Socioeconomic inequalities in type 2 diabetes mellitus: a study based on a population-based survey in Iran
Type 2 diabetes mellitus (T2DM) is the most prevalent form of Diabetes Mellitus (DM), with social and economic determinants significantly influencing its prevalence. This study aimed to analyze the socioeconom...
- View Full Text

Proximity to public green spaces and depressive symptoms among South African residents: a population-based study
Exposure to green spaces has been suggested to improve mental health and may reduce the risk of depression. However, there is generally limited evidence on the association between green spaces and depression o...
Influenza vaccine coverage and factors associated with non-vaccination among caregiving and care-receiving adults in the Canadian Longitudinal Study on Aging (CLSA)
Influenza vaccination is recommended for those at increased risk of influenza complications and their household contacts to help reduce influenza exposure. Adults who require care often experience health issue...
Adulterants present in the San Diego county fentanyl supply: a laboratory analysis of seized law enforcement samples
The opioid overdose crisis is one of the worst public health crises ever to face the US and emerging evidence suggests its effects are compounded by the presence of drug adulterants. Here we report our efforts...
Knowledge, attitude, and practice toward weight management among diabetic patients in Qidong City, Jiangsu Province
Weight management is an effective prevention and treatment strategy for diabetes mellitus. This study aimed to assess the knowledge, attitude, and practice (KAP) of diabetic patients towards weight management.
Who chooses “healthy” meals? An analysis of lunchtime meal quality in a workplace cafeteria
The workplace can play an important role in shaping the eating behaviors of U.S. adults. Unfortunately, foods obtained in the workplace tend to be low in nutritional quality. Questions remain about the best wa...
Study on the measurement of coupling and coordinated development level between China’s internet and elderly care services and its influencing factors
With the intensification of China’s aging population, the demand for elderly care services has become increasingly prominent. At the same time, rapid development of internet technology provides more convenienc...
Chronic diseases and determinants of community health services utilization among adult residents in southern China: a community-based cross-sectional study
The burden of chronic diseases has become a major public health concern, and high-efficiency use of community health services is essential in combating chronic diseases. This study described the status of chro...
Malaria infection and predictor factors among Chadian nomads’ children
In Chad, malaria remains a significant public health concern, particularly among nomadic populations. Geographical factors and the mobility of human populations have shown to be associated with the diversity of P...
Inspecting the “health poverty trap” mechanism: self-reinforcing effect and endogenous force
The term “health poverty trap” describes a vicious cycle in which developing countries or regions become trapped in low levels of health and poverty during the process of modernization. Although significant pr...
Dietary diversity and its determinants among women of reproductive age residing in the urban area of Nouakchott, Mauritania
The intake of nutrient-rich foods from diverse diets ensures adequate nutrition for women. This study aims to determine dietary diversity among women of reproductive age (WRA) using the MDD-W indicator and how...
How do people with long COVID utilize COVID-19 vaccination and rehabilitation services and what are their experiences with these services? results of a qualitative study with 48 participants from Germany
Studies estimate that at least 7.5% of adults are affected by long-term symptoms such as fatigue or cognitive impairment after the acute phase of COVID-19. COVID-19 vaccination may reduce the risk of long COVI...
One-year trajectories of nutritional status in perimenopausal women: a community-based multi-centered prospective study
Nutritional status is a modifiable factor associated with perimenopausal women’s health and quality of life. Assessing body composition indicators helps to comprehensively understand nutritional status compare...
Connecting families: a qualitative study examining the experiences of parenting young children under financial strain in Ontario, Canada
There is little research investigating the subjective experiences of parenting young children while living in poverty and experiencing financial strain using qualitative methodologies. Therefore, the objective...
Absorbent hygiene products disposal behaviour in informal settlements: identifying determinants and underlying mechanisms in Durban, South Africa
Within South Africa, many low-income communities lack reliable waste management services. Within these contexts, absorbent hygiene product (AHP) waste, including nappies (diapers), are not recycled, and are of...
Racial/ethnic differences in the association between transgender-related U.S. state policies and self-rated health of transgender women
Policy protections for transgender adults in the United States are consistently associated with positive health outcomes. However, studies over-represent non-Latinx White transgender people and obscure variati...
Coverage and determinants of HIV testing and counseling services among mothers attending antenatal care in sub-Saharan African countries: a multilevel analysis
HIV/AIDS is one of the top global public health threats that causes significant cases, deaths, and socioeconomic impact. Even though both HIV testing and counseling are identified as essential HIV intervention...
Menstruating while homeless: navigating access to products, spaces, and services
People experiencing homelessness (PEH) in the United States face substantial challenges related to menstruation, exacerbated by the COVID-19 pandemic. Limited access to period products, heightened stigma, and ...
Digital health literacy and associated factors among internet users from China: a cross-sectional study
As the internet develops and 5G technology becomes increasingly prominent, the internet has become a major source of health-related information. Increasingly, people use the internet to find health-related inf...
Job boredom as an antecedent of four states of mental health: life satisfaction, positive functioning, anxiety, and depression symptoms among young employees – a latent change score approach
Job boredom has been generally associated with poorer self-rated health but the evidence is mainly cross-sectional and there is a lack of a holistic mental health approach. We examined the temporal relationshi...
Psychometric analysis and linguistic adaptation of the Persian version of Contraceptive Self-Efficacy Scale (CSES-P)
This study was aimed to test adaptability of the Contraceptive Self-Efficacy Scale (CSES) for use on Persian-speaking women of reproductive age.
The individuals’ awareness and adoption of electronic health records in China: a questionnaire survey of 1,337 individuals
Electronic health records (EHRs) are digital records of individual health information. However, their adoption and utilization remain low. This study explores the factors influencing the implementation of EHRs...
Linkages between the Sustainable Development Goals and health in Somalia
The Sustainable Development Goals (SDGs) adopted in 2015 compromises 17 universal and indivisible goals for sustainable development, however the interactions between the SDGs in Somalia is not known which is v...
Food insecurity in urban American Indian and Alaska Native populations during the COVID-19 pandemic
Food insecurity is an important social determinant of health that was exacerbated by the COVID-19 pandemic. Both food insecurity and COVID-19 infection disproportionately affect racial and ethnic minority grou...
Cyberchondria severity and utilization of health services in Polish society: a cross-sectional study
It has been suggested that cyberchondria leads to increased utilization of healthcare services. Unfortunately, not many studies have analyzed this effect comprehensively. The aim of this study was to analyze t...
A novel correction method for modelling parameter-driven autocorrelated time series with count outcome
Count time series (e.g., daily deaths) are a very common type of data in environmental health research. The series is generally autocorrelated, while the widely used generalized linear model is based on the as...
Publisher Correction: Association of urinary chlorpyrifos, paraquat, and cyproconazole levels with the severity of fatty liver based on MRI
The original article was published in BMC Public Health 2024 24 :807
Knowledge, attitudes, and practices towards Kawasaki disease from caregivers of children with Kawasaki disease: a cross-sectional study
To examine the knowledge, attitudes, and practices (KAP) of caregivers of children with Kawasaki disease toward Kawasaki disease.
Cross-country variations in the caregiver role: evidence from the ENTWINE-iCohort study
Globally, economically developed countries face similar ageing demographics and the challenge of a ‘care gap’, yet they vary due to different care and formal support systems, and different cultural and societa...
ICT penetration and life expectancy in emerging market economies: panel evidence from asymmetric causality analysis
Life expectancy is a significant result indicator of public health and sustainable development. Therefore, one of the final objectives of all economic and social policies is to increase the life expectancy. In...
Differences in nutritional status and level of physical activity among adolescents living in urban and rural areas of Montenegro - national study
Nutritional status and physical activity are important factors for adolescent health. These factors may vary by the place of residence. This study aims to assess the nutritional status and physical activity le...
Changes in social mixing and attitudes and practices to precautionary measures in a maturing COVID-19 pandemic in six communities in Sudan: a qualitative study
With low COVID-19 vaccination coverage, non-pharmaceutical interventions were critical to mitigating the COVID-19 pandemic in Sudan. We explored changes in social contact patterns, risk perception, attitudes, ...
The relationship between psychological distress and weight maintenance in weight cycling: mediating role of eating behavior
Obesity is a global public health concern. The goal of this study was to see if eating habits could mediate the relationship between psychological distress and weight maintenance in a population with a history...
Barriers and enabling factors for utilizing physical rehabilitation services by Afghan immigrants and refugees with disabilities in Iran: a qualitative study
Individuals with a migrant background often underutilize physical rehabilitation services (PRS) compared to the host population. This disparity is attributed to various barriers, including limited access to in...
Design and usability evaluation of a mobile application for self-care among Iranian adolescents
Mobile phones can be an ideal platform to engage adolescents to maintain, improve, and promote self-care. Therefore, the current study aims to design and evaluate the usability of a mobile application for self...
Changes in disease burden and global inequalities in bladder, kidney and prostate cancers from 1990 to 2019: a comparative analysis based on the global burden of disease study 2019
Bladder, kidney and prostate cancers make significant contributors to cancer burdens. Exploring their cross-country inequalities may inform equitable strategies to meet the 17 sustainable development goals bef...
A great way to bring up health behaviour topics at playgroup: a qualitative evaluation of the Healthy Conversations @ Playgroup program
The early years is a critical stage to establish optimal nutrition and movement behaviours. Community playgroups are a relaxed environment for parents with a focus on social connection and supporting parents i...
Neighborhood-level factors associated with COVID-19 vaccination rates: a case study in Chicago
Chicago’s deeply-rooted racial and socioeconomic residential segregation is a pattern mirrored in other major cities, making it a prototype for studying the uptake of public health interventions across the US....
Food safety and dietary diversity in African urban cities: evidence from Ghana
Food safety is integral to food security and is increasingly becoming a significant concern in the urban areas of Africa, which are rapidly growing in population. In the case of Ghana, many urban households de...
Exploring the medical decision-making patterns and influencing factors among the general Chinese public: a binary logistic regression analysis
With the ongoing evolution of the healthcare system and shifts in cultural paradigms, there is a pressing need to delve into the medical decision-making behaviors of general Chinese public and understand their...
Pregnancy health in a multi-state U.S. population of systemically underserved patients and their children: PROMISE cohort design and baseline characteristics
Gestational weight gain (GWG) is a routinely monitored aspect of pregnancy health, yet critical gaps remain about optimal GWG in pregnant people from socially marginalized groups, or with pre-pregnancy body ma...
Key predictors of food security and nutrition in Africa: a spatio-temporal model-based study
There is voluminous literature on Food Security in Africa. This study explicitly considers the spatio-temporal factors in addition to the usual FAO-based metrics in modeling and understanding the dynamics of f...
Systematic review of empiric studies on lockdowns, workplace closures, and other non-pharmaceutical interventions in non-healthcare workplaces during the initial year of the COVID-19 pandemic: benefits and selected unintended consequences
We conducted a systematic review aimed to evaluate the effects of non-pharmaceutical interventions within non-healthcare workplaces and community-level workplace closures and lockdowns on COVID-19 morbidity an...
Racial discrimination is associated with food insecurity, stress, and worse physical health among college students
Students of color disproportionately experience racial discrimination and food insecurity, which both lead to poor academic and health outcomes. This study explores the extent to which the location of racial d...
Efficacy of health literacy interventions aimed to improve health gains of higher education students—a systematic review
Health literacy (HL) among higher education students is low, making them vulnerable about their health. To reverse this trend, higher education institutions promote HL interventions with various topics and met...
Covid-19 skepticism and public health norms during refugee assistance: does skepticism always lead to poor safety protocol adherence?
Skepticism about COVID-19’s existence or severity has spread as fast as the disease itself, and in some populations has been shown to undermine protective public health behaviors that can mitigate infection. F...
Correction to: Impact of COVID-19 on mental health of health care workers in Spain: a mix-methods study
The original article was published in BMC Public Health 2024 24 :463
Trends in psychosomatic symptoms among adolescents and the role of lifestyle factors
Adolescent mental health problems are on the rise globally, including in Sweden. One indicator of this trend is increased psychosomatic symptoms (PSS) over time. Lifestyle factors such as physical activity (PA...
Content and face validity of Workplace COVID-19 Knowledge & Stigma Scale (WoCKSS)
The COVID-19 pandemic has led to fear, rumours, and stigma, particularly against those infected with the virus. In Malaysia, the manufacturing industry is particularly vulnerable to COVID-19 clusters, making i...
Risk of diabetes and hypertension in a population with alcohol use disorders
A population-based follow-up study assessing the risk of developing hypertension and diabetes associated with alcohol use disorder (AUD) is crucial. We investigated this relationship by using insurance claims ...
Important information
Editorial board
For authors
For editorial board members
For reviewers
- Manuscript editing services
Annual Journal Metrics
2022 Citation Impact 4.5 - 2-year Impact Factor 4.7 - 5-year Impact Factor 1.661 - SNIP (Source Normalized Impact per Paper) 1.307 - SJR (SCImago Journal Rank)
2023 Speed 32 days submission to first editorial decision for all manuscripts (Median) 173 days submission to accept (Median)
2023 Usage 24,332,405 downloads 24,308 Altmetric mentions
- More about our metrics
Peer-review Terminology
The following summary describes the peer review process for this journal:
Identity transparency: Single anonymized
Reviewer interacts with: Editor
Review information published: Review reports. Reviewer Identities reviewer opt in. Author/reviewer communication
More information is available here
- Follow us on Twitter
BMC Public Health
ISSN: 1471-2458
- Submission enquiries: [email protected]
- General enquiries: [email protected]

- Mission and history
- Platform features
- Library Advisory Group
- What’s in JSTOR
- For Librarians
- For Publishers
Open and free content on JSTOR and Artstor
Our partnerships with libraries and publishers help us make content discoverable and freely accessible worldwide
Search open content on JSTOR
Explore our growing collection of Open Access journals
Early Journal Content , articles published prior to the last 95 years in the United States, or prior to the last 143 years if initially published internationally, are freely available to all
Even more content is available when you register to read – millions of articles from nearly 2,000 journals
Thousands of Open Access ebooks are available from top scholarly publishers, including Brill, Cornell University Press, University College of London, and University of California Press – at no cost to libraries or users.
This includes Open Access titles in Spanish:
- Collaboration with El Colegio de México
- Partnership with the Latin American Council of Social Sciences
Images and media
JSTOR hosts a growing number of public collections , including Artstor’s Open Access collections , from museums, archives, libraries, and scholars worldwide.
Research reports
A curated set of more than 34,000 research reports from more than 140 policy institutes selected with faculty, librarian, and expert input.
Resources for librarians
Open content title lists:
- Open Access Journals (xlsx)
- Open Access Books (xlsx)
- JSTOR Early Journal Content (txt)
- Research Reports
Open Access ebook resources for librarians
Library-supported collections
Shared Collections : We have a growing corpus of digital special collections published on JSTOR by our institutional partners.
Reveal Digital : A collaboration with libraries to fund, source, digitize and publish open access primary source collections from under-represented voices.
JSTOR Daily
JSTOR Daily is an online publication that contextualizes current events with scholarship. All of our stories contain links to publicly accessible research on JSTOR. We’re proud to publish articles based in fact and grounded by careful research and to provide free access to that research for all of our readers.
An official website of the United States government
The .gov means it’s official. Federal government websites often end in .gov or .mil. Before sharing sensitive information, make sure you’re on a federal government site.
