An official website of the United States government
The .gov means it’s official. Federal government websites often end in .gov or .mil. Before sharing sensitive information, make sure you’re on a federal government site.
The site is secure. The https:// ensures that you are connecting to the official website and that any information you provide is encrypted and transmitted securely.
- Publications
- Account settings
Preview improvements coming to the PMC website in October 2024. Learn More or Try it out now .
- Advanced Search
- Journal List
- J Grad Med Educ
- v.12(3); 2020 Jun

Academic Writing, and How to Learn How to Write
Marcin kozak.
Associate Professor, Department of Media, Journalism and Social Communication, University of Information Technology and Management, Rzeszow, Poland
I read with great interest the editorial by Yarris and colleagues on academic writing, 1 and I fully agree that academic writing is going to change. It must change, to be true—not only because it should align with technological development, but also because far too often academic texts are unclear, clumsy, and inefficient. We need articles like Yarris et al's and similar initiatives to change this for the better.
A man of the written word, I see academic writing mainly through the prism of actual writing—which does not mean I do not agree with everything else Yarris and colleagues wrote about, because I do. But let me focus on academic writing as an actual writing process. Even if the written word is to be partly replaced with other means, such as visualization, we will continue to write, at least because this is likely the best means of showing what we think . Most visualizations, be it a graph or a table, also show what we think, because they show how we interpret the data: For a given data set, we can often present various charts, offering quite different interpretations. But to show what you think, it's best to write it, even if other measures can help.
The authors emphasize, and I fully agree, that academic writers will have to change their approach to writing, switching from an incomprehensible language full of jargon to an understandable one—and even, I would say, to pleasurable writing. 2 Sad but true, more often than not academic texts are difficult to understand, and the future of academic writing should change that.
To this end, we not only need to put more emphasis on teaching young researchers how to write, but also on convincing not so young ones to further develop their writing skills. While many among the former can be taught, most of the latter would prefer to self-learn. For this, they need to practice, and they need good resources—Yarris and colleagues proposed at least a couple of them. 1
While I really like Stephen King's On Writing 3 and Anne Lamott's Bird by Bird: Some Instructions on Writing and Life , 4 and I love Helen Sword's Air & Light & Time & Space: How Successful Academics Write , 5 these are by no means writing resources. I am afraid that beginning writers starting off with these books would learn what the life of a writer is like, not how to write. Explaining how to organize your work in order to write more, Paul J. Silva also does not offer advice on how to write well. 6
There are quite a few books that do not tell stories about writers and writing, but that show what good writing is and how to write well. Yarris and colleagues provided a perfect example: Helen Sword's Stylish Academic Writing —but unlike the authors stated, it deals with academic, not general, writing. I think academic authors would learn a lot from Thomas S. Kane's The Oxford Essential Guide to Writing 7 and Joseph M. Williams's Style: Ten Lessons in Charity and Grace , 8 both being general writing books; and from Anne E. Greene's Writing Science in Plain English , focused on academic writing, particularly on biology. 9 Let's not forget William Zinsser's On Writing Well: The Classic Guide to Writing Nonfiction , another general writing book of useful advice, very well-known among nonfiction writers. 10 Michael Swan's Practical English Usage 11 might not offer the most pleasant read, since it's a usage guide—but it's known of great usefulness for anyone writing in English.
Of course, these are just my choices. I have enjoyed 20 or 30 other books (by such authors as Roy Peter Clark, Patricia T. O'Conner, Lynne Truss, Constance Hale, June Casagrande, and Mark Forsyth), but the brevity of this letter does not enable me to provide that long a list. If you wish and have the time, find your own favorites, but I would advise beginning with the ones described above.
I have always treated general writing books as more useful than most academic writing ones, for the simple reason that often the latter are too … academic. There are exceptions, though, like the above-mentioned Sword's and Greene's books. I am afraid that too few academics and educators have time to spend on reading about writing. So, unless you are, like me, a rare specimen of a minority population finding pleasure in reading about writing, and do so not only to learn how to write, but also to enjoy your scarce free time—start off with Greene and Sword, and then, if you can, follow with Williams, Zinsser, and Kane.
- I nfographics
- Show AWL words
- Subscribe to newsletter
What is academic writing?
- Academic Style
- What is the writing process?
- Understanding the title
- Brainstorming
- Researching
- First draft
- Proofreading
- Report writing
- Compare & contrast
- Cause & effect
- Problem-solution
- Classification
- Essay structure
- Introduction
- Literature review
- Book review
- Research proposal
- Thesis/dissertation
- What is cohesion?
- Cohesion vs coherence
- Transition signals
- What are references?
- In-text citations
- Reference sections
- Reporting verbs
- Band descriptors
Show AWL words on this page.
Levels 1-5: grey Levels 6-10: orange
Show sorted lists of these words.
Any words you don't know? Look them up in the website's built-in dictionary .
Choose a dictionary . Wordnet OPTED both
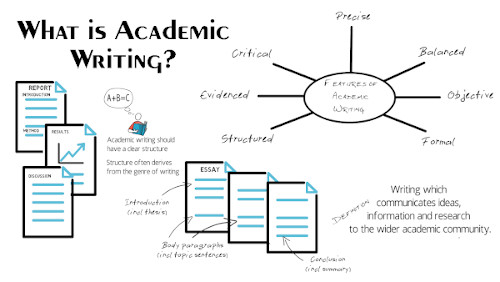
Academic Writing Seven features of academic writing
Academic writing is arguably the most important skill in academic contexts, since writing is the main method of academic communication. It is also the most difficult skill for most students to master. This page considers what academic writing is , looking in detail at the main features of academic writing , as well as suggesting ways to develop academic writing . There is a checklist at the end for you to check your understanding.
For another look at the same content, check out YouTube or Youku , or the infographic . There is a worksheet (with answers and teacher's notes) for this video.
Academic writing is writing which communicates ideas, information and research to the wider academic community. It can be divided into two types: student academic writing, which is used as a form of assessment at university, as well as at schools as preparation for university study; and expert academic writing, which is writing that is intended for publication in an academic journal or book. Both types of academic writing (student and expert) are expected to adhere to the same standards, which can be difficult for students to master. The characteristics of academic writing which together distinguish it from other forms of writing are that it is:
- structured ;
- evidenced ;
- objective ;
Features of academic writing

Check out the features of academic writing infographic »
Academic writing should have a clear structure. The structure will often derive from the genre of writing . For example, a report will have an introduction (including the aim or aims), a method section, a discussion section and so on, while an essay will have an introduction (including a thesis statement ), clear body paragraphs with topic sentences , and a conclusion. The writing should be coherent , with logical progression throughout, and cohesive , with the different parts of the writing clearly connected. Careful planning before writing is essential to ensure that the final product will be well structured, with a clear focus and logical progression of ideas.
Opinions and arguments in academic writing should be supported by evidence. Often the writing will be based on information from experts in the field, and as such, it will be important to reference the information appropriately, for example via the use of in-text citations and a reference section .
Academic writing does more than just describe. As an academic writer, you should not simply accept everything you read as fact. You need to analyse and evaluate the information you are writing about, in other words make judgements about it, before you decide whether and how to integrate it into your own writing. This is known as critical writing . Critical writing requires a great deal of research in order for the writer to develop a deep enough understanding of the topic to be truly critical about it.
Academic writing should be balanced. This means giving consideration to all sides of the issue and avoiding bias. As noted above, all research, evidence and arguments can be challenged, and it is important for the academic writer to show their stance on a particular topic, in other words how strong their claims are. This can be done using hedges , for example phases such as the evidence suggests... or this could be caused by... , or boosters , that is, phrases such as clearly or the research indicates .
Academic writing should use clear and precise language to ensure the reader understands the meaning. This includes the use of technical (i.e. subject-specific) vocabulary , which should be used when it conveys the meaning more precisely than a similar non-technical term. Sometimes such technical vocabulary may need defining , though only if the term is not commonly used by others in the same discipline and will therefore not be readily understood by the reader.
Academic writing is objective. In other words, the emphasis is placed on the arguments and information, rather than on the writer. As a result, academic writing tends to use nouns and noun phrases more than verbs and adverbs. It also tends to use more passive structures , rather than active voice, for example The water was heated rather than I heated the water .
Finally, academic writing is more formal than everyday writing. It tends to use longer words and more complex sentences , while avoiding contractions and colloquial or informal words or expressions that might be common in spoken English. There are words and collocations which are used in academic writing more frequently than in non-academic writing, and researchers have developed lists of these words and phrases to help students of academic English, such as the Academic Word List , the Academic Vocabulary List , and the Academic Collocation List .
Developing your academic writing
Given the relatively specialist nature of academic writing, it can seem daunting when you first begin. You can develop your academic writing by paying attention to feedback from tutors or peers and seeking specific areas to improve. Another way to develop your academic writing is to read more. By reading academic journals or texts, you can develop a better understanding of the features that make academic writing different from other forms of writing.
Alexander, O., Argent, S. and Spencer, J. (2008) EAP Essentials: A teacher's guide to principles and practice . Reading: Garnet Publishing Ltd.
Cardiff Metropolitan University (n.d.) Academic Writing: Principles and Practice . Available at: https://study.cardiffmet.ac.uk/AcSkills/Documents/Guides/AS_Guide_Academic_Writing.pdf (Access date: 4/2/21).
Gillett, A. (n.d.) Features of academic writing . Available at: http://www.uefap.com/writing/feature/featfram.htm (Access date: 4/2/21).
Staffordshire University (2020) Academic writing . https://libguides.staffs.ac.uk/ld.php?content_id=33103104 (Access date: 4/2/21).
Staffordshire University (2021) Academic writing . https://libguides.staffs.ac.uk/academic_writing/explained (Access date: 4/2/21).
University of Leeds (2021) Academic writing . https://library.leeds.ac.uk/info/14011/writing/106/academic_writing (Access date: 4/2/21).

GET FREE EBOOK
Like the website? Try the books. Enter your email to receive a free sample from Academic Writing Genres .
Below is a checklist for this page. Use it to check your understanding.
Next section
Find out more about the academic style in the next section.

