
Essays About Religion: Top 5 Examples and 7 Writing Prompts
Essays about religion include delicate issues and tricky subtopics. See our top essay examples and prompts to guide you in your essay writing.
With over 4,000 religions worldwide, it’s no wonder religion influences everything. It involves faith, lessons on humanity, spirituality, and moral values that span thousands of years. For some, it’s both a belief and a cultural system. As it often clashes with science, laws, and modern philosophies, it’s also a hot debate topic. Religion is a broad subject encompassing various elements of life, so you may find it a challenging topic to write an essay about it.
1. Wisdom and Longing in Islam’s Religion by Anonymous on Ivypanda.com
2. consequences of following religion blindly essay by anonymous on ivypanda.com, 3. religion: christians’ belief in god by anonymous on ivypanda.com, 4. mecca’s influence on today’s religion essay by anonymous on ivypanda.com, 5. religion: how buddhism views the world by anonymous on ivypanda.com , 1. the importance of religion, 2. pros and cons of having a religion, 3. religions across the world, 4. religion and its influence on laws, 5. religion: then and now, 6. religion vs. science, 7. my religion.
“Portraying Muslims as radical religious fanatics who deny other religions and violently fight dissent has nothing to do with true Islamic ideology. The knowledge that is presented in Islam and used by Muslims to build their worldview system is exploited in a misinterpreted form. This is transforming the perception of Islam around the world as a radical religious system that supports intolerance and conflicts.”
The author discusses their opinion on how Islam becomes involved with violence or terrorism in the Islamic states. Throughout the essay, the writer mentions the massive difference between Islam’s central teachings and the terrorist groups’ dogma. The piece also includes a list of groups, their disobediences, and punishments.
This essay looks at how these brutalities have nothing to do with Islam’s fundamental ideologies. However, the context of Islam’s creeds is distorted by rebel groups like The Afghan mujahideen, Jihadis, and Al-Qa’ida. Furthermore, their activities push dangerous narratives that others use to make generalized assumptions about the entire religion. These misleading generalizations lead to misunderstandings amongst other communities, particularly in the western world. However, the truth is that these terrorist groups are violating Islamic doctrine.
“Following religion blindly can hinder one’s self-actualization and interfere with self-development due to numerous constraints and restrictions… Blind adherence to religion is a factor that does not allow receiving flexible education and adapting knowledge to different areas.”
The author discusses the effects of blindly following a religion and mentions that it can lead to difficulties in self-development and the inability to live independently. These limitations affect a person’s opportunity to grow and discover oneself. Movies like “ The Da Vinci Code ” show how fanatical devotion influences perception and creates constant doubt.
“…there are many religions through which various cultures attain their spiritual and moral bearings to bring themselves closer to a higher power (deity). Different religions are differentiated in terms of beliefs, customs, and purpose and are similar in one way or the other.”
The author discusses how religion affects its followers’ spiritual and moral values and mentions how deities work in mysterious ways. The essay includes situations that show how these supreme beings test their followers’ faith through various life challenges. Overall, the writer believes that when people fully believe in God, they can be stronger and more capable of coping with the difficulties they may encounter.
“Mecca represents a holy ground that the majority of the Muslims visit; and is only supposed to be visited by Muslims. The popularity of Mecca has increased the scope of its effects, showing that it has an influence on tourism, the financial aspects of the region and lastly religion today.”
The essay delves into Mecca’s contributions to Saudi Arabia’s tourism and religion. It mentions tourism rates peaking during Hajj, a 5-day Muslim pilgrimage, and visitors’ sense of spiritual relief and peace after the voyage. Aside from its tremendous touristic benefits, it also brings people together to worship Allah. You can also check out these essays about values and articles about beliefs .
“Buddhism is seen as one of the most popular and widespread religions on the earth the reason of its pragmatic and attractive philosophies which are so appealing for people of the most diversified backgrounds and ways of thinking .”
To help readers understand the topic, the author explains Buddhism’s worldviews and how Siddhatta Gotama established the religion that’s now one of the most recognized on Earth. It includes teachings about the gift of life, novel thinking, and philosophies based on his observations. Conclusively, the author believes that Buddhism deals with the world as Gotama sees it.
Check out our guide packed full of transition words for essays .
7 Prompts on Essays About Religion

Religion’s importance is embedded in an individual or group’s interpretation of it. They hold on to their faith for various reasons, such as having an idea of the real meaning of life and offering them a purpose to exist. Use this prompt to identify and explain what makes religion a necessity. Make your essay interesting by adding real-life stories of how faith changed someone’s life.
Although religion offers benefits such as positivity and a sense of structure, there are also disadvantages that come with it. Discuss what’s considered healthy and destructive when people follow their religion’s gospels and why. You can also connect it to current issues. Include any personal experience you have.
Religion’s prevalence exhibits how it can significantly affect one’s daily living. Use this prompt to discuss how religions across the world differ from one another when it comes to beliefs and if traditions or customs influence them. It’s essential to use relevant statistical data or surveys in this prompt to support your claims and encourage your readers to trust your piece.
There are various ways religion affects countries’ laws as they adhere to moral and often humanitarian values. Identify each and discuss how faith takes part in a nation’s decision-making regarding pressing matters. You can focus on one religion in a specific location to let the readers concentrate on the case. A good example is the latest abortion issue in the US, the overturning of “Wade vs. Roe.” Include people’s mixed reactions to this subject and their justifications.

In this essay, talk about how the most widespread religions’ principles or rituals changed over time. Then, expound on what inspired these changes. Add the religion’s history, its current situation in the country, and its old and new beliefs. Elaborate on how its members clash over these old and new principles. Conclude by sharing your opinion on whether the changes are beneficial or not.
There’s a never-ending debate between religion and science. List the most controversial arguments in your essay and add which side you support and why. Then, open discourse about how these groups can avoid quarreling. You can also discuss instances when religion and science agreed or worked together to achieve great results.
Use this prompt if you’re a part of a particular religion. Even if you don’t believe in faith, you can still take this prompt and pick a church you’ll consider joining. Share your personal experiences about your religion. Add how you became a follower, the beliefs that helped you through tough times, and why you’re staying as an active member in it. You can also speak about miraculous events that strengthen your faith. Or you can include teachings that you disagree with and think needs to be changed or updated.
For help with your essay, check out our top essay writing tips !

Maria Caballero is a freelance writer who has been writing since high school. She believes that to be a writer doesn't only refer to excellent syntax and semantics but also knowing how to weave words together to communicate to any reader effectively.
View all posts
- Share full article
Advertisement
Supported by
student opinion
What Role Does Religion Play in Your Life?
Did you attend religious services or observe religious traditions as a child? How has religion shaped who you are today?

By Nicole Daniels and Michael Gonchar
When you were younger, did you attend religious services or participate in religious observations with your family? Did you belong to any kind of religious community? What about now, as a teenager?
Has religion played an important role in your life? If so, in what ways?
In her recent Opinion essay, “ I Followed the Lives of 3,290 Teenagers. This Is What I Learned About Religion and Education ,” Ilana M. Horwitz discusses the effects of a religious upbringing on academic success:
American men are dropping out of college in alarming numbers. A slew of articles over the past year depict a generation of men who feel lost , detached and lacking in male role models . This sense of despair is especially acute among working-class men, fewer than one in five of whom completes college. Yet one group is defying the odds: boys from working-class families who grow up religious. As a sociologist of education and religion, I followed the lives of 3,290 teenagers from 2003 to 2012 using survey and interview data from the National Study of Youth and Religion , and then linking those data to the National Student Clearinghouse in 2016. I studied the relationship between teenagers’ religious upbringing and its influence on their education: their school grades, which colleges they attend and how much higher education they complete. My research focused on Christian denominations because they are the most prevalent in the United States. I found that what religion offers teenagers varies by social class. Those raised by professional-class parents, for example, do not experience much in the way of an educational advantage from being religious. In some ways, religion even constrains teenagers’ educational opportunities (especially girls’) by shaping their academic ambitions after graduation; they are less likely to consider a selective college as they prioritize life goals such as parenthood, altruism and service to God rather than a prestigious career. However, teenage boys from working-class families, regardless of race, who were regularly involved in their church and strongly believed in God were twice as likely to earn bachelor’s degrees as moderately religious or nonreligious boys. Religious boys are not any smarter , so why are they doing better in school? The answer lies in how religious belief and religious involvement can buffer working-class Americans — males in particular — from despair.
Students, read the entire article , then tell us:
What role, if any, did religion play in your childhood? Do you consider religion and religious faith to be important parts of your life? Why or why not?
According to Dr. Horwitz’s research, religious belief and religious involvement help working-class teenage boys achieve academic success. Do you think religion has helped you succeed in the classroom? Why or why not?
Dr. Horwitz discusses some of the social benefits — including a sense of community, a shared outlook on life and the presence of trusting relationships and adult role models — that religion can have for young people. Has religion provided any of these benefits to you? Has it provided other benefits?
Not every person sees religion as beneficial. Are you one of those people? If so, why?
The author explains the importance of “social capital” — the social ties that provide a web of support for families and young people. Do you feel that you are surrounded by a web of support? Does it include family, friends, neighbors, teachers, coaches, religious leaders or others? In what ways do these people — or the communities in which they operate — support you and your family? Do you wish that you had more social capital or a larger web of support? Why or why not?
Dr. Horwitz has found that social class and gender can affect what religion offers teenagers. Do those findings surprise you? Is there anything else from her research that strikes you as unexpected? How so?
What else do you think people should know about teenagers and religion that was not discussed in the essay?
Want more writing prompts? You can find all of our questions in our Student Opinion column . Teachers, check out this guide to learn how you can incorporate them into your classroom.
Students 13 and older in the United States and Britain, and 16 and older elsewhere, are invited to comment. All comments are moderated by the Learning Network staff, but please keep in mind that once your comment is accepted, it will be made public.
Nicole Daniels joined The Learning Network as a staff editor in 2019 after working in museum education, curriculum writing and bilingual education. More about Nicole Daniels
Read our research on: Gun Policy | International Conflict | Election 2024
Regions & Countries
Religion in everyday life, highly religious americans are happier and more involved with family but are no more likely to exercise, recycle or make socially conscious consumer choices.
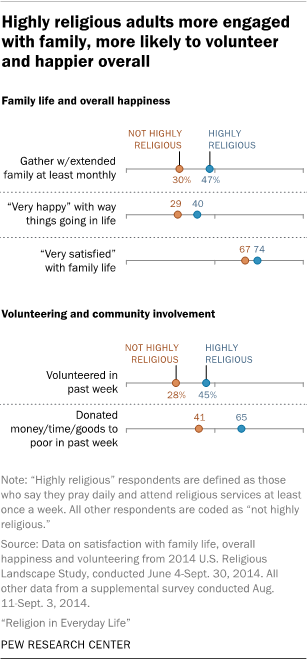
These differences are found not only in the U.S. adult population as a whole but also within a variety of religious traditions (such as between Catholics who are highly religious and those who are less religious), and they persist even when controlling for other factors, including age, income, education, geographic region of residence, marital status and parental status.
For instance, highly religious people are about as likely as other Americans to say they lost their temper recently, and they are only marginally less likely to say they told a white lie in the past week. When it comes to diet and exercise, highly religious Americans are no less likely to have overeaten in the past week, and they are no more likely to say they exercise regularly. Highly religious people also are no more likely than other Americans to recycle their household waste. And when making decisions about what goods and services to buy, they are no more inclined to consider the manufacturers’ environmental records or whether companies pay employees a fair wage.
These are among the latest findings of Pew Research Center’s U.S. Religious Landscape Study. The study and this report were made possible by The Pew Charitable Trusts, which received support for the project from Lilly Endowment Inc.
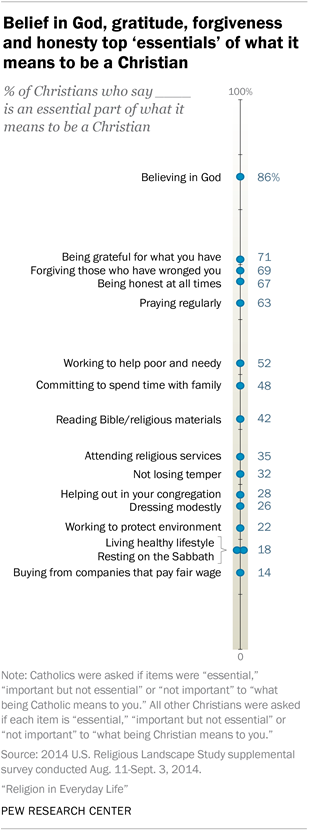
Among Christians, believing in God tops the list, with fully 86% saying belief in God is “essential” to their Christian identity. In addition, roughly seven-in-ten Christians say being grateful for what they have (71%), forgiving those who have wronged them (69%) and always being honest (67%) are essential to being Christian. Far fewer say that attending religious services (35%), dressing modestly (26%), working to protect the environment (22%) or resting on the Sabbath (18%) are essential to what being Christian means to them, personally.
The survey posed similar questions to members of non-Christian faiths and religiously unaffiliated Americans (sometimes called religious “nones”), asking whether various behaviors are essential to “what being a moral person means to you.” 4 Among the unaffiliated, honesty (58%) and gratitude (53%) are the attributes most commonly seen as essential to being a moral person. (Findings about non-Christians are discussed in more detail at the end of Chapter 2 .)
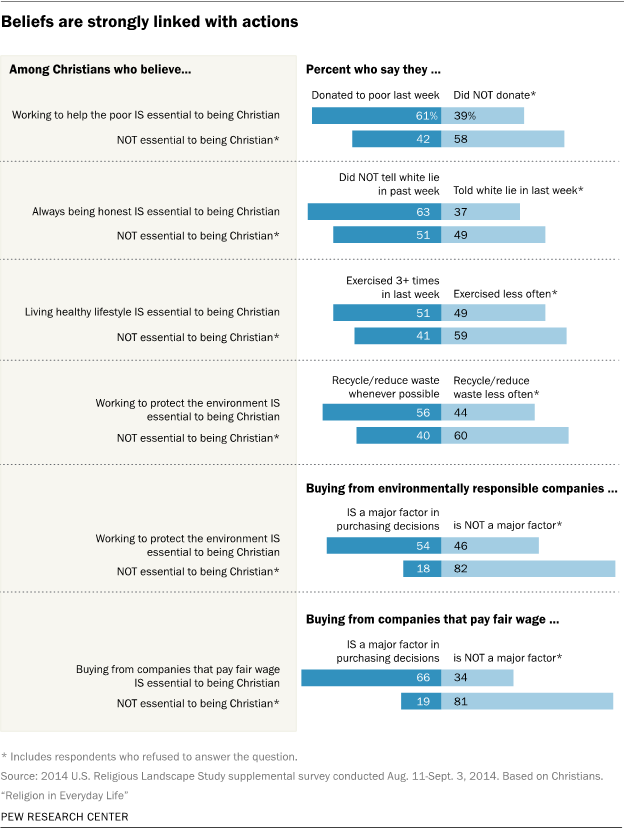
The survey shows a clear link between what people see as essential to their faith and their self-reported day-to-day behavior. Simply put, those who believe that behaving in a particular way or performing certain actions are key elements of their faith are much more likely to say they actually perform those actions on a regular basis.
For example, among Christians who say that working to help the poor is essential to what being Christian means to them, about six-in-ten say they donated time, money or goods to help the poor in the past week. By comparison, fewer Christians who do not see helping the poor as central to their religious identity say they worked to help the poor during the previous week (42%).
The same pattern is seen in the survey’s questions about interpersonal interactions, health and social consciousness. Relatively few Christians see living a healthy lifestyle, buying from companies that pay fair wages or protecting the environment as key elements of their faith. But those who do see these things as essential to what it means to be a Christian are more likely than others to say they live a healthy lifestyle (by exercising, for example), consider how a company treats its employees and the environment when making purchasing decisions, or attempt to recycle or reduce waste as much as possible.
Of course, survey data like these cannot prove that believing certain actions are obligatory for Christians actually causes Christians to behave in particular ways. The causal arrow could point in the other direction: It may be easier for those who regularly engage in particular behaviors to cite those behaviors as essential to their faith. Conversely, it may be harder for those who do not regularly engage in particular activities (such as helping the poor) to describe those activities as essential to their faith. Nevertheless, the survey data suggest that Christians are more likely to live healthy lives, work on behalf of the poor and behave in environmentally conscious ways if they consider these things essential to what it means to be a Christian.
But while relatively few people look to religious leaders for guidance on major decisions, many Americans do turn to prayer when faced with important choices. Indeed, among those who are highly religious, nearly nine-in-ten (86%) say they rely “a lot” on prayer and personal religious reflection when making major life decisions, which exceeds the share of the highly religious who say they rely a lot on their own research.
Other key findings in this report include:
- Three-quarters of adults – including 96% of members of historically black Protestant churches and 93% of evangelical Protestants – say they thanked God for something in the past week. And two-thirds, including 91% of those in the historically black Protestant tradition and 87% of evangelicals, say they asked God for help during the past week. Fewer than one-in-ten adults (8%) say they got angry with God in the past week. (For more details on how Americans say they relate to God, see Chapter 1 .)
- One-third of religiously unaffiliated Americans say they thanked God for something in the past week, and one-in-four have asked God for help in the past week. (For more details, see Chapter 1 .)
- Nearly half of Americans (46%) say they talk with their immediate families about religion at least once or twice a month. About a quarter (27%) say they talk about religion at least once a month with their extended families, and 33% say they discuss religion as often with people outside their families. Having regular conversations about religion is most common among evangelicals and people who belong to churches in the historically black Protestant tradition. By contrast, relatively few religious “nones” say they discuss religion with any regularity. (For more details on how often Americans talk about religion, see Chapter 1 .)
- One-third of American adults (33%) say they volunteered in the past week. This includes 10% who say they volunteered mainly through a church or religious organization and 22% who say their volunteering was not done through a religious organization. (For more details on volunteering, see Chapter 1 .) 5
- Three-in-ten adults say they meditated in the past week to help cope with stress. Regularly using meditation to cope with stress is more common among highly religious people than among those who are less religious (42% vs. 26%). (For more details on meditation and stress, see Chapter 1 .)
- Nine-in-ten adults say the quality of a product is a “major factor” they take into account when making purchasing decisions, and three-quarters focus on the price. Far fewer – only about one-quarter of adults – say a company’s environmental responsibility (26%) or whether it pays employees a fair wage (26%) are major factors in their purchasing decisions. Highly religious adults are no more or less likely than those who are less religious to say they consider a company’s environmental record and fair wage practices in making purchasing decisions. (For more details on how Americans make purchasing decisions, see Chapter 1 .)
- Three-quarters of Catholics say they look to their own conscience “a great deal” for guidance on difficult moral questions. Far fewer Catholics say they look a great deal to the Catholic Church’s teachings (21%), the Bible (15%) or the pope (11%) for guidance on difficult moral questions. (For more details, see Chapter 3 .)
- One-quarter of Christians say dressing modestly is essential to what being Christian means to them, and an additional four-in-ten say it is “important, but not essential.” (For more details, see Chapter 2 .)
- When asked to describe, in their own words, what being a “moral person” means to them, 23% of religious “nones” cite the golden rule or being kind to others, 15% mention being a good person and 12% mention being tolerant and respectful of others. (For more details, see Chapter 2 .)
The remainder of this report explores these and other findings in greater depth. Chapter 1 provides greater detail on how Americans from various religious backgrounds say they live their day-to-day lives. Chapter 2 examines the essentials of religious and moral identity – what do Christians see as “essential” to what it means to be a Christian, and what do members of non-Christian faiths and religious “nones” see as essential to being a moral person? Chapter 3 reports on where members of various religious groups say they look for guidance when making major life decisions or thinking about tough moral questions. On most of these questions, the report compares highly religious Americans with those who are less religious and also looks at differences among members of a variety of religious groups. For comparisons of highly religious people with those who are less religious within particular religious groups (e.g., highly religious Catholics vs. less religious Catholics), see the detailed tables .
Profile of those who are highly religious, less religious
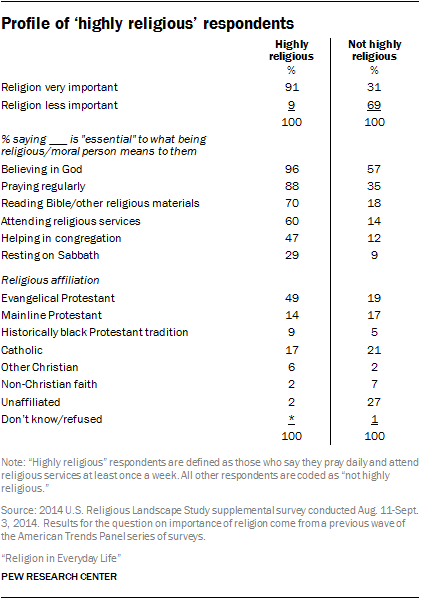
As this report highlights, these standard measures of traditional religious practice do not capture the full breadth of what it means to be religious; many respondents also say attributes such as gratitude, forgiveness and honesty are essential to what being religious means to them, personally. Nevertheless, these two indicators (prayer and religious attendance) are closely related to a variety of other measures of religious commitment.
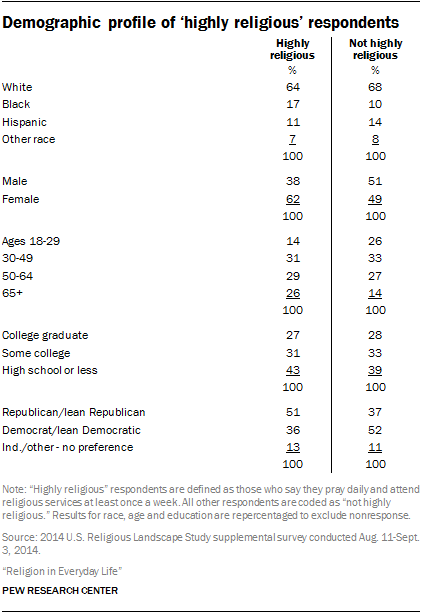
As might be expected, the religious makeup of the highly religious and less religious also are quite distinct. Fully half of highly religious American adults (49%) identify with evangelical Protestant denominations, compared with about one-in-five (19%) of those who are not highly religious. And while only a handful of highly religious people are religiously unaffiliated, about a quarter of less religious respondents (27%) identify as atheist, agnostic or “nothing in particular.”
There also are important demographic differences between the highly religious and those who are less religious. 8 They also are more likely to align with the Republican Party than the Democratic Party, and they are somewhat older, on average, than those who are less religious. However, there are few differences by level of education.
If respondents who seldom or never pray and seldom or never attend religious services are analyzed separately from others who are “not highly religious,” many of these differences are even larger.
- There are many possible ways to define “highly religious.” For example, Pew Research Center used an index of four measures (frequency of prayer, worship service attendance, belief in God and importance of religion) to create a “highly religious” category in a recently published interactive tool titled “ How religious is your state? ” The definition of “highly religious” in this report is based on two of these standard measures of religiosity – self-reported rates of prayer and worship service attendance – that were asked of all respondents in a supplemental survey to the U.S. Religious Landscape Study, the main source of data for this report. ↩
- Some previous studies have found that highly religious Americans Are more likely to volunteer not only for religious causes but also for secular ones. See Putnam, Robert D. and David E. Campbell. 2010. “American Grace: How Religion Divides and Unites Us.” Chapter 13, pages 443-454. Some prior studies also have found linkages between religious behavior and better health outcomes, though the reasons for this are debated. See, for example, Blasi, Anthony J. ed. 2011. “Toward a Sociological Theory of Religion and Health.” ↩
- In recent years, religious leaders across a wide range of faiths have urged followers to put their religious beliefs into practice through everyday behaviors such as consumer choices, environmentalism, hospitality, charity, honesty, forgiveness and healthy living. See, for example, Pope Francis’ 2015 environmental encyclical “Laudato Si.” Also see Bass, Dorothy C. ed. 2010. “Practicing Our Faith: A Way of Life for a Searching People.” However, the underlying question in this report is not normative – e.g., how religious people should behave in daily life – but sociological: Do Americans who are highly religious by conventional measures (prayer and worship service attendance) also have different beliefs or behave differently from less religious Americans in other areas of life? ↩
- Ideally, the survey would have asked about the “essentials” of religious identity across a wider range of religious groups. For example, Jewish, Muslim and Buddhist respondents would have been asked if these behaviors are essential to what being Jewish, Muslim and Buddhist means to them. Because some respondents completed the survey by mail in a paper-and-pencil format, however, it was not feasible to program the questionnaire with language specific to more than a few religious groups. ↩
- Readers should note that surveys may overstate the extent to which respondents engage in volunteering, since people who participate in activities such as volunteering also are more likely to participate in surveys. For more details, see “ The challenges of polling when fewer people are available to be polled .” ↩
- Estimates of the highly religious share of the population come from the 2014 U.S. Religious Landscape Study national telephone survey. Among respondents in the supplemental survey, 28% are highly religious by the definition employed here, and 72% are not. ↩
- The question asking respondents how important religion is in their lives was asked in a previous wave of the American Trends Panel series of surveys; as a result, not everyone in the supplemental survey to the Religious Landscape Study was asked this question. For more details about the American Trends Panel, see the Methodology . ↩
- For more on the link between gender and religiosity, see Pew Research Center’s report “ The Gender Gap in Religion Around the World .” ↩
Sign up for our Religion newsletter
Sent weekly on Wednesday
Report Materials
Table of contents, how common is religious fasting in the united states, rising numbers of americans say jews and muslims face a lot of discrimination, how u.s. muslims are experiencing the israel-hamas war, 5 facts about muslims and christians in indonesia, what the data says about abortion in the u.s., most popular.
About Pew Research Center Pew Research Center is a nonpartisan fact tank that informs the public about the issues, attitudes and trends shaping the world. It conducts public opinion polling, demographic research, media content analysis and other empirical social science research. Pew Research Center does not take policy positions. It is a subsidiary of The Pew Charitable Trusts .

