
Essay On Young Generation And Technology
The younger generation and technology Technology has become an inseparable part of the social, working and leisure life of people. Communication via emails, using multi-media sites, searching information or internet shopping are part of the daily routine in a high percentage of homes. Until a few years ago, analysis on the use of these devices was focused on adult users. However, this tendency has changed in recent times and child and youth audience begins to play a major role, especially in social networking, the most popular activity online. Is the young society getting worse as technology takes over the world? In little more than five years, this age group has become dominant, as more than thirty per cent of internet users are up to twenty years old. More than 75% of all teenagers have a mobile phone , used mainly to take and share pictures, …show more content…
Teens may also become obsessed with the Internet, looking at their mobile phones every few minutes to check new statuses, messages or notifications. This addiction can interfere with responsibilities, like chores and homework. Furthermore, health-related issues can be developed, including obesity, vision disorders, insomnia or side effects of harmful radiations of smartphones. These are some of the negative effects of the internet on youth proven by scientific investigations. These issues with technology are the deductible ones, which are easily identifiable; but could there be some side effects of these network connections still unknown to the humanity? Possibly there are, and the biggest concern is we do not know their consequences. The previous generation did not have the access to gadgets as the younger generation has, whose development is greatly affected by digitalisation in today’s world. Information on all topics circulates around the Internet and it is accessible to everyone. False information is spread online in terms of seconds, influencing negatively young people who are in process of development and
Fahrenheit 451 Technology Quotes
There is really no limit to the things that can be done on a smartphone. Yet, with all this information streaming through our population’s mind, no knowledge or substance is gained. The likelihood that a teenager would pick up a book or go outside when they could instantly be absorbed in their phone is doubtful, even though this is often the less mentally and physically fulfilling option. With phones always at our fingertips, society is becoming increasingly immersed in technology and media,
Have Smartphones Destroyed A Generation: Article Analysis
Behavioral changes from one generation to the next naturally occur little by little. Nonetheless, changes in adolescent behavior from the millennial generation triumphing it have been substantial and revolutionary. Today’s teens have never witnessed a world without internet. The majority of them possess smartphones and waste several hours each week on social media. But while numerous parents may feel allayed about their teens’ seeming uninterested in drinking, driving and dating, they could perhaps be overlooking the effects that continuous internet access has on their teens’ mental well-being.
Analysis Of Kristin Lewis 'Your Phone Could Ruin Your Life'
Kristin Lewis, the author of "Your Phone Could Ruin Your Life", believes that smartphones do more harm than good. First off, one piece of evidence is that the author writes "58% of pedestrian deaths are kids under 19. Experts believe these tragedies are mainly due to digital distraction. " This means that when crossing streets many people are looking at their phones and not checking the road like they should. Also, another piece of evidence is in the article the author said, "80% of teenagers sleep with their phone nearby.
Henig's 'What Is It About 20-Somethings'
Some of the negative results of the increasing use of social media are a greater change of friend groups and acquaintances, increased awareness of the livelihood of our fellow peers, and more exposure to the world around us. With all these results, it is easy to see why young adults continue to become distant and flexible later on in their lives than those of previous generations. One of the most prominent consequences of the continued use of social media is the increase in average age of
Summary: The Influence Of Technology On Teenagers
Technology has been expeditiously changing over previous generations. Those born between 1946 - 1964 are classified as Baby Boomers, and from 1995 - 2012 are catergorised as Generation Z. Over the years, youths become more connected to their mobile phones and given up and lost real connections and relationships? The behaviour standards and the influence from Baby Boomers has significantly altered towards the youths over the past decades. Generation Z has an overall population of 82 million worldwide, with the oldest turning 23 and the youngest turning 6 (Robinson, 2018). As part of the research, Shane Lynch was interviewed from the Generation Baby Boomers.
The Effects Of Movies And TV Shows On Teenagers
Do you think movies and TV shows influence teenagers? Nowadays, people spend time watching movies and TV shows more than setting all together having launch. People’s behavior including teenagers the most spend a lot of time on social media and this can change their behavior due to the things that they see. The media in general has a huge impact in our society on teenagers.
How Social Media Affect Teenagers
Since social media came around , there’s have been a decrease in real-life conversations , More people are building a relationship online and drifting away from the real world. It's starting to cause a lack of face to face communication. Teenagers don't even pay attention to the outside world or their surroundings when they’re on their phones. You get easily distracted when you are on your phone. Also technology causes you to miss out on your sleep and losing sleep have negative effects on your brain.
Technology Synthesis Essay
Nowadays, technology devices become plays an important role in our daily lives, especially in adolescents’ categories. While there is a very clear argument for how the technology is effected on us and causing social isolation as we know, but in another way is also the argument that these technologies are helping us to become more social in our society. This is very probably because we have a good and perfect ability to communicate with each other. Despite long distances. We all know that the goal of technology is to make our lives easier and more efficient.
The Positive And Negative Effects Of Technology On Teens
Literature Review There are various studies that shows the effects of the use of technology on teenagers. Several studies show the positive effects of the technological gadgets and services. Other studies reveal the negative effects of these technological products. Some of the studies have found both positive and negative effects of technology on teenagers. Positive Effects of Technology
Argumentative Essay On Cell Phones
Cell Phones: The average teenager who gets on their phone, just for a second, each hour has the same mind as a 30 year old cocaine addict. Teens have their minds tricked into thinking they can’t live without their cell phones and social media. Teens need to be able to talk to and connect with others and learn face-to-face communication skills. Nowadays teens can get harmed very easily, and teens do not really know who is on the other side of the screen. Studies have shown that phones can ruin lives with the blink of an eye.
Social Media And Social Depression
As the technology era change over time, the social media becomes an important part of our life. We use social media to connect with friends and family, also to found out the latest news or fashion trends. Especially after the great success of Facebook, many other social media follow along such as Snapchat and Instagram. Numerous young age children gradually sink into the virtual world of Social Media. According to the Pew Research Center survey, that majority of Americans use Facebook and YouTube, but young adults are especially heavy users of Snapchat and Instagram.
Smartphone Addiction Research Paper
Smartphone is one of the best invention in twenty first century. Smartphone is an all-in device that provide functionality of other device such as calculator, torch light, media player and camera. According to Pei and Lionel (2006), unspecific promoting planner had started to use the term smartphone to bring up new type of cell phone that can enable information access and use computing power to process. Smartphone allow us to contract with people, access information and make transaction within our finger tips. Although smartphone is convenient to us but the overuse of smartphone can lead to smartphone addiction.
Argumentative Essay On Social Media Advantages And Disadvantages
Imagine that 20 years ago the only way to stay in touch with a person was to mail a letter. In a modern world with the invention of social media, people can converse with someone using the internet and get a response within seconds. Although in the course of time all generations have started to take advantage of the novations that social media has brought about, teenagers and young adults are the most active users of these networks. According to numerous research studies in the area of online social networks, it has been shown that such sites are impacting the lives of the youth significantly. Understandably, there are a lot of different opinions about its positive and negative influence.
Technology Essay: How Technology Affects Our Lives
We depend too much on technology. There is no doubt about it. Many places of work are at a loss if their internet connection stops working. Many businesses and institutions are left high and dry if the internet or computer crashes. Every bit of information regarding business is entered into the computer.
Excessive Use Of Social Media
In the fast developing contemporary world, it seems to be that people cannot spend a day without social media, despite the fact of its numerous negative effects. The vulnerable teenagers should limit the use of social media by spending less time on the Internet as it can cause a number of negative consequences: it can lead to health as well as social problems. Proponents, however, argue that social media changed lives to the better as it made communication easier and faster and there are no negative effects from social media. They might also say it is impossible to withdraw from the Internet at all. This may be true and their argument is valid, nevertheless, all the negative impacts on one’s physical as well as mental health and social life outweigh the mentioned advantages.
More about Essay On Young Generation And Technology
Related topics.
- Mobile phone
- Social network service
- Communication
- Entertainment
- Environment
- Information Science and Technology
- Social Issues
Home Essay Samples Information Science and Technology Modern Technology
Modern Technology and the Younger Generation
Table of contents, introduction, empowered learning through technology, changing social dynamics, impact on mental health, cultivating digital literacy and skills, challenges in digital citizenship, fostering creativity and innovation, works cited.
*minimum deadline
Cite this Essay
To export a reference to this article please select a referencing style below

- Children and Technology
- Virtual Reality
- Impact of Video Games
- Network Security
- Cloud Computing
Related Essays
Need writing help?
You can always rely on us no matter what type of paper you need
*No hidden charges
100% Unique Essays
Absolutely Confidential
Money Back Guarantee
By clicking “Send Essay”, you agree to our Terms of service and Privacy statement. We will occasionally send you account related emails
You can also get a UNIQUE essay on this or any other topic
Thank you! We’ll contact you as soon as possible.

25,000+ students realised their study abroad dream with us. Take the first step today
Meet top uk universities from the comfort of your home, here’s your new year gift, one app for all your, study abroad needs, start your journey, track your progress, grow with the community and so much more.

Verification Code
An OTP has been sent to your registered mobile no. Please verify

Thanks for your comment !
Our team will review it before it's shown to our readers.

- School Education /
Essay on Information Technology in 400 Words
- Updated on
- Dec 2, 2023

Essay on Information Technology: Information Technology is the study of computer systems and telecommunications for storing, retrieving, and transmitting information using the Internet. Today, we rely on information technology to collect and transfer data from and on the internet. Say goodbye to the conventional lifestyle and hello to the realm of augmented reality (AR) and virtual reality (VR).
Check out all the latest updates on all board exams 2024
Also Read: Essay on Internet
Scientific discoveries have given birth to Information Technology (IT), which has revolutionized our way of living. Sudden developments in technology have given a boost to IT growth, which has changed the entire world. Students are taught online using smartboards, virtual meetings are conducted between countries to enhance diplomatic ties, online surveys are done to spread social awareness, e-commerce platforms are used for online shopping, etc.
Information Technology has made sharing and collecting information at our fingertips easier. We can learn new things with just a click. IT tools have enhanced global communication, through which we can foster economic cooperation and innovation. Almost every business in the world relies on Information Technology for growth and development. The addiction to information technology is thriving throughout the world.
Also Read: Essay on 5G Technology
- Everyday activities like texting, calling, and video chatting have made communication more efficient.
- E-commerce platforms like Amazon and Flipkart have become a source of online shopping.
- E-learning platforms have made education more accessible.
- The global economy has significantly improved.
- The healthcare sector has revolutionized with the introduction of Electronic Health Records (EHR) and telemedicine.
- Local businesses have expanded into global businesses.
- Access to any information on the internet in real-time.
Also Read: Essay on Mobile Phone
Disadvantages
Apart from the above-mentioned advantages of Information Technology, there are some disadvantages also.
- Cybersecurity and data breaches are one of the most important issues.
- There is a digital divide in people having access to information technology.
- Our over-relying attitude towards the IT sector makes us vulnerable to technical glitches, system failures and cyber-attacks.
- Excessive use of electronic devices and exposure to screens contribute to health issues.
- Short lifecycles of electronic devices due to rapid changes in technological developments.
- Challenges like copyright infringement and intellectual property will rise because of ease in digital reproduction and distribution.
- Our traditional ways of entertainment have been transformed by online streaming platforms, where we can watch movies and play games online.
The modern world heavily relies on information technology. Indeed, it has fundamentally reshaped our way of living and working, but, we also need to strike a balance between its use and overuse. We must pay attention to the challenges it brings for a sustainable and equitable society.
Also Read: Essay on Technology
Paragraph on Information Technology
Also Read: Essay on Wonder of Science
Ans: Information technology is an indispensable part of our lives and has revolutionized the way we connect, work, and live. The IT sector involves the use of computers and electronic gadgets to store, transmit, and retrieve data. In recent year, there has been some rapid changes in the IT sector, which has transformed the world into a global village, where information can be exchanged in real-time across vast distances.
Ans: The IT sector is one of the fastest-growing sectors in the world. The IT sector includes IT services, e-commerce, the Internet, Software, and Hardware products. IT sector helps boost productivity and efficiency. Computer applications and digital systems have allowed people to perform multiple tasks at a faster rate. IT sector creates new opportunities for everyone; businesses, professionals, and consumers.
Ans: There are four basic concepts of the IT sector: Information security, business software development, computer technical support, and database and network management.
Related Articles
For more information on such interesting topics, visit our essay writing page and follow Leverage Edu .
Shiva Tyagi
With an experience of over a year, I've developed a passion for writing blogs on wide range of topics. I am mostly inspired from topics related to social and environmental fields, where you come up with a positive outcome.
Leave a Reply Cancel reply
Save my name, email, and website in this browser for the next time I comment.
Contact no. *

Connect With Us

25,000+ students realised their study abroad dream with us. Take the first step today.

Resend OTP in

Need help with?
Study abroad.
UK, Canada, US & More
IELTS, GRE, GMAT & More
Scholarship, Loans & Forex
Country Preference
New Zealand
Which English test are you planning to take?
Which academic test are you planning to take.
Not Sure yet
When are you planning to take the exam?
Already booked my exam slot
Within 2 Months
Want to learn about the test
Which Degree do you wish to pursue?
When do you want to start studying abroad.
January 2024
September 2024
What is your budget to study abroad?

How would you describe this article ?
Please rate this article
We would like to hear more.
Have something on your mind?

Make your study abroad dream a reality in January 2022 with
India's Biggest Virtual University Fair

Essex Direct Admission Day
Why attend .

Don't Miss Out
The Importance of Technological Change in Shaping Generational Perspectives
If we name each generation based on the technological conditions it experienced, generations may soon encompass only a few years apiece.

“There are a number of labels to describe the young people currently studying at school, college and university,” Ellen John Helsper and Rebecca Evnon wrote in a 2010 article in the British Educational Research Journal . “They include the digital natives, the net generation, the Google generation or the millenials. All of these terms are being used to highlight the significance and importance of new technologies within the lives of young people.”

