- PRO Courses Guides New Tech Help Pro Expert Videos About wikiHow Pro Upgrade Sign In
- EDIT Edit this Article
- EXPLORE Tech Help Pro About Us Random Article Quizzes Request a New Article Community Dashboard This Or That Game Popular Categories Arts and Entertainment Artwork Books Movies Computers and Electronics Computers Phone Skills Technology Hacks Health Men's Health Mental Health Women's Health Relationships Dating Love Relationship Issues Hobbies and Crafts Crafts Drawing Games Education & Communication Communication Skills Personal Development Studying Personal Care and Style Fashion Hair Care Personal Hygiene Youth Personal Care School Stuff Dating All Categories Arts and Entertainment Finance and Business Home and Garden Relationship Quizzes Cars & Other Vehicles Food and Entertaining Personal Care and Style Sports and Fitness Computers and Electronics Health Pets and Animals Travel Education & Communication Hobbies and Crafts Philosophy and Religion Work World Family Life Holidays and Traditions Relationships Youth
- Browse Articles
- Learn Something New
- Quizzes Hot
- This Or That Game New
- Train Your Brain
- Explore More
- Support wikiHow
- About wikiHow
- Log in / Sign up
- Education and Communications
- Autobiographies

How to Write a Personal Recount
Last Updated: January 17, 2024 Fact Checked
This article was reviewed by Gerald Posner . Gerald Posner is an Author & Journalist based in Miami, Florida. With over 35 years of experience, he specializes in investigative journalism, nonfiction books, and editorials. He holds a law degree from UC College of the Law, San Francisco, and a BA in Political Science from the University of California-Berkeley. He’s the author of thirteen books, including several New York Times bestsellers, the winner of the Florida Book Award for General Nonfiction, and has been a finalist for the Pulitzer Prize in History. He was also shortlisted for the Best Business Book of 2020 by the Society for Advancing Business Editing and Writing. This article has been fact-checked, ensuring the accuracy of any cited facts and confirming the authority of its sources. This article has been viewed 127,226 times.
Writing a personal recount requires you to retell an activity or event that happened in your own life. You must structure your story in a way that makes sense while using language that matches the same purpose.
Considerations

- The first thing you need to understand is the writing prompt itself. If your teacher asks you to write about a favorite holiday memory, your recount needs to describe something that happened during a holiday. It should not describe a favorite memory that happened in school, after class on a normal school day, or during a normal weekend.
- Pay attention to requirements concerning length, as well. Your teacher may tell you how many words, pages, or paragraphs your recount needs to be. If these instructions are not included and you aren't sure about how long the piece must be, consider asking your teacher directly.

- Most recounts are meant to inform, entertain, or do some combination of the two. Personal recounts are generally written for entertainment, but if your teacher asks you to describe an event he or she was not present for—like what happened during your last sports game or during a time when a substitute teacher led class—you also need to make sure that you provide plenty of accurate information about that event.

- For classroom purposes, your recount will usually be written for either your teacher or your peers. Your teacher will want to see that you followed the instructions he or she provided. Your classmates will usually want to be entertained with a story they can enjoy or relate to.

- For example, if you need or want to write a personal recount about a fun summer memory, you probably shouldn't write about your best friend moving away. As a sad memory, describing the loss of your friend won't create the “fun” mood your recount is supposed to have.

- Choose something simple. For instance, a recount about your favorite pet might be titled, “My Favorite Pet.”

- Identify the participants. Even though a personal recount must retell a story from your own life, other people will probably be involved in your story, too. Mentioning these individuals early on will prevent the reader from being surprised or confused later.
- Explain when the activity happened and where it happened, as well. These details are crucial if you want your readers to understand the events of your story.
- For example, if you choose to write about a beach vacation spent with your family, consider starting with something like, “I spent the first week of July with my mother, father, sister, Uncle Eric, and Aunt Lydia. We stayed at a hotel on the beach.”

- For instance, if school was canceled for the day because of a major blizzard, you should mention the blizzard first, followed by the discovery that school was canceled. Write about what you did with your day off only after explaining why you had that day off.

- As a general rule, only describe events that the reader would not be able to predict. When writing a personal recount about your weekend, you could describe the games you played, the people you met with, and any special treats you may have enjoyed. You do not need to explain that you went to sleep each night or ate breakfast each morning, however, since those are things your teacher expects you to do every weekend.

- For personal recounts that cover an extended period of time, each paragraph might describe one easily separated portion of that time. A recount about your weekend might include one paragraph for Friday evening, one paragraph for Saturday, and one paragraph for Sunday. A recount about your summer might include one paragraph for May, one paragraph for June, one paragraph for July, and one paragraph for August.

- This is especially important when you are writing a personal recount about someone or something important. Personal recounts about your favorite pet should include a description of how your pet looks. Personal recounts about your grandparents should include descriptions of how your grandparents look and sound.

- Consider including a personal opinion about what happened. For instance, you might say conclude a personal recount about your Christmas with a statement like, “This past Christmas was very fun.”
- You may also need to conclude by describing the outcome of the activity. If you are telling a recount about your visit to the doctor, end with an explanation of what your doctor told you or what medicine he or she gave you. [3] X Research source

- For a personal recount, you need to describe how you felt and what you did. Doing this will be impossible if you do not tell the story from your perspective.