The site is secure. The https:// ensures that you are connecting to the official website and that any information you provide is encrypted and transmitted securely.
- Publications
- Account settings
Preview improvements coming to the PMC website in October 2024. Learn More or Try it out now .
PubMed Central (PMC) Home Page
PubMed Central ® (PMC) is a free full-text archive of biomedical and life sciences journal literature at the U.S. National Institutes of Health's National Library of Medicine (NIH/NLM)
Discover a digital archive of scholarly articles, spanning centuries of scientific research.
Learn how to find and read articles of interest to you.
Collections
Browse the PMC Journal List or learn about some of PMC's unique collections.
For Authors
Navigate the PMC submission methods to comply with a funder mandate, expand access, and ensure preservation.
For Publishers
Learn about deposit options for journals and publishers and the PMC selection process.
For Developers
Find tools for bulk download, text mining, and other machine analysis.
9.8 MILLION articles are archived in PMC.
Content provided in part by:, full participation journals.
Journals deposit the complete contents of each issue or volume.
NIH Portfolio Journals
Journals deposit all NIH-funded articles as defined by the NIH Public Access Policy.
Selective Deposit Programs
Publisher deposits a subset of articles from a collection of journals.
March 21, 2024
Preview upcoming improvements to pmc.
We are pleased to announce the availability of a preview of improvements planned for the PMC website. These…
Dec. 15, 2023
Update on pubreader format.
The PubReader format was added to PMC in 2012 to make it easier to read full text articles on tablet, mobile, and oth…

We are pleased to announce the availability of a preview of improvements planned for the PMC website. These improvements will become the default in October 2024.
- Search by keyword
- Search by citation
Page 1 of 86
Comparing the clinical practice and prescribing safety of locum and permanent doctors: observational study of primary care consultations in England
Temporary doctors, known as locums, are a key component of the medical workforce in the NHS but evidence on differences in quality and safety between locum and permanent doctors is limited. We aimed to examine...
- View Full Text
SARS-CoV-2, influenza A/B and respiratory syncytial virus positivity and association with influenza-like illness and self-reported symptoms, over the 2022/23 winter season in the UK: a longitudinal surveillance cohort
Syndromic surveillance often relies on patients presenting to healthcare. Community cohorts, although more challenging to recruit, could provide additional population-wide insights, particularly with SARS-CoV-...
A phase II study of belumosudil for chronic graft-versus-host disease in patients who failed at least one line of systemic therapy in China
Chronic graft-versus-host disease (cGVHD) is an immune-related disorder that is the most common complication post-allogenic hematopoietic stem cell transplant. Corticosteroids with or without calcineurin inhib...
Association between genetic risk and adherence to healthy lifestyle for developing age-related hearing loss
Previous studies have shown that lifestyle/environmental factors could accelerate the development of age-related hearing loss (ARHL). However, there has not yet been a study investigating the joint association...
Associations between maternal pre-pregnancy BMI and infant striatal mean diffusivity
It is well-established that parental obesity is a strong risk factor for offspring obesity. Further, a converging body of evidence now suggests that maternal weight profiles may affect the developing offspring...
Evaluation of a hospital-initiated tobacco dependence treatment service: uptake, smoking cessation, readmission and mortality
The National Health Service in England aims to implement tobacco dependency treatment services in all hospitals by 2024. We aimed to assess the uptake of a new service, adapted from the Ottawa Model of Smoking...
Delivering synaptic protein mRNAs via extracellular vesicles ameliorates cognitive impairment in a mouse model of Alzheimer’s disease
Synaptic dysfunction with reduced synaptic protein levels is a core feature of Alzheimer’s disease (AD). Synaptic proteins play a central role in memory processing, learning, and AD pathogenesis. Evidence sugg...
Association between inflammatory bowel disease and cancer risk: evidence triangulation from genetic correlation, Mendelian randomization, and colocalization analyses across East Asian and European populations
Inflammatory bowel disease (IBD), which includes Crohn’s disease (CD) and ulcerative colitis (UC), has been associated with several cancer risks in observational studies, but the observed associations have bee...
Medication non-adherence and self-inflicted violence behaviors among 185,800 patients with schizophrenia in the community: a 12-year cohort study
Despite the importance of medication adherence in treatment effectiveness, little is known about the association between medication non-adherence and self-inflicted violence behaviors. We aimed to assess wheth...
Childhood maltreatment and health in the UK Biobank: triangulation of outcome-wide and polygenic risk score analyses
Childhood maltreatment is common globally and impacts morbidity, mortality, and well-being. Our understanding of its impact is constrained by key substantive and methodological limitations of extant research, ...
Sleep alterations as a function of 88 health indicators
Alterations in sleep have been described in multiple health conditions and as a function of several medication effects. However, evidence generally stems from small univariate studies. Here, we apply a large-s...
Sarcopenic obesity is part of obesity paradox in dementia development: evidence from a population-based cohort study
Sarcopenic obesity, a clinical and functional condition characterized by the coexistence of obesity and sarcopenia, has not been investigated in relation to dementia risk and its onset.
Sex-specific associations between sodium and potassium intake and overall and cause-specific mortality: a large prospective U.S. cohort study, systematic review, and updated meta-analysis of cohort studies
The impact of sodium intake on cardiovascular disease (CVD) health and mortality has been studied for decades, including the well-established association with blood pressure. However, non-linear patterns, dose...
Progress with the Learning Health System 2.0: a rapid review of Learning Health Systems’ responses to pandemics and climate change
Pandemics and climate change each challenge health systems through increasing numbers and new types of patients. To adapt to these challenges, leading health systems have embraced a Learning Health System (LHS...
Regional disparities and risk factors of mortality among patients at high risk of sudden cardiac death in emerging countries: a nonrandomized controlled trial
Comprehensive data on patients at high risk of sudden cardiac death (SCD) in emerging countries are lacking. The aim was to deepen our understanding of the SCD phenotype and identify risk factors for death amo...
Association of in utero HIV exposure with child brain structure and language development: a South African birth cohort study
There is a growing population of children with in utero HIV exposure who are at risk of poor neurodevelopmental outcomes despite avoiding HIV infection. However, the underlying neurobiological pathways are not...
Correction: Transient increased risk of influenza infection following RSV infection in South Africa: findings from the PHIRST study, South Africa, 2016–2018
The original article was published in BMC Medicine 2023 21 :441
Incidence of new-onset hypertension before, during, and after the COVID-19 pandemic: a 7-year longitudinal cohort study in a large population
While the augmented incidence of diabetes after COVID-19 has been widely confirmed, controversial results are available on the risk of developing hypertension during the COVID-19 pandemic.
Incorporating social vulnerability in infectious disease mathematical modelling: a scoping review
Highlighted by the rise of COVID-19, climate change, and conflict, socially vulnerable populations are least resilient to disaster. In infectious disease management, mathematical models are a commonly used too...
SARS-CoV-2 infection is detrimental to pregnancy outcomes after embryo transfer in IVF/ICSI: a prospective cohort study
To explore whether SARS-CoV-2 infection affects the pregnancy outcomes of assisted reproductive techniques (ART).

Risk of encephalitis and meningitis after COVID-19 vaccination in South Korea: a self-controlled case series analysis
Several neurological manifestations shortly after a receipt of coronavirus infectious disease 2019 (COVID-19) vaccine have been described in the recent case reports. Among those, we sought to evaluate the risk...
Autotaxin inhibition attenuates the aortic valve calcification by suppressing inflammation-driven fibro-calcific remodeling of valvular interstitial cells
Patients with fibro-calcific aortic valve disease (FCAVD) have lipid depositions in their aortic valve that engender a proinflammatory impetus toward fibrosis and calcification and ultimately valve leaflet ste...
Improved emotion differentiation under reduced acoustic variability of speech in autism
Socio-emotional impairments are among the diagnostic criteria for autism spectrum disorder (ASD), but the actual knowledge has substantiated both altered and intact emotional prosodies recognition. Here, a Bay...
Polygenic risk score-based phenome-wide association study of head and neck cancer across two large biobanks
Numerous observational studies have highlighted associations of genetic predisposition of head and neck squamous cell carcinoma (HNSCC) with diverse risk factors, but these findings are constrained by design l...
Safety and efficacy of sirolimus in recurrent intravenous leiomyomatosis, pulmonary benign metastatic leiomyomatosis, and leiomyomatosis peritonealis disseminata: a pilot study
Intravenous leiomyomatosis (IVL), pulmonary benign metastatic leiomyomatosis (PBML), and leiomyomatosis peritonealis disseminata (LPD) are leiomyomas with special growth patterns and high postoperative recurre...
The medication-based Rx-Risk Comorbidity Index and risk of hip fracture - a nationwide NOREPOS cohort study
Few previous studies have assessed overall morbidity at the individual level with respect to future risk of hip fracture. The aim of this register-based cohort study was to examine the association between morb...
Paxlovid use is associated with lower risk of cardiovascular diseases in COVID-19 patients with autoimmune rheumatic diseases: a retrospective cohort study
Paxlovid has been shown to be effective in reducing mortality and hospitalization rates in patients with coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19). It is not known whether Paxlovid can reduce the risk of cardiovascu...
Evidence linking COVID-19 and the health/well-being of children and adolescents: an umbrella review
Experiences during childhood and adolescence have enduring impacts on physical and mental well-being, overall quality of life, and socioeconomic status throughout one’s lifetime. This underscores the importanc...
Investigating the nexus of metabolic syndrome, serum uric acid, and dementia risk: a prospective cohort study
The global dementia prevalence is surging, necessitating research into contributing factors. We aimed to investigate the association between metabolic syndrome (MetS), its components, serum uric acid (SUA) lev...
Assessing the impact of type 2 diabetes on mortality and life expectancy according to the number of risk factor targets achieved: an observational study
Type 2 diabetes (T2D) is associated with an increased risk of premature death. Whether multifactorial risk factor modification could attenuate T2D-related excess risk of death is unclear. We aimed to examine t...
The optimal antithrombotic strategy for post-stroke patients with atrial fibrillation and extracranial artery stenosis—a nationwide cohort study
In post-stroke atrial fibrillation (AF) patients who have indications for both oral anticoagulant (OAC) and antiplatelet agent (AP), e.g., those with carotid artery stenosis, there is debate over the best anti...
Low awareness of the transitivity assumption in complex networks of interventions: a systematic survey from 721 network meta-analyses
The transitivity assumption is the cornerstone of network meta-analysis (NMA). Violating transitivity compromises the credibility of the indirect estimates and, by extent, the estimated treatment effects of th...
Malaria vaccination: hurdles to reach high-risk children
Ensuring that malaria vaccines deliver maximum public health impact is non-trivial. Drawing on current research, this article examines hurdles that malaria immunization may face to reach high-risk children and...
Efficacy and safety of gut microbiota-based therapies in autoimmune and rheumatic diseases: a systematic review and meta-analysis of 80 randomized controlled trials
Previous randomized controlled trials (RCTs) suggested that gut microbiota-based therapies may be effective in treating autoimmune diseases, but a systematic summary is lacking.
The influence of n-3 polyunsaturated fatty acids on cognitive function in individuals without dementia: a systematic review and dose–response meta-analysis
Omega-3 polyunsaturated fatty acids (n-3 PUFA) have been suggested as a cognitive enhancing agent, though their effect is doubtful. We aimed to examine the effect of n-3 PUFA on the cognitive function of middl...
Correlates of protection and determinants of SARS-CoV-2 breakthrough infections 1 year after third dose vaccination
The emergence of new SARS-CoV-2 variants and the waning of immunity raise concerns about vaccine effectiveness and protection against COVID-19. While antibody response has been shown to correlate with the risk...
Degree of joint risk factor control and hazard of mortality in diabetes patients: a matched cohort study in UK Biobank
Diabetes patients are at higher risk for mortality than the general population; however, little is known about whether the excess mortality risk associated with diabetes could be mitigated or nullified via con...
Camrelizumab plus gemcitabine and oxaliplatin for relapsed or refractory classical Hodgkin lymphoma: a phase II trial
Classical Hodgkin lymphoma (cHL) is a highly curable disease, while novel therapy is needed for refractory or relapsed (R/R) patients. This phase II trial aimed to evaluate the role of camrelizumab plus gemcit...
Breastfeeding is associated with enhanced intestinal gluconeogenesis in infants
Breastfeeding (BF) confers metabolic benefits to infants, including reducing risks of metabolic syndrome such as obesity and diabetes later in life. However, the underlying mechanism is not yet fully understoo...
Characterization and trajectories of hematological parameters prior to severe COVID-19 based on a large-scale prospective health checkup cohort in western China: a longitudinal study of 13-year follow-up
The relaxation of the “zero-COVID” policy on Dec. 7, 2022, in China posed a major public health threat recently. Complete blood count test was discovered to have complicated relationships with COVID-19 after t...
Gut microbiome features and metabolites in non-alcoholic fatty liver disease among community-dwelling middle-aged and older adults
The specific microbiota and associated metabolites linked to non-alcoholic fatty liver disease (NAFLD) are still controversial. Thus, we aimed to understand how the core gut microbiota and metabolites impact N...
Influence of lack of blinding on the estimation of medication-related harms: a retrospective cohort study of randomized controlled trials
Empirical evidence suggests that lack of blinding may be associated with biased estimates of treatment benefit in randomized controlled trials, but the influence on medication-related harms is not well-recogni...
Medication adherence in patients with type 2 diabetes after disability onset: a difference-in-differences analysis using nationwide data
Effectively managing the coexistence of both diabetes and disability necessitates substantial effort. Whether disability onset affects adherence to type 2 diabetes medication remains unclear. This study invest...
Global epidemiology of type 2 diabetes in patients with NAFLD or MAFLD: a systematic review and meta-analysis
Non-alcoholic fatty liver disease (NAFLD) and metabolic-associated fatty liver disease (MAFLD) shares common pathophysiological mechanisms with type 2 diabetes, making them significant risk factors for type 2 ...
A self-controlled case series study to measure the risk of SARS-CoV-2 infection associated with attendance at sporting and cultural events: the UK Events Research Programme events
In 2021, whilst societies were emerging from major social restrictions during the SARS-CoV-2 pandemic, the UK government instigated an Events Research Programme to examine the risk of COVID-19 transmission fro...
Subsidized gestational diabetes mellitus screening and management program in rural China: a pragmatic multicenter, randomized controlled trial
The increasing prevalence of gestational diabetes mellitus (GDM) is a major challenge, particularly in rural areas of China where control rates are suboptimal. This study aimed to evaluate the effectiveness of...
Carbohydrate quality, not quantity, linked to reduced colorectal cancer incidence and mortality in US populations: evidence from a prospective study
Carbohydrates have been implicated in colorectal cancer (CRC) risk, but the specific impact of carbohydrate quality and quantity on CRC susceptibility in US populations remains unclear.
Thrombospondin 1 enhances systemic inflammation and disease severity in acute-on-chronic liver failure
The key role of thrombospondin 1 (THBS1) in the pathogenesis of acute-on-chronic liver failure (ACLF) is unclear. Here, we present a transcriptome approach to evaluate THBS1 as a potential biomarker in ACLF di...

Autoimmune diseases and adverse pregnancy outcomes: an umbrella review
There is a high prevalence of autoimmune conditions in women specially in the reproductive years; thus, the association with adverse pregnancy outcomes has been widely studied. However, few autoimmune conditio...