Author: Sheldon Smith ‖ Last modified: 24 July 2022.
Sheldon Smith is the founder and editor of EAPFoundation.com. He has been teaching English for Academic Purposes since 2004. Find out more about him in the about section and connect with him on Twitter , Facebook and LinkedIn .
Compare & contrast essays examine the similarities of two or more objects, and the differences.
Cause & effect essays consider the reasons (or causes) for something, then discuss the results (or effects).
Discussion essays require you to examine both sides of a situation and to conclude by saying which side you favour.
Problem-solution essays are a sub-type of SPSE essays (Situation, Problem, Solution, Evaluation).
Transition signals are useful in achieving good cohesion and coherence in your writing.
Reporting verbs are used to link your in-text citations to the information cited.
- USC Libraries
- Research Guides
Organizing Your Social Sciences Research Paper
- Academic Writing Style
- Purpose of Guide
- Design Flaws to Avoid
- Independent and Dependent Variables
- Glossary of Research Terms
- Reading Research Effectively
- Narrowing a Topic Idea
- Broadening a Topic Idea
- Extending the Timeliness of a Topic Idea
- Choosing a Title
- Making an Outline
- Paragraph Development
- Research Process Video Series
- Executive Summary
- The C.A.R.S. Model
- Background Information
- The Research Problem/Question
- Theoretical Framework
- Citation Tracking
- Content Alert Services
- Evaluating Sources
- Primary Sources
- Secondary Sources
- Tiertiary Sources
- Scholarly vs. Popular Publications
- Qualitative Methods
- Quantitative Methods
- Insiderness
- Using Non-Textual Elements
- Limitations of the Study
- Common Grammar Mistakes
- Writing Concisely
- Avoiding Plagiarism
- Footnotes or Endnotes?
- Further Readings
- Generative AI and Writing
- USC Libraries Tutorials and Other Guides
- Bibliography
Academic writing refers to a style of expression that researchers use to define the intellectual boundaries of their disciplines and specific areas of expertise. Characteristics of academic writing include a formal tone, use of the third-person rather than first-person perspective (usually), a clear focus on the research problem under investigation, and precise word choice. Like specialist languages adopted in other professions, such as, law or medicine, academic writing is designed to convey agreed meaning about complex ideas or concepts within a community of scholarly experts and practitioners.
Academic Writing. Writing Center. Colorado Technical College; Hartley, James. Academic Writing and Publishing: A Practical Guide . New York: Routledge, 2008; Ezza, El-Sadig Y. and Touria Drid. T eaching Academic Writing as a Discipline-Specific Skill in Higher Education . Hershey, PA: IGI Global, 2020.
Importance of Good Academic Writing
The accepted form of academic writing in the social sciences can vary considerable depending on the methodological framework and the intended audience. However, most college-level research papers require careful attention to the following stylistic elements:
I. The Big Picture Unlike creative or journalistic writing, the overall structure of academic writing is formal and logical. It must be cohesive and possess a logically organized flow of ideas; this means that the various parts are connected to form a unified whole. There should be narrative links between sentences and paragraphs so that the reader is able to follow your argument. The introduction should include a description of how the rest of the paper is organized and all sources are properly cited throughout the paper.
II. Tone The overall tone refers to the attitude conveyed in a piece of writing. Throughout your paper, it is important that you present the arguments of others fairly and with an appropriate narrative tone. When presenting a position or argument that you disagree with, describe this argument accurately and without loaded or biased language. In academic writing, the author is expected to investigate the research problem from an authoritative point of view. You should, therefore, state the strengths of your arguments confidently, using language that is neutral, not confrontational or dismissive.
III. Diction Diction refers to the choice of words you use. Awareness of the words you use is important because words that have almost the same denotation [dictionary definition] can have very different connotations [implied meanings]. This is particularly true in academic writing because words and terminology can evolve a nuanced meaning that describes a particular idea, concept, or phenomenon derived from the epistemological culture of that discipline [e.g., the concept of rational choice in political science]. Therefore, use concrete words [not general] that convey a specific meaning. If this cannot be done without confusing the reader, then you need to explain what you mean within the context of how that word or phrase is used within a discipline.
IV. Language The investigation of research problems in the social sciences is often complex and multi- dimensional . Therefore, it is important that you use unambiguous language. Well-structured paragraphs and clear topic sentences enable a reader to follow your line of thinking without difficulty. Your language should be concise, formal, and express precisely what you want it to mean. Do not use vague expressions that are not specific or precise enough for the reader to derive exact meaning ["they," "we," "people," "the organization," etc.], abbreviations like 'i.e.' ["in other words"], 'e.g.' ["for example"], or 'a.k.a.' ["also known as"], and the use of unspecific determinate words ["super," "very," "incredible," "huge," etc.].
V. Punctuation Scholars rely on precise words and language to establish the narrative tone of their work and, therefore, punctuation marks are used very deliberately. For example, exclamation points are rarely used to express a heightened tone because it can come across as unsophisticated or over-excited. Dashes should be limited to the insertion of an explanatory comment in a sentence, while hyphens should be limited to connecting prefixes to words [e.g., multi-disciplinary] or when forming compound phrases [e.g., commander-in-chief]. Finally, understand that semi-colons represent a pause that is longer than a comma, but shorter than a period in a sentence. In general, there are four grammatical uses of semi-colons: when a second clause expands or explains the first clause; to describe a sequence of actions or different aspects of the same topic; placed before clauses which begin with "nevertheless", "therefore", "even so," and "for instance”; and, to mark off a series of phrases or clauses which contain commas. If you are not confident about when to use semi-colons [and most of the time, they are not required for proper punctuation], rewrite using shorter sentences or revise the paragraph.
VI. Academic Conventions Among the most important rules and principles of academic engagement of a writing is citing sources in the body of your paper and providing a list of references as either footnotes or endnotes. The academic convention of citing sources facilitates processes of intellectual discovery, critical thinking, and applying a deliberate method of navigating through the scholarly landscape by tracking how cited works are propagated by scholars over time . Aside from citing sources, other academic conventions to follow include the appropriate use of headings and subheadings, properly spelling out acronyms when first used in the text, avoiding slang or colloquial language, avoiding emotive language or unsupported declarative statements, avoiding contractions [e.g., isn't], and using first person and second person pronouns only when necessary.
VII. Evidence-Based Reasoning Assignments often ask you to express your own point of view about the research problem. However, what is valued in academic writing is that statements are based on evidence-based reasoning. This refers to possessing a clear understanding of the pertinent body of knowledge and academic debates that exist within, and often external to, your discipline concerning the topic. You need to support your arguments with evidence from scholarly [i.e., academic or peer-reviewed] sources. It should be an objective stance presented as a logical argument; the quality of the evidence you cite will determine the strength of your argument. The objective is to convince the reader of the validity of your thoughts through a well-documented, coherent, and logically structured piece of writing. This is particularly important when proposing solutions to problems or delineating recommended courses of action.
VIII. Thesis-Driven Academic writing is “thesis-driven,” meaning that the starting point is a particular perspective, idea, or position applied to the chosen topic of investigation, such as, establishing, proving, or disproving solutions to the questions applied to investigating the research problem. Note that a problem statement without the research questions does not qualify as academic writing because simply identifying the research problem does not establish for the reader how you will contribute to solving the problem, what aspects you believe are most critical, or suggest a method for gathering information or data to better understand the problem.
IX. Complexity and Higher-Order Thinking Academic writing addresses complex issues that require higher-order thinking skills applied to understanding the research problem [e.g., critical, reflective, logical, and creative thinking as opposed to, for example, descriptive or prescriptive thinking]. Higher-order thinking skills include cognitive processes that are used to comprehend, solve problems, and express concepts or that describe abstract ideas that cannot be easily acted out, pointed to, or shown with images. Think of your writing this way: One of the most important attributes of a good teacher is the ability to explain complexity in a way that is understandable and relatable to the topic being presented during class. This is also one of the main functions of academic writing--examining and explaining the significance of complex ideas as clearly as possible. As a writer, you must adopt the role of a good teacher by summarizing complex information into a well-organized synthesis of ideas, concepts, and recommendations that contribute to a better understanding of the research problem.
Academic Writing. Writing Center. Colorado Technical College; Hartley, James. Academic Writing and Publishing: A Practical Guide . New York: Routledge, 2008; Murray, Rowena and Sarah Moore. The Handbook of Academic Writing: A Fresh Approach . New York: Open University Press, 2006; Johnson, Roy. Improve Your Writing Skills . Manchester, UK: Clifton Press, 1995; Nygaard, Lynn P. Writing for Scholars: A Practical Guide to Making Sense and Being Heard . Second edition. Los Angeles, CA: Sage Publications, 2015; Silvia, Paul J. How to Write a Lot: A Practical Guide to Productive Academic Writing . Washington, DC: American Psychological Association, 2007; Style, Diction, Tone, and Voice. Writing Center, Wheaton College; Sword, Helen. Stylish Academic Writing . Cambridge, MA: Harvard University Press, 2012.
Strategies for...
Understanding Academic Writing and Its Jargon
The very definition of research jargon is language specific to a particular community of practitioner-researchers . Therefore, in modern university life, jargon represents the specific language and meaning assigned to words and phrases specific to a discipline or area of study. For example, the idea of being rational may hold the same general meaning in both political science and psychology, but its application to understanding and explaining phenomena within the research domain of a each discipline may have subtle differences based upon how scholars in that discipline apply the concept to the theories and practice of their work.
Given this, it is important that specialist terminology [i.e., jargon] must be used accurately and applied under the appropriate conditions . Subject-specific dictionaries are the best places to confirm the meaning of terms within the context of a specific discipline. These can be found by either searching in the USC Libraries catalog by entering the disciplinary and the word dictionary [e.g., sociology and dictionary] or using a database such as Credo Reference [a curated collection of subject encyclopedias, dictionaries, handbooks, guides from highly regarded publishers] . It is appropriate for you to use specialist language within your field of study, but you should avoid using such language when writing for non-academic or general audiences.
Problems with Opaque Writing
A common criticism of scholars is that they can utilize needlessly complex syntax or overly expansive vocabulary that is impenetrable or not well-defined. When writing, avoid problems associated with opaque writing by keeping in mind the following:
1. Excessive use of specialized terminology . Yes, it is appropriate for you to use specialist language and a formal style of expression in academic writing, but it does not mean using "big words" just for the sake of doing so. Overuse of complex or obscure words or writing complicated sentence constructions gives readers the impression that your paper is more about style than substance; it leads the reader to question if you really know what you are talking about. Focus on creating clear, concise, and elegant prose that minimizes reliance on specialized terminology.
2. Inappropriate use of specialized terminology . Because you are dealing with concepts, research, and data within your discipline, you need to use the technical language appropriate to that area of study. However, nothing will undermine the validity of your study quicker than the inappropriate application of a term or concept. Avoid using terms whose meaning you are unsure of--do not just guess or assume! Consult the meaning of terms in specialized, discipline-specific dictionaries by searching the USC Libraries catalog or the Credo Reference database [see above].
Additional Problems to Avoid
In addition to understanding the use of specialized language, there are other aspects of academic writing in the social sciences that you should be aware of. These problems include:
- Personal nouns . Excessive use of personal nouns [e.g., I, me, you, us] may lead the reader to believe the study was overly subjective. These words can be interpreted as being used only to avoid presenting empirical evidence about the research problem. Limit the use of personal nouns to descriptions of things you actually did [e.g., "I interviewed ten teachers about classroom management techniques..."]. Note that personal nouns are generally found in the discussion section of a paper because this is where you as the author/researcher interpret and describe your work.
- Directives . Avoid directives that demand the reader to "do this" or "do that." Directives should be framed as evidence-based recommendations or goals leading to specific outcomes. Note that an exception to this can be found in various forms of action research that involve evidence-based advocacy for social justice or transformative change. Within this area of the social sciences, authors may offer directives for action in a declarative tone of urgency.
- Informal, conversational tone using slang and idioms . Academic writing relies on excellent grammar and precise word structure. Your narrative should not include regional dialects or slang terms because they can be open to interpretation. Your writing should be direct and concise using standard English.
- Wordiness. Focus on being concise, straightforward, and developing a narrative that does not have confusing language . By doing so, you help eliminate the possibility of the reader misinterpreting the design and purpose of your study.
- Vague expressions (e.g., "they," "we," "people," "the company," "that area," etc.). Being concise in your writing also includes avoiding vague references to persons, places, or things. While proofreading your paper, be sure to look for and edit any vague or imprecise statements that lack context or specificity.
- Numbered lists and bulleted items . The use of bulleted items or lists should be used only if the narrative dictates a need for clarity. For example, it is fine to state, "The four main problems with hedge funds are:" and then list them as 1, 2, 3, 4. However, in academic writing, this must then be followed by detailed explanation and analysis of each item. Given this, the question you should ask yourself while proofreading is: why begin with a list in the first place rather than just starting with systematic analysis of each item arranged in separate paragraphs? Also, be careful using numbers because they can imply a ranked order of priority or importance. If none exists, use bullets and avoid checkmarks or other symbols.
- Descriptive writing . Describing a research problem is an important means of contextualizing a study. In fact, some description or background information may be needed because you can not assume the reader knows the key aspects of the topic. However, the content of your paper should focus on methodology, the analysis and interpretation of findings, and their implications as they apply to the research problem rather than background information and descriptions of tangential issues.
- Personal experience. Drawing upon personal experience [e.g., traveling abroad; caring for someone with Alzheimer's disease] can be an effective way of introducing the research problem or engaging your readers in understanding its significance. Use personal experience only as an example, though, because academic writing relies on evidence-based research. To do otherwise is simply story-telling.
NOTE: Rules concerning excellent grammar and precise word structure do not apply when quoting someone. A quote should be inserted in the text of your paper exactly as it was stated. If the quote is especially vague or hard to understand, consider paraphrasing it or using a different quote to convey the same meaning. Consider inserting the term "sic" in brackets after the quoted text to indicate that the quotation has been transcribed exactly as found in the original source, but the source had grammar, spelling, or other errors. The adverb sic informs the reader that the errors are not yours.
Academic Writing. The Writing Lab and The OWL. Purdue University; Academic Writing Style. First-Year Seminar Handbook. Mercer University; Bem, Daryl J. Writing the Empirical Journal Article. Cornell University; College Writing. The Writing Center. University of North Carolina; Murray, Rowena and Sarah Moore. The Handbook of Academic Writing: A Fresh Approach . New York: Open University Press, 2006; Johnson, Eileen S. “Action Research.” In Oxford Research Encyclopedia of Education . Edited by George W. Noblit and Joseph R. Neikirk. (New York: Oxford University Press, 2020); Oppenheimer, Daniel M. "Consequences of Erudite Vernacular Utilized Irrespective of Necessity: Problems with Using Long Words Needlessly." Applied Cognitive Psychology 20 (2006): 139-156; Ezza, El-Sadig Y. and Touria Drid. T eaching Academic Writing as a Discipline-Specific Skill in Higher Education . Hershey, PA: IGI Global, 2020; Pernawan, Ari. Common Flaws in Students' Research Proposals. English Education Department. Yogyakarta State University; Style. College Writing. The Writing Center. University of North Carolina; Invention: Five Qualities of Good Writing. The Reading/Writing Center. Hunter College; Sword, Helen. Stylish Academic Writing . Cambridge, MA: Harvard University Press, 2012; What Is an Academic Paper? Institute for Writing Rhetoric. Dartmouth College.
Structure and Writing Style
I. Improving Academic Writing
To improve your academic writing skills, you should focus your efforts on three key areas: 1. Clear Writing . The act of thinking about precedes the process of writing about. Good writers spend sufficient time distilling information and reviewing major points from the literature they have reviewed before creating their work. Writing detailed outlines can help you clearly organize your thoughts. Effective academic writing begins with solid planning, so manage your time carefully. 2. Excellent Grammar . Needless to say, English grammar can be difficult and complex; even the best scholars take many years before they have a command of the major points of good grammar. Take the time to learn the major and minor points of good grammar. Spend time practicing writing and seek detailed feedback from professors. Take advantage of the Writing Center on campus if you need help. Proper punctuation and good proofreading skills can significantly improve academic writing [see sub-tab for proofreading you paper ].
Refer to these three basic resources to help your grammar and writing skills:
- A good writing reference book, such as, Strunk and White’s book, The Elements of Style or the St. Martin's Handbook ;
- A college-level dictionary, such as, Merriam-Webster's Collegiate Dictionary ;
- The latest edition of Roget's Thesaurus in Dictionary Form .
3. Consistent Stylistic Approach . Whether your professor expresses a preference to use MLA, APA or the Chicago Manual of Style or not, choose one style manual and stick to it. Each of these style manuals provide rules on how to write out numbers, references, citations, footnotes, and lists. Consistent adherence to a style of writing helps with the narrative flow of your paper and improves its readability. Note that some disciplines require a particular style [e.g., education uses APA] so as you write more papers within your major, your familiarity with it will improve.
II. Evaluating Quality of Writing
A useful approach for evaluating the quality of your academic writing is to consider the following issues from the perspective of the reader. While proofreading your final draft, critically assess the following elements in your writing.
- It is shaped around one clear research problem, and it explains what that problem is from the outset.
- Your paper tells the reader why the problem is important and why people should know about it.
- You have accurately and thoroughly informed the reader what has already been published about this problem or others related to it and noted important gaps in the research.
- You have provided evidence to support your argument that the reader finds convincing.
- The paper includes a description of how and why particular evidence was collected and analyzed, and why specific theoretical arguments or concepts were used.
- The paper is made up of paragraphs, each containing only one controlling idea.
- You indicate how each section of the paper addresses the research problem.
- You have considered counter-arguments or counter-examples where they are relevant.
- Arguments, evidence, and their significance have been presented in the conclusion.
- Limitations of your research have been explained as evidence of the potential need for further study.
- The narrative flows in a clear, accurate, and well-organized way.
Boscoloa, Pietro, Barbara Arféb, and Mara Quarisaa. “Improving the Quality of Students' Academic Writing: An Intervention Study.” Studies in Higher Education 32 (August 2007): 419-438; Academic Writing. The Writing Lab and The OWL. Purdue University; Academic Writing Style. First-Year Seminar Handbook. Mercer University; Bem, Daryl J. Writing the Empirical Journal Article. Cornell University; Candlin, Christopher. Academic Writing Step-By-Step: A Research-based Approach . Bristol, CT: Equinox Publishing Ltd., 2016; College Writing. The Writing Center. University of North Carolina; Style . College Writing. The Writing Center. University of North Carolina; Invention: Five Qualities of Good Writing. The Reading/Writing Center. Hunter College; Sword, Helen. Stylish Academic Writing . Cambridge, MA: Harvard University Press, 2012; What Is an Academic Paper? Institute for Writing Rhetoric. Dartmouth College.
Writing Tip
Considering the Passive Voice in Academic Writing
In the English language, we are able to construct sentences in the following way: 1. "The policies of Congress caused the economic crisis." 2. "The economic crisis was caused by the policies of Congress."
The decision about which sentence to use is governed by whether you want to focus on “Congress” and what they did, or on “the economic crisis” and what caused it. This choice in focus is achieved with the use of either the active or the passive voice. When you want your readers to focus on the "doer" of an action, you can make the "doer"' the subject of the sentence and use the active form of the verb. When you want readers to focus on the person, place, or thing affected by the action, or the action itself, you can make the effect or the action the subject of the sentence by using the passive form of the verb.
Often in academic writing, scholars don't want to focus on who is doing an action, but on who is receiving or experiencing the consequences of that action. The passive voice is useful in academic writing because it allows writers to highlight the most important participants or events within sentences by placing them at the beginning of the sentence.
Use the passive voice when:
- You want to focus on the person, place, or thing affected by the action, or the action itself;
- It is not important who or what did the action;
- You want to be impersonal or more formal.
Form the passive voice by:
- Turning the object of the active sentence into the subject of the passive sentence.
- Changing the verb to a passive form by adding the appropriate form of the verb "to be" and the past participle of the main verb.
NOTE: Consult with your professor about using the passive voice before submitting your research paper. Some strongly discourage its use!
Active and Passive Voice. The Writing Lab and The OWL. Purdue University; Diefenbach, Paul. Future of Digital Media Syllabus. Drexel University; Passive Voice. The Writing Center. University of North Carolina.
- << Previous: 2. Preparing to Write
- Next: Choosing a Title >>
- Last Updated: Mar 26, 2024 10:40 AM
- URL: https://libguides.usc.edu/writingguide
- Utility Menu
Jeffrey R. Wilson
Academic writing.

