So What Do You Think? Writing a Review

- Resources & Preparation
- Instructional Plan
- Related Resources
Teenagers are often outspoken and opinionated. Writing reviews of the literature they read gives them a chance to express their ideas while developing style and voice. This lesson uses discussion of student opinions about yesterday's lunch or a popular TV show serves as an introduction to the genre of reviews. Students then read and analyze conflicting reviews. After examining samples of movie, music, restaurant, and book reviews, students devise guidelines for writing interesting and informative reviews. They then produce their own reviews of the literature they're reading in class. Finally, students compare their ideas and their pieces with published reviews of the same piece of literature. Though this lesson is illustrated with examples from student and professional reviews of Raymond Carver's writing, the techniques can be used with whatever literature students are reading.

Featured Resources
Components of a Review : This handout gives an overview of what is normally included in a critical review.
Review Guidelines : Students can use these guidelines when writing their own critical reviews.
From Theory to Practice
While it's important for students to learn to read and evaluate critical commentary, "Each reader has a right-and even a responsibility-to form his or her own opinions, based on that reader's reading and understanding of a piece of literature, and to be able to support those opinions with solid reasons" (97).
When students express ideas on an author's work that are also noted by critics, "it presents a perfect opportunity to introduce critical commentary naturally into class discussion in order to promote a deeper understanding of the literature" (100).
Further Reading
Common Core Standards
This resource has been aligned to the Common Core State Standards for states in which they have been adopted. If a state does not appear in the drop-down, CCSS alignments are forthcoming.
State Standards
This lesson has been aligned to standards in the following states. If a state does not appear in the drop-down, standard alignments are not currently available for that state.
NCTE/IRA National Standards for the English Language Arts
- 1. Students read a wide range of print and nonprint texts to build an understanding of texts, of themselves, and of the cultures of the United States and the world; to acquire new information; to respond to the needs and demands of society and the workplace; and for personal fulfillment. Among these texts are fiction and nonfiction, classic and contemporary works.
- 3. Students apply a wide range of strategies to comprehend, interpret, evaluate, and appreciate texts. They draw on their prior experience, their interactions with other readers and writers, their knowledge of word meaning and of other texts, their word identification strategies, and their understanding of textual features (e.g., sound-letter correspondence, sentence structure, context, graphics).
- 4. Students adjust their use of spoken, written, and visual language (e.g., conventions, style, vocabulary) to communicate effectively with a variety of audiences and for different purposes.
- 5. Students employ a wide range of strategies as they write and use different writing process elements appropriately to communicate with different audiences for a variety of purposes.
- 6. Students apply knowledge of language structure, language conventions (e.g., spelling and punctuation), media techniques, figurative language, and genre to create, critique, and discuss print and nonprint texts.
- 7. Students conduct research on issues and interests by generating ideas and questions, and by posing problems. They gather, evaluate, and synthesize data from a variety of sources (e.g., print and nonprint texts, artifacts, people) to communicate their discoveries in ways that suit their purpose and audience.
- 8. Students use a variety of technological and information resources (e.g., libraries, databases, computer networks, video) to gather and synthesize information and to create and communicate knowledge.
- 9. Students develop an understanding of and respect for diversity in language use, patterns, and dialects across cultures, ethnic groups, geographic regions, and social roles.
- 12. Students use spoken, written, and visual language to accomplish their own purposes (e.g., for learning, enjoyment, persuasion, and the exchange of information).
Materials and Technology
- Sample reviews of various types (movie, music, restaurant, book, etc.), both print and online
- Specific reviews of the literature students are reading
- Components of a Review
- Creating Classroom Discussion about Reviews
- Student Example of a Book Review
- Review Guidelines
- Writing a Review Checklist
- Student Reflection Sheet
Preparation
- two conflicting reviews of a current movie, television show, or CD with which students are likely familiar.
- reviews specific to the writer(s) who students are reading. The Stauffer Library Reference and Book Reviews in the Yahoo! Directory may be helpful in finding those reviews.
- Make appropriate number of copies of handouts.
- Test the ReadWriteThink Pinting Press on your computers to familiarize yourself with the tool and ensure that you have the Flash plug-in installed. You can download the plug-in from the technical support page.
Student Objectives
Students will
- read a variety of different kinds of reviews.
- determine the qualities and characteristics of an effective review.
- use critical thinking skills to formulate their own opinions about a writer's work.
- apply their knowledge to write their own reviews.
- compare their ideas and their work to that of professional reviewers.
Session One
- In this first class session, work to generate interest in writing a review-and to convince students that they do have strong and valid opinions.
- If lunch was "gross," what made it so?
- If the show was "really funny," why did it make them laugh?
- Ask students why they go to certain movies, buy specific CDs, or choose to eat in particular restaurants. Encourage them to explore where they get their "recommendations" from.
- Invite students to share both positive and negative experiences they have had as a result of listening to someone else's opinion.
- Lead the discussion to a point where students begin to see that word-of-mouth recommendations and published reviews essentially serve the same purpose: to comment on and evaluate a work or an event.
- Share two conflicting reviews with students.
- the kind of information included in both reviews.
- the specific points the reviewers agree and disagree about.
- any differences in focus between the reviews.
- which review is more entertaining—and why.
- which review is more convincing—and why.
- Ask students to list various kinds of reviews and to suggest where they can find these reviews (newspapers, magazines, journals, and online).
- For homework, ask each student bring one to three reviews to class.
Session Two
- In this second session, focus on helping students determine the qualities and characteristics of a good review.
- the name of what is being reviewed
- a clear statement of the reviewer's opinion (i.e., a thesis)
- specific examples that support the reviewer's opinion
- a particular tone (use of humor, sarcasm, authority, etc.).
- book reviews may include quotations from the work.
- restaurant reviews may discuss atmosphere.
- both music and literary reviews may trace developments in the writer/musician's history.
- Each small group should choose one review to read to the class along with their own short oral analysis.
- As a conclusion to the activity, the class as a whole should compile a list on the board or on chart paper of qualities that contribute to a good review. If desired, share the Components of a Review handout, which reviews the parts of a review.
- The teacher should collect all reviews students brought in for homework for use in future sessions.
Session Three
- In this third session, work to get students to focus on the particular attributes of a book review in preparation for writing their own reviews of the literature they're reading.
- Ideally, the teacher should have a selection of book reviews from those collected from students the previous day. In case students have not brought in book reviews, the teacher should have such reviews available. These reviews should be carefully chosen so that their content is accessible to students. It's best if some reviews focus on works students may have read while others are of work unfamiliar to students.)
- In small groups of three or four, have students examine a book review and break it down into its components to determine how the introduction, the body, and the conclusion allow the writer to make his/her points.
- Next, students should examine the particular style of their group's review and determine how the writer achieves a unique voice. Each group should try to determine the tone of their review (i.e., pompous and authoritative, humorous, enthusiastic, analytical, etc.) by noting such things as word choice, sentence structure, and use of detail. If students have collected reviews written by the same reviewer, these "elusive" qualities may be easier to spot.
- Invite a class discussion about how a review combines the informative aspects of straight journalism with the "pizzazz" of personal narrative.
- Where did your review appear?
- What do you know about this publication?
- Who do you think the audience for this publication would be?
- What would a reader who had read the book take from the review?
- What would a reader unfamiliar with the book take from the review?
- By the end of the session, ask students to compile a class list of broad, basic guidelines for writing a review. Example guidelines are also available.
- Invite students to begin writing the first draft of a review based on the particular piece(s) of literature the class is studying.
- If students are reading one book, that one work would be the focus of the review.
- If students are reading more than one work (i.e., a number of short stories, poems, or essays) by an author, the review can cover any or all of this material.
- Ask students to design a rating system to include with the written review. The system can be as traditional as 1-5 stars or something more creative.
NOTE: Older students tend to get the style and tone of a review quite quickly, while younger students often produce something more like a book report in the early drafts. Writing instruction should be geared to the ability of each class.
- Use the Writing a Review Checklist as a guide to help students draft and edit their reviews.
Session Four
- In this fourth session, introduce critical commentary into class discussion.
- When the students have completed their reviews, invite them to publish their reviews using one of the options on the ReadWriteThink Printing Press . Print them when they are complete.
- With their final drafts complete, have students read professionally written reviews on the same text and compare their ideas as well as their writing to these reviews. Depending on the accessibility of these reviews, you can collect all published material or students can be assigned this task. (It's for this reason that this aspect of the assignment works best if the writers reviewed are contemporary.)
- When comparing their reviews with the published pieces, students should find points that are raised in both. This process demystifies critical commentary and allows students to feel comfortable discussing the work of reviewers. For example, one of my students writes of his appreciation of Carver's "deadpan humor."
- Teachers can use such excerpts to generate lively classroom discussion. If desired, use the this suggestion for creating a classroom discussion.
- After all students have reacted to each excerpt, invite the class to break into pairs or small groups, with each group responsible for sifting through the material on one of the papers.
- Finally, have students present conclusions based on their peers' responses to the critical commentary.
- a classroom bulletin board displaying reviews, accompanied by artwork and photographs of the authors.
- a class compilation of reviews. Students can use the ReadWriteThink Printing Press to compile their reviews in a reader-friendly format.
- a class publication with all reviews collected in a booklet, brochure, or binder and saved for future classes who will be studying the same author. This collection can be added to over the years to create an "historical perspective" on a particular works/authors.
- submissions to print and online publications that seek reviews. (Note: Teen Ink seeks student written reviews on all topics.)
- writing an individual response to a review to then share with the class.
- revising and rewriting their own original reviews to address points raised by the professional reviewer.
- working with a partner and each taking a side in response to a review, with one student proving the reviewer is "right" and the other proving him/her "wrong."
- When students are comparing different types of reviews, invite them to use the Venn Diagram interactive.
Student Assessment / Reflections
- Grade the review as a complete writing assignment.
- As students write and revise their reviews, guide their work with the Review Checklist , a worksheet that outlines the vital features of a good review and asks students to verify that their final review includes these specific features. This checklist can be used by the teacher in evaluating the review.
- Students can assess their own work and learning by completing a Reflection Sheet that is handed in with the review. As with all reflection sheets, the form should include 4–5 questions that make writers really think about their pieces and the process that led to their creation.
- Publish student reviews using one of the options listed above to provide further feedback and assessment for students.
- Calendar Activities
- Professional Library
- Student Interactives
- Lesson Plans
The interactive Printing Press is designed to assist students in creating newspapers, brochures, and flyers.
Add new comment
- Print this resource
Explore Resources by Grade
- Kindergarten K
Book Review Lesson Plan: Teach Students How to Write a Successful Book Report
- Categories : High school english lesson plans grades 9 12
- Tags : High school lesson plans & tips
Teaching Students to Write a Book Review
I’ve always been an avid reader, but I hit a snag around high school and college when it came to choosing books for reading pleasure. I started reading book reviews out of my People magazine and online to help narrow down my choices. Through reading reviews, I was introduced to some of my all-time favorite novels, like The Lovely Bones by Alice Sebold and The Time Traveler’s Wife by Audrey Niffenegger. Book reviews are a useful resource for reading fans, but can also be an alternative assessment tool for teachers.
Before students can write a book review, you must introduce them to professionally written pieces. Take them to the computer lab and go to sites that have notable book reviews, like the New York Times or Barnes and Noble Review. If you do not have access to the internet, you can always clip reviews from magazines, like People or from the newspaper. Read several reviews as a class and discuss the format reviewers use when writing about a book. Be sure to point out that reviews provide a general summary, name major characters, introduce the major conflicts in the story, and give either a positive, negative, or neutral opinion of the work. Good reviews will never reveal the resolution to the conflict, so encourage them to avoid giving away the ending!
I also use this time discuss how reviewing books, movies, and other media can easily turn into a profession. We discuss how writing and expressing one’s opinions clearly can benefit a future reviewer. Students are in awe at the many different types of reviewers that are in our mainstream media today. There are reviewers for video games, phone apps, computer software, as well as the typical book and movie reviewers. As a class we discuss how much fun a career in reviewing could bring to someone who has an avid interest in the subject matter they are critiquing. Tying a real-world application to the assignment helps middle school kids to see the answer to the eternal adolescent question, “Why do I need to know this” that every teacher seems to encounter on a daily (if not on a daily basis)!
How to Implement and Assess Student Reviews
Develop a structure for the book review, depending on the length you desire the review to be. I usually like students to implement the “Plot Pyramid” structure that they learn early on in the year, which follows the five steps of plot organization: Exposition, Conflict/Rising Action, Climax, Falling Action/denouement, and Resolution. Of course, I have them leave off resolution, so the ending to the novel is not revealed to the reader. This ends up being a four paragraph structure (minus the resolution), and then I have them add an “opinion paragraph” at the end of their plot assessment to make the structure a five-paragraph essay form.
If you have advanced students, or if you think your students are ready, you can also require quote integration into the article. Using the Quote Burger Method , assign students to integrate a certain number of quotes within their writing to bring a flavor and voice to the article that mirror’s the book. You will also be able to pick up on who actually read the book, and who is “writing blind”, based on the relevance of their quotes. At the end of the article, students can also rank the book on a four star system (one star being a horrible book and four stars being an awesome book). Students can draw the stars and color them in, or you can use clip art in Microsoft Word….either way, assigning a star ranking adds visual appeal to their review and peaks student interest in the review.
- Teacher experience.

