Have a language expert improve your writing
Run a free plagiarism check in 10 minutes, generate accurate citations for free.
- Knowledge Base
- What Is a Modal Verb? | Definition & Examples

What Is a Modal Verb? | Definition & Examples
Published on February 14, 2023 by Eoghan Ryan . Revised on December 6, 2023.
A modal verb (also called a modal auxiliary verb ) is used along with a main verb to express possibility, ability, permission, or necessity. For example, in the statement “you must leave,” “must” is a modal verb indicating that it’s necessary for the subject (“you”) to perform the action of the verb (“leave”).
The modal verb “will” is used to form the future tense, indicating an action that has not yet occurred (e.g., “I will clean the garage”).
Can you drive me to the airport?
Table of contents
How are modal verbs used in sentences, modal verbs list, modal verbs and auxiliary verbs, modal verbs and mood, other uses of modal verbs, other interesting language articles, frequently asked questions.
Modal verbs are used along with a main verb to indicate ability, necessity, possibility, and permission. In sentences containing modal verbs, the main verb typically takes the infinitive form. Modal verbs come before main verbs and never change form.
You may have as many cookies as you’d like.
Check for common mistakes
Use the best grammar checker available to check for common mistakes in your text.
Fix mistakes for free
Below is a table that illustrates some of the various uses of modal verbs. Note that modal verbs are very commonly used in a wide variety of senses—this table doesn’t cover every possible usage.
Modal verbs are classed as a type of auxiliary verb . Auxiliary verbs are used along with a main verb to express tense, mood, or voice. However, unlike modal verbs, regular auxiliary verbs follow subject-verb agreement and must be conjugated for tense and mood.
Gordon has burned the toast.
Modal verbs can be used along with auxiliary verbs to refer to possible past, continuous, or future action.
When a modal verb is followed by another auxiliary verb (e.g., “have,” “be”), the main verb takes either the past participle form (typically ending in “-ed,” “-n,” or “-t”) or the present participle form (ending in “-ing”).
The modal verb “will” is used in all aspects of the future tense (e.g., “I will talk,” “you will be traveling ”).
You may be wondering what I mean.
The grammatical mood of a verb indicates the intention of the sentence. Modal verbs and auxiliary verbs are used along with a main verb to express mood.
Modal verbs have various other functions in English. They can also be used:
- In indirect speech
- In negative statements
- For emphasis
Indirect speech
Modal verbs are used in indirect speech to indicate what someone else said. While most modal verbs stay the same when used in indirect speech, the past form of some modal verbs is used instead (e.g., “can” becomes “could”).
Negative statements
In negative statements containing modal verbs, the adverb “not” comes immediately after the modal verb and before all other verbs. The negative form is often contracted (e.g., “would not” becomes “wouldn’t”).
In everyday conversation, people sometimes place emphasis on a modal verb to refute a previous statement or question. The emphasized word is often italicized when written down.
If you want to know more about commonly confused words, definitions, common mistakes, and differences between US and UK spellings, make sure to check out some of our other language articles with explanations, examples, and quizzes.
Nouns & pronouns
- Common nouns
- Proper nouns
- Collective nouns
- Personal pronouns
- Uncountable and countable nouns
- Verb tenses
- Phrasal verbs
- Sentence structure
- Active vs passive voice
- Subject-verb agreement
- Interjections
- Determiners
- Prepositions
Modal verbs (also called modal auxiliary verbs ) are used along with a main verb to express ability, possibility, necessity, and permission. They are a type of auxiliary verb .
For example, in the statement “I can drive,” “can” is a modal verb indicating that the subject (“I”) has the ability to perform the action of the verb (“drive”).
“Would” is a modal verb that’s often used along with the auxiliary verb “have” to indicate that something was possible in the past but no longer is (e.g., “She would have been a professional athlete if she hadn’t broken her leg”). It can be contracted to “would’ve.”
People sometimes mistakenly write “would of” because of its similar pronunciation. However, “would of” is never correct.
“May” is a modal verb used to indicate possibility (e.g., “I may miss the bus”), make a request (e.g., “May I have a drink?”), or indicate permission (e.g., “You may sit down”).
Sources in this article
We strongly encourage students to use sources in their work. You can cite our article (APA Style) or take a deep dive into the articles below.
Ryan, E. (2023, December 06). What Is a Modal Verb? | Definition & Examples. Scribbr. Retrieved April 11, 2024, from https://www.scribbr.com/verbs/modal-verb/
Aarts, B. (2011). Oxford modern English grammar . Oxford University Press.
Butterfield, J. (Ed.). (2015). Fowler’s dictionary of modern English usage (4th ed.). Oxford University Press.
Garner, B. A. (2016). Garner’s modern English usage (4th ed.). Oxford University Press.
Is this article helpful?

Eoghan Ryan
Other students also liked, what is an auxiliary verb | definition & examples, what is a linking verb | definition & examples, what is a transitive verb | examples, definition & quiz, unlimited academic ai-proofreading.
✔ Document error-free in 5minutes ✔ Unlimited document corrections ✔ Specialized in correcting academic texts

Want to create or adapt books like this? Learn more about how Pressbooks supports open publishing practices.
Part Three Editing / Grammar Skills
Unit 15 Modals
Learning Objectives
- To understand what modals are and what principles they follow
- To learn the challenges and strategies in using appropriate modals
- To learn the meanings and uses of modals and modal-like expressions through multiple examples
- To practice using modals through a variety of writing situations

The following ten sentences are about some customs from different countries. The modal and main verb are bold-faced in each sentence. If the bold-faced part is correct, choose “correct”. If not, choose the other answer. After you finish one sentence, you will get instant feedback on your answer before the next sentence. If you make mistakes, you can retry all the questions or see all the answers at the end of the pre-test.
II. Principles of Using Modals
As you have learned in Unit 9 Verb Basics in Academic Writing ( Open Unit 9 here ) , modals are an important part of the verb family. They are considered helping verbs, also called auxiliary verbs. Most modals follow the following principles:
1. They cannot exist by themselves. They are followed by the base form of main verbs to show different meanings and tones.
modal + base form of main verb = complete verb
- In the United States, people should call ahead before visiting someone. ( no “calls, called, calling, to call” )
- People must not show the “OK” gesture [1] with the thumb and index finger in Mexico. ( no “shows, showed, showing, to show” )
2. Contractions are common are in modals, such as “shouldn’t” and “mustn’t”. However, “may” and “might” do not have a contraction form. It is wrong to write “mayn’t” and “mightn’t”.

- Small children mayn’t stay ( may not stay ) alone at home in the United States.
- It mightn’t be ( might not be ) a good idea for children to stay in their friend’s home overnight.
3. Some expressions are called modal-like expressions. There is a “to” in them, and the base form of the verb follows the “to”. These expressions include: be able to, be supposed to, have to, have got to, ought to, and some others.
- People have to come on time for an appointment in the United States.
- They are supposed to explain the reasons if they are late.
4. Some modals and modal-like expressions are often used in conversations only.
- In Thailand, people had better not touch the head of a statue.
- In the U.S. restaurants, customers have got to tip the waiters and waitresses.
Exercise 1. The following sentences are about dining customs in some countries. There are mistakes in the form of modals and main verbs. Identify each mistake by underlining the whole verb (modal + main verb) and then correct the mistake. If the main verb is missing, add it.
Example :
People can to learn ( can learn ) about different customs and traditions when they travel abroad.

- Dinning traditions may the most interesting to most people.
- In Kenya, guests should to wash their hands both before and after the meal. They cannot sitting with their feet and toes pointing toward any of the other guests or the food. Kenyans do not use utensils [2] . They eat with their right hand. They must not to use their left hand during the whole meal.
- Americans and Europeans have opposite dinning etiquettes [3] . Americans should holds the knife in their right hand and the fork in their left hand, but the Europeans are suppose to hold the knife in their left hand and the fork in their right hand.
- People in Morocco practice communal [4] eating. This means that they eat from the communal bowl closest to them. A person must eats using his or her right hand. The left hand mayn’t be used to get food. If a bone is taken, the person supposed to suck the marrow [5] from it.
III. Challenges in Learning Modals and the Strategies in Using Them
1. The same modal may have different meanings in different contexts.
- I can drive a car because I have a driver’s license. (permission)
- I can drive a car because I know how to drive. (ability)
2. The same meaning can be expressed with different modals, but the tone or level of strength is different.
- In order to drive in the U.S, a person must have a driver’s license. (stronger)
- In order to drive in the U.S, a person has to have a driver’s license. (less strong)
3. Some modals have the appearance of past tense, but they have a present or future meaning.
- Most cultural traditions stay for generations, but some might change quickly.
- People had better learn the customs of another country when they travel there.
Strategies:
1. Understand a modal, its meaning, its time (past, present, future), and its form together as a “package”.
- In many countries in the past, young people had to follow the custom of the arranged marriage.
- In some countries nowadays and in the near future, some young people still must follow the custom of the arranged marriage.
In both sentences, “had to follow” and “must follow” have the same meaning: obligation, responsibility, necessity.
However, the first sentence shows the meaning in the past, and its form is “had to + follow”.
In the second sentence, the same meaning is expressed in present and future sense, and its form is “must + follow”.
Therefore, try not to study modals in isolation [6] . Instead, understand them in the context and study the “package”.
2. Use the same strategy as in learning other aspects of English: practice, practice, and practice.
IV. Uses of Modals and Modal-Like Expressions
Meaning : advice, suggestions
- In the United States, customers should tip the waiters or waitresses for their service. (present)
- Customers ought to tip the waiters or waitresses for their service. (less common) (present)
- They can tip /could tip 10 – 20% of the food bill. (present, softer tone)
- Customers should not leave the restaurant without tipping the waiters or waitresses. (present)
Exercise 2. Give at least two suggestions for each of the following situations.
One of your classmates is going to visit your country as a tourist in summer .
Suggestion #1 : You should bring a few extra bottles of sunscreen because my country Colombia is near the equator and the sun is very intense.
Suggestion #2: You ought to try bandeja paisa. It is Colombia’s unofficial national dish.
- One of your siblings has found an American boyfriend (or girlfriend)
- One of your relatives is planning to study at Harper College for the first time.
- One of your American friends is going to study at a university in your native country.
- One of your professors is considering studying your native language.
- One of your friends is nervous about meeting his parents-in-law for the first time.
Meaning: abilities

- There are many languages in India. Many people there can speak more than 5 different ones. (present)
- They are able to speak Hindi, English, and some regional dialects. (present)
- The Indian government recognizes twenty-three official languages, but most people cannot speak all of them. (present)
- People in ancient Indian could speak Sanskrit, one of the earliest languages. (past)
- They were able to speak Sanskrit as early as 2000 BC. (past)
Meaning: permissions
- In Canada, college students can address / may address their professors by the first name. (present)
- In Canada, college students could not drink alcohol in class fifty years ago, and they still cannot . (past, present)
- In Ukraine, college students cannot call / may not call their professors by the first name. It is considered very impolite. (present)
Exercise 3. Finish the following sentences to express ability and permission.
When I was a child, I could climb a tree . (ability)
- When I was a child, I could ____________________. (ability)
- When I was a child, I could not ____________________ (ability)
- Now I am an adult. I can ____________________ (ability)
- Now I am an adult. I cannot ____________________. (ability)
- When I was a student in my home country, I could ____________________ (permission)
- When I was a student in my home country, I could not ____________________ (permission)
- Now I am a student in the U.S. I can ____________________ (permission)
- Now I am a student in the U.S. I cannot ____________________ (permission)
Meaning: necessity, obligation, responsibility
- In Iraqi formal greetings, people must use a person’s surname and title, for example, Dr. Kazem. (present)
- Men have to stand to greet a woman when she enters the room. (present)
- A long time ago in Iraq, everyone had to stand when an elderly person arrived. This custom has remained to this day. (past)
- In Iraqi culture, people do not have to kiss each other as a way of greeting. Handshaking is common. (present)

Meaning: prohibition [7]
- People must not whistle inside a Mongolian ger, a round-shaped dwelling. (present)
- In a ger, people must not point their feet to the north end. (present)
Exercise 4. Discuss the following questions. What are the answers in your home country? What are the answers in the United States?
- Must people get married first if they want to live together?
- Do people have to get their parents’ permission to get married?
- Must men serve in the military?
- Do school children have to wear uniforms?
- What are the things you must not do on the street?
- What are the things you must not do during a test?
- What are the questions you must not ask a lady?
Meaning: possibilities
- In Japan, parents do not kiss each other in front of their children. They must think / may think / might think / could think it improper [8] for the children to see their intimacy [9] . (present)
- This custom may change / might change /could change in the near future. The young generation should welcome / may welcome / might welcome / could welcome this change. (future)
- Some words are the same in writing in both Chinese and Japanese. However, the meanings of these words may not be / might not be the same. (present)
Meaning: expectations
- On March 8, the International Women’s Day, men are supposed to buy flowers for women in Russia and many other Eastern European countries. (present)
- On that day, women are not supposed to do much housework. They are supposed to take a day off. (present)
- Last year, Natalia’s husband was supposed to buy flowers for her, but he forgot. (past)
Meaning: preferences
- In some countries, people prefer arranged marriages. Parents would rather pick someone as their future son-in-law or daughter-in-law than let their child decide. (present)
- Some young people would rather not get into a marriage than marry someone they do not love. (present)
Exercise 5. Write sentences according to the instructions.
- Use modals of possibility to write three guesses why seafood is popular on Valentine’s Day in the U.S.
- Use modals of expectation to write three things you are supposed to know when you go to an American family for dinner.
- Use modals of preference to write three choices of food on New Year’s Eve in your home country.
V. Unit Review Practice
Exercise 6. Read the following sayings. Each contains a modal. Discuss what the saying means and whether you agree with it. Do you have similar sayings in your native language? How do you say them? If you can think of additional sayings with modals, please list them below.