- Table of Contents
- Random Entry
- Chronological
- Editorial Information
- About the SEP
- Editorial Board
- How to Cite the SEP
- Special Characters
- Advanced Tools
- Support the SEP
- PDFs for SEP Friends
- Make a Donation
- SEPIA for Libraries
- Entry Contents
Bibliography
Academic tools.
- Friends PDF Preview
- Author and Citation Info
- Back to Top
The Concept of Religion
It is common today to take the concept religion as a taxon for sets of social practices, a category-concept whose paradigmatic examples are the so-called “world” religions of Judaism, Christianity, Islam, Hinduism, Buddhism, Confucianism, and Daoism. [ 1 ] Perhaps equally paradigmatic, though somewhat trickier to label, are forms of life that have not been given a name, either by practitioners or by observers, but are common to a geographical area or a group of people—for example, the religion of China or that of ancient Rome, the religion of the Yoruba or that of the Cherokee. In short, the concept is today used for a genus of social formations that includes several members, a type of which there are many tokens.
The concept religion did not originally refer to a social genus, however. Its earliest references were not to social kinds and, over time, the extension of the concept has evolved in different directions, to the point that it threatens incoherence. As Paul Griffiths notes, listening to the discussions about the concept religion
rapidly suggests the conclusion that hardly anyone has any idea what they are talking about—or, perhaps more accurately, that there are so many different ideas in play about what religion is that conversations in which the term figures significantly make the difficulties in communication at the Tower of Babel seem minor and easily dealt with. These difficulties are apparent, too, in the academic study of religion, and they go far toward an explanation of why the discipline has no coherent or widely shared understanding of its central topic. (2000: 30)
This entry therefore provides a brief history of the how the semantic range of religion has grown and shifted over the years, and then considers two philosophical issues that arise for the contested concept, issues that are likely to arise for other abstract concepts used to sort cultural types (such as “literature”, “democracy”, or “culture” itself). First, the disparate variety of practices now said to fall within this category raises a question of whether one can understand this social taxon in terms of necessary and sufficient properties or whether instead one should instead treat it as a family resemblance concept. Here, the question is whether the concept religion can be said to have an essence. Second, the recognition that the concept has shifted its meanings, that it arose at a particular time and place but was unknown elsewhere, and that it has so often been used to denigrate certain cultures, raises the question whether the concept corresponds to any kind of entity in the world at all or whether, instead, it is simply a rhetorical device that should be retired. This entry therefore considers the rise of critical and skeptical analyses of the concept, including those that argue that the term refers to nothing.
1. A History of the Concept
2.1 monothetic approaches, 2.2 polythetic approaches, 3. reflexivity, reference, and skepticism, other internet resources, related entries.
The concept religion did not originally refer to a social genus or cultural type. It was adapted from the Latin term religio , a term roughly equivalent to “scrupulousness”. Religio also approximates “conscientiousness”, “devotedness”, or “felt obligation”, since religio was an effect of taboos, promises, curses, or transgressions, even when these were unrelated to the gods. In western antiquity, and likely in many or most cultures, there was a recognition that some people worshipped different gods with commitments that were incompatible with each other and that these people constituted social groups that could be rivals. In that context, one sometimes sees the use of nobis religio to mean “our way of worship”. Nevertheless, religio had a range of senses and so Augustine could consider but reject it as the right abstract term for “how one worships God” because the Latin term (like the Latin terms for “cult” and “service”) was used for the observance of duties in both one’s divine and one’s human relationships (Augustine City of God [1968: Book X, Chapter 1, 251–253]). In the Middle Ages, as Christians developed monastic orders in which one took vows to live under a specific rule, they called such an order religio (and religiones for the plural), though the term continued to be used, as it had been in antiquity, in adjective form to describe those who were devout and in noun form to refer to worship (Biller 1985: 358; Nongbri 2013: ch. 2).
The most significant shift in the history of the concept is when people began to use religion as a genus of which Christian and non-Christian groups were species. One sees a clear example of this use in the writings of Edward Herbert (1583–1648). As the post-Reformation Christian community fractured into literal warring camps, Herbert sought to remind the different protesting groups of what they nevertheless had in common. Herbert identified five “articles” or “elements” that he proposed were found in every religion, which he called the Common Notions, namely: the beliefs that
- there is a supreme deity, [ 2 ]
- this deity should be worshipped,
- the most important part of religious practice is the cultivation of virtue,
- one should seek repentance for wrong-doing, and
- one is rewarded or punished in this life and the next.
Ignoring rituals and group membership, this proposal takes an idealized Protestant monotheism as the model of religion as such. Herbert was aware of peoples who worshipped something other than a single supreme deity. He noted that ancient Egyptians, for instance, worshipped multiple gods and people in other cultures worshipped celestial bodies or forces in nature. Herbert might have argued that, lacking a belief in a supreme deity, these practices were not religions at all but belonged instead in some other category such as superstition, heresy, or magic. But Herbert did include them, arguing that they were religions because the multiple gods were actually servants to or even aspects of the one supreme deity, and those who worshiped natural forces worshipped the supreme deity “in His works”.
The concept religion understood as a social genus was increasingly put to use by to European Christians as they sought to categorize the variety of cultures they encountered as their empires moved into the Americas, South Asia, East Asia, Africa, and Oceania. In this context, fed by reports from missionaries and colonial administrators, the extension of the generic concept was expanded. The most influential example is that of anthropologist Edward Burnett Tylor (1832–1917) who had a scholarly interest in pre-Columbian Mexico. Like Herbert, Tylor sought to identify the common denominator of all religions, what Tylor called a “minimal definition” of religion, and he proposed that the key characteristic was “belief in spiritual beings” (1871 [1970: 8]). This generic definition included the forms of life predicated on belief in a supreme deity that Herbert had classified as religion. But it could also now include—without Herbert’s procrustean assumption that these practices were really directed to one supreme being—the practices used by Hindus, ancient Athenians, and the Navajo to connect to the gods they revere, the practices used by Mahayana Buddhists to connect to Bodhisattvas, and the practices used by Malagasy people to connect to the cult of the dead. The use of a unifying concept for such diverse practices is deliberate on Tylor’s part as he sought to undermine assumptions that human cultures poorly understood in Christian Europe—especially those despised ones, “painted black on the missionary maps” (1871 [1970: 4])—were not on the very same spectrum as the religion of his readers. This opposition to dividing European and non-European cultures into separate categories underlies Tylor’s insistence that all human beings are equivalent in terms of their intelligence. He argued that so-called “primitive” peoples generate their religious ideas when they wrestle with the same questions that all people do, such as the biological question of what explains life, and they do so with the same cognitive capacities. They may lack microscopes or telescopes, but Tylor claims that they seek to answer these questions in ways that are “rational”, “consistent”, and “logical”. Tylor repeatedly calls the Americans, Africans, and Asians he studies “thinking men” and “philosophers”. Tylor was conscious that the definition he proposed was part of a shift: though it was still common to describe some people as so primitive that they had no religion, Tylor complains that those who speak this way are guilty of “the use of wide words in narrow senses” because they are only willing to describe as religion practices that resemble their own expectations (1871 [1970: 3–4]).
In the twentieth century, one sees a third and last growth spurt in the extension of the concept. Here the concept religion is enlarged to include not only practices that connect people to one or more spirits, but also practices that connect people to “powers” or “forces” that lack minds, wills, and personalities. One sees this shift in the work of William James, for example, when he writes,
Were one asked to characterize the life of religion in the broadest and most general terms possible, one might say that it consists of the belief that there is an unseen order, and our supreme good lies in harmoniously adjusting ourselves thereto. (1902 [1985: 51]; cf. Proudfoot 2000)
By an “unseen order”, James presumably means a structure that is non-empirical, though he is not clear about why the term would not also include political, economic, or other invisible but human-created orders. The same problem plagues James’s description of “a MORE” operating in the universe that is similar to but outside oneself (1902 [1985: 400], capitalization in the original). The anthropologist Clifford Geertz addresses this issue, also defining religion in terms of an “order” but specifying that he means practices tied to conceptions of “a general order of existence”, that is, as he also says, something whose existence is “fundamental”, “all-pervading”, or “unconditioned” (1973: 98, emphasis added). The practices that are distinctly religious for Geertz are those tied to a culture’s metaphysics or worldview, their conception of “the overall shape of reality” (1973: 104). Like James, then, Geertz would include as religions not only the forms of life based on the theistic and polytheistic (or, more broadly, animist or spiritualist) beliefs that Herbert and Tylor recognized, but also those based on belief in the involuntary, spontaneous, or “natural” operations of the law of karma, the Dao in Daoism, the Principle in Neo-Confucianism, and the Logos in Stoicism. This expansion also includes Theravada Buddhism because dependent co-origination ( pratītyasamutpāda ) is a conception of the general order of existence and it includes Zen Buddhism because Buddha-nature is said to pervade everything. This third expansion is why non-theistic forms of Buddhism, excluded by the Herbert’s and Tylor’s definitions but today widely considered religions, can serve as “a litmus test” for definitions of the concept (Turner 2011: xxiii; cf. Southwold 1978). In sum, then, one can think of the growth of the social genus version of the concept religion as analogous to three concentric circles—from a theistic to a polytheistic and then to a cosmic (or “cosmographic” [Dubuisson 1998]) criterion. Given the near-automatic way that Buddhism is taken as a religion today, the cosmic version now seems to be the dominant one.
Some scholars resist this third expansion of the concept and retain a Tylorean definition, and it is true that there is a marked difference between practices that do and practices that do not involve interacting with person-like beings. In the former, anthropomorphic cases, practitioners can ask for help, make offerings, and pray with an understanding that they are heard. In the latter, non-anthropomorphic cases, practitioners instead typically engage in actions that put themselves “in accord with” the order of things. The anthropologist Robert Marett marks this difference between the last two extensions of the concept religion by distinguishing between “animism” and “animatism” (1909), the philosopher John Hick by distinguishing between religious “personae” and religious “impersonae” (1989: ch. 14–15). This difference raises a philosophical question: on what grounds can one place the practices based on these two kinds of realities in the same category? The many loa spirits, the creator Allah, and the all-pervading Dao are not available to the methods of the natural sciences, and so they are often called “supernatural”. If that term works, then religions in all three concentric circles can be understood as sets of practices predicated on belief in the supernatural. However, “supernatural” suggests a two-level view of reality that separates the empirically available natural world from some other realm metaphorically “above” or “behind” it. Many cultures lack or reject a distinction between natural and supernatural (Saler 1977, 2021). They believe that disembodied persons or powers are not in some otherworldly realm but rather on the top of a certain mountain, in the depths of the forest, or “everywhere”. To avoid the assumption of a two-level view of reality, then, some scholars have replaced supernatural with other terms, such as “superhuman”. Hick uses the term “transcendent”:
the putative reality which transcends everything other than itself but is not transcended by anything other than itself. (1993: 164)
In order to include loa , Allah, and the Dao but to exclude nations and economies, Kevin Schilbrack (2013) proposes the neologism “superempirical” to refer to non-empirical things that are also not the product of any empirical thing. Wouter Hanegraaff (1995), following J. G. Platvoet (1982: 30) uses “meta-empirical”. Whether a common element can be identified that will coherently ground a substantive definition of “religion” is not a settled question.
Despite this murkiness, all three of these versions are “substantive” definitions of religion because they determine membership in the category in terms of the presence of a belief in a distinctive kind of reality. In the twentieth century, however, one sees the emergence of an importantly different approach: a definition that drops the substantive element and instead defines the concept religion in terms of a distinctive role that a form of life can play in one’s life—that is, a “functional” definition. One sees a functional approach in Emile Durkheim (1912), who defines religion as whatever system of practices unite a number of people into a single moral community (whether or not those practices involve belief in any unusual realities). Durkheim’s definition turns on the social function of creating solidarity. One also sees a functional approach in Paul Tillich (1957), who defines religion as whatever dominant concern serves to organize a person’s values (whether or not that concern involve belief in any unusual realities). Tillich’s definition turns on the axiological function of providing orientation for a person’s life.
Substantive and functional approaches can produce non-overlapping extensions for the concept. Famously, a functional approach can hold that even atheistic forms of capitalism, nationalism, and Marxism function as religions. The literature on these secular institutions as functionally religions is massive. As Trevor Ling says,
the bulk of literature supporting the view that Marxism is a religion is so great that it cannot easily be set aside. (1980: 152)
On capitalism as a religion, see, e.g., McCarraher (2019); on nationalism, see, e.g., Omer and Springs (2013: ch. 2). One functionalist might count white supremacy as a religion (Weed 2019; Finley et al. 2020) and another might count anti-racism as a religion (McWhorter 2021). Here, celebrities can reach a religious status and fandom can be one’s religious identity (e.g., Lofton 2011; Lovric 2020). Without a supernatural, transcendent, or superempirical element, these phenomena would not count as religious for Herbert, Tylor, James, or Geertz. Conversely, interactions with supernatural beings may be categorized on a functional approach as something other than religion. For example, the Thai villager who wears an apotropaic amulet and avoids the forest because of a belief that malevolent spirits live there, or the ancient Roman citizen who takes a bird to be sacrificed in a temple before she goes on a journey are for Durkheim examples of magic rather than religion, and for Tillich quotidian rather than ultimate concerns.
It is sometimes assumed that to define religion as a social genus is to treat it as something universal, as something that appears in every human culture. It is true that some scholars have treated religion as pan-human. For example, when a scholar defines religion functionally as the beliefs and practices that generate social cohesion or as the ones that provide orientation in life, then religion names an inevitable feature of the human condition. The universality of religion that one then finds is not a discovery but a product of one’s definition. However, a social genus can be both present in more than one culture without being present in all of them, and so one can define religion , either substantively or functionally, in ways that are not universal. As common as beliefs in disembodied spirits or cosmological orders have been in human history, for instance, there were people in the past and there are people in the present who have no views of an afterlife, supernatural beings, or explicit metaphysics.
2. Two Kinds of Analysis of the Concept
The history of the concept religion above shows how its senses have shifted over time. A concept used for scrupulous devotion was retooled to refer to a particular type of social practice. But the question—what type?—is now convoluted. The cosmic version of the concept is broader than the polytheistic version, which is in turn broader than the theistic version, and the functional definitions shift the sense of the term into a completely different register. What is counted as religion by one definition is often not counted by others. How might this disarray be understood? Does the concept have a structure? This section distinguishes between two kinds of answer to these questions. Most of the attempts to analyze the term have been “monothetic” in that they operate with the classical view that every instance that is accurately described by a concept will share a defining property that puts them in that category. The last several decades, however, have seen the emergence of “polythetic” approaches that abandon the classical view and treat religion , instead, as having a prototype structure. For incisive explanations of the classical theory and the prototype theory of concepts, see Laurence and Margolis (1999).
Monothetic approaches use a single property (or a single set of properties) as the criterion that determines whether a concept applies. The key to a monothetic approach is that it proposes necessary and sufficient conditions for membership in the given class. That is, a monothetic approach claims that there is some characteristic, or set of them, found in every religion and that if a form of life has it, then that form of life is a religion. Most definitions of the concept religion have been of this type. For example, as we saw above, Edward Tylor proposes belief in spiritual beings as his minimal definition of religion, and this is a substantive criterion that distinguishes religion from non-religion in terms of belief in this particular kind of entity. Similarly, Paul Tillich proposes ultimate concern as a functional criterion that distinguishes religion from non-religion in terms of what serves this particular role in one’s life. These are single criterion monothetic definitions.
There are also monothetic definitions that define religion in terms of a single set of criteria. Herbert’s five Common Notions are an early example. More recently, Clifford Geertz (1973: ch. 4) proposes a definition that he breaks down into five elements:
- a system of symbols
- about the nature of things,
- that inculcate dispositions for behavior
- through ritual and cultural performance, [ 3 ]
- so that the conceptions held by the group are taken as real.
One can find each of these five elements separately, of course: not all symbols are religious symbols; historians (but not novelists) typically consider their conceptions factual; and so on. For Geertz, however, any religious form of life will have all five. Aware of functional approaches like that of Tillich, Geertz is explicit that symbols and rituals that lack reference to a metaphysical framework—that is, those without the substantive element he requires as his (2)—would be secular and not religious, no matter how intense or important one’s feelings about them are (1973: 98). Reference to a metaphysical entity or power is what marks the other four elements as religious. Without it, Geertz writes, “the empirical differentia of religious activity or religious experience would not exist” (1973: 98). As a third example, Bruce Lincoln (2006: ch. 1) enumerates four elements that a religion would have, namely:
- “a discourse whose concerns transcend the human, temporal, and contingent, and that claims for itself a similarly transcendent status”,
- practices connected to that discourse,
- people who construct their identity with reference to that discourse and those practices, and
- institutional structures to manage those people.
This definition is monothetic since, for Lincoln, religions always have these four features “at a minimum” (2006: 5). [ 4 ] To be sure, people constantly engage in practices that generate social groups that then have to be maintained and managed by rules or authorities. However, when the practices, communities, and institutions lack the distinctive kind of discourse that claims transcendent status for itself, they would not count for Lincoln as religions.
It is worth noting that when a monothetic definition includes multiple criteria, one does not have to choose between the substantive and functional strategies for defining religion , but can instead include both. If a monothetic definition include both strategies, then, to count as a religion, a form of life would have to refer to a distinctive substantive reality and also play a certain role in the participants’ lives. This double-sided approach avoids the result of purely substantive definitions that might count as religion a feckless set of beliefs (for instance, “something must have created the world”) unconnected from the believers’ desires and behavior, while also avoiding the result of purely functional definitions that might count as religion some universal aspect of human existence (for instance, creating collective effervescence or ranking of one’s values). William James’s definition of religion (“the belief that there is an unseen order, and our supreme good lies in harmoniously adjusting ourselves thereto”) is double-sided in this way, combining a belief in the existence of a distinctive referent with the spiritual disciplines with which one seeks to embody that belief. Geertz’s definition of religion also required both substantive and functional aspects, which he labelled “worldview” and “ethos” (1973: ch. 5). To treat religion as “both/and” in this way is to refuse to abstract one aspect of a complex social reality but instead recognizes, as Geertz puts it, both “the dispositional and conceptual aspects of religious life” (1973: 113). [ 5 ]
These “monothetic-set definitions” treat the concept of religion as referring to a multifaceted or multidimensional complex. It may seem avant garde today to see religion described as a “constellation”, “assemblage”, “network”, or “system”, but in fact to treat religion as a complex is not new. Christian theologians traditionally analyzed the anatomy of their way of life as simultaneously fides , fiducia , and fidelitas . Each of these terms might be translated into English as “faith”, but each actually corresponds to a different dimension of a social practice. Fides refers to a cognitive state, one in which a person assents to a certain proposition and takes it as true. It could be translated as “belief” or “intellectual commitment”. Beliefs or intellectual commitments distinctive to participation in the group will be present whether or not a religious form of life has developed any authoritative doctrines. In contrast, fiducia refers to an affective state in which a person is moved by a feeling or experience that is so positive that it bonds the recipient to its source. It could be translated as “trust” or “emotional commitment”. Trust or emotional commitment will be present whether or not a religious form of life teaches that participation in their practices aims at some particular experience of liberation, enlightenment, or salvation. And fidelitas refers to a conative state in which a person commits themselves to a path of action, a path that typically involves emulating certain role models and inculcating the dispositions that the group considers virtuous. It could be translated as “loyalty” or “submission”. Loyalty or submission will be present whether or not a religious form of life is theistic or teaches moral rules. By the time of Martin Luther, Christian catechisms organized these aspects of religious life in terms of the “three C’s”: the creed one believed, the cult or worship one offered, and the code one followed. When Tillich (1957: ch. 2) argues that religious faith is distorted when one treats it not as a complex but instead as a function of the intellect alone, emotion alone, or the will alone, he is speaking from within this tradition. These three dimensions of religious practices—symbolically, the head, the heart, and the hand—are not necessarily Christian. In fact, until one adds a delimiting criterion like those discussed above, these dimensions are not even distinctively religious. Creed, cult, and code correspond to any pursuit of what a people considers true, beautiful, and good, respectively, and they will be found in any collective movement or cultural tradition. As Melford Spiro says, any human institution will involve a belief system, a value system, and an action system (Spiro 1966: 98).
Many have complained that arguments about how religion should be defined seem unresolvable. To a great extent, however, this is because these arguments have not simply been about a particular aspect of society but rather have served as proxy in a debate about the structure of human subjectivity. There is deep agreement among the rival positions insofar as they presuppose the cognitive-affective-conative model of being human. However, what we might call a “Cartesian” cohort argues that cognition is the root of religious emotions and actions. This cohort includes the “intellectualists” whose influence stretches from Edward Tylor and James Frazer to E. E. Evans-Pritchard, Robin Horton, Jack Goody, Melford Spiro, Stewart Guthrie, and J. Z. Smith, and it shapes much of the emerging field of cognitive science of religion (e.g., Boyer 2001). [ 6 ] A “Humean” cohort disagrees, arguing that affect is what drives human behavior and that cognition serves merely to justify the values one has already adopted. In theology and religious studies, this feelings-centered approach is identified above all with the work of Friedrich Schleiermacher and Rudolf Otto, and with the tradition called phenomenology of religion, but it has had a place in anthropology of religion since Robert Marett (Tylor’s student), and it is alive and well in the work of moral intuitionists (e.g., Haidt 2012) and affect theory (e.g., Schaefer 2015). A “Kantian” cohort treats beliefs and emotions regarding supernatural realities as relatively unimportant and argues instead that for religion the will is basic. [ 7 ] This approach treats a religion as at root a set of required actions (e.g., Vásquez 2011; C. Smith 2017). These different approaches disagree about the essence of religion, but all three camps operate within a shared account of the human. Thus, when William James describes religion as
the feelings, acts, and experiences of individual [people] in their solitude, so far as they apprehend themselves to stand in relation to whatever they may consider the divine. (1902 [1985: 34])
he is foregrounding an affective view and playing down (though not denying) the cognitive. When James’s Harvard colleague Alfred North Whitehead corrects him, saying that “[r]eligion is what a person does with their solitariness” (1926: 3, emphasis added), Whitehead stresses the conative, though Whitehead also insists that feelings always play a role. These are primarily disagreements of emphasis that do not trouble this model of human subjectivity. There have been some attempts to leave this three-part framework. For example, some in the Humean camp have suggested that religion is essentially a particular feeling with zero cognition. But that romantic suggestion collapses under the inability to articulate how an affective state can be noncognitive but still identifiable as a particular feeling (Proudfoot 1985).
Although the three-sided model of the true, the beautiful, and the good is a classic account of what any social group explicitly and implicitly teaches, one aspect is still missing. To recognize the always-presupposed material reality of the people who constitute the social group, even when this reality has not been conceptualized by the group’s members, one should also include the contributions of their bodies, habits, physical culture, and social structures. To include this dimension mnemonically, one can add a “fourth C”, for community. Catherine Albanese (1981) may have been the first to propose the idea of adding this materialist dimension. Ninian Smart’s famous anatomy of religion (1996) has seven dimensions, not four, but the two models are actually very similar. Smart calls the affective dimension the “experiential and emotional”, and then divides the cognitive dimension into two (“doctrinal and philosophical” and “narrative and mythological”), the conative into two (“ethical and legal” and “ritual”), and the communal into two (“social and institutional” and “material”). In an attempt to dislodge the focus on human subjectivity found in the three Cs, some have argued that the material dimension is the source of the others. They argue, in other words, that the cognitive, affective, and conative aspects of the members of a social group are not the causes but rather the effects of the group’s structured practices (e.g., Asad 1993: ch. 1–4; Lopez 1998). Some argue that to understand religion in terms of beliefs, or even in terms of any subjective states, reflects a Protestant bias and that scholars of religion should therefore shift attention from hidden mental states to the visible institutional structures that produce them. Although the structure/agency debate is still live in the social sciences, it is unlikely that one can give a coherent account of religion in terms of institutions or disciplinary practices without reintroducing mental states such as judgements, decisions, and dispositions (Schilbrack 2021).
Whether a monothetic approach focuses on one essential property or a set, and whether that essence is the substance or the function of the religion, those using this approach ask a Yes/No question regarding a single criterion. This approach therefore typically produces relatively clear lines between what is and is not religion. Given Tylor’s monothetic definition, for instance, a form of life must include belief in spiritual beings to be a religion; a form of life lacking this property would not be a religion, even if it included belief in a general order of existence that participants took as their ultimate concern, and even if that form of life included rituals, ethics, and scriptures. In a famous discussion, Melford Spiro (1966) works with a Tylorean definition and argues exactly this: lacking a belief in superhuman beings, Theravada Buddhism, for instance, is something other than a religion. [ 8 ] For Spiro, there is nothing pejorative about this classification.
Having combatted the notion that “we” have religion (which is “good”) and “they” have superstition (which is “bad”), why should we be dismayed if it be discovered that that society x does not have religion as we have defined the term? (1966: 88)
That a concept always corresponds to something possessing a defining property is a very old idea. This assumption undergirds Plato’s Euthyphro and other dialogues in which Socrates pushes his interlocutors to make that hidden, defining property explicit, and this pursuit has provided a model for much not only of philosophy, but of the theorizing in all fields. The traditional assumption is that every entity has some essence that makes it the thing it is, and every instance that is accurately described by a concept of that entity will have that essence. The recent argument that there is an alternative structure—that a concept need not have necessary and sufficient criteria for its application—has been called a “conceptual revolution” (Needham 1975: 351), “one of the greatest and most valuable discoveries that has been made of late years in the republic of letters” (Bambrough 1960–1: 207).
In discussions of the concept religion , this anti-essentialist approach is usually traced to Ludwig Wittgenstein (1953, posthumous). Wittgenstein argues that, in some cases, when one considers the variety of instances described with a given concept, one sees that among them there are multiple features that “crop up and disappear”, the result being “a complicated network of similarities overlapping and criss-crossing” (Wittgenstein 1953, §68). The instances falling under some concepts lack a single defining property but instead have a family resemblance to each other in that each one resembles some of the others in different ways. All polythetic approaches reject the monothetic idea that a concept requires necessary and sufficient criteria. But unappreciated is the fact that polythetic approaches come in different kinds, operating with different logics. Here are three.
The most basic kind of polythetic approach holds that membership in a given class is not determined by the presence of a single crucial characteristic. Instead, the concept maps a cluster of characteristics and, to count as a member of that class, a particular case has to have a certain number of them, no particular one of which is required. To illustrate, imagine that there are five characteristics typical of religions (call this the “properties set”) and that, to be a religion, a form of life has to have a minimum of three of them (call this the “threshold number”). Because this illustration limits the number of characteristics in the properties set, I will call this first kind a “bounded” polythetic approach. For example, the five religion-making characteristics could be these:
- belief in superempirical beings or powers,
- ethical norms,
- worship rituals,
- participation believed to bestow benefits on participants, and
- those who participate in this form of life see themselves as a distinct community.
