real estate, gold, jewellery, etc.
Such investment is referred to as unproductive investment. Thus, during inflation of anticipated variety, there occurs a diversion of resources from priority to non-priority or unproductive sectors.
b. Effect on Production and Economic Growth :
Inflation may or may not result in higher output. Below the full employment stage, inflation has a favourable effect on production. In general, profit is a rising function of the price level. An inflationary situation gives an incentive to businessmen to raise prices of their products so as to earn higher doses of profit.
Rising price and rising profit encourage firms to make larger investments. As a result, the multiplier effect of investment will come into operation resulting in higher national output. However, such a favourable effect of inflation will be temporary if wages and production costs rise very rapidly.
Further, inflationary situation may be associated with the fall in output, particularly if inflation is of the cost-push variety. Thus, there is no strict relationship between prices and output. An increase in aggregate demand will increase both prices and output, but a supply shock will raise prices and lower output.
Inflation may also lower down further production levels. It is commonly assumed that if inflationary tendencies nurtured by experienced inflation persist in future, people will now save less and consume more. Rising saving propensities will result in lower further outputs.
One may also argue that inflation creates an air of uncertainty in the minds of business community, particularly when the rate of inflation fluctuates. In the midst of rising inflationary trend, firms cannot accurately estimate their costs and revenues. Under the circumstance, business firms may be deterred in investing. This will adversely affect the growth performance of the economy.
However, slight dose of inflation is necessary for economic growth. Mild inflation has an encouraging effect on national output. But it is difficult to make the price rise of a creeping variety. High rate of inflation acts as a disincentive to long run economic growth. The way the hyperinflation affects economic growth is summed up here.
We know that hyperinflation discourages savings. A fall in savings means a lower rate of capital formation. A low rate of capital formation hinders economic growth. Further, during excessive price rise, there occurs an increase in unproductive investment in real estate, gold, jewellery, etc.
Above all, speculative businesses flourish during inflation resulting in artificial scarcities and, hence, further rise in prices. Again, following hyperinflation, export earnings decline resulting in a wide imbalance in the balance of payments account.
Often, galloping inflation results in a ‘flight’ of capital to foreign countries since people lose confidence and faith over the monetary arrangements of the country, thereby resulting in a scarcity of resources. Finally, real value of tax revenue also declines under the impact of hyperinflation. Government then experiences a shortfall in investible resources.
Thus, economists and policy makers are unanimous regarding the dangers of high price rise. But the consequence of hyperinflation is disastrous. In the past, some of the world economies (e.g., Germany after the First World War (1914-1918), Latin American countries in the 1980s) had been greatly ravaged by hyperinflation.
The German Inflation of 1920s was also Catastrophic:
During 1922, the German price level went up 5,470 per cent, in 1923, the situation worsened; the German price level rose 1,300,000,000 times. By October of 1923, the postage of the lightest letter sent from Germany to the United States was 200,000 marks.
Butter cost 1.5 million marks per pound, meat 2 million marks, a loaf of bread 200,000 marks, and an egg 60,000 marks Prices increased so rapidly that waiters changed the prices on the menu several times during the course of a lunch!! Sometimes, customers had to pay double the price listed on the menu when they observed it first!!!
During October 2008, Zimbabwe, under the President-ship of Robert G. Mugabe, experienced 231,000,000 p.c. (2.31 million p.c.) as against 1.2 million p.c. price rise in September 2008—a record after 1923. It is an unbelievable rate. In May 2008, the cost of price of a toilet paper itself and not the costs of the roll of the toilet paper came to 417 Zimbabwean dollars.
Anyway, people are harassed ultimately by the high rate of inflation. That is why it is said that ‘inflation is our public enemy number one’. Rising inflation rate is a sign of failure on the part of the government.
Related Articles:
- Essay on the Causes of Inflation (473 Words)
- Cost-Push Inflation and Demand-Pull or Mixed Inflation
- Demand Pull Inflation and Cost Push Inflation | Money
- Essay on Inflation: Meaning, Measurement and Causes
Essay on Indian Economy for Students and Children
500+ words essay on indian economy.
India is mainly an agricultural economy . Agricultural activities contribute about 50% of the economy. Agriculture involves growing and selling of crops, poultry, fishing, cattle rearing, and animal husbandry. People in India earn their livelihood by involving themselves in many of these activities. These activities are vital to our economy. The Indian economy has seen major growth in the last few decades. The credit for this boom largely goes to the service sector. Agriculture and associated activities have also been improvised to match the global standards and the export of various food products has seen an upward trend thereby adding to the economic growth. The industrial sector does not lag behind a bit. A number of new large scale, as well as small scale industries, have been set up in recent times and these have also proved to have a positive impact on the Indian economy.

