
- Walden University
- Faculty Portal

Common Assignments: Journal Entries
Basics of journal entries, related webinar.
Didn't find what you need? Search our website or email us .
Read our website accessibility and accommodation statement .
- Previous Page: Writing a Successful Response to Another's Post
- Next Page: Read the Prompt Carefully
- Office of Student Disability Services
Walden Resources
Departments.
- Academic Residencies
- Academic Skills
- Career Planning and Development
- Customer Care Team
- Field Experience
- Military Services
- Student Success Advising
- Writing Skills
Centers and Offices
- Center for Social Change
- Office of Academic Support and Instructional Services
- Office of Degree Acceleration
- Office of Research and Doctoral Services
- Office of Student Affairs
Student Resources
- Doctoral Writing Assessment
- Form & Style Review
- Quick Answers
- ScholarWorks
- SKIL Courses and Workshops
- Walden Bookstore
- Walden Catalog & Student Handbook
- Student Safety/Title IX
- Legal & Consumer Information
- Website Terms and Conditions
- Cookie Policy
- Accessibility
- Accreditation
- State Authorization
- Net Price Calculator
- Contact Walden
Walden University is a member of Adtalem Global Education, Inc. www.adtalem.com Walden University is certified to operate by SCHEV © 2024 Walden University LLC. All rights reserved.
Have a language expert improve your writing
Run a free plagiarism check in 10 minutes, generate accurate citations for free.
- Knowledge Base
- Research paper
How to Write a Research Paper | A Beginner's Guide
A research paper is a piece of academic writing that provides analysis, interpretation, and argument based on in-depth independent research.
Research papers are similar to academic essays , but they are usually longer and more detailed assignments, designed to assess not only your writing skills but also your skills in scholarly research. Writing a research paper requires you to demonstrate a strong knowledge of your topic, engage with a variety of sources, and make an original contribution to the debate.
This step-by-step guide takes you through the entire writing process, from understanding your assignment to proofreading your final draft.
Instantly correct all language mistakes in your text
Upload your document to correct all your mistakes in minutes

Table of contents
Understand the assignment, choose a research paper topic, conduct preliminary research, develop a thesis statement, create a research paper outline, write a first draft of the research paper, write the introduction, write a compelling body of text, write the conclusion, the second draft, the revision process, research paper checklist, free lecture slides.
Completing a research paper successfully means accomplishing the specific tasks set out for you. Before you start, make sure you thoroughly understanding the assignment task sheet:
- Read it carefully, looking for anything confusing you might need to clarify with your professor.
- Identify the assignment goal, deadline, length specifications, formatting, and submission method.
- Make a bulleted list of the key points, then go back and cross completed items off as you’re writing.
Carefully consider your timeframe and word limit: be realistic, and plan enough time to research, write, and edit.
Prevent plagiarism. Run a free check.
There are many ways to generate an idea for a research paper, from brainstorming with pen and paper to talking it through with a fellow student or professor.
You can try free writing, which involves taking a broad topic and writing continuously for two or three minutes to identify absolutely anything relevant that could be interesting.
You can also gain inspiration from other research. The discussion or recommendations sections of research papers often include ideas for other specific topics that require further examination.
Once you have a broad subject area, narrow it down to choose a topic that interests you, m eets the criteria of your assignment, and i s possible to research. Aim for ideas that are both original and specific:
- A paper following the chronology of World War II would not be original or specific enough.
- A paper on the experience of Danish citizens living close to the German border during World War II would be specific and could be original enough.
Note any discussions that seem important to the topic, and try to find an issue that you can focus your paper around. Use a variety of sources , including journals, books, and reliable websites, to ensure you do not miss anything glaring.
Do not only verify the ideas you have in mind, but look for sources that contradict your point of view.
- Is there anything people seem to overlook in the sources you research?
- Are there any heated debates you can address?
- Do you have a unique take on your topic?
- Have there been some recent developments that build on the extant research?
In this stage, you might find it helpful to formulate some research questions to help guide you. To write research questions, try to finish the following sentence: “I want to know how/what/why…”
A thesis statement is a statement of your central argument — it establishes the purpose and position of your paper. If you started with a research question, the thesis statement should answer it. It should also show what evidence and reasoning you’ll use to support that answer.
The thesis statement should be concise, contentious, and coherent. That means it should briefly summarize your argument in a sentence or two, make a claim that requires further evidence or analysis, and make a coherent point that relates to every part of the paper.
You will probably revise and refine the thesis statement as you do more research, but it can serve as a guide throughout the writing process. Every paragraph should aim to support and develop this central claim.
Receive feedback on language, structure, and formatting
Professional editors proofread and edit your paper by focusing on:
- Academic style
- Vague sentences
- Style consistency
See an example

A research paper outline is essentially a list of the key topics, arguments, and evidence you want to include, divided into sections with headings so that you know roughly what the paper will look like before you start writing.
A structure outline can help make the writing process much more efficient, so it’s worth dedicating some time to create one.
Your first draft won’t be perfect — you can polish later on. Your priorities at this stage are as follows:
- Maintaining forward momentum — write now, perfect later.
- Paying attention to clear organization and logical ordering of paragraphs and sentences, which will help when you come to the second draft.
- Expressing your ideas as clearly as possible, so you know what you were trying to say when you come back to the text.
You do not need to start by writing the introduction. Begin where it feels most natural for you — some prefer to finish the most difficult sections first, while others choose to start with the easiest part. If you created an outline, use it as a map while you work.
Do not delete large sections of text. If you begin to dislike something you have written or find it doesn’t quite fit, move it to a different document, but don’t lose it completely — you never know if it might come in useful later.
Paragraph structure
Paragraphs are the basic building blocks of research papers. Each one should focus on a single claim or idea that helps to establish the overall argument or purpose of the paper.
Example paragraph
George Orwell’s 1946 essay “Politics and the English Language” has had an enduring impact on thought about the relationship between politics and language. This impact is particularly obvious in light of the various critical review articles that have recently referenced the essay. For example, consider Mark Falcoff’s 2009 article in The National Review Online, “The Perversion of Language; or, Orwell Revisited,” in which he analyzes several common words (“activist,” “civil-rights leader,” “diversity,” and more). Falcoff’s close analysis of the ambiguity built into political language intentionally mirrors Orwell’s own point-by-point analysis of the political language of his day. Even 63 years after its publication, Orwell’s essay is emulated by contemporary thinkers.
Citing sources
It’s also important to keep track of citations at this stage to avoid accidental plagiarism . Each time you use a source, make sure to take note of where the information came from.
You can use our free citation generators to automatically create citations and save your reference list as you go.
APA Citation Generator MLA Citation Generator
The research paper introduction should address three questions: What, why, and how? After finishing the introduction, the reader should know what the paper is about, why it is worth reading, and how you’ll build your arguments.
What? Be specific about the topic of the paper, introduce the background, and define key terms or concepts.
Why? This is the most important, but also the most difficult, part of the introduction. Try to provide brief answers to the following questions: What new material or insight are you offering? What important issues does your essay help define or answer?
How? To let the reader know what to expect from the rest of the paper, the introduction should include a “map” of what will be discussed, briefly presenting the key elements of the paper in chronological order.
The major struggle faced by most writers is how to organize the information presented in the paper, which is one reason an outline is so useful. However, remember that the outline is only a guide and, when writing, you can be flexible with the order in which the information and arguments are presented.
One way to stay on track is to use your thesis statement and topic sentences . Check:
- topic sentences against the thesis statement;
- topic sentences against each other, for similarities and logical ordering;
- and each sentence against the topic sentence of that paragraph.
Be aware of paragraphs that seem to cover the same things. If two paragraphs discuss something similar, they must approach that topic in different ways. Aim to create smooth transitions between sentences, paragraphs, and sections.
The research paper conclusion is designed to help your reader out of the paper’s argument, giving them a sense of finality.
Trace the course of the paper, emphasizing how it all comes together to prove your thesis statement. Give the paper a sense of finality by making sure the reader understands how you’ve settled the issues raised in the introduction.
You might also discuss the more general consequences of the argument, outline what the paper offers to future students of the topic, and suggest any questions the paper’s argument raises but cannot or does not try to answer.
You should not :
- Offer new arguments or essential information
- Take up any more space than necessary
- Begin with stock phrases that signal you are ending the paper (e.g. “In conclusion”)
There are four main considerations when it comes to the second draft.
- Check how your vision of the paper lines up with the first draft and, more importantly, that your paper still answers the assignment.
- Identify any assumptions that might require (more substantial) justification, keeping your reader’s perspective foremost in mind. Remove these points if you cannot substantiate them further.
- Be open to rearranging your ideas. Check whether any sections feel out of place and whether your ideas could be better organized.
- If you find that old ideas do not fit as well as you anticipated, you should cut them out or condense them. You might also find that new and well-suited ideas occurred to you during the writing of the first draft — now is the time to make them part of the paper.
The goal during the revision and proofreading process is to ensure you have completed all the necessary tasks and that the paper is as well-articulated as possible. You can speed up the proofreading process by using the AI proofreader .
Global concerns
- Confirm that your paper completes every task specified in your assignment sheet.
- Check for logical organization and flow of paragraphs.
- Check paragraphs against the introduction and thesis statement.
Fine-grained details
Check the content of each paragraph, making sure that:
- each sentence helps support the topic sentence.
- no unnecessary or irrelevant information is present.
- all technical terms your audience might not know are identified.
Next, think about sentence structure , grammatical errors, and formatting . Check that you have correctly used transition words and phrases to show the connections between your ideas. Look for typos, cut unnecessary words, and check for consistency in aspects such as heading formatting and spellings .
Finally, you need to make sure your paper is correctly formatted according to the rules of the citation style you are using. For example, you might need to include an MLA heading or create an APA title page .
Scribbr’s professional editors can help with the revision process with our award-winning proofreading services.
Discover our paper editing service
Checklist: Research paper
I have followed all instructions in the assignment sheet.
My introduction presents my topic in an engaging way and provides necessary background information.
My introduction presents a clear, focused research problem and/or thesis statement .
My paper is logically organized using paragraphs and (if relevant) section headings .
Each paragraph is clearly focused on one central idea, expressed in a clear topic sentence .
Each paragraph is relevant to my research problem or thesis statement.
I have used appropriate transitions to clarify the connections between sections, paragraphs, and sentences.
My conclusion provides a concise answer to the research question or emphasizes how the thesis has been supported.
My conclusion shows how my research has contributed to knowledge or understanding of my topic.
My conclusion does not present any new points or information essential to my argument.
I have provided an in-text citation every time I refer to ideas or information from a source.
I have included a reference list at the end of my paper, consistently formatted according to a specific citation style .
I have thoroughly revised my paper and addressed any feedback from my professor or supervisor.
I have followed all formatting guidelines (page numbers, headers, spacing, etc.).
You've written a great paper. Make sure it's perfect with the help of a Scribbr editor!
Open Google Slides Download PowerPoint
Is this article helpful?
Other students also liked.
- Writing a Research Paper Introduction | Step-by-Step Guide
- Writing a Research Paper Conclusion | Step-by-Step Guide
- Research Paper Format | APA, MLA, & Chicago Templates
More interesting articles
- Academic Paragraph Structure | Step-by-Step Guide & Examples
- Checklist: Writing a Great Research Paper
- How to Create a Structured Research Paper Outline | Example
- How to Write a Discussion Section | Tips & Examples
- How to Write Recommendations in Research | Examples & Tips
- How to Write Topic Sentences | 4 Steps, Examples & Purpose
- Research Paper Appendix | Example & Templates
- Research Paper Damage Control | Managing a Broken Argument
- What Is a Theoretical Framework? | Guide to Organizing
What is your plagiarism score?
- International edition
- Australia edition
- Europe edition

Writing for an academic journal: 10 tips
1) Have a strategy, make a plan
Why do you want to write for journals? What is your purpose? Are you writing for research assessment? Or to make a difference? Are you writing to have an impact factor or to have an impact? Do you want to develop a profile in a specific area? Will this determine which journals you write for? Have you taken their impact factors into account?
Have you researched other researchers in your field – where have they published recently? Which group or conversation can you see yourself joining? Some people write the paper first and then look for a 'home' for it, but since everything in your article – content, focus, structure, style – will be shaped for a specific journal, save yourself time by deciding on your target journal and work out how to write in a way that suits that journal.
Having a writing strategy means making sure you have both external drivers – such as scoring points in research assessment or climbing the promotion ladder – and internal drivers – which means working out why writing for academic journals matters to you. This will help you maintain the motivation you'll need to write and publish over the long term. Since the time between submission and publication can be up to two years (though in some fields it's much less) you need to be clear about your motivation.
2) Analyse writing in journals in your field
Take a couple of journals in your field that you will target now or soon. Scan all the abstracts over the past few issues. Analyse them: look closely at all first and last sentences. The first sentence (usually) gives the rationale for the research, and the last asserts a 'contribution to knowledge'. But the word 'contribution' may not be there – it's associated with the doctorate. So which words are used? What constitutes new knowledge in this journal at this time? How can you construct a similar form of contribution from the work you did? What two sentences will you write to start and end your abstract for that journal?
Scan other sections of the articles: how are they structured? What are the components of the argument? Highlight all the topic sentences – the first sentences of every paragraph – to show the stages in the argument. Can you see an emerging taxonomy of writing genres in this journal? Can you define the different types of paper, different structures and decide which one will work best in your paper? Select two types of paper: one that's the type of paper you can use as a model for yours, and one that you can cite in your paper, thereby joining the research conversation that is ongoing in that journal.
3) Do an outline and just write
Which type of writer are you: do you always do an outline before you write, or do you just dive in and start writing? Or do you do a bit of both? Both outlining and just writing are useful, and it is therefore a good idea to use both. However, make your outline very detailed: outline the main sections and calibrate these with your target journal.
What types of headings are normally used there? How long are the sections usually? Set word limits for your sections, sub-sections and, if need be, for sub-sub-sections. This involves deciding about content that you want to include, so it may take time, and feedback would help at this stage.
When you sit down to write, what exactly are you doing:using writing to develop your ideas or writing to document your work? Are you using your outline as an agenda for writing sections of your article? Define your writing task by thinking about verbs – they define purpose: to summarise, overview, critique, define, introduce, conclude etc.
4) Get feedback from start to finish
Even at the earliest stages, discuss your idea for a paper with four or five people, get feedback on your draft abstract. It will only take them a couple of minutes to read it and respond. Do multiple revisions before you submit your article to the journal.
5) Set specific writing goals and sub-goals
Making your writing goals specific means defining the content, verb and word length for the section. This means not having a writing goal like, 'I plan to have this article written by the end of the year' but 'My next writing goal is to summarise and critique twelve articles for the literature review section in 800 words on Tuesday between 9am and 10.30'. Some people see this as too mechanical for academic writing, but it is a way of forcing yourself to make decisions about content, sequence and proportion for your article.
6) Write with others
While most people see writing as a solitary activity, communal writing – writing with others who are writing – can help to develop confidence, fluency and focus. It can help you develop the discipline of regular writing. Doing your academic writing in groups or at writing retreats are ways of working on your own writing, but – if you unplug from email, internet and all other devices – also developing the concentration needed for regular, high-level academic writing.
At some point – ideally at regular intervals – you can get a lot more done if you just focus on writing. If this seems like common sense, it isn't common practice. Most people do several things at once, but this won't always work for regular journal article writing. At some point, it pays to privilege writing over all other tasks, for a defined period, such as 90 minutes, which is long enough to get something done on your paper, but not so long that it's impossible to find the time.
7) Do a warm up before you write
While you are deciding what you want to write about, an initial warm up that works is to write for five minutes, in sentences, in answer to the question: 'What writing for publication have you done [or the closest thing to it], and what do you want to do in the long, medium and short term?'
Once you have started writing your article, use a variation on this question as a warm up – what writing for this project have you done, and what do you want to do in the long, medium and short term? Top tip: end each session of writing with a 'writing instruction' for yourself to use in your next session, for example, 'on Monday from 9 to 10am, I will draft the conclusion section in 500 words'.
As discussed, if there are no numbers, there are no goals. Goals that work need to be specific, and you need to monitor the extent to which you achieve them. This is how you learn to set realistic targets.
8) Analyse reviewers' feedback on your submission
What exactly are they asking you to do? Work out whether they want you to add or cut something. How much? Where? Write out a list of revision actions. When you resubmit your article include this in your report to the journal, specifying how you have responded to the reviewers' feedback. If your article was rejected, it is still useful to analyse feedback, work out why and revise it for somewhere else.
Most feedback will help you improve your paper and, perhaps, your journal article writing, but sometimes it may seem overheated, personalised or even vindictive. Some of it may even seem unprofessional. Discuss reviewers' feedback – see what others think of it. You may find that other people – even eminent researchers – still get rejections and negative reviews; any non-rejection is a cause for celebration. Revise and resubmit as soon as you can.
9) Be persistent, thick-skinned and resilient
These are qualities that you may develop over time – or you may already have them. It may be easier to develop them in discussion with others who are writing for journals.
10) Take care of yourself
Writing for academic journals is highly competitive. It can be extremely stressful. Even making time to write can be stressful. And there are health risks in sitting for long periods, so try not to sit writing for more than an hour at a time. Finally, be sure to celebrate thoroughly when your article is accepted. Remind yourself that writing for academic journals is what you want to do – that your writing will make a difference in some way.
These points are taken from the 3rd edition of Writing for Academic Journals .
Rowena Murray is professor in education and director of research at the University of the West of Scotland – follow it on Twitter @UniWestScotland
This content is brought to you by Guardian Professional . Looking for your next university role? Browse Guardian jobs for thousands of the latest academic, administrative and research posts
- Universities
- Professional development
- Higher education
- Arts and humanities
Comments (…)
Most viewed.
How to Write and Publish a Research Paper for a Peer-Reviewed Journal
- Open access
- Published: 30 April 2020
- Volume 36 , pages 909–913, ( 2021 )
Cite this article
You have full access to this open access article
- Clara Busse ORCID: orcid.org/0000-0002-0178-1000 1 &
- Ella August ORCID: orcid.org/0000-0001-5151-1036 1 , 2
261k Accesses
15 Citations
703 Altmetric
Explore all metrics
Communicating research findings is an essential step in the research process. Often, peer-reviewed journals are the forum for such communication, yet many researchers are never taught how to write a publishable scientific paper. In this article, we explain the basic structure of a scientific paper and describe the information that should be included in each section. We also identify common pitfalls for each section and recommend strategies to avoid them. Further, we give advice about target journal selection and authorship. In the online resource 1 , we provide an example of a high-quality scientific paper, with annotations identifying the elements we describe in this article.
Similar content being viewed by others

How to Choose the Right Journal

The Point Is…to Publish?