Understanding the concept religion in this polythetic way produces a graded hierarchy of instances. [ 9 ] A form of life that has all five of these characteristics would be a prototypical example of a religion. Historically speaking, prototypical examples of the concept are likely to be instances to which the concept was first applied. Psychologically speaking, they are also likely to be the example that comes to mind first to those who use the concept. For instance, robins and finches are prototypical examples of a bird, and when one is prompted to name a bird, people are more likely to name a robin or a finch than an ostrich or a penguin. A form of life that has only four of these characteristics would nevertheless still be a clear example of a religion. [ 10 ] If a form of life has only three, then it would be a borderline example. A form of life that has only two of these characteristics would not be included in the category, though such cases might be considered “quasi-religions” and they might be the most interesting social forms to compare to religions (J. E. Smith 1994). A form of life that only had one of the five characteristics would be unremarkable. The forms of life that had three, four, or five of these characteristics would not be an unrelated set but rather a “family” with multiple shared features, but no one characteristic (not even belief in superempirical beings or powers) possessed by all of them. On this polythetic approach, the concept religion has no essence, and a member of this family that only lacked one of the five characteristics— no matter which one —would still clearly be a religion. [ 11 ] As Benson Saler (1993) points out, one can use this non-essentialist approach not only for the concept religion but also for the elements within a religion (sacrifice, scripture, and so on) and to individual religions (Christianity, Hinduism, and so on).
Some have claimed that, lacking an essence, polythetic approaches to religion make the concept so vague that it becomes useless (e.g., Fitzgerald 2000: 72–3; Martin 2009: 167). Given the focused example of a “bounded” approach in the previous paragraph and the widespread adoption of polythetic approaches in the biological sciences, this seems clearly false. However, it is true that one must pay attention to the parameters at work in a polythetic approach. Using a properties set with only five elements produces a very focused class, but the properties set is simply a list of similarities among at least two of the members of a class, and since the class of religions might have hundreds of members, one could easily create a properties set that is much bigger. Not long after Wittgenstein’s death, a “bounded” polythetic approach was applied to the concept religion by William Alston who identified nine religion-making characteristics. [ 12 ] Southwold (1978) has twelve; Rem Edwards (1972) has fourteen and leaves room for more. But there is no reason why one might not work with a properties set for religion with dozens or even hundreds of shared properties. Half a century ago, Rodney Needham (1975: 361) mentions a computer program that sorted 1500 different bacterial strains according to 200 different properties. As J. Z. Smith (1982: ch. 1) argues, treating the concept religion in this way can lead to surprising discoveries of patterns within the class and the co-appearance of properties that can lead to explanatory theories. The second key parameter for a polythetic approach is the threshold number. Alston does not stipulate the number of characteristics a member of the class has to have, saying simply, “When enough of these characteristics are present to a sufficient degree, we have a religion” (1967: 142). Needham (1975) discusses the sensible idea that each member has a majority of the properties, but this is not a requirement of polythetic approaches. The critics are right that as one increases the size of the properties set and decreases the threshold number, the resulting category becomes more and more diffuse. This can produce a class that is so sprawling that it is difficult to use for empirical study.
Scholars of religion who have used a polythetic approach have typically worked with a “bounded” approach (that is, with a properties set that is fixed), but this is not actually the view for which Wittgenstein himself argues. Wittgenstein’s goal is to draw attention to the fact that the actual use of concepts is typically not bound: “the extension of the concept is not closed by a frontier” (Wittgenstein 1953, §67). We can call this an “open” polythetic approach. To grasp the open approach, consider a group of people who have a concept they apply to a certain range of instances. In time, a member of the group encounters something new that resembles the other instances enough in her eyes that she applies the concept to it. When the linguistic community adopts this novel application, the extension of the concept grows. If their use of the concept is “open”, however, then, as the group adds a new member to the category named by a concept, properties of that new member that had not been part of the earlier uses can be added to the properties set and thereby increase the range of legitimate applications of the concept in the future. We might say that a bounded polythetic approach produces concepts that are fuzzy, and an open polythetic approach produces concepts that are fuzzy and evolving . Timothy Williamson calls this “the dynamic quality of family resemblance concepts” (1994: 86). One could symbolize the shift of properties over time this way:
Wittgenstein famously illustrated this open polythetic approach with the concept game , and he also applied it to the concepts of language and number (Wittgenstein 1953, §67). If we substitute our concept as Wittgenstein’s example, however, his treatment fits religion just as well:
Why do we call something a “religion”? Well, perhaps because it has a direct relationship with several things that have hitherto been called religion; and this can be said to give an indirect relationship to other things we call the same name. (Wittgenstein 1953, §67)
Given an open polythetic approach, a concept evolves in the light of the precedents that speakers recognize, although, over time, what people come to label with the concept can become very different from the original use.
In the academic study of religions, discussions of monothetic and polythetic approaches have primarily been in service of developing a definition of the term. [ 13 ] How can alternate definitions of religion be assessed? If one were to offer a lexical definition (that is, a description of what the term means in common usage, as with a dictionary definition), then the definition one offers could be shown to be wrong. In common usage, for example, Buddhism typically is considered a religion and capitalism typically is not. On this point, some believe erroneously that one can correct a definition by pointing to some fact about the referents of the term. One sees this assumption, for example, in those who argue that the western discovery of Buddhism shows that theistic definitions of religion are wrong (e.g., Southwold 1978: 367). One can correct a real or lexical definition in this way, but not a stipulative definition, that is, a description of the meaning that one assigns to the term. When one offers a stipulative definition, that definition cannot be wrong. Stipulative definitions are assessed not by whether they are true or false but rather by their usefulness, and that assessment will be purpose-relative (cf. Berger 1967: 175). De Muckadell (2014) rejects stipulative definitions of religion for this reason, arguing that one cannot critique them and that they force scholars simply to “accept whatever definition is offered”. She gives the example of a problematic stipulative definition of religion as “ice-skating while singing” which, she argues, can only be rejected by using a real definition of religion that shows the ice-skating definition to be false. However, even without knowing the real essence of religion, one can critique a stipulative definition, either for being less adequate or appropriate for a particular purpose (such as studying forms of life across cultures) or, as with the ice-skating example, for being so far from a lexical definition that it is adequate or appropriate for almost no purpose.
Polythetic definitions are increasingly popular today as people seek to avoid the claim that an evolving social category has an ahistorical essence. [ 14 ] However, the difference between these two approaches is not that monothetic definitions fasten on a single property whereas polythetic definitions recognize more. Monothetic definitions can be multifactorial, as we have seen, and they can recognize just as many properties that are “common” or even “typical” of religions, without being essential. The difference is also not that the monothetic identification of the essence of religion reflects an ethnocentrism that polythetic approaches avoid. The polythetic identification of a prototypical religion is equally ethnocentric. The difference between them, rather, is that a monothetic definition sorts instances with a Yes/No mechanism and is therefore digital, and a polythetic definition produces gradations and is therefore analog. It follows that a monothetic definition treats a set of instances that all possess the one defining property as equally religion, whereas a polythetic definition produces a gray area for instances that are more prototypical or less so. This makes a monothetic definition superior for cases (for example, legal cases) in which one seeks a Yes/No answer. Even if an open polythetic approach accurately describes how a concept operates, therefore, one might, for purposes of focus or clarity, prefer to work with a closed polythetic account that limits the properties set, or even with a monothetic approach that limits the properties set to one. That is, one might judge that it is valuable to treat the concept religion as structurally fuzzy or temporally fluid, but nevertheless place boundaries on the forms of life one will compare.
This strategy gives rise to a third kind of polythetic approach, one that stipulates that one property (or one set of properties) is required. Call this an “anchored” polythetic definition. Consistently treating concepts as tools, Wittgenstein suggests this “anchored” idea when he writes that when we look at the history of a concept,
what we see is something constantly fluctuating … [but we might nevertheless] set over against this fluctuation something more fixed, just as one paints a stationary picture of the constantly altering face of the landscape. (1974: 77)
Given a stipulated “anchor”, a concept will then possess a necessary property, and this property reintroduces essentialism. Such a definition nevertheless still reflects a polythetic approach because the presence of the required property is not sufficient to make something a religion. To illustrate this strategy, one might stipulate that the only forms of life one will consider a religion will include
(thereby excluding nationalism and capitalism, for example), but the presence of this property does not suffice to count this form of life as a religion. Consider the properties set introduced above that also includes
If the threshold number is still three, then to be a religion, a form of life would have to have three of these properties, one of which must be (A) . An anchored definition of religion like this would have the benefits of the other polythetic definitions. For example, it would not produce a clear line between religion and nonreligion but would instead articulate gradations between different forms of life (or between versions of one form of life at different times) that are less or more prototypically religious. However, given its anchor, it would produce a more focused range of cases. [ 15 ] In this way, the use of an anchor might both reflect the contemporary cosmological view of the concept religion and also address the criticism that polythetic approaches make a concept too vague.
Over the past forty years or so, there has been a reflexive turn in the social sciences and humanities as scholars have pulled the camera back, so to speak, to examine the constructed nature of the objects previously taken for granted as unproblematically “there”. Reflexive scholars have argued that the fact that what counts as religion shifts according to one’s definition reflects an arbitrariness in the use of the term. They argue that the fact that religion is not a concept found in all cultures but rather a tool invented at a certain time and place, by certain people for their own purposes, and then imposed on others, reveals its political character. The perception that religion is a politically motivated conceptual invention has therefore led some to skepticism about whether the concept picks out something real in the world. As with instrumentalism in philosophy of science, then, reflection on religion has raised doubts about the ontological status of the referent of one’s technical term.
A watershed text for the reflexive turn regarding the concept religion is Jonathan Z. Smith’s Imagining Religion (1982). Smith engages simultaneously in comparing religions and in analyzing the scholarly practice of comparison. A central theme of his essays is that the concept religion (and subcategories such as world religions , Abrahamic faiths , or nonliterate traditions ) are not scientific terms but often reflect the unrecognized biases of those who use these concepts to sort their world into those who are or are not “like us”. [ 16 ] Smith shows that, again and again, the concept religion was shaped by implicit Protestant assumptions, if not explicit Protestant apologetics. In the short preface to that book, Smith famously says,
[ T ] here is no data for religion . Religion is solely the creation of the scholar’s study. It is created for the scholar’s analytic purposes by his imaginative acts of comparison and generalization. Religion has no independent existence apart from the academy. (1982: xi, italics in original)
This dramatic statement has sometimes been taken as Smith’s assertion that the concept religion has no referent. However, in his actual practice of comparing societies, Smith is not a nonrealist about religion . In the first place, he did not think that the constructed nature of religion was something particular to this concept: any judgement that two things were similar or different in some respect presupposed a process of selection, juxtaposition, and categorization by the observer. This is the process of imagination in his book’s title. Second, Smith did not think that the fact that concepts were human products undermined the possibility that they successfully corresponded to entities in the world: an invented concept for social structures can help one discover religion—not “invent” it—even in societies whose members did not know the concept. [ 17 ] His slogan is that one’s (conceptual) map is not the same as and should be tested and rectified by the (non-conceptual) territory (J. Z. Smith 1978). Lastly, Smith did not think that scholars should cease to use religion as a redescriptive or second-order category to study people in history who lacked a comparable concept. On the contrary, he chastised scholars of religion for resting within tradition-specific studies, avoiding cross-cultural comparisons, and not defending the coherence of the generic concept. He writes that scholars of religion should be
prepared to insist, in some explicit and coherent fashion, on the priority of some generic category of religion. (1995: 412; cf. 1998: 281–2)
Smith himself repeatedly uses religion and related technical terms he invented, such as “locative religion”, to illuminate social structures that operate whether or not those so described had named those structures themselves—social structures that exist, as his 1982 subtitle says, from Babylon to Jonestown.
The second most influential book in the reflexive turn in religious studies is Talal Asad’s Genealogies of Religion (1993). Adopting Michel Foucault’s “genealogical” approach, Asad seeks to show that the concept religion operating in contemporary anthropology has been shaped by assumptions that are Christian (insofar as one takes belief as a mental state characteristic of all religions) and modern (insofar as one treats religion as essentially distinct from politics). Asad’s Foucauldian point is that though people may have all kinds of religious beliefs, experiences, moods, or motivations, the mechanism that inculcates them will be the disciplining techniques of some authorizing power and for this reason one cannot treat religion as simply inner states. Like Smith, then, Asad asks scholars to shift their attention to the concept religion and to recognize that assumptions baked into the concept have distorted our grasp of the historical realities. However, also like Smith, Asad does not draw a nonrealist conclusion. [ 18 ] For Asad, religion names a real thing that would operate in the world even had the concept not been invented, namely, “a coherent existential complex” (2001: 217). Asad’s critical aim is not to undermine the idea that religion exists qua social reality but rather to undermine the idea that religion is essentially an interior state independent of social power. He points out that anthropologists like Clifford Geertz adopt a hermeneutic approach to culture that treats actions as if they are texts that say something, and this approach has reinforced the attention given to the meaning of religious symbols, deracinated from their social and historical context. Asad seeks to balance this bias for the subjective with a disciplinary approach that sees human subjectivity as also the product of social structures. Smith and Asad are therefore examples of scholars who critique the concept religion without denying that it can still refer to something in the world, something that exists even before it is named. They are able, so to speak, to look at one’s conceptual window without denying that the window provides a perspective on things outside.
Other critics have gone farther. They build upon the claims that the concept religion is an invented category and that its modern semantic expansion went hand in hand with European colonialism, and they argue that people should cease treating religion as if it corresponds to something that exists outside the sphere of modern European influence. It is common today to hear the slogan that there is no such “thing” as religion. In some cases, the point of rejecting thing-hood is to deny that religion names a category, all the instances of which focus on belief in the same kind of object—that is, the slogan is a rejection of substantive definitions of the concept (e.g., Possamai 2018: ch. 5). In this case, the objection bolsters a functional definition and does not deny that religion corresponds to a functionally distinct kind of form of life. Here, the “no such thing” claim reflects the unsettled question, mentioned above, about the grounds of substantive definitions of “religion”. In other cases, the point of this objection is to deny that religion names a defining characteristic of any kind—that is, the slogan is a rejection of all monothetic definitions of the concept. Perhaps religion (or a religion, like Judaism) should always be referred to in the plural (“Judaisms”) rather than the singular. In this case, the objection bolsters a polythetic definition and does not deny that religion corresponds to a distinct family of forms of life. Here, the “no such thing” claim rejects the assumption that religion has an essence. Despite their negativity, these two objections to the concept are still realist in that they do not deny that the phrase “a religion” can correspond to a form of life operating in the world.
More radically, one sees a denial of this realism, for example, in the critique offered by Wilfred Cantwell Smith (1962). Smith’s thesis is that in many different cultures, people developed a concept for the individuals they considered pious, but they did not develop a concept for a generic social entity, a system of beliefs and practices related to superempirical realities. Before modernity, “there is no such entity [as religion and] … the use of a plural, or with an article, is false” (1962: 326, 194; cf. 144). Smith recommends dropping religion . Not only did those so described lack the concept, but the use of the concept also treats people’s behavior as if the phrase “a religion” names something in addition to that behavior. A methodological individualist, Smith denies that groups have any reality not explained by the individuals who constitute them. What one finds in history, then, is religious people, and so the adjective is useful, but there are no religious entities above and beyond those people, and so the noun reifies an abstraction. Smith contends that
[n]either religion in general nor any one of the religions … is in itself an intelligible entity, a valid object of inquiry or of concern either for the scholar or for the [person] of faith. (1962: 12)
More radical still are the nonrealists who argue that the concepts religion, religions, and religious are all chimerical. Often drawing on post-structuralist arguments, these critics propose that the notion that religions exist is simply an illusion generated by the discourse about them (e.g., McCutcheon 1997; 2018; Fitzgerald 2000; 2007; 2017; Dubuisson 1998; 2019). As Timothy Fitzgerald writes, the concept religion
picks out nothing and it clarifies nothing … the word has no genuine analytical work to do and its continued use merely contributes to the general illusion that it has a genuine referent …. (2000: 17, 14; also 4)
Advocates of this position sometimes call their approach the “Critical Study of Religion” or simply “Critical Religion”, a name that signals their shift away from the pre-critical assumption that religion names entities in the world and to a focus on who invented the concept, the shifting contrast terms it has had, and the uses to which it has been put. [ 19 ] Like the concept of witches or the concept of biological races (e.g., Nye 2020), religion is a fiction (Fitzgerald 2015) or a fabrication (McCutcheon 2018), a concept invented and deployed not to respond to some reality in the world but rather to sort and control people. The classification of something as “religion” is not neutral but
a political activity, and one particularly related to the colonial and imperial situation of a foreign power rendering newly encountered societies digestible and manipulable in terms congenial to its own culture and agenda. (McCutcheon & Arnal 2012: 107)
As part of European colonial projects, the concept has been imposed on people who lacked it and did not consider anything in their society “their religion”. In fact, the concept was for centuries the central tool used to rank societies on a scale from primitive to civilized. To avoid this “conceptual violence” or “epistemic imperialism” (Dubuisson 2019: 137), scholars need to cease naturalizing this term invented in modern Europe and instead historicize it, uncovering the conditions that gave rise to the concept and the interests it serves. The study of religions outside Europe should end. As Timothy Fitzgerald writes, “The category ‘religion’ should be the object, not the tool, of analysis” (2000: 106; also 2017: 125; cf. McCutcheon 2018: 18).
Inspired by the post-structuralist critiques that religion does not apply to cultures that lack the concept, some historians have argued that the term should no longer be used to describe any premodern societies, even in Europe. For example, Brent Nongbri (2013), citing McCutcheon, argues that though it is common to speak of religions existing in the past, human history until the concept emerged in modernity is more accurately understood as a time “before religion”. His aim is “to dispel the commonly held idea that there is such a thing as ‘ancient religion’” (2013: 8). Citing Nongbri, Carlin Barton and Daniel Boyarin (2016) argue that the Latin religio and the Greek thrēskeia do not correspond to the modern understanding of religion and those studying antiquity should cease translating them with that concept. There was no “Roman religious reality”, they say (2016: 19). These historians suggest that if a culture does not have the concept of X , then the reality of X does not exist for that culture. Boyarin calls this position “nominalism”, arguing that religion is
not in any possible way a “real” object, an object that is historical or ontological, before the term comes to be used. (2017: 25)
These critics are right to draw attention to the fact that in the mind of most contemporary people, the concept religion does imply features that did not exist in ancient societies, but the argument that religion did not exist in antiquity involves a sleight of hand. None of these historians argues that people in antiquity did not believe in gods or other spiritual beings, did not seek to interact with them with sacrifices and other rituals, did not create temples or scriptures, and so on. If one uses Tylor’s definition of religion as belief in spiritual beings or James’s definition of religion as adjusting one’s life to an unseen order— or any of the other definitions considered in this entry —then religion did exist in antiquity. What these historians are pointing out is that ancient practices related to the gods permeated their cultures . As Nongbri puts it,
To be sure, ancient people had words to describe proper reverence of the gods, but … [t]he very idea of “being religious” requires a companion notion of what it would mean to be “not religious” and this dichotomy was not part of the ancient world; (2013: 4)
there was no “discrete sphere of religion existing prior to the modern period” (2019: 1, typo corrected). And Barton and Boyarin:
The point is not … that there weren’t practices with respect to “gods” (of whatever sort) but that these practices were not divided off into separate spheres …. (2016: 4)
Steve Mason also argues that religion did not exist in antiquity since religion is “a voluntary sphere of activity, separate in principle” from politics, work, entertainment, and military service (2019: 29). In short, what people later came to conceptualize as religion was in antiquity not a freestanding entity. The nominalist argument, in other words, adds to the definition of the concept religion a distinctively modern feature (usually some version of “the separation of church and state”), and then argues that the referent of this now-circumscribed concept did not exist in antiquity. Their argument is not that religion did not exist outside modernity, but that modern religion did not exist outside modernity.
These post-structuralist and nominalist arguments that deny that religion is “out there” have a realist alternative. According to this alternative, there is a world independent of human conceptualization, and something can be real and it can even affect one’s life, whether or not any human beings have identified it. This is true of things whose existence does not depend on collective agreement, like biochemical signaling cascades or radioactive beta particles, and it is equally true of things whose existence does depend on collective agreement, like kinship structures, linguistic rules, and religious commitments. A realist about social structures holds that a person can be in a bilateral kinship system, can speak a Uralic language, and can be a member of a religion—even if they lack these concepts.
This realist claim that social structures have existed without being conceptualized raises the question: if human beings had different ways of practicing religion since prehistoric times, why and when did people “finally” create the taxon? Almost every scholar involved in the reflexive turn says that religion is a modern invention. [ 20 ] The critique of the concept religion then becomes part of their critique of modernity. Given the potent uses of religion —to categorize certain cultures as godless and therefore inferior or, later, to categorize certain cultures as superstitious and therefore backwards—the significance of the critique of religion for postcolonial and decolonial scholarship is undeniable. Nevertheless, it is not plausible that modern Europeans were the first to want a generic concept for different ways of interacting with gods. It is easy to imagine that if the way that a people worship their gods permeates their work, art, and politics, and they do not know of alternative ways, then it would not be likely that they would have created a concept for it. There is little need for a generic concept that abstracts a particular aspect of one’s culture as one option out of many until one is in a sustained pluralistic situation. The actions that today are categorized as religious practices—burial rites, the making of offerings, the imitation of divinized ancestors—may have existed for tens of thousands of years without the practitioners experiencing that diversity or caring to name it. Nevertheless, it is likely that a desire to compare the rules by which different people live in relation to their gods would have emerged in many parts of the world long before modernity. One would expect to find people developing such social abstractions as cities and then empires emerged and their cultures came into contact with each other. From this realist perspective, it is no surprise that, according to the detailed and example-filled argument of Barton and Boyarin (2016), the first use of religion as a generic social category, distinct from the concept of politics , for the ways that people interact with gods is not a product of the Renaissance, the Reformation, or modern colonialism at all, but can be found in the writings of Josephus (37–c. 100 CE) and Tertullian (c. 155–c. 220 CE). [ 21 ] From the realist perspective, it is no surprise to see the development of analogous terms in medieval China, centuries before interaction with Europeans (Campany 2003, 2012, 2018) and in medieval Islam (Abbasi 2020, 2021). The emergence of social kinds does not wait on language, and the development of language for social kinds is not only a Western project. If this is right, then the development of a concept for religion as a social genus is at least two thousand years old, though the social reality so labeled would be much older.
- Abbasi, Rushain, 2020, “Did Premodern Muslims Distinguish the Religious and the Secular? The Dīn-Dunyā Binary in Medieval Islamic Thought”, Journal of Islamic Studies , 31(2): 185–225. doi:10.1093/jis/etz048
- –––, 2021, “Islam and the Invention of Religion: A Study of Medieval Muslim Discourses on Dīn ”, Studia Islamica , 116(1): 1–106.
- Albanese, Catherine, 1981, America: Religions and Religion , Belmont, CA: Wadsworth.
- Alston, William P., 1964, The Philosophy of Language , Englewood Cliffs, NJ: Prentice-Hall.
- –––, 1967, “Religion”, The Encyclopedia of Philosophy , Paul Edwards (ed.), New York: Macmillan.
- Asad, Talal, 1993, Genealogies of Religion: Discipline and Reasons of Power in Christianity and Islam , Baltimore, MD: John Hopkins University Press.
- –––, 2001, “Reading a Modern Classic: W. C. Smith’s The Meaning and End of Religion ”, History of Religions , 40(3): 205–222. doi:10.1086/463633
- Asad, Talal and Craig Martin, 2014, “ Genealogies of Religion , Twenty Years On: An Interview with Talal Asad”, Bulletin for the Study of Religion , 43(1): 12–17. doi:10.1558/bsor.v43i1.12
- Augustine, City of God, Volume III: Books 8–11 , David S. Wiesen (trans.), Cambridge, MA: Harvard University Press, 1968.
- Bambrough, Renford, 1960–1, “Universals and Family Resemblances”, Proceedings of the Aristotelian Society , 61: 207–222. doi:10.1093/aristotelian/61.1.207
- Barton, Carlin A. and Daniel Boyarin, 2016, Imagine No Religion: How Modern Abstractions Hide Ancient Realities , New York: Fordham University Press.
- Berger, Peter L., 1967, The Sacred Canopy: Elements of a Sociological Theory of Religion , New York: Doubleday.
- –––, 1974, “Some Second Thoughts on Substantive versus Functional Definitions of Religion”, Journal for the Scientific Study of Religion , 13(2): 125–133. doi:10.2307/1384374
- Biller, Peter, 1985, “Words and the Medieval Notion of ‘Religion’”, Journal of Ecclesiastical History , 36(3): 351–369. 10.1017/S0022046900041142
- Boyarin, Daniel, 2017, “Nominalist ‘Judaism’ and the Late-Antique Invention of Religion”, in Religion, Theory, Critique: Classic and Contemporary Approaches and Methodologies , Richard King (ed.), New York: Columbia University Press, ch. 2.
- Boyer, Pascal, 2001, Religion Explained: The Evolutionary Origins of Religious Thought , New York: Basic Books.
- Burley, Mikel, 2019, “‘Being Near Enough to Listen’: Wittgenstein and Interreligious Understanding”, in Interpreting Interreligious Relations with Wittgenstein: Philosophy, Theology, and Religious Studies , Gorazd Andrejč and Daniel H. Weiss (eds), Leiden: Brill, 33–53.
- Campany, Robert Ford, 2003, “On the Very Idea of Religions (in the Modern West and Early Medieval China)”, History of Religions , 42(4): 287–319. doi:10.1086/378757
- –––, 2012, “Chinese History and Writing about ‘Religion(s)’: Reflections at a Crossroads”, in Dynamics in the History of Religions between Asia and Europe: Encounters, Notions, and Comparative Perspectives , Marion Steineke and Volkhard Krech (eds), Leiden: Brill, 273–294.
- –––, 2018, “‘Religious’ as a Category: A Comparative Case Study”, Numen , 65(4): 333–376. doi:10.1163/15685276-12341503
- Casadio, Giovanni, 2016, “Historicizing and Translating Religion”, in The Oxford Handbook of the Study of Religion , Michael Stausberg and Steven Engler (eds), Oxford: Oxford University Press.
- De Muckadell, Caroline Schaffalitzky, 2014, “On Essentialism and Real Definitions of Religion”, Journal of the American Academy of Religion , 82(2): 495–520. doi:10.1093/jaarel/lfu015
- Dubuisson, Daniel, 1998 [2003], L’Occident et la religion: mythes, science et idéologie , Bruxelles: Editions Complexe. Translated as The Western Construction of Religion: Myths, Knowledge, and Ideology , William Sayers (trans.), Baltimore: Johns Hopkins University Press, 2003.
- –––, 2019, The Invention of Religions , Martha Cunningham (trans.), Sheffield: Equinox. French original published as L’invention Des Religions: Impérialisme Cognitif et Violence Épistémique , Paris: CNRS éditions, 2020.
- Durkheim, Emile, 1912 [1915], Les formes élémentaires de la vie religieuse, le système totémique en Australie , Paris: F. Alcan. Translated as The Elementary Forms of the Religious Life, a Study in Religious Sociology , Joseph Ward Swain (trans.), London: George Allen & Unwin, 1915.
- Edwards, Rem, 1972, Reason and Religion: An Introduction to the Philosophy of Religion , New York: Harcourt Brace Jovanavich.
- Ferro-Luzzi, Gabriella Eichinger, 1989, “The Polythetic-Prototype Approach to Hinduism”, in Hinduism Reconsidered , Günther-Dietz Sontheimer and Hermann Kulke (eds), New Delhi: Manohar, pp. 294–304.
- Finley, Stephen C., Biko Mandela Gray, and Lori Latrice Martin (eds.), 2020, The Religion of White Rage: Religious Fervor, White Workers and the Myth of Black Racial Progress , Edinburgh: Edinburgh University Press.
- Fitzgerald, Timothy, 2000, The Ideology of Religious Studies , New York: Oxford University Press.
- –––, 2007, Discourse on Civility and Barbarity: A Critical History of Religion and Related Categories , New York: Oxford University Press. doi:10.1093/acprof:oso/9780195300093.001.0001
- –––, 2015, “Critical Religion and Critical Research on Religion: Religion and Politics as Modern Fictions”, Critical Research on Religion , 3(3): 303–319. doi:10.1177/2050303215613123
- –––, 2017, “ The Ideology of Religious Studies Revisited: The Problem with Politics”, in Method and Theory in the Study of Religion: Working Papers from Hannover , Steffen Führding (ed.), Leiden: Brill, 124–152.
- Geertz, Armin W., 2016, “Conceptions of Religion in the Cognitive Science of Religion”, in Contemporary Views on Comparative Religion , Peter Antes, Armin W. Geertz, and Mikael Rothstein (eds), Sheffield: Equinox, 127–139.
- Geertz, Clifford, 1973, The Interpretation of Cultures , New York: Basic Books.
- Griffiths, Paul J., 2000, “The Very Idea of Religion”, First Things , 103(May): 30–35. [ Griffiths 2000 available online ]
- Haidt, Jonathan, 2012, The Righteous Mind: Why Good People are Divided by Politics and Religion , New York: Vintage.
- Hanegraaff, Wouter J., 1995, “Empirical Method in the Study of Esotericism”, Method and Theory in the Study of Religion , 7(2): 99–129.
- Harrison, Peter, 1990, ‘Religion’ and the Religions in the English Enlightenment , Cambridge: Cambridge University Press. doi:10.1017/CBO9780511627972
- Hick, John, 1989, An Interpretation of Religion: Human Responses to the Transcendent , New Haven, CT: Yale University Press.
- –––, 1993, Disputed Questions in Theology and the Philosophy of Religion , New Haven, CT: Yale University Press.
- James, William, 1902 [1985], The Varieties of Religious Experience , London: Longmans, Green, and Co.; reprinted, Cambridge, MA: Harvard University Press, 1985.
- –––, 1912 [1979], The Will to Believe , London: Longmans, Green, and Co.; reprinted, Cambridge, MA: Harvard University Press, 1979.