- You can lead a horse to water, but you can’t make it drink.
- You can’t teach an old dog new tricks.
- You can’t have your cake and eat it too.
- Beggars can’t be choosers.
- People in glass houses shouldn’t throw stones.
- Children should be seen, not heard.
- Bitter pills may have blessed effects.
- Be careful what you wish for; you just might get it.
________________________________________
Exercise 7. The following sentences are about school uniforms. The modals and main verbs are underlined. Discuss their different meanings and time references (past, present, future) in the context. The first one is an example.

- School uniforms could be ( possibility, present) an important part of school traditions. Students in some schools must wear the school uniform. They may not attend school without their uniform. The uniform must be important.
- A uniform reflects [10] the school and its reputation. Therefore, students are supposed to be in their best behavior.
- Students with totally different uniforms cannot belong to the same school even though they may be siblings. They must not exchange their uniforms with students from other schools.
- In some schools, uniforms are optional. Students may choose to wear one. They could also wear their own clothes. Some students would rather have the uniform. They would rather not spen d half an hour each morning choosing what to wear.
- In most cases, uniforms are not free. Students have to purchase them. Most families are able to afford them, but some are not. This might increase the financial burden for some families.
- Even though the students must wear their uniform while in school, they do not have to wear one after school.
- Should schools require uniforms? There have been many debates [11] . If most students do not like them, they may disappear in the near future. Otherwise, they should stay for a long, long time.
Exercise 8. The follow is an essay on how high school students in different countries spend time in the summer. Underlined the modals and their main verbs. Then discuss what they means in the context and whether they express present, past, or future time. The first one is an example.
After you finish reading and understanding the first three paragraphs, write a new supporting paragraph about a person you know who spent last summer vacationing and relaxing. Then write a conclusion for the essay. Include at least five modals and modal-like expressions. You may write in the box below or in your own notebook. (Warning: Once you leave this page, you will lose what you have written in the box.)

How to Spend the Summer?
High school students in different countries may spend (possibility, present) their summer very differently. Some might value life experiences by working on a job, some could use the time catching up with their academic work, and others might consider it an opportunity to relax and have fun. How they spend their summer might reflect some of the customs and values of their cultures.
It is common for many high school students in the United States to work during the summer months. They could work in any type of job: food, travel, secretarial, health care, summer camp, and many others. Last summer, Joan worked as a summer camp activity leader. She was happy that the job provided her with valuable work experience as well as a small income. Both the experience and the money should be helpful in her future college study.
In Korea, however, it is not usual for high school students to hold a job in summer. They are supposed to take extra classes to prepare for university. Last summer, Ji-hoon kept himself busy by taking a few science and English classes in a cram school. Though he was very busy, he had to do so. He was determined to be better prepared for his university entrance exam.
Exercise 9. Choose two of the following topics and write a paragraph for each. Use proper modals.
- Describe one of the holiday dinning traditions in your native country.
- Describe some customs about naming a baby in your native country.
- Explain one of the taboos [12] for a wedding ceremony in your native country.
- Some people say that elderly parents should live with their adult children. Do you agree or disagree? Why do you think so?
- In America, it is common to “go Dutch” (split the food bill in the restaurant) when people dine out. Is this practice common in your native culture? If not, why not? who usually pays for the meals?
- Write about the joys and challenges of living in two cultures (your native culture and the American culture). What was your biggest cultural shock during your first two weeks in the U.S.?
NSNT Practice

Go to The NSNT Free Writing Approach and Additional Weekly Prompts for Writing in Appendix A. ( Open Appendix A here. ) Choose two topics that involve modals. You may start with the NSNT approach. Then revise and edit your paragraphs. Pay attention to the use of modals. You are encouraged to share your writing with your partner and help each other improve.
Vocabulary Review

