Nature vs. Nurture Debate In Psychology
Saul Mcleod, PhD
Editor-in-Chief for Simply Psychology
BSc (Hons) Psychology, MRes, PhD, University of Manchester
Saul Mcleod, PhD., is a qualified psychology teacher with over 18 years of experience in further and higher education. He has been published in peer-reviewed journals, including the Journal of Clinical Psychology.
Learn about our Editorial Process
Olivia Guy-Evans, MSc
Associate Editor for Simply Psychology
BSc (Hons) Psychology, MSc Psychology of Education
Olivia Guy-Evans is a writer and associate editor for Simply Psychology. She has previously worked in healthcare and educational sectors.
On This Page:
The nature vs. nurture debate in psychology concerns the relative importance of an individual’s innate qualities (nature) versus personal experiences (nurture) in determining or causing individual differences in physical and behavioral traits. While early theories favored one factor over the other, contemporary views recognize a complex interplay between genes and environment in shaping behavior and development.

Key Takeaways
- Nature is what we think of as pre-wiring and is influenced by genetic inheritance and other biological factors.
- Nurture is generally taken as the influence of external factors after conception, e.g., the product of exposure, life experiences, and learning on an individual.
- Behavioral genetics has enabled psychology to quantify the relative contribution of nature and nurture concerning specific psychological traits.
- Instead of defending extreme nativist or nurturist views, most psychological researchers are now interested in investigating how nature and nurture interact in a host of qualitatively different ways.
- For example, epigenetics is an emerging area of research that shows how environmental influences affect the expression of genes.
The nature-nurture debate is concerned with the relative contribution that both influences make to human behavior, such as personality, cognitive traits, temperament and psychopathology.
Examples of Nature vs. Nurture
Nature vs. nurture in child development.
In child development, the nature vs. nurture debate is evident in the study of language acquisition . Researchers like Chomsky (1957) argue that humans are born with an innate capacity for language (nature), known as universal grammar, suggesting that genetics play a significant role in language development.
Conversely, the behaviorist perspective, exemplified by Skinner (1957), emphasizes the role of environmental reinforcement and learning (nurture) in language acquisition.
Twin studies have provided valuable insights into this debate, demonstrating that identical twins raised apart may share linguistic similarities despite different environments, suggesting a strong genetic influence (Bouchard, 1979)
However, environmental factors, such as exposure to language-rich environments, also play a crucial role in language development, highlighting the intricate interplay between nature and nurture in child development.
Nature vs. Nurture in Personality Development
The nature vs. nurture debate in personality psychology centers on the origins of personality traits. Twin studies have shown that identical twins reared apart tend to have more similar personalities than fraternal twins, indicating a genetic component to personality (Bouchard, 1994).
However, environmental factors, such as parenting styles, cultural influences, and life experiences, also shape personality.
For example, research by Caspi et al. (2003) demonstrated that a particular gene (MAOA) can interact with childhood maltreatment to increase the risk of aggressive behavior in adulthood.
This highlights that genetic predispositions and environmental factors contribute to personality development, and their interaction is complex and multifaceted.
Nature vs. Nurture in Mental Illness Development
The nature vs. nurture debate in mental health explores the etiology of depression. Genetic studies have identified specific genes associated with an increased vulnerability to depression, indicating a genetic component (Sullivan et al., 2000).
However, environmental factors, such as adverse life events and chronic stress during childhood, also play a significant role in the development of depressive disorders (Dube et al.., 2002; Keller et al., 2007)
The diathesis-stress model posits that individuals inherit a genetic predisposition (diathesis) to a disorder, which is then activated or exacerbated by environmental stressors (Monroe & Simons, 1991).
This model illustrates how nature and nurture interact to influence mental health outcomes.
Nature vs. Nurture of Intelligence
The nature vs. nurture debate in intelligence examines the relative contributions of genetic and environmental factors to cognitive abilities.
Intelligence is highly heritable, with about 50% of variance in IQ attributed to genetic factors, based on studies of twins, adoptees, and families (Plomin & Spinath, 2004).
Heritability of intelligence increases with age, from about 20% in infancy to as high as 80% in adulthood, suggesting amplifying effects of genes over time.
However, environmental influences, such as access to quality education and stimulating environments, also significantly impact intelligence.
Shared environmental influences like family background are more influential in childhood, whereas non-shared experiences are more important later in life.
Research by Flynn (1987) showed that average IQ scores have increased over generations, suggesting that environmental improvements, known as the Flynn effect , can lead to substantial gains in cognitive abilities.
Molecular genetics provides tools to identify specific genes and understand their pathways and interactions. However, progress has been slow for complex traits like intelligence. Identified genes have small effect sizes (Plomin & Spinath, 2004).
Overall, intelligence results from complex interplay between genes and environment over development. Molecular genetics offers promise to clarify these mechanisms. The nature vs nurture debate is outdated – both play key roles.
Nativism (Extreme Nature Position)
It has long been known that certain physical characteristics are biologically determined by genetic inheritance.
Color of eyes, straight or curly hair, pigmentation of the skin, and certain diseases (such as Huntingdon’s chorea) are all a function of the genes we inherit.
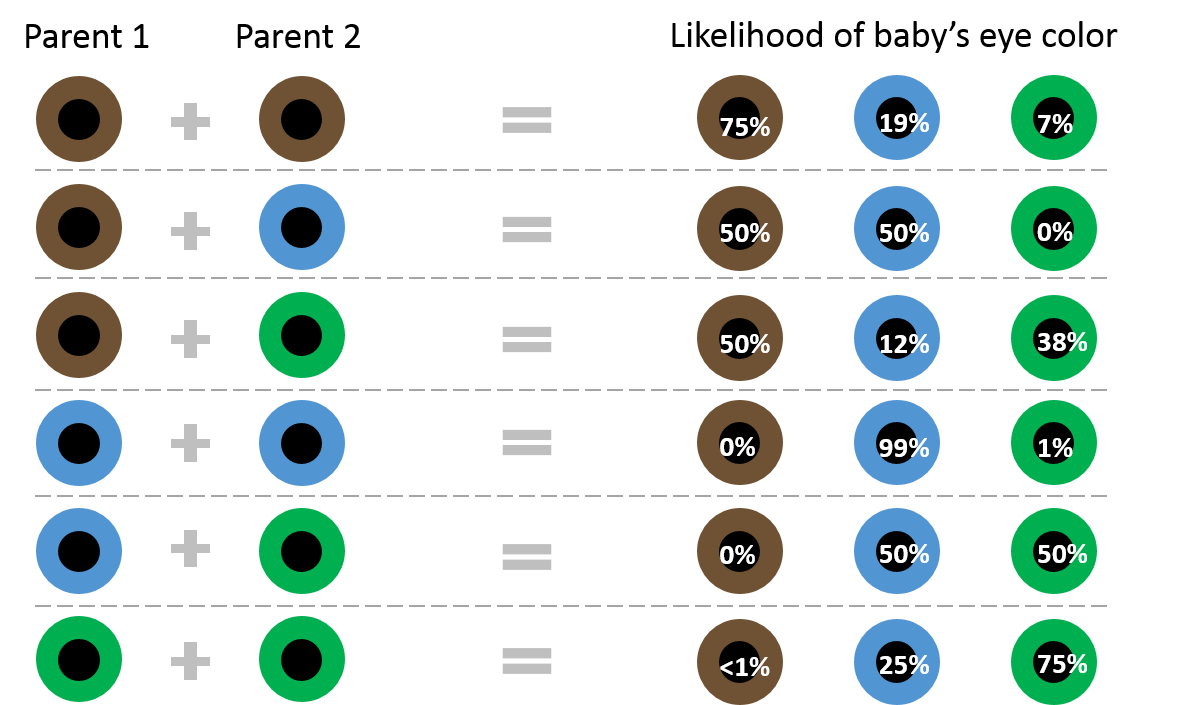
These facts have led many to speculate as to whether psychological characteristics such as behavioral tendencies, personality attributes, and mental abilities are also “wired in” before we are even born.
Those who adopt an extreme hereditary position are known as nativists. Their basic assumption is that the characteristics of the human species as a whole are a product of evolution and that individual differences are due to each person’s unique genetic code.
In general, the earlier a particular ability appears, the more likely it is to be under the influence of genetic factors. Estimates of genetic influence are called heritability.
Examples of extreme nature positions in psychology include Chomsky (1965), who proposed language is gained through the use of an innate language acquisition device. Another example of nature is Freud’s theory of aggression as being an innate drive (called Thanatos).
Characteristics and differences that are not observable at birth, but which emerge later in life, are regarded as the product of maturation. That is to say, we all have an inner “biological clock” which switches on (or off) types of behavior in a pre-programmed way.
The classic example of the way this affects our physical development are the bodily changes that occur in early adolescence at puberty.
However, nativists also argue that maturation governs the emergence of attachment in infancy , language acquisition , and even cognitive development .
Empiricism (Extreme Nurture Position)
At the other end of the spectrum are the environmentalists – also known as empiricists (not to be confused with the other empirical/scientific approach ).
Their basic assumption is that at birth, the human mind is a tabula rasa (a blank slate) and that this is gradually “filled” as a result of experience (e.g., behaviorism ).
From this point of view, psychological characteristics and behavioral differences that emerge through infancy and childhood are the results of learning. It is how you are brought up (nurture) that governs the psychologically significant aspects of child development and the concept of maturation applies only to the biological.
For example, Bandura’s (1977) social learning theory states that aggression is learned from the environment through observation and imitation. This is seen in his famous bobo doll experiment (Bandura, 1961).
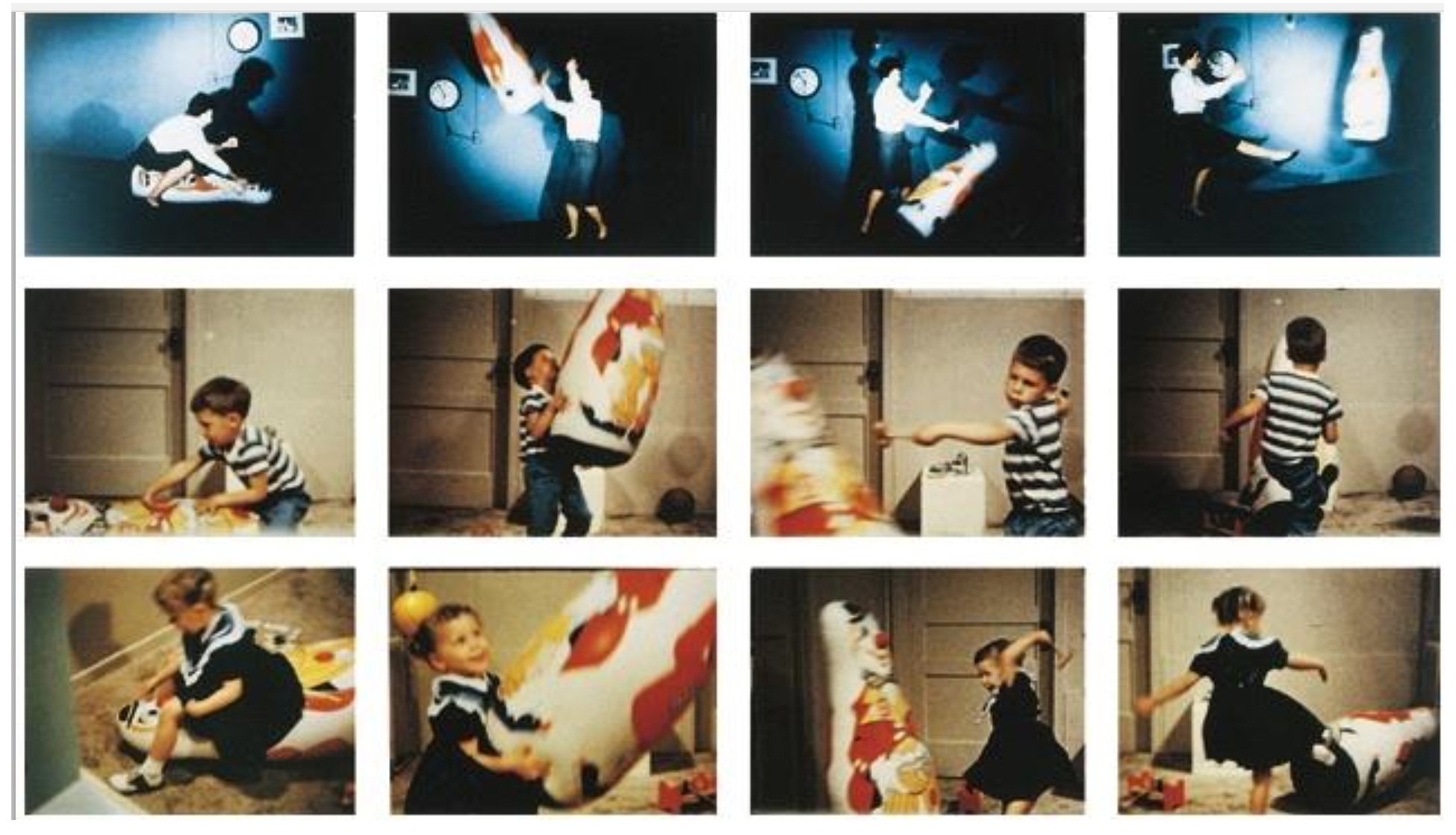