- The words “played,” “raced,” and “painted” describe the actions you and your cousin performed.
- It makes more sense to say that you performed these actions than to describe these events without saying anything about doing them. A description of the park you raced to won't make sense if you don't first explain that you raced to it.

- This means converting all of your verbs to the past tense. Instead of saying that you “enjoy” eating at your favorite restaurant, you will need to write that you “enjoyed” eating at your favorite restaurant.
- For most verbs, you can change them to the past tense by add “-ed” to the end of the verb. Examples include: enjoyed (enjoy), played (play), visited (visit), walked (walk)
- For some verbs, several letters within the word will change and no “-ed” is needed. A few common examples include: ran (run), ate (eat), went (go)

- Transitions describe the order of events. A few examples include: first, next, later, meanwhile, then, finally
- First , I did _________.
- Next , we went to the ______.
- Later , I decided to ______.
- Meanwhile , my parents were ______.
- Then , all of us ______.
- Finally , we ended the day by ______.
Community Q&A
You Might Also Like

- ↑ https://englishonline.tki.org.nz/English-Online/Planning-for-my-students-needs/Resources-research-and-professional-support/Features-of-text-forms/Recounts
- ↑ https://www.ziptales.com/pdfs/scripts/write-recount.pdf
About This Article

- Send fan mail to authors
Reader Success Stories
Antonio Criscione
Jun 6, 2016
Did this article help you?

Ismail Khan
Oct 14, 2016
Aug 24, 2018
Mar 1, 2017

Featured Articles

Trending Articles

Watch Articles

- Terms of Use
- Privacy Policy
- Do Not Sell or Share My Info
- Not Selling Info
Get all the best how-tos!
Sign up for wikiHow's weekly email newsletter
- MOE Updates
- Primary School
- English P1 Essay Resources
- English P2 Comprehension
- English P3 LC Resources
- English P4 Oral Resources
- Singapore News
- Free Test Papers
- Model Essays
- Early Concepts
- Fun with Mandarin
- Malay Language Worksheets
- Math Mastery
- Chinese Audio Books
- English Audio Books
- International Baccalaureate (IB) Primary Years Programme (PYP)
- School Placement Exercise for Returning Singaporeans-Secondary (SPERS-Sec)
- All you need to know about the SPERS exam for returning Singaporeans
- Admissions Exercise for International Students (AEIS)
- Singapore Best Online Tuition
- Find a Tutor
- Tuition Rates
- Tuition Centres
- 新加坡一对一补习 – AEIS, GP Tuition Testimonials
- Sign up as a Tutor
- Member Registration
The Learning Space
O’levels Paper 1: Continuous Writing (Sample Narrative / Personal Recount Essay)

O’levels Paper 1 Student’s Model Essay:
Question: Write about an occasion when an inconsiderate act leads to drastic consequences
“Bang, bang, bang, buzzzzz,” the sound of the relentless pounding of the drill reverberated throughout the walls of my flat. The cacophonous sound had jolted me from my deep slumber. Bleary-eyed, I dragged myself towards the main door, hoping to find out who or what is causing such a din.
I opened my door and was livid to find that the entire common corridor has been filled with tools, wooden planks, stacks of old newspaper and old furniture. A long extension ladder was also placed against the parapet. It turns out that my new neighbour Dashen has been using the common corridor like his own workshop.
“Oh my gosh! Can you please STOP?!” I yelled, my voice shooting up 50 octaves, my eyes flashing angrily.
“Why are you making so much noise so early in the morning? Don’t you know you cannot block the common corridor? You are obstructing everyone. This is very inconsiderate!” I hollered again. Rage gripping me and anger flooding through my veins.
Dashen darted me a baleful look, flicked his cigarette, turned his head, walked back into his flat, ignoring me completely.
At this point, I could feel a vein popped out in my neck, my jaw thrust forward with indignation. I stomped back to my room to put on some proper clothing so that I can confront him.
Suddenly, an acrid smell hit my nostrils. It was smoky campfire-ish smell. I raced to the front door only to find thick gray smoke billowing in. Like a monstrous beast, it wolfed everything in its way. Nothing was spared. Flames ripped across the ceiling as if they had been shot from a flamethrower. At the corner of my eyes, I caught a glimpse of a burning cigarette that landed on the pile of newspaper.
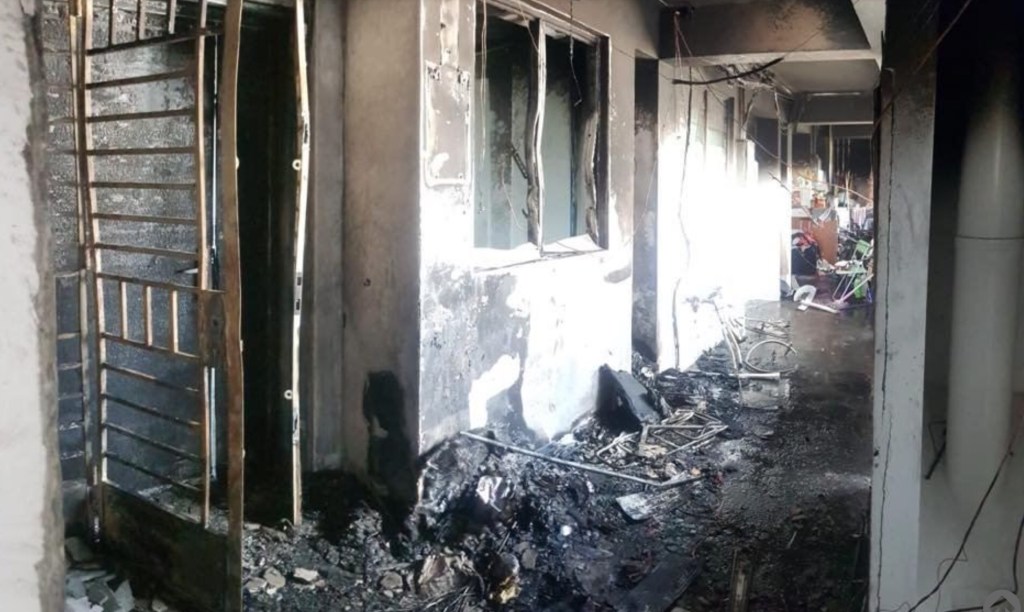