Some Opinions on the Review Process of Research Papers Destined for Publication
Ehsan Roohi & Omid Mahian
Avoid common mistakes on your manuscript.
Introduction
Writing a scientific paper is an important component of the research process, yet researchers often receive little formal training in scientific writing. This is especially true in low-resource settings. In this article, we explain why choosing a target journal is important, give advice about authorship, provide a basic structure for writing each section of a scientific paper, and describe common pitfalls and recommendations for each section. In the online resource 1 , we also include an annotated journal article that identifies the key elements and writing approaches that we detail here. Before you begin your research, make sure you have ethical clearance from all relevant ethical review boards.
Select a Target Journal Early in the Writing Process
We recommend that you select a “target journal” early in the writing process; a “target journal” is the journal to which you plan to submit your paper. Each journal has a set of core readers and you should tailor your writing to this readership. For example, if you plan to submit a manuscript about vaping during pregnancy to a pregnancy-focused journal, you will need to explain what vaping is because readers of this journal may not have a background in this topic. However, if you were to submit that same article to a tobacco journal, you would not need to provide as much background information about vaping.
Information about a journal’s core readership can be found on its website, usually in a section called “About this journal” or something similar. For example, the Journal of Cancer Education presents such information on the “Aims and Scope” page of its website, which can be found here: https://www.springer.com/journal/13187/aims-and-scope .
Peer reviewer guidelines from your target journal are an additional resource that can help you tailor your writing to the journal and provide additional advice about crafting an effective article [ 1 ]. These are not always available, but it is worth a quick web search to find out.
Identify Author Roles Early in the Process
Early in the writing process, identify authors, determine the order of authors, and discuss the responsibilities of each author. Standard author responsibilities have been identified by The International Committee of Medical Journal Editors (ICMJE) [ 2 ]. To set clear expectations about each team member’s responsibilities and prevent errors in communication, we also suggest outlining more detailed roles, such as who will draft each section of the manuscript, write the abstract, submit the paper electronically, serve as corresponding author, and write the cover letter. It is best to formalize this agreement in writing after discussing it, circulating the document to the author team for approval. We suggest creating a title page on which all authors are listed in the agreed-upon order. It may be necessary to adjust authorship roles and order during the development of the paper. If a new author order is agreed upon, be sure to update the title page in the manuscript draft.
In the case where multiple papers will result from a single study, authors should discuss who will author each paper. Additionally, authors should agree on a deadline for each paper and the lead author should take responsibility for producing an initial draft by this deadline.
Structure of the Introduction Section
The introduction section should be approximately three to five paragraphs in length. Look at examples from your target journal to decide the appropriate length. This section should include the elements shown in Fig. 1 . Begin with a general context, narrowing to the specific focus of the paper. Include five main elements: why your research is important, what is already known about the topic, the “gap” or what is not yet known about the topic, why it is important to learn the new information that your research adds, and the specific research aim(s) that your paper addresses. Your research aim should address the gap you identified. Be sure to add enough background information to enable readers to understand your study. Table 1 provides common introduction section pitfalls and recommendations for addressing them.

The main elements of the introduction section of an original research article. Often, the elements overlap
Methods Section
The purpose of the methods section is twofold: to explain how the study was done in enough detail to enable its replication and to provide enough contextual detail to enable readers to understand and interpret the results. In general, the essential elements of a methods section are the following: a description of the setting and participants, the study design and timing, the recruitment and sampling, the data collection process, the dataset, the dependent and independent variables, the covariates, the analytic approach for each research objective, and the ethical approval. The hallmark of an exemplary methods section is the justification of why each method was used. Table 2 provides common methods section pitfalls and recommendations for addressing them.
Results Section
The focus of the results section should be associations, or lack thereof, rather than statistical tests. Two considerations should guide your writing here. First, the results should present answers to each part of the research aim. Second, return to the methods section to ensure that the analysis and variables for each result have been explained.
Begin the results section by describing the number of participants in the final sample and details such as the number who were approached to participate, the proportion who were eligible and who enrolled, and the number of participants who dropped out. The next part of the results should describe the participant characteristics. After that, you may organize your results by the aim or by putting the most exciting results first. Do not forget to report your non-significant associations. These are still findings.
Tables and figures capture the reader’s attention and efficiently communicate your main findings [ 3 ]. Each table and figure should have a clear message and should complement, rather than repeat, the text. Tables and figures should communicate all salient details necessary for a reader to understand the findings without consulting the text. Include information on comparisons and tests, as well as information about the sample and timing of the study in the title, legend, or in a footnote. Note that figures are often more visually interesting than tables, so if it is feasible to make a figure, make a figure. To avoid confusing the reader, either avoid abbreviations in tables and figures, or define them in a footnote. Note that there should not be citations in the results section and you should not interpret results here. Table 3 provides common results section pitfalls and recommendations for addressing them.
Discussion Section
Opposite the introduction section, the discussion should take the form of a right-side-up triangle beginning with interpretation of your results and moving to general implications (Fig. 2 ). This section typically begins with a restatement of the main findings, which can usually be accomplished with a few carefully-crafted sentences.
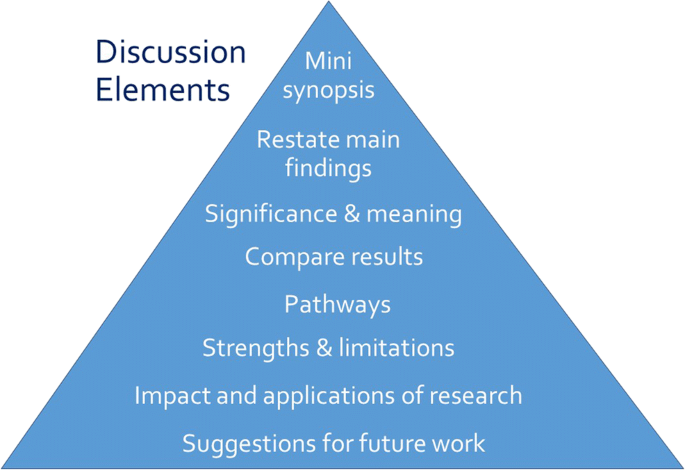
Major elements of the discussion section of an original research article. Often, the elements overlap
Next, interpret the meaning or explain the significance of your results, lifting the reader’s gaze from the study’s specific findings to more general applications. Then, compare these study findings with other research. Are these findings in agreement or disagreement with those from other studies? Does this study impart additional nuance to well-accepted theories? Situate your findings within the broader context of scientific literature, then explain the pathways or mechanisms that might give rise to, or explain, the results.
Journals vary in their approach to strengths and limitations sections: some are embedded paragraphs within the discussion section, while some mandate separate section headings. Keep in mind that every study has strengths and limitations. Candidly reporting yours helps readers to correctly interpret your research findings.
The next element of the discussion is a summary of the potential impacts and applications of the research. Should these results be used to optimally design an intervention? Does the work have implications for clinical protocols or public policy? These considerations will help the reader to further grasp the possible impacts of the presented work.
Finally, the discussion should conclude with specific suggestions for future work. Here, you have an opportunity to illuminate specific gaps in the literature that compel further study. Avoid the phrase “future research is necessary” because the recommendation is too general to be helpful to readers. Instead, provide substantive and specific recommendations for future studies. Table 4 provides common discussion section pitfalls and recommendations for addressing them.
Follow the Journal’s Author Guidelines
After you select a target journal, identify the journal’s author guidelines to guide the formatting of your manuscript and references. Author guidelines will often (but not always) include instructions for titles, cover letters, and other components of a manuscript submission. Read the guidelines carefully. If you do not follow the guidelines, your article will be sent back to you.
Finally, do not submit your paper to more than one journal at a time. Even if this is not explicitly stated in the author guidelines of your target journal, it is considered inappropriate and unprofessional.
Your title should invite readers to continue reading beyond the first page [ 4 , 5 ]. It should be informative and interesting. Consider describing the independent and dependent variables, the population and setting, the study design, the timing, and even the main result in your title. Because the focus of the paper can change as you write and revise, we recommend you wait until you have finished writing your paper before composing the title.
Be sure that the title is useful for potential readers searching for your topic. The keywords you select should complement those in your title to maximize the likelihood that a researcher will find your paper through a database search. Avoid using abbreviations in your title unless they are very well known, such as SNP, because it is more likely that someone will use a complete word rather than an abbreviation as a search term to help readers find your paper.
After you have written a complete draft, use the checklist (Fig. 3 ) below to guide your revisions and editing. Additional resources are available on writing the abstract and citing references [ 5 ]. When you feel that your work is ready, ask a trusted colleague or two to read the work and provide informal feedback. The box below provides a checklist that summarizes the key points offered in this article.

Checklist for manuscript quality
Data Availability
Michalek AM (2014) Down the rabbit hole…advice to reviewers. J Cancer Educ 29:4–5
Article Google Scholar
International Committee of Medical Journal Editors. Defining the role of authors and contributors: who is an author? http://www.icmje.org/recommendations/browse/roles-and-responsibilities/defining-the-role-of-authosrs-and-contributors.html . Accessed 15 January, 2020
Vetto JT (2014) Short and sweet: a short course on concise medical writing. J Cancer Educ 29(1):194–195
Brett M, Kording K (2017) Ten simple rules for structuring papers. PLoS ComputBiol. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pcbi.1005619
Lang TA (2017) Writing a better research article. J Public Health Emerg. https://doi.org/10.21037/jphe.2017.11.06
Download references
Acknowledgments
Ella August is grateful to the Sustainable Sciences Institute for mentoring her in training researchers on writing and publishing their research.
Code Availability
Not applicable.
Author information
Authors and affiliations.
Department of Maternal and Child Health, University of North Carolina Gillings School of Global Public Health, 135 Dauer Dr, 27599, Chapel Hill, NC, USA
Clara Busse & Ella August
Department of Epidemiology, University of Michigan School of Public Health, 1415 Washington Heights, Ann Arbor, MI, 48109-2029, USA
Ella August
You can also search for this author in PubMed Google Scholar
Corresponding author
Correspondence to Ella August .
Ethics declarations
Conflicts of interests.
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Additional information
Publisher’s note.
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Electronic supplementary material
(PDF 362 kb)
Rights and permissions
Open Access This article is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License, which permits use, sharing, adaptation, distribution and reproduction in any medium or format, as long as you give appropriate credit to the original author(s) and the source, provide a link to the Creative Commons licence, and indicate if changes were made. The images or other third party material in this article are included in the article's Creative Commons licence, unless indicated otherwise in a credit line to the material. If material is not included in the article's Creative Commons licence and your intended use is not permitted by statutory regulation or exceeds the permitted use, you will need to obtain permission directly from the copyright holder. To view a copy of this licence, visit http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/ .
Reprints and permissions
About this article
Busse, C., August, E. How to Write and Publish a Research Paper for a Peer-Reviewed Journal. J Canc Educ 36 , 909–913 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1007/s13187-020-01751-z
Download citation
Published : 30 April 2020
Issue Date : October 2021
DOI : https://doi.org/10.1007/s13187-020-01751-z
Share this article
Anyone you share the following link with will be able to read this content:
Sorry, a shareable link is not currently available for this article.
Provided by the Springer Nature SharedIt content-sharing initiative
- Manuscripts
- Scientific writing
- Find a journal
- Publish with us
- Track your research
Writing a Research Paper for an Academic Journal: A Five-step Recipe for Perfection
The answer to writing the perfect research paper is as simple as following a step-by-step recipe. Here we bring to you a recipe for effortlessly planning, writing, and publishing your paper as a peer reviewed journal article.
Updated on March 15, 2022

As a young researcher, getting your paper published as a journal article is a huge milestone; but producing it may seem like climbing a mountain compared to, perhaps, the theses, essays, or conference papers you have produced in the past.
You may feel overwhelmed with the thought of carrying innumerable equipment and may feel incapable of completing the task. But, in reality, the answer to writing the perfect research paper is as simple as following a recipe with step-by-step instructions.
In this blog, I aim to bring to you the recipe for effortlessly planning, writing, and publishing your paper as a peer reviewed journal article. I will give you the essential information, key points, and resources to keep in mind before you begin the writing process for your research papers.
Secret ingredient 1: Make notes before you begin the writing process
Because I want you to benefit from this article on a personal level, I am going to give away my secret ingredient for producing a good research paper right at the beginning. The one thing that helps me write literally anything is — cue the drum rolls — making notes.
Yes, making notes is the best way to remember and store all that information, which is definitely going to help you throughout the process of writing your paper. So, please pick up a pen and start making notes for writing your research paper.
Step 1. Choose the right research topic
Although it is important to be passionate and curious about your research article topic, it is not enough. Sometimes the sheer excitement of having an idea may take away your ability to focus on and question the novelty, credibility, and potential impact of your research topic.
On the contrary, the first thing that you should do when you write a journal paper is question the novelty, credibility, and potential impact of your research question.
It is also important to remember that your research, along with the aforementioned points, must be original and relevant: It must benefit and interest the scientific community.
All you have to do is perform a thorough literature search in your research field and have a look at what is currently going on in the field of your topic of interest. This step in academic writing is not as daunting as it may seem and, in fact, is quite beneficial for the following reasons:
- You can determine what is already known about the research topic and the gaps that exist.
- You can determine the credibility and novelty of your research question by comparing it with previously published papers.
- If your research question has already been studied or answered before your first draft, you first save a substantial amount of time by avoiding rejections from journals at a much later stage; and second, you can study and aim to bridge the gaps of previous studies, perhaps, by using a different methodology or a bigger sample size.
So, carefully read as much as you can about what has already been published in your field of research; and when you are doing so, make sure that you make lots of relevant notes as you go along in the process. Remember, your study does not necessarily have to be groundbreaking, but it should definitely extend previous knowledge or refute existing statements on the topic.
Secret ingredient 2: Use a thematic approach while drafting your manuscript
For instance, if you are writing about the association between the level of breast cancer awareness and socioeconomic status, open a new Word or Notes file and create subheadings such as “breast cancer awareness in low- and middle-income countries,” “reasons for lack of awareness,” or “ways to increase awareness.”
Under these subheadings, make notes of the information that you think may be suitable to be included in your paper as you carry out your literature review. Ensure that you make a draft reference list so that you don't miss out on the references.
Step 2: Know your audience
Finding your research topic is not synonymous with communicating it, it is merely a step, albeit an important one; however, there are other crucial steps that follow. One of which is identifying your target audience.
Now that you know what your topic of interest is, you need to ask yourself “Who am I trying to benefit with my research?” A general mistake is assuming that your reader knows everything about your research topic. Drafting a peer reviewed journal article often means that your work may reach a wide and varied audience.
Therefore, it is a good idea to ponder over who you want to reach and why, rather than simply delivering chunks of information, facts, and statistics. Along with considering the above factors, evaluate your reader's level of education, expertise, and scientific field as this may help you design and write your manuscript, tailoring it specifically for your target audience.
Here are a few points that you must consider after you have identified your target audience:
- Shortlist a few target journals: The aims and scope of the journal usually mention their audience. This may help you know your readers and visualize them as you write your manuscript. This will further help you include just the right amount of background and details.
- View your manuscript from the reader's perspective: Try to think about what they might already know or what they would like more details on.
- Include the appropriate amount of jargon: Ensure that your article text is familiar to your target audience and use the correct terminology to make your content more relatable for readers - and journal editors as your paper goes through the peer review process.
- Keep your readers engaged: Write with an aim to fill a knowledge gap or add purpose and value to your reader's intellect. Your manuscript does not necessarily have to be complex, write with a simple yet profound tone, layer (or sub-divide) simple points and build complexity as you go along, rather than stating dry facts.
- Be specific: It is easy to get carried away and forget the essence of your study. Make sure that you stick to your topic and be as specific as you can to your research topic and audience.
Secret ingredient 3: Clearly define your key terms and key concepts
Do not assume that your audience will know your research topic as well as you do, provide compelling details where it is due. This can be tricky. Using the example from “Secret ingredient 2,” you may not need to define breast cancer while writing about breast cancer awareness. However, while talking about the benefits of awareness, such as early presentation of the disease, it is important to explain these benefits, for instance, in terms of superior survival rates.
Step 3: Structure your research paper with care
After determining the topic of your research and your target audience, your overflowing ideas and information need to be structured in a format generally accepted by journals.
Most academic journals conventionally accept original research articles in the following format: Abstract, followed by the Introduction, Methods, Results, and Discussion sections, also known as the IMRaD, which is a brilliant way of structuring a research paper outline in a simplified and layered format. In brief, these sections comprise the following information:
In closed-access journals, readers have access to the abstract/summary for them to decide if they wish to purchase the research paper. It's an extremely important representative of the entire manuscript.
All information provided in the abstract must be present in the manuscript, it should include a stand-alone summary of the research, the main findings, the abbreviations should be defined separately in this section, and this section should be clear, decluttered, and concise.
Introduction
This section should begin with a background of the study topic, i.e., what is already known, moving on to the knowledge gaps that exist, and finally, end with how the present study aims to fill these gaps, or any hypotheses that the authors may have proposed.
This section describes, with compelling details, the procedures that were followed to answer the research question.
The ultimate factor to consider while producing the methods section is reproducibility; this section should be detailed enough for other researchers to reproduce your study and validate your results. It should include ethical information (ethical board approval, informed consent, etc.) and must be written in the past tense.
This section typically presents the findings of the study, with no explanations or interpretations. Here, the findings are simply stated alongside figures or tables mentioned in the text in the correct sequential order. Because you are describing what you found, this section is also written in the past tense.
Discussion and conclusion
This section begins with a summary of your findings and is meant for you to interpret your results, compare them with previously published papers, and elaborate on whether your findings are comparable or contradictory to previous literature.
This section also contains the strengths and limitations of your study, and the latter can be used to suggest future research. End this section with a conclusion paragraph, briefly summarizing and highlighting the main findings and novelty of your study.
Step 4: Cite credible research sources
Now that you know who and what you are writing for, it's time to begin the writing process for your research paper. Another crucial factor that determines the quality of your manuscript is the detailed information within. The introduction and discussion sections, which make a massive portion of the manuscript, majorly rely on external sources of information that have already been published.
Therefore, it is absolutely indispensable to extract and cite these statements from appropriate, credible, recent, and relevant literature to support your claims. Here are a few pointers to consider while choosing the right sources:
Cite academic journals
These are the best sources to refer to while writing your research paper, because most articles submitted to top journals are rejected, resulting in high-quality articles being filtered-out. In particular, peer reviewed articles are of the highest quality because they undergo a rigorous process of editorial review, along with revisions until they are judged to be satisfactory.
But not just any book, ideally, the credibility of a book can be judged by whether it is published by an academic publisher, is written by multiple authors who are experts in the field of interest, and is carefully reviewed by multiple editors. It can be beneficial to review the background of the author(s) and check their previous publications.
Cite an official online source
Although it may be difficult to judge the trustworthiness of web content, a few factors may help determine its accuracy. These include demographic data obtained from government websites (.gov), educational resources (.edu), websites that cite other pertinent and trustworthy sources, content meant for education and not product promotion, unbiased sources, or sources with backlinks that are up to date. It is best to avoid referring to online sources such as blogs and Wikipedia.
Do not cite the following sources
While citing sources, you should steer clear from encyclopedias, citing review articles instead of directly citing the original work, referring to sources that you have not read, citing research papers solely from one country (be extensively diverse), anything that is not backed up by evidence, and material with considerable grammatical errors.
Although these sources are generally most appropriate and valid, it is your job to critically read and carefully evaluate all sources prior to citing them.
Step 5: Pick the correct journal
Selecting the correct journal is one of the most crucial steps toward getting published, as it not only determines the weightage of your research but also of your career as a researcher. The journals in which you choose to publish your research are part of your portfolio; it directly or indirectly determines many factors, such as funding, professional advancement, and future collaborations.
The best thing you can do for your work is to pick a peer-reviewed journal. Not only will your paper be polished to the highest quality for editors, but you will also be able to address certain gaps that you may have missed out.
Besides, it always helps to have another perspective, and what better than to have it from an experienced peer?
A common mistake that researchers tend to make is leave the task of choosing the target journal after they have written their paper.
Now, I understand that due to certain factors, it can be challenging to decide what journal you want to publish in before you start drafting your paper, therefore, the best time to make this decision is while you are working on writing your manuscript. Having a target journal in mind while writing your paper has a great deal of benefits.
- As the most basic benefit, you can know beforehand if your study meets the aims and scope of your desired journal. It will ensure you're not wasting valuable time for editors or yourself.
- While drafting your manuscript, you could keep in mind the requirements of your target journal, such as the word limit for the main article text and abstract, the maximum number of figures or tables that are allowed, or perhaps, the maximum number of references that you may include.
- Also, if you choose to submit to an open-access journal, you have ample amount of time to figure out the funding.
- Another major benefit is that, as mentioned in the previous section, the aims and scope of the journal will give you a fair idea on your target audience and will help you draft your manuscript appropriately.
It is definitely easier to know that your target journal requires the text to be within 3,500 words than spending weeks writing a manuscript that is around, say, 5,000 words, and then spending a substantial amount of time decluttering. Now, while not all journals have very specific requirements, it always helps to short-list a few journals, if not concretely choose one to publish your paper in.
AJE also offers journal recommendation services if you need professional help with finding a target journal.
Secret ingredient 4: Follow the journal guidelines
Perfectly written manuscripts may get rejected by the journal on account of not adhering to their formatting requirements. You can find the author guidelines/instructions on the home page of every journal. Ensure that as you write your manuscript, you follow the journal guidelines such as the word limit, British or American English, formatting references, line spacing, line/page numbering, and so on.
Our ultimate aim is to instill confidence in young researchers like you and help you become independent as you write and communicate your research. With the help of these easy steps and secret ingredients, you are now ready to prepare your flavorful manuscript and serve your research to editors and ultimately the journal readers with a side of impact and a dash of success.