Also, Skinner (1957) believed that language is learned from other people via behavior-shaping techniques.
Evidence for Nature
- Biological Approach
- Biology of Gender
- Medical Model
Freud (1905) stated that events in our childhood have a great influence on our adult lives, shaping our personality.
He thought that parenting is of primary importance to a child’s development , and the family as the most important feature of nurture was a common theme throughout twentieth-century psychology (which was dominated by environmentalists’ theories).
Behavioral Genetics
Researchers in the field of behavioral genetics study variation in behavior as it is affected by genes, which are the units of heredity passed down from parents to offspring.
“We now know that DNA differences are the major systematic source of psychological differences between us. Environmental effects are important but what we have learned in recent years is that they are mostly random – unsystematic and unstable – which means that we cannot do much about them.” Plomin (2018, xii)
Behavioral genetics has enabled psychology to quantify the relative contribution of nature and nurture with regard to specific psychological traits. One way to do this is to study relatives who share the same genes (nature) but a different environment (nurture). Adoption acts as a natural experiment which allows researchers to do this.
Empirical studies have consistently shown that adoptive children show greater resemblance to their biological parents, rather than their adoptive, or environmental parents (Plomin & DeFries, 1983; 1985).
Another way of studying heredity is by comparing the behavior of twins, who can either be identical (sharing the same genes) or non-identical (sharing 50% of genes). Like adoption studies, twin studies support the first rule of behavior genetics; that psychological traits are extremely heritable, about 50% on average.
The Twins in Early Development Study (TEDS) revealed correlations between twins on a range of behavioral traits, such as personality (empathy and hyperactivity) and components of reading such as phonetics (Haworth, Davis, Plomin, 2013; Oliver & Plomin, 2007; Trouton, Spinath, & Plomin, 2002).
Implications
Jenson (1969) found that the average I.Q. scores of black Americans were significantly lower than whites he went on to argue that genetic factors were mainly responsible – even going so far as to suggest that intelligence is 80% inherited.
The storm of controversy that developed around Jenson’s claims was not mainly due to logical and empirical weaknesses in his argument. It was more to do with the social and political implications that are often drawn from research that claims to demonstrate natural inequalities between social groups.
For many environmentalists, there is a barely disguised right-wing agenda behind the work of the behavioral geneticists. In their view, part of the difference in the I.Q. scores of different ethnic groups are due to inbuilt biases in the methods of testing.
More fundamentally, they believe that differences in intellectual ability are a product of social inequalities in access to material resources and opportunities. To put it simply children brought up in the ghetto tend to score lower on tests because they are denied the same life chances as more privileged members of society.
Now we can see why the nature-nurture debate has become such a hotly contested issue. What begins as an attempt to understand the causes of behavioral differences often develops into a politically motivated dispute about distributive justice and power in society.
What’s more, this doesn’t only apply to the debate over I.Q. It is equally relevant to the psychology of sex and gender , where the question of how much of the (alleged) differences in male and female behavior is due to biology and how much to culture is just as controversial.
Polygenic Inheritance
Rather than the presence or absence of single genes being the determining factor that accounts for psychological traits, behavioral genetics has demonstrated that multiple genes – often thousands, collectively contribute to specific behaviors.
Thus, psychological traits follow a polygenic mode of inheritance (as opposed to being determined by a single gene). Depression is a good example of a polygenic trait, which is thought to be influenced by around 1000 genes (Plomin, 2018).
This means a person with a lower number of these genes (under 500) would have a lower risk of experiencing depression than someone with a higher number.
The Nature of Nurture
Nurture assumes that correlations between environmental factors and psychological outcomes are caused environmentally. For example, how much parents read with their children and how well children learn to read appear to be related. Other examples include environmental stress and its effect on depression.
However, behavioral genetics argues that what look like environmental effects are to a large extent really a reflection of genetic differences (Plomin & Bergeman, 1991).
People select, modify and create environments correlated with their genetic disposition. This means that what sometimes appears to be an environmental influence (nurture) is a genetic influence (nature).
So, children that are genetically predisposed to be competent readers, will be happy to listen to their parents read them stories, and be more likely to encourage this interaction.
Interaction Effects
However, in recent years there has been a growing realization that the question of “how much” behavior is due to heredity and “how much” to the environment may itself be the wrong question.
Take intelligence as an example. Like almost all types of human behavior, it is a complex, many-sided phenomenon which reveals itself (or not!) in a great variety of ways.
The “how much” question assumes that psychological traits can all be expressed numerically and that the issue can be resolved in a quantitative manner.
Heritability statistics revealed by behavioral genetic studies have been criticized as meaningless, mainly because biologists have established that genes cannot influence development independently of environmental factors; genetic and nongenetic factors always cooperate to build traits. The reality is that nature and culture interact in a host of qualitatively different ways (Gottlieb, 2007; Johnston & Edwards, 2002).
Instead of defending extreme nativist or nurturist views, most psychological researchers are now interested in investigating how nature and nurture interact.
For example, in psychopathology , this means that both a genetic predisposition and an appropriate environmental trigger are required for a mental disorder to develop. For example, epigenetics state that environmental influences affect the expression of genes.
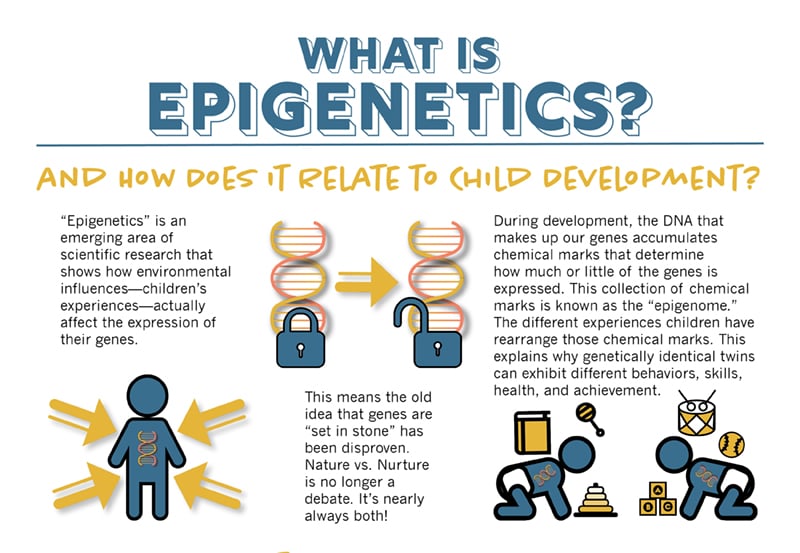
What is Epigenetics?
Epigenetics is the term used to describe inheritance by mechanisms other than through the DNA sequence of genes. For example, features of a person’s physical and social environment can effect which genes are switched-on, or “expressed”, rather than the DNA sequence of the genes themselves.
Stressors and memories can be passed through small RNA molecules to multiple generations of offspring in ways that meaningfully affect their behavior.
One such example is what is known as the Dutch Hunger Winter, during last year of the Second World War. What they found was that children who were in the womb during the famine experienced a life-long increase in their chances of developing various health problems compared to children conceived after the famine.
Epigenetic effects can sometimes be passed from one generation to the next, although the effects only seem to last for a few generations. There is some evidence that the effects of the Dutch Hunger Winter affected grandchildren of women who were pregnant during the famine.
Therefore, it makes more sense to say that the difference between two people’s behavior is mostly due to hereditary factors or mostly due to environmental factors.
This realization is especially important given the recent advances in genetics, such as polygenic testing. The Human Genome Project, for example, has stimulated enormous interest in tracing types of behavior to particular strands of DNA located on specific chromosomes.
If these advances are not to be abused, then there will need to be a more general understanding of the fact that biology interacts with both the cultural context and the personal choices that people make about how they want to live their lives.
There is no neat and simple way of unraveling these qualitatively different and reciprocal influences on human behavior.
Epigenetics: Licking Rat Pups
Michael Meaney and his colleagues at McGill University in Montreal, Canada conducted the landmark epigenetic study on mother rats licking and grooming their pups.
This research found that the amount of licking and grooming received by rat pups during their early life could alter their epigenetic marks and influence their stress responses in adulthood.
Pups that received high levels of maternal care (i.e., more licking and grooming) had a reduced stress response compared to those that received low levels of maternal care.
Meaney’s work with rat maternal behavior and its epigenetic effects has provided significant insights into the understanding of early-life experiences, gene expression, and adult behavior.
It underscores the importance of the early-life environment and its long-term impacts on an individual’s mental health and stress resilience.
Epigenetics: The Agouti Mouse Study
Waterland and Jirtle’s 2003 study on the Agouti mouse is another foundational work in the field of epigenetics that demonstrated how nutritional factors during early development can result in epigenetic changes that have long-lasting effects on phenotype.
In this study, they focused on a specific gene in mice called the Agouti viable yellow (A^vy) gene. Mice with this gene can express a range of coat colors, from yellow to mottled to brown.
This variation in coat color is related to the methylation status of the A^vy gene: higher methylation is associated with the brown coat, and lower methylation with the yellow coat.
Importantly, the coat color is also associated with health outcomes, with yellow mice being more prone to obesity, diabetes, and tumorigenesis compared to brown mice.
Waterland and Jirtle set out to investigate whether maternal diet, specifically supplementation with methyl donors like folic acid, choline, betaine, and vitamin B12, during pregnancy could influence the methylation status of the A^vy gene in offspring.
Key findings from the study include:
Dietary Influence : When pregnant mice were fed a diet supplemented with methyl donors, their offspring had an increased likelihood of having the brown coat color. This indicated that the supplemented diet led to an increased methylation of the A^vy gene.
Health Outcomes : Along with the coat color change, these mice also had reduced risks of obesity and other health issues associated with the yellow phenotype.
Transgenerational Effects : The study showed that nutritional interventions could have effects that extend beyond the individual, affecting the phenotype of the offspring.
The implications of this research are profound. It highlights how maternal nutrition during critical developmental periods can have lasting effects on offspring through epigenetic modifications, potentially affecting health outcomes much later in life.
The study also offers insights into how dietary and environmental factors might contribute to disease susceptibility in humans.
Bandura, A. Ross, D., & Ross, S. A. (1961). Transmission of aggression through the imitation of aggressive models. Journal of Abnormal and Social Psychology , 63, 575-582
Bandura, A. (1977). Social learning theory . Englewood Cliffs, NJ: Prentice Hall.
Bouchard, T. J. (1994). Genes, Environment, and Personality. Science, 264 (5166), 1700-1701.
Bowlby, J. (1969). Attachment. Attachment and loss: Vol. 1. Loss . New York: Basic Books.
Caspi, A., Sugden, K., Moffitt, T. E., Taylor, A., Craig, I. W., Harrington, H., … & Poulton, R. (2003). Influence of life stress on depression: moderation by a polymorphism in the 5-HTT gene. Science , 301 (5631), 386-389.
Chomsky, N. (1957). Syntactic structures. Mouton de Gruyter.
Chomsky, N. (1965). Aspects of the theory of syntax . MIT Press.
Dube, S. R., Anda, R. F., Felitti, V. J., Edwards, V. J., & Croft, J. B. (2002). Adverse childhood experiences and personal alcohol abuse as an adult. Addictive Behaviors , 27 (5), 713-725.
Flynn, J. R. (1987). Massive IQ gains in 14 nations: What IQ tests really measure. Psychological Bulletin , 101 (2), 171.
Freud, S. (1905). Three essays on the theory of sexuality . Se, 7.
Galton, F. (1883). Inquiries into human faculty and its development . London: J.M. Dent & Co.
Gottlieb, G. (2007). Probabilistic epigenesis. Developmental Science, 10 , 1–11.
Haworth, C. M., Davis, O. S., & Plomin, R. (2013). Twins Early Development Study (TEDS): a genetically sensitive investigation of cognitive and behavioral development from childhood to young adulthood . Twin Research and Human Genetics, 16(1) , 117-125.
Jensen, A. R. (1969). How much can we boost I.Q. and scholastic achievement? Harvard Educational Review, 33 , 1-123.
Johnston, T. D., & Edwards, L. (2002). Genes, interactions, and the development of behavior . Psychological Review , 109, 26–34.
Keller, M. C., Neale, M. C., & Kendler, K. S. (2007). Association of different adverse life events with distinct patterns of depressive symptoms. American Journal of Psychiatry , 164 (10), 1521-1529.
Monroe, S. M., & Simons, A. D. (1991). Diathesis-stress theories in the context of life stress research: implications for the depressive disorders. Psychological Bulletin , 110 (3), 406.
Oliver, B. R., & Plomin, R. (2007). Twins” Early Development Study (TEDS): A multivariate, longitudinal genetic investigation of language, cognition and behavior problems from childhood through adolescence . Twin Research and Human Genetics, 10(1) , 96-105.
Petrill, S. A., Plomin, R., Berg, S., Johansson, B., Pedersen, N. L., Ahern, F., & McClearn, G. E. (1998). The genetic and environmental relationship between general and specific cognitive abilities in twins age 80 and older. Psychological Science , 9 (3), 183-189.
Plomin, R., & Petrill, S. A. (1997). Genetics and intelligence: What’s new?. Intelligence , 24 (1), 53-77.
Plomin, R. (2018). Blueprint: How DNA makes us who we are . MIT Press.
Plomin, R., & Bergeman, C. S. (1991). The nature of nurture: Genetic influence on “environmental” measures. behavioral and Brain Sciences, 14(3) , 373-386.
Plomin, R., & DeFries, J. C. (1983). The Colorado adoption project. Child Development , 276-289.
Plomin, R., & DeFries, J. C. (1985). The origins of individual differences in infancy; the Colorado adoption project. Science, 230 , 1369-1371.
Plomin, R., & Spinath, F. M. (2004). Intelligence: genetics, genes, and genomics. Journal of personality and social psychology , 86 (1), 112.
Plomin, R., & Von Stumm, S. (2018). The new genetics of intelligence. Nature Reviews Genetics , 19 (3), 148-159.
Skinner, B. F. (1957). Verbal behavior . Acton, MA: Copley Publishing Group.
Sullivan, P. F., Neale, M. C., & Kendler, K. S. (2000). Genetic epidemiology of major depression: review and meta-analysis. American Journal of Psychiatry , 157 (10), 1552-1562.
Szyf, M., Weaver, I. C., Champagne, F. A., Diorio, J., & Meaney, M. J. (2005). Maternal programming of steroid receptor expression and phenotype through DNA methylation in the rat . Frontiers in neuroendocrinology , 26 (3-4), 139-162.
Trouton, A., Spinath, F. M., & Plomin, R. (2002). Twins early development study (TEDS): a multivariate, longitudinal genetic investigation of language, cognition and behavior problems in childhood . Twin Research and Human Genetics, 5(5) , 444-448.
Waterland, R. A., & Jirtle, R. L. (2003). Transposable elements: targets for early nutritional effects on epigenetic gene regulation . Molecular and cellular biology, 23 (15), 5293-5300.
Further Information
- Genetic & Environmental Influences on Human Psychological Differences
Evidence for Nurture
- Classical Conditioning
- Little Albert Experiment
- Operant Conditioning
- Behaviorism
- Social Learning Theory
- Bronfenbrenner’s Ecological Systems Theory
- Social Roles
- Attachment Styles
- The Hidden Links Between Mental Disorders
- Visual Cliff Experiment
- Behavioral Genetics, Genetics, and Epigenetics
- Epigenetics
- Is Epigenetics Inherited?
- Physiological Psychology
- Bowlby’s Maternal Deprivation Hypothesis
- So is it nature not nurture after all?
Evidence for an Interaction
- Genes, Interactions, and the Development of Behavior
- Agouti Mouse Study
- Biological Psychology
What does nature refer to in the nature vs. nurture debate?
In the nature vs. nurture debate, “nature” refers to the influence of genetics, innate qualities, and biological factors on human development, behavior, and traits. It emphasizes the role of hereditary factors in shaping who we are.
What does nurture refer to in the nature vs. nurture debate?
In the nature vs. nurture debate, “nurture” refers to the influence of the environment, upbringing, experiences, and social factors on human development, behavior, and traits. It emphasizes the role of external factors in shaping who we are.
Why is it important to determine the contribution of heredity (nature) and environment (nurture) in human development?
Determining the contribution of heredity and environment in human development is crucial for understanding the complex interplay between genetic factors and environmental influences. It helps identify the relative significance of each factor, informing interventions, policies, and strategies to optimize human potential and address developmental challenges.
- Type 2 Diabetes
- Heart Disease
- Digestive Health
- Multiple Sclerosis
- COVID-19 Vaccines
- Occupational Therapy
- Healthy Aging
- Health Insurance
- Public Health
- Patient Rights
- Caregivers & Loved Ones
- End of Life Concerns
- Health News
- Thyroid Test Analyzer
- Doctor Discussion Guides
- Hemoglobin A1c Test Analyzer
- Lipid Test Analyzer
- Complete Blood Count (CBC) Analyzer
- What to Buy
- Editorial Process
- Meet Our Medical Expert Board
What Are Nature vs. Nurture Examples?
How is nature defined, how is nurture defined, the nature vs. nurture debate, nature vs. nurture examples, what is empiricism (extreme nurture position), contemporary views of nature vs. nurture.
Nature vs. nurture is an age-old debate about whether genetics (nature) plays a bigger role in determining a person's characteristics than lived experience and environmental factors (nurture). The term "nature vs. nature" was coined by English naturalist Charles Darwin's younger half-cousin, anthropologist Francis Galton, around 1875.
In psychology, the extreme nature position (nativism) proposes that intelligence and personality traits are inherited and determined only by genetics.
On the opposite end of the spectrum, the extreme nurture position (empiricism) asserts that the mind is a blank slate at birth; external factors like education and upbringing determine who someone becomes in adulthood and how their mind works. Both of these extreme positions have shortcomings and are antiquated.
This article explores the difference between nature and nurture. It gives nature vs. nurture examples and explains why outdated views of nativism and empiricism don't jibe with contemporary views.
Thanasis Zovoilis / Getty Images
In the context of nature vs. nurture, "nature" refers to genetics and heritable factors that are passed down to children from their biological parents.
Genes and hereditary factors determine many aspects of someone’s physical appearance and other individual characteristics, such as a genetically inherited predisposition for certain personality traits.
Scientists estimate that 20% to 60% percent of temperament is determined by genetics and that many (possibly thousands) of common gene variations combine to influence individual characteristics of temperament.
However, the impact of gene-environment (or nature-nurture) interactions on someone's traits is interwoven. Environmental factors also play a role in temperament by influencing gene activity. For example, in children raised in an adverse environment (such as child abuse or violence), genes that increase the risk of impulsive temperamental characteristics may be activated (turned on).
Trying to measure "nature vs. nurture" scientifically is challenging. It's impossible to know precisely where the influence of genes and environment begin or end.
How Are Inherited Traits Measured?
“Heritability” describes the influence that genes have on human characteristics and traits. It's measured on a scale of 0.0 to 1.0. Very strong heritable traits like someone's eye color are ranked a 1.0.
Traits that have nothing to do with genetics, like speaking with a regional accent ranks a zero. Most human characteristics score between a 0.30 and 0.60 on the heritability scale, which reflects a blend of genetics (nature) and environmental (nurture) factors.
Thousands of years ago, ancient Greek philosophers like Plato believed that "innate knowledge" is present in our minds at birth. Every parent knows that babies are born with innate characteristics. Anecdotally, it may seem like a kid's "Big 5" personality traits (agreeableness, conscientiousness, extraversion, neuroticism, and openness) were predetermined before birth.
What is the "Big 5" personality traits
The Big 5 personality traits is a theory that describes the five basic dimensions of personality. It was developed in 1949 by D. W. Fiske and later expanded upon by other researchers and is used as a framework to study people's behavior.
From a "nature" perspective, the fact that every child has innate traits at birth supports Plato's philosophical ideas about innatism. However, personality isn't set in stone. Environmental "nurture" factors can change someone's predominant personality traits over time. For example, exposure to the chemical lead during childhood may alter personality.
In 2014, a meta-analysis of genetic and environmental influences on personality development across the human lifespan found that people change with age. Personality traits are relatively stable during early childhood but often change dramatically during adolescence and young adulthood.
It's impossible to know exactly how much "nurture" changes personality as people get older. In 2019, a study of how stable personality traits are from age 16 to 66 found that people's Big 5 traits are both stable and malleable (able to be molded). During the 50-year span from high school to retirement, some traits like agreeableness and conscientiousness tend to increase, while others appear to be set in stone.
Nurture refers to all of the external or environmental factors that affect human development such as how someone is raised, socioeconomic status, early childhood experiences, education, and daily habits.
Although the word "nurture" may conjure up images of babies and young children being cared for by loving parents, environmental factors and life experiences have an impact on our psychological and physical well-being across the human life span. In adulthood, "nurturing" oneself by making healthy lifestyle choices can offset certain genetic predispositions.
For example, a May 2022 study found that people with a high genetic risk of developing the brain disorder Alzheimer's disease can lower their odds of developing dementia (a group of symptoms that affect memory, thinking, and social abilities enough to affect daily life) by adopting these seven healthy habits in midlife:
- Staying active
- Healthy eating
- Losing weight
- Not smoking
- Reducing blood sugar
- Controlling cholesterol
- Maintaining healthy blood pressure
The nature vs. nurture debate centers around whether individual differences in behavioral traits and personality are caused primarily by nature or nurture. Early philosophers believed the genetic traits passed from parents to their children influence individual differences and traits. Other well-known philosophers believed the mind begins as a blank slate and that everything we are is determined by our experiences.
While early theories favored one factor over the other, experts today recognize there is a complex interaction between genetics and the environment and that both nature and nurture play a critical role in shaping who we are.
Eye color and skin pigmentation are examples of "nature" because they are present at birth and determined by inherited genes. Developmental delays due to toxins (such as exposure to lead as a child or exposure to drugs in utero) are examples of "nurture" because the environment can negatively impact learning and intelligence.
In Child Development
The nature vs. nurture debate in child development is apparent when studying language development. Nature theorists believe genetics plays a significant role in language development and that children are born with an instinctive ability that allows them to both learn and produce language.
Nurture theorists would argue that language develops by listening and imitating adults and other children.
In addition, nurture theorists believe people learn by observing the behavior of others. For example, contemporary psychologist Albert Bandura's social learning theory suggests that aggression is learned through observation and imitation.
In Psychology
In psychology, the nature vs. nurture beliefs vary depending on the branch of psychology.
- Biopsychology: Researchers analyze how the brain, neurotransmitters, and other aspects of our biology influence our behaviors, thoughts, and feelings. emphasizing the role of nature.
- Social psychology: Researchers study how external factors such as peer pressure and social media influence behaviors, emphasizing the importance of nurture.
- Behaviorism: This theory of learning is based on the idea that our actions are shaped by our interactions with our environment.
In Personality Development
Whether nature or nurture plays a bigger role in personality development depends on different personality development theories.
- Behavioral theories: Our personality is a result of the interactions we have with our environment, such as parenting styles, cultural influences, and life experiences.
- Biological theories: Personality is mostly inherited which is demonstrated by a study in the 1990s that concluded identical twins reared apart tend to have more similar personalities than fraternal twins.
- Psychodynamic theories: Personality development involves both genetic predispositions and environmental factors and their interaction is complex.
In Mental Illness
Both nature and nurture can contribute to mental illness development.
For example, at least five mental health disorders are associated with some type of genetic component ( autism , attention-deficit hyperactivity disorder (ADHD) , bipolar disorder , major depression, and schizophrenia ).
Other explanations for mental illness are environmental, such as:
- Being exposed to drugs or alcohol in utero
- Witnessing a traumatic event, leading to post-traumatic stress disorder (PTSD)
- Adverse life events and chronic stress during childhood
In Mental Health Therapy
Mental health treatment can involve both nature and nurture. For example, a therapist may explore life experiences that may have contributed to mental illness development (nurture) as well as family history of mental illness (nature).
At the same time, research indicates that a person's genetic makeup may impact how their body responds to antidepressants. Taking this into consideration is important for finding the right treatment for each individual.
What Is Nativism (Extreme Nature Position)?
Innatism emphasizes nature's role in shaping our minds and personality traits before birth. Nativism takes this one step further and proposes that all of people's mental and physical characteristics are inherited and predetermined at birth.
In its extreme form, concepts of nativism gave way to the early 20th century's racially-biased eugenics movement. Thankfully, "selective breeding," which is the idea that only certain people should reproduce in order to create chosen characteristics in offspring, and eugenics, arranged breeding, lost momentum during World War II. At that time, the Nazis' ethnic cleansing (killing people based on their ethnic or religious associations) atrocities were exposed.
Philosopher John Locke's tabula rasa theory from 1689 directly opposes the idea that we are born with innate knowledge. "Tabula rasa" means "blank slate" and implies that our minds do not have innate knowledge at birth.
Locke was an empiricist who believed that all the knowledge we gain in life comes from sensory experiences (using their senses to understand the world), education, and day-to-day encounters after being born.
Today, looking at nature vs. nature in black-and-white terms is considered a misguided dichotomy (two-part system). There are so many shades of gray where nature and nurture overlap. It's impossible to tease out how inherited traits and learned behaviors shape someone's unique characteristics or influence how their mind works.
The influences of nature and nurture in psychology are impossible to unravel. For example, imagine someone growing up in a household with an alcoholic parent who has frequent rage attacks. If that child goes on to develop a substance use disorder and has trouble with emotion regulation in adulthood, it's impossible to know precisely how much genetics (nature) or adverse childhood experiences (nurture) affected that individual's personality traits or issues with alcoholism.
Epigenetics Blurs the Line Between Nature and Nurture
"Epigenetics " means "on top of" genetics. It refers to external factors and experiences that turn genes "on" or "off." Epigenetic mechanisms alter DNA's physical structure in utero (in the womb) and across the human lifespan.
Epigenetics blurs the line between nature and nurture because it says that even after birth, our genetic material isn't set in stone; environmental factors can modify genes during one's lifetime. For example, cannabis exposure during critical windows of development can increase someone's risk of neuropsychiatric disease via epigenetic mechanisms.
Nature vs. nurture is a framework used to examine how genetics (nature) and environmental factors (nurture) influence human development and personality traits.
However, nature vs. nurture isn't a black-and-white issue; there are many shades of gray where the influence of nature and nurture overlap. It's impossible to disentangle how nature and nurture overlap; they are inextricably intertwined. In most cases, nature and nurture combine to make us who we are.
Waller JC. Commentary: the birth of the twin study--a commentary on francis galton’s “the history of twins.” International Journal of Epidemiology . 2012;41(4):913-917. doi:10.1093/ije/dys100
The New York Times. " Major Personality Study Finds That Traits Are Mostly Inherited ."
Medline Plus. Is temperament determined by genetics?
Feldman MW, Ramachandran S. Missing compared to what? Revisiting heritability, genes and culture . Phil Trans R Soc B . 2018;373(1743):20170064. doi:10.1098/rstb.2017.0064
Winch C. Innatism, concept formation, concept mastery and formal education: innatism, concept formation and formal education . Journal of Philosophy of Education . 2015;49(4):539-556. doi:10.1111/1467-9752.12121
Briley DA, Tucker-Drob EM. Genetic and environmental continuity in personality development: A meta-analysis . Psychological Bulletin . 2014;140(5):1303-1331. doi:10.1037/a0037091
Damian RI, Spengler M, Sutu A, Roberts BW. Sixteen going on sixty-six: A longitudinal study of personality stability and change across 50 years . Journal of Personality and Social Psychology . 2019;117(3):674-695. doi:10.1037/pspp0000210
Tin A, Bressler J, Simino J, et al. Genetic risk, midlife life’s simple 7, and incident dementia in the atherosclerosis risk in communities study . Neurology . Published online May 25, 2022. doi:10.1212/WNL.0000000000200520
Levitt M. Perceptions of nature, nurture and behaviour . Life Sci Soc Policy . 2013;9(1):13. doi:10.1186/2195-7819-9-13
Ross EJ, Graham DL, Money KM, Stanwood GD. Developmental consequences of fetal exposure to drugs: what we know and what we still must learn . Neuropsychopharmacology. 2015 Jan;40(1):61-87. doi: 10.1038/npp.2014.14
World Health Organization. Lead poisoning .
Bandura, A., Ross, D., & Ross, S. A. Transmission of aggression through imitation of aggressive models . The Journal of Abnormal and Social Psychology, 1961; 63 (3), 575–582 doi:10.1037/h0045925
Krapfl JE. Behaviorism and society . Behav Anal. 2016;39(1):123-9. doi:10.1007/s40614-016-0063-8
Bouchard TJ Jr, Lykken DT, McGue M, Segal NL, Tellegen A. Sources of human psychological differences: the Minnesota Study of Twins Reared Apart . Science. 1990 Oct 12;250(4978):223-8. doi: 10.1126/science.2218526
National Institutes of Health. Common genetic factors found in 5 mental disorders .
Franke HA. Toxic Stress: Effects, Prevention and Treatment . Children (Basel). 2014 Nov 3;1(3):390-402. doi: 10.3390/children1030390
Pain O, Hodgson K, Trubetskoy V, et al. Identifying the common genetic basis of antidepressant response . Biol Psychiatry Global Open Sci . 2022;2(2):115-126. doi:10.1016/j.bpsgos.2021.07.008
National Human Genome Research Institute. Eugenics and Scientific Racism .
OLL. The Works of John Locke in Nine Volumes .
Toraño EG, García MG, Fernández-Morera JL, Niño-García P, Fernández AF. The impact of external factors on the epigenome: in utero and over lifetime . BioMed Research International . 2016;2016:1-17. doi:10.1155/2016/2568635
Smith A, Kaufman F, Sandy MS, Cardenas A. Cannabis exposure during critical windows of development: epigenetic and molecular pathways implicated in neuropsychiatric disease . Curr Envir Health Rpt . 2020;7(3):325-342. doi:10.1007/s40572-020-00275-4
By Christopher Bergland Christopher Bergland is a retired ultra-endurance athlete turned medical writer and science reporter.
- Bipolar Disorder
- Therapy Center
- When To See a Therapist
- Types of Therapy
- Best Online Therapy
- Best Couples Therapy
- Best Family Therapy
- Managing Stress
- Sleep and Dreaming
- Understanding Emotions
- Self-Improvement
- Healthy Relationships
- Student Resources
- Personality Types
- Guided Meditations
- Verywell Mind Insights
- 2023 Verywell Mind 25
- Mental Health in the Classroom
- Editorial Process
- Meet Our Review Board
- Crisis Support
The Nature vs. Nurture Debate
Genetic and Environmental Influences and How They Interact
Kendra Cherry, MS, is a psychosocial rehabilitation specialist, psychology educator, and author of the "Everything Psychology Book."
:max_bytes(150000):strip_icc():format(webp)/IMG_9791-89504ab694d54b66bbd72cb84ffb860e.jpg)
Verywell / Joshua Seong
- Definitions
- Interaction
- Contemporary Views
Nature refers to how genetics influence an individual's personality, whereas nurture refers to how their environment (including relationships and experiences) impacts their development. Whether nature or nurture plays a bigger role in personality and development is one of the oldest philosophical debates within the field of psychology .
Learn how each is defined, along with why the issue of nature vs. nurture continues to arise. We also share a few examples of when arguments on this topic typically occur, how the two factors interact with each other, and contemporary views that exist in the debate of nature vs. nurture as it stands today.
Nature and Nurture Defined
To better understand the nature vs. nurture argument, it helps to know what each of these terms means.
- Nature refers largely to our genetics . It includes the genes we are born with and other hereditary factors that can impact how our personality is formed and influence the way that we develop from childhood through adulthood.
- Nurture encompasses the environmental factors that impact who we are. This includes our early childhood experiences, the way we were raised , our social relationships, and the surrounding culture.
A few biologically determined characteristics include genetic diseases, eye color, hair color, and skin color. Other characteristics are tied to environmental influences, such as how a person behaves, which can be influenced by parenting styles and learned experiences.
For example, one child might learn through observation and reinforcement to say please and thank you. Another child might learn to behave aggressively by observing older children engage in violent behavior on the playground.
The Debate of Nature vs. Nurture
The nature vs. nurture debate centers on the contributions of genetics and environmental factors to human development. Some philosophers, such as Plato and Descartes, suggested that certain factors are inborn or occur naturally regardless of environmental influences.
Advocates of this point of view believe that all of our characteristics and behaviors are the result of evolution. They contend that genetic traits are handed down from parents to their children and influence the individual differences that make each person unique.
Other well-known thinkers, such as John Locke, believed in what is known as tabula rasa which suggests that the mind begins as a blank slate . According to this notion, everything that we are is determined by our experiences.
Behaviorism is a good example of a theory rooted in this belief as behaviorists feel that all actions and behaviors are the results of conditioning. Theorists such as John B. Watson believed that people could be trained to do and become anything, regardless of their genetic background.
People with extreme views are called nativists and empiricists. Nativists take the position that all or most behaviors and characteristics are the result of inheritance. Empiricists take the position that all or most behaviors and characteristics result from learning.
Examples of Nature vs. Nurture
One example of when the argument of nature vs. nurture arises is when a person achieves a high level of academic success . Did they do so because they are genetically predisposed to elevated levels of intelligence, or is their success a result of an enriched environment?
The argument of nature vs. nurture can also be made when it comes to why a person behaves in a certain way. If a man abuses his wife and kids, for instance, is it because he was born with violent tendencies, or is violence something he learned by observing others in his life when growing up?
Nature vs. Nurture in Psychology
Throughout the history of psychology , the debate of nature vs. nurture has continued to stir up controversy. Eugenics, for example, was a movement heavily influenced by the nativist approach.
Psychologist Francis Galton coined the terms 'nature versus nurture' and 'eugenics' and believed that intelligence resulted from genetics. Galton also felt that intelligent individuals should be encouraged to marry and have many children, while less intelligent individuals should be discouraged from reproducing.
The value placed on nature vs. nurture can even vary between the different branches of psychology , with some branches taking a more one-sided approach. In biopsychology , for example, researchers conduct studies exploring how neurotransmitters influence behavior, emphasizing the role of nature.
In social psychology , on the other hand, researchers might conduct studies looking at how external factors such as peer pressure and social media influence behaviors, stressing the importance of nurture. Behaviorism is another branch that focuses on the impact of the environment on behavior.
Nature vs. Nurture in Child Development
Some psychological theories of child development place more emphasis on nature and others focus more on nurture. An example of a nativist theory involving child development is Chomsky's concept of a language acquisition device (LAD). According to this theory, all children are born with an instinctive mental capacity that allows them to both learn and produce language.
An example of an empiricist child development theory is Albert Bandura's social learning theory . This theory says that people learn by observing the behavior of others. In his famous Bobo doll experiment , Bandura demonstrated that children could learn aggressive behaviors simply by observing another person acting aggressively.
Nature vs. Nurture in Personality Development
There is also some argument as to whether nature or nurture plays a bigger role in the development of one's personality. The answer to this question varies depending on which personality development theory you use.
According to behavioral theories, our personality is a result of the interactions we have with our environment, while biological theories suggest that personality is largely inherited. Then there are psychodynamic theories of personality that emphasize the impact of both.
Nature vs. Nurture in Mental Illness Development
One could argue that either nature or nurture contributes to mental health development. Some causes of mental illness fall on the nature side of the debate, including changes to or imbalances with chemicals in the brain. Genetics can also contribute to mental illness development, increasing one's risk of a certain disorder or disease.
Mental disorders with some type of genetic component include autism , attention-deficit hyperactivity disorder (ADHD), bipolar disorder , major depression , and schizophrenia .
Other explanations for mental illness are environmental. This includes being exposed to environmental toxins, such as drugs or alcohol, while still in utero. Certain life experiences can also influence mental illness development, such as witnessing a traumatic event, leading to the development of post-traumatic stress disorder (PTSD).
Nature vs. Nurture in Mental Health Therapy
Different types of mental health treatment can also rely more heavily on either nature or nurture in their treatment approach. One of the goals of many types of therapy is to uncover any life experiences that may have contributed to mental illness development (nurture).
However, genetics (nature) can play a role in treatment as well. For instance, research indicates that a person's genetic makeup can impact how their body responds to antidepressants. Taking this into consideration is important for getting that person the help they need.
Interaction Between Nature and Nurture
Which is stronger: nature or nurture? Many researchers consider the interaction between heredity and environment—nature with nurture as opposed to nature versus nurture—to be the most important influencing factor of all.
For example, perfect pitch is the ability to detect the pitch of a musical tone without any reference. Researchers have found that this ability tends to run in families and might be tied to a single gene. However, they've also discovered that possessing the gene is not enough as musical training during early childhood is needed for this inherited ability to manifest itself.
Height is another example of a trait influenced by an interaction between nature and nurture. A child might inherit the genes for height. However, if they grow up in a deprived environment where proper nourishment isn't received, they might never attain the height they could have had if they'd grown up in a healthier environment.
A newer field of study that aims to learn more about the interaction between genes and environment is epigenetics . Epigenetics seeks to explain how environment can impact the way in which genes are expressed.
Some characteristics are biologically determined, such as eye color, hair color, and skin color. Other things, like life expectancy and height, have a strong biological component but are also influenced by environmental factors and lifestyle.
Contemporary Views of Nature vs. Nurture
Most experts recognize that neither nature nor nurture is stronger than the other. Instead, both factors play a critical role in who we are and who we become. Not only that but nature and nurture interact with each other in important ways all throughout our lifespan.
As a result, many in this field are interested in seeing how genes modulate environmental influences and vice versa. At the same time, this debate of nature vs. nurture still rages on in some areas, such as in the origins of homosexuality and influences on intelligence .
While a few people take the extreme nativist or radical empiricist approach, the reality is that there is not a simple way to disentangle the multitude of forces that exist in personality and human development. Instead, these influences include genetic factors, environmental factors, and how each intermingles with the other.
Schoneberger T. Three myths from the language acquisition literature . Anal Verbal Behav . 2010;26(1):107-31. doi:10.1007/bf03393086
National Institutes of Health. Common genetic factors found in 5 mental disorders .
Pain O, Hodgson K, Trubetskoy V, et al. Identifying the common genetic basis of antidepressant response . Biol Psychiatry Global Open Sci . 2022;2(2):115-126. doi:10.1016/j.bpsgos.2021.07.008
Moulton C. Perfect pitch reconsidered . Clin Med J . 2014;14(5):517-9 doi:10.7861/clinmedicine.14-5-517
Levitt M. Perceptions of nature, nurture and behaviour . Life Sci Soc Policy . 2013;9:13. doi:10.1186/2195-7819-9-13
Bandura A, Ross D, Ross, SA. Transmission of aggression through the imitation of aggressive models . J Abnorm Soc Psychol. 1961;63(3):575-582. doi:10.1037/h0045925
Chomsky N. Aspects of the Theory of Syntax .
Galton F. Inquiries into Human Faculty and Its Development .
Watson JB. Behaviorism .
By Kendra Cherry, MSEd Kendra Cherry, MS, is a psychosocial rehabilitation specialist, psychology educator, and author of the "Everything Psychology Book."
Nature vs. Nurture

The nature versus nurture debate is about the relative influence of an individual's innate attributes as opposed to the experiences from the environment one is brought up in, in determining individual differences in physical and behavioral traits. The philosophy that humans acquire all or most of their behavioral traits from "nurture" is known as tabula rasa ("blank slate").
In recent years, both types of factors have come to be recognized as playing interacting roles in development. So several modern psychologists consider the question naive and representing an outdated state of knowledge . The famous psychologist, Donald Hebb, is said to have once answered a journalist's question of "Which, nature or nurture, contributes more to personality?" by asking in response, "Which contributes more to the area of a rectangle, its length or its width?"
Comparison chart
Nature vs. nurture in the iq debate.
Evidence suggests that family environmental factors may have an effect upon childhood IQ, accounting for up to a quarter of the variance. On the other hand, by late adolescence this correlation disappears, such that adoptive siblings are no more similar in IQ than strangers. Moreover, adoption studies indicate that, by adulthood, adoptive siblings are no more similar in IQ than strangers (IQ correlation near zero), while full siblings show an IQ correlation of 0.6. Twin studies reinforce this pattern: monozygotic (identical) twins raised separately are highly similar in IQ (0.86), more so than dizygotic (fraternal) twins raised together (0.6) and much more than adoptive siblings (almost 0.0). Consequently, in the context of the "nature versus nurture" debate, the "nature" component appears to be much more important than the "nurture" component in explaining IQ variance in the general adult population of the United States .
The TEDx Talk below, featuring renowned entomologist Gene Robinson , discusses how the science of genomics strongly suggests both nature and nurture actively affect genomes, thus playing important roles in development and social behavior:
Nature vs. Nurture in Personality Traits
Personality is a frequently-cited example of a heritable trait that has been studied in twins and adoptions. Identical twins reared apart are far more similar in personality than randomly selected pairs of people. Likewise, identical twins are more similar than fraternal twins. Also, biological siblings are more similar in personality than adoptive siblings. Each observation suggests that personality is heritable to a certain extent.
However, these same study designs allow for the examination of environment as well as genes. Adoption studies also directly measure the strength of shared family effects. Adopted siblings share only family environment. Unexpectedly, some adoption studies indicate that by adulthood the personalities of adopted siblings are no more similar than random pairs of strangers. This would mean that shared family effects on personality wane off by adulthood. As is the case with personality, non-shared environmental effects are often found to out-weigh shared environmental effects. That is, environmental effects that are typically thought to be life-shaping (such as family life) may have less of an impact than non-shared effects, which are harder to identify.
Moral Considerations of the Nature vs. Nurture Debate

Some observers offer the criticism that modern science tends to give too much weight to the nature side of the argument, in part because of the potential harm that has come from rationalized racism. Historically, much of this debate has had undertones of racist and eugenicist policies — the notion of race as a scientific truth has often been assumed as a prerequisite in various incarnations of the nature versus nurture debate. In the past, heredity was often used as "scientific" justification for various forms of discrimination and oppression along racial and class lines. Works published in the United States since the 1960s that argue for the primacy of "nature" over "nurture" in determining certain characteristics, such as The Bell Curve, have been greeted with considerable controversy and scorn. A recent study conducted in 2012 has come up with the verdict that racism, after all, isn't innate.
A critique of moral arguments against the nature side of the argument could be that they cross the is-ought gap. That is, they apply values to facts. However, such appliance appears to construct reality. Belief in biologically determined stereotypes and abilities has been shown to increase the kind of behavior that is associated with such stereotypes and to impair intellectual performance through, among other things, the stereotype threat phenomenon.
The implications of this are brilliantly illustrated by the implicit association tests (IATs) out of Harvard . These, along with studies of the impact of self-identification with either positive or negative stereotypes and therefore "priming" good or bad effects, show that stereotypes, regardless of their broad statistical significance, bias the judgements and behaviours of members and non-members of the stereotyped groups.
Homosexuality
Being gay is now considered a genetic phenomenon rather than being influenced by the environment. This is based on observations such as:
- About 10% of the population is gay. This number is consistent across cultures throughout the world. If culture and society — i.e., nurture — were responsible for homosexuality, the percentage of population that is gay would vary across cultures.
- Studies of identical twins have shown that if one sibling is gay, the probability that the other sibling is also gay is greater than 50%.
More recent studies have indicated that both gender and sexuality are spectrums rather than strictly binary choices.
Epigenetics
Genetics is a complex and evolving field. A relatively newer idea in genetics is the epigenome . Changes happen to DNA molecules as other chemicals attach to genes or proteins in a cell. These changes constitute the epigenome. The epigenome regulates activity of cells by "turning genes off or on", i.e., by regulating which genes are expressed. This is why even though all cells have the same DNA (or genome), some cells grow into brain cells while others turn into liver and others into skin.
Epigenetics suggests a model for how the environment (nurture) may affect an individual by regulating the genome (nature). More information about epigenetics can be found here .
Philosophical Considerations of the Nature vs. Nurture Debate
Are the traits real.
It is sometimes a question whether the "trait" being measured is even a real thing. Much energy has been devoted to calculating the heritability of intelligence (usually the I.Q., or intelligence quotient), but there is still some disagreement as to what exactly "intelligence" is.
Determinism and Free Will
If genes do contribute substantially to the development of personal characteristics such as intelligence and personality, then many wonder if this implies that genes determine who we are. Biological determinism is the thesis that genes determine who we are. Few , if any, scientists would make such a claim; however, many are accused of doing so.
Others have pointed out that the premise of the "nature versus nurture" debate seems to negate the significance of free will. More specifically, if all our traits are determined by our genes, by our environment, by chance , or by some combination of these acting together, then there seems to be little room for free will. This line of reasoning suggests that the "nature versus nurture" debate tends to exaggerate the degree to which individual human behavior can be predicted based on knowledge of genetics and the environment. Furthermore, in this line of reasoning, it should also be pointed out that biology may determine our abilities, but free will still determines what we do with our abilities.
- Wikipedia: Nature versus nurture
- Nature vs Nurture: Racism isn't Innate - National Journal
- Nature vs. Nurture: The Debate on Psychological Development - YouTube
- Epigenetics - PBS
Related Comparisons

Share this comparison via:
If you read this far, you should follow us:
"Nature vs Nurture." Diffen.com. Diffen LLC, n.d. Web. 24 Mar 2024. < >
Comments: Nature vs Nurture
Anonymous comments (5).
October 10, 2012, 8:50am Somewhere, someone has to be scratching their head and saying...what about free will? What about man's ability to reason? Nature and nurture do not complete the picture. They are influences, but we should not reduce the human mind and spirit to such base concepts. — 69.✗.✗.87
September 13, 2012, 1:25pm we were assigned to be on the "nature" side, to defend it. and the information I got from here made me "encouraged" to win on our debate, and has provided me a chance of having a high grade tomorrow. thanks.. — 109.✗.✗.162
February 28, 2013, 7:28pm nature all the way — 170.✗.✗.19
June 18, 2009, 1:54pm we were assigned to be on the "nature" side, to defend it. and the information I got from here made me "encouraged" to win on our debate, and has provided me a chance of having a high grade tomorrow. thanks.. — 124.✗.✗.255
May 9, 2014, 2:03pm Nurture an nature can change becose it is unchangeble to the personality. — 141.✗.✗.231
- Fraternal Twins vs Identical Twins
- Psychiatry vs Psychology
- Genotype vs Phenotype
- Left Brain vs Right Brain
- Behaviourism vs Constructivism
- Anthropology vs Sociology
- Ethnicity vs Race
- Allele vs Gene
Edit or create new comparisons in your area of expertise.
Stay connected
© All rights reserved.