The role of lifestyle in the association between long-term ambient air pollution exposure and cardiovascular disease: a national cohort study in China
Cardiovascular disease (CVD) caused by air pollution poses a considerable burden on public health. We aim to examine whether lifestyle factors mediate the associations of air pollutant exposure with the risk o...
- Editorial Team
- Editorial Board
- Call for papers
- Editor’s choice
- Sign up for article alerts and news from this journal
- Manuscript editing services
Annual Journal Metrics
2022 Citation Impact 9.3 - 2-year Impact Factor 10.4 - 5-year Impact Factor 3.011 - SNIP (Source Normalized Impact per Paper) 3.447 - SJR (SCImago Journal Rank)
2023 Speed 6 days submission to first editorial decision for all manuscripts (Median) 145 days submission to accept (Median)
2023 Usage 6,375,113 downloads 24,228 Altmetric mentions
- More about our metrics
Announcements
medRxiv transfers
BMC Medicine is happy to consider manuscripts that have been, or will be, posted on a preprint server. Authors are able to submit their manuscripts directly from medRxiv , without having to re-upload files.
Registered reports
BMC Medicine is accepting Registered Reports. Find out more about this innovative format in our Submission Guidelines .
- Follow us on Twitter
BMC Medicine
ISSN: 1741-7015
- Submission enquiries: [email protected]
- General enquiries: [email protected]
Help | Advanced Search
Computer Science > Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition
Title: mm1: methods, analysis & insights from multimodal llm pre-training.
Abstract: In this work, we discuss building performant Multimodal Large Language Models (MLLMs). In particular, we study the importance of various architecture components and data choices. Through careful and comprehensive ablations of the image encoder, the vision language connector, and various pre-training data choices, we identified several crucial design lessons. For example, we demonstrate that for large-scale multimodal pre-training using a careful mix of image-caption, interleaved image-text, and text-only data is crucial for achieving state-of-the-art (SOTA) few-shot results across multiple benchmarks, compared to other published pre-training results. Further, we show that the image encoder together with image resolution and the image token count has substantial impact, while the vision-language connector design is of comparatively negligible importance. By scaling up the presented recipe, we build MM1, a family of multimodal models up to 30B parameters, including both dense models and mixture-of-experts (MoE) variants, that are SOTA in pre-training metrics and achieve competitive performance after supervised fine-tuning on a range of established multimodal benchmarks. Thanks to large-scale pre-training, MM1 enjoys appealing properties such as enhanced in-context learning, and multi-image reasoning, enabling few-shot chain-of-thought prompting.
Submission history
Access paper:.
- Download PDF
- Other Formats
References & Citations
- Google Scholar
- Semantic Scholar
BibTeX formatted citation
Bibliographic and Citation Tools
Code, data and media associated with this article, recommenders and search tools.
- Institution
arXivLabs: experimental projects with community collaborators
arXivLabs is a framework that allows collaborators to develop and share new arXiv features directly on our website.
Both individuals and organizations that work with arXivLabs have embraced and accepted our values of openness, community, excellence, and user data privacy. arXiv is committed to these values and only works with partners that adhere to them.
Have an idea for a project that will add value for arXiv's community? Learn more about arXivLabs .
Disclaimer » Advertising
- HealthyChildren.org
Selection Criteria
Search strategy, data extraction, risk of bias and applicability, data synthesis and analysis, parent ratings, teacher ratings, youth self-reports, combined rating scales, additional clinician tools, neuropsychological tests, biospecimen, neuroimaging, variation in diagnostic accuracy with clinical setting or patient subgroup, measures for diagnostic performance, available tools, importance of the comparator sample, clinical implications, future research, conclusions, acknowledgments, tools for the diagnosis of adhd in children and adolescents: a systematic review.
FUNDING: The work is based on research conducted by the Southern California Evidence-based Practice Center under contract to the Agency for Healthcare Research and Quality (AHRQ), Rockville, MD (Contract 75Q80120D00009). The Patient-Centered Outcomes Research Institute (PCORI) funded the research (PCORI Publication No. 2023-SR-03). The findings and conclusions in this manuscript are those of the authors, who are responsible for its contents; the findings and conclusions do not necessarily represent the views of AHRQ or PCORI, its Board of Governors, or Methodology Committee. Therefore, no statement in this report should be construed as an official position of PCORI, AHRQ or of the US Department of Health and Human Services.
CONFLICT OF INTEREST DISCLOSURES: The authors have indicated they have no conflicts of interest to disclose.
- Split-Screen
- Article contents
- Figures & tables
- Supplementary Data
- Peer Review
- CME Quiz Close Quiz
- Open the PDF for in another window
- Get Permissions
- Cite Icon Cite
- Search Site
Bradley S. Peterson , Joey Trampush , Morah Brown , Margaret Maglione , Maria Bolshakova , Mary Rozelle , Jeremy Miles , Sheila Pakdaman , Sachi Yagyu , Aneesa Motala , Susanne Hempel; Tools for the Diagnosis of ADHD in Children and Adolescents: A Systematic Review. Pediatrics 2024; e2024065854. 10.1542/peds.2024-065854
Download citation file:
- Ris (Zotero)
- Reference Manager
Correct diagnosis is essential for the appropriate clinical management of attention-deficit/hyperactivity disorder (ADHD) in children and adolescents.
This systematic review provides an overview of the available diagnostic tools.
We identified diagnostic accuracy studies in 12 databases published from 1980 through June 2023.
Any ADHD tool evaluation for the diagnosis of ADHD, requiring a reference standard of a clinical diagnosis by a mental health specialist.
Data were abstracted and critically appraised by 1 reviewer and checked by a methodologist. Strength of evidence and applicability assessments followed Evidence-based Practice Center standards.
In total, 231 studies met eligibility criteria. Studies evaluated parental ratings, teacher ratings, youth self-reports, clinician tools, neuropsychological tests, biospecimen, EEG, and neuroimaging. Multiple tools showed promising diagnostic performance, but estimates varied considerably across studies, with a generally low strength of evidence. Performance depended on whether ADHD youth were being differentiated from neurotypically developing children or from clinically referred children.
Studies used different components of available tools and did not report sufficient data for meta-analytic models.
A valid and reliable diagnosis of ADHD requires the judgment of a clinician who is experienced in the evaluation of youth with and without ADHD, along with the aid of standardized rating scales and input from multiple informants across multiple settings, including parents, teachers, and youth themselves.
Attention-deficit/hyperactivity disorder (ADHD) is one of the most prevalent neurodevelopmental conditions in youth. Its prevalence has remained constant at ∼5.3% worldwide over the years, and diagnostic criteria have remained constant when based on rigorous diagnostic procedures. 1 Clinical diagnoses, however, have increased steadily over time, 2 and currently, ∼10% of US children receive an ADHD diagnosis. 3 Higher rates of clinical compared with research-based diagnoses are because of an increasing clinician recognition of youth who have ADHD symptoms that are functionally impairing but do not fully meet formal diagnostic criteria. 4 The higher diagnostic rates over time in clinical samples also results from youth receiving a diagnosis incorrectly. Some youth, for example, are misdiagnosed as having ADHD when they have symptoms of other disorders that overlap with ADHD symptoms, such as difficulty concentrating, which occurs in many other conditions. 5 Moreover, ADHD is more than twice as likely to be diagnosed in boys than in girls, 3 in lower-income families, 6 and in white compared with nonwhite youth 7 ; differences that derive at least in part from diagnostic and cultural biases. 8 , – 11
Improving clinical diagnostic accuracy is essential to ensure that youth who truly have ADHD benefit from receiving treatment without delay. Similarly, youth who do not have ADHD should not be diagnosed since an incorrect diagnosis risks exposing them to unbeneficial treatments. 12 , 13 Clinician judgement alone, however, especially by nonspecialist clinicians, is poor in diagnosing ADHD 14 compared with expert, research-grade diagnoses made by mental health clinicians. 15 Accurately diagnosing ADHD is difficult because diagnoses are often made using subjective clinical impressions, and putative diagnostic tools have a confusing, diverse, and poorly described evidence base that is not widely accessible. The availability of valid diagnostic tools would especially help to reduce misdiagnoses from cultural biases and symptom overlap with ADHD. 12 , 16 , – 19
This review summarizes evidence for the performance of tools for children and adolescents with ADHD. We did not restrict to a set of known diagnostic tools but instead explored the range of available diagnostic tools, including machine-learning assisted and virtual reality-based tools. The review aimed to assess how diagnostic performance varies by clinical setting and patient characteristics.
The review aims were developed in consultation with the Agency for Healthcare Research and Quality (AHRQ), the Patient-Centered Outcomes Research Institute, the topic nominator American Academy of Pediatrics, key informants, a technical expert panel (TEP), and public input. The TEP reviewed the protocol and advised on key outcomes. Subgroup analyses and key outcomes were prespecified. The review is registered in PROSPERO (CRD42022312656) and the protocol is available on the AHRQ Web site as part of a larger evidence report on ADHD. The systematic review followed Methods of the (AHRQ) Evidence-based Practice Center Program. 20
Population: age <18 years.
Interventions: any ADHD tool for the diagnosis of ADHD.
Comparators: diagnosis by a mental health specialist, such as a psychologist, psychiatrist, or other provider, who often used published scales or semistructured diagnostic interviews to ensure a reliable DSM-based diagnosis of ADHD.
Key outcomes: diagnostic accuracy (eg, sensitivity, specificity, area under the curve).
Setting: any.
Study design: diagnostic accuracy studies.
Other: English language, published from 1980 to June 2023.
We searched PubMed, Embase, PsycINFO, ERIC, and ClinicalTrials.gov. We identified reviews for reference-mining through PubMed, Cochrane Database of Systematic Reviews, Campbell Collaboration, What Works in Education, PROSPERO, ECRI Guidelines Trust, G-I-N, and ClinicalKey. The peer reviewed strategy is in the Supplemental Appendix . All citations were screened by trained literature reviewers supported by machine learning ( Fig 1 ). Two independent reviewers assessed full text studies for eligibility. The TEP reviewed studies to ensure all were captured. Publications reporting on the same participants were consolidated into 1 record.

Literature flow diagram.
The data abstraction form included extensive guidance to aid reproducibility and standardization in recording study details, results, risk of bias, and applicability. One reviewer abstracted data and a methodologist checked accuracy and completeness. Data are publicly available in the Systematic Review Data Repository.
We assessed characteristics pertaining to patient selection, index test, reference standard, flow and timing that may have introduced bias, and evaluated applicability of study results, such as whether the test, its conduct, or interpretation differed from how the test is used in clinical practice. 21 , 22
We differentiated parent, teacher, and youth self-report ratings; tools for clinicians; neuropsychological tests; biospecimens; EEG; and neuroimaging. We organized analyses according to prespecified outcome measures. A narrative overview summarized the range of diagnostic performance for key outcomes. Because lack of reported detail in many individual studies hindered use of meta-analytic models, we created summary figures to document the diagnostic performance reported in each study. We used meta-regressions across studies to assess the effects of age, comorbidities, racial and ethnic composition, and diagnostic setting (differentiating primary care, specialty care, school settings, mixed settings, and not reported) on diagnostic performance. One researcher with experience in use of specified standardized criteria 23 initially assessed the overall strength of evidence (SoE) (see Supplemental Appendix ) for each study, then discussed it with the study team to communicate our confidence in each finding.
We screened 23 139 citations and 7534 publications retrieved as full text against the eligibility criteria. In total, 231 studies reported in 290 publications met the eligibility criteria (see Fig 1 ).
Methodological quality of the studies varied. Selection bias was likely in two-thirds of studies; several were determined to be problematic in terms of reported study flow and timing of assessments (eg, not stating whether diagnosis was known before the results of the index test); and several lacked details on diagnosticians or diagnostic procedures ( Supplemental Fig 1 ). Applicability concerns limited the generalizability of findings ( Supplemental Fig 2 ), usually because youth with comorbidities were excluded. Many different tools were assessed within the broader categories (eg, within neuropsychological tests), and even when reporting on the same diagnostic tool, studies often used different components of the tool (eg, different subscales of rating scales), or they combined components in a variety of ways (eg, across different neuropsychological test parameters).
The evidence table ( Supplemental Table 10 , Supplemental Appendix ) shows each study’s finding. The following highlights key findings across studies.
Fifty-nine studies used parent ratings to diagnose ADHD ( Fig 2 ). The most frequently evaluated tool was the CBCL (Child Behavior Checklist), alone or in combination with other tools, often using different score cutoffs for diagnosis, and evaluating different subscales (most frequently the attention deficit/hyperactivity problems subscale). Sensitivities ranged from 38% (corresponding specificity = 96%) to 100% (specificity = 4% to 92%). 24 , 25

Diagnostic performance parent and teacher ratings. For a complete list of scales see Supplemental Appendix .
Area under the curve (AUC) for receiver operator characteristic curves ranged widely from 0.55 to 0.95 but 3 CBCL studies reported AUCs of 0.83 to 0.84. 26 , – 28 Few studies reported measurement of reliability. SoE was downgraded for study limitation (lack of detailed reporting), imprecision (large performance variability), and inconsistent findings ( Supplemental Table 1 ).
Twenty-three studies used teacher ratings to diagnose ADHD ( Fig 2 ). No 2 studies reported on rater agreement, internal consistency, or test-retest reliability for the same teacher rating scale. The highest sensitivity was 97% (specificity = 26%). 25 The Teacher Report Form, alone or in combination with Conners teacher rating scales, yielded sensitivities of 72% to 79% 29 and specificities of 64% to 76%. 30 , 32 reported AUCs ranged from 0.65 to 0.84. 32 SoE was downgraded to low for imprecision (large performance variability) and inconsistency (results for specific tools not replicated), see Supplemental Table 2 .
Six studies used youth self-reports to diagnose ADHD. No 2 studies used the same instrument. Sensitivities ranged from 53% (specificity = 98%) to 86% (specificity = 70%). 35 AUCs ranged from 0.56 to 0.85. 36 We downgraded SoE for domain inconsistency (only 1 study reported on a given tool and outcome), see Supplemental Table 3 .
Thirteen studies assessed diagnostic performance of ratings combined across informants, often using machine learning for variable selection. Only 1 study compared performance of combined data to performance from single informants, finding negligible improvement (AUC youth = 0.71; parent = 0.85; combined = 0.86). 37 Other studies reported on limited outcome measures and used ad hoc methods to combine information from multiple informants. The best AUC was reported by a machine learning supported study combining parent and teacher ratings (AUC = 0.98). 38
Twenty-four studies assessed additional tools, such as interview guides, that can be used by clinicians to aid diagnosis of ADHD. Sensitivities varied, ranging from 67% (specificity = 65%) to 98% (specificity = 100%); specificities ranged from 36% (sensitivity = 89%) to 100% (sensitivity = 98%). 39 Some of the tools measured activity levels objectively using an actometer or commercially available activity tracker, either alone or as part of a diagnostic test battery. Reported performance was variable (sensitivity range 25% to 100%, 40 specificity range 66% to 100%, 40 AUCs range 0.75–0.9996 41 ). SoE was downgraded for imprecision (large performance variability) and inconsistency (outcomes and results not replicated), see Supplemental Table 4 .