How to Write a Book Review: The Ultimate Guide
WHAT IS A BOOK REVIEW?

Traditionally, book reviews are evaluations of a recently published book in any genre. Usually, around the 500 to 700-word mark, they briefly describe a text’s main elements while appraising the work’s strengths and weaknesses. Published book reviews can appear in newspapers, magazines, and academic journals. They provide the reader with an overview of the book itself and indicate whether or not the reviewer would recommend the book to the reader.
WHAT IS THE PURPOSE OF A BOOK REVIEW?
There was a time when book reviews were a regular appearance in every quality newspaper and many periodicals. They were essential elements in whether or not a book would sell well. A review from a heavyweight critic could often be the deciding factor in whether a book became a bestseller or a damp squib. In the last few decades, however, the book review’s influence has waned considerably, with many potential book buyers preferring to consult customer reviews on Amazon, or sites like Goodreads, before buying. As a result, book review’s appearance in newspapers, journals, and digital media has become less frequent.
WHY BOTHER TEACHING STUDENTS TO WRITE BOOK REVIEWS AT ALL?
Even in the heyday of the book review’s influence, few students who learned the craft of writing a book review became literary critics! The real value of crafting a well-written book review for a student does not lie in their ability to impact book sales. Understanding how to produce a well-written book review helps students to:
● Engage critically with a text
● Critically evaluate a text
● Respond personally to a range of different writing genres
● Improve their own reading, writing, and thinking skills.
Not to Be Confused with a Book Report!
WHAT’S THE DIFFERENCE BETWEEN A BOOK REVIEW AND A BOOK REPORT?

While the terms are often used interchangeably, there are clear differences in both the purpose and the format of the two genres. Generally speaking, book reports aim to give a more detailed outline of what occurs in a book. A book report on a work of fiction will tend to give a comprehensive account of the characters, major plot lines, and themes in the book. Book reports are usually written around the K-12 age range, while book reviews tend not to be undertaken by those at the younger end of this age range due to the need for the higher-level critical skills required in writing them. At their highest expression, book reviews are written at the college level and by professional critics.
Learn how to write a book review step by step with our complete guide for students and teachers by familiarizing yourself with the structure and features.
BOOK REVIEW STRUCTURE
ANALYZE Evaluate the book with a critical mind.
THOROUGHNESS The whole is greater than the sum of all its parts. Review the book as a WHOLE.
COMPARE Where appropriate compare to similar texts and genres.
THUMBS UP OR DOWN? You are going to have to inevitably recommend or reject this book to potential readers.
BE CONSISTENT Take a stance and stick with it throughout your review.
FEATURES OF A BOOK REVIEW
PAST TENSE You are writing about a book you have already read.
EMOTIVE LANGUAGE Whatever your stance or opinion be passionate about it. Your audience will thank you for it.
VOICE Both active and passive voice are used in recounts.
A COMPLETE UNIT ON REVIEW AND ANALYSIS OF TEXTS

⭐ Make MOVIES A MEANINGFUL PART OF YOUR CURRICULUM with this engaging collection of tasks and tools your students will love. ⭐ All the hard work is done for you with NO PREPARATION REQUIRED.
This collection of 21 INDEPENDENT TASKS and GRAPHIC ORGANIZERS takes students beyond the hype, special effects and trailers to look at visual literacy from several perspectives offering DEEP LEARNING OPPORTUNITIES by watching a SERIES, DOCUMENTARY, FILM, and even VIDEO GAMES.
ELEMENTS OF A BOOK REVIEW
As with any of the writing genres we teach our students, a book review can be helpfully explained in terms of criteria. While there is much to the ‘art’ of writing, there is also, thankfully, a lot of the nuts and bolts that can be listed too. Have students consider the following elements before writing:
● Title: Often, the title of the book review will correspond to the title of the text itself, but there may also be some examination of the title’s relevance. How does it fit into the purpose of the work as a whole? Does it convey a message or reveal larger themes explored within the work?
● Author: Within the book review, there may be some discussion of who the author is and what they have written before, especially if it relates to the current work being reviewed. There may be some mention of the author’s style and what they are best known for. If the author has received any awards or prizes, this may also be mentioned within the body of the review.
● Genre: A book review will identify the genre that the book belongs to, whether fiction or nonfiction, poetry, romance, science-fiction, history etc. The genre will likely tie in, too with who the intended audience for the book is and what the overall purpose of the work is.
● Book Jacket / Cover: Often, a book’s cover will contain artwork that is worthy of comment. It may contain interesting details related to the text that contribute to, or detract from, the work as a whole.
● Structure: The book’s structure will often be heavily informed by its genre. Have students examine how the book is organized before writing their review. Does it contain a preface from a guest editor, for example? Is it written in sections or chapters? Does it have a table of contents, index, glossary etc.? While all these details may not make it into the review itself, looking at how the book is structured may reveal some interesting aspects.
● Publisher and Price: A book review will usually contain details of who publishes the book and its cost. A review will often provide details of where the book is available too.

BOOK REVIEW KEY ELEMENTS
As students read and engage with the work they will review, they will develop a sense of the shape their review will take. This will begin with the summary. Encourage students to take notes during the reading of the work that will help them in writing the summary that will form an essential part of their review. Aspects of the book they may wish to take notes on in a work of fiction may include:
● Characters: Who are the main characters? What are their motivations? Are they convincingly drawn? Or are they empathetic characters?
● Themes: What are the main themes of the work? Are there recurring motifs in the work? Is the exploration of the themes deep or surface only?
● Style: What are the key aspects of the writer’s style? How does it fit into the wider literary world?
● Plot: What is the story’s main catalyst? What happens in the rising action? What are the story’s subplots?
A book review will generally begin with a short summary of the work itself. However, it is important not to give too much away, remind students – no spoilers, please! For nonfiction works, this may be a summary of the main arguments of the work, again, without giving too much detail away. In a work of fiction, a book review will often summarise up to the rising action of the piece without going beyond to reveal too much!