Encyclopedia of Personality and Individual Differences pp 1–5 Cite as
Nature-Nurture Debate
- Christian Montag 3 , 4 &
- Elisabeth Hahn 5
- Living reference work entry
- First Online: 02 February 2018
574 Accesses
3 Citations
Epigenome , Gene by environment , Intelligence , Molecular genetics , Nature , Nurture , Personality
Introduction
Among the earliest testimonials of human civilization is a deep intuition that some aspects of human behavior originate in our genetic makeup, while others feel like the result of upbringing or exercise. A central question posed by both ancient philosophers such as Aristotle and modern researchers in the twenty-first century deals with the impact of nature and nurture on human characteristics such as personality or intelligence. While Aristotle questioned how resemblances between parents and their offspring can be explained (Henry 2006 ), Sir Francis Galton ( 1869 ) as one of the first scientists already dealt in his famous work Hereditary Genius with the genetics of intelligence.
The nature versus nurture debate represents one of the oldest issues in the research of human behavior dealing with the question whether inherited traits or life experiences (e.g., upbringing)...
This is a preview of subscription content, log in via an institution .
Arslan, R. C., & Penke, L. (2015). Zeroing in on the genetics of intelligence. Journal of Intelligence, 3 (2), 41–45.
Article Google Scholar
Bakermans-Kranenburg, M. J., Van IJzendoorn, M. H., Pijlman, F. T., Mesman, J., & Juffer, F. (2008). Experimental evidence for differential susceptibility: Dopamine D4 receptor polymorphism (DRD4 VNTR) moderates intervention effects on toddlers’ externalizing behavior in a randomized controlled trial. Developmental Psychology, 44 (1), 293–300.
Article PubMed Google Scholar
Caspi, A., Sugden, K., Moffitt, T. E., Taylor, A., Craig, I. W., Harrington, H., et al. (2003). Influence of life stress on depression: Moderation by a polymorphism in the 5-HTT gene. Science, 301 (5631), 386–389.
Galton, F. (1876). The history of twins, as a criterion of the relative powers of nature and nurture. The Journal of the Anthropological Institute of Great Britain and Ireland, 5 , 391–406.
Galton, F. (1869). Hereditary genius: An inquiry into its laws and consequences . New York: Macmillan.
Book Google Scholar
Gillham, N. W. (2001). Sir Francis Galton and the birth of eugenics. Annual review of genetics, 35 (1), 83–101.
Haas, B. W., Filkowski, M. M., Cochran, R. N., Denison, L., Ishak, A., Nishitani, S., & Smith, A. K. (2016). Epigenetic modification of OXT and human sociability. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences, 113 (27), E3816–E3823.
Hahn, E., & Spinath, F. M. (2017). Quantitative behavior genetics of internet addiction. In Internet addiction (pp. 125–140). Cham: Springer International Publishing.
Chapter Google Scholar
Henry, D. (2006). Aristotle on the mechanism of inheritance. Journal of the History of Biology, 39 (3), 425–455.
Jang, K. L., Livesley, W. J., & Vemon, P. A. (1996). Heritability of the big five personality dimensions and their facets: A twin study. Journal of Personality, 64 (3), 577–592.
Karg, K., Burmeister, M., Shedden, K., & Sen, S. (2011). The serotonin transporter promoter variant (5-HTTLPR), stress, and depression meta-analysis revisited: Evidence of genetic moderation. Archives of General Psychiatry, 68 (5), 444–454.
Article PubMed PubMed Central Google Scholar
Knopik, V. S., Neiderhiser, J. M., DeFries, J. C., & Plomin, R. (2016). Behavioral genetics . New York: Worth.
Google Scholar
Langbehn, D. R., Brinkman, R. R., Falush, D., Paulsen, J. S., & Hayden, M. R. (2004). A new model for prediction of the age of onset and penetrance for Huntington’s disease based on CAG length. Clinical Genetics, 65 (4), 267–277.
Meaney, M. J. (2001). Nature, nurture, and the disunity of knowledge. Annals of the New York Academy of Sciences, 935 (1), 50–61.
Meaney, M. J. (2010). Epigenetics and the biological definition of gene × environment interactions. Child Development, 81 (1), 41–79.
Mitchell, C., Notterman, D., Brooks-Gunn, J., Hobcraft, J., Garfinkel, I., Jaeger, K., et al. (2011). Role of mother’s genes and environment in postpartum depression. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences, 108 (20), 8189–8193.
Montag, C., & Reuter, M. (2014). Disentangling the molecular genetic basis of personality: From monoamines to neuropeptides. Neuroscience & Biobehavioral Reviews, 43 , 228–239.
Montag, C., Jurkiewicz, M., & Reuter, M. (2012). The role of the catechol-O-methyltransferase (COMT) gene in personality and related psychopathological disorders. CNS & Neurological Disorders-Drug Targets (Formerly Current Drug Targets-CNS & Neurological Disorders), 11 (3), 236–250.
Montag, C., Hall, J., Plieger, T., Felten, A., Markett, S., Melchers, M., & Reuter, M. (2015). The DRD3 Ser9Gly polymorphism, Machiavellianism, and its link to schizotypal personality. Journal of Neuroscience, Psychology, & Economics, 8 (1), 48–57.
Montag, C., Hahn, E., Reuter, M., Spinath, F. M., Davis, K., & Panksepp, J. (2016). The role of nature and nurture for individual differences in primary emotional systems: Evidence from a twin study. PloS One, 11 (3), e0151405.
Plieger, T., Felten, A., Melchers, M., Markett, S., Montag, C., & Reuter, M. (2018). Association between a functional polymorphism on the dopamine-β-hydroxylase gene and reward dependence in two independent samples. Personality and Individual Differences,121 , 218–222.
Polderman, T. J., Benyamin, B., De Leeuw, C. A., Sullivan, P. F., Van Bochoven, A., Visscher, P. M., & Posthuma, D. (2015). Meta-analysis of the heritability of human traits based on fifty years of twin studies. Nature Genetics, 47 (7), 702–709.
Purcell, S. (2002). Variance components models for gene–environment interaction in twin analysis. Twin Research and Human Genetics, 5 (6), 554–571.
Reiss, D., Leve, L. D., & Neiderhiser, J. M. (2013). How genes and the social environment moderate each other. American Journal of Public Health, 103 (S1), S111–S121.
Riemann, R., Angleitner, A., & Strelau, J. (1997). Genetic and environmental influences on personality: A study of twins reared together using the self-and peer report NEO-FFI scales. Journal of Personality, 65 (3), 449–475.
Risch, N., Herrell, R., Lehner, T., Liang, K. Y., Eaves, L., Hoh, J., et al. (2009). Interaction between the serotonin transporter gene (5-HTTLPR), stressful life events, and risk of depression: A meta-analysis. Jama, 301 (23), 2462–2471.
Toyokawa, S., Uddin, M., Koenen, K. C., & Galea, S. (2012). How does the social environment ‘get into the mind’? Epigenetics at the intersection of social and psychiatric epidemiology. Social Science & Medicine, 74 (1), 67–74.
VanTassel-Baska, J. (2005). Gifted programs and services: What are the nonnegotiables? Theory Into Practice, 44 (2), 90–97.
Youngson, N. A., & Whitelaw, E. (2008). Transgenerational epigenetic effects. Annual Review of Genomics and Human Genetics, 9 , 233–257.
Zhang, T. Y., & Meaney, M. J. (2010). Epigenetics and the environmental regulation of the genome and its function. Annual Review of Psychology, 61 , 439–466.
Download references
Acknowledgment
The position of Christian Montag is funded by a Heisenberg grant awarded to him by the German Research Foundation (DFG, MO2363/3-2).
Author information
Authors and affiliations.
Institute of Psychology and Education, Ulm University, Ulm, Germany
Christian Montag
Key Laboratory for NeuroInformation/Center for Information in Medicine, School of Life Science and Technology, University of Electronic Science and Technology of China, Chengdu, China
Department of Psychology, Saarland University, Saarbrücken, Germany
Elisabeth Hahn
You can also search for this author in PubMed Google Scholar
Corresponding author
Correspondence to Christian Montag .
Editor information
Editors and affiliations.
Oakland University, Rochester, USA
Virgil Zeigler-Hill
Todd K. Shackelford
Section Editor information
Department of Educational Sciences, University of Genoa, Genoa, Italy
Patrizia Velotti
Sapienza University of Rome, Rome, Italy
Rights and permissions
Reprints and permissions
Copyright information
© 2018 Springer International Publishing AG
About this entry
Cite this entry.
Montag, C., Hahn, E. (2018). Nature-Nurture Debate. In: Zeigler-Hill, V., Shackelford, T. (eds) Encyclopedia of Personality and Individual Differences. Springer, Cham. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-319-28099-8_822-1
Download citation
DOI : https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-319-28099-8_822-1
Received : 09 August 2017
Accepted : 18 December 2017
Published : 02 February 2018
Publisher Name : Springer, Cham
Print ISBN : 978-3-319-28099-8
Online ISBN : 978-3-319-28099-8
eBook Packages : Springer Reference Behavioral Science and Psychology Reference Module Humanities and Social Sciences Reference Module Business, Economics and Social Sciences
- Publish with us
Policies and ethics
- Find a journal
- Track your research
- Subject List
- Take a Tour
- For Authors
- Subscriber Services
- Publications
- African American Studies
- African Studies
- American Literature
- Anthropology
- Architecture Planning and Preservation
- Art History
- Atlantic History
- Biblical Studies
- British and Irish Literature
- Childhood Studies
- Chinese Studies
- Cinema and Media Studies
- Communication
- Criminology
- Environmental Science
- Evolutionary Biology
- International Law
- International Relations
- Islamic Studies
- Jewish Studies
- Latin American Studies
- Latino Studies
- Linguistics
- Literary and Critical Theory
- Medieval Studies
- Military History
- Political Science
- Public Health
- Renaissance and Reformation
- Social Work
- Urban Studies
- Victorian Literature
- Browse All Subjects
How to Subscribe
- Free Trials
In This Article Expand or collapse the "in this article" section Nature versus Nurture Debate in Psychology
Introduction, general overviews.
- Conceptual Problems
- Biological Constraints, Predispositions, and Preparedness in Learning
- Critical Periods
- Innate Knowledge
- Heritability
- Behavioral Epigenetics
Related Articles Expand or collapse the "related articles" section about
About related articles close popup.
Lorem Ipsum Sit Dolor Amet
Vestibulum ante ipsum primis in faucibus orci luctus et ultrices posuere cubilia Curae; Aliquam ligula odio, euismod ut aliquam et, vestibulum nec risus. Nulla viverra, arcu et iaculis consequat, justo diam ornare tellus, semper ultrices tellus nunc eu tellus.
- Developmental Psychology (Cognitive)
- Developmental Psychology (Social)
- Evolutionary Psychology
- Life-Span Development
Other Subject Areas
Forthcoming articles expand or collapse the "forthcoming articles" section.
- Data Visualization
- Remote Work
- Workforce Training Evaluation
- Find more forthcoming articles...
- Export Citations
- Share This Facebook LinkedIn Twitter
Nature versus Nurture Debate in Psychology by Hunter Honeycutt LAST MODIFIED: 12 January 2023 DOI: 10.1093/obo/9780199828340-0305
The nature-nurture dichotomy is a long-standing and pervasive framework for thinking about the causal influences believed to be operating during individual development. In this dichotomy, nature refers to factors (e.g., genes, genetic programs, and/or biological blueprints) or forces (e.g., heredity and/or maturation) inherent to the individual that predetermine the development of form and function. Nurture generally refers to all the remaining, typically “external,” causal factors (e.g., physical and social conditions) and processes (e.g., learning and experience) that influence development. The nature versus nurture debate in psychology deals with disagreements about the extent to which the development of traits in humans and animals reflects the relative influence of nature and nurture. It is commonly stated that psychologists have moved on from asking whether traits (or variation in traits) develop from nature or nurture, to recognize instead that both nature and nurture work together or “interact” to produce outcomes, although exactly how to view the interaction is a matter of much debate. While acknowledging the interaction of nature and nurture, one’s theoretical models and research focus might emphasize the prominence of one over the other. Thus, nativists focus more on the importance of innate factors or forces operating on development, whereas empiricists focus more on experiential or environmental factors. However, not everyone finds value in thinking about development in terms of nature and nurture. By the middle of the twentieth century, some psychologists, biologists, and philosophers began to view nature-nurture as a conceptually deficient and biologically implausible dichotomy that oversimplifies the dynamics of behavior and development. Such people espouse some variant of “developmental systems theory” and seek to eliminate or otherwise fuse the nature-nurture division.
The works in this section are mostly trade books that provide general introductions to the nature-nurture debate across a variety of topical areas in psychology, all of which would be suitable for use in classes with undergraduate students at all levels. Goldhaber 2012 contrasts four popular perspectives on the nature-nurture issue and would be a good place to start for anyone unfamiliar with the nature-nurture debate in psychology. Nativist perspectives are represented by Pinker 2002 , Plomin 2018 , and Vallortigara 2021 . An empiricist-leaning position on behavior development is put forth in Schneider 2012 . Developmental systems theory is promoted in Blumberg 2005 and Moore 2002 . Two edited books are included and both are better suited for advanced undergraduate- or graduate-level students. The first edited book, Coll, et al. 2013 , focuses on the nature-nurture issue across a range of topics and perspectives in psychology. The other, Mayes and Lewis 2012 , presents empiricist (or environmentalist) perspectives on child development.
Bateson, P. 2017. Behaviour, development and evolution . Cambridge, UK: OpenBook Publishers.
DOI: 10.11647/OBP.0097
Written by a distinguished ethologist who draws extensively from his work on animal behavior, this book argues that the nature-nurture division is neither valid nor helpful in capturing the complex system of factors that influence behavioral development. Topics include imprinting and attachment, parent-offspring relations, the influence of early-life experiences on later-life outcomes, problems with genetic determinism, and the role of behavior in evolutionary change.
Blumberg, M. S. 2005. Basic instinct: The genesis of novel behavior . New York: Thunder’s Mouth Press.
Consistent with developmental systems theory, Blumberg presents an overview of the conceptual and empirical limitations of nativism in explanations of behavioral and neural development in animals and cognitive development in humans.
Coll, C. G., E. L. Bearer, and R. M. Lerner, eds. 2013. Nature-nurture: The complex interplay of genetic and environmental influences on human behavior and development . New York: Psychology Press.
The contents of this edited volume are almost entirely original works with commentary that span multiple disciplines (psychology, biology, economics, philosophy) and multiple perspectives (behavioral genetics and developmental systems theory) on the nature-nurture issue.
Goldhaber, D. 2012. The nature-nurture debates: Bridging the gap . Cambridge, UK: Cambridge Univ. Press.
DOI: 10.1017/CBO9781139022583
Goldhaber reviews four major perspectives (behavior genetics, environmentalism, evolutionary psychology, and developmental systems theory) on the nature-nurture issue. He argues we should reject reductionist views based on either genetic determinism or environmental determinism in favor of more holistic, interactionist approaches.
Mayes, L. C., and M. Lewis, eds. 2012. The Cambridge handbook of environment in human development . Cambridge, UK: Cambridge Univ. Press.
This handbook explores a wide variety of ways in which the environment influences child development. Chapters cover conceptual frameworks and methodological issues in thinking about and studying environmental influences as well reviewing ways in which environmental contexts and systems influence specific aspects of child development.
Moore, D. S. 2002. The dependent gene: The fallacy of nature vs. nurture . New York: Henry Holt.
This book provides an introduction to the developmental systems theory take on the nature-nurture issue particularly as it relates to genetic determinism, heritability and heredity.
Pinker, S. 2002. The blank slate: The modern denial of human nature . New York: Viking.
In this best-selling book, Pinker draws on evidence from behavioral genetics, evolutionary psychology, and cognitive psychology to argue for a nativist position concerning human nature.
Plomin, R. 2018. Blueprint: How DNA makes us who we are . Cambridge, MA: MIT Press.
Plomin reviews traditional and more modern evidence from behavioral genetics to argue that genes are the primary factor in bringing about psychological differences between people. Moreover, he argues that many “environmental” factors operating on development are themselves strongly influenced by genetic differences.
Schneider, S. M. 2012. The science of consequences: How they affect genes, change the brain, and impact our world . Amherst, NY: Prometheus Books.
Schneider presents a view grounded in behavior analysis to argue for the critical role that the consequences of genetic activity, neural activity, and behavioral activity play in individual development. While emphasizing environmental (or experiential) factors influencing development, this book also highlights the systemic and interactive nature of developmental systems across multiple levels of analysis.
Vallortigara, G. 2021. Born knowing: Imprinting and the origins of knowledge . Cambridge, MA: MIT Press.
DOI: 10.7551/mitpress/14091.001.0001
Drawing upon research in comparative cognition and comparative neuroscience, much of it his own, Vallortigara argues that animals, including humans, enter the world with a set of unlearned, innate or instinctive behaviors and neural circuits that bias or predispose subsequent learning and development.
back to top
Users without a subscription are not able to see the full content on this page. Please subscribe or login .
Oxford Bibliographies Online is available by subscription and perpetual access to institutions. For more information or to contact an Oxford Sales Representative click here .
- About Psychology »
- Meet the Editorial Board »
- Abnormal Psychology
- Academic Assessment
- Acculturation and Health
- Action Regulation Theory
- Action Research
- Addictive Behavior
- Adolescence
- Adoption, Social, Psychological, and Evolutionary Perspect...
- Advanced Theory of Mind
- Affective Forecasting
- Affirmative Action
- Ageism at Work
- Allport, Gordon
- Alzheimer’s Disease
- Ambulatory Assessment in Behavioral Science
- Analysis of Covariance (ANCOVA)
- Animal Behavior
- Animal Learning
- Anxiety Disorders
- Art and Aesthetics, Psychology of
- Artificial Intelligence, Machine Learning, and Psychology
- Assessment and Clinical Applications of Individual Differe...
- Attachment in Social and Emotional Development across the ...
- Attention-Deficit/Hyperactivity Disorder (ADHD) in Adults
- Attention-Deficit/Hyperactivity Disorder (ADHD) in Childre...
- Attitudinal Ambivalence
- Attraction in Close Relationships
- Attribution Theory
- Authoritarian Personality
- Bayesian Statistical Methods in Psychology
- Behavior Therapy, Rational Emotive
- Behavioral Economics
- Behavioral Genetics
- Belief Perseverance
- Bereavement and Grief
- Biological Psychology
- Birth Order
- Body Image in Men and Women
- Bystander Effect
- Categorical Data Analysis in Psychology
- Childhood and Adolescence, Peer Victimization and Bullying...
- Clark, Mamie Phipps
- Clinical Neuropsychology
- Clinical Psychology
- Cognitive Consistency Theories
- Cognitive Dissonance Theory
- Cognitive Neuroscience
- Communication, Nonverbal Cues and
- Comparative Psychology
- Competence to Stand Trial: Restoration Services
- Competency to Stand Trial
- Computational Psychology
- Conflict Management in the Workplace
- Conformity, Compliance, and Obedience
- Consciousness
- Coping Processes
- Correspondence Analysis in Psychology
- Counseling Psychology
- Creativity at Work
- Critical Thinking
- Cross-Cultural Psychology
- Cultural Psychology
- Daily Life, Research Methods for Studying
- Data Science Methods for Psychology
- Data Sharing in Psychology
- Death and Dying
- Deceiving and Detecting Deceit
- Defensive Processes
- Depressive Disorders
- Development, Prenatal
- Diagnostic and Statistical Manual of Mental Disorders (DSM...
- Discrimination
- Dissociative Disorders
- Drugs and Behavior
- Eating Disorders
- Ecological Psychology
- Educational Settings, Assessment of Thinking in
- Effect Size
- Embodiment and Embodied Cognition
- Emerging Adulthood
- Emotional Intelligence
- Empathy and Altruism
- Employee Stress and Well-Being
- Environmental Neuroscience and Environmental Psychology
- Ethics in Psychological Practice
- Event Perception
- Expansive Posture
- Experimental Existential Psychology
- Exploratory Data Analysis
- Eyewitness Testimony
- Eysenck, Hans
- Factor Analysis
- Festinger, Leon
- Five-Factor Model of Personality
- Flynn Effect, The
- Forensic Psychology
- Forgiveness
- Friendships, Children's
- Fundamental Attribution Error/Correspondence Bias
- Gambler's Fallacy
- Game Theory and Psychology
- Geropsychology, Clinical
- Global Mental Health
- Habit Formation and Behavior Change
- Health Psychology
- Health Psychology Research and Practice, Measurement in
- Heider, Fritz
- Heuristics and Biases
- History of Psychology
- Human Factors
- Humanistic Psychology
- Implicit Association Test (IAT)
- Industrial and Organizational Psychology
- Inferential Statistics in Psychology
- Insanity Defense, The
- Intelligence
- Intelligence, Crystallized and Fluid
- Intercultural Psychology
- Intergroup Conflict
- International Classification of Diseases and Related Healt...
- International Psychology
- Interviewing in Forensic Settings
- Intimate Partner Violence, Psychological Perspectives on
- Introversion–Extraversion
- Item Response Theory
- Law, Psychology and
- Lazarus, Richard
- Learned Helplessness
- Learning Theory
- Learning versus Performance
- LGBTQ+ Romantic Relationships
- Lie Detection in a Forensic Context
- Locus of Control
- Loneliness and Health
- Mathematical Psychology
- Meaning in Life
- Mechanisms and Processes of Peer Contagion
- Media Violence, Psychological Perspectives on
- Mediation Analysis
- Memories, Autobiographical
- Memories, Flashbulb
- Memories, Repressed and Recovered
- Memory, False
- Memory, Human
- Memory, Implicit versus Explicit
- Memory in Educational Settings
- Memory, Semantic
- Meta-Analysis
- Metacognition
- Metaphor, Psychological Perspectives on
- Microaggressions
- Military Psychology
- Mindfulness
- Mindfulness and Education
- Minnesota Multiphasic Personality Inventory (MMPI)
- Money, Psychology of
- Moral Conviction
- Moral Development
- Moral Psychology
- Moral Reasoning
- Nature versus Nurture Debate in Psychology
- Neuroscience of Associative Learning
- Nonergodicity in Psychology and Neuroscience
- Nonparametric Statistical Analysis in Psychology
- Observational (Non-Randomized) Studies
- Obsessive-Complusive Disorder (OCD)
- Occupational Health Psychology
- Olfaction, Human
- Operant Conditioning
- Optimism and Pessimism
- Organizational Justice
- Parenting Stress
- Parenting Styles
- Parents' Beliefs about Children
- Path Models
- Peace Psychology
- Perception, Person
- Performance Appraisal
- Personality and Health
- Personality Disorders
- Personality Psychology
- Phenomenological Psychology
- Placebo Effects in Psychology
- Play Behavior
- Positive Psychological Capital (PsyCap)
- Positive Psychology
- Posttraumatic Stress Disorder (PTSD)
- Prejudice and Stereotyping
- Pretrial Publicity
- Prisoner's Dilemma
- Problem Solving and Decision Making
- Procrastination
- Prosocial Behavior
- Prosocial Spending and Well-Being
- Protocol Analysis
- Psycholinguistics
- Psychological Literacy
- Psychological Perspectives on Food and Eating
- Psychology, Political
- Psychoneuroimmunology
- Psychophysics, Visual
- Psychotherapy
- Psychotic Disorders
- Publication Bias in Psychology
- Reasoning, Counterfactual
- Rehabilitation Psychology
- Relationships
- Reliability–Contemporary Psychometric Conceptions
- Religion, Psychology and
- Replication Initiatives in Psychology
- Research Methods
- Risk Taking
- Role of the Expert Witness in Forensic Psychology, The
- Sample Size Planning for Statistical Power and Accurate Es...
- Schizophrenic Disorders
- School Psychology
- School Psychology, Counseling Services in
- Self, Gender and
- Self, Psychology of the
- Self-Construal
- Self-Control
- Self-Deception
- Self-Determination Theory
- Self-Efficacy
- Self-Esteem
- Self-Monitoring
- Self-Regulation in Educational Settings
- Self-Report Tests, Measures, and Inventories in Clinical P...
- Sensation Seeking
- Sex and Gender
- Sexual Minority Parenting
- Sexual Orientation
- Signal Detection Theory and its Applications
- Simpson's Paradox in Psychology
- Single People
- Single-Case Experimental Designs
- Skinner, B.F.
- Sleep and Dreaming
- Small Groups
- Social Class and Social Status
- Social Cognition
- Social Neuroscience
- Social Support
- Social Touch and Massage Therapy Research
- Somatoform Disorders
- Spatial Attention
- Sports Psychology
- Stanford Prison Experiment (SPE): Icon and Controversy
- Stereotype Threat
- Stereotypes
- Stress and Coping, Psychology of
- Student Success in College
- Subjective Wellbeing Homeostasis
- Taste, Psychological Perspectives on
- Teaching of Psychology
- Terror Management Theory
- Testing and Assessment
- The Concept of Validity in Psychological Assessment
- The Neuroscience of Emotion Regulation
- The Reasoned Action Approach and the Theories of Reasoned ...
- The Weapon Focus Effect in Eyewitness Memory
- Theory of Mind
- Therapies, Person-Centered
- Therapy, Cognitive-Behavioral
- Thinking Skills in Educational Settings
- Time Perception
- Trait Perspective
- Trauma Psychology
- Twin Studies
- Type A Behavior Pattern (Coronary Prone Personality)
- Unconscious Processes
- Video Games and Violent Content
- Virtues and Character Strengths
- Women and Science, Technology, Engineering, and Math (STEM...
- Women, Psychology of
- Work Well-Being
- Wundt, Wilhelm
- Privacy Policy
- Cookie Policy
- Legal Notice
- Accessibility
Powered by:
- [66.249.64.20|195.158.225.244]
- 195.158.225.244
Nature Vs. Nurture: What Matters Most?
Have you ever questioned how much of your personality or difficulties you’ve faced may be due to your biology, and how much may be due to the environment you’ve lived in and learned from? If so, you aren’t alone. This is one of the fundamental bases of nature vs nurture psychology, which has been studied by experts for decades. It’s even been featured in countless articles from publishers as prominent as the New York Times for decades.
The debate over what drives human culture, personality, and behavior is actually believed by many to go back thousands of years to Ancient Greece. It can involve cultural, philosophical, and scientific elements to identify a variant or a hypothesis of the primary force behind human nature. Understanding this element of scope and pursuing ongoing education in this area can help you to determine how either element affects your present-day experience and how you can live well in your current situation.
Read on to learn more about the nature vs nurture debate in psychology and how both can affect your daily experiences.
Nature vs. nurture psychology
Nature refers to inherent characteristics while nurture refers to outside factors. The topic has been debated for millennia, and many have found that science has yet to arrive at a definitive answer—possibly suggesting that human nature is complex and not easy to define with labels.
The history of the nature vs. nurture debate
Galen, a philosopher in Ancient Greece, is thought by many to have first proposed that a person’s personality can arise from the levels of four types of bodily fluids (or “humors”), also known by many as the humorism or humoralism theory.
Later on, in the 1870s, Sir Francis Galton is quoted in historical texts using the terms “nature” and “nurture” when explaining his theory that traits, like intelligence and personality, could be developed by genetics and inherited at birth. During the same period, philosopher John Locke proposed that children were born as blank slates, and their characters developed from what they learned.
According to medical history, many behavioral and psychoanalytic theories in the early 1900s relied on the assumption that learning, environment and experience might be the most critical elements that can contribute to a person’s mental health. However, as time progressed to the later years of the 20th century, genetics and neuroscience gained popularity—and many medical professionals may have shifted back toward the nature “side” of the argument.
Current research generally indicates that individual differences in personality, behavior patterns, and mental health can all have intricate ties to genetic and environmental factors.
The interactionist position in the nature–nurture debate
Many field experts appear to support the interactionist position in the nature vs nurture debate—which is thought to state that genetics and environmental factors work within a fully interactive system that can determine a person’s personality and overall mental well-being.
As parents can provide someone with both genetic makeup and early environment and childhood lessons, in most cases, it can be argued that one of the most influential factors in human and child development—childhood caregivers—is, by definition, driven by both nature and nurture.
“Nature vs nurture is one of the oldest questions in science. The answer is not an either/or, but rather it is both nature and nurture, acting in various degrees”. — Grand Challenge: Nature Versus Nurture
Why does the nature vs nurture debate matter?
Your opinion on what matters most may affect how you approach your mental health. For example: If you stand firmly on the nature side, you may feel powerless to change something you believe was determined before birth. If nurture is the basis of your philosophy, however, you may feel powerless in pursuit or ownership of your unique fusion of personality traits.
Understanding both sides of the debate can give you an open mind regarding mental health treatment options, as you can change your experience in a range of ways. Those who favor the interactionist position may work with all the factors that could influence them—possibly empowering them to make an informed decision about improving their well-being with varied methods.
To help you to determine your own set of personal beliefs, we’ve listed a summary of both nature- and nurture-related elements below.
Nature: Biological factors
Nature can refer to your genetics and other biological factors that can influence your mental health and personality development.
Elements included on the nature side of the debate
While there can be a range of elements included in this area of the nature vs nurture argument, some of the most includes:
- Genetic diseases and disorders
- Appearance-related elements, such as eye, hair or skin color