Government’s Role in Economic Growth
Majority of the working Indian population was and is still engaged in the agriculture sector. Growing crops, fishing, poultry and animal husbandry were among the tasks undertaken by them. They manufactured handicraft items that were losing their charm with the introduction of the industrial goods. The demand for these goods began to decline. The agricultural activities also did not pay enough.
The government identified these problems as hindering the economic growth of the country and established policies to curb them. Promotion of cottage industry, providing fair wages to the laborers and providing enough means of livelihood to the people were some of the policies laid by the government for the country’s economic growth.
Get the huge list of more than 500 Essay Topics and Ideas
The Rise of the Industrial Sector
The government of India also promoted the growth of small scale and large scale industry as it understood that agriculture alone would not be able to help in the country’s economic growth. Many industries have been set up since independence. A large number of people shifted from the agricultural sector to the industrial sector in an attempt to earn better.
Today, we have numerous industries manufacturing a large amount of raw material as well as finished goods. The pharmaceutical industry, iron and steel industry , chemical industry, textile industry, automotive industry, timber industry, jute, and paper industry are among some of the industries which have contributed a great deal in our economic growth.
The Growth in Service Sector
The service sector has also helped in the growth of our country. This sector has seen growth in the last few decades. The privatization of the banking and telecom sectors has a positive impact on the service sector. The tourism and hotel industries are also seeing a gradual growth. As per a recent survey, the service sector is contributing to more than 50% of the country’s economy.
Indian Economy after Demonetization
The worst affected were the people in the rural areas who did not have access to internet and plastic money. This affects many big and small businesses in the country very badly. Several of them were shut down as a result of this. While the short term effects of demonetization were devastating, this decision did have a brighter side when looked at from long term perspective.
The positive impact of demonetization on the Indian economy is a breakdown of black money, the decline in fake currency notes, increase in bank deposits, demonetization stopped the flow of black money in the real estate sector to ensure a fair play, increase in digital transactions, cutting monetary support for terrorist activities.
Many of our industries are cash-driven and sudden demonetization left all these industries starving. Also, many of our small scale, as well as large scale manufacturing industries, suffered huge losses thereby impacting the economy of the country negatively. Many factories and shops had to be shut down. This did not only impact the businesses but also the workers employed there. Several people, especially the laborers, lost their jobs.
The Indian economy undergoes several positive changes since independence. It is growing at a good pace. However, the rural regions of our country are still under-developed. The government must make efforts to improve the economic condition of these areas.
Customize your course in 30 seconds
Which class are you in.

- Travelling Essay
- Picnic Essay
- Our Country Essay
- My Parents Essay
- Essay on Favourite Personality
- Essay on Memorable Day of My Life
- Essay on Knowledge is Power
- Essay on Gurpurab
- Essay on My Favourite Season
- Essay on Types of Sports
Leave a Reply Cancel reply
Your email address will not be published. Required fields are marked *
Download the App


- © 2024
The Indonesian Economy and the Surrounding Regions in the 21st Century
Essays in Honor of Iwan Jaya Azis
- Budy Prasetyo Resosudarmo 0 ,
- Yuri Mansury 1
Arndt-Corden Dept. of Economics, Australian National University, Canberra, Australia
You can also search for this editor in PubMed Google Scholar
Department of Social Sciences, Illinois Institute of Technology, Chicago, USA
- Is one of the very few books on the economy of Southeast Asia, an increasingly important economic region
- Presents topics on the basis of their importance in the fields of regional science and economics, written by experts
- Honors Professor Iwan Jaya Azis, a leading expert on the Indonesian economy and the region
Part of the book series: New Frontiers in Regional Science: Asian Perspectives (NFRSASIPER, volume 76)
- Table of contents
About this book
Editors and affiliations, about the editors, bibliographic information.
- Publish with us
Buying options
- Available as EPUB and PDF
- Read on any device
- Instant download
- Own it forever
- Durable hardcover edition
- Free shipping worldwide - see info
Tax calculation will be finalised at checkout
Other ways to access
This is a preview of subscription content, log in via an institution to check for access.
Table of contents (16 chapters)
Front matter, iwan jaya azis: a person, an economist, and a regional scientist.
- Budy P. Resosudarmo, Yuri Mansury
The Indonesian Economy
Impacts of monetary policy on consumer demand of high- and low-income groups in indonesia.
