

How to Teach Essay Writing in Secondary ELA

Teaching students how to write a multi-paragraph essay is a process, and it isn’t something that can be taught in one class period, nor is it a skill that we should expect our incoming students to know. Before I even assign my students a multi-paragraph essay, I first take several weeks to teach paragraph writing, and I typically do this with my short story unit.
However, once my students are ready to make the jump from paragraphs to an essay, I still continue to break down my writing instruction. When I teach essay writing in my high school English students, I break it down paragraph-by-paragraph to encourage them to be the best writer they can be. All of the lessons that I will refer to throughout this blog post are included in this print and digital essay writing teaching unit .
Teach Essay Writing in Middle School and High School ELA
Start with brainstorming.
I am a huge fan of group brainstorming, especially since I usually have some EL and SPED students mainstreamed in my college prep English classes. I usually dedicate an entire class period to brainstorming where students gather ideas, paragraph topics, and supporting quotes. You can read more about group brainstorming in this blog post where I discuss brainstorming with my students and I teach them how to brainstorm an essay.
Outline the essay
After brainstorming, I move my students to the outlining phase of the writing process. This step is essential because it helps students organize their papers and stay on topic. Ever since I started dedicating an entire class period to in-class essay outlining, I’ve noticed a significant improvement in my students’ essays. You can read more about how I teach essay outlining in this blog post . When we focus on outlining the essay, I make sure that we focus on all of the essential components of an essay: thesis statement, topic sentences, and evidence.
Write the thesis statement
After the class has completed the brainstorming and outlining, I then move on to direct instruction for essay writing. Since students have already outlined their main ideas, they can start working on their thesis statement. I use my introduction and thesis statement lesson to help students write a meaningful thesis statement. I also look at examples of good thesis statements with my students and have students turn in their draft thesis statements to me before moving on.

Write the introduction
Once students have a solid working thesis statement (and I say working because it is possible for it to change throughout this process), I then have them move on to the introduction. Using the same introduction and thesis writing lesson, I then have my students work on drafting a hook and background information to complete their introduction. Now that students are in high school, I don’t accept a question as an acceptable hook. However, if my students get stuck, especially some of my lower students, I have them write their questions and then help them turn them into a statement.
Also, I’ve noticed that students sometimes have a hard time jumping on the hook. They tend to get stuck there, and when this happens, I have them jump right into the background information. In doing so, students get started writing, and they can go back to the hook later.
Topic Sentences
When I complete essay outlining with my students before the drafting process, I typically have them outline each paragraph with a topic sentence and then the quotes they want to use. Once we move from the introduction to the body paragraphs, I have them work on their topic sentence first. I use my topic sentences and body paragraphs essay writing lesson with my students at this point in the essay. Once students have a good topic sentence for their body paragraph, they write the rest of their body paragraph.
Write the body paragraphs
The next step in the writing process, especially for the first essay of the school year, is for students to write out the rest of their body paragraphs. If they’ve done their outlining correctly, they have a good idea about what they want to include in their body paragraphs. In this step, I really emphasize that my students need to provide support and analysis. They should be providing more explanation than simply restating their quotes.
Write the conclusion
Once students have their introduction and body paragraphs complete, I then have them move on to writing the conclusion. At this step, I teach conclusion writing to my students and have them restate the thesis and add a general thought to the end of the paragraph. At this point, I emphasize that students should not be adding in any new information. Also, one way to help students rephrase their thesis statement is to have them rewrite it in two sentences since a thesis statement is typically a one-sentence statement.
Complete peer editing

Provide time for essay revisions
Once students revise their essays and turn them in, I still like to provide students with some time to revise their essays after I grade them. This is where true learning and growth happen. It is when a student thinks they are done but then goes back to try to improve their essay. In this blog post about essay revisions , you can read more about how I conduct them in the classroom.
An entire year of writing instruction
What if I told you that you could have all of your writing instruction for the ENTIRE SCHOOL YEAR planned and ready to go? I’m talking about all the major writing strands and peer editing to grading rubrics. Just imagine how much time and stress you’ll save!
It almost sounds too good to be true, right?
It’s not! My Ultimate Writing Bundle is your one-stop shop for all of your writing instruction needs! Plus, your students will thrive with the built-in scaffolding and consistency throughout the year!
Join the Daring English Teacher community!
Subscribe to receive freebies, teaching ideas, and my latest content by email.
I won’t send you spam. Unsubscribe at any time.
Built with ConvertKit
Leave a Reply Cancel reply
Your email address will not be published. Required fields are marked *
Save my name, email, and website in this browser for the next time I comment.

SUBSCRIBE NOW

Essay Writing: A complete guide for students and teachers
P LANNING, PARAGRAPHING AND POLISHING: FINE-TUNING THE PERFECT ESSAY
Essay writing is an essential skill for every student. Whether writing a particular academic essay (such as persuasive, narrative, descriptive, or expository) or a timed exam essay, the key to getting good at writing is to write. Creating opportunities for our students to engage in extended writing activities will go a long way to helping them improve their skills as scribes.
But, putting the hours in alone will not be enough to attain the highest levels in essay writing. Practice must be meaningful. Once students have a broad overview of how to structure the various types of essays, they are ready to narrow in on the minor details that will enable them to fine-tune their work as a lean vehicle of their thoughts and ideas.

In this article, we will drill down to some aspects that will assist students in taking their essay writing skills up a notch. Many ideas and activities can be integrated into broader lesson plans based on essay writing. Often, though, they will work effectively in isolation – just as athletes isolate physical movements to drill that are relevant to their sport. When these movements become second nature, they can be repeated naturally in the context of the game or in our case, the writing of the essay.
THE ULTIMATE NONFICTION WRITING TEACHING RESOURCE

- 270 pages of the most effective teaching strategies
- 50+ digital tools ready right out of the box
- 75 editable resources for student differentiation
- Loads of tricks and tips to add to your teaching tool bag
- All explanations are reinforced with concrete examples.
- Links to high-quality video tutorials
- Clear objectives easy to match to the demands of your curriculum
Planning an essay

The Boys Scouts’ motto is famously ‘Be Prepared’. It’s a solid motto that can be applied to most aspects of life; essay writing is no different. Given the purpose of an essay is generally to present a logical and reasoned argument, investing time in organising arguments, ideas, and structure would seem to be time well spent.
Given that essays can take a wide range of forms and that we all have our own individual approaches to writing, it stands to reason that there will be no single best approach to the planning stage of essay writing. That said, there are several helpful hints and techniques we can share with our students to help them wrestle their ideas into a writable form. Let’s take a look at a few of the best of these:
BREAK THE QUESTION DOWN: UNDERSTAND YOUR ESSAY TOPIC.
Whether students are tackling an assignment that you have set for them in class or responding to an essay prompt in an exam situation, they should get into the habit of analyzing the nature of the task. To do this, they should unravel the question’s meaning or prompt. Students can practice this in class by responding to various essay titles, questions, and prompts, thereby gaining valuable experience breaking these down.
Have students work in groups to underline and dissect the keywords and phrases and discuss what exactly is being asked of them in the task. Are they being asked to discuss, describe, persuade, or explain? Understanding the exact nature of the task is crucial before going any further in the planning process, never mind the writing process .
BRAINSTORM AND MIND MAP WHAT YOU KNOW:
Once students have understood what the essay task asks them, they should consider what they know about the topic and, often, how they feel about it. When teaching essay writing, we so often emphasize that it is about expressing our opinions on things, but for our younger students what they think about something isn’t always obvious, even to themselves.
Brainstorming and mind-mapping what they know about a topic offers them an opportunity to uncover not just what they already know about a topic, but also gives them a chance to reveal to themselves what they think about the topic. This will help guide them in structuring their research and, later, the essay they will write . When writing an essay in an exam context, this may be the only ‘research’ the student can undertake before the writing, so practicing this will be even more important.
RESEARCH YOUR ESSAY
The previous step above should reveal to students the general direction their research will take. With the ubiquitousness of the internet, gone are the days of students relying on a single well-thumbed encyclopaedia from the school library as their sole authoritative source in their essay. If anything, the real problem for our students today is narrowing down their sources to a manageable number. Students should use the information from the previous step to help here. At this stage, it is important that they:
● Ensure the research material is directly relevant to the essay task
● Record in detail the sources of the information that they will use in their essay
● Engage with the material personally by asking questions and challenging their own biases
● Identify the key points that will be made in their essay
● Group ideas, counterarguments, and opinions together
● Identify the overarching argument they will make in their own essay.
Once these stages have been completed the student is ready to organise their points into a logical order.
WRITING YOUR ESSAY
There are a number of ways for students to organize their points in preparation for writing. They can use graphic organizers , post-it notes, or any number of available writing apps. The important thing for them to consider here is that their points should follow a logical progression. This progression of their argument will be expressed in the form of body paragraphs that will inform the structure of their finished essay.
The number of paragraphs contained in an essay will depend on a number of factors such as word limits, time limits, the complexity of the question etc. Regardless of the essay’s length, students should ensure their essay follows the Rule of Three in that every essay they write contains an introduction, body paragraphs, and a conclusion.
Generally speaking, essay paragraphs will focus on one main idea that is usually expressed in a topic sentence that is followed by a series of supporting sentences that bolster that main idea. The first and final sentences are of the most significance here with the first sentence of a paragraph making the point to the reader and the final sentence of the paragraph making the overall relevance to the essay’s argument crystal clear.
Though students will most likely be familiar with the broad generic structure of essays, it is worth investing time to ensure they have a clear conception of how each part of the essay works, that is, of the exact nature of the task it performs. Let’s review:
Common Essay Structure
Introduction: Provides the reader with context for the essay. It states the broad argument that the essay will make and informs the reader of the writer’s general perspective and approach to the question.
Body Paragraphs: These are the ‘meat’ of the essay and lay out the argument stated in the introduction point by point with supporting evidence.
Conclusion: Usually, the conclusion will restate the central argument while summarising the essay’s main supporting reasons before linking everything back to the original question.
ESSAY WRITING PARAGRAPH WRITING TIPS

● Each paragraph should focus on a single main idea
● Paragraphs should follow a logical sequence; students should group similar ideas together to avoid incoherence
● Paragraphs should be denoted consistently; students should choose either to indent or skip a line
● Transition words and phrases such as alternatively , consequently , in contrast should be used to give flow and provide a bridge between paragraphs.
HOW TO EDIT AN ESSAY

Students shouldn’t expect their essays to emerge from the writing process perfectly formed. Except in exam situations and the like, thorough editing is an essential aspect in the writing process.
Often, students struggle with this aspect of the process the most. After spending hours of effort on planning, research, and writing the first draft, students can be reluctant to go back over the same terrain they have so recently travelled. It is important at this point to give them some helpful guidelines to help them to know what to look out for. The following tips will provide just such help:
One Piece at a Time: There is a lot to look out for in the editing process and often students overlook aspects as they try to juggle too many balls during the process. One effective strategy to combat this is for students to perform a number of rounds of editing with each focusing on a different aspect. For example, the first round could focus on content, the second round on looking out for word repetition (use a thesaurus to help here), with the third attending to spelling and grammar.
Sum It Up: When reviewing the paragraphs they have written, a good starting point is for students to read each paragraph and attempt to sum up its main point in a single line. If this is not possible, their readers will most likely have difficulty following their train of thought too and the paragraph needs to be overhauled.
Let It Breathe: When possible, encourage students to allow some time for their essay to ‘breathe’ before returning to it for editing purposes. This may require some skilful time management on the part of the student, for example, a student rush-writing the night before the deadline does not lend itself to effective editing. Fresh eyes are one of the sharpest tools in the writer’s toolbox.
Read It Aloud: This time-tested editing method is a great way for students to identify mistakes and typos in their work. We tend to read things more slowly when reading aloud giving us the time to spot errors. Also, when we read silently our minds can often fill in the gaps or gloss over the mistakes that will become apparent when we read out loud.
Phone a Friend: Peer editing is another great way to identify errors that our brains may miss when reading our own work. Encourage students to partner up for a little ‘you scratch my back, I scratch yours’.
Use Tech Tools: We need to ensure our students have the mental tools to edit their own work and for this they will need a good grasp of English grammar and punctuation. However, there are also a wealth of tech tools such as spellcheck and grammar checks that can offer a great once-over option to catch anything students may have missed in earlier editing rounds.

Putting the Jewels on Display: While some struggle to edit, others struggle to let go. There comes a point when it is time for students to release their work to the reader. They must learn to relinquish control after the creation is complete. This will be much easier to achieve if the student feels that they have done everything in their control to ensure their essay is representative of the best of their abilities and if they have followed the advice here, they should be confident they have done so.
WRITING CHECKLISTS FOR ALL TEXT TYPES

ESSAY WRITING video tutorials

Classroom Q&A
With larry ferlazzo.
In this EdWeek blog, an experiment in knowledge-gathering, Ferlazzo will address readers’ questions on classroom management, ELL instruction, lesson planning, and other issues facing teachers. Send your questions to [email protected]. Read more from this blog.
Four Strategies for Effective Writing Instruction

- Share article
(This is the first post in a two-part series.)
The new question-of-the-week is:
What is the single most effective instructional strategy you have used to teach writing?
Teaching and learning good writing can be a challenge to educators and students alike.
The topic is no stranger to this column—you can see many previous related posts at Writing Instruction .
But I don’t think any of us can get too much good instructional advice in this area.
Today, Jenny Vo, Michele Morgan, and Joy Hamm share wisdom gained from their teaching experience.
Before I turn over the column to them, though, I’d like to share my favorite tool(s).
Graphic organizers, including writing frames (which are basically more expansive sentence starters) and writing structures (which function more as guides and less as “fill-in-the-blanks”) are critical elements of my writing instruction.
You can see an example of how I incorporate them in my seven-week story-writing unit and in the adaptations I made in it for concurrent teaching.
You might also be interested in The Best Scaffolded Writing Frames For Students .
Now, to today’s guests:
‘Shared Writing’
Jenny Vo earned her B.A. in English from Rice University and her M.Ed. in educational leadership from Lamar University. She has worked with English-learners during all of her 24 years in education and is currently an ESL ISST in Katy ISD in Katy, Texas. Jenny is the president-elect of TexTESOL IV and works to advocate for all ELs:
The single most effective instructional strategy that I have used to teach writing is shared writing. Shared writing is when the teacher and students write collaboratively. In shared writing, the teacher is the primary holder of the pen, even though the process is a collaborative one. The teacher serves as the scribe, while also questioning and prompting the students.
The students engage in discussions with the teacher and their peers on what should be included in the text. Shared writing can be done with the whole class or as a small-group activity.
There are two reasons why I love using shared writing. One, it is a great opportunity for the teacher to model the structures and functions of different types of writing while also weaving in lessons on spelling, punctuation, and grammar.
It is a perfect activity to do at the beginning of the unit for a new genre. Use shared writing to introduce the students to the purpose of the genre. Model the writing process from beginning to end, taking the students from idea generation to planning to drafting to revising to publishing. As you are writing, make sure you refrain from making errors, as you want your finished product to serve as a high-quality model for the students to refer back to as they write independently.
Another reason why I love using shared writing is that it connects the writing process with oral language. As the students co-construct the writing piece with the teacher, they are orally expressing their ideas and listening to the ideas of their classmates. It gives them the opportunity to practice rehearsing what they are going to say before it is written down on paper. Shared writing gives the teacher many opportunities to encourage their quieter or more reluctant students to engage in the discussion with the types of questions the teacher asks.
Writing well is a skill that is developed over time with much practice. Shared writing allows students to engage in the writing process while observing the construction of a high-quality sample. It is a very effective instructional strategy used to teach writing.

‘Four Square’
Michele Morgan has been writing IEPs and behavior plans to help students be more successful for 17 years. She is a national-board-certified teacher, Utah Teacher Fellow with Hope Street Group, and a special education elementary new-teacher specialist with the Granite school district. Follow her @MicheleTMorgan1:
For many students, writing is the most dreaded part of the school day. Writing involves many complex processes that students have to engage in before they produce a product—they must determine what they will write about, they must organize their thoughts into a logical sequence, and they must do the actual writing, whether on a computer or by hand. Still they are not done—they must edit their writing and revise mistakes. With all of that, it’s no wonder that students struggle with writing assignments.
In my years working with elementary special education students, I have found that writing is the most difficult subject to teach. Not only do my students struggle with the writing process, but they often have the added difficulties of not knowing how to spell words and not understanding how to use punctuation correctly. That is why the single most effective strategy I use when teaching writing is the Four Square graphic organizer.
The Four Square instructional strategy was developed in 1999 by Judith S. Gould and Evan Jay Gould. When I first started teaching, a colleague allowed me to borrow the Goulds’ book about using the Four Square method, and I have used it ever since. The Four Square is a graphic organizer that students can make themselves when given a blank sheet of paper. They fold it into four squares and draw a box in the middle of the page. The genius of this instructional strategy is that it can be used by any student, in any grade level, for any writing assignment. These are some of the ways I have used this strategy successfully with my students:
* Writing sentences: Students can write the topic for the sentence in the middle box, and in each square, they can draw pictures of details they want to add to their writing.
* Writing paragraphs: Students write the topic sentence in the middle box. They write a sentence containing a supporting detail in three of the squares and they write a concluding sentence in the last square.
* Writing short essays: Students write what information goes in the topic paragraph in the middle box, then list details to include in supporting paragraphs in the squares.
When I gave students writing assignments, the first thing I had them do was create a Four Square. We did this so often that it became automatic. After filling in the Four Square, they wrote rough drafts by copying their work off of the graphic organizer and into the correct format, either on lined paper or in a Word document. This worked for all of my special education students!
I was able to modify tasks using the Four Square so that all of my students could participate, regardless of their disabilities. Even if they did not know what to write about, they knew how to start the assignment (which is often the hardest part of getting it done!) and they grew to be more confident in their writing abilities.
In addition, when it was time to take the high-stakes state writing tests at the end of the year, this was a strategy my students could use to help them do well on the tests. I was able to give them a sheet of blank paper, and they knew what to do with it. I have used many different curriculum materials and programs to teach writing in the last 16 years, but the Four Square is the one strategy that I have used with every writing assignment, no matter the grade level, because it is so effective.

‘Swift Structures’
Joy Hamm has taught 11 years in a variety of English-language settings, ranging from kindergarten to adult learners. The last few years working with middle and high school Newcomers and completing her M.Ed in TESOL have fostered stronger advocacy in her district and beyond:
A majority of secondary content assessments include open-ended essay questions. Many students falter (not just ELs) because they are unaware of how to quickly organize their thoughts into a cohesive argument. In fact, the WIDA CAN DO Descriptors list level 5 writing proficiency as “organizing details logically and cohesively.” Thus, the most effective cross-curricular secondary writing strategy I use with my intermediate LTELs (long-term English-learners) is what I call “Swift Structures.” This term simply means reading a prompt across any content area and quickly jotting down an outline to organize a strong response.
To implement Swift Structures, begin by displaying a prompt and modeling how to swiftly create a bubble map or outline beginning with a thesis/opinion, then connecting the three main topics, which are each supported by at least three details. Emphasize this is NOT the time for complete sentences, just bulleted words or phrases.
Once the outline is completed, show your ELs how easy it is to plug in transitions, expand the bullets into detailed sentences, and add a brief introduction and conclusion. After modeling and guided practice, set a 5-10 minute timer and have students practice independently. Swift Structures is one of my weekly bell ringers, so students build confidence and skill over time. It is best to start with easy prompts where students have preformed opinions and knowledge in order to focus their attention on the thesis-topics-supporting-details outline, not struggling with the rigor of a content prompt.
Here is one easy prompt example: “Should students be allowed to use their cellphones in class?”
Swift Structure outline:
Thesis - Students should be allowed to use cellphones because (1) higher engagement (2) learning tools/apps (3) gain 21st-century skills
Topic 1. Cellphones create higher engagement in students...
Details A. interactive (Flipgrid, Kahoot)
B. less tempted by distractions
C. teaches responsibility
Topic 2. Furthermore,...access to learning tools...
A. Google Translate description
B. language practice (Duolingo)
C. content tutorials (Kahn Academy)
Topic 3. In addition,...practice 21st-century skills…
Details A. prep for workforce
B. access to information
C. time-management support
This bare-bones outline is like the frame of a house. Get the structure right, and it’s easier to fill in the interior decorating (style, grammar), roof (introduction) and driveway (conclusion). Without the frame, the roof and walls will fall apart, and the reader is left confused by circuitous rubble.
Once LTELs have mastered creating simple Swift Structures in less than 10 minutes, it is time to introduce complex questions similar to prompts found on content assessments or essays. Students need to gain assurance that they can quickly and logically explain and justify their opinions on multiple content essays without freezing under pressure.

Thanks to Jenny, Michele, and Joy for their contributions!
Please feel free to leave a comment with your reactions to the topic or directly to anything that has been said in this post.
Consider contributing a question to be answered in a future post. You can send one to me at [email protected] . When you send it in, let me know if I can use your real name if it’s selected or if you’d prefer remaining anonymous and have a pseudonym in mind.
You can also contact me on Twitter at @Larryferlazzo .
Education Week has published a collection of posts from this blog, along with new material, in an e-book form. It’s titled Classroom Management Q&As: Expert Strategies for Teaching .
Just a reminder; you can subscribe and receive updates from this blog via email (The RSS feed for this blog, and for all Ed Week articles, has been changed by the new redesign—new ones are not yet available). And if you missed any of the highlights from the first nine years of this blog, you can see a categorized list below.
- This Year’s Most Popular Q&A Posts
- Race & Racism in Schools
- School Closures & the Coronavirus Crisis
- Classroom-Management Advice
- Best Ways to Begin the School Year
- Best Ways to End the School Year
- Student Motivation & Social-Emotional Learning
- Implementing the Common Core
- Facing Gender Challenges in Education
- Teaching Social Studies
- Cooperative & Collaborative Learning
- Using Tech in the Classroom
- Student Voices
- Parent Engagement in Schools
- Teaching English-Language Learners
- Reading Instruction
- Writing Instruction
- Education Policy Issues
- Differentiating Instruction
- Math Instruction
- Science Instruction
- Advice for New Teachers
- Author Interviews
- Entering the Teaching Profession
- The Inclusive Classroom
- Learning & the Brain
- Administrator Leadership
- Teacher Leadership
- Relationships in Schools
- Professional Development
- Instructional Strategies
- Best of Classroom Q&A
- Professional Collaboration
- Classroom Organization
- Mistakes in Education
- Project-Based Learning
I am also creating a Twitter list including all contributors to this column .
The opinions expressed in Classroom Q&A With Larry Ferlazzo are strictly those of the author(s) and do not reflect the opinions or endorsement of Editorial Projects in Education, or any of its publications.
Sign Up for EdWeek Update
Edweek top school jobs.

Sign Up & Sign In

- Share full article
Advertisement
Supported by
Our 2020-21 Writing Curriculum for Middle and High School
A flexible, seven-unit program based on the real-world writing found in newspapers, from editorials and reviews to personal narratives and informational essays.