How does nature affect you?
In a 2021 study , researchers sought to determine genetic influence on one’s experience and understanding of self with the removal of the environmental factors provided by parents to avoid errors related to causation. As a result, they suggested using the Familial Control Method as a workaround when genetically sensitive information isn’t available.
This could be a plausible measure to determine how nature truly can affect you. Per current psychological understanding, your genetic code is thought to be the source of your nature—while your genes might determine your brain structure, and your individual neurochemistry may shape your thought patterns, emotions and behaviors.
Nurture: Environmental factors
Nurture generally refers to the environmental factors, such as relationships, experiences and culture, which can impact who you are and how your mental health develops.
Elements included on the nurture side of the debate
Many people might have common nurture-related experiences, such as:
- Parenting and attachment style variations during childhood
- Learned experiences (facilitated by school or extracurricular activities)
- Social relationships
- Culture-related achievements (variable)
How does nurture affect you?
As you might imagine, your experiences and everything you’ve been through can impact your life and experiences. For example: Your experiences as an infant and throughout childhood substantially influence who you become, from your attachment style affecting how you form and maintain relationships to traumatic experiences changing how you react to certain situations.
Can nurture be changed?
Psychotherapy is generally defined as a proven method to help change one’s behavior and thought patterns. It can be regarded as an effective treatment for various mental health conditions.
Many may have nearly limitless ways to alter your environment—and psychotherapy can help you rebuild your cognitive pathways , according to data presented in a 2017 study. This published work alone shows the potential of change that nurture can hold, encouraging those who may wish to change facets of their personality or thought processes over time.
What are examples of nature vs. nurture in psychology?
You can see practical examples of nature vs nurture in everyday life, specifically in the area of behavioral psychology. Many believe that rather than showing definitive evidence for one side or the other, the evidence can show how integral and widespread the connection between nature and nurture truly is.
Nature vs nurture: Abusive behaviors
If a person exhibits abusive behavior, is it because they learned it by observing violence during their formative years, or is it due to being born with violent tendencies? This can be a common topic that’s brought up in the nature vs nurture debate.
If you or a loved one is experiencing abuse, contact the Domestic Violence Hotline at 1-800-799-SAFE (7233). Support is available 24/7.
If you are experiencing trauma, support is available. Please see our Get Help Now page for more resources.
Nature vs nurture: Intelligence
Does a person who demonstrates a high level of intelligence owe that to their genetic makeup or years of studying? How do we account for people who are born geniuses?
Looking to improve your mental health? Speak with a licensed therapist
Nature vs nurture: personality.
Twins can offer a unique view into how genetics and environment can shape your personality, mental health and emotional stability. For example, why would identical twins develop separate personalities and interests when they have the exact same genetics? Or how could children adopted into a home develop personality characteristics like their non-biological siblings?
Nature vs nurture: Mental health conditions
Some mental health conditions, like schizophrenia, might have a significant genetic component, while others can be directly caused by experiences—such as post-traumatic stress disorder. There are several brain issues, like Huntington’s disease, known to be passed on through genetics as well. What role would nature vs nurture have in these instances? How would one account for that?
Nature vs. nurture debate status
According to a 2018 study the medical community suggests that there’s not a single answer to the nature vs. nurture debate . The solution for many may be to allow both nature and nurture to interact throughout your life, shaping you into the person you are and influencing your mental health and stability in many complex ways.
How can online therapy help you establish mental stability
Mental health conditions can often leave you feeling overwhelmed. This level of overwhelm can make it difficult for you to leave the home, especially to confront your nervousness head on through in-person therapeutic intervention. Working with a licensed therapist online through virtual therapy platforms like BetterHelp can empower you to work on your mental health from the convenience and comfort of your own home—possibly offering a sense of safety when speaking about vulnerable topics.
Is online therapy effective?
Studies published by the American Psychological Association (APA) suggest that online therapy can be a viable, affordable option for many mental health conditions. It can also effectively boost the overall mental well-being of people who are not currently diagnosed with a mental condition. The APA has been quoted stating that virtual options for therapy can make treatment available in areas that did not previously have in-person option, possibly maximizing the amount of benefit that a larger pool of people can gain.
Why is Nature Vs Nurture important to psychology?
The nature versus nurture debate is the extent to which aspects of our behavior are the product of either inherited (i.e., nature) or learned (i.e., nurture) influences. Nature is what we think of as what we are pre-destined to become and is influenced by genetic inheritance (i.e., hair color). On the other hand, nurture is the influence of external factors after conception (i.e., personality characteristics).
Breaking down nature versus nurture within the psychological science disciplines involves a discussion around the two extreme schools of thought – Nativism and Empiricism. The first is nativism. Eye color, hair texture, skin pigmentation and predisposition to genetic diseases are all a function of the genes we inherit. These facts have led nativists to speculate whether psychological characteristics such as behavioral tendencies, personality attributes, and mental abilities are also genetically influenced. The basic assumption amongst nativists is that the characteristics of the human species is entirely a product of evolution and individual differences can be explained by each person’s unique genetic code.
Empiricism is the opposite of nativism in that it takes the extreme nurture position. Their basic assumption is that at birth, the human mind is a blank slate, or a tabula rasa, and that it is gradually filled as a result of experience. Psychological characteristics and behavioral differences that emerge from birth through childhood are the results of learning and being part of an environment.
Researchers in the field of behavioral genetics study how genes affect behavior and therefore relate variation in behavior between people. Behavioral genetics allows psychology to quantify just how much nature and nurture impact specific psychological traits. Adoption also acts a natural experiment that allows researchers to determine whether certain traits are more or less a product of either nature or nurture or a combination of the two. Studies have consistently shown that adopted children show greater physical resemblance to their biological parents , rather than their adoptive parents.
Another way researchers have studied nature versus nurture is through twin studies. Like adoption studies, twin studies support that psychological traits are extremely inheritable, about 50% on average. In a Twins in Early Development Study , there was found to be correlations between twins on a range of behavioral traits such as personality (empathy and hyperactivity) and the reach of phonetics.
Nature versus nurture is just one way that developmental psychology tries to explain and understand the differences in human behavior and how genetic and environmental factors contribute to those differences.
Is Developmental Psychology a nature or nurture?
Developmental psychology is the scientific study of changes that occur in human beings over the course of their lives and examines change and development across a broad range of topics, such as motor skills, cognitive development, problem-solving skills, personality and emotional development, among others.
When explaining development, considering both nature and nurture is important. Developmental psychology seeks to answer two big questions around nature versus nurture. The first is how much weight does each contribute? And the second is how do nature and nurture interact? Developmental psychology considers both nature and nurture when it comes to explaining human development since they are both seen as playing a crucial role in determining the development of personality and other behaviors.
Was Freud nature or nurture?
Sigmund Freud stated that events in our childhood have a great influence on our adult lives, shaping our personality characteristics. Freud was of the belief that parenting is of primary importance to a child’s development. These aspects of the theory led Freud to believe early childhood was crucial to the development of personality as an adult. In fact, he focused primarily on the first five years of life as being critical to healthy outcomes.
While Freud was primarily interested in how nurture influences a person’s behavior, Freud’s theory of aggression is steeped in nature. Freud believed that aggression was an innate drive propelled by thoughts and feelings of the subconscious mind. Unlike his belief that personality traits are influenced by a person’s environment during early childhood, he saw aggression as something that was innate in everyone.
Despite Freud’s flourishing success and contributions to the psychology field, it is clear that even he struggled with the nature versus nurture debate.
How does nature and nurture affect personality?
As discussed above, there are various schools of thoughts around whether nature or nurture influence personality. However, the contemporary school of thought is that person’s personality is multi-faceted and is therefore a combination of both influences, rather than one being solely responsible.
Personality is not determined by any single gene. Rather, genes work together to determine certain actions. There is no “IQ gene” that determines intelligence. Genes are also not so powerful that they can control or create our personalities solely by themselves. In the same way that personality is not determined solely by genes, it is also not solely determined by environmental influences. Personality is affected by both genetic and environmental influences and because of this, it is something that can continue to be shaped throughout a person’s life.
How does nature and nurture affect intelligence?
Intelligence is a complex, multi-faceted phenomenon that cannot simply be boiled down to whether one’s genetics or environment influence intelligence.
Throughout the history of psychology, the nature versus nurture debate has caused quite a bit of controversy. Eugenics, for example, was a movement heavily influenced by the nativist approach.
Psychologist Francis Galton , a cousin of naturalist Charles Darwin, coined the terms nature versus nurture as well as eugenics and believes that intelligences were the result of genetics. Galton believed that intelligent individuals should be encouraged to marry and have many children, while less intelligent individuals should be prevented from reproducing.
Today, the majority of experts believe that a combination of nature and nurture impact behavior and development, including intelligence.
How does nature and nurture influence child development?
In the past, children were viewed as blank slates, which led to parents believing they could mod their child’s development solely through their actions. The idea put a lot of pressure on parents as it suggested that any decision would impact their child. We now know that this is not the case as their genetic makeup influences aspects of their behavior and personality. Beginning at conception, how a child develops and behaviors is partly influenced by the genes they inherit. Examples of nature influencing characteristics include sleeping behavior and parts of a child’s personality. However, the child’s environment plays a crucial role in influencing which genetic influences play a prominent role.
The reality is that nature and nurture both play a crucial role in influencing child development. In fact, new research demonstrates that environmental influences can actually affect genetic expression and whether or how the genes are expressed in the first place. The research found that adverse fetal and early childhood experiences can, and oftentimes do, lead to physical and chemical changes in the brain that can last a lifetime. Additionally, the study found that variations in DNA sequences between individuals influences the way genes are expressions, but the environment in which one develops, before and soon after birth, provides an impactful experience that chemically modify certain genes.
What are the 6 principles of nurture?
The six principles of nurture include: environmental variables, childhood experiences, how we were raised, social relationships, surrounding culture, and having a sense of belonging.
Is anxiety caused by nature or nurture
Around 40 million people are diagnosed with anxiety annually. When it comes to mental illness, the nature nurture debate can be quite helpful in shedding light on why some people develop issues whereas others do not. Anxiety researchers cite social learning theory as significant to the development of clinical anxiety conditions. Four ways the development of anxiety can be explained is:
- Exposure to a traumatic event can lead to fear and anxiety.
- Anxiety and fear are learned by people through watching the reactions and experiences of those around them.
- Simply talking about situations, objects, or people can lead to fear or anxiety.
- Children may negatively reinforce anxiety by avoiding it, which can lead to the development of a clinically significant anxiety condition.
On the other side of the debate, nature plays a pivotal role in understanding anxiety. Twin studies on anxiety disorders have found a genetic foundation for developing anxiety . However, gene-mapping findings have been less clear. This has led researchers to believe that there may be different genes responsible for the development of specific anxiety disorders, such as Generalized Anxiety Disorder.
When it comes to the nature nurture discussion for just about any topic, it becomes clear that both likely play a role in determining why certain behaviors and health problems arise.
Is aggression Nature or nurture?
Examples of nature influencing aggression include Sigmund Freud’s belief that aggression is innate and therefore is influenced by nature. In contrast to this view, Albert Bandura’s social learning theory states that aggression is learned from the environment through observation and imitation. In 1961, Bandura sought to prove this through his famous Bobo Doll experiment. During the experiment, 24 children were shown an aggressive model, 24 children were shown a non-aggressive model, and 24 children were shown no model. The study found that children are able to learn social behavior such as aggression through the process of observing another person’s behavior.
Is high IQ nature or nurture?
A high IQ is not determined by nature or nurture, rather it is a combination of the two. As stated previously, there is no single “IQ gene” that will predetermine whether a person is destined to have a higher IQ than someone else. Rather, it is a combination of genetic predisposition and environmental influences that truly impact a person’s IQ.
Does nature affect intelligence?
Intelligence is a complex trait that is influenced by both genetic and environmental factors. Intelligence is strongly influenced by the environment a person grows up in. Many psych reports show that factors related to a child’s home environment and parenting, education and availability of learning resources, and nutrition are just some of the environmental contributions to a person’s intelligence. Examples of nature influencing intelligence have been studied extensively , however the studies have not conclusively identified any genes that play a major role in differences in intelligence.
Which one is more important between nature and nurture?
The current school of thought is that nature and nurture are equally important and that both influence a person’s overall behavior and personality.
Why is nurture important?
While certain genetic factors may create an increased chance for a particular illness or behavior, the probability that a person develops either is oftentimes dependent on environment. One example of this is that the basis for addiction is not thought to be entirely genetic by most researchers. Environmental aspects, such as the habits of parents, friends, or a partner might also be significant factors contributing to whether a person develops an addiction. Similarly, researchers found that while a family history of mental health conditions was the second strongest predictor of mental illness, the strongest predictors were life events and experiences, such as childhood bullying, abuse, or other trauma. Nurture plays a crucial role in how we develop and evolve into who we are in the world.
How do you nurture yourself?
There are many ways to nurture yourself and doing so will have many positive impacts. A technique for treating yourself better is by developing your “ Inner Nurturing Parent .” Even if you did not have the most nurturing of familial relationships, you can create your inner nurturing parent by forgiving your past mistakes, making every effort to keep yourself healthy and safe,to love and support yourself. Some tips to get started include telling yourself “I love you and appreciate who you are” at the end of each day or saying “I believe in you” when you’ve had a particularly tough day. Making time each day for things you enjoy and prioritizing your health and well-being by starting a weekly exercise routine are other ways to begin to nurture yourself.
What is a nurturing woman?
There is no one “right” way to be a nurturing person. However, some characteristics of a nurturing person is someone who makes an effort to keep loved ones healthy and safe, listens to and acknowledges their feelings, forgives mistakes, and lets their loved ones know how loved they are. A nurturing person makes mistakes, lets others know when they have made a mistake and accepts responsibility for those mistakes.
- Evolutionary Psychology: How Evolutionary Psychologists View Human Behavior Medically reviewed by April Brewer , DBH, LPC
- What Is A Military Psychologist And How To Become One Medically reviewed by Melissa Guarnaccia , LCSW
- Psychologists
- Relationships and Relations
Biopsychology
Introduction to nature and nurture, what you’ll learn to do: explain how nature, nurture, and epigenetics influence personality and behavior.

H ow do we become who we are? Traditionally, people’s answers have placed them in one of two camps: nature or nurture. The one says genes determine an individual while the other claims the environment is the linchpin for development. Since the 16th century, when the terms “nature” and “nurture” first came into use, many people have spent ample time debating which is more important, but these discussions have more often led to ideological cul-de-sacs rather than pinnacles of insight.
New research into epigenetics—the science of how the environment influences genetic expression—is changing the conversation. As psychologist David S. Moore explains in his newest book, The Developing Genome , this burgeoning field reveals that what counts is not what genes you have so much as what your genes are doing . And what your genes are doing is influenced by the ever-changing environment they’re in. Factors like stress, nutrition, and exposure to toxins all play a role in how genes are expressed—essentially which genes are turned on or off. Unlike the static conception of nature or nurture, epigenetic research demonstrates how genes and environments continuously interact to produce characteristics throughout a lifetime.
Learning Objectives
- Examine the historic nature vs. nurture debate
- Explain the basic principles of the theory of evolution by natural selection, genetic variation, and mutation
- Describe epigenetics and examine how gene-environment interactions are critical for expression of physical and psychological characteristics
Contribute!
Improve this page Learn More
- Modification, adaptation, and original content. Provided by : Lumen Learning. License : CC BY: Attribution
- DNA image. Provided by : Wikimedia. Located at : https://simple.wikipedia.org/wiki/DNA_methylation#/media/File:DNA_methylation.jpg . License : CC BY-SA: Attribution-ShareAlike
- The End of Nature Versus Nurture. Authored by : Evan Nesterak. Located at : http://thepsychreport.com/books/the-end-of-nature-versus-nurture/ . Project : The Psych Report. License : CC BY-NC-SA: Attribution-NonCommercial-ShareAlike


The Nature-Nurture Question
Learning objectives.
- Investigate the historic nature vs. nurture debate
Nature vs. Nurture Debate
Are you the way you are because you were born that way, or because of the way you were raised? Do your genetics and biology dictate your personality and behavior, or is it your environment and how you were raised? These questions are central to the age-old nature-nurture debate. In the history of psychology, no other question has caused so much controversy and offense: We are so concerned with nature–nurture because our very sense of moral character seems to depend on it. While we may admire the athletic skills of a great basketball player, we think of his height as simply a gift, a payoff in the “genetic lottery.” For the same reason, no one blames a short person for his height or someone’s congenital disability on poor decisions: To state the obvious, it’s “not their fault.” But we do praise the concert violinist (and perhaps her parents and teachers as well) for her dedication, just as we condemn cheaters, slackers, and bullies for their bad behavior.The problem is, most human characteristics aren’t usually as clear-cut as height or instrument-mastery, affirming our nature–nurture expectations strongly one way or the other. In fact, even the great violinist might have some inborn qualities—perfect pitch, or long, nimble fingers—that support and reward her hard work. And the basketball player might have eaten a diet while growing up that promoted his genetic tendency for being tall. When we think about our own qualities, they seem under our control in some respects, yet beyond our control in others. And often the traits that don’t seem to have an obvious cause are the ones that concern us the most and are far more personally significant. What about how much we drink or worry? What about our honesty, or religiosity, or sexual orientation? They all come from that uncertain zone, neither fixed by nature nor totally under our own control.

One major problem with answering nature-nurture questions about people is, how do you set up an experiment? In nonhuman animals, there are relatively straightforward experiments for tackling nature–nurture questions. Say, for example, you are interested in aggressiveness in dogs. You want to test for the more important determinant of aggression: being born to aggressive dogs or being raised by them. You could mate two aggressive dogs—angry Chihuahuas—together, and mate two nonaggressive dogs—happy beagles—together, then switch half the puppies from each litter between the different sets of parents to raise. You would then have puppies born to aggressive parents (the Chihuahuas) but being raised by nonaggressive parents (the Beagles), and vice versa, in litters that mirror each other in puppy distribution. The big questions are: Would the Chihuahua parents raise aggressive beagle puppies? Would the beagle parents raise non aggressive Chihuahua puppies? Would the puppies’ nature win out, regardless of who raised them? Or… would the result be a combination of nature and nurture? Much of the most significant nature–nurture research has been done in this way (Scott & Fuller, 1998), and animal breeders have been doing it successfully for thousands of years. In fact, it is fairly easy to breed animals for behavioral traits.
With people, however, we can’t assign babies to parents at random, or select parents with certain behavioral characteristics to mate, merely in the interest of science (though history does include horrific examples of such practices, in misguided attempts at “eugenics,” the shaping of human characteristics through intentional breeding). In typical human families, children’s biological parents raise them, so it is very difficult to know whether children act like their parents due to genetic (nature) or environmental (nurture) reasons. Nevertheless, despite our restrictions on setting up human-based experiments, we do see real-world examples of nature-nurture at work in the human sphere—though they only provide partial answers to our many questions. The science of how genes and environments work together to influence behavior is called behavioral genetics . The easiest opportunity we have to observe this is the adoption study . When children are put up for adoption, the parents who give birth to them are no longer the parents who raise them. This setup isn’t quite the same as the experiments with dogs (children aren’t assigned to random adoptive parents in order to suit the particular interests of a scientist) but adoption still tells us some interesting things, or at least confirms some basic expectations. For instance, if the biological child of tall parents were adopted into a family of short people, do you suppose the child’s growth would be affected? What about the biological child of a Spanish-speaking family adopted at birth into an English-speaking family? What language would you expect the child to speak? And what might these outcomes tell you about the difference between height and language in terms of nature-nurture?

Another option for observing nature-nurture in humans involves twin studies . There are two types of twins: monozygotic (MZ) and dizygotic (DZ). Monozygotic twins, also called “identical” twins, result from a single zygote (fertilized egg) and have the same DNA. They are essentially clones. Dizygotic twins, also known as “fraternal” twins, develop from two zygotes and share 50% of their DNA. Fraternal twins are ordinary siblings who happen to have been born at the same time. To analyze nature–nurture using twins, we compare the similarity of MZ and DZ pairs. Sticking with the features of height and spoken language, let’s take a look at how nature and nurture apply: Identical twins, unsurprisingly, are almost perfectly similar for height. The heights of fraternal twins, however, are like any other sibling pairs: more similar to each other than to people from other families, but hardly identical. This contrast between twin types gives us a clue about the role genetics plays in determining height.
Now consider spoken language. If one identical twin speaks Spanish at home, the co-twin with whom she is raised almost certainly does too. But the same would be true for a pair of fraternal twins raised together. In terms of spoken language, fraternal twins are just as similar as identical twins, so it appears that the genetic match of identical twins doesn’t make much difference. Twin and adoption studies are two instances of a much broader class of methods for observing nature-nurture called quantitative genetics , the scientific discipline in which similarities among individuals are analyzed based on how biologically related they are. We can do these studies with siblings and half-siblings, cousins, twins who have been separated at birth and raised separately (Bouchard, Lykken, McGue, & Segal, 1990; such twins are very rare and play a smaller role than is commonly believed in the science of nature–nurture), or with entire extended families (see Plomin, DeFries, Knopik, & Neiderhiser, 2012, for a complete introduction to research methods relevant to nature–nurture).
For better or for worse, contentions about nature–nurture have intensified because quantitative genetics produces a number called a heritability coefficient , varying from 0 to 1, that is meant to provide a single measure of genetics’ influence of a trait. In a general way, a heritability coefficient measures how strongly differences among individuals are related to differences among their genes. But beware: Heritability coefficients, although simple to compute, are deceptively difficult to interpret. Nevertheless, numbers that provide simple answers to complicated questions tend to have a strong influence on the human imagination, and a great deal of time has been spent discussing whether the heritability of intelligence or personality or depression is equal to one number or another.

One reason nature–nurture continues to fascinate us so much is that we live in an era of great scientific discovery in genetics, comparable to the times of Copernicus, Galileo, and Newton, with regard to astronomy and physics. Every day, it seems, new discoveries are made, new possibilities proposed. When Francis Galton first started thinking about nature–nurture in the late-19th century he was very influenced by his cousin, Charles Darwin, but genetics per se was unknown. Mendel’s famous work with peas, conducted at about the same time, went undiscovered for 20 years; quantitative genetics was developed in the 1920s; DNA was discovered by Watson and Crick in the 1950s; the human genome was completely sequenced at the turn of the 21st century; and we are now on the verge of being able to obtain the specific DNA sequence of anyone at a relatively low cost. No one knows what this new genetic knowledge will mean for the study of nature–nurture, but as we will see in the next section, answers to nature–nurture questions have turned out to be far more difficult and mysterious than anyone imagined.
What Have We Learned About Nature–Nurture?
It would be satisfying to be able to say that nature–nurture studies have given us conclusive and complete evidence about where traits come from, with some traits clearly resulting from genetics and others almost entirely from environmental factors, such as childrearing practices and personal will; but that is not the case. Instead, everything has turned out to have some footing in genetics. The more genetically-related people are, the more similar they are—for everything : height, weight, intelligence, personality, mental illness, etc. Sure, it seems like common sense that some traits have a genetic bias. For example, adopted children resemble their biological parents even if they have never met them, and identical twins are more similar to each other than are fraternal twins. And while certain psychological traits, such as personality or mental illness (e.g., schizophrenia), seem reasonably influenced by genetics, it turns out that the same is true for political attitudes, how much television people watch (Plomin, Corley, DeFries, & Fulker, 1990), and whether or not they get divorced (McGue & Lykken, 1992).