The summary should also provide some orientation for the reader. Given the nature of the purpose of a review, it is important that students’ consider their intended audience in the writing of their review. Readers will most likely not have read the book in question and will require some orientation. This is often achieved through introductions to the main characters, themes, primary arguments etc. This will help the reader to gauge whether or not the book is of interest to them.
Once your student has summarized the work, it is time to ‘review’ in earnest. At this point, the student should begin to detail their own opinion of the book. To do this well they should:
i. Make It Personal
Often when teaching essay writing we will talk to our students about the importance of climbing up and down the ladder of abstraction. Just as it is helpful to explore large, more abstract concepts in an essay by bringing it down to Earth, in a book review, it is important that students can relate the characters, themes, ideas etc to their own lives.
Book reviews are meant to be subjective. They are opinion pieces, and opinions grow out of our experiences of life. Encourage students to link the work they are writing about to their own personal life within the body of the review. By making this personal connection to the work, students contextualize their opinions for the readers and help them to understand whether the book will be of interest to them or not in the process.
ii. Make It Universal
Just as it is important to climb down the ladder of abstraction to show how the work relates to individual life, it is important to climb upwards on the ladder too. Students should endeavor to show how the ideas explored in the book relate to the wider world. The may be in the form of the universality of the underlying themes in a work of fiction or, for example, the international implications for arguments expressed in a work of nonfiction.
iii. Support Opinions with Evidence
A book review is a subjective piece of writing by its very nature. However, just because it is subjective does not mean that opinions do not need to be justified. Make sure students understand how to back up their opinions with various forms of evidence, for example, quotations, statistics, and the use of primary and secondary sources.
EDIT AND REVISE YOUR BOOK REVIEW

As with any writing genre, encourage students to polish things up with review and revision at the end. Encourage them to proofread and check for accurate spelling throughout, with particular attention to the author’s name, character names, publisher etc.
It is good practice too for students to double-check their use of evidence. Are statements supported? Are the statistics used correctly? Are the quotations from the text accurate? Mistakes such as these uncorrected can do great damage to the value of a book review as they can undermine the reader’s confidence in the writer’s judgement.
The discipline of writing book reviews offers students opportunities to develop their writing skills and exercise their critical faculties. Book reviews can be valuable standalone activities or serve as a part of a series of activities engaging with a central text. They can also serve as an effective springboard into later discussion work based on the ideas and issues explored in a particular book. Though the book review does not hold the sway it once did in the mind’s of the reading public, it still serves as an effective teaching tool in our classrooms today.

Teaching Resources
Use our resources and tools to improve your student’s writing skills through proven teaching strategies.
BOOK REVIEW GRAPHIC ORGANIZER (TEMPLATE)

101 DIGITAL & PRINT GRAPHIC ORGANIZERS FOR ALL CURRICULUM AREAS

Introduce your students to 21st-century learning with this GROWING BUNDLE OF 101 EDITABLE & PRINTABLE GRAPHIC ORGANIZERS. ✌ NO PREP REQUIRED!!! ✌ Go paperless, and let your students express their knowledge and creativity through the power of technology and collaboration inside and outside the classroom with ease.
Whilst you don’t have to have a 1:1 or BYOD classroom to benefit from this bundle, it has been purpose-built to deliver through platforms such as ✔ GOOGLE CLASSROOM, ✔ OFFICE 365, ✔ or any CLOUD-BASED LEARNING PLATFORM.
Book and Movie review writing examples (Student Writing Samples)
Below are a collection of student writing samples of book reviews. Click on the image to enlarge and explore them in greater detail. Please take a moment to both read the movie or book review in detail but also the teacher and student guides which highlight some of the key elements of writing a text review
Please understand these student writing samples are not intended to be perfect examples for each age or grade level but a piece of writing for students and teachers to explore together to critically analyze to improve student writing skills and deepen their understanding of book review writing.
We would recommend reading the example either a year above and below, as well as the grade you are currently working with to gain a broader appreciation of this text type .

BOOK REVIEW VIDEO TUTORIALS

OTHER GREAT ARTICLES RELATED TO BOOK REVIEWS
Transactional Writing

How to write a text response


How to Write a Compare and Contrast Essay

How to Write Excellent Expository Essays
404 Not found

Book Review Writing Examples
Examples: learn from the efforts of others.
Learning how to write strong reviews takes time and not a little effort. Reading the reviews others have done can help you get a feel for the flow and flavor of reviews.
If I Never Forever Endeavor Review by Hayden, age 4, Southeast Michigan Mensa

This book was about a bird who didn't yet know how to fly.
The bird has to decide if it will try to fly, but it was not sure if it wants to. The bird thought, "If I never forever endeavor" then I won't ever learn. On one wing, he worries he might fail and on the other wing he thinks of how he may succeed. He worries that if he tries, he may get lost in the world. That makes him want to stay in his nest where he's safe.
I think this book would help other children to learn that trying new things can be scary, but sometimes when we try, we can find things that make us happy too. And this book will help others know that mistakes are okay and part of learning.
My favorite part is that the bird tried and learned that she could fly. I also liked that I read this book because it gave me a chance to talk to mom about making mistakes and how I don't like making them. Then I learned they are good and part of learning.
Boys and girls who are 3 to 8 years old would like this book because it teaches about trying a new thing and how it's important to get past being scared so you can learn new things.
I give the book 5 stars since I think it's important for other children to learn about courage.
Flesh & Blood So Cheap Review by Umar B., age 8, Central New Jersy Mensa

I liked this book. People who are interested in national disasters and US history as well as immigration will most probably be interested in reading this book.
Readers can gain knowledge of what it was like to work in New York City in the early 1900s. One of the things that was especially interesting was that there were no safety laws at work. Also, there was a big contrast between the rich and the poor. Some people may not like this book because it is very depressing, but it is an important event in history to remember.
This book was very well written. It has black and white photos along with descriptions of the photos. These photos give us a better idea of what people's lives were like. This book is suitable for 9-20 year olds.
I give this book 5 stars.
Galaxy Zach: Journey to Juno Review by Young Mensan Connor C., age 6, Boston Mensa

Journey To Juno is the second book of the Galaxy Zack series. It is just as good as the first one. It's awesome!
Zack joins the Sprockets Academy Explorers Club at school. They fly on a special trip to Juno, a new planet no one has ever visited. Zack gets paired up with Seth, the class bully, and that's dreadful but Zack is excited when he finds a huge galaxy gemmite. A gemmite that large had not been found in 100 years! Kids will love this book!
Boys and girls will both like it. It's an easy chapter book with pictures on every page. I love the illustrations. I think ages 6-8 would like this but younger kids would like the story being read to them.
My favorite parts are the galactic blast game (it is similar to baseball except there are robots playing), recess at Zack's school where everything is 3-D holographic images, the rainbow river in a crystal cave on Juno, and the galaxy gemmite that Zack finds on Juno. I also loved when a life-size holographic image of his Earth friend appears in Zack's room because he calls him on a hyperphone. I give this book one hundred stars! There is a "to be continued" at the end so you have to read the next book see what's in store. I can't wait to find out what happens!!!
I Capture the Castle Review by Lauren W., age 17, Mensa in Georgia

Dodie Smith's novel I Capture the Castle is a journey through the mind of a young writer as she attempts to chronicle her daily life. Seventeen-year-old Cassandra Mortmain has recently learned to speed-write, and she decides to work on her writing skills by describing the actions and conversations of those around her.
Cassandra lives in a fourteenth-century English castle with an interesting cast of characters: her beautiful older sister, Rose; her rather unsociable author father and his second wife, artist-model Topaz; Stephen, the garden boy; a cat and a bull terrier; and sometimes her brother Thomas when he is home from school. One fateful day they make the acquaintance of the Cotton family, including the two sons, and a web of tangled relationships ensues.
While I definitely recommend this book to other readers, I would recommend it to older teenagers, mainly because it will resonate better with them. The writing is tame enough that younger teens could also read it, but most of the characters are adults or on the verge of adulthood. Older readers would take the most from it since they can not only relate, but they may also better pick up on and appreciate Cassandra's sometimes subtle humor.
Over the course of the novel, Cassandra undergoes a definite transformation from child to mature young adult, even though it's only over the course of several months. I love that I could see into her mindset and read exactly what she was feeling when she thought out situations. Her thoughts flowed well and moved the book along very quickly.
Cassandra's narrative voice is wonderful. She is serious at times, but also very witty, which makes for an engaging read. It feels absolutely real, as though I'm reading someone's actual journal. Sometimes I forget that I am reading a story and not a real-life account. Her emotions and the dialogue are so genuine, and they are spot-on for a seventeen-year-old girl in her situation.
Cassandra has many wonderful insights on life, on topics ranging from writing to faith to matters of the heart. I personally have had some of the same thoughts as Cassandra, except Ms. Smith was able to put them into words.
Capture the Castle should be essential reading for aspiring writers, those looking for historical fiction or romance, or anyone who loves reading amazing classic books. Dodie Smith is an exceptional writer, and I Capture the Castle is a book that will never become obsolete.
Frankenstein's Cat Review by Zander H., age 12, Mid-America Mensa

I appreciated Frankenstein's Cat for its fascinating explanation about the often baffling subject of bioengineering and its sister sciences. Emily Anthes explains the many sides of today's modern technology, such as gene modification, cloning, pharmaceutical products (from the farm), prosthesis, animal tag and tracking and gene cryogenics. This book provides a well-rounded summary of these complicated sciences without being boring or simply factual. Her real world examples take us on a journey from the farm, to the pet store and then from the pharmacy to the frozen arc.
Have you ever wondered if the neighborhood cat is spying on you? Read about Operation Acoustic Kitty and find out if this feline fantasy fiction or fact. Do you think bugs are creepy? What about a zombified cyborg beetle? Is Fido so special that you want two of him? Money can buy you an almost exact copy of your pooch BUT don't expect the same personality. Emily Anthes makes you crave more information. She makes you want to know the future of Earth's flora and fauna, as well as humanity itself.
I would highly recommend this book to anyone who desires a guide to the future of biological science and technology. Frankenstein's Cat is best read by the light of a glow-in-the-dark fish, while cuddling your favorite cloned dog and drinking a glass of genetically modified milk.
About Marsupials Review by Connor C., age 6, Boston Mensa