The words here have appeared in this unit. The best way to learn them is to guess the meaning of each word from the context. Then hover your computer mouse over the number beside each word to check its meaning and part of speech. These words are also listed in the footnote area at the end of each unit.
Here, you can use the flashcards below to review these words.
- Modals are helping verbs (also called auxiliary verbs). They must be used with a main verb to serve as the complete verb in a sentence: Modal + Main Verb = Complete Verb
- A modal is followed by the base form of the main verb.
- The same modals may mean differently in different contexts, and some others may share similar meanings but have differences in tone and level of emphasis.
- Some modals have their unique forms of past tense. Some of them look like the past tense but mean present or future.
- Do not use “mayn’t” and “mightn’t”.
- A good strategy is to understand modals is by learning each modal, its meaning, its time reference, and its form together as a “package”.
Media Attributions
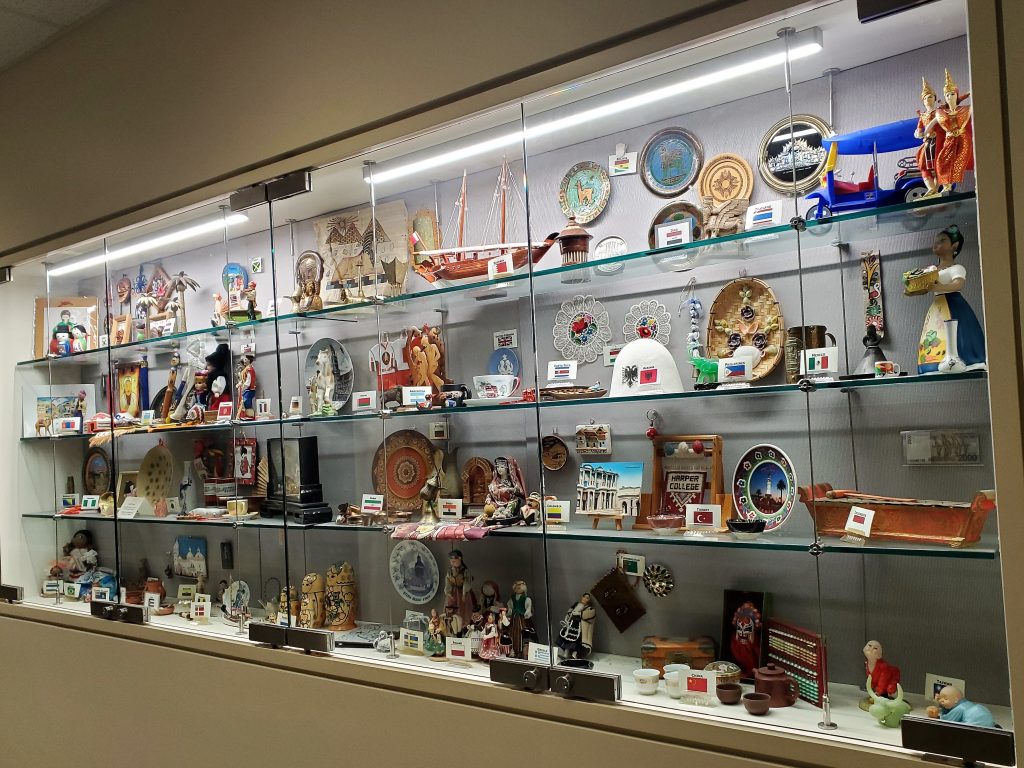
- showcase of culture artifacts at entrance of ESL Department at Harper College © Lin Cui is licensed under a CC0 (Creative Commons Zero) license
- two words “yes” and “no” with “yes” crossed out © Photo by cottonbro from Pexels
- a plate of food with a fork and a knife © medium:after_download_modal.copy_text.photo: https://www.pexels.com/photo/boiled-potatoes-with-salad-and-meat-rissole-4210862/
- A 19th-century illustrated Sanskrit manuscript from the Bhagavad Gita, composed c. 400 BCE – 200 BCE. © Unknown artist is licensed under a Public Domain license
- three Mongolia gers © Photo by Audrius Sutkus on Unsplash
- a dog balancing a ball © Photo by RODNAE Productions from Pexels
- four girls in school uniform doing hand signs © Photo by 周 康 from Pexels
- sunglasses on sand © Photo by Ylanite Koppens from Pexels
- a pen writing in a notebook © Photo by Aaron Burden on Unsplash
- a page in a dictionary © Pixabay
- gesture: noun, a movement of hands, arms, or another part of the body to express an idea or emotion ↵
- utensil: noun, a dining tool such as a spoon or a fork ↵
- etiquette: noun, a rule or tradition for proper social behavior ↵
- communal: adjective, used or shared by everyone in the group ↵
- marrow: noun, the soft, fatty part inside a bone ↵
- in isolation: prepositional phrase, separately, apart from each other ↵
- prohibition: noun, things that are not allowed ↵
- improper: adjective, not appropriate, not right ↵
- intimacy: noun, a very close, loving relationship ↵
- reflect: verb, show, represent ↵
- debate: noun, an argument ↵
- taboo: noun, an unacceptable word or behavior especially in a group setting ↵
Building Academic Writing Skills Copyright © 2022 by Cui, Lin is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial-ShareAlike 4.0 International License , except where otherwise noted.
You are using an outdated browser. Please upgrade your browser or activate Google Chrome Frame to improve your experience.
English Modal Verbs: What Are Modal Verbs and When Are They Used?
Everybody can use a little help now and then!
That goes for English verbs , too.
Sometimes, one verb alone just won’t cut it.
A modal verb can help the main verb do its job.
Modal verbs add more meaning to your sentences and let you express more complex ideas.
But what are modal verbs? How do you use them?
In this post, I’ll introduce you to the most important English modal verbs. I’ll show you how they work and how to use them correctly.
What Are Modal Verbs?
When do we use english modal verbs, all of the english modal verbs, how to use modal verbs in business english, where to practice modal verbs, and one more thing....
Download: This blog post is available as a convenient and portable PDF that you can take anywhere. Click here to get a copy. (Download)
Modal verbs are a type of “auxiliary verb,” also called a “helping verb” as we hinted above. That means they work alongside other verbs to give your sentence a new meaning .
For example, they can change the tense of your main verb, or indicate the possibility, permission or necessity for something to happen.
Common English modal verbs are:
Modal verbs are used very frequently in English, in a variety of contexts. Here are some of the main things modal verbs can be used to express:
- Possibility
- Suggestions
- Probability
Modal verbs are also often used to ask questions, especially Wh questions .
Once you understand how modal verbs work, it’ll help you speak English conversationally and in an academic setting .
One of the most common uses for this modal verb is to express ability . In this case, can is another way of saying “be able to.”
I can play piano.
This also works if you’re asking a question. To ask about someone’s ability to do something, typically you would say: Can you _____?
Can you speak English?
In a similar way, can is also used sometimes as a way to offer help or to ask for permission .
I can watch your dog while you’re on vacation.
Can you please pass the butter?
You’ll also often hear this modal verb used to express the possibility of something happening.
Houses can flood in this region during rainstorms.
Could expresses the past tense of can . Use it to express ability, but when talking about the past.
I could understand German when I was a kid.
Could you hear the birds chirping yesterday morning?
Could is sometimes used to express possibility, similar to can . However, unlike can , it’s used for less concrete possibilities and suggestions.
We could go to the park or we could go to the mall.
Will is most commonly used to put an English sentence in the future tense . It indicates that something’s going to happen in the future.
I will wash my plates after I finish eating.
They will visit their grandmom next month.
In question form, will is used to ask if something’s going to happen in the future.
Will there be a storm tomorrow?
Will we have a quiz in English class?
Would often talks about a habitual action in the past . That means an action repeated more than once, often by routine.
When I was a kid I would play with dolls every day.
Would can also show a willingness to do something in the future, often as part of the phrase “would like to…”
She would like to come to the party.
Would is used in a question to ask someone to do something. In this way, it’s similar to can —however, using would sounds more polite .
Would you please close the door?
Another very common usage of would is in conditionals —showing that something depends on something else. You may recognize the sentence structure would … if , as in the examples below:
She would go to the mall if you asked her.
He would become fluent in English if he practiced more often.
Finally, would often pairs up with the verb wish to express a desire .
I wish you would stop tapping your pencil.
You’ll often hear should used to as a way to give or ask for advice or an opinion .
You should do your homework.
The governor should visit our neighborhood.
Should I meet you at your apartment?
In a similar way, it can be used to describe something necessary but perhaps not wanted .
She should comb her hair but she doesn’t want to.
Should is also used to show an expectation .
He should be back by 10 p.m.
The mall should be empty at this time of night.
May is another modal verb that’s similar to can , but more formal and polite. It’s used to express or ask for permission , and is often considered the most polite way to do so .
May I sit beside you?
You may pour yourself a cup of tea.
May is also often used to describe a possibility .
We may go downtown tonight.
Like may , might can present a possibility . It’s not uncommon to hear may and might used interchangeably in this context, although may is slightly more formal.
He might get the job at the factory.
Might can also be used to suggest something . Within the phrase “might as well,” it indicates that there isn’t a good alternative.
I might as well go home since there’s no one else here.
Must is a way of saying “have to” or “need to,” though it’s more formal than either of those.
You must finish your homework by Wednesday.
Must also expresses a strong suggestion .
You must see the Louvre while you’re in Paris!
Must can also be used as a guess , though only if you think that your guess is correct or if you have evidence to back up your guess.
He must be smart because he studied engineering.
Shall is a good modal verb to recognize, but it’s rarely used in everyday language because it feels so formal and polite to native English speakers. Its use is similar to will . You may see it most often in literature from past eras .
I shall call your mother if you misbehave.
We shall arrive at 5:00.
Now we’ll cover some useful modal verb phrases you can use in different business situations.
Arranging a Meeting
Of course, there are many business situations where you might need to arrange a meeting. Modal verbs will be invaluable in setting up these meetings politely and efficiently.
Could we meet at _____?
I can meet at _____. / I can’t meet at _____.
Should I reserve the conference room?
Might we discuss it over lunch?
The meeting should take about 30 minutes.
Conducting an Online Meeting
In today’s business world, online meetings, video calls or conference calls are very common. If you work for a foreign company, it’s likely that you’ll have to participate in an online meeting at some point.
Modal verbs will help you keep the meeting on track in a clear and formal way.
Could you please mute your microphone when you’re not speaking?
Can everyone hear/see me?
Before we begin, we should each introduce ourselves.
Giving a Presentation
Giving presentations in any language can be nerve-wracking, but it can be especially overwhelming if you have to give a presentation in English. Fortunately, there are several modal verb phrases you can learn in business English to help you give your best presentation.
Might/may I have your attention, please?
Could you please save your questions until the end?
Today, I would like to discuss…
In conclusion, we must find a way to decrease costs/to increase profits/to find our niche/etc.
Speaking to an Employee as a Manager
If you’re a manager, one of the most common relationships you’ll have to navigate in the business world is between you and your employees. Here are some modal phrases that can help you speak with your employees in a respectful, yet commanding manner.
When can you give me the numbers from this quarter?
When will you be finished with the project?
Could you email me a detailed update?
We should plan to move forward with the merger.
Speaking to a Manager as an Employee
When you’re an employee at a company, you’ll most likely need to report to a manager or some other type of superior . It’s important to speak with respect and confidence when communicating with your boss. Here are some types of modal verb phrases that might be useful.
Could you please give me your thoughts on…?
I will finish _____ by _____.
I can find time for theses tasks today.
I would welcome your feedback on…
Speaking to Your Colleagues
Another important relationship in the workplace is the relationship between you and your colleagues. When you’re speaking with employees of a company that are at your same level, it’s nice to be able to talk both about business and more casually. Here are some modal phrases that you might try.
I might attend the conference. What about you?
I could use a day off. What about you?
Can/could I give you some advice?
Can/could I ask you a favor?
Speaking with a Client or Customer
Speaking with a client or customer is an important part of many jobs. It’s important to speak clearly, confidently and politely with them. If you often work directly with clients and customers, you may want to add some of these general business modal verb phrases to your vocabulary.
We would like to set up a face-to-face meeting.
May I offer you …?
It would be my pleasure to…
I might be able to…
Would you like to renew your account/subscription?
Could you give us a list of your requirements?
Taking a Phone Call
No matter what department you work in, making and receiving phone calls is probably a daily occurrence. It’s important to be able to successfully engage in a phone conversation at work . Here are some standard modal verb phrases you can use the next time your desk phone rings.
Could I ask who’s calling, please?
How may I help you?
Can I take a message?
Should I call back later?
Could you repeat that?
Hiring an Employee
One of the most common business interactions is hiring new employees.
Sometimes it can be challenging to interview potential employees, especially if you’re speaking in a second language such as English. Here are some useful phrases you’ll need during the hiring process.
Can/could you tell me more about your work experience?
You must arrive on time for the interview.
You should submit three references with your application.
As with many English grammar concepts, the trick to learning modal verbs is to practice them as much as you can!
- Ginger Software has some helpful exercises where you’ll choose the correct modal verb to put in a sentence .
- Mad Libs is a popular English word game that’ll expose you to modal verbs among many other types of English vocabulary.
- Journaling is a great technique to practice your English while incorporating modal verbs. Write about your plans for the upcoming day or week, like what you will do, what you should do, etc.
- FluentU is a language learning platform with a curated library of English videos.
This should help you express a range of ideas in English more fluently. Don’t forget to keep practicing!
If you like learning English through movies and online media, you should also check out FluentU. FluentU lets you learn English from popular talk shows, catchy music videos and funny commercials , as you can see here:
If you want to watch it, the FluentU app has probably got it.
The FluentU app and website makes it really easy to watch English videos. There are captions that are interactive. That means you can tap on any word to see an image, definition, and useful examples.
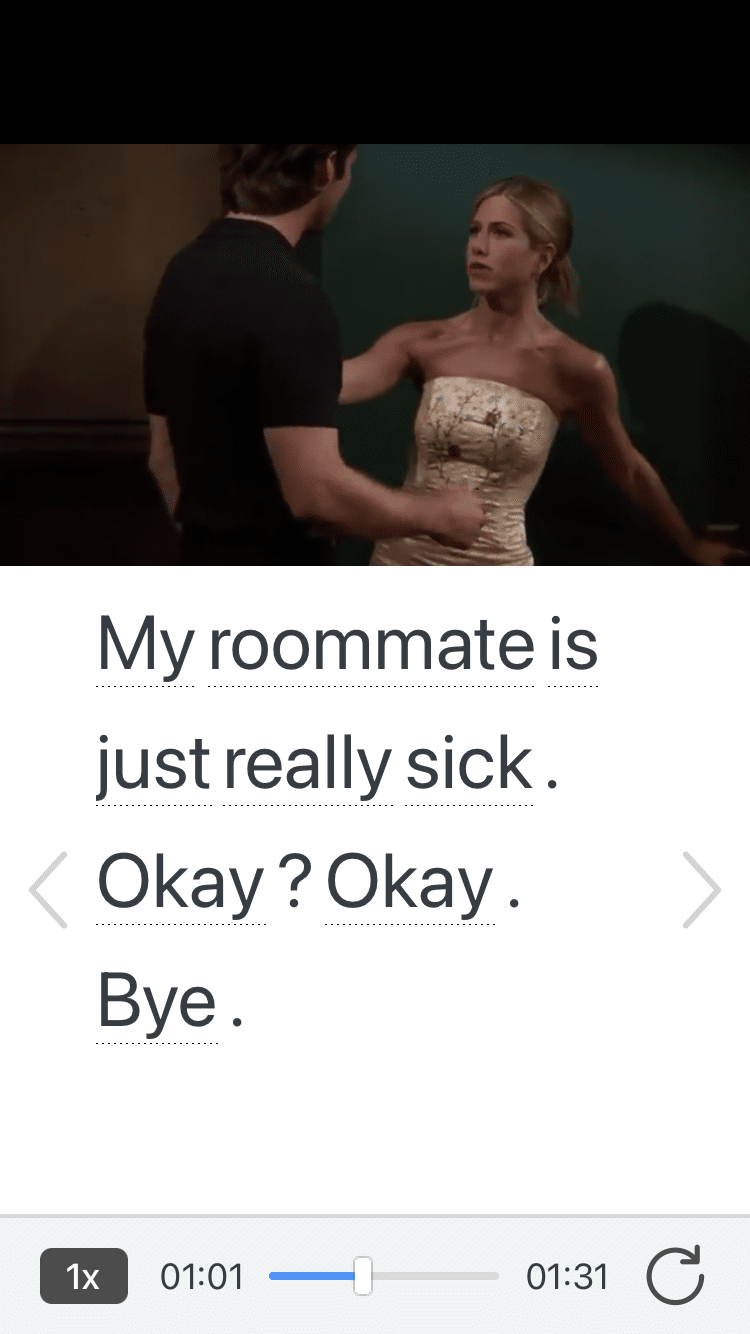
FluentU lets you learn engaging content with world famous celebrities.
For example, when you tap on the word "searching," you see this:
FluentU lets you tap to look up any word.
Learn all the vocabulary in any video with quizzes. Swipe left or right to see more examples for the word you’re learning.
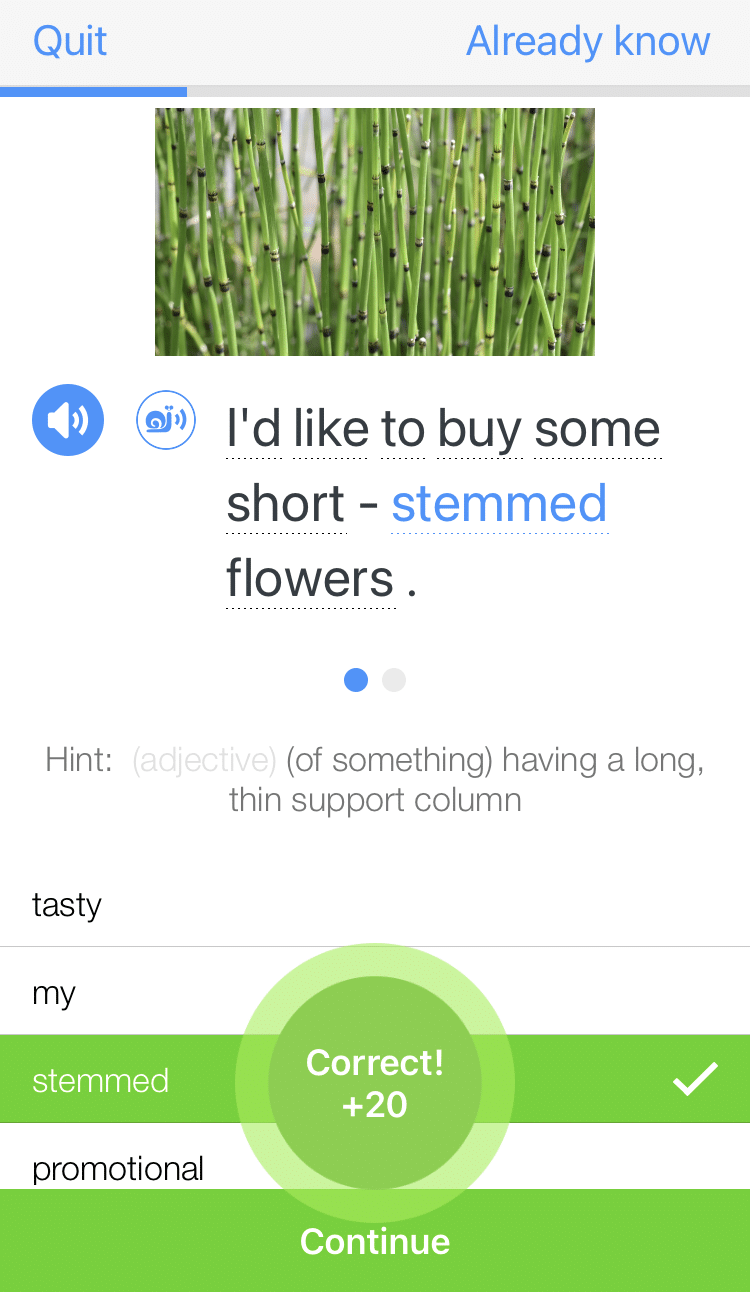
FluentU helps you learn fast with useful questions and multiple examples. Learn more.
The best part? FluentU remembers the vocabulary that you’re learning. It gives you extra practice with difficult words—and reminds you when it’s time to review what you’ve learned. You have a truly personalized experience.
Start using the FluentU website on your computer or tablet or, better yet, download the FluentU app from the iTunes or Google Play store. Click here to take advantage of our current sale! (Expires at the end of this month.)
Enter your e-mail address to get your free PDF!
We hate SPAM and promise to keep your email address safe