What seemed noteworthy a decade ago is now commonplace: Slicing the population into ever-narrower generations, each defined by its very specific relationship to technology, is fundamental to how we think about the relationship between age, culture, and technology.
But generation gaps did not begin with the invention of the microchip. What’s new is the fine-slicing of generational divides, the centrality of technology to defining each successive generation. Both of these developments rest on a remarkably intellectual innovation: the idea of generations as socially significant categories.
As Marius Hentea points out in his article “ The Problem of Literary Generations :” “[t]he sociological meaning of ‘generation’ is a post-Enlightenment development.” We’ve moved from a view of generations as biological “in the sense of the generation of a butterfly from a caterpillar,” as Hentea puts it, to a view of generations as sociological. Hentea argues that three nineteenth-century developments were responsible for this emergent concept of generational divides, the first of which was democratization :
By no longer limiting political power to a defined group but rather encouraging political participation across social strata, democracy eased youth into public life in a way other regimes had proven incapable of doing. At the same time, democratization paradoxically created generational categories. With aristocratic privileges abolished and republican duties diminished, the generation provided a fallback for social belonging: not everyone can belong to my generation, so the vestigial desire for distinction is satisfied, but at the same time, no one remains without a generation, so the democratic impulse toward equality is met.
Another important factor was centralization : “the spectacular rise of the bureaucratic state and its disciplinary instruments of control and categorization.” Last but not least, Hentea notes, was the role of technologization :
As technology advanced ever more quickly in the nineteenth century, differentiation based on age became even more important: the young had at their disposal tools their elders did not. The concentration of rapid technological change in urban centers led to youth gaining economic and social advantages at the same time that the transmission of accumulated knowledge and experience from elders lost its relevance for changing industries.
If the role of technology in shaping an emergent generational consciousness seems obvious to us now, however, it far from evident to earlier observers. “Why does contemporary western civilization manifest an extraordinary amount of parent-adolescent conflict?” Kinsley Davis asked in his article “ The Sociology of Parent-Youth Conflict .” In 1940, apparently, it was still possible to see inter-generational conflict as a novel and perplexing mystery.
To one of Davis’ contemporaries, the answer was clear: “the two generations in question have lived under such different economic conditions,” wrote Julien Brenda in a 1938 article, “ The Conflict of Generations in France .” “The old generation was a happy one—unusually happy, I venture to say; the young generation is unhappy, hard pressed by circumstances.”
Wallace Stegner picks up the theme of generational angst in his 1949 article, “ The Anxious Generation .” Writing of the twenty-somethings who came of age during or just after World War II, Stegner says:
They could no more have missed awareness of the tension and fear in their world than a bird could avoid awareness of wind. Far more has been taken from them than had been taken from preceding generations: politically, only uncertainty and fear and the Cold War is left them; the atom bomb is a threat such as the world has a never faced; if by a miracle we escape another war and the bomb, there is always the longer-term disaster of an incredibly multiplying world population and the shrinkage and wastage of world resources and the diminishing of world food supplies.
If that rather grim assessment implicitly rests on a set of assumptions about the impact of technological change—for what else is an atom bomb, if not a technological innovation?—then that assessment only seems apparent through our twenty-first century lens. In the middle of the last century, many still thought it preposterous to attribute generational differences to technological innovation. Writing in the middle of World War II, C. E. Ayres wrote that:
No serious student attributes the evils of the age to its machines. Popular essayists sometimes write as though tanks and airplanes were responsible for the bloodshed which is now going on, and novelists occasionally draw pictures of the horrors of a future in which life will have become wholly mechanized, with babies germinating in test tubes, “scientifically” maimed for the “more efficient” performance of industrial tasks. But this of course is literary nonsense…
Just a few years later, however, A. J. Jaffe would take a very different position in the pages of Scientific Monthly. “ Of the factors causing change in our society, one of the most important is technology—important new inventions as well as minor technical innovations,” Jaffe wrote in “ Technological Innovations and the Changing Socioeconomic Structure .” Making the case for the importance of studying technological change, Jaffe argued that:
Perhaps the single most important reason for studying technological change is to afford society a mechanism for predicting the social changes which are expected to occur… any thinking that will permit a society to better adapt itself to the inevitable changes which will occur—changes stemming in large measure from technological innovations—will be better able to meet such changes.
If that seems like a rather rapid turnaround on the importance of technological change in shaping generational perspectives, well, the pace of change was very much the point. In a 1945 article, “ Characteristics of an Age of Change ,” J. B. McKinney observed that “change, which was hitherto a gradual process, has become, for us, cataclysmic; it has become a tidal wave that threatens to overwhelm us. A decade to-day is the equivalent of a generation, and standards and values topple over like ninepins.”
From this rapid change, it was perceived, sprang generational discord. In his 1940 article, Davis argued that:
Extremely rapid change in modern civilization… tends to increase parent-youth conflict, for within a fast-changing social order the time-interval between generations, ordinarily but a mere moment in the life of a social system, become historically significant, thereby creating a hiatus between one generation and the next. Inevitably, under such a condition, youth is reared in a milieu different from that of the parents; hence the parents become old-fashioned, youth rebellious, and clashes occur which, in the closely confined circle of the immediate family, generate sharp emotion.
This 80-year-old assertion does an excellent job of anticipating our current tendency to label a new generation every decade, based on its unique relationship to emergent technology. Smartphones have only been in widespread use for a decade, but they’re now so fundamental to our daily lives that it’s hard to remember life without them. How could we possibly see those who can remember life before the smartphone as part of the same generation as those who’ve known nothing else? How could we see kids who’ve grown up on YouTube as part of the same generation that still watched actual TV? Doesn’t the leap from Facebook to SnapChat constitute its own profound generational divide?
Weekly Newsletter
Get your fix of JSTOR Daily’s best stories in your inbox each Thursday.
Privacy Policy Contact Us You may unsubscribe at any time by clicking on the provided link on any marketing message.
As the pace of technological innovation continues to accelerate, and as each successive round of innovation becomes more widely disseminated, it’s hard to imagine a return to the days when sociological generations spanned multiple decades. If you believe that technological conditions profoundly shape the life experience and perspectives of each successive generation, then those generations will only get narrower.
But that accuracy will come at a price. If we name each generation based on the specific technological conditions it experienced during childhood or adolescence, we may soon be dealing with generations that encompass only a few years apiece. At that point, the very idea of “generations” will cease to have much utility for social scientists, since it will be very hard to analyze attitudinal or behavioral differences between generations that are just a few years part. We’ll have come full circle, back to the early nineteenth century, when the only way to think of generations was in terms of biology, not sociology.

JSTOR is a digital library for scholars, researchers, and students. JSTOR Daily readers can access the original research behind our articles for free on JSTOR.
Get Our Newsletter
More stories.

- Beware the Volcanoes of Alaska (and Elsewhere)

Saffron: The Story of the World’s Most Expensive Spice

“Spaghettification”: How Black Holes Stretch Objects into Oblivion

Why Not Just Be a Nurse?
Recent posts.
- Seeing the World Through Missionaries’ Eyes
- The Border Presidents and Civil Rights
- The Genius of Georgette Chen
- Eurasianism: A Primer
Support JSTOR Daily
Sign up for our weekly newsletter.
An official website of the United States government
The .gov means it’s official. Federal government websites often end in .gov or .mil. Before sharing sensitive information, make sure you’re on a federal government site.
The site is secure. The https:// ensures that you are connecting to the official website and that any information you provide is encrypted and transmitted securely.
- Publications
- Account settings
Preview improvements coming to the PMC website in October 2024. Learn More or Try it out now .
- Advanced Search
- Journal List
- Dialogues Clin Neurosci
- v.22(2); 2020 Jun
Language: English | Spanish | French
The impact of digital technology use on adolescent well-being
El impacto del empleo de la tecnología digital en el bienestar de los adolescents, impact de l’usage des technologies numériques sur le bien-être de l’adolescent, tobias dienlin.
School of Communication, University of Hohenheim, Germany
Niklas Johannes
Institute of Neuroscience and Psychology, University of Glasgow, UK
This review provides an overview of the literature regarding digital technology use and adolescent well-being. Overall, findings imply that the general effects are on the negative end of the spectrum but very small. Effects differ depending on the type of use: whereas procrastination and passive use are related to more negative effects, social and active use are related to more positive effects. Digital technology use has stronger effects on short-term markers of hedonic well-being (eg, negative affect) than long-term measures of eudaimonic well-being (eg, life satisfaction). Although adolescents are more vulnerable, effects are comparable for both adolescents and adults. It appears that both low and excessive use are related to decreased well-being, whereas moderate use is related to increased well-being. The current research still has many limitations: High-quality studies with large-scale samples, objective measures of digital technology use, and experience sampling of well-being are missing.
Esta revisión entrega una panorámica de la literatura acerca del empleo de la tecnología digital y el bienestar de los adolescentes. En general, los resultados traducen que los efectos globales son negativos, aunque muy insignificantes. Los efectos difieren según el tipo de empleo: la procastinación y el empleo pasivo están relacionados con efectos más negativos; en cambio, el empleo social y activo se asocia con efectos más positivos. El empleo de la tecnología digital tiene efectos más potentes en los indicadores de corto plazo del bienestar hedónico (como los afectos negativos) que las mediciones a largo plazo del bienestar eudaimónico (como la satisfacción con la vida). Aunque los adolescentes son más vulnerables, los efectos son comparables para adolescentes y adultos. Parece que tanto el empleo reducido como el excesivo están relacionados con una disminución del bienestar, mientras que el empleo moderado se vincula con un mayor bienestar. La investigación actual todavía tiene muchas limitaciones: faltan estudios de alta calidad con muestras numerosas, mediciones objetivas del empleo de tecnología digital y muestras de experiencia de bienestar.
Nous proposons ici une revue de la littérature sur la pratique des technologies numériques et le bien-être de l’adolescent. Les données générales sont en faveur d’un effet négatif mais qui reste négligeable. L’usage définit la nature de l’effet : la procrastination et la passivité sont associées à un effet plus négatif alors qu’une pratique active et tournée vers la socialisation s’associe à un effet plus positif. Les effets sont plus importants sur les marqueurs à court terme du bien-être hédonique (comme les affects négatifs) que sur ceux à long terme du bien-être eudémonique (épanouissement personnel) ; ils sont comparables chez les adultes et les adolescents, même si ces derniers sont plus fragiles. Une utilisation excessive ou à l’inverse insuffisante semble diminuer le bien-être, alors qu’une pratique modérée l’augmenterait. Cependant, la recherche actuelle manque encore d’études de qualité élevée à grande échelle, de mesures objectives de la pratique des technologies numériques et d’expérience d’échantillonnage du bien-être.
With each new technology come concerns about its potential impact on (young) people’s well-being. 1 In recent years, both scholars and the public have voiced concerns about the rise of digital technology, with a focus on smartphones and social media. 2 To ascertain whether or not these concerns are justified, this review provides an overview of the literature regarding digital technology use and adolescent well-being.
Digital technology use and well-being are broad and complex concepts. To understand how technology use might affect well-being, we first define and describe both concepts. Furthermore, adolescence is a distinct stage of life. To obtain a better picture of the context in which potential effects unfold, we then examine the psychological development of adolescents. Afterward, we present current empirical findings about the relation between digital technology use and adolescent well-being. Because the empirical evidence is mixed, we then formulate six implications in order to provide some general guidelines, and end with a brief conclusion.
Digital technology use
Digital technology use is an umbrella term that encompasses various devices, services, and types of use. Most adolescent digital technology use nowadays takes place on mobile devices. 3 , 4 Offering the functions and affordances of several other media, smartphones play a pivotal role in adolescent media use and are thus considered a “metamedium.” 5 Smartphones and other digital devices can host a vast range of different services. A representative survey of teens in the US showed that the most commonly used digital services are YouTube (85%), closely followed by the social media Instagram (72%), and Snapchat (69%). Notably, there exist two different types of social media: social networking sites such as Instagram or TikTok and instant messengers such as WhatsApp or Signal.
All devices and services offer different functionalities and affordances, which result in different types of use . 6 When on social media, adolescents can chat with others, post, like, or share. Such uses are generally considered active . In contrast, adolescents can also engage in passive use, merely lurking and watching the content of others. The binary distinction between active and passive use does not yet address whether behavior is considered as procrastination or goal-directed. 7 , 8 For example, chatting with others can be considered procrastination if it means delaying work on a more important task. Observing, but not interacting with others’ content can be considered to be goal-directed if the goal is to stay up to date with the lives of friends. Finally, there is another important distinction between different types of use: whether use is social or nonsocial. 9 Social use captures all kinds of active interpersonal communication, such as chatting and texting, but also liking photos or sharing posts. Nonsocial use includes (specific types of) reading and playing, but also listening to music or watching videos.
When conceptualizing and measuring these different types of digital technology use, there are several challenges. Collapsing all digital behaviors into a single predictor of well-being will inevitably decrease precision, both conceptually and empirically. Conceptually, subsuming all these activities and types of use under one umbrella term fails to acknowledge that they serve different functions and show different effects. 10 Understanding digital technology use as a general behavior neglects the many forms such behavior can take. Therefore, when asking about the impact of digital technology use on adolescent well-being, we need to be aware that digital technology use is not a monolithic concept.
Empirically, a lack of validated measures of technology use adds to this imprecision. 11 Most work relies on self-reports of technology use. Self-reports, however, have been shown to be imprecise and of low validity because they correlate poorly with objective measures of technology use. 12 In the case of smartphones, self-reported duration of use correlated moderately, at best, with objectively logged use. 13 These findings are mirrored when comparing self-reports of general internet use with objectively measured use. 14 Taken together, in addition to losing precision by subsuming all types of technology use under one behavioral category, the measurement of this category contributes to a lack of precision. To gain precision, it is necessary that we look at effects for different types of use, ideally objectively measured.
Well-being
Well-being is a subcategory of mental health. Mental health is generally considered to consist of two parts: negative and positive mental health. 15 Negative mental health includes subclinical negative mental health, such as stress or negative affect, and psychopathology, such as depression or schizophrenia. 16 Positive mental health is a synonym for well-being; it comprises hedonic well-being and eudaimonic well-being. 17 Whereas hedonic well-being is affective, focusing on emotions, pleasure, or need satisfaction, eudaimonic well-being is cognitive, addressing meaning, self-esteem, or fulfillment.
Somewhat surprisingly, worldwide mental health problems have not increased in recent decades. 18 Similarly, levels of general life satisfaction remained stable during the last 20 years. 19 , 20 Worth noting, the increase in mental health problems that has been reported 21 could merely reflect increased awareness of psychosocial problems. 22 , 23 In other words, an increase in diagnoses might not mean an increase in psychopathology.
Which part of mental health is the most likely to be affected by digital technology use? Empirically, eudaimonic well-being, such as life satisfaction, is stable. Although some researchers maintain that 40% of happiness is volatile and therefore malleable, 24 more recent investigations argued that the influences of potentially stabilizing factors such as genes and life circumstances are substantially larger. 25 These results are aligned with the so-called set-point hypothesis, which posits that life satisfaction varies around a fixed level, showing much interpersonal but little intrapersonal variance. 26 The hypothesis has repeatedly found support in empirical studies, which demonstrate the stability of life satisfaction measures. 27 , 28 Consequently, digital technology use is not likely to be a strong predictor of eudaimonic well-being. In contrast, hedonic well-being such as positive and negative affect is volatile and subject to substantial fluctuations. 17 Therefore, digital technology use might well be a driver of hedonic well-being: Watching entertaining content can make us laugh and raise our spirits, while reading hostile comments makes us angry and causes bad mood. In sum, life satisfaction is stable, and technology use is more likely to affect temporary measures of hedonic well-being instead of more robust eudaimonic well-being. If this is the case, we should expect small to medium-sized effects on short-term affect, but small to negligible effects on both long-term affect and life satisfaction.
Adolescents
Adolescence is defined as “the time between puberty and adult independence,” 29 during which adolescents actively develop their personalities. Compared with adults, adolescents are more open-minded, more social-oriented, less agreeable, and less conscientious 30 ; more impulsive and less capable of inhibiting behavior 31 ; more risk-taking and sensation seeking 29 ; and derive larger parts of their well-being and life satisfaction from other peers. 32 During adolescence, general levels of life satisfaction and self-esteem drop and are often at their all-time lowest. 33 , 34 At the same time, media use increases and reaches a first peak in late adolescence. 3 Analyzing the development of several well-being-related variables across the last two decades, the answers of 46 817 European adolescents and young adults show that, whereas overall internet use has risen strongly, both life satisfaction and health problems remained stable. 19 Hence, although adolescence is a critical life stage with substantial intrapersonal fluctuations related to well-being, the current generation does not seem to do better or worse than those before.
Does adolescent development make them particularly susceptible to the influence of digital technology? Several scholars argue that combining the naturally occurring trends of low self-esteem, a spike in technology use, and higher suggestibility into a causal narrative can take the form of a foregone conclusion. 35 For one, although adolescents are in a phase of development, there might be more similarities between adolescents and adults than differences. 30 Concerns about the effects of a new technology on an allegedly vulnerable group has historically often taken the form of paternalization. 36 For example, and maybe in contrast to popular opinion, adolescents already possess much media literacy or privacy literacy. 3
This has two implications. First, asking what technology does to adolescents ascribes an unduly passive role to adolescents, putting them in the place of simply responding to technology stimuli. Recent theoretical developments challenge such a one-directional perspective and advise to rather ask what adolescents do with digital technology , including their type of use. 37 Second, in order to understand the effects of digital technology use on well-being, it might not be necessary to focus on adolescents. It is likely that similar effects can be found for both adolescents and adults. True, in light of the generally decreased life satisfaction and the generally increased suggestibility, results might be more pronounced for adolescents; however, it seems implausible that they are fundamentally different. When assessing how technology might affect adolescents compared with adults, we can think of adolescents as “canaries in the coalmine.” 38 If digital technology is indeed harmful, it will affect people from all ages, but adolescents are potentially more vulnerable.
Effects
What is the effect of digital technology use on well-being? If we ask US adolescents directly, 31% are of the opinion that the effects are mostly positive, 45% estimate the effects to be neither positive nor negative, and 24% believe that effects are mostly negative. 4 Teens who considered the effects to be positive stated that social media help (i) connect with friend; (ii) obtain information; and (c) find like-minded people. 4 Those who considered the effects to be negative explained that social media increase the risks of (i) bullying; (ii) neglecting face-to-face contacts; (iii) obtaining unrealistic impressions of other people’s lives. 4
Myriad studies lend empirical support to adolescents’ mixed feelings, reporting a wide range of positive, 39 neutral, 40 or negative 41 relations between specific measures of digital technology use and well-being. Aligned with these mixed results of individual studies, several meta-analyses support the lack of a clear effect. 42 In an analysis of 43 studies on the effects of online technology use on adolescent mental well-being, Best et al 43 found that “[t]he majority of studies reported either mixed or no effect(s) of online social technologies on adolescent wellbeing.” Analyzing eleven studies on the relation between social media use and depressive symptoms, McCrae et al 44 report a small positive relationship. Similarly, Lissak 45 reports positive relations between excessive screen time and insufficient sleep, physiological stress, mind wandering, attention deficit-hyperactivity disorder (ADHD)-related behavior, nonadaptive/negative thinking styles, decreased life satisfaction, and potential health risks in adulthood. On the basis of 12 articles, Wu et al 46 find that “the use of [i]nternet technology leads to an increased sense of connectedness to friend[s] and school, while at the same time increasing levels of anxiety and loneliness among adolescents.” Relatedly, meta-analyses on the relation between social media use and adolescent academic performance find no or negligible effects. 47
It is important to note that the overall quality of the literature these meta-analyses rely upon has been criticized. 48 This is problematic because low quality of individual studies biases meta-analyses. 49 To achieve higher quality, scholars have called for more large-scale studies using longitudinal designs, objective measures of digital technology use that differentiate types of use, experience sampling measures of well-being (ie, in-the-moment measures of well-being; also known as ambulant assessment or in situ assessment), and a statistical separation of between-person variance and within-person variance. 50 In addition, much research cannot be reproduced because the data and the analysis scripts are not shared. 51 In what follows, we look at studies that implemented some of these suggestions.
Longitudinal studies generally find a complex pattern of effects. In an 8 year study of 500 adolescents in the US, time spent on social media was positively related to anxiety and depression on the between-person level. 52 At the within-person level, these relationships disappeared. The study concludes that those who use social media more often might also be those with lower mental health; however, there does not seem to be a causal link between the two. A study on 1157 Croatians in late adolescence supports these findings. Over a period of 3 years, changes in social media use and life satisfaction were unrelated, speaking to the stability of life satisfaction. 40 In a sample of 1749 Australian adolescents, Houghton et al 53 distinguished between screen activities (eg, web browsing or gaming) and found overall low within-person relations between total screen time and depressive symptoms. Out of all activities, only web surfing was a significant within-person predictor of depressive symptoms. However, the authors argue that this effect might not survive corrections for multiple testing. Combining a longitudinal design with experience sampling in a sample of 388 US adolescents, Jensen et al 54 did not find a between-person association between baseline technology use and mental health. Interestingly, they only observed few and small within-person effects. Heffer et al 55 found no relation between screen use and depressive symptoms in 594 Canadian adolescents over 2 years. These results emphasize the growing need for more robust and transparent methods and analysis. In large adolescent samples from the UK and the US, a specification curve analysis, which provides an overview of many different plausible analyses, found small, negligible relations between screen use and well-being, both cross-sectionally and longitudinally. 56 Employing a similar analytical approach, Orben, Dienlin, and Przybylski 57 found small negative between-person relations between social media use and life satisfaction in a large UK sample of adolescents over 7 years. However, there was no robust within-person effect. Similarly, negligible effect sizes between adolescent screen use and well-being are found in cross-sectional data sets representative of the population in the UK and US. 58 In analyzing the potential effects of social media abstinence on well-being, two large-scale studies using adult samples found small positive effects of abstinence on well-being. 59 , 60 Two studies with smaller and mostly student samples instead found mixed 61 or no effects of abstinence on well-being. 62
The aforementioned studies often relied on composite measures of screen use, possibly explaining the overall small effects. In contrast, work distinguishing between different types of use shows that active use likely has different effects than passive use. Specifically, active use may contribute to making meaningful social connections, whereas passive use does not. 9 For example, meaningful social interactions have been shown to increase social gratification in adults, 63 , 64 whereas passive media use or media use as procrastination has been negatively related to well-being. 6 , 8 This distinction should also apply to adolescents. 6 The first evidence for this proposition already exists. In a large sample of Icelandic adolescents, passive social media use was positively related to anxiety and depressive symptoms; the opposite was the case for active use. 65
Furthermore, longitudinal work so far relies on self-reports of media use. Self-reported media use has been shown to be inaccurate compared with objectively measured use. 14 Unfortunately, there is little work employing objective measures to test whether the results of longitudinal studies using self-reports hold up when objective use is examined. The limited existing evidence suggests that effects remain small. In a convenience sample of adults, only phone use at night negatively predicted well-being. 66 Another study that combined objective measures of social smartphone applications with experience sampling in young adults found a weak negative relation between objective use and well-being. 67
Effects might also not be linear. Whereas both low and high levels of internet use have been shown to be associated with slightly decreased life satisfaction, moderate use has been shown to be related to slightly increased life satisfaction. 10 , 35 , 68 However, evidence for this position is mixed; other empirical studies did not find this pattern of effects. 53 , 54
Taken together, do the positive or the negative effects prevail? The literature implies that the relationship between technology use and adolescent well-being is more complicated than an overall negative linear effect. In line with meta-analyses on adults, effects of digital technology use in general are mostly neutral to small. In their meta-review of 34 meta-analyses and systematic reviews, Meier and Reinecke 42 summarize that “[f]indings suggest an overall (very) small negative association between using SNS [social networking sites], the most researched CMC [computer mediated communication] application, and mental health.” In conclusion, the current literature is mostly ambivalent, although slightly emphasizing the negative effects of digital tech use.