- Kant, Immanuel, 1793 [1934], Die Religion innerhalb der Grenzen der bloßen Vernunft , Königsberg. Translated as Religion within the Limits of Reason Alone , Theodore M. Greene and Hoyt H. Hudson (trans.), La Salle, IL: The Open Court, 1934.
- Laurence, Stephen and Eric Margolis, 1999, “Concepts and Cognitive Science”, in Concepts: Core Readings , Eric Margolis and Stephen Laurence (eds), Cambridge: MIT Press, 1–81.
- Lehrich, Christopher I., 2021, Jonathan Z. Smith on Religion , London: Routledge.
- Lincoln, Bruce, 2006, Holy Terrors: Thinking about Religion after September 11 . Second edition. Chicago: The University of Chicago Press.
- Ling, Trevor, 1980, Karl Marx and Religion: In Europe and India , London: Palgrave Macmillan.
- Lofton, Kathryn, 2011, Oprah: The Gospel of an Icon , Berkeley, CA: University of California Press.
- –––, 2012, “Religious History as Religious Studies”, Religion , 42(3): 383–394. doi:10.1080/0048721X.2012.681878
- Lopez, Donald S., Jr., 1998, “Belief”, in Critical Terms for Religious Studies , Mark C. Taylor (ed), Chicago, IL: University of Chicago Press.
- Lovric, Bruno, 2020, “Pokémon Fandom as a Religion: Construction of Identity and Cultural Consumption in Hong Kong”, in Handbook of Research on the Impact of Fandom in Society and Consumerism , Cheng Lu Wang (ed.), Hershey, PA: IGI Global, 460–479.
- Luther, Martin, 1526 [1973], Der Prophet Jonah , Nuremberg. Translated in Lectures on the Minor Prophets, Volume II , Hilton Oswald (ed.), (Luther’s Works, 19), Saint Louis, MO: Concordia.
- Marett, Robert Ranulph, 1909, The Threshold of Religion , London: Methuen and Co.
- Martin, Craig, 2009, “Delimiting Religion”, Method and Theory in the Study of Religion , 21(2): 157–176. doi:10.1163/157006809X431015
- Mason, Steve, 2019, “Our Language and Theirs: ‘Religious’ Categories and Identities”, in Roubekas 2019: 11–31.
- Masuzawa, Tomoko, 2005, The Invention of World Religions: Or, How European Universalism was Preserved in the Language of Pluralism , Chicago: University of Chicago Press.
- McCarraher, Eugene, 2019, The Enchantments of Mammon: How Capitalism Became the Religion of Modernity , Cambridge, MA: Harvard University Press.
- McCutcheon, Russell T., 1997, Manufacturing Religion: The Discourse on Sui Generis Religion and the Politics of Nostalgia , New York: Oxford University Press.
- –––, 2018, Fabricating Religion: Fanfare for the Common e.g. , Berlin: de Gruyter. doi:10.1515/9783110560831
- McCutcheon, Russell, and Arnal, William, 2012, The Sacred is the Profane: The Political Nature of “Religion” , New York: Oxford University Press. doi:10.1093/acprof:oso/9780199757114.001.0001
- McWhorter, John, 2021, Woke Racism: How a New Religion has Betrayed Black America , New York: Portfolio/Penguin.
- Needham, Rodney, 1975, “Polythetic Classification: Convergence and Consequences”, Man , New Series 10(3): 349–369. doi:10.2307/2799807
- Nongbri, Brent, 2013, Before Religion: A History of a Modern Concept , New Haven, CT: Yale University Press.
- –––, 2019, “Introduction: The Present and Future of Ancient Religion”, in Roubekas 2019: 1–8.
- Omer, Atalia and Jason A. Springs, 2013, Religious Nationalism: A Reference Handbook , Santa Barbara, CA: ABC-CLIO.
- Platvoet, J. G., 1982, Comparing Religions: A Limitative Approach , The Hague: Mouton.
- Possamai, Adam, 2018, The i-zation of Society, Religion, and Neoliberal Post-Secularization , Singapore: Palgrave Macmillan. doi:10.1007/978-981-10-5942-1
- Proudfoot, Wayne, 1985, Religious Experience , Berkeley, CA: University of California Press.
- –––, 2000, “William James on an Unseen Order”, Harvard Theological Review , 93(1): 51–66. doi:10.1017/S0017816000016667
- Riesebrodt, Martin, 2007 [2010], Cultus und Heilsversprechen: eine Theorie der Religionen , München : Verlag C.H. Beck. Translated as The Promise of Salvation: A Theory of Religion , Steven Rendall (trans.), Chicago: The University of Chicago Press.
- Roubekas, Nickolas P. (ed.), 2019, Theorizing “Religion” in Antiquity , (Studies in Ancient Religion and Culture), Bristol, UK: Equinox Publishing.
- Saler, Benson, 1977, “Supernatural as a Western Category”, Ethos , 5(1): 31–53. doi:10.1525/eth.1977.5.1.02a00040
- –––, 1993, Conceptualizing Religion: Immanent Anthropologists, Transcendent Natives, and Unbounded Categories , Leiden: E. J. Brill.
- –––, 1999, “Family Resemblance and the Definition of Religion”, Historical Reflections / Réflexions Historiques , 25(3): 391–404.
- –––, 2021, The Construction of the Supernatural in Euro-American Cultures: Something Nice about Vampires , London: Bloomsbury.
- Schaefer, Donovan O., 2015, Religious Affects: Animals, Evolution, and Power , Durham, NC: Duke University Press.
- Schellenberg, J. L., 2005, Prolegomena to a Philosophy of Religion , Ithaca, NY: Cornell University Press.
- Schilbrack, Kevin, 2013, “What Isn’t Religion?”, Journal of Religion , 93(3): 291–318. doi:10.1086/670276
- –––, 2018, “Mathematics and the Definitions of Religion”, International Journal for Philosophy of Religion , 83(2): 145–160. doi:10.1007/s11153-017-9621-6
- –––, 2021, “Religious Practices and the Formation of Subjects”, in The Future of the Philosophy of Religion , M. David Eckel, C. Allen Speight, and Troy DuJardin (eds), (Boston Studies in Philosophy, Religion and Public Life 8), Cham: Springer International Publishing, 43–60. doi:10.1007/978-3-030-44606-2_4
- Smart, Ninian, 1996, Dimensions of the Sacred: An Anatomy of the World’s Beliefs , Berkeley, CA: University of California Press.
- Smith, Christian, 2017, Religion: What it is, How it Works, and Why it Matters , Princeton, NJ: Princeton University Press.
- Smith, John E., 1994, Quasi-religions: Humanism, Marxism, and Nationalism , New York: St. Martin’s Press.
- Smith, Jonathan Z., 1978, Map is Not Territory: Studies in the History of Religions , Leiden: Brill.
- –––, 1982, Imagining Religion: From Babylon to Jonestown , Chicago, IL: University of Chicago Press.
- –––, 1995, “Afterword: Religious Studies: Whither (Wither) and Why?”, Method and Theory in the Study of Religion , 7(4): 407–414. doi:10.1163/157006895X00171
- –––, 1998, “Religion, Religions, Religious”, Critical Terms for Religious Studies , Mark C. Taylor (ed.), Chicago, IL: University of Chicago Press.
- Smith, Wilfred Cantwell, 1962, The Meaning and End of Religion , New York: Macmillan.
- Southwold, Martin, 1978, “Buddhism and the Definition of Religion”, Man , New Series 13(3): 362–379. doi:10.2307/2801935
- Spiro, Melford, 1966, “Religion: Problems of Definition and Explanation”, in Anthropological Approaches to the Study of Religion , Michael Banton (ed.), London: Tavistock, 85–126.
- Taves, Ann, 2009, Religious Experience Reconsidered: A Building-Block Approach to the Study of Religion and other Special Things. , Princeton, NJ: Princeton University Press.
- Tillich, Paul, 1957, Dynamics of Faith , New York: Harper and Row.
- –––, 1963, Christianity and the Encounter of the World Religions , New York: Columbia University Press.
- Turner, Bryan S., 2011, Religion and Modern Society: Citizenship, Secularization and the State , Cambridge: Cambridge University Press. doi:10.1017/CBO9780511975660
- Tylor, Edward Burnett, 1871 [1970], Primitive Culture , two vols., London: John Murray, 1871; vol. 2 reprinted as Religion in Primitive Culture , Gloucester: Peter Smith, 1970.
- Vásquez, Manuel A., 2011, More than Belief: A Materialist Theory of Religion , Oxford: Oxford University Press.
- Weed, Eric, 2019, The Religion of White Supremacy in the United States , Lanham, MD: Lexington.
- Whitehead, Alfred North, 1926, Religion in the Making , Cambridge: Cambridge University Press.
- Williamson, Timothy, 1994, Vagueness , London: Routledge.
- Wittgenstein, Ludwig, 1953 [2009], Philosophical Investigations , G. E. M. Armstrong (trans.), Oxford: Basil Blackwell; reprinted: 4 th edition, Malden: Blackwell, 2009.
- –––, 1974, Philosophical Grammar , Anthony Kenny (trans.), Oxford: Blackwell.
How to cite this entry . Preview the PDF version of this entry at the Friends of the SEP Society . Look up topics and thinkers related to this entry at the Internet Philosophy Ontology Project (InPhO). Enhanced bibliography for this entry at PhilPapers , with links to its database.
- Nye, Malory, 2020, “ Religion is Not a Thing ”, Religion Bites , 31 January 2020.
- The Critical Religion Association
- The Religious Studies Project
- Centre for Critical Realism
definitions | religion: philosophy of | skepticism | Wittgenstein, Ludwig
Copyright © 2022 by Kevin Schilbrack < schilbrackke @ appstate . edu >
- Accessibility
Support SEP
Mirror sites.
View this site from another server:
- Info about mirror sites
The Stanford Encyclopedia of Philosophy is copyright © 2023 by The Metaphysics Research Lab , Department of Philosophy, Stanford University
Library of Congress Catalog Data: ISSN 1095-5054
- Skip to primary navigation
- Skip to main content
- Skip to primary sidebar
Student Essays
Essays-Paragraphs-Speeches
Essay on Importance of Religion | Purpose, Role & Importance in Life
Leave a Comment
Religions provides the base, an ideology for living. Throughout the years, the religions have been important part of our lives. The following essay focuses on religion, importance of religions and what role religion has to play in life.
List of Topics
Essay on Religions | Meaning, Purpose & Importance of Religion in Life
It simply means a set of beliefs and rituals that people hold sacred, which in most cases is the belief in some form of higher power or powers. In a sense, it is a very personal belief system. Religion is important because it serves as a moral guide for how people are expected to act in their world. For some, it provides a sense of peace and comfort. For others, it can provide a sense of purpose in life.
Major Religions of World
There are so many religions in the world, it would be hard to cover just five of those religions. Christianity is the largest religion with over 2 billion followers all over the world.
Islam is the second largest religion in the world with around 1.5 billion followers today, which originated from middle-east. Hinduism is the third largest religion in the world with over 900 million followers. It originated from India and Nepal and it has some flexibility in its beliefs. Buddhism is the fourth largest religion in the world, with over 500 million followers around the globe. It originated from middle-east and China.
>>>>>>>> Also Read: Essay on Charity Begins at Home
Judaism is the fifth largest religion in the world with over 14 million followers around the globe. It originated from middle-east and Africa. Jainism is the major religion in India and has around 4 million followers all over the world. It originated from India. Baha’i is the major religion in Iran with 2 million followers around the world. It originated from Israel and Syria. Sikhism is the major religion in India with 23 million followers all over the world. It originated from Middle East.
Founders of Religions:
There is no single founder of the major world religions. Most of them evolved over centuries. However, founders like Gautam Buddha, Jesus Christ and Prophet Muhammad are the major founders of three major world religions Buddhism, Christianity and Islam respectively.
Importance of Religions in Life
- Religion provides a sense of community / belonging to something greater than ourselves. Many people have the need to be part of something bigger, and religion provides that. Belonging to a group of like-minded believers gives people a sense of purpose and fulfillment.
- Religion provides a sense of identity. In the face of ever-changing trends and fads, religion gives people a sense of belonging to something more timeless and constant—a bond that transcends time.
- Religion can unite people in service towards a common good. Whether it is in the form of relief efforts during times of natural disasters, or fighting for social justice, people’s ability to work together on shared challenges is strengthened when there is a common belief system to unite them.
- Religion brings hope, comfort and peace during difficult times. Many people have turned to religion when faced with a terminal illness or a loved one is taken away from them through death. In those moments, it shines as a beacon of hope and provides inspiration.
- It is a source of guidance and provides lessons on how to live. Many religions provide practical advice for individuals on how to lead a moral life. We can all learn from each other, and religion provides a baseline for what is right and wrong.
- It gives a structure / a set of rules for how to live life. Having a religion provides a framework on what is acceptable and unacceptable behavior, as well as how to answer the difficult questions of the universe, such as “What happens after I die?”
- Religion can be a source of comfort for those who are grieving. Many people rely on their faith in times of crisis, when there seems to be no explanation for what is happening around them. Offering emotional support and comfort, religion can provide solace to those who may be confused or uncertain.
Religions Spread Peace & Love
All religions basically preach the message of love, peace and compassion. They provide the best way for humanity to find true happiness and believe that all human beings are equal. We all have been made from one essence and we must learn to live together as a collective whole
Role of Religion in Modern World
Today, many people are abandoning religion because they do not believe in the existence of God. They are thus creating their own path without religious guidance, which can be dangerous. People have become increasingly self-centered, and are unable to look beyond their own needs without some form of spirituality.
Religion still plays a very important part as it affects people’s thinking and concerns as well as defines and ratifies their behavior and morals. It also brings unity amongst the people of a particular faith and guides them to be good human beings as well as to help others in need.
>>>>>>> Read Also: Essay on Beggars
Religion helps make people connect to their inner-self and also look beyond. It is a source of hope for many, particularly in times of crisis. It brings us together to fight for a common cause and motivates us to be compassionate towards others. It is an important part of our life that shouldn’t be ignored or overlooked, for our own good.
Related Posts:
Reader Interactions
Leave a reply cancel reply.
Your email address will not be published. Required fields are marked *
Save my name, email, and website in this browser for the next time I comment.
- Entertainment
- Environment
- Information Science and Technology
- Social Issues
Home Essay Samples
Essay Samples on Religion
Composing your student essay about religion, it’s essential to research your subject first and avoid controversial subjects. The trick is to provide a clear structure that will focus on theological aspects of things. When you strive to compare different religions, do not write in a biased tone and work on your compare-and-contrast essay. The body parts of your religion essay must start with a good topic sentence as you address a particular concept or the roots of some religious notions. It’s always good if you can find reliable sources to support the facts. If you are not sure about some source or an idea that must be explored, you can either talk to an academic advisor or focus on a good religion essay example that we have prepared for you. These will help you get a basic idea of how such essays must be written. See the introduction part in every essay sample provided and don’t forget to stay respectful as you work on the differences and similarities. Check your grading rubric requirements twice. Regarding a good thesis statement, religious essays should only pose assumptions or compose specific claims that are supported with another sentence to avoid misreading or confusion.
Why Is Freedom of Religion Important
Freedom of religion stands as one of the fundamental pillars of a democratic and pluralistic society. It safeguards an individual's right to practice their chosen faith without fear of discrimination or persecution. This essay delves into the resons why freedom of religion is important, exploring...
- Religious Tolerance
Who is God in Your Life: Personal Beliefs and Spiritual Connections
The concept of God holds profound significance across cultures and belief systems, shaping individuals' values, perspectives, and sense of purpose. So who is God in your life? This essay delves into the diverse ways people perceive God in their lives, whether through religious traditions, personal...
- Religious Beliefs
Should Religion Be Taught in Schools
Should religion be taught in schools? This question is a topic that evokes discussions about cultural diversity, freedom of religion, and the role of education in shaping students' worldviews. Advocates argue that including religion in the curriculum can foster understanding, promote tolerance, and provide students...
How Does Religion Affect Your Life
How does religion affect your life? Religion is a deeply personal and influential aspect of human experience, shaping beliefs, values, behaviors, and perspectives. The impact of religion extends beyond mere rituals; it permeates various dimensions of life. This essay explores the intricate ways in which...
How Are Religion and Culture Connected in Various Ways
The intricate relationship between religion and culture is a subject of immense significance, shaping the values, behaviors, and traditions of societies worldwide. While religion and culture are distinct concepts, they are profoundly interconnected, often influencing and informing one another. This essay delves into how religion...
- Culture and Communication
Stressed out with your paper?
Consider using writing assistance:
- 100% unique papers
- 3 hrs deadline option
Buddhism and Hinduism: Exploring Similarities and Differences
Buddhism and Hinduism, two of the world's most ancient and complex religions, share both commonalities and distinctions that have shaped the spiritual and cultural landscapes of Asia. This essay delves into Buddhism and Hinduism and the core similarities and differences between these two belief systems,...
Death is a Passage Beyond Life
Introduction In virtually every culture and religion around the world, death is not regarded as an end, but as a passage to a different form of existence. This belief, deeply rooted in human history and psyche, has shaped rituals, philosophies, and the way we perceive...
Why Should We Respect Our Parents: Exploring Islamic Arguments
What islam says about why should we respect our parents? In this essay I want to emphasize that Allah is telling us to treat our parents kindly and to make effort in pleasing them. He says that our mother most deserves our respect and service,...
- Parent-Child Relationship
Respect Your Parents and Take Care of Your Children: Ephesians 6:1-9
I chose the following passage Ephesians 6:1-9. The main reason that I chose this passage was because the other passages had already been taken. Now after researching this passage I discovered that there was more than meets the eye and I want to learn how...
The Importance of Respect and Obedience to Our Parents in Islam
DedicationI dedicate this research to God Almighty my creator, my strong pillar, my source of inspiration, wisdom, knowledge and understanding. He has been the source of my strength throughout this research and on His wings only have I soared. I also dedicate this work to...
Respect for Life: the Issue of Death Penalty in Catholic Teachings
An essential principle of a human rights is that each and every human being has an innate dignity that must be respected. Respect for one's human dignity is the original human right from which other human being had as a gift from our almighty God....
- Catholic Church
- Death Penalty
What Does Respect Mean to You: Christian Explanation
A few days ago a friend of mine asked 'what does respect mean to you?' Later this question inspired me to write this essay about the meaning of respect from christian believer's point of view. Paradise is something that many people think they can...
- Biblical Worldview
- Christian Worldview
Implementing the Four Noble Truths in Everyday Life
Introduction One of the fundamental doctrines of Buddhism set forth by Buddha himself are the Four Noble Truths. These contain the very essence of the Buddha's pragmatic teachings. The Buddha is known to attain enlightenment only after the realization of these four truths during his...
Euthanasia and the Catholic Church in Australia
An ethical issue is a problem or dilemma that involves a person having to decide whether or not it is morally right or wrong. Euthanasia is a clear example of an ethical issue currently present in Australia. Euthanasia is a process whereby a person who...
- Assisted Suicide
Islamic Traditions and Practices: A Focus on Asian Muslims
Asia is home to one of the largest Muslim populations in the world. Muslim population accounts for approximately 62% of the total population of Asia. Pakistan, India, Malaysia, Indonesia, and Bangladesh are Muslim-majority countries of Asia. As Muslims have different cultures, values, and histories, their...
The Divine Love: Understanding God's Love for Humanity
There is a multitude of attributes of God, what He is and that any human being can also become. Among these countless attributes or characteristics, we have love. A 'simple' characteristic present in some way in the life of all humanity, from the rich to...
- Image of God
Comparison of Islamic Religious Texts: the Quran and Hadith
The Quran is the most important text in the Islamic faith, believed to be the word of God communicated to the prophet Muhammad who spoke to his followers, and what he said was written down in the Quran years after his death. The Hadith is...
- Religious texts
The Virtue and Significance of the Quran: Exploring its Divine Revelation, Recitation, and Impact on the Muslim Community
The Quran is defined as the miraculous word of God, devoted to its recitation, the house of the Prophet Muhammad (PBUH) by revelation by Jibril, peace be upon him, and transmitted to us in frequency. It should be noted that the Quran came down in...
Human Experience of Illness and the Key Role of the Environment
The key goal of the healthcare facility is to offer a environment where the sick will be at ease and to enable their body to regenerate. There are three principles for a healthy environment: seen, unseen, and storied environments. These ideas give us a deeper...
The Trustworthiness of the Bible: Exploration of Its Foundations
The Bible, a collection of sacred texts revered by millions around the world, has endured for centuries as a source of moral guidance, spiritual enlightenment, and historical insight. Its trustworthiness stems from a multifaceted examination of its historical, literary, and spiritual foundations, which collectively affirm...
- Personal Experience
Exploring of the Five Meanings of Science of the Quran
Sciences of the Quran are each science that is intended to serve the Holy Quran and attempt to investigate its privileged insights and uncover its puzzles, for example, the exploration in the Quranic disclosure and Quranic contents, the gathering and grouping of the Quran, the...
Exploring Invaluable Role of Jesus Christ for the World
Jesus Christ is one of the most well known historical figures that could be considered heroic and relatively important to the development of Western Civilization. The existence of Jesus and the eternal legacy he left after he sacrificed himself was one that dramatically influenced the...
- Historical Figures
- Influence of Christianity
- Jesus Christ
Is Jesus a Myth: One of the World’s Most Controversial Figures
It would be hard to find a person in history that has been met with so much controversy than Jesus of Nazareth. According to those who wrote the New Testament, Jesus is God, who was born of a virgin, who lived a sinless life, was...
- World History
Why Jesus Is a Hero: an Example of Love and Forgiveness
Is Jesus a hero or not? The meaning of a hero is someone who shows bravery, courage, determination, justice and more. A hero doesn’t need to save the world for people to say that is what a hero is, like Jesus, he reached out to...
- Influential Person
The Life and Achievemnts of Muhammad - a Founder of Islam
I chose Muhammad because he did a lot from the day he was born till the day he died. One of the many things that Muhammad did was when Muhammad founded Islam and made it the way it is now. Muhammad was born in Mecca,...
Unveiling Jesus as the Heroic Figure of True Faith and Love
A hero is someone who gives themselves, often putting their own life at great risk, for the greater good of others . A hero shows courage and is determined and dedicated to helping others in need by showing selflessness and sacrifice for the good of...
Jesus as the Greatest Hero: Being Gifted With Godlike DNA
A hero is a person who is admired for their courage, outstanding achievements, or noble qualities. Jesus shown these quality’s in different bible readings. Jesus was not only a hero that did miracles to heal people, he was a hero that sacrificed his own life...
Personal Reflections: Three Lessons I Have Learnt From Hosea's Story
David was chosen to be king at a young age when he was only a shepherd, but wasn’t the king until he was 30 years old, David had been working for king Saul and throughout that time he had been taken to court by king...
The Menace of Terrorism Around the World: Emerging Threats and Issues
The menace of terrorism has been increasing over the years though there have been several efforts to counter it. The evils of terrorism have become widespread, and the world has become too familiar to them. There has been a lot of debate on the definition...
- Religious Conflict
- Social Problems
Understanding Islam: Beliefs, Practices, and History
What is Islam? What do they believe in? Who are they? Well continue reading and you will find out a lot about this religion. Islam is an Abrahamic monotheistic religion teaching that there is only one God and that Muhammad is the messenger of God....
- Five Pillars of Islam
The Unique World of Buddhism: Its Origins, Beliefs, and Practices
The World is today is unique, religion being a huge part of that uniqueness. The religions shaped many of the well- known religions today. There are a lot of well-known religions today adapted some of practices of many older religions that today depending on the...
Submission to Allah: The Core Concept of Islam
The concept at the core of Islam is the intention that a Muslim follows the will of Allah as closely as possible in hopes that each moment of each day is to be lived in an attitude of complete submission to Him. Allah’s greatest revelation,...
The Increased Violence in New Terrorism: What Is Going On
The 1990s recalls a series of extremist acts that ushered a new and more violent form of terrorism. Propelled by religious motivations, decentralized organization, and technological advancement, the new terrorism distinguished itself from old terrorism with its inclination to indiscriminate killing and mass casualties. Rapoport’s...
The Sacred Mystery of Plants in Eastern Religion Cultures
Sacred plants are specific plants those are usually devoted to gods and goddess. The human relation with sacred plant stands basically on religion which is considered with Hindu, Buddhist and Jain culture. During the ancient period, the worship of sacred plants is most of the...
Understanding Islam: The Complete Submission to the Will of God
Religion is often a fundamental part of one’s identity. The word religion originates from a Latin word meaning “to tie or bind together.” As new and modern religions continue to develop, religion defines as “an organized system of beliefs and rituals centring on a spiritual...
Difference Between Islam and Christianity: Perspectives on Racism
Islam and Christianity are two of the largest religions in the world, with billions of followers combined. While there are significant difference between islam and christianity in this essay we will also analyse similarities between islam and christianity. For this paper we have interviewed several...
Postulates and Principles of Islamic Moral Economic System
In this paper we will take a short review of main principles and postulates, its subsequent objectives of the Islamic moral economic system. Tawhid or the Unity of God is the fundamental principle of IME. It refers to the human beings being equal before the...
- Economic systems
Muhammad and the Birth of Islam: Unraveling the History and Teachings
Chapter 10 of Islam of “Living Religions” by Mary Fisher talks about how Islam is viewed by society and how Islam came about. Reading this chapter from the point of view of the author who is not Muslim made me feel like she was with...
- History of Islam
The Journey to Nirvana: The Teachings and Beliefs of Buddhism
Buddhism is among the world's biggest religions, with origins in India dating back 2,500 years. Buddhists think that human existence is full of misery, believing the way to obtain happiness, or nirvana, is via meditation, spiritual and physical effort, and moral behavior. Buddhists believe life...
Gautama and the Middle Way: The Birth of Buddhism
Although we think of Buddhism as being created by Buddha, Gautama a young prince, was the creator and he is now referred to as Buddha, also known as the enlightened one. Since Gautama was a prince that meant that his father was a king and...
The Intersection of Religion and Abortion: A Comparative Analysis
Abortion has been a hot topic for several years. People are very opinionated about the case and there's an ethical side to the subject. The abortion debate asks whether it may be morally right to terminate a pregnancy before normal childbirth. Some people believe that...
- Abortion Debate
Buddhism in Asia: A Cultural and Historical Perspective
The story of the life of Gautama Buddha According to the legend the person now commonly known as the Buddha was a prince named Siddhartha Gautama. His father, Suddhodana Gautama, was the ruler of the Shakya clan. Siddhartha’s birth was attended by many unusual events....
- Zen Buddhism
From India to China: The Spread of Buddhism along the Silk Road
Introduction The silk road spread religions, philosophies, education, goods, and people. The people who embarked for a journey on the silk road were monks from India. India, during the iron age, between the fourth and sixth centuries, began urbanization and in this process, the influence...
Exploring Buddhism at a Traditional Mon Buddhist Dharma Session
Introduction Sunday, February 16th at two-thirty, I visited the Mon Buddhist Monastery Community in Akron Ohio. This was a traditional Mon Buddhist Dharma session. I was very pleased by the turnout of the session and was able to grasp a better understanding of the Buddhism...
The Rise and Spread of Islam: History and Impact
Introduction Islam is probably the most youthful religion and has the biggest followers in the world and is predominant in Africa, the Middle East, and Asia (Hopfe and Woodward 330). Islam is a significant religion in the world and has in excess of billion followers...
The Dichotomy of Annihilationism and Non-Annihilationism in Buddhism
Introduction Buddhism can be split into two distinct schools of thought: annihilationism and eternal rebirth. The argument that the state of nirvana is achieved through the blowing out of what fuels one’s self is the one generally accepted by most Buddhists and scholars. The minority...
Islam: The Role of Gender, Storytelling, and Conflict
Introduction: The emergence of the Muslim minority in Western nations has spurred discussion over which Muslim behaviors should be accepted, with many people considering certain customs a rejection. In Western countries, societies based on the Islamic belief system have wrestled with gender roles, the importance...
The Ethical Code of Islam: A Comprehensive Overview
Introduction: In Islam, there is a strict ethical code that must be followed in order to abide by Allah. This code is highlighted in the Koran and is practiced through traditions, actions, clothing, and food consumption. Furthermore, every Muslim is expected to adhere to the...
Religion and Abortion: Understanding the Pro-Life Movement
Introduction Death sentences, guns, religion, and abortion are among the top debated subjects in conversations. These topics are discussed frequently, especially if it’s a hot topic for a political debate. There are supporters and opponents on these subjects due to their strong points of view....
Organ Donation and Brain Death from Buddhist's Perspectives
Modern scientific and technological developments have contributed to mass production. There have arisen many issues which affect human health both physical and mental are related, regarding to ethical criteria in physical medicine. This paper will discuss brain death and organ transplantation from Buddhists perspectives. There...
- Organ Donation
- Organ Transplant
Hinduism and Buddhism as Most Popular Religions in India
Located in northern India that flows from the Himalayan Mountains to the Bay of Bengal lies the Ganges River. Known as a sacred entity, many Hindus bathe in its waters to cleanse past sins and to facilitate Moksha, liberation of reincarnation; thus, many faithful customs,...
Faith and Reason Are Compatible: Suspension of Disbelief
Art is a platform that dares reality. It stretches the limits of reality and tends to over step these boundaries all to serve the purpose of the piece of art. This is where the suspension of disbelief comes in. One must set aside their typical...
The Baptism Experience: Passing God's Love Through Baptism
One simple act creates an endless ripple where people passes it on and pays it forward. This is due to the interconnected nature of human beings – when we are happy, we influence the people around us to have a positive outlook in life. And...
The Idea That Faith and Reason Are Compatible in Religious Texts
There are four fundamental claims of the Catholic intellectual tradition and the one I choose is, the dignity of the human being inviolable and the commitment to justice for the common good is necessary. These four fundamental claims are very important in the catholic religion...
The Baptism Experience in the Life of Children in the Medieval Ages
Of all the misconceptions of the Medieval Ages, some of the most prevalent include the life of a child during this era. During this time it is believed that many children were shown no recognition and they were treated as though they were adults as...
- Middle Ages
Hinduism and Buddhism: The Values and Purposes of Both Religions
Today there are many different religions in the world. In Asia, Buddhism and Hinduism are popular beliefs in general. Hinduism is the religion of Antigua known and very rich in literally hundreds of divinities, rituals and symbolic beliefs. Believes is that was founded around 1500...
Nacirema Culture and Buddhism Religious Practices
Religion is a topic that provokes or brings about different thoughts and ideas between people. We all have our own beliefs and traditions that make each one of our religions stand out. It is what makes us who we are. Myths and rituals are a...
The Freedom Of Religion And Why Is The First Amendment Important
First Amendment “Congress shall make no law respecting an establishment of religion or prohibiting the free exercise or abridging the freedom of speech, or of the press; or the right of the people peaceably to assemble, and to petition the Government for a redress of...
- American Constitution
- First Amendment
Belief In God: Relationships Between Science and Religion
The conflict between science and spirituality (religion) usually refers to an assumed conflict between science and belief in God. For the purpose of this talk “religion” refers to the monotheistic religion which is the belief in the existence of a good, personal and transcendent creator....
- Science Vs. Religion
- Spirituality
Why Do You Believe In God
Well, God can do all of these and even more. Sometimes, situations can make anyone forget or doubt God's abilities irrespective of how strong you have been in faith. Remember, no one is ever ready for hard situations to hit them, it just happens, but...
- Kingdom of God