Want to create or adapt books like this? Learn more about how Pressbooks supports open publishing practices.
5.6 Modal Auxiliaries
Learning objectives.
- Define and identify modal auxiliaries.
- Learn how and when to use modal auxiliaries.
We all need to express our moods and emotions, both in writing and in our everyday life. We do this by using modal auxiliaries .
Modal Auxiliaries
Modal auxiliaries are a type of helping verb that are used only with a main verb to help express its mood.
The following is the basic formula for using a modal auxiliary:
There are ten main modal auxiliaries in English.
Table 5.11 Modal Auxiliaries
Use the following format to form a yes-no question with a modal auxiliary:
Be aware of these four common errors when using modal auxiliaries:
Using an infinitive instead of a base verb after a modal
Incorrect: I can to move this heavy table.
Correct: I can move this heavy table.
Using a gerund instead of an infinitive or a base verb after a modal
Incorrect: I could moving to the United States.
Correct: I could move to the United States.
Using two modals in a row
Incorrect: I should must renew my passport.
Correct: I must renew my passport.
Correct : I should renew my passport.
Leaving out a modal
Incorrect: I renew my passport.
Edit the following paragraph by correcting the common modal auxiliary errors.
Modals and Present Perfect Verbs
In the previous section, we defined present perfect verb tense as describing a continuing situation or something that has just happened.
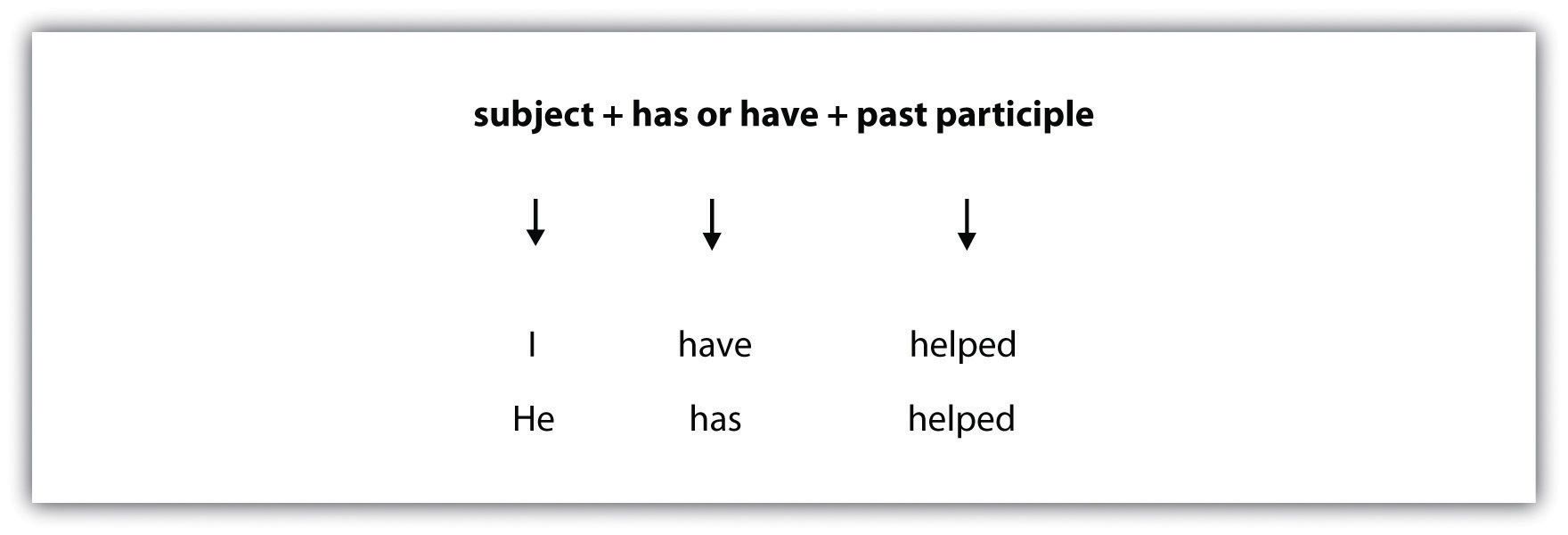
Remember, when a sentence contains a modal auxiliary before the verb, the helping verb is always have .
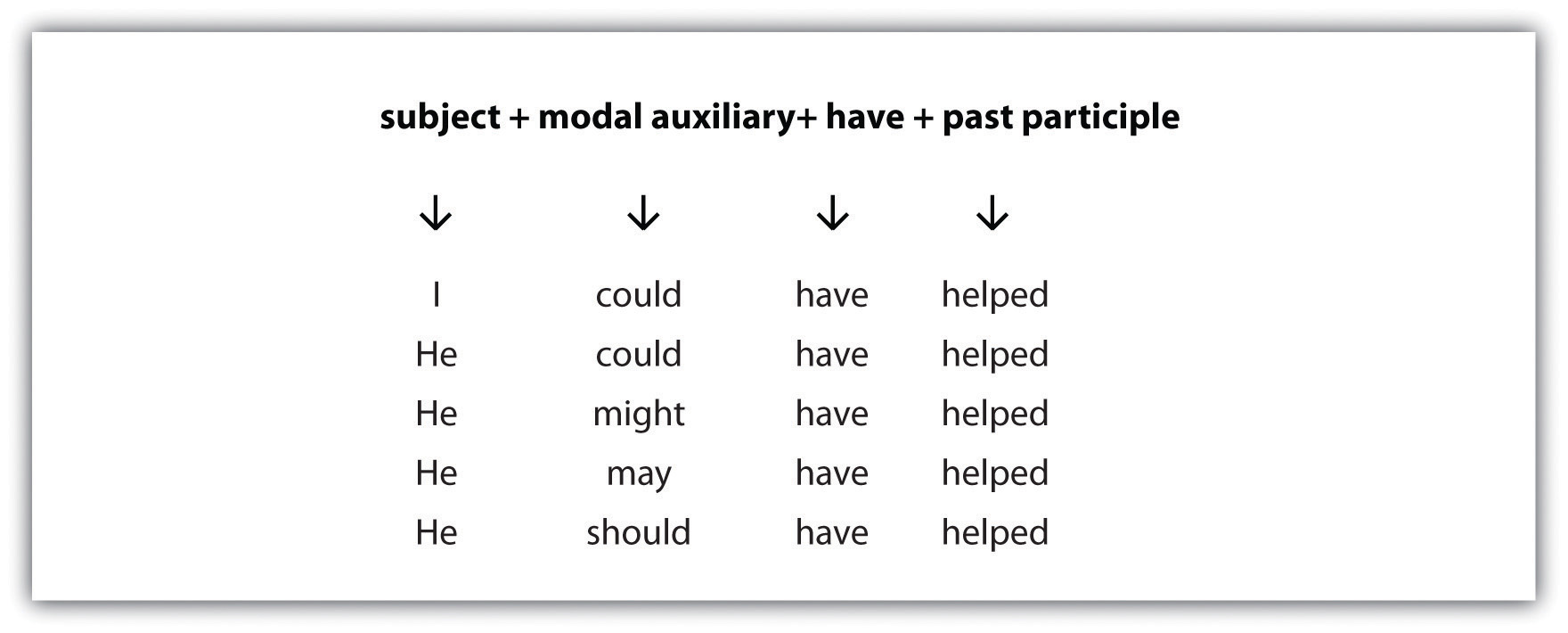
Be aware of the following common errors when using modal auxiliaries in the present perfect tense:
Using had instead of have
Incorrect: Jamie would had attended the party, but he was sick.
Correct: Jamie would have attended the party, but he was sick.
Leaving out have
Incorrect: Jamie would attended the party, but he was sick.
On a separate sheet of paper, complete the following sentences by changing the given verb form to a modal auxiliary in present perfect tense.
- The man ________ (laugh).
- The frogs ________ (croak).
- My writing teacher ________ (smile).
- The audience ________ (cheer) all night.
- My best friend ________ (giggled).
Key Takeaways
The basic formula for using a modal auxiliary is
- There are ten main modal auxiliaries in English: can , could , may , might , shall , should , will , would , must , and ought to .
- The four common types of errors when using modals include the following: using an infinitive instead of a base verb after a modal, using a gerund instead of an infinitive or a base verb after a modal, using two modals in a row, and leaving out a modal.
- In the present perfect tense, when a sentence has a modal auxiliary before the verb, the helping verb is always have .
- The two common errors when using modals in the present perfect tense include using had instead of have and leaving out have .
Writing Application
On a separate sheet of paper, write ten original sentences using modal auxiliaries.
Writing for Success Copyright © 2015 by University of Minnesota is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial-ShareAlike 4.0 International License , except where otherwise noted.
- A Beginner’s Guide to IELTS
- Common Grammar Mistakes [for IELTS Writing Candidates]
Writing Correction Service
- Free IELTS Resources
- Practice Speaking Test
Select Page
A Complete Guide to Modal Verbs
Posted by David S. Wills | Sep 22, 2023 | Grammar | 0
Have you ever wondered how to talk about possibility, obligation, or ability in English? If so, welcome to the world of modal verbs! Modal verbs are incredibly versatile and essential for expressing various tones, moods, and attitudes in English. In this guide, we will explore what modal verbs are, delve into their usage, and examine some common rules and examples.
Table of Contents
What are modal verbs, types of modal verbs, rules for using modal verbs, common mistakes.
Modal verbs are auxiliary, or “helping,” verbs that modify the main verb in a sentence to express possibility, ability, necessity, or other conditions. These include words like “can,” “could,” “will,” “would,” “shall,” “should,” “may,” “might,” and “must.”
- This shows ability.
- This is a suggestion.
Additional Examples:
- Can : She can play the piano well.
- Could : When she was younger, she could climb trees easily.
Possibility and Speculation
- May : It may rain tomorrow.
- Might : I might visit my grandparents this weekend.
- Can : Can I use your phone?
- May : May I come in?
Obligation and Necessity
- Must : You must report to the office immediately.
- Have to : I have to pick up my kids from school.
Prohibition
- Cannot/Can’t : You can’t park here.
- Mustn’t : You mustn’t smoke in this area.
Offers and Invitations
- Will : Will you have some coffee?
- Would : Would you like to join us for dinner?
Suggestions
- Shall : Shall we go for a walk?
- Should : We should take a break.
- Could : Could you please pass the salt?
- Would : Would you mind helping me with this?
Future Probability
- Will : She will probably come to the party.
- Shall : They shall succeed with enough effort.
Past Probability
- Would have : She would have succeeded if she had tried.
- Could have : He could have won the race but decided to stop and help an injured runner
These examples showcase the various contexts and conditions in which modal verbs are often used. They allow for a nuanced expression of mood, probability, ability, necessity, and more. By understanding how to use them appropriately, you can convey your ideas and attitudes much more clearly and effectively. Remember that accuracy is very important!
Possibility
- Can : Can you finish the project by tomorrow?
- Might : He might come to the party later.
- Can : Maria can speak four languages.
- Could : I could run fast when I was young.
- Must : We must complete the assignment.
- Have to : They have to take the medicine.
Request and Offers
- Will : Will you marry me?
- Would : Would you like some tea?
- May : You may find the book interesting.
- Could : They could arrive late due to traffic.
- Will be able to : She will be able to finish the project by next week.
- Would be able to : If she had more time, she would be able to complete it sooner.
- Should : You should take an umbrella; it looks like it’ll rain.
- Ought to : They ought to apologise for their behaviour.
- Can : Can you help me with my homework?
- Shall : Shall I open the window for you?
These additional examples should provide a broader understanding of the different ways modal verbs can be employed for various purposes. Whether you’re indicating possibility, showing ability, emphasising necessity, or making requests and offers, modal verbs are your go-to tool for nuanced communication.
- No Conjugation : Modal verbs do not change form based on the subject.
- Incorrect: She cans swim.
- Correct: She can swim.
- Incorrect : He wills go to the market.
- Correct : He will go to the market.
- Incorrect : They musts complete the project by tomorrow.
- Correct : They must complete the project by tomorrow.
- Incorrect : She coulds read when she was four.
- Correct : She could read when she was four.
- Incorrect : We cans see the mountains from here.
- Correct : We can see the mountains from here.
As you can see, the modal verb stays the same form irrespective of the subject, thus making it simpler than regular verbs, which often require conjugation based on the subject. (Learn more in this article on subject-verb agreement .) Understanding this rule is essential as it simplifies the process of constructing sentences.
- Double Modals Are Rare : Using two modal verbs together is generally avoided.
- Incorrect: She might can go.
- Correct: She might be able to go.
- Incorrect : They should must complete the project.
- Correct : They should complete the project. / They must complete the project.
- Incorrect : He will can join us later.
- Correct : He will be able to join us later.
- Incorrect : She may should attend the meeting.
- Correct : She may need to attend the meeting. / She should attend the meeting.
- Incorrect : We could will win the game.
- Correct : We could win the game. / We will probably win the game.
- Incorrect : I would can help you with that.
- Correct : I would be able to help you with that.
By avoiding double modals, the sentences remain clearer and easier to understand. If you feel the need to use two modal-like ideas, consider replacing one with an equivalent phrase, like “be able to,” “have to,” or “need to,” among others. This will help you maintain the clarity and grammatical integrity of your sentences.
- Always Use Base Form : Always use the base form of the main verb after a modal.
- Incorrect: He must to go.
- Correct: He must go.
- Incorrect : She can runs fast.
- Correct : She can run fast.
- Incorrect : They should eats healthily.
- Correct : They should eat healthily.
- Incorrect : We will sees you tomorrow.
- Correct : We will see you tomorrow.
- Incorrect : He might goes there.
- Correct : He might go there.
- Incorrect : She would likes some coffee.
- Correct : She would like some coffee.
As shown, the main verb that follows a modal should always be in its base form. This is crucial for constructing grammatically correct sentences. Ensuring you follow this rule will make your English sound more natural and accurate. It will also help you to get a better score for Grammatical Range and Accuracy .
Confusing “Should” and “Must”
- You should eat more fruits.
- You must obey the law.
“Should” for Advice or Recommendation
- Here, “should” offers a suggestion for maintaining good health.
- In this example, “should” advises more frequent contact with parents.
- “Should” here recommends contemplating alternative approaches.
- This is a suggestion aimed at a better environmental future.
“Must” for Stronger Necessity or Obligation
- “Must” indicates a firm deadline that is non-negotiable.
- Here, “must” emphasises the crucial nature of taking medication for health.
- The necessity of being punctual for the meeting is stressed by using “must.”
- This statement indicates an urgent need to act for environmental reasons.
As you can see, “should” is less forceful and is generally used for giving advice or making recommendations. In contrast, “must” implies a stronger sense of obligation or necessity. Choosing the appropriate modal verb can greatly influence the tone and meaning of your sentences.
Confusing “would” and “could”
These two modals are often confused by English learners. This is understandable because they can have slightly similar meanings. Both can be used in polite requests and both can appear in conditionals .
However, the main difference is that “could” shows possibility and “would” shows intention. For example:
- This shows the intention to do something.
- This shows the possibility of being able to do it.
Confusing “can” and “would
These two modals are often confused. Again, it comes down to their basic function: “can” shows the ability to do something. Meanwhile, “would” has a range of uses as we can see above.
Here’s a visual lesson that I made for my social media followers:
Misplacing the Modal Verb
Sometimes, beginners struggle with placing a modal verb in a sentence.
- Incorrect: He swim can.
- Correct: He can swim.
- Incorrect: She drive should carefully.
- Here, “should” should be placed before the main verb “drive” to offer advice about driving.
- Incorrect: They must go will to college.
- “Must” should directly precede the main verb “go” to express necessity.
- Incorrect: You sing can well.
- The modal “can” should come before the main verb “sing” to indicate ability.
- Incorrect: He soon will arrive.
- “Will” should be placed right before “arrive” to denote future action.
- Incorrect: We may late be.
- The modal “may” should directly precede the main verb “be” to express possibility.
As shown, misplacing the modal verb can cause confusion and make the sentence grammatically incorrect. Ensure that the modal verb is placed right before the main verb to maintain the intended meaning and grammatical structure of the sentence.
In summary, understanding modal verbs is essential for mastering the English language. By knowing how to use them correctly, you can express a range of ideas—from possibility to obligation—clearly and efficiently.
Remember, the key is practice. The more you use them, the more natural they will become.
About The Author
David S. Wills
David S. Wills is the author of Scientologist! William S. Burroughs and the 'Weird Cult' and the founder/editor of Beatdom literary journal. He lives and works in rural Cambodia and loves to travel. He has worked as an IELTS tutor since 2010, has completed both TEFL and CELTA courses, and has a certificate from Cambridge for Teaching Writing. David has worked in many different countries, and for several years designed a writing course for the University of Worcester. In 2018, he wrote the popular IELTS handbook, Grammar for IELTS Writing and he has since written two other books about IELTS. His other IELTS website is called IELTS Teaching.
Related Posts
Present Simple vs Present Perfect
October 20, 2023
How to Use Pronouns
September 15, 2023
Less vs Fewer
October 9, 2023
Understanding Question Word Order in English Grammar
November 13, 2023
Leave a reply Cancel reply
Your email address will not be published. Required fields are marked *
This site uses Akismet to reduce spam. Learn how your comment data is processed .
Download my IELTS Books
Recent Posts
- Past Simple vs Past Perfect
- Complex Sentences
- How to Score Band 9 [Video Lesson]
- Taxing Fast Food: Model IELTS Essay
- Airport Vocabulary
Recent Comments
- David S. Wills on Writing Correction Service
- James Oluwasegun on Writing Correction Service
- Daisey Lachut on IELTS Discussion Essays [Discuss Both Views/Sides]
- David S. Wills on Describe a Historical Period
- Siavash on Describe a Historical Period
- Lesson Plans
- Model Essays
- TED Video Lessons
- Weekly Roundup
- English Grammar