Implications
Although there are several conflicting positions and research findings, some general implications emerge:
1. The general effects of digital technology use on well-being are likely in the negative spectrum, but very small—potentially too small to matter.
2. No screen time is created equal; different uses will lead to different effects.
3. Digital technology use is more likely to affect short-term positive or negative affect than long-term life satisfaction.
4. The dose makes the poison; it appears that both low and excessive use are related to decreased well-being, whereas moderate use is related to increased well-being.
5. Adolescents are likely more vulnerable to effects of digital technology use on well-being, but it is important not to patronize adolescents—effects are comparable and adolescents not powerless.
6. The current empirical research has several limitations: high-quality studies with large-scale samples, objective measures of digital technology use, and experience sampling of well-being are still missing.
Conclusion
Despite almost 30 years of research on digital technology, there is still no coherent empirical evidence as to whether digital technology hampers or fosters well-being. Most likely, general effects are small at best and probably in the negative spectrum. As soon as we take other factors into account, this conclusion does not hold up. Active use that aims to establish meaningful social connections can have positive effects. Passive use likely has negative effects. Both might follow a nonlinear trend. However, research showing causal effects of general digital technology use on well-being is scarce. In light of these limitations, several scholars argue that technology use has a mediating role69: already existing problems increase maladapted technology use, which then decreases life satisfaction. Extreme digital technology use is more likely to be a symptom of an underlying sociopsychological problem than vice versa. In sum, when assessing the effects of technology use on adolescent well-being, one of the best answers is that it’s complicated.
This lack of evidence is not surprising, because there is no consensus on central definitions, measures, and methods. 42 Specifically, digital technology use is an umbrella term that encompasses many different behaviors. Furthermore, it is theoretically unclear as to why adolescents in particular should be susceptible to the effects of technology and what forms of well-being are candidates for effects. At the same time, little research adopts longitudinal designs, differentiates different types of technology use, or measures technology use objectively. Much work in the field has also been criticized for a lack of transparency and rigor. 51 Last, research (including this review) is strongly biased toward a Western perspective. In other cultures, adolescents use markedly different services (such as WeChat or Renren, etc). Although we assume most effects to be comparable, problems seem to differ somewhat. For example, online gaming addiction is more prevalent in Asian than Western cultures. 70
Adults have always criticized the younger generation, and media (novels, rock music, comic books, or computer games) have often been one of the culprits. 1 Media panics are cyclical, and we should refrain from simply blaming the unknown and the novel. 1 In view of the public debate, we should rather emphasize that digital technology is not good or bad per se. Digital technology does not “happen” to individuals. Individuals, instead, actively use technology, often with much competence. 3 The current evidence suggests that typical digital technology use will not harm a typical adolescent. That is not to say there are no individual cases and scenarios in which effects might be negative and large. Let’s be wary, but not alarmist.
Acknowledgments
Both authors declare no conflicts of interest. Both authors contributed equally to this manuscript. Tobias Dienlin receives funding from the Volkswagen Foundation. We would like to thank Amy Orben for valuable feedback and comments
Read our research on: Abortion | Podcasts | Election 2024
Regions & Countries
Millennials stand out for their technology use, but older generations also embrace digital life.
Our approach to generational analysis has evolved to incorporate new considerations. Learn more about how we currently report on generations , and read tips for consuming generations research .
Millennials have often led older Americans in their adoption and use of technology, and this largely holds true today. But there has been significant growth in tech adoption since 2012 among older generations – particularly Gen Xers and Baby Boomers.
More than nine-in-ten Millennials (93% of those who turn ages 23 to 38 this year ) own smartphones, compared with 90% of Gen Xers (those ages 39 to 54 this year), 68% of Baby Boomers (ages 55 to 73) and 40% of the Silent Generation (74 to 91), according to a new analysis of a Pew Research Center survey of U.S. adults conducted in early 2019.
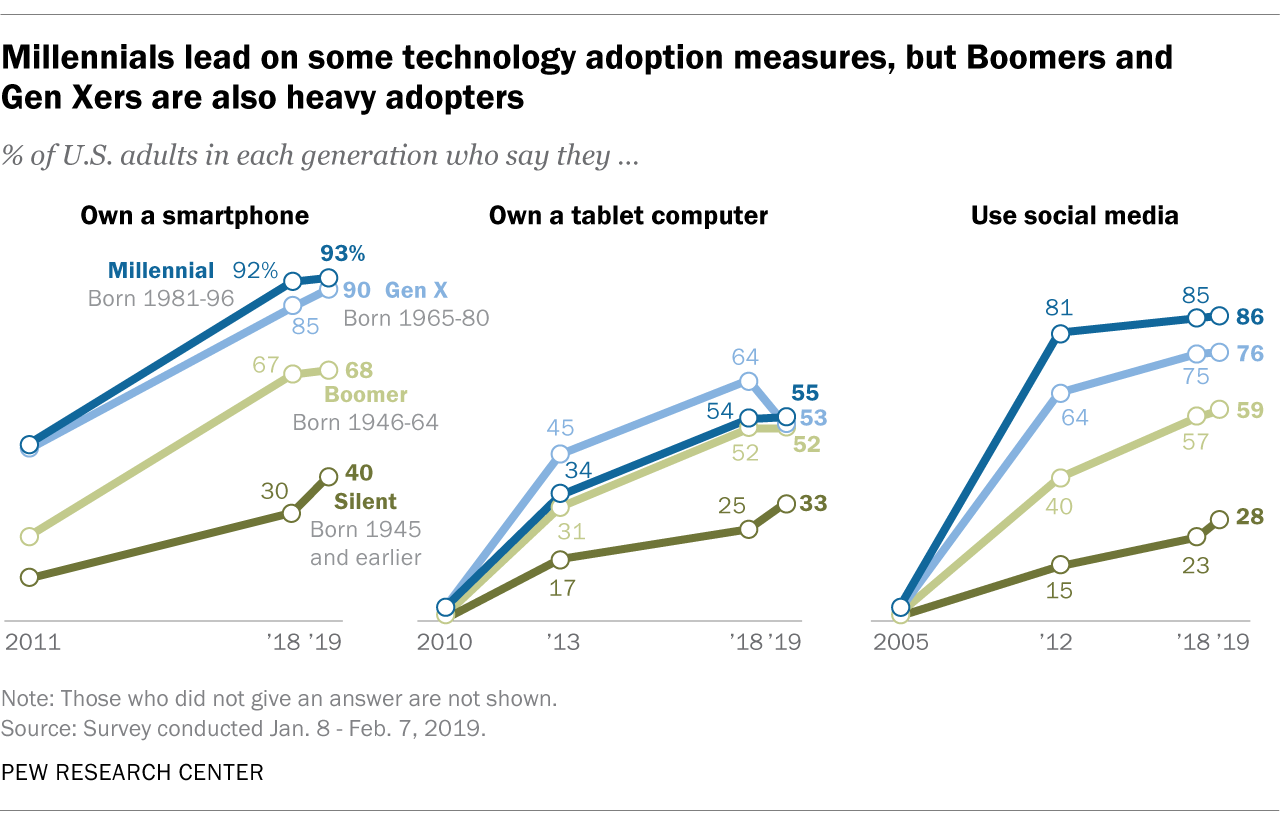
Unlike with smartphones and social media, tablet ownership is now comparable across most generations. Today, 55% of Gen Xers, 53% of Millennials and 52% of Boomers say they own tablets. A smaller share of Silents (33%) report owning tablets.
Those in the Silent Generation also lag when it comes to having broadband service at home. Whereas most Millennials (78%), Gen Xers (78%) and Boomers (74%) say they subscribe to home broadband, fewer than half of Silents (45%) say this.
Almost all Millennials (nearly 100%) now say they use the internet, and 19% of them are smartphone-only internet users – that is, they own a smartphone but do not have broadband internet service at home. Large shares of Gen Xers (91%) and Boomers (85%) use the internet, compared with just 62% of Silents. When it comes to smartphone-only internet users, 17% of Gen Xers go online primarily via a smartphone, as do 11% of Boomers and 15% of Silents.
Baby Boomers continue to trail both Gen Xers and Millennials on most measures of technology adoption, but adoption rates for this group have been growing rapidly in recent years. For example, Boomers are now far more likely to own a smartphone than they were in 2011 (68% now vs. 25% then).
Although Boomers have been adopting a range of technologies in recent years, members of the Silent Generation are less likely to have done so. Four-in-ten Silents (40%) report owning a smartphone, and fewer (33%) indicate that they have a tablet computer or use social media (28%). Previous Pew Research Center surveys have found that the oldest adults face some unique barriers to adopting new technologies – from a lack of confidence in using new technologies to physical challenges manipulating various devices.
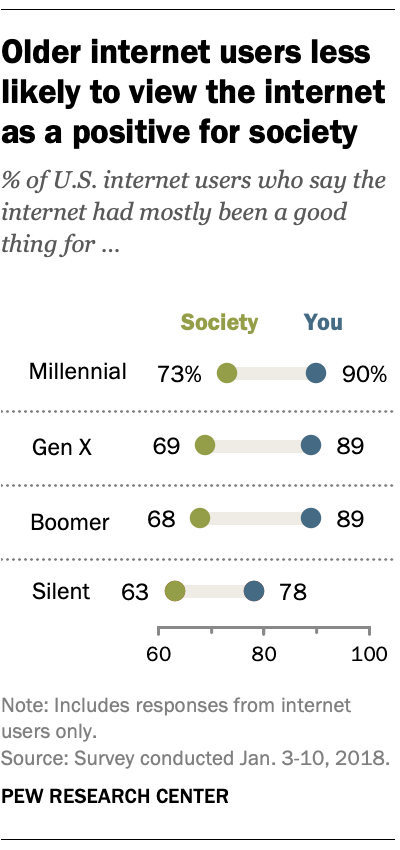
While generations differ in their use of various technologies, a 2018 Center survey found that younger internet users also were more likely than older Americans who use the internet to say the internet has had a positive impact on society: 73% of online Millennials said the internet has been mostly a good thing for society, compared with 63% of users in the Silent Generation.
Americans were also less positive about the societal impact of the internet last year than four years earlier. Gen Xers’ views of the internet’s impact on society declined the most in that time. In 2014, 80% of Gen X internet users believed the internet had been mostly a positive thing for society, a number that dropped to 69% in 2018. Millennial and Silent internet users were also somewhat less optimistic last year than in 2014.
Note: This is an update of a post originally published May 2, 2018, and written by Jingjing Jiang, a former research analyst focusing on internet and technology. See full topline results and methodology here .
Sign up for our weekly newsletter
Fresh data delivered Saturday mornings
Assessing the effects of generation using age-period-cohort analysis
How pew research center will report on generations moving forward, 5 things to keep in mind when you hear about gen z, millennials, boomers and other generations, millennials overtake baby boomers as america’s largest generation, defining generations: where millennials end and generation z begins, most popular.
About Pew Research Center Pew Research Center is a nonpartisan fact tank that informs the public about the issues, attitudes and trends shaping the world. It conducts public opinion polling, demographic research, media content analysis and other empirical social science research. Pew Research Center does not take policy positions. It is a subsidiary of The Pew Charitable Trusts .