About Marsupials is the title so the book is about...marsupials, of course. It's non-fiction. I really think everyone would like the book. I think someone who likes animals would especially like to read it.
The glossary of facts in the back of About Marsupials is the most useful part. I thought the most interesting parts were that some marsupials have their pouch at their back legs and one marsupial, the Yellow-footed Rock Wallaby, is very small but can jump 13 feet wide!
Kids in the 4-8 age range would like this book. Even though it's not a story book, 4 year olds would like the few words on each page and they would love the beautiful pictures. But older kids would like it because of all the facts in the back of the book. There's a lot of information for each animal. I think boys and girls (and parents) would enjoy reading it. This book is very interesting. I give it 4 stars.
Mapping the World Review by Umar A., age 10, Central New Jersey Mensa

Every day, people around the world use maps. Whether it is an airplane pilot or businessman, housewife or museum group, maps have always and will continue to provide useful information for all.
Mapping the World talks about the uses of maps, as well as how to differentiate between the type of map projection and type of map.
In this series, we travel to the past and learn about historical mapmakers, from Claudius Ptolemy (who stated the idea that the Earth is at the center of the universe) to Gerardus Mercator (who created one of the most widely used map projections) and more. This series goes into tremendous detail on the cartographer's life and maps. We then journey to the present era to learn about map projections and the diverse types of maps used today. You might ask, "What is the difference between the two? They sound the same to me." No map projection is perfect, because you cannot really flatten a sphere into a rectangle. An uncolored projection could be used in many ways. We could use it for population concentration, highways, land elevation, and so many other things!
For example, we could make a topographic map of the U.S., which shows land elevation. We could make it a colorful map that shows the amount of pollution in different areas, or it could be a population map, or it could even be a map that shows the 50 states, their capitals and borders! Our last step in this amazing excursion is the near future, where we see some hypothetical solutions as to what maps will be used for. Currently, we are working on better virtual map technology.
Now, scientists have been able to put maps on phones. Back in the early 1900s, people had to lug a lot of maps around to find your way from place to place, or just keep asking for directions. Now, all the information is on a phone or global positioning system (GPS). It is amazing how much maps have changed technology and the world in this century.
The Mapping the World 8-book set goes into amazing levels of detail. It is a long read, but it gives an immense range and amount of information that you would not find in any other book or series on maps. The flowing way the chapters and books are organized makes it easy to link passages from different books in this series together. Mapping the World is a treasure box, filled with the seeds of cartography. Collect and plant them, and you soon will have the fruits of cartography, beneficial to those who want to be cartographers. Use this series to the utmost, then the fruits of mapping will be sweet for all who endeavor to succeed in cartography.
This series of lessons was designed to meet the needs of gifted children for extension beyond the standard curriculum with the greatest ease of use for the educator. The lessons may be given to the students for individual self-guided work, or they may be taught in a classroom or a home-school setting. Assessment strategies and rubrics are included at the end of each section. The rubrics often include a column for "scholar points," which are invitations for students to extend their efforts beyond that which is required, incorporating creativity or higher level technical skills.

- All topics A-Z
- Grammar
- Vocabulary
- Speaking
- Reading
- Listening
- Writing
- Pronunciation
- Virtual Classroom
- Worksheets by season
- 600 Creative Writing Prompts
- Warmers, fillers & ice-breakers
- Coloring pages to print
- Flashcards
- Classroom management worksheets
- Emergency worksheets
- Revision worksheets
- Resources we recommend
- Copyright 2007-2021 пїЅ
- Submit a worksheet
- Mobile version
Writing A Book Review
Students will read a book a book of their choice and take notes while they read. Then, they will write a book review about the book they read. This is for fourth through fifth grade students.
Learn to read and take notes Write a book review State the positive and negative aspects of the book
Book of their choice Notebook paper to take notes Notebook paper to write their review Pencils and Erasers Pens
Before they write their book review, you will need to explain how to write one. After you explain about book reviews, then they can choose a book they would like to read, and they will take notes while they read. Then, they will write a book review of their book. After that, they will submit their review for you to grade.
You can grade the students on how they wrote their book review.
- Find a School Near You
- Read K-12 Articles
- Browse Lesson Plans
- Descriptive Paper - and then There Were None The students will read the book, And Then there Were None by Agatha Christie. While you read, you will take notes on the different characters. They will write a descriptive paper of the characters...
- Your Future Occupation This lesson could be used with fourth and fifth grade students as well as with middle school. Have students think about their future occupation and write a story with them as the main character in a...
- Learning About Editing Students will write a short story in any genre for their homework assignment. After that, they will bring their stories to class the next day. They will exchange their stories and learn about...
- Compare and Contrast Two Books Students will read two books and write a comparison and contrast paper on their views of the two books. They can discuss a specific element of fiction such as plot, theme, characters, or...
- Writing Children should be able to write at least their First name, by the end of the school year....

Join Discovery, the new community for book lovers
Trust book recommendations from real people, not robots 🤓
Blog – Posted on Friday, Mar 29
17 book review examples to help you write the perfect review.