Modal verbs
Level: beginner
The modal verbs are:
We use modals to show if we believe something is certain, possible or impossible :
My keys must be in the car. It might rain tomorrow. That can't be Peter's coat. It's too small.
We also use them to do things like talk about ability , ask permission , and make requests and offers :
I can't swim. May I ask a question? Could I have some tea, please? Would you like some help?
MultipleChoice_MTYzNDI=
Hello Team. Could you please help me? Does "had to" mean that the action happened or might not? For example, is the following sentence correct? Some teachers say that it is not correct while others say it is OK, what do you say? - I had to call my friend but I forgot. Thank you.
- Log in or register to post comments
Hello Ahmed Imam,
It is possible to say this. Had to does not necessarily imply that the obligation/requirement was met. For example, it's fine to say this:
I had to get there by 8.00 to go to the meeting, but unfortunately the train was delayed.
The LearnEnglish Team
Hello, "Had to" as the positive and "didn't have to" as the negative form are in the past. And therefore what I gather from your sentence is = you were supposed to call your friend but you didn't (Now, it's too late). Bye :)
I had to call my friend but i forgot this sentence is fine. But when ever you talk about the past, you always need two actions and a time scale. Two actions is what you have but no time scale. I had to call my friend(when?) yesterday or last week? I had to call my friend yesterday but I completely forgot. Giving the sentence a little more emphasis by using an adverb (completely).
This sentence is right.I see no problem with this.
"i had to call my friend" this sentence alone can not express whether you called your friend or not but it shows that you were in urgent need or situation.
but when you added "but i forgot" then you are assuring that you didn't call your friend.
Instead of but i forgot you could have also used ,"i had forgotten".
I was reading about this online recently and someone said that their dictionary from 1982 shows the verb "can" as an auxiliary intransitive verb, which was fully congugated and the past and conditional tenses were "could" and the conditional past was "could have". Please could you tell me when the fully conjugated verb became obsolete and was replaced with the two modal verbs "can" and "could" and also why this happened? Thank you for your help!
Hi helenaw,
It's an interesting question, but one that is outside what we do on this site, which is focused on learning English as a foreign/second/additional language. For what it's worth, I'm not sure we can say "can" has ever been fully conjugated in modern English, as to my knowledge it's never had a past participle. But users of sites such as Stack Exchange may be able to shed more light on this. I hope you can find answers there to your interesting question!
LearnEnglish team
I have always wondered why WILL, SHALL and WOULD are considered modal verbs as they don't have meaning and they are closer to the auxiliaries DO; DOES; DID
Hi MRamos2022,
It's an interesting question. A modal verb, as defined by the Cambridge Dictionary , is "a verb used with another verb to express an idea such as possibility that is not expressed by the main verb". Will , shall and would fit this description - they are all used with another verb and cannot be used alone, and they express some kind of meaning or attitude that modifies the main verb (broadly speaking, will and shall are about willingness or beliefs about the future, and would is about unreal and hypothetical actions). For example, I like coffee is different in meaning from I would like a coffee , and I don't agree is not the same as I wouldn't agree (using "would" makes it a hypothetical disagreement, thus less direct and possibly more polite).
Dear respected team, Even superman wouldn't be able to defeat him. What does "would" refer to? Does it refer to possibility or point of view of the speaker? Thank you
Hi Hosseinpour,
"Would" indicates an unreal situation. It is unreal either because Superman is a fictional character and doesn't exist in the real world, or (if this sentence comes from a story in which Superman does exist) because in the speaker's view, Superman and the other person have not yet had a fight and are not really going to fight.
Thank you sir for the help and time. Thank you
This is very helpful! Thanks
Hello, I have more questions about texts from the 19th century. The text is "Mrs Hutchinson" by Nathaniel Hawthorne. My first question is about the meaning of a question appears in the subjunctive mode in the text. The author writes, "Is the prize worth her [woman's] having if she win it [fame]?" I understand "if she win it" to mean "should she win it", which in turn means that the author has doubts about "her winning it". Therefore, is it correct to conclude that Hawthorne in using the subjunctive mode is expressing a disparaging view about a woman's potential. Isn't he saying "I don't think women can win it". The other question is from the same document, but comes from the opening statement. "The character of this female suggests a train of thoughts which will form as natural an introduction to her story as most of the prefaces to Gay's Fables or the tales of Prior, besides that the general soundness of the moral may excuse any want to present applicability". I am not sure what the author means by the second half of this sentence (after "besides"). Does he mean "in addition to that the validity of the moral point we gather from Hutchinson's character allows for an introduction here"? I interpreted "want for" to mean "preference for", not as "lack of". I am not sure how "lack of" can work in this case. I hope that my questions don't bore you. thanks
Hello Ahmed,
I should start off by saying that I'm not familiar with this text or the context in which the sentences you ask about occur. So please know that my answers might well be different if I were.
Re: your first question, I think that 'should she win it' is a good gloss of 'if she win it'. You could also say 'if she wins it'. I'd have to have a closer look at the text (or be more familiar with 19th-century American literature than I am) to say for sure, but I don't think the subjunctive here indicates any extra meaning. In other words, from this sentence alone, I don't think one can conclude that Hawthorne has doubts about this woman's (or women's?) ability to win fame. I think he's simply saying that she/they might win it, or she/they might not. And really what he seems to be doing isn't so much doubting whether this woman/women can win it, but whether winning fame is something worth winning.
Re: your second question, I'm afraid I'd need to know more about what's Hawthorne's talking about (the woman, her story, her train of thoughts, the moral, etc.) to make any useful sense of this sentence. Perhaps you have a teacher you could ask about this?
All the best, Kirk LearnEnglish team
Hell, In reading 19th century prose, I have often come across a strange usage of "would". Take for instance the following sentence: "Even on a small scale, how often will it happen that the term best corresponding to a new world in the original will be one that in our language is already old and worn out, so that the translator, would he show the work's contribution to the development of the language, will be forced to introduce foreign content into the passage, deviating into the realm of imitation!" Am I right to think of "would he show" to mean "if he wants to show"? Also, under what subtopic in modals can I find more about this usage?
Hi Ahmed Nidal,
Yes, that's right. The meaning of "would" here is the desire to do something, and this meaning is rarely used today. The conditional meaning ("if") comes from the subject/modal inversion, rather than from "would".
It is meaning 2.8 on this Wiktionary page . I hope that helps.
Thank you Jonathan. Much appreciated. Ahmed
Hello Sir, "We may have to live with the coronavirus." 1. In this sentence 'have' is main verb or it is modal verb(have to) 2. Can we place two modal verbs (may & have to) together 3. Further, 'to' is attached to 'have'(have to) or it is attached to 'live'(to live)
Hello Mordhvaj,
The main verb in this sentence is 'live'.
'May' is a modal verb. 'Have to' is sometimes called a semi-modal verb in that it has some elements of modality but not others. The wikipedia page for modal verbs describes it thus:
...there are numerous other verbs that can be viewed as modal verbs insofar as they clearly express modality in the same way that the verbs in this list do, e.g. appear, have to, seem etc. In the strict sense, though, these other verbs do not qualify as modal verbs in English because they do not allow subject-auxiliary inversion, nor do they allow negation with not. Verbs such as be able to and be about to allow subject-auxiliary inversion and do not require do-support in negatives but these are rarely classified as modal verbs because they inflect and are a modal construction involving the verb to be which itself is not a modal verb. If, however, one defines modal verb entirely in terms of meaning contribution, then these other verbs would also be modals and so the list here would have to be greatly expanded.
https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Modal_verb
It is possible to use a modal verb before 'have to', but it is not possible to use 'have to' before a modal verb. Thus, 'we may have to...' is fine, but *'we have to may...'* is incorrect.
We describe the form as have to + verb rather than have + to verb . The 'to' is still included when the verb is omitted:
We need to leave for the party. Is it really important I go? Yes, you have to. No complaining!
Hello Sir, I feel honoured to have my question answered by you. Point by point you have cleared each and every doubt of mine. I have always been a big fan of your answers. It is almost a miracle to have one's answer 'succinct' and 'detailed' simultaneously; and you are a wizard who can do that miracle. Thanks🌹
Hello Mordhvaj,
It's nice of you to say so. We're a small team here but we try our best!
Hello, thanks for the grammar. I have a question in relation to adverbs of frequency, and modal verbs. These two sentences: They could never divide us. They never could divide us. Which one is grammatically correct? Also are there some situations you could use the second one, and it would be correct? Thanks.
Hi Howard Manzi,
Thanks for your question :) They are both grammatically correct. The typical position is as in sentence 1, between the modal verb and the main verb. Sentence 2 is grammatical too, but the position of "never" seems to make it more emphatic than in sentence 1. Somebody may say this if they really want to emphasise "never".
"Never" can also be emphasised by putting it as the first word in the sentence (this also needs an inversion of subject and modal verb): Never could they divide us .
I hope that helps.
Thanks. I appreciate it.
"May" has PERMISSION meaning also "Might" has?
I found this following question on this web page.
->I know you're busy, but MIGHT I ask you a quick question? (and right answer of meaning is PERMISSION)
I understood that "MIGHT" doesn't have PERMISSION meaning. So I am confused..
Hello Jiwon LEE,
As is explained on our 'may' and 'might' page , 'might' can be used to ask for permission in a very polite way.
This use is quite rare in ordinary speaking and many grammars don't even mention it. 'may' and 'can' are far more commonly used.
All the best, Kirk The LearnEnglish Team
Hi Jonathan, I would like to ask for your help and hope you're available to answer me this time.
If someone gives me a present, I might say :
(A) How could you have known it was my birthday today ?
[1] Does the use of "could have known" in this sentence express surprise about how he could know that today is my birthday ? Or [2] Is it a conditional sentence with the implied if clause that is not mentioned ? For example :
(B) How could you have known....if my mother had not told you ? (No surprise is conveyed here)
[3] If we can use this pattern to express surprise, can we say this sentence ?
(C) I don't know how the thief could have known the key code, but he did (= I'm surprised how he got to know the key code).
[4] To express surprise in examples (A) and (C), can we change "could have" to "can have" ?
I would really appreciate your explanation. Thank you.
Best regards,
Hello melvinthio,
(A) is grammatically correct, but in the situation you describe in [1], a more natural statement would be 'How did you know it was my birthday today?'. Both (A) and my suggestion could certainly express surprise, though they don't necessarily do so. Even if you thought the gift giver was giving you the present for a different reason, I still don't think they'd use a sentence with 'could have known' here.
Your analysis of (B) in [2] sounds correct to me, though I don't think the grammar tells us anything about surprise. It could express simple curiosity, though it certainly can also be used to express surprise.
Similar to (A), a more natural way of saying (C) is 'I don't know how the thief knew ...' (assuming we can see evidence of the thief knowing this), but (C) is also possible here. I'd understand it to express some degree of surprise, but I don't think it has anything to do with the grammar, but rather the situation.
I think the difference between the two situations is that in (A), we see the action with our own eyes -- we've seen the person giving the gift or somehow know it came from them. In contrast, in (C), we see the result of the thief's actions -- an open safe -- but haven't seen the thief open it. It also more possible for another person to discover our birthday than it is for a thief to open a safe (at least to my mind).
As for [4], no, 'could have' better expresses the idea of an unlikely possibility. Perhaps 'can have' would be possible in some unusual situations, but in most cases and certainly in the way I've imagined them now, it wouldn't work.
Hope this helps.
Hii, I am Manish. One of my teachers told me modal are ( be and Have ) Be has 3 forms BE =1. Is/am/ are 2. Was/ were 3. Been You are a teacher. I am a student. You were a child 10 years ago. I was a child too.
Have = possession I have a car.= I have got a car.
Was he right?
Hello Manish,
Modal verbs are verbs like should, can, could, might, will etc.
'Be' and 'have' are not modal verbs. They are normal verbs but can also be used as auxiliary verbs to form questions and other forms.
Base form - be ~ have
First form (present) - am/is/are ~ have/has
Second form (past) - was/were ~ had
Third form (past participle) - been ~ had
For possession, have and have got are alternatives.
You can read more about the verb 'be' on this page:
https://learnenglish.britishcouncil.org/grammar/english-grammar-reference/the-verb-be
Can I use articles with collective noun ? (a,an,the)
Yes, you can :) If you have any questions about it, you can post them on our Articles page.
Hi everyone, is the following sentence correct? I can English.
When can it be accepted? Thank you so much!
Hello mivu,
No, I'm afraid 'I can English' is not correct in any context I can think of.
It's possible to say 'I can' or 'I can do' in a short answer , but the direct object of the verb is omitted in short answers.
Hey there Well, every modal verb will be followed by another verb, which is missing in that statement. It might be the verb "to speak". I can SPEAK English.
Hello. I have a question. Why is WOULD considered a modal verb? As I understand, WOULD has no meaning as the other modals verbs. It has a function, which is to make the sentence conditional. And if it is considered, why the other auxiliaries are not? Thank you very much for your help.
Hello MRamos,
' would ' actually has a number of uses beyond its use in second conditional structures -- for example, it can be used to make polite requests, or to talk about frequent past events. In older styles of English, it was also used to express desires, though this is almost never heard these days.
In general, modal verbs add different kinds of meaning to a statement -- for example, certainty, possibility or obligation. I'd suggest having a look at our Modal verbs page, where you can see more on this, and you might also find the Cambridge Dictionary Grammar's page on Modal verbs and modality useful.
I couldn't have explained it better. Amazing!
Hello Mussorie,
There is no difference in meaning here. In this and similar constructions you can use either the object pronoun or the possessive adjective with the -ing form. Both are in common use and are acceptable but I think the form with the object pronoun ( me ) is more informal and less likely to be used in formal contexts.
You can read a brief discussion of the topic here:
https://english.stackexchange.com/questions/515247/my-ing-possessive-form-ing-vs-me-ing-object-form-ing
In both 1 and 2, you are reporting that the thing you imagined has been confirmed, but the verb form in 1 suggests that someone else was doubting your supposition.
In the other sentence, 'will have started' is used because the time reference point is the present time (6:00). We use 'would' to speak about the future from the perspective of the past, but the time reference point here is present. The beginning of the match in the past is suggested, but not stated.
All the best,
Hello Nevı,
No, I'm afraid that doesn't work. Normally the verb forms in reduced relative clauses replace non-modal verbs, usually in the present continuous, present simple or past simple.
Best wishes,
Hello Hemam,
'would' (and 'wouldn't') can be used to express unwillingness, in other words, the idea that someone or something doesn't want to do something. So in the first sentence, the idea is that the car didn't want to start. Most people don't actually believe that a car has desires, but sometimes when we feel we are unlucky, we speak this way to show the feeling of being unlucky. Other than this, these two sentences mean the same thing.
The sentence about Reddington could mean that we think he would never tell us this in any circumstance (here 'would' refers to hypothetical situations) or, if it's speaking about the past, it could mean that Redding refused to tell us. Which meaning it has depends on the context.
Online courses