Search form
- Find Stories
- For Journalists
Gen Z are not ‘coddled.’ They are highly collaborative, self-reliant and pragmatic, according to new Stanford-affiliated research
Generation Z, the first generation never to know the world without the internet, value diversity and finding their own unique identities, says Stanford scholar Roberta Katz.
Generation Z – also known as Gen Z, iGen or postmillennial – are a highly collaborative cohort that cares deeply about others and have a pragmatic attitude about how to address a set of inherited issues like climate change, according to research by Roberta Katz, a senior research scholar at Stanford’s Center for Advanced Study in the Behavioral Sciences (CASBS) .

Roberta Katz (Image credit: Charles Katz)
Since 2017, Katz, along with her co-authors, Sarah Ogilvie, a linguist at the University of Oxford and formerly at Stanford; Jane Shaw, a historian who is the principal of Harris Manchester College at Oxford and was previously dean for Religious Life at Stanford; and Linda Woodhead, a sociologist at King’s College London, collaborated as part of a multi-year CASBS research project to better understand a generation who, born between the mid-1990s to around 2010, grew up with digital tools always at their fingertips.
Their findings are based on some 120 interviews gathered on three college campuses – Stanford University; Foothill College, a community college in Los Altos Hills, California; and Lancaster University, a research university in Lancaster, England. A set of focus groups and two surveys in the U.S. and the U.K. were administered to a representative sample of over 2,000 adults aged between 18 and 25 years old.
Contributing further to the scholar’s understanding of Gen Z was the creation of the “ iGen corpus ,” a 70 million item digital repository of spoken and written language of people aged 16 to 25 years that included transcripts from the researchers’ interviews and focus groups, as well as public data from the social media platforms Twitter, Reddit, Twitch, 4chan and YouTube, as well as memes and copypastas from Facebook and Instagram. Ogilvie, the principal investigator on the corpus research team, along with a team of Stanford student research assistants, applied machine learning algorithms to discover the many ways in which young people today express themselves.
Taken together, the scholars’ research offers a snapshot of who Gen Zers really are, what matters to them and why. Findings from Katz’s and her co-authors’ research are detailed in a new book, Gen Z, Explained: The Art of Living in a Digital Age (University of Chicago Press, 2021).
Here, Katz discusses some of what she and her colleagues learned from their extensive research into how Gen Zers, the most diverse generation yet , experience and understand the world.
Based on your research, can you briefly describe the typical Gen Zer?
In summary, a typical Gen Zer is a self-driver who deeply cares about others, strives for a diverse community, is highly collaborative and social, values flexibility, relevance, authenticity and non-hierarchical leadership, and, while dismayed about inherited issues like climate change, has a pragmatic attitude about the work that has to be done to address those issues.
How has growing up in an internet-connected society shaped how Gen Zers see and experience the world and everyday life?
Internet-related technologies have dramatically changed the speed, scale and scope of human communications, resulting in significant changes in how people work, play, shop, find friends and learn about other people. For Gen Zers living in the United States and Britain (the two places we studied), the “norm” they experienced as children was a world that operated at speed, scale and scope. They developed an early facility with powerful digital tools that allowed them to be self-reliant as well as collaborative. Similarly, because they could learn about people and cultures around the globe from an early age, they developed a greater appreciation for diversity and the importance of finding their own unique identities.
What do people most misunderstand or get wrong about Gen Zers?
For quite a while, people were critical of what they saw as a generation that was too coddled and “soft.” Gen Zers were called “snowflakes” and “unwilling to grow up.” But much of that negative judgment came from a misunderstanding of what it is like to grow up in today’s world when compared with how their elders grew up. As an example, Gen Zers have been criticized as lazy because they don’t have after-school or summer jobs. But many Gen Zers have been earning significant dollars online through a variety of activities, even including product placements on fashion-advice sites. Another example concerns drivers’ licenses: older people, for whom getting a driver’s license was a rite of passage toward adulthood, have criticized Gen Zers who do not rush to take their driver’s tests when they turn 16, but this criticism fails to consider that Gen Zers have no need to drive when they have ready access to ride services like Uber and Lyft.
Do you think Gen Zers get an undeserved bad rap?
Yes, but that is changing. Of late, many people are beginning to appreciate the strength and pragmatism of Gen Zers.
What were you most surprised to learn about Gen Zers?
Our biggest surprise came in response to this interview question: “What type of communication do you like best?” We expected the interviewees to respond with their favorite type of digital communication – e.g., text, email, chat group, DM, FaceTime, Skype, etc. – but instead nearly every single person said their favorite form of communication was “in person.”
As Gen Zers enter the workforce, what would be helpful for other generations to know about their post-millennial colleagues?
For those who are now experiencing Gen Zers in the workplace, my advice is to recognize that these new colleagues are used to working collaboratively and flexibly, with an eye to being efficient in getting the job done. They are pragmatic and value direct communication, authenticity and relevance. They also value self-care. They may be more likely than older people were when they were the age of the Gen Zers to question rules and authority because they are so used to finding what they need on their own. They are not always right; often they don’t know what they need, especially in a new setting, and this is where inter-generational dialogue can be so helpful. Both the older and the younger colleagues can learn from the other, in each case by listening with more respect, appreciation and trust. The older colleague can learn some helpful new ways of getting a job done, while the younger colleague may learn good reasons for why things have long been done in a certain way. Without that dialogue, we’ll have a wasteful tug of war between the past and the future. The goal is for older and younger generations to work together, with openness and trust, to ensure that the wisdom – but not what has become the excess baggage – of the past is not lost to the future.
How has studying Gen Zers changed your own interactions with this generation?
I came to understand that Gen Zers are, on the whole, much better adapted to life in a digital age than those of us who are older and that they can be very frustrated by what appear to them to be outdated and often irrelevant ways of doing things. As one simple example that we cite in the book, an older person would likely assume that any organization needs a set of officers, for that has been the norm in their experience, but a Gen Zer would say, from their lived experience, that there is no need to elect officers (or other leaders) if the group can accomplish its mission through online collaborations that take advantage of the participants’ diverse skills.
In my own interactions with Gen Zers, I am much more likely than I used to be to listen closely to what they say, and to refrain from making a judgment about their ideas, values and behaviors based on an assumption that they are wrong and I am right. They often do things differently, have some different values and have some different ideas about the future than I do, and I have come to appreciate and trust that they often have a new and better approach. Many of us who are older have a different understanding of how the world works, which is rooted in our own early experiences, so it’s easy for us to assume that the world will continue to operate in much the same way going forward and that the young people need to adapt to that older way of living. But the younger people are necessarily future-oriented, and as we all are increasingly coming to appreciate, the digital-age future is quite different from the industrial-age past.
For 13 years, Katz served under Stanford University Presidents John Hennessy and Marc Tessier-Lavigne as the associate vice president for strategic planning. She also served as President Tessier-Lavigne’s interim chief of staff until early 2017. Katz has been deeply involved in the facilitation of a variety of interdisciplinary research initiatives at Stanford, and she is a current member of the CASBS board of directors.
This research was funded by the Knight Foundation.

Home | About Us Contact Us | Privacy Policy

Advantages and Disadvantages of Technology on Youth
Technology has become an integral part of our daily lives, and its impact on the younger generation is undeniable.
While it has brought about numerous benefits, such as increased access to information and improved communication, it has also raised concerns about its potential negative effects on youth.
In this article, we will explore the advantages and disadvantages of technology for youth.
Advantages of Technology on Youth
Technology has become an integral part of our lives, and its impact on the younger generation cannot be ignored.
While some may argue that technology has negative effects on youth, there are also many advantages that cannot be overlooked.
From improved communication and social networking to access to information and new learning opportunities, technology has opened up a world of possibilities for young people.

1. Increased Opportunities for Career Development and Entrepreneurship
Technology has brought about numerous advantages for the youth, including increased opportunities for career development and entrepreneurship.
With the rise of STEM education and the growing emphasis on an entrepreneurial mindset, young people are now better equipped to identify and capitalize on opportunities, change course when needed, and view mistakes as an opportunity to learn and improve.
Moreover, technology has made it easier for young people to access education and training, regardless of their location or financial situation.
This has opened up new avenues for personal and professional growth, allowing young people to pursue rewarding careers and achieve their full potential.
As we look to the future, it is clear that entrepreneurship and innovation will play a critical role in driving economic growth and creating new job opportunities.
By investing in technology and supporting the development of young entrepreneurs, we can ensure that the next generation has the tools and resources they need to succeed in an ever-changing world
2. Greater Creative and Productive Opportunities through Technology
Technology has opened up greater creative and productive opportunities for the youth.
With the use of modern hardware and software, young people can gain a sustainable competitive advantage and achieve great things with relatively simple technologies.
Technology also empowers young people to maintain autonomy, choose the lifestyle they want, and promote dignity.
Moreover, technology can help reduce bias, diversify talent pools, and benchmark diversity and inclusion, which brings a host of benefits to businesses in terms of profitability, innovation, decision-making, and employee engagement.
By fostering unique ideas, technology encourages creativity, which is a key component of innovation.
Therefore, the advantages of technology for youth are immense, and it is essential to continue to leverage technology to create more opportunities for young people to thrive.
3. Improved Quality of Life through Technological Conveniences
Technology has improved the quality of life for the youth. With the advent of the internet and smartphones, young people can easily access information, connect with friends and family, and engage in various activities that promote their mental and physical well-being.
Technology has also made it possible for young people to learn new skills and pursue their passions through online courses and platforms.
Additionally, technology has made life easier for young people by providing them with various technological conveniences such as smart homes, wearable devices, and virtual assistants that make daily tasks more manageable.
These technological advancements have not only made life more convenient but have also contributed to the safety and protection of young people, allowing them to live longer and healthier lives.
4. Enhanced Access to Social Services and Support Networks
One of the most significant advantages of technology is enhanced access to social services and support networks.
With the help of digital technologies , vulnerable youth can receive social protection and support from governments and other organizations.
Having a social support system is crucial for overall mental health, and technology has made it easier for youth to connect with others and build supportive networks.
Young adults are more likely to mention social media as a resource for social connectedness, and technology has made it easier for them to access support networks.
With the help of technology, youth can increase their social support by connecting with others, sharing experiences, and receiving help and advice.
Overall, technology has had a positive impact on youth by enhancing their access to social services and support networks, which is crucial for their mental health and well-being.
5. Increased Awareness and Understanding of Global Issues and Challenges
Technology has increased awareness and understanding of global issues and challenges. With the spread of technology around the world, students now have access to information and resources that enable them to develop global competence.
They can learn about the effects of globalization on the environment, the importance of international collaboration, and the need for a more peaceful and just society.
Through technology, they can also stay informed about global issues such as climate change, poverty, and human rights, and take action to address them.
The United Nations continues to promote justice and international law, and technology has made it easier for young people to get involved in these efforts.
Overall, technology has opened up new opportunities for the youth to learn about and engage with the world, and this increased awareness and understanding can help them become more informed and responsible global citizens.
Disadvantages of Technology on Youth
Technology’s impact on the younger generation cannot be ignored. While it has brought about numerous benefits, such as increased connectivity and access to information, it also has its downsides.
The negative effects of technology on youth are becoming increasingly apparent, with studies linking excessive social media use to poor sleep quality, anxiety, and depression.
Furthermore, the constant use of technology can lead to a lack of focus and exposure to harmful content, such as cyberbullying and sexual exploitation.

1. Increased Dependence on Technology and Reduced Attention Span
The increased dependence on technology among youth has led to a reduction in attention span. Studies have shown that our average attention span has decreased by 4 seconds, down from 12 to 8, which is shorter than that of a goldfish.
This is due to the fact that technology has made it easier for us to access information quickly, leading to a decrease in our ability to focus for extended periods of time.
Furthermore, kids aged 5 or younger who experience two or more hours of daily screen time are nearly eight times more likely to be diagnosed with focus-related conditions including attention deficit hyperactivity disorder (ADHD).
It is important for parents and educators to monitor the amount of time children spend on technology and encourage them to engage in activities that promote focus and attention.
2. Increased Exposure to Inappropriate and Harmful Content Online
The increased exposure to inappropriate and harmful content online is a major disadvantage of technology for youth.
With the pandemic worsened mental health stressors and social isolation for teens, millions of youth have increased their social media use, leading to a higher risk of exposure to toxic content.
Spending more time online may expose children to potentially harmful and violent content as well as a greater risk of cyberbullying.
Inappropriate content includes information or images that upset children, material that’s directed at adults, inaccurate information, or information that might lead or tempt children into unlawful or dangerous behavior.
Exposure to such content can lead to increased anxiety, depression, loneliness, and risky behaviors.
As parents and guardians, it is important to monitor children’s online activity and educate them on safe internet practices to protect them from exposure to inappropriate content.
3. The Challenge of Balancing Online and Offline Life
The rise of technology has created a challenge for young people in balancing their online and offline lives.
Spending too much time online can lead to negative effects on mental health, such as anxiety and depression.
It is important for young people to develop healthy digital habits and engage in activities that don’t involve devices, apps, or the internet.
Creating a balance between online and offline activities is crucial for maintaining a healthy lifestyle.
Encouraging students to use their internet activities as a reward for completing other meaningful and necessary tasks can help them develop a healthy balance.
As technology continues to advance, it is important for young people to be mindful of their digital habits and strive for a healthy balance between their online and offline lives.
4. The Potential for Digital Disinformation and Misinformation
The potential for digital disinformation and misinformation is a major disadvantage of technology on youth.
With the rise of social media and the ease of spreading information online, it has become increasingly challenging to address the spread of false information.
Disinformation can spread quickly and anonymously, making it difficult to identify and combat. This can have serious consequences, such as affecting public health, climate change, and democracy.
While digital literacy can help identify misinformation, it does not necessarily stop its spread of it. It is important to educate youth on the dangers of disinformation and provide them with the tools to identify and respond to it.
Emerging technologies like blockchain have the potential to address the root causes of disinformation and combat its spread.
It is crucial to address this issue to ensure that youth are equipped with the skills and knowledge to navigate the digital world safely and responsibly.
5. The Challenge of Keeping Up with Rapid Technological Advancements
The rapid advancement of technology poses a significant challenge for youth today. While technology has its advantages, it also has its disadvantages, and keeping up with the latest trends can be overwhelming.
The constant evolution of technology means that young people must continually learn new skills to remain relevant in the job market.
Additionally, the unexpected consequences of technological advancements can have a significant impact on society, and it is essential to recognize and anticipate these consequences.
Furthermore, technological change has not delivered its full potential in boosting productivity and economic growth, and it has pushed income inequality higher.
Companies also face challenges in developing technological capabilities that provide a competitive advantage.
As technology continues to change the world, it is crucial to understand its impact and adapt to the changes to ensure a better future for all.
Conclusion on Advantages and Disadvantages of Technology on Youth
In conclusion, technology has both advantages and disadvantages for the youth. On one hand, it has made education more accessible and provided new opportunities for communication and socialization.
On the other hand, it has also led to issues such as cyberbullying, addiction, and a lack of face-to-face interaction.
It is important for parents, educators, and society as a whole to recognize these potential drawbacks and work to mitigate them while still embracing the benefits of technology.
Ultimately, it is up to individuals to use technology responsibly and in moderation to ensure a healthy and balanced lifestyle.
Relevant Resources:
- Advantages and Disadvantages of Technology in Human Life
- Advantages and Disadvantages of Technology in Organizations
- Advantages and Disadvantages of Technology in Culture
- Advantages and Disadvantages of Technology in Child Development
- Advantages and Disadvantages of Science and Technology in Politics

Ahmad Ali (Author)
Ahmad Ali has been a technology enthusiast and writer for the past 5 years having vast knowledge of technology.