It may seem surprising, but genetic influence on behavior is a relatively recent discovery. In the middle of the 20th century, psychology was dominated by the doctrine of behaviorism, which held that behavior could only be explained in terms of environmental factors. Psychiatry concentrated on psychoanalysis, which probed for roots of behavior in individuals’ early life-histories. The truth is, neither behaviorism nor psychoanalysis is incompatible with genetic influences on behavior, and neither Freud nor Skinner was naive about the importance of organic processes in behavior. Nevertheless, in their day it was widely thought that children’s personalities were shaped entirely by imitating their parents’ behavior, and that schizophrenia was caused by certain kinds of “pathological mothering.”
Whatever the outcome of our broader discussion of nature–nurture, the basic fact that the best predictors of an adopted child’s personality or mental health are found in the biological parents he or she has never met, rather than in the adoptive parents who raised him or her, presents a significant challenge to purely environmental explanations of personality or psychopathology. The message is clear: You can’t leave genes out of the equation. But keep in mind, no behavioral traits are completely inherited, so you can’t leave the environment out altogether, either. Trying to untangle the various ways nature-nurture influences human behavior can be messy, and often common-sense notions can get in the way of good science. One very significant contribution of behavioral genetics that has changed psychology for good can be very helpful to keep in mind: When your subjects are biologically-related, no matter how clearly a situation may seem to point to environmental influence, it is never safe to interpret a behavior as wholly the result of nurture without further evidence. For example, when presented with data showing that children whose mothers read to them often are likely to have better reading scores in third grade, it is tempting to conclude that reading to your kids out loud is important to success in school; this may well be true, but the study as described is inconclusive, because there are genetic as well as environmental pathways between the parenting practices of mothers and the abilities of their children. This is a case where “correlation does not imply causation,” as they say. To establish that reading aloud causes success, a scientist can either study the problem in adoptive families (in which the genetic pathway is absent) or by finding a way to randomly assign children to oral reading conditions.
Think It Over
- Is your personality more like one of your parents than the other? If you have a sibling, is his or her personality like yours? In your family, how did these similarities and differences develop? What do you think caused them?
- Can you think of a human characteristic for which genetic differences would play almost no role? Defend your choice.
- Do you think the time will come when we will be able to predict almost everything about someone by examining their DNA on the day they are born?
- Identical twins are more similar than fraternal twins for the trait of aggressiveness, as well as for criminal behavior. Do these facts have implications for the courtroom? If it can be shown that a violent criminal had violent parents, should it make a difference in culpability or sentencing?
attributions
Modification and adaptation. Provided by: Lumen Learning. License: CC BY-NC-SA: Attribution-NonCommercial-ShareAlike
The Nature-Nurture Question . Authored by: Eric Turkheimer. License: CC BY-NC-SA: Attribution-NonCommercial-ShareAlike
the empirical science of how genes and environments combine to generate behavior
a behavior genetic research method that involves comparison of adopted children to their adoptive and biological parents
a behavior genetic research method that involves comparison of the similarity of identical (monozygotic; MZ) and fraternal (dizygotic; DZ) twins
scientific and mathematical methods for inferring genetic and environmental processes based on the degree of genetic and environmental similarity among organisms
an easily misinterpreted statistical construct that purports to measure the role of genetics in the explanation of differences among individuals
Introduction to Psychology Copyright © by Utah Tech University Psychology Department is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial-ShareAlike 4.0 International License , except where otherwise noted.
Share This Book
- Tools and Resources
- Customer Services
- Affective Science
- Biological Foundations of Psychology
- Clinical Psychology: Disorders and Therapies
- Cognitive Psychology/Neuroscience
- Developmental Psychology
- Educational/School Psychology
- Forensic Psychology
- Health Psychology
- History and Systems of Psychology
- Individual Differences
- Methods and Approaches in Psychology
- Neuropsychology
- Organizational and Institutional Psychology
- Personality
- Psychology and Other Disciplines
- Social Psychology
- Sports Psychology
- Share This Facebook LinkedIn Twitter
Article contents
Nature and nurture as an enduring tension in the history of psychology.
- Hunter Honeycutt Hunter Honeycutt Bridgewater College, Department of Psychology
- https://doi.org/10.1093/acrefore/9780190236557.013.518
- Published online: 30 September 2019
Nature–nurture is a dichotomous way of thinking about the origins of human (and animal) behavior and development, where “nature” refers to native, inborn, causal factors that function independently of, or prior to, the experiences (“nurture”) of the organism. In psychology during the 19th century, nature-nurture debates were voiced in the language of instinct versus learning. In the first decades of the 20th century, it was widely assumed that that humans and animals entered the world with a fixed set of inborn instincts. But in the 1920s and again in the 1950s, the validity of instinct as a scientific construct was challenged on conceptual and empirical grounds. As a result, most psychologists abandoned using the term instinct but they did not abandon the validity of distinguishing between nature versus nurture. In place of instinct, many psychologists made a semantic shift to using terms like innate knowledge, biological maturation, and/or hereditary/genetic effects on development, all of which extend well into the 21st century. Still, for some psychologists, the earlier critiques of the instinct concept remain just as relevant to these more modern usages.
The tension in nature-nurture debates is commonly eased by claiming that explanations of behavior must involve reference to both nature-based and nurture-based causes. However, for some psychologists there is a growing pressure to see the nature–nurture dichotomy as oversimplifying the development of behavior patterns. The division is seen as both arbitrary and counterproductive. Rather than treat nature and nurture as separable causal factors operating on development, they treat nature-nurture as a distinction between product (nature) versus process (nurture). Thus there has been a longstanding tension about how to define, separate, and balance the effects of nature and nurture.
- nature–nurture
- development
- nativism–empiricism
- innate–learned
- behavioral genetics
- epigenetics
Nature and Nurture in Development
The oldest and most persistent ways to frame explanations about the behavioral and mental development of individuals is to distinguish between two separate sources of developmental causation: (a) intrinsic, preformed, or predetermined causes (“nature”) versus (b) extrinsic, experiential, or environmental causes (“nurture”). Inputs from these two sources are thought to add their own contribution to development (see Figure 1 ).
Figure 1. The traditional view of nature and nurture as separate causes of development. In the traditional view, nature and nurture are treated as independent causal influences that combine during development to generate outcomes. Note that, during development, the effects of nature and nurture (shown in horizontal crossing lines) remain independent so that their effects on outcomes are theoretically separable.
Because some traits seem to derive more from one source than the other, much of the tension associated with the nature–nurture division deals with disagreements about how to balance the roles of nature and nurture in the development of a trait.
Evidence of Nature in Development
Evidence to support the nature–nurture division usually derives from patterns of behavior that suggest a limited role of environmental causation, thus implying some effect of nature by default. Table 1 depicts some common descriptors and conditions used to infer that some preference, knowledge, or skill is nature based.
Table 1. Common Descriptors and Associated Conditions for Inferring the Effects of Nature on Development
It is important to reiterate that nature-based causation (e.g., genetic determination) is inferred from these observations. Such inferences can generate tension because each of the observations listed here can be explained by nurture-based (environmental) factors. Confusion can also arise when evidence of one descriptor (e.g., being hereditary) is erroneously used to justify a different usage (e.g., that the trait is unlearned).
The Origins of Nature Versus Nurture
For much of recorded history, the distinction between nature and nurture was a temporal divide between what a person is innately endowed with at birth, prior to experience (nature), and what happens thereafter (nurture). It was not until the 19th century that the temporal division was transformed into a material division of causal influences (Keller, 2010 ). New views about heredity and Darwinian evolution justified distinguishing between native traits and genetic causes from acquired traits and environmental causes. More so than before, the terms nature and nurture were often juxtaposed in an opposition famously described by Sir Francis Galton ( 1869 ) as that between “nature versus nurture.”
Galton began writing about heredity in the mid-1860s. He believed we would discover laws governing the transmission of mental as well as physical qualities. Galton’s take on mental heredity, however, was forged by his desire to improve the human race in a science he would later call “eugenics.” In the mid- 19th century , British liberals assumed humans were equivalent at birth. Their social reform efforts were geared to enhancing educational opportunities and improving living conditions. Galton, a political conservative, opposed the notion of natural equality, arguing instead that people were inherently different at birth (Cowan, 2016 ), and that these inherited mental and behavioral inequalities were transmitted through lineages like physical qualities. Because Galton opposed the widely held Lamarckian idea that the qualities acquired in one’s lifetime could modify the inherited potential of subsequent generations, he believed long-lasting improvement of the human stock would only come by controlling breeding practices.
To explain the biological mechanisms of inheritance, Galton joined a growing trend in the 1870s to understand inheritance as involving the transmission of (hypothetical) determinative, germinal substances across generations. Foreshadowing a view that would later become scientific orthodoxy, Galton believed these germinal substances to be uninfluenced by the experiences of the organism. His theory of inheritance, however, was speculative. Realizing he was not equipped to fully explicate his theory of biological inheritance, Galton abandoned this line of inquiry by the end of that decade and refocused his efforts on identifying statistical laws of heredity of individual differences (Renwick, 2011 ).
Historians generally agree that Galton was the first to treat nature (as heredity) and nurture (everything else) as separate causal forces (Keller, 2010 ), but the schism gained biological legitimacy through the work of the German cytologist Auguste Weismann in the 1880s. Whereas Galton’s theory was motivated by his political agenda, Weismann was motivated by a scientific, theoretical agenda. Namely, Weismann opposed Lamarckian inheritance and promoted a view of evolution driven almost entirely by natural selection.
Drawing upon contemporary cytological and embryological research, Weismann made the case that the determinative substances found in the germ cells of plants and animals (called the “germ-plasm”) that are transmitted across generations were physically sequestered very early in embryogenesis and remained buffered from the other cells of the body (“somato-plasm”). This so-called, Weismann’s barrier meant that alterations in the soma that develop in the lifetime of the organism through the use or disuse of body parts would not affect the germinal substances transmitted during reproduction (see Winther, 2001 , for review). On this view, Lamarckian-style inheritance of acquired characteristics was not biologically possible.
Galton and Weismann’s influence on the life sciences cannot be overstated. Their work convinced many to draw unusually sharp distinctions between the inherited (nature) and the acquired (nurture). Although their theories were met with much resistance and generated significant tension in the life sciences from cytology to psychology, their efforts helped stage a new epistemic space through which to appreciate Mendel’s soon to be rediscovered breeding studies and usher in genetics (Muller-Wille & Rheinberger, 2012 ).
Ever since, psychology has teetered between nature-biased and nurture-biased positions. With the rise of genetics, the wedge between nature–nurture was deepened in the early to mid- 20th century , creating fields of study that focused exclusively on the effects of either nature or nurture.
The “Middle Ground” Perspective on Nature–Nurture
Twenty-first-century psychology textbooks often state that the nature–nurture debates have been resolved, and the tension relaxed, because we have moved on from emphasizing nature or nurture to appreciating that development necessarily involves both nature and nurture. In this middle-ground position, one asks how nature and nurture interact. For example, how do biological (or genetic) predispositions for behaviors or innate knowledge bias early learning experiences? Or how might environmental factors influence the biologically determined (maturational) unfolding of bodily form and behaviors?
Rejection of the Nature–Nurture Divide
For some, the “middle-ground” resolution is as problematic as “either/or” views and does not resolve a deeper source of tension inherent in the dichotomy. On this view, the nature–nurture divide is neither a legitimate nor a constructive way of thinking about development. Instead, developmental analysis reveals that the terms commonly associated with nature (e.g., innate, genetic, hereditary, or instinctual) and nurture (environmental or learned) are so entwined and confounded (and often arbitrary) that their independent effects cannot be meaningfully discussed. The nature–nurture division oversimplifies developmental processes, takes too much for granted, and ultimately hinders scientific progress. Thus not only is there a lingering tension about how to balance the effects of nature and nurture in the middle-ground view, but there is also a growing tension to move beyond the dichotomous nature–nurture framework.
Nativism in Behavior: Instincts
Definitions of instinct can vary tremendously, but many contrast (a) instinct with reason (or intellect, thought, will), which is related to but separable from contrasting (b) instinct with learning (or experience or habit).
Instinct in the Age of Enlightenment
Early usages of the instinct concept, following Aristotle, treated instinct as a mental, estimative faculty ( vis aestimativa or aestimativa naturalis ) in humans and animals that allowed for the judgments of objects in the world (e.g., seeing a predator) to be deemed beneficial or harmful in a way that transcends immediate sensory experience but does not involve the use of reason (Diamond, 1971 ). In many of the early usages, the “natural instinct” of animals even included subrational forms of learning.
The modern usage of instincts as unlearned behaviors took shape in the 17th century . By that point it was widely believed that nature or God had implanted in animals and humans innate behaviors and predispositions (“instincts”) to promote the survival of the individual and the propagation of the species. Disagreements arose as to whether instincts derived from innate mental images or were mindlessly and mechanically (physiologically) generated from innately specified bodily organization (Richards, 1987 ).
Anti-Instinct Movement in the Age of Enlightenment
Challenges to the instinct concept can be found in the 16th century (see Diamond, 1971 ), but they were most fully developed by empiricist philosophers of the French Sensationalist tradition in the 18th century (Richards, 1987 ). Sensationalists asserted that animals behaved rationally and all of the so-called instincts displayed by animals could be seen as intelligently acquired habits.
For Sensationalists, instincts, as traditionally understood, did not exist. Species-specificity in behavior patterns could be explained by commonalities in physiological organization, needs, and environmental conditions. Even those instinctual behaviors seen at birth (e.g., that newly hatched chicks peck and eat grain) might eventually be explained by the animal’s prenatal experiences. Erasmus Darwin ( 1731–1802 ), for example, speculated that the movements and swallowing experiences in ovo could account for the pecking and eating of grain by young chicks. The anti-instinct sentiment was clearly expressed by the Sensationalist Jean Antoine Guer ( 1713–1764 ), who warned that instinct was an “infantile idea” that could only be held by those who are ignorant of philosophy, that traditional appeals to instincts in animals not only explained nothing but served to hinder scientific explanations, and that nothing could be more superficial than to explain behavior than appealing to so-called instincts (Richards, 1987 ).
The traditional instinct concept survived. For most people, the complex, adaptive, species-specific behaviors displayed by naïve animals (e.g., caterpillars building cocoons; infant suckling behaviors) appeared to be predetermined and unlearned. Arguably as important, however, was the resistance to the theological implications of Sensationalist philosophy.
One of the strongest reactions to Sensationalism was put forward in Germany by Herman Samuel Reimarus ( 1694–1768 ). As a natural theologian, Reimarus, sought evidence of a God in the natural world, and the species-specific, complex, and adaptive instincts of animals seemed to stand as the best evidence of God’s work. More so than any other, Reimarus extensively catalogued instincts in humans and animals. Rather than treat instincts as behaviors, he defined instincts as natural impulses (inner drives) to act that were expressed perfectly, without reflection or practice, and served adaptive goals (Richards, 1987 ). He even proposed instincts for learning, a proposal that would resurface in the mid- 20th century , as would his drive theory of instinct (Jaynes & Woodward, 1974 ).
Partly as a result of Reimarus’ efforts, the instinct concept survived going into the 19th century . But many issues surrounding the instinct concept were left unsettled. How do instincts differ from reflexive behaviors? What role does learning play in the expression of instincts, if any? Do humans have more or fewer instincts than animals? These questions would persist well into the first decades of the 20th century and ultimately fuel another anti-instinct movement.
Instinct in the 19th Century
In the 19th century , the tension about the nature and nurture of instincts in the lifetime of animals led to debates about the nature and nurture of instincts across generations . These debates dealt with whether instincts should be viewed as “inherited habits” from previous generations or whether they result from the natural selection. Debating the relative roles of neo-Lamarckian use-inheritance versus neo-Darwinian natural selection in the transmutation of species became a significant source of tension in the latter half of the 19th century . Although the neo-Lamarckian notion of instincts as being inherited habits was rejected in the 20th century , it has resurged in recent years (e.g., see Robinson & Barron, 2017 ).
Darwinian evolutionary theory required drawing distinctions between native and acquired behaviors, and, perhaps more so than before, behaviors were categorized along a continuum from the purely instinctive (unlearned), to the partially instinctive (requiring some learning), to the purely learned. Still, it was widely assumed that a purely instinctive response would be modified by experience after its first occurrence. As a result, instinct and habit were very much entangled in the lifetime of the organism. The notion of instincts as fixed and unmodifiable would not be widely advanced until after the rise of Weismann’s germ-plasm theory in the late 19thcentury .
Given their importance in evolutionary theory, there was greater interest in more objectively identifying pure instincts beyond anecdotal reports. Some of the most compelling evidence was reported by Douglas Spalding ( 1844–1877 ) in the early 1870s (see Gray, 1967 ). Spalding documented numerous instances of how naïve animals showed coordinated, seemingly adaptive responses (e.g., hiding) to objects (e.g., sight of predators) upon their first encounter, and he helped pioneer the use of the deprivation experiment to identify instinctive behaviors. This technique involved selectively depriving young animals of seemingly critical learning experiences or sensory stimulation. Should animals display some species-typical action following deprivation, then, presumably, the behavior could be labeled as unlearned or innate. In all, these studies seemed to show that animals displayed numerous adaptive responses at the very start, prior to any relevant experience. In a variety of ways, Spalding’s work anticipated 20th-century studies of innate behavior. Not only would the deprivation experiment be used as the primary means of detecting native tendencies by European zoologists and ethologists, but Spalding also showed evidence of what would later be called imprinting, critical period effects and evidence of behavioral maturation.
Reports of pure instinct did not go unchallenged. Lloyd Morgan ( 1896 ) questioned the accuracy of these reports in his own experimental work with young animals. In some cases, he failed to replicate the results and in other cases he found that instinctive behaviors were not as finely tuned to objects in the environment as had been claimed. Morgan’s research pointed to taking greater precision in identifying learned and instinctive components of behavior, but, like most at the turn of the 20th century , he did not question that animal behavior involved both learned and instinctive elements.
A focus on instinctive behaviors intensified in the 1890s as Weismann’s germ-plasm theory grew in popularity. More so than before, a sharp distinction was drawn between native and acquired characteristics, including behavior (Johnston, 1995 ). Although some psychologists continued to maintain neo-Lamarckian notions, most German (Burnham, 1972 ) and American (Cravens & Burnham, 1971 ) psychologists were quick to adopt Weismann’s theory. They envisioned a new natural science of psychology that would experimentally identify the germinally determined, invariable set of native psychological traits in species and their underlying physiological (neural) basis. However, whereas English-speaking psychologists tended to focus on how this view impacted our understanding of social institutions and its social implications, German psychologists were more interested in the longstanding philosophical implications of Weismann’s doctrine as it related to the differences (if any) between man and beast (Burnham, 1972 ).
Some anthropologists and sociologists, however, interpreted Weismann’s theory quite differently and used it elevate sociology as its own scientific discipline. In the 1890s, the French sociologist Emil Durkheim, for example, interpreted Weismann’s germinal determinants as a generic force on human behavior that influenced the development of general predispositions that are molded by the circumstances of life (Meloni, 2016 ). American anthropologists reached similar conclusions in the early 20th century (Cravens & Burnham, 1971 ). Because Weismann’s theory divorced biological inheritance from social inheritance, and because heredity was treated as a generic force, sociologists felt free to study social (eventually, “cultural”) phenomena without reference to biological or psychological concerns.
Anti-Instinct Movement in the 1920s
Despite their differences, in the first two decades of the 20th century both psychologists and sociologists generally assumed that humans and animals had some native tendencies or instincts. Concerns were even voiced that instinct had not received enough attention in psychology. Disagreements about instincts continued to focus on (the now centuries old debates of) how to conceptualize them. Were they complex reflexes, impulses, or motives to act, or should instinct be a mental faculty (like intuition), separate from reasoning and reflex (Herrnstein, 1972 )?
In America, the instinct concept came under fire following a brief paper in 1919 by Knight Dunlap titled “Are There Any Instincts?” His primary concern dealt with teleological definitions of instincts in which an instinct referred to all the activities involved in obtaining some end-state (e.g., instincts of crying, playing, feeding, reproduction, war, curiosity, or pugnacity). Defined in this way, human instincts were simply labels for human activities, but how these activities were defined was arbitrarily imposed by the researchers. Is feeding, for instance, an instinct, or is it composed of more basic instincts (like chewing and swallowing)? The arbitrariness of classifying human behavior had led to tremendous inconsistencies and confusion among psychologists.
Not all of the challenges to instinct dealt with its teleological usage. Some of the strongest criticisms were voiced by Zing-Yang Kuo throughout the 1920s. Kuo was a Chinese animal psychologist who studied under Charles Tolman at the University of California, Berkeley. Although Kuo’s attacks on instinct changed throughout the 1920s (see Honeycutt, 2011 ), he ultimately argued that all behaviors develop in experience-dependent ways and that appeals to instinct were statements of ignorance about how behaviors develop. Like Dunlap, he warned that instincts were labels with no explanatory value. To illustrate, after returning to China, he showed how the so-called rodent-killing instinct in cats often cited by instinct theorists is not found in kittens that are reared with rodents (Kuo, 1930 ). These kittens, instead, became attached to the rodents, and they resisted attempts to train rodent-killing. Echoing the point made by Guer, Kuo claimed that appeals to instinct served to stunt scientific inquiry into the developmental origins of behavior.
But Kuo did not just challenge the instinct concept. He also argued against labeling behaviors as “learned.” After all, whether an animal “learns” depends on the surrounding environmental conditions, the physiological and developmental status of the animal, and, especially, the developmental (or experiential) history of that animal. Understanding learning also required developmental analysis. Thus Kuo targeted the basic distinction between nature and nurture, and he was not alone in doing so (e.g., see Carmichael, 1925 ), but his call to reject it did not spread to mainstream American psychologists.
By the 1930s, the term instinct had fallen into disrepute in psychology, but experimental psychologists (including behaviorists) remained committed to a separation of native from acquired traits. If anything, the dividing line between native and acquired behaviors became more sharply drawn than before (Logan & Johnston, 2007 ). For some psychologists, instinct was simply rebranded in the less contentious (but still problematic) language of biological drives or motives (Herrnstein, 1972 ). Many other psychologists simply turned to describing native traits as due to “maturation” and/or “heredity” rather than “instinct.”
Fixed Action Patterns
The hereditarian instinct concept received a reboot in Europe in the 1930s with the rise of ethology led by Konrad Lorenz, Niko Tinbergen, and others. Just as animals inherit organs that perform specific functions, ethologists believed animals inherit behaviors that evolved to serve adaptive functions as well. Instincts were described as unlearned (inherited), blind, stereotyped, adaptive, fixed action patterns, impervious to change that are initiated (released) by specific stimuli in the environment.
Ethologists in 1930s and 1940s were united under the banner of innateness. They were increasingly critical of the trend by American psychologists (i.e., behaviorists) to focus on studying on how a limited number of domesticated species (e.g., white rat) responded to training in artificial settings (Burkhardt, 2005 ). Ethologists instead began with rich descriptions of animal behavior in more natural environments along with detailed analyses of the stimulus conditions that released the fixed action patterns. To test whether behavioral components were innate, ethologists relied primarily on the deprivation experiment popularized by Spalding in the 19th century . Using these methods (and others), ethologists identified numerous fascinating examples of instinctive behaviors, which captured mainstream attention.
In the early 1950s, shortly after ethology had gained professional status (Burkhardt, 2005 ), a series of challenges regarding instinct and innateness were put forth by a small cadre of North American behavioral scientists (e.g., T. C. Schneirla, Donald Hebb, Frank Beach). Arguably the most influential critique was voiced by comparative psychologist Daniel Lehrman ( 1953 ), who presented a detailed and damning critique of deprivation experiments on empirical and logical grounds. Lehrman explained that deprivation experiments isolate the animal from some but not all experiences. Thus deprivation experiments simply change what an animal experiences rather than eliminating experience altogether, and so they cannot possibly determine whether a behavior is innate (independent of experience). Instead, these experiments show what environmental conditions do not matter in the development of a behavior but do not speak to what conditions do matter .
Lehrman went on to argue that the whole endeavor to identify instinctive or innate behavior was misguided from the start. All behavior, according to Lehrman, develops from a history of interactions between an organism and its environment. If a behavior is found to develop in the absence of certain experiences, the researcher should not stop and label it as innate. Rather, research should continue to identify the conditions under which the behavior comes about. In line with Kuo, Lehrman repeated the warning that to label something as instinctive (or inherited or maturational) is a statement of ignorance about how that behavior develops and does more to stunt than promote research.
Lehrman’s critique created significant turmoil among ethologists. As a result, ethologists took greater care in using the term innate , and it led to new attempts to synthesize or re-envision learning and instinct .
Some of these attempts focused on an increased role for learning and experience in the ontogeny of species-typical behaviors. These efforts spawned significant cross-talk between ethologists and comparative psychologists to more thoroughly investigate behavioral development under natural conditions. Traditional appeals to instinct and learning (as classical and operant conditioning) were both found to be inadequate for explaining animal behavior. In their stead, these researchers focused more closely on how anatomical, physiological, experiential, and environmental conditions influenced the development of species-typical behaviors.
Tinbergen ( 1963 ) was among those ethologists who urged for greater developmental analysis of species-typical behaviors, and he included it as one of his four problems in the biological study of organisms, along with causation (mechanism), survival value (function), and evolution. Of these four problems, Tinbergen believed ethologists were especially well suited to study survival value, which he felt had been seriously neglected (Burkhardt, 2005 ).
The questions of survival value coupled with models of population genetics would gain significant momentum in the 1960s and 1970s in England and the United States with the rise of behavioral ecology and sociobiology (Griffiths, 2008 ). But because these new fields seemed to promote some kind of genetic determinism in behavioral development, they were met with much resistance and reignited a new round of nature–nurture debates in the 1970s (see Segerstrale, 2000 ).
However, not all ethologists abandoned the instinct concept. Lorenz, in particular, continued to defend the division between nature and nurture. Rather than speaking of native and acquired behaviors, Lorenz later spoke of two different sources of information for behavior (innate/genetic vs. acquired/environmental), which was more a subtle shift in language than it was an actual change in theory, as Lehrman later pointed out.
Some ethologists followed Lorenz’s lead and continued to maintain more of a traditional delineation between instinct and learning. Their alternative synthesis viewed learning as instinctive (Gould & Marler, 1987 ). They proposed that animals have evolved domain-specific “instincts to learn” that result from the its genetic predispositions and innate knowledge. To support the idea of instincts for learning, ethologists pointed to traditional ethological findings (on imprinting and birdsong learning), but they also drew from the growing body of work in experimental psychology that seemed to indicate certain types of biological effects on learning.
Biological Constraints and Preparedness
While ethology was spreading in Europe in the 1930s–1950s, behaviorism reigned in the United States. Just as ethologists were confronted with including a greater role of nurture in their studies, behaviorists were challenged to consider a greater role of nature.
Behaviorists assumed there to be some behavioral innateness (e.g., fixed action patterns, unconditioned reflexes, primary reinforcers and drives). But because behaviorists focused on learning, they tended to study animals in laboratory settings using biologically (or ecologically) irrelevant stimuli and responses to minimize any role of instinct (Johnston, 1981 ). It was widely assumed that these studies would identify general laws of learning that applied to all species regardless of the specific cues, reinforcers, and responses involved.
Challenges to the generality assumption began to accumulate in the 1960s. Some studies pointed to failures that occurred during conditioning procedures. Breland and Breland ( 1961 ), for example, reported that some complex behaviors formed through operant conditioning would eventually become “displaced” by conditioned fixed action patterns in a phenomenon they called “instinctive drift.” Studies of taste-aversion learning (e.g., Garcia & Koelling, 1966 ) also reported the failure of rats to associate certain events (e.g., flavors with shock or audiovisual stimuli with toxicosis).
Other studies were pointing to enhanced learning. In particular, it was found that rats could form strong conditioned taste aversions after only a single pairing between a novel flavor and illness. (This rapid “one trial learning” was a major focus in the research from Niko Tinbergen’s ethological laboratory.) Animals, it seemed, had evolved innate predispositions to form (or not form) certain associations.
In humans, studies of biological constraints on learning were mostly limited to fear conditioning. Evidence indicated that humans conditioned differently to (biologically or evolutionarily) fear-relevant stimuli like pictures of spiders or snakes than to fear-irrelevant stimuli like pictures of mushrooms or flowers (Ohman, Fredrikson, Hugdahl, & Rimmö, 1976 ).
These findings and others were treated as a major problem in learning theory and led to calls for a new framework to study learning from a more biologically oriented perspective that integrated the evolutionary history and innate predispositions of the species. These predispositions were described as biological “constraints” on, “preparedness,” or “adaptive specializations” for learning, all of which were consistent with the “instincts to learn” framework proposed by ethologists.
By the 1980s it was becoming clear that the biological preparedness/constraint view of learning suffered some limitations. For example, what constraints count as “biological” was questioned. It was well established that there were general constraints on learning associated with the intensity, novelty, and timing of stimuli. But, arbitrarily it seemed, these constraints were not classified as “biological” (Domjan & Galef, 1983 ). Other studies of “biological constraints” found that 5- and 10-day old rats readily learned to associated a flavor with shock (unlike in adults), but (like in adults) such conditioning was not found in 15-day-old rats (Hoffman & Spear, 1988 ). In other words, the constraint on learning was not present in young rats but developed later in life, suggesting a possible role of experience in bringing about the adult-like pattern.
Attempts to synthesize these alternatives led to numerous calls for more ecologically oriented approaches to learning not unlike the synthesis between ethology and comparative psychology in the 1960s. All ecological approaches to learning proposed that learning should be studied in the context of “natural” (recurrent and species-typical) problems that animals encounter (and have evolved to encounter) using ecologically meaningful stimuli and responses. Some argued (e.g., Johnston, 1981 ) that studies of learning should take place within the larger context of studying how animals develop and adapt to their surround. Others (Domjan & Galef, 1983 ) pointed to more of a comparative approach in studying animal learning in line with behavioral ecology that takes into account how learning can be influenced by the possible selective pressures faced by each species. Still, how to synthesize biological constraints (and evolutionary explanations) on learning with a general process approach remains a source of tension in experimental psychology.
Nativism in Mind: Innate Ideas
Nativism and empiricism in philosophy.
In the philosophy of mind, nature–nurture debates are voiced as debates between nativists and empiricists. Nativism is a philosophical position that holds that our minds have some innate (a priori to experience) knowledge, concepts, or structure at the very start of life. Empiricism, in contrast, holds that all knowledge derives from our experiences in the world.
However, rarely (if ever) were there pure nativist or empiricist positions, but the positions bespeak a persistent tension. Empiricists tended to eschew innateness and promote a view of the mental content that is built by general mechanisms (e.g., association) operating on sensory experiences, whereas nativists tend to promote a view of mind that contains domain-specific, innate processes and/or content (Simpson, Carruthers, Laurence, & Stich, 2005 ). Although the tension about mental innateness would loosen as empiricism gained prominence in philosophy and science, the strain never went away and would intensify again in the 20th century .
Nativism in 20th Century Psychology: The Case of Language Development
In the first half of the 20th century , psychologists generally assumed that knowledge was gained or constructed through experience with the world. This is not to say that psychologists did not assume some innate knowledge. The Swiss psychologist Jean Piaget, for example, believed infants enter the world with some innate knowledge structures, particularly as they relate to early sensory and motor functioning (see Piaget, 1971 ). But the bulk of his work dealt with the construction of conceptual knowledge as children adapt to their worlds. By and large, there were no research programs in psychology that sought to identify innate factors in human knowledge and cognition until the 1950s (Samet & Zaitchick, 2017 )
An interest in psychological nativism was instigated in large part by Noam Chomsky’s ( 1959 ) critique of B. F. Skinner’s book on language. To explain the complexity of language, he argued, we must view language as the knowledge and application of grammatical rules. He went on to claim that the acquisition of these rules could not be attributed to any general-purpose, learning process (e.g., reinforcement). Indeed, language acquisition occurs despite very little explicit instruction. Moreover, language is special in terms of its complexity, ease, and speed of acquisition by children and in its uniqueness to humans. Instead, he claimed that our minds innately contain some language-specific knowledge that kick-starts and promotes language acquisition. He later claimed this knowledge can be considered some sort of specialized mental faculty or module he called the “language acquisition device” (Chomsky, 1965 ) or what Pinker ( 1995 ) later called the “language instinct.”
To support the idea of linguistic nativism, Chomsky and others appealed to the poverty of the stimulus argument. In short, this argument holds that our experiences in life are insufficient to explain our knowledge and abilities. When applied to language acquisition, this argument holds children’s knowledge of language (grammar) goes far beyond the limited, and sometimes broken, linguistic events that children directly encounter. Additional evidence for nativism drew upon the apparent maturational quality of language development. Despite wide variations in languages and child-rearing practices across the world, the major milestones in language development appear to unfold in children in a universal sequence and timeline, and some evidence suggested a critical period for language acquisition.
Nativist claims about language sparked intense rebuttals by empiricist-minded psychologists and philosophers. Some of these retorts tackled the logical limitations of the poverty of stimulus argument. Others pointed to the importance of learning and social interaction in driving language development, and still others showed that language (grammatical knowledge) may not be uniquely human (see Tomasello, 1995 , for review). Nativists, in due course, provided their own rebuttals to these challenges, creating a persistent tension in psychology.
Extending Nativism Beyond Language Development
In the decades that followed, nativist arguments expanded beyond language to include cognitive domains that dealt with understanding the physical, psychological, and social worlds. Developmental psychologists were finding that infants appeared to be much more knowledgeable in cognitive tasks (e.g., on understanding object permanence) and skillful (e.g., in imitating others) than had previously been thought, and at much younger ages. Infants also showed a variety of perceptual biases (e.g., preference for face-like stimuli over equally complex non-face-like stimuli) from very early on. Following the standard poverty of the stimulus argument, these findings were taken as evidence that infants enter the world with some sort of primitive, innate, representational knowledge (or domain-specific neural mechanisms) that constrains and promotes subsequent cognitive development. The nature of this knowledge (e.g., as theories or as core knowledge), however, continues to be debated (Spelke & Kinzler, 2007 ).
Empiricist-minded developmental psychologists responded by demonstrating shortcomings in the research used to support nativist claims. For example, in studies of infants’ object knowledge, the behavior of infants (looking time) in nativist studies could be attributed to relatively simple perceptual processes rather than to the infants’ conceptual knowledge (Heyes, 2014 ). Likewise, reports of human neonatal imitation not only suffered from failures to replicate but could be explained by simpler mechanisms (e.g., arousal) than true imitation (Jones, 2017 ). Finally, studies of perceptual preferences found in young infants, like newborn preferences for face-like stimuli, may not be specific preferences for faces per se but instead may reflect simpler, nonspecific perceptual biases (e.g., preferences for top-heavy visual configurations and congruency; Simion & Di Giorgio, 2015 ).