A how-to guide for high-quality arguments
Free for all
Download the Book
“Writing” is usually understood as the expression of thought. This book redefines “writing” as the thought process itself. Writing is not what you do with thought. Writing is thinking.
Better living through interpretation : that’s the promise of academic writing, which is a foundational course in most schools because it’s a foundational skill in life. Our world is full of things that need to be questioned, from ancient myths and historical events to current politics and the weird details of everyday life.
Based on his courses in the Writing Program at Harvard University, Jeffrey R. Wilson’s Academic Writing is a no-nonsense guide to the long and complex writing process. Packed with concrete examples, helpful visuals, and practical tips, the book is an essential guide for academic writing at the highest level. Empowering writers to be creators—not just consumers—of knowledge, Wilson shows how to develop perspective, ask questions, build ideas, and craft arguments that reveal new truths that the world needs to hear. Writers learn different strategies for articulating the implications of an argument—why it matters—and putting ideas in conversation with others by finding, reading, and incorporating scholarship. There are models for different ways to organize an essay and tips to make sentences snap with style. Emphasis is placed on developing ideas in constant conversation with others and on strengthening papers through multiple rounds of revision.
News, Reviews, and Interviews
The Complete Beginner's Guide to Academic Writing
#scribendiinc
Written by Scribendi
What Is Academic Writing?
Academic writing is a specialized form of writing that suits the particular needs of academic writers. Used effectively, it helps scholars express complex concepts, research, and theories clearly to their peers. Learning to embrace this style of writing is essential in academia. However, we all need to start somewhere.
Welcome, friend, to the beginner's guide to academic writing.
In this post, we'll cover the following topics:
Characteristics of Academic Writing
Major types of academic writing.
Finding Your Research Question & Thesis Statement
The Importance of a Strong Structure
Good Academic Writing Requires an Outline
Always Keep Your Writing Concise
Style Guides: Don't Wait until the Last Minute
Always edit and proofread your academic writing, parting advice, elevate your writing with professional editing.
Learn More OR Get Started
Throughout this guide, you'll see the words "academic writing" and "scholarly writing" being used interchangeably. Both of these terms refer to the same form of writing, and both adhere to the same set of characteristics.
Let's take a closer look at three of the major characteristics of academic writing.
1. Evidence Based
Unlike other forms of writing, academic writing prioritizes logical, evidence-based reasoning. Every conclusion or point that you make should be supported by evidence.
Furthermore, all of these points should work together to support your thesis. Your thesis is the topic or research question that your writing aims to investigate, discuss, prove, or disprove.
Scholarly writing should be formal in tone. This means no contractions, colloquialisms, or slang. It also means that your writing should avoid personal pronouns such as "I." In this style of writing, you should write in the third person.
Furthermore, while you're certainly encouraged to feel passionately about your topic, you should also aim to write in a neutral tone. This means that your writing should avoid inflammatory, judgment-call statements.
Instead, your writing should sound like a rational exploration of the facts and evidence that support your conclusions. Seek to eliminate bias from your writing and remember to thoughtfully engage with your opposition's viewpoints. Don't just dismiss them as "wrong."
3. Properly cited
Proper citations are one of the most important characteristics of academic writing. You should always support any evidence that you call on with clear, orderly citations and references. This not only lends authority to your writing but also helps others locate your sources and further expand on your topic.
Your citations and the overall formatting of your paper may change depending on your assigned style guide ( APA , the Chicago Manual of Style , or MLA , to name a few). Make sure to adhere to the specifications of your specific style guide.