Seventy-four studies used measures from various neuropsychological tests, including continuous performance tests (CPTs). Four of these included 3- and 4-year-old children. 42 , – 44 A large majority used a CPT, which assessed omission errors (reflecting inattention), commission errors (impulsivity), and reaction time SD (response time variability). Studies varied in use of traditional visual CPTs, such as the Test of Variables of Attention, more novel, multifaceted “hybrid” CPT paradigms, and virtual reality CPTs built upon environments designed to emulate real-world classroom distractibility. Studies used idiosyncratic combinations of individual cognitive measures to achieve the best performance, though many reported on CPT attention and impulsivity measures.
Sensitivity for all neuropsychological tests ranged from 22% (specificity = 96%) to 100% (specificity = 100%) 45 ( Fig 3 ), though the latter study reported performance for unique composite measures without replication. Specificities ranged from 22% (sensitivity = 91%) 46 to 100% (sensitivity = 100% to 75%). 45 , 47 AUCs ranged from 0.59 to 0.93. 48 Sensitivity for all CPT studies ranged from 22% ( specificity = 96) to 100% (specificity = 75%). 49 Specificities for CPTs ranged from 22% (sensitivity = 91%) to 100% (sensitivity = 89%) 47 ( Fig 3 ). AUCs ranged from 0.59 to 0.93. 50 , 51 SoE was deemed low for imprecise studies (large performance variability), see Supplemental Table 5.

Diagnostic performance neuropsychological tests, CPTs, activity monitors, biospecimen, EEG.
Seven studies assessed blood or urine biomarkers to diagnose ADHD. These measured erythropoietin or erythropoietin receptor, membrane potential ratio, micro RNA levels, or urine metabolites. Sensitivities ranged from 56% (specificity = 95%) to 100% (specificity = 100% for erythropoietin and erythropoietin receptors levels). 52 Specificities ranged from 25% (sensitivity = 79%) to 100% (sensitivity = 100%). 52 AUCs ranged from 0.68 to 1.00. 52 Little information was provided on reliability of markers or their combinations. SoE was downgraded for inconsistent and imprecise studies ( Supplemental Table 6 ).
Forty-five studies used EEG markers to diagnose ADHD. EEG signals were obtained in a variety of patient states, even during neuropsychological test performance. Two-thirds used machine learning algorithms to select classification parameters. Several combined EEG with demographic variables or rating scales. Sensitivity ranged widely from 46% to 100% (corresponding specificities 74 and 71%). 53 , 54 One study that combined EEG with demographics data supported by machine learning reported perfect sensitivity and specificity. 54 Specificity was also variable and ranged from 38% (sensitivity = 95%) to 100% (specificities = 71% or 100%). 53 , – 56 Reported AUCs ranged from 0.63 to 1.0. 57 , 58 SoE was downgraded for study imprecision (large performance variability) and limitations (diagnostic approaches poorly described), see Supplemental Table 7 .
Nineteen studies used neuroimaging for diagnosis. One public data set (ADHD-200) produced several analyses. All but 2 used MRI: some functional MRI (fMRI), some structural, and some in combination, with or without magnetic resonance spectroscopy (2 used near-infrared spectroscopy). Most employed machine learning to detect markers that optimized diagnostic classifications. Some combined imaging measures with demographic or other clinical data in the prediction model. Sensitivities ranged from 42% (specificity = 95%) to 99% (specificity = 100%) using resting state fMRI and a complex machine learning algorithm 56 to differentiate ADHD from neurotypical youth. Specificities ranged from 55% (sensitivity = 95%) to 100% 56 using resting state fMRI data. AUCs ranged from 0.58 to over 0.99, 57 SoE was downgraded for imprecision (large performance variability) and study limitations (diagnostic models are often not well described, and the number and type of predictor variables entering the model were unclear). Studies generally did not validate diagnostic algorithms or assess performance measures in an independent sample ( Supplemental Table 8 ).
Regression analyses indicated that setting was associated with both sensitivity ( P = .03) and accuracy ( P = .006) but not specificity ( P = .68) or AUC ( P = .28), with sensitivities lowest in primary care ( Fig 4 ). Sensitivity, specificity, and accuracy were also lower when differentiating youth with ADHD from a clinical sample than from typically developing youth (sensitivity P = .04, specificity P < .001, AUC P < .001) ( Fig 4 ), suggesting that clinical population is a source of heterogeneity in diagnostic performance. Findings should be interpreted with caution, however, as they were not obtained in meta-analytic models and, consequently, do not take into account study size or quality.

Diagnostic performance by setting and population.
Supplemental Figs 3–5 in the Supplemental Appendix document effects by age and gender. We did not detect statistically significant associations of age with sensitivity ( P = .54) or specificity ( P = .37), or associations of the proportion of girls with sensitivity ( P = .63), specificity ( P = .80), accuracy ( P = .34), or AUC ( P = .90).
We identified a large number of publications reporting on ADHD diagnostic tools. To our knowledge, no prior review of ADHD diagnostic tools has been as comprehensive in the range of tools, outcomes, participant ages, and publication years. Despite the large number of studies, we deemed the strength of evidence for the reported performance measures across all categories of diagnostic tools to be low because of large performance variability across studies and various limitations within and across studies.
We required that studies report diagnoses when using the tool compared with diagnoses made by expert mental health clinicians. Studies most commonly reported sensitivity (true-positive rate) and specificity (true-negative rate) when a study-specific diagnostic threshold was applied to measures from the tool being assessed. Sensitivity and specificity depend critically on that study-specific threshold, and their values are inherently a trade-off, such that varying the threshold to increase either sensitivity or specificity reduces the other. Interpreting diagnostic performance in terms of sensitivity and specificity, and comparing those performance measures across studies, is therefore challenging. Consequently, researchers more recently often report performance for sensitivity and specificity in terms of receiver operating characteristics (ROC) curves, a plot of sensitivity versus specificity across the entire range of possible diagnostic thresholds. The area under this ROC curve (AUC) provides an overall, single index of performance that ranges from 0.5 (indicating that the tool provides no information above chance for classification) to 1.0 (indicating a perfect test that can correctly classify all participants as having ADHD and all non-ADHD participants as not having it). AUC values of 90 to 100 are commonly classified as excellent performance; 80 to 90 as good; 70 to 80 as fair; 60 to 70 as poor; and 50 to 60 failed performance.
Most research is available on parental ratings. Overall, AUCs for parent rating scales ranged widely from “poor” 58 to “excellent.” 59 Analyses restricted to the CBCL, the most commonly evaluated scale, yielded more consistent “good” AUCs for differentiating youth with ADHD from others in clinical samples, but the number of studies contributing data were small. Internal consistency for rating scale items was generally high across most rating scales. Test-retest reliability was good, though only 2 studies reported it. One study reported moderate rater agreement between mothers and fathers for inattention, hyperactivity, and impulsivity symptoms. Few studies included youth under 7 years of age.
AUCs for teacher rating scales ranged from “failed” 33 to “good.” 34 Internal consistency for scale items was generally high. Teacher ratings demonstrated very low rater agreement with corresponding parent scales, suggesting either a problem with the instruments or a large variability in symptom presentation with environmental context (home or school).
Though data were limited, self-reports from youth seemed to perform less well than corresponding parent and teacher reports, with AUCs ranging from “failed” for CBCL or ASEBA when distinguishing ADHD from other patients 33 to “good” for the SWAN in distinguishing ADHD from neurotypical controls. 36 , 37
Studies evaluating neuropsychological tests yielded AUCs ranging from “poor” 60 , 61 to “excellent.” 50 Many used idiosyncratic combinations of cognitive measures, which complicates interpretation of the results across studies. Nevertheless, extracting specific, comparable measures of inattention and impulsivity from CPTs yielded diagnostic performance ranging from “poor” to “excellent” in differentiating ADHD youth from neurotypical controls and “fair” in differentiating ADHD youth from other patients. 42 , 60 , 62 No studies provided an independent replication of diagnosis using the same measure.
Blood biomarkers yielded AUCs ranging from “poor” (serum miRNAs) 63 to “excellent” (erythropoietin and erythropoietin receptors levels) 52 in differentiating ADHD from neurotypical youth. None have been independently replicated, and test-retest reliability was not reported. Most EEG studies used machine learning for diagnostic classification. AUCs ranged from “poor” 64 to “excellent” when differentiating ADHD youth from neurotypical controls. 65 Diagnostic performance was not prospectively replicated in any independent samples.
Most neuroimaging studies relied on machine learning to develop diagnostic algorithms. AUCs ranged from “poor” 66 to “excellent” for distinguishing ADHD youth from neurotypically developing controls. 57 Most studies used pre-existing data sets or repositories to retrospectively discriminate youths with ADHD from neurotypical controls, not from other clinical populations and not prospectively, and none assessed test-retest reliability or the independent reproducibility of findings. Reporting of final mathematical models or algorithms for diagnosis was limited. Activity monitors have the advantage of providing inexpensive, objective, easily obtained, and quantified measures that can potentially be widely disseminated and scaled.
Studies of combined approaches, such as integrating diagnostic tools with clinician impressions, were limited. One study reported increased sensitivity and specificity when an initial clinician diagnosis combined EEG indicators (the reference standard was a consensus diagnosis from a panel of ADHD experts). 67 These findings were not independently replicated, however, and no test-retest reliability was reported.
Many studies aimed to distinguish ADHD youth from neurotypical controls, which is a distinction of limited clinical relevance. In clinically referred youth, most parents, teachers, and clinicians are reasonably confident that something is wrong, even if they are unsure whether the cause of their concern is ADHD. To be informed by a tool that the child is not typically developing is not particularly helpful. Moreover, we cannot know whether diagnostic performance for tools that discriminate ADHD youth only from neurotypical controls is determined by the presence of ADHD or by the presence of any other characteristics that accompany clinical “caseness,” such as the presence of comorbid illnesses or symptoms shared or easily confused with those of other conditions, or the effects of chronic stress or current or past treatment. The clinically more relevant and difficult question is, therefore, how well the tool distinguishes youth with ADHD from those who have other emotional and behavioral problems. Consistent with these conceptual considerations that argue for assessing diagnostic performance in differentiating youth with ADHD from those with other clinical conditions, we found significant evidence that, across all studies, sensitivity, specificity, and AUC were all lower when differentiating youth with ADHD from a clinical sample than when differentiating them from neurotypical youth. These findings also suggest that the comparison population was a significant source of heterogeneity in diagnostic performance.
Despite the large number of studies on diagnostic tools, a valid and reliable diagnosis of ADHD ultimately still requires the judgement of a clinician who is experienced in the evaluation of youth with and without ADHD, along with the aid of standardized rating scales and input from multiple informants across multiple settings, including parents, teachers, and youth themselves. Diagnostic tools perform best when the clinical question is whether a youth has ADHD or is healthy and typically developing, rather than when the clinical question is whether a youth has ADHD or another mental health or behavioral problem. Diagnostic tools yield more false-positive and false-negative diagnoses of ADHD when differentiating youth with ADHD from youth with another mental health problem than when differentiating them from neurotypically developing youth.
Scores for rating scales tended to correlate poorly across raters, and ADHD symptoms in the same child varied across settings, indicating that no single informant in a single setting is a gold-standard for diagnosis. Therefore, diagnosis using rating scales will likely benefit from a more complete representation of symptom expression across multiple informants (parents, school personnel, clinicians, and youth) across more than 1 setting (home, school, and clinic) to inform clinical judgement when making a diagnosis, thus, consistent with current guidelines. 68 , – 70 Unfortunately, methods for combining scores across raters and settings that improve diagnosis compared with scores from single raters have not been developed or prospectively replicated.
Despite the widespread use of neuropsychological testing to “diagnose” youth with ADHD, often at considerable expense, indirect comparisons of AUCs suggest that performance of neuropsychological test measures in diagnosing ADHD is comparable to the diagnostic performance of ADHD rating scales from a single informant. Moreover, the diagnostic accuracy of parent rating scales is typically better than neuropsychological test measures in head-to-head comparisons. 44 , 71 Furthermore, the overall SoE for estimates of diagnostic performance with neuropsychological testing is low. Use of neuropsychological test measures of executive functioning, such as the CPT, may help inform a clinical diagnosis, but they are not definitive either in ruling in or ruling out a diagnosis of ADHD. The sole use of CPTs and other neuropsychological tests to diagnose ADHD, therefore, cannot be recommended. We note that this conclusion regarding diagnostic value is not relevant to any other clinical utility that testing may have.
No independent replication studies have been conducted to validate EEG, neuroimaging, or biospecimen to diagnose ADHD, and no clinical effectiveness studies have been conducted using these tools to diagnose ADHD in the real world. Thus, these tools do not seem remotely close to being ready for clinical application to aid diagnosis, despite US Food and Drug Administration approval of 1 EEG measure as a purported diagnostic aid. 67 , 72
All studies of diagnostic tools should report data in more detail (ie, clearly report false-positive and -negative rates, the diagnostic thresholds used, and any data manipulation undertaken to achieve the result) to support meta-analytic methods. Studies should include ROC analyses to support comparisons of test performance across studies that are independent of the diagnostic threshold applied to measures from the tool. They should also include assessment of test-retest reliability to help discern whether variability in measures and test performance is a function of setting or of measurement variability over time. Future studies should address the influence of co-occurring disorders on diagnostic performance and how well the tools distinguish youth with ADHD from youth with other emotional and behavioral problems, not simply from healthy controls. More studies should compare the diagnostic accuracy of different test modalities, head-to-head. Independent, prospective replication of performance measures of diagnostic tools in real-world settings is essential before US Food and Drug Administration approval and before recommendations for widespread clinical use.
Research is needed to identify consensus algorithms that combine rating scale data from multiple informants to improve the clinical diagnosis of ADHD, which at present is often unguided, ad hoc, and suboptimal. Diagnostic studies using EEG, neuroimaging, and neuropsychological tests should report precise operational definitions and measurements of the variable(s) used for diagnosis, any diagnostic algorithm employed, the selected statistical cut-offs, and the number of false-positives and false-negatives the diagnostic tool yields to support future efforts at synthetic analyses.
Objective, quantitative neuropsychological test measures of executive functioning correlate only weakly with the clinical symptoms that define ADHD. 73 Thus, many youth with ADHD have normal executive functioning profiles on neuropsychological testing, and many who have impaired executive functioning on testing do not have ADHD. 74 Future research is needed to understand how test measures of executive functioning and the real-world functional problems that define ADHD map on to one another and how that mapping can be improved.
One of the most important potential uses of systematic reviews and meta-analyses in improving the clinical diagnosis of ADHD and treatment planning would be identification of effect modifiers for the performance of diagnostic tools: determining, for example, whether tools perform better in patients who are younger or older, in ethnic minorities, or those experiencing material hardship, or who have a comorbid illness or specific ADHD presentation. Future studies of ADHD should more systematically address the modifier effects of these patient characteristics. They should make available in public repositories the raw, individual-level data and the algorithms or computer code that will aid future efforts at replication, synthesis, and new discovery for diagnostic tools across data sets and studies.
Finally, no studies meeting our inclusion criteria assessed the consequences of being misdiagnosed or labeled as either having or not having ADHD, the diagnosis of ADHD specifically in preschool-aged children, or the potential adverse consequences of youth being incorrectly diagnosed with or without ADHD. This work is urgently needed.