Update, Aug. 3, 2023: Find our 2023-24 writing curriculum here.
Our 2019-20 Writing Curriculum is one of the most popular new features we’ve ever run on this site, so, of course, we’re back with a 2020-21 version — one we hope is useful whether you’re teaching in person , online , indoors , outdoors , in a pod , as a homeschool , or in some hybrid of a few of these.
The curriculum detailed below is both a road map for teachers and an invitation to students. For teachers, it includes our writing prompts, mentor texts, contests and lesson plans, and organizes them all into seven distinct units. Each focuses on a different genre of writing that you can find not just in The Times but also in all kinds of real-world sources both in print and online.
But for students, our main goal is to show young people they have something valuable to say, and to give those voices a global audience. That’s always been a pillar of our site, but this year it is even more critical. The events of 2020 will define this generation, and many are living through them isolated from their ordinary communities, rituals and supports. Though a writing curriculum can hardly make up for that, we hope that it can at least offer teenagers a creative outlet for making sense of their experiences, and an enthusiastic audience for the results. Through the opportunities for publication woven throughout each unit, we want to encourage students to go beyond simply being media consumers to become creators and contributors themselves.
So have a look, and see if you can find a way to include any of these opportunities in your curriculum this year, whether to help students document their lives, tell stories, express opinions, investigate ideas, or analyze culture. We can’t wait to hear what your students have to say!
Each unit includes:
Writing prompts to help students try out related skills in a “low stakes” way.
We publish two writing prompts every school day, and we also have thematic collections of more than 1,000 prompts published in the past. Your students might consider responding to these prompts on our site and using our public forums as a kind of “rehearsal space” for practicing voice and technique.
Daily opportunities to practice writing for an authentic audience.
If a student submits a comment on our site, it will be read by Times editors, who approve each one before it gets published. Submitting a comment also gives students an audience of fellow teenagers from around the world who might read and respond to their work. Each week, we call out our favorite comments and honor dozens of students by name in our Thursday “ Current Events Conversation ” feature.
Guided practice with mentor texts .
Each unit we publish features guided practice lessons, written directly to students, that help them observe, understand and practice the kinds of “craft moves” that make different genres of writing sing. From how to “show not tell” in narratives to how to express critical opinions , quote or paraphrase experts or craft scripts for podcasts , we have used the work of both Times journalists and the teenage winners of our contests to show students techniques they can emulate.
“Annotated by the Author” commentaries from Times writers — and teenagers.
As part of our Mentor Texts series , we’ve been asking Times journalists from desks across the newsroom to annotate their articles to let students in on their writing, research and editing processes, and we’ll be adding more for each unit this year. Whether it’s Science writer Nicholas St. Fleur on tiny tyrannosaurs , Opinion writer Aisha Harris on the cultural canon , or The Times’s comics-industry reporter, George Gene Gustines, on comic books that celebrate pride , the idea is to demystify journalism for teenagers. This year, we’ll be inviting student winners of our contests to annotate their work as well.
A contest that can act as a culminating project .
Over the years we’ve heard from many teachers that our contests serve as final projects in their classes, and this curriculum came about in large part because we want to help teachers “plan backwards” to support those projects.
All contest entries are considered by experts, whether Times journalists, outside educators from partner organizations, or professional practitioners in a related field. Winning means being published on our site, and, perhaps, in the print edition of The New York Times.
Webinars and our new professional learning community (P.L.C.).
For each of the seven units in this curriculum, we host a webinar featuring Learning Network editors as well as teachers who use The Times in their classrooms. Our webinars introduce participants to our many resources and provide practical how-to’s on how to use our prompts, mentor texts and contests in the classroom.
New for this school year, we also invite teachers to join our P.L.C. on teaching writing with The Times , where educators can share resources, strategies and inspiration about teaching with these units.
Below are the seven units we will offer in the 2020-21 school year.
September-October
Unit 1: Documenting Teenage Lives in Extraordinary Times
This special unit acknowledges both the tumultuous events of 2020 and their outsized impact on young people — and invites teenagers to respond creatively. How can they add their voices to our understanding of what this historic year will mean for their generation?
Culminating in our Coming of Age in 2020 contest, the unit helps teenagers document and respond to what it’s been like to live through what one Times article describes as “a year of tragedy, of catastrophe, of upheaval, a year that has inflicted one blow after another, a year that has filled the morgues, emptied the schools, shuttered the workplaces, swelled the unemployment lines and polarized the electorate.”
A series of writing prompts, mentor texts and a step-by-step guide will help them think deeply and analytically about who they are, how this year has impacted them, what they’d like to express as a result, and how they’d like to express it. How might they tell their unique stories in ways that feel meaningful and authentic, whether those stories are serious or funny, big or small, raw or polished?
Though the contest accepts work across genres — via words and images, video and audio — all students will also craft written artist’s statements for each piece they submit. In addition, no matter what genre of work students send in, the unit will use writing as a tool throughout to help students brainstorm, compose and edit. And, of course, this work, whether students send it to us or not, is valuable far beyond the classroom: Historians, archivists and museums recommend that we all document our experiences this year, if only for ourselves.
October-November
Unit 2: The Personal Narrative
While The Times is known for its award-winning journalism, the paper also has a robust tradition of publishing personal essays on topics like love , family , life on campus and navigating anxiety . And on our site, our daily writing prompts have long invited students to tell us their stories, too. Our 2019 collection of 550 Prompts for Narrative and Personal Writing is a good place to start, though we add more every week during the school year.
In this unit we draw on many of these resources, plus some of the 1,000-plus personal essays from the Magazine’s long-running Lives column , to help students find their own “short, memorable stories ” and tell them well. Our related mentor-text lessons can help them practice skills like writing with voice , using details to show rather than tell , structuring a narrative arc , dropping the reader into a scene and more. This year, we’ll also be including mentor text guided lessons that use the work of the 2019 student winners.
As a final project, we invite students to send finished stories to our Second Annual Personal Narrative Writing Contest .
DECEMBER-January
Unit 3: The Review
Book reports and literary essays have long been staples of language arts classrooms, but this unit encourages students to learn how to critique art in other genres as well. As we point out, a cultural review is, of course, a form of argumentative essay. Your class might be writing about Lizzo or “ Looking for Alaska ,” but they still have to make claims and support them with evidence. And, just as they must in a literature essay, they have to read (or watch, or listen to) a work closely; analyze it and understand its context; and explain what is meaningful and interesting about it.
In our Mentor Texts series , we feature the work of Times movie , restaurant , book and music critics to help students understand the elements of a successful review. In each one of these guided lessons, we also spotlight the work of teenage contest winners from previous years.
As a culminating project, we invite students to send us their own reviews of a book, movie, restaurant, album, theatrical production, video game, dance performance, TV show, art exhibition or any other kind of work The Times critiques.
January-February
Unit 4: Informational Writing
Informational writing is the style of writing that dominates The New York Times as well as any other traditional newspaper you might read, and in this unit we hope to show students that it can be every bit as engaging and compelling to read and to write as other genres. Via thousands of articles a month — from front-page reporting on politics to news about athletes in Sports, deep data dives in The Upshot, recipes in Cooking, advice columns in Style and long-form investigative pieces in the magazine — Times journalists find ways to experiment with the genre to intrigue and inform their audiences.
This unit invites students to take any STEM-related discovery, process or idea that interests them and write about it in a way that makes it understandable and engaging for a general audience — but all the skills we teach along the way can work for any kind of informational writing. Via our Mentor Texts series, we show them how to hook the reader from the start , use quotes and research , explain why a topic matters and more. This year we’ll be using the work of the 2020 student winners for additional mentor text lessons.
At the end of the unit, we invite teenagers to submit their own writing to our Second Annual STEM writing contest to show us what they’ve learned.
March-April
Unit 5: Argumentative Writing
The demand for evidence-based argumentative writing is now woven into school assignments across the curriculum and grade levels, and you couldn’t ask for better real-world examples than what you can find in The Times Opinion section .
This unit will, like our others, be supported with writing prompts, mentor-text lesson plans, webinars and more. We’ll also focus on the winning teenage writing we’ve received over the six years we’ve run our related contest.
At a time when media literacy is more important than ever, we also hope that our annual Student Editorial Contest can serve as a final project that encourages students to broaden their information diets with a range of reliable sources, and learn from a variety of perspectives on their chosen issue.
To help students working from home, we also have an Argumentative Unit for Students Doing Remote Learning .
Unit 6: Writing for Podcasts
Most of our writing units so far have all asked for essays of one kind or another, but this spring contest invites students to do what journalists at The Times do every day: make multimedia to tell a story, investigate an issue or communicate a concept.
Our annual podcast contest gives students the freedom to talk about anything they want in any form they like. In the past we’ve had winners who’ve done personal narratives, local travelogues, opinion pieces, interviews with community members, local investigative journalism and descriptions of scientific discoveries.
As with all our other units, we have supported this contest with great examples from The Times and around the web, as well as with mentor texts by teenagers that offer guided practice in understanding elements and techniques.
June-August
Unit 7: Independent Reading and Writing
At a time when teachers are looking for ways to offer students more “voice and choice,” this unit, based on our annual summer contest, offers both.
Every year since 2010 we have invited teenagers around the world to add The New York Times to their summer reading lists and, so far, 70,000 have. Every week for 10 weeks, we ask participants to choose something in The Times that has sparked their interest, then tell us why. At the end of the week, judges from the Times newsroom pick favorite responses, and we publish them on our site.
And we’ve used our Mentor Text feature to spotlight the work of past winners , explain why newsroom judges admired their thinking, and provide four steps to helping any student write better reader-responses.
Because this is our most open-ended contest — students can choose whatever they like, and react however they like — it has proved over the years to be a useful place for young writers to hone their voices, practice skills and take risks . Join us!
12 Lesson Plans for Teaching Writing to Secondary Students

Blog category: Education Date: 21 September 2017

It can be tough to think of ways to keep things interesting when teaching writing to high school students. Fortunately, there are so many great lesson plans out there to give you a starting point. We’ve compiled a list of 12 great lesson plans for teaching different writing techniques and styles to high school students.
1. News stories
It’s important for students to learn that different types of writing require different styles. For example, the structure and tone of a newspaper article differs greatly from a creative narrative. This news story writing lesson is a great way to help students produce writing with more lexical variation, complex sentences and passive structures.
2. Calling all characters
Writing fictional narratives can be daunting to many students who feel uncomfortable sharing their ideas, so breaking down the creative writing process is a good way to help students get the ball rolling. This lesson plan requires students to brainstorm character traits, behaviours and actions, then write scenes about that character. Although this lesson plan was designed for primary students, it can be adapted for secondary-level creative writing by removing the simpler games.
3. Drafting your essay
Essay writing is a major part of high school so it’s important to find different ways of engaging students to reinforce their learning of this type of text. This activity has students deconstruct other essays to learn about essay structure, which will help them when they go to write their own essays. Again, because this is a lesson plan for primary school students, it should be adapted to suit the grade of high school you’re teaching, for example, substitute the picture book for a secondary school novel.
4. Object creative writing
Rather than starting with characters, another way to prompt students to write stories is the object creative writing lesson plan. By giving students an object to describe, they learn to think creatively in response to a stimulus and develop their descriptive writing skills. Thinking on their feet will help them develop the skills to formulate their own creative ideas in the future.
5. Letter of complaint
Letters are a common text type that your students will be familiar with. The purpose of this lesson plan is to encourage students to use phrases that express attitude and emotion, which are found in letters of complaint.
6. Advertising
Advertising uses persuasive language, so practicing this type of writing can help students in forming arguments in essays and debates. Learning how to sell something can also help develop confidence in students.
7. Peer editing
This lesson plan involves students editing the writing of their peers. Marking the work of others can help a student develop an understanding of their own writing skills by analysing what they would do differently. Responding to feedback from peers also encourages students to develop a positive attitude towards criticism and learning.
8. Self-reflection
Writing about writing is one of the best ways to help students reduce the number of errors in their work. This lesson plan requires students to read over their work and identify one error that occurs frequently, then rewrite the piece without the error. This activity helps students learn how to correct their work and address habits so that they occur less frequently in the future.
9. Writing for a real purpose
Writing for a hypothetical purpose can leave students feeling unmotivated to produce their best work. For this lesson plan, students respond to real life scenarios that they’re personally interested in. This way, students adopt an authentic voice, based on real life experience, making their work more engaging.
10. The 100-word challenge
Being able to write clearly and succinctly is an important writing skill for students in high school and beyond. This lesson idea teaches students how to get to the point in a small number of words, by asking student to respond to a prompt in 100 words or less.
11. Start a pseudonym project
If you have a students who are particularly shy about sharing their writing with others, you can introduce an anonymous system. Allow students to choose a pseudonym they will use for handing in work. The idea is that students will feel less conscious about being personal or passionate in their work, and therefore produce higher quality work.
12. Copy cat
Some types of writing, like poetry and creative writing, are harder for students than structured essays and short responses. To help students adopt more creative tones in their writing, this lesson asks students to bring in a piece of writing (poetry or novel) and write their own original piece using the same style and tone.
Get creative
Learning to write different text types, from essays and letters, to creative stories and poetry, can be challenging for students. To help them along the way, it’s important to introduce lesson plans that encourage imagination and help develop lifelong skills that will improve their writing.
Select your localisation:

- Privacy Overview
- Strictly Necessary Cookies
- 3rd Party Cookies
- Cookie Policy
This website uses cookies so that we can provide you with the best user experience possible. Cookie information is stored in your browser and performs functions such as recognising you when you return to our website and helping our team to understand which sections of the website you find most interesting and useful.
Strictly Necessary Cookie should be enabled at all times so that we can save your preferences for cookie settings.
If you disable this cookie, we will not be able to save your preferences. This means that every time you visit this website you will need to enable or disable cookies again.
This website uses third-party tools to collect anonymous information such as the number of visitors to the site, the source of those visitors and the most popular pages.
Keeping this cookie enabled helps us to improve our website and marketing activities.
Please enable Strictly Necessary Cookies first so that we can save your preferences!
More information about our Cookie Policy
A Step-by-Step Plan for Teaching Argumentative Writing
February 7, 2016
Can't find what you are looking for? Contact Us

Listen to this post as a podcast:
This page contains Amazon Affiliate and Bookshop.org links. When you make a purchase through these links, Cult of Pedagogy gets a small percentage of the sale at no extra cost to you. What’s the difference between Amazon and Bookshop.org?
For seven years, I was a writing teacher. Yes, I was certified to teach the full spectrum of English language arts—literature, grammar and usage, speech, drama, and so on—but my absolute favorite, the thing I loved doing the most, was teaching students how to write.
Most of the material on this site is directed at all teachers. I look for and put together resources that would appeal to any teacher who teaches any subject. That practice will continue for as long as I keep this up. But over the next year or so, I plan to also share more of what I know about teaching students to write. Although I know many of the people who visit here are not strictly English language arts teachers, my hope is that these posts will provide tons of value to those who are, and to those who teach all subjects, including writing.
So let’s begin with argumentative writing, or persuasive writing, as many of us used to call it. This overview will be most helpful to those who are new to teaching writing, or teachers who have not gotten good results with the approach you have taken up to now. I don’t claim to have the definitive answer on how to do this, but the method I share here worked pretty well for me, and it might do the same for you. If you are an experienced English language arts teacher, you probably already have a system for teaching this skill that you like. Then again, I’m always interested in how other people do the things I can already do; maybe you’re curious like that, too.
Before I start, I should note that what I describe in this post is a fairly formulaic style of essay writing. It’s not exactly the 5-paragraph essay, but it definitely builds on that model. I strongly believe students should be shown how to move past those kinds of structures into a style of writing that’s more natural and fitting to the task and audience, but I also think they should start with something that’s pretty clearly organized.
So here’s how I teach argumentative essay writing.
Step 1: Watch How It’s Done
One of the most effective ways to improve student writing is to show them mentor texts, examples of excellent writing within the genre students are about to attempt themselves. Ideally, this writing would come from real publications and not be fabricated by me in order to embody the form I’m looking for. Although most experts on writing instruction employ some kind of mentor text study, the person I learned it from best was Katie Wood Ray in her book Study Driven (links to the book: Bookshop.org | Amazon ).
Since I want the writing to be high quality and the subject matter to be high interest, I might choose pieces like Jessica Lahey’s Students Who Lose Recess Are the Ones Who Need it Most and David Bulley’s School Suspensions Don’t Work .
I would have students read these texts, compare them, and find places where the authors used evidence to back up their assertions. I would ask students which author they feel did the best job of influencing the reader, and what suggestions they would make to improve the writing. I would also ask them to notice things like stories, facts and statistics, and other things the authors use to develop their ideas. Later, as students work on their own pieces, I would likely return to these pieces to show students how to execute certain writing moves.
Step 2: Informal Argument, Freestyle
Although many students might need more practice in writing an effective argument, many of them are excellent at arguing in person. To help them make this connection, I would have them do some informal debate on easy, high-interest topics. An activity like This or That (one of the classroom icebreakers I talked about last year) would be perfect here: I read a statement like “Women have the same opportunities in life as men.” Students who agree with the statement move to one side of the room, and those who disagree move to the other side. Then they take turns explaining why they are standing in that position. This ultimately looks a little bit like a debate, as students from either side tend to defend their position to those on the other side.
Every class of students I have ever had, from middle school to college, has loved loved LOVED this activity. It’s so simple, it gets them out of their seats, and for a unit on argument, it’s an easy way to get them thinking about how the art of argument is something they practice all the time.
Step 3: Informal Argument, Not so Freestyle
Once students have argued without the support of any kind of research or text, I would set up a second debate; this time with more structure and more time to research ahead of time. I would pose a different question, supply students with a few articles that would provide ammunition for either side, then give them time to read the articles and find the evidence they need.
Next, we’d have a Philosophical Chairs debate (learn about this in my discussion strategies post), which is very similar to “This or That,” except students use textual evidence to back up their points, and there are a few more rules. Here they are still doing verbal argument, but the experience should make them more likely to appreciate the value of evidence when trying to persuade.
Before leaving this step, I would have students transfer their thoughts from the discussion they just had into something that looks like the opening paragraph of a written argument: A statement of their point of view, plus three reasons to support that point of view. This lays the groundwork for what’s to come.
Step 4: Introduction of the Performance Assessment
Next I would show students their major assignment, the performance assessment that they will work on for the next few weeks. What does this look like? It’s generally a written prompt that describes the task, plus the rubric I will use to score their final product.
Anytime I give students a major writing assignment, I let them see these documents very early on. In my experience, I’ve found that students appreciate having a clear picture of what’s expected of them when beginning a writing assignment. At this time, I also show them a model of a piece of writing that meets the requirements of the assignment. Unlike the mentor texts we read on day 1, this sample would be something teacher-created (or an excellent student model from a previous year) to fit the parameters of the assignment.
Step 5: Building the Base
Before letting students loose to start working on their essays, I make sure they have a solid plan for writing. I would devote at least one more class period to having students consider their topic for the essay, drafting a thesis statement, and planning the main points of their essay in a graphic organizer.
I would also begin writing my own essay on a different topic. This has been my number one strategy for teaching students how to become better writers. Using a document camera or overhead projector, I start from scratch, thinking out loud and scribbling down my thoughts as they come. When students see how messy the process can be, it becomes less intimidating for them. They begin to understand how to take the thoughts that are stirring around in your head and turn them into something that makes sense in writing.
For some students, this early stage might take a few more days, and that’s fine: I would rather spend more time getting it right at the pre-writing stage than have a student go off willy-nilly, draft a full essay, then realize they need to start over. Meanwhile, students who have their plans in order will be allowed to move on to the next step.
Step 6: Writer’s Workshop
The next seven to ten days would be spent in writer’s workshop, where I would start class with a mini-lesson about a particular aspect of craft. I would show them how to choose credible, relevant evidence, how to skillfully weave evidence into an argument, how to consider the needs of an audience, and how to correctly cite sources. Once each mini-lesson was done, I would then give students the rest of the period to work independently on their writing. During this time, I would move around the room, helping students solve problems and offering feedback on whatever part of the piece they are working on. I would encourage students to share their work with peers and give feedback at all stages of the writing process.
If I wanted to make the unit even more student-centered, I would provide the mini-lessons in written or video format and let students work through them at their own pace, without me teaching them. (To learn more about this approach, read this post on self-paced learning ).
As students begin to complete their essays, the mini-lessons would focus more on matters of style and usage. I almost never bother talking about spelling, punctuation, grammar, or usage until students have a draft that’s pretty close to done. Only then do we start fixing the smaller mistakes.
Step 7: Final Assessment
Finally, the finished essays are handed in for a grade. At this point, I’m pretty familiar with each student’s writing and have given them verbal (and sometimes written) feedback throughout the unit; that’s why I make the writer’s workshop phase last so long. I don’t really want students handing in work until they are pretty sure they’ve met the requirements to the best of their ability. I also don’t necessarily see “final copies” as final; if a student hands in an essay that’s still really lacking in some key areas, I will arrange to have that student revise it and resubmit for a higher grade.
So that’s it. If you haven’t had a lot of success teaching students to write persuasively, and if the approach outlined here is different from what you’ve been doing, give it a try. And let’s keep talking: Use the comments section below to share your techniques or ask questions about the most effective ways to teach argumentative writing.
Want this unit ready-made?
If you’re a writing teacher in grades 7-12 and you’d like a classroom-ready unit like the one described above, including mini-lessons, sample essays, and a library of high-interest online articles to use for gathering evidence, take a look at my Argumentative Writing unit. Just click on the image below and you’ll be taken to a page where you can read more and see a detailed preview of what’s included.
What to Read Next