Immediately, everything clicked.
Our inconsiderate new neighbour, Dashen, must have flung his cigarette onto the newspapers that he had left outside. The cigarette must have stabbed into a tottering stack of cardboard boxes intermixed with old newspapers and an old cabinet that was missing a leg. The suffocating smoke jolted me to my senses. I quickly reached for my phone and dialled 995. As I put down the phone, a thought struck me like lightning. Oh no! I have to alert Auntie Wong, our recently widowed, octogenarian neighbour who is living alone. I knocked furiously and frantically at her door. Just as I thought, she was home and had just woken up too.
“We have to get out of here! There is a fire!” I bellowed. Mrs Wong was hyperventilating. I took her hand and helped her out of her flat. There was choking smoke, so black and thick that it seemed you could grab it by the handful. Suddenly, out of nowhere, I heard a lot sound. Crack! Thud! The ladder that Dashen left outside the corridor had fallen, landing on Mrs Wong’s left leg. Gasping for breath, I mustered all my strength and pushed the ladder away, almost tripping over the debris. I picked the frail Mrs Wong up and carried her down the stairs. Just as we were able to go down the stairs, a loud boom echoed behind me and we were hurled forward. At this point, the firemen had arrived and managed to bring the both of us to safety.
After battling with the fire for close to four hours, the fire was finally extinguished. The police had also arrived and told us that there some flammable substances such as cleaning agents and electronic items in the old cabinet that Dashen had left outside the corridor. Dashen was also questioned by the authorities and the police took him away to assist with further investigation.

Dashen’s terribly selfish, horribly reckless act endangered everyone. Lives could have been lost because of such thoughtless act and careless oversights. Dashen’s inconsiderate act has started a disastrous fire which took have taken a heavy toll on innocent lives.
What exactly do examiners look for in a well written narrative or personal recount essay?
Content: Students need a well-organized story will have all three parts, and the ideas will be presented in a clear and logical way. Your story must be credible and not too far-fetched.
Language: To get The paragraphs will be set appropriately, with colons and semicolons used as they should, and the ideas presented should be easy to connect and understand, making it a smooth read for the reader.
For more insider’s tips and sample essays, subscribe here . You can also reach out to our team of professional and experienced tutors to give you a head start today.
Share this:
Leave a reply cancel reply.
Your email address will not be published. Required fields are marked *
You may use these HTML tags and attributes:
Free Exam Papers and Study Notes
Every student should be given the opportunity to maximize their educational potential. Looking for professional tutors? Get help from our team of MOE, NIE trained teachers and full time tutors. Looking for free study notes and resources? We provide the latest test papers and quality study notes for Primary, Secondary, IGCSE, IB, JC students. Subscribe to our Youtube Channel and exclusive access to PSLE, O’levels, A’Levels materials. WhatsApp us today,
新加玻补习老师, 试卷和学习笔记
寻找 专业导师,补习老师?我们的 MOE、NIE 培训教师和全职导师团队可以帮助您的孩子补习英文。要上英文网课?那里有最好的IB英文老师补习?寻找免费的学习笔记和资源? 我们为AEIS,小学、中学、IGCSE、IB、JC学生提供最新的试卷和优质的学习笔记。 订阅我们的 Youtube 频道 并独家访问 PSLE、O’levels、A’Levels 材料。今天就 WhatsApp 我们。

Personal Narrative Writing Guide
WHAT IS A PERSONAL NARRATIVE?