Group and one-to-one classes with expert teachers.

Learn English in your own time, at your own pace.

One-to-one sessions focused on a personal plan.

Get the score you need with private and group classes.
- Cambridge Dictionary +Plus
Modal verbs and modality
Modality is about a speaker’s or a writer’s attitude towards the world. A speaker or writer can express certainty, possibility, willingness, obligation, necessity and ability by using modal words and expressions.
Speakers often have different opinions about the same thing.
These speakers are looking at the same thing.
Modal verbs
Here are the main verbs we use to express modal meanings:
Core modal verbs: can , could , may , might , will , shall , would , should , must
Semi-modals: dare, need , ought to , used to
Other verbs with modal meanings: have (got) to, be going to and be able to
Be going to : form
Have got to and have to
Modal words and expressions
There are a number of other words and expressions in English, apart from the main modal verbs, which also express modal meanings.
Here are some examples:
Modality: meanings and uses
Modality: other modal words and expressions
Be expressions ( be able to , be due to )

Word of the Day
pitch-perfect
Your browser doesn't support HTML5 audio
singing each musical note perfectly, at exactly the right pitch (= level)

Alike and analogous (Talking about similarities, Part 1)

Learn more with +Plus
- Recent and Recommended {{#preferredDictionaries}} {{name}} {{/preferredDictionaries}}
- Definitions Clear explanations of natural written and spoken English English Learner’s Dictionary Essential British English Essential American English
- Grammar and thesaurus Usage explanations of natural written and spoken English Grammar Thesaurus
- Pronunciation British and American pronunciations with audio English Pronunciation
- English–Chinese (Simplified) Chinese (Simplified)–English
- English–Chinese (Traditional) Chinese (Traditional)–English
- English–Dutch Dutch–English
- English–French French–English
- English–German German–English
- English–Indonesian Indonesian–English
- English–Italian Italian–English
- English–Japanese Japanese–English
- English–Norwegian Norwegian–English
- English–Polish Polish–English
- English–Portuguese Portuguese–English
- English–Spanish Spanish–English
- English–Swedish Swedish–English
- Dictionary +Plus Word Lists
Add ${headword} to one of your lists below, or create a new one.
{{message}}
Something went wrong.
There was a problem sending your report.

What is a modal verb in English? - Easy Learning Grammar
- to express different degrees of doubt and possibility about the action of the main verb.
- to express degrees of future possibility, ranging from the definite future, will , to the possible future, may , and the conditional future, could .
- to request or give permission for an action to take place.
- to make a prohibition, when used with a negative.
- to speculate.
- to express obligation and duty.
- to refer to typical behaviour.
- to add politeness to a request which might otherwise sound abrupt.
- to make conditional sentences.
- in reported speech.
Quick word challenge
Quiz Review
Score: 0 / 5

- All topics A-Z
- Grammar
- Vocabulary
- Speaking
- Reading
- Listening
- Writing
- Pronunciation
- Virtual Classroom
- Worksheets by season
- 600 Creative Writing Prompts
- Warmers, fillers & ice-breakers
- Coloring pages to print
- Flashcards
- Classroom management worksheets
- Emergency worksheets
- Revision worksheets
- Resources we recommend
- Copyright 2007-2021 пїЅ
- Submit a worksheet
- Mobile version
Modal Verbs: Useful Rules, List and Examples in English
Are you struggling to understand the concept of modal verbs? Look no further! In this article, we will dive into the basics of modal verbs and provide you with a clear understanding of their function in English grammar.
It is important to note that modal verbs have a unique set of rules that differ from regular verbs. For example, they do not use an “s” for the third person singular, and they make questions by inversion. It is also important to understand the different nuances of each modal verb and how they are used in context. So, let’s get started and explore the world of modal verbs together!