Categories: Instruction , Podcast
Tags: English language arts , Grades 6-8 , Grades 9-12 , teaching strategies
58 Comments
This is useful information. In teaching persuasive speaking/writing I have found Monroe’s Motivated sequence very useful and productive. It is a classic model that immediately gives a solid structure for students.
Thanks for the recommendation, Bill. I will have to look into that! Here’s a link to more information on Monroe’s Motivated sequence, for anyone who wants to learn more: https://www.mindtools.com/pages/article/MonroeMotivatedSequence.htm
What other sites do you recommend for teacher use on providing effective organizational structure in argumentative writing? As a K-12 Curriculum Director, I find that when teachers connect with and understand the organizational structure, they are more effective in their teaching/delivery.
Hey Jessica, in addition to the steps outlined here, you might want to check out Jenn’s post on graphic organizers . Graphic organizers are a great tool that you can use in any phase of a lesson. Using them as a prewrite can help students visualize the argument and organize their thoughts. There’s a link in that post to the Graphic Organizer Multi-Pack that Jenn has for sale on her Teachers Pay Teachers site, which includes two versions of a graphic organizer you can use specifically for argument organization. Otherwise, if there’s something else you had in mind, let us know and we can help you out. Thanks!
Dear Jennifer Gonzalez,
You are generous with your gift of lighting the path… I hardly ever write (never before) , but I must today… THANK YOU… THANK YOU….THANK YOU… mostly for reading your great teachings… So your valuable teachings will even be easy to benefit all the smart people facing challenge of having to deal with adhd…
I am not a teacher… but forever a student…someone who studied English as 2nd language, with a science degree & adhd…
You truly are making a difference in our World…
Thanks so much, Rita! I know Jenn will appreciate this — I’ll be sure to share with her!
Love it! Its simple and very fruitful . I can feel how dedicated you are! Thanks alot Jen
Great examples of resources that students would find interesting. I enjoyed reading your article. I’ve bookmarked it for future reference. Thanks!
You’re welcome, Sheryl!
Students need to be writing all the time about a broad range of topics, but I love the focus here on argumentative writing because if you choose the model writing texts correctly, you can really get the kids engaged in the process and in how they can use this writing in real-world situations!
I agree, Laura. I think an occasional tight focus on one genre can help them grow leaps and bounds in the skills specific to that type of writing. Later, in less structured situations, they can then call on those skills when that kind of thinking is required.
This is really helpful! I used it today and put the recess article in a Google Doc and had the kids identify anecdotal, statistic, and ‘other’ types of evidence by highlighting them in three different colors. It worked well! Tomorrow we’ll discuss which of the different types of evidence are most convincing and why.
Love that, Shanna! Thanks for sharing that extra layer.
Greetings Ms. Gonzales. I was wondering if you had any ideas to help students develop the cons/against side of their argument within their writing? Please advise. Thanks.
Hi Michael,
Considering audience and counterarguments are an important part of the argumentative writing process. In the Argumentative Writing unit Jenn includes specific mini-lessons that teach kids how, when and where to include opposing views in their writing. In the meantime, here’s a video that might also be helpful.
Hi, Thank you very much for sharing your ideas. I want to share also the ideas in the article ‘Already Experts: Showing Students How Much They Know about Writing and Reading Arguments’ by Angela Petit and Edna Soto…they explain a really nice activity to introduce argumentative writing. I have applied it many times and my students not only love it but also display a very clear pattern as the results in the activity are quite similar every time. I hope you like it.
Lorena Perez
I’d like to thank you you for this excellence resource. It’s a wonderful addition to the informative content that Jennifer has shared.
What do you use for a prize?
I looked at the unit, and it looks and sounds great. The description says there are 4 topics. Can you tell me the topics before I purchase? We start argument in 5th grade, and I want to make sure the topics are different from those they’ve done the last 5 years before purchasing. Thanks!
Hi Carrie! If you go to the product page on TPT and open up the preview, you’ll see the four topics on the 4th page in more detail, but here they are: Social Networking in School (should social media sites be blocked in school?), Cell Phones in Class, Junk Food in School, and Single-Sex Education (i.e., genders separated). Does that help?
I teach 6th grade English in a single gendered (all-girls) class. We just finished an argument piece but I will definitely cycle back your ideas when we revisit argumentation. Thanks for the fabulous resources!
Glad to hear it, Madelyn!
I’m not a writing teacher and honestly haven’t been taught on how to teach writing. I’m a history teacher. I read this and found it helpful but have questions. First I noticed that amount of time dedicated to the task in terms of days. My questions are how long is a class period? I have my students for about 45 minutes. I also saw you mentioned in the part about self-paced learning that mini-lessons could be written or video format. I love these ideas. Any thoughts on how to do this with almost no technology in the room and low readers to non-readers? I’m trying to figure out how to balance teaching a content class while also teaching the common core skills. Thank you for any consideration to my questions.
Hey Jones, To me, a class period is anywhere from 45 minutes to an hour; definitely varies from school to school. As for the question about doing self-paced with very little tech? I think binders with written mini-lessons could work well, as well as a single computer station or tablet hooked up to a class set of videos. Obviously you’d need to be more diligent about rotating students in and out of these stations, but it’s an option at least. You might also give students access to the videos through computers in other locations at school (like the library) and give them passes to watch. The thing about self-paced learning, as you may have seen in the self-paced post , is that if students need extra teacher support (as you might find with low readers or non-readers), they would spend more one-on-one time with the teacher, while the higher-level students would be permitted to move more quickly on their own. Does that help?
My primary goal for next semester is to increase academic discussion and make connections from discussion to writing, so I love how you launch this unit with lessons like Philosophical Chairs. I am curious, however, what is the benefit of the informal argument before the not-so-informal argument? My students often struggle to listen to one another, so I’m wondering if I should start with the more formal, structured version. Or, am I overthinking the management? Thanks so much for input.
Yikes! So sorry your question slipped through, and we’re just now getting to this, Sarah. The main advantage of having kids first engage in informal debate is that it helps them get into an argumentative mindset and begin to appreciate the value of using research to support their claims. If you’ve purchased the unit, you can read more about this in the Overview.
My 6th graders are progressing through their argumentative essay. I’m providing mini lessons along the way that target where most students are in their essay. Your suggestions will be used. I’ve chosen to keep most writing in class and was happy to read that you scheduled a lot of class time for the writing. Students need to feel comfortable knowing that writing is a craft and needs to evolve over time. I think more will get done in class and it is especially important for the struggling writers to have peers and the teacher around while they write. Something that I had students do that they liked was to have them sit in like-topic groups to create a shared document where they curated information that MIGHT be helpful along the way. By the end of the essay, all will use a fantastic add-on called GradeProof which helps to eliminate most of the basic and silly errors that 6th graders make.
Debbi! I LOVE the idea of a shared, curated collection of resources! That is absolutely fantastic! Are you using a Google Doc for this? Other curation tools you might consider are Padlet and Elink .
thanks v much for all this information
Love this! What do you take as grades in the meantime? Throughout this 2 week stretch?
Ideally, you wouldn’t need to take grades at all, waiting until the final paper is done to give one grade. If your school requires more frequent grades, you could assign small point values for getting the incremental steps done: So in Step 3 (when students have to write a paragraph stating their point of view) you could take points for that. During the writer’s workshop phase, you might give points for completion of a rough draft and participation points for peer review (ideally, they’d get some kind of feedback on the quality of feedback they give to one another). Another option would be to just give a small, holistic grade for each week based on the overall integrity of their work–are they staying on task? Making small improvements to their writing each day? Taking advantage of the resources? If students are working diligently through the process, that should be enough. But again, the assessment (grades) should really come from that final written product, and if everyone is doing what they’re supposed to be doing during the workshop phase, most students should have pretty good scores on that final product. Does that help?
Awesome Step 2! Teaching mostly teenagers in Northern Australia I find students’ verbal arguments are much more finely honed than their written work.
To assist with “building the base” I’ve always found sentence starters an essential entry point for struggling students. We have started using the ‘PEARL’ method for analytical and persuasive writing.
If it helps here a free scaffold for the method:
https://www.teacherspayteachers.com/Product/FREE-Paragraph-Scaffold-PEEL-to-PEARL-3370676
Thanks again,
Thank you for sharing this additional resource! It’s excellent!
I’ve been scouring the interwebs looking for some real advice on how I can help my struggling 9th grader write better. I can write. Since it comes naturally for me, I have a hard time breaking it down into such tiny steps that he can begin to feel less overwhelmed. I LOVE the pre-writing ideas here. My son is a fabulous arguer. I need to help him use those powers for the good of his writing skills. Do you have a suggestion on what I else I can be using for my homeschooled son? Or what you may have that could work well for home use?
Hi Melinda,
You might be interested in taking a look at Jenn’s Argumentative Writing unit which she mentions at the end of the post . Hope this helps!
Mam it would be good if you could post some steps of different writing and some samples as well so it can be useful for the students.
Hi Aalia! My name is Holly, and I work as a Customer Experience Manager for Cult of Pedagogy. It just so happens that in the near future, Jenn is going to release a narrative writing unit, so keep an eye out for that! As far as samples, the argumentative writing unit has example essays included, and I’m sure the narrative unit will as well. But, to find the examples, you have to purchase the unit from Teachers Pay Teachers.
I just want to say that this helped me tremendously in teaching argument to 8th Graders this past school year, which is a huge concept on their state testing in April. I felt like they were very prepared, and they really enjoyed the verbal part of it, too! I have already implemented these methods into my unit plan for argument for my 11th grade class this year. Thank you so much for posting all of these things! : )
-Josee` Vaughn
I’m so glad to hear it, Josee!!
Love your blog! It is one of the best ones.
I am petrified of writing. I am teaching grade 8 in September and would love some suggestions as I start planning for the year. Thanks!
This is genius! I can’t wait to get started tomorrow teaching argument. It’s always something that I have struggled with, and I’ve been teaching for 18 years. I have a class of 31 students, mostly boys, several with IEPs. The self-paced mini-lessons will help tremendously.
So glad you liked it, Britney!
My students will begin the journey into persuasion and argument next week and your post cemented much of my thinking around how to facilitate the journey towards effective, enthusiastic argumentative writing.
I use your rubrics often to outline task expectations for my students and the feedback from them is how useful breaking every task into steps can be as they are learning new concepts.
Additionally, we made the leap into blogging as a grade at https://mrsdsroadrunners.edublogs.org/2019/01/04/your-future/ It feels much like trying to learn to change a tire while the car is speeding down the highway. Reading your posts over the past years was a factor in embracing the authentic audience. Thank You! Trish
I love reading and listening to your always helpful tips, tricks, and advice! I was wondering if you had any thoughts on creative and engaging ways to have students share their persuasive writing? My 6th students are just finishing up our persuasive writing where we read the book “Oh, Rats” by Albert Marrin and used the information gathered to craft a persuasive piece to either eliminate or protect rats and other than just reading their pieces to one another, I have been trying to think of more creative ways to share. I thought about having a debate but (un)fortunately all my kids are so sweet and are on the same side of the argument – Protect the Rats! Any ideas?
Hi Kiley! Thanks for the positive feedback! So glad to hear that you are finding value in Cult of Pedagogy! Here are a few suggestions that you may be interested in trying with your students:
-A gallery walk: Students could do this virtually if their writing is stored online or hard copies of their writing. Here are some different ways that you could use gallery walks: Enliven Class Discussions With Gallery Walks
-Students could give each other feedback using a tech tool like Flipgrid . You could assign students to small groups or give them accountability partners. In Flipgrid, you could have students sharing back and forth about their writing and their opinions.
I hope this helps!
I love the idea of mentor texts for all of these reading and writing concepts. I saw a great one on Twitter with one text and it demonstrated 5-6 reasons to start a paragraph, all in two pages of a book! Is there a location that would have suggestions/lists of mentor texts for these areas? Paragraphs, sentences, voice, persuasive writing, expository writing, etc. It seems like we could share this info, save each other some work, and curate a great collection of mentor text for English Language Arts teachers. Maybe it already exists?
Hi Maureen,
Here are some great resources that you may find helpful:
Craft Lessons Second Edition: Teaching Writing K-8 Write Like This: Teaching Real-World Writing Through Modeling and Mentor Texts and Mentor Texts, 2nd edition: Teaching Writing Through Children’s Literature, K-6
Thanks so much! I’ll definitely look into these.
I love the steps for planning an argumentative essay writing. When we return from Christmas break, we will begin starting a unit on argumentative writing. I will definitely use the steps. I especially love Step #2. As a 6th grade teacher, my students love to argue. This would set the stage of what argumentative essay involves. Thanks for sharing.
So glad to hear this, Gwen. Thanks for letting us know!
Great orientation, dear Jennifer. The step-by-step carefully planned pedagogical perspectives have surely added in the information repository of many.
Hi Jennifer,
I hope you are well. I apologise for the incorrect spelling in the previous post.
Thank you very much for introducing this effective instruction for teaching argumentative writing. I am the first year PhD student at Newcastle University, UK. My PhD research project aims to investigate teaching argumentative writing to Chinese university students. I am interested in the Argumentative Writing unit you have designed and would like to buy it. I would like to see the preview of this book before deciding to purchase it. I clicked on the image BUT the font of the preview is so small and cannot see the content clearly. I am wondering whether it could be possible for you to email me a detailed preview of what’s included. I would highly appreciate if you could help me with this.
Thank you very much in advance. Looking forward to your reply.
Take care and all the very best, Chang
Hi Chang! Jenn’s Argumentative Writing Unit is actually a teaching unit geared toward grades 7-12 with lessons, activities, etc. If you click here click here to view the actual product, you can click on the green ‘View Preview’ button to see a pretty detailed preview of what’s offered. Once you open the preview, there is the option to zoom in so you can see what the actual pages of the unit are like. I hope this helps!
Great Content!
Another teacher showed me one of your posts, and now I’ve read a dozen of them. With teaching students to argue, have you ever used the “What’s going on in this picture?” https://www.nytimes.com/column/learning-whats-going-on-in-this-picture?module=inline I used it last year and thought it was a non-threatening way to introduce learners to using evidence to be persuasive since there was no text.
I used to do something like this to help kids learn how to make inferences. Hadn’t thought of it from a persuasive standpoint. Interesting.
this is a very interesting topic, thanks!
Hi! I’m a teacher too! I was looking for inspiration and I found your article and thought you might find this online free tool interesting that helps make all students participate meaningfully and engage in a topic. https://www.kialo-edu.com/
This tool is great for student collaboration and to teach argumentative writing in an innovative way. I hope this helps!
Leave a Reply
Your email address will not be published.
- PRO Courses Guides New Tech Help Pro Expert Videos About wikiHow Pro Upgrade Sign In
- EDIT Edit this Article
- EXPLORE Tech Help Pro About Us Random Article Quizzes Request a New Article Community Dashboard This Or That Game Popular Categories Arts and Entertainment Artwork Books Movies Computers and Electronics Computers Phone Skills Technology Hacks Health Men's Health Mental Health Women's Health Relationships Dating Love Relationship Issues Hobbies and Crafts Crafts Drawing Games Education & Communication Communication Skills Personal Development Studying Personal Care and Style Fashion Hair Care Personal Hygiene Youth Personal Care School Stuff Dating All Categories Arts and Entertainment Finance and Business Home and Garden Relationship Quizzes Cars & Other Vehicles Food and Entertaining Personal Care and Style Sports and Fitness Computers and Electronics Health Pets and Animals Travel Education & Communication Hobbies and Crafts Philosophy and Religion Work World Family Life Holidays and Traditions Relationships Youth
- Browse Articles
- Learn Something New
- Quizzes Hot
- This Or That Game New
- Train Your Brain
- Explore More
- Support wikiHow
- About wikiHow
- Log in / Sign up
- Education and Communications
- College University and Postgraduate
- Academic Writing
How to Teach Essay Writing
Last Updated: June 26, 2023 Fact Checked
This article was co-authored by Christopher Taylor, PhD . Christopher Taylor is an Adjunct Assistant Professor of English at Austin Community College in Texas. He received his PhD in English Literature and Medieval Studies from the University of Texas at Austin in 2014. There are 12 references cited in this article, which can be found at the bottom of the page. This article has been fact-checked, ensuring the accuracy of any cited facts and confirming the authority of its sources. This article has been viewed 88,767 times.
Teaching students how to write an essay is a big undertaking, but this is a crucial process for any high school or college student to learn. Start by assigning essays to read and then encourage students to choose an essay topic of their own. Spend class time helping students understand what makes a good essay. Then, use your assignments to guide students through writing their essays.
Choosing Genres and Topics

- Narrative , which is a non-fiction account of a personal experience. This is a good option if you want your students to share a story about something they did, such as a challenge they overcame or a favorite vacation they took. [2] X Trustworthy Source Purdue Online Writing Lab Trusted resource for writing and citation guidelines Go to source
- Expository , which is when you investigate an idea, discuss it at length, and make an argument about it. This might be a good option if you want students to explore a specific concept or a controversial subject. [3] X Trustworthy Source Purdue Online Writing Lab Trusted resource for writing and citation guidelines Go to source
- Descriptive , which is when you describe a person, place, object, emotion, experience, or situation. This can be a good way to allow your students to express themselves creatively through writing. [4] X Trustworthy Source Purdue Online Writing Lab Trusted resource for writing and citation guidelines Go to source
- Argumentative or persuasive essays require students to take a stance on a topic and make an argument to support that stance. This is different from an expository essay in that students won't be discussing a concept at length and then taking a position. The goal of an argumentative essay is to take a position right away and defend it with evidence. [5] X Trustworthy Source Purdue Online Writing Lab Trusted resource for writing and citation guidelines Go to source

- Make sure to select essays that are well-structured and interesting so that your students can model their own essays after these examples. Include essays written by former students, if you can, as well as professionally written essays.
Tip : Readers come in many forms. You can find readers that focus on a specific topic, such as food or pop culture. You can also find reader/handbook combos that will provide general information on writing along with the model essays.

- For example, for each of the essays you assign your students, you could ask them to identify the author's main point or focus, the structure of the essay, the author's use of sources, and the effect of the introduction and conclusion.
- Ask the students to create a reverse outline of the essay to help them understand how to construct a well-written essay. They'll identify the thesis, the main points of the body paragraphs, the supporting evidence, and the concluding statement. Then, they'll present this information in an outline. [8] X Research source

- For example, if you have assigned your students a narrative essay, then encourage them to choose a story that they love to tell or a story they have always wanted to tell but never have.
- If your students are writing argumentative essays, encourage them to select a topic that they feel strongly about or that they'd like to learn more about so that they can voice their opinion.
Explaining the Parts of an Essay

- For example, if you read an essay that begins with an interesting anecdote, highlight that in your class discussion of the essay. Ask students how they could integrate something like that into their own essays and have them write an anecdotal intro in class.
- Or, if you read an essay that starts with a shocking fact or statistic that grabs readers' attention, point this out to your students. Ask them to identify the most shocking fact or statistic related to their essay topic.

- For example, you could provide a few model thesis statements that students can use as templates and then ask them to write a thesis for their topic as an in-class activity or have them post it on an online discussion board.
Tip : Even though the thesis statement is only 1 sentence, this can be the most challenging part of writing an essay for some students. Plan to spend a full class session on writing thesis statements and review the information multiple times as well.

- For example, you could spend a class session going over topic sentences, and then look at how the authors of model essays have used topic sentences to introduce their claims. Then, identify where the author provides support for a claim and how they expand on the source.

- For example, you might direct students to a conclusion in a narrative essay that reflects on the significance of an author's experience. Ask students to write a paragraph where they reflect on the experience they are writing about and turn it in as homework or share it on class discussion board.
- For an expository or argumentative essay, you might show students conclusions that restate the most important aspect of a topic or that offer solutions for the future. Have students write their own conclusions that restate the most important parts of their subject or that outline some possible solutions to the problem.
Guiding Students Through the Writing Process

- Try giving students a sample timeline for how to work on their essays. For example, they might start brainstorming a topic, gathering sources (if required), and taking notes 4 weeks before the paper is due.
- Then, students might begin drafting 2 weeks before the paper is due with a goal of having a full draft 1 week before the essay's due date.
- Students could then plan to start revising their drafts 5 days before the essay is due. This will provide students with ample time to read through their papers a few times and make changes as needed.

- Freewriting, which is when you write freely about anything that comes to mind for a set amount of time, such as 10, 15, or 20 minutes.
- Clustering, which is when you write your topic or topic idea on a piece of paper and then use lines to connect that idea to others.
- Listing, which is when you make a list of any and all ideas related to a topic and ten read through it to find helpful information for your paper.
- Questioning, such as by answering the who, what, when, where, why, and how of their topic.
- Defining terms, such as identifying all of the key terms related to their topic and writing out definitions for each one.

- For example, if your students are writing narrative essays, then it might make the most sense for them to describe the events of a story chronologically.
- If students are writing expository or argumentative essays, then they might need to start by answering the most important questions about their topic and providing background information.
- For a descriptive essay, students might use spatial reasoning to describe something from top to bottom, or organize the descriptive paragraphs into categories for each of the 5 senses, such as sight, sound, smell, taste, and feel.

- For example, if you have just gone over different types of brainstorming strategies, you might ask students to choose 1 that they like and spend 10 minutes developing ideas for their essay.

- Try having students post a weekly response to a writing prompt or question that you assign.
- You may also want to create a separate discussion board where students can post ideas about their essay and get feedback from you and their classmates.

- You could also assign specific parts of the writing process as homework, such as requiring students to hand in a first draft as a homework assignment.

- For example, you might suggest reading the paper backward 1 sentence at a time or reading the paper out loud as a way to identify issues with organization and to weed out minor errors. [21] X Trustworthy Source University of North Carolina Writing Center UNC's on-campus and online instructional service that provides assistance to students, faculty, and others during the writing process Go to source
- Try peer-review workshops that ask students to review each others' work. Students can work in pairs or groups during the workshop. Provide them with a worksheet, graphic organizer, or copy of the assignment rubric to guide their peer-review.
Tip : Emphasize the importance of giving yourself at least a few hours away from the essay before you revise it. If possible, it is even better to wait a few days. After this time passes, it is often easier to spot errors and work out better ways of describing things.
Community Q&A
- Students often need to write essays as part of college applications, for assignments in other courses, and when applying for scholarships. Remind your students of all the ways that improving their essay writing skills can benefit them. Thanks Helpful 0 Not Helpful 0

You Might Also Like

- ↑ https://owl.purdue.edu/owl/general_writing/academic_writing/essay_writing/index.html
- ↑ https://owl.purdue.edu/owl/general_writing/academic_writing/essay_writing/narrative_essays.html
- ↑ https://owl.purdue.edu/owl/general_writing/academic_writing/essay_writing/expository_essays.html
- ↑ https://owl.purdue.edu/owl/general_writing/academic_writing/essay_writing/descriptive_essays.html
- ↑ https://owl.purdue.edu/owl/general_writing/academic_writing/essay_writing/argumentative_essays.html
- ↑ https://wac.colostate.edu/jbw/v1n2/petrie.pdf
- ↑ https://www.uww.edu/learn/restiptool/improve-student-writing
- ↑ https://twp.duke.edu/sites/twp.duke.edu/files/file-attachments/reverse-outline.original.pdf
- ↑ https://www.niu.edu/citl/resources/guides/instructional-guide/brainstorming.shtml
- ↑ https://writingcenter.unc.edu/faculty-resources/tips-on-teaching-writing/situating-student-writers/
- ↑ https://writingcenter.unc.edu/faculty-resources/tips-on-teaching-writing/in-class-writing-exercises/
- ↑ https://writingcenter.unc.edu/tips-and-tools/revising-drafts/
About This Article

- Send fan mail to authors
Reader Success Stories
Oct 13, 2017
Did this article help you?