Rehmat Ullah (Content Reviewer)
Rehmat Ullah is a software engineer and CEO of Softhat IT Solutions. He is an expert technologist, entrepreneur, and educationist.
Leave a Comment Cancel Reply
Your email address will not be published. Required fields are marked *
Save my name, email, and website in this browser for the next time I comment.
The Technology Influence on Youth Essay
Today, the importance of technology makes many people prefer to scroll through the timeline rather than get a few hours of sleep. Teenagers who are deprived of controlling their free time or filtering information coming from social networks are especially susceptible to this. Absorbing all the information that the Internet introduces, teenagers tend to stop evaluating the acquired knowledge sensibly. This leads to a deterioration of mental state physical health and increases the risk of falling into the hands of fraudsters. Since the spread of the Internet provides easier access to extensive knowledge and carries hidden harm, research has been conducted to analyze the impact of the Internet on adolescents. These studies were aimed at identifying the dangers that teenagers face on the Internet, finding their causes and measures that can help overcome them. This paper examines some of the main effects of new technologies on adolescents and young people, including deterioration of the physical and mental condition, increased risk of becoming a victim of a fraudster, and the gradual loss of moral values in an entire generation.
The interest of young people in social networks has specific consequences in the form of mental and physical health problems. For example, sitting in a constantly uncomfortable posture while checking social networks leads to the deterioration of the neck and back, provoking chronic pain in these areas. Moreover, bright light contributes to the damage of vision and sleep disorders, such as lack of sleep or even insomnia. Online interactions affect a teen’s emotional state, which can never be restored when it comes to mental health. Adolescents have learned to interact with people while staying behind the curve, which disrupts communication abilities (Bibi et al. 480). This proves that when technology is used incorrectly, it harms comprehensively.
The use of social networks by young people also weakens the institution of moral education and disregard for moral values. Uncontrolled publications on the social network Instagram with a demonstration of tobacco or the smoking process lead to the popularization of smoking among teenagers. Another problem is the distribution of images with alcohol consumption in the same social network, which erases the boundaries of what is permissible for minors. In addition, the lack of filtering of images of aggression and cruelty also leads to an increase in the risks of immoral behavior among adolescents whose personality has not yet been fully formed (Krylova 498). Having a negative impact on teenagers’ vision of tobacco and alcohol, technologies, where not all information is filtered and suitable for children and adolescents, also harm moral values.
The growing popularity of technology among young people has also led to an increase in their involvement in the sex industry, leading to a rise in crime and the experience of traumatic experiences by adolescents. Viewing prohibited materials causes the appearance of curiosity, which means the risk of harmful sexual contact even with the right person is becoming possible. New technologies and poor awareness of teenagers have also led to an increased risk of sharing an intimate photo on the Internet with an unfamiliar person. The possibility of involving children in the porn industry is also greatly simplified, which sometimes happens by the voluntary consent of a teenager due to the influence of the availability of sexual content (Senadjki et al. 63). As a result, the number of sexual crimes, where the victims are teenagers, is increasing because of the lack of filtering information in social networks.
From all of the above, it follows that the Internet has a huge negative impact of unverified information on the still unformed personalities of teenagers. All this leads to the understanding that the quantity and quality of resources viewed by teenagers must be controlled. Moreover, it is worth raising awareness among young people about the dangers and risks that await them with excessive use of technology.
Works Cited
Bibi, Arifa, et al. “Effect of Latest Technology and Social Media on Interpersonal Communication on Youth of Balochistan.” Journal of Managerial Sciences , vol. 11, n. 3, 2018, pp. 475-490.
Krylova, Palageya. “The Impact of the Social Networks Having Name Instagram on Values of Youth.” Culture and Education: Social Transformations and Multicultural Communication, 2019, pp. 494-501
Senadjki, Abdelhak, et al. “The Influence of Technology on Youth Sexual Prevalence: Evidences from Malaysia.” Malaysian Journal of Youth Studies, 2017, pp. 38-68.
- Chicago (A-D)
- Chicago (N-B)
IvyPanda. (2023, January 11). The Technology Influence on Youth. https://ivypanda.com/essays/the-technology-influence-on-youth/
"The Technology Influence on Youth." IvyPanda , 11 Jan. 2023, ivypanda.com/essays/the-technology-influence-on-youth/.
IvyPanda . (2023) 'The Technology Influence on Youth'. 11 January.
IvyPanda . 2023. "The Technology Influence on Youth." January 11, 2023. https://ivypanda.com/essays/the-technology-influence-on-youth/.
1. IvyPanda . "The Technology Influence on Youth." January 11, 2023. https://ivypanda.com/essays/the-technology-influence-on-youth/.
Bibliography
IvyPanda . "The Technology Influence on Youth." January 11, 2023. https://ivypanda.com/essays/the-technology-influence-on-youth/.
- Internet Filtering Positives and Negatives
- Internet Censorship: Blocking and Filtering
- Analysis and Evaluation of Statistical Spam Filtering.
- Internet Filtering: Debating the Positives & Negatives
- Censorship on the Internet
- Internet Censorship in Saudi Arabia
- Who Should Be Allowed to Filter the Internet?
- Benthic Macroinvertebrate
- Computer Literacy: Parents and Guardians Role
- Tobacco Smoking and Its Dangers
- Smartwatches: Developments of Niche Devices
- Human Impact on Technology: Ethics for the Information Age
- COVID-19 Pandemic in Singapore
- Future Innovations and Their Role in People’s Life
- Science and Technology: Impact on Human Life
Greater Good Science Center • Magazine • In Action • In Education
Parenting & Family Articles & More
How teens today are different from past generations, a psychologist mines big data on teens and finds many ways this generation—the “igens"—is different from boomers, gen xers, and millennials..
Every generation of teens is shaped by the social, political, and economic events of the day. Today’s teenagers are no different—and they’re the first generation whose lives are saturated by mobile technology and social media.
In her new book, psychologist Jean Twenge uses large-scale surveys to draw a detailed portrait of ten qualities that make today’s teens unique and the cultural forces shaping them. Her findings are by turn alarming, informative, surprising, and insightful, making the book— iGen:Why Today’s Super-Connected Kids Are Growing Up Less Rebellious, More Tolerant, Less Happy—and Completely Unprepared for Adulthood—and What That Means for the Rest of Us —an important read for anyone interested in teens’ lives.
Who are the iGens?

Twenge names the generation born between 1995 and 2012 “iGens” for their ubiquitous use of the iPhone, their valuing of individualism, their economic context of income inequality, their inclusiveness, and more.
She identifies their unique qualities by analyzing four nationally representative surveys of 11 million teens since the 1960s. Those surveys, which have asked the same questions (and some new ones) of teens year after year, allow comparisons among Boomers, Gen Xers, Millennials, and iGens at exactly the same ages. In addition to identifying cross-generational trends in these surveys, Twenge tests her inferences against her own follow-up surveys, interviews with teens, and findings from smaller experimental studies. Here are just a few of her conclusions.
iGens have poorer emotional health thanks to new media. Twenge finds that new media is making teens more lonely, anxious, and depressed, and is undermining their social skills and even their sleep.
iGens “grew up with cell phones, had an Instagram page before they started high school, and do not remember a time before the Internet,” writes Twenge. They spend five to six hours a day texting, chatting, gaming, web surfing, streaming and sharing videos, and hanging out online. While other observers have equivocated about the impact, Twenge is clear: More than two hours a day raises the risk for serious mental health problems.
She draws these conclusions by showing how the national rise in teen mental health problems mirrors the market penetration of iPhones—both take an upswing around 2012. This is correlational data, but competing explanations like rising academic pressure or the Great Recession don’t seem to explain teens’ mental health issues. And experimental studies suggest that when teens give up Facebook for a period or spend time in nature without their phones, for example, they become happier.
The mental health consequences are especially acute for younger teens, she writes. This makes sense developmentally, since the onset of puberty triggers a cascade of changes in the brain that make teens more emotional and more sensitive to their social world.
Social media use, Twenge explains, means teens are spending less time with their friends in person. At the same time, online content creates unrealistic expectations (about happiness, body image, and more) and more opportunities for feeling left out—which scientists now know has similar effects as physical pain . Girls may be especially vulnerable, since they use social media more, report feeling left out more often than boys, and report twice the rate of cyberbullying as boys do.
Social media is creating an “epidemic of anguish,” Twenge says.
iGens grow up more slowly. iGens also appear more reluctant to grow up. They are more likely than previous generations to hang out with their parents, postpone sex, and decline driver’s licenses.
More on Teens
Discover five ways parents can help prevent teen depression .
Learn how the adolescent brain transforms relationships .
Understand the purpose of the teenage brain .
Explore how to help teens find purpose .
Twenge floats a fascinating hypothesis to explain this—one that is well-known in social science but seldom discussed outside academia. Life history theory argues that how fast teens grow up depends on their perceptions of their environment: When the environment is perceived as hostile and competitive, teens take a “fast life strategy,” growing up quickly, making larger families earlier, and focusing on survival. A “slow life strategy,” in contrast, occurs in safer environments and allows a greater investment in fewer children—more time for preschool soccer and kindergarten violin lessons.
“Youths of every racial group, region, and class are growing up more slowly,” says Twenge—a phenomenon she neither champions nor judges. However, employers and college administrators have complained about today’s teens’ lack of preparation for adulthood. In her popular book, How to Raise an Adult , Julie Lythcott-Haims writes that students entering college have been over-parented and as a result are timid about exploration, afraid to make mistakes, and unable to advocate for themselves.
Twenge suggests that the reality is more complicated. Today’s teens are legitimately closer to their parents than previous generations, but their life course has also been shaped by income inequality that demoralizes their hopes for the future. Compared to previous generations, iGens believe they have less control over how their lives turn out. Instead, they think that the system is already rigged against them—a dispiriting finding about a segment of the lifespan that is designed for creatively reimagining the future .
iGens exhibit more care for others. iGens, more than other generations, are respectful and inclusive of diversity of many kinds. Yet as a result, they reject offensive speech more than any earlier generation, and they are derided for their “fragility” and need for “ trigger warnings ” and “safe spaces.” (Trigger warnings are notifications that material to be covered may be distressing to some. A safe space is a zone that is absent of triggering rhetoric.)
Today’s colleges are tied in knots trying to reconcile their students’ increasing care for others with the importance of having open dialogue about difficult subjects. Dis-invitations to campus speakers are at an all-time high, more students believe the First Amendment is “outdated,” and some faculty have been fired for discussing race in their classrooms. Comedians are steering clear of college campuses, Twenge reports, afraid to offend.
The future of teen well-being
Social scientists will discuss Twenge’s data and conclusions for some time to come, and there is so much information—much of it correlational—there is bound to be a dropped stitch somewhere. For example, life history theory is a useful macro explanation for teens’ slow growth, but I wonder how income inequality or rising rates of insecure attachments among teens and their parents are contributing to this phenomenon. And Twenge claims that childhood has lengthened, but that runs counter to data showing earlier onset of puberty.
So what can we take away from Twenge’s thoughtful macro-analysis? The implicit lesson for parents is that we need more nuanced parenting. We can be close to our children and still foster self-reliance. We can allow some screen time for our teens and make sure the priority is still on in-person relationships. We can teach empathy and respect but also how to engage in hard discussions with people who disagree with us. We should not shirk from teaching skills for adulthood, or we risk raising unprepared children. And we can—and must—teach teens that marketing of new media is always to the benefit of the seller, not necessarily the buyer.
Yet it’s not all about parenting. The cross-generational analysis that Twenge offers is an important reminder that lives are shaped by historical shifts in culture, economy, and technology. Therefore, if we as a society truly care about human outcomes, we must carefully nurture the conditions in which the next generation can flourish.
We can’t market technologies that capture dopamine, hijack attention, and tether people to a screen, and then wonder why they are lonely and hurting. We can’t promote social movements that improve empathy, respect, and kindness toward others and then become frustrated that our kids are so sensitive. We can’t vote for politicians who stall upward mobility and then wonder why teens are not motivated. Society challenges teens and parents to improve; but can society take on the tough responsibility of making decisions with teens’ well-being in mind?
The good news is that iGens are less entitled, narcissistic, and over-confident than earlier generations, and they are ready to work hard. They are inclusive and concerned about social justice. And they are increasingly more diverse and less partisan, which means they may eventually insist on more cooperative, more just, and more egalitarian systems.
Social media will likely play a role in that revolution—if it doesn’t sink our kids with anxiety and depression first.
About the Author

Diana Divecha
Diana Divecha, Ph.D. , is a developmental psychologist, an assistant clinical professor at the Yale Child Study Center and Yale Center for Emotional Intelligence, and on the advisory board of the Greater Good Science Center. Her blog is developmentalscience.com .
You May Also Enjoy

This article — and everything on this site — is funded by readers like you.
Become a subscribing member today. Help us continue to bring “the science of a meaningful life” to you and to millions around the globe.
- Get involved
Youth and technology: 5 ways we're changing the world
August 10, 2018.

Scarlet Clemente
Intern, Digital and Online team, UNDP
As a user of digital platforms and a professional in the communications field, I see how quickly and effectively technology has opened doors, connected people from remote communities with the same interests, and provided new opportunities to women, vulnerable groups and especially to young people.
Technology has helped immensely to boost access to large amounts of information and has supported changes that have transformed our lives forever. The innovative potential of young people, combined with the power of technology, is already proving to be a powerful force on the road to achieving the Sustainable Development Goals.
Today, youth actively contribute to the creation of new jobs, economic empowerment of vulnerable groups, the promotion of better health systems and access to inclusive and quality education.
Here are five stories where avant-garde technology, creative ideas and young and passionate visionaries intertwine to give life to development initiatives that are changing the world.
1. Green thinking
RecLeb - Recycle the Smart Way is a project developed by Khalil, a 23-year-old electrical and computer engineer, aiming to the high levels of pollution in Lebanon resulting from improper waste management.
RecLeb will help residents classify their solid waste through a mobile web platform, promoting "green thinking" among the community and healthy environments for young people .
2. Enterprising solutions
Hayfa Sdiri is a 19-year-old Tunisian social activist, blogger and founder of Entr@crush . This is an online platform designed for young entrepreneurs, where people with similar ideas and interests converge: young entrepreneurs, investors and sponsors.
This non-profit initiative, initially developed by five members and with almost no seed capital, promotes entrepreneurship and innovation and Sustainable Development Goal (SDG) 8, which promotes inclusive and sustainable economic growth and decent work for all.
The platform has brought together young entrepreneurs willing to provide their knowledge for free, teaching virtual learning courses on a variety of topics that serve future entrepreneurs. For women who live in remote areas, this platform is a way to gain new skills and set up businesses, without the need to travel to the cities.

3. Preventing violence
Putting an end to physical and verbal violence and sexual harassment in commercial establishments in Brazil, together with reducing the gender gap in information technology, was the goal of the creators of the application Não me calo (I will not shut up, in English).
This app classifies commercial premises according to the number of incidents reported by users and identifies those areas of higher risk for being harassed or assaulted.
At the same time, Não me calo encourages diners to make complaints and request the owner of the premises and government representatives to take measures to improve security in the place.
4. Robot-assisted participation
Badia is a messaging robot designed to shorten the communication gap between government authorities and citizens. It was developed by Montassar, a 25 year-old architect and university professor in Tunisia.
This entrepreneur has devised an innovative solution to address the lack of citizen participation in his hometown of Sidi Bouzid. The chatbot answers questions from residents on issues related to the local budget, promoting the flow of information and citizen participation.
5. Multi-dimensional thinking
Supporting the entry of youth who have suffered some disability during migratory processes or as a result of violence in the labour market was the vision of the young doctors, engineers and industrial designers in Honduras who gave life to an orthopaedic prosthesis model produced with 3D printing technology.
The prototype, which has been developed using only the printer, a laser cutter and a computer with design software, offers a better quality of life of people with disabilities and a big step towards achieving the SDGs.
These are just a few of the millions of young people who are helping to bring about change around the world. Promoting the wellbeing of the most vulnerable people and communities is a challenge that young people have taken on with passion and commitment. They just need support and opportunities from governments, civil society and the private sector, and the involvement of their own communities. Providing access to education and financing, boosting their creativity and innovation and simply believing in their ideas will help them make their projects and visions a reality. With this kind of support, youth can play a huge role in bringing about the world we want by 2030 – a world of peace, prosperity and inclusion, leaving no one behind.