Other arguments from empiricist-minded developmental psychologists focused on the larger rationale for inferring innateness. Even if it is conceded that young infants, like two-month-olds, or even two-day-olds, display signs of conceptual knowledge, there is no good evidence to presume the knowledge is innate. Their knowledgeable behaviors could still be seen as resulting from their experiences (many of which may be nonobvious to researchers) leading up to the age of testing (Spencer et al., 2009 ).
In the 21st century , there is still no consensus about the reality, extensiveness, or quality of mental innateness. If there is innate knowledge, can experience add new knowledge or only expand the initial knowledge? Can the doctrine of innate knowledge be falsified? There are no agreed-upon answers to these questions. The recurring arguments for and against mental nativism continue to confound developmental psychologists.
Maturation Theory
The emergence of bodily changes and basic behavioral skills sometimes occurs in an invariant, predictable, and orderly sequence in a species despite wide variations in rearing conditions. These observations are often attributed to the operation of an inferred, internally driven, maturational process. Indeed, 21st-century textbooks in psychology commonly associate “nature” with “maturation,” where maturation is defined as the predetermined unfolding of the individual from a biological or genetic blueprint. Environmental factors play a necessary, but fundamentally supportive, role in the unfolding of form.
Preformationism Versus Epigenesis in the Generation of Form
The embryological generation of bodily form was debated in antiquity but received renewed interest in the 17th century . Following Aristotle, some claimed that embryological development involved “epigenesis,” defined as the successive emergence of form from a formless state. Epigenesists, however, struggled to explain what orchestrated development without appealing to Aristotelean souls. Attempts were made to invoke to natural causes like physical and chemical forces, but, despite their best efforts, the epigenesists were forced to appeal to the power of presumed, quasi-mystical, vitalistic forces (entelechies) that directed development.
The primary alternative to epigenesis was “preformationism,” which held that development involved the growth of pre-existing form from a tiny miniature (homunculus) that formed immediately after conception or was preformed in the egg or sperm. Although it seems reasonable to guess that the invention and widespread use of the microscope would immediately lay to rest any claim of homuncular preformationism, this was not the case. To the contrary, some early microscopists claimed to see signs of miniature organisms in sperm or eggs, and failures to find these miniatures were explained away (e.g., the homunculus was transparent or deflated to the point of being unrecognizable). But as microscopes improved and more detailed observations of embryological development were reported in the late 18th and 19th centuries , homuncular preformationism was finally refuted.
From Preformationism to Predeterminism
Despite the rejection of homuncular preformationism, preformationist appeals can be found throughout the 19th century . One of the most popular preformationist theories of embryological development was put forth by Ernst Haeckel in the 1860s (Gottlieb, 1992 ). He promoted a recapitulation theory (not original to Haeckel) that maintained that the development of the individual embryo passes through all the ancestral forms of its species. Ontogeny was thought to be a rapid, condensed replay of phylogeny. Indeed, for Haeckel, phylogenesis was the mechanical cause of ontogenesis. The phylogenetic evolution of the species created the maturational unfolding of embryonic form. Exactly how this unfolding takes place was less important than its phylogenetic basis.
Most embryologists were not impressed with recapitulation theory. After all, the great embryologist Karl Ernst von Baer ( 1792–1876 ) had refuted strict recapitulation decades earlier. Instead, there was greater interest in how best to explain the mechanical causes of development ushering in a new “experimental embryology.” Many experimental embryologists followed the earlier epigenesists by discussing vitalistic forces operating on the unorganized zygote. But it soon became clear that the zygote was structured, and many people believed the zygote contained special (unknown) substances that specified development. Epigenesis-minded experimental embryologists soon warned that the old homuncular preformationism was being transformed into a new predetermined preformationism.
As a result, the debates between preformationism and epigenesis were reignited in experimental embryology, but the focus of these debates shifted to the various roles of nature and nurture during development. More specifically, research focused on the extent to which early cellular differentiation was predetermined by factors internal to cells like chromosomes or cytoplasm (preformationism, nature) or involved factors (e.g., location) outside of the cell (epigenesis, nurture). The former emphasized reductionism and developmental programming, whereas the latter emphasized some sort of holistic, regulatory system responsive to internal and external conditions. The tension between viewing development as predetermined or “epigenetic” persists into the 21st century .
Preformationism gained momentum in the 20th century following the rediscovery of Mendel’s studies of heredity and the rapid rise of genetics, but not because of embryological research on the causes of early differentiation. Instead, preformationism prevailed because it seemed embryological research on the mechanisms of development could be ignored in studies of hereditary patterns.
The initial split between heredity and development can be found in Galton’s speculations but is usually attributed to Weismann’s germ-plasm theory. Weismann’s barrier seemed to posit that the germinal determinants present at conception would be the same, unaltered determinants transmitted during reproduction. This position, later dubbed as “Weismannism,” was ironically not one promoted by Weismann. Like nearly all theorists in the 19th century , he viewed the origins of variation and heredity as developmental phenomena (Amundson, 2005 ), and he claimed that the germ-plasm could be directly modified in the lifetime of the organism by environmental (e.g., climactic and dietary) conditions (Winther, 2001 ). Still, Weismann’s theory treated development as a largely predetermined affair driven by inherited, germinal determinants buffered from most developmental events. As such, it helped set the stage for a more formal divorce between heredity and development with the rise of Mendelism in the early 20th century .
Mendel’s theory of heredity was exceptional in how it split development from heredity (Amundson, 2005 ). More so than in Weismann’s theory, Mendel’s theory assumed that the internal factors that determine form and are transmitted across generations remain unaltered in the lifetime of the organism. To predict offspring outcomes, one need only know the combination of internal factors present at conception and their dominance relations. Exactly how these internal factors determined form could be disregarded. The laws of hereditary transmission of the internal factors (e.g., segregation) did not depend on the development or experiences of the organism or the experiences the organism’s ancestors. Thus the experimental study of heredity (i.e., breeding) could proceed without reference to ancestral records or embryological concerns (Amundson, 2000 ). By the mid-1920s, the Mendelian factors (now commonly called “genes”) were found to be structurally arranged on chromosomes, and the empirical study of heredity (transmission genetics) was officially divorced from studies of development.
The splitting of heredity and development found in Mendel’s and Weismann’s work met with much resistance. Neo-Lamarckian scientists, especially in the United States (Cook, 1999 ) and France (Loison, 2011 ), sought unsuccessfully to experimentally demonstrate the inheritance of acquired characteristics into the 1930s.
In Germany during the 1920s and 1930s, resistance to Mendelism dealt with the chromosomal view of Mendelian heredity championed by American geneticists who were narrowly focused on studying transmission genetics at the expense of developmental genetics. German biologists, in contrast, were much more interested in the broader roles of genes in development (and evolution). In trying to understand how genes influence development, particularly of traits of interest to embryologists, they found the Mendelian theory to be lacking. In the decades between the world wars, German biologists proposed various expanded views of heredity that included some form of cytoplasmic inheritance (Harwood, 1985 ).
Embryologists resisted the preformationist view of development throughout the early to mid- 20th century , often maintaining no divide between heredity and development, but their objections were overshadowed by genetics and its eventual synthesis with evolutionary theory. Consequently, embryological development was treated by geneticists and evolutionary biologists as a predetermined, maturational process driven by internal, “genetic” factors buffered from environmental influence.
Maturation Theory in Psychology
Maturation theory was applied to behavioral development in the 19th century in the application of Haeckel’s recapitulation theory. Some psychologists believed that the mental growth of children recapitulated the history of the human race (from savage brute to civilized human). With this in mind, many people began to more carefully document child development. Recapitulationist notions were found in the ideas of many notable psychologists in the 19th and early 20th centuries (e.g., G. S. Hall), and, as such, the concept played an important role in the origins of developmental psychology (Koops, 2015 ). But for present purposes what is most important is that children’s mental and behavioral development was thought to unfold via a predetermined, maturational process.
With the growth of genetics, maturational explanations were increasingly invoked to explain nearly all native and hereditary traits. As the instinct concept lost value in the 1920s, maturation theory gained currency, although the shift was largely a matter of semantics. For many psychologists, the language simply shifted from “instinct versus learning” to “maturation versus practice/experience” (Witty & Lehman, 1933 ).
Initial lines of evidence for maturational explanations of behavior were often the same as those that justified instinct and native traits, but new embryological research presented in the mid-1920s converged to show support for strict maturational explanations of behavioral development. In these experiments (see Wyman, 2005 , for review), spanning multiple laboratories, amphibians (salamanders and frogs) were exposed to drugs that acted as anesthetics and/or paralytics throughout the early stages of development, thus reducing sensory experience and/or motor practice. Despite the reduced sensory experiences and being unable to move, these animals showed no delays in the onset of motor development once the drugs wore off.
This maturational account of motor development in amphibians fit well with contemporaneous studies of motor development in humans. The orderly, invariant, and predictable (age-related) sequential appearance of motor skills documented in infants reared under different circumstances (in different countries and across different decades) was seen as strong evidence for a maturational account. Additional evidence was reported by Arnold Gessell and Myrtle McGraw, who independently presented evidence in the 1920s to show that the pace and sequence of motor development in infancy were not altered by special training experiences. Although the theories of these maturation theorists were more sophisticated when applied to cognitive development, their work promoted a view in which development was primarily driven by neural maturation rather than experience (Thelen, 2000 ).
Critical and Sensitive Periods
As the maturation account of behavioral development gained ground, it became clear that environmental input played a more informative role than had previously been thought. Environmental factors were found to either disrupt or induce maturational changes at specific times during development. Embryological research suggested that there were well-delineated time periods of heightened sensitivity in which specific experimental manipulations (e.g., tissue transplantations) could induce irreversible developmental changes, but the same manipulation would have no effect outside of that critical period.
In the 1950s–1960s a flurry of critical period effects were reported in birds and mammals across a range of behaviors including imprinting, attachment, socialization, sensory development, bird song learning, and language development (Michel & Tyler, 2005 ). Even though these findings highlighted an important role of experience in behavioral development, evidence of critical periods was usually taken to imply some rigid form of biological determinism (Oyama, 1979 ).
As additional studies were conducted on critical period effects, it became clear that many of the reported effects were more gradual, variable, experience-dependent, and not necessarily as reversible as was previously assumed. In light of these reports, there was a push in the 1970s (e.g., Connolly, 1972 ) to substitute “sensitive period” for “critical period” to avoid the predeterminist connotations associated with the latter and to better appreciate that these periods simply describe (not explain) certain temporal aspects of behavioral development. As a result, a consensus emerged that behaviors should not be attributed to “time” or “age” but to the developmental history and status of the animal under investigation (Michel & Tyler, 2005 ).
Heredity and Genetics
In the decades leading up to and following the start of the 20th century , it was widely assumed that many psychological traits (not just instincts) were inherited or “due to heredity,” although the underlying mechanisms were unknown. Differences in intelligence, personality, and criminality within and between races and sexes were largely assumed to be hereditary and unalterable by environmental intervention (Gould, 1996 ). The evidence to support these views in humans was often derived from statistical analyses of how various traits tended to run in families. But all too frequently, explanations of data were clouded by pre-existing, hereditarian assumptions.
Human Behavioral Genetics
The statistical study of inherited human (physical, mental, and behavioral) differences was pioneered by Galton ( 1869 ). Although at times Galton wrote that nature and nurture were so intertwined as to be inseparable, he nevertheless devised statistical methods to separate their effects. In the 1860s and 1870s, Galton published reports purporting to show how similarities in intellect (genius, talent, character, and eminence) in European lineages appeared to be a function of degree of relatedness. Galton considered, but dismissed, environmental explanations of his data, leading him to confirm his belief that nature was stronger than nurture.
Galton also introduced the use of twin studies to tease apart the relative impact of nature versus nurture, but the twin method he used was markedly different from later twin studies used by behavioral geneticists. Galton tracked the life history of twins who were judged to be very similar or very dissimilar near birth (i.e., by nature) to test the power of various postnatal environments (nurture) that might make them more or less similar over time. Here again, Galton concluded that nature overpowers nurture.
Similar pedigree (e.g., the Kallikak study; see Zenderland, 2001 ) and twin studies appeared in the early 1900s, but the first adoption study and the modern twin method (which compares monozygotic to dizygotic twin pairs) did not appear until the 1920s (Rende, Plomin, & Vandenberg, 1990 ). These reports led to a flurry of additional work on the inheritance of mental and behavioral traits over the next decade.
Behavioral genetic research peaked in the 1930s but rapidly lost prominence due in large part to its association with the eugenics movement (spearheaded by Galton) but also because of the rise and eventual hegemony of behaviorism and the social sciences in the United States. Behavioral genetics resurged in the 1960s with the rising tide of nativism in psychology, and returned to its 1930s-level prominence in the 1970s (McGue & Gottesman, 2015 ).
The resurgence brought with a new statistical tool: the heritability statistic. The origins of heritability trace back to early attempts to synthesize Mendelian genetics with biometrics by Ronald Fisher and others. This synthesis ushered in a new field of quantitative genetics and it marked a new way of thinking about nature and nurture. The shift was to no longer think about nature and nurture as causes of traits in individuals but as causes of variation in traits between populations of individuals. Eventually, heritability came to refer to the amount of variance in a population sample that could be statistically attributed to genetic variation in that sample. Kinship (especially twin) studies provided seemingly straightforward ways of partitioning variation in population trait attributes into genetic versus environmental sources.
Into the early 21st century , hundreds of behavioral genetic studies of personality, intelligence, and psychopathology were reported. With rare exceptions, these studies converge to argue for a pervasive influence of genetics on human psychological variation.
These studies have also fueled much controversy. Citing in part behavioral genetic research, the educational psychologist Arthur Jensen ( 1969 ) claimed that the differences in intelligence and educational achievement in the United States between black and white students appeared to have a strong genetic basis. He went on to assume that because these racial differences appeared hereditary, they were likely impervious to environmental (educational) intervention. His article fanned the embers of past eugenics practices and ignited fiery responses (e.g., Hirsch, 1975 ). The ensuing debates not only spawned a rethinking of intelligence and how to measure it, but they ushered in a more critical look at the methods and assumptions of behavioral genetics.
Challenges to Behavioral Genetics
Many of the early critiques of behavioral genetics centered on interpreting the heritability statistic commonly calculated in kinship (family, twin, and adoption) studies. Perhaps more so than any other statistic, heritability has been persistently misinterpreted by academics and laypersons alike (Lerner, 2002 ). Contrary to popular belief, heritability tells us nothing about the relative impact of genetic and environmental factors on the development of traits in individuals. It deals with accounting for trait variation between people, not the causes of traits within people. As a result, a high heritability does not indicate anything about the fixity of traits or their imperviousness to environmental influence (contra Jensen), and a low heritability does not indicate an absence of genetic influence on trait development. Worse still, heritability does not even indicate anything about the role of genetics in generating the differences between people.
Other challenges to heritability focused not on its interpretation but on its underlying computational assumptions. Most notably, heritability analyses assume that genetic and environmental contributions to trait differences are independent and additive. The interaction between genetic and environmental factors were dismissed a priori in these analyses. Studies of development, however, show that no factor (genes, hormones, parenting, schooling) operates independently, making it impossible to quantify how much of a given trait in a person is due to any causal factor. Thus heritability analyses are bound to be misleading because they are based on biologically implausible and logically indefensible assumptions about development (Gottlieb, 2003 ).
Aside from heritability, kinship studies have been criticized for not being able to disentangle genetic and environmental effects on variation. It had long been known that that in family (pedigree) studies, environmental and genetic factors are confounded. Twin and adoption studies seemed to provide unique opportunities to statistically disentangle these effects, but these studies are also deeply problematic in assumptions and methodology. There are numerous plausible environmental reasons for why monozygotic twin pairs could resemble each other more than dizygotic twin pairs or why adoptive children might more closely resemble their biological than their adoptive parents (Joseph & Ratner, 2013 ).
A more recent challenge to behavioral genetics came from an unlikely source. Advances in genomic scanning in the 21st century made it possible in a single study to correlate thousands of genetic polymorphisms with variation in the psychological profiles (e.g., intelligence, memory, temperament, psychopathology) of thousands of people. These “genome-wide association” studies seemed to have the power and precision to finally identify genetic contributions to heritability at the level of single nucleotides. Yet, these studies consistently found only very small effects.
The failure to find large effects came to be known as the “missing heritability” problem (Maher, 2008 ). To account for the missing heritability, some behavioral geneticists and molecular biologists asserted that important genetic polymorphisms remain unknown, they may be too rare to detect, and/or that current studies are just not well equipped to handle gene–gene interactions. These studies were also insensitive to epigenetic profiles (see the section on Behavioral Epigenetics), which deal with differences in gene expression. Even when people share genes, they may differ in whether those genes get expressed in their lifetimes.
But genome-wide association studies faced an even more problematic issue: Many of these studies failed to replicate (Lickliter & Honeycutt, 2015 ). For those who viewed heritability analyses as biologically implausible, the small effect sizes and failures to replicate in genome-wide association studies were not that surprising. The search for independent genetic effects was bound to fail, because genes simply do not operate independently during development.
Behavioral Epigenetics
Epigenetics was a term coined in the 1940s by the developmental biologist Conrad Waddington to refer to a new field of study that would examine how genetic factors interact with local environmental conditions to bring about the embryological development of traits. By the end of the 20th century , epigenetics came to refer to the study of how nongenetic, molecular mechanisms physically regulate gene expression patterns in cells and across cell lineages. The most-studied mechanisms involve organic compounds (e.g., methyl-groups) that physically bind to DNA or the surrounding proteins that package DNA. The addition or removal of these compounds can activate or silence gene transcription. Different cell types have different, stable epigenetic markings, and these markings are recreated during cell division so that cells so marked give rise to similar types of cells. Epigenetic changes were known to occur during developmental periods of cellular differentiation (e.g., during embryogenesis), but not until 2004 was it discovered that these changes can occur at other periods in the life, including after birth (Roth, 2013 )
Of interest to psychologists were reports that different behavioral and physiological profiles (e.g., stress reactivity) of animals were associated with different epigenetic patterns in the nervous system (Moore, 2015 ). Furthermore, these different epigenetic patterns could be established or modified by environmental factors (e.g., caregiving practices, training regimes, or environmental enrichment), and, under certain conditions, they remain stable over long periods of time (from infancy to adulthood).
Because epigenetic research investigates the physical interface between genes and environment, it represents an exciting advance in understanding the interaction of nature and nurture. Despite some warnings that the excitement over behavioral epigenetic research may be premature (e.g., Miller, 2010 ), for many psychologists, epigenetics underscores how development involves both nature and nurture.
For others, what is equally exciting is the additional evidence epigenetics provides to show that the genome is an interactive and regulated system. Once viewed as the static director of development buffered from environment influence, the genome is better described as a developing resource of the cell (Moore, 2015 ). More broadly, epigenetics also points to how development is not a genetically (or biologically) predetermined affair. Instead, epigenetics provides additional evidence that development is a probabilistic process, contingent upon factors internal and external to the organism. In this sense, epigenetics is well positioned to help dissolve the nature–nurture dichotomy.
Beyond Nature–Nurture
In the final decades of the 20th century , a position was articulated to move beyond the dichotomous nature–nurture framework. The middle-ground position on nature–nurture did not seem up to the task of explaining the origins of form, and it brought about more confusion than clarity. The back-and-forth (or balanced) pendulum between nature- and nurture-based positions throughout history had only gone in circles. Moving forward would require moving beyond such dichotomous thinking (Johnston, 1987 ).
The anti-dichotomy position, referred to as the Developmentalist tradition, was expressed in a variety of systems-based, metatheoretical approaches to studying development, all of which extended the arguments against nature–nurture expressed earlier by Kuo and Lehrman. The central problem with all nativist claims according to Developmentalists is a reliance on preformationism (or predeterminism).
The problem with preformationism, they argue, besides issues of evidence, is that it is an anti-developmental mindset. It presumes the existence of the very thing(s) one wishes to explain and, consequently, discourages developmental analyses. To claim that some knowledge is innate effectively shuts down research on the developmental origins of that knowledge. After all, why look for the origins of conceptual knowledge if that knowledge is there all along? Or why search for any experiential contributions to innate behaviors if those behaviors by definition develop independently of experience? In the words of Developmentalists Thelen and Adolph ( 1992 ), nativism “leads to a static science, with no principles for understanding change or for confronting the ultimate challenge of development, the source of new forms in structure and function” (p. 378).
A commitment to maturational theory is likely one of the reasons why studies of motor development remained relatively dormant for decades following its heyday in the 1930–1940s (Thelen, 2000 ). Likewise, a commitment to maturational theory also helps explain the delay in neuroscience to examine how the brain physically changes in response to environmental conditions, a line of inquiry that only began in the 1960s.
In addition to the theoretical pitfalls of nativism, Developmentalists point to numerous studies that show how some seemingly native behaviors and innate constraints on learning are driven by the experiences of animals. For example, the comparative psychologist Gilbert Gottlieb ( 1971 ) showed that newly hatched ducklings display a naïve preference for a duck maternal call over a (similarly novel) chicken maternal call (Gottlieb, 1971 ), even when duck embryos were repeatedly exposed to the chicken call prior to hatching (Gottlieb, 1991 ). It would be easy to conclude that ducklings have an innate preference to approach their own species call and that they are biologically constrained (contraprepared) in learning a chicken call. However, Gottlieb found that the naïve preference for the duck call stemmed from exposure to the duck embryos’ own (or other) vocalizations in the days before hatching (Gottlieb, 1971 ). Exposure to these vocalizations not only made duck maternal calls more attractive, but it hindered the establishment of a preference for heterospecific calls. When duck embryos were reared in the absence of the embryonic vocalizations (by devocalizing embryos in ovo ) and exposed instead to chicken maternal calls, the newly hatched ducklings preferred chicken over duck calls (Gottlieb, 1991 ). These studies clearly showed how seemingly innate, biologically based preferences and constraints on learning derived from prenatal sensory experiences.
For Developmentalists, findings like these suggest that nativist explanations of any given behavior are statements of ignorance about how that behavior actually develops. As Kuo and Lehrman made clear, nativist terms are labels, not explanations. Although such appeals are couched in respectable, scientific language (e.g., “X is due to maturation, genes, or heredity”), they argue it would be more accurate simply to say that “We don’t know what causes X” or that “X is not due to A, B, or C.” Indeed, for Developmentalists, the more we unpack the complex dynamics about how traits develop, the less likely we are to use labels like nature or nurture (Blumberg, 2005 ).
On the other hand, Developmentalists recognize that labeling a behavior as “learned” also falls short as an explanatory construct. The empiricist position that knowledge or behavior is learned does not adequately take into account that what is learned and how easily something is learned depends on (a) the physiological and developmental status of the person, (b) the nature of the surrounding physical and social context in which learning takes place, and the (c) experiential history of the person. The empiricist tendency to say “X is learned or acquired through experience” can also short-circuit developmental analyses in the same way as nativist claims.
Still, Developmentalists appreciate that classifying behaviors can be useful. For example, the development of some behaviors may be more robust, reliably emerging across a range of environments and/or remaining relatively resistant to change, whereas others are more context-specific and malleable. Some preferences for stimuli require direct experience with those stimuli. Other preferences require less obvious (indirect) types of experiences. Likewise, it can still be useful to describe some behaviors in the ways shown in Table 1 . Developmentalists simply urge psychologists to resist the temptation to treat these behavioral classifications as implying different kinds of explanations (Johnston, 1987 ).
Rather than treat nature and nurture as separate developmental sources of causation (see Figure 1 ), Developmentalists argue that a more productive way of thinking about nature–nurture is to reframe the division as that between product and process (Lickliter & Honeycutt, 2015 ). The phenotype or structure (one’s genetic, epigenetic, anatomical, physiological, behavioral, and mental profile) of an individual at any given time can be considered one’s “nature.” “Nurture” then refers to the set of processes that generate, maintain, and transform one’s nature (Figure 2 ). These processes involve the dynamic interplay between phenotypes and environments.
Figure 2. The developmentalist alternative view of nature–nurture as product–process. Developmentalists view nature and nurture not as separate sources of causation in development (see Figure 1 ) but as a distinction between process (nurture) and product (nature).
It is hard to imagine any set of findings that will end debates about the roles of nature and nurture in human development. Why? First, more so than other assumptions about human development, the nature–nurture dichotomy is deeply entrenched in popular culture and the life sciences. Second, throughout history, the differing positions on nature and nurture were often driven by other ideological, philosophical, and sociopolitical commitments. Thus the essential source of tension in debates about nature–nurture is not as much about research agendas or evidence as about basic differences in metatheoretical positions (epistemological and ontological assumptions) about human behavior and development (Overton, 2006 ).
- Amundson, R. (2000). Embryology and evolution 1920–1960: Worlds apart? History and Philosophy of the Life Sciences , 22 , 335–352.
- Amundson, R. (2005). The changing role of the embryo in evolutionary thought: Roots of evo-devo . New York, NY: Cambridge University Press.
- Blumberg, M. S. (2005). Basic instinct: The genesis of novel behavior . New York, NY: Thunder’s Mouth Press.
- Breland, K. , & Breland, M. (1961). The misbehavior of organisms. American Psychologist , 16 , 681–684.
- Burkhardt, R. (2005). Patterns of behavior: Konrad Lorenz, Niko Tinbergen and the founding of ethology . Chicago, IL: University of Chicago Press.
- Burnham, J. C. (1972). Instinct theory and the German reaction to Weismannism. Journal of the History of Biology , 5 , 321–326.
- Carmichael, L. (1925). Heredity and environment: Are they antithetical? The Journal of Abnormal and Social Psychology , 20 (3), 245–260.
- Chomsky, N. (1959). A review of B. F. Skinner’s verbal behavior. Language , 35 , 26–57.
- Chomsky, N. (1965). Aspects of the theory of syntax . Cambridge, MA: MIT Press.
- Connolly, K. (1972). Learning and the concept of critical periods in infancy. Developmental Medicine & Child Neurology , 14 (6), 705–714.
- Cook, G. M. (1999). Neo-Lamarckian experimentalism in America: Origins and consequences. Quarterly Review of Biology , 74 , 417–437.
- Cowan, R. S. C. (2016). Commentary: Before Weismann and germplasm there was Galton and eugenics: The biological and political meaning of the inheritance of acquired characteristics in the late 19th century . International Journal of Epidemiology , 45 , 15–20.
- Cravens, H. , & Burnham, J. C. (1971). Psychology and evolutionary naturalism in American thought, 1890–1940. American Quarterly , 23 , 635–657.
- Diamond, S. (1971). Gestation of the instinct concept. History of the Behavioral Sciences , 7 (4), 323–336.
- Domjan, M. , & Galef, B. G. (1983). Biological constraints on instrumental and classical conditioning: Retrospect and prospect. Animal Learning & Behavior , 11 (2), 151–161.
- Dunlap, K. (1919). Are there any instincts? Journal of Abnormal Psychology , 14 , 307–311.
- Galton, F. (1869). Hereditary genius . London, U.K.: Macmillan.
- Garcia, J. , & Koelling, R. A. (1966). Relation of cue to consequence in avoidance learning. Psychonomics , 4 (1), 123–124.
- Gottlieb, G. (1971). Development of species identification in birds . Chicago, IL: University of Chicago Press.
- Gottlieb, G. (1991). Experiential canalization of behavioral development: Results. Developmental Psychology , 27 (1), 35–39.
- Gottlieb, G. (1992). Individual development and evolution: The genesis of novel behavior . New York, NY: Oxford University Press.
- Gottlieb, G. (2003). On making behavioral genetics truly developmental. Human Development , 46 , 337–355.
- Gould, J. L. , & Marler, P. (1987). Learning by instinct. Scientific American , 256 (1), 74–85.
- Gould, S. J. (1996). The mismeasure of man (2nd ed.). New York, NY: Norton.
- Gray, P. H. (1967). Spalding and his influence on research in developmental behavior. Journal of the History of the Behavioral Sciences , 3 , 168–179.
- Griffiths, P. E. (2008). Ethology, sociobiology, and evolutionary psychology. In S. Sarkar & A. Plutnsky (Eds.), A companion to the philosophy of biology (pp. 393–414). New York, NY: Blackwell.
- Harwood, J. (1985). Geneticists and the evolutionary synthesis in interwar Germany. Annals of Science , 42 , 279–301.
- Herrnstein, R. J. (1972). Nature as nurture: Behaviorism and the instinct doctrine. Behaviorism , 1 (1), 23–52.
- Heyes, C. (2014). False belief in infancy: A fresh look. Developmental Science , 17 (5), 647–659.
- Hirsch, J. (1975). Jensenism: The bankruptcy of “science” without scholarship. Educational Theory , 25 , 3–27.
- Hoffman, H. , & Spear, N. E. (1988). Ontogenetic differences in conditioning of an aversion to a gustatory CS with a peripheral US. Behavioral and Neural Biology , 50 , 16–23.
- Honeycutt, H. (2011). The “enduring mission” of Zing-Yang Kuo to eliminate the nature–nurture dichotomy in psychology. Developmental Psychobiology , 53 (4), 331–342.
- Jaynes, J. , & Woodward, W. (1974). In the shadow of the enlightenment. II. Reimarus and his theory of drives. Journal of the History of the Behavioral Sciences , 10 , 144–159.
- Jensen, A. (1969). How much can we boost IQ and scholastic achievement. Harvard Educational Review , 39 , 1–123.
- Johnston, T. (1981). Contrasting approaches to a theory of learning. Behavioral and Brain Sciences , 4 , 125–173.
- Johnston, T. (1987). The persistence of dichotomies in the study of behavior. Developmental Review , 7 , 149–172.
- Johnston, T. (1995). The influence of Weismann’s germ-plasm theory on the distinction between learned and innate behavior. Journal of the History of the Behavioral Sciences , 31 , 115–128.
- Jones, S. (2017). Can newborn infants imitate? Wiley Interdisciplinary Reviews: Cognitive Science , 8 , e1410.
- Joseph, J. , & Ratner, C. (2013). The fruitless search for genes in psychiatry and psychology: Time to reexamine a paradigm. In S. Krimsky & J. Gruber (Eds.), Genetic explanations: Sense and nonsense (pp. 94–106). Cambridge, MA: Harvard University Press.
- Keller, E. F. (2010). The mirage of space between nature and nurture . Durham, NC: Duke University Press.
- Koops, W. (2015). No developmental psychology without recapitulation theory . European Journal of Developmental Psychology , 12 (6), 630–639.
- Kuo, Z. Y. (1930). The genesis of the cat’s response to the rat. Journal of Comparative Psychology , 11 , 1–36.
- Lehrman, D. S. (1953). A critique of Konrad Lorenz’s theory of instinctive behavior. Quarterly Review of Biology , 28 , 337–363.
- Lerner, R. (2002). Concepts and theories of human development (3rd ed.). Mahwah, NJ: Erlbaum.
- Lickliter, R. , & Honeycutt, H. (2015). Biology, development and human systems . In W. Overton & P. C. M. Molenaar (Eds.), Handbook of child psychology and developmental science . Vol. 1: Theory and method (7th ed., pp. 162–207). Hoboken, NJ: Wiley.
- Logan, C. A. , & Johnston, T. D. (2007). Synthesis and separation in the history of “nature” and “nurture.” Developmental Psychobiology , 49 (8), 758–769.
- Loison, L. (2011). French roots of French neo-Lamarckisms,1879–1985 . Journal of the History of Biology , 44 , 713–744.
- Maher, B. (2008). Personal genomes: The case of the missing heritability . Nature , 456 , 18–21.
- McGue, M. , & Gottesman, I. I. (2015). Behavior genetics . In R. L. Cautin & S. O. Lilienfeld (Eds.), The encyclopedia of clinical psychology (Vol. 1). Chichester, U.K.: Wiley Blackwell.
- Meloni, M. (2016). The transcendence of the social: Durkheim, Weismann and the purification of sociology . Frontiers in Sociology , 1 , 1–13.
- Michel, G. F. , & Tyler, A. N. (2005). Critical period: A history of transition of questions of when, to what, to how . Developmental Psychobiology , 46 (3), 156–162.
- Miller, G. (2010).The seductive allure of behavioral epigenetics. Science , 329 (5987), 24–27.
- Moore, D. S. (2015). The developing genome. An introduction to behavioral epigenetics . New York, NY: Oxford University Press
- Morgan, C. L. (1896). Habit and instinct . New York, NY: Edward Arnold.
- Muller-Wille, S. , & Rheinberger, H.-J. (2012). A cultural history of heredity . Chicago, IL: University of Chicago Press.
- Ohman, A. , Fredrikson, M. , Hugdahl, K. , & Rimmö, P.A. (1976). The premise of equipotentiality in human classical conditioning: Conditioned electrodermal responses to potentially phobic stimuli. Journal of Experimental Psychology: General , 105 (4), 313–337.
- Overton, W. F. (2006). Developmental psychology: Philosophy, concepts, methodology. In R. Lerner (Ed.), Handbook of child psychology: Vol. 1. Theoretical models of human development (pp. 18–88). New York, NY: Wiley.
- Oyama, S. (1979). The concept of the sensitive period in developmental studies. Merrill-Palmer Quarterly , 25 (2), 83–103.
- Piaget, J. (1971). Biology and knowledge: An essay on the relation between organic regulations and cognitive processes . Chicago, IL: University of Chicago Press.
- Pinker, S. (1995). The language instinct: How the mind creates language . London, U.K.: Penguin.
- Rende, R. D. , Plomin, R. , & Vandenberg, S. G. (1990). Who discovered the twin method? Behavioral Genetics , 20 (2), 277–285.
- Renwick, C. (2011). From political economy to sociology: Francis Galton and the social-scientific origins of eugenics . British Journal for the History of Science , 44 , 343–369.
- Richards, R. J. (1987). Darwin and the emergence of evolutionary theories of mind and behavior . Chicago, IL: University of Chicago Press.
- Robinson, G. E. , & Barron, A. B. (2017). Epigenetics and the evolution of instincts. Science , 356 (6333), 26–27.
- Roth, T. L. (2013). Epigenetic mechanisms in the development of behavior: Advances, challenges, and future promises of a new field . Development and Psychopathology , 25 , 1279–1291.
- Samet, J. , & Zaitchick, D. (2017). Innateness and contemporary theories of cognition . In E. N. Zalta (Ed.), The Stanford encyclopedia of philosophy . Stanford, CA: Stanford University.
- Segerstrale, U. (2000). Defenders of the truth: The battle for science in the sociobiology debate and beyond . New York, NY: Oxford University Press.
- Simion, F. , & Di Giorgio, E. (2015). Face perception and processing in early infancy: Inborn predispositions and developmental changes . Frontiers in Psychology , 6 , 969.
- Simpson, T. , Carruthers, P. , Laurence, S. , & Stich, S. (2005). Introduction: Nativism past and present . In P. Carruthers , S. Laurence , & S. Stich (Eds.), The innate mind: Structure and contents (pp. 3–19). New York, NY: Oxford University Press.
- Spelke, E. , & Kinzler, K. D. (2007). Core knowledge . Developmental Science , 10 (1), 89–96.
- Spencer, J. P. , Samuelson, L. K. , Blumberg, M. S. , McMurray, R. , Robinson, S. R. , & Tomblin, J. B. (2009). Seeing the world through a third eye: Developmental systems theory looks beyond the nativist-empiricist debate. Child Development Perspectives , 3 , 103–105.
- Thelen, E. (2000). Motor development as foundation and future of developmental psychology. International Journal of Behavioral Development , 24 (4), 385–397.
- Thelen, E. , & Adolph, K. E. (1992). Arnold L. Gesell: The paradox of nature and nurture. Developmental Psychology , 28 (3), 368–380.
- Tinbergen, N. (1963). On the aims and methods of ethology. Zeitschrift für Tierpsychologie , 20 , 410–433.
- Tomasello, M. T. (1995). Language is not an instinct. Cognitive Development , 10 , 131–156.
- Winther, R. G. (2001). Weismann on germ-plasm variation. Journal of the History of Biology , 34 , 517–555.
- Witty, P. A. , & Lehman, H. C. (1933). The instinct hypothesis versus the maturation hypothesis. Psychological Review , 40 (1), 33–59.
- Wyman, R. J. (2005). Experimental analysis of nature–nurture. Journal of Experimental Zoology , 303 , 415–421.
- Zenderland, L. (2001). Measuring minds. Henry Herbert Goddard and the origins of American intelligence testing . New York, NY: Cambridge University Press.
Printed from Oxford Research Encyclopedias, Psychology. Under the terms of the licence agreement, an individual user may print out a single article for personal use (for details see Privacy Policy and Legal Notice).
date: 04 April 2024
- Cookie Policy
- Privacy Policy
- Legal Notice
- Accessibility
- [66.249.64.20|195.158.225.244]
- 195.158.225.244
Character limit 500 /500