Jul 11, 2017
Jan 26, 2017

Featured Articles

Trending Articles

Watch Articles

- Terms of Use
- Privacy Policy
- Do Not Sell or Share My Info
- Not Selling Info
Get all the best how-tos!
Sign up for wikiHow's weekly email newsletter
- CORE CURRICULUM
- LITERACY > CORE CURRICULUM > Into Literature, 6-12" data-element-type="header nav submenu" title="Into Literature, 6-12" aria-label="Into Literature, 6-12"> Into Literature, 6-12
- LITERACY > CORE CURRICULUM > Into Reading, K-6" data-element-type="header nav submenu" title="Into Reading, K-6" aria-label="Into Reading, K-6"> Into Reading, K-6
- INTERVENTION
- LITERACY > INTERVENTION > English 3D, 4-12" data-element-type="header nav submenu" title="English 3D, 4-12" aria-label="English 3D, 4-12"> English 3D, 4-12
- LITERACY > INTERVENTION > Read 180, 3-12" data-element-type="header nav submenu" title="Read 180, 3-12" aria-label="Read 180, 3-12"> Read 180, 3-12
- LITERACY > READERS > Hero Academy Leveled Libraries, PreK-4" data-element-type="header nav submenu" title="Hero Academy Leveled Libraries, PreK-4" aria-label="Hero Academy Leveled Libraries, PreK-4"> Hero Academy Leveled Libraries, PreK-4
- LITERACY > READERS > HMH Reads Digital Library, K-5" data-element-type="header nav submenu" title="HMH Reads Digital Library, K-5" aria-label="HMH Reads Digital Library, K-5"> HMH Reads Digital Library, K-5
- LITERACY > READERS > inFact Leveled Libraries, K-5" data-element-type="header nav submenu" title="inFact Leveled Libraries, K-5" aria-label="inFact Leveled Libraries, K-5"> inFact Leveled Libraries, K-5
- LITERACY > READERS > Rigby PM, K-5" data-element-type="header nav submenu" title="Rigby PM, K-5" aria-label="Rigby PM, K-5"> Rigby PM, K-5
- LITERACY > READERS > Science & Engineering Leveled Readers, K-5" data-element-type="header nav submenu" title="Science & Engineering Leveled Readers, K-5" aria-label="Science & Engineering Leveled Readers, K-5"> Science & Engineering Leveled Readers, K-5
- SUPPLEMENTAL
- LITERACY > SUPPLEMENTAL > A Chance in the World SEL, 8-12" data-element-type="header nav submenu" title="A Chance in the World SEL, 8-12" aria-label="A Chance in the World SEL, 8-12"> A Chance in the World SEL, 8-12
- LITERACY > SUPPLEMENTAL > Amira Learning, K-6" data-element-type="header nav submenu" title="Amira Learning, K-6" aria-label="Amira Learning, K-6"> Amira Learning, K-6
- LITERACY > SUPPLEMENTAL > Classcraft, K-8" data-element-type="header nav submenu" title="Classcraft, K-8" aria-label="Classcraft, K-8"> Classcraft, K-8
- LITERACY > SUPPLEMENTAL > JillE Literacy, K-3" data-element-type="header nav submenu" title="JillE Literacy, K-3" aria-label="JillE Literacy, K-3"> JillE Literacy, K-3
- LITERACY > SUPPLEMENTAL > Waggle, K-8" data-element-type="header nav submenu" title="Waggle, K-8" aria-label="Waggle, K-8"> Waggle, K-8
- LITERACY > SUPPLEMENTAL > Writable, 3-12" data-element-type="header nav submenu" title="Writable, 3-12" aria-label="Writable, 3-12"> Writable, 3-12
- LITERACY > SUPPLEMENTAL > ASSESSMENT" data-element-type="header nav submenu" title="ASSESSMENT" aria-label="ASSESSMENT"> ASSESSMENT
- MATH > CORE CURRICULUM > Arriba las Matematicas, K-8" data-element-type="header nav submenu" title="Arriba las Matematicas, K-8" aria-label="Arriba las Matematicas, K-8"> Arriba las Matematicas, K-8
- MATH > CORE CURRICULUM > Go Math!, K-6" data-element-type="header nav submenu" title="Go Math!, K-6" aria-label="Go Math!, K-6"> Go Math!, K-6
- MATH > CORE CURRICULUM > Into Algebra 1, Geometry, Algebra 2, 8-12" data-element-type="header nav submenu" title="Into Algebra 1, Geometry, Algebra 2, 8-12" aria-label="Into Algebra 1, Geometry, Algebra 2, 8-12"> Into Algebra 1, Geometry, Algebra 2, 8-12
- MATH > CORE CURRICULUM > Into Math, K-8" data-element-type="header nav submenu" title="Into Math, K-8" aria-label="Into Math, K-8"> Into Math, K-8
- MATH > CORE CURRICULUM > Math Expressions, PreK-6" data-element-type="header nav submenu" title="Math Expressions, PreK-6" aria-label="Math Expressions, PreK-6"> Math Expressions, PreK-6
- MATH > CORE CURRICULUM > Math in Focus, K-8" data-element-type="header nav submenu" title="Math in Focus, K-8" aria-label="Math in Focus, K-8"> Math in Focus, K-8
- MATH > SUPPLEMENTAL > Classcraft, K-8" data-element-type="header nav submenu" title="Classcraft, K-8" aria-label="Classcraft, K-8"> Classcraft, K-8
- MATH > SUPPLEMENTAL > Waggle, K-8" data-element-type="header nav submenu" title="Waggle, K-8" aria-label="Waggle, K-8"> Waggle, K-8
- MATH > INTERVENTION > Math 180, 5-12" data-element-type="header nav submenu" title="Math 180, 5-12" aria-label="Math 180, 5-12"> Math 180, 5-12
- SCIENCE > CORE CURRICULUM > Into Science, K-5" data-element-type="header nav submenu" title="Into Science, K-5" aria-label="Into Science, K-5"> Into Science, K-5
- SCIENCE > CORE CURRICULUM > Into Science, 6-8" data-element-type="header nav submenu" title="Into Science, 6-8" aria-label="Into Science, 6-8"> Into Science, 6-8
- SCIENCE > CORE CURRICULUM > Science Dimensions, K-12" data-element-type="header nav submenu" title="Science Dimensions, K-12" aria-label="Science Dimensions, K-12"> Science Dimensions, K-12
- SCIENCE > READERS > inFact Leveled Readers, K-5" data-element-type="header nav submenu" title="inFact Leveled Readers, K-5" aria-label="inFact Leveled Readers, K-5"> inFact Leveled Readers, K-5
- SCIENCE > READERS > Science & Engineering Leveled Readers, K-5" data-element-type="header nav submenu" title="Science & Engineering Leveled Readers, K-5" aria-label="Science & Engineering Leveled Readers, K-5"> Science & Engineering Leveled Readers, K-5
- SCIENCE > READERS > ScienceSaurus, K-8" data-element-type="header nav submenu" title="ScienceSaurus, K-8" aria-label="ScienceSaurus, K-8"> ScienceSaurus, K-8
- SOCIAL STUDIES > CORE CURRICULUM > HMH Social Studies, 6-12" data-element-type="header nav submenu" title="HMH Social Studies, 6-12" aria-label="HMH Social Studies, 6-12"> HMH Social Studies, 6-12
- SOCIAL STUDIES > SUPPLEMENTAL > Writable" data-element-type="header nav submenu" title="Writable" aria-label="Writable"> Writable
- For Teachers
- PROFESSIONAL DEVELOPMENT > For Teachers > Coachly" data-element-type="header nav submenu" title="Coachly" aria-label="Coachly"> Coachly
- PROFESSIONAL DEVELOPMENT > For Teachers > Teacher's Corner" data-element-type="header nav submenu" title="Teacher's Corner" aria-label="Teacher's Corner"> Teacher's Corner
- PROFESSIONAL DEVELOPMENT > For Teachers > Live Online Courses" data-element-type="header nav submenu" title="Live Online Courses" aria-label="Live Online Courses"> Live Online Courses
- For Leaders
- PROFESSIONAL DEVELOPMENT > For Leaders > The Center for Model Schools (formerly ICLE)" data-element-type="header nav submenu" title="The Center for Model Schools (formerly ICLE)" aria-label="The Center for Model Schools (formerly ICLE)"> The Center for Model Schools (formerly ICLE)
- MORE > undefined > Assessment" data-element-type="header nav submenu" title="Assessment" aria-label="Assessment"> Assessment
- MORE > undefined > Early Learning" data-element-type="header nav submenu" title="Early Learning" aria-label="Early Learning"> Early Learning
- MORE > undefined > English Language Development" data-element-type="header nav submenu" title="English Language Development" aria-label="English Language Development"> English Language Development
- MORE > undefined > Homeschool" data-element-type="header nav submenu" title="Homeschool" aria-label="Homeschool"> Homeschool
- MORE > undefined > Intervention" data-element-type="header nav submenu" title="Intervention" aria-label="Intervention"> Intervention
- MORE > undefined > Literacy" data-element-type="header nav submenu" title="Literacy" aria-label="Literacy"> Literacy
- MORE > undefined > Mathematics" data-element-type="header nav submenu" title="Mathematics" aria-label="Mathematics"> Mathematics
- MORE > undefined > Professional Development" data-element-type="header nav submenu" title="Professional Development" aria-label="Professional Development"> Professional Development
- MORE > undefined > Science" data-element-type="header nav submenu" title="Science" aria-label="Science"> Science
- MORE > undefined > undefined" data-element-type="header nav submenu">
- MORE > undefined > Social and Emotional Learning" data-element-type="header nav submenu" title="Social and Emotional Learning" aria-label="Social and Emotional Learning"> Social and Emotional Learning
- MORE > undefined > Social Studies" data-element-type="header nav submenu" title="Social Studies" aria-label="Social Studies"> Social Studies
- MORE > undefined > Special Education" data-element-type="header nav submenu" title="Special Education" aria-label="Special Education"> Special Education
- MORE > undefined > Summer School" data-element-type="header nav submenu" title="Summer School" aria-label="Summer School"> Summer School
- BROWSE RESOURCES
- BROWSE RESOURCES > Classroom Activities" data-element-type="header nav submenu" title="Classroom Activities" aria-label="Classroom Activities"> Classroom Activities
- BROWSE RESOURCES > Customer Success Stories" data-element-type="header nav submenu" title="Customer Success Stories" aria-label="Customer Success Stories"> Customer Success Stories
- BROWSE RESOURCES > Digital Samples" data-element-type="header nav submenu" title="Digital Samples" aria-label="Digital Samples"> Digital Samples
- BROWSE RESOURCES > Events" data-element-type="header nav submenu" title="Events" aria-label="Events"> Events
- BROWSE RESOURCES > Grants & Funding" data-element-type="header nav submenu" title="Grants & Funding" aria-label="Grants & Funding"> Grants & Funding
- BROWSE RESOURCES > International" data-element-type="header nav submenu" title="International" aria-label="International"> International
- BROWSE RESOURCES > Research Library" data-element-type="header nav submenu" title="Research Library" aria-label="Research Library"> Research Library
- BROWSE RESOURCES > Shaped - HMH Blog" data-element-type="header nav submenu" title="Shaped - HMH Blog" aria-label="Shaped - HMH Blog"> Shaped - HMH Blog
- BROWSE RESOURCES > Webinars" data-element-type="header nav submenu" title="Webinars" aria-label="Webinars"> Webinars
- CUSTOMER SUPPORT
- CUSTOMER SUPPORT > Contact Sales" data-element-type="header nav submenu" title="Contact Sales" aria-label="Contact Sales"> Contact Sales
- CUSTOMER SUPPORT > Customer Service & Technical Support Portal" data-element-type="header nav submenu" title="Customer Service & Technical Support Portal" aria-label="Customer Service & Technical Support Portal"> Customer Service & Technical Support Portal
- CUSTOMER SUPPORT > Platform Login" data-element-type="header nav submenu" title="Platform Login" aria-label="Platform Login"> Platform Login
- Learn about us
- Learn about us > About" data-element-type="header nav submenu" title="About" aria-label="About"> About
- Learn about us > Diversity, Equity, and Inclusion" data-element-type="header nav submenu" title="Diversity, Equity, and Inclusion" aria-label="Diversity, Equity, and Inclusion"> Diversity, Equity, and Inclusion
- Learn about us > Environmental, Social, and Governance" data-element-type="header nav submenu" title="Environmental, Social, and Governance" aria-label="Environmental, Social, and Governance"> Environmental, Social, and Governance
- Learn about us > News Announcements" data-element-type="header nav submenu" title="News Announcements" aria-label="News Announcements"> News Announcements
- Learn about us > Our Legacy" data-element-type="header nav submenu" title="Our Legacy" aria-label="Our Legacy"> Our Legacy
- Learn about us > Social Responsibility" data-element-type="header nav submenu" title="Social Responsibility" aria-label="Social Responsibility"> Social Responsibility
- Learn about us > Supplier Diversity" data-element-type="header nav submenu" title="Supplier Diversity" aria-label="Supplier Diversity"> Supplier Diversity
- Join Us > Careers" data-element-type="header nav submenu" title="Careers" aria-label="Careers"> Careers
- Join Us > Educator Input Panel" data-element-type="header nav submenu" title="Educator Input Panel" aria-label="Educator Input Panel"> Educator Input Panel
- Join Us > Suppliers and Vendors" data-element-type="header nav submenu" title="Suppliers and Vendors" aria-label="Suppliers and Vendors"> Suppliers and Vendors
- Divisions > Center for Model Schools (formerly ICLE)" data-element-type="header nav submenu" title="Center for Model Schools (formerly ICLE)" aria-label="Center for Model Schools (formerly ICLE)"> Center for Model Schools (formerly ICLE)
- Divisions > Heinemann" data-element-type="header nav submenu" title="Heinemann" aria-label="Heinemann"> Heinemann
- Divisions > NWEA" data-element-type="header nav submenu" title="NWEA" aria-label="NWEA"> NWEA
- Platform Login
SOCIAL STUDIES
PROFESSIONAL DEVELOPMENT
5 Effective Tips for Teaching High School Writing

Writing is an acquired skill that takes many years of practice and feedback to master. High school writing instruction poses a unique challenge for teachers who must ensure their soon-to-be graduated students, whether they opt for college or career, can communicate their ideas in writing. Here, I share five tips for teachers to use in the high school classroom as their students continue to master the writing process.
How to Teach Writing to High School Students
At the end of students' high school careers, they should have mastered the art of writing in various formats, including persuasive , narrative , informative , research, short constructed responses, and analysis of literature and nonfiction. The array of formats may make teaching writing to high school students seem overwhelming. Luckily, research has given us a clear approach to accelerating writing gains—practice, feedback, and revision—principles that are integrated into the design of HMH's program Writable for Grades 3–12.
At the high school level, this trifecta may take place independently, with peers, in groups, or with the guidance of a teacher. Researchers suggest that carefully planned instruction include opportunities for writing practice, peer review, and revision based on feedback. Additionally, feedback from the teacher is paramount throughout the entire writing process. Support in the form of writing examples, models, and specific, measurable feedback is needed to improve student writing.

Writing Strategies for High School Students
Boost writing skills for high school students with these tried-and-true strategies that ensure students get the practice, feedback, and revision experience they need for success. Teaching multilingual students? Use these strategies to support them in the writing process.
Strategy 1: The Tour Guide
This strategy, aptly called The Tour Guide , is a tour of an exemplary essay. If students are expected to write a proficient essay, they must be guided through the components of one.
How is the essay structured? Are there multiple paragraphs? Are there citations woven throughout? What does it look like? How does the content reflect the prompt? How does the grammar, punctuation, and sentence structure contribute to the overall read of the essay? These are all questions that are asked, and subsequently answered, as the teacher takes the class on a guided tour of an essay.
Take this strategy up a notch by allowing students to annotate an essay on their own computer using extensions like Kami or apps like Google Docs. As the teacher reviews each component on the tour, students can annotate the essay using the tools for highlighting or commenting. HMH's program Writable has built-in annotation tools, plus teachers can save time using the program's AI-generated editable feedback in English or Spanish (see example below), draft scoring, and originality check.
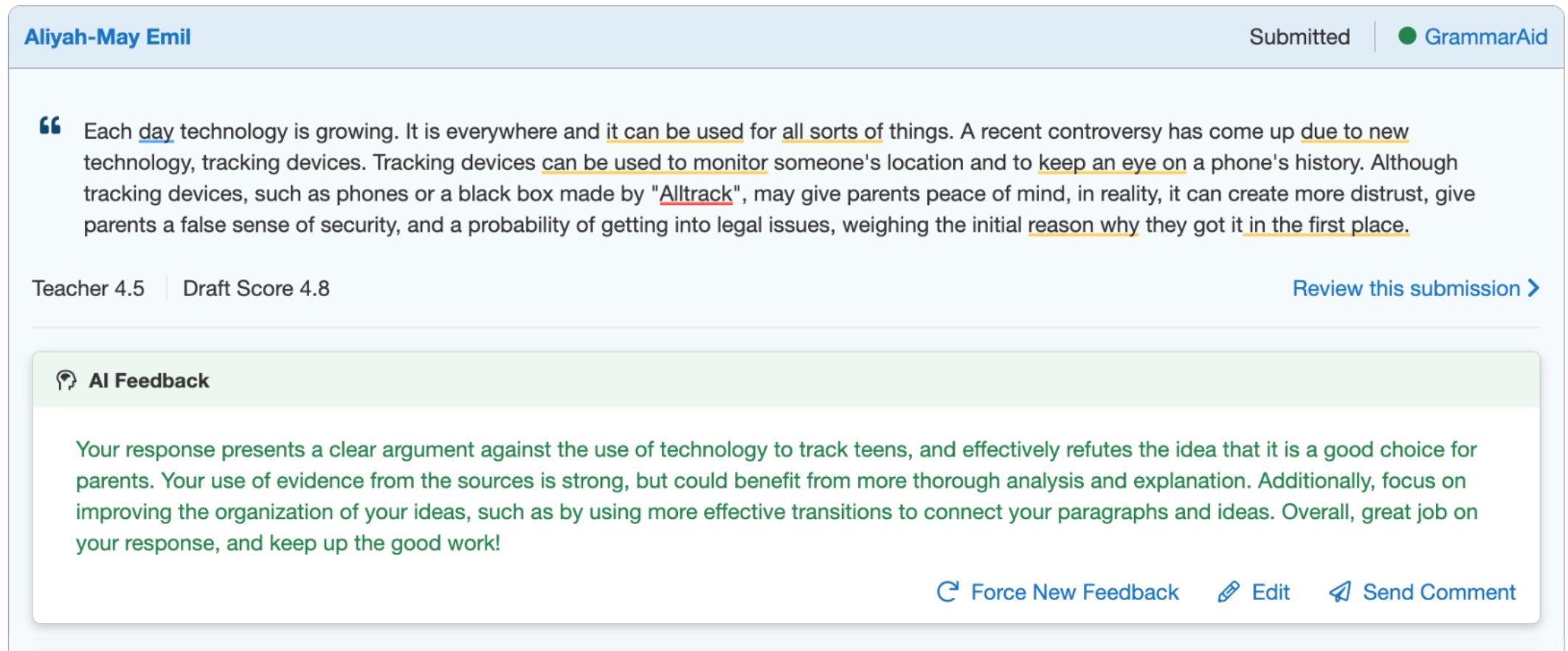
Strategy 2: Read Like a Writer
When students are tasked with writing essays such as a literary analysis or argument, a key indicator of success is seamlessly incorporating cited text from multiple sources. This synthesis of research, culminated in a student essay, is critical for high school writing and beyond. Oftentimes, the first part of this process is overlooked: gathering the text evidence that will be utilized in the essay. So let's not skip this important step. Students should read multiple sources in preparation. Read like a writer , a common phrase amongst teachers, is a strategy that will set students up for success when it comes time to write the essay.
Give each student a graphic organizer along with a writing prompt. Next, leave space for the student to fill in the title of the text they are reading, the author, and the cited evidence as it pertains to the prompt. As students read multiple texts, they will have an organized outline of the information they are to include in the essay. Doing this proactive step benefits students when it comes time to synthesize across multiple texts and produce an essay. Instead of having to retrace their steps, students can refer to their graphic organizer and begin to write. This has been one of the most successful strategies in my experience to get students on task and engaged because they have a starting point.
Strategy 3: Puzzle Pieces
How many times have you heard a student say, "I don’t know how to start?" I’ve heard it countless times and my response is always, " Do you know how to finish?" Students can feel overwhelmed when starting an essay and, in my experience, starting has always been the hardest part for them. But I've also found that students often have some parts of their essay pieced together in their head.
The Puzzle Pieces strategy encourages students to begin writing at any part of the essay. For example, maybe a student can perfectly describe a character they’ve envisioned and are ready to get that character down on paper! Why should the student wait for the character to be introduced in the story they’re writing? The same applies to a literary analysis essay. If students have a firm grasp on certain parts of the text they are analyzing, they should begin to write their ideas down.
Letting students write their essay in pieces, and then put it together like a puzzle, is beneficial for students who need the task broken down in smaller chunks. As students start to build momentum with their essay, their confidence and motivation also increases. After they have pieced their essay puzzle together, they will need to revise and add transitions to make the essay flow from one paragraph to the next. This is a great time to provide some feedback using student review or teacher review .
Strategy 4: Revise Out Loud
Once students are in the revision stage of the writing process, a great strategy is to have students record themselves reading their essays aloud using their phone or laptop. When students record themselves, they are not only practicing their fluency, but getting a good first read of what their essay would sound like to an audience. Oftentimes, this is a skipped step in the revision process, but an important one for students to do.
When students are done recording themselves, they can play it back and listen for grammatical errors, sentences that may need more description for clarity, or editing of punctuation. Students really love this new twist on revising. Give this strategy a try in your classroom and see students embrace the power of revision!
Strategy 5: Red Light, Yellow Light, Green Light
It is no secret that writing conferences with a teacher are beneficial to a successful writing piece. Students need plenty of practice and specific feedback to write an exemplary essay. While it is always a goal to conference with all students multiple times throughout the writing process, it may be difficult to do so in a formal conference. Therefore, this strategy is differentiated for students at their various writing levels.
Using an interactive whiteboard like Google Jamboard, or sticky notes on an anchor chart, create three headings—“Red, Yellow, Green.” Each student should write their name or student ID number (if you use a number system in your classroom) and move their sticky note under the heading that they feel best represents the conference they need for that class period. If students place their sticky note under the red heading, this indicates they would like a writing conference with their teacher. If a student places their sticky note under the yellow heading, this means they are proceeding with caution, but would like to conference with either a teacher or peer. And you guessed it—if students place their sticky note under the green heading, they are ready to work independently for the class period.
This strategy allows teachers to be mindful of what students need as they write. And it allows students to self-assess their needs, direct their learning, and voice what works best for them—whether it be a conference with a teacher or peer, or to work by themselves. Give this strategy a try and watch students become self-directed writers!
Share Your Best Writing Strategies
What are your go-to writing strategies for high school students? We'd love to hear how you help them master the writing process. Share ideas with us on Facebook , Instagram , or via email at [email protected] .
Try Writable for Grades 3–12 to support your ELA curriculum, district benchmarks, and state standards with more than 1,000 customizable writing assignments and rubrics, plus AI-generated feedback and originality check that will save teachers time while boosting student skills.
Be the first to read the latest from Shaped .
- Professional Learning
- Grades 9-12
Related Reading

Differentiated Instruction Strategies and Examples for Teacher and Student Success
Shaped Contributor
March 26, 2024

What Is Academic Vocabulary?
Jennifer Corujo Shaped Editor
March 25, 2024

Podcast: Partnering with Families to Build Early Literacy Skills with Melissa Hawkins in HI on Teachers in America
March 21, 2024

ChatGPT for Teachers
Trauma-informed practices in schools, teacher well-being, cultivating diversity, equity, & inclusion, integrating technology in the classroom, social-emotional development, covid-19 resources, invest in resilience: summer toolkit, civics & resilience, all toolkits, degree programs, trauma-informed professional development, teacher licensure & certification, how to become - career information, classroom management, instructional design, lifestyle & self-care, online higher ed teaching, current events, 5 tips for teachers assigning essays to high school students.