It’s an exciting time to be a book reviewer. Once confined to print newspapers and journals, reviews now dot many corridors of the Internet — forever helping others discover their next great read. That said, every book reviewer will face a familiar panic: how can you do justice to a great book in just a thousand words?
As you know, the best way to learn how to do something is by immersing yourself in it. Luckily, the Internet (i.e. Goodreads and other review sites , in particular) has made book reviews more accessible than ever — which means that there are a lot of book reviews examples out there for you to view!
In this post, we compiled 17 prototypical book review examples in multiple genres to help you figure out how to write the perfect review . If you want to jump straight to the examples, you can skip the next section. Otherwise, let’s first check out what makes up a good review.
Are you interested in becoming a book reviewer? We recommend you check out Reedsy Discovery , where you can earn money for writing reviews — and are guaranteed people will read your reviews! To register as a book reviewer, sign up here.
Pro-tip : But wait! How are you sure if you should become a book reviewer in the first place? If you're on the fence, or curious about your match with a book reviewing career, take our quick quiz:
Should you become a book reviewer?
Find out the answer. Takes 30 seconds!
What must a book review contain?
Like all works of art, no two book reviews will be identical. But fear not: there are a few guidelines for any aspiring book reviewer to follow. Most book reviews, for instance, are less than 1,500 words long, with the sweet spot hitting somewhere around the 1,000-word mark. (However, this may vary depending on the platform on which you’re writing, as we’ll see later.)
In addition, all reviews share some universal elements, as shown in our book review templates . These include:
- A review will offer a concise plot summary of the book.
- A book review will offer an evaluation of the work.
- A book review will offer a recommendation for the audience.
If these are the basic ingredients that make up a book review, it’s the tone and style with which the book reviewer writes that brings the extra panache. This will differ from platform to platform, of course. A book review on Goodreads, for instance, will be much more informal and personal than a book review on Kirkus Reviews, as it is catering to a different audience. However, at the end of the day, the goal of all book reviews is to give the audience the tools to determine whether or not they’d like to read the book themselves.
Keeping that in mind, let’s proceed to some book review examples to put all of this in action.
How much of a book nerd are you, really?
Find out here, once and for all. Takes 30 seconds!
Book review examples for fiction books
Since story is king in the world of fiction, it probably won’t come as any surprise to learn that a book review for a novel will concentrate on how well the story was told .
That said, book reviews in all genres follow the same basic formula that we discussed earlier. In these examples, you’ll be able to see how book reviewers on different platforms expertly intertwine the plot summary and their personal opinions of the book to produce a clear, informative, and concise review.
Note: Some of the book review examples run very long. If a book review is truncated in this post, we’ve indicated by including a […] at the end, but you can always read the entire review if you click on the link provided.
Examples of literary fiction book reviews
Kirkus Reviews reviews Ralph Ellison’s The Invisible Man :
An extremely powerful story of a young Southern Negro, from his late high school days through three years of college to his life in Harlem.
His early training prepared him for a life of humility before white men, but through injustices- large and small, he came to realize that he was an "invisible man". People saw in him only a reflection of their preconceived ideas of what he was, denied his individuality, and ultimately did not see him at all. This theme, which has implications far beyond the obvious racial parallel, is skillfully handled. The incidents of the story are wholly absorbing. The boy's dismissal from college because of an innocent mistake, his shocked reaction to the anonymity of the North and to Harlem, his nightmare experiences on a one-day job in a paint factory and in the hospital, his lightning success as the Harlem leader of a communistic organization known as the Brotherhood, his involvement in black versus white and black versus black clashes and his disillusion and understanding of his invisibility- all climax naturally in scenes of violence and riot, followed by a retreat which is both literal and figurative. Parts of this experience may have been told before, but never with such freshness, intensity and power.
This is Ellison's first novel, but he has complete control of his story and his style. Watch it.
Lyndsey reviews George Orwell’s 1984 on Goodreads:
YOU. ARE. THE. DEAD. Oh my God. I got the chills so many times toward the end of this book. It completely blew my mind. It managed to surpass my high expectations AND be nothing at all like I expected. Or in Newspeak "Double Plus Good." Let me preface this with an apology. If I sound stunningly inarticulate at times in this review, I can't help it. My mind is completely fried.
This book is like the dystopian Lord of the Rings, with its richly developed culture and economics, not to mention a fully developed language called Newspeak, or rather more of the anti-language, whose purpose is to limit speech and understanding instead of to enhance and expand it. The world-building is so fully fleshed out and spine-tinglingly terrifying that it's almost as if George travelled to such a place, escaped from it, and then just wrote it all down.
I read Fahrenheit 451 over ten years ago in my early teens. At the time, I remember really wanting to read 1984, although I never managed to get my hands on it. I'm almost glad I didn't. Though I would not have admitted it at the time, it would have gone over my head. Or at the very least, I wouldn't have been able to appreciate it fully. […]
The New York Times reviews Lisa Halliday’s Asymmetry :
Three-quarters of the way through Lisa Halliday’s debut novel, “Asymmetry,” a British foreign correspondent named Alistair is spending Christmas on a compound outside of Baghdad. His fellow revelers include cameramen, defense contractors, United Nations employees and aid workers. Someone’s mother has FedExed a HoneyBaked ham from Maine; people are smoking by the swimming pool. It is 2003, just days after Saddam Hussein’s capture, and though the mood is optimistic, Alistair is worrying aloud about the ethics of his chosen profession, wondering if reporting on violence doesn’t indirectly abet violence and questioning why he’d rather be in a combat zone than reading a picture book to his son. But every time he returns to London, he begins to “spin out.” He can’t go home. “You observe what people do with their freedom — what they don’t do — and it’s impossible not to judge them for it,” he says.
The line, embedded unceremoniously in the middle of a page-long paragraph, doubles, like so many others in “Asymmetry,” as literary criticism. Halliday’s novel is so strange and startlingly smart that its mere existence seems like commentary on the state of fiction. One finishes “Asymmetry” for the first or second (or like this reader, third) time and is left wondering what other writers are not doing with their freedom — and, like Alistair, judging them for it.
Despite its title, “Asymmetry” comprises two seemingly unrelated sections of equal length, appended by a slim and quietly shocking coda. Halliday’s prose is clean and lean, almost reportorial in the style of W. G. Sebald, and like the murmurings of a shy person at a cocktail party, often comic only in single clauses. It’s a first novel that reads like the work of an author who has published many books over many years. […]
Emily W. Thompson reviews Michael Doane's The Crossing on Reedsy Discovery :
In Doane’s debut novel, a young man embarks on a journey of self-discovery with surprising results.
An unnamed protagonist (The Narrator) is dealing with heartbreak. His love, determined to see the world, sets out for Portland, Oregon. But he’s a small-town boy who hasn’t traveled much. So, the Narrator mourns her loss and hides from life, throwing himself into rehabbing an old motorcycle. Until one day, he takes a leap; he packs his bike and a few belongings and heads out to find the Girl.
Following in the footsteps of Jack Kerouac and William Least Heat-Moon, Doane offers a coming of age story about a man finding himself on the backroads of America. Doane’s a gifted writer with fluid prose and insightful observations, using The Narrator’s personal interactions to illuminate the diversity of the United States.
The Narrator initially sticks to the highways, trying to make it to the West Coast as quickly as possible. But a hitchhiker named Duke convinces him to get off the beaten path and enjoy the ride. “There’s not a place that’s like any other,” [39] Dukes contends, and The Narrator realizes he’s right. Suddenly, the trip is about the journey, not just the destination. The Narrator ditches his truck and traverses the deserts and mountains on his bike. He destroys his phone, cutting off ties with his past and living only in the moment.
As he crosses the country, The Narrator connects with several unique personalities whose experiences and views deeply impact his own. Duke, the complicated cowboy and drifter, who opens The Narrator’s eyes to a larger world. Zooey, the waitress in Colorado who opens his heart and reminds him that love can be found in this big world. And Rosie, The Narrator’s sweet landlady in Portland, who helps piece him back together both physically and emotionally.
This supporting cast of characters is excellent. Duke, in particular, is wonderfully nuanced and complicated. He’s a throwback to another time, a man without a cell phone who reads Sartre and sleeps under the stars. Yet he’s also a grifter with a “love ‘em and leave ‘em” attitude that harms those around him. It’s fascinating to watch The Narrator wrestle with Duke’s behavior, trying to determine which to model and which to discard.
Doane creates a relatable protagonist in The Narrator, whose personal growth doesn’t erase his faults. His willingness to hit the road with few resources is admirable, and he’s prescient enough to recognize the jealousy of those who cannot or will not take the leap. His encounters with new foods, places, and people broaden his horizons. Yet his immaturity and selfishness persist. He tells Rosie she’s been a good mother to him but chooses to ignore the continuing concern from his own parents as he effectively disappears from his old life.
Despite his flaws, it’s a pleasure to accompany The Narrator on his physical and emotional journey. The unexpected ending is a fitting denouement to an epic and memorable road trip.
The Book Smugglers review Anissa Gray’s The Care and Feeding of Ravenously Hungry Girls :
I am still dipping my toes into the literally fiction pool, finding what works for me and what doesn’t. Books like The Care and Feeding of Ravenously Hungry Girls by Anissa Gray are definitely my cup of tea.
Althea and Proctor Cochran had been pillars of their economically disadvantaged community for years – with their local restaurant/small market and their charity drives. Until they are found guilty of fraud for stealing and keeping most of the money they raised and sent to jail. Now disgraced, their entire family is suffering the consequences, specially their twin teenage daughters Baby Vi and Kim. To complicate matters even more: Kim was actually the one to call the police on her parents after yet another fight with her mother. […]
Examples of children’s and YA fiction book reviews
The Book Hookup reviews Angie Thomas’ The Hate U Give :
♥ Quick Thoughts and Rating: 5 stars! I can’t imagine how challenging it would be to tackle the voice of a movement like Black Lives Matter, but I do know that Thomas did it with a finesse only a talented author like herself possibly could. With an unapologetically realistic delivery packed with emotion, The Hate U Give is a crucially important portrayal of the difficulties minorities face in our country every single day. I have no doubt that this book will be met with resistance by some (possibly many) and slapped with a “controversial” label, but if you’ve ever wondered what it was like to walk in a POC’s shoes, then I feel like this is an unflinchingly honest place to start.
In Angie Thomas’s debut novel, Starr Carter bursts on to the YA scene with both heart-wrecking and heartwarming sincerity. This author is definitely one to watch.
♥ Review: The hype around this book has been unquestionable and, admittedly, that made me both eager to get my hands on it and terrified to read it. I mean, what if I was to be the one person that didn’t love it as much as others? (That seems silly now because of how truly mesmerizing THUG was in the most heartbreakingly realistic way.) However, with the relevancy of its summary in regards to the unjust predicaments POC currently face in the US, I knew this one was a must-read, so I was ready to set my fears aside and dive in. That said, I had an altogether more personal, ulterior motive for wanting to read this book. […]
The New York Times reviews Melissa Albert’s The Hazel Wood :
Alice Crewe (a last name she’s chosen for herself) is a fairy tale legacy: the granddaughter of Althea Proserpine, author of a collection of dark-as-night fairy tales called “Tales From the Hinterland.” The book has a cult following, and though Alice has never met her grandmother, she’s learned a little about her through internet research. She hasn’t read the stories, because her mother, Ella Proserpine, forbids it.
Alice and Ella have moved from place to place in an attempt to avoid the “bad luck” that seems to follow them. Weird things have happened. As a child, Alice was kidnapped by a man who took her on a road trip to find her grandmother; he was stopped by the police before they did so. When at 17 she sees that man again, unchanged despite the years, Alice panics. Then Ella goes missing, and Alice turns to Ellery Finch, a schoolmate who’s an Althea Proserpine superfan, for help in tracking down her mother. Not only has Finch read every fairy tale in the collection, but handily, he remembers them, sharing them with Alice as they journey to the mysterious Hazel Wood, the estate of her now-dead grandmother, where they hope to find Ella.
“The Hazel Wood” starts out strange and gets stranger, in the best way possible. (The fairy stories Finch relays, which Albert includes as their own chapters, are as creepy and evocative as you’d hope.) Albert seamlessly combines contemporary realism with fantasy, blurring the edges in a way that highlights that place where stories and real life convene, where magic contains truth and the world as it appears is false, where just about anything can happen, particularly in the pages of a very good book. It’s a captivating debut. […]
James reviews Margaret Wise Brown’s Goodnight, Moon on Goodreads:
Goodnight Moon by Margaret Wise Brown is one of the books that followers of my blog voted as a must-read for our Children's Book August 2018 Readathon. Come check it out and join the next few weeks!
This picture book was such a delight. I hadn't remembered reading it when I was a child, but it might have been read to me... either way, it was like a whole new experience! It's always so difficult to convince a child to fall asleep at night. I don't have kids, but I do have a 5-month-old puppy who whines for 5 minutes every night when he goes in his cage/crate (hopefully he'll be fully housebroken soon so he can roam around when he wants). I can only imagine! I babysat a lot as a teenager and I have tons of younger cousins, nieces, and nephews, so I've been through it before, too. This was a believable experience, and it really helps show kids how to relax and just let go when it's time to sleep.
The bunny's are adorable. The rhymes are exquisite. I found it pretty fun, but possibly a little dated given many of those things aren't normal routines anymore. But the lessons to take from it are still powerful. Loved it! I want to sample some more books by this fine author and her illustrators.
Publishers Weekly reviews Elizabeth Lilly’s Geraldine :
This funny, thoroughly accomplished debut opens with two words: “I’m moving.” They’re spoken by the title character while she swoons across her family’s ottoman, and because Geraldine is a giraffe, her full-on melancholy mode is quite a spectacle. But while Geraldine may be a drama queen (even her mother says so), it won’t take readers long to warm up to her. The move takes Geraldine from Giraffe City, where everyone is like her, to a new school, where everyone else is human. Suddenly, the former extrovert becomes “That Giraffe Girl,” and all she wants to do is hide, which is pretty much impossible. “Even my voice tries to hide,” she says, in the book’s most poignant moment. “It’s gotten quiet and whispery.” Then she meets Cassie, who, though human, is also an outlier (“I’m that girl who wears glasses and likes MATH and always organizes her food”), and things begin to look up.