Nature vs. Nurture
Reviewed by Psychology Today Staff
The expression “nature vs. nurture” describes the question of how much a person's characteristics are formed by either “nature” or “nurture.” “Nature” means innate biological factors (namely genetics ), while “nurture” can refer to upbringing or life experience more generally.
Traditionally, “nature vs. nurture” has been framed as a debate between those who argue for the dominance of one source of influence or the other, but contemporary experts acknowledge that both “nature” and “nurture” play a role in psychological development and interact in complex ways.
- The Meaning of Nature vs. Nurture
- The Nature-vs.-Nurture Debate
- Identifying Genetic and Environmental Factors

The wording of the phrase “nature vs. nurture” makes it seem as though human individuality— personality traits, intelligence , preferences, and other characteristics—must be based on either the genes people are born with or the environment in which they grew up. The reality, as scientists have shown, is more complicated, and both these and other factors can help account for the many ways in which individuals differ from each other.
The words “nature” and “nurture” themselves can be misleading. Today, “ genetics ” and “environment” are frequently used in their place—with one’s environment including a broader range of experiences than just the nurturing received from parents or caregivers. Further, nature and nurture (or genetics and environment) do not simply compete to influence a person, but often interact with each other; “nature and nurture” work together. Finally, individual differences do not entirely come down to a person’s genetic code or developmental environment—to some extent, they emerge due to messiness in the process of development as well.
A person’s biological nature can affect a person’s experience of the environment. For example, a person with a genetic disposition toward a particular trait, such as aggressiveness, may be more likely to have particular life experiences (including, perhaps, receiving negative reactions from parents or others). Or, a person who grows up with an inclination toward warmth and sociability may seek out and elicit more positive social responses from peers. These life experiences could, in turn, reinforce an individual’s initial tendencies. Nurture or life experience more generally may also modify the effects of nature—for example, by expanding or limiting the extent to which a naturally bright child receives encouragement, access to quality education , and opportunities for achievement.
Epigenetics—the science of modifications in how genes are expressed— illustrates the complex interplay between “nature” and “nurture.” An individual’s environment, including factors such as early-life adversity, may result in changes in the way that parts of a person’s genetic code are “read.” While these epigenetic changes do not override the important influence of genes in general, they do constitute additional ways in which that influence is filtered through “nurture” or the environment.

Theorists and researchers have long battled over whether individual traits and abilities are inborn or are instead forged by experiences after birth. The debate has had broad implications: The real or perceived sources of a person’s strengths and vulnerabilities matter for fields such as education, philosophy , psychiatry , and clinical psychology. Today’s consensus—that individual differences result from a combination of inherited and non-genetic factors—strikes a more nuanced middle path between nature- or nurture-focused extremes.
The debate about nature and nurture has roots that stretch back at least thousands of years, to Ancient Greek theorizing about the causes of personality. During the modern era, theories emphasizing the role of either learning and experience or biological nature have risen and fallen in prominence—with genetics gaining increasing acknowledgment as an important (though not exclusive) influence on individual differences in the later 20th century and beyond.
“Nature versus nurture” was used by English scientist Francis Galton. In 1874, he published the book English Men of Science: Their Nature and Nurture , arguing that inherited factors were responsible for intelligence and other characteristics.
Genetic determinism emphasizes the importance of an individual’s nature in development. It is the view that genetics is largely or totally responsible for an individual’s psychological characteristics and behavior. The term “biological determinism” is often used synonymously.
The blank slate (or “tabula rasa”) view of the mind emphasizes the importance of nurture and the environment. Notably described by English philosopher John Locke in the 1600s, it proposed that individuals are born with a mind like an unmarked chalkboard and that its contents are based on experience and learning. In the 20th century, major branches of psychology proposed a primary role for nurture and experience , rather than nature, in development, including Freudian psychoanalysis and behaviorism.

Modern scientific methods have allowed researchers to advance further in understanding the complex relationships between genetics, life experience, and psychological characteristics, including mental health conditions and personality traits. Overall, the findings of contemporary studies underscore that with some exceptions—such as rare diseases caused by mutations in a single gene—no one factor, genetic or environmental, solely determines how a characteristic develops.
Scientists use multiple approaches to estimate how important genetics are for any given trait, but one of the most influential is the twin study. While identical (or monozygotic) twins share the same genetic code, fraternal (or dizygotic) twins share about 50 percent of the same genes, like typical siblings. Scientists are able to estimate the degree to which the variation in a particular trait, like extraversion , is explained by genetics in part by analyzing how similar identical twins are on that trait, compared to fraternal twins. ( These studies do have limitations, and estimates based on one population may not closely reflect all other populations.)
It’s hard to call either “nature” or “nurture,” genes or the environment, more important to human psychology. The impact of one set of factors or the other depends on the characteristic, with some being more strongly related to one’s genes —for instance, autism appears to be more heritable than depression . But in general, psychological traits are shaped by a balance of interacting genetic and non-genetic influences.
Both genes and environmental factors can contribute to a person developing mental illness. Research finds that a major part of the variation in the risk for psychiatric conditions such as autism spectrum disorder, anxiety disorders, depression, and schizophrenia can be attributed to genetic differences. But not all of that risk is genetic, and life experiences, such as early-life abuse or neglect, may also affect risk of mental illness (and some individuals, based on their genetics, are likely more susceptible to environmental effects than others).
Like other psychological characteristics, personality is partly heritable. Research suggests less than half of the difference between people on measures of personality traits can be attributed to genes (one recent overall estimate is 40 percent). Non-genetic factors appear to be responsible for an equal or greater portion of personality differences between individuals. Some theorize that the social roles people adopt and invest in as they mature are among the more important non-genetic factors in personality development.

How do we make sense of new experiences? Ultimately, it's about how we categorize them—which we often do by "lumping" or "splitting" them.

How are twin studies used to answer questions related to the nature-and-nurture debate?

All I ask of strangers in the store—don't judge me as being less competent because my hair is grey and my skin well-textured. I’m just out doing my best, as we all are.

The new Biophilia Reactivity Hypothesis argues our attraction to the natural world is not an instinct but a measurable temperament trait.

A Personal Perspective: How can Adam Grant's newest book help OCD sufferers? In more ways than you think.

Do selfish genes mean that humans are designed to be selfish?

Are classical musicians more "craft" and jazz musicians more "creative"? A question for debate.
Where all beliefs and behavior come from.
Many people will outlive their money because of not saving for the future. Sadly, many people are also going to run out of health before they run out of life. Here's how not to.

Our cultures shape us in profound ways. The latest research from cultural psychology offers fascinating insights into the nature-nurture interaction.
- Find Counselling
- Find Online Therapy
- Bukit Merah
- Choa Chu Kang
- Downtown Core
- Jurong West
- Asperger's
- Bipolar Disorder
- Chronic Pain
- Eating Disorders
- Passive Aggression
- Personality
- Goal Setting
- Positive Psychology
- Stopping Smoking
- Low Sexual Desire
- Relationships
- Child Development
- Therapy Center NEW
- Diagnosis Dictionary
- Types of Therapy

Understanding what emotional intelligence looks like and the steps needed to improve it could light a path to a more emotionally adept world.
- Coronavirus Disease 2019
- Affective Forecasting
- Neuroscience

Nature vs Nurture: Genes or Environment
Categories Development
Sharing is caring!
The nature versus nurture debate focuses on the question of whether genetic or environmental factors matter most in the course of human development.
What is it that makes you who you are? Some might say that it is your genes that have the greatest influence in controlling your personality and preferences. Others might say that it is your environment and the unique experiences you have had over the course of your life that have a greater role.
In this article, learn more about the nature vs. nurture debate and what research has found about the contributions of genetic and environmental factors.
What Is the Nature vs Nurture Debate?
The nature vs. nurture debate is often described as one of the big philosophical and scientific questions facing psychologists. So what exactly does this debate mean? Why is it important for understanding the human mind and behavior?
Let’s start by learning more about each of these factors.
- Nature: This side of the debate argues that genes have the greatest influence over who we are, from the way we look to the way we behave. Genes determine physical traits such as height, eye color, hair color, and face shape, but they can also contribute to other attributes such as your personality traits and cognitive abilities.
- Nurture: This side of the debate argues that environmental variables such as how we were raised, individual experience, and other social relationships play a more important role. Your upbringing, your early social interactions, school, and peers all play a role in shaping who you are and how you behave.
Let’s consider an example. If a student excels at math, is it because they inherited that ability from their parents or is it because they work hard to learn the subject?
Nature would suggest that they do well because they are genetically inclined to do so, while nature argues that their talent stems from their upbringing and educational background.
History of Nature vs. Nurture
The debate over nature and nurture predates psychology and goes back to the days of the ancient philosophers. In philosophy, this is often referred to as the nativism versus empiricism debate. What do these two terms mean and how do they relate to nature and nurture.
The nativist approach suggests that inheritance plays the greatest role in determining characteristics. Nativism proposes that people’s characteristics, both physical and mental, are innate. These are things that are passed down genetically from our ancestors. The nativist approach essentially espouses the nature side of the argument.
Noam Chomsky’s theory of language acquisition is one of the best-known examples of nativism in psychology. Chomsky suggested that language develops as a result of an innate language acquisition device. He believed that people are able to learn language because they have an innate, hard-wired capacity for what he referred to as universal grammar.
Empiricism represents the nurture side of the debate. The empiricist approach suggests that all learning is the result of experience and environmental factors.
The philosopher John Locke took an empiricist approach and proposed a concept known as tabula rasa, which means “blank slate.” This approach that the mind is essentially that —a blank slate—and that it is through learning and experience that all knowledge, skill, and behavioral patterns are acquired.
Behaviorism is one example of an empirical approach to understanding human behavior. Behaviorists such as John B. Watson and B.F. Skinner believed that all human behavior was the result of conditioning, either classical (associative) or operant ( reinforcement and punishment ).
Watson was famously known for proclaiming that he could train anyone to be anything using the principles of conditioning, regardless of that individual’s genetics and background.
Approaches to Psychology
While few contemporary psychologists take an extreme, hard-lined empiricist or nativist approach, different branches of psychology do sometimes tend to emphasize one influence over the other.
Biological Psychology
Biological psychology, for example, tends to focus more on the nature side of the debate. This area of psychology focuses on how biological factors influence human behavior, so things such as the brain, neurons, and neurotransmitters are of greater interest than external factors.
Behavioral Psychology
Behavioral psychology tends to take the nurture side of the debate, focusing on how environmental factors and learned associations contribute to how people think and act.
Health Psychology
Health psychology is an example of an approach that tends to lie somewhere in the middle. Health psychologists are focused on understanding how both biological and environmental factors contribute and interact to affect an individual’s health.
Examples of Nature vs. Nurture
Looking at examples can be helpful to understand why the nature vs nurture debate has been so crucial throughout psychology’s history. The topic is not just an important philosophical debate. It has been critical for understanding what factors influence different aspects of human behavior and has been the source of considerable controversy at times.
Consider the long debate over the factors that influence intelligence. Those on the nature side of the debate suggest that the greatest influence on IQ is inheritance. Some early thinkers such as Francis Galton believed that intelligence could largely be attributed to genetic factors.
Such views have been used to justify discriminatory social policies and attitudes. When some research suggested that some groups of people had lower IQ scores, for example, some researchers interpreted such results to suggest that these individuals scored lower as a result of genetics.
Those taking the nurture side of the debate point out that other factors such as biased test construction, racism, and systemic discrimination impacting educational access and quality play a more important role.
Inequality, discrimination, and lack of access play a role in shaping how well people perform on intelligence tests and other assessments of educational outcomes.
Gender Differences and Education
Sex differences in school performance and attainment is another area where the debate between the contributions of nature vs nurture comes into play. Girls often perform better on verbal tests but less well on math. As they advance in school, girls also become less likely to enter STEM courses and STEM fields.
Those taking a nature perspective might suggest that girls are inherently less capable in these subjects. Nature advocates, however, would point out that social variables including gender stereotypes and discrimination have a greater influence.
Many researchers today believe that human behavior is influenced by both nature and nurture, and that it is often the interaction of the two variables that is even more important.
Impact of the Nature and Nurture Debate
Few modern psychologists would take an extreme nature or nurture position. Rather than asking which one controls specific variables, researchers are more likely to wonder about the degree to which each of these forces plays a role. So what exactly are the relative contributions of nature and nurture?
According to the research, the answer is about 50/50. Researchers collected the results of nearly every twin study conducted over the last half-century. Doing this allowed them to determine which factors played a role in determining certain characteristics.
Twin studies examine similarities and differences by looking at twins who are either raised together or raised apart. This allows researchers to determine the impact of genes versus the environment.
Researchers analyzed more than 2,700 twin studies involving a whopping 14.5 million pairs of twins from 39 different countries and discovered that genes and environment share a roughly equal role in determining who we are.
Variations in personality traits and disease were determined to be 49% due to genetics and 51% due to environment.
One important thing to note is that while the research suggests a 50/50 split, the findings did reveal that genes do play a greater role in the risk of certain diseases. Bipolar disorder, for example, was found to be approximately 70% heritable.
How Nature and Nurture Interact
Today, many experts suggest that we should be more concerned with how nature and nurture interact to determine how we develop. We might be genetically inclined toward a certain trait, for example, but our experiences can determine to what degree that trait is expressed.
Height is a good example of how genes and the environment can interact to make you who you are. Even if you inherit genes for tallness, proper nourishment is important for reaching that height. Kids who come from tall families might not become tall if they do not receive proper nutrition during their childhood.
So while we know that both factors are equally important, the question we are left to ponder is just how much of a role each factor plays in the development of certain characteristics. As the research suggests, some diseases are more strongly linked to genetics than to the environment.
As researchers continue to explore how nature and nurture interact, we will continue to gain a deeper understanding of the factors that contribute to who we are.
Haworth CM, Davis OS, Plomin R. Twins Early Development Study (TEDS): a genetically sensitive investigation of cognitive and behavioral development from childhood to young adulthood . Twin Res Hum Genet . 2013;16(1):117-125. doi:10.1017/thg.2012.91
This page has been archived and is no longer updated