Essay assignments are a nightmare for many high school students. The fear of essay writing is often the result of not fully understanding the purpose of an essay or the writing process for completing one. A helpful tactic when teaching essay writing is to start with essay concepts, which may help to reduce the student’s apprehension.
What kind of essay should students write?
There are several types of essays and it’s important to explain the kind essay you wish the student to create. This clarity helps the student focus on techniques specific to that essay type. Is this to be a persuasive essay to bring the reader into agreement with the author on a topic? If so, then students should understand how to present a thesis and the supporting evidence behind it. These two concepts can be taught in separate classes since they are complicated issues to understand.
If you are assigning a narrative essay then the process of describing an experience becomes important. The students learn how to establish a setting, with a plot and characters, much as in fiction writing. Unlike fiction, the purpose of this type of essay is to make a point instead of entertain.
Because these two essay genres have quite different purposes, it is good to work with one until students are comfortable before moving to the other type. The knowledge of both of these types of essays will serve the student well when applying for college, performing their college-level work or later when applying for jobs.
Teach how to outline
A typical classroom scenario is assigning an essay to a roomful of high school students and then watching them stare at a blank sheet of paper. At this point in their education, the words may not come easily and they need a tool to get them started. Teaching good outlining techniques gives the student a way to organize random thoughts into a structure.
A useful outline for a persuasive essay might be:
- State the thesis
- Present Topic No. 1
- Present the supportive evidence for Topic No. 1
- Present Topic No. 2
- Present the supportive evidence for Topic No. 2
- Present Topic No. 3
- Present the supportive evidence for Topic No. 3
- Summarize the thesis
Discuss what information is a fit for each section and what is not. A verifiable fact that supports the thesis might be appropriate while an anecdote may not.
Using class time to write
Have the students spend some time in class working on their essays. This gives you a chance to observe and comment on the students’ process. Good examples can be highlighted to the class so they learn by the scenario. Questionable examples or ones that the student is “on the fence” about can be posed to the class for discussion.
Your presence while the students write is as an authoritative resource, something they may not have when writing at home, in the library or in study hall. This also facilitates a “learning as you go” environment which means the student need not fully understand a concept before continuing to write.
Teach the mechanics
High school students rarely have the opportunity to practice writing essays over and over to develop expertise. By focusing on the structure and how to assemble thoughts on the paper, you give the student a foundation on which to build their skills. Practicing the use of good essay structure frees up the student to begin to think about content.
Introduce and reinforce creativity
Along with the mechanics, encourage students to be original and creative in their work. High school students may still look outside of themselves for content when they already have a wealth of information within from which to draw. Show them how to tap into their own experiences to create unique content. Explain the use of anecdotes and metaphors. Give examples of good openers and summaries. This promotes more ownership of the words than if they are left to rewrite other content they have found.
Teaching essay styles and techniques to high school students helps reduce their fear of writing exercises. It gives students tools they will use in college and throughout their adult lives. It teaches them good writing habits and why writing is so important.
You may also like to read
- 5 Educational Apps for High School Students
- How Teachers Can Help Prevent High School Dropouts
- Critical Thinking Resources for High School Teachers
- Classroom Management Strategies for High School Teachers
- How Students Can Get the Most Out of High School Through Work and Play
- Websites that Help Students with High School Math
Categorized as: Tips for Teachers and Classroom Resources
Tagged as: High School (Grades: 9-12) , Language Arts
- Online & Campus Doctorate in Education (EdD) ...
- Certificates in Early Childhood Education
- Master's in Education Technology & Learning D...
How To Teach Argumentative Essay Writing

Teaching argumentative essay writing can be a real challenge. In addition to teaching writing, you’re also teaching skills like research and refutation. Luckily, this post includes the tips you need for effectively teaching argumentative essay writing.
I have great news for any of you gearing up to teach argumentative essay writing. Those students of yours love to argue. (Don’t believe me? Just ask their parents!) Students love to stand up for their opinion, proving their view is correct. The challenge, then, is getting them to look at the whole picture, find supporting evidence and understand the opposing viewpoints. Only then can they craft an argument that is both factually strong and persuasive. Overall, it’s about moving them beyond the blinders of their opinions and taking a more sound evidence-based approach.
Teaching argumentative essay writing doesn’t have to be such a painful experience for both you and your students. Follow the steps and strategies below to learn how to approach the dreaded argumentative essay more easily.
The Challenge with Teaching Argumentative Essay Writing
Why is teaching argumentative essay writing so difficult, you ask? I’ve been there. The truth is, when teaching argumentative essay writing, you’re teaching more than writing . You’re also teaching research skills and encouraging critical thought and analysis. You also need to explain how to evaluate sources and evidence and the difference between fact and opinion. In many ways, you’re teaching tolerance and perspective. (The list goes on.)
Long story short, it makes sense that it’s a challenge. The key is to not rush into it. Take it step-by-step, building upon what students already know.
Moving Beyond Persuasion
The good news? Many of your students have a foundational knowledge of persuasive writing that you can use as a springboard for teaching argumentative essay writing. However, it’s important to note that, while many use the terms interchangeably, they’re not quite the same. The main difference? Factual evidence. Your students might be used to persuasive writing, meaning writing to convince the reader of a claim rooted in their personal opinion . While it’s likely that students will argue something they are in favor of, argumentative essay writing involves using claims supported by factual evidence. Additionally, a hallmark of the argumentative essay is addressing the opposing viewpoint, a step that many students are unfamiliar with– and find rather challenging.
Consider the following steps as you move from persuasion to argumentative essay writing:
Step 1: Start with Casual Augmentation
Engage your students in a low-stakes debate before formally teaching argumentative essay writing. This approach will help get students in the right mindset as you begin to lay the foundation for effective argumentation. Don’t even mention the word essay at this point. Keep it fun and casual to break the ice.
There are many ways to approach casual argumentation in class. You can begin with an anticipation guide of controversial yet appropriate statements. After students fill it out, foster a group discussion in which students share their thoughts regarding each statement. Encourage them to move beyond simple opinions by asking why to get them to dig deeper as they support their stance.
To get your students up and moving, consider playing a game like Four Corners to get them to take a stance on a topic. Regardless of which activity you choose, spend time discussing the students’ stances. Small debates are likely to unfold right then and there.
Step 2: Add In Evidence, But Still Keep It Casual
You’ve causally engaged students in basic argumentation. However, before moving into a full-blown argumentative essay, dip students’ toes into the world of supporting evidence. Use the same activity above or write a simple yet controversial topic on the board for them to take a stance on. This time, give students a chance to gather supporting evidence. It might be worth quickly reviewing what makes a sound piece of evidence (research, studies, statistics, expert quotes, etc.). Then, once they pick their stance, allow five to ten minutes to gather the best piece of supportive evidence they can find. After, give them another five to ten minutes to work with the others in their corner/on their side to determine the strongest two or three pieces of evidence to share with the class. Once each team does this, have them take turns sharing their stance and supporting evidence. I like to leave room at the end for “final words” where they can respond to a point made by the other side.
During this simple activity, begin to unpack the importance of solid and relevant supporting evidence.
Step 3: Bring in the Opposing Viewpoints
Don’t stop there. One of the most challenging aspects of argumentative writing for students to grasp is acknowledging and responding to the opposition. They are often blinded by their experiences, perspectives, and opinions that they neglect the opposing side altogether.
Here’s what you can do: Repeat either activity above with a slight twist. Once students pick their side, switch it up. Instead of supporting the side they chose, ask them to research the other side and find the best supporting evidence to bring back to the class. Therefore, students will engage in a casual debate, supporting an opposing viewpoint. (For a simpler, more independent version of this, write a controversial statement on the board, have students take a stance, and then find evidence for the opposing side, putting it all into a written response.) While many students might complain at first, you’d be surprised how quickly they get into the task. Activities like these lay the groundwork for making evidence-based claims. Additionally, students will begin to recognize the role of perspective in argumentation.
Step 4: Introduce the Argumentative Essay
Now it’s time to introduce the argumentative essay. Many students will be tempted to jump right into writing. Therefore, make it clear that argumentative essay writing involves deeply investigating a topic before writing.
Next, explain how argumentative writing aims to take a stance on a topic and back it up with substantial supporting evidence. Additionally, include how argumentative essay writing requires acknowledging the opposing viewpoint. As for persuasion, explain that it must work in coordination with collected evidence rather than being rooted solely in one’s opinion.
When introducing the argumentative essay, it helps to outline the essay structure, showing students where it is both similar and different from the essays they are used to:
- Begin with an introductory paragraph. This is where the students will hook their readers and provide a summary of the issue, any relative background information, and a well-defined claim. (This is a great place to explain that claim is another word for a thesis statement used in argumentative writing.)
- Then comes the logically organized body paragraphs, each unpacking evidential support of the claim. While students are used to using body paragraphs to support their claim, remind them one body paragraph must reference and refute the opposing side.
- Finally comes the conclusion. Students are no strangers to writing conclusions. However, they should be moving beyond simply restating the thesis at the secondary level. Guide them through readdressing it in a way that acknowledges the presented evidence and leaves the author with something to think about.
Students will likely recognize the similarity between this and the traditional five-paragraph essay. Therefore, focus your teaching on the newer elements thrown into the mix that truly make it an argumentative essay.
Teacher Tip.
Incorporate various mentor texts to help students grasp the elements of argumentative essay writing. There are tons you can pull offline written by students and experts alike. ( The New York Times Learning Network has some great mentor text resources!) The more interesting your students find the subject matter, the better. Controversial topics always stir up an engaging conversation as well.
Teaching the Argumentative Essay Writing Process
Remember, students can quickly fall into old habits, neglecting some of the most imperative aspects of argumentative writing. Take it slow, walking students through the following steps – trust me, you’ll be thankful you did when it comes time to read a pile of these essays:
- Choose a topic. I recommend providing a list of argumentative essay writing topics for students to choose from. This prevents students’ classic “I can’t think of anything” roadblock. However, encourage students to choose a topic they are interested in or feel passionate about. With that said, I always give the option of letting students convince me (ha!) to let them use a topic they came up with if not on the list.
- Start the research. This is where students begin gathering evidence and is an opportunity to review what constitutes strong evidence in the first place.
- Understand the opposing side: Students are always confused about why I have them start here. One reason? It’s more challenging for students to see the other side, so this gets it out of the way first. Another? Some students never took the time to understand the other side, and in some cases, they switch their stance before writing their argument. It’s better to do so now than after you’ve done all your research and drafting. Lastly, I explain how understanding the opposing side can help guide your research for your side.
- Make a claim. While students may have an idea of their claim, the strongest claims are driven by evidence . Therefore, remind students that a claim is a statement that can be supported with evidence and reasoning and debated. Playing a quick game of two truths and an opinion (a spin on two truths and a lie) can reinforce the notion of facts vs. opinions.
- Write the body paragraphs. Each body paragraph should focus on supporting the claim with specific evidence. However, don’t forget to rebut the opposition! While they find it challenging, students learn to love this part. (After all, they love being right.) However, their instinct tends to be just to prove the other side wrong without using evidence as to why.
- Round out the intro and the conclusion, put it all together, and voila! An argumentative essay is born.
More Tips for Teaching Argumentative Essay Writing
- Begin with what they know: Build on the well-known five-paragraph essay model. Start with something students know. Many are already familiar with the classic five-paragraph essay, right? Use that as a reference point, noting out where they will add new elements, such as opposing viewpoints and rebuttal.
- Use mentor texts: Mentor texts help give students a frame of reference when learning a new genre of writing. However, don’t stop at reading the texts. Instead, have students analyze them, looking for elements such as the authors’ claims, types of evidence, and mentions of the opposing side. Additionally, encourage students to discuss where the author made the most substantial arguments and why.
- In [ARTICLE NAME/STUDY], the author states…
- According to…,
- This shows/illustrates/explains…
- This means/confirms/suggests…
- Opponents of this idea claim/maintain that… however…
- Those who disagree/are against these ideas may say/ assert that… yet…
- On the other hand…
- This is not to say that…
- Provide clear guidelines: I love using rubrics, graphic organizers, and checklists to help students stay on track throughout the argumentative essay writing process. Use these structured resources to help them stay on track every step of the way– and makes grading much easier for you .
The bottom line? Teaching argumentative essay writing is a skill that transcends the walls of our classrooms. The art of making and supporting a sound, evidence-based argument is a real-life skill. If our goal as teachers is to prepare students to be skilled, active, and engaged citizens of the 21st century, effectively teaching argumentative essay writing is a must. So, what are you waiting for? Teach those kids how to argue the write way.
1 thought on “How To Teach Argumentative Essay Writing”
This is very helpful. I am preparing to teach my student how to write an argumentative essay. This help me know that I am on the right path and to change how I organize some things in a different way. I really like how you recommended they pick out the elements of the writing. This will help them focus on the parts they dislike doing the most. Thanks for the writing.
Leave a Reply Cancel reply
Your email address will not be published. Required fields are marked *
Save my name, email, and website in this browser for the next time I comment.
It's Lit Teaching
High School English and TPT Seller Resources
- Creative Writing
- Teachers Pay Teachers Tips
- Shop My Teaching Resources!
- Sell on TPT
How to Teach Creative Writing to High School Students

Creative Writing was forced onto my schedule; I didn’t ask for it. But it ended up becoming my favorite class period of the day. While academic English courses can feel high-stakes and always short on time, Creative Writing can be a refreshingly relaxed elective class. In many districts with loose curriculums, Creative Writing is what you make of it. In this post, I outline six steps to show you how to teach creative writing to high school students.
Why Teach Creative Writing
Before we get into the how , let’s first address the why . Why bother teaching Creative Writing in the first place? Students’ basic skills are lower than ever; is now really the time to encourage them to break the rules?
If you want to get really deep into why you should teach Creative Writing, I have a whole post about it here.
But think about why you love reading. Is it because you were made to annotate or close read a bunch of classic novels? Probably not. You probably fell in love with reading while you were reading something that was fun. And because it was fun, you read more, and your skills as a reader grew.
The same principle applies to writing. If we can make it fun for our students, perhaps we can foster a love for it. And passion is what leads, eventually, to mastery.
Giving our students the opportunity to fall in love with writing is a gift that might help them grow in their academic writing later.

Teach Creative Writing to High School Students Step #1: Decide on Your Standards or Goals
Your school or district may have a mandated syllabus or curriculum. Mine did not.
Whether you’re given student goals or have to create them, you must have an overall vision for what your Creative Writing class will accomplish.
Is this a laid-back, engaging course designed to help students discover the fun in writing? Or is it a supplement to rigorous academics for college-bound high school students?
If you know your school’s student population well, I encourage you to think about their needs. Some students just need to write more–more of anything, but lots more. Some students are high achieving and ready to write their first novels! If possible, design your course around the needs and interests of the general student population in your school or district.
Regardless of how rigorous your Creative Writing course will be, deciding on these goals first will help you in backwards planning.
Teach Creative Writing to High School Students Step #2: Choose Your Final Assessments and Big Projects
Before we can start planning our lessons, we have to decide what skills or knowledge our students will need. And to know what they need, we have to decide on their summative assessments.

Will your final assessment be a short story? A collection of poetry? Are you required to offer a final exam?
Once you know what students will need to do, you can make a list of the skill they’ll need. This list will become a list of lessons you’ll need to teach.
Fairy Tale Retelling Project
My Fairy Tale Retelling Project is a great Creative Writing assessment. For this project, students had to first choose a fairy tale. Then, they rewrote the story from the perspective of the villain.
This project works really well because students have structure. They can pick any fairy tale they want, but they can’t write about just anything.

Secondly, students already know the story, so they don’t have to worry about a beginning, middle, and end. The open-endedness of writing a story completely from scratch has paralyzed my students before. Structure allows students lots of creative freedom without the excuse of “I don’t know what to write.”
Author Study Project
If you’d like your Creative Writing class to help beginner writers have fun and just get some practice with fiction writing, a Fairy Tale Retelling Project would probably be perfect for your class.
Another project I’ve done with my students is an Author Study . In this project, students choose one author to study in-depth. Then, they attempt to replicate that author’s style in an original work.

If you’d like your class to also include lots of exposure to other writers or classic literature, then this might be a great assessment for your class.
Learn more about doing an author study in this step-by-step post.
Test or Final Exam
I also gave my students a final exam focused on literary terms.
This Literary Terms Test allowed me to test students on the academic knowledge they gained throughout class instead of their writing ability. This test also helped me fulfill my district’s requirement of having a final exam at the end of each course.
Once you’ve decided on your class’s major projects and assessments, you can begin designing the rest of your class.
Teach Creative Writing to High School Students Step #3: Backwards Plan
Now that you know what your students will need to do at the end of this class, you can list out everything you need to teach them in order for them to be successful.
For example, if you opt for an author study as a final project, you know what you will need to cover. You will need to teach students some literary terms so that they can describe an author’s style. You’ll need to show them how to analyze a poem.
During the course of your class, you’ll also want to expose students to a variety of authors and mentor texts. Students will need to practice basic writing techniques in order to replicate those of their chosen authors.
If you need some inspiration for what kinds of lessons to teach, check out this post on essential Creative Writing lessons.
Teach Creative Writing to High School Students Step #4: Decide on Your Class Structure
Once you’ve decided on the end goals for your Creative Writing class, you can use them to help create day-to-day plans.
What will your class look like? Will it be full of lots of quiet and independent work time? Will it be full of frenetic energy with students working in collaborative groups? Are students writing in notebooks or on laptops?

Of course, a successful class will most likely include a mixture of all of the above. But it’s up to you to decide on your ratio.
Again, I encourage you to think about your school’s population. If you’re on ninety-minute blocks, is it realistic for students to be quietly writing that whole time? If you have high-achieving students, might they benefit from working independently at home and then getting and giving peer feedback during class time?
Use your goals to help decide on a general class structure.
Warm-ups for Creative Writing
You’ll need a consistent way to begin each class.
When I initially began teaching Creative Writing, I just wanted to provide my students with more time to write. We began every class period with free writing. I gave students a couple of prompts to choose from each day, and then we’d write for about ten minutes.
( Those journal prompts are right here . Every day includes two prompts plus a third option of freewriting.)
Students were given the option to share part of their writing if they wanted to. Every couple of weeks I’d flip through their notebooks to make sure they were keeping up, but I only read the entries they starred for me in advance.

Later, I wanted to add some rigor to my Creative Writing class and leverage more mentor texts. I created a Poem of the Week activity for each week of the course.
This gave students the opportunity to study professional writing before using it as a mentor text for a new, original piece.
(You can read more about using these Poem of the Week activities here.)
As my goals for the class and my students change, so did the way we began class.
How can you begin your class in a way that supports the end goals or teaches the desired standards? How often will peers work together?

Teach Creative Writing to High School Students Step #5: Focus on Engagement Strategies
Now you can actually start planning lessons and projects!
But as you do so, focus on creating engaging ones–especially if your class is meant to be a fun elective.
Need more tips? Check out this post full of Creative Writing teaching tips!
Use Mentor Texts and Lots of Examples
Have you ever tried putting a puzzle together without knowing what the image was going to look like? It would be pretty difficult! Similarly, students need lots of examples of strong writing to aspire to.
Without clear models or mentor texts , students will happily turn in unread drafts. They’ll choose the first word that comes to their mind instead of searching for a better one.
But if you surround students with great writing, highlight strong technique when discussing the writing of others, and challenge them to notice the details in their own writing, they’ll naturally become better at self-editing.
I don’t believe that you can provide students with too many mentor texts or examples of strong writing. As you teach Creative Writing, keep or take pictures of strong writing samples from students to use as examples later.
Nearly all of my lessons and projects include an example along with instruction.
Model and Create with Your Students
You can even use your own writing as an example. When I had students free write to creative writing prompts, I always wrote with them. Sometimes I would then put my notebook under the document camera and model reading my own work.
I would cross out words and replace them or underline phrases I thought were strong enough to keep. Model for students not just great writing, but the process of strengthening writing.
And then give them plenty of time to edit theirs. This is when having students engage in peer feedback is a game-changer.
Without great writing to aspire to, however, students easily become lazy and turn in work that is “good enough” in their eyes. Don’t let them get lazy in their writing. Keep throwing greater and greater work in front of them and challenge them to push themselves.
(This is another reason I love using Poem of the Week warm-ups –they expose students to a new writer every week!)
Set Clear Expectations
Creative writing causes a lot of students anxiety. There’s no “right” answer, so how will they know if they creatively wrote “correctly?”
Help them out by setting clear expectations. Offering a rubric for every project is great for this. If you can, give them specifics to include. “At least 500 words” or “three or more similes” are nice, concrete guidelines that students can follow.
Give Students Choice
Offering students choice always boosts engagement. It lets students take charge of their learning and pursue something that interests them.
For example, when I teach odes , students are given the opportunity to write about something they love.
With an author study , students can study a writer whose style and work they admire.

Teach Creative Writing to High School Students Step #6: Use Clear and Structured Expectations
While showing students excellent prose or perfect poetry should help inspire students, your writers will still need some hard parameters to follow.
Academic writing is often easier for students than creative writing. Usually, academic writing follows a structure or certain formula. The rubric dictates exactly how many quotes need to be included or how long an essay needs to be. MLA or APA formats tell students how to punctuate quotes and citations.
These rules don’t apply to creative writing. And while that’s exactly what makes creative writing awesome, it’s often overwhelming.
So do your students a favor and give them some clear expectations (without, of course, entirely dictating what they need to write about).
The project also includes a rubric, so young writers know what should be included in their stories.
Don’t give your students so much creative freedom that it paralyzes them! Your writers are still students; give them the same level of structure and organization that you would in any other class.

Engage your students in more creative writing!
Sign up and get five FREE Creative Writing journal prompts to use with your students!
Opt in to receive news and updates.
Keep an eye on your inbox for your FREE journal prompts!
Teach Creative Writing to High School Students Step #7: Give Students Choices
So how do you give students frameworks, requirements, and uphold high expectations without stifling their creativity?
Give students choices. You can write about A, B, or C, as long as you meet requirements 1, 2, and 3.
Offering choices works with small one-day assignments or lessons as well as bigger, longer-term projects.