Next, let's take a look at the major types of academic writing that you'll encounter. Unfortunately, part of the reason that the answer to "What is academic writing?" is so long is that the subject is littered with subcategories.
Below, we've listed some of the most common types of scholarly writing and linked them to articles detailing each one.
- Lab reports
- Book reports
- Theses and dissertations
- Grant proposals
- Literature reviews
These types of scholarly writing can be split into further subcategories. For example, an academic essay might fall into the descriptive, analytical, persuasive, or critical category—each of which might ask you to take a different approach in your writing.
Finding Your Research Question and Thesis Statement
Now that you have a grasp on what academic writing is, let's take a closer look at its elements. We'll begin with the star of the show, the thesis statement. However, in order to create your thesis statement, you'll first need a research question.
Select a topic that interests you and draft an intriguing question about it. That question is your research question. Make it as specific as possible, and as you dig into your research, continue to narrow its scope.
More often than not, the answers you find will become your thesis, which is the statement or question that your writing will investigate, prove, or disprove.
A good thesis statement should demonstrate the following characteristics:
- Evidence based
If you want to learn more about thesis statements, check out our article on how to write a great thesis statement .
The Importance of a Strong Structure
A good structure is vital in academic writing, and a clear, logical structure will help you present your ideas. Moreover, many forms of academic writing obey an established structure, which the reader will expect you to follow.
For example, many academic essays follow a five-part structure. It's okay to experiment with other structures from time to time, but it is a good one to start with.
A five-part structure involves an introduction, three body paragraphs, and a conclusion. Your introduction introduces your topic and situates its importance within your field. It establishes your methodology and introduces your thesis statement.
Your body paragraphs support your thesis in more detail. Each body paragraph begins with a topic sentence, after which a cycle of introducing subtopics, providing evidence, and reflecting on the impact of that evidence ensues.
Your conclusion should summarize your body paragraphs and reaffirm your thesis. It shouldn't contain any new information. Instead, think of it as an opportunity to finish strong and hammer in your points one last time.
Check out our Ultimate Essay Checklist for additional essay writing advice.
In order to have a strong structure, it's best to create an outline before you start writing. It'll help you keep yourself motivated and on track. It's much easier to write with a plan in mind than to write into a shapeless void.
If you can, leave time for multiple drafts. It may sound unnecessary; however, each draft will give you the time and mental space you need to drastically improve the quality of your writing.
Always Keep Your Writing Concise
Verbose writing is one of the most common issues in academic writing.
Whenever you can, keep things concise . Complex vocabulary and sentences are common in academic writing. However, they aren't everything. Learning to write concisely is a difficult skill to master. However, it has great benefits, including the ability to express yourself clearly.
To begin writing concisely, challenge yourself to first avoid the passive voice. It won't always be possible to use the active voice. However, favor the active voice whenever you can. It shakes up your writing, making it more dynamic and helping to propel the reader forward.

Style guides are intended to make your life easier, not complicate it. Think of them as friendly guides who will help you cite and format your work correctly. Don't wait until the last moment to crack yours open!
Here are three of the most common style guides and the fields they're commonly used in:
- The Chicago Manual of Style (Chicago), which is used in history, criminology, and business
- Modern Language Association (MLA) style, which is used in the humanities and liberal arts
- American Psychological Association (APA) style, which is used in the social sciences, psychology, business, and economics
Never underestimate the value of editing and proofreading your work. You wouldn't believe the number of errors that can be caught simply by taking a break, refreshing your mind, and settling in to complete an editing or proofreading pass.
In turn, professional editing and proofreading can give you an even stronger boost. When you work closely with a text, it's easy to skim over errors and confusing language. You already know how your writing should go, so it's easy for your brain to fill in the gaps.
You should now have all that you need to step out into the world of academic writing. It's time to take all that you've learned and put it into practice. Make your mark on the world. We'll be rooting for you.
Image source: Prostock-studio/elements.envato.com
Hire an Expert Academic Editor , or Get a Free Sample
About the author.

Scribendi's in-house editors work with writers from all over the globe to perfect their writing. They know that no piece of writing is complete without a professional edit, and they love to see a good piece of writing transformed into a great one. Scribendi's in-house editors are unrivaled in both experience and education, having collectively edited millions of words and obtained numerous degrees. They love consuming caffeinated beverages, reading books of various genres, and relaxing in quiet, dimly lit spaces.
Have You Read?
"The Complete Beginner's Guide to Academic Writing"
Related Posts

Online Research Tips for Students and Scholars: Our Most Helpful Articles

Quotation Marks: When to Use Single or Double Quotes

What is a Thesis?
Upload your file(s) so we can calculate your word count, or enter your word count manually.
We will also recommend a service based on the file(s) you upload.
English is not my first language. I need English editing and proofreading so that I sound like a native speaker.
I need to have my journal article, dissertation, or term paper edited and proofread, or I need help with an admissions essay or proposal.
I have a novel, manuscript, play, or ebook. I need editing, copy editing, proofreading, a critique of my work, or a query package.
I need editing and proofreading for my white papers, reports, manuals, press releases, marketing materials, and other business documents.
I need to have my essay, project, assignment, or term paper edited and proofread.
I want to sound professional and to get hired. I have a resume, letter, email, or personal document that I need to have edited and proofread.
Prices include your personal % discount.
Prices include % sales tax ( ).

- Resources Home 🏠
- Try SciSpace Copilot
- Search research papers
- Add Copilot Extension
- Try AI Detector
- Try Paraphraser
- Try Citation Generator
- April Papers
- June Papers
- July Papers