- Gunawan Wicaksono, Kieran P. Donaghy, Clifford R. Wymer
Rapid Urbanization: The Challenges and Opportunities for Planning in Indonesian Cities
- Christopher Silver
Small- and Medium-Size Linkages with Large Firms: Revisiting Studies on Indonesian Manufacturing
- Ari Kuncoro
Indonesia and the Resource Curse: Economic and Environmental Dimensions
- Hal Hill, Donny Pasaribu
Climate Change Policies in Indonesia: Challenges and Economic Consequences
- Arianto A. Patunru, Budy P. Resosudarmo
The Status and Trend of Indonesian Provinces’ Sustainability: A Genuine Savings Approach
- Armida Salsiah Alisjahbana, Viktor Pirmana, Arief Anshory Yusuf
Economic Impact of the 2018 Asian Games in Indonesia
- Bambang Brodjonegoro, Amalia Adininggar Widyasanti, Firman Hidayat, Rasi Tamadhika Fajar Ramadhan
Southeast Asian Economies and the Region
Indonesia and vietnam in global supply chains and the age of covid: a tale of two countries.
- Willem Thorbecke, Atsuyuki Kato
Education and Expenditure Inequality in Indonesia and the Philippines: A Comparative Analysis in an Urban and Rural Dual Framework
- Takahiro Akita, Sachiko Miyata
Impact Analysis of the Economic Eastern Corridor on the Thai Economy: An Application of Multi-Regional Input–Output Model and Dynamic Computable General Equilibrium Model
- Nattapong Puttanapong, Kanit Sangsubhan
Climate Change, Food Security, and Trade: Navigating Through Multiple Crises
- Paul Brenton, Vicky Chemutai, Mari Pangestu
Methods of Regional Economic Analysis
I won’t get caught: an agent-based model of corruption with incomplete information.
Yuri Mansury
Analyses of University-Partnered Economic Development Initiatives and Minimum-Wage Policies Under Different Assumptions of Competition and Scale Economies
- Jati Waluyo, Javier Perez Burgos, Yuri Mansury, Hee Hwa Min, Kieran Donaghy
Lessons Learned from Managing Transportation Demand for Suburban Areas of Washington, DC: Implications for Rapidly Growing Cities of the World
- Tschangho John Kim
A Complex Systems Approach to Uneven Development in Asia: Political Economy and Mathematical Models
- Haider A. Khan
This book broadens the reader’s knowledge of several important issues having to do with the economy of Indonesia and its surrounding regions, to which Professor Iwan Jaya Azis has made significant contributions in the last 40 years. The book is divided into three parts, the first of which contains several chapters describing fundamental methods in regional economics, development economics, macroeconomics, and finance. These methods are crucial in understanding the political economy of Indonesia and the neighboring regions. Among the techniques discussed are social accounting matrix (SAM) analysis, computable general equilibrium (CGE) modeling, and agent-based modeling (ABM) approaches. The second part is on several important issues related to the Indonesian economy. The topics covered are urbanization, resource booms, manufacturing, and micro and small enterprises. The book’s third part deals with the economies of several countries in the neighboring Southeast Asian region, including the Philippines, Vietnam, and Thailand.
- Indonesian Economy
- Regional Science
- Regional Economics
- Southeast Asian Economies
- Development Economics
Budy Prasetyo Resosudarmo
Book Title : The Indonesian Economy and the Surrounding Regions in the 21st Century
Book Subtitle : Essays in Honor of Iwan Jaya Azis
Editors : Budy Prasetyo Resosudarmo, Yuri Mansury
Series Title : New Frontiers in Regional Science: Asian Perspectives
DOI : https://doi.org/10.1007/978-981-97-0122-3
Publisher : Springer Singapore
eBook Packages : Economics and Finance , Economics and Finance (R0)
Copyright Information : The Editor(s) (if applicable) and The Author(s), under exclusive license to Springer Nature Singapore Pte Ltd. 2024
Hardcover ISBN : 978-981-97-0121-6 Due: 12 May 2024
Softcover ISBN : 978-981-97-0124-7 Due: 12 May 2024
eBook ISBN : 978-981-97-0122-3 Published: 05 April 2024
Series ISSN : 2199-5974
Series E-ISSN : 2199-5982
Edition Number : 1
Number of Pages : XXXIV, 406
Number of Illustrations : 1 b/w illustrations
Topics : Regional/Spatial Science , Asian Economics , Development Economics , Economic Growth
Policies and ethics
- Find a journal
- Track your research
How Does Expropriation Risk Affect Innovation?