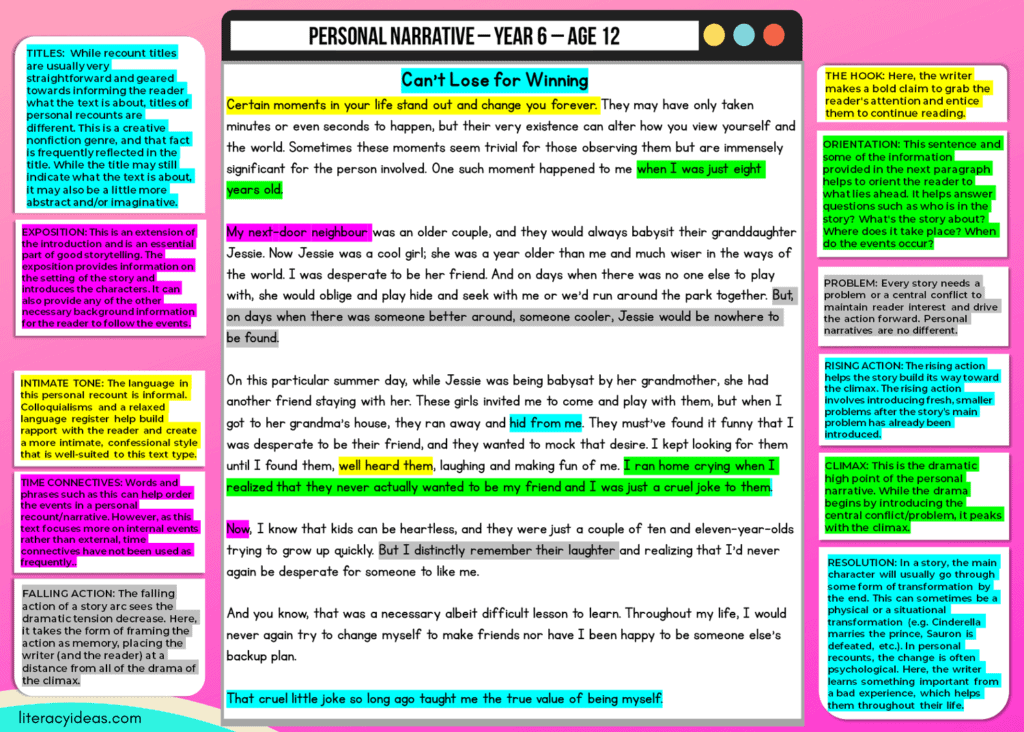
A Personal Narrative recounts an event or experience from the writer’s life in story form and often in intimate detail. This text type not only relates to the events happening around the author but also often reveals the writer’s inner thoughts and emotions also.
A personal narrative can be understood as nonfiction storytelling based on the writer’s thoughts, feelings, and experiences. Told in the first person, the writer draws on their life events to construct a story.
Combining elements of nonfiction recount writing with introspection and the frequent use of literary devices more commonly associated with fiction and poetry, a personal narrative can be best understood as a type of creative nonfiction .
PERSONAL NARRATIVE VERSUS A PERSONAL RECOUNT: SO WHAT’S THE DIFFERENCE?
Personal narratives are also frequently referred to as personal recounts. They share much in common but are unique text types, so let’s explore how they compare and contrast.
When we first instruct our students to write stories based on the events of their own lives, they will inevitably write simple recounts. These recounts are based on retelling personal incidents of their lives but lack the depth we can typically expect to find in a personal narrative.
While personal narratives also recount events from the writer’s life, with greater emphasis placed on exploring the writer’s thoughts and feelings on these events rather than just what happened.
A personal narrative is a means for the writer to explore the meaning of the events in their life. It is, at its core, an introspective and creative endeavor that focuses as much on the interior life of the writer as it does on external events.

While the conclusion of a traditional recount usually provides some of the writer’s insights, in a personal narrative, these are woven throughout the text.
STRUCTURE AND FEATURES OF A PERSONAL NARRATIVE
Personal narrative structure.
ORIENTATION Explain the who, what, when, and where of the experience in your introduction to your audience.
FOCUS Mainly focus on meaningful events.
CHRONOLOGY Events are described in the sequence in which they occurred.
ORGANIZATION Relevant information is organized into paragraphs
INSIGHT & MEANING Include personal comments, opinions or interpretations of the experience or event in your personal narrative.
PERSONAL NARRATIVE FEATURES
TENSE The first and third person are used most frequently and recall is always written in the past tense. Present tense can be used for analysis and opinion.
NOUNS Use proper nouns to refer to specific people, places times and events
VOICE Both active and passive voice are used in recounts. Use these to express your emotions and thinking clearly.
CONNECTIVES Use conjunctions and connectives to link events and indicate time sequence in your personal narrative.
A COMPLETE TEACHING UNIT ON PERSONAL NARRATIVE WRITING