The Tangle of the Nature-Nurture Debate


Email your Friend

- May 27, 2015 Fish Skin Band-Aids: a natural way to speed wou...
- March 19, 2014 Do “Smart Pills” Really Make You Sm...
- February 24, 2014 The Invasive Species Wriggling Beneath Your Feet
- December 09, 2013 Getting the Straight Dope on Weed
- October 07, 2013 The Delta Fingerprint: Anthropogenic Climate Ch...
- September 30, 2013 Keep It Simple Students: Mapping the Biological...
- September 25, 2013 Keep It Simple Students: How You Were Copied
- September 19, 2013 Keep It Simple Students: Camouflage
- September 04, 2013 Nietzsche's Butterfly: An Introduction to Chaos...
- August 23, 2013 Obituary: Kepler Spacecraft “Planet Hunte...
- July 26, 2013 The Poets of Starlight
- July 10, 2013 Socks, the Doctor and the End of the Universe
- June 18, 2013 Poo Transplants: Sniffing Out the Story
- May 23, 2013 We’re Launching Ten New Blogs and One New...
- May 16, 2013 Misophonia: Enraged by Everyday Sounds
- May 14, 2013 Male Black Widows Sniff Out Femme Fatales
- May 13, 2013 The Science of Earth and the Human Policies tha...
- May 08, 2013 Dream Catcher: The Neuroscience Behind Decoding...
- February 04, 2013 If Your Head Is In the Clouds At Least It Won't...
- October 11, 2012 The Foundation of Cosmetics
- October 05, 2012 #30DayGreen Day 19: Synthetic Meat
- September 28, 2012 #30DayGreen Day 12: Hard Times
- September 24, 2012 #30DayGreen Day 8: Green Bathroom
- September 23, 2012 #30DayGreen Day 5: Recycling Right
- September 20, 2012 #30DayGreen Day 3: Carnivores
- September 20, 2012 The Designer's Detritus: ENCODE, Junk DNA, and ...
- September 19, 2012 #30DayGreen Day 2. Talking Rubbish: The Indian ...
- September 17, 2012 30 Days of Green: Day 1
- September 10, 2012 #30DayGreen: A Scitable Recycling Challenge
- August 30, 2012 How We Represent Risk Isn't Helping Medical Scr...
- August 21, 2012 An Ecology of Houses
- August 10, 2012 Occupy ALOHA 2012: A tribute to Bob Dylan
- August 01, 2012 Once upon a time: The possible story of viruses
- July 26, 2012 Skepticism And The Second Enlightenment
- July 19, 2012 Of (misplaced) Pride and (everlasting) Prejudice
- July 13, 2012 How About That Cup Of Coffee?
- July 10, 2012 The Great “Detox” Deception
- July 08, 2012 Painless Injections
- June 29, 2012 Why walk when you can jump?
- June 21, 2012 To be or not to be good science
- June 12, 2012 Cell Phones and Health Hazards: Mythbusting in ...
- June 04, 2012 What Statistics Can Teach Us About History (and...
- June 01, 2012 I'm not a speciesist, but...
- May 07, 2012 How Whales Fly?
- April 28, 2012 A Case for Oral Contraceptives
- March 17, 2012 Managing views and expectations in science
- March 05, 2012 A Peek on “Lenses on Biology”
- February 23, 2012 The messenger goddess of exercise
- February 01, 2012 Preparing for the pandemic
- December 16, 2011 Veggie Tales and the Environment
- November 28, 2011 Do Our Brains Determine Our Facebook Friend Count?
- November 28, 2011 Flying Frogs
- November 09, 2011 A Closer Look at Quantum Levitation
- October 26, 2011 Shortcuts for supercentenarians
- October 05, 2011 Reconstructing the Mind's Eye
- October 03, 2011 Peptic Ulcers and a Nobel Prize
- September 15, 2011 Genetic Algorithms: Harnessing Natural Selection
- September 10, 2011 Spore Ballistics
- September 04, 2011 Chasing Earthquakes
- September 02, 2011 Earthquakes and Social Media
- August 23, 2011 Artificial Photosynthesis: Adapting Nature̵...
- August 21, 2011 Butterflies Prevent Forgery?
- August 09, 2011 Fluid Dynamics from Felis catus
- August 08, 2011 Keeping Cool with Biomimicry
- August 04, 2011 The Age of Mind-Controlled Computers
- August 04, 2011 In athletics, a technological arms race
- July 12, 2011 Getting in Shape to Go into Space
- July 08, 2011 Of Biomimicry and Learning From Ants
- July 07, 2011 Of Love Handles and Losing Weight
- June 27, 2011 Guest Post: Synthetic Biology Gets More Digital
- June 24, 2011 Inspirational Research Has Re-opened My Eyes
- June 17, 2011 Smelly Hangups for Mosquitoes... and Bedbugs?
- June 10, 2011 To Use or Not to Use: Cellphones and Health
- June 09, 2011 Nutrition Guidelines: From Pyramid to ‘Pi...
- June 02, 2011 Gas Hub Threatens Dinosaur Footprints
- May 26, 2011 An X-Ray of the Sky
- May 16, 2011 What Google's Chromebook Means To Education
- April 26, 2011 Richard Branson: Noble Conservationist or Meddl...
- April 21, 2011 New Particle Could Signal End of Standard Model
- April 12, 2011 Melbourne Says No to Medical Research Funding Cuts
- March 31, 2011 Some Like It Very, Very Hot
- March 29, 2011 Big Crayfish Could Be Key to Population Stability
- March 24, 2011 Left-Hand Man
- March 22, 2011 The Unchanging Face of Drug Discovery
- March 17, 2011 The Rise and Fall of Helium
- March 16, 2011 The Sound of Epigenetics
- March 15, 2011 The False Dichotomy Of the Nature-Nurture Debate
- March 10, 2011 The Tangle of the Nature-Nurture Debate
- March 08, 2011 Rave Culture: Correlation Doesn't Equal Causation
- March 03, 2011 The End of the Shuttle Era
- March 01, 2011 The Cocaine Vaccine
- February 15, 2011 Engineering Solar Bacteria
- February 10, 2011 The Importance of Translation
- February 08, 2011 Guest Post: The World Through Wired Eyes
- February 03, 2011 Earth Calling Space
- January 28, 2011 Pandas Need More Than Just Shoots and Leaves
- January 25, 2011 Blaming Ourselves
- January 20, 2011 Still Don't Drink the Water?
- January 18, 2011 The Forgotten Fathers
- January 11, 2011 Not Mentally Crazy
- January 04, 2011 Storytime
- December 28, 2010 Artificial Human Ovary
- December 21, 2010 The Debate Around IVF
- December 17, 2010 Guest Post: Engineering the Science of Today
- December 14, 2010 Such Great Heights
- December 07, 2010 Pregnant While Already Pregnant
- December 03, 2010 Barcoding Guts
- November 30, 2010 Genomic Sequencing and Information Bottleneck
- November 25, 2010 An Interview with Melinda Wenner Moyer
- November 22, 2010 Guest Post: A Year in Neuroscience
- November 18, 2010 Lessons from the Dam
- November 16, 2010 An Interview with Ferris Jabr
- November 11, 2010 The Architecture of Choice
- November 09, 2010 Guest Post: Learning from the Luminaries
- November 04, 2010 Cracking the Turing Test
- November 02, 2010 Can miRNA Cure Cocaine Addiction?
- October 28, 2010 If You're Reading This, You're Probably Weird
- October 26, 2010 Lindau Meetings: Hamilton Smith on Miniature Ro...
- October 26, 2010 Lindau Meetings: Francoise Barre-Sinoussi on th...
- October 20, 2010 World Statistics Day
- October 15, 2010 The Golgi Apparatus
- October 12, 2010 Lindau Meetings: Jack Szostak on the Origin of ...
- October 07, 2010 Mighty Mitochondria
- October 04, 2010 Lindau Meetings: Tim Hunt on Systems Biology
- October 01, 2010 A Long Wait in the Que
- September 27, 2010 My ER Play
- September 21, 2010 Cell Bio at Scitable is Coming!
- September 10, 2010 Stem Cells, Please?
- August 30, 2010 An Eye for an Eye?
- August 24, 2010 Under the Scalpel
- August 18, 2010 Color and Depression in the Eye of the Beholder
- August 10, 2010 Guest Post: If You Build It, They Will Come
- August 06, 2010 Guest Post: Assessing the Risks of Personal Gen...
- August 05, 2010 Guest Post: The Limits of Science in Medicine a...
- August 04, 2010 Guest Post: Introduction to Terry
- July 30, 2010 A Whiff of Bee Evolution
- July 27, 2010 Naturally Obsessed: The Making of a Scientist
- July 15, 2010 When We Share Ideas, We All Get More
- July 13, 2010 Bee Happy?
- July 02, 2010 Of Exams and World Cup
- June 23, 2010 Summer Science Fiction
- June 14, 2010 The Colorful Life of the Rainbow Eucalyptus
- June 07, 2010 Oil and Water
- June 04, 2010 A Science Student's Typical Day: Colombian Edition
- May 24, 2010 The Art of the Sloth
- May 21, 2010 Synthetic Life and Other News
- May 17, 2010 Guest Post: Scary Diseases Part 3
- May 07, 2010 Guest Post: Matt Schiller of the AMSJ
- April 29, 2010 Get Contaminated
- April 22, 2010 Learning without Brains?
- April 15, 2010 Goes Down the Drain
- April 08, 2010 Don't Drink The Water?
- April 06, 2010 Deciphering Water
- March 31, 2010 The Water Series
- March 29, 2010 Predicting Upsets
- March 25, 2010 Miraculous Miraculin
- March 16, 2010 3.14159 . . . Day
- March 12, 2010 Working "5 to 9"
- March 05, 2010 The Mathematics and Neurology of Wonderland
- February 26, 2010 Whitney's Favorite Links
- February 23, 2010 Khalil's Favorite Links
- February 19, 2010 Justine's Favorite Links
- February 16, 2010 Tara's Favorite Links
- February 12, 2010 Film and Flora
- February 08, 2010 Are We Friends with Them?
- February 01, 2010 Of Gorgeous Sceneries and Giant Lizards
- January 25, 2010 R2D2 Go; 3D2 Stay?
- January 20, 2010 Avatar : Power in Surrender
- January 20, 2010 Avatar in Review
- January 11, 2010 Prize Fight
- January 08, 2010 Copenhagen: Far from the End
- January 07, 2010 Getting It Write
- December 30, 2009 What Would Jesus Do?
- December 21, 2009 Finals: The Real Grinch
- December 14, 2009 Let It Snow
- December 07, 2009 The Mouse Is Mightier, or Is It?
- November 30, 2009 Chemistry Magic
- November 24, 2009 Stupak, or a Step Back?
- November 04, 2009 Creative science photography
- October 29, 2009 Pre-med Don't Ask, Dont Tell
- October 27, 2009 Memorizing techniques from around the world
- October 22, 2009 How to Make a Scitable Classroom
- October 15, 2009 An Interview with Nobel Prize Winner Dr. Carol ...
- October 14, 2009 Songs for a New Age
- October 13, 2009 An Interview with Jorge Cham
- October 06, 2009 Three's Company: A Trio of Americans Wins the N...
- September 30, 2009 Scary diseases Part 2: Fatal Familial Insomnia ...
- September 23, 2009 A New Perspective on Vision
- September 22, 2009 “I See,” Said the Color Blind Man
- August 25, 2009 A typical day of a Science Student in Malaysia
- August 20, 2009 The Write Choice
- August 19, 2009 Scary Diseases Part I: PAM
- August 18, 2009 Chasing the Red Queen in Academia
- August 11, 2009 Debunking Biofuels (or not): Part 3
- August 04, 2009 Debunking Biofuels: Part 2
- July 31, 2009 Patience with Patients
- July 29, 2009 iEureka
- July 23, 2009 Debunking Biofuels: Part I
- July 22, 2009 Brain Games: Part II
- July 15, 2009 Genetics Fail
- July 14, 2009 Undoing pollution with plants
- July 13, 2009 Sofasaurus Rex: King of the Prehistoric Jungle
- July 09, 2009 Pass me that cheeseburger -- and a shake!
- July 07, 2009 Brain Games: Part I
- July 06, 2009 The toxic underbelly of green lightbulbs
- June 29, 2009 To Drink or Not to Drink? First, Ask the Right ...
- June 26, 2009 A Squid Named Ishmael
- June 25, 2009 Nanoparticle Concerns Getting Under Your Skin?
- June 25, 2009 E pluribus unum: out of many, one
- June 11, 2009 A twisted tango: the falsification of research ...
- May 28, 2009 Of mice and men: recent developments in the fie...
- May 26, 2009 Nonprofit harnesses business strategy to cure d...
- May 26, 2009 One reason for decreased cancer incidence among...
- May 21, 2009 Sticky situation reveals part of our evolutiona...
- May 21, 2009 Fractions of a second can ruin a well-developed...
- May 18, 2009 Blood cells in the right place at the right time
- May 15, 2009 America, where the streets are paved with therm...
- May 14, 2009 We got the beat! (and so do they.)
- May 13, 2009 Milk: it does some bodies good
- May 12, 2009 When marketing campaigns direct scientific rese...
- May 08, 2009 Don’t count your chickens before they hat...
- May 06, 2009 In search of a one-track mind
- May 01, 2009 Botox for the brain
- April 28, 2009 Some flu facts in the midst of a media frenzy
- April 08, 2009 Are sharp teeth necessary to survive the rat race?
- April 07, 2009 Fighter or forager? It depends on a brain gene.
- April 06, 2009 Ants change the rules of an evolutionary arms race
- April 02, 2009 Gender ratios around the globe
- April 01, 2009 Pheromones: the key ingredient missing from on-...
- March 31, 2009 The physiology of scaling Mt. Everest
- March 30, 2009 Three's company: symbiosis, drug discovery, and...
- March 27, 2009 Attack of the supermodel tomatoes
- March 26, 2009 The genetics of achondroplasia
- March 25, 2009 X-chromosome inactivation in the calico cat
- March 24, 2009 Freedom, liberty and fraternity
- March 23, 2009 The drought faced by science education in Calif...
- March 20, 2009 Natural rainbow gene expression
- March 19, 2009 I've got the horse right here, his name is Paul...
- March 18, 2009 Taking the next step: facilitating the process ...
- March 17, 2009 The elusive gentleman scientist
- March 16, 2009 Champagne supernova: when the interests of Holl...
- March 16, 2009 Chimeras: the perfect experiment
- March 13, 2009 A really expensive Band-Aid
- March 13, 2009 Science: today's guild system
© 2014 Nature Education
- Press Room |
- Terms of Use |
- Privacy Notice |


- school Campus Bookshelves
- menu_book Bookshelves
- perm_media Learning Objects
- login Login
- how_to_reg Request Instructor Account
- hub Instructor Commons
- Download Page (PDF)
- Download Full Book (PDF)
- Periodic Table
- Physics Constants
- Scientific Calculator
- Reference & Cite
- Tools expand_more
- Readability
selected template will load here
This action is not available.

4.1B: Nature vs. Nurture- A False Debate
- Last updated
- Save as PDF
- Page ID 7962
Is nature (an individual’s innate qualities) or nurture (personal experience) more important in determining physical and behavioral traits?
Learning Objectives
- Discuss both sides of the nature versus nurture debate, understanding the implications of each
- Nature refers to innate qualities like human nature or genetics.
- Nurture refers to care given to children by parents or, more broadly, to environmental influences such as media and marketing.
- The nature versus nurture debate raises philosophical questions about determinism and free will.
- nurture : The environmental influences that contribute to the development of an individual; see also nature.
- nature : The innate characteristics of a thing. What something will tend by its own constitution, to be or do. Distinct from what might be expected or intended.
- determinism : The doctrine that all actions are determined by the current state and immutable laws of the universe, with no possibility of choice.
The nature versus nurture debate rages over whether an individual’s innate qualities or personal experiences are more important in determining physical and behavioral traits.
In the social and political sciences, the nature versus nurture debate may be compared with the structure versus agency debate, a similar discussion over whether social structure or individual agency (choice or free will) is more important for determining individual and social outcomes.

Historically, the “nurture” in the nature versus nurture debate has referred to the care parents give to children. But today, the concept of nurture has expanded to refer to any environmental factor – which may arise from prenatal, parental, extended family, or peer experiences, or even from media, marketing, and socioeconomic status. Environmental factors could begin to influence development even before it begins: a substantial amount of individual variation might be traced back to environmental influences that affect prenatal development.
The “nature” in the nature versus nurture debate generally refers to innate qualities. In historical terms, nature might refer to human nature or the soul. In modern scientific terms, it may refer to genetic makeup and biological traits. For example, researchers have long studied twins to determine the influence of biology on personality traits. These studies have revealed that twins, raised separately, still share many common personality traits, lending credibility to the nature side of the debate. However, sample sizes are usually small, so generalization of the results must be done with caution.
The nature versus nurture debate conjures deep philosophical questions about free will and determinism. The “nature” side may be criticized for implying that we behave in ways in which we are naturally inclined, rather than in ways we choose. Similarly, the “nurture” side may be criticized for implying that we behave in ways determined by our environment, not ourselves.
Of course, sociologists point out that our environment is, at least in part, a social creation.
ReviseSociology
A level sociology revision – education, families, research methods, crime and deviance and more!
Nature and Nurture Explanations of Human Behaviour
Nature = biology explains behaviour, Nurture = social factors explains human behaviour.
Table of Contents
Last Updated on June 5, 2023 by Karl Thompson
Nature explanations argue that biological inheritance and genetics determine human behaviour; nurture explanations argue that society, culture and social processes such as socialisation explain human behaviour.
While not denying the role of biology in explaining some aspects of human behaviour, sociology very much emphasises the role of society (nurture) rather than nature in explaining human action. The material below forms part of lesson one of an eight lesson introduction to Sociology.

Nature Explanations of Behaviour
In Sociology, we are looking at human behaviour. Human behaviour is the term we use that refers to all of the things that people do. There are many ways of explaining why certain people do things in particular ways.
Some biologists and psychologists think that people behave as they do because they are animals who primarily act according to their instincts. This is known as the “nature theory” of human behaviour. Other scientists and psychologists are researching whether our behaviour is “genetic” i.e. certain types of behaviour are passed down from parent to child. Again, this is a nature theory of human behaviour because it supports the belief that our behaviour is pre-programmed to a large extent. For example, it has been debated whether there is a criminal gene which means some people are more likely to commit crime.
Nurture explanations of behaviour
Nurture arguments focus on the way people are brought up and how their environment moulds their personality and behaviour. Sociologists argue that some people are brought up to be kind and caring, and others are brought up to display very different forms of behaviour.
An individual’s personality and identify are moulded and developed in response to their social environments and the people they meet. They are by taught others around them telling them what is right and wrong, including teachers, siblings and most importantly parents. This is why sociologists study the family and education (the two topics on the AS course) amongst other topics because it allows to investigate how these institutions effect human behaviour.
Nurture explains more than nature
We have two different ways of explaining human behaviour. One uses nature to explain behaviour, the other uses nurture. The question is, which is the best explanation?
If you explain human behaviour as being the same as animal behaviour, that means that humans would all behave in the same way. French cats behave in the same way as British cats. Do British people behave like French people? People in Britain do tend to behave in a similar way. They do similar things and wear certain types of clothing. Do all people all over the world behave in the same way? Sociologists tend to say ‘no’ and use two main types of evidence to prove the point:
- historical comparative evidence
- Anthropological (cross cultural) comparative evidence.
Historical Evidence against Nature theories
Nature arguments suggest human behaviour isn’t dissimilar to animal behaviour, which is based on automatic responses and pre-determined modes of behaviour or that our behaviour is pre-determined by our genes. However, human behaviour has changed significantly throughout history whilst animal behaviour has changed only slightly over a very long period of time. This suggests humans interact with their environments in a unique manner, both moulding and being moulded by it.

Anthropological Evidence against Nature theories
The second argument uses anthropological evidence. Anthropologists are people who study and compare societies from all over the world. If our behaviour was in our genes then people all around the world would behave in the same way. This is because other than the external physical difference between humans, the actual biological difference between people from different parts of the world is tiny. However, anthropologists show that people behave differently in different societies.

Further evidence against nature theories
The Analaysis podcast below demonstrates the importance of nurture over nature explanations of human action…
“ I should be a psychopath, but I’m not?” 5:30 – 11:44 http://www.bbc.co.uk/programmes/b010mcl1 (2011)
What was the pattern in the professor’s family history? What genetic pattern did the professor have?What factors does researcher suggest prevented him from becoming a killer, criminal etc?How do the researchers view of genetics vs surroundings explanations of behaviour change?
Nature or Nurture: Conclusions
NOTE – the Nature Vs. Nurture debate is hotly debated topic. No side can claim to provide compelling evidence that entirely disputes the other i.e. neither side can completely disregard nature or nurture in explanation of human behaviour.
Signposting and Related Posts
I usually teach this material as part of an introduction to sociology module.
Please click here to return to the homepage – ReviseSociology.com
Share this:
- Share on Tumblr
Leave a Reply Cancel reply
This site uses Akismet to reduce spam. Learn how your comment data is processed .
Discover more from ReviseSociology
Subscribe now to keep reading and get access to the full archive.
Continue reading

IMAGES
VIDEO
COMMENTS
The nature vs. nurture debate in psychology concerns the relative importance of an individual's innate qualities (nature) versus personal experiences (nurture) in determining or causing individual differences in physical and behavioral traits. While early theories favored one factor over the other, contemporary views recognize a complex interplay between genes and environment in shaping ...
Summary. Nature vs. nurture is a framework used to examine how genetics (nature) and environmental factors (nurture) influence human development and personality traits. However, nature vs. nurture isn't a black-and-white issue; there are many shades of gray where the influence of nature and nurture overlap. It's impossible to disentangle how ...
The Nature vs. Nurture Debate. Nature refers to how genetics influence an individual's personality, whereas nurture refers to how their environment (including relationships and experiences) impacts their development. Whether nature or nurture plays a bigger role in personality and development is one of the oldest philosophical debates within ...
The expression "nature vs. nurture" describes the question of how much a person's characteristics are formed by either "nature" or "nurture." "Nature" means innate biological ...
Nurture. On the other side of the nature vs. nurture debate are scientists who argue that most of what matters in our lives are things that we learn as we grow. Since much of our learning occurs under the care of older humans, this is the nurture side of the debate. On this side of the debate, scientists are concerned with arguing that there is ...
Nature vs. Nurture Debate. The nature vs. nurture debate is the scientific, cultural, and philosophical debate about whether human culture, behavior, and personality are caused primarily by nature ...
In the "nature vs nurture" debate, nature refers to an individual's innate qualities (nativism). In the "nature vs nurture" debate, nurture refers to personal experiences (i.e. empiricism or behaviorism). Example. Nature is your genes. The physical and personality traits determined by your genes stay the same irrespective of where you were born ...
The expression "nature vs. nurture" describes the question of how much a person's characteristics are formed by either "nature" or "nurture." "Nature" means innate biological ...
The expression "nature vs. nurture" describes the question of how much a person's characteristics are formed by either "nature" or "nurture." "Nature" means innate biological ...
The nature versus nurture debate represents one of the oldest issues in the research of human behavior dealing with the question whether inherited traits or life experiences (e.g., upbringing) play a greater role in shaping, for example, our personality.
The nature vs. nurture debate has both been influenced by and has influenced psychology, sociology, and genetics. Psychology is largely concerned with the mind and behavior of the individual. Sociology is concerned with the collective experiences and behavior of society. Genetics studies how genes and traits are passed down through families.
Nature versus nurture is a long-standing debate in biology and society about the relative influence on human beings of their genetic inheritance (nature) and the environmental conditions of their development ().The alliterative expression "nature and nurture" in English has been in use since at least the Elizabethan period and goes back to medieval French.
The nature versus nurture debate in psychology deals with disagreements about the extent to which the development of traits in humans and animals reflects the relative influence of nature and nurture. It is commonly stated that psychologists have moved on from asking whether traits (or variation in traits) develop from nature or nurture, to ...
The interactionist position in the nature-nurture debate. Many field experts appear to support the interactionist position in the nature vs nurture debate—which is thought to state that genetics and environmental factors work within a fully interactive system that can determine a person's personality and overall mental well-being.
Traditionally, people's answers have placed them in one of two camps: nature or nurture. The one says genes determine an individual while the other claims the environment is the linchpin for development. Since the 16th century, when the terms "nature" and "nurture" first came into use, many people have spent ample time debating which ...
Another option for observing nature-nurture in humans involves twin studies. There are two types of twins: monozygotic (MZ) and dizygotic (DZ). Monozygotic twins, also called "identical" twins, result from a single zygote (fertilized egg) and have the same DNA. They are essentially clones. Dizygotic twins, also known as "fraternal ...
The "Middle Ground" Perspective on Nature-Nurture. Twenty-first-century psychology textbooks often state that the nature-nurture debates have been resolved, and the tension relaxed, because we have moved on from emphasizing nature or nurture to appreciating that development necessarily involves both nature and nurture. In this middle-ground position, one asks how nature and nurture ...
The expression "nature vs. nurture" describes the question of how much a person's characteristics are formed by either "nature" or "nurture." "Nature" means innate biological ...
Nature: This side of the debate argues that genes have the greatest influence over who we are, from the way we look to the way we behave. Genes determine physical traits such as height, eye color, hair color, and face shape, but they can also contribute to other attributes such as your personality traits and cognitive abilities. Nurture: This ...
These questions deal with individual causes of traits, differences between individuals, and average differences in a population — all very different levels of explanation. Yet all three kinds of ...
The nature vs. nurture theory has been discussed since Hippocrates was alive. Nature refers to how our genetic makeup affects our physical and mental health, while nurture refers to how our environment affects our physical and mental health. For example, if heart disease runs in your family, you can decrease your risk of developing the disease ...
The "nature" in the nature versus nurture debate generally refers to innate qualities. In historical terms, nature might refer to human nature or the soul. In modern scientific terms, it may refer to genetic makeup and biological traits. For example, researchers have long studied twins to determine the influence of biology on personality ...
Nature or Nurture: Conclusions . NOTE - the Nature Vs. Nurture debate is hotly debated topic. No side can claim to provide compelling evidence that entirely disputes the other i.e. neither side can completely disregard nature or nurture in explanation of human behaviour.