We thank Cynthia Ramirez, Erin Tokutomi, Jennifer Rivera, Coleman Schaefer, Jerusalem Belay, Anne Onyekwuluje, and Mario Gastelum for help with data acquisition. We thank Kymika Okechukwu, Lauren Pilcher, Joanna King, and Robyn Wheatley from the American Academy of Pediatrics (AAP), Jennie Dalton and Paula Eguino Medina from PCORI, Christine Chang and Kim Wittenberg from AHRQ, and Mary Butler from the Minnesota Evidence-based Practice Center. We thank Glendy Burnett, Eugenia Chan, MD, MPH, Matthew J. Gormley, PhD, Laurence Greenhill, MD, Joseph Hagan, Jr, MD, Cecil Reynolds, PhD, Le'Ann Solmonson, PhD, LPC-S, CSC, and Peter Ziemkowski, MD, FAAFP who served as key informants. We thank Angelika Claussen, PhD, Alysa Doyle, PhD, Tiffany Farchione, MD, Matthew J. Gormley, PhD, Laurence Greenhill, MD, Jeffrey M. Halperin, PhD, Marisa Perez-Martin, MS, LMFT, Russell Schachar, MD, Le'Ann Solmonson, PhD, LPC-S, CSC, and James Swanson, PhD who served as a technical expert panel. Finally, we thank Joel Nigg, PhD, and Peter S. Jensen, MD for their peer review of the data.
Drs Peterson and Hempel conceptualized and designed the study, collected data, conducted the analyses, drafted the initial manuscript, and critically reviewed and revised the manuscript; Dr Trampush conducted the critical appraisal; Ms Brown, Ms Maglione, Drs Bolshakova and Padkaman, and Ms Rozelle screened citations and abstracted the data; Dr Miles conducted the analyses; Ms Yagyu designed and executed the search strategy; Ms Motala served as data manager; and all authors provided critical input for the manuscript, approved the final manuscript as submitted, and agree to be accountable for all aspects of the work.
This trial has been registered at PROSPERO (identifier CRD42022312656).
COMPANION PAPER: A companion to this article can be found online at https://www.pediatrics.org/cgi/doi/10.1542/peds.2024-065787 .
Data sharing statement: Data are available in SRDRPlus.
attention-deficit/hyperactivity disorder
area under the curve
Child Behavior Checklist
continuous performance test
functional magnetic resonance imaging
receiver operating characteristics
strength of evidence
technical expert panel
Competing Interests
Supplementary data.
Advertising Disclaimer »
Citing articles via
Email alerts.

Affiliations
- Editorial Board
- Editorial Policies
- Journal Blogs
- Pediatrics On Call
- Online ISSN 1098-4275
- Print ISSN 0031-4005
- Pediatrics Open Science
- Hospital Pediatrics
- Pediatrics in Review
- AAP Grand Rounds
- Latest News
- Pediatric Care Online
- Red Book Online
- Pediatric Patient Education
- AAP Toolkits
- AAP Pediatric Coding Newsletter
First 1,000 Days Knowledge Center
Institutions/librarians, group practices, licensing/permissions, integrations, advertising.
- Privacy Statement | Accessibility Statement | Terms of Use | Support Center | Contact Us
- © Copyright American Academy of Pediatrics
This Feature Is Available To Subscribers Only
Sign In or Create an Account
Thank you for visiting nature.com. You are using a browser version with limited support for CSS. To obtain the best experience, we recommend you use a more up to date browser (or turn off compatibility mode in Internet Explorer). In the meantime, to ensure continued support, we are displaying the site without styles and JavaScript.
- View all journals
- My Account Login
- Explore content
- About the journal
- Publish with us
- Sign up for alerts
- Open access
- Published: 26 March 2024
Predicting and improving complex beer flavor through machine learning
- Michiel Schreurs ORCID: orcid.org/0000-0002-9449-5619 1 , 2 , 3 na1 ,
- Supinya Piampongsant 1 , 2 , 3 na1 ,
- Miguel Roncoroni ORCID: orcid.org/0000-0001-7461-1427 1 , 2 , 3 na1 ,
- Lloyd Cool ORCID: orcid.org/0000-0001-9936-3124 1 , 2 , 3 , 4 ,
- Beatriz Herrera-Malaver ORCID: orcid.org/0000-0002-5096-9974 1 , 2 , 3 ,
- Christophe Vanderaa ORCID: orcid.org/0000-0001-7443-5427 4 ,
- Florian A. Theßeling 1 , 2 , 3 ,
- Łukasz Kreft ORCID: orcid.org/0000-0001-7620-4657 5 ,
- Alexander Botzki ORCID: orcid.org/0000-0001-6691-4233 5 ,
- Philippe Malcorps 6 ,
- Luk Daenen 6 ,
- Tom Wenseleers ORCID: orcid.org/0000-0002-1434-861X 4 &
- Kevin J. Verstrepen ORCID: orcid.org/0000-0002-3077-6219 1 , 2 , 3
Nature Communications volume 15 , Article number: 2368 ( 2024 ) Cite this article
36k Accesses
741 Altmetric
Metrics details
- Chemical engineering
- Gas chromatography
- Machine learning
- Metabolomics
- Taste receptors
The perception and appreciation of food flavor depends on many interacting chemical compounds and external factors, and therefore proves challenging to understand and predict. Here, we combine extensive chemical and sensory analyses of 250 different beers to train machine learning models that allow predicting flavor and consumer appreciation. For each beer, we measure over 200 chemical properties, perform quantitative descriptive sensory analysis with a trained tasting panel and map data from over 180,000 consumer reviews to train 10 different machine learning models. The best-performing algorithm, Gradient Boosting, yields models that significantly outperform predictions based on conventional statistics and accurately predict complex food features and consumer appreciation from chemical profiles. Model dissection allows identifying specific and unexpected compounds as drivers of beer flavor and appreciation. Adding these compounds results in variants of commercial alcoholic and non-alcoholic beers with improved consumer appreciation. Together, our study reveals how big data and machine learning uncover complex links between food chemistry, flavor and consumer perception, and lays the foundation to develop novel, tailored foods with superior flavors.
Similar content being viewed by others
BitterSweet: Building machine learning models for predicting the bitter and sweet taste of small molecules
Rudraksh Tuwani, Somin Wadhwa & Ganesh Bagler
Sensory lexicon and aroma volatiles analysis of brewing malt
Xiaoxia Su, Miao Yu, … Tianyi Du
Predicting odor from molecular structure: a multi-label classification approach
Kushagra Saini & Venkatnarayan Ramanathan
Introduction
Predicting and understanding food perception and appreciation is one of the major challenges in food science. Accurate modeling of food flavor and appreciation could yield important opportunities for both producers and consumers, including quality control, product fingerprinting, counterfeit detection, spoilage detection, and the development of new products and product combinations (food pairing) 1 , 2 , 3 , 4 , 5 , 6 . Accurate models for flavor and consumer appreciation would contribute greatly to our scientific understanding of how humans perceive and appreciate flavor. Moreover, accurate predictive models would also facilitate and standardize existing food assessment methods and could supplement or replace assessments by trained and consumer tasting panels, which are variable, expensive and time-consuming 7 , 8 , 9 . Lastly, apart from providing objective, quantitative, accurate and contextual information that can help producers, models can also guide consumers in understanding their personal preferences 10 .
Despite the myriad of applications, predicting food flavor and appreciation from its chemical properties remains a largely elusive goal in sensory science, especially for complex food and beverages 11 , 12 . A key obstacle is the immense number of flavor-active chemicals underlying food flavor. Flavor compounds can vary widely in chemical structure and concentration, making them technically challenging and labor-intensive to quantify, even in the face of innovations in metabolomics, such as non-targeted metabolic fingerprinting 13 , 14 . Moreover, sensory analysis is perhaps even more complicated. Flavor perception is highly complex, resulting from hundreds of different molecules interacting at the physiochemical and sensorial level. Sensory perception is often non-linear, characterized by complex and concentration-dependent synergistic and antagonistic effects 15 , 16 , 17 , 18 , 19 , 20 , 21 that are further convoluted by the genetics, environment, culture and psychology of consumers 22 , 23 , 24 . Perceived flavor is therefore difficult to measure, with problems of sensitivity, accuracy, and reproducibility that can only be resolved by gathering sufficiently large datasets 25 . Trained tasting panels are considered the prime source of quality sensory data, but require meticulous training, are low throughput and high cost. Public databases containing consumer reviews of food products could provide a valuable alternative, especially for studying appreciation scores, which do not require formal training 25 . Public databases offer the advantage of amassing large amounts of data, increasing the statistical power to identify potential drivers of appreciation. However, public datasets suffer from biases, including a bias in the volunteers that contribute to the database, as well as confounding factors such as price, cult status and psychological conformity towards previous ratings of the product.
Classical multivariate statistics and machine learning methods have been used to predict flavor of specific compounds by, for example, linking structural properties of a compound to its potential biological activities or linking concentrations of specific compounds to sensory profiles 1 , 26 . Importantly, most previous studies focused on predicting organoleptic properties of single compounds (often based on their chemical structure) 27 , 28 , 29 , 30 , 31 , 32 , 33 , thus ignoring the fact that these compounds are present in a complex matrix in food or beverages and excluding complex interactions between compounds. Moreover, the classical statistics commonly used in sensory science 34 , 35 , 36 , 37 , 38 , 39 require a large sample size and sufficient variance amongst predictors to create accurate models. They are not fit for studying an extensive set of hundreds of interacting flavor compounds, since they are sensitive to outliers, have a high tendency to overfit and are less suited for non-linear and discontinuous relationships 40 .
In this study, we combine extensive chemical analyses and sensory data of a set of different commercial beers with machine learning approaches to develop models that predict taste, smell, mouthfeel and appreciation from compound concentrations. Beer is particularly suited to model the relationship between chemistry, flavor and appreciation. First, beer is a complex product, consisting of thousands of flavor compounds that partake in complex sensory interactions 41 , 42 , 43 . This chemical diversity arises from the raw materials (malt, yeast, hops, water and spices) and biochemical conversions during the brewing process (kilning, mashing, boiling, fermentation, maturation and aging) 44 , 45 . Second, the advent of the internet saw beer consumers embrace online review platforms, such as RateBeer (ZX Ventures, Anheuser-Busch InBev SA/NV) and BeerAdvocate (Next Glass, inc.). In this way, the beer community provides massive data sets of beer flavor and appreciation scores, creating extraordinarily large sensory databases to complement the analyses of our professional sensory panel. Specifically, we characterize over 200 chemical properties of 250 commercial beers, spread across 22 beer styles, and link these to the descriptive sensory profiling data of a 16-person in-house trained tasting panel and data acquired from over 180,000 public consumer reviews. These unique and extensive datasets enable us to train a suite of machine learning models to predict flavor and appreciation from a beer’s chemical profile. Dissection of the best-performing models allows us to pinpoint specific compounds as potential drivers of beer flavor and appreciation. Follow-up experiments confirm the importance of these compounds and ultimately allow us to significantly improve the flavor and appreciation of selected commercial beers. Together, our study represents a significant step towards understanding complex flavors and reinforces the value of machine learning to develop and refine complex foods. In this way, it represents a stepping stone for further computer-aided food engineering applications 46 .
To generate a comprehensive dataset on beer flavor, we selected 250 commercial Belgian beers across 22 different beer styles (Supplementary Fig. S1 ). Beers with ≤ 4.2% alcohol by volume (ABV) were classified as non-alcoholic and low-alcoholic. Blonds and Tripels constitute a significant portion of the dataset (12.4% and 11.2%, respectively) reflecting their presence on the Belgian beer market and the heterogeneity of beers within these styles. By contrast, lager beers are less diverse and dominated by a handful of brands. Rare styles such as Brut or Faro make up only a small fraction of the dataset (2% and 1%, respectively) because fewer of these beers are produced and because they are dominated by distinct characteristics in terms of flavor and chemical composition.
Extensive analysis identifies relationships between chemical compounds in beer
For each beer, we measured 226 different chemical properties, including common brewing parameters such as alcohol content, iso-alpha acids, pH, sugar concentration 47 , and over 200 flavor compounds (Methods, Supplementary Table S1 ). A large portion (37.2%) are terpenoids arising from hopping, responsible for herbal and fruity flavors 16 , 48 . A second major category are yeast metabolites, such as esters and alcohols, that result in fruity and solvent notes 48 , 49 , 50 . Other measured compounds are primarily derived from malt, or other microbes such as non- Saccharomyces yeasts and bacteria (‘wild flora’). Compounds that arise from spices or staling are labeled under ‘Others’. Five attributes (caloric value, total acids and total ester, hop aroma and sulfur compounds) are calculated from multiple individually measured compounds.
As a first step in identifying relationships between chemical properties, we determined correlations between the concentrations of the compounds (Fig. 1 , upper panel, Supplementary Data 1 and 2 , and Supplementary Fig. S2 . For the sake of clarity, only a subset of the measured compounds is shown in Fig. 1 ). Compounds of the same origin typically show a positive correlation, while absence of correlation hints at parameters varying independently. For example, the hop aroma compounds citronellol, and alpha-terpineol show moderate correlations with each other (Spearman’s rho=0.39 and 0.57), but not with the bittering hop component iso-alpha acids (Spearman’s rho=0.16 and −0.07). This illustrates how brewers can independently modify hop aroma and bitterness by selecting hop varieties and dosage time. If hops are added early in the boiling phase, chemical conversions increase bitterness while aromas evaporate, conversely, late addition of hops preserves aroma but limits bitterness 51 . Similarly, hop-derived iso-alpha acids show a strong anti-correlation with lactic acid and acetic acid, likely reflecting growth inhibition of lactic acid and acetic acid bacteria, or the consequent use of fewer hops in sour beer styles, such as West Flanders ales and Fruit beers, that rely on these bacteria for their distinct flavors 52 . Finally, yeast-derived esters (ethyl acetate, ethyl decanoate, ethyl hexanoate, ethyl octanoate) and alcohols (ethanol, isoamyl alcohol, isobutanol, and glycerol), correlate with Spearman coefficients above 0.5, suggesting that these secondary metabolites are correlated with the yeast genetic background and/or fermentation parameters and may be difficult to influence individually, although the choice of yeast strain may offer some control 53 .

Spearman rank correlations are shown. Descriptors are grouped according to their origin (malt (blue), hops (green), yeast (red), wild flora (yellow), Others (black)), and sensory aspect (aroma, taste, palate, and overall appreciation). Please note that for the chemical compounds, for the sake of clarity, only a subset of the total number of measured compounds is shown, with an emphasis on the key compounds for each source. For more details, see the main text and Methods section. Chemical data can be found in Supplementary Data 1 , correlations between all chemical compounds are depicted in Supplementary Fig. S2 and correlation values can be found in Supplementary Data 2 . See Supplementary Data 4 for sensory panel assessments and Supplementary Data 5 for correlation values between all sensory descriptors.
Interestingly, different beer styles show distinct patterns for some flavor compounds (Supplementary Fig. S3 ). These observations agree with expectations for key beer styles, and serve as a control for our measurements. For instance, Stouts generally show high values for color (darker), while hoppy beers contain elevated levels of iso-alpha acids, compounds associated with bitter hop taste. Acetic and lactic acid are not prevalent in most beers, with notable exceptions such as Kriek, Lambic, Faro, West Flanders ales and Flanders Old Brown, which use acid-producing bacteria ( Lactobacillus and Pediococcus ) or unconventional yeast ( Brettanomyces ) 54 , 55 . Glycerol, ethanol and esters show similar distributions across all beer styles, reflecting their common origin as products of yeast metabolism during fermentation 45 , 53 . Finally, low/no-alcohol beers contain low concentrations of glycerol and esters. This is in line with the production process for most of the low/no-alcohol beers in our dataset, which are produced through limiting fermentation or by stripping away alcohol via evaporation or dialysis, with both methods having the unintended side-effect of reducing the amount of flavor compounds in the final beer 56 , 57 .