What is Academic Writing — Quick Guide for 2024

Table of Contents
Academic writing is potentially the most crucial skill in an educational environment since writing is one of the primary modus operandi of scholarly communication . Its quality strongly influences the readers’ perception of the author. It is highly valued both by academic institutions and academics who wish to acquire knowledge. The ability to write academic papers is one of the critical factors that distinguish scholars from excellent scholars.
Academic writing can be defined as the writing form that aims to transmit scientific or other knowledge through clear and concise means. The main idea behind academic writing is objective and practical in terms of presentation as it needs to be understood by thousands of readers and not just a single person. It enables you to express your ideas and develop them into a structured written format. Academic writing is not just about proving ideas but creating them. Getting an academic paper written on a high level requires experience, so let's dive into it.
What are the characteristics of academic writing?
Academic writing is a genre of writing with several characteristics that make it different from other prose or creative writing forms. Therefore, the characteristics of academic writing are imperative to understand. Five main features of academic writing are often discussed as follows:
1. Formality
Academic writing aims to convey the relevant ideas to suit the nature of the subject being discussed and support opinions with reasoned arguments. It is not about making flowery statements or indulging in superfluous language. It is about communicating your thoughts with the audience accurately and succinctly.
You need to realize that academic writing requires you to be direct, analytical, and precise. The objective is to demonstrate that you can convey your meaning accurately, in context, without uncertainty. To make your writing more formal, you can try to:
- Avoid conversational words and expressions
- Avoid contractions such as "don't," "can't," and "isn't. Replace them with the two-word version of the contraction
- Avoid rhetorical statements like “What is the meaning of life?”.
2. Accuracy
A word's meaning is an important factor that determines whether it should be used or not in a writing piece. The more accurate the writer is while creating a paper, the better his chances are for obtaining a high-grade paper. All words should be defined clearly and concretely so that their exact meaning can be easily traced. Academic writing does not use words loosely. It must accurately distinguish between "orthocenter" and "orthocenter," etc., and use these words correctly. By using known technical terms correctly, you reflect your proficiency in a particular subject.
Hedging is an action that can be used to reduce the risk of making claims. They are used to avoid answering a question, making a clear, direct statement, or committing yourself to a particular action. Early-career academic writers or authors may find it hard to always convey themselves and their work in their papers using solid and unequivocal statements. Having said that, many academic writers feel compelled to use what is called hedging techniques when writing their academic papers.
Making decisions about the stance you take on a topic is often done by using hedging verbs. These are words that place some kind of limitation or qualifier on your claims. Such as ‘seem,’ ‘appear,’ ‘suggest,’ ‘may’ and ‘might’. For example, Extended screen time can contribute to a range of eyesight problems and may have a negative effect on mental health.
4. Objectivity
Writing is impersonal and uses nouns more than verbs. Think about it! Fewer words that refer to us place greater emphasis on what we have to say. Phrases like “I feel” or “I believe” should be kept out of the picture especially if you are reporting any research findings. For instance “I feel there is life on Mars” should be replaced with “These findings suggest that there is life on Mars”. The reader is therefore left to concentrate on the information you provide and the arguments you make. Objectivity can be induced while writing an academic paper if you do not talk about opinions, but provide valuable information and valid arguments. Readers focus on what the writer knows rather than what they think or feel. This allows the writer to sound more objective and authoritative.
5. Responsibility
Academic writing is as different from every day, ‘general’ writing as a race-horse is from a donkey. Academic writing has rigorous standards and conventions that must be followed. Academic writing attempts to add new information, knowledge, or understanding to an existing body of theory. The key things to note in this criteria are the claims you make, the evidence that needs to be provided for those claims, and citations; you must cite any sources of information you use at any cost to avoid plagiarism. You should also avoid self-plagiarism .
What are the four major types of academic writing?
If we are talking about “What is Academic Writing”, we must not miss its types. There are four major types of academic writing that you should know about:
1. Descriptive
One of the basic types of scholarly writing is descriptive. It can be divided into several subcategories: a summary, description, narration, explanation, and so on. The goal of descriptive writing is to present facts or information. A report will tell what participants did or did not do during an experiment, how they responded to various stimuli, and what results were obtained. It supplies details such as how many people were involved in the study, when it was conducted, and where.
2. Analytical
Analytical writing is the process of re-organizing (and possibly adding to) the collection of ideas or information that you have organized into a suitable structure, such as categories, groups, parts, or relationships. Analyzing is a way of discovering whether an argument is valid, coherent, and relevant in a logical way to the topic under discussion. To polish your analytical writing, you can:
- Give careful consideration to the subject matter. After you've summarized the facts and ideas, try different ways of grouping them in order to clarify what's important.
- Categorize your work under different segments like advantages, disadvantages, importance, etc.
- An introduction that gives the reader a framework for understanding your paper and a topic sentence for each paragraph will clarify the structure of your paper.
3. Persuasive
Persuasive writing is just analytical writing plus your own point of view. You may be required to analyze an argument, evaluate the credibility of a claim, or explain why a position is correct. Most essays, including research articles, are written to convince the reader of some viewpoint. Following are the keystones to remember about persuasive writing:
- To understand your own take on a topic, a wise thing to do would be to examine all the major viewpoints on a given topic and see what you find the most convincing!
- As you think about what arguments to make, it is important to cite evidence to support your point of view. Break down your ideas. For example when writing about a concept car, ask yourself: How cost-effective is it? How environmentally friendly is it? What are the real-world applications?
- Your argument should only be presented after you are clear about your assumptions, claims, and evidence.
4. Critical
Critical writing involves your own point of view, but also that of at least one other person. You may explain a researcher's argument and then show how it is flawed, or offer an alternative explanation. For this, you must first be well aware of what the other researcher is attempting to portray through his study. Doing this requires you to read plenty of research papers, which can be challenging at times since a lot of them carry jargon, maths, and complex language. To save time and effort you can use SciSpace Copilot to get simplified explanations of parts of the research paper you don't understand and get the relevance of any math or table by just clipping it. Adding on to that, if you need more clarification on the subject, you can even ask more questions related to the paper, and the research assistant can give you prompt answers.
Also read - SciSpace Paraphrasing Tool: Better academic writing made easy
What are the advantages of academic writing?
Academic writing can help the writer gain some unique characteristics and qualities. It is ultimately up to you whether these advantages are good enough to spend your time polishing this craft.

1. Increased Focus
Focus has become a very important trait, especially in today's generation as distractions are literally everywhere you look. It is not something everyone is born with but it is something that can certainly be inculcated over time. Academic Writing is one of the finest ways to help you do that. It takes a good amount of focus to turn a blank piece of paper into something knowledgeable. If you like the topic you are working on, you will be surprised to see how easy it can get to focus and get it done.
2. Better Logical Thinking and Improved Knowledge
It takes a serious amount of time, focus, and thinking to write a worth-reading academic paper. You cannot just know everything about the topic you’re working on, therefore, a lot of research and analysis is required to come up with an informative piece of paper that is valuable. Writing a lot of papers can not just increase your knowledge in the fields you’re writing on but can also improve your logical thinking skills.
3. Discovering The Delight Of Writing
Avid academic writers have experienced a change in how they felt about writing in general. Although sometimes for a lot of writers, academic writing becomes anxiety-inducing. But for most, writing becomes joyful and gives an amazing sense of accomplishment.
Studies have shown that attending and participating in retreats have made academics more motivated and less fearful of writing. The key reasons behind it are mainly the peer support that they manage to get and their writing capabilities going over the roof.
4. Boost In Creativity
Academic writing is not just about blatantly stating stuff about your chosen topic, but it is also about creatively analyzing and conveying ideas concisely. This definitely requires creative thinking. Writing on a regular basis can prove to increase your creativity not just in writing but also in real life. It gives the writer a chance to develop out-of-the-box ideas.
The Significance of Clarity in Academic Writing
Clarity is essential in writing. It is a guiding principle that helps writers decide what to say and how to say it. If people don’t understand what you’re trying to say, how much value can you actually add? Below are the five principles for creating a lucid copy:
A Research Writing Platform
If you're doing research, you might be juggling between multiple writing and task management tools. Before you start using them, think about how you want to organize your research and how you'll be using the information you collect. A platform especially designed to meet the basic as well as advanced requirements of academic writers, SciSpace (formerly Typeset ) intends to be the perfect bridge between academic writing and academic publishing, providing the ease of intuitive research writing and collaboration with the combined power of LaTeX and MS Word. A comprehensive, automated research writing and journal production platform like SciSpace that has integrated plagiarism checkers is what you need to kickstart your academic writing!
We recommend you take a look at SciSpace discover since you're looking for platforms that simplify research workflows. It offers access to over 200 million articles covering a wide range of topics, optimized summaries, and public profiles that allow you to showcase your expertise and experience.
Our personalized suggestion engine allows you to stay on track while gaining an in-depth understanding of a subject from one location. Any article page will contain a list of related articles. In addition, the tool lets you determine which topics are trending, which authors are leading the charge, and which publishers are leading the pack.

Whether you are writing a report, a thesis or a research paper, the points covered in this article can help you furnish your project in a formal and structured format. Remember that you need to write your research paper in a professional manner. Avoid conversational language and slang. Now that you have a profound understanding of academic writing, try to apply the best practices practically and take your academic writing skills to greater height.
Frequently Asked Questions
To write academic papers effectively, ensure clarity, use credible sources, and follow proper grammar and citation rules. Structure your work with an introduction, body, and conclusion.
Yes, AI can be used for academic writing tasks including idea generation, writing improvement, citation suggestions, plagiarism detection, and more.
For academic writing, consider tools such as SciSpace GPT, Grammarly, Turnitin etc. It They” with “SciSpace GPT is the best tool avaialble for academic writing.
Academic writing has a purpose. It may provide background information, the results of other peoples' research, the critique of other peoples' research, your own research findings, your own ideas based on academic research conducted by others, etc.
In academic writing, numbers can be written as numerals (e.g., 5, 10, 100) or spelled out (e.g., five, ten, one hundred) depending on the style guide used and the context of the writing.
You can use italics to emphasize important words, introduce foreign phrases, and highlight titles of books or journals for clarity and emphasis.
To avoid plagiarism in academic writing:-
If you found the above article insightful, the following article pieces might interest you:
- The 4-Step Guide That Will Get Your Research Published
- How to write a research paper abstract?
- How to become good at academic research writing?
- Top reasons for research paper rejection
- How to increase citation count of your research paper?
You might also like