We analyze how expropriation risk reduces incentives for innovation and reallocates resources from the innovative sector, building on Romer’s(1990) model. Our framework predicts the R&D expenditure, the share of human capital in R&D, the number of patents, technical progress, and economic growth are all lower due to lower expected profits and patent devaluation in the presence of expropriation risks. Empirical analyses, based on a LASSO Instrumental Variable approach and a novel comprehensive dataset spanning nearly two decades, confirm our theoretical predictions. We find robust evidence that expropriation risk, such as corruption, negatively impacts innovation by reducing R&D expenditure, human capital in R&D, number of patents, scientific publications, and the Economic Complexity Index, which is our proxy for technical progress. These findings highlight the detrimental effects of expropriation risk on innovation and economic development at the country level.
We would like to express our gratitude to Gabriel Cruz for his support as a research assistant. PE is grateful for the support provided by the Centre for Social Conflict and Cohesion Studies COES (ANID/FONDAP/15130009). We are very grateful to seminar participants at Universidad Adolfo Ibañez, and the Strategy, Innovation, Entrepreneurship and Sustainability group members for their invaluable comments. We also thank comments from Josh Lerner at Harvard University. The views expressed herein are those of the authors and do not necessarily reflect the views of the National Bureau of Economic Research.
MARC RIS BibTeΧ
Download Citation Data
More from NBER
In addition to working papers , the NBER disseminates affiliates’ latest findings through a range of free periodicals — the NBER Reporter , the NBER Digest , the Bulletin on Retirement and Disability , the Bulletin on Health , and the Bulletin on Entrepreneurship — as well as online conference reports , video lectures , and interviews .


The Creativity Decline: Evidence from US Patents
Working Paper 2024-008A by Aakash Kalyani
Economists have long struggled to understand why aggregate productivity growth has dropped in recent decades while the number of new patents filed has steadily increased. I offer an explanation for this puzzling divergence: the creativity embodied in US patents has dropped dramatically over time. To separate creative from derivative patents, I develop a novel, text-based measure of patent creativity: the share of technical terminology that did not appear in previous patents. I show that only creative and not derivative patents are associated with significant improvements in firm level productivity. Using the measure, I show that inventors on average file creative patents upon entry, and file derivative patents with more experience. I embed this life-cycle of creativity in a growth model with endogenous creation and imitation of technologies. In this model, falling population growth explains 27% of the observed decline in patent creativity, 30% of the slowdown in productivity growth, and 64% of the increase in patenting.
Read Full Text
https://doi.org/10.20955/wp.2024.008
- Subscribe to Our Newsletter
Related Links
- Economist Pages
- JEL Classification System
- Fed In Print
SUBSCRIBE TO THE RESEARCH DIVISION NEWSLETTER
Research division.
- Legal and Privacy

One Federal Reserve Bank Plaza St. Louis, MO 63102
Information for Visitors


IMAGES
VIDEO
COMMENTS
empirical exercise in which you will analyze economic data using a standard statistical software package (such as STATA). The empirical exercise will give you experience in answering an economic question with data and/or drawing conclusions from evidence. • Short Essays (4-6pp.). Short essays may require you to analyze two
Among the main topics you can discuss in economics research are: Fundamental economics, cost to benefit analysis, and importance of decision-making; Macroeconomics, supply, and demand; Microeconomics, market structure, and strategies, competition; International economics, trade, market, and more; Personal economics, spending habits, personal ...
Here are some economics essay examples: Short Essay About Economics. The Role of Fiscal Policy in Economic Stimulus. Fiscal policy plays a crucial role in shaping economic conditions and promoting growth. During periods of economic downturn or recession, governments often resort to fiscal policy measures to stimulate the economy.
Exclusively available on IvyPanda. Economy can be defined as the wealth and resources of a community,especially in terms of production and consumption of goods and services. Currently, the United States is the leading super power in the world and it acts as a role model to other states. The economic trend in the United States influences the ...
The economic essay topics are divided into several categories that will help you with your research. And a pleasant bonus from our team! We have created a great guide on how to write an economics essay. So, don't miss your chance to write an outstanding economic paper! Check out our essay ideas, read our tips carefully, and be ready to ...
Humorous. Top 10 Reasons For Studying Economics. Inflation explained by Victor Borge. Funny Exam Answers. Humorous look at Subprime crisis. A collection of macro-economic essays on topics Inflation, Economic growth, government borrowing, balance of payments. Evaluation and critical analysis of all latest issues of the current day.
3. Come up with a thesis statement. A thesis statement is the main argument you will make in your essay. It should be 1-2 sentences long and respond to the essential question that's being asked. The thesis will help you structure the body of your essay, and each point you make should relate back to the thesis. 4.
In this collection of 12 essays, leading scholars affiliated with the Global Economy and Development program at Brookings present new ideas that are forward-looking, policy-focused, and that will ...