Lubaina Koti, BS
Scientific Writer
See our "Privacy Policy"
Thank you for visiting nature.com. You are using a browser version with limited support for CSS. To obtain the best experience, we recommend you use a more up to date browser (or turn off compatibility mode in Internet Explorer). In the meantime, to ensure continued support, we are displaying the site without styles and JavaScript.
- View all journals
- Explore content
- About the journal
- Publish with us
- Sign up for alerts
- CAREER BRIEF
- 08 May 2019
Toolkit: How to write a great paper
A clear format will ensure that your research paper is understood by your readers. Follow:
1. Context — your introduction
2. Content — your results
3. Conclusion — your discussion
Plan your paper carefully and decide where each point will sit within the framework before you begin writing.

Collection: Careers toolkit
Straightforward writing
Scientific writing should always aim to be A, B and C: Accurate, Brief, and Clear. Never choose a long word when a short one will do. Use simple language to communicate your results. Always aim to distill your message down into the simplest sentence possible.
Choose a title
A carefully conceived title will communicate the single core message of your research paper. It should be D, E, F: Declarative, Engaging and Focused.
Conclusions
Add a sentence or two at the end of your concluding statement that sets out your plans for further research. What is next for you or others working in your field?
Find out more
See additional information .
doi: https://doi.org/10.1038/d41586-019-01362-9
Related Articles
How to get published in high impact journals

So you’re writing a paper
Writing for a Nature journal

Africa’s postdoc workforce is on the rise — but at what cost?
Career Feature 02 APR 24

Impact factors are outdated, but new research assessments still fail scientists
World View 02 APR 24

How scientists are making the most of Reddit
Career Feature 01 APR 24
How can we make PhD training fit for the modern world? Broaden its philosophical foundations
Correspondence 02 APR 24
Allow researchers with caring responsibilities ‘promotion pauses’ to make research more equitable
Faculty Positions, Aging and Neurodegeneration, Westlake Laboratory of Life Sciences and Biomedicine
Applicants with expertise in aging and neurodegeneration and related areas are particularly encouraged to apply.
Hangzhou, Zhejiang, China
Westlake Laboratory of Life Sciences and Biomedicine (WLLSB)
Faculty Positions in Chemical Biology, Westlake University
We are seeking outstanding scientists to lead vigorous independent research programs focusing on all aspects of chemical biology including...
School of Life Sciences, Westlake University
Faculty Positions in Neurobiology, Westlake University
We seek exceptional candidates to lead vigorous independent research programs working in any area of neurobiology.
Head of the histopathology and imaging laboratory
GENETHON recruits: Head of the histopathology and imaging laboratory (H/F)
Evry-Sud, Evry (FR)
Seeking Global Talents, the International School of Medicine, Zhejiang University
Welcome to apply for all levels of professors based at the International School of Medicine, Zhejiang University.
Yiwu, Zhejiang, China
International School of Medicine, Zhejiang University
Sign up for the Nature Briefing newsletter — what matters in science, free to your inbox daily.
Quick links
- Explore articles by subject
- Guide to authors
- Editorial policies

Writing in a Journal: A Short Course on Journal Writing for 2023
Do any of the following statements or questions sound like you?
- “I don’t have time to write a journal!”
- “I don’t know what to write about!”
- “How do I get started?
- “I’m a lousy writer!”
If so, then this short course on journal writing is for you! Here are five easy steps to get started with writing, eight suggestions for new journal writers, and 14 writing techniques for your journal.
How to Get Started with Journal Writing
It’s Easy to W.R.I.T.E.
Just try these five easy steps. You’ll be writing in no time!
W – What do you want to write about? What’s going on? How do you feel? What are you thinking about? What do you want? Name it.
R – Review or reflect on it. Close your eyes. Take three deep breaths. Focus. You can start with “I feel…” or “I want…” or “I think…” or “Today….” or “Right now…” or “In this moment…”
I – Investigate your thoughts and feelings. Start writing and keep writing. Follow the pen/keyboard. If you get stuck or run out of juice, close your eyes and re-center yourself. Re-read what you’ve already written and continue writing.
T – Time yourself. Write for 5-15 minutes. Write the start time and the projected end time at the top of the page. If you have an alarm/timer on your PDA or cell phone, set it.
E – Exit smart by re-reading what you’ve written and reflecting on it in a sentence or two: “As I read this, I notice—” or “I’m aware of—” or “I feel—”. Note any action steps to take.
In summary….it’s easy to W.R.I.T.E. ! W hat topic? R eview/reflect I nvestigate T ime yourself E xit smart
Looking for free journaling workshops? Check out our on-demand courses including “ J is for Journal: A Short Course on Writing for Healing, Growth, and Change ,” with seven lessons containing a total of 68 writing prompts!
Eight Suggestions for New Journal Writers
1. protect your privacy..
Store your journal in its own special place so that the temptation for others to read is diminished. Ask for agreement with your housemates that your journal is private. Reserve the first page of any new journal for your name and phone number or e-mail address, along with a notice: This is my personal journal. Please do not read it without my permission. If none of that would stop whoever might read your journal, get a shredder. Find a creative way to protect your privacy, such as a new gmail or yahoo account, freshly passworded, from which to write yourself at that address. Or keep your journal on a flash drive. Make your privacy an intentional act.
2. Start with an entrance meditation.
Nearly every journal technique benefits from a few minutes of focused quieting. Use visualization, soft music, candles, deep breathing, stretches, whatever works for you.
3. Date every entry.
If you only establish one habit in your journal, let it be this one! Dating every entry allows you to chronologically reconstruct your journal by date. It also lets you hear the silence between your entries.
4. Keep (and re-read) what you write.
Often the writes that feel like throw-aways contain the seeds for future insight. Keep it, re-read it later, and surprise yourself with how much you knew that you didn’t know you knew!
5. Write quickly.
You can outsmart dreaded “journal block” by writing so fast that the Internal Critic and the Internal Censor can’t keep up. Keep your pen moving!
6. Start writing; keep writing.
Start with the present moment (“What’s going on?”) Or start with a feeling (“I’m so mad I could bust!”) Or start with a story (“Today the weirdest thing happened….”) Once you’ve started, don’t go back to edit or rewrite. And don’t think too much. Let it flow.
7. Tell yourself the truth.
Your own truth is not your enemy. Don’t try to talk yourself out of knowing what you know or feeling what you feel. Give yourself permission to tell the truth. Also give yourself permission to pace yourself. If the truth seems too bright or harsh, then slow it down.
8. Write naturally.
If there is one inviolate rule of journal writing, it is that there simply are no rules! Do what works. Don’t worry about what you’re not doing. Give yourself permission. Let yourself enjoy the process!
14 Writing Techniques for Your Journal
1. sentence stem..
A sentence-completion process. Fill in the blank with a word or phrase. May be very universal (Right now I feel———-) or highly customized to an individual’s immediate question, problem or interest.
Start with the beginning of a sentence:
- Today I will—
- Right now I feel—
- The most important thing to do—
- I want—
- I need—-
- What I wish I could say to you—
- If only I could—
- I wonder–
—and finish it with a word, a thought, the rest of the sentence.
Boom. You’re done.
2. Five-Minute Sprint .
A timed writing process designed to bring focus and intensity in short bursts. Excellent for those who are resistant or aversive to journal writing, or who are uncertain about how to start, or who state they do not have time to write journals.
It’s a two-step process that couldn’t be more simple:
- Set the timer on your phone or kitchen stove. Stop writing when signaled!
- Keep your pen or fingers moving the entire time. It’s only five minutes. It goes fast.
Ready? Set your timers–and WRITE! Start with this prompt: What’s going on?
3. Inventory.
An assessment of life balance in major areas of living (health, family, home, work, spiritual/religious, emotional well-being, etc.) Gives a quick picture of which life areas might need attention.
4. Structured Write.
A series of Sentence Stems grouped and sequenced to reveal consistently deepening layers of information and awareness.

5. Clustering.
Visual free-association from a central word or phrase. Lines and circles connect key thoughts and associations to the central core. Work quickly to maximize results. A brief writing to synthesize findings may follow.

6. Lists of 100.
A list of 100 items, many of which will probably be repetitions, on a predetermined theme or topic. Repetition is an important part of the process. Topics can be about any current issue (for example: 100 Things I’m Sad About; 100 Things I Need or Want to Do; 100 Places I Would Like to See). At the end of the list, group the responses into themes and synthesize the information.
In this video, Kathleen Adams, Founder of the Center for Journal Therapy, shares what she likes about using short lists as a journaling technique.
7. Alphapoem.
Write the alphabet, A-Z, or any collection of letters, vertically down the side of a page. Then write a poem in which each successive line begins with the next letter. Excellent for groups as it promotes a high level of participation and sharing. Adolescents and reluctant writers respond well.
Check out this example of an Alphapoem:
An Alphapoem on Alphapoems
by Kay Adams and Scribe (journal group members)
A nticipate a B lossoming of C reative D elight! E asy, really, once you F ind the rhythm and the pace. G ather up the thoughts you H old secret in your heart. I magine them J ust drifting out, a K aleidoscope of L etters M aking words. N o rules to follow–except the O bvious one. P erhaps you’ll find a poet inside? Q uite likely! R ead your Alphapoems; you’ll find them S tartlingly T rue–an U nusual way to give V oice to the W himpers, wonderings, whys, wins. X hilerating feeling to find Y ou’ve reached the Z enith of the poem!
8. Captured Moments.
Vignettes capturing the sensations of a particularly meaningful or emotional experience. Written from the senses with strong descriptors. Captured Moments of beauty, joy, blessing, calm can add balance, hope and perspective to a challenging time.
9. Unsent Letters .
A metaphoric communication to another that is written with the specific intention that it will not be shared.
10. Character Sketch .
A written portrait of another person or of an aspect of the self. Can also be written about emotions by personifying an emotion and giving it a characterization – an appearance, a style of dress, a personality and temperament.
11. Dialogue.
A metaphoric conversation written in two voices. Anyone or anything is an appropriate dialogue partner. There is no constriction by time, space, physical reality or literal voice.
On the page, it looks like a script:
Me: So how do I do this?
Dialogue Partner: Just ask me a question, and I’ll respond.
Me: Seems a little silly.
D.P.: Just make it up! Write the next thing in your head.
You can write a dialogue with anyone or anything: Your Wise Self, your spouse/partner/child, your job, your body, your feelings, your dreams and desires – anything goes!
12. Perspectives .
An alteration in point of view that provides a different perspective on an event or situation. Through magical realism, we can jump time, compare alternative realities and walk a mile in another’s moccasins. The writer experiences a new dimension of time, place or voice.
- A different time: Using imagery, time-travel to a date in the near or distant past or future. Write that altered date at the top of the page. Imagine who you are, how you feel, what is different, how a problem got solved or an issue resolved. Write in the present tense, as if it were that time.
- A different place: When faced with a tough choice or decision, jump time and write Perspectives entries in the present tense as if you’d made each choice. One man, conflicted about applying to medical school or a psychology program, saw himself miserable as a psychiatrist and fully engaged as a psychotherapist working with veterans and their families. See what nudges forward from your subconscious mind!
- A different voice: Write in someone else’s “I” voice, in the present tense, as if that person were writing in a journal about you or a disagreement (argument, conflict, painful difference) the two of you are experiencing.
- Another different voice: Alter your own voice by writing in past tense, in the third-person voice (s/he, her/his), about your own experience. This pulls back the camera lens, puts you in the role of omniscient narrator/compassionate witness and allows useful distance and objectivity. This is particularly helpful if you are working with difficult stories that can create intense emotional states.
13. Springboard.
A free-write with a prompt. Starting a free-write with the smallest structure of a question, thought or topic can focus and frame the writing session.
Here are some sample springboards:
- What’s the next thing to do?
- A year from today, I will ….
- Why don’t I … ?
- I’m sorry I didn’t….
- What am I avoiding?
- If I knew I would succeed, I would ….
- I want to overcome….
- Where am I going?
- What do I want?
- If I weren’t scared….
- What’s the best thing? What’s the worst thing?
In this video, Kathleen Adams, Founder of the Center for Journal Therapy, talks about using props to get started with writing.
14. Free Writing.
Unboundaried, unstructured, unpaced narrative writing. Useful for creative flow or spontaneous writing sessions. Can be structured by adding a time limit or page limit.
(c) Kathleen Adams. All rights reserved. For reprint permission please email us .
Center for Journal Therapy
3440 youngfield st., #411 wheat ridge, co. 80033 phone: (303) 209-9599 contact us >>.
This document originally came from the Journal of Mammalogy courtesy of Dr. Ronald Barry, a former editor of the journal.
Journal Writing
View in pdf format, common goals of a journal.
- To encourage regular writing
- To make connections between class material, lectures, and personal observations
- To raise questions and issues that can fuel classroom discussions
- To generate ideas for future paper topics
- To provide a forum for inquiry, analysis, and evaluation of ideas
- Write regularly
- Try to make concrete connections between journal entries
- Link personal reactions to the class material
- Approach the exercise with the intention of being challenged
- Present your ideas in a coherent and thought-provoking manner
- Ignore basic rules of grammar and punctuation
- Write to fill pages; the process is more important than the product
- Wait until the last minute to make your entries
- Confuse your journal with a personal diary. Although this is your journal, the main focus should be on class assignments and their connections. Try not to focus too much on your personal feelings, such as whether or not you liked the book or the film. Instead concentrate on why your professor assigned the material.
- Simply summarize — analyze. Avoid describing what you have read. Ask probing questions: are the points well-argued? Does the writer come to a logical conclusion? What other issues should be considered?
Take your journal seriously. Keeping a journal helps develop writing, reading, analytical and critical skills that are necessary in all disciplines.
Faculty Comments on the Value of Journal Writing
“I’ll be looking for evidence of thought and clarity of expression. The journal needn’t be polished to gem-like lustre, but it should be coherent and, I hope, thought-provoking.” — Richard Decker, Professor of Computer Science “Journals are ultimately very useful for developing good work habits by providing a venue and location for thinking through ideas in an ongoing and consistent way.” — Ella Gant, Professor of Art

by Molly Soule ’97 & Andresse St. Rose ’97
Office / Department Name
Nesbitt-Johnston Writing Center
Contact Name
Jennifer Ambrose
Writing Center Director