The previously mentioned Fairy Tale Retelling Project is a great example of offering a narrow selection of choices that uphold expectations without dictating what students write.
Another one of my favorite examples of offering students choices is my “Show. Don’t Tell” Mini-lesson . This lesson touches on everything students need to successfully learn creative writing.
First I teach them the concept of showing vs. telling in writing through direct instruction. I show them lots of examples of expanding a “telling sentence” into a “showing paragraph.”
Then I model for students how I would write a paragraph that shows crucial information, rather than telling it.
Lastly, I have students pick a strip of paper from a hat or a bag. Each strip of paper contains a “telling sentence” that they must then write as a “showing paragraph.” Students are limited by the sentences I provide, but they still have complete freedom over how they achieve that detailed paragraph.
If you wanted to give students even more freedom, you could let them pick their sentences or trade with a peer rather than blindly choosing.
Any time you can give students a choice, you give them permission to use their creativity and allow them to take some of the initiative in their own learning.
Teach Creative Writing to High School Students Step #8: Encourage Peer Collaboration and Feedback
We can tell students something a hundred times, but they won’t listen until a peer says the same thing. Us educators know the value of positive peer interaction, so don’t limit it in a creative writing class!
There are a ton of ways to implement peer interaction in a creative writing class. I often do this on the first day of class with a writing game. You’ve probably heard of it: everyone writes a sentence on a piece of paper, then everyone passes the paper and adds a sentence, and so on.
I highly encourage you to use peer feedback throughout the class. I usually start having students share their work from day one with my free “I Am” Poem Lesson so that they can start getting used to having their work read by others immediately.

Make getting feedback so routine in your room that students don’t even question it.
It’s really tempting to let students get away without sharing their work. We don’t want to make shy or anxious students uncomfortable. I mean, what better way to completely ruin creative writing for a student than to make them feel embarrassed all the time, right?
But keep trying to encourage shy students to share. Even if that means you share it anonymously or read it aloud for them.
I recommend including some kind of peer feedback with every writing assignment . Yes, even short practice assignments. This will work as a kind of “immersion therapy” for receiving feedback on more involved work.
After some time, you might find that your students even begin to share their work without your prompting!
I like to organize the desks in my Creative Writing class so that students are in little groups. I’ve found that at least half of my classes will begin talking and sharing with one another in their little groups while working on projects.
They’ll ask each other questions or to remind them of a word. They’ll read sentences aloud and ask if they sound right. Personally, I would much rather hear this kind of chatter in my class than have a dead silent room of boring writers!
However you decide to allow students to work together, be sure to provide the opportunity. Reading and getting feedback from peers could possibly teach students more about writing than any of your instruction (sorry!).

One of the truly great things about teaching creative writing to high school students is that there often isn’t a rigid curriculum. Of course, this is also sometimes one of the worst things about teaching creative writing to high school students!
You have total freedom over the assignments you give, the standards you teach, and how you organize and structure your classroom. After a few years of teaching Creative Writing, however, I’ve found that sticking to these six steps is a great way to have a successful semester.
If you’re excited about teaching your Creative Writing class, but are running low on prep time, check out my complete 9-week Creative Writing course ! Included are two different types of warm-ups, poetry analysis activities from well-known authors, mini-lesson, projects, and more!


- Teaching Persuasive Writing in a Fun Way
by Gordana S | Feb 14, 2021 | Student Skills | 0 comments

Table of Contents
Teaching Persuasive Writing in High School—Theory and Practice
Teaching different writing skills to high school students is crucial if you want them to develop the soft skills they’ll need in life. When considering the reasons why reading and writing skills are important , it’s a mistake to think only in terms of language conventions and an excellent GPA.
Your students will have to use different writing skills and strategies in life. For example, they will need to write personal statements to get into the college of their choice. When they are enrolled, they will do college essays and write motivational letters to get internships . Adolescents enjoy coming up with creative ways to express themselves in their personal lives too. Research shows high school students enjoy writing — 93% of them do it for pleasure.
Your students will benefit from learning persuasive writing strategies in a variety of ways. Not only will they need to master persuasion for everyday exchanges, but also for their personal statement essays and college applications. To that end, let’s see what persuasive writing encompasses and how you can teach it to your students effectively.
Take the Right Approach to Teaching Persuasive Writing
Persuasive writing is used in any text that aims to nudge readers to form an opinion or take action. While it’s a given that most persuasive writing belongs to the non-fiction genre, fiction writers can use persuasion to influence their readers’ worldviews too.
Even though your students read persuasive texts, they don’t necessarily know how to write an effective persuasive essay themselves. This means that you need to teach them the specific skills that go into composing a persuasive essay one by one.
In your teaching, you cannot miss a lesson on effective opening and closing paragraphs or the importance of outlining. You also have to teach students how to do research effectively and choose the right words to construct their sentences. Only when your students know each of the techniques used in writing persuasive texts can they compose a solid persuasive essay.
Characteristics of Persuasive Writing

Credit: Elijah Macleod
Readers are more likely to believe a professional in the field than someone who has no connection or experience with the subject of a text. Experienced writers know that the first step to writing a persuasive piece is gaining knowledge on the topic.
To do it, your students have to know how to do research first. When it’s clear from their essays that they know what they are writing about, their texts will be more effective and convincing. Whether they can write persuasively depends on the techniques of persuasive writing that you teach them.
Some of the most common characteristics of persuasive essays are:
- Current statistics that support the author’s argument
- Examples from real life
- Observation of current events and phenomena
- Acknowledgment and rebuttal of the opposing argument
- Additional research from reputable institutions
These characteristics contribute to the validity of the statements in an essay and the credibility of the author. Sound, well-researched arguments should sway the reader to take the author’s point of view .
Essential Persuasion Techniques
Whether it’s used in writing or speech, persuasion has three essential elements:
Take a look at the table demonstrating what each of the three is:
You should teach your students about ethos, pathos, and logos to show them why it’s important to use those elements of persuasion. They will not only learn how to use them to their advantage but also be more successful in recognizing when their intellect and emotions are being appealed to.
Teach Your Students Persuasive Writing Skills

Credit: Kelly Sikkema
Ethos, pathos, and logos are the backbone of persuasion. There are many techniques your students can employ to use these three elements effectively.
Teaching your students persuasive writing isn’t much different from teaching them critical or argumentative writing . Some skills—such as an excellent command of vocabulary and critical thinking—are needed for any type of writing.
The next time you are planning a persuasive writing activity, think about how you can teach these techniques to your students:
- Establishing tone
- Targeting a specific audience
- Using the right words
- Locating evidence
- Presenting data
- Telling a story
- Refuting an argument
- Appealing to the readers’ emotions
- Rephrasing effectively
Outlining is a prewriting activity that your students should employ when creating any type of essay. Your students should learn that a clear outline will help them in each stage of their writing process. Outlining makes it easier for them to organize their ideas into specific parts of the essay and serves as a reference they can use to check whether they are straying off topic.
If time and curricula allow, you should have a lesson dedicated to writing effective outlines only. You can distribute a sample outline of a persuasive essay to all your students to introduce them to the technique. They can see that an outline consists of:
- The introduction —in which authors determine how they will present the topic, opposing views, and thesis statements
- Body paragraphs —in which authors decide how they will back up their claims
- The conclusion —which summarizes the thesis effectively and calls to action
When students have studied the outline structure, give them a sample essay to examine how well the author executed their plan. You can have a class discussion about the usefulness of an effective outline.
An interesting exercise is to allow your students to construct outlines for already written essays before they make outlines for their texts.
When your students compose outlines for their persuasive texts, make sure you give them feedback on their work. Help them see if they are on the right path.
Establishing Tone
Tone is essential for persuasive writing. The tone your students set in their essays will build trust more than the topic of the assignment. Teach your students what tone they should use to sound confident when defending their arguments in essays.
For example, imagine your students are arguing against the rule of wearing uniforms in high schools. Rather than writing “wearing uniforms in high schools may impact the students’ self-expression negatively,” they should write “wearing uniforms in high schools eliminates the students’ self-expression.” The second sentence is more confident, and the essay assumes a stronger stand and convinces the reader that uniforms aren’t a good idea.
Targeting a Specific Audience
Instead of aiming to appeal to as many people as possible, persuasive writing is more effective if targeted at a specific audience. Depending on the argument that your students want to support or the field for which they are writing, the type of audience will vary.
When your students hand in their persuasive writing essays, you will be their only judge, but they shouldn’t see you as their target audience. Teach your students they should also appeal to a specific audience rather than the masses. You can give them a list of questions they can go over, such as:
- Who will benefit from what I have to say the most?
- What problems do people I address experience?
- Who is this issue important to?
- What has the best chance to trigger emotions in my target audience?
Using the Right Words
A careful selection of words can influence readers to feel more deeply about the problem students present in their essays, so make sure you work with them on expanding their vocabulary. Having a large number of synonyms and topic-specific vocabulary in their arsenal will help them pick the most efficient word for what they want to express.
You should also equip your students with the words and phrases that are commonly used in persuasive writing. Give them a reference list of phrases they can use and show them how specific vocabulary helps their essay convince the reader that they are knowledgeable on the topic.
An excellent exercise is to have a quick vocabulary brainstorming session with the whole class based on the topic of the essay your students need to write. For example, if they need to write a topic on pollution, your class should brainstorm on the topic-related words and phrases. This gives your students useful vocabulary for the essay, ideas on what to write about, and in turn, how to outline their texts.
Finding Evidence
The best technique to prove a point is to refer to concrete evidence that supports it. Your students may not be familiar with academic research yet, which is why it’s a good idea to teach them how to do research in high school. They will not be overwhelmed when the same is required of them in college.
Make sure your students know these rules of effective research:
- Knowing which keywords to use to get the results fast online
- Checking whether the information is relevant and up-to-date
- Choosing statistics published by reputable institutions
- Selecting the most relevant type of information for their essays
Same as outlining, research is part of almost all longer writing. If possible, dedicate a lesson to teaching the importance of research to your high school students. Another lesson should be devoted to teaching your students how they can locate data successfully.
You can start with a fun topic that is interesting to your students. For example, if there are rumors about their favorite celebrities, you can tell them to research the validity of those rumors.
Presenting Data
If the research your students do involves data, they need to present it in their essay effectively. Knowing how to present data in a persuasive essay might be more work for your students than finding it in the first place. If they clutter their essays with numbers for the sake of having them, they will probably do their writing a disservice.
The best course of action is to give students a text that presents statistics clearly and effectively. They should also learn the vocabulary that is used to explain data. Your students can then practice presenting data themselves in their essays.
Telling a Story
Telling a story can be a great way to connect with readers. Your students need to learn how to use narration to their benefit. Make sure they don’t turn their persuasive essays into fiction, though. A story element should appeal to the reader’s emotions and influence them to take the author’s side .
Providing examples from real life can back up your students’ arguments as effectively as presenting a precedent or striking statistics. Relating real-life experience can be a neat way your students can start a speech in a school competition , for example. Teach your students they don’t have to tell stories from their personal lives if they don’t have any they would like to share.
Refuting an Argument
Acknowledging the other side of an argument is essential for successful persuasion. Readers will hardly be convinced to side with a certain opinion if the opposite one isn’t refuted.
You should make it clear to your students that they must not run from opposing viewpoints. When they present them in their persuasive essays and explain why those arguments are not as valid as their own, their essays will be that more compelling.
When you present the topics for the essay to your students, have a class discussion on the opposing views first. Each student can pick one side of the argument and practice how to refute the opposing one with their partner.
Appealing to Readers’ Emotions
Your students can appeal to their readers’ emotions by the use of narration or the right word choices—but these aren’t the only techniques. Others include:
- Creating an effective hook in the introductory sentence
- Addressing the reader directly
- Making the reader relate to the author’s experience
- Using direct questions to make readers think about what they have read
When your students master these nuances of persuasive writing, they should use them to a steady degree. Logic should be the primary focus of their essays rather than emotional manipulation.
You should also engage your students in acknowledging how other writers do it. The best example would be the advertisements that your students are bombarded with on the daily. The ads your students see on their phones or in the newspapers use persuasive language and appeal to their emotions. When your students recognize it, they can get ideas on how to use persuasion in their own essays and be more mindful when they are the target of persuasive writing themselves.
Rephrasing Effectively
Your students will have to repeat themselves in their persuasive essays. Most notably, their concluding paragraph will have to restate their thesis statement. You should teach them how to paraphrase it effectively.
Teach your students to express the same idea again in other words. When they are invested in the topic of their assignment and have researched it thoroughly, they should have no problem doing that.
When you devote one lesson to closing paragraphs, give your students other authors’ intros to rephrase. They need to connect their conclusions to the hook in the original intro, but they mustn’t introduce new concepts in that final paragraph.
Activities for Teaching Persuasive Writing

Credit: Free-Photos
You can come up with various activities to teach your students persuasive writing, but make sure to have one main goal for each activity.
To practice persuasive writing through class activities, your students can:
- Watch and learn from other writers
- Look for relevant sources
- Outline their essays
Watch and Learn
For this activity, pick a good example of persuasive writing and distribute it to your students. They should single out the specific techniques the author used to influence readers.
Ask your students which persuasive methods are prevalent in the text. You can also tell them to jot down any words and phrases they believe are there for a specific reason—to make readers adopt the author’s viewpoint.
Look for Sources
If your students have little experience with research, prepare an activity that can introduce them to it carefully. You can give them a list of specific questions they can find answers to. Their answers should be backed up by relevant sources.
Organize Your Ideas
Having your students create an outline for their persuasive essay should be an individual activity. Teach them the main parts of an outline and let them try their hand at writing one.
Here’s an idea of what a persuasive essay outline should cover:
How To Teach Persuasive Writing—Your Ideas
If you have ample experience in teaching, you might be familiar with many of the points mentioned in this article. Perhaps you would like to add your own.
Many believe that high school students don’t learn writing skills effectively. Despite wanting to unleash their creativity, your students often don’t have sufficient tools to do so. If you feel it’s time for that to change, we want to hear what innovations you would bring to American education.
Write to us, and we’ll be glad to share your ideas with our readers.
Submit a Comment Cancel reply
Your email address will not be published. Required fields are marked *
Save my name, email, and website in this browser for the next time I comment.
Recent Posts
- How to become a writer after high school
- Effective Stress Management Activities for Teenagers
- The Importance of Financial Literacy for High School Students
- Career Assessment for High School Students

- All topics A-Z
- Grammar
- Vocabulary
- Speaking
- Reading
- Listening
- Writing
- Pronunciation
- Virtual Classroom
- Worksheets by season
- 600 Creative Writing Prompts
- Warmers, fillers & ice-breakers
- Coloring pages to print
- Flashcards
- Classroom management worksheets
- Emergency worksheets
- Revision worksheets
- Resources we recommend
- Copyright 2007-2021 пїЅ
- Submit a worksheet
- Mobile version
- How to Teach Essay Writing
Don't just throw your homeschooled-student intoformal essay crafting. Focus on sentence structure and basic paragraph composition before movingto more complicated formal essay composition.
Are you a competent essay writer? Even if you know how to write an essay , chances are you are dreading the coming years of teaching homeschool writing just as much as your novice writer could be dreading learning how to write . Writing comes naturally for very few, but most view writing as an insurmountable abstract mountain. The Write Foundation writing curriculum is a divide and conquer method of teaching writing. Focusing on small portions of writing paragraphs and later five-paragraph college level essays, eventually you and your students will be able to use all the necessary writing skills to easily compose wonderfully crafted formal essays .
Start with a good foundation
That is, of course, what The Write Foundation teaches. Don’t just throw your homeschooled-child into the middle of essay crafting. Focus on sentence structure and basic paragraph composition before moving to more complicated formal essay composition . Learn to write essays one bite at a time. This helps students develop writing skills by using writing tools which helps them gain confidence and enables parents who are insecure about their own writing skills learn with their students.
Hold their hand as much as they need you hold their hand.
An abstract assignment with limited instructions can appear quite daunting to a reluctant, struggling, or new writer; tiny decisions can become writing blocks in a new writer’s mind.
Share the experience with your homeschooler. Discuss writing blocks and ways to overcome them. Discuss the planning process and experience how it helps flesh out an essay. Walk them through each lesson making sure they complete each step successfully before attempting to move on in the writing process. Working side by side with your student also helps you become a better instructor by solidifying the lesson for yourself. As students gain confidence with their new skills they will need your help less and less so they will shoo you away as they learn writing is much easier using the complete writing process.
Use concrete assignments
Creative writing is very subjective, and it is also very abstract for a new writer. You need a writing curriculum which focuses on concrete assignments and provides a variety of writing topics that fit the type of writing being taught in that assignment. Give your students a structure to work into a paragraph using their creative information. Leaving several factors to the unknown, such as type of writing, structure, and so on, leaves more decisions that the novice writer is not ready to determine. An abstract assignment with limited instructions can appear quite daunting to a reluctant, struggling, or just new writer; tiny decisions can become writing blocks in a new writer’s mind. Even experienced writers face writer’s block. Students need to be given tools and taught skills that overcome “But, what do I write about?”
Know your audience
Let your child select from a list of possible writing topics that may be interesting to them. Your child may enjoy the experience more if he is writing about his favorite pastime instead of writing about your favorite pastime. Choosing topics about things that directly influence your child, such as different views about their favorite sport, the influence of network TV or political topics that hit close to home may open the doors for lively discussion and insight into your child’s mind.
Writing is a necessary life skill. When teaching writing remember you are not alone. If you are worried about teaching formal writing to your homeschooler, use the support system of The Write Foundation for any questions you may have through the process, and know that you are not alone. Look into a homeschool writing co-op in your area to lighten the burden and give new perspective on your child’s essay writing development. Use The Write Foundation and use a proven writing system.
Questions or Comments?
Recent articles.
- Correcting Run-on Sentences
- How Does Skipping the Writing Process Affect your Writing?
- Graduating Homeschooling
- Is My Child Ready for Formal Writing?
- Teaching Spelling
- Evaluating Homeschool Writing Curriculums
- Why Most Writing Curriculums Fail (and How to Make Sure your Homeschooler Doesn't!)
- Top Five Reasons Students Hate to Write (and How You can Help!)
- College Preparation for Homeschooled Students
H e is like a man building a house, who dug deep and laid the foundation on the rock. Luke 6:48

View, Print, and Practice the Sample Lessons
(We're here to help you teach!)
Now Available!
Free Reading Lists Get your copy today!
Have a struggling writer? Maybe he hates writing? Does your student just need to learn how to write? Long for teacher-friendly lesson plans you can quickly prepare and teach? Desire a writing curriculum your children will enjoy while learning creatively?
- Complete Lesson Plans
- Free Assessment Tests
- Free Reading Lists
- Organization for Writing
- Checklists & Guidelines
- Brainstorm & Outline Forms
Open doors to writing success!
Contact Rebecca . Rebecca Celsor will answer your questions regarding how to easily teach your child to write.
" Generally speaking, level 1 does not require your child to come up with content out of thin air or make the assumption that she has tons of ideas she can’t wait to get on paper. One example: Lesson 20 will have your child rewriting fables by taking well-known fables and changing aspects about them to make new stories. (Imitation is a worthwhile way of improving one’s own writing, by the way.) The "

- Course Selection Assistance
- Suggested Age Levels for Homeschool Writing
- Entry Level I - Prepare to Write
- Entry Level II - Creating Sentences
- Level 1 - Sentence to Paragraph
- Level 2 - Paragraph
- Level 3 - Essay
- Free Curriculum Writing Samples
- Example Teaching Videos
- Online Grading Service
- Writing Skills Reference Folder
- How to Present a Lesson
- Grading Writing
- Key Points for Grading Writing
- MindBenders®
- Order Curriculum Packages
- Order Worksheets Only
- Refund/Return Policy
- Selecting Home School Curriculum
- Writing Preparation
- Writing Development
- High School and Beyond
- Homeschool Co-ops
- Homeschool How To
- The Story Behind TWF
- Why Another Writing Curriculum?
- Copyright Information

He is like a man building a house, who dug deep and laid the foundation on the rock . Luke 6:48
Dedicated to equipping God's children with the ability to communicate His Truth to the world.
- Teaching Tools
- Curriculum Ordering
- homeschool writing curriculum
- home school writing samples
- Mind Benders®
- Online Grading
Copyright © 2021 TheWriteFoundation.org
web site design - evolvethebrand.com
Essay Writing Tips and Resources for Junior & High School Students
- Haley Drucker
- Categories : Help with writing assignments paragraphs, essays, outlines & more
- Tags : Homework help & study guides
Essay Writing as a Skill
Students sometimes see essay writing as something you are either good at or you aren’t. This is a mistake, and leads to a lack of effort and a lot of essays that don’t live up to their potential. Writing a good essay is a skill, one that can be practiced and improved upon. With these essay writing tips and the resources linked to in the sections below, students can learn to start producing papers they can be proud of.
Brainstorming and Preparation
Picking a Topic: A good essay starts long before any actual writing happens. The first thing you’ll need to do is select a topic. Good essay topics take careful thought—don’t just decide to write about the first thing that comes to mind. One guideline to remember is that, in general, the narrower your topic is the better. A specific, restricted topic helps you keep your essay organized and focused. It’s also best to choose a topic you find interesting—even in the most boring of subjects or books there’s likely to be one aspect that interests you on some level.
Doing Research: Depending on the type of essay, the next step may be to do some research. Be sure to allocate plenty of time for this very important task. Use as many different kinds of materials as possible—from websites to books to documentaries—and keep an eye out for themes and ideas that keep popping up. These are the kinds of things that should probably make an appearance in your essay. And don’t forget to take notes during the research process, so you’ll be able to find the information and quotes you need later on.
Outlining: Then you’re ready to starting outlining your essay. This can be as specific or as general as you want, but it’s best to approach each essay with a plan in mind rather than writing it from scratch. If you at least have an idea of what main ideas you are going to cover and in what order, you’ll take a lot of stress out of the actual writing process. Graphic organizers such as mind maps and Venn diagrams can really help you get your ideas in order and make sense of all your notes and information.
Types of Essays
The other thing you’ll want to do before you start writing is consider the essay’s genre. Each type of essay has its own rules and conventions. You don’t want to finish the conclusion just to realize that your persuasive essay has somehow turned into a research paper. These are a few of the essay writing genres most commonly assigned:
Research Papers: A research paper is meant to educate the reader about something, so this type of essay is the one that requires the most research. It should also be very formal, and should include plenty of quotes and citations.
Persuasive Essays : The whole point of this kind of paper is to convince your audience to agree with you about something. Everything you write, every fact and quote you use, should be focused on strengthening your argument and the persuasive power of your essay.
Literary Analysis: These essays are about a particular book or other text, but this isn’t a book report. You’ll want to summarize the book briefly, but the bulk of the paper needs to be about analyzing and interpreting it (or certain aspects like a particular character or theme).
Compare and Contrast Essays: This is pretty straightforward—in this type of essay you’ll need to compare and contrast two or more things (books, time periods, countries, paintings, etc). The most common issue students have with these papers is focusing too much on comparing and forgetting to contrast, or vice versa.
Reflective Essays : Also called personal essays or narrative essays, these papers are about your personal experiences. They will be structured more like a story, and so won’t follow the usual five-paragraph format. Also, this is the only kind of essay you probably won’t need to do any research for.
Writing the Essay
It’s finally time to start writing the first draft. Don’t worry about editing at this point, or about getting everything perfect. It’s best to just write a full first draft, then go back to revise it and make sure it sounds smooth and is well-organized. It can even help to skip the introduction and go straight to the body paragraphs , then come back and write the introduction at the end. After all, you won’t be completely sure what your paper is about until it’s actually written. Make sure to be familiar with the five-paragraph essay format as many teachers require you to write this way, and even if they don’t, it provides a helpful structure to follow.
Your most powerful tools for keeping yourself organized and focused during the essay writing process are your thesis and topic sentences. The thesis statement can usually be found at the end of the first paragraph, and provides a general guideline for what you’re going to discuss throughout the essay. Each body paragraph should then start with a topic sentence , which is like a mini thesis that provides an outline for just that paragraph. Everything in a paragraph should relate back to its topic sentence, and every topic sentence should relate back to the thesis statement. This keeps you from rambling and makes your essay easier to read (and grade).
Intros and Conclusions
These two parts of your paper deserve a special mention for two reasons. Many students find these paragraphs the hardest to write, and at the same time they are arguably the two most important paragraphs. After all, the introduction and conclusion are the first and last parts of your writing the teacher will see, and so are very influential on their impressions about your essay.
Introductions : The most crucial part of the intro paragraph is the last sentence or two, which constitutes the thesis statement (see above). But what about the rest of the paragraph? A good strategy is to start general and narrow down into your specific topic. For example, you might start by mentioning the tragic effects of war in general, and then move into discussing WWII is particular. It can also help draw reader interest to start the introduction with a quote, question, brief story, or personal experience (avoid starting with a dictionary definition though—that tactic is overused and not terribly professional).
Conclusions : It’s a good idea to devote the first few sentences of the conclusion to giving a brief summary of what you’ve discussed in your essay—in short, to restating your thesis statement. But you don’t want to just summarize in your conclusion. That’s redundant, and not very interesting. Instead, use the second half of the conclusion to answer the questions “So what?” and “Who cares?” Consider relating your paper to a current event or important issue, introducing an interesting question for the reader to ponder, or providing a call to action.
Revising and Proofreading
A lot of students skip over these steps. But a first draft hardly ever makes for a good essay. You’ll need to go though and tighten the focus and organization, improve the grammar and sentence structures, and scan for typos and mistakes. Editing is a part of essay writing, not something separate or less important.
Good editing takes place in two steps. First is the revision stage, where you pay attention to the large-scale issues. This is where you add and delete sentences, move paragraphs, and rewrite or delete anything that isn’t working or distracts from your thesis. Make sure every paragraph addresses a single idea, and that idea is reflected in the topic sentence. Check your thesis statement—does it accurately reflect what your paper is about? During this stage you’ll also want to pay attention to how the paper sounds. Does it flow well? Are there transitions? Are all the sentences too long or too short, or is there a good variety? And consider the format of your paper—does it look professional?
Then, when you’re happy with the paper as a whole, you can begin to proofread. This involves editing for good grammar and spelling, eliminating unnecessary words , and checking facts, page numbers, and quotes to make sure they’re accurate. This reason you should do this last is that, if you don’t, you might spend a lot of time fixing the grammar in a sentence only to realize later that sentence needs to be deleted because it’s off topic. And remember not to rely on Microsoft to do these tasks for you—spell check doesn’t catch everything, and grammar check is just plain wrong at least half the time.
Avoiding Perfectionism
No essay will ever be perfect. All the same, essay writing can be a frustrating task because it’s hard to figure out exactly when you’ve finished. Put plenty of time and effort into your paper, but don’t stress yourself out by trying to write the world’s best essay. A good rule of thumb is that when you start changing things back to the way they were in your previous revision, you should probably stop and call the essay complete. Writing doesn’t have to be a stressful process, after all—and these essay writing tips will hopefully go a long way towards making it an easy and maybe even a fun process.
Just added to your cart
The Art of Teaching Essay Writing to Middle and High School Students
Are you a middle or high school teacher tasked with teaching essay writing to your students, do you want to ensure that your students become confident and proficient writers.
We have compiled some answers to the most commonly asked questions about teaching essay writing to middle and high school students.