Lilly’s watercolor-and-ink drawings are as vividly comic and emotionally astute as her writing; just when readers think there are no more ways for Geraldine to contort her long neck, this highly promising talent comes up with something new.
Examples of genre fiction book reviews
Karlyn P reviews Nora Roberts’ Dark Witch , a paranormal romance novel , on Goodreads:
4 stars. Great world-building, weak romance, but still worth the read.
I hesitate to describe this book as a 'romance' novel simply because the book spent little time actually exploring the romance between Iona and Boyle. Sure, there IS a romance in this novel. Sprinkled throughout the book are a few scenes where Iona and Boyle meet, chat, wink at each, flirt some more, sleep together, have a misunderstanding, make up, and then profess their undying love. Very formulaic stuff, and all woven around the more important parts of this book.
The meat of this book is far more focused on the story of the Dark witch and her magically-gifted descendants living in Ireland. Despite being weak on the romance, I really enjoyed it. I think the book is probably better for it, because the romance itself was pretty lackluster stuff.
I absolutely plan to stick with this series as I enjoyed the world building, loved the Ireland setting, and was intrigued by all of the secondary characters. However, If you read Nora Roberts strictly for the romance scenes, this one might disappoint. But if you enjoy a solid background story with some dark magic and prophesies, you might enjoy it as much as I did.
I listened to this one on audio, and felt the narration was excellent.
Emily May reviews R.F. Kuang’s The Poppy Wars , an epic fantasy novel , on Goodreads:
“But I warn you, little warrior. The price of power is pain.”
Holy hell, what did I just read??
➽ A fantasy military school
➽ A rich world based on modern Chinese history
➽ Shamans and gods
➽ Detailed characterization leading to unforgettable characters
➽ Adorable, opium-smoking mentors
That's a basic list, but this book is all of that and SO MUCH MORE. I know 100% that The Poppy War will be one of my best reads of 2018.
Isn't it just so great when you find one of those books that completely drags you in, makes you fall in love with the characters, and demands that you sit on the edge of your seat for every horrific, nail-biting moment of it? This is one of those books for me. And I must issue a serious content warning: this book explores some very dark themes. Proceed with caution (or not at all) if you are particularly sensitive to scenes of war, drug use and addiction, genocide, racism, sexism, ableism, self-harm, torture, and rape (off-page but extremely horrific).
Because, despite the fairly innocuous first 200 pages, the title speaks the truth: this is a book about war. All of its horrors and atrocities. It is not sugar-coated, and it is often graphic. The "poppy" aspect refers to opium, which is a big part of this book. It is a fantasy, but the book draws inspiration from the Second Sino-Japanese War and the Rape of Nanking.
Crime Fiction Lover reviews Jessica Barry’s Freefall , a crime novel:
In some crime novels, the wrongdoing hits you between the eyes from page one. With others it’s a more subtle process, and that’s OK too. So where does Freefall fit into the sliding scale?
In truth, it’s not clear. This is a novel with a thrilling concept at its core. A woman survives plane crash, then runs for her life. However, it is the subtleties at play that will draw you in like a spider beckoning to an unwitting fly.
Like the heroine in Sharon Bolton’s Dead Woman Walking, Allison is lucky to be alive. She was the only passenger in a private plane, belonging to her fiancé, Ben, who was piloting the expensive aircraft, when it came down in woodlands in the Colorado Rockies. Ally is also the only survivor, but rather than sitting back and waiting for rescue, she is soon pulling together items that may help her survive a little longer – first aid kit, energy bars, warm clothes, trainers – before fleeing the scene. If you’re hearing the faint sound of alarm bells ringing, get used to it. There’s much, much more to learn about Ally before this tale is over.
Kirkus Reviews reviews Ernest Cline’s Ready Player One , a science-fiction novel :
Video-game players embrace the quest of a lifetime in a virtual world; screenwriter Cline’s first novel is old wine in new bottles.
The real world, in 2045, is the usual dystopian horror story. So who can blame Wade, our narrator, if he spends most of his time in a virtual world? The 18-year-old, orphaned at 11, has no friends in his vertical trailer park in Oklahoma City, while the OASIS has captivating bells and whistles, and it’s free. Its creator, the legendary billionaire James Halliday, left a curious will. He had devised an elaborate online game, a hunt for a hidden Easter egg. The finder would inherit his estate. Old-fashioned riddles lead to three keys and three gates. Wade, or rather his avatar Parzival, is the first gunter (egg-hunter) to win the Copper Key, first of three.
Halliday was obsessed with the pop culture of the 1980s, primarily the arcade games, so the novel is as much retro as futurist. Parzival’s great strength is that he has absorbed all Halliday’s obsessions; he knows by heart three essential movies, crossing the line from geek to freak. His most formidable competitors are the Sixers, contract gunters working for the evil conglomerate IOI, whose goal is to acquire the OASIS. Cline’s narrative is straightforward but loaded with exposition. It takes a while to reach a scene that crackles with excitement: the meeting between Parzival (now world famous as the lead contender) and Sorrento, the head of IOI. The latter tries to recruit Parzival; when he fails, he issues and executes a death threat. Wade’s trailer is demolished, his relatives killed; luckily Wade was not at home. Too bad this is the dramatic high point. Parzival threads his way between more ’80s games and movies to gain the other keys; it’s clever but not exciting. Even a romance with another avatar and the ultimate “epic throwdown” fail to stir the blood.
Too much puzzle-solving, not enough suspense.
Book review examples for non-fiction books
Nonfiction books are generally written to inform readers about a certain topic. As such, the focus of a nonfiction book review will be on the clarity and effectiveness of this communication . In carrying this out, a book review may analyze the author’s source materials and assess the thesis in order to determine whether or not the book meets expectations.
Again, we’ve included abbreviated versions of long reviews here, so feel free to click on the link to read the entire piece!
The Washington Post reviews David Grann’s Killers of the Flower Moon :
The arc of David Grann’s career reminds one of a software whiz-kid or a latest-thing talk-show host — certainly not an investigative reporter, even if he is one of the best in the business. The newly released movie of his first book, “The Lost City of Z,” is generating all kinds of Oscar talk, and now comes the release of his second book, “Killers of the Flower Moon: The Osage Murders and the Birth of the FBI,” the film rights to which have already been sold for $5 million in what one industry journal called the “biggest and wildest book rights auction in memory.”
Grann deserves the attention. He’s canny about the stories he chases, he’s willing to go anywhere to chase them, and he’s a maestro in his ability to parcel out information at just the right clip: a hint here, a shading of meaning there, a smartly paced buildup of multiple possibilities followed by an inevitable reversal of readerly expectations or, in some cases, by a thrilling and dislocating pull of the entire narrative rug.
All of these strengths are on display in “Killers of the Flower Moon.” Around the turn of the 20th century, oil was discovered underneath Osage lands in the Oklahoma Territory, lands that were soon to become part of the state of Oklahoma. Through foresight and legal maneuvering, the Osage found a way to permanently attach that oil to themselves and shield it from the prying hands of white interlopers; this mechanism was known as “headrights,” which forbade the outright sale of oil rights and granted each full member of the tribe — and, supposedly, no one else — a share in the proceeds from any lease arrangement. For a while, the fail-safes did their job, and the Osage got rich — diamond-ring and chauffeured-car and imported-French-fashion rich — following which quite a large group of white men started to work like devils to separate the Osage from their money. And soon enough, and predictably enough, this work involved murder. Here in Jazz Age America’s most isolated of locales, dozens or even hundreds of Osage in possession of great fortunes — and of the potential for even greater fortunes in the future — were dispatched by poison, by gunshot and by dynamite. […]
Stacked Books reviews Malcolm Gladwell’s Outliers :
I’ve heard a lot of great things about Malcolm Gladwell’s writing. Friends and co-workers tell me that his subjects are interesting and his writing style is easy to follow without talking down to the reader. I wasn’t disappointed with Outliers. In it, Gladwell tackles the subject of success – how people obtain it and what contributes to extraordinary success as opposed to everyday success.
The thesis – that our success depends much more on circumstances out of our control than any effort we put forth – isn’t exactly revolutionary. Most of us know it to be true. However, I don’t think I’m lying when I say that most of us also believe that we if we just try that much harder and develop our talent that much further, it will be enough to become wildly successful, despite bad or just mediocre beginnings. Not so, says Gladwell.
Most of the evidence Gladwell gives us is anecdotal, which is my favorite kind to read. I can’t really speak to how scientifically valid it is, but it sure makes for engrossing listening. For example, did you know that successful hockey players are almost all born in January, February, or March? Kids born during these months are older than the others kids when they start playing in the youth leagues, which means they’re already better at the game (because they’re bigger). Thus, they get more play time, which means their skill increases at a faster rate, and it compounds as time goes by. Within a few years, they’re much, much better than the kids born just a few months later in the year. Basically, these kids’ birthdates are a huge factor in their success as adults – and it’s nothing they can do anything about. If anyone could make hockey interesting to a Texan who only grudgingly admits the sport even exists, it’s Gladwell. […]
Quill and Quire reviews Rick Prashaw’s Soar, Adam, Soar :
Ten years ago, I read a book called Almost Perfect. The young-adult novel by Brian Katcher won some awards and was held up as a powerful, nuanced portrayal of a young trans person. But the reality did not live up to the book’s billing. Instead, it turned out to be a one-dimensional and highly fetishized portrait of a trans person’s life, one that was nevertheless repeatedly dubbed “realistic” and “affecting” by non-transgender readers possessing only a vague, mass-market understanding of trans experiences.
In the intervening decade, trans narratives have emerged further into the literary spotlight, but those authored by trans people ourselves – and by trans men in particular – have seemed to fall under the shadow of cisgender sensationalized imaginings. Two current Canadian releases – Soar, Adam, Soar and This One Looks Like a Boy – provide a pointed object lesson into why trans-authored work about transgender experiences remains critical.
To be fair, Soar, Adam, Soar isn’t just a story about a trans man. It’s also a story about epilepsy, the medical establishment, and coming of age as seen through a grieving father’s eyes. Adam, Prashaw’s trans son, died unexpectedly at age 22. Woven through the elder Prashaw’s narrative are excerpts from Adam’s social media posts, giving us glimpses into the young man’s interior life as he traverses his late teens and early 20s. […]
Book Geeks reviews Elizabeth Gilbert’s Eat, Pray, Love :
WRITING STYLE: 3.5/5
SUBJECT: 4/5
CANDIDNESS: 4.5/5
RELEVANCE: 3.5/5
ENTERTAINMENT QUOTIENT: 3.5/5
“Eat Pray Love” is so popular that it is almost impossible to not read it. Having felt ashamed many times on my not having read this book, I quietly ordered the book (before I saw the movie) from amazon.in and sat down to read it. I don’t remember what I expected it to be – maybe more like a chick lit thing but it turned out quite different. The book is a real story and is a short journal from the time when its writer went travelling to three different countries in pursuit of three different things – Italy (Pleasure), India (Spirituality), Bali (Balance) and this is what corresponds to the book’s name – EAT (in Italy), PRAY (in India) and LOVE (in Bali, Indonesia). These are also the three Is – ITALY, INDIA, INDONESIA.
Though she had everything a middle-aged American woman can aspire for – MONEY, CAREER, FRIENDS, HUSBAND; Elizabeth was not happy in her life, she wasn’t happy in her marriage. Having suffered a terrible divorce and terrible breakup soon after, Elizabeth was shattered. She didn’t know where to go and what to do – all she knew was that she wanted to run away. So she set out on a weird adventure – she will go to three countries in a year and see if she can find out what she was looking for in life. This book is about that life changing journey that she takes for one whole year. […]
Emily May reviews Michelle Obama’s Becoming on Goodreads:
Look, I'm not a happy crier. I might cry at songs about leaving and missing someone; I might cry at books where things don't work out; I might cry at movies where someone dies. I've just never really understood why people get all choked up over happy, inspirational things. But Michelle Obama's kindness and empathy changed that. This book had me in tears for all the right reasons.
This is not really a book about politics, though political experiences obviously do come into it. It's a shame that some will dismiss this book because of a difference in political opinion, when it is really about a woman's life. About growing up poor and black on the South Side of Chicago; about getting married and struggling to maintain that marriage; about motherhood; about being thrown into an amazing and terrifying position.
I hate words like "inspirational" because they've become so overdone and cheesy, but I just have to say it-- Michelle Obama is an inspiration. I had the privilege of seeing her speak at The Forum in Inglewood, and she is one of the warmest, funniest, smartest, down-to-earth people I have ever seen in this world.
And yes, I know we present what we want the world to see, but I truly do think it's genuine. I think she is someone who really cares about people - especially kids - and wants to give them better lives and opportunities.
She's obviously intelligent, but she also doesn't gussy up her words. She talks straight, with an openness and honesty rarely seen. She's been one of the most powerful women in the world, she's been a graduate of Princeton and Harvard Law School, she's had her own successful career, and yet she has remained throughout that same girl - Michelle Robinson - from a working class family in Chicago.
I don't think there's anyone who wouldn't benefit from reading this book.
Hopefully, this post has given you a better idea of how to write a book review. You might be wondering how to put all of this knowledge into action now! Many book reviewers start out by setting up a book blog. If you don’t have time to research the intricacies of HTML, check out Reedsy Discovery — where you can read indie books for free and review them without going through the hassle of creating a blog. To register as a book reviewer , go here .
And if you’d like to see even more book review examples, simply go to this directory of book review blogs and click on any one of them to see a wealth of good book reviews. Beyond that, it's up to you to pick up a book and pen — and start reviewing!
Continue reading
More posts from across the blog.
50 Best Self-Help Books of All Time
Want to better yourself, but don't know where to start? Our list of 50 titles is sure to give you the guiding hand you need to start improving your life today.
60 Children's Books About Diversity To Read With Little Ones
Children's books about diversity are crucial: they introduce difficult but important topics to little ones in engaging and thoughtful ways. Take a look at these enchanting books to see how.
40 Transformative Poems About Life Everyone Should Know
When life gets confusing, it might be useful to turn to the wisdom of poetry. In this post we’ve put together a list of the 40 greatest poems about life. From classics like Robert Frost and Rumi to the more contemporary Rupi Kaur, you’re guaranteed to find a poem about life ...
Heard about Reedsy Discovery?
Trust real people, not robots, to give you book recommendations.
Or sign up with an
Or sign up with your social account
- Submit your book
- Reviewer directory