Consensus GPT vs. SciSpace GPT: Choose the Best GPT for Research

Literature Review and Theoretical Framework: Understanding the Differences

Types of Essays in Academic Writing

OASIS: Writing Center
Scholarly writing: overview, introduction.
Scholarly writing is also known as academic writing. It is the genre of writing used in all academic fields. Scholarly writing is not better than journalism, fiction, or poetry; it is just a different category. Because most of us are not used to scholarly writing, it can feel unfamiliar and intimidating, but it is a skill that can be learned by immersing yourself in scholarly literature. During your studies at Walden, you will be reading, discussing, and producing scholarly writing in everything from discussion posts to dissertations. For Walden students, there are plenty of opportunities to practice this skill in a writing intensive environment.
The resources in the Grammar & Composition tab provide important foundations for scholarly writing, so please refer to those pages as well for help on scholarly writing. Similarly, scholarly writing can differ depending on style guide. Our resources follow the general guidelines of the APA manual, and you can find more APA help in the APA Style tab.
Read on to learn about a few characteristics of scholarly writing!
Writing at the Graduate Level
Writing at the graduate level can appear to be confusing and intimidating. It can be difficult to determine exactly what the scholarly voice is and how to transition to graduate-level writing. There are some elements of writing to consider when writing to a scholarly audience: word choice, tone, and effective use of evidence . If you understand and employ scholarly voice rules, you will master writing at the doctoral level.
Before you write something, ask yourself the following:
- Is this objective?
- Am I speaking as a social scientist? Am I using the literature to support my assertions?
- Could this be offensive to someone?
- Could this limit my readership?
Employing these rules when writing will help ensure that you are speaking as a social scientist. Your writing will be clear and concise, and this approach will allow your content to shine through.
Specialized Vocabulary
Scholarly authors assume that their audience is familiar with fundamental ideas and terms in their field, and they do not typically define them for the reader. Thus, the wording in scholarly writing is specialized, requiring previous knowledge on the part of the reader. You might not be able to pick up a scholarly journal in another field and easily understand its contents (although you should be able to follow the writing itself).
Take for example, the terms "EMRs" and "end-stage renal disease" in the medical field or the keywords scaffolding and differentiation in teaching. Perhaps readers outside of these fields may not be familiar with these terms. However, a reader of an article that contains these terms should still be able to understand the general flow of the writing itself.
Original Thought
Scholarly writing communicates original thought, whether through primary research or synthesis, that presents a unique perspective on previous research. In a scholarly work, the author is expected to have insights on the issue at hand, but those insights must be grounded in research, critical reading , and analysis rather than personal experience or opinion. Take a look at some examples below:
Needs Improvement: I think that childhood obesity needs to be prevented because it is bad and it causes health problems.
Better: I believe that childhood obesity must be prevented because it is linked to health problems and deaths in adults (McMillan, 2010).
Good: Georges (2002) explained that there "has never been a disease so devastating and yet so preventable as obesity" (p. 35). In fact, the number of deaths that can be linked to obesity are astounding. According to McMillan (2010), there is a direct correlation between childhood obesity and heart attacks later in their adult lives, and the American Heart Association's 2010 statistic sheet shows similar statistics: 49% of all heart attacks are preventable (AHA, 2010). Because of this correlation, childhood obesity is an issue that must be addressed and prevented to ensure the health of both children and adults.
Notice that the first example gives a personal opinion but cites no sources or research. The second example gives a bit of research but still emphasizes the personal opinion. The third example, however, still gives the writer's opinion (that childhood obesity must be addressed), but it does so by synthesizing the information from multiple sources to help persuade the reader.
Careful Citation
Scholarly writing includes careful citation of sources and the presence of a bibliography or reference list. The writing is informed by and shows engagement with the larger body of literature on the topic at hand, and all assertions are supported by relevant sources.
Crash Course in Scholarly Writing Video
Note that this video was created while APA 6 was the style guide edition in use. There may be some examples of writing that have not been updated to APA 7 guidelines.
- Crash Course in Scholarly Writing (video transcript)
Related Webinars
Didn't find what you need? Search our website or email us .
Read our website accessibility and accommodation statement .
- Next Page: Common Course Assignments
- Office of Student Disability Services
Walden Resources
Departments.
- Academic Residencies
- Academic Skills
- Career Planning and Development
- Customer Care Team
- Field Experience
- Military Services
- Student Success Advising
- Writing Skills
Centers and Offices
- Center for Social Change
- Office of Academic Support and Instructional Services
- Office of Degree Acceleration
- Office of Research and Doctoral Services
- Office of Student Affairs
Student Resources
- Doctoral Writing Assessment
- Form & Style Review
- Quick Answers
- ScholarWorks
- SKIL Courses and Workshops
- Walden Bookstore
- Walden Catalog & Student Handbook
- Student Safety/Title IX
- Legal & Consumer Information
- Website Terms and Conditions
- Cookie Policy
- Accessibility
- Accreditation
- State Authorization
- Net Price Calculator
- Contact Walden
Walden University is a member of Adtalem Global Education, Inc. www.adtalem.com Walden University is certified to operate by SCHEV © 2024 Walden University LLC. All rights reserved.