What are the essential components of an essay, and how can I effectively teach them to students?
The essential components of an essay include an introduction, body paragraphs, and a conclusion. To teach these components effectively, break them down into smaller sections and provide examples of well-written essays. Teach students how to structure their essays by creating an outline before writing the first draft. For teaching basic essay components, check out our Essay Writing Basics Bundle
How can I help students develop and organize their ideas and arguments effectively?
To help students develop and organize their ideas and arguments effectively, start by teaching them how to brainstorm and create a mind map. Encourage them to group their ideas into categories and teach them how to order their thoughts logically. Also, show them how to use transitions to link their ideas and ensure a smooth flow throughout the essay.
How can I teach students to write clear and concise thesis statements that accurately reflect the main argument of their essay?
Teaching students how to write a clear and concise thesis statement is essential. Show them examples of good and bad thesis statements and teach them how to use precise language to convey their argument. Encourage them to avoid vague or general statements and ensure that their thesis statement is specific and relevant to their essay topic.
How can I encourage students to use evidence and examples to support their claims?
Encourage students to use evidence and examples to support their claims by teaching them how to research and gather information from reliable sources. Teach them how to analyze and evaluate their sources to determine their credibility. Encourage them to use quotes and statistics to support their arguments and ensure that they cite their sources properly.
How can I teach students to write effective introductions and conclusions?
Teaching students how to write effective introductions and conclusions is crucial. Encourage them to start their essay with a hook, such as a quote, anecdote, or a rhetorical question. Teach them how to write a clear thesis statement and preview the main points they will be discussing in their essay. For the conclusion, teach them to restate the thesis statement and summarize the main points of their essay.
How can I help students understand the importance of editing and revising their work?
Teach students to understand the importance of editing and revising their work by showing them examples of poorly written essays and the impact of careless mistakes. Encourage them to take breaks between writing and revising to help them see their work from a fresh perspective. Teach them how to proofread their work for grammar, punctuation, and spelling errors.
How can I provide feedback that is both constructive and helpful to students?
Provide feedback that is both constructive and helpful to students by focusing on specific areas that need improvement. Avoid criticism and instead provide suggestions for improvement. Use positive language and encourage students to take risks and experiment with their writing.
How can I differentiate instruction to meet the needs of students with different learning styles and abilities?
Differentiate instruction to meet the needs of students with different learning styles and abilities by using a variety of teaching methods. Incorporate visual aids, group work, and hands-on activities to engage students with different learning styles. Provide extra support and resources for students who need additional help.
How can I help students develop their own voice and style in their writing?
Help students develop their own voice and style in their writing by encouraging them to write about topics they are passionate about. Teach them to write in their own voice, using a tone that reflects their personality. Encourage them to experiment with different writing styles and techniques to help them find their own unique style.
How can I create assignments and assessments that accurately measure students' understanding of essay writing concepts and skills?
To create assignments and assessments that accurately measure students' understanding of essay writing concepts and skills, create rubrics that clearly define the expectations for the assignment. Provide students with clear instructions and expectations for the assignment. Assess their essays based on the essential components of an essay, including the thesis statement, evidence, organization, and writing style.
Teaching essay writing to middle and high school students can be a challenging task, but with the right strategies and techniques, you can help your students become confident and proficient writers.
By breaking down the essential components of an essay, teaching students how to develop and organize their ideas, and providing feedback that is both constructive and helpful, you can help your students master the art of essay writing.
- Share Share on Facebook
- Tweet Tweet on Twitter
- Pin it Pin on Pinterest
Leave a comment
Please note, comments must be approved before they are published
- choosing a selection results in a full page refresh
- press the space key then arrow keys to make a selection
You are using an outdated browser. Please upgrade your browser or activate Google Chrome Frame to improve your experience.
ESL Essay Writing: 7 Important Tips to Teach Students Plus Resources for Writing Lessons
“Every good story has a beginning, a middle and an end.”
This is true for a good essay, too.
An essay needs a coherent structure to successfully articulate its arguments. Strong preparation and planning is crucial to providing that structure.
Of course, essay writing can be challenging for ESL students. They must order their thoughts and construct their arguments—all in their second language.
So, here are seven ESL essay writing tips that will allow your students to weave together a coherent and persuasive essay, plus teacher resources for writing activities, prompts and lessons!
1. Build the Essay Around a Central Question
2. use the traditional 5-paragraph essay structure, 3. plan the essay carefully before writing, 4. encourage research and rewriting, 5. practice utilizing repetition, 6. aim to write a “full circle” essay, 7. edit the essay to the end, esl essay writing resources.
Download: This blog post is available as a convenient and portable PDF that you can take anywhere. Click here to get a copy. (Download)
Encourage your students to build all their writing around one central question.
That central question is the engine of the writing—it should drive everything!
If a word or sentence is not assisting that forward motion toward the explication of that question and its possible answers, then it needs to be reworded, rephrased or just plain cut out and discarded.
Lean writing is merciless. Focusing on a central question throughout the prewriting, writing and rewriting stages helps develop the critical faculties required to discern what to keep and what to throw away.
Providing a clear structure for the student to approach essay writing can do a lot to build their confidence. The 5-paragraph essay, or “hamburger” essay, provides that clear structure for ESL writers.
Generally, this structure employs five separate paragraphs for the entire essay. Each paragraph serves a specific purpose, melding together to form a coherent whole:
- Paragraph 1: The introductory paragraph. This includes the thesis statement, orientating the reader to the purpose of the essay.
- Paragraphs 2 to 4: The body paragraphs. These make individual points that are further backed up by various forms of evidence.
- Paragraph 5: The conclusion paragraph. This provides a summation of the arguments and a final statement of the thesis.
While students do not need to rigidly follow this format forever, the simple structure outlined above can serve as excellent training wheels for your writers.
Using the 5-paragraph structure as outlined above makes planning clear cut.
Once they have their theses and are planning their paragraphs, share with the students the ridiculously useful acronym P.E.E. This stands for Point, Explanation and Evidence.
Each body paragraph should make a point or argument in favor of the central thesis, followed by an explanation of this point and relevant evidence to back it up.
Students can make note of all their points, explanations and evidence before they start writing them in essay form. This helps take away some of the pressure ESL writers feel when faced with a blank page.
Extol the necessity for students to constantly refer to their planning. The mind-mapping techniques popularized by Tony Buzan can be useful at the planning stage and make for easy reference points to ensure focus is maintained throughout the essay.
Having a visual reference such as this can help ensure that your student-writers see each piece of the whole as well as that elusive “bigger picture,” so it becomes a case of seeing the forest and the trees!
Just as planning is crucial, so too is research.
Often ideas or connections do not occur until the writing process has begun. This is a good thing! Essay writing is a creative act, so students can have more ideas along the way and work them in as they go.
The key is to always be able to back up these ideas. Students who have done their research on their subject will be much more confident and articulate in expressing their arguments in their writing.
One way you can help students with context and research is to show relevant video content via FluentU . This language learning program uses authentic videos made by and for native speakers to help students learn English.
You can watch videos as a class or assign them directly to students for individual viewing. Videos come equipped with interactive bilingual subtitles and other learning tools such as multimedia flashcards and personalized quizzes so you can see how each student is doing.
No matter how your students do their research, the important thing is that they explore and understand their topic area before beginning the big task of writing their essay.
Even with thorough planning and research, writing oneself into a linguistic cul-de-sac is a common error. Especially with higher-level students, unforeseen currents can pull the student-writer off course.
Sometimes abandoning such a sentence helps. Going back to the drawing board and rewriting it is often best.
Students can be creative with their sentence structures when expressing simpler ideas and arguments. However, when it comes to more complex concepts, help them learn to use shorter sentences to break their arguments into smaller, more digestible chunks.
Essay writing falls firmly in the camp of non-fiction. However, that doesn’t mean that essay writers can’t use some of the techniques more traditionally associated with fiction, poetry and drama .
One technique that’s particularly useful in essay writing is repetition. Just as poetry relies heavily on rhythm, so too does argument. Repetition can provide that sense of rhythm.
This is because written language has its origins in oral language. Think of the great orators and demagogues and their use of repetition. Speechwriters, too, are well aware of the power of repetition.
The writing principle of the “rule of 3” states that ideas expressed in these terms are more convincing and memorable. This is true of both spoken and written words and the ideas they express. Teach your students to use this method in their essay writing.
The very structure of the 5-paragraph essay lends itself to planning for this repetition, in fact. Each idea that is explored in a body paragraph should be outlined first in the introductory paragraph.
Then, the single body paragraph devoted to the idea will explore it at greater length, supported by evidence. And the third rap of the hammer occurs in the summation of the concluding paragraph, driving the point securely and convincingly home.
As mentioned at the start of this post, every good essay has a beginning, a middle and an end.
Each point made, explained and supported by evidence is a step toward what the writing teacher Roy Peter Clark calls “closing the circle of meaning.”
In planning for the conclusion of the essay, the students should take the opportunity to reaffirm their position. By referring to the points outlined in the introduction and driving them home one last time, the student-writer is bringing the essay to a satisfying full circle.
This may be accomplished by employing various strategies: an apt quotation, referring to future consequences or attempting to inspire and mobilize the reader.
Ending with a succinct quotation has the double benefit of lending some authoritative weight to the argument while also allowing the student to select a well-written, distilled expression of their central thesis. This can make for a strong ending, particularly for ESL students.
Often the essay thesis will suggest its own ending. If the essay is structured around a problem, it’s frequently appropriate to end the essay by offering solutions to the problem and outlining potential consequences if those solutions are not followed.
In the more polemical type of essay, the student may end with a call to arms, a plea for action on the part of the reader.
The strategy chosen by the student will depend largely on what fits the central thesis of their essay best.
For the ESL student, the final edit is especially important.
It offers a final chance to check form and meaning. For all writers, this process can be daunting, but more so for language students.
Often, ESL students will use the same words over and over again due to a limited vocabulary. Encourage your students to employ a thesaurus in the final draft before submission. This will freshen up their work, making it more readable, and will also increase their active vocabulary in the long run!
Another useful strategy at this stage is to encourage students to read their work aloud before handing it in.
This can be good pronunciation practice , but it also provides an opportunity to listen for grammatical errors. Further, it helps students hear where punctuation is required in the text, helping the overall rhythm and readability of the writing.
To really help your students become master essay writers, you’ll want to provide them with plenty of opportunities to test and flex their skills.
Writing prompts and exercises are a good place to start:
Descriptive writing activities encourage students to get creative and use their five senses, literary devices and diverse vocabulary. Read on for eight descriptive writing…
https://www.fluentu.com/blog/educator-english/esl-writing-projects/ https://www.fluentu.com/blog/educator-english/esl-picture-description/
Giving good ESL writing prompts is important because inspiring prompts inspire students to write more and writing more is how they improve. Read this post to learn 50…
You’ll likely also want to teach them more about the mechanics of writing :
Are you looking for ESL writing skills to share with your ESL students? In this guide, you’ll find different ESL writing techniques, such as helping students understand…
Would you like to introduce journal writing into your ESL classes? Fantastic idea! Here are 9 essential tips to make it creative, engaging and fun.
https://www.fluentu.com/blog/educator-english/esl-writing-lessons/
Essays are a great way not only for students to learn how the language works, but also to learn about themselves.
Formulating thoughts and arguments about various subjects is good exercise for not only the students’ linguistic faculties, but also for understanding who they are and how they see the world.
Enter your e-mail address to get your free PDF!
We hate SPAM and promise to keep your email address safe

How to Teach Essay Writing to ESL Students Better
23 December 2020 Guest posts

Teaching essay writing to ESL students is no easy feat. There's a lot of things to consider, such as making sure the language is correct, of course, as well things like structure, accurate covering of the topic, the context of the essay, and how well the points are represented.
Throughout this guide, I'm going to detail some of the ways you can make every essay writing task as beneficial as possible. Your students can take on board these tips with the aim of making their essays better than ever before.
There are lots of tips and advice I could share, but today I'm going to focus on the most important, hopefully giving you a great place to get started when it comes to improving your students essay writing abilities
Start with the Basics
The absolute first place you want to start is with improving your student's sentence structure since sentences, after all, are what go into making an essay what it is. You'll want to start with teaching your students about basic sentences and then move onto compound and then complex.
Build it up slowly and highlight the key differences between each sentence type and why they would be used and what effect each sentence type has.
There's plenty of information online on how you can approach the basics of essay writing, such as on websites like Revieweal , Boomessays , Studydemic , Ukservicesreviews , and Assignment writing service , or you can simply ask a question you may have in your preferred search engine.
Understanding the Topic
A student will not be able to write a proper essay if they don't truly understand the topic they're writing about. Whether your students get to choose their topics or not, it's important that you explain that they should take their time to research and have a proper grasp on the topic they're writing about.
"It's important to remember that you can also suggest topics if the students are struggling to think of their own, ones that you believe will play to their strengths. Remember, essay writing within the ESL community is all about building confidence. If the students believe they can do a task, then they will be able to do it," explains Fergie Marie, a writer at Ukwritings and Custom Writing .
It's all about overcoming that first hurdle.
Break the Essay Down
Most essays are written in the same way, very similar to how stories are written. They have a start, a middle, and an end, and highlighting this structure form is a great way to make essays seem a little less daunting.
After all, being tasked with a 1,000-word essay can feel overwhelming at first, but when you break it down into three main sections that can be focused on individually, the task seems a little more manageable.
Of course, each section of the essay has a specific purpose. The introduction is meant to grab the reader, hook them into the writing, and sets the tone for the essay ahead. The middle is for laying down and explaining the points that would answer the question of whatever the essay topic is about.
Finally, you have the conclusion, which wraps everything up, answers any questions that were asked, and rounds off the essay nicely. Focusing on these points can help massively when it comes to writing an essay because there's less thought needed on what you need to write and more focus on what the actual writing will be.
Practice, Practice, Practice
"It might seem a bit mean to set regular essays all the time, and you don't want to be that kind of teacher, but the best way to get better at essay writing, as with everything else in life, is to practice. This means giving your students essay tasks to complete, and then reviewing the mistakes and highlighting what they did well," shares Duncan Turner, an educator at Assignment Help and Essayroo .
And that's the important bit. Not only do you want to highlight the areas where your students can improve or perhaps correcting mistakes they made, you always want to make sure you're showcasing what they did well and congratulating them on the bits they got right.
This inspires confidence and will encourage your students to keep trying, keep writing, and keep getting better.
Katherine Rundell is a book writer at Essay Writing Service and BigAssignments . She writes about teaching and helping ESL students make the most of their educational efforts. Also, she is a proof-reader at Essay writing services reviews .
Previous post: 7 Debunked Myths On Teaching English
- Features (34)
- Guest posts (37)
- Argentina (10)
- Colombia (6)
- Ecuador (2)
- Hong Kong (5)
- Thailand (15)
- Vietnam (5)
9 tips to improve your academic writing
These are nine easy tips that can help any student overcome their writer’s block and develop their academic writing.

Academic writing is a skill that takes a while to develop. Here are nine tips to help you start your journey to becoming a stronger writer.
1. Consider your purpose
It is your job as the writer to help readers understand what they will gain from reading your work.
What will they learn? What questions will they have that you can answer? Considering the lessons and perhaps even emotional responses a reader might have will help you to understand the purpose of your work.
2. Find inspiration in your daily life
When facing writer’s block, think about your daily life instead. Our lives might seem unrelated to academic writing topics such as economics, politics and justice. However, your anger at Google raising YouTube premium prices might create ideas for your next economics essay on monopoly structures. Most academic topics can be connected to daily life in some way.
3. Focus your ideas
You’ve done all your reading, your deadlines are approaching and yet somehow your ideas seem more scattered than ever.
To overcome this, write one or two sentences describing what each paragraph will cover.
These will then serve as a starting point for you to develop your ideas. Writing your focus point down gives you a concrete idea to develop and work on, instead of allowing the essay to run away from you.
4. Stay specific
Academic writing requires you to discuss facts, interpret past ideas and create your arguments. If the scope of your topic is too large, you might find that you are doing too much research, which then makes it difficult to narrow down your essay.
Although this will differ across each writing project, academic writing is most successful when it is limited to a specific aspect or approach. When in doubt, discuss with writing tutors or professors whether your topic is of appropriate scope.
5. Find your voice
Most of the time, every sentence you write might feel (and often is) too informal and awkward. And after poring over the dictionary, doing 20 rounds of revisions and incorporating feedback from 10 people, you might find your writing has been sucked dry of your voice.
To develop your voice, writing needs to flow from your mind and feel natural. Although it’s important to keep re-reading and editing your work, sometimes this can be done too much.
6. Absorb English
Read everything that you can, including fiction and non-fiction. Academic writers might not write fiction themselves, but fiction teaches writers how to create rhythm and tension. Notice how authors manipulate language and use it creatively.
You can also listen to audiobooks and music, and watch movies and documentaries. Continuously absorbing English in many different mediums can help you to gain a better grasp of the language.
7. Write in short sentences
Readers will not want to wade through excessively long, formal and sophisticated sentences. Instead, shorter, conversational sentences are easier to read.
However, this might not come naturally, so consider writing long sentences then cutting them up into simpler ones. Or pretend you are talking to someone as you write. You might find that creates a more natural flow to your work.
8. Take small steps
Writing is a skill that takes time to develop. Even if you write for only 10 minutes a day, a regular practice will help you to develop that skill. One paragraph a day can build into a book or a PhD thesis.
Simply get into the habit of writing. Write about anything you want – describe how last night’s dinner tasted, rant about your roommate, celebrate your accomplishments. Just one paragraph a day can help you to develop your language, sentence structure and vocabulary.
9. Visit writing centres at your university
Writing centres provide valuable services, including writing workshops, one-on-one tutoring, writing groups, writing classes and writing resources such as textbooks, vocabulary lists and templates.
While teachers and tutors are great at giving you resources and advice, you can share writing experiences and exchange feedback with peers in writing workshops.
You may also like

.css-185owts{overflow:hidden;max-height:54px;text-indent:0px;} How to use digital advisers to improve academic writing

Five resources to help students with academic writing

How to write a successful research piece at university
Maggie Tighe
Register free and enjoy extra benefits
Ultimate Guide to Writing Your College Essay
Tips for writing an effective college essay.
College admissions essays are an important part of your college application and gives you the chance to show colleges and universities your character and experiences. This guide will give you tips to write an effective college essay.
Want free help with your college essay?
UPchieve connects you with knowledgeable and friendly college advisors—online, 24/7, and completely free. Get 1:1 help brainstorming topics, outlining your essay, revising a draft, or editing grammar.
Writing a strong college admissions essay
Learn about the elements of a solid admissions essay.
Avoiding common admissions essay mistakes
Learn some of the most common mistakes made on college essays
Brainstorming tips for your college essay
Stuck on what to write your college essay about? Here are some exercises to help you get started.
How formal should the tone of your college essay be?
Learn how formal your college essay should be and get tips on how to bring out your natural voice.
Taking your college essay to the next level
Hear an admissions expert discuss the appropriate level of depth necessary in your college essay.
Student Stories
Student Story: Admissions essay about a formative experience
Get the perspective of a current college student on how he approached the admissions essay.
Student Story: Admissions essay about personal identity
Get the perspective of a current college student on how she approached the admissions essay.
Student Story: Admissions essay about community impact
Student story: admissions essay about a past mistake, how to write a college application essay, tips for writing an effective application essay, sample college essay 1 with feedback, sample college essay 2 with feedback.
This content is licensed by Khan Academy and is available for free at www.khanacademy.org.
- Our Mission
5 High-Impact Writing Strategies for the Elementary Grades
Simple, effective exercises can help elementary students develop the foundational writing skills they need for their academic journey.