Help us provide an accessible education, offer innovative resources and programs, and foster intellectual exploration.
Site Search
Writing an Abstract for Your Research Paper
Definition and Purpose of Abstracts
An abstract is a short summary of your (published or unpublished) research paper, usually about a paragraph (c. 6-7 sentences, 150-250 words) long. A well-written abstract serves multiple purposes:
- an abstract lets readers get the gist or essence of your paper or article quickly, in order to decide whether to read the full paper;
- an abstract prepares readers to follow the detailed information, analyses, and arguments in your full paper;
- and, later, an abstract helps readers remember key points from your paper.
It’s also worth remembering that search engines and bibliographic databases use abstracts, as well as the title, to identify key terms for indexing your published paper. So what you include in your abstract and in your title are crucial for helping other researchers find your paper or article.
If you are writing an abstract for a course paper, your professor may give you specific guidelines for what to include and how to organize your abstract. Similarly, academic journals often have specific requirements for abstracts. So in addition to following the advice on this page, you should be sure to look for and follow any guidelines from the course or journal you’re writing for.
The Contents of an Abstract
Abstracts contain most of the following kinds of information in brief form. The body of your paper will, of course, develop and explain these ideas much more fully. As you will see in the samples below, the proportion of your abstract that you devote to each kind of information—and the sequence of that information—will vary, depending on the nature and genre of the paper that you are summarizing in your abstract. And in some cases, some of this information is implied, rather than stated explicitly. The Publication Manual of the American Psychological Association , which is widely used in the social sciences, gives specific guidelines for what to include in the abstract for different kinds of papers—for empirical studies, literature reviews or meta-analyses, theoretical papers, methodological papers, and case studies.
Here are the typical kinds of information found in most abstracts:
- the context or background information for your research; the general topic under study; the specific topic of your research
- the central questions or statement of the problem your research addresses
- what’s already known about this question, what previous research has done or shown
- the main reason(s) , the exigency, the rationale , the goals for your research—Why is it important to address these questions? Are you, for example, examining a new topic? Why is that topic worth examining? Are you filling a gap in previous research? Applying new methods to take a fresh look at existing ideas or data? Resolving a dispute within the literature in your field? . . .
- your research and/or analytical methods
- your main findings , results , or arguments
- the significance or implications of your findings or arguments.
Your abstract should be intelligible on its own, without a reader’s having to read your entire paper. And in an abstract, you usually do not cite references—most of your abstract will describe what you have studied in your research and what you have found and what you argue in your paper. In the body of your paper, you will cite the specific literature that informs your research.
When to Write Your Abstract
Although you might be tempted to write your abstract first because it will appear as the very first part of your paper, it’s a good idea to wait to write your abstract until after you’ve drafted your full paper, so that you know what you’re summarizing.
What follows are some sample abstracts in published papers or articles, all written by faculty at UW-Madison who come from a variety of disciplines. We have annotated these samples to help you see the work that these authors are doing within their abstracts.
Choosing Verb Tenses within Your Abstract
The social science sample (Sample 1) below uses the present tense to describe general facts and interpretations that have been and are currently true, including the prevailing explanation for the social phenomenon under study. That abstract also uses the present tense to describe the methods, the findings, the arguments, and the implications of the findings from their new research study. The authors use the past tense to describe previous research.
The humanities sample (Sample 2) below uses the past tense to describe completed events in the past (the texts created in the pulp fiction industry in the 1970s and 80s) and uses the present tense to describe what is happening in those texts, to explain the significance or meaning of those texts, and to describe the arguments presented in the article.
The science samples (Samples 3 and 4) below use the past tense to describe what previous research studies have done and the research the authors have conducted, the methods they have followed, and what they have found. In their rationale or justification for their research (what remains to be done), they use the present tense. They also use the present tense to introduce their study (in Sample 3, “Here we report . . .”) and to explain the significance of their study (In Sample 3, This reprogramming . . . “provides a scalable cell source for. . .”).
Sample Abstract 1
From the social sciences.
Reporting new findings about the reasons for increasing economic homogamy among spouses
Gonalons-Pons, Pilar, and Christine R. Schwartz. “Trends in Economic Homogamy: Changes in Assortative Mating or the Division of Labor in Marriage?” Demography , vol. 54, no. 3, 2017, pp. 985-1005.
![how to write a journal paper for college “The growing economic resemblance of spouses has contributed to rising inequality by increasing the number of couples in which there are two high- or two low-earning partners. [Annotation for the previous sentence: The first sentence introduces the topic under study (the “economic resemblance of spouses”). This sentence also implies the question underlying this research study: what are the various causes—and the interrelationships among them—for this trend?] The dominant explanation for this trend is increased assortative mating. Previous research has primarily relied on cross-sectional data and thus has been unable to disentangle changes in assortative mating from changes in the division of spouses’ paid labor—a potentially key mechanism given the dramatic rise in wives’ labor supply. [Annotation for the previous two sentences: These next two sentences explain what previous research has demonstrated. By pointing out the limitations in the methods that were used in previous studies, they also provide a rationale for new research.] We use data from the Panel Study of Income Dynamics (PSID) to decompose the increase in the correlation between spouses’ earnings and its contribution to inequality between 1970 and 2013 into parts due to (a) changes in assortative mating, and (b) changes in the division of paid labor. [Annotation for the previous sentence: The data, research and analytical methods used in this new study.] Contrary to what has often been assumed, the rise of economic homogamy and its contribution to inequality is largely attributable to changes in the division of paid labor rather than changes in sorting on earnings or earnings potential. Our findings indicate that the rise of economic homogamy cannot be explained by hypotheses centered on meeting and matching opportunities, and they show where in this process inequality is generated and where it is not.” (p. 985) [Annotation for the previous two sentences: The major findings from and implications and significance of this study.]](https://writing.wisc.edu/wp-content/uploads/sites/535/2019/08/Abstract-1.png)
Sample Abstract 2
From the humanities.
Analyzing underground pulp fiction publications in Tanzania, this article makes an argument about the cultural significance of those publications
Emily Callaci. “Street Textuality: Socialism, Masculinity, and Urban Belonging in Tanzania’s Pulp Fiction Publishing Industry, 1975-1985.” Comparative Studies in Society and History , vol. 59, no. 1, 2017, pp. 183-210.
![how to write a journal paper for college “From the mid-1970s through the mid-1980s, a network of young urban migrant men created an underground pulp fiction publishing industry in the city of Dar es Salaam. [Annotation for the previous sentence: The first sentence introduces the context for this research and announces the topic under study.] As texts that were produced in the underground economy of a city whose trajectory was increasingly charted outside of formalized planning and investment, these novellas reveal more than their narrative content alone. These texts were active components in the urban social worlds of the young men who produced them. They reveal a mode of urbanism otherwise obscured by narratives of decolonization, in which urban belonging was constituted less by national citizenship than by the construction of social networks, economic connections, and the crafting of reputations. This article argues that pulp fiction novellas of socialist era Dar es Salaam are artifacts of emergent forms of male sociability and mobility. In printing fictional stories about urban life on pilfered paper and ink, and distributing their texts through informal channels, these writers not only described urban communities, reputations, and networks, but also actually created them.” (p. 210) [Annotation for the previous sentences: The remaining sentences in this abstract interweave other essential information for an abstract for this article. The implied research questions: What do these texts mean? What is their historical and cultural significance, produced at this time, in this location, by these authors? The argument and the significance of this analysis in microcosm: these texts “reveal a mode or urbanism otherwise obscured . . .”; and “This article argues that pulp fiction novellas. . . .” This section also implies what previous historical research has obscured. And through the details in its argumentative claims, this section of the abstract implies the kinds of methods the author has used to interpret the novellas and the concepts under study (e.g., male sociability and mobility, urban communities, reputations, network. . . ).]](https://writing.wisc.edu/wp-content/uploads/sites/535/2019/08/Abstract-2.png)
Sample Abstract/Summary 3
From the sciences.
Reporting a new method for reprogramming adult mouse fibroblasts into induced cardiac progenitor cells
Lalit, Pratik A., Max R. Salick, Daryl O. Nelson, Jayne M. Squirrell, Christina M. Shafer, Neel G. Patel, Imaan Saeed, Eric G. Schmuck, Yogananda S. Markandeya, Rachel Wong, Martin R. Lea, Kevin W. Eliceiri, Timothy A. Hacker, Wendy C. Crone, Michael Kyba, Daniel J. Garry, Ron Stewart, James A. Thomson, Karen M. Downs, Gary E. Lyons, and Timothy J. Kamp. “Lineage Reprogramming of Fibroblasts into Proliferative Induced Cardiac Progenitor Cells by Defined Factors.” Cell Stem Cell , vol. 18, 2016, pp. 354-367.
![how to write a journal paper for college “Several studies have reported reprogramming of fibroblasts into induced cardiomyocytes; however, reprogramming into proliferative induced cardiac progenitor cells (iCPCs) remains to be accomplished. [Annotation for the previous sentence: The first sentence announces the topic under study, summarizes what’s already known or been accomplished in previous research, and signals the rationale and goals are for the new research and the problem that the new research solves: How can researchers reprogram fibroblasts into iCPCs?] Here we report that a combination of 11 or 5 cardiac factors along with canonical Wnt and JAK/STAT signaling reprogrammed adult mouse cardiac, lung, and tail tip fibroblasts into iCPCs. The iCPCs were cardiac mesoderm-restricted progenitors that could be expanded extensively while maintaining multipo-tency to differentiate into cardiomyocytes, smooth muscle cells, and endothelial cells in vitro. Moreover, iCPCs injected into the cardiac crescent of mouse embryos differentiated into cardiomyocytes. iCPCs transplanted into the post-myocardial infarction mouse heart improved survival and differentiated into cardiomyocytes, smooth muscle cells, and endothelial cells. [Annotation for the previous four sentences: The methods the researchers developed to achieve their goal and a description of the results.] Lineage reprogramming of adult somatic cells into iCPCs provides a scalable cell source for drug discovery, disease modeling, and cardiac regenerative therapy.” (p. 354) [Annotation for the previous sentence: The significance or implications—for drug discovery, disease modeling, and therapy—of this reprogramming of adult somatic cells into iCPCs.]](https://writing.wisc.edu/wp-content/uploads/sites/535/2019/08/Abstract-3.png)
Sample Abstract 4, a Structured Abstract
Reporting results about the effectiveness of antibiotic therapy in managing acute bacterial sinusitis, from a rigorously controlled study
Note: This journal requires authors to organize their abstract into four specific sections, with strict word limits. Because the headings for this structured abstract are self-explanatory, we have chosen not to add annotations to this sample abstract.
Wald, Ellen R., David Nash, and Jens Eickhoff. “Effectiveness of Amoxicillin/Clavulanate Potassium in the Treatment of Acute Bacterial Sinusitis in Children.” Pediatrics , vol. 124, no. 1, 2009, pp. 9-15.
“OBJECTIVE: The role of antibiotic therapy in managing acute bacterial sinusitis (ABS) in children is controversial. The purpose of this study was to determine the effectiveness of high-dose amoxicillin/potassium clavulanate in the treatment of children diagnosed with ABS.
METHODS : This was a randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled study. Children 1 to 10 years of age with a clinical presentation compatible with ABS were eligible for participation. Patients were stratified according to age (<6 or ≥6 years) and clinical severity and randomly assigned to receive either amoxicillin (90 mg/kg) with potassium clavulanate (6.4 mg/kg) or placebo. A symptom survey was performed on days 0, 1, 2, 3, 5, 7, 10, 20, and 30. Patients were examined on day 14. Children’s conditions were rated as cured, improved, or failed according to scoring rules.
RESULTS: Two thousand one hundred thirty-five children with respiratory complaints were screened for enrollment; 139 (6.5%) had ABS. Fifty-eight patients were enrolled, and 56 were randomly assigned. The mean age was 6630 months. Fifty (89%) patients presented with persistent symptoms, and 6 (11%) presented with nonpersistent symptoms. In 24 (43%) children, the illness was classified as mild, whereas in the remaining 32 (57%) children it was severe. Of the 28 children who received the antibiotic, 14 (50%) were cured, 4 (14%) were improved, 4(14%) experienced treatment failure, and 6 (21%) withdrew. Of the 28children who received placebo, 4 (14%) were cured, 5 (18%) improved, and 19 (68%) experienced treatment failure. Children receiving the antibiotic were more likely to be cured (50% vs 14%) and less likely to have treatment failure (14% vs 68%) than children receiving the placebo.
CONCLUSIONS : ABS is a common complication of viral upper respiratory infections. Amoxicillin/potassium clavulanate results in significantly more cures and fewer failures than placebo, according to parental report of time to resolution.” (9)
Some Excellent Advice about Writing Abstracts for Basic Science Research Papers, by Professor Adriano Aguzzi from the Institute of Neuropathology at the University of Zurich:

Academic and Professional Writing
This is an accordion element with a series of buttons that open and close related content panels.
Analysis Papers
Reading Poetry
A Short Guide to Close Reading for Literary Analysis
Using Literary Quotations
Play Reviews
Writing a Rhetorical Précis to Analyze Nonfiction Texts
Incorporating Interview Data
Grant Proposals
Planning and Writing a Grant Proposal: The Basics
Additional Resources for Grants and Proposal Writing
Job Materials and Application Essays
Writing Personal Statements for Ph.D. Programs
- Before you begin: useful tips for writing your essay
- Guided brainstorming exercises
- Get more help with your essay
- Frequently Asked Questions
Resume Writing Tips
CV Writing Tips
Cover Letters
Business Letters
Proposals and Dissertations
Resources for Proposal Writers
Resources for Dissertators
Research Papers
Planning and Writing Research Papers
Quoting and Paraphrasing
Writing Annotated Bibliographies
Creating Poster Presentations
Thank-You Notes
Advice for Students Writing Thank-You Notes to Donors
Reading for a Review
Critical Reviews
Writing a Review of Literature
Scientific Reports
Scientific Report Format
Sample Lab Assignment
Writing for the Web
Writing an Effective Blog Post
Writing for Social Media: A Guide for Academics
How to Write a Journal: 6 Tips to Get Started
by Pamela Hodges | 61 comments
Writers are collectors of ideas, and where do we keep them? On scraps of paper, napkins, the notes app of our phones, and sometimes in journals. But as anyone who's started a journal can attest, sometimes it's hard to begin and even harder to keep one going. So how to write a journal? What to write in a journal? Let's look at some simple ways to start capturing ideas.

There are a number of ways to capture ideas, from keeping a gratitude journal, to a reading journal, to a project journal. No matter what type of journal you keep, let me share with you some tips from my journaling experience for how to keep a journal and why a journaling habit pays off for writers.
4 Advantages of Keeping a Journal
Julia Cameron, acclaimed author of The Artist's Way and more recently a 6-week program outlined in a book called Write for Life, begins the writing and artistic life with a practice she calls morning pages. In essence, she suggests writing three pages each morning to explore ideas and life, and to clear the mind.
The benefits of journaling this way are numerous. Writers who establish regular journaling time may find it helps them clear their minds and explore new ideas.
There are many reasons why it is a good idea to keep a journal. I want to share four big reasons this daily habit may help you with your writing process and develop your writing skills.
1. Remember details
When I traveled to Europe in 1978, I kept a journal of my daily life. I have notes from the trip to Greece where I wiped out on a moped, weeded sugar beets on Kibbutz Reshafim in Israel, and hitchhiked through occupied territory in the south of Israel.
There were several details of my trip that I had completely forgotten until I re-read my personal journals.
Recording the details of your life can enrich your stories. One year when for The Spring Writing Contest at The Write Practice, I wrote a story about when the IRS called me to say I owed money.
In my first draft, I wrote that the amount they said I owed was, $638. After I had completed the first draft I went back to the notes I had written in my journal, and the correct amount was over six thousand dollars: $6,846.48 to be exact. Well, maybe there are some things we don't want to remember.
Thankfully, I didn't send the money. It wasn't the real IRS. But it was even better than a writing prompt for a story idea.
2. Find old friends
Keeping a journal can help you find old friends. One of the women I met on November 26th, 1978, wrote down her address. I found her on Facebook and just sent her a message. (Social media and Google can also help, but the journal did remind me of her name.)
We'll see if she responds to my Facebook message. It has been almost forty years since she lent me a pair of gloves when I scraped my hand on the pavement when I fell off my moped.
3. Help process feelings and ideas
When you keep thoughts in your head it can be hard to know how you think and feel. Writing down how you feel will help you process your emotions , as feelings become words, which can be then be edited.
Processing your feelings and ideas can lead to personal growth and peace, but that's not all. Expressive writing can be therapeutic, but it can also help you flesh out characters later.
4. Preserve the writer's history
When you are dead and a famous writer, your journals will give your readers insight into your life, thoughts, and process.
You may never sell more than one hundred copies of your book, you may never publish your writing, or your journals may only be read by the mice that crawl through your basement. Or your journals will be read by zombies after the zombie apocalypse, sharing insight into your life and daily routines.
If you don't want anyone to read your journal, keep it in a locked box and swallow the key. (Please don't really swallow the key. It would be unpleasant to have to find it again, and you might choke.) Put the key in a safe spot, and then remember where you put it.
6 Tips for How to Keep a Journal (and What to Write in a Journal!)
Now you know why journaling can be helpful. But how should you journal? It is very personal, and you should do what works best for you. But I will give you some tips to help you get started on a journaling practice.
1. Choose your kind of journal
You have several options for how to keep your journal.
A book, where you write with a pen or pencil onto paper: Write in a book that is not so pretty you are afraid to write in it. Keep the size small enough you don't mind carrying it in your messenger bag, and big enough you can read your handwriting. Do not try journaling at night when the only paper you have on your bedside table is a bandaid. The next morning I couldn't read my writing on the band-aid, and the idea I wanted to journal was lost.
The advantage of pen to paper is you can write without having to be plugged into an electronic device. You don’t have to worry about a dead battery, and you can write even when the sun is bright or the airline makes you turn off your electronic devices.
The disadvantage to a paper journal is if you lose the journal and you didn’t make a copy of it, you have lost all of the writing. But either way, the journal writing helps you pay attention and record the moments of everyday life that will fade with time otherwise.
Software: There are several software applications and journaling apps on the market you can use to keep a digital journal. Be sure they sync to the cloud, as you don’t want to lose your entries because you fry your computer's hard-drive.
Journey and Day One can add photographs and text, and export all of your entries into a PDF. You can also journal in Google Docs, Microsoft Word, or Scrivener and save your files to a cloud-based program that will keep your files safe if you lose your computer or pour water on your keyboard.
2. Date your entry
You think you will remember when it happened, but without a written date, you might forget. Make it a part of your journal writing routine to date the entry.
3. Tell the truth
The journal is a record of how you felt and what you did. Telling the truth will make you a reliable storyteller.
If you haven’t cleaned the seven litter boxes for a week, don’t write that you clean them every day simply because you want your readers one hundred years from now to think you had good habits. The beauty of journal writing is that you can record things honestly for yourself that you might not otherwise record or share.
4. Write down details
Record details like the time, location, who you were with, and what you were wearing. Details will help bring the memory alive when you record using your five senses .
To this day, if I smell a certain kind of Japanese soup, I can remember vividly the day I flew to Korea to renew my Japanese visa, only to discover the Japanese embassy was closed for a traditional Japanese holiday.
5. Write down what you felt
What you were thinking? Were you mad? Sad? Happy? Write down why.
6. Write a lot or a little
A journal entry doesn’t have to be three pages long. It can be a few words that describe what happened, a few sentences about the highlight of your day, or it can be a short description of an event from your day, where you describe details to help you remember what happened. What time of day was it? What sound do you remember?
Your journal entry might be a drawing, a poem, or a list of words or cities you drove through. It is your journal, and you have the freedom to be creative.
You can use journal writing prompts or simply tap into a memory that floats into your mind.
Bonus tip: How to write a journal entry
Aside from the date, you can write your journal entry in a number of ways. You can write stream-of-consciousness, try bullet points written rapid fire, you can use various art materials, or any form that speaks to you. Try a list or a mix of writing and doodling, or even dialogue exchanges.
The most important thing is just to take the journaling time and make a regular habit of it, even if it isn't on a daily basis. The words will show up when you do.
When to Journal
There is no right or wrong time to write in a journal. Write when you will remember to do it. Do you always brush your teeth before you go to bed? Have writing in your journal be part of your bedtime routine. Perhaps put it on your bedside table, or beside your hammock, or on the floor beside your futon.
If you are a morning person, consider keeping your journal on the table where you drink your morning coffee, tea, water, milk, or orange juice.
These are only suggestions. You don’t have to write down your feelings or why you felt a certain way. I hate being told what to do. Even if it is a good idea. But I hope you'll give it a try and see if you find it unlocks your own writing.
Do you write in a journal? Why is keeping a journal a valuable practice? Please tell us in the comment s.
Do you write in a journal? Do you think writing in a journal is a good idea for a writer, or a bad idea? Please tell us why in the comments .
Write for fifteen minutes about some aspect of your day as though you were writing in a journal. Your journal entry might be a drawing, a poem, a list of words, or a list of cities you drove through.
Please share your writing in the Pro Practice Workshop here and leave feedback on someone else’s practice today. We learn by writing and by reading.
Pamela Hodges
Pamela writes stories about art and creativity to help you become the artist you were meant to be. She would love to meet you at pamelahodges.com .