Teach your students to write AMAZING PERSONAL NARRATIVES using a proven model of research skills, writing strategies and engaging content. ALL CONTENT, RESOURCES AND ASSESSMENT TOOLS INCLUDED covering.
Download this COMPLETE 85 PAGE UNIT today. NO PREPARATION REQUIRED.
HOW LONG SHOULD A PERSONAL NARRATIVE BE?
The personal narrative is a modern text type and therefore has no traditionally defined optimum length, and we can find texts ranging from a couple of hundred words to a multi-volume series in this genre.
However, for our students, this text type can be thought of in terms of length as similar to an essay. Like an essay, the text needs to be long enough to comprehensively answer the question, prompt, or the event/experience the student is retelling.
David Sedaris, the American writer and one of the best-known writers of humorous personal narratives, has written many books that could accurately be classified in this genre.
While these full-length books are often built around a loose theme, each chapter could stand alone as a personal narrative essay in its own right, each built around a single identifiable experience or event.
As with an essay, the length of a personal narrative can be based on a variety of factors, including:
- Age and ability of the students
- Specifics of the question or writing prompt
- Any limitation imposed by a word count
- The complexity of the event/experience being written about.
Regardless of length, given its structural similarity with the essay, personal narratives usually follow a basic three-part structure.
HOW TO WRITE A PERSONAL NARRATIVE STEP-BY-STEP
We mentioned previously that this text type is relatively modern, so there aren’t many fixed rules concerning structure. That said, we can usually identify three distinct parts of a personal narrative corresponding to the three parts outlined in the hamburger essay or the 5-paragraph essay format. These are:

- The introduction
- The body paragraphs
- The conclusion
If you want an in-depth guide to this format, check out our comprehensive article here . But, for now, let’s take a brief look at the purpose of each section as it relates to a personal narrative.
WRITING THE INTRODUCTION OF A PERSONAL NARRATIVE

The introduction of a personal narrative performs several functions.
1: It hooks the Reader
The first job of the introduction is to ‘hook’ the reader. If we can’t catch the reader’s interest initially, there will be no middle or end for the reader. A strong hook is needed at the very outset, and it can take several forms.
Some effective hooks to open a personal narrative with include:
- A bold claim
- An interesting anecdote
- A fascinating fact or revealing statistic
- A compelling quotation
Whichever technique the student chooses to open their narrative with, they should ensure it is relevant to the subject matter explored, whether it focuses on external or internal events or experiences or a mixture of both.
2: It orients the Reader
Like many other nonfiction and fiction text types, the opening paragraph (or paragraphs) will also orient the reader by answering some basic questions such as:
- What is the text about?
- Who is in this story?
- Where is it set?
- When do the events or experiences occur?
While it may also hint at why these events or experiences matter, a detailed answer to the why of a personal narrative may be saved for the text’s conclusion.
This section of the personal narrative can also be thought of as The Exposition .
3: It Sets the Tone
The introduction reveals not only what the text will be about but also how the writer (and, by extension, the reader) will treat the topic. This is the tone.
For example, a more sombre tone has been established where the language used is serious and formal. In this instance, the reader will adopt a more serious approach to the work.
On the other hand, if the treatment of the event or experience is humorous, this will be apparent in the language choices the writer makes and the mood they establish. Going forward, the reader can reasonably expect to be amused by what’s to come in the text.
THE BODY PARAGRAPHS OF A PERSONAL NARRATIVE
The body paragraphs of a personal narrative comprise the bulk of the text.
As with any type of recount, this section will generally focus on the chronological retelling of an event or experience.
However, there is another significant difference between this type of recount and the other types.’ The root of this difference can be found in the word ‘narrative’.
While the body paragraphs of a personal narrative can make use of some of the defining characteristics of more traditional types of recount, if the introduction acts as the exposition of the setting and character of the story, the body paragraphs move the text along its story arc.
Though we will cover the main elements briefly, structuring a story is an art in itself and if you want to find out more about it, check out our detailed article on the subject here.
Also, if you want to learn more about the structure of general recounts, find out more here .
While we’ve seen that the introduction of a personal narrative corresponds to a story’s exposition, the following elements of a story arc can be found in the text’s body.
1: The Problem
The problem or conflict is an essential ingredient in any story worth the name. It creates the story’s focal point, ignites the reader’s interest, and drives the story forward. In a personal narrative, this problem can be internal or external, however, there is often an emphasis placed on how the issues affect the writer psychologically. 2: The Rising Action
As the narrative develops, the dramatic tension will tend to increase. The main problem will intensify, or the writer may introduce additional more minor problems to amp things up. 3: The Climax
This is where the story reaches its dramatic high point. In the case of a personal narrative where the conflict or problem is psychological, this drama and its climax may play out internally.
WRITING THE CONCLUSION OF YOUR PERSONAL NARRATIVE ESSAY

This third and final section of the personal narrative performs a slightly different function to a regular essay’s conclusion.
While the conclusions of most nonfiction text types focus on restating a central thesis and/or providing a summary of arguments, the conclusion in a personal narrative follows a story’s final section more closely.
That is, it usually contains the story’s falling action and resolution.
Let’s take a quick look at each.
1: The Falling Action
The story arc dips in dramatic tension after the dramatic high point of the climax. As personal narratives often focus on ‘internal’ events, this ‘action’ can also occur internally. 2: Resolution
The resolution marks the end of the story, and in this text type, it usually involves some personal change in circumstances or transformation. It can also take the form of a lesson learned or new knowledge attained.
TIPS FOR WRITING A GREAT PERSONAL NARRATIVE ESSAY
- Begin with a clear and compelling story: Your personal narrative essay should focus on a significant event or experience in your life that you want to share with the reader.
- Write in the first person perspective: Use “I” statements to describe your experiences and thoughts and take us inside your mind.
- Be descriptive: To bring your story to life, use descriptive language to paint a picture of the sights, sounds, and emotions of your experience.
- Focus on what matters the most: Tell a powerful story with just a few key details. When writing your personal narrative, focus on the most impactful events and thoughts that help convey your message.
- Emphasize the impact the experience had upon you: Leave the reader with a clear understanding of the impact that the experience had on your life.
- Be true to yourself: Ensure your personal narrative essay is honest and genuine in your descriptions and reflections.
- Deliver a powerful ending: The conclusion should summarize the major points of your essay and leave the reader with a lasting impression.
- Review and Revise: Don’t be afraid to proofread your essay several times to ensure it is the best it can be.