Peter`s The Great Reforms: A Knot Between Church And State
Christians all over the world have been persecuted for their religious beliefs. Although the situation became better with time, it was still not ideal in the 18th century. Peter the Great, the first emperor of Russia, introduced the Most Holy Synod, and it changed the...
- Russian Empire
The Nature Of Confucianism and Daoism, And The Gender Roles
The story of Cui Ying Ying was composed during the late Tang dynasty and is regarded as famous romantic prose. The story explores cultural dynamics during the Tang period and displays the contrasting views of Chinese philosophy in the era. To truly comprehend the symbolism...
- Confucianism
- Gender Roles
"Paradise Lost" By John Milton: Book Review
In this review, I hope to put forward two different approaches to interpreting Milton’s Paradise Lost. I will be exploring Archie Burnett’s article ‘Sense Variously Drawn Own’ published in 2003 which examines the relation between Lineation, syntax, and meaning in Milton’s Paradise Lost. I will...
- Adam and Eve
- Paradise Lost
"Does Science Threaten Religion?" By Gerber and Macionis: A Review
The article “Controversy and Debate: Does Science Threaten Religion?” has demonstrated the changing relationship between science and religion, from apparent contradictions in the past to recognizing and accepting each other in the present (Gerber & Macionis, 2018, pp. 553). The author has incorporated a structural-functional...
The History Of The Emergence And Spread Of Christianity And Islam
Christianity is one of the most spread religions in the world. It centers its belief in the public life of Jesus Christ. The term Christianity is a derivation of the followers of Christ. Therefore, Jesus is the pioneer of this faith. Christians base their teaching...
- Spread of Christianity
The Second Coming By Yeats: Powerful Warning To Society
In a world full of hostility and loss of faith surrounded by war and technological developments, the modernist era of literature developments, the modernists era of literature arose. The sinking of the Titanic symbolized the falling of the Great Britain empire and newly invented standardized...
- The Second Coming
- William Butler Yeats
Acceptance Concepts Through the Bible Topics
I believe that God creates all of us to be good genuinely and kindhearted. God believes that we are most beautiful & unique the way he created us. So, bullies should stop their intimidating behaviors towards others, they don’t need to be so, they should...
Humble, Mainwairing and Pompous Pride
This is probably something that none of you know about me and that is I am a massive Dads Army fan, I have all the available episodes and movies on DVD. It’s been great to watch the lost episodes on Gold this week, now I...
Apuleius’ Metamorphoses and Picture of Human Nature
This essay will explore Apuleius’ Metamorphoses with special regard to what picture of human nature and society it presents and whether or not the gods offer the prospect of salvation. Dealing with the tale of Lucius whose overly curious nature results in him being turned...
- Human Nature
- Metamorphoses
The Shinto Religion and the Root of Japanese Culture
Shintōism is frequently portrayed in art from all over the world, especially in Japan. The Shintō religion is at the root of Japanese culture and history and therefore has a profound impact on its popular culture today, from manga and anime to film to video...
- Personal Beliefs
Biblical Archaeology: How the Study of God Is Look Like
Archaeology is defined as the scientific study of historic or prehistoric peoples and their cultures by analysis of their artifacts, inscriptions, monuments, and other such remains, especially those that have been excavated. (Dictionary, Archaeology) Archaeology is used throughout history and in many ways. Biblical Archaeology...
- Archaeology
The Development of Islamic Art
Islamic art is created not only for the Muslim faith, but it consists of artworks such as textiles, architecture, paintings and drawings that were produced in the regions that were once ruled by Muslim empires. Artists from various disciplines take part in collaborative projects and...
- Islamic Art
Unforgiveness Steals Away Your Joy, Peace, and Happiness
Forgiveness is one of the topics most Christians don't like to talk about especially if they were truly hurt by someone close to their heart. Sometimes, we feel it is better to carry the burden of hatred rather than forgive those that have wronged us....
- Forgiveness
Role of Cultural and Religious Pluralism
Cultural pluralism is a term used when smaller groups within a larger society maintain their own unique cultural identities. Migration is a key process that makes significant contribution to the growth of urbanism. Often immigrants belonging to particular region, language, religion ,tribe etc tend to...
- Art and Religion
- Religious Pluralism
Political Correctness and Occidental International Law
The uniformity of European political thought canon as asserted by postcolonialists has created a ‘residual sense that the Christian faith is an expression of white Western privilege ’. This deficit in postcolonial theory, to account for Grotius and theorists who argued for the separation of...
- Political Correctness
The Portrayal of the Culture of Death and Afterlife in Art
Throughout history, different cultures dealt with the concept of death and afterlife according to their beliefs, and developed different perspectives about what happens after the body dies. These ideas were often reflected in their art, literature, and their lifestyle as well. Most cultures produce art...
The Tattoo of Cherry Blossom Bracelets in China
The armband tattoos were a popular excitement 10 to 15 years ago. Today, however, it is gradually becoming a hot trend again. These types of tattoos are appealing because they are easy to show and can be quickly hidden in the sleeve. What do bracelet...
- Chinese Culture
- Christianity
Amazon's Upload is All About the Digital Afterlife
Take Black Mirror's dystopian tech analysis, The Good Place's thoughtful investigation of the afterlife, and the workplace pranks of The Office, squeeze them together, and you have Amazon’s Upload. It takes place in a world that could simply be 10 years from now. You can...
Hagia Sophia and Eastern Roman Empire
Hagia Sophia is the great rich remain and an important monument for the Eastern Roman Empire commonly known as the Byzantine Empire. It remain the Centre for Orthodox Church for nearly a thousand years. The current version was built in the year 532. This iconic...
- Ancient Rome
- Byzantine Empire
- Hagia Sophia
Life After Death for the One Whose Heart Is Light
Built in the 27th century BC for the burial of Pharaoh Djoser by his vizier; architect and later known as the God of Medicine, Imhotep. Pyramids were built for religious purposes and the Egyptian civilization were one of the first to believe in an afterlife....
Insurance Regarding the Existence of an Individual’s Afterlife
Under the rational choice model, decisions individuals make are based on perfect information. This implies that people do not undergo any risks or uncertainties when making a choice. However, religious choices of individuals cannot be based on perfect information, for there are no verified sources...
Johann Christoph Blumhardt and Christology
Johann Christoph Blumhardt (1805-1880) was a Lutheran pastor in Württemberg. He was known among the Lutheran Pietists who built the relation between Southwest Germany [then] with the Basel University of Switzerland mission Society. Certain authors consider this relationship as fostering the trans-Atlantic faith healing movement....
- Christology
- Martin Luther King
Finding What Is The Biblical Purpose Of Govenrment
One day a man was walking down the streets of his city, headed to the capitol, and then he saw a car wreck right in front of him. His first instinct is to go help, so he rushes over and sees the scene. Now with...
- Role of Government
The Creation Myth And Human Evolution: The Everlasting Debate
Every generation of people, young and old as well, come to ask questions about the origin of the universe: Where did it come from? When did it start? or How did it come into existence? Scientists, philosophers or religious believers have all tried to explain...
- Creation Myth
- Human Evolution
Considering Religious Beliefs And Freedom Of Expression
Whether you believe in something or not, the idea of religion has probably crossed your mind. Some people see it as a way to make sense of the world around us and some see it as way of life. the idea that a higher power,...
The Foundational Beliefs Of The Biblical Worldview
To build a biblical framework, or foundational beliefs about God, His character, His world, and His plan one must go to Scripture, for these are His words. Here answers are found to life’s questions; why are we here, good and evil, our purpose, and where...
The Truths About Real Life In The Biblical Worldview
Introduction Every person has a worldview that is either biblical or secular (humanistic). A person’s worldview is the lens through which they view the world. It dictates the decisions they make, the way they treat themselves and others, and their ideas of life after death....
The Perception Of The World In The Christian Worldview
A worldview, this is easy to say its self-explanatory, but it’s much more than that. A worldview can be defined as, “a particular philosophy of life or conception of the world” (Google Dictionary). Another idea is, how a Christian worldview is defined. A Christian Worldview...
The Correlation Between Christian Worldview And Criminal Justice System
Abstract This criminal justice research paper will discuss how people in law enforcement have demonstrated and or expressed their integration of Christen Worldviews into the field of criminal justice. It will show how their Christian beliefs are the driving force behind their ethical and moral...
The Age Of The Earth: Creation Vs. Evolution
There are four great questions of life that everyone asks. The questions are; Who am I? Where did I come from? Why am I here? And where am I going when I die? These questions are answered completely different depending on if you are an...
The Impact Of Religion On Defining What Is Value Of Life
What might most people on this earth value? You guessed it right, it’s Life! Life brings a lot of meaning and purpose that is I feel is an ideal answer to the society and lets just face it, what could someone value other than life?...
- Meaning of Life
Exploration Of Buddhism And Hinduism: Similarities And Differences
Nearly, all people chose at least one religion which is suitable for their thoughts and believes. Due to that fact, people of the same religion come together usually. For instance, there are islamic countries in one community which is called Muslim countries or Ummah. Moreover,...
Buddhism And Hinduism: The Similarities And Differences Of Views
There are three ways to achieve moksha which is when a person’s atman (individual soul) is released from the eternal cycle of reincarnation. Reincarnation is a core idea of Hinduism as according to Upanishad (the third and final Vedic scripture) literature the atman would go...
The Similarities And Differences Between Worldviews Of Hinduism And Buddhism
I will start with the greeting of each religion since it gives a good first impression about you if you greet them in their own way. “Namaste” is the common greeting or salutation in Hinduism, it is usually said with body gestures where they bend...
A Biblical Worldview: The Values Of A Devoted Christian
There comes a point in everyone's life that they must start making decisions on their own, it is at this point they choose what lenses they will use to drive their decisions. For Christians that lense is the Bible and the Holy Spirit is the...
Christian Worldview: Faith And Forgiveness As A Basis
Throughout history, different point of views arose and changed the way people looked at the past of the world. One specific viewpoint is the Christian’s worldview. Christians sin just like everyone else and they recognize that, just like how they recognize the faith of God....
The Biblical Worldview On The Human Trafficking
Choices to commit a crime, fight against crime, or generate justice for criminal acts are all motivated by our worldview. Incorporating a Christian worldview into the Criminal Justice approach allows you to view behavior and response through the lens of God's expectations. This perspective creates...
- Human Trafficking
The Christian Worldview: Philosophy And Values
Today's culture has multiple worldviews. Many individuals prefer to select various religions views but mostly keep to one central worldview. A worldview is the gathering of values that form our everyday work and define our overall vision of existence. Looking seriously at my beliefs, my...
The Effect Of Prophet Muhammad On The Quick Spread Of Islam
This paper will deeply investigate the following interesting question on Islam and it’s spread. What effect did the spread of Islam by Prophet Muhammad in Mecca have on the already religious Saudi Arabian society? In order to compose this paper with reliable facts, mostly primary...
Understanding the Power of a Biblical Worldview in Psychology
A biblical worldview is a transformative lens through which we view the world, based on the teachings of the Bible. It impacts our perspectives on various situations, facts, and aspects of life. This worldview has profound implications for psychology, influencing even the smallest details, such...
Best topics on Religion
1. Why Is Freedom of Religion Important
2. Who is God in Your Life: Personal Beliefs and Spiritual Connections
3. Should Religion Be Taught in Schools
4. How Does Religion Affect Your Life
5. How Are Religion and Culture Connected in Various Ways
6. Buddhism and Hinduism: Exploring Similarities and Differences
7. Death is a Passage Beyond Life
8. Why Should We Respect Our Parents: Exploring Islamic Arguments
9. Respect Your Parents and Take Care of Your Children: Ephesians 6:1-9
10. The Importance of Respect and Obedience to Our Parents in Islam
11. Respect for Life: the Issue of Death Penalty in Catholic Teachings
12. What Does Respect Mean to You: Christian Explanation
13. Implementing the Four Noble Truths in Everyday Life
14. Euthanasia and the Catholic Church in Australia
15. Islamic Traditions and Practices: A Focus on Asian Muslims
- Seven Deadly Sins
Need writing help?
You can always rely on us no matter what type of paper you need
*No hidden charges
100% Unique Essays
Absolutely Confidential
Money Back Guarantee
By clicking “Send Essay”, you agree to our Terms of service and Privacy statement. We will occasionally send you account related emails
You can also get a UNIQUE essay on this or any other topic
Thank you! We’ll contact you as soon as possible.
- Why Is Religion So Important In Culture?