Want to be a book reviewer?
Review new books and start building your portfolio.
Book Reports Lesson Plan: Self and Peer Evaluation
Submitted by: angela watson.
In this lesson plan, which is adaptable for grades K-12, students use BrainPOP and/or BrainPOP Jr. resources to identify the elements of a comprehensive book report. Students then create a book report and present it to the class. They will also use a class-generated set of criteria to self-assess and evaluate the book reports of peers.
Lesson Plan Common Core State Standards Alignments
Students will:.
- Identify the elements of a comprehensive book report.
- Create a book report and present it to the class.
- Use a class-generated set of criteria to self-assess and evaluate the book reports of peers.
- Computer and projector to watch BrainPOP as a class
- Printed class set of BrainPOP Worksheet
- Printed class set of student-generated book report criteria for scoring and assessment
Vocabulary:
Preparation:, lesson procedure:.
- Brainstorm what students know about formal book reports. What is their purpose? Guide children to understand that book reports are a chance to share stories and information you enjoy, and help other people discover books they might love, as well.
- What do students think makes a compelling report on a book? If students do not have prior experiences with reports, talk about the information they would typically share when recommending a good book to a friend. Share real-world examples of book reports in the form of online book reviews and blog posts, or even clips from the book reports given on the former show Reading Rainbow . Encourage students who do have background knowledge and experience to think of outstanding presentations they've seen and talk about what made them interesting. Record their responses.
- Show either the BrainPOP Jr. or BrainPOP Book Report movie (depending on your students' ability levels.)
- Ask students to consider what they learned from the movie and revisit their original list of book report criteria. You may want to include criteria for being an attentive audience member during others' reports and discuss specifically what that looks like. Students who have more experience with book reports may want to talk about original and creative book report ideas; use the "In Practice" Related Reading page as a springboard for discussion.
- Tell students that they will have the opportunity to create and present a report on the book of their choosing. Explain any deadlines or special instructions you have for the assignment. You may wish to type the class' list of book report components and provide each student with a copy. The list might also include a grading scale that explains how many points each component is worth.
- Provide very young students and/or those who are emerging English readers/writers with the BrainPOP Jr. activity page as a guide for their reports. More advanced students may use the BrainPOP Worksheet to help them organize their thoughts and ideas prior to writing a formal report.
- Check in with students regularly as they read their books and form their reports. Keep the class list of components displayed for student reference. You can use various BrainPOP resources to reinforce expectations and keep students motivated and excited about sharing their reports.
- When students are ready to present their reports, review the criteria for book reports as well as audience participation. Have students assess themselves as well as their classmates through informal class discussion and/or by writing down feedback on photocopies of the report criteria that students generated.
- Display the reports (and, if possible, a copy of the books students read) in your class library to encourage students to read the books their peers recommended. You could also take a digital photo of each child holding his/her report and book and display it online or in the class library as a reminder of each book title and the person who reported on it.
Extension Activities:

- BrainPOP Jr. (K-3)
- BrainPOP ELL
- BrainPOP Science
- BrainPOP Español
- BrainPOP Français
- Set Up Accounts
- Single Sign-on
- Manage Subscription
- Quick Tours
- About BrainPOP

- Terms of Use
- Privacy Policy
- Trademarks & Copyrights
- Our Mission
Planning Writing Lessons for the Early Elementary Grades
Teachers can provide thoughtful instruction that supports the sustained development of young students’ literacy skills.

Often, attempting to plan effective and purposeful writing instruction raises many questions: What does lesson planning look like? How will I manage so many students who may be in different stages of their writing? How often should they be editing and revising? The list doesn’t stop there.
By utilizing on-demand writing for assessment and long-range writing for scaffolded practice of applying various writing techniques, teachers can approach their instruction with intentional and tailored lessons that meet the needs of the learners in the classroom, as well as help students develop self-regulated behaviors when crafting a piece of text.
On-Demand Writing
Just like any area of instruction, assessment is critical for knowing what the students’ strengths and areas of growth are, and on-demand writing is how teachers can gather that evidence. An on-demand piece of writing simply means that the teacher provides a specific prompt for the student to write to for the purpose of anecdotal data. For example, let’s say a second-grade teacher prepares for a narrative writing cycle. In the first couple of days before the cycle begins, they’ll ask students to write a narrative about something fun they’ve experienced (with their family or a friend).
After the prompt is given, students get one or two days to write and are provided with all necessary tools to carry out the process of developing a piece of writing without additional modeling or instruction. Effective tools might include graphic organizers, writing paper, tools for editing, and a writing checklist. However, the teacher will not model how to use the tools. The teacher is informally assessing if the students know how to use these resources to develop a story.
After students complete their piece, the teacher collects them for analysis. It is critically important to determine realistic expectations for what writing should look like throughout various points of the year, so creating a common rubric as a grade level is a great way to stay on the same page for analyzing the assessment.
Writing growth, similar to reading, happens along a continuum of skills. At the beginning of the year, a second grader can’t be expected to write like an end-of-the-year second grader because they haven’t been taught the grade-level skills necessary to do so yet. On-demand benchmark assessments along the way will gradually raise the expectation of what that student should be able to do. Websites such as Reading Rockets and Achieve the Core provide useful anchor examples of real student writing in various genres that provide annotated explanations of students’ overall writing ability and possible next steps for instruction.
As students engage in daily lessons about crafting a narrative within the instructional cycle of a long-range writing piece, another on-demand prompt may be given at the halfway point of the cycle to track growth and drive future instruction. This could be the same prompt as before or a prompt given in response to a story or passage the student has read.
It’s important to remember that it’s easy to fall into the trap of using writing prompts daily for students to produce writing simply because it’s easy to manage. If we use this approach exclusively, we rob our students of the opportunity to dive deeply into producing self-chosen, elaborate pieces full of voice and author’s craft.
Long-Range Writing
Long-range pieces give students the autonomy to choose their own writing topic while the teacher assists in walking them through the process. This type of instruction instills the executive-functioning behaviors needed when students are asked to write a piece on demand. When considering how to implement this type of writing instruction, it can be overwhelming. Breaking down long-range instruction using the following components allows for a more manageable approach.
Keep your lesson mini: A mini lesson is 15 to 20 minutes long and organized in a gradual release format, and it allows the teacher to model a specific, focused lesson. For example, narrative writing could be broken into the following mini lessons for a beginning-of-the-year cycle for second grade: introduce and describe a setting, introduce and describe the character, edit on the go (this means to stop and edit before we add more writing), describe the first event in the narrative, introduce a problem, etc. Essentially, each lesson will invite students to add to their story one chunk at a time.
Model, provide independent practice: The teacher begins by modeling one learning target using a well-crafted organizer . An effective organizer teaches students that each genre has a specific structure. As learners begin to recognize the pattern in text structure, they can replicate it when assessed in on-demand pieces. For example, the teacher can start by using a text that clearly introduces and describes the setting, and then read that page out loud and ask students what they notice about how the author introduced the setting.
Next, students are invited to help the teacher write a setting to a story together by offering verbal suggestions. The teacher records the students’ ideas and writes an example introduction in the organizer. Then students think about an idea for an introduction of a setting on their own and are prompted to talk to a partner about their story. The students verbally rehearse what they plan to write, as this provides them an opportunity to organize their thoughts and prepares them to get started as soon as they are released to write independently, using the same organizer that the teacher used to model the mini lesson.
The benefit of this approach is that it gives the teacher time to provide specific feedback over the same crafting element. Having every student write their complete thoughts directly in the organizer in a chunked manner allows for a better visual of where to correct capitalization and punctuation. Essentially, each lesson should invite students to write one or two complete sentences that can be quickly edited before adding the next part of the story.
Share and reflect: Close each lesson by bringing students back together so that they have an opportunity to share what they’ve produced. This time celebrates students’ creativity, as well as giving them an opportunity to reflect on how they can improve their writing.
Both on-demand writing and long-range writing are vital in developing confident writers across various genres. It’s important to approach them with a cyclical scope and sequence that allows students to learn the craft, structure, and development of narrative, informative, and opinion styles of writing. By scaffolding and supporting students’ growth in each genre of writing, learners will begin to automatically apply these techniques more independently as the year progresses because of the solid foundation that has been built.
- International
- Schools directory
- Resources Jobs Schools directory News Search
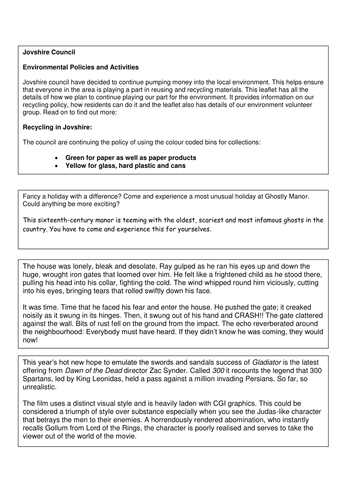
Writing a review
Subject: English
Age range: 11-14
Resource type: Lesson (complete)
Last updated
21 May 2013
- Share through email
- Share through twitter
- Share through linkedin
- Share through facebook
- Share through pinterest

Tes classic free licence
Your rating is required to reflect your happiness.
It's good to leave some feedback.
Something went wrong, please try again later.
Thank you so very much for sharing! A really useful resource!
Empty reply does not make any sense for the end user
tania_ester
Thank you so much for sharing!
This has saved my bacon - thanks so much for sharing!
Great resource, it was very helpful and saved lots of time. Thank you!
Report this resource to let us know if it violates our terms and conditions. Our customer service team will review your report and will be in touch.
Not quite what you were looking for? Search by keyword to find the right resource:

IMAGES
VIDEO
COMMENTS
Overview. Teenagers are often outspoken and opinionated. Writing reviews of the literature they read gives them a chance to express their ideas while developing style and voice. This lesson uses discussion of student opinions about yesterday's lunch or a popular TV show serves as an introduction to the genre of reviews.
Book reviews are a useful resource for reading fans, but can also be an alternative assessment tool for teachers. Before students can write a book review, you must introduce them to professionally written pieces. Take them to the computer lab and go to sites that have notable book reviews, like the New York Times or Barnes and Noble Review.
A general guideline is that the longer the book, the longer the review, and a review shouldn't be fewer than 100 words or so. For a long book, the review may be 500 words or even more. If a review is too short, the review may not be able to fulfill its purpose. Too long, and the review may stray into too much plot summary or lose the reader's ...
The real value of crafting a well-written book review for a student does not lie in their ability to impact book sales. Understanding how to produce a well-written book review helps students to: Engage critically with a text. Critically evaluate a text. Respond personally to a range of different writing genres.
learn how to write a book reviewing with our guide that walks students through the process of writing a systematic book review with proven teacher strategies and writing skills. learn how the write one book review with our guide that trips students through the process of type a structure book review using proven teaching strategies and writings ...
Based on the number of questions you answered "yes" for: 0-4- You may want to take some more time reviewing other reviews available. 5-7- You are on your way to writing a great review. With a little bit of love and care, it will be ready in no time! 8-9- Sounds like you are ready to publish. Way to go! 10- Wow.
This lesson plan will help students learn how to construct an effective book review. After observing the teacher model the process, students will write their own book review about a favorite book ...
Examples: Learn from the efforts of others. Learning how to write strong reviews takes time and not a little effort. Reading the reviews others have done can help you get a feel for the flow and flavor of reviews. This book was about a bird who didn't yet know how to fly. The bird has to decide if it will try to fly, but it was not sure if it ...
Include the target structures and key vocabulary from each chapter and any diagrams or maps that they should be familiar with. This does a lot to build student confidence because they have a hard copy of what they should review and what sections of the course you feel are most important. The study guide should include every type of question ...
doc, 92 KB. pdf, 636.37 KB. Year 3/4 English - writing a book review lesson plan and other resources: - writing a book review lesson plan. - writing a book review model review. - writing a book review writing frame. There is a PDF of all of the files and an editable version of each file (you just need to delete the watermark logo from each of ...
Questions to prompt the creation of a quality book review. Webinars; For AFT Members; Featured This Month: Winter Holidays Lesson Plans and Resources
Procedure. Before they write their book review, you will need to explain how to write one. After you explain about book reviews, then they can choose a book they would like to read, and they will take notes while they read. Then, they will write a book review of their book. After that, they will submit their review for you to grade.
It is a fantasy, but the book draws inspiration from the Second Sino-Japanese War and the Rape of Nanking. Crime Fiction Lover reviews Jessica Barry's Freefall, a crime novel: In some crime novels, the wrongdoing hits you between the eyes from page one. With others it's a more subtle process, and that's OK too.
Xu 2. Procedure [50 minutes]: Step 1: Provide the format and review the steps to writing a review article. [15 minutes] 1. Show the third slide. Explain that there are different types of review articles, depending on the work being reviewed and the primary purpose the review article serves.
Home > Legends and Heroes - Lesson Plan ... Although the questions prompt students for thoughts about the book, it is not a process guide for "how to" write a book review. Liberty5. February 08, 2014. Good book report resource jtucker24. July 17, 2012. Thank you so much. Can be used with all year ages SML Member. May 31, 2012.
Grade Levels: 3-5, 6-8, 9-12, K-3. In this lesson plan, which is adaptable for grades K-12, students use BrainPOP and/or BrainPOP Jr. resources to identify the elements of a comprehensive book report. Students then create a book report and present it to the class. They will also use a class-generated set of criteria to self-assess and evaluate ...
Steps to building your lesson plan. Once you've identified the components that need to go into teaching your class, you're ready to use these eight steps to build your lesson plan: 1. Identify the objectives. To build a lesson, you first need to identify the objectives of each class.
Writing a Book Review. Subject: English. Age range: 11-14. Resource type: Worksheet/Activity. File previews. pptx, 68.2 KB. Basic powerpoint about how to write a book review. Not quite what you were looking for? Search by keyword to find the right resource:
Keep your lesson mini: A mini lesson is 15 to 20 minutes long and organized in a gradual release format, and it allows the teacher to model a specific, focused lesson. For example, narrative writing could be broken into the following mini lessons for a beginning-of-the-year cycle for second grade: introduce and describe a setting, introduce and ...
Empty reply does not make any sense for the end user. Submit reply Cancel