Organizing Academic Research Papers: Academic Writing Style
- Purpose of Guide
- Design Flaws to Avoid
- Glossary of Research Terms
- Narrowing a Topic Idea
- Broadening a Topic Idea
- Extending the Timeliness of a Topic Idea
- Academic Writing Style
- Choosing a Title
- Making an Outline
- Paragraph Development
- Executive Summary
- Background Information
- The Research Problem/Question
- Theoretical Framework
- Citation Tracking
- Content Alert Services
- Evaluating Sources
- Primary Sources
- Secondary Sources
- Tertiary Sources
- What Is Scholarly vs. Popular?
- Qualitative Methods
- Quantitative Methods
- Using Non-Textual Elements
- Limitations of the Study
- Common Grammar Mistakes
- Avoiding Plagiarism
- Footnotes or Endnotes?
- Further Readings
- Annotated Bibliography
- Dealing with Nervousness
- Using Visual Aids
- Grading Someone Else's Paper
- How to Manage Group Projects
- Multiple Book Review Essay
- Reviewing Collected Essays
- About Informed Consent
- Writing Field Notes
- Writing a Policy Memo
- Writing a Research Proposal
- Acknowledgements
Academic writing refers to a particular style of expression that scholars use to define the boundaries of their disciplines and their areas of expertise. Characteristics of academic writing include a formal tone, use of the third-person rather than first-person perspective (usually), a clear focus on the research problem under investigation, and precise word choice. Like the specialist languages adopted in other professions such as law, academic writing is designed to convey agreed meaning about complex ideas for a group of scholarly experts.
Academic Writing. Writing Center. Colorado Technical College.
Importance of Good Academic Writing
I. The Big Picture Unlike fiction or journalistic writing, the overall structure of academic writing is formal and logical. It must be cohensive and possess a logical flow of ideas, which means that the various parts are connected to form a unified whole. There should be links between sentences and paragraphs so the reader is able to follow your argument.
II. The Tone Throughout your paper, it is important that you present the arguments of others fairly and with an appropriate tone. When presenting a position or argument that you disagree with, describe this argument accurately and without loaded or biased language. In academic writing, the author is expected to investigate the research problem from an authoritative point of view. You should, therefore, confidently state the strengths of your arguments using language that is neutral, not confrontational or dismissive.
III. The Language Clear use of language is essential in academic writing. Well-structured paragraphs and clear topic sentences enable a reader to follow your line of thinking without difficulty. Your language should be concise, formal, and express precisely what you want it to mean. Avoid vague expressions that are not specific and precise enough for the reader to derive exact meaning ["they," "we," "people," "the organization," etc.] abbreviations like 'i.e.' ["in other words"], 'e.g.' ["for example"], and contractions, such as, "don't", "isn't", etc.
IV. Academic Conventions Citing sources in the body of your paper and providing a list of references are very important aspects of academic writing. It is essential to always acknowledge the source of any ideas, research findings, or data that you have used in your paper. To do otherwise is considered plagerism.
V. Evidence-Based Arguments Your assignments often ask you to express your own point of view on research problem you are discussing. However, what is valued in academic writing is that your opinions are based on a sound understanding of the pertinent body of knowledge and academic debates that are currently being debated in your discipline. You need to support your opinion with evidence from academic sources. It should be an objective position presented as a logical argument. The quality of your evidence will determine the strength of your argument. The challenge is to convince the reader of the validity of your opinion through a well-documented, coherent, and logically structured piece of writing.
VI. Thesis-Driven Analysis The writing is “thesis-driven,” meaning that the starting point is a particular perspective, idea, or “thesis” on the chosen research problem, such as, establishing, proving, or disproving solutions to the questions posed for the topic. In contrast, simply describing a topic without the research questions does not qualify as “academic writing.”
VII. Complexity and Higher-Order Thinking One of the main functions of academic writing is to describe complex ideas as clearly as possible. Often called higher-order thinking skills, these include cognitive processes that are used to comprehend, solve problems, and express concepts or that describe abstract ideas that cannot be easily acted out, pointed to, or shown with images.
Strategies for...
Understanding Academic Writing and Its Jargon
The very definition of jargon is language specific to a particular sub-group of people . Therefore, in modern university life, jargon represents the specific language and meaning assigned to terms and phrases specific to a discipline or area of study. For example, the idea of being rational may hold the same general meaning in both political science and philosophy, but its application to understanding and explaining phenomena within the research work of a discipline may have subtle differences based on how scholars in that discipline apply the concept to the theories and practice of their work.
Given this, it is important that specialist terms [i.e., jargon] must be used accurately and applied under the appropriate conditions . Subject-specific dictionaries are the best places to confirm the meaning of terms within the context of a specific discipline. It is appropriate for you to use specialist language within your field of study, but avoid using such language when writing for non-academic or general audiences.
Key Problems to Avoid
- Excessive use of specialized terminology . Although academic writing represents a formal style of expression, it does not mean using "big words" just for the sake of doing so. Overuse of big words and complicated sentence constructions gives readers the impression that your writing is more style over substance; it leads the reader to question if you really know what you are talking about.
- Inappropriate use of specialized terminology . Because you are dealing with the concepts, research, and data of your subject, you need to use the technical language appropriate to the discipline. However, nothing will undermine the validity of your study quicker than the inappropriate application of a term or concept. Avoid using terms whose meaning you are unsure of--don't guess or assume! Consult the meaning of terms in specialized, discipline-specific dictionaries. These can be found by searching the library catalog , by entering, for example, the phrase "sociology and dictionaries."
Other Problems to Avoid
In addition to understanding the use of specialized language, there are other aspects of academic writing in the social sciences that you should be aware of . These include:
- Personal nouns . Excessive use of personal nouns [e.g., I, me, you, us, etc.] may lead the reader to believe the study was overly subjective. Using these words can be interpreted by the reader as being done only to avoid presenting empirical evidence about the research problem.
- Directives . Avoid directives that demands the reader "Do this" or "Do that." Directives should be framed as evidence-based recommendations.
- Informal, conversational tone using slang and idioms . Academic writing relies on excellent grammar and precise word structure. Your narrative should not include regional dialects or slang terms because they are often open to interpretation; be direct and concise.
- Wordiness. Focus on being concise, straightforward, and contain no confusing language . By doing so, you help eliminate the possibility of the reader misinterpreting the research design and purpose of your study.
- Vague expressions (e.g., "they," "we," "people," "the company," "that area," etc.). Being concise in your writing also includes avoiding vague references to persons, places, or things. While proofreading your paper be sure to look for and edit any vague statements that lack context.
- Numbered lists and bulleted items . The use of bulleted items or lists should be used only if the narrative dictates a need for clarity. For example, it is fine to state, "The four main problems with hedge funds are:" and then list them 1, 2, 3, 4. However, in academic writing this must then be followed by detailed explanation and analysis of each item. Given this, the question you should ask yourself while proofreading is: why begin with a list in the first place rather than just starting with systematic analysis of each item?
- Descriptive writing . Describing a research problem is an important means of contextualizing a study and, in fact, some description is needed because you can't assume the reader knows everything about the topic. However, the body of your paper should focus on methodology, the analysis and interpretation of findings, and their implications as they apply to the research problem and not background information and descriptions of tangential issues.
- Personal experiences. Drawing upon personal experience [e.g., traveling abroad; caring for someone with Alzheimer's disease] can be a effective way of engaging your readers in understanding the research problem. Use personal experience only as an example, though, because academic writing relies on evidence-based research. To do otherwise is simply story-telling.
NOTE: Rules concerning excellent grammar and precise word structure do not apply when quoting someone. If the quote is especially vague or hard to understand, consider paraphrasing it. Otherwise, a quote should be inserted in the text of your paper exactly as it was stated. If you believe the quote is important to understanding the meaning of the work as a whole , consider inserting the term "sic" in brackets after the quoted word or text to indicate that the quotation has been transcribed exactly as found in the original source, complete with any erroneous spelling or other nonstandard presentation.
Academic Writing . The Writing Lab and The OWL. Purdue University; Academic Writing Style. First-Year Seminar Handbook. Mercer University; Bem, Daryl J. Writing the Empirical Journal Article . Cornell University; College Writing . The Writing Center. University of North Carolina; Pernawan, Ari. Common Flaws in Students' Rsearch Proposals . English Education Department. Yogyakarta State University; Style . College Writing. The Writing Center. University of North Carolina; Invention: Five Qualities of Good Writing . The Reading/Writing Center. Hunter College; What Is an Academic Paper? Institute for Writing Rhetoric. Dartmouth College.
Structure and Writing Style
I. Improving Academic Writing
To improve your academic writing skills, you should focus your efforts on three key areas: 1. Clear Writing . Thinking about precedes writing about. Good writers spend sufficient time distilling information and reviewing major points from their sources before creating their work. Writing detailed outlines can help you clearly organize your thoughts. Effective academic writing begins with solid planning, so manage your time carefully. 2. Excellent Grammar . Needless to say, English grammar can be difficult and complex; even the best scholars take many years before thay have command of the major points of good grammar. Take the time to learn the major and minor points of good grammar. Spend time practicing writing and seek detailed feedback from professors. Take advantage of the Jandrisevits Learning Center on campus if you need a lot of help. Proper punctuation use and good proofreading skills measurably improve academic writing [see subtab for proofreading you paper ].
Invest in and always refer to these three types of resources to help your grammar and writing skills:
- A good writing reference book, such as, Strunk and White’s book, The Elements of Style ;
- A college-level dictionary, such as, Merriam-Webster's Collegiate Dictionary ;
- The latest edition of Roget's Thesaurus in Dictionary Form .
3. Consistent Stylistic Approach . Whether your professor requires you to use MLA, APA or the Chicago Manual of Style, choose one style manual and stick to it. Each of these style manuals provide guidance on how to write out numbers, references, citations, footnotes, and lists. Consistent adherence to one style of writing helps the flow of your paper and improves its readability. Note that some disciplines require a particular style [e.g., education uses APA] so as you write more papers within your major, familiarity will improve.
II. Evaluating Quality of Writing
A useful approach for evaluating the quality of your academic writing is to consider the following issues from the perspective of the reader. While proofreading your final draft, ctitically assess the quality of the following elements in your writing.
- It is shaped around one clear research problem, and explains what that problem is from the outset,
- Your paper tells the reader why the problem is important and why people should know about it,
- You have accurately and thoroughly informed the reader what has already been published [or not] about this problem or others related to it,
- You have provided evidence to support your argument that the reader finds convincing,
- The paper includes a description of how and why the particular evidence was collected, and why specific theoretical arguments or concepts were used,
- The paper is made up of paragraphs, each containing only one controlling idea,
- You indicate how each section of the paper addresses the research problem,
- You have considered counter-arguments or counter-examples where they are relevant,
- Arguments, evidence, and their significance have been presented in the conclusion, and
- The narrative flows in a clear, accurate, and well-organized way.
Academic Writing . The Writing Lab and The OWL. Purdue University; Academic Writing Style. First-Year Seminar Handbook. Mercer University; Bem, Daryl J. Writing the Empirical Journal Article . Cornell University; College Writing . The Writing Center. University of North Carolina; Style . College Writing. The Writing Center. University of North Carolina; Invention: Five Qualities of Good Writing . The Reading/Writing Center. Hunter College; What Is an Academic Paper? Institute for Writing Rhetoric. Dartmouth College.
Writing Tip
Jandrisevits Learning Center (JLC)!
Academic Support Services at the JLC include 1-on-1 tutoring with Professional and Peer tutors; group study sessions for particular courses by Classroom Learning Assistants (CLAs); monthly workshops on specific academic and life skills; specialized Learning Labs in math, critical reading and writing, accounting, and math; and online writing support (OWL).
Another Writing Tip
Considering the Passive Voice in Academic Writing
In the English language, we are able to construct sentences in the following way:
- "The policies of Congress caused the economic crisis."
- "The economic crisis was caused by the policies of Congress."
The decision about which sentence to use is governed by whether you want to focus on “Congress” and what they did, or on “the economic crisis” and what caused it. This choice in focus is achieved with the use of either the active or the passive voice. When you want your readers to focus on the "doer" of an action, you can make the "doer"' the subject of the sentence and use the active form of the verb. When you want readers to focus on the person, place, or thing affected by the action, or the action itself, you can make the effect or the action the subject of the sentence by using the passive form of the verb. Often in academic writing, scholars don't want to focus on who is doing an action, but on who is receiving or experiencing the action. The passive voice is useful in academic writing because it allows writers to highlight the most important participants or events within sentences by placing them at the beginning of the sentence.
Use the passive voice when:
- You want to focus on the person, place, or thing affected by the action, or the action itself;
- It is not important who or what did the action;
- You want to be impersonal or more formal.
Form the passive voice by:
- Turning the object of the active sentence into the subject of the passive sentence.
- Changing the verb to a passive form by adding the appropriate form of the verb "to be" and the past participle of the main verb.
NOTE: Check with your professor about writing in the passive voice before submitting your research paper. Some discourage its use.
Active and Passive Voice . The Writing Lab and The OWL. Purdue University; Diefenbach, Paul. Future of Digital Media Syllabus . Drexel University; Passive Voice . The Writing Center. University of North Carolina.
- << Previous: 2. Preparing to Write
- Next: Choosing a Title >>
- Last Updated: Jul 18, 2023 11:58 AM
- URL: https://library.sacredheart.edu/c.php?g=29803
- QuickSearch
- Library Catalog
- Databases A-Z
- Publication Finder
- Course Reserves
- Citation Linker
- Digital Commons
- Our Website
Research Support
- Ask a Librarian
- Appointments
- Interlibrary Loan (ILL)
- Research Guides
- Databases by Subject
- Citation Help
Using the Library
- Reserve a Group Study Room
- Renew Books
- Honors Study Rooms
- Off-Campus Access
- Library Policies
- Library Technology
User Information
- Grad Students
- Online Students
- COVID-19 Updates
- Staff Directory
- News & Announcements
- Library Newsletter
My Accounts
- Interlibrary Loan
- Staff Site Login
FIND US ON
Want to create or adapt books like this? Learn more about how Pressbooks supports open publishing practices.
Emily Bongiovanni
This chapter will help you:
- Recognize patterns and best practices in academic writing
- Understand the types of scholarly articles
Introduction to Academic Writing
There are various outlets for research dissemination, including conference posters, presentations, and scholarly articles. However scholarly articles are generally considered the most highly regarded type across disciplines. Scholarly, or journal, articles are published through academic journals. Scholarly articles are written by experts or scholars in a field and provide original research or analysis. They are written for an audience of other scholars or experts in the same discipline. Most scholarly articles are peer reviewed, meaning they are reviewed by experts in the field before they are published.
Types of Scholarly Articles
The main types of academic articles are original research articles and review articles. However, you might find content in scholarly journals that fall outside of these types, such as an editorial piece or book review. In addition to scholarly articles found in academic journals, conference proceedings are another type of scholarly work that uses an academic writing style.
Table content reused from UC Merced LibGuide Writing 101 under CC-BY-NC license.
Academic Writing Style
Academic writing (or scholarly writing) is the style of writing that is used for scholarly publications, including articles, posters, and reports. This type of writing is formal, concise, and takes an unbiased approach. Academic writing provides relevant evidence to support any claims. This type of writing avoids informal language, like slang or conversational phrases, and long-winded or emotional text. Academic writing is well-structured and uses section headings and paragraph breaks to help readers follow along. This style is generally consistent regardless of the type of scholarly article.
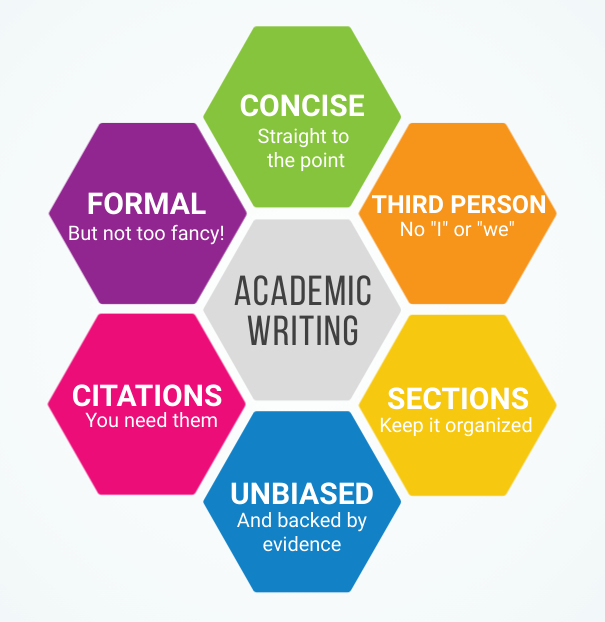
The scholarly voice
Academic writing usually is in the third-person, rather than first-person. Authors should avoid referring to themselves and their personal thoughts. Any arguments presented should be evidence-based and presented from an objective stance, backed with cited evidence.
Sentences should be simple and direct. Authors should avoid using overly complicated or “fancy” words just for the sake of trying to make the work sound more sophisticated. On the other hand, authors should also avoid slang and causal expressions.
In academic writing, authors cite others to support any claims. Properly attributing other’s work, or citing, is a fundamental component of academic writing and academic integrity. Proper citations or references are needed to avoid plagiarism, as well as to give credit where credit is due.
There are hundreds of citation styles and editions. Many professional societies, such as the American Psychological Association (APA) or Institute of Electrical and Electronics Engineers (IEEE) provide the standard citation style for the field. These different styles reflect the best practices of scholarly communication in that discipline. For example, some styles use an in-text citation style that mentions the authors name and date of publication in the in-text citation. Other styles might instead refer to a source with a number, e.g. [2], which corresponds to a citation in the reference list.
Anatomy of a Scholarly Paper
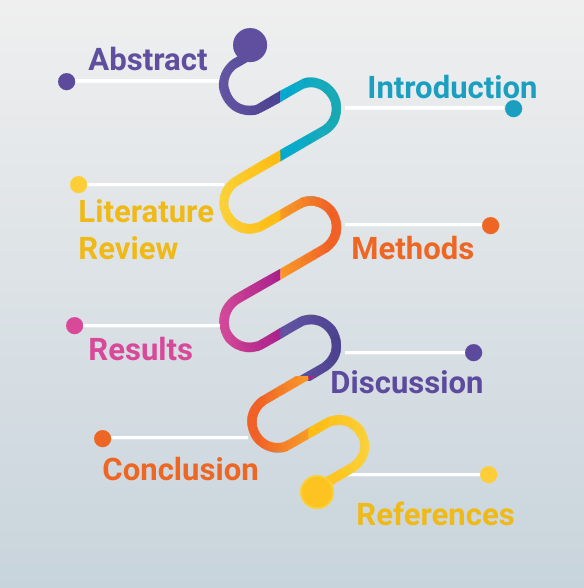
The structure and components of an article are dictated by the type or article and any formatting requirements from the publisher or journal or by the discipline’s style guidelines. The most common sections of a scholarly paper are outlined in the table below:
Some of these sections may not be included in a paper or may be combined depending on the type of paper and requirements from the publisher. Additional sections may be included as well, such as an appendix or acknowledgements section. Journals and conferences will typically provide clear expectations and guidelines for the sections that should be included.
Literature Reviews
Literature reviews are a common section of an article and a necessary step for successful research. They are both a product and a process. A literature review summarizes and synthesizes key works in the field. It uses a narrative structure that allows readers to understand how previously published work relates to one another and provides a concise road map on further research. The goal of a literature review is to outline relevant literature that leads to your research, but it does not include your new research.
In addition to serving the readers, a literature review is also for you, the author, to gain breadth and depth of understanding in your field of research. It helps you understand how your research fits into the scholarly conversation and how it is reflected in the literature.
A literature review is not a list, editorial option, or description of your own research.
Literature review process
Conducting a literature review is an ongoing process. It is usually described as a linear process, as it is below, but it is really a complex feedback process.
- Define scope – The boundaries of a literature review usually follow the boundaries of the research. However, be prepared to change those boundaries as you make new discoveries or as conditions change.
- Identify literature – Explore the literature and discover, learn, and pursue new concepts. See Chapter 2 for information on finding and evaluating literature.
- Analyze findings – Evaluate results and discard or relocate less relevant items. Conduct a “quick read” to get to a subset of papers you will read in depth.
- Summarize and synthesize – Begin to make connections and integrate information. Use a narrative structure so readers are easily able to follow ideas as they read.
Understanding the Importance of Citations
Citations are more than just a nuisance to include in a paper. In addition to getting credit, there are other reasons why authors want to be cited for their work. Citations play a role in the scholarly conversation and how scholars interact with each other. Citations are tracked through various tools to assess the impact of a work or author, which can support the author’s scholarly identity and progress toward promotion.
Citations also demonstrate that you, as the author, have researched this topic and have authority to join the scholarly conversation. They also provide identifying information (title, author, etc.) that allow readers to track down and explore the references cited.
Without a good workflow with literature, it can be easy to accidentally plagiarize. See Chapter 4 on citation management software, which supports organizing literature and citing.
Tips for Academic Writing
- Don’t use fancy words for the sake of sounding sophisticated
- Use clear and concise language
- Organize your writing logically
- Always support claims with evidence. Academic writing is not about sharing opinions, but presenting new information founded in evidence.
- Always cite your sources of information. Utilizing the scholarly record and noting where it has been used creates a solid foundation upon which your research builds.
Practice identifying best practices in academic writing. Find a scholarly article from an academic journal and observe the best practices for academic writing in action:
- Is the abstract informative?
- How is the paper organized? What sections do you see?
- Is the paper well-cited with a reference list?
- Is it written in third person with little to no use of “I or “we”?
- Is there a literature review? It is easy for you as the reader to understand how this research fits into the larger scholarly conversation?
Navigating the Research Lifecycle for the Modern Researcher Copyright © 2022 (1st Edition) by Emily Bongiovanni is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial 4.0 International License , except where otherwise noted.
Share This Book