Definition of Modal Verbs
Modal verbs are a special class of auxiliary verbs that are used to modify the meaning of the main verb in a sentence. They are also known as modal auxiliary verbs or simply modals. Modal verbs are used to express different kinds of meanings such as possibility, ability, permission, necessity, and more.
Modal verbs are always used in combination with ordinary verbs and they change the meaning of the verb to something different from simple fact. They are commonly used in English and are an essential part of the language.
The following are some of the most common modal verbs in English:
Each of these modal verbs has a specific meaning and usage in English. For example, “can” is used to express ability, “may” is used to express possibility, and “must” is used to express necessity.
Modal verbs are also used to create different tenses in English. For example, “could” is used to create the past conditional tense, while “will” is used to create the future tense.
It is important to note that modal verbs do not have infinitive or participle forms. They are always used in their base form, and they do not take the -ing or -ed endings.
In summary, modal verbs are a special class of auxiliary verbs that are used to modify the meaning of the main verb in a sentence. They are used to express different kinds of meanings such as possibility, ability, permission, necessity, and more. Understanding the usage of modal verbs is essential for effective communication in English.
Types of Modal Verbs
Modal verbs are auxiliary verbs that express a range of meanings such as ability, permission, possibility, obligation, and advice. Here are the different types of modal verbs:
Modal verbs of ability express whether you are capable of doing something or not. The most common modal verbs of ability are “can” and “could.” Here are some examples:
- You can speak English fluently.
- I could run a marathon when I was younger.
Modal verbs of permission express whether you are allowed to do something or not. The most common modal verbs of permission are “may” and “can.” Here are some examples:
- May I leave early today?
- Can I borrow your car for the weekend?
Possibility
Modal verbs of possibility express the likelihood of something happening. The most common modal verbs of possibility are “may,” “might,” “could,” and “can.” Here are some examples:
- It may rain later today.
- The train might be delayed.
- She could be at home.
Modal verbs of obligation express whether you are required to do something or not. The most common modal verbs of obligation are “must” and “should.” Here are some examples:
- You must submit your report by Friday.
- You should apologize for your mistake.
Modal verbs of advice express recommendations or suggestions. The most common modal verbs of advice are “should” and “ought to.” Here are some examples:
- You should exercise regularly to stay healthy.
- You ought to try the new restaurant in town.
In summary, modal verbs are essential in expressing different meanings in English. Understanding the different types of modal verbs can help you communicate more effectively and accurately.
Modal Verbs: Rules & Examples
Learn how and when to use modal verbs in English with rules and example sentences.
1. To indicate that something is probable or possible, or not so.
For example:
- It is sunny today; it must be warm outside. = It is sunny today; it is probably warm outside.
- His mobile is not reachable; he may/might/could be travelling by metro. = His mobile is not reachable; it is possible that he is travelling by metro.
- This can’t be our bill. = It is not possible that this is our bill.
2. ‘Can’ and ‘could’ are used to refer to skills and abilities.
- He can cover a hundred metres in under ten seconds.
- My father could see perfectly before the age of fifty.
- I can’t ride a horse.
3. ‘Must’ is used to indicate that something is necessary or of extreme importance, and ‘should’ is used to suggest that something is advisable.
- You must do your homework.
- You mustn’t skip school.
- You should say sorry.
- You shouldn’t smoke.
4. ‘Can’, ‘could’ and ‘may’ are used to ask for, give and withhold permission.
- Can I try my hand at it?
- Could we disperse early today?
- You may not enter the premises.
5. ‘Will’ and ‘would’ are used to refer to habits and inclinations.
- When I was a child, I would often climb trees.
- I will never refuse you anything.
- He would never do such a thing.
Note : These verbs differ from ordinary verbs in 3 respects.
- When used with the third person singular (he, she), they don’t require the addition of an ‘s’.
- They can be used to form questions by inverting the structure of the sentence.
- They can be followed directly by the verb, without the use of ‘to’.
Usage of Modal Verbs
Modal verbs are an essential part of English grammar. They are used to express a variety of meanings such as ability, possibility, permission, and obligation. In this section, we will discuss the usage of modal verbs in statements, questions, and negative sentences.
In Statements
Modal verbs are often used in statements to express various meanings. Here are some examples:
- Ability: “I can speak French fluently.”
- Possibility: “It may rain tomorrow.”
- Permission: “You may leave the room now.”
- Obligation: “You must finish your homework before going out.”
Note that when using modal verbs in statements, the main verb is always in its base form (infinitive) without “to.”
In Questions
Modal verbs are also commonly used in questions to ask for permission, ability, or possibility. Here are some examples:
- Permission: “May I leave the room now?”
- Ability: “Can you swim?”
- Possibility: “Could it be true?”
In questions, the modal verb is usually placed at the beginning of the sentence.
In Negative Sentences
Modal verbs can also be used in negative sentences to express the absence of ability, permission, or obligation. Here are some examples:
- Ability: “I cannot speak French fluently.”
- Permission: “You may not leave the room now.”
- Obligation: “You must not forget to lock the door.”
In negative sentences, the word “not” is added after the modal verb.
It is important to note that some modal verbs have different meanings depending on the context. For example, “must” can express obligation, but it can also be used to express a strong recommendation or deduction. In addition, some modal verbs have more than one form, such as “may” and “might,” which can both be used to express possibility.
Overall, modal verbs are an important part of English grammar and are used in a variety of contexts. By understanding their usage in statements, questions, and negative sentences, you can improve your English communication skills.
Common Modal Verb Phrases
Modal verbs are often used with other verbs to create phrases that convey a specific meaning. Here are some common modal verb phrases and their meanings:
- Can’t help but – This phrase is used to express that you cannot stop yourself from doing something. For example, “I can’t help but smile when I see puppies.”
- Have to – This phrase is used to express obligation or necessity. For example, “I have to finish my homework before I can go out.”
- Need to – This phrase is used to express that something is necessary. For example, “I need to drink water after exercising.”
- Should have – This phrase is used to express regret about something that was not done in the past. For example, “I should have studied more for the test.”
- Would rather – This phrase is used to express a preference. For example, “I would rather stay at home than go to the party.”
- Must have – This phrase is used to express certainty about something that happened in the past. For example, “He must have left his phone at home.”
- Might as well – This phrase is used to suggest doing something because there is no reason not to. For example, “Since we have some extra time, we might as well go for a walk.”
Modal verb phrases can be very useful in expressing specific meanings and adding nuance to your language. It’s important to use them correctly and in the appropriate context.
Modal Verbs vs Auxiliary Verbs
When it comes to understanding the English language, it’s important to know the difference between modal verbs and auxiliary verbs. While both of these types of verbs are used to help the main verb in a sentence, there are some key differences between them.
Modal Verbs
Modal verbs, also known as modal auxiliary verbs, are a group of verbs that give additional information about the function of the main verb. They show possibility, intent, ability, or necessity. Modal verbs do not change their appearance, and they are used alongside the infinitive form of the main verb of a sentence.
Some common examples of modal verbs include:
Modal verbs are used to show if you believe something is certain, possible, or impossible. They can also be used to talk about ability, ask permission, and make requests and offers.
Auxiliary Verbs
Auxiliary verbs , also known as helping verbs, are used to help the main verb in a sentence. They change according to certain factors in the sentence, such as tense, person, and number.
Some common examples of auxiliary verbs include:
Auxiliary verbs can be used to form different tenses, such as the present perfect or past continuous. They can also be used to form questions and negatives.
In summary, the main difference between modal verbs and auxiliary verbs is that modal verbs do not change their appearance, while auxiliary verbs change according to certain factors in the sentence. Understanding the difference between these two types of verbs can help you to use them correctly in your writing and speaking.
Modal Verbs in Different Tenses
When it comes to tenses, modal verbs are quite unique. Unlike regular verbs, modal verbs do not change their form to indicate different tenses. They are used in their base form regardless of the time frame.
Modal verbs can refer to present and future time, but only some of them can refer to past time. Here is a table showing the modal verbs that can be used to refer to past time:
For example, “I could swim when I was younger” or “He would always help me with my homework.”
It’s important to note that when using modal verbs to refer to past time, the main verb in the sentence should be in the base form as well. For example, “I could have gone to the party, but I decided not to.”
In addition to the past time usage, here are some examples of how modal verbs can be used in different tenses:
- Present: “You should eat more vegetables.”
- Future: “We will have to leave early tomorrow.”
- Perfect: “He must have forgotten his phone at home.”
- Continuous: “They might be playing tennis right now.”
Overall, modal verbs are a versatile and useful tool in English grammar. By understanding how they can be used in different tenses, you can effectively communicate your intentions and convey meaning in your writing and speech.
Frequently Asked Questions
What are some examples of modal verbs in English?
Modal verbs are used to express ability, possibility, necessity, and permission. Some examples of modal verbs in English include can, may, must, shall, will, could, might, should, and would.
How many modal verbs are there in English?
There are nine modal verbs in English: can, may, must, shall, will, could, might, should, and would.
What is the definition of modal verbs and how are they used?
Modal verbs are auxiliary verbs that are used to express various meanings such as ability, possibility, necessity, and permission. They are followed by the base form of a verb and do not change their form based on the subject of the sentence. Modal verbs can also be used to make requests, give advice, and express opinions.
What is a good worksheet for practicing modal verbs?
There are many worksheets available online for practicing modal verbs. One good worksheet is the “Modal Verbs Practice” worksheet from Englishlinx.com. This worksheet includes exercises for practicing the different uses of modal verbs in English.
What are some common sentences using modal verbs?
Some common sentences using modal verbs include:
- I can swim.
- You should study for the test.
- He may arrive late.
- We must finish the project by Friday.
- They could come to the party.
How do you pronounce modal verbs correctly?
Modal verbs are pronounced with stress on the first syllable. For example, can is pronounced as “kan,” may is pronounced as “may,” and must is pronounced as “must.”
Related Posts:

thank you so much
Its amazing
Thank you. This would help me with my students.
- No category
English Quarter 2 Module 4 Argumentative Texts Modal Verbs and Modal Adverbs (1)

Related documents

Study collections
- My collection
Add this document to collection(s)
You can add this document to your study collection(s)
Add this document to saved
You can add this document to your saved list
Suggest us how to improve StudyLib
(For complaints, use another form )
Input it if you want to receive answer
404 Not found

- The English Farm's blog
Grammar essentials: Introduction to modals
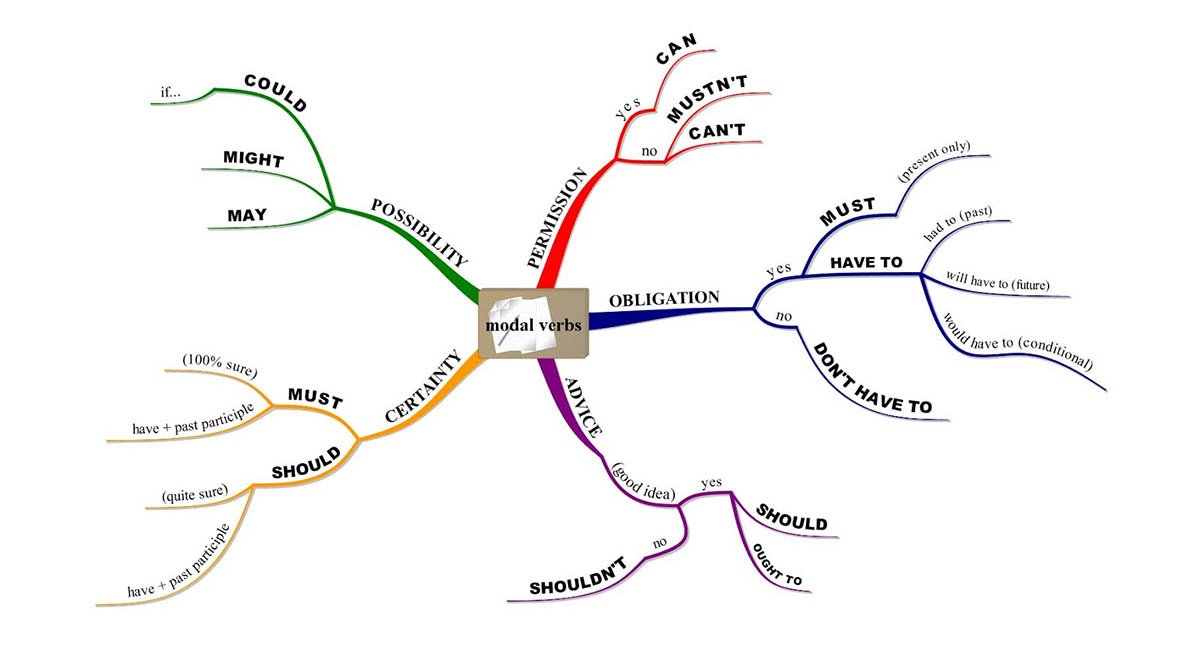
What are modal verbs?
Very simply put, a modal verb is a helping verb, also known as a type of auxiliary verb, that adds meaning to the main verb. Modals enable you to use a single main verb in different ways, or modes .
The 8 most common modals are:
(There are others, such as ought to , that are not as commonly used.)
You use modals all the time. The sentences, "I study," and, "I should study," and "I will study," all have obviously different meanings. The difference is the modal verb.
But you may not know just how versatile modals are. So, let's get into it. How do you think about them? How do you use them?
First, let's see how much you know already.
Look at the sentences below. What is the difference in meaning between a and b? [Answers are at the bottom of the page.]
Simple examples
Let's start simply. If you say, " I can dance ," the main verb is dance , and the modal verb , can , adds the function of ability .
Compare this to the sentence, " I don't dance ." Notice how dance is still the main verb, but the modal, don't , adds the idea of the negative .
So modals are not like regular verbs, but they accompany and attenuate regular verbs, like auxiliaries. But auxiliaries are used to form tenses, questions and negatives, whereas modals add different ideas , as we have seen with " I can dance " above. More below about this.
Simple mistakes
Modals are unlike regular verbs in that they do not decline or conjugate like regular verbs.
- Negatives : you can say, " I dance" and, " I don't dance" , but while you can say, " I can dance", you cannot say, " I can don't dance ".
- Time : you can say I danced , but you cannot say I canned dance .
- Questions : some modals use an auxiliary, eg, " I have to go" changes to " Do I have to go ?"; but some don't, eg, " I must go " changes to " Must I go ?"
- Continuous form : there is no continuous form attached to the modal, eg, I am canning dance .
- Third person 's': the modal does not take the extra letter, eg, He cans dance .
So all these reasons mean that they can be confusing, both in meaning, function and formation.
Which modal does what?
A big problem is that often one modal has many uses. For instance, must can be used to express many things:
- You must be tired after your long journey.
- You must pay tax.
- You must stop tapping your foot.
- You must see the new Batman movie!"
- Must you go so soon?
Therefore, you can see that a bad question to ask is, "how do I use must?" It's bad because there are too many possible answers. It is better to ask, "How do I express obligation?" This is a question of category.
So, let's look at the possible categories.
List of uses
Modals can be used to express the following ideas—you can call them modalities , or you can simply say functions or categories.
Looking at the categories and trying to think of an example for yourself is a kind of "backward learning." You know the necessary modals (there are just 8 basic ones), but this analysis is a way of thinking about it you might not have done before.
Take a look at each one. How many ways can you think to express it?
- denial of permission
- lack of obligation
- lack of necessity
- possibility
- probability
- lack of ability
- positive assumption
- negative assumption
- prohibition
- willingness
If you don't know any modals that fit into an above category, then that means you need to study it! Book a lesson with a teacher and ask, for instance, "how do I express probability?" Alternatively, you can google that question.
With time and practice, you can master modals.
Quiz Answers
- a) I didn’t need to go . (I knew it was not necessary for me to go and for that reason, I did not go.) b) I needn’t have gone . (I didn't know it was not necessary for me to go so I went.)
- a) You must be very careful . (I command you to be careful.) b) You must be very careless . (I conclude from the evidence that you are careless.)
- a) You shouldn’t have done that . (I am criticising the fact that you did that.) b) A gift ? You shouldn’t have ! (expression of surprise/gratitude at receiving an unexpected gift.)
- a) He could have told me . (Maybe he told me but I am not sure.) b) He could have told me ! (I am disappointed he didn't tell me although he had the opportunity or ability to do so.)
- a) I would say that . (I agree.) b) You would say that ! (It's typical of you to say that, and I disapprove somewhat.)
- a) I can’t tell . (I do not have permission to give you that information.) b) I can’t tell . (I am unable to understand, or unable to differentiate between two things.)