61 Comments
I found writing a journal to be a learning experience in itself. When I started, I soon realised I didn’t really know what I was trying to achieve. It seems obvious now but I had to keep at it a while for that to become apparent. Everyone has to find their personal journalling style. A few pointers certainly help, so thanks for your post. I completely agree about the sensory aspect. It’s not the result of a to-do list we’re writing, it’s shades of what gave meaning to our day.
Hello Saul Marchant, I love your description, “shades of what gave meaning to our day.” So, not just a list, but what has meaning. Best, xo Pamela
I also like your “shades of what gave meaning to our day.” Sometimes I find myself lamenting that I want more meaning in my activities—as evidenced by my journal entry above. I need to remember that the purpose and the meaning come from my perspective of the experiences, in all the various colors and shades. Thank you.
I agree with Pamela I to love your description “shades of what gave meaning to our day. I think I fall more into a listing journalistic style but time has lead me to include more meaning as I progress.
Pamela, Thank you for a great article on journaling. I started out writing a diary when I was twelve years old, then moved into journaling as an adult, which I did for twenty years, and dropped off for about five years. I renewed my journaling practice in September 2002 and began daily journaling shortly after that. I record the date and time of the entry and number my pages. I am now on page 6515 (since 2002). Some days I journal just a paragraph—other days, I write up to ten pages. It depends on what is happening in my life, and how I am feeling. The time of day and my energy level also play a part—sometimes, I am too tired to write much, but I arrange my day so that I journal every day. I am in the process of reading previous entries and harvesting them for prompts for my fiction writing and blog posts. The depth and wisdom of some of my entries amaze me. Journaling enriches my life and allows me to process my feelings and emotions which contribute to my well-being.
Hello Billie L Wade, Thank you for sharing your journaling experience. I love the idea of numbering the pages. I regret not keeping a journal when I lived in Tokyo, I have some of my letters a friend saved, but there is so much I don’t remember. Would you like to share a short excerpt from when you were twelve, or something more recent, in the comment section on The Write Practice? xo Pamela
Hi Pamela. Unfortunately, I no longer have my journaling prior to 2002 (long stories). The following entry is indicative of a frequent experience with me in which I start out with with a challenge, problem, or issue and come to some resolution by the end of the session. This entry spans pages 6447-6449. This is not edited except to remove names of people. Thank You.
Monday, 3/20/17, 9:38 p.m. I’ve been afraid I’ll die before I’m ready, before I feel fulfilled, before I’ve done what I want to do, before I’m successful, before I’m “self-actualized,” before I’m joyous. At the same time, I hear of young people—22, 35, 38—with plans and futures and young children, dying of cancer and strokes. I’m 67. I’ve lived to see my son grow into adulthood. Really puts things into perspective. I’m not financially wealthy, but I have enough—my bills are paid; I have life, car, renters, health, and supplemental insurance; I have food; I enjoy dining out with friends; I can afford my medications; I have a car; I have books and magazines to read; I can think and feel and love; I can see and hear; I have my natural teeth; I have a new cell phone; I have leather-bound journals and hand-crafted pens; I drink bottled water that is delivered to me; I live in a beautiful apartment with a nice, green view; if I’m frugal, I can afford a few extras each month. I have people in my life who care about me; by many standards, I’ve had three successful careers, I’m educated and articulate; I can taste and smell and feel the sensuousness of touch; I can write; I have challenging projects to work on; I have a therapist who “gets” me and respects me; I have [my family]. The future is uncertain—always has been—and I sometimes feel frightened when I hear the prospects. I read an article within the past few days in which the author wrote something similar to “our acceptance and behavior in the present moment are predictors of our future.” When I am joyful and grateful and fully alive in the present moment, I have a better chance that I will do so in the future. The more I cultivate an attitude of gratitude, faith, and hope today, the more likely I will feel those attitudes in the future. And, how great it would be to die as [my partner] did—with joyful anticipation and expectancy; with gratitude; with hope; in peace. I can feel fulfilled every day by bringing acceptance and awareness and appreciation to everything I do.
…exquisite … and inspiring
thank you for your gift of words and reflection
Thank you Susan.
I started keeping a journal in the third grade, after reading “Harriet the Spy.” I have a drawer full of them, dated and numbered, and I get them out to browse whenever I’m working on a kids story or something YA. It’s a great resource for me to be able to see how a twelve year old mind worked. I’m so glad I kept them. My five year old keeps a drawing journal of the things he sees during the week, which I hope will eventually grow into something he does for a lifetime.
Hello Amanda Niehaus-Hard, Wow! How exciting to have writing from when you were twelve. I am happy you kept them too. What a treasure. A drawing journal is a great idea, a way to journal for children who might not be writing yet. If you would like to, please share a short excerpt from one of your third grade journals with the date, and/or one of your child’s drawing, if they don’t mind. All my best, xo Pamela
Hi Amanda, I am impressed that you have your journaling from age twelve, organized so you can easily use them. Everything I wrote before 2002 was destroyed, and I miss not having all of my writing. I am glad you can use your journaling to inform what you are writing now. Happy writing to you.
Hi, I did not want to do it this way, but this is regarding my guest post submission idea that I proposed on 31st March. I got the email of confirmation from the automatic mailing system, but did not recieve any manual response for the idea that I had submitted. What has brought me here today is that just six days later, a guest post was published on this very website titled “Show, Don’t Tell : How to Inject Drama Into Your Writing.” This did not seem to be a coincidence, since when I read the article, most of it seemed to be derived from the idea that I had proposed to you, and got no response to. I wrote another email, and that too has not recieved a reply regarding the state of my query. I know that this is not how this matter is appropriately resolved, but since I have got no response from your side, I am becoming both ancious and disappointed. The publication of the guest post resembling my idea might have been a coincidence, albeit a strange one. But the fact that I have recieved no response troubles me. All of us are writers here, and I think that beyond a moment of doubt, all of us would agree that it isn’t in the best interest of the art of writing and all the virtues which come with it. Again, I know this is not the way things are supposed to be dealt with, but right now, I seem to have no other option left to retrieve the creative right over what is beyond a doubt my own idea, credited to someone else right now. Thanking you, and hoping for a legitimate response, Abhijato. (I would have provided my email here, but I do not want any spam. I request you to kindly respond to my enquirery.)
Great article. I have tried in the past to journal but have never kept it up. Perhaps my life is not interesting enough or I’m not disciplined enough to form the habit. I’m going to start again and not put so much pressure on myself thanks to this article.
Hello Marieca Lashawn, I don’t journal every day either. I treasure the journals I have from my trip to Europe in 1978. It never occurred to me that every day life also had value. I am going to start again too. We don’t have to be perfect, and there are no rules to keeping a journal. I will floss all of my teeth, and write something every day. A new habit for me too. xo Pamela
Hello Marieca; I think one for the reasons I journal is that I feel I don’t have to be interesting. Sometimes years go by before I reread what I have written. Some is boring, so what? Now if I am writing a story, and article or a memoir,, I try to be literate and interesting. But journaling, hey the pressure is off and at least I am writing.
The great travel writer Tim Cahill just taught a writing class in Morocco, which I was part of .. and the biggest take away I got (he said if you only remember one thing..it’s this) : “take copious notes” (as life happens, whether traveling or whatnot). Great post and in the exact same vein as Mr. Cahill’ instructions!
Hello Jacqueline Gu, Morocco, how fun. A writing class with Tim Cahill. “Take copious notes.” I love this. It is worthy of a tattoo. Or at least writing it on my chalkboard. Thank you for sharing your adventure, and the lessons you learned. Now I will look up Tim Cahill, I am not familiar with his work. Do you have a favorite book written by him? What book do you recommend I read first? What do you like to write? xo Pamela p.s. Where in Morocco were you? I was Casablanca in 1989 talking photographs for a Japanese client.
Hi Pam – nice to meet you. always great to be acquainted with a fellow writer. I’m reading Tim’s “Pass the Butterworm” but I also heard good things about “Hold the Enlightenment”. I do creative nonfiction/travel/memoir writing but I haven’t shared my stuff with many ppl yet so i’m working on becoming published. I was in Fez/Moulay Idriss/Sahara/Chefchouwen for my 2 week trek in Morocco. So much material (so much copious notes) now to write from! And 1989? That’s awesome – sounds like a trip too! Did you ever write about Morocco?
Cheers to you Pam! I will look up your blog and url now. Jackie
Writing a journal is the only consistent form of writing I have done for the past few years. My journal consists of Writing down which of my 12 daily disciplines I have accomplished and which ones are left to do. I began this practice when I retired and found my days slipping by without accomplishing much and giving into a lifelong leaning towards depression. After some time I changed the disciplines around and found the exercise helped me in many ways. Life, however intervened and heart attacks, strokes, and major moves intervened in the practice since my life priorities changed. So to the twelve disciplines I added a daily description of the foods I eat in a day; the physical activity and exercise I have done; and a spiritual insight along with five things for which I am grateful on each specific day. Today’s post is timely, because I was thinking the practice was getting me nowhere; but I think I will continue since so many successful writers do journal. Thanks for the timely post.
I like the sound of daily disciplines. Life has begun to slide recently. A reformed depressive, a serial dropper outer, I love writing but have not allowed myself to recently, ditto dancing and yoga. I love lists and the daily disciplines sound list like, something with a big tick beside it to feel like achievements until they build up into something big and can count as such. I used to blog and make copious entries and notes and have let that slide too. So thanks for the timely post and for contributions, and here’s to getting back to good habits.
Hello Maryjhowell, Yes, here’s to getting back to good habits. There is a yoga class I keep meaning to get to, I am a serial do it tomorrower. Wishing you all the best, and hope you find time to dance, stretch and journal. Please share your url for the next blog post you write, as you find your way back to yourself. xo Pamela
Hello retrogeegee, I love the name you use here, very creative. I hope you are feeling well, I am sorry to hear you have experienced heart attacks and strokes. Thank you for sharing how you write in our journal with your daily disciplines. What did you eat today? Today I will also write down five things I am grateful for. Sometimes I lean towards depression too, exercise has helped me. Looking at what is good in my life will help too. Thank you for sharing your life. I appreciate your honesty. xo Pamela
I have kept a diary since childhood, although those are long gone. It was a good habit, and I have been journaling since I am an adult. Now I am writing Our Story – 45 years in Japan – and some details that I needed were in there. My son thought the dog under our house gave birth to eight puppies. I checked my journal – it was only six! I have separate loose page journals for the visits we made to our missionary kids in Zaire (now Congo), and the ones in Nepal volunteering for six years with MCC. Wonderful memories preserved.
Hello Mary Derksen, The journals sound really helpful in remembering details. “45 Years in Japan”, sounds like a great title for a memoir. I lived in Tokyo for seven years, and wish I had kept a journal when I was there. What happened to the puppies? That must have been a fun memory. Hope you are well. So nice to meet you and hear of your and your children’s adventures. xo Pamela
Hi Pam, great inspiring article. I have been journal writing and keeping diaries for years. For some reason I started this practice in the 5th grade. I went back to read the first entry in this diary hoping to find why I started this practice, but unfortunately I didn’t write the reason Why. You are right, journaling helps people keep personal records of their life. Mine have taken me from grade school to high school, to college. Through dating, marriage, kids, divorce, death and now back to a long term relationship, that I could probably turn into a never ending novel.. Some things that were too painful to write about, I put them in these journal writings as short stories to make it seem as if these were things that happened to someone else. To date I have 38 diaries/journals. Most recently I started a journal for my writing ideas and a personal one for my everyday happenings. So really I now have 40 journals.
Hi Cheryl, Yes, our journals get us through so much. Mine are a constant repository of self-nurturing as I wrestle with the gamut of feelings and emotions, challenges and resolutions. Rereading my entries validates my perseverance and resilience. I am up to 18 journals now, lots more to go. Best to you.
Thank you Billie, all the writing instructors always say write daily. So when I’m not writing on a story, I make it a habit to write something in my journals. So that’s my way of writing everyday.
Hello Cheryl Sams, Your approach of writing the hard parts of your story as short stories is a great idea. A record of what happened, but keeping the pain in the third person. I hope your story has more sunshine in it today, and in your tomorrows. I wonder what your 5th grade self thought. How special that you have all of your journals. Wishing you all my best. xo Pamela
Sorry to get back to you so late Pam, but you had me wondering about what did I write about in my first diary. Well I dug it out of my pile of journals, and my first entry was dated January 1, 1979. I introduced my immediate family, my grandmother, mom, aunt, uncle, stepdad, siblings and half siblings, and my 5year old cousin. It was the deep south and on that day it was windy, wet, cold, and there was a chance of snow. Christmas vacation was over and I was ready to go back to school. I didn’t want to be at home, school was more exciting(I stayed in a very rural area). Well I caught a cold and I was miserable, and I stated “I’m tired of writing now, I’m going to bed.” Well I guess I went to bed for a very long time, because my next entry was dated January 1984 and I was in college getting ready to go out on a date with an upperclassman. This was a one year diary, but I wrote in it throughout the years. My last entry Jan.2016. I updated my life. Three more pages left in this 38 year old diary. So I’m going to finally close it out on a very positive life update. Just needed to share. thanks.
Yes! Creativity doesn’t recognize boundaries or rules! I write, am an artist too, many mediums for both. I think it’s a pretty healthy, natural condition. Haven’t had the rich overseas experiences, but lived in a good many U.S. states and Canada, amassed 37 addresses so far, leaving fingerprints and/or words/artwork in my wake. Many journals created, some with people whose names I’ve forgotten but whose sketched faces I recognize. Hope to check in with you often. Cheers! 😀
wow … “whose sketched faces I recognize.” … I can just imagine the lovely nature of your journal with sketches intertwined with your written thoughts.
Definitely do come back to The Write Practice to visit … it’s a welcoming place, as is Pamela Hodges’ wonderful website!
Thx Susan. I’m a fan of The Write Practice, visited Pam’s site as well. My site’s a bit wonky at present–but c’mon over if you don’t mind stepping over the mess! { kdadams.com }
I thought I might have been making a wrong assumption based on your “check in” phrase. Nevertheless, I’m glad I commented and got your response so I could visit your website. LOVELY! Looks like you do remarkable, meaningful work. Loved, for instance, reading the glowing feedback from your memoir workshop participants. I’ll visit again.
Sorry for delay- my digital myopia caused lapse in finding your note. Have not yet launched newsletter but hope to find reliable tech soon! What’s your writing?
Hello Kristine Adams, Love your description of leaving fingerprints in your wake. Words and artwork. You have lived in a lot of places, so many memories. Where in Canada? I grew up in Saskatoon, Saskatchewan. Hugs to you. xo Pamela
Sorry for delay- email folder used w/ Write Practice exchange was misplaced. I lived just into southern Ontario–first near Petrolia, and later near Sarnia. Shared communal houses with friends who now are in B.C. Wow, with our bogus potus, Canada’s appeal is skyrocketing!
I absolutely LOVE this article. I’ve been writing journals since i was a kid but quit writing for a very long. I’ve again started to write down my journals. It’s the best thing I’ve discovered. I’m more aware of my thoughts and myself now. It’s the best practice for a winter of any sort. Be it a beginner or a published author. I’m not sure if I want to share it with anyone but i just enjoy the whole process of writing my journal
Hello shiwangi agarwal, Thank you for confirming that journal writing has helped you be more aware of your thoughts. You don’t have to share your thoughts. I like having a private place to write and think. Now to find a safe spot to hide a key, where no one else will find it and I can remember where I put it. xo Pamela
This doesn’t relate to this post, but feedback is greatly appreciated.
Mara shivered, pulling her ratty, practically obsolete sweater closer around her torso. Tevrah was cold this time of year. And drizzly. A drop of rain landed on her nose, freezing and unexpected. She wished she had warm pants instead of her school dress and her mother’s cardigan.
Her younger brother, Deo, tugged on her hand and pulled her off-course toward a stand selling jewelry. A young woman was standing behind the tables, smiling benevolently at her customers. She eyed Mara and Deo. “We don’t have long,” Mara warned him in their language, trying to smile innocently at the shopkeeper. It wasn’t as if they were going to steal something, but they certainly had the stink of poverty around them, accentuated especially by their thin, dark features. Deo’s hair was sticking up all over the place, his face the only inch of cleanliness on his body. Their mother was quite persistent about the need for washing your face twice a day, even if nothing else was clean. “It is important to make a good impression,” she had warned. Mara could only imagine what the people of this town thought of her and Deo, as she surely looked just the same as her six-year-old brother. She wished she hadn’t disregarded the necessity of neatness that morning. Every sort of person on earth could be observed in this market. The rich, the seedy, the fine, the poor, the gaudy, the drab. And Mara and Deo looked like beggars.