- More than 1.2 billion people today do not consider themselves religious, associate themselves as atheists, agnostics, or secular.
- Religion can be a key factor in the cultural identity of many people, influencing their behavior and traditions.
- Rituals, sacrifices, prayer, art, are one of the many ways people show their allegiance to a particular religion.
There are more than 10,000 religions in the world, some of which you probably never heard of or knew they existed. The majority of the world population is associated with Christianity (the largest religion), Islam, and Hinduism. However, around 1.2 billion people are without religious affiliation, those that associate themselves as atheists, agnostic, or secular.
Religion and culture have both been subjects of much scholarly debate throughout history, and remain in the spotlight of many discussions. Their relationship is complicated at best, and not easy to explain, but they are both important in the lives of humans and how they construct and make sense of the world around us. Even the terms themselves, "religion" and "culture," ask for explanations that are out of the scope of this article. However, we will try to make this as simple as possible.
Why Is It Hard To Define Religion?
Ever since the 9/11 attacks on the United States of America, there has been a significant increase in the study of religion and its impact on society and culture. Because of the attacks, there has been a growth of interest in the religion of Islam, as well as the increase in the critique of Islam. However, it also reinforced fundamentalism in faith, which provides a way of dealing with the plethora of choices offered by our societies.
Anthropologists like Clifford Geertz considered religion to be a cultural system, containing symbols that establish powerful moods and motivations by constructing a realistic order of existence. No academic will tell you an identical definition of religion or agree over what exactly makes a religion. However, many will agree that religion is a system of different behaviors and practices and that every religion has its set of morals, ethics, and sacred sites dedicated to figures they respect (they can be people, supernatural beings, or any form of transcendence that provides guidance or afterlife).