Can you speak English? Using CAN naturally

Which should you use: GOING TO or WILL?

The simple difference between GET and BECOME

Use the singular "they" to include everyone

ESSAY SAUCE
FOR STUDENTS : ALL THE INGREDIENTS OF A GOOD ESSAY
Modal verbs
A modal verb is a verb which is used with another verb to express such ideas as possibility, ability, and necessity, e.g. computers can perform a wide range of tasks. Modal verbs in English can present some difficulties for learners. They occur quite frequently in the academic context and the range and variety of their use can make understanding and using them correctly quite a challenge.
The nine main modal verbs express a range of meanings, which may differ very subtly.
Modal verbs are used to indicate the writer’s or speaker’s attitude to what he or she is writing or saying. There are three main categories of meaning.
- possibility/ability/permission
- obligation/necessity
- intention/prediction
Expressing possibility, ability and permission
The most common meaning for modal verbs in the category of possibility, ability and permission is logical possibility: indicating what is or is not possible from what we know about a situation. All four modals in this category (can, could, may, might) are used in this way.
Can is frequently used to indicate ability.
The use of can and may to ask or give someone permission is common in speech but rare in formal writing, because it involves personal interaction.
Expressing obligation and necessity, intention and prediction
In the category of modal verbs expressing obligation and necessity there are two main meanings found in formal writing. The first meaning is that of personal obligation; the writer states what he/she and perhaps the reader is obliged to do/believe etc. using a modal verb such as must or should.
The second meaning is that of logical necessity; the writer states what he/she wants the reader to conclude from the information presented using a modal verb such as must or should.
Using modal verbs to express intention and prediction clearly relates to future time. This is a large and complex area of English grammar, and here the focus is on the modals will, would and shall; how they are used and how they can be distinguished.
will and would are commonly used in formal writing to predict future events or states that are not caused by anyone. Very often the period or point in time is not mentioned.
shall is used to indicate the writer’s personal intention. This is a formal and conventional use of this modal.
Helpful sites for practice
Online English Grammar http://www.edufind.com/english/grammar/index.cfm Online grammar explanations with examples.
Gerunds and Infinitives http://www.reocities.com/gwyni_99/gerinfless.html Grammar explanation plus links to practice exercises and a useful verb list.
Gerunds, Participle and Infinitives http://owl.english.purdue.edu/handouts/grammar/g_verbals.html Detailed information with practice in this area of grammar.
Language and Learning Online http://www.monash.edu.au/lls/llonline/index.xml A comprehensive set of resources for grammar. Provided by Monash University, Australia.
Dependent Prepositions http://www.wordskills.com/general/prepositions.pdf A pdf reference list of common dependent prepositions.
British Council Learnenglish Grammar Games http://learnenglish.britishcouncil.org/en/grammar-games Grammar games to practise most aspects of grammar.
Grammar Terms Quiz http://esl.about.com/library/quiz/bl_grammarterms.htm Test your knowledge of grammar terminology by matching examples to grammar terms.
Using English.com – Glossary of grammatical terms http://www.usingenglish.com/glossary.html A comprehensive online glossary of grammatical terms.
Englishpage.com http://www.englishpage.com/index.html Grammar practice website.
Englishclub.com http://www.englishclub.com/grammar/index.htm Grammar practice website.
SOURCE: The Open University, 2011
Essay Categories:
- Accounting essays
- Architecture essays
- Business essays
- Computer science essays
- Criminology essays
- Economics essays
- Education essays
- Engineering essays
- English language essays
- Environmental studies essays
- Essay examples
- Finance essays
- Geography essays
- Health essays
- History essays
- Hospitality and tourism essays
- Human rights essays
- Information technology essays
- International relations
- Leadership essays
- Linguistics essays
- Literature essays
- Management essays
- Marketing essays
- Mathematics essays
- Media essays
- Medicine essays
- Military essays
- Miscellaneous essays
- Music Essays
- Nursing essays
- Philosophy essays
- Photography and arts essays
- Politics essays
- Project management essays
- Psychology essays
- Religious studies and theology essays
- Sample essays
- Science essays
- Social work essays
- Sociology essays
- Sports essays
- Types of essay
- Zoology essays

IMAGES
VIDEO
COMMENTS
Modal verbs show possibility, intent, ability, or necessity. Common examples of modal verbs include can, should, and must . Because they're a type of auxiliary verb (helper verb), they're used alongside the infinitive form of the main verb of a sentence. Modal verbs are used to express certain hypothetical conditions, such as advisability ...
Revised on December 6, 2023. A modal verb (also called a modal auxiliary verb) is used along with a main verb to express possibility, ability, permission, or necessity. For example, in the statement "you must leave," "must" is a modal verb indicating that it's necessary for the subject ("you") to perform the action of the verb ...
modal + base form of main verb = complete verb. 2. Contractions are common are in modals, such as "shouldn't" and "mustn't". However, "may" and "might" do not have a contraction form. It is wrong to write "mayn't" and "mightn't". Small children mayn't stay ( may not stay) alone at home in the United States.
Modal Verbs Modal verbs (modals) are verbs that add the meaning of logical possibility, ability, necessity, and permission to verbs, which have a degree of strength from stronger to weaker. Modals come before infinitive verbs and the "to" is removed. Modals do not need to match their subject in plural agreement, so there is no need to add ...
Modal verbs are a type of "auxiliary verb," also called a "helping verb" as we hinted above. That means they work alongside other verbs to give your sentence a new meaning. For example, they can change the tense of your main verb, or indicate the possibility, permission or necessity for something to happen. Common English modal verbs ...
What this handout is about. Modal verbs (will, would, should, may, can, could, might, must) precede another verb. Modals do not have subject-verb agreement or take the infinitive "to" before the next verb. This handout shows how modals in academic writing can change a sentence's meaning into a prediction, suggestion, or a question.
Grammatical Form. Modals are a special type of verbs; they are followed by the base form of verbs (e.g. I should go, she must see, he can swim ). In addition to the simple form of modals, there are also other forms to express: past time 1: modal + have + Past Participle (e.g., may have submitted) passive voice 2: modal + be + Past Participle (e ...
modal auxiliary. +. main verb. There are ten main modal auxiliaries in English: can, could, may, might, shall, should, will, would, must, and ought to. The four common types of errors when using modals include the following: using an infinitive instead of a base verb after a modal, using a gerund instead of an infinitive or a base verb after a ...
Modal verbs are auxiliary, or "helping," verbs that modify the main verb in a sentence to express possibility, ability, necessity, or other conditions. These include words like "can," "could," "will," "would," "shall," "should," "may," "might," and "must.". Example: He can swim. This shows ability. You ...
The modal verbs are: We use modals to show if we believe something is certain, possible or impossible: My keys must be in the car. It might rain tomorrow. That can't be Peter's coat. It's too small. We also use them to do things like talk about ability, ask permission, and make requests and offers: I can't swim.
Modal verbs (must, will, would, should, may, can, could, might, must) precede another verb. Modals do not have subject-verb agreement or take the infinitive "to" before the next verb. This handout shows how modals in academic writing can change a sentence's meaning into a prediction, suggestion, or a question.
Modal verbs and modality - English Grammar Today - a reference to written and spoken English grammar and usage - Cambridge Dictionary
to make conditional sentences. in reported speech. Modals can refer to a time range that reaches from the immediate present to some future time, so that they can all be used for future reference, especially when they are used with a time adverbial. You will be seeing her on Friday at Jackie's house.
This is a writing aimed at pre-intermediate and intermediate level students. They have to describe life in the year 3012, using modal verbs to talk about different things like: education, jobs, cities, clothes, etc. They are given some examples: what students/teachers can/can't do, what means of transport can/can't do, etc.
Should. Will. Would. Each of these modal verbs has a specific meaning and usage in English. For example, "can" is used to express ability, "may" is used to express possibility, and "must" is used to express necessity. Modal verbs are also used to create different tenses in English. For example, "could" is used to create the past ...
CO_Q2_English 10_ Module 4. What is It. Modal Adverbs are used to modify specific verbs that consist of a linking verb (verb of. being) and sometimes another verb. Here are examples of modal adverbs: probably, possibly, evidently, certainly, surely, undoubtedly, seriously, clearly, obviously. 1.
Here's an example of how a modal verb gives shades of meaning to a sentence. Trina and Joan play the piano. Trina and Joan might play the piano. Another verb always follows modal verbs in base form. Remember not to conjugate the verb. For example: Incorrect: She can plays the piano. Correct: She can play the piano.
With modal verbs, use the infinitive submit of the main verb. With most but not all modal verbs, the your declined from the verb. So if you want to brag nearly is ability to eat an entire pizza, yourself use the modal verb can before the infinitive form of swallow without to—which is simply eat. The rest of the catch continues as normalize.
Modals enable you to use a single main verb in different ways, or modes. The 8 most common modals are: (There are others, such as ought to, that are not as commonly used.) You use modals all the time. The sentences, "I study," and, "I should study," and "I will study," all have obviously different meanings. The difference is the modal verb.
When the modal verb 'will' is used, that means that the action is certain to take place. Would. The modal verb 'would' indicates a condition. It is possible that the action will take place, but another condition has to be met. The phrase including the modal verb will be followed by a connective such as 'if'.
A response to 'Taming English modals - how a construction grammar approach helps to understand modal verbs' by Sergio Torres-Martínez, English Today 138, 35 (2), 50-57, 2019. English Today CrossRef Google Scholar. Goldberg, A. E. 1995. Constructions: A Construction Grammar Approach to Argument Structure. Chicago: Chicago University Press.
Modal verbs. A modal verb is a verb which is used with another verb to express such ideas as possibility, ability, and necessity, e.g. computers can perform a wide range of tasks. Modal verbs in English can present some difficulties for learners. They occur quite frequently in the academic context and the range and variety of their use can make ...
Will - here, the plan is that the essay is completed.... In addition, this part of speech cannot form a negation on its own, only with the help of an auxiliary verb with the particle not. Modal verbs... How to improve your IELTS Writing Task 2 essay (2023)... Modal verbs (will, would, should, may, can, could, might, must) precede another verb.