When considering writing as part of the instructional day, teachers may think only of the type of writing where students engage in storytelling or informational pieces. While the ability to leverage student choice and produce fiction and nonfiction text is beneficial for all grade levels, it’s important to consider how writing can be incorporated and layered across all content areas, as well as develop the deep foundational understanding to prepare young writers for authoring texts.
For us as teachers, it’s vital that we share a common language and understanding about the types of high-impact writing strategies that students can engage in and how to effectively implement them in the classroom.
1. Handwriting in the Early Grades
In the digital age, prioritizing handwriting education during phonics instruction remains instrumental in nurturing well-rounded learners and sets them up for success when more stamina is required of them. The tactile experience of handwriting establishes a profound connection between language and sensory perception, contributing increased cognitive development .
Teachers can adopt a common path of movement language (language used to describe how to form the letters) when teaching the letters. In addition to that, providing students with multisensory ways of forming the letters helps create a strong understanding of the letters’ features.
A practical example of this type of instruction is having students trace a lowercase a in a tray full of salt, repeating the path of movement language, “over, around, down.” Then, students practice writing the letter using a pencil or dry erase marker. As the teacher models the directionality, it’s important to ensure that students know what “over,” “around,” and “down” mean and look like and that the teacher is using on-the-spot intervention for correction.
2. Dictated Sentences
Utilizing dictated sentences in elementary phonics instruction holds profound importance in nurturing early literacy skills. This strategy serves as a powerful bridge between decoding individual phonemes and comprehending them within a meaningful context.
For example, in a phonics lesson where students are practicing decoding and spelling words with a short i vowel and have practiced reading the high-frequency words they and the , the teacher may end the lesson with students writing the dictated sentence, ”They will fill the big bin with wigs.”
This method encourages the application of phonics knowledge in real-word scenarios, promoting fluency and automaticity. In addition, dictated sentences provide a valuable opportunity for students to hone their listening skills, enhancing their ability to discern and reproduce distinct phonetic elements accurately and to authentically apply irregularly spelled high-frequency words in context. This practice benefits students of any grade level working on phonics skills.
3. Writing to Read
Another foundational type of writing that prepares students for more demanding types of writing in later grades is writing to read. This is an interactive approach to early writing instruction where the teacher models early literacy and print concepts starting as early as prekindergarten through early kindergarten. Through collaboration with the students, the teacher models drawing pictures and sentence creation.
Teachers can start by engaging students in a conversation around an event in a book or nursery rhyme they read together. Then, the teacher offers a prompt: “In the story, the characters went to play at the park. That gives me an idea for a story. What kinds of things do you like to do at the park?” Students can share multiple ideas for the story, and the teacher chooses one to model.
While the teacher explicitly models drawing and develops a sentence about the drawing, the students offer ideas on where to start writing, count the words in the story, identify the sounds they hear as the teacher spells out each word, and notice where spaces will occur. The more that students engage in this type of instruction, the more responsibility we can hand over to them, and they can write the story along with us. As students are given more opportunities to apply early writing principles and rereading strategies, they begin to understand the reciprocal relationship between reading and writing.
4. Reading to Write
When the foundations for early writing have been established, students can quickly move into another layer of high-impact writing, which is writing about the texts that they’re reading.
Even starting in kindergarten, encouraging students to write and/or draw in response to reading across multiple content areas is a valuable strategy that helps deepen comprehension and understanding of a particular topic, as explored in Linda J. Dorn and Carla Soffos’s book Teaching for Deep Comprehension .
These “writing about the reading” prompts require students to analyze, synthesize, and connect ideas, fostering a deeper understanding of the material. For example, if first-grade students are working on story elements, after reading a story, a student might write, “The character in the story is a bear who lives in the forest. The problem in the story is that he is sad, but he solves his problem when he learns to be happy.”
This expression encapsulates comprehension, language reinforcement, and academic vocabulary. As students progress through grade levels upward to 12th grade, the scaffold of giving the students a prompt for writing about the text should decrease as they develop enough self-regulation to write about their own thinking.
5. Writing About Learning
Similar to reading to write, this strategy is solely focused on writing about what the student has learned, why the learning is important, and when to use the learning. This type of writing can happen as early as kindergarten, but in a highly scaffolded manner that mostly focuses on articulating why the learning is important.
Students up to 12th grade can benefit from writing about their learning because it keeps the purpose of what they’re learning in various content areas relevant and promotes quick retrieval of the information.
This strategy also promotes metacognition , because it helps learners organize their thoughts and reflect on their learning process. For instance, a second-grade class could collaboratively study the nature of bees in a nonfiction text. Then, because the teacher focuses on the skill of identifying and explaining main ideas and details, a student may write, “I learned the main idea by using headings and key details. Knowing main ideas helps us understand the most important information in a text.”

Woodland Joint Unified School Distirct Board…
Share this:.
- Click to share on Facebook (Opens in new window)
- Click to share on Twitter (Opens in new window)
- Click to print (Opens in new window)
- A&E Source
- Best of 2023 Magazine
Latest Headlines
Subscriber only, woodland joint unified school distirct board honors students, teachers for spanish creative writing contest.

The Woodland Joint Unified School District Board of Trustees honored students and teachers from Pioneer and Woodland High School for recently winning awards for Spanish creative writing as part of the Sacramento region’s “Voces de Sacramento Writing Contest.”
According to a WJUSD press release, the third-annual writing contest, organized by Sacramento State’s Department of World Languages and Literatures, invited students and community members in the Sacramento area to submit creative writing in the Spanish language.
During a March 28 board meeting, WJUSD trustees recognized students from Pioneer and Woodland high schools who won first place, second place and honorable mention awards in the Young Writers category, as well as teachers from both schools who won in the adults category.
For Pioneer High School, student winners included Mildred Victoria Saldaña (first place), María Jaime Hernández (second place), and Melanie Salazar (honorable mention).
“Please join me in congratulating these talented students who participated and won the Voces de Sacramento Writing Contest, in Spanish,” stated Pioneer High School Spanish teacher Delia Zamudio, who won second place in the adults category for her piece called “Ojotes” (Big Eyes). “Every year, since the contest started, I extend the invitation to all my students. I know all my Spanish-speaking students can write in Spanish. They just need motivation and a little push (‘un empujoncito’). Seeing their faces, full of joy, saying, ‘Maestra, lo logré’ (teacher, I did it) makes me proud of them and keeps me inspiring others.”
At Woodland High School, student Alejandra Vargas Reyes and teacher Jaime Rocha both won honorable mentions for their categories.

“When I won my award of honorable mention and saw that my poem was going to be published, I felt a mixture of happiness, but gratitude as well,” said Melanie Salazar, a junior at Pioneer High School, who wrote a poem dedicated to her grandfather called “Mis raíces en la música” (My Roots in Music).
“I wanted everyone to know how nice of a man my grandfather was and that I will forever be thankful to have his last name,” she said.
Mildred Victoria Saldaña, a junior at Pioneer High School, won first place for a short story called “El caballo que quería correr” (The Horse that Wanted to Run).
“The story is about animal abuse,” Saldaña said. “It is based on the point of view of a young horse who narrates the entire story as if he were a great racing competitor, but it is not until the last paragraph that everything takes a different turn.”
Alejandra Vargas Reyes, a junior from Woodland High School, won honorable mention for a personal story called “Cómo mi vida cambió de la noche a la mañana” (How my Life Changed Overnight).
“I felt honored to have won an honorable mention,” Reyes said. “I think it is important to not only write in Spanish but also to be able to speak and read it well. It’s sad that so many people lose their native language. That is why if I don’t read in Spanish, I try my best every day to speak with my friends, family, and teachers in Spanish. Another way that I do not lose my Spanish is to watch Mexican movies or shows in Spanish.”
María Jaime Hernández, a senior at Pioneer High School, won second place for a story called “El espíritu de la juventud” (The Spirit of Youth).
Woodland High School teacher Jaime Rocha won honorable mention in the adults category for a short story called “Ya no es lo mesmo” (It’s No Longer the Same).
“Voces de Sacramento gives both young and adult writers a unique opportunity to share their written voices with the greater Spanish-speaking population in the Sacramento area,” he said. “And having their writing published in the compilation book is an exceptional accomplishment for all participants, for it tells them, ‘Sí tienes madera de escritor/a’ (You have the makings of a writer).”
You can read their stories at the Voces de Sacramento website.
More in News

National Politics | Yes, we’re divided. But new AP-NORC poll shows Americans still agree on most core American values

State’s community colleges are losing millions to financial aid fraud

Yolo County Partnership HealthPlan members left scrambling after Dignity Health contract ends

National Politics | Young voters are more concerned with the economy. That’s bad for Biden
$2,000 No Essay Scholarship
Help cover the cost of college without writing a single essay!
Niche is giving one student $2,000 to put toward tuition, housing, books or other college expenses — no essay required.
Apply below for your chance to win so you can focus on your education, not your finances. Good luck!
Min 7 characters
By proceeding you acknowledge and agree to our Privacy Policy and Terms of Use .
By proceeding you acknowledge and agree to our Privacy Policy and Terms of Use and Scholarship Rules .
Who Can Apply
All high school and college students, as well as anyone looking to attend college or graduate school in the next year. Please note: Not everyone is eligible for this scholarship. Niche sponsored scholarships and sweepstakes are for people with US citizenship or a valid Visa/US passport only. Read the scholarship rules for full eligibility requirements.
How It Works
The $2,000 “No Essay” Scholarship is an easy scholarship with no essay required! Only one entry allowed per person. The winner will be determined by random drawing and then contacted directly and announced in Niche's email newsletter and on the Scholarship Winners page.
About Niche scholarships
We believe cost shouldn’t keep anyone from pursuing a higher education, so we connect students with thousands of scholarships — many of which don’t require an essay — to help them afford college. In 2023 alone, we offered over $285,000 in Niche scholarships. Read more about Niche scholarships here or visit our FAQs .
- Today's news
- Reviews and deals
- Climate change
- 2024 election
- Fall allergies
- Health news
- Mental health
- Sexual health
- Family health
- So mini ways
- Unapologetically
- Buying guides
Entertainment
- How to Watch
- My watchlist
- Stock market
- Biden economy
- Personal finance
- Stocks: most active
- Stocks: gainers
- Stocks: losers
- Trending tickers
- World indices
- US Treasury bonds
- Top mutual funds
- Highest open interest
- Highest implied volatility
- Currency converter
- Basic materials
- Communication services
- Consumer cyclical
- Consumer defensive
- Financial services
- Industrials
- Real estate
- Mutual funds
- Credit cards
- Credit card rates
- Balance transfer credit cards
- Business credit cards
- Cash back credit cards
- Rewards credit cards
- Travel credit cards
- Checking accounts
- Online checking accounts
- High-yield savings accounts
- Money market accounts
- Personal loans
- Student loans
- Car insurance
- Home buying
- Options pit
- Investment ideas
- Research reports
- Fantasy football
- Pro Pick 'Em
- College Pick 'Em
- Fantasy baseball
- Fantasy hockey
- Fantasy basketball
- Download the app
- Daily fantasy
- Scores and schedules
- GameChannel
- World Baseball Classic
- Premier League
- CONCACAF League
- Champions League
- Motorsports
- Horse racing
- Newsletters
New on Yahoo
- Privacy Dashboard
Teen columnists wanted for 2024-25 school year
Apr. 2—The Post Bulletin is accepting applications from high school students interested in being a teen columnist for the 2024-25 school year. All high school students in southeastern Minnesota are eligible to be considered.
What do columnists do? Teens write 500- to 700-word personal essays or columns published Tuesdays in the Post Bulletin Life section. Typically, 10 teens are selected and scheduled to write columns once every five weeks.
What do you need? Send your name, mailing address, email address, phone number, year in high school, high school you attend and age.
Please include a cover letter telling us why you want to be a teen columnist and why you should be selected. Also include three examples that show your writing ability.
Deadline? July 15.
How? Send information via email to Jeff Pieters, Post Bulletin editor, at [email protected] , or via USPS to Jeff Pieters, RE: Teen columnists, 1700 Greenview Drive SW, Rochester, MN 55902. If you have questions, call 507-285-7748.
What's next? We'll let everyone know whom we've selected by early August. Writing will start in September.
Recommended Stories
Nba daily playoff picture: the one where brooklyn's playoff life is on the line.
With the regular season winding down, here's an updated look at the playoff picture and the stakes for Wednesday's slate of games.
Dark circles? Grab Amazon's No. 1 bestselling under-eye masks while they're just 25 cents apiece — that's 65% off
Double discount alert! 'My puffiness and bags were gone,' says one of 24,000 fans of these revitalizing, collagen-infused patches.
Stock market today: Stocks cling to gains as Powell says rate cuts likely at 'some point' this year
Investors looked ahead to a speech by Federal Reserve Chair Jerome Powell amid worries that interest rates will stay higher for longer.
Americans who switch jobs are seeing pay gains nearly double of those who stay put
Workers who leave their jobs are seeing big pay increases compared to those who don't, potentially forestalling inflation's path downward.
Vince Carter, Chauncey Billups will reportedly be part of 2024 Basketball Hall of Fame class
The other inductees will be revealed during the NCAA men's Final Four on Saturday.
Our favorite cheap smartphone is on sale for $250 right now
Our pick for the best cheap phone is on sale, making it an even better deal. The OnePlus Nord N30 5G is now $50 off.
Eclipse weather forecast: Where you'll be able to see it — and where viewing could be difficult
Preliminary local forecasts in 13 states along the so-called path of totality show viewing the highly-anticipated celestial event may be a problem for some, less so for others.
Clean up your yard in no time thanks to this 31% off DeWalt deal
This pruner allows you to tackle branches that would typically require larger manual loppers, all in the compact size of a one-handed tool.
The best smartphone cameras for 2024: How to choose the phone with the best photography chops
Your phone's camera is probably the one you'll use the most on a regular basis. These are the best camera phones you can buy right now.
Bills reportedly trading Stefon Diggs to Texans for 2025 second-round draft pick
Diggs has spent the past four seasons with the Bills.
'A Brief History of the Future' offers a hopeful antidote to cynical tech takes
"A Brief History of the Future," hosted by Ari Wallach, also has the compelling quality of, as a PBS production, being completely free. The thesis of the show is simply that, while the dangers and disappointments of technology (often due to its subversion by business interests) are worth considering and documenting, the other side of the coin also should be highlighted not out of naiveté but because it is genuinely important and compelling.
2024 Mazda Miata sales: the Autoblog Miata Index
One way to track auto sales is by counting the number of 2024 Mazda Miatas sold. We didn't say it was good way.
The FCC will vote to restore net neutrality later this month
The Federal Communications Commission (FCC) plans to vote to restore net neutrality later this month. With the Democrats finally holding an FCC majority in the final year of President Biden’s first term.
The best electric bikes of 2024
The best electric bikes available at Amazon to help you get where you need to go.
Angel Reese declares for WNBA Draft
Reese, a 2023 first-team All-American, had until Wednesday night to decide on her future.
Scandinavian math: Polestar will replace the 2 with a new model called 7
Polestar confirmed it will replace the 2 with a new model called 7 rather than releasing a second-generation model. We should see the EV in the late 2020s.
OnePlus rolls out its own version of Google's Magic Eraser
OnePlus has announced a new tool called AI Eraser, which removes unwanted objects from photos.
Disneyland's Tomorrowland cars are ditching fossil fuel
Tomorrowland's Autopia attraction is embracing the future with a transition away from fossil fuels.
Stability AI’s audio generator can now crank out 3 minute ‘songs’
Stability AI just unveiled Stable Audio 2.0, which now creates three minute AI-generated songs via prompt. Musicians, for now, have nothing to worry about.
Drew Barrymore says this cleanser is 'by far the best' — and it's now just $10 on Amazon
More than 39,000 five-star fans agree: It's the easiest way to remove makeup, no harsh scrubbing required.

IMAGES
VIDEO
COMMENTS
Effective writing is a vital component of students' literacy achievement, and writing is a critical communication tool for students to convey thoughts and opinions, describe ideas and events, and analyze information. Indeed, writing is a life-long skill that plays a key role in post-secondary success across academic and vocational disciplines.1
Teach Essay Writing in Middle School and High School ELA Start with brainstorming. I am a huge fan of group brainstorming, especially since I usually have some EL and SPED students mainstreamed in my college prep English classes. I usually dedicate an entire class period to brainstorming where students gather ideas, paragraph topics, and ...
270 pages of the most effective teaching strategies; 50+ digital tools ready right out of the box 75 editable resources for student differentiation ; Loads of tricks and tips to add to your teaching tool bag; All explanations are reinforced with concrete examples.; Links to high-quality video tutorials; Clear objectives easy to match to the demands of your curriculum
The Four Square is a graphic organizer that students can make themselves when given a blank sheet of paper. They fold it into four squares and draw a box in the middle of the page. The genius of ...
New for this school year, we also invite teachers to join our P.L.C. on teaching writing with The Times, where educators can share resources, strategies and inspiration about teaching with these ...
We've compiled a list of 12 great lesson plans for teaching different writing techniques and styles to high school students. 1. News stories. It's important for students to learn that different types of writing require different styles. For example, the structure and tone of a newspaper article differs greatly from a creative narrative.
If you're a writing teacher in grades 7-12 and you'd like a classroom-ready unit like the one described above, including mini-lessons, sample essays, and a library of high-interest online articles to use for gathering evidence, take a look at my Argumentative Writing unit. Just click on the image below and you'll be taken to a page where you can read more and see a detailed preview of ...
Try having students post a weekly response to a writing prompt or question that you assign. You may also want to create a separate discussion board where students can post ideas about their essay and get feedback from you and their classmates. 6. Give students homework to help them develop their essays.
Strategy 2: Read Like a Writer. When students are tasked with writing essays such as a literary analysis or argument, a key indicator of success is seamlessly incorporating cited text from multiple sources. This synthesis of research, culminated in a student essay, is critical for high school writing and beyond.
Essay assignments are a nightmare for many high school students. The fear of essay writing is often the result of not fully understanding the purpose of an essay or the writing process for completing one. A helpful tactic when teaching essay writing is to start with essay concepts, which may help to reduce the student's apprehension.
Step 1: Start with Casual Augmentation. Engage your students in a low-stakes debate before formally teaching argumentative essay writing. This approach will help get students in the right mindset as you begin to lay the foundation for effective argumentation. Don't even mention the word essay at this point.
Students learn organizational groundwork for writing simple paragraphs and then advance to college level essays. With a variety of topics and types of paragraphs this curriculum guides you as you teach how to logically and easily write formal papers that "Wow!" professors. Every lesson in TWF is arranged with detailed, specific guidelines ...
4 Engaging Writing Tasks for High School Students. Short, authentic writing tasks can encourage high school students to compose richer long pieces. It's quite likely that many of your students dislike writing. After all, they're often expected to compose lengthy pieces that typically require lots of brainstorming, researching, planning ...
Teach Creative Writing to High School Students Step #6: Use Clear and Structured Expectations. While showing students excellent prose or perfect poetry should help inspire students, your writers will still need some hard parameters to follow. Academic writing is often easier for students than creative writing.
You're Getting a List of Writing Strategies With Examples. Prewriting—A Writing Strategy That Comes Before All Others. Mind-Mapping. Outlining. Researching. Targeting Readers. Getting Feedback on Your Outline. Strategies for Your Initial Drafts—Find What Works Best for You. Freewriting.
You can come up with various activities to teach your students persuasive writing, but make sure to have one main goal for each activity. To practice persuasive writing through class activities, your students can: Watch and learn from other writers. Look for relevant sources. Outline their essays.
Outline. The last thing to do before starting to write an essay is to make its outline. Choose some topic and make a list of points your students would need to mention if they wrote an essay on it. Such a technique will give them a better understanding of what and essay is, and how it should be written. Make sure that all students perfectly ...
Discuss writing blocks and ways to overcome them. Discuss the planning process and experience how it helps flesh out an essay. Walk them through each lesson making sure they complete each step successfully before attempting to move on in the writing process. Working side by side with your student also helps you become a better instructor by ...
The first thing you'll need to do is select a topic. Good essay topics take careful thought—don't just decide to write about the first thing that comes to mind. One guideline to remember is that, in general, the narrower your topic is the better. A specific, restricted topic helps you keep your essay organized and focused.
Teaching students how to write effective introductions and conclusions is crucial. Encourage them to start their essay with a hook, such as a quote, anecdote, or a rhetorical question. Teach them how to write a clear thesis statement and preview the main points they will be discussing in their essay. For the conclusion, teach them to restate ...
A simple and effective strategy for how to teach writing is to have students write about the texts that they are reading. Research supports the benefits of this evidence-based writing practice as a way to increase and enlarge opportunities for all students to be successful. This strategy is in contrast to having students simply brainstorm or ...
So, here are seven ESL essay writing tips that will allow your students to weave together a coherent and persuasive essay, plus teacher resources for writing activities, prompts and lessons! Contents. 1. Build the Essay Around a Central Question; 2. Use the Traditional 5-paragraph Essay Structure; 3. Plan the Essay Carefully Before Writing; 4.
Practice, Practice, Practice. "It might seem a bit mean to set regular essays all the time, and you don't want to be that kind of teacher, but the best way to get better at essay writing, as with everything else in life, is to practice. This means giving your students essay tasks to complete, and then reviewing the mistakes and highlighting ...
4. Stay specific. Academic writing requires you to discuss facts, interpret past ideas and create your arguments. If the scope of your topic is too large, you might find that you are doing too much research, which then makes it difficult to narrow down your essay.
Want free help with your college essay? UPchieve connects you with knowledgeable and friendly college advisors—online, 24/7, and completely free. Get 1:1 help brainstorming topics, outlining your essay, revising a draft, or editing grammar.
This method encourages the application of phonics knowledge in real-word scenarios, promoting fluency and automaticity. In addition, dictated sentences provide a valuable opportunity for students to hone their listening skills, enhancing their ability to discern and reproduce distinct phonetic elements accurately and to authentically apply irregularly spelled high-frequency words in context.
The Woodland Joint Unified School District Board of Trustees honored students and teachers from Pioneer and Woodland High School for recently winning awards for Spanish creative writing as part of ...
Help cover the cost of college without writing a single essay! Niche is giving one student $2,000 to put toward tuition, housing, books or other college expenses — no essay required. ... All high school and college students, as well as anyone looking to attend college or graduate school in the next year. Please note: Not everyone is eligible ...
According to US News, the average child sits for 8.5 hours a day. Combine that with high-calorie foods, and weight gain …show more content… It's the law that they need a break. The average school day at our high school starts at 7:35 and ends at 2:35. That's 8 hours of work. The average workday for an adult is 8 hours.
All high school students in southeastern Minnesota are eligible to be considered. What do columnists do? Teens write 500- to 700-word personal essays or columns published Tuesdays in the Post ...