Besides expected associations, our data also reveals less trivial associations between beer styles and specific parameters. For example, geraniol and citronellol, two monoterpenoids responsible for citrus, floral and rose flavors and characteristic of Citra hops, are found in relatively high amounts in Christmas, Saison, and Brett/co-fermented beers, where they may originate from terpenoid-rich spices such as coriander seeds instead of hops 58 .
Tasting panel assessments reveal sensorial relationships in beer
To assess the sensory profile of each beer, a trained tasting panel evaluated each of the 250 beers for 50 sensory attributes, including different hop, malt and yeast flavors, off-flavors and spices. Panelists used a tasting sheet (Supplementary Data 3 ) to score the different attributes. Panel consistency was evaluated by repeating 12 samples across different sessions and performing ANOVA. In 95% of cases no significant difference was found across sessions ( p > 0.05), indicating good panel consistency (Supplementary Table S2 ).
Aroma and taste perception reported by the trained panel are often linked (Fig. 1 , bottom left panel and Supplementary Data 4 and 5 ), with high correlations between hops aroma and taste (Spearman’s rho=0.83). Bitter taste was found to correlate with hop aroma and taste in general (Spearman’s rho=0.80 and 0.69), and particularly with “grassy” noble hops (Spearman’s rho=0.75). Barnyard flavor, most often associated with sour beers, is identified together with stale hops (Spearman’s rho=0.97) that are used in these beers. Lactic and acetic acid, which often co-occur, are correlated (Spearman’s rho=0.66). Interestingly, sweetness and bitterness are anti-correlated (Spearman’s rho = −0.48), confirming the hypothesis that they mask each other 59 , 60 . Beer body is highly correlated with alcohol (Spearman’s rho = 0.79), and overall appreciation is found to correlate with multiple aspects that describe beer mouthfeel (alcohol, carbonation; Spearman’s rho= 0.32, 0.39), as well as with hop and ester aroma intensity (Spearman’s rho=0.39 and 0.35).
Similar to the chemical analyses, sensorial analyses confirmed typical features of specific beer styles (Supplementary Fig. S4 ). For example, sour beers (Faro, Flanders Old Brown, Fruit beer, Kriek, Lambic, West Flanders ale) were rated acidic, with flavors of both acetic and lactic acid. Hoppy beers were found to be bitter and showed hop-associated aromas like citrus and tropical fruit. Malt taste is most detected among scotch, stout/porters, and strong ales, while low/no-alcohol beers, which often have a reputation for being ‘worty’ (reminiscent of unfermented, sweet malt extract) appear in the middle. Unsurprisingly, hop aromas are most strongly detected among hoppy beers. Like its chemical counterpart (Supplementary Fig. S3 ), acidity shows a right-skewed distribution, with the most acidic beers being Krieks, Lambics, and West Flanders ales.
Tasting panel assessments of specific flavors correlate with chemical composition
We find that the concentrations of several chemical compounds strongly correlate with specific aroma or taste, as evaluated by the tasting panel (Fig. 2 , Supplementary Fig. S5 , Supplementary Data 6 ). In some cases, these correlations confirm expectations and serve as a useful control for data quality. For example, iso-alpha acids, the bittering compounds in hops, strongly correlate with bitterness (Spearman’s rho=0.68), while ethanol and glycerol correlate with tasters’ perceptions of alcohol and body, the mouthfeel sensation of fullness (Spearman’s rho=0.82/0.62 and 0.72/0.57 respectively) and darker color from roasted malts is a good indication of malt perception (Spearman’s rho=0.54).

Heatmap colors indicate Spearman’s Rho. Axes are organized according to sensory categories (aroma, taste, mouthfeel, overall), chemical categories and chemical sources in beer (malt (blue), hops (green), yeast (red), wild flora (yellow), Others (black)). See Supplementary Data 6 for all correlation values.
Interestingly, for some relationships between chemical compounds and perceived flavor, correlations are weaker than expected. For example, the rose-smelling phenethyl acetate only weakly correlates with floral aroma. This hints at more complex relationships and interactions between compounds and suggests a need for a more complex model than simple correlations. Lastly, we uncovered unexpected correlations. For instance, the esters ethyl decanoate and ethyl octanoate appear to correlate slightly with hop perception and bitterness, possibly due to their fruity flavor. Iron is anti-correlated with hop aromas and bitterness, most likely because it is also anti-correlated with iso-alpha acids. This could be a sign of metal chelation of hop acids 61 , given that our analyses measure unbound hop acids and total iron content, or could result from the higher iron content in dark and Fruit beers, which typically have less hoppy and bitter flavors 62 .
Public consumer reviews complement expert panel data
To complement and expand the sensory data of our trained tasting panel, we collected 180,000 reviews of our 250 beers from the online consumer review platform RateBeer. This provided numerical scores for beer appearance, aroma, taste, palate, overall quality as well as the average overall score.
Public datasets are known to suffer from biases, such as price, cult status and psychological conformity towards previous ratings of a product. For example, prices correlate with appreciation scores for these online consumer reviews (rho=0.49, Supplementary Fig. S6 ), but not for our trained tasting panel (rho=0.19). This suggests that prices affect consumer appreciation, which has been reported in wine 63 , while blind tastings are unaffected. Moreover, we observe that some beer styles, like lagers and non-alcoholic beers, generally receive lower scores, reflecting that online reviewers are mostly beer aficionados with a preference for specialty beers over lager beers. In general, we find a modest correlation between our trained panel’s overall appreciation score and the online consumer appreciation scores (Fig. 3 , rho=0.29). Apart from the aforementioned biases in the online datasets, serving temperature, sample freshness and surroundings, which are all tightly controlled during the tasting panel sessions, can vary tremendously across online consumers and can further contribute to (among others, appreciation) differences between the two categories of tasters. Importantly, in contrast to the overall appreciation scores, for many sensory aspects the results from the professional panel correlated well with results obtained from RateBeer reviews. Correlations were highest for features that are relatively easy to recognize even for untrained tasters, like bitterness, sweetness, alcohol and malt aroma (Fig. 3 and below).
RateBeer text mining results can be found in Supplementary Data 7 . Rho values shown are Spearman correlation values, with asterisks indicating significant correlations ( p < 0.05, two-sided). All p values were smaller than 0.001, except for Esters aroma (0.0553), Esters taste (0.3275), Esters aroma—banana (0.0019), Coriander (0.0508) and Diacetyl (0.0134).
Besides collecting consumer appreciation from these online reviews, we developed automated text analysis tools to gather additional data from review texts (Supplementary Data 7 ). Processing review texts on the RateBeer database yielded comparable results to the scores given by the trained panel for many common sensory aspects, including acidity, bitterness, sweetness, alcohol, malt, and hop tastes (Fig. 3 ). This is in line with what would be expected, since these attributes require less training for accurate assessment and are less influenced by environmental factors such as temperature, serving glass and odors in the environment. Consumer reviews also correlate well with our trained panel for 4-vinyl guaiacol, a compound associated with a very characteristic aroma. By contrast, correlations for more specific aromas like ester, coriander or diacetyl are underrepresented in the online reviews, underscoring the importance of using a trained tasting panel and standardized tasting sheets with explicit factors to be scored for evaluating specific aspects of a beer. Taken together, our results suggest that public reviews are trustworthy for some, but not all, flavor features and can complement or substitute taste panel data for these sensory aspects.
Models can predict beer sensory profiles from chemical data
The rich datasets of chemical analyses, tasting panel assessments and public reviews gathered in the first part of this study provided us with a unique opportunity to develop predictive models that link chemical data to sensorial features. Given the complexity of beer flavor, basic statistical tools such as correlations or linear regression may not always be the most suitable for making accurate predictions. Instead, we applied different machine learning models that can model both simple linear and complex interactive relationships. Specifically, we constructed a set of regression models to predict (a) trained panel scores for beer flavor and quality and (b) public reviews’ appreciation scores from beer chemical profiles. We trained and tested 10 different models (Methods), 3 linear regression-based models (simple linear regression with first-order interactions (LR), lasso regression with first-order interactions (Lasso), partial least squares regressor (PLSR)), 5 decision tree models (AdaBoost regressor (ABR), extra trees (ET), gradient boosting regressor (GBR), random forest (RF) and XGBoost regressor (XGBR)), 1 support vector regression (SVR), and 1 artificial neural network (ANN) model.
To compare the performance of our machine learning models, the dataset was randomly split into a training and test set, stratified by beer style. After a model was trained on data in the training set, its performance was evaluated on its ability to predict the test dataset obtained from multi-output models (based on the coefficient of determination, see Methods). Additionally, individual-attribute models were ranked per descriptor and the average rank was calculated, as proposed by Korneva et al. 64 . Importantly, both ways of evaluating the models’ performance agreed in general. Performance of the different models varied (Table 1 ). It should be noted that all models perform better at predicting RateBeer results than results from our trained tasting panel. One reason could be that sensory data is inherently variable, and this variability is averaged out with the large number of public reviews from RateBeer. Additionally, all tree-based models perform better at predicting taste than aroma. Linear models (LR) performed particularly poorly, with negative R 2 values, due to severe overfitting (training set R 2 = 1). Overfitting is a common issue in linear models with many parameters and limited samples, especially with interaction terms further amplifying the number of parameters. L1 regularization (Lasso) successfully overcomes this overfitting, out-competing multiple tree-based models on the RateBeer dataset. Similarly, the dimensionality reduction of PLSR avoids overfitting and improves performance, to some extent. Still, tree-based models (ABR, ET, GBR, RF and XGBR) show the best performance, out-competing the linear models (LR, Lasso, PLSR) commonly used in sensory science 65 .
GBR models showed the best overall performance in predicting sensory responses from chemical information, with R 2 values up to 0.75 depending on the predicted sensory feature (Supplementary Table S4 ). The GBR models predict consumer appreciation (RateBeer) better than our trained panel’s appreciation (R 2 value of 0.67 compared to R 2 value of 0.09) (Supplementary Table S3 and Supplementary Table S4 ). ANN models showed intermediate performance, likely because neural networks typically perform best with larger datasets 66 . The SVR shows intermediate performance, mostly due to the weak predictions of specific attributes that lower the overall performance (Supplementary Table S4 ).
Model dissection identifies specific, unexpected compounds as drivers of consumer appreciation
Next, we leveraged our models to infer important contributors to sensory perception and consumer appreciation. Consumer preference is a crucial sensory aspects, because a product that shows low consumer appreciation scores often does not succeed commercially 25 . Additionally, the requirement for a large number of representative evaluators makes consumer trials one of the more costly and time-consuming aspects of product development. Hence, a model for predicting chemical drivers of overall appreciation would be a welcome addition to the available toolbox for food development and optimization.
Since GBR models on our RateBeer dataset showed the best overall performance, we focused on these models. Specifically, we used two approaches to identify important contributors. First, rankings of the most important predictors for each sensorial trait in the GBR models were obtained based on impurity-based feature importance (mean decrease in impurity). High-ranked parameters were hypothesized to be either the true causal chemical properties underlying the trait, to correlate with the actual causal properties, or to take part in sensory interactions affecting the trait 67 (Fig. 4A ). In a second approach, we used SHAP 68 to determine which parameters contributed most to the model for making predictions of consumer appreciation (Fig. 4B ). SHAP calculates parameter contributions to model predictions on a per-sample basis, which can be aggregated into an importance score.
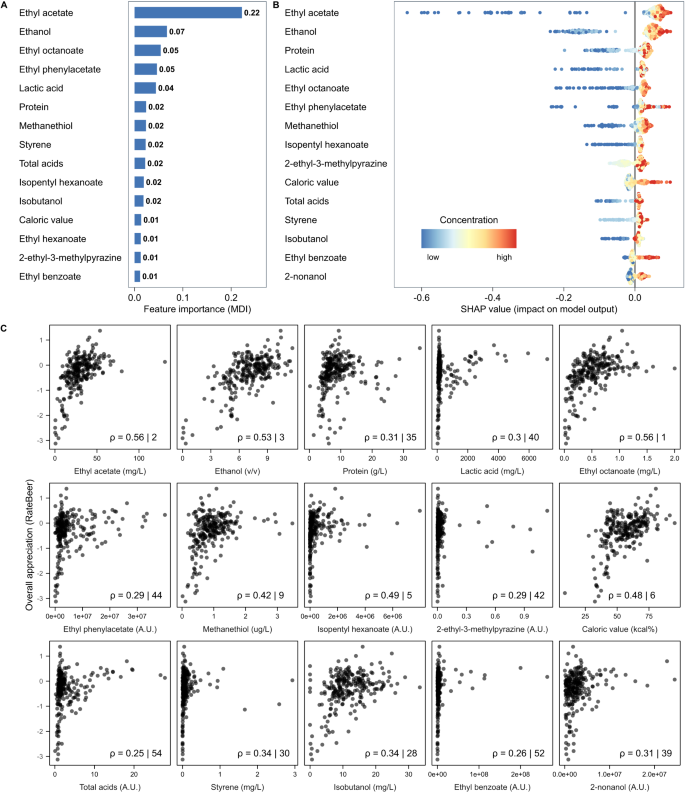
A The impurity-based feature importance (mean deviance in impurity, MDI) calculated from the Gradient Boosting Regression (GBR) model predicting RateBeer appreciation scores. The top 15 highest ranked chemical properties are shown. B SHAP summary plot for the top 15 parameters contributing to our GBR model. Each point on the graph represents a sample from our dataset. The color represents the concentration of that parameter, with bluer colors representing low values and redder colors representing higher values. Greater absolute values on the horizontal axis indicate a higher impact of the parameter on the prediction of the model. C Spearman correlations between the 15 most important chemical properties and consumer overall appreciation. Numbers indicate the Spearman Rho correlation coefficient, and the rank of this correlation compared to all other correlations. The top 15 important compounds were determined using SHAP (panel B).
Both approaches identified ethyl acetate as the most predictive parameter for beer appreciation (Fig. 4 ). Ethyl acetate is the most abundant ester in beer with a typical ‘fruity’, ‘solvent’ and ‘alcoholic’ flavor, but is often considered less important than other esters like isoamyl acetate. The second most important parameter identified by SHAP is ethanol, the most abundant beer compound after water. Apart from directly contributing to beer flavor and mouthfeel, ethanol drastically influences the physical properties of beer, dictating how easily volatile compounds escape the beer matrix to contribute to beer aroma 69 . Importantly, it should also be noted that the importance of ethanol for appreciation is likely inflated by the very low appreciation scores of non-alcoholic beers (Supplementary Fig. S4 ). Despite not often being considered a driver of beer appreciation, protein level also ranks highly in both approaches, possibly due to its effect on mouthfeel and body 70 . Lactic acid, which contributes to the tart taste of sour beers, is the fourth most important parameter identified by SHAP, possibly due to the generally high appreciation of sour beers in our dataset.