Teaching Resources
Use our resources and tools to improve your student’s writing skills through proven teaching strategies.
PERSONAL NARRATIVE TEACHING STRATEGIES AND ACTIVITIES
PERSONAL NARRATIVE PRACTICE EXERCISE: ACTIVITY 1
- Organise your students into small groups of four or five
- Provide each group with a selection of personal recounts
- Can the students identify how each sample text attempts to hook the reader in the opening paragraph?
- How effectively does the introduction of each text orient the reader?
- What is the tone of the text? How has this tone been created?
PERSONAL NARRATIVE PRACTICE EXERCISE: ACTIVITY 2
In their groups, with their sample personal narrative texts, ask students to identify how the writer deals with each element as listed below and discuss how effectively they have done so.
- The Problem
- The Rising Action
PERSONAL NARRATIVE PRACTICE EXERCISE: ACTIVITY 3
Now students understand how to structure and write each stage of their personal narrative, encourage them to spend some time brainstorming events and experiences from their lives that could serve as the topic for their writing.
When they have chosen a suitable topic, instruct them to begin planning the writing of their text using the categories listed above. They might even wish to create a simple graphic organizer to help.
For example:
Introduction
- What is the opening hook?
Body Paragraphs
- What is the central problem?
- What happens in the rising action?
- How does the climax play out?
- What happens in the falling action?
- What is the resolution of the story?
Once students have their narrative adequately planned, it’s time to get them writing earnestly to put all that theory into practice.
PERSONAL NARRATIVE WRITING TEMPLATE / GRAPHIC ORGANIZER

PERSONAL NARRATIVE WRITING EXAMPLES
VIDEO TUTORIAL ON PERSONAL NARRATIVE WRITING

NARRATIVE WRITING CHECKLIST BUNDLE

RELEVANT ARTICLES

How to Write a Recount Text (And Improve your Writing Skills)

How to Write a Historical Recount Text

5 Easy Recount Writing Lesson Plans students love.

15 Awesome Recount & Personal Narrative Topics

Explore our Teaching Unit on PERSONAL NARRATIVES
- (65) 9646 0930

Personal Recount: Using FATS to Develop Dilemmas
- Posted By Randall Chew
Hi everyone, I’m Ms Atifa, an English teacher at Lil’ but Mighty. Have you ever had a tough time in a situation where making a choice seemed impossible? I’m sure that you have, and you might also know that such a situation is called a dilemma.
A dilemma refers to a situation where a difficult choice has to be made, and often, both of the choices carry some form of undesirability. For instance, imagine you and your best friend won tickets to a concert by your favourite artist. When you asked your parents if you could go, they firmly told you that you couldn’t. However, your best friend told you that you could lie to your parents in order to attend the concert without their knowledge. Your mind was fraught with the question: Do you listen to your best friend and tell a lie to your parents, or do you listen to your parents and miss an opportunity of a lifetime?
When writing a Personal Recount essay, you can use this particular literary device to add depth to the incident that you are retelling. In case you have forgotten, let’s briefly recap what a Personal Recount entails. This particular type of essay requires you to recount an incident that you have experienced which is related to the topic. When writing a Personal Recount, you can use the following structure to organise your ideas:
- Introduction – start with an interesting hook to entice your reader
- Background Information – this is where you provide important information that willhelp your reader understand the recounted experience
- Recount • Rising Action – this retells the events the lead to the climax • Climax – this represents the most exciting part • Falling Action – this part recounts the events that resulted from the climax
- Reflections – this last paragraph usually shows what you took away from the recounted experience
The Climax of the Recount would be the most important part of your entire essay. This would be where the writer encounters a problem and displays some form of struggle that needs to be overcome in the Falling Action. Hence, the Climax is a great place for you to introduce a dilemma.
When writing a dilemma, you can use the F.A.T.S. technique, which stands for:
- F acial Expressions
Let’s see how we can apply F.A.T.S. to develop a dilemma according to the following essay question:
Write about a time when you did something just to impress someone which you later regretted. (O Level 2020 Paper 1 Section C)
First, think of a dilemma you would have that is relevant to the topic. To do so, use the 5W1H questions to help you, for example: Who did I want to impress? What did I do to impress him/her? Where did this incident take place? The resulting dilemma could be something like this:
The most popular student in school dares me to steal a book. Do I listen to him or do I refuse?
Then, plan how you can develop the dilemma using F.A.T.S. Take a look at the table below. In the left column are questions for you to consider to help you think of some ideas for each part. On the right are some examples of phrases you can use when describing the above- mentioned dilemma:

The final step is to put everything together. The paragraph should look something like this:

Take note of how the final choice made by the writer relates closely to the question, i.e. since the first part of the question is about doing something to impress someone, the writer makes the final decision to steal the book in order to impress Ben the bully. Remember this when you are crafting your dilemma for the Personal Recount that you are writing.
Now, it’s your turn to try! Using F.A.T.S. , think of a dilemma you would have for the following topic, and how you can apply F.A.T.S. to develop it:
Write about a time when you disappointed someone close to you.
Remember to follow the steps I have outlined above to help you get started. First, think of a dilemma that is related to the question. Use the 5W1H questions to help you brainstorm some ideas, for instance: Who was the person that I disappointed? What action did I do that disappointed this person? When did this take place?
Here is an example of a possible response:
While sitting for my end-of-year examination, I notice my best friend cheating and looking at answers from a slip of paper under the table. Do I tell our teacher about her actions and risk disappointing my beloved friend, or do I keep quiet and carry the burden of ignoring her dishonest actions?
Next, develop the dilemma using F.A.T.S. by using the questions below to help you. Remember to jot down your ideas next to the questions:

Putting everything together, you should have written something like this:

Again, remember to show how the final choice made is closely linked to the question, i.e. the writer makes the final decision to inform the teacher about her friend’s dishonest act and in this way, disappoints her friend who would have expected the writer to cover for her.
Also, notice how S (Speech) is not present in the dilemma. This is because the situation the writer finds herself in (taking an exam) does not lend itself to the use of speech. Hence, whilst using F.A.T.S. will help you to develop your dilemma, you should also take heed to ensure that its usage fits the situation in the recount. If you find yourself being unable to use any part of F.A.T.S. , you can try to describe more of the other parts, like how in the example above I have included more descriptions for A (Actions) and T (Thoughts), to ensure that the dilemma is still well-elaborated.
I hope you give this practice a try, and remember to explore using a dilemma in your Personal Recounts if it is relevant to the topic. Don’t forget to apply the F.A.T.S. technique to develop your dilemmas as well. Happy writing!

ENGLISH COMPOSITION PLAN? WHAT’S THAT?
Good writers plan. They think through what they want to write before they actually write.
Before writing a story, some good writers may write their plans down or draw a mind map.
Sometimes, they SEEM like they are not planning but actually, they already know what is necessary for a good English Composition (due to numerous practice!) and have formed a mental plan in their minds.
It all starts with a plan. With a good plan, half the battle is won before you even start writing.
- Find Out More

In her time teaching, she has incorporated elements of drama into her classes to engage her lower primary students. She tries her best to get to know all of her students and is always keen to find out each of their interests and hobbies. She believes that each student has personalised needs, and aims to make lessons fun and helpful for all of her students.
Have something to share? Drop us a comment below!
Leave a reply.
You must be logged in to post a comment.
Other related posts


Creative Writing | 3 Easy Steps to Write Your Own Haiku!
- Creative Writing & Compo
Verbs: More than Just Action Words! | Part 3: Changes in Verb Forms
Ketchup on english – is, are, was and were.
- Grammar , Lower Primary
Audience In Visual Text | Visual Text Comprehension
- Visual Text Comprehension

Exploring Points of View (POV) in Composition Writing
Metaphors for | part ii – implied metaphors.

10 Beautiful Vivid Verbs to Boost Your Writing and Oral! | Primary School English
- Creative Writing & Compo , Oral
Metaphors For? | Part I – An Introduction to Metaphors

3 Family-Friendly Shows on Netflix (Educational & Entertaining)!
- English in the real world

Verbs: More than Just Action Words! | Part 2: Tenses
2021 father’s day contest winners.
- Company News
Verbs: More than Just Action Words! | Part 1: Subject-Verb Agreement

10 Beautiful Words You Can Use in Narrative / Descriptive Writing | Secondary School
- Secondary School English

Ways To Create A Well-Rounded Character | Creative Writing
Understanding purpose-related questions in visual text comprehension.

How Playing Video Games Can Improve Our English (With Practical Tips for Parents!)

Primary School Composition | Onomatopoeia – What’s That?
2021 mother’s day contest winners + our founder’s journey (mother’s day special).

Composition Revision: Using Your 5 Senses in Your Writing
How to create a dynamic piece of writing using idioms, ketchup on english – subject-verb agreement, punctuation marks: colon vs. semicolon.

4 steps to Create Suspense

Earth Hour – Oral Topic
That simile though 2 | using stronger similes.