She still had a few coins left in the pockets of her sweater. Her bag was filled with day-old bread, bruised apples, and several rolls of bandages. They still hadn’t found someplace selling sponges for cheap, which was unfortunate since the younger kids cried when you scrubbed them with the rougher brush. And that was Mara’s job. She would have taken a used oil cloth by now to avoid Skya Menyon’s sharp glance whenever she heard the wail of her toddler, who was the whiniest child Mara had ever met.
It had been her job back at the village, at least three hundred kilometers from Tevrah’s town of North Market. They were three hundred kilometers from the place Mara had never left in her life– until now. The people were different here, even not so far away. The area was drizzly and brown and green, filled with grays. The people here had lighter hair, while the skin on Mara’s arm was dark as a macadamia nut’s shell. Her village was all but disappeared, nothing but ashes on the gods’ gentle breeze.
The day after the fires, the women of the village had shorn their hair to shoulder length, Mara included since her fifteenth birthday had passed two weeks prior. She wasn’t used to it. She liked to twirl strands of her hair, mindlessly twist them together as a nervous habit, and with it so short it was hard to wrap her black locks around her index finger. She kept reaching up only for her hand to stop short and sink back down to her side.
Deo was gawking at a gold necklace. The shopkeeper’s hawk eyes stayed locked on him, drawn as a moth to a flame. She was clearly suspicious. “Deo,” Mara hissed. He barely looked up.
“What?” he muttered. “Stop it.”
Mara tugged him a few feet away from the necklace, the shopkeeper still watching them. “Stop looking at that like you’re going to grab it.”
“I wasn’t going–” “She doesn’t know that!” Mara protested. Deo frowned, looking at his grubby hands curiously.
“Is it time for lunch yet?”
“Deo!” she chastised. The woman had begun to emerge from behind the booth. Mara turned toward her, widening her eyes. “Yes?” she inquired politely, switching to Tevranian for the shopkeeper’s sake.
“You kids like my jewelry?” she demanded.
Mara smiled shakily. “I apologize, miss, but my brother, he is not so smart,” she said, patting Deo’s hair and shushing his protests with a hand over his mouth. She tried to adjust the bag on her hip so the woman could peer into it and see there was nothing out of the ordinary inside.
“Oh?” the woman said, raising an eyebrow.
“He does not know how much the necklace does cost, you see?”
She grunted again.
“The cost is too much for us, anyway, because you see–” Mara saw something out of the corner of her eye. A glint of silver. A flash of crimson red. She stopped short, aware of the shopkeeper’s eyes trained on her dubiously. A girl had slipped in behind the stand, wearing vibrant red pants and a gray shirt, hair that must have been white as ivory when it was clean hanging in strands down her back.
“Yes?” the woman prompted.
“Yes…” Mara forced herself to look away. “I, um, we were not taking the necklace.” The fair-haired girl’s hand danced out of her pocket and hooked the bracelet onto a finger. She stuffed it into her overcoat.
Mara stared for a second before coming to her senses. “Hey!”
The shopkeeper whirled around. “What–”
The girl’s green eyes darted up to meet her accuser’s, and then she nimbly slipped into the crowd, that white hair a blur behind her. Mara began to run after her, leaving Deo and the shopkeeper behind, but stumbled over a man’s shoe. He sneered at her. “S-sorry,” she stammered. “Sir.”
A warm, dry hand grasped Mara’s hand in its grip. She looked down to see Deo staring up at her, his hair wet from the rain. “Deo,” she said , trying to see over the crowd’s heads, “go… go find Thyme and Yuri.” She shoved the basket of goods into his hands.
He began to whine, but Mara was already gone. She darted around a fruit cart, a few berries falling to the ground as she bumped it. The boy selling the fruits cursed at her in a language she didn’t understand. Mara kept going. Where had that girl gone? And why hadn’t she yelled “Thief!” and left other people to take care of it?
She was an idiot, Mara reminded herself, that’s why.
She tripped over her own shoes, a size and a half too large, not once but twice. Her gray dress was small on her, barely modest as it ended a few inches above her knees. The only reason Mara could get away with it was because she didn’t look her age. She’d kept a bit of baby fat, and she hadn’t shot up like a bamboo stalk. At least, not yet.
Ah. Under that bridge over there, stretching across the rushing river below, its banks mossy and wet. Mara saw a flash of blonde hair and those strange red pants the girl was wearing before she took off again. By now, the rain was coming down hard, clumping Mara’s dark eyelashes together and blurring her vision. She stumbled over the muddy ground beyond the market, the sounds of the city disappearing from her ears, and ducked under the cover of the old bridge.
It was quiet but for the sound of rain pattering the stone above.
“Hello?” Mara called out softly. There were no footprints in the mud leading off into the forest on the other side of the tunnel, but she couldn’t see where else the girl could have gone. Perhaps she’d disappeared, like in the Yaba’s stories back home. “Hello?” Mara said again, louder this time. She took a tentative step forward, then froze in her tracks when a voice responded.
“It’s not worth that much.”
Mara startled, whirling around. No one. “What?”
“The bracelet,” the voice explained. “Didn’t cost as much as that lady was selling it for.”
“Ay.” Mara didn’t know what to say to an invisible person. The distant sounds of shouting salesman only just reached her ears.
“You can leave and pretend this never happened.”
Mara seethed. “No.”
“Why not?” the disembodied voice challenged.
“You took it!”
“I stole something deserving of a halved coin.”
“What in ny anaran’Andriamanitra is a half coin?” Mara retorted. She wrung the rainwater out of her hair, and it splattered on her already-soaked dress, hanging limp around her knees. She wasn’t sure where to look, as she couldn’t see the person she was talking to.
“Oh, you know.” Mara didn’t. “A copper. Not even a single silver. She was marking it three times its worth.” They didn’t have much of silver where Mara was from.
“And who are you,” Mara said, “to judge?”
“And who are you?” the voice echoed.
“I–” Mara started, then cut herself off. “You are a criminal.”
“Hm.” The girl’s body dropped from the top of the bridge, and she landed perfectly balanced, wearing that red sweater and brown, unfitted pants. Mara stumbled back, surprised at the girl’s entrance, and almost tripped over a rock behind her. “I disagree,” the girl said.
“Are quite good at climbing things,” the girl said. She stared at Mara unblinkingly, her green eyes startling against the gray of the day. A gust of wind picked up her wispy blonde hair on its wings. “I’ll tell you what. You let me go, I’ll give you this bracelet.”
“That is not a deal!” Mara said, indignant. “You took it! Here is the idea: give it back and I will not… tell. Tell the police.”
The girl chuckled, flashing a crooked smile, dimples appearing at the corners of her mouth. “Let me guess. You aren’t from around here?”
Hello, Pamela. Nearly every journal I’ve ever written starts with, “Well, I’m not good at journal writing, but I’ll try again” or some such lame thing, and invariably that entry is followed by a handful of dated entries, followed by some more six months or six years later. I try to let go of that feeling of “defeat before I’ve even started” because what’s the point? I tell myself, “Let go of thoughts of perfection because it ain’t coming to my doorstep any time soon.”
I’m going to include here an entry in my journal from the month after my mother passed away in 2014. I’m guessing that I was using your writing style as part of my inspiration because I included a level and type of detail that I may not have previously.
I was reflecting on why I am thankful. It reads, …
The piece I’m going to start with is the sweet gesture that Mehrzad [my husband] made yesterday, showing me his deep love and such a respectful honoring of Mom. We sold her car yesterday at Carmax [2003 Lexus ES 300 silver/light blue, “wood” steering wheel and other trim areas, 40,708 miles bought for about $30,000 new – mom’s decision with no consultation – sold for $7,000] Carmax gave us back the license plate [NWSTOY] and license plate frames [“I’d rather be stitching”]. I’m thinking, “OK, What do we do with these? Should we keep them? No, we’re trying to declutter not reclutter.” A bit later on, Mehrzad lovingly says, “Shall we hang these up in the garage? It’s part of your mom’s life and we want to keep that history. We’ll need to find a place to hang it.” WOW! … THANKFUL! —- [I just now took a picture of the license plate on our pegboard in the garage to include here, but I guess an upload option is not included; forgot that.] —– As always, I’m thankful for you, Pamela.
Hello Susan WA, Thank you for sharing the excerpt from your journal about your mom. The detail about the car, including the milage brought me emotionally into the story. Life is made up of concrete details. Little bits of reality that allow me the reader to feel the story. I am so sorry your mom died. And, so thankful to read of the kindness of your husband who hung the license in the garage. So nice to hear from you Susan. I am thankful for you also. xo Pamela
One of my biggest heartaches is that I accidentally threw out a notebook that I thought was empty … turns out it was my son’s reflections on quotes from when he was in 8th grade … it was a daily exercise by his history teacher, a man who inspired my son deeply, and is his favorite teacher of all time. Love those amazing connections when a teacher has such an impact on a student’s life.
Hi, Pamela! Here is a way to have both the handwritten and the electronic record: https://store.moleskine.com/usa/en-us/Moleskine-/Evernote/C26
I haven’t tried this system, but it looks pretty interesting. I also like the idea of using Scrivener. I prefer to journal with pen and paper, but am currently doing a hybrid: early morning brain dump online at http://750words.com , and then a notebook and my pretty new purple fountain pen throughout the day.
Hi GirlGriot, So nice to see you here! Thank you for the suggestion to combine the handwritten and the electronic. Maybe I need to get a pretty purple fountain pen too. Something to remind me to take notes on my life. I will check out the 750 words site, and dump out my brains too. Hope you are well. xo Pamela
(FYI, 750 words is a paid site now. Not sure what it costs. I joined when it was free and was grandfathered in when they switched over.)
Hello TerriblyTerrific, You could always swallow the key. (This is meant to be funny, and is not a real suggestion, in case you do swallow the key, and then want to hire a lawyer and say we told you to eat a key) How old is your daughter? Maybe she needs to find a safe spot to hide her journal. 🙂 xo Pamela
I started writing journals when my children grew up and went to college. I felt lost in myself and wanted to get the emotions out of my system. I then began to cycle long distances with some friends. We cycled from coast to coast in various countries including Australia, Vietnam; parts of Europe and the Himalayas. I have recently been expanding some of my journals and one thing I noticed is that, throughout all the scary parts of the journeys; when we thought we were in dire states, someone came out of the blue and saved the day. When the bike broke, when we ran out of food or water on the mountains, or when we had no shelter. I call them the Angels on my journeys all of which I am deeply thankful for.
The journal in 2014 helped me deal with a lot of sudden deaths of close family and friends, there was almost one a month that year. When I look at that year I realise we are all challenged and no matter how hard that challenge with a bit of help we can get through it. Journals can be lifesavers reminding us to be grateful and how lucky we are.
Hello Elizabeth McKenna, You have lived some amazing adventures. I love your perspective on how “journals can be lifesavers reminding us to be grateful and how lucky we are.” I am sorry about the sudden deaths of family and friends in 2014. That sounds like a hard year. Sending you hugs and sunshine, xo Pamela
In Julia Cameron’s book “The Artist’s Way,” she teaches her students to writing their “Morning Pages,” as a way to get back their creativity. Sometimes they are referred to as our “Mourning Pages,” because we mourn the ills of our life. I wrote faithfully for about a year then quit. It’s something that cleansed the soul and helped me dig down deep to the heart of my frustration with a certain family members and clear out some junk. Journalling is so important to our mental health and to bring us clarity. It can help us clear our mental blocks to our creativity as well. Thanks for the post.
April 20, 2008
We had breakfast with Uncle Jerry today after church. He made waffles, and we brought the side dishes: sausage, fried potatoes, cheese soufflé, and crunchy cantaloupe. It was nice to be together. He’s having more trouble with his breathing, but he isn’t taking any treatments for it. He’s refused what treatment the doctors have offered, although for his condition—interstitial lung disease—there really isn’t much they can do. He is allowing the disease to run its course. It’s strange seeing it happen to him because I know that I will follow soon.
In truth, I’m simply afraid. I have always had a horror of drowning, of suffocation, of being unable to breathe. Since I’ve got late-stage pulmonary hypertension, that’s exactly how I’ll die: one gasp at a time. I might get lucky, though. People with this disease often die of sudden cardiac death. The heart just stops, and they’re dead before they hit the ground. I like Door Number 2 much better than Door Number 1.
“Writing is the only way I have to explain my own life to myself.” Love that. Must try it, but I need to be ‘plugged in’. I thought I’d never write again after the shakes got me. Now I can even read my writing!
Hello Pamela, Many thanks for your article on keeping a journal. Very handy. I wrote a journal in the past, for a year, when I was grieving. There was no one to confide in, and writing my feelings and the events that filled my day, brought a little solace. Now I write daily, (in longhand, in a small blue booklet) to record my husband’s medication, (the names of his medicines and the hour in which he took them) his moods, and in brackets, a little about myself. The journal is a verification of what we did. My husband contests me on many things, declaring that ‘we did not’. Out comes my journal to satisfy his verification. I’m glad I recorded it on paper. In the blue booklet, I write the day, then the date, and below, the weather and mean temperature. I record where we went and why, like, shopping for shoes, meat, presents, etc:. I write of guests who came to lunch or to visit.
I write a line about Minnie and her friends. Yesterday I recored that she vomited… a bunch of grass.
Please give our love to Harper and the users of the other six litter boxes.
With love, Lilian
I love journaling and have even taught journal workshops. It is what helps untangle my thoughts and make sense of life. I make a practice of re-reading (currently once a week). That’s when I’m reminded of things I need to follow up on. It’s about the only time I use paper and pencil now, which really sets it apart from all other activities.
Great article. I took a trip to Europe a few years ago and I was so happy when I came across my travel journal. All the details that I had forgotten are in there! I’ve now converted to a digital journal since it’s accessible from anywhere and I usually have my phone on me to jot down entries when I have a few minutes. (Disclaimer: I blog for JRNL.)
I have an urgent need to journal, and I do so, but always with a feeling of trepidation because am afraid my kids will judge me poorly when I’m gone. Haven’t committed crimes or anything like that but am somehow ashamed of the strong feelings of insecurities that come up again and again. But I need very much to write them. Anyone else have this problem?
Yes. I sometimes feel like you as well. That is why, I write a lot and then get rid of it. This helps me with my self awareness. When you write everything down as true as it has happened and you read back to yourself, you somehow judge yourself and that would become very valuable to you for many reasons. 1) you might realise, it was not as important, good or bad or even important as you first thought. 2) You can realise what went wrong or right in that occasion and you might have the opportunity to make it better or try to accept it and draw a line under it. 3) you have become your own best imaginary friend whom you can talk to in confidence and get help without any worry of it going further or be judged. The list of benefits are endless and can go on and on and on, but I am sure, you got the gist of it. 🙂
I love this articular because it explain how writing journals makes you a better writes. it help you express your emotions also your daily lifestyle. I never really writing a journal before but I starting to write down my thought in my journal. it’s the best way to practice writing or express yourself for example I wake up seven in the mourning eat breakfast brush my tooth and wash my face.I get dress walk out the front door to wait at the bus stop.
Journaling leads to growth, which is especially important for a writer. Benjamin Franklin had the habit of keeping a journal, which helped him to become healthy and wealthy: https://constantrenewal.com/keeping-a-journal/
Great post. I have journaled ever since junior high and maybe even a bit earlier. As time goes on I think I’m writing down better things, descriptions and such and digging deep into my real feelings about things and life. It’s a good way to explore and figure out who I am and what I’m thinking. 🙂
I started journaling few months ago and I think it really improved my mental health a bit lol. Usually, I write at night and sometimes, I forget what just happened hours ago (which I have to reopen my gallery to find some specific photos that have to do with my “day”). Anyways, it’s a great and a helpful article btw!
Trackbacks/Pingbacks
- Creative Resource Links (04.13.17) - bohemianizm - […] How to Write a Journal: 6 Tips (The Write […]
- What to Write in a Journal - Allenia Renee Writes - […] I found a solution to this….wait for it. I started journaling. As I write this my chest is poked…
- Junk food is a cheap drug: Research explores the link between income, obesity, and psychological distress – FREE SPEECH DAILY - […] instead of a chocolate bar. Rather than venting out by eating junk food, release your emotions by writing them…
- I admit it… | Rainey Dewey Blog | Life * Art * Things That Matter - […] nice thing about writing – whether in a journal or here on a public blog – is that writing…
- How to Journal during this Unprecedented Historical Time – Legacy Of Love - […] write about this time is crucial. Expressing your thoughts, feelings, hopes, and fears, along with what is happening with…
- 6 Ways to Take Care Of Yourself During The Pandemic - TheUrbanRealist - […] 3. Write in a Journal. […]
- 10 Tips for Maintaining Mental Health During COVID-19 – Fashion Cluba - […] outlets you can use to deal with your emotions and get them off your chest. Something as simple as…
- Appreciation for the little things makes a difference – A Liddle Sunshine - […] things that sometimes helps the most. This can be as simple as baking cookies, reading a book, journaling, or…
- Discover your safe haven and burst with growth – A Liddle Sunshine - […] you love to journal, read books, take pictures, play music or fill in the blank, remember that the Lord…
- How to Write a Journal: 6 Tips - - […] article How to Write a Journal: 6 Tips appeared first on The Write […]
- The Best Gifts For New Mums - A Mum Reviews - […] to share. Some mothers may even fall into postpartum depression. Get the new mother a perfect little journal that…
- Quotes About Self-Improvement – Boost your personal growth - […] Print them off and frame them and hang them on a wall in your kitchen or bedroom. If you…
Submit a Comment Cancel reply
Your email address will not be published. Required fields are marked *
Submit Comment
Join over 450,000 readers who are saying YES to practice. You’ll also get a free copy of our eBook 14 Prompts :
Popular Resources
Book Writing Tips & Guides Creativity & Inspiration Tips Writing Prompts Grammar & Vocab Resources Best Book Writing Software ProWritingAid Review Writing Teacher Resources Publisher Rocket Review Scrivener Review Gifts for Writers
Books By Our Writers