Interestingly, some of the most important predictive parameters for our model are not well-established as beer flavors or are even commonly regarded as being negative for beer quality. For example, our models identify methanethiol and ethyl phenyl acetate, an ester commonly linked to beer staling 71 , as a key factor contributing to beer appreciation. Although there is no doubt that high concentrations of these compounds are considered unpleasant, the positive effects of modest concentrations are not yet known 72 , 73 .
To compare our approach to conventional statistics, we evaluated how well the 15 most important SHAP-derived parameters correlate with consumer appreciation (Fig. 4C ). Interestingly, only 6 of the properties derived by SHAP rank amongst the top 15 most correlated parameters. For some chemical compounds, the correlations are so low that they would have likely been considered unimportant. For example, lactic acid, the fourth most important parameter, shows a bimodal distribution for appreciation, with sour beers forming a separate cluster, that is missed entirely by the Spearman correlation. Additionally, the correlation plots reveal outliers, emphasizing the need for robust analysis tools. Together, this highlights the need for alternative models, like the Gradient Boosting model, that better grasp the complexity of (beer) flavor.
Finally, to observe the relationships between these chemical properties and their predicted targets, partial dependence plots were constructed for the six most important predictors of consumer appreciation 74 , 75 , 76 (Supplementary Fig. S7 ). One-way partial dependence plots show how a change in concentration affects the predicted appreciation. These plots reveal an important limitation of our models: appreciation predictions remain constant at ever-increasing concentrations. This implies that once a threshold concentration is reached, further increasing the concentration does not affect appreciation. This is false, as it is well-documented that certain compounds become unpleasant at high concentrations, including ethyl acetate (‘nail polish’) 77 and methanethiol (‘sulfury’ and ‘rotten cabbage’) 78 . The inability of our models to grasp that flavor compounds have optimal levels, above which they become negative, is a consequence of working with commercial beer brands where (off-)flavors are rarely too high to negatively impact the product. The two-way partial dependence plots show how changing the concentration of two compounds influences predicted appreciation, visualizing their interactions (Supplementary Fig. S7 ). In our case, the top 5 parameters are dominated by additive or synergistic interactions, with high concentrations for both compounds resulting in the highest predicted appreciation.
To assess the robustness of our best-performing models and model predictions, we performed 100 iterations of the GBR, RF and ET models. In general, all iterations of the models yielded similar performance (Supplementary Fig. S8 ). Moreover, the main predictors (including the top predictors ethanol and ethyl acetate) remained virtually the same, especially for GBR and RF. For the iterations of the ET model, we did observe more variation in the top predictors, which is likely a consequence of the model’s inherent random architecture in combination with co-correlations between certain predictors. However, even in this case, several of the top predictors (ethanol and ethyl acetate) remain unchanged, although their rank in importance changes (Supplementary Fig. S8 ).
Next, we investigated if a combination of RateBeer and trained panel data into one consolidated dataset would lead to stronger models, under the hypothesis that such a model would suffer less from bias in the datasets. A GBR model was trained to predict appreciation on the combined dataset. This model underperformed compared to the RateBeer model, both in the native case and when including a dataset identifier (R 2 = 0.67, 0.26 and 0.42 respectively). For the latter, the dataset identifier is the most important feature (Supplementary Fig. S9 ), while most of the feature importance remains unchanged, with ethyl acetate and ethanol ranking highest, like in the original model trained only on RateBeer data. It seems that the large variation in the panel dataset introduces noise, weakening the models’ performances and reliability. In addition, it seems reasonable to assume that both datasets are fundamentally different, with the panel dataset obtained by blind tastings by a trained professional panel.
Lastly, we evaluated whether beer style identifiers would further enhance the model’s performance. A GBR model was trained with parameters that explicitly encoded the styles of the samples. This did not improve model performance (R2 = 0.66 with style information vs R2 = 0.67). The most important chemical features are consistent with the model trained without style information (eg. ethanol and ethyl acetate), and with the exception of the most preferred (strong ale) and least preferred (low/no-alcohol) styles, none of the styles were among the most important features (Supplementary Fig. S9 , Supplementary Table S5 and S6 ). This is likely due to a combination of style-specific chemical signatures, such as iso-alpha acids and lactic acid, that implicitly convey style information to the original models, as well as the low number of samples belonging to some styles, making it difficult for the model to learn style-specific patterns. Moreover, beer styles are not rigorously defined, with some styles overlapping in features and some beers being misattributed to a specific style, all of which leads to more noise in models that use style parameters.
Model validation
To test if our predictive models give insight into beer appreciation, we set up experiments aimed at improving existing commercial beers. We specifically selected overall appreciation as the trait to be examined because of its complexity and commercial relevance. Beer flavor comprises a complex bouquet rather than single aromas and tastes 53 . Hence, adding a single compound to the extent that a difference is noticeable may lead to an unbalanced, artificial flavor. Therefore, we evaluated the effect of combinations of compounds. Because Blond beers represent the most extensive style in our dataset, we selected a beer from this style as the starting material for these experiments (Beer 64 in Supplementary Data 1 ).
In the first set of experiments, we adjusted the concentrations of compounds that made up the most important predictors of overall appreciation (ethyl acetate, ethanol, lactic acid, ethyl phenyl acetate) together with correlated compounds (ethyl hexanoate, isoamyl acetate, glycerol), bringing them up to 95 th percentile ethanol-normalized concentrations (Methods) within the Blond group (‘Spiked’ concentration in Fig. 5A ). Compared to controls, the spiked beers were found to have significantly improved overall appreciation among trained panelists, with panelist noting increased intensity of ester flavors, sweetness, alcohol, and body fullness (Fig. 5B ). To disentangle the contribution of ethanol to these results, a second experiment was performed without the addition of ethanol. This resulted in a similar outcome, including increased perception of alcohol and overall appreciation.
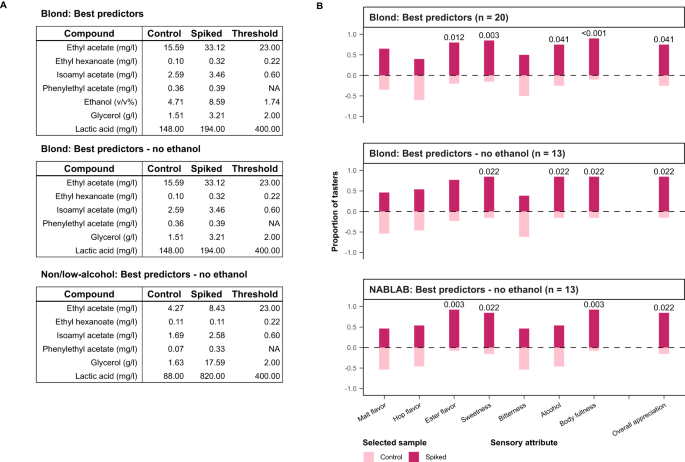
Adding the top chemical compounds, identified as best predictors of appreciation by our model, into poorly appreciated beers results in increased appreciation from our trained panel. Results of sensory tests between base beers and those spiked with compounds identified as the best predictors by the model. A Blond and Non/Low-alcohol (0.0% ABV) base beers were brought up to 95th-percentile ethanol-normalized concentrations within each style. B For each sensory attribute, tasters indicated the more intense sample and selected the sample they preferred. The numbers above the bars correspond to the p values that indicate significant changes in perceived flavor (two-sided binomial test: alpha 0.05, n = 20 or 13).
In a last experiment, we tested whether using the model’s predictions can boost the appreciation of a non-alcoholic beer (beer 223 in Supplementary Data 1 ). Again, the addition of a mixture of predicted compounds (omitting ethanol, in this case) resulted in a significant increase in appreciation, body, ester flavor and sweetness.
Predicting flavor and consumer appreciation from chemical composition is one of the ultimate goals of sensory science. A reliable, systematic and unbiased way to link chemical profiles to flavor and food appreciation would be a significant asset to the food and beverage industry. Such tools would substantially aid in quality control and recipe development, offer an efficient and cost-effective alternative to pilot studies and consumer trials and would ultimately allow food manufacturers to produce superior, tailor-made products that better meet the demands of specific consumer groups more efficiently.
A limited set of studies have previously tried, to varying degrees of success, to predict beer flavor and beer popularity based on (a limited set of) chemical compounds and flavors 79 , 80 . Current sensitive, high-throughput technologies allow measuring an unprecedented number of chemical compounds and properties in a large set of samples, yielding a dataset that can train models that help close the gaps between chemistry and flavor, even for a complex natural product like beer. To our knowledge, no previous research gathered data at this scale (250 samples, 226 chemical parameters, 50 sensory attributes and 5 consumer scores) to disentangle and validate the chemical aspects driving beer preference using various machine-learning techniques. We find that modern machine learning models outperform conventional statistical tools, such as correlations and linear models, and can successfully predict flavor appreciation from chemical composition. This could be attributed to the natural incorporation of interactions and non-linear or discontinuous effects in machine learning models, which are not easily grasped by the linear model architecture. While linear models and partial least squares regression represent the most widespread statistical approaches in sensory science, in part because they allow interpretation 65 , 81 , 82 , modern machine learning methods allow for building better predictive models while preserving the possibility to dissect and exploit the underlying patterns. Of the 10 different models we trained, tree-based models, such as our best performing GBR, showed the best overall performance in predicting sensory responses from chemical information, outcompeting artificial neural networks. This agrees with previous reports for models trained on tabular data 83 . Our results are in line with the findings of Colantonio et al. who also identified the gradient boosting architecture as performing best at predicting appreciation and flavor (of tomatoes and blueberries, in their specific study) 26 . Importantly, besides our larger experimental scale, we were able to directly confirm our models’ predictions in vivo.
Our study confirms that flavor compound concentration does not always correlate with perception, suggesting complex interactions that are often missed by more conventional statistics and simple models. Specifically, we find that tree-based algorithms may perform best in developing models that link complex food chemistry with aroma. Furthermore, we show that massive datasets of untrained consumer reviews provide a valuable source of data, that can complement or even replace trained tasting panels, especially for appreciation and basic flavors, such as sweetness and bitterness. This holds despite biases that are known to occur in such datasets, such as price or conformity bias. Moreover, GBR models predict taste better than aroma. This is likely because taste (e.g. bitterness) often directly relates to the corresponding chemical measurements (e.g., iso-alpha acids), whereas such a link is less clear for aromas, which often result from the interplay between multiple volatile compounds. We also find that our models are best at predicting acidity and alcohol, likely because there is a direct relation between the measured chemical compounds (acids and ethanol) and the corresponding perceived sensorial attribute (acidity and alcohol), and because even untrained consumers are generally able to recognize these flavors and aromas.
The predictions of our final models, trained on review data, hold even for blind tastings with small groups of trained tasters, as demonstrated by our ability to validate specific compounds as drivers of beer flavor and appreciation. Since adding a single compound to the extent of a noticeable difference may result in an unbalanced flavor profile, we specifically tested our identified key drivers as a combination of compounds. While this approach does not allow us to validate if a particular single compound would affect flavor and/or appreciation, our experiments do show that this combination of compounds increases consumer appreciation.
It is important to stress that, while it represents an important step forward, our approach still has several major limitations. A key weakness of the GBR model architecture is that amongst co-correlating variables, the largest main effect is consistently preferred for model building. As a result, co-correlating variables often have artificially low importance scores, both for impurity and SHAP-based methods, like we observed in the comparison to the more randomized Extra Trees models. This implies that chemicals identified as key drivers of a specific sensory feature by GBR might not be the true causative compounds, but rather co-correlate with the actual causative chemical. For example, the high importance of ethyl acetate could be (partially) attributed to the total ester content, ethanol or ethyl hexanoate (rho=0.77, rho=0.72 and rho=0.68), while ethyl phenylacetate could hide the importance of prenyl isobutyrate and ethyl benzoate (rho=0.77 and rho=0.76). Expanding our GBR model to include beer style as a parameter did not yield additional power or insight. This is likely due to style-specific chemical signatures, such as iso-alpha acids and lactic acid, that implicitly convey style information to the original model, as well as the smaller sample size per style, limiting the power to uncover style-specific patterns. This can be partly attributed to the curse of dimensionality, where the high number of parameters results in the models mainly incorporating single parameter effects, rather than complex interactions such as style-dependent effects 67 . A larger number of samples may overcome some of these limitations and offer more insight into style-specific effects. On the other hand, beer style is not a rigid scientific classification, and beers within one style often differ a lot, which further complicates the analysis of style as a model factor.
Our study is limited to beers from Belgian breweries. Although these beers cover a large portion of the beer styles available globally, some beer styles and consumer patterns may be missing, while other features might be overrepresented. For example, many Belgian ales exhibit yeast-driven flavor profiles, which is reflected in the chemical drivers of appreciation discovered by this study. In future work, expanding the scope to include diverse markets and beer styles could lead to the identification of even more drivers of appreciation and better models for special niche products that were not present in our beer set.
In addition to inherent limitations of GBR models, there are also some limitations associated with studying food aroma. Even if our chemical analyses measured most of the known aroma compounds, the total number of flavor compounds in complex foods like beer is still larger than the subset we were able to measure in this study. For example, hop-derived thiols, that influence flavor at very low concentrations, are notoriously difficult to measure in a high-throughput experiment. Moreover, consumer perception remains subjective and prone to biases that are difficult to avoid. It is also important to stress that the models are still immature and that more extensive datasets will be crucial for developing more complete models in the future. Besides more samples and parameters, our dataset does not include any demographic information about the tasters. Including such data could lead to better models that grasp external factors like age and culture. Another limitation is that our set of beers consists of high-quality end-products and lacks beers that are unfit for sale, which limits the current model in accurately predicting products that are appreciated very badly. Finally, while models could be readily applied in quality control, their use in sensory science and product development is restrained by their inability to discern causal relationships. Given that the models cannot distinguish compounds that genuinely drive consumer perception from those that merely correlate, validation experiments are essential to identify true causative compounds.
Despite the inherent limitations, dissection of our models enabled us to pinpoint specific molecules as potential drivers of beer aroma and consumer appreciation, including compounds that were unexpected and would not have been identified using standard approaches. Important drivers of beer appreciation uncovered by our models include protein levels, ethyl acetate, ethyl phenyl acetate and lactic acid. Currently, many brewers already use lactic acid to acidify their brewing water and ensure optimal pH for enzymatic activity during the mashing process. Our results suggest that adding lactic acid can also improve beer appreciation, although its individual effect remains to be tested. Interestingly, ethanol appears to be unnecessary to improve beer appreciation, both for blond beer and alcohol-free beer. Given the growing consumer interest in alcohol-free beer, with a predicted annual market growth of >7% 84 , it is relevant for brewers to know what compounds can further increase consumer appreciation of these beers. Hence, our model may readily provide avenues to further improve the flavor and consumer appreciation of both alcoholic and non-alcoholic beers, which is generally considered one of the key challenges for future beer production.
Whereas we see a direct implementation of our results for the development of superior alcohol-free beverages and other food products, our study can also serve as a stepping stone for the development of novel alcohol-containing beverages. We want to echo the growing body of scientific evidence for the negative effects of alcohol consumption, both on the individual level by the mutagenic, teratogenic and carcinogenic effects of ethanol 85 , 86 , as well as the burden on society caused by alcohol abuse and addiction. We encourage the use of our results for the production of healthier, tastier products, including novel and improved beverages with lower alcohol contents. Furthermore, we strongly discourage the use of these technologies to improve the appreciation or addictive properties of harmful substances.