- Youth Program
- Wharton Online
- Business Journal Articles
- Entrepreneurs & Leaders
- Science & Technology
- Student Essays
Student Essay: Helping the Older Generation Embrace Technology

Share Article:
Google Classroom:
Jordan Mittler, a sophomore at The Ramaz Upper School in New York City and a participant in the Wharton Global Youth Summer Program, is the founder of Mittler Senior Technology, a company that helps senior citizens adapt to the world of technology. In this student essay, Jordan shares the story of how he started his business and why it has become so critical during this time of social isolation — especially in New York City, the epicenter of the coronavirus pandemic in the U.S.
In the next few months, Wharton Global Youth will be featuring a new essay every week, written by students around the world who are at home and eager to share their stories of entrepreneurship, leadership and experiences with business.
Five years ago, I gifted my grandparents, Janet and Mark Mittler, iPhones because it was painful for me to watch them still using flip phones! I have always been passionate about technology. I needed to get my grandparents, with whom I am very close, on board with the latest gadgets. It never even occurred to me that they would have no idea how to use an iPhone. They did not know how to perform many of the basic functions that come so easily to my generation, such as texting, Facetiming, photographing — and the list goes on.
And so, the idea for my business was born. I knew I needed to help this older generation, who missed the technology boom and was literally scared of trying to figure out our new connected world. As a result of this very real fear, they were often left alone and out of touch because they couldn’t communicate like everyone else.
Bonnie’s Got Mail
I decided to test my market concept at the local nursing home. I will never forget walking through those doors. I was only 11 at the time, and the director looked at me as if I had 10 heads. I went to the recreation floor and asked over a microphone: “Who would like free technology help?” I only had one taker. Her name was Bonnie Fisher, and I sat with her one-on-one for more than a year providing technology lessons. You should have seen Bonnie light up when she figured out how to connect with her sister and friends over email! I needed to figure out a way to reach a bigger audience.
I reached out to my synagogue, Congregation Kehilath Jeshrun, and asked if they would send a letter by mail promoting free technology help to all of their members over the age of 65. The synagogue was flooded with phone calls from interested seniors looking to enroll in tech class each Sunday. My temple, affiliated with my school, also let me use the school’s computer lab to hold my weekly classes. So many seniors showed interest that I had to maintain a waitlist. I got them into the classroom and taught them everything from texting to FaceTime and how to navigate the internet.
Fast forward to February 2020, and my classes were booming. I had even inspired some of my friends to join me in volunteering their time as teaching assistants. I had just added another class to fit in as many beginner and intermediate seniors as possible, and I felt like I was in a very good position to start scaling my business to reach even more learners.
We all know what happened next. Coronavirus swept through the world and our country, hitting the senior population the hardest and having a grim impact on New York City (reporting nearly 4,500 deaths through the beginning of April). During this time, I canceled my Sunday classes as my own schedule moved to at-home online learning.
I also realized, however, that senior citizens were suddenly even more cut off than ever. This new world of distancing was going to throw the older generation into more social isolation than they had ever experienced. One of my students, Roz Zuger, is 94 years old. I knew she would be disappointed without her weekly dose of tech class. So, I decided that I would attempt to continue my classes online via Zoom and walk all of my seniors through setting up the application and account. I started with Roz, spending endless phone calls with her to get her set up and comfortable with the online meeting platform. Roz had lots of trouble with the audio function on Zoom, and we slowly worked through this together.
After missing only one in-person class – and sending multiple texts and reminder calls — I had my whole class plus others online with me for our first virtual session. I updated my curriculum to be most helpful for seniors during this time when they were homebound and alone. For example, Rabbi Haskel Lookstein, the Rabbi Emeritus of my synagogue and Principal Emeritus of my school, needed help creating a group chat so he could communicate with all his children at one time. He was having particular trouble setting this up. I was able to show him virtually how to work through all the issues.
Facetiming and Ordering Groceries Online
The key to my teaching success with the older generation is showing, not just explaining. For seniors, talking in technology terms is less effective than presenting them with a visual of how to do something. They’re just not used to the language of technology. Roz, for example, was only able to launch Zoom after I Facetimed with her and sent her pictures via text of the next steps she needed to take. I helped Rabbi Lookstein by sharing visuals with him from my own computer screen.
In the past few weeks, we have been figuring this out as we go along – and it’s working. I started to record all of my Zoom sessions, so the seniors could replay any section of our class for review. After each online session, I send out a link to the recording, as well as a message with everything covered in class that day. My updated curriculum includes showing my students (which total some 80 seniors) how to order groceries online, how to order from Amazon, how to Facetime to stay connected, how to access online newspapers, and, of course, how to mute and unmute their Zoom audio.
It has been really rewarding for me to help so many people become tech-savvy during a time when technology has never been more fundamental to our daily lives. Social distancing has helped me bridge even further the gap between generations – and empower older people with the very valuable tool of connection.
Related Links
- Teen Vogue: Teens Are Helping Seniors Stay Connected
Conversation Starters
How did Jordan Mittler think like an entrepreneur in a time of crisis? Need help? Check out this Wharton Global Youth article for guidance.
Initially, Jordan only had one customer. Why was Bonnie so important to the growth of his idea and his business?
Have you used innovation to respond to needs during the coronavirus pandemic? Share your story in the Comment section of this article.
33 comments on “ Student Essay: Helping the Older Generation Embrace Technology ”
Wow! It’s incredible how technology can connect everyone. Many people often say that technology drifts us apart, but I’d like to disagree. In the current age, technology lets people from all walks of life to seamlessly connect. From Jordan’s example of how he helped local senior citizens be accustom to technology, it indeed shows how something as small as a smartphone can bridge generational divides.
Moreover, I’d like to add that I’ve seen a similar experience with my grandparents. My grandparents currently reside in India while I live in the US. This poses a problem as we cannot communicate readily. However, I found a solution to that vexing issue last summer. My family and I decided it was time for a change in the technology my grandparents were using, so we bought them iPhones. I helped them understand the ins and outs of how to use the technology which they were not familiar with. Because of this, they often facetime us from India and have even become like teenagers, as now they are glued to their phones.
Hi Vishnu, I really enjoyed reading your anecdote about your grandparents in India. I could relate to this issue since my grandparents live in Maryland, while I reside in New Jersey. Pre-isolation, my extended family and I would visit them almost bimonthly. This was crucial to their well-being, as they live alone in a rural area. During the quarantine, I helped introduce them to Zoom, which has been a useful online tool. Now that they are capable of using it, our entire family has weekly digital chats. In relation to this article, our examples of giving help to our grandparents exemplify the responsibility of younger generations to take initiative with technology. Jordan allowing the Rabbi Emeritus of his synagogue to communicate with all his children at once is an important example of lending knowledge and skills to older generations to maximize efficiency and happiness during these times of uncertainty.
I understand that technology helps connect people, especially during this time of endless quarantines. It is beneficial that the older generation is taking an interest in technology, breaking the stereotype that the elderly reject new ideas. After all, technology was and is made to make humans’ lives easier. However, while reading both your comments, Vishnu and Charlie, along with the article, I see that in all the cases of older people using technology, it is because the elderly generation have no other ways to stay connected. Now, this sparked a curious thought inside me—the elderly are using tech because especially during this time period, they really need it to prevent themselves from becoming isolated. But when it comes to young people, we just use tech because we are so addicted to it. We reach for a phone because it’s just what teens do. We text, FaceTime, and play multiplayer games with each other simultaneously. For the elderly, the chance to be able to connect with their loved ones is a big highlight in their life. They have not experienced such ease and luxury for much of their lives.
In contrast, teens have grown up around technology. We should try to bring back a culture that is less focused on technology usage to grow up appreciating the time we use technology, especially to connect with others. The younger generation is so desensitized by constant interaction through texting and voice/video calls that we often fail to appreciate it. I was surprised by the enthusiasm of the elderly when Jordan offered classes, but now I realize that it’s because they have realized its value and are taking efforts to gain the most out of it. For me, it took spending some time in quarantine to realize this. My friends and I are always complaining how we are so lonely, when we have actually been texting and calling daily before the COVID-19 outbreak. Teens need to shift a little bit away from the constant technology usage and take time to do other things that do not require technology—perhaps even teaching their elderly relatives about technology, as Jordan did.
I also have another major concern: older people are already at huge risk to scams and privacy issues, and presenting them with increased technology would give others more opportunities to take advantage of the elderly. I already admire Jordan very much for being able to accomplish the feat of teaching the elderly about technology, and I am also very impressed at how he runs his program so professionally and in such an organized way. But I also hope that Jordan, along with you, Vishnu and Charlie, for your grandparents, have presented the gift of technology as well as explained the dangers that come with technology. There are many scammers and hackers that target the elderly, as they are known to take weaker security measures without knowing the consequences. They are more susceptible to common false alerts on the internet and on phone calls. When we think of introducing technology to the elderly, thinking about their tech security and scam-awareness are not the first things that come to mind, so I think there should be further steps taken to make that a priority. Still, I understand that connecting with loved ones is a priority in this case, as it is a good thing that your grandparents have been able to establish a system of communication to maximize the time you all share. I hope there will be more cases similar to that of yours and Jordan’s students. That way, the world can truly be connected and everyone will FEEL connected!
Daniel It is interesting that you note that students now are doing school from home and despite being tech savvy, they miss the socialization of school and may have to find other ways of relating to their friends or spending their time. They can stimulate their minds thinking about how they can contribute to society, or better their reading and writing skills.
Charlie It is important for children and grandchildren to recognize that their senior relatives can benefit from learning technology, and a little patience in instructing them will make them so happy. On a personal note, my Rabbi has done so much for my family and has been there for all of our family’s life events, so it gave me personal pleasure to help teach him how to connect with his family in new ways during these challenging times.
I love your personal experience with your grandparents. Your thoughts remind me that helping the older generation learn the use of technology also help us connects our lives with theirs.
Vishnu This is wonderful to hear that you got your grandparents iPhones and they are now using FaceTime. It is interesting that you point out that technology sometimes causes people to drift apart, maybe because it is often something people do alone without communicating with others. There are so many elements of technology like face time or zoom that allow people to connect virtually.
Hey Vishnu,
It sounds like we both share Jordan’s experience with the elderly population. I definitely agree that technology has connected us all and bridged generations. While your grandparents are in India, mine are in Florida. I know it’s not quite as far away, but for them, it’s far enough. Similar to how you guys had to cater your lessons to what their generation was used to, I have had my share of challenging but also rewarding experiences. For Jordan, it was FaceTime and Zoom; for me, it was Gmail.
My grandpa called me one day because his friend had sent out a party invite as a list. Grandpa spent about forty minutes trying to find it. I told him to look carefully and like Santa, check his list twice. He didn’t think that was funny. I realized that his friend’s email probably went to his Spambox. I told him to look to the left to find Spambox and click on it. He replied “My Gmail must be different from yours; I don’t have a Spambox folder.” After a few minutes of trying to describe it to him, I FaceTimed him. I looked on his screen and realized that he needed to scroll down in order to find Spambox.
For me, I had always automatically scrolled down to find it without even realizing that I did this. To me, every action or click is like a knee-jerk reflex, but I realized that for grandpa, his reflexes needed a bit more time to kick in. Jordan is absolutely right in that the elderly need more hands-on and visual support. Remember, they grew up with things that required more physical interaction like holding a thick hardcovered book or applying their index finger on a rotary phone. Even my mom tells me she used to love watching each digit of the rotary phone make its way back!
Anyways, thank goodness for FaceTime. I showed grandpa how to scroll down to find his Spambox. And sure enough, the mysterious party invite miraculously appeared. I thought about teaching Grandpa how to move that conversation to his Inbox, but he was so elated that I decided to save this lesson for another day.
I found this article very relatable as I have as well tried to teach my grandparents how to use a mobile phone. At the end I was only able to teach my grandmother how to play candy crush and how to select who she wanted to call without needing to type the number every time. But nothing more. She kept refusing to learn the “new and unnecessary technologies”.
What he is doing very important, specially during the coronavirus epidemic. I have found the elderly are the ones who suffer the most isolation, as they are the ones that are less connected. It reminds me of a video what was viral in social media about a grandmother who sang happy birthday to herself, alone, in her house. It broke my heart. This is why seemingly-small ideas like these can really make an impact and change people’s lives for the better.
Hi Alejandra! I can totally relate to your experience. Due to the COVID-19 pandemic, I have been sympathizing for the elderly in nursing homes, who are not able to interact with families. Therefore, I started Facetime sessions with the elderly, either playing piano for them or chatting with them to help time pass by for them. However, I came across some obstacles, such as having difficulties getting on the video chat. She told me that although she enjoys having a companion to talk to, it is really hard for her to work with the technology, such as logging onto the computer. I was dejected for not being able to teach her about technology usage due to the quarantine lockdown.
Furthermore, I live on the opposite side of the globe from my grandmother. The only form of communicating and interacting is through technology. However, she also has hard time using it as well, and it really is painful to think that I am not able to spend most of the time actually talking rather than being lost on using the technology to communicate, especially when I want to spend as much time with her.
As of in the near future, I would like to create a nonprofit business, putting an emphasis on sharing our knowledge of technology to those who are not efficient with it.
Alejandra Seniors are often fixed in their ways and unwilling to change. They like what has been working for so many years. They have to be told that is ok to try things with their phone and not to be afraid to make a mistake. Your grandmother liked to make calls but she may like to learn how to text if she is encouraged to do so, and understand this is a popular way to communicating these days. If she tries it maybe she will like it. She may appreciate someone texting her an image or picture, something you can’t do over the phone.
This article really reflects the present situation of contemporary society.In just 20 years, from cover phones to smartphones, from 2G to 5G, from 8GB to 512GB, the change is so fast and dramatic that the elderly feel disjointed by the society. Take my family for instance. In the 5 years ago, my grandparents don’t know how to use the smartphones. But now, they can use the app like Wechat to communicate with others. When they go out and buy stuffs, they use the apple pay instead of paying the cash. This paves the convenient for them because the elderly will be easy to lost cash or coins on the way home. You know that they will be disappointed and complaint when they know they just lost several dollars. This problem can be solved now. The another advantage that I discovered is that seeing the doctor online. In the past, my grandfather had to get up early around 5.am and go to the hospital to make an appointment. In the morning, the temperature is very low and it is so tired for him to register. But now, they can make the appointment online through the app. This can largely save the time on the way to the hospital and queuing outside the gate. After finishing the doctor, The medicine will be mailed to the home, so that grandpa would not have to go to the hospital to get it again and again. This class sounds great since it helped a lot of “students” to learn the advanced technology. Nowadays, many young people are busy with their work and don’ have enough time to teach their parents to use the phones. This class just solves this embarrassment. Recently, my grandparents know a lot of knowledge about the prevention of COVID-19 and buying the food online without going to the market to reduce the risk of infection. The phones really make the life more convenient and these classes should be encouraged by the public. We should try our best to make the contribution to the society.
I agree with you, YuTao. The article really emphasizes the change that technology has brought onto the modern world and the transformational effect it can have on someone’s life. As technology evolves every day, so does mankind. And in this time and day, it’s up to the newer generation to educate the older generations about this change. Being part of the new generation myself, I’ve had to teach many family members about technology as well, such as setting up an app, purchasing something, or helping them understand how to communicate with their friends through the use of WeChat and similar apps. A couple of years ago, we went back to China to visit our family, and at the end of the trip, because the thought of saying goodbye and not speaking to them for a long time was so painful, we decided to get them new phones and teach them how to use them so we could communicate with the touch of a button whenever we missed each other. My cousin and I had to teach our uncles, aunts, and grandparents how to set up their new phones and WeChat because technology was still foreign to them at the time. And now, they use their phones just like anyone would in this day and time, despite the large age gap between us. At home, my mom constantly asks me questions about technology because she isn’t very technologically advanced, due to the fact that she immigrated here from China back when there was little technology available. However, now that she has one, she constantly asks me how to set things up, how to search things up, or how to manage her WeChat when she wants to call or FaceTime some of her friends. She’s also learned to use her phone to go places by using Google Maps. Using handheld maps and knowing the routes by heart is no longer needed with the advancement of technology. Because of the elderly’s age, getting places and doing things by themselves is not as easy as it was when they were younger. They aren’t able to support themselves, and their kids may be too busy with work and their own lives to be around them every hour of the day. With their newfound technology, they can call for assistance by simply pressing a button that will notify help, or call someone in case of an emergency. Technology could very well save someone’s life. Moreover, I feel like the class that Jordan has decided to teach could end up helping everyone, not just his students. His teaching the classes means that the elderly’s kids don’t need to teach them themselves, and instead can focus on working and supporting their family as a whole. They can rest assured knowing that their parents are safe and that they know what to do in case of an emergency. In addition, they could also learn to download some games for their own entertainment. It’s important to acknowledge Jordan for everything he’s done and to appreciate him for giving us this opportunity to experience something new that can help many. This example shows just how much technology has evolved over these years.
YuTao Thank you for your kind words. More people are no longer using money, so it would be helpful for seniors to use their phone to pay for things, maybe with credit card or Apple Pay. It is very helpful for seniors to be able to use electronics for medical purposes, like emailing with a doctor. I also teach in my class about a healthcare app where seniors can keep all of their medical information.
Experience is key in entrepreneurship. One of the few ways we have to better ourselves as entrepreneurs, and our businesses as life experiences, is going through an initial process of practice and learning, often a synonym for failure. Bonnie’s role in the case of this fantastic entrepreneurial story is exactly this one: giving Jordan a starting point, from which acknowledging the actions necessary to improve the quality of the business. As often stated throughout the article, connecting people has never had such an importance in the terrible crisis we are facing due to the Coronavirus outbreak. Older people are being left behind, not only technologically, but unfortunately socially too: missing tools, such as the previously discussed iPhones and laptops, and absent experience, make it much more difficult for grandmas and grandpas to go beyond the standard, old-fashioned phone call, in a world, in a time, where the closer we can get to having real-life meeting with our loved ones is joining a Zoom call. I personally find this a wonderful example of how we, as youngsters, can personally engage in making these terrible times lighter and less burdensome: each small action can make a difference, regardless of the size of our targeted audience, and our duty as world-citizen, I think, has never had such an important role in our everyday life.
Jacopo I’ve been very fortunate to have this entrepreneurial experience at this early age, and I hope to continue through my high school years so that I will be able to expand this program and scale it so it helps so many more people.
Similar to your experiences, I am also a sophomore and also volunteer to aid senior individuals in adapting to new technology! As a branch director in an organization called Teach Seniors Technology, I could not relate more on the initial difficulties in gaining customers. A few years ago, when I walked into my local community center to give my first lesson, there were only one or two students. In fact, there were many times during my first couple of months volunteering where no students had signed up for my weekly lessons! Though I wasn’t necessarily successful at first, I was also forced to adapt for these reasons. After reaching out to the community center staff, I was able to secure a classroom and promotion materials for my service which now serves several seniors each week.
Yet, I believe the “success” of my organization is determined by much more than the number of seniors who I teach. I often serve seniors from China, who have to bridge both the language barrier and the technological gap here in the United States. One of the ladies at my branch literally burst into joy when I taught her how to use Google Translate! In a world which is becoming increasingly interconnected and reliant on technology, I find that “success” of my volunteering branch rests on reintegrating these seniors into the technological area of society. I am overjoyed by the fact that there are other who share so much similarity with me. As more and more technological advancements are made, we must learn to bridge generational gaps so that our society as a whole can progress together with the technology that is being invented.
Jason It is wonderful to hear of another sophomore participating in a similar type of program.