Get a Month of Journal Prompts
Enter your email for a free calendar with 31 daily journal prompts to jumpstart your writing habit today!
You've got it! Just us where to send your guide.
Enter your email to get our free 10-step guide to becoming a writer.
You've got it! Just us where to send your book.
Enter your first name and email to get our free book, 14 Prompts.
Purdue Online Writing Lab Purdue OWL® College of Liberal Arts
Academic Proposals

Welcome to the Purdue OWL
This page is brought to you by the OWL at Purdue University. When printing this page, you must include the entire legal notice.
Copyright ©1995-2018 by The Writing Lab & The OWL at Purdue and Purdue University. All rights reserved. This material may not be published, reproduced, broadcast, rewritten, or redistributed without permission. Use of this site constitutes acceptance of our terms and conditions of fair use.
This resource introduces the genre of academic proposals and provides strategies for developing effective graduate-level proposals across multiple contexts.
Introduction
An important part of the work completed in academia is sharing our scholarship with others. Such communication takes place when we present at scholarly conferences, publish in peer-reviewed journals, and publish in books. This OWL resource addresses the steps in writing for a variety of academic proposals.
For samples of academic proposals, click here .
Important considerations for the writing process
First and foremost, you need to consider your future audience carefully in order to determine both how specific your topic can be and how much background information you need to provide in your proposal. While some conferences and journals may be subject-specific, most will require you to address an audience that does not conduct research on the same topics as you. Conference proposal reviewers are often drawn from professional organization members or other attendees, while journal proposals are typically reviewed by the editorial staff, so you need to ensure that your proposal is geared toward the knowledge base and expectations of whichever audience will read your work.
Along those lines, you might want to check whether you are basing your research on specific prior research and terminology that requires further explanation. As a rule, always phrase your proposal clearly and specifically, avoid over-the-top phrasing and jargon, but do not negate your own personal writing style in the process.
If you would like to add a quotation to your proposal, you are not required to provide a citation or footnote of the source, although it is generally preferred to mention the author’s name. Always put quotes in quotation marks and take care to limit yourself to at most one or two quotations in the entire proposal text. Furthermore, you should always proofread your proposal carefully and check whether you have integrated details, such as author’s name, the correct number of words, year of publication, etc. correctly.
Methodology is often a key factor in the evaluation of proposals for any academic genre — but most proposals have such a small word limit that writers find it difficult to adequately include methods while also discussing their argument, background for the study, results, and contributions to knowledge. It's important to make sure that you include some information about the methods used in your study, even if it's just a line or two; if your proposal isn't experimental in nature, this space should instead describe the theory, lens, or approach you are taking to arrive at your conclusions.
Reasons proposals fail/common pitfalls
There are common pitfalls that you might need to improve on for future proposals.
The proposal does not reflect your enthusiasm and persuasiveness, which usually goes hand in hand with hastily written, simply worded proposals. Generally, the better your research has been, the more familiar you are with the subject and the more smoothly your proposal will come together.
Similarly, proposing a topic that is too broad can harm your chances of being accepted to a conference. Be sure to have a clear focus in your proposal. Usually, this can be avoided by more advanced research to determine what has already been done, especially if the proposal is judged by an important scholar in the field. Check the names of keynote speakers and other attendees of note to avoid repeating known information or not focusing your proposal.
Your paper might simply have lacked the clear language that proposals should contain. On this linguistic level, your proposal might have sounded repetitious, have had boring wording, or simply displayed carelessness and a lack of proofreading, all of which can be remedied by more revisions. One key tactic for ensuring you have clear language in your proposal is signposting — you can pick up key phrases from the CFP, as well as use language that indicates different sections in academic work (as in IMRAD sections from the organization and structure page in this resource). This way, reviewers can easily follow your proposal and identify its relatedness to work in the field and the CFP.
Conference proposals
Conference proposals are a common genre in graduate school that invite several considerations for writing depending on the conference and requirements of the call for papers.
Beginning the process
Make sure you read the call for papers carefully to consider the deadline and orient your topic of presentation around the buzzwords and themes listed in the document. You should take special note of the deadline and submit prior to that date, as most conferences use online submission systems that will close on a deadline and will not accept further submissions.
If you have previously spoken on or submitted a proposal on the same topic, you should carefully adjust it specifically for this conference or even completely rewrite the proposal based on your changing and evolving research.
The topic you are proposing should be one that you can cover easily within a time frame of approximately fifteen to twenty minutes. You should stick to the required word limit of the conference call. The organizers have to read a large number of proposals, especially in the case of an international or interdisciplinary conference, and will appreciate your brevity.
Structure and components
Conference proposals differ widely across fields and even among individual conferences in a field. Some just request an abstract, which is written similarly to any other abstract you'd write for a journal article or other publication. Some may request abstracts or full papers that fit into pre-existing sessions created by conference organizers. Some request both an abstract and a further description or proposal, usually in cases where the abstract will be published in the conference program and the proposal helps organizers decide which papers they will accept.
If the conference you are submitting to requires a proposal or description, there are some common elements you'll usually need to include. These are a statement of the problem or topic, a discussion of your approach to the problem/topic, a discussion of findings or expected findings, and a discussion of key takeaways or relevance to audience members. These elements are typically given in this order and loosely follow the IMRAD structure discussed in the organization and structure page in this resource.
The proportional size of each of these elements in relation to one another tends to vary by the stage of your research and the relationship of your topic to the field of the conference. If your research is very early on, you may spend almost no time on findings, because you don't have them yet. Similarly, if your topic is a regular feature at conferences in your field, you may not need to spend as much time introducing it or explaining its relevance to the field; however, if you are working on a newer topic or bringing in a topic or problem from another discipline, you may need to spend slightly more space explaining it to reviewers. These decisions should usually be based on an analysis of your audience — what information can reviewers be reasonably expected to know, and what will you have to tell them?
Journal Proposals
Most of the time, when you submit an article to a journal for publication, you'll submit a finished manuscript which contains an abstract, the text of the article, the bibliography, any appendices, and author bios. These can be on any topic that relates to the journal's scope of interest, and they are accepted year-round.
Special issues , however, are planned issues of a journal that center around a specific theme, usually a "hot topic" in the field. The editor or guest editors for the special issue will often solicit proposals with a call for papers (CFP) first, accept a certain number of proposals for further development into article manuscripts, and then accept the final articles for the special issue from that smaller pool. Special issues are typically the only time when you will need to submit a proposal to write a journal article, rather than submitting a completed manuscript.
Journal proposals share many qualities with conference proposals: you need to write for your audience, convey the significance of your work, and condense the various sections of a full study into a small word or page limit. In general, the necessary components of a proposal include:
- Problem or topic statement that defines the subject of your work (often includes research questions)
- Background information (think literature review) that indicates the topic's importance in your field as well as indicates that your research adds something to the scholarship on this topic
- Methodology and methods used in the study (and an indication of why these methods are the correct ones for your research questions)
- Results or findings (which can be tentative or preliminary, if the study has not yet been completed)
- Significance and implications of the study (what will readers learn? why should they care?)
This order is a common one because it loosely follows the IMRAD (introduction, methods, results and discussion) structure often used in academic writing; however, it is not the only possible structure or even always the best structure. You may need to move these elements around depending on the expectations in your field, the word or page limit, or the instructions given in the CFP.
Some of the unique considerations of journal proposals are:
- The CFP may ask you for an abstract, a proposal, or both. If you need to write an abstract, look for more information on the abstract page. If you need to write both an abstract and a proposal, make sure to clarify for yourself what the difference is. Usually the proposal needs to include more information about the significance, methods, and/or background of the study than will fit in the abstract, but often the CFP itself will give you some instructions as to what information the editors are wanting in each piece of writing.
- Journal special issue CFPs, like conference CFPs, often include a list of topics or questions that describe the scope of the special issue. These questions or topics are a good starting place for generating a proposal or tying in your research; ensuring that your work is a good fit for the special issue and articulating why that is in the proposal increases your chances of being accepted.
- Special issues are not less valuable or important than regularly scheduled issues; therefore, your proposal needs to show that your work fits and could readily be accepted in any other issue of the journal. This means following some of the same practices you would if you were preparing to submit a manuscript to a journal: reading the journal's author submission guidelines; reading the last several years of the journal to understand the usual topics, organization, and methods; citing pieces from this journal and other closely related journals in your research.
Book Proposals
While the requirements are very similar to those of conference proposals, proposals for a book ought to address a few other issues.
General considerations
Since these proposals are of greater length, the publisher will require you to delve into greater detail as well—for instance, regarding the organization of the proposed book or article.
Publishers generally require a clear outline of the chapters you are proposing and an explication of their content, which can be several pages long in its entirety.
You will need to incorporate knowledge of relevant literature, use headings and sub-headings that you should not use in conference proposals. Be sure to know who wrote what about your topic and area of interest, even if you are proposing a less scholarly project.
Publishers prefer depth rather than width when it comes to your topic, so you should be as focused as possible and further outline your intended audience.
You should always include information regarding your proposed deadlines for the project and how you will execute this plan, especially in the sciences. Potential investors or publishers need to know that you have a clear and efficient plan to accomplish your proposed goals. Depending on the subject area, this information can also include a proposed budget, materials or machines required to execute this project, and information about its industrial application.
Pre-writing strategies
As John Boswell (cited in: Larsen, Michael. How to Write a Book Proposal. Writers Digest Books , 2004. p. 1) explains, “today fully 90 percent of all nonfiction books sold to trade publishers are acquired on the basis of a proposal alone.” Therefore, editors and agents generally do not accept completed manuscripts for publication, as these “cannot (be) put into the usual channels for making a sale”, since they “lack answers to questions of marketing, competition, and production.” (Lyon, Elizabeth. Nonfiction Book Proposals Anybody Can Write . Perigee Trade, 2002. pp. 6-7.)
In contrast to conference or, to a lesser degree, chapter proposals, a book proposal introduces your qualifications for writing it and compares your work to what others have done or failed to address in the past.
As a result, you should test the idea with your networks and, if possible, acquire other people’s proposals that discuss similar issues or have a similar format before submitting your proposal. Prior to your submission, it is recommended that you write at least part of the manuscript in addition to checking the competition and reading all about the topic.
The following is a list of questions to ask yourself before committing to a book project, but should in no way deter you from taking on a challenging project (adapted from Lyon 27). Depending on your field of study, some of these might be more relevant to you than others, but nonetheless useful to reiterate and pose to yourself.
- Do you have sufficient enthusiasm for a project that may span years?
- Will publication of your book satisfy your long-term career goals?
- Do you have enough material for such a long project and do you have the background knowledge and qualifications required for it?
- Is your book idea better than or different from other books on the subject? Does the idea spark enthusiasm not just in yourself but others in your field, friends, or prospective readers?
- Are you willing to acquire any lacking skills, such as, writing style, specific terminology and knowledge on that field for this project? Will it fit into your career and life at the time or will you not have the time to engage in such extensive research?
Essential elements of a book proposal
Your book proposal should include the following elements:
- Your proposal requires the consideration of the timing and potential for sale as well as its potential for subsidiary rights.
- It needs to include an outline of approximately one paragraph to one page of prose (Larsen 6) as well as one sample chapter to showcase the style and quality of your writing.
- You should also include the resources you need for the completion of the book and a biographical statement (“About the Author”).
- Your proposal must contain your credentials and expertise, preferably from previous publications on similar issues.
- A book proposal also provides you with the opportunity to include information such as a mission statement, a foreword by another authority, or special features—for instance, humor, anecdotes, illustrations, sidebars, etc.
- You must assess your ability to promote the book and know the market that you target in all its statistics.
The following proposal structure, as outlined by Peter E. Dunn for thesis and fellowship proposals, provides a useful guide to composing such a long proposal (Dunn, Peter E. “Proposal Writing.” Center for Instructional Excellence, Purdue University, 2007):
- Literature Review
- Identification of Problem
- Statement of Objectives
- Rationale and Significance
- Methods and Timeline
- Literature Cited
Most proposals for manuscripts range from thirty to fifty pages and, apart from the subject hook, book information (length, title, selling handle), markets for your book, and the section about the author, all the other sections are optional. Always anticipate and answer as many questions by editors as possible, however.
Finally, include the best chapter possible to represent your book's focus and style. Until an agent or editor advises you to do otherwise, follow your book proposal exactly without including something that you might not want to be part of the book or improvise on possible expected recommendations.
Publishers expect to acquire the book's primary rights, so that they can sell it in an adapted or condensed form as well. Mentioning any subsidiary rights, such as translation opportunities, performance and merchandising rights, or first-serial rights, will add to the editor's interest in buying your book. It is enticing to publishers to mention your manuscript's potential to turn into a series of books, although they might still hesitate to buy it right away—at least until the first one has been a successful endeavor.
The sample chapter
Since editors generally expect to see about one-tenth of a book, your sample chapter's length should reflect that in these building blocks of your book. The chapter should reflect your excitement and the freshness of the idea as well as surprise editors, but do not submit part of one or more chapters. Always send a chapter unless your credentials are impeccable due to prior publications on the subject. Do not repeat information in the sample chapter that will be covered by preceding or following ones, as the outline should be designed in such a way as to enable editors to understand the context already.
How to make your proposal stand out
Depending on the subject of your book, it is advisable to include illustrations that exemplify your vision of the book and can be included in the sample chapter. While these can make the book more expensive, it also increases the salability of the project. Further, you might consider including outstanding samples of your published work, such as clips from periodicals, if they are well-respected in the field. Thirdly, cover art can give your potential publisher a feel for your book and its marketability, especially if your topic is creative or related to the arts.
In addition, professionally formatting your materials will give you an edge over sloppy proposals. Proofread the materials carefully, use consistent and carefully organized fonts, spacing, etc., and submit your proposal without staples; rather, submit it in a neat portfolio that allows easy access and reassembling. However, check the submission guidelines first, as most proposals are submitted digitally. Finally, you should try to surprise editors and attract their attention. Your hook, however, should be imaginative but inexpensive (you do not want to bribe them, after all). Make sure your hook draws the editors to your book proposal immediately (Adapted from Larsen 154-60).
- PRO Courses Guides New Tech Help Pro Expert Videos About wikiHow Pro Upgrade Sign In
- EDIT Edit this Article
- EXPLORE Tech Help Pro About Us Random Article Quizzes Request a New Article Community Dashboard This Or That Game Popular Categories Arts and Entertainment Artwork Books Movies Computers and Electronics Computers Phone Skills Technology Hacks Health Men's Health Mental Health Women's Health Relationships Dating Love Relationship Issues Hobbies and Crafts Crafts Drawing Games Education & Communication Communication Skills Personal Development Studying Personal Care and Style Fashion Hair Care Personal Hygiene Youth Personal Care School Stuff Dating All Categories Arts and Entertainment Finance and Business Home and Garden Relationship Quizzes Cars & Other Vehicles Food and Entertaining Personal Care and Style Sports and Fitness Computers and Electronics Health Pets and Animals Travel Education & Communication Hobbies and Crafts Philosophy and Religion Work World Family Life Holidays and Traditions Relationships Youth
- Browse Articles
- Learn Something New
- Quizzes Hot
- This Or That Game New
- Train Your Brain
- Explore More
- Support wikiHow
- About wikiHow
- Log in / Sign up
- Education and Communications
- Journal Writing
How to Write a Journal Entry
Last Updated: February 21, 2024 Fact Checked
This article was co-authored by Nicolette Tura, MA and by wikiHow staff writer, Danielle Blinka, MA, MPA . Nicolette Tura is an Empowerment Expert based in the San Francisco Bay Area. She holds a decade of experience creating change in various non-profits then went on to operate her own wellness business for 10 years. Most recently, she worked as a Therapy Associate to a chiropractic neurologist for 15 months working hands-on with patients, helping them heal from neurological disorders like concussions, long covid, migraines, and more. Nicolette guides groups and individuals on transformative meditation journeys and game-changing mindset management workshops and retreats on empowering everyone to keep expanding beyond past conditioning and self-limiting beliefs. Nicolette is a 500-hour Registered Yoga Teacher with a Psychology & Mindfulness Major, a NASM certified Corrective Exercise Specialist, and an expert in psychophysiology with experience in nervous system regulation and breath work. She holds a BA in Sociology from the University of California, Berkeley, and a Master’s degree is Sociology from San Jose State University There are 16 references cited in this article, which can be found at the bottom of the page. This article has been fact-checked, ensuring the accuracy of any cited facts and confirming the authority of its sources. This article has been viewed 2,834,830 times.
Keeping a journal allows you to record what’s happening in your life and to work through your thoughts and feelings. Sometimes, you might write a journal for school to help you deepen your understanding of what you’re studying. Fortunately, writing a journal entry is a simple process. First, choose a topic to write about, like what's happening in your life. Then, write an opening for your entry and express your thoughts.
Choosing a Topic

- This is a great way to help you document things you want to remember.
- For instance, you might write about something funny that happened at lunch, scoring the winning goal in a soccer game, or a fight you had with your friend. The events can be positive or negative.

- Let’s say you’re feeling sad because you’re going through a breakup. You could write about how you feel and what you’ll miss about the relationship. This will help you release your feelings so you can start to feel better .

- Write about what you’d like to do this weekend.
- Discuss a place you’d like to visit.
- Pretend that you found a fantasy creature.
- Write about something you want to change.
- Write from the perspective of your favourite book or movie character.

- A summary of a reading or lecture.
- Your analysis of the course material.
- Connections between topics you’ve studied.
- Personal connections you made with the coursework.
- Questions you have about the text or lecture.
Tip: Keep a journal for school focused on studying and analyzing your course material. For instance, you might summarize your coursework, record your reflections on it, and write down questions you have. Leave out how you feel about what you’re reading or studying.
Opening Your Journal Entry

- Your instructor has assigned journaling to help you deepen your understanding of your coursework and to improve your writing skills . Following their instructions will help you best achieve these goals.

- For instance, you might write, “July 24, 2019,” “07-24-19,” or “24 July 2019.”

- For instance, you might write “Good Beans Coffee House,” “School,” “Paris,” or “My bedroom” for your location. For the time, you could write the actual time, such as “12:25 p.m.,” or the time of day, like “Early morning.”

Tip: You usually don’t include a salutation when you’re writing a journal for school.
Expressing Yourself in a Personal Journal

- If mistakes really bother you, it’s okay to go back and correct them after you finish writing your journal entry.

- Turn a memory into a story.
- Record what you dreamed last night.
- Write a list, such as what you did that day or what you’re grateful for.
- Doodle or paste pictures into your journal.
- Record song lyrics or quotes that mean something to you.
- Write your own lyrics or a poem.
- Write in stream of consciousness.

- For instance, you’d write, “I went to lunch with Sari today,” not “Amy had lunch with Sari today.”

- For instance, let’s say you’re on vacation at the beach. You might include details like, “sea spray hitting my face,” “the smell of burning wood from bonfires on the beach,” “the taste of salt on my lips,” “the sun glinting off the surface of the water,” and “the shouts from other beach goers having fun.”

- With journaling, it’s more important to write often than to write a lot.
Drafting an Academic Journal Entry

- If you’re telling a story, try to follow a narrative structure to give it a beginning, middle, and end.
- Read over your journal entry before your submit it to check that it makes sense.

- For handwritten journals, your instructor may require that you simply fill up a page. Make sure you know the exact requirements so you can do your assignment correctly.
- If you’re struggling to think of something to write, make a mind map about the topic to help you brainstorm some new ideas.

- If you’re struggling with your grammar, visit your school’s writing center or ask your instructor about tutoring options. Additionally, you can find online programs that help you with grammar.