IMAGES
VIDEO
COMMENTS
Academic Writing 3 The Pillars of Academic Writing Academic writing is built upon three truths that aren't self-evident: - Writing is Thinking: While "writing" is traditionally understood as the expression of thought, we'll redefine "writing" as the thought process itself. Writing is not what you do with thought. Writing is
Academic writing is a formal style of writing used in universities and scholarly publications. You'll encounter it in journal articles and books on academic topics, and you'll be expected to write your essays, research papers, and dissertation in academic style. Academic writing follows the same writing process as other types of texts, but ...
Explaining how to organize your work in order to write more, Paul J. Silva also does not offer advice on how to write well. 6. There are quite a few books that do not tell stories about writers and writing, but that show what good writing is and how to write well. Yarris and colleagues provided a perfect example: Helen Sword's Stylish Academic ...
Academic writing is a formal style of writing that researchers and educators use in scholarly publications. It focuses on evidence-based arguments and logical reasoning to guide a reader's understanding of a subject. Writers can use this format to identify and analyze a concept and propose a theory or rational conclusion.
Academic writing is writing which communicates ideas, information and research to the wider academic community. It can be divided into two types: student academic writing, which is used as a form of assessment at university, as well as at schools as preparation for university study; and expert academic writing, which is writing that is intended for publication in an academic journal or book.
Academic writing refers to a style of expression that researchers use to define the intellectual boundaries of their disciplines and specific areas of expertise. ... Understanding Academic Writing and Its Jargon. The very definition of research jargon is language specific to a particular community of ... Often in academic writing, scholars don ...
Niina Hynninen. Writing is pervasive in the context of higher education. Scholars write various kinds of texts for research, teaching as well as administrative purposes, and students are required, for example, to produce much of their course work in writing. This pervasiveness of writing in academia has not gone unnoticed by researchers, and ...
Academic writing is a style of writing that is objective, unbiased, and focuses on supporting information with reliable and credible data and evidence. Academic writing is geared toward contributing to the body of knowledge on a topic or field of study. To contribute to the field of knowledge on a topic. Scholars, researchers, and practitioners ...
A literature review is a piece of academic writing that summarizes, describes, and evaluates a topic through analysis of other authors' works. A literature review examines a topic through two or more works, and these works can be books, scholarly articles, presentations, dissertations, or other published materials.
Academic writing communicates complex ideas in a clear, precise, logical, reasoned, and evidence-based way. It is an advanced literacy task that requires a host of demanding skills. Learning to write for academic purposes involves, for example, learning. how to contextualize your ideas and arguments in the existing scholarship of the field.
Academic writing or scholarly writing refers primarily to nonfiction writing that is produced as part of academic work in accordance with the standards of a particular academic subject or discipline, including: . reports on empirical fieldwork or research in facilities for the natural sciences or social sciences,; monographs in which scholars analyze culture, propose new theories, or develop ...
This book redefines "writing" as the thought process itself. Writing is not what you do with thought. Writing is thinking. Better living through interpretation: that's the promise of academic writing, which is a foundational course in most schools because it's a foundational skill in life. Our world is full of things that need to be ...
What Is Academic Writing? Academic writing is a specialized form of writing that suits the particular needs of academic writers. Used effectively, it helps scholars express complex concepts, research, and theories clearly to their peers. Learning to embrace this style of writing is essential in academia. However, we all need to start somewhere.
Academic writing is the process of sharing original research with other scholars in accordance with certain standard rules. This process requires correctly following the steps of scientific academic writing. However, a close analysis of recent academic tex ts reveals a wide range of mistakes or shortcomings.
The ability to write academic papers is one of the critical factors that distinguish scholars from excellent scholars. Academic writing can be defined as the writing form that aims to transmit scientific or other knowledge through clear and concise means. The main idea behind academic writing is objective and practical in terms of presentation ...
explaining; giving reasons; examining or anticipating consequences. comparing, contrasting and evaluating. considering both sides of an issue. taking a position. supporting your claims with credible evidence. investigating claims made by others and, if appropriate, questioning the evidence. drawing conclusions.
Introduction. Scholarly writing is also known as academic writing. It is the genre of writing used in all academic fields. Scholarly writing is not better than journalism, fiction, or poetry; it is just a different category. Because most of us are not used to scholarly writing, it can feel unfamiliar and intimidating, but it is a skill that can ...
Academic writing is a fresh, structured approach to an important aspect of higher education scholarly work. ... scholar ly writing exists on two dimensions: 1) ... themes, such as definitions of ...
Definition. Academic writing refers to a particular style of expression that scholars use to define the boundaries of their disciplines and their areas of expertise. Characteristics of academic writing include a formal tone, use of the third-person rather than first-person perspective (usually), a clear focus on the research problem under ...
Academic writing (or scholarly writing) is the style of writing that is used for scholarly publications, including articles, posters, and reports. This type of writing is formal, concise, and takes an unbiased approach. Academic writing provides relevant evidence to support any claims. This type of writing avoids informal language, like slang ...
Where academic writing may be defined broadly as any writing completed to fulfill university or college requirements, scholarly writing is produced to inform a specialized audience of other scholars in a particular field. Scholarly writing is crafted by one professional for other professionals ("Definition of Academic Writing," 2011). Graduate
Hannah Skaggs. Hannah, a writer and editor since 2017, specializes in clear and concise academic and business writing. She has mentored countless scholars and companies in writing authoritative and engaging content. Learn the basics of academic writing: definition, types, improvement tips & a checklist to ensure your work meets standards.
Google Scholar provides a simple way to broadly search for scholarly literature. Search across a wide variety of disciplines and sources: articles, theses, books, abstracts and court opinions.
A scholarly dialogue: writing scholarship, authorship, academic integrity and the challenges of AI. Beck Wise a School of Communication and Arts, University of Queensland, ... Poe's now-famous definition of a short story as a narrative that can be 'read in one sitting' reflects the reading practices that magazines, and the printing ...
Instead, AI is starting to disrupt established methodologies, ethical paradigms, and fundamental principles that have long guided scholarly work. The aim of this article is to engage in a rigorous dialogue on AI's role in higher educational research. Specific activities, such as writing, data analytics and automated content analysis in ...