Just like you, I help senior citizens but also adults from Central and South America with the technology and language barrier that thousands of people face in the United States. Technology is not common for lower classes in third world countries which makes it difficult for these adults and senior citizens to understand what seems like the basics of a smartphone for the majority of people in the US. It is such a joy when I see those which I help finally being able to communicate through Google Translate (An incredible tool I must say) and doing tasks like buying on Amazon, Instacart, or any online store. Observing this has made me come to the conclusion that we must come together as the new technology generation and help all of those individuals who have not gotten the opportunity to learn the incredible benefits the tech world brings; together we can close the digital divide across all ages, races, and socioeconomic statuses. We are the future and have yet to see great things created through technology.
Great response, Rossana! Do I see a team of digital-divide change makers forming here?
Technology helps join people, specially for the duration of this time of infinite quarantines. It is recommended that the older era is taking an hobby in technology, breaking the stereotype that the elderly reject new ideas. After all, technological know-how was once and is made to make humans’ lives easier. However, whilst analyzing each your comments, Vishnu and Charlie, alongside with the article, I see that in all the instances of older humans the use of technology, it is due to the fact the aged era have no different approaches to remain connected. Now, this sparked a curious thinking internal me—the aged are the use of tech due to the fact particularly at some stage in this time period, they genuinely want it to forestall themselves from turning into isolated. But when it comes to younger people, we simply use tech due to the fact we are so addicted to it. We attain for a smartphone due to the fact it’s simply what teenagers do. We text, FaceTime, and play multiplayer video games with every different simultaneously. For the elderly, the hazard to be in a position to join with their cherished ones is a massive spotlight in their life. They have no longer skilled such ease and luxurious for a great deal of their lives.
Despite efforts to teach the older generation about the newest developments in technology, it is saddening how much of the older generation is still very ignorant about it, especially since it is an era of technology.
One summer, I went to China to see my relatives, especially my grandmother. My grandmother lived in more rural parts of Sichuan, in Dazu. She didn’t need to use any technology; as long as she knew how to open the television and call using her corded home telephone, she could live happily growing plants in the back yard and raising chickens. She rarely went into the city to where my other relatives lived, they always visited her instead. However, to my delightful surprise, she proactively volunteered to wait for my arrival in Chongqing, one of the busiest cities in Sichuan.
When I arrived at my aunt’s apartment, where my grandma stayed, I asked jokingly why she decided to finally come to the city, she replied that it was because she hadn’t been here for so long. It was boring back home, and my grandma wanted to experience what life is like in the city for a while. She said that she would stay in the city until I left for America in a few weeks.
I was delighted and planned to take her to all sorts of fun places with great food that I had remembered from my last visit here. In Dazu, you could hardly find such boisterousness due to the lack of crowds. I was sure that she would enjoy it.
One morning, after I had officially settled in at my aunt’s house, my aunt and her husband told me that they were going to go somewhere for the rest of the day and needed me to take care of my grandmother. They said I could take my grandmother out to walk or do some other activities, but to be careful. I agreed with a smile.
My grandma was very happy this particular morning as well. She told me that she wanted to try exercising in the nearby park with some other old people; she wanted to make some friends here. I happily agreed. I walked her to the park and watched her dance and make merry with the folks there. After a few minutes, she could tell that I was a little restless and told me to play on my own and insisted that she could manage herself well. She said that she would go home when she wanted to and told me not to worry. I reluctantly agreed, told her the directions to the apartment building, and gave her the corresponding card. The apartment wasn’t that far, only one block away from the park. Then, I went off to a nearby stationary store to buy some souvenirs for my friends in America.
After some time, I picked the gifts that caught my fancy and went on the line to pay. The store was very popular and so the line was very long as well. After waiting for a quarter of an hour, I finally got out of the line and started my way home. In the distance, I saw a familiar figure. I panicked and hurriedly ran to the entrance of the apartment.
My grandma stood in the burning sun, her arms hung down at her sides, watching the pedestrians. Apparently, she had a squabble with the people from the park almost immediately after I left. She wasn’t in the mood to dance anymore, so she went home. However, the problem is that she didn’t know how to open the more technologically advanced apartment door. To me, the door system was very simple, you just had to swipe a card, but my grandmother never had to use this sort of system, she only ever needed a key. My grandma thought that you just had to press the card against the door or something. She also forgot how to call using the smartphone that was given to her. I also didn’t think it was necessary enough to teach my grandmother how to open the door since it seemed natural to me.
This story truly shows the importance of communication and the need to help the older generation with technology.
“When are you coming back?” These words were music to my 15-year-old ears. I had just helped fix the internet connectivity issue for Ms. Jacobson, one of the residents at Sequoias’, a senior residential facility, where I was volunteering to help seniors with their tech issues in the summer after my freshman year. Ms. Jacobson sent a very nice thank you note about the help she received from me to the Services Director at Sequoias who passed it on to me. The note, painstakingly written in spidery cursive must have taken Ms. Jacobson some time to write and is still cherished by me. The experience with helping seniors with their tech issues and entertaining them with piano recitals helped me get more attuned to the needs of my own grandparents. My two sets of grandparents are separated by a decade and come from similar backgrounds but have very different life experiences. One set of grandparents who live with us are older, technologically challenged, and can call on us anytime to help them operate the phone, the TV and other gadgets. They prefer to read the actual newspaper despite efforts to get them to read news online, and prefer talking on the phone instead of using Facetime. The younger set of grandparents who live in India have a large social circle, live on their own, and while still technologically challenged, have learned the basics of how to use a smartphone, browse the internet, and order online. Jordan’s article made me reflect on my experience working with seniors, both in my own family and outside and I realized that seniors face the same challenges that students of all ages face. First of all, every student learns in their own unique way, much like some of Jordan’s students – Roz and Rabbi Haskel. Some are visual learners, some need more time to read and absorb information on their own, etc. Secondly, each student has different capabilities and interests. Some like one set of my grandparents did not have much interest in learning how to use technology as they were happy with the old ways and could always ask us for help if they needed it. The other set of grandparents found ways to learn the basics that they needed to fulfill their needs as they were living on their own. There is also a social and cultural context to this. More and more seniors are now forced to live on their own, either in their homes or in senior facilities. Those that do not live with family face loneliness among other issues, and do need to know some basics such as texting, online searching and ordering, connecting with their medical provider online, etc. to stay safe, independent, and connected. The need to stay connected has been exacerbated by the COVID-19 pandemic. However, the issue with being connected is that not only are seniors more vulnerable to scams, they are also very gullible when it comes to fake news. I have had to constantly remind my grandparents who treat WhatsApp and Facebook as reliable news sources that everything they read there is not always true. The other issue is the plethora of apps, tools, and websites that can be overwhelming for seniors. I noticed this issue after working with a couple of seniors at Sequoias and created a home page for every senior I worked with, that contained shortcuts/icons for their most frequently used apps and websites for easy access. Perhaps in all of this, there is an opportunity to create senior-friendly apps and devices, but unfortunately, this is not a coveted demographic for tech companies and marketers. There is certainly a need to help seniors learn tech basics which can enrich and simplify their life. I applaud Jordan’s efforts to provide this valuable service to seniors in his community. However, the bigger question I ponder is that why are seniors put into this position in the first place where instead of enjoying time with their families, they are forced to learn new skills, especially when many have impacted cognitive skills which makes learning new things harder. Additionally, we are only talking about a subset of the senior population. There is a big population of seniors living in poverty who have more pressing issues such as survival to deal with. My own experience with my grandparents and with seniors I worked with is that every single one of them would have preferred to live with their families, surrounded by their children and grandchildren instead of connecting with them over facetime and group chats. In fact, the percentage of multigenerational families in the United States has continued to rise, primarily due to financial necessity. While one size does not fit all and every family has their own unique challenges, perhaps it’s time for us as a society to take a closer look at how best to support the needs of our senior population, given the increased life expectancy in the United States.
Hey, Jatin. I really enjoyed reading your thoughtful post and response. What I love most is that you bring up some broader issues that really add value to the “seniors and technology” conversation. I’ve always admired certain cultures — India for one — where families place more emphasis on caring for and living with their elders, the people without whom they would not even exist. The questions you raise about supporting our senior population are so important! We deliver them meals, help them connect, even give them a ride to the market, but we don’t go beyond to the point of human companionship and connection at a time when they need it most.
The age of smartphones has progressed so quickly that the fact the first iPhone originated just over ten years ago may come as a surprise to many. This development is only one example of a world industrializing at an unprecedented rate. Despite making communication and practically every other aspect of life easier, this revolution may not apply to all — the elderly, as you stated, are often not kept up to date to these new technologies. However, it must be noted that other adults may also not be kept up to date. I believe my parents are a prime example of this. They both immigrated to the United States in the 1980s and made a decent living running a restaurant. However, when it came time to digitalize, they struggled and required my older sister’s assistance to facilitate this new aspect of the business. Now that she’s off to college, it’s my turn to fulfill this position of filling out online documents and forms. This is a growing problem as it is a given that technology will only advance forward, regardless of whether there are those who are unable to utilize these new advantages. That is why I find programs like yours to be so fascinating and thoughtful. My mother has recently taken up taking computer classes, where she learns basic computer navigation skills. It is essential for the whole population to collectively adapt as a whole.
Alvin I appreciate the idea of showing seniors how to fill out forms online, and all of the elements involved in that process.
I certainly agree with Jordan that technology helps us stay connected. It is very important that we help the elderly members of the society on the use of technology. It is not easy to teach the older generation to use technology, as they are not quite familiar with it.
Moreover, I have also had a similar experience with my grandmother who just got a new iPhone and she did not know how to use it properly. Though she was able to make her daily phone calls and read her WhatsApp messages, she did not know how to access the Internet, do Face time and little other stuff. One day during the never-ending lockdown, I decided to teach my grandmother how to use her new phone. Since, she was having sleepless nights due to the change in her sleep cycle because of lockdown, I first taught her how to use YouTube so that she could put spiritual music on it and have good sleep. As days progressed I taught her how to access the daily news online, face timing, texting and many more things. This also gave me an opportunity to spend quality time with my grandmother, which I could not during my school days. My grandmother had a habit of doing all her office-work on paper so, later I started teaching her to use the laptop to check few mails and tally her accounts. This whole process not only helped her a great deal by making her work a lot easier, but also it helped me become more patient by answering the same quarries that she had again and again.
There have been vast advancements in technology over the years and it has helped us in many ways, such as online classes and courses, which are the most helpful things at the moment. By helping the elderly members of the society as to how technology can be used, bridges the generation gap and will help the society progress faster.
I’ve spent a lot of time helping relatives with technology and sometimes it can get very frustrating but I remember that they didn’t grow up with this like we did. So I am more patient and don’t get mad because I love my relatives. What Jordan is doing is really important, especially during this pandemic. The elderly are the most impacted in my opinion, because many of them lack technological experience. His Zoom meetings are a great idea though, keeping the elderly learning and up to date with technology so they can stay connected.
The younger generation is lucky. Since we were young, we have had access to electronic products. Elders often see their grandchildren typing like a speed of light with two thumbs on the keyboard or on the phone, while they themselves can only type letter by letter or word by word with their index fingers. Many elders have only had access to technologies in the past 15 to 20 years. We sometimes get annoyed when they want to learn how to use technology. But when thinking about our situations, aren’t we like them when we are trying to figure out how to solve a simple math question? We see the technologies are easy for us to learn and use, but the elders must take a long time to get used to using technologies.
The last time I saw my grandmother in person was five years ago, but we are able to FaceTime each other at least once a week. When I visited her in China five years ago, I saw her struggling to send a message on WeChat or even make a simple phone call. She would forget which group chat is which and would constantly send private messages in group chats with other family members in it. When I started teaching her how to use WeChat, I saw my grandma was listening to what I was saying very carefully. I taught her how to use WeChat for video calls, voice calls, and many other functions of the app. Later, she took her cellphone and just pressed on it casually trying to use the phone herself. This makes me think that the elders are still very curious to learn new things and look forward to more connections with others so as not to be disconnected from society.
Although she still struggles with using keyboards, my grandma has greatly increased her ability to use her phone. Now she is able to shop online and play simple games on her phone like mahjong and Candy Crush. She sends us many photos of places she has visited and writes that she wishes to take me on one of her trips. Communication is a bridge to build interpersonal relationships. From sharing feelings to expressing ideas, the world requires us to communicate with others. Not just through face-to-face communication, but also through technologies, we are able to share our feelings with others through a simple call or message. Especially during the COVID-19 pandemic, we find communication important with family members or friends or co-workers through technologies. We have stayed home for more than one and a half months, and we would need to communicate with our parents almost every day and stay with them 24/7 face-to-face. We might not know how to have a conversation with them before, but with this pandemic, we might have no choice but to speak with them. We have learned that communicating with them is not as hard as we thought, and moreover, it is enjoyable to hear stories from our parents or other elders in the family. The elders are aging every day and we are growing up every day. It is hard for us to frequently see each other in real life, so technology is how we would connect and communicate with them.
What a sensational experience, Jordan! I enjoyed reading your stories, and I was astonished at how your involvement with elders related to mine.
As another member of Generation Z, technology and the rapid advancement of modern devices have always piqued my interest. Due to my eagerness, I grew up as a tech nerd, earning the title of “tech guy” in the family. “Alvin, why is my wifi not connecting?” “Alvin, what’s wrong with our TV?” “Alvin, why is my Bluetooth not connecting?” At least five times a day, I would hear such questions from my parents and brothers. From simple wifi connection problems to complicated home appliance control systems, I had to be present if the issues involved technology.
My title became significant as COVID invaded our lives. Similar to your experience, my grandparents struggled the most as the majority of platforms and services turned online. Since my grandparents were in a higher-risk group for exposure to COVID, they had to be extremely cautious. They could not go outside to get food or to their workplace. Whether they liked it or not, they had to stay home and adapt to online platforms to order food and attend Zoom meetings. And, as the “tech guy” of the family, I was responsible for providing comfort for my grandparents. Starting from scratch, I had to water down difficult technological terminologies such as Airdrop, iCloud, and Bluetooth to help them rapidly adapt to new lifestyles. Such experiences were similar to teaching elementary schoolers about calculus, in which I realized how uncomfortable it was for my grandparents to utilize new technologies. For instance, Bluetooth features offer wireless connections within the comfort of one’s own vicinity, which is one of the reasons why younger generations utilize Bluetooth: it provides comfort. On the other hand, older generations have an arduous time figuring out how to connect devices using Bluetooth since they are unfamiliar with such features. It is true that consumers are attracted to more comfortable features, and businesses provide new technologies that could reduce time management for consumers. However, it creates a downside for older generations, making them take longer to do something. While convenience for the younger generations increases with the use of technology, the older generations are having difficulty adapting to rapid technological advancement.
By observing the hardships of older generations from my grandparents’ perspective, I thought there was a need for action. Although there are various ways to address such issues, I focused on a fundamental need for everyone: food.
Therefore, I gathered up my close friends, Robert and Kaiden, who shared similar visions regarding this issue, and we came up with an accessible software that will make it approachable for elders to order food from nearby food centers. Essentially, our solution focused on a sustainable, healthy, and accessible approach that is similar to your experience helping elders order groceries. We developed a food ordering app that sends prepackaged, nutritious meals to seniors who sign up for it. Our sign-up system is very simple since it could be pre-installed on phones, involves one click of a button, and has well-explained and accessible payment methods; for example, this service allows the program to automatically extract money from the elder’s source of payment which minimizes the complicated process of payment process every. Ultimately, elders can readily receive healthy and hearty meals at their doorstep. We also utilized the Zoom recording function to create tutorials to help elders navigate through our process. These methods of solution could sound ironic at first, but I believe the most effective solution for elders who are uncomfortable with technology is to expose them to an extent of unfamiliarity to reduce their discomfort.
Like most other start-ups, our application lacks feasibility, so initially, we must test it on a small group of elders and make adjustments. If our test proves to be successful, we will launch our application, which will familiarize elders with technology and aid them in accepting and embracing modern devices. Moreover, I would like to expand this business into providing food and holding online classes about ordering goods, entertainment, media, and safe technology use for elders. I would happily like to share words with you about this matter, and I want to resemble your helping and enthusiastic attitude towards social advancement.
Wow! This is a really beautiful essay. It inspires me to see a fellow teenager making such a positive impact in the world today.
Technology is one of the major generational gaps we have today, and it is very refreshing and encouraging to see someone trying to bridge that gap. I love your teaching strategy of showing instead of just telling. That is truly one of the best ways to explain. You made an astounding impact in a dreary and challenging time for many. As someone who teaches children in a local orphanage home, I can relate to the indescribable feeling of joy you get when your student finally understands.
I will also like to place emphasis on not just teaching seniors how to navigate the internet, but also on teaching them how to be safe while navigating the internet! Cyber crimes are increasing in a very tremendous way all over the world, as more people look for illegal means to usurp unknowing people. This is one of the major fears of seniors and the older generation concerning technology. I believe that teaching them how to best stay safe in the ‘dangerous’ global world provided by the internet would not just be beneficial to them, but it would also help in further bridging the generational gap.
Chidera, your comment is one that caught my attention. Your comment highlights a crucial aspect of our society today: the technology generation gap. Most importantly, the issue of cyber crimes. Indeed, with the rapid advancement of technology, it becomes increasingly challenging for elderly to keep up. Even some of us from younger generations struggle with mastering the intricacies of various tools and software, like navigating Google spreadsheets.
But you draw attention to the pressing issue of cybersecurity and cybercrime, which poses a significant threat to people of all ages, including the elderly. Even myself, who is clearly not an elderly person, receives tons and tons of spam messages and emails trying to trick me of my money. While these scams may not work on us, they can be extremely tempting for the elderly, who may be more vulnerable to such tactics.
For example, my friend’s grandma was a victim to these scams, falling victim to a company promising to save money for her granddaughter’s college tuition fee. This just highlights your point on the emphasis and awareness that should be put on cyber crimes. It demonstrates how easily elderly individuals can be targeted and deceived and the urgency of addressing the dangers they face while navigating the Internet.
Likewise, in the effort to bridge the technology generation gap, I believe that it is crucial to not only teach the elderly how to use technology but also raise awareness to the public about the prevalence of cybercrime and the importance of robust cybersecurity. By empowering people of all ages with knowledge and strategies to protect themselves online, we can help them become more confident and secure users of digital tools.
I truly believe that with stronger cybersecurity implementation and the awareness we can teach people about, the challenges of cyber crimes is one we can focus less on. Allowing us to focus more on bridging this generational gap, being able to facetime our loved ones, and even send them cool gadgets.
I think this is an amazing and much needed program! People tend to alienate the elderly from our evolving world, waving them off as they say, “You can’t teach an old dog new tricks.” This is incredibly isolating and unfair to them. A month ago, I helped organize a ceremony for my high school, and many senior citizens came to support their grandchildren. The program for the ceremony was online, and I watched many of them struggle to scan a QR code. It was clear they were embarrassed, and they deserve to spend the day celebrating their family rather than feeling ashamed.
It’s also important to recognize that technology can help them stay busy. Many of the elderly cannot drive or live very far from their families. My grandparents live across the world in India. They are retired, and travel is very hard for them. They don’t typically have much to do, and they can get bored and demoralized. However, my grandpa stays busy and keeps his mind sharp by playing sudoku on his iPad. My grandma loves to play candy crush or call her relatives. Teaching the elderly how to use technology can be more helpful than most realize.
Leave a Reply Cancel reply
Your email address will not be published. Required fields are marked *
Save my name, email, and website in this browser for the next time I comment.
Related Articles
A data project explores gun ownership in new york city, future of the business world: sanjana yeddula on raising gen z’s political awareness.
Home — Essay Samples — Information Science and Technology — Internet — The Impact Of Internet On Younger Generations
The Impact of Internet on Younger Generations
- Categories: Impact of Technology Internet
About this sample