- This is especially important if you’re keeping your journal as a graded assignment.
- If you’re typing your journal entries in an online portal, there may be a spellcheck tool you can use. However, you should still proofread the entry to look for other errors.
Journal Entry Template

Community Q&A
- It’s best to write regularly so that journaling becomes a habit. To help you remember, write in your journal at the same time everyday. [19] X Research source Thanks Helpful 1 Not Helpful 0
- You can write about anything you want, so don’t feel like you can only write about how you feel. You might instead prefer to write about your daily accomplishments or what you enjoyed that day. Thanks Helpful 24 Not Helpful 4
- While you can use a paper journal, there are journaling apps and websites you can try. Additionally, it’s okay to use a word processor like Google Docs or Microsoft Word for journaling. Thanks Helpful 15 Not Helpful 8

- Since your journal is private, prevent people from reading it by keeping it in a safe place. If it’s a digital journal, you might even password protect it. Thanks Helpful 25 Not Helpful 3
You Might Also Like

- ↑ https://libguides.usc.edu/writingguide/title
- ↑ Nicolette Tura, MA. Empowerment Expert. Expert Interview. 23 January 2020.
- ↑ https://positivepsychology.com/benefits-of-journaling/
- ↑ https://www.readingrockets.org/article/journal-writing
- ↑ https://www.hamilton.edu/academics/centers/writing/writing-resources/journal-writing
- ↑ https://writing.wisc.edu/handbook/assignments/writing-an-abstract-for-your-research-paper/
- ↑ https://www.niu.edu/citl/resources/guides/instructional-guide/reflective-journals-and-learning-logs.shtml
- ↑ https://psychcentral.com/blog/ready-set-journal-64-journaling-prompts-for-self-discovery
- ↑ https://psychcentral.com/lib/the-health-benefits-of-journaling
- ↑ https://www.bates.edu/biology/files/2010/06/How-to-Write-Guide-v10-2014.pdf
- ↑ https://files.eric.ed.gov/fulltext/EJ1081806.pdf
- ↑ https://writing.wisc.edu/handbook/style/connectingideas/
- ↑ https://positivepsychology.com/writing-therapy/
- ↑ https://apastyle.apa.org/style-grammar-guidelines/capitalization
- ↑ https://libguides.usc.edu/writingguide/proofreading
- ↑ https://www.psychologytoday.com/us/blog/modern-minds/202301/10-good-reasons-to-keep-a-journal
About This Article

To write a journal entry, first find a quiet, comfortable spot where you won’t be disturbed. Take a moment to brainstorm what you want to write about. You can journal about anything, like your day, your dreams, work, school, friends, or an upcoming project. If you’re not sure, choose a writing prompt for your entry, like “What was your earliest childhood memory?” or “What is your biggest secret?” Open to a new page in your journal and write the date at the top. Then, start writing. Let your thoughts flow and don’t edit yourself. Write whatever comes to mind. It’s okay to be honest since nobody else will be reading what you write. Draw pictures if specific images come to mind while you’re writing. Try to journal for somewhere between 5 and 20 minutes every day. The more you journal, the easier it will become! Keep reading to learn how to write a journal entry for school! Did this summary help you? Yes No
- Send fan mail to authors
Reader Success Stories
Sep 1, 2017
Did this article help you?
Enolisa Tigga
Sep 8, 2016
Nesma Mansour
Apr 9, 2016
Jun 23, 2017
Apr 25, 2017

Featured Articles

Trending Articles

Watch Articles

- Terms of Use
- Privacy Policy
- Do Not Sell or Share My Info
- Not Selling Info
Get all the best how-tos!
Sign up for wikiHow's weekly email newsletter
Ultimate Guide to Writing Your College Essay
Tips for writing an effective college essay.
College admissions essays are an important part of your college application and gives you the chance to show colleges and universities your character and experiences. This guide will give you tips to write an effective college essay.
Want free help with your college essay?
UPchieve connects you with knowledgeable and friendly college advisors—online, 24/7, and completely free. Get 1:1 help brainstorming topics, outlining your essay, revising a draft, or editing grammar.
Writing a strong college admissions essay
Learn about the elements of a solid admissions essay.
Avoiding common admissions essay mistakes
Learn some of the most common mistakes made on college essays
Brainstorming tips for your college essay
Stuck on what to write your college essay about? Here are some exercises to help you get started.
How formal should the tone of your college essay be?
Learn how formal your college essay should be and get tips on how to bring out your natural voice.
Taking your college essay to the next level
Hear an admissions expert discuss the appropriate level of depth necessary in your college essay.
Student Stories
Student Story: Admissions essay about a formative experience
Get the perspective of a current college student on how he approached the admissions essay.
Student Story: Admissions essay about personal identity
Get the perspective of a current college student on how she approached the admissions essay.
Student Story: Admissions essay about community impact
Student story: admissions essay about a past mistake, how to write a college application essay, tips for writing an effective application essay, sample college essay 1 with feedback, sample college essay 2 with feedback.
This content is licensed by Khan Academy and is available for free at www.khanacademy.org.
Journaling For Mental Health: How To Do It Effectively To Improve Mood And Well-Being
Here's what the science says.

“Journaling can be a powerful way to organize your thoughts, feelings, and ideas, leading to increased self-awareness, self-discovery, and growth,” says Jaci Witmer Lopez, PsyD, a licensed clinical psychologist based in New York City. “In my practice, I've seen firsthand how regular journaling can transform lives.”
Maybe you've kept a fitness journal in the past to help you stay on track toward your wellness goals, or you currently have a gratitude journal to stay grounded. There are travel journals to help you document your adventures, and if you’re less artistically inclined, there are even journaling apps to help you stay mindful on the go. Below, experts share the benefits of journaling for mental health, how to start one yourself, and specific writing prompts for inspiration.
Meet the experts: Jaci Witmer Lopez, PsyD , is a clinical psychologist based in New York City. Marc Campbell, LMHC , is a licensed therapist based in Orlando, Florida, and the author of I Love My Queer Kid .
Common Benefits Of Journaling
Apart from having a dedicated place for juicy diary entries, there are several general benefits of journaling. The practice has been shown to help people process stressful events, according to a study published in Annals of Behavioral Medicine . In another study about college students, researchers found that journaling may improve self-efficacy —in other words, it can help you believe in yourself. Writing has even been studied as a behavioral intervention for children—so if you have kiddos at home, encouraging them to write may not be such a bad idea.
Common benefits of journaling include:
- Finding inspiration
- Creative expression
- Tracking your goals
- Fun freewriting
- General reflection
- Brainstorming ideas
5 Mental Health Benefits Of Journaling
Apart from its general benefits, here's how journaling can impact your mental health, specifically, according to experts.
1. It can help you process (and learn from) your emotions.
“Remembering the events from your day—both the ups and the downs—can help your brain practice processing and regulating your emotions,” says Marc Campbell, LMHC, a licensed therapist based in Orlando, Florida. For instance, if you’re feeling rejected from a recent breakup or you're burned out at work, writing about how you feel and reading it back to yourself can help you process the difficult emotions. Journaling can also help you recognize certain patterns, practice more acceptance, and have more empathy for yourself, Campbell says.
2. It can help you heal from traumatic events.
Journaling can significantly impact your ability to process and heal from trauma, Lopez says. “ Research has shown that writing can reduce symptoms of depression, anxiety, and post-traumatic stress disorder (PTSD),” she says. “When you write things down as opposed to just thinking about them, you hold yourself accountable to reframing or changing your narrative.” Although the mental health effects of trauma won’t disappear by simply writing down how you feel, journaling can be a helpful practice in addition to seeking therapy and trauma treatment .
3. It may help you manage anxiety and depression.
Anxiety and depression are among the most commonly cited mental health struggles in America, per the American Psychological Association (APA). And although having a writing practice won't cure these conditions overnight, journaling may have the potential to decrease depression and anxiety and improve resilience over time, according to a recent study . Plus, if you’re struggling to find meaning in everyday life or you feel generally disengaged—both of which are common experiences when facing mental health challenges— some studies suggest that journaling may help.
4. It can help you track your therapy progress.
If you're seeing a therapist right now, journaling can help you check in with yourself daily or weekly about how it’s going—or even help you hold yourself accountable for certain behaviors you’d like to change, Campbell says. “Through the process of journaling, you can reflect on past entries and potentially learn about any patterns you have,” he says.
You can also use a journal to reflect on what, exactly you speak about during your therapy sessions and begin to process how you’re feeling about it, Lopez adds. An added benefit? One day, you can look back at your journal and celebrate how far you've come.
5. It can help you practice self-compassion.
Whether you're dealing with a specific mental health issue or you're simply feeling overwhelmed, negative self-talk, shame, and embarrassment are common. It can be difficult to be kind to yourself, however, practicing self-compassion can go a long way, experts say. A recent study in the American Journal of Speech-Language Pathology found that daily journaling as a mindfulness practice led to increased levels of self-compassion, and another study on registered nurses found that journaling can boost compassion and help manage burnout.
How To Start Journaling For Mental Health
If you aren't someone who spilled your heart out in a childhood diary, don't worry—journaling can be as simple as jotting things down on your phone, in a notebook, or responding to a specific prompt to get inspiration (more on that soon).
There’s no “right” or “wrong” way to journal, but it should be a personal process, Campbell says. “I recommend starting journaling in the way that feels most authentic to you. If you prefer pen and paper, start with that. If you prefer typing things out in your notes app, that works, too. If you aren’t sure, try both and more—a laptop or even typewriter if you’re feeling adventurous,” he says. Also, writing for mental health is personal, but you shouldn't feel pressured to document your whole life story all at once (unless you want to).
Whether you incorporate journaling into your morning routine or you attempt five minutes before bedtime to free-write, experts recommend starting slow. “If you're new to journaling, my advice is to start small and be patient with yourself. Set aside just a few minutes a day to begin with, and gradually increase the time as you build the habit. It’s important to find a method that you'll stick with consistently," Lopez says. Try to pace yourself and make the practice as manageable as possible so that it becomes a habit formed over time, she adds.
10 Journal Prompts For Mental Health
- What was the highlight of my day?
- What was a lot moment of my day?
- What's a challenge I'm facing right now?
- What people, places, or things am I grateful for and why?
- Who is someone that's inspired me lately and why?
- What are three things I'm proud of myself for, and why?
- What is a small act of kindness I can do for myself this week?
- What is one limiting belief I have about myself? (And is there a way I can begin to reframe it)?
- Describe something you are struggling with. Then, read it from the perspective of someone you care about. What would they have to say about it?
- If I could change an aspect of my mental health and well-being right now, what would it be and why?
When it comes to journaling for mental health, consistency is key. Whatever method, prompt, or format you choose, your mental health will thank you.
Best Journals For Mental Health

The Five Minute Journal
Looking for a simple, sleek journal that will help you practice more mindfulness and gratitude? This popular option might be a good fit for you. It encourages you to cultivate a sense of calm for just five minutes a day, but there are plenty of helpful tools packed into the journal itself—like prompts, daily highlights, weekly challenges, affirmations, and more. If you're brand new to journaling for mental health, this one provides clear cues and outlines to help you self-reflect and feel more confident. Plus, it's aesthetically pleasing. What could be better?

The Big Feelings Survival Guide
This colorful, activity-filled workbook by licensed art therapist Alyse Ruriani, LPC, is a great option if you're ready to dive into mental health in a fun, accessible, yet meaningful way. The workbook includes practical and creative activities that are all rooted in dialectical behavior therapy (DBT), which, ICYMI, is a revolutionary treatment that helps people move through emotions. Not only will you gain major insight about your mental health journey, but the workbook itself is super bright and engaging—the helpful illustrations and eye-opening exercises are sure to help you reflect and gain inspiration.

Self-Love Workbook for Women
This self-love workbook by therapist Megan Logan, LCSW, is uniquely designed to help you release self-doubt and have more self-compassion. The journal includes quizzes, writing prompts, and fun activities to help you cultivate more self-love, like writing a message to your younger self and making a "happy playlist." You'll also find empowering affirmations for those days when your mental health isn't so good—plus, the journal provides helpful resources for goal-tracking, identifying emotions, and embracing who you are.

90-Day Mental Health Journal
This easy-to-follow journal encourages you to care for your mental health in a holistic way. If you're dealing with stress, anxiety, or uncertainty about the future, the journal claims to help you self-reflect and gain self-awareness while focusing on the power of the present moment. This journal is ideal for anyone who wants to breathe, reconnect with themselves, and cultivate more mindfulness. It comes with grounding activities and daily check-ins to help you keep track of your emotions—and understand their roots.
Lexi Inks (she/her) is a lifestyle journalist based in Jacksonville, Florida. She has reported on countless topics, including sexual wellness, astrology, relationship issues, non-monogamy, mental health, pop culture, and more. In addition to Women’s Health, her work has been published on Bustle, Cosmopolitan, Well + Good, Byrdie, Popsugar, and others. As a queer and plus-size woman with living with mental illness, Lexi strives for intersectionality and representation in all of her writing. She holds a BFA in Musical Theatre from Jacksonville University, which she has chosen to make everyone’s problem.
Mental Health

20 Best Guided Journals For Your Wellness Journey

‘I Had SCAD As A Healthy, Fit 36-Year-Old Woman’

'How I Trained For An Ironman With Parkinson's'

WNBA's Diamond DeShields Reflects On Spinal Tumor

'I Did 7 Marathons In 7 Days With Type 1 Diabetes'

'Ultra-Running Helps Me Cope With Lupus Symptoms'

‘What It's Like To Be A Dancer With Hearing Loss’
'How I Progressed To Deadlift 375 Pounds'

What Is Anticipatory Grief?

What Is Body Neutrality, Exactly? Experts Weigh In

Why Don’t We Prescribe Exercise For Mental Health?

IMAGES
VIDEO
COMMENTS
Basics of Journal Entries. Both in traditional and online classrooms, journal entries are used as tools for student reflection. By consciously thinking about and comparing issues, life experiences, and course readings, students are better able to understand links between theory and practice and to generate justifiable, well-supported opinions.
Abstract. The purpose of your abstract is to express the key points of your research, clearly and concisely. An abstract must always be well considered, as it is the primary element of your work that readers will come across. An abstract should be a short paragraph (around 300 words) that summarizes the findings of your journal article.
tutorial. That said, writing conventions vary widely across countries, cultures, and even disciplines. For example, although the hourglass model introduces the most important point right from the beginning as a guide to the rest of the paper, some traditions build the argument gradually and deliver the main idea as a punchline.
Choose a research paper topic. Conduct preliminary research. Develop a thesis statement. Create a research paper outline. Write a first draft of the research paper. Write the introduction. Write a compelling body of text. Write the conclusion. The second draft.
This article provides an overview of writing for publication in peer-reviewed journals. While the main focus is on writing a research article, it also provides guidance on factors influencing journal selection, including journal scope, intended audience for the findings, open access requirements, and journal citation metrics.
9) Be persistent, thick-skinned and resilient. These are qualities that you may develop over time - or you may already have them. It may be easier to develop them in discussion with others who ...
Double-space the whole title page. Place the paper title three or four lines down from the top of the page. Add an extra double-spaced blank like between the paper title and the byline. Then, list the other title page elements on separate lines, without extra lines in between.
The introduction section should be approximately three to five paragraphs in length. Look at examples from your target journal to decide the appropriate length. This section should include the elements shown in Fig. 1. Begin with a general context, narrowing to the specific focus of the paper.
So, please pick up a pen and start making notes for writing your research paper. Step 1. Choose the right research topic. Although it is important to be passionate and curious about your research article topic, it is not enough. Sometimes the sheer excitement of having an idea may take away your ability to focus on and question the novelty ...
A clear format will ensure that your research paper is understood by your readers. Follow: 1. Context — your introduction. 2. Content — your results. 3. Conclusion — your discussion. Plan ...
academic writing skills. Target a Specific Journal Sometimes people write a paper and then look for a home for it. Authors can save time by deciding on a target journal first, then writing the article to suit that journal. Become familiar with the focus and content of the target journal and its typical readers. Everything in
Abstract. Writing an effective manuscript is one of the pivotal steps in the successful closure of the research project, and getting it published in a peer-reviewed and indexed journal adds to the academic profile of a researcher. Writing and publishing a scientific paper is a tough task that researchers and academicians must endure in staying ...
Watch on. In this video, Kathleen Adams, Founder of the Center for Journal Therapy, shares what she likes about using short lists as a journaling technique. 7. Alphapoem. Write the alphabet, A-Z, or any collection of letters, vertically down the side of a page. Then write a poem in which each successive line begins with the next letter.
- The Writing Process: These features show all the steps taken to write a paper, allowing you to follow it from initial idea to published article. - Into the Essay: Excerpts from actual papers show the ideas from the chapters in action because you learn to write best by getting examples rather than instructions. Much of my approach to ...
Start Here. Simply put, writing a college paper is about picking a topic or position, researching it, and sharing what you've learned in an academic format. A paper often has you making an argument - your thesis - and explaning why you have picked that position. You do this by tying your thoughts together with the words and ideas of multiple ...
The Sections of the Paper. Most journal-style scientific papers are subdivided into the following sections: Title , Authors and Affiliation , Abstract, Introduction , Methods, Results, Discussion , Acknowledgments, and Literature Cited , which parallel the experimental process. This is the system we will use.
How to format your research paper. Go to Taylor & Francis Online and search for the title of your chosen journal using the search bar. Select the relevant journal and click on the instructions for authors tab. Read your target journal's instructions for authors, and find out about its formatting guidelines. Below are a list of Word templates ...
Common Goals of a Journal. To encourage regular writing. To make connections between class material, lectures, and personal observations. To raise questions and issues that can fuel classroom discussions. To generate ideas for future paper topics. To provide a forum for inquiry, analysis, and evaluation of ideas.
Definition and Purpose of Abstracts An abstract is a short summary of your (published or unpublished) research paper, usually about a paragraph (c. 6-7 sentences, 150-250 words) long. A well-written abstract serves multiple purposes: an abstract lets readers get the gist or essence of your paper or article quickly, in order to decide whether to….
But I will give you some tips to help you get started on a journaling practice. 1. Choose your kind of journal. You have several options for how to keep your journal. A book, where you write with a pen or pencil onto paper: Write in a book that is not so pretty you are afraid to write in it.
An important part of the work completed in academia is sharing our scholarship with others. Such communication takes place when we present at scholarly conferences, publish in peer-reviewed journals, and publish in books. This OWL resource addresses the steps in writing for a variety of academic proposals. For samples of academic proposals ...
2. Start your first entry by setting the scene. To begin writing in your journal, label your first entry with the date, time and, optionally, location. For instance, you might start with "Monday, January 1, 1.00p.m., Bedroom". Next, if you'd like to, write a salutation.
1. Organize your thoughts to make them coherent. A journal entry doesn't need to be as organized as an essay, even if it's for school. However, it should be possible to follow your train of thought. Use complete sentences to express your thoughts, and start a new paragraph when you switch to a new idea. [15]
Sample College Essay 2 with Feedback. This content is licensed by Khan Academy and is available for free at www.khanacademy.org. College essays are an important part of your college application and give you the chance to show colleges and universities your personality. This guide will give you tips on how to write an effective college essay.
You will have a maximum number of words, so the secret is not to try to cover everything in your essay. Create a plan before you actually start writing, organize your essay in three parts (introduction, body and conclusion), and decide on the main ideas you want to express. 7. Ask someone to proofread your work.
Apart from its general benefits, here's how journaling can impact your mental health, specifically, according to experts. 1. It can help you process (and learn from) your emotions. "Remembering ...