3 Tips for English Comprehension (Open-Ended)
- Comprehension

PSLE ORAL | Compiled Prelim 2021 Oral Topics + Questions!
- Free Downloads , Oral

5 Steps to Convert a Newspaper Article into a Cloze Passage
- Cloze Passage and Editing , Free Downloads , Primary School English

PSLE English | Oral Conversation: Free SG50 Sample Practice + Model Answers
- Free Downloads , Oral , Primary School English

PSLE English | Oral Conversation: Filling your Story with Details Easily + Free Revision Cards

PSLE English | Situational Writing: Q&A + Formal vs Informal Writing Comparison Chart
- Free Downloads , Primary School English , Situational Writing

PSLE English Tips | Oral: Stimulus-Based Conversation Checklist

A Little Encouragement | DIY Motivational Bookmark (Easy to personalise too!)
- English in the real world , Free Downloads , Reading

Situational Writing: Step-by-Step Guide + Free Revision Card

I Love Reading | 5 Ways to Motivate Reluctant Readers
- English in the real world , Free Downloads

PSLE English | Printable Ultimate Grammar & Synthesis Summary
- Free Downloads , Grammar , Sentence Synthesis

How Well Do You Know Your Past Participles?
- Free Downloads , Grammar

Primary Composition Writing | Starting Sentences with Introductory Clauses
- Creative Writing & Compo , Free Downloads

The Sentence Train | Lower Primary English

PSLE English Tips | Oral: Reading Checklist

Language of COVID | 10 Words Added to the Dictionary
- English in the real world , Vocabulary

Using Personification to Show, Not Tell!
- Creative Writing & Compo , Primary School English
Expressing Character Feelings Too! | Using Show-Not-Tell (Part 2)
How to choose a book to read: 8 ways.

How to Dress Up A Boring Paragraph | Creative Writing
Ketchup on english – halloween special: prepositions of time.
- Lower Primary
Ketchup on English! – Verbs Are Not Just Action Words!

Expressing Character Feelings | Using Show-Not-Tell
Which picture should i use | choosing the best picture to use for composition.

Oral: Reading Passage | Long Vowels – Have You Been Reading Your Vowels Correctly?
Like what you are reading.
Subscribe now to receive news and tips hot off the press!
The greatest joy in giving small group tuition is a teacher’s ability to create greater impact in the children that have been entrusted to her care.
Our Programmes
- Primary English
- Secondary English
- Self-Paced Online Courses
- School Clients
- Copyright Terms & Conditions
- Personal Data Protection Policy
- Registration Terms & Conditions
- Contest Terms & Conditions
Lil’ but Mighty Clementi Block 432 Clementi Avenue 3, #01-282, Singapore 120432
Lil’ but Mighty Bukit Timah 170 Upper Bukit Timah Road, #B2-02 Bukit Timah Shopping Centre, Singapore 588179
Lil’ but Mighty Hougang Block 211 Hougang Street 21, #01-305 (Back entrance), Singapore 530211
Lil’ but Mighty Novena 1 Goldhill Plaza, #02-25, Singapore 308899
Lil’ but Mighty Marine Parade 1 Marine Parade, #04-05 Parkway Centre, Singapore 449408
Lil’ but Mighty Tampines 3 Tampines Central 1, #06-03 Tampines Plaza 1, Singapore 529540

IMAGES
VIDEO
COMMENTS
Types of Essays •Factual Recount-Facts presented in chronological order (in sequence)-Contains no emotions or personal opinions •Narrative-Fictional story -Contains emotions and personal opinions-Third person (She/He/They) point of view •Personal Recount -Non-fiction story -Based on a past experience-Contains emotions and personal opinions
If these instructions are not included and you aren't sure about how long the piece must be, consider asking your teacher directly. 2. Understand the purpose. Ask yourself what you hope to achieve by writing your recount. You need to accurately portray a real event you were personally involved in.
While writing an essay, you should always keep the following points in mind: Use of first-person pronouns: I, me, myself, mine, my, we, us, ourselves, ours, our. Use of simple past tense. Use of connectors. Connectors are words such as however, furthermore, then etc. and are used to give flow.
Browse essays about Personal Recount and find inspiration. Learn by example and become a better writer with Kibin's suite of essay help services. Essay Examples
When used in the context of writing a recount, the 5-paragraph essay will look something like this: The Orientation: Paragraph 1. In the introductory paragraph, the student will establish the setting and introduce the characters and the topic of the recount. The Events: Paragraphs 2-4.
The Childhood is considering as the most innocent phase of man's life. Yet when I look back those innocent days of my early childhood, actually I could not remember much. But those pleasant memories of my childhood linger on time to time due to the incidents that I face presently. Those experiences that I have gathered can be good or bad and ...
O’levels Paper 1 Student’s Model Essay: Question: Write about an occasion when an inconsiderate act leads to drastic consequences. “Bang, bang, bang, buzzzzz,” the sound of the relentless pounding of the drill reverberated throughout the walls of my flat. The cacophonous sound had jolted me from my deep slumber.
A personal narrative is a means for the writer to explore the meaning of the events in their life. It is, at its core, an introspective and creative endeavor that focuses as much on the interior life of the writer as it does on external events. While the conclusion of a traditional recount usually provides some of the writer’s insights, in a ...
When writing a Personal Recount essay, you can use this particular literary device to add depth to the incident that you are retelling. In case you have forgotten, let’s briefly recap what a Personal Recount entails. This particular type of essay requires you to recount an incident that you have experienced which is related to the topic.
Clear structure. Use paragraphs to separate the beginning, middle and end.Your middle section should include at least three events or experiences. Recounts are written in the order in which they ...