Religion incorporates the relation of human beings to supernatural, spiritual aspects of existence. Religious practices are one of the most common ways people show their allegiance or respect towards a particular religion. Such practices can be, or not, limited to rituals, sacrifices, prayer, art, the commemoration of the dead , going to churches, and many more, extending into various facets of human culture that we witness and experience daily.
The Cultural Importance Of Religion
"God is Dead," said Nietzsche , alluding to the secularization in the West, and the decline of the idea that a divine entity governed our universe. Because of the scientific revolution, the post-enlightenment period of history no longer needed God, according to Nietzsche. Today, more than 1 billion people are those with no religious affiliation, but can we be responsible for creating our value systems and moral guidelines without the divine intervention?
Even if we think we are, can religion ever be fully removed from our daily life and our culture? Whatever the answer is, it might not be important in exploring the ways of how religion is linked with cultural beliefs . Religion influences cultures, but it is also influenced by culture. Religion can play a big part in the cultural identity of people, influencing how they dress, what and when they eat, and how they behave.
Many of the cultural traditions are closely associated with religion, and many religious practices and behaviors have become so rooted in the daily lives of people all over the world that it is hard to make a distinct difference between culture and religion.
More in Society

Countries With Zero Income Tax For Digital Nomads

The World's 10 Most Overcrowded Prison Systems

Manichaeism: The Religion that Went Extinct

The Philosophical Approach to Skepticism

How Philsophy Can Help With Your Life

3 Interesting Philosophical Questions About Time

What Is The Antinatalism Movement?

The Controversial Philosophy Of Hannah Arendt
- Essay Samples
- College Essay
- Writing Tools
- Writing guide

↑ Return to College Essay
Why is Religion Important Essay
If we are not governed by a set of values, then our principles and idea of right and wrong are only based on opinion. The Nazis were not evil. They had a set of values that do not match many of the values that exist today. If they had kept to the religious promises they made the Vatican as they rose to power, then they would have had a hard time taking life in the way they did. My hypothesis is that religion is a human creation, but without some form of faith in more than human opinion, we are lost because only have ourselves to account to.
Human nature is bad. We are not born with a knowledge of right or wrong. That is why people turn out so differently. It is not because a person is born good or bad, but the way they are treated and the values they are taught is what makes them the person they become. Religion has sets of rules that people follow on mass. These rules are more than laws with punishments and rewards, they are based on a set of values, and those are the things that help a person grow to be well adjusted.
Imagine kids without the rule of parents. If a child was allowed to run around and do what he or she wished in an unchecked manner, then children would kill themselves by accident, become sociopaths, and become savages. There would be no way of knowing what would happen. Kids need a parental figure to give out rules and teach values, and that is what religion does for adults. It gives them a set of values and rules to live by.
We are taught what is right and wrong, and religion allows a certain unification that governments are unable to instill. The law tells us not to kill. We are not born with that knowledge. We are born to kill, which is why kids are often merciless insect (and pet) killers. We have both eyes facing front, which means we are born predators. The law tells us not to kill and not to steal. Most will never do such things, and part of that is due to religion. Religion came up with the idea that we shouldn’t kill and steal long before the law did.
The law simply tells us what to do, but religion tries to explain why we should do things. One may say that we do not do things because the law tells us not to, and that is a good enough reason for them, but it is too black and white for most people. Religion helps us shape values so we can make our own choices. For example, the law may say do not kill, but religion (the good religions) teaches us the sanctity of life, so if we had to kill a single person in order to save thousands–then religion allows us to make that choice where the law does not.
The law is the government’s way of trying to instill values, but they simply cannot do it with rules alone. The government would hope that if you follow the law, then you will see why it works and learn your values that way–but it is doing it all backwards. With peace-loving and good religions that do not condone killing, such as any religion “other than” the Arian brotherhood, Islam, and Satanism, you are taught why something is wrong so that you may then choose what you do. Good religions that do not condone killing say you can break the law because you have choices, but it first gives you the reasons and values needed to make the right decision (which usually involves following the law).

Follow Us on Social Media
Get more free essays

Send via email
Most useful resources for students:.
- Free Essays Download
- Writing Tools List
- Proofreading Services
- Universities Rating
Contributors Bio

Find more useful services for students
Free plagiarism check, professional editing, online tutoring, free grammar check.

Essay on The Importance of Religion in the World
We live in a world today filled with: low self-esteem, bullying, hate crimes, lying, abuse, child molestation, depression, racism, addiction(s), murder, corruption, violence, rape, self-mutilation, witchcraft, pornography, sexual immorality, broken hearts, hatred, greed, eating disorders, jealousy, suicide, starvation, torture, hypocrisy, and death. Religion is important because it teaches people about themselves. It gives them hope for a future free from all this sorrow and heartache, and through stories, parables, and quotes from prudent prophets of old said to be hearing the voice of God , or recalling evidence of miracles and extreme faith it provides a lifeline to God, and spiritual fulfillment. It teaches people morals, principal, …show more content…
This goes to say that there would be no government, hypocrisy, violence, rebellion, greed, divorce, power-trips, control freaks, war, bad parents, or anarchy. Parents would govern their own household and teach their children Gods will for their lives according to the bible which would be considered their daily bread of life, so that by the time the child has matured into adulthood they would be whole-heartedly devoted to Christlikeness by the unconditional love and perfect example their parents would imbue them with. Surprisingly, I’m not really the religious type. I believe in God, and have a personal relationship with him. Although I have seen miracles preformed in God’s name, heard his voice, felt his encumbering love and compassion wash over me, tasted his amazing blessings, and been shown his never-ending mercies, there was once a time where even though I have been baptized since the age of four, have grown up in the church/private school, and have received the gift of the holy spirit /spoken in tongues for as long as I can remember…I questioned the legitimacy of God’s presence in my life, or His existence at all. I saw religion as a way to shelter and brainwash multitudes of
World History Argumentative Paper- Religion’s Effect on Society
- 5 Works Cited
From the start of civilization, religion has played a crucial role in the development of most societies. The proof of its influence is evident in the way daily life was carried out. Religion had the power to affect everything from social status to common law, thus dominating a large portion of the culture. In ancient Egyptian, Islamic, and Indian society, religion had the capacity to establish how the average person would conduct their daily life.
What Does Religion Mean To You Essay
Religion is most basically defined as the belief and worship of a higher power, more specifically a belief in one or many Gods. Although no two religions are exactly the same, all religions are based off of some belief. My own personal belief is based off of Catholicism. While I do not agree with all the teachings of the catholic church, I do believe that Jesus is our lord and savior. He symbolizes hope and forgiveness for me and is a constant in my life.
Why Religion Is Good Or Bad Essay
Religion is constructed on faith and belief of an individual even though it is the individual choice to follow it or not. It has stirred a lot of debates for years; those who are trying to prove that God exists throughout history and follow to modern day. While, those who are atheist are trying to prove their point of God does not exist. There are still more and more theories and debate over the subject of religious view. It is a matter of theism versus atheism; new and old philosophers have joined the debate and all with different sides to another philosopher’s theory or view on the matter. In this paper, I will attempt to illustrate the reasons given by Louis Pojman of why religion is good or bad, as well as evaluating Bertrand Russell argument about religion. This can define the meaning of life and the creation of life as we know it. It can change views or switch sides for there is always another explanation to exactly what religion is all about and having a superior ruler that created all.
Brave New World Essay
Religion forms as a method for dealing with life and the world it makes up. It answers the questions that are beyond science and logic. It eliminates the question of "Why?", and brings the fellow believers together to cope with the community and personal problems. People come to religion to find stability, a sense of understanding, and help from other believers. These are the needs that religion fulfills.
Religion In Brave New World By Mustapha Mond
“A man's ethical behavior should be based effectually on sympathy, education, and social ties; no religious basis is necessary. Man would indeed be in a poor way if he had to be restrained by fear of punishment and hope of reward after death.” - Albert Einstein. While Albert Einstein is most certainly correct about the idea of religion not being a necessity for an individual or a society as a whole, religion still has a large influence over society whether it is necessary or not. And with the large influence of religion comes the large importance of religion.
American Grace: The Importance Of Religion In The United States
Through out history religion has played a major role in history. For many people who settled in Northern New England came for religious freedom and the colonies were spread because of that. Believing in religion is often the spiritual thing that they lead their life with. Robert Putnam, in his book, American Grace; How Religion Divides and Unites Us claims that religion, when taken in high doses is toxic to civil life, this is true to an extent. Although many people can agree with his claim he isn’t completely right because religion can still be beneficial for people who truly believe in it. Its true religion has set back society a few steps with the prosecution of many innocent people and the deaths of thousands of people but, religion has also helped many people get through hardships they face.
Essay on World Religion Final Hum 130
In this paper I will be discussing what I learned about Christianity and Islamic faiths. How that even though these two religions have differences that they have core similarities and history that show that they have more in common than they do not have in common. I will discuss my interview at a Christian church and what I learned from it. Then I will discuss how much all the religions I have studied in this class have in common. Touching on their philosophies, beliefs, virtues and traditions and any areas that show areas they have in common.
Religion In Beowulf
Religion has been important to mankind since he discovered that he could think. Especially when the questions arose on where man came from. Thus, the invention of a supreme being and ideas on how man came about. In a time before scientific discovery, man had tales of the beginning of life on Earth. The stories were passed down from generation to generation and each corner of the world had their own take on how life was created.
Pei was asking me the biggest decision that makes me started studying again. I shared about how God saved me when I was in my lowest point and He was the One who brought me into the light. She was surprised as she said that she would only find someone to express her sadness, instead to Buddha. They would only go to the Chinese Temple when they need money or asking for peace and health upon them. I was happy that finally I got the chance to share the main point of my faith! I shared her some Bible verses about Christ carries our burdens and sadness, especially John 14 where Jesus comforts His disciples.
Social Conditioning Influences
Religion has been out for many years, and many people believe that religion is important, because it helps them to figure out what is right and what is wrong. Even though it helps in the sense of morality, it has also somewhat ruin society in a way where people today seem to isolate each other from many other cultures because they are not the “same”. Because of religion, people are always trying to go by what their religion tells them, in other words, people go by their beliefs throughout life. One example of religion used in an everyday life, is when sinning in the Christian religion, is known to be a horrible idea and if you do not follow the religion exactly you will be sent to hell rather than heaven. Also, Christians have a specific way of dressing. Girls should wear a long skirt and are not allowed to wear jeans because it does not follow what the bible says. Not to forget that depending on your gender or sex is an should be the only good way of living, which means that changing genders is not okay. Religion has also created stereotypes. For example, women should be nurturing, and men should be the men of the house. Religion separates the importance of being human beings and manages the way someone can think or
Essay on Why Is Religion Important?
In this essay we will discuss the importance of religion in society. We will attempt to explain why societies have religions and what functions their belief system has for them. We will also ask if these functions are now out-dated and if religions have any meaningful function in today's world or are they just stained glass windows into a bygone era? 'Religion' can be defined by two main groupings. 'The inclusive definition' covers all topics and subjects of a persons life including, not only, their belief in a deity but also their belief and belongingness to music, sport and any other interests the person may hold. 'The exclusive definition' refers to just their belief system regarding a 'supra-human' (Browne 2005, p. 311). It is mainly
My Utopi My Vision Of A Perfect Society
The forests would be kept as nature to look at and not destroy. All people could believe whichever religion they wanted. Children would be taught education about all subjects. There would be no hurtful comments made to people about appearance and looks. If people need anything people would be friendly and share if they have what the other person needs. If a law is broken the person or people would be sentence to working on the farms for a few weeks growing crops and.
Without Religion Research Paper
Whinking back to some of my first days in English and World History class, I can remember my teacher asking about religion. Why was it important? How did I feel about it? Without religion, where would the world be today? I was honestly puzzled, because you usually wouldn't sit back and think about things such as this. In response to her questions, I would say that I feel religion is important because it gives aid to helping people understand themselves and others. I feel that religion is important because humans need something to look up to. Such as a God, a Goddess, Buddha, or even many Gods. We need something that can encourage cooperation and tolerance among relative strangers. Without religion, I feel that there would be no grounded morality
Example Of A Worldview Essay
However, over the years, my faith began to wane. I don’t know If I always doubted my religion, but slowly over the years I began to slowly slip away from my religious upbringing. This all culminated in a youth camp my church held when I was around thirteen years old. During this youth camp, we were scheduled to do all sorts of service work and spiritual experiences. I had been told for years that this camp was where people finally “experienced” God, and where people finally saw God’s impact in their lives. While I appreciated the service work I got to do for others, I never had any spiritual experiences, and this moment really impacted me, and caused me to doubt the existence of a higher
Religion and Civilization Essay
- 2 Works Cited
They became the cornerstone of many earlier and later civilizations. Even today many countries, especially those in the Middle East, have religious leaders who work with the government to enact laws and “guide” the spiritual aspect of the lives of their citizens. Unfortunately, with such strong beliefs and convictions can come conflict. This conflict can be on a small scale, such as discrimination against those who don’t share the same beliefs to full-scale war which was the case in the first Crusades. In more recent times we have seen mass genocides of people based in part on religious beliefs such as the annihilation of the Jews during the Second World War. Today we see it played out in acts of terrorism, jihads. Religion is a powerful tool that can be used both to help and enrich the lives of people or used as justification for intolerance against others.
Related Topics
- Holy Spirit
- Christian terms
Home — Essay Samples — Religion — Religious Freedom — Freedom of Religion
Freedom of Religion
- Categories: Religious Freedom Religious Tolerance
About this sample

Words: 693 |
Published: Jan 30, 2024
Words: 693 | Pages: 2 | 4 min read
Table of contents
Historical context of freedom of religion, the significance of freedom of religion, challenges and dilemmas in ensuring freedom of religion, case studies of freedom of religion in practice.
- Rousseau, Jean-Jacques. The Social Contract. Penguin Classics, 2003.
- Jefferson, Thomas. The U.S. Constitution.
- Walker, Phil. Religious Freedom. McGraw-Hill, 2021.
- Hill, Jonathan P. The Freedom to Be Different: Religious Diversity in the US. Harvard University Press, 2018.