Words: 573 |
Published: Feb 8, 2022
Words: 573 | Page: 1 | 3 min read

Cite this Essay
Let us write you an essay from scratch
- 450+ experts on 30 subjects ready to help
- Custom essay delivered in as few as 3 hours
Get high-quality help

Dr. Heisenberg
Verified writer
- Expert in: Information Science and Technology

+ 120 experts online
By clicking “Check Writers’ Offers”, you agree to our terms of service and privacy policy . We’ll occasionally send you promo and account related email
No need to pay just yet!
Related Essays
4 pages / 1753 words
2 pages / 812 words
3 pages / 1579 words
2 pages / 985 words
Remember! This is just a sample.
You can get your custom paper by one of our expert writers.
121 writers online

Still can’t find what you need?
Browse our vast selection of original essay samples, each expertly formatted and styled
Related Essays on Internet
Valkenburg, P. M., & Peter, J. (2007). Online communication and adolescent well-being: Testing the stimulation versus the displacement hypothesis. Journal of Computer-Mediated Communication, 12(4), 1169-1182.
The excessive use of the internet has become a prevalent concern in today's digital age. The internet, once a revolutionary tool for communication and information, has now transformed into an integral part of our daily lives. [...]
Alton, L. (2017, May 15). Is Working From Home Making You Feel Miserable?. NBC news. Retrieved from https://www.inc.com/amy-morin/heres-why-internet-has-made-us-lonelier-than-ever.html
Hawkley, L., Cacioppo, J. (2010). Loneliness is a bodily function like hunger. AoBM.Anderson, W. A. (n.d.). The Impact of ICT on Loneliness in Elder Individuals. University of Alabama.Sharifpoor, E., Mohammadzadeh, M. J., & [...]
Are humans being replaced with new technology? Nicolas Carr says reading is not the same anymore, after a few pages the brain and mind start wandering off. In this essay Carr talks about how Google’s search engine makes it easy [...]
Do you ever lose focus while reading? Find yourself constantly on your phone scrolling through emails, articles, and social feeds?The Shallows: What The Internet Is Doing To Our Brains by Nicholas Carr deeply examines the [...]
Related Topics
By clicking “Send”, you agree to our Terms of service and Privacy statement . We will occasionally send you account related emails.
Where do you want us to send this sample?
By clicking “Continue”, you agree to our terms of service and privacy policy.
Be careful. This essay is not unique
This essay was donated by a student and is likely to have been used and submitted before
Download this Sample
Free samples may contain mistakes and not unique parts
Sorry, we could not paraphrase this essay. Our professional writers can rewrite it and get you a unique paper.
Please check your inbox.
We can write you a custom essay that will follow your exact instructions and meet the deadlines. Let's fix your grades together!
Get Your Personalized Essay in 3 Hours or Less!
We use cookies to personalyze your web-site experience. By continuing we’ll assume you board with our cookie policy .
- Instructions Followed To The Letter
- Deadlines Met At Every Stage
- Unique And Plagiarism Free

IMAGES
VIDEO
COMMENTS
The younger generation and technology. Technology has become an inseparable part of the social, working and leisure life of people. Communication via emails, using multi-media sites, searching information or internet shopping are part of the daily routine in a high percentage of homes. Until a few years ago, analysis on the use of these devices ...
Introduction. This essay has explored the intricate relationship between modern technology and the younger generation, analyzing its impact on education, social interactions, mental health, digital literacy, and responsible citizenship.
Essay on Information Technology in 400 Words. Essay on Information Technology: Information Technology is the study of computer systems and telecommunications for storing, retrieving, and transmitting information using the Internet. Today, we rely on information technology to collect and transfer data from and on the internet.
With so much of our personal and professional worlds now inextricably tied to digital technology, Gen X and especially Baby Boomers can feel frustrated and intimidated by the idea of younger generations mastering complex modern technology with such ease — and usually while walking (or, unfortunately, driving!).
"There are a number of labels to describe the young people currently studying at school, college and university," Ellen John Helsper and Rebecca Evnon wrote in a 2010 article in the British Educational Research Journal. "They include the digital natives, the net generation, the Google generation or the millenials.
The most recent nationally representative surveys of the Pew Internet Project show how immersed teens and young adults are in the tech environment and how tied they are to the mobile and social sides of it. Some 95% of teens ages 12-17 are online, 76% use social networking sites, and 77% have cell phones. Moreover, 96% of those ages 18-29 are ...
The literature implies that the relationship between technology use and adolescent well-being is more complicated than an overall negative linear effect. In line with meta-analyses on adults, effects of digital technology use in general are mostly neutral to small. In their meta-review of 34 meta-analyses and systematic reviews, Meier and ...
While generations differ in their use of various technologies, a 2018 Center survey found that younger internet users also were more likely than older Americans who use the internet to say the internet has had a positive impact on society: 73% of online Millennials said the internet has been mostly a good thing for society, compared with 63% of ...
Digital technologies have profoundly changed childhood and adolescence. The internet and the means to access it, such as tablets and smartphones, along with social media platforms and messaging apps, have become integral to the lives of youth around the world. They have transformed their education and learning, the way they make and maintain friendships, how they spend their leisure time, and ...
Digitalized everyday life of the young generation. Children of today have been surrounded by digital technology since their birth; ever since, their everyday life and practices have been entwined with social media, smart phone, tablet, and Internet use. Digital technology has been thoroughly embedded with how they live and learn.
Technology empowers us to store, retrieve, and disseminate information across the globe, ensuring that knowledge is never lost. In the interconnected world of the 21st century, these two forces ...
January 3, 2022. Gen Z are not 'coddled.'. They are highly collaborative, self-reliant and pragmatic, according to new Stanford-affiliated research. Generation Z, the first generation never to ...
Technology's impact on the younger generation cannot be ignored. While it has brought about numerous benefits, such as increased connectivity and access to information, it also has its downsides. The negative effects of technology on youth are becoming increasingly apparent, with studies linking excessive social media use to poor sleep ...
The most influenced category of the population could be considered the young generation, and there are various reasons that could be listed for that statement. This study presents an analysis of the impacts of the modern technology on the communication skills, personalities and social behaviors of the youth in the technological context that ...
The Generations - Demographics tell only part of the story. For clarity, I will use the generational ranges provided by The Center For Generational Kinetics: Gen X: Born 1965 to 1976 - Coming ...
Moreover, it is worth raising awareness among young people about the dangers and risks that await them with excessive use of technology. Works Cited. Bibi, Arifa, et al. "Effect of Latest Technology and Social Media on Interpersonal Communication on Youth of Balochistan." Journal of Managerial Sciences, vol. 11, n. 3, 2018, pp. 475-490.
Every generation of teens is shaped by the social, political, and economic events of the day. Today's teenagers are no different—and they're the first generation whose lives are saturated by mobile technology and social media. In her new book, psychologist Jean Twenge uses large-scale surveys to draw a detailed portrait of ten qualities ...
The dynamics between the older generation and the younger generation offer a compelling study in contrasts and evolutionary societal norms. ... Analysis Of The Book 'The Dumbest Generation' By Mark Bauerlein Essay. In today's generation, technology has become a day to day necessity. ... Today's generation is very different from their parents ...
Here are five stories where avant-garde technology, creative ideas and young and passionate visionaries intertwine to give life to development initiatives that are changing the world. 1. Green thinking. RecLeb - Recycle the Smart Way is a project developed by Khalil, a 23-year-old electrical and computer engineer, aiming to the high levels of ...
However, as it has negatively impacted on life of young generation like health issues, poor social interaction, privacy threats etc. Hongnguyen (2015) highlights that smartphones act as a quickest communication tool, helps in contact with loved ones easily, entertainer to listen music & games and also help in study.
Google Classroom: Jordan Mittler, a sophomore at The Ramaz Upper School in New York City and a participant in the Wharton Global Youth Summer Program, is the founder of Mittler Senior Technology, a company that helps senior citizens adapt to the world of technology. In this student essay, Jordan shares the story of how he started his business ...
The Impact of Internet on Younger Generations. Nowadays, people spend most of their time online whether its with friends, streaming videos or conducting business. While there are many advantages due to the ever-changing technology to us humans, it bears many disadvantages. One of the most serious problems we face now is the safety of our ...
Parents and educators should monitor the influence of modern technology and gadgets on the younger generation, and even more so on the early age of young people. Gone are the days of having more personal interactions with the family members, friends, and acquaintances.