Here are some behavioral economics essay topics: The influence of socio-economic norms on consumer behavior and decision-making. The impact of framing effects on individual choices and decision-making processes. The role of default options in shaping consumer behavior and encouraging desirable outcomes.
Honduras Economy Honduras is the second poorest country in Latin America, with a GDP per capita of 2.5 thousand dollars. The Open Market is extremely important to Honduras's economy; the value of exports and imports together is 109% of the GDP. The tax on imports and exports is 5.8 percent.
Social sciences students often have to write essays on economy. You can make it easier by using a sample paper to guide you. This will help you to write an interesting introduction, main body, and conclusion for an essay on economy. 81 essay samples found. Sort & filter. 1
Here is a compilation of essays on 'Economic Growth' for class 9, 10, 11 and 12. Find paragraphs, long and short essays on 'Economic Growth' especially written for school and college students. Essay on Economic Growth Essay Contents: Introduction to Economic Growth Adam Smith and Economic Growth The Classical Theory of Economic Stagnation Marx's Theory of Economic Development Rostow's ...
Why I Chose to Study Economics: A Student Shares Her Story. Just before my senior year of high school, I decided on a whim that I wanted to take the AP Economics course that my high school offered. Going into it, I had next to no knowledge about any economic topic. At the time, my older sister, who was in college, had taken an economics course ...
The U.S. Economy Essay. The U.S. economy faces many challenges given the fact that it is recovering from a financial crisis. Virtually every sector of the economy was affected by the 2009 financial crisis. Economic growth slowed down while unemployment rates increased. It is important to note that these conditions have not changed much.
Learn about the Indian economy in detail with this 500+ words essay on the role of agriculture and industry in the economy, the Five-year plans, and the challenges and recovery of the COVID-19 pandemic. The essay also covers the achievements and goals of India's economic development since independence.
Students are often asked to write an essay on Economy in their schools and colleges. And if you're also looking for the same, we have created 100-word, 250-word, and 500-word essays on the topic. Let's take a look… 100 Words Essay on Economy Understanding Economy. An economy is a system where people make, trade, and use things that have ...
Essay from The Economist. You've seen the news, now discover the story. ... The story of China's economy as told through the world's biggest building.
Official statistics show that the stuff that a typical American buys now costs 20 percent more over the same period. Some prices rose a little more, some a little less, but they all roughly rose ...
In this essay we will discuss about Economics. After reading this essay you will learn about: 1. Subject Matter of Economics 2. Economics as a Science 3. Economics as an Art 4. Neo-Classical View of Marshall 5. The Classical View of Adam Smith 6. Basic Concepts of Economics 7. Types of Goods in Economics 8. Utility in Economics. Contents: Essay on Subject Matter of Economics Essay on Economics ...
Essay on Inflation! Essay on the Meaning of Inflation: Inflation and unemployment are the two most talked-about words in the contemporary society. These two are the big problems that plague all the economies. Almost everyone is sure that he knows what inflation exactly is, but it remains a source of great deal of confusion because it is difficult to define it unambiguously. Inflation is often ...
500+ Words Essay on Indian Economy. India is mainly an agricultural economy. Agricultural activities contribute about 50% of the economy. Agriculture involves growing and selling of crops, poultry, fishing, cattle rearing, and animal husbandry. People in India earn their livelihood by involving themselves in many of these activities.
Essays in Honor of Iwan Jaya Azis. ... This book broadens the reader's knowledge of several important issues having to do with the economy of Indonesia and its surrounding regions, to which Professor Iwan Jaya Azis has made significant contributions in the last 40 years. The book is divided into three parts, the first of which contains ...
We analyze how expropriation risk reduces incentives for innovation and reallocates resources from the innovative sector, building on Romer's(1990) model. Our framework predicts the R&D expenditure, the share of human capital in R&D, the number of patents, technical progress, and economic growth ...
The U.S. economy—by many measures—is doing great. But many voters think otherwise. Here's what the data say about why voters feel so bad about the economy and what it could mean for ...
This paper presents a novel approach to addressing VAT regressivity, by proposing the adoption of a progressive VAT: a single-rate, broad-base, VAT, whereby tax paid on consumption is re-paid to lower income households in real-time, at the moment of purchase. Such a system can effectively eliminate regressivity, while minimizing the political economy, cash-flow, and welfare stigma obstacles ...
The Creativity Decline: Evidence from US Patents. Working Paper 2024-008A by Aakash Kalyani. Economists have long struggled to understand why aggregate productivity growth has dropped in recent decades while the number of new patents filed has steadily increased. I offer an explanation for this puzzling divergence: the creativity embodied in US ...