Cite this Essay
Let us write you an essay from scratch
- 450+ experts on 30 subjects ready to help
- Custom essay delivered in as few as 3 hours
Get high-quality help

Dr. Heisenberg
Verified writer
- Expert in: Religion

+ 120 experts online
By clicking “Check Writers’ Offers”, you agree to our terms of service and privacy policy . We’ll occasionally send you promo and account related email
No need to pay just yet!
Related Essays
5 pages / 2348 words
2 pages / 905 words
4 pages / 1781 words
4 pages / 1789 words
Remember! This is just a sample.
You can get your custom paper by one of our expert writers.
121 writers online
Still can’t find what you need?
Browse our vast selection of original essay samples, each expertly formatted and styled
Related Essays on Religious Freedom
The right to freedom of religion is a fundamental human right that plays a pivotal role in shaping personal and societal values. In this essay, we will delve into the significance of this right and how it can be harnessed to [...]
Dearden, Lizzie. “France Burkini Ban: What Is It and Why Is It Controversial?” The Independent, 17 Aug. 2016, [...]
Religious freedom is a fundamental human right that encompasses the freedom to practice, change, or abstain from any religion or belief system. It is recognized as a cornerstone of democratic societies, ensuring individuals' [...]
Freedom of religion is a fundamental human right that has been recognized and protected by various international treaties and conventions. The right to practice one's religion, or to have no religion at all, is essential for the [...]
In the time period of 1692, when the Puritans came to this country for religious freedom, they had a strict moral code which everyone in the village lived by. Religion was especially important. The state was founded on religion, [...]
It has been made clear to me that there is no such thing as "religious liberty" within this once great country of ours. We have completely fallen short of what our forefathers intended us to be. Foundations and religious [...]
Related Topics
By clicking “Send”, you agree to our Terms of service and Privacy statement . We will occasionally send you account related emails.
Where do you want us to send this sample?
By clicking “Continue”, you agree to our terms of service and privacy policy.
Be careful. This essay is not unique
This essay was donated by a student and is likely to have been used and submitted before
Download this Sample
Free samples may contain mistakes and not unique parts
Sorry, we could not paraphrase this essay. Our professional writers can rewrite it and get you a unique paper.
Please check your inbox.
We can write you a custom essay that will follow your exact instructions and meet the deadlines. Let's fix your grades together!
Get Your Personalized Essay in 3 Hours or Less!
We use cookies to personalyze your web-site experience. By continuing we’ll assume you board with our cookie policy .
- Instructions Followed To The Letter
- Deadlines Met At Every Stage
- Unique And Plagiarism Free
How Does Shakespeare Use Banqou In Macbeth
In Shakespeare's didactic tragedy, Shakespeare uses Banqou's character to make a clear assertion about the importance of religion, using him as an example of what happens if you stray from god. Throughout the play, Shakespeare uses Banqou's character to deliver a clear message about the importance of resisting the temptations of evil, although it may be a struggle. Shakespeare advocates turning to God for support. The internal battle Banqou experiences emphasises his humanity and allows the audience to connect with him on a deeper level than they can Macbeth. We first see this religious nature of Banqou come to light in Act 1 Scene 3 after meeting the witches. Banqou says, 'If you can look into the seeds of time'. Here, we see him try to use …show more content…
Although Banqou suffers a moral decline similar to Macbeth, it is neither as severe nor as rapid. Shakespeare's source material for the play was Holinshed's chronicles. A history book in which there is the genuine tale of Macbeth. However, the play of Macbeth differs from this book because, in the book, Banqou is involved in the murderous plot to kill Duncan. Although Banqous's consciousness remains clear after meeting the witches as the play progresses, his temptation grows. Like Macbeth, he says he can no longer sleep soundly and admits to his son Fleance that he is struggling to restrain 'cursed thoughts' and is troubled by the prophecies of the three sisters. However, there are significant differences between Macbeth and Banquo. When Banquo feels his temptation growing, he asks his son Fleance to take his sword. This demonstrates that only Macbeth takes matters into his own hands and embarks on his bloody campaign of violence. Banquo is morally stronger and doesn't succumb to the prophecies. Banqou doesn't have the same humour and ambition as Macbeth. We can assume Shakespeare changed the original tale of Banqou to paint him in a more positive light because it was believed that King James the First (Shakespeare patreon) was a descendant of Banqou. The imperative verb 'take' conveys a sense of urgency and importance. This suggests Banquo has dark thoughts and does not trust himself to act on them. In this way, Shakespeare highlights the difference between the two
More about How Does Shakespeare Use Banqou In Macbeth
Origins of Religion Response Essay
Introduction, origins of religion, works cited.
In the book, the second chapter on the origin of religion is the important since it is speculative and fascinating, as the author suggests. The author notes in the introduction that a number of studies are simply concerned with explaining the reasons why people are religious, but they do not delve into the issue touching on the origin of religion. The focus of the chapter is to report on where religious ideas and practices came from.
Moreover, the chapter evaluates the idea of God or supernatural powers since such powers are sacred forces that influence the behaviour of individuals in a number of ways. The author is of the view that answers to the origin of religion are numerous, even though they can be grouped into a few categories.
To establish the real origin of religion, the use of scientific methods is inadequate hence the use of theories is the only valid method of tracing the origins of religion. Before proceeding to look at the theories that the author provides regarding the origin of religion, it is prudent to define sociology of religion.
Sociology of religion refers to the study of cultural beliefs, practices, and forms of organizations. Sociologists study religion through some of the established tools and methods. Sociological explanation of the origin of religion is very different from the views of other scholars from different fields.
Prehistoric people had no reason to trace the origin of religion since they were not concerned with understanding the dynamics of society. In the modern society, religion plays a critical role of uniting people.
This paper discusses various theories that explain the origin religion in the modern society. Religion in the modern society is very complex, unlike in the traditional society whereby it was considered an individual’s belief system.
Revelation is one of the theories that sociologists employ in trying to explain how people started worshiping the supernatural being. The author notes that people believed in God, who was the creator, in the early days of Christianity. In this regard, God was the originator of all religions in the world, including the traditional ones. The theory suggests that God created everything on earth, including people.
In the Garden of Eden God instituted some principles and laws that were supposed to govern the first man. Later on, God would pass his message through prophets, as he did in the Old Testament. Through this process, he was creating religion since he expected people to follow his commandments. A number of religions believe in this theory, including Buddhism, Christianity, and Judaism.
Gautama Buddha claimed that he had a revelation, which inspired him to spread the Buddha teachings. Mormonism was inspired by a revelation that was in form of golden plates that were buried in a hill referred to as Cumorah in New York State (Johnstone 23).
One of the founders of religion, John Smith, claimed that God gave him the power to interpret and translate what was in the plates. In the Islamic religion, Muhammad claimed to have received visions from one of the angels referred to as Gabriel in a cave near Mecca.
Christian theologians who claim that they received direct revelation from God for the gift of true religion hold the natural knowledge of God theory (Johnstone 23). Those who believe in the Holy Bible give such explanations. In fact, the existence of other religions disturbs them so much.
In this regard, Christian theologians wonder how other religions came about since God revealed himself through the chosen people of Israel. The theory answers their question since it claims that people have a fundamental knowledge regarding the existence of God.
Johnstone is of the view that all human beings are born with an elementary knowledge of the heavenly, which is a basic awareness that God or some power is, in due course, responsible for what they witness around them (24). Other religion, other than Christianity, tries to be aware of their surrounding and make sense out of the little knowledge they have in relation to God.
Anthropologists have a different theory explaining the origins of religion. According to anthropological theories, religion emerged as a response to the experiences of various individuals, who tried to construe the world around them. Individuals in the traditional society came across awesome, mysterious, and terrifying events that forced them to reconsider their religious positions.
Some of these terrifying events include sickness, thunder and lightning, earthquakes, tidal waves, and floods (Johnstone 24). Many people sought to find the real causes of these horrifying events. Traditional religious systems were relied upon in explaining these events, which facilitated the growth of religion. People would then allocate causes for the so-called natural observable facts, as well as other recurrent incidents.
Within anthropological explanations, at least two schools of thoughts exist, one of them being naturalistic school headed by Max Muller. This school of thought insists that physical acts of nature, such as storms, sunrises, and tides, contributed to the development of religion (Muller 88).
In this regard, individuals in the prehistoric societies were fearful and defenceless since they existed at the mercy of these horrifying events. Some were worried why a tragic even would happen to them and not other people. Such individuals were of the believe that all natural disasters were either caused by human beings or other human-like agents since they witnessed people killing each other and pushing rocks.
Through this reasoning, this believe, believe in sprits was eminent since individuals thought that some agents must be hiding somewhere, with the power to natural disasters, such as death. Edward Tylor led a different school of thought that held an animistic view, which believed in personal experiences, such as dreams and reflections (Johnstone 25).
Psychologists have a different view as regards the origin of religion, which treats the origin of religion in terms of people’s emotional needs (Johnstone 25). As anthropologists focused on cognitive needs in explaining inexplicable events, psychologists are more focused on giving an emotional explanation.
In this regard, they note that people are always in need of maintaining an emotional stability whenever they experience danger, uncertainty, and interference. People ask themselves how they would get out of danger, particularly when faced with disruptions such as sickness, accident, and threats of death.
An individual would wonder why a disaster would happen to him or her or even to those he or she loves. At this stage, an individual tries to make sense out of the disaster by asking how he or she can find strength to move on. An individual would be aiming at finding some hope in the future. Brown was of the view that religion is a response to constant threats to security, safety, and future existence (12).
Sociologists offer a different explanation concerning the origins of religion. In fact, sociologists do not use the term origins, but instead they employ the word correlates in their analysis of religion to explain its origins. This means that religion is an ever-present aspect in the lives of individuals. Sociologists are focused on establishing the relationships between modern religion and other social forces.
According to modern sociologists, religion is everywhere meaning that tracing its origins would be an exercise in futility since it exists in a number of varieties. George Simmel was one of the sociologists who analyzed religion, as well as its interactions with other social variables. He was of the view that a number of no-religious aspects influence tremendous effect to various forms of religions in the modern society.
In this regard, a number of views and prototypes of expressions frequently referred to as spiritual are also found in other areas of life (Johnstone 30). These patterns are general ingredients of social interactions. They include adulation, loyalty, fervour and worship. Durkheim analyzed the role of religion in legitimizing social values and norms. Through setting standards, religion offers divine sanctions for human behaviour.
When people come together to perform rituals, their feeling of unity is strengthened. Durkheim went ahead to discuss two important concepts, which are totem and totemic principle. He observed that a totem is an object or something alive, including a bird, an animal and plants (Johnstone 31). The object is not so important to human life, but what matters is what the object worships.
Brown, Laurence. Advances in the Psychology of Religion . Oxford: Pergamon Press, 1985. Print.
Johnstone, Ronald. Religion in Society: Sociology of Religion . Upper Saddle River, NJ: Prentice Hall, 2007. Print.
Muller, Max. Anthropological Religion . Whitefish: Kessinger Publication, 2005. Print.
- Chicago (A-D)
- Chicago (N-B)
IvyPanda. (2019, June 3). Origins of Religion. https://ivypanda.com/essays/origins-of-religion/
"Origins of Religion." IvyPanda , 3 June 2019, ivypanda.com/essays/origins-of-religion/.
IvyPanda . (2019) 'Origins of Religion'. 3 June.
IvyPanda . 2019. "Origins of Religion." June 3, 2019. https://ivypanda.com/essays/origins-of-religion/.
1. IvyPanda . "Origins of Religion." June 3, 2019. https://ivypanda.com/essays/origins-of-religion/.
Bibliography
IvyPanda . "Origins of Religion." June 3, 2019. https://ivypanda.com/essays/origins-of-religion/.
- Revelation, Apocalyptic Literature, and Prophecy
- Bible. Objective and Subjective Revelation.
- “The Book of Revelation”: The Revelation of Jesus Christ
- Revelation in the World Religions
- The interpretation of Revelation 20: 1-6
- Elements of a Sociological Theory of Religion
- Concept of Deviance and Sociologists Researches
- Origin of Major World Religions
- Religion Study: Sociological Approach
- Abrahamic Religions: Judaism, Christianity, Islam
- Comparative Analysis on Nature and Grace in the Augustinian and Thomistic Schools
- Discipleship
- Definition of Gospel Parables
- Elements of a Religion
- The Holy Spirit in Acts

IMAGES
VIDEO
COMMENTS
Importance of Religion. Three-quarters of U.S. adults say religion is at least "somewhat" important in their lives, with more than half (53%) saying it is "very" important. Approximately one-in-five say religion is "not too" (11%) or "not at all" important in their lives (11%). Although religion remains important to many ...
A good example is the latest abortion issue in the US, the overturning of "Wade vs. Roe." Include people's mixed reactions to this subject and their justifications. 5. Religion: Then and Now. On your essay, ddd the religion's history, its current situation in the country, and its old and new beliefs.
The Importance of Religion in Human Lives Essay. Some contend that humans require religion to be moral, to instill in them a sense of right and evil, and to motivate them to act morally. It penalizes bad behavior and establishes a standard for good behavior. Others might contend that morality and happiness can be attained without religion.
A large part of humanity believes in the existence of gods and follow their norms religion. Believing in God and consequently in a religion would work. For example, as a comfort in the face of the inevitability of death. Thus, giving a purpose to existence for their passage through the Earth would be only one of the stages to be fulfilled.
In her recent Opinion essay, " I Followed the Lives of 3,290 Teenagers. This Is What I Learned About Religion and Education ," Ilana M. Horwitz discusses the effects of a religious upbringing ...
Similarly, religion is as old as the mankind. The reason why religion plays an important role in any society indeed rests on the major roles it plays in society. In this paper, it has been found that the belief that someone or something is watching us from above, the ability to give mankind a sense of belonging and identity and solve societal ...
religion, human beings' relation to that which they regard as holy, sacred, absolute, spiritual, divine, or worthy of especial reverence. It is also commonly regarded as consisting of the way people deal with ultimate concerns about their lives and their fate after death.In many traditions, this relation and these concerns are expressed in terms of one's relationship with or attitude ...
By contrast, only three-in-ten people who are classified as not highly religious (31%) say religion is very important in their lives, and most of the rest (38%) say religion is "not too" or "not at all" important to them. 7. Nearly all people who are highly religious say believing in God is essential to their religious identity (96% ...
1. A History of the Concept. The concept religion did not originally refer to a social genus or cultural type. It was adapted from the Latin term religio, a term roughly equivalent to "scrupulousness".Religio also approximates "conscientiousness", "devotedness", or "felt obligation", since religio was an effect of taboos, promises, curses, or transgressions, even when these ...
Essay on Religions | Meaning, Purpose & Importance of Religion in Life. It simply means a set of beliefs and rituals that people hold sacred, which in most cases is the belief in some form of higher power or powers. In a sense, it is a very personal belief system.
Essay On Importance Of Religion. 927 Words4 Pages. Whether religion is important to one's life is a debatable issue. This is a topic where many people would agree to disagree the importance of religion in people's life. Every society 's standards and laws are based on some form of religion. Throughout history, we have seen many societies ...
Collectively, the intercultural work examining religion demonstrates the increasing importance of the intersection between religion and culture in communication studies. Collectively, communication studies discourse about religion has focused on how religion is an integral part of an individual's culture.
Religion is relevantly important to different people in the world. That is the reason why as much as religion faces so much criticism from disciplines like science and theories as evolution it will stand the test of time. Religion deals with the bigger criticism but some people have proved to stand the tests. Works Cited. Haley, Alex.
Why Is Freedom of Religion Important. Freedom of religion stands as one of the fundamental pillars of a democratic and pluralistic society. It safeguards an individual's right to practice their chosen faith without fear of discrimination or persecution. This essay delves into the resons why freedom of religion is important, exploring...
It gives a purpose to our lives, helps guide us through our lives, helps us appreciate our world and one other, and it plays a crucial part in the evolution in our society. (Reuters 1) Religion is not only a necessary but a vital part of our lives. Without faith, people would find it difficult to live their lives.
Essay on the Importance of Religion in Our Lives. Man sometimes confronts some such situations in life which he is not able to understand. He expresses his curiosities to others about the same and concedes his utter helplessness in the matter. It is difficult to say how religion has come to the modern form. It may be said that on the basis of ...
Religion influences cultures, but it is also influenced by culture. Religion can play a big part in the cultural identity of people, influencing how they dress, what and when they eat, and how they behave. Many of the cultural traditions are closely associated with religion, and many religious practices and behaviors have become so rooted in ...
Why is Religion Important Essay. If we are not governed by a set of values, then our principles and idea of right and wrong are only based on opinion. The Nazis were not evil. They had a set of values that do not match many of the values that exist today. If they had kept to the religious promises they made the Vatican as they rose to power ...
Religion is important because it teaches people about themselves. It gives them hope for a future free from all this sorrow and heartache, and through stories, parables, and quotes from prudent prophets of old said to be hearing the voice of God, or recalling evidence of miracles and extreme faith it provides a lifeline to God, and spiritual ...
Importance for Social Harmony. Freedom of religion is essential for the promotion of social harmony and peaceful coexistence. In diverse societies, individuals hold a wide range of religious beliefs, and the freedom to practice these beliefs without fear of persecution or discrimination is vital for maintaining unity and understanding.
Introduction. Religious tolerance is imperative in modern societies because it allows people with separate faiths, beliefs or values to coexist with one another. Acknowledgment of the validity of other people's religions requires placing these different religions in their traditional contexts in order to understand them.
Religious freedom protects the members of a community from being discriminated against and oppressed on the basis of their religion.Moreover, freedom of religion is vital in promoting societal diversity and tolerance. It fosters cultural and religious pluralism, encouraging the ability of members of society to coexist peacefully with each other.
In Shakespeare's didactic tragedy, Shakespeare uses Banqou's character to make a clear assertion about the importance of religion, using him as an example of what happens if you stray from god. Throughout the play, Shakespeare uses Banqou's character to deliver a clear message about the importance of resisting the temptations of evil, although ...
Origins of Religion. Revelation is one of the theories that sociologists employ in trying to explain how people started worshiping the supernatural being. The author notes that people believed in God, who was the creator, in the early days of Christianity. In this regard, God was the originator of all religions in the world, including the ...