The present work demonstrates that despite some important remaining hurdles, combining the latest developments in chemical analyses, sensory analysis and modern machine learning methods offers exciting avenues for food chemistry and engineering. Soon, these tools may provide solutions in quality control and recipe development, as well as new approaches to sensory science and flavor research.
Beer selection
250 commercial Belgian beers were selected to cover the broad diversity of beer styles and corresponding diversity in chemical composition and aroma. See Supplementary Fig. S1 .
Chemical dataset
Sample preparation.
Beers within their expiration date were purchased from commercial retailers. Samples were prepared in biological duplicates at room temperature, unless explicitly stated otherwise. Bottle pressure was measured with a manual pressure device (Steinfurth Mess-Systeme GmbH) and used to calculate CO 2 concentration. The beer was poured through two filter papers (Macherey-Nagel, 500713032 MN 713 ¼) to remove carbon dioxide and prevent spontaneous foaming. Samples were then prepared for measurements by targeted Headspace-Gas Chromatography-Flame Ionization Detector/Flame Photometric Detector (HS-GC-FID/FPD), Headspace-Solid Phase Microextraction-Gas Chromatography-Mass Spectrometry (HS-SPME-GC-MS), colorimetric analysis, enzymatic analysis, Near-Infrared (NIR) analysis, as described in the sections below. The mean values of biological duplicates are reported for each compound.
HS-GC-FID/FPD
HS-GC-FID/FPD (Shimadzu GC 2010 Plus) was used to measure higher alcohols, acetaldehyde, esters, 4-vinyl guaicol, and sulfur compounds. Each measurement comprised 5 ml of sample pipetted into a 20 ml glass vial containing 1.75 g NaCl (VWR, 27810.295). 100 µl of 2-heptanol (Sigma-Aldrich, H3003) (internal standard) solution in ethanol (Fisher Chemical, E/0650DF/C17) was added for a final concentration of 2.44 mg/L. Samples were flushed with nitrogen for 10 s, sealed with a silicone septum, stored at −80 °C and analyzed in batches of 20.
The GC was equipped with a DB-WAXetr column (length, 30 m; internal diameter, 0.32 mm; layer thickness, 0.50 µm; Agilent Technologies, Santa Clara, CA, USA) to the FID and an HP-5 column (length, 30 m; internal diameter, 0.25 mm; layer thickness, 0.25 µm; Agilent Technologies, Santa Clara, CA, USA) to the FPD. N 2 was used as the carrier gas. Samples were incubated for 20 min at 70 °C in the headspace autosampler (Flow rate, 35 cm/s; Injection volume, 1000 µL; Injection mode, split; Combi PAL autosampler, CTC analytics, Switzerland). The injector, FID and FPD temperatures were kept at 250 °C. The GC oven temperature was first held at 50 °C for 5 min and then allowed to rise to 80 °C at a rate of 5 °C/min, followed by a second ramp of 4 °C/min until 200 °C kept for 3 min and a final ramp of (4 °C/min) until 230 °C for 1 min. Results were analyzed with the GCSolution software version 2.4 (Shimadzu, Kyoto, Japan). The GC was calibrated with a 5% EtOH solution (VWR International) containing the volatiles under study (Supplementary Table S7 ).
HS-SPME-GC-MS
HS-SPME-GC-MS (Shimadzu GCMS-QP-2010 Ultra) was used to measure additional volatile compounds, mainly comprising terpenoids and esters. Samples were analyzed by HS-SPME using a triphase DVB/Carboxen/PDMS 50/30 μm SPME fiber (Supelco Co., Bellefonte, PA, USA) followed by gas chromatography (Thermo Fisher Scientific Trace 1300 series, USA) coupled to a mass spectrometer (Thermo Fisher Scientific ISQ series MS) equipped with a TriPlus RSH autosampler. 5 ml of degassed beer sample was placed in 20 ml vials containing 1.75 g NaCl (VWR, 27810.295). 5 µl internal standard mix was added, containing 2-heptanol (1 g/L) (Sigma-Aldrich, H3003), 4-fluorobenzaldehyde (1 g/L) (Sigma-Aldrich, 128376), 2,3-hexanedione (1 g/L) (Sigma-Aldrich, 144169) and guaiacol (1 g/L) (Sigma-Aldrich, W253200) in ethanol (Fisher Chemical, E/0650DF/C17). Each sample was incubated at 60 °C in the autosampler oven with constant agitation. After 5 min equilibration, the SPME fiber was exposed to the sample headspace for 30 min. The compounds trapped on the fiber were thermally desorbed in the injection port of the chromatograph by heating the fiber for 15 min at 270 °C.
The GC-MS was equipped with a low polarity RXi-5Sil MS column (length, 20 m; internal diameter, 0.18 mm; layer thickness, 0.18 µm; Restek, Bellefonte, PA, USA). Injection was performed in splitless mode at 320 °C, a split flow of 9 ml/min, a purge flow of 5 ml/min and an open valve time of 3 min. To obtain a pulsed injection, a programmed gas flow was used whereby the helium gas flow was set at 2.7 mL/min for 0.1 min, followed by a decrease in flow of 20 ml/min to the normal 0.9 mL/min. The temperature was first held at 30 °C for 3 min and then allowed to rise to 80 °C at a rate of 7 °C/min, followed by a second ramp of 2 °C/min till 125 °C and a final ramp of 8 °C/min with a final temperature of 270 °C.
Mass acquisition range was 33 to 550 amu at a scan rate of 5 scans/s. Electron impact ionization energy was 70 eV. The interface and ion source were kept at 275 °C and 250 °C, respectively. A mix of linear n-alkanes (from C7 to C40, Supelco Co.) was injected into the GC-MS under identical conditions to serve as external retention index markers. Identification and quantification of the compounds were performed using an in-house developed R script as described in Goelen et al. and Reher et al. 87 , 88 (for package information, see Supplementary Table S8 ). Briefly, chromatograms were analyzed using AMDIS (v2.71) 89 to separate overlapping peaks and obtain pure compound spectra. The NIST MS Search software (v2.0 g) in combination with the NIST2017, FFNSC3 and Adams4 libraries were used to manually identify the empirical spectra, taking into account the expected retention time. After background subtraction and correcting for retention time shifts between samples run on different days based on alkane ladders, compound elution profiles were extracted and integrated using a file with 284 target compounds of interest, which were either recovered in our identified AMDIS list of spectra or were known to occur in beer. Compound elution profiles were estimated for every peak in every chromatogram over a time-restricted window using weighted non-negative least square analysis after which peak areas were integrated 87 , 88 . Batch effect correction was performed by normalizing against the most stable internal standard compound, 4-fluorobenzaldehyde. Out of all 284 target compounds that were analyzed, 167 were visually judged to have reliable elution profiles and were used for final analysis.
Discrete photometric and enzymatic analysis
Discrete photometric and enzymatic analysis (Thermo Scientific TM Gallery TM Plus Beermaster Discrete Analyzer) was used to measure acetic acid, ammonia, beta-glucan, iso-alpha acids, color, sugars, glycerol, iron, pH, protein, and sulfite. 2 ml of sample volume was used for the analyses. Information regarding the reagents and standard solutions used for analyses and calibrations is included in Supplementary Table S7 and Supplementary Table S9 .
NIR analyses
NIR analysis (Anton Paar Alcolyzer Beer ME System) was used to measure ethanol. Measurements comprised 50 ml of sample, and a 10% EtOH solution was used for calibration.
Correlation calculations
Pairwise Spearman Rank correlations were calculated between all chemical properties.
Sensory dataset
Trained panel.
Our trained tasting panel consisted of volunteers who gave prior verbal informed consent. All compounds used for the validation experiment were of food-grade quality. The tasting sessions were approved by the Social and Societal Ethics Committee of the KU Leuven (G-2022-5677-R2(MAR)). All online reviewers agreed to the Terms and Conditions of the RateBeer website.
Sensory analysis was performed according to the American Society of Brewing Chemists (ASBC) Sensory Analysis Methods 90 . 30 volunteers were screened through a series of triangle tests. The sixteen most sensitive and consistent tasters were retained as taste panel members. The resulting panel was diverse in age [22–42, mean: 29], sex [56% male] and nationality [7 different countries]. The panel developed a consensus vocabulary to describe beer aroma, taste and mouthfeel. Panelists were trained to identify and score 50 different attributes, using a 7-point scale to rate attributes’ intensity. The scoring sheet is included as Supplementary Data 3 . Sensory assessments took place between 10–12 a.m. The beers were served in black-colored glasses. Per session, between 5 and 12 beers of the same style were tasted at 12 °C to 16 °C. Two reference beers were added to each set and indicated as ‘Reference 1 & 2’, allowing panel members to calibrate their ratings. Not all panelists were present at every tasting. Scores were scaled by standard deviation and mean-centered per taster. Values are represented as z-scores and clustered by Euclidean distance. Pairwise Spearman correlations were calculated between taste and aroma sensory attributes. Panel consistency was evaluated by repeating samples on different sessions and performing ANOVA to identify differences, using the ‘stats’ package (v4.2.2) in R (for package information, see Supplementary Table S8 ).
Online reviews from a public database
The ‘scrapy’ package in Python (v3.6) (for package information, see Supplementary Table S8 ). was used to collect 232,288 online reviews (mean=922, min=6, max=5343) from RateBeer, an online beer review database. Each review entry comprised 5 numerical scores (appearance, aroma, taste, palate and overall quality) and an optional review text. The total number of reviews per reviewer was collected separately. Numerical scores were scaled and centered per rater, and mean scores were calculated per beer.
For the review texts, the language was estimated using the packages ‘langdetect’ and ‘langid’ in Python. Reviews that were classified as English by both packages were kept. Reviewers with fewer than 100 entries overall were discarded. 181,025 reviews from >6000 reviewers from >40 countries remained. Text processing was done using the ‘nltk’ package in Python. Texts were corrected for slang and misspellings; proper nouns and rare words that are relevant to the beer context were specified and kept as-is (‘Chimay’,’Lambic’, etc.). A dictionary of semantically similar sensorial terms, for example ‘floral’ and ‘flower’, was created and collapsed together into one term. Words were stemmed and lemmatized to avoid identifying words such as ‘acid’ and ‘acidity’ as separate terms. Numbers and punctuation were removed.
Sentences from up to 50 randomly chosen reviews per beer were manually categorized according to the aspect of beer they describe (appearance, aroma, taste, palate, overall quality—not to be confused with the 5 numerical scores described above) or flagged as irrelevant if they contained no useful information. If a beer contained fewer than 50 reviews, all reviews were manually classified. This labeled data set was used to train a model that classified the rest of the sentences for all beers 91 . Sentences describing taste and aroma were extracted, and term frequency–inverse document frequency (TFIDF) was implemented to calculate enrichment scores for sensorial words per beer.
The sex of the tasting subject was not considered when building our sensory database. Instead, results from different panelists were averaged, both for our trained panel (56% male, 44% female) and the RateBeer reviews (70% male, 30% female for RateBeer as a whole).
Beer price collection and processing
Beer prices were collected from the following stores: Colruyt, Delhaize, Total Wine, BeerHawk, The Belgian Beer Shop, The Belgian Shop, and Beer of Belgium. Where applicable, prices were converted to Euros and normalized per liter. Spearman correlations were calculated between these prices and mean overall appreciation scores from RateBeer and the taste panel, respectively.
Pairwise Spearman Rank correlations were calculated between all sensory properties.
Machine learning models
Predictive modeling of sensory profiles from chemical data.
Regression models were constructed to predict (a) trained panel scores for beer flavors and quality from beer chemical profiles and (b) public reviews’ appreciation scores from beer chemical profiles. Z-scores were used to represent sensory attributes in both data sets. Chemical properties with log-normal distributions (Shapiro-Wilk test, p < 0.05 ) were log-transformed. Missing chemical measurements (0.1% of all data) were replaced with mean values per attribute. Observations from 250 beers were randomly separated into a training set (70%, 175 beers) and a test set (30%, 75 beers), stratified per beer style. Chemical measurements (p = 231) were normalized based on the training set average and standard deviation. In total, three linear regression-based models: linear regression with first-order interaction terms (LR), lasso regression with first-order interaction terms (Lasso) and partial least squares regression (PLSR); five decision tree models, Adaboost regressor (ABR), Extra Trees (ET), Gradient Boosting regressor (GBR), Random Forest (RF) and XGBoost regressor (XGBR); one support vector machine model (SVR) and one artificial neural network model (ANN) were trained. The models were implemented using the ‘scikit-learn’ package (v1.2.2) and ‘xgboost’ package (v1.7.3) in Python (v3.9.16). Models were trained, and hyperparameters optimized, using five-fold cross-validated grid search with the coefficient of determination (R 2 ) as the evaluation metric. The ANN (scikit-learn’s MLPRegressor) was optimized using Bayesian Tree-Structured Parzen Estimator optimization with the ‘Optuna’ Python package (v3.2.0). Individual models were trained per attribute, and a multi-output model was trained on all attributes simultaneously.
Model dissection
GBR was found to outperform other methods, resulting in models with the highest average R 2 values in both trained panel and public review data sets. Impurity-based rankings of the most important predictors for each predicted sensorial trait were obtained using the ‘scikit-learn’ package. To observe the relationships between these chemical properties and their predicted targets, partial dependence plots (PDP) were constructed for the six most important predictors of consumer appreciation 74 , 75 .
The ‘SHAP’ package in Python (v0.41.0) was implemented to provide an alternative ranking of predictor importance and to visualize the predictors’ effects as a function of their concentration 68 .
Validation of causal chemical properties
To validate the effects of the most important model features on predicted sensory attributes, beers were spiked with the chemical compounds identified by the models and descriptive sensory analyses were carried out according to the American Society of Brewing Chemists (ASBC) protocol 90 .
Compound spiking was done 30 min before tasting. Compounds were spiked into fresh beer bottles, that were immediately resealed and inverted three times. Fresh bottles of beer were opened for the same duration, resealed, and inverted thrice, to serve as controls. Pairs of spiked samples and controls were served simultaneously, chilled and in dark glasses as outlined in the Trained panel section above. Tasters were instructed to select the glass with the higher flavor intensity for each attribute (directional difference test 92 ) and to select the glass they prefer.
The final concentration after spiking was equal to the within-style average, after normalizing by ethanol concentration. This was done to ensure balanced flavor profiles in the final spiked beer. The same methods were applied to improve a non-alcoholic beer. Compounds were the following: ethyl acetate (Merck KGaA, W241415), ethyl hexanoate (Merck KGaA, W243906), isoamyl acetate (Merck KGaA, W205508), phenethyl acetate (Merck KGaA, W285706), ethanol (96%, Colruyt), glycerol (Merck KGaA, W252506), lactic acid (Merck KGaA, 261106).
Significant differences in preference or perceived intensity were determined by performing the two-sided binomial test on each attribute.
Reporting summary
Further information on research design is available in the Nature Portfolio Reporting Summary linked to this article.
Data availability
The data that support the findings of this work are available in the Supplementary Data files and have been deposited to Zenodo under accession code 10653704 93 . The RateBeer scores data are under restricted access, they are not publicly available as they are property of RateBeer (ZX Ventures, USA). Access can be obtained from the authors upon reasonable request and with permission of RateBeer (ZX Ventures, USA). Source data are provided with this paper.
Code availability
The code for training the machine learning models, analyzing the models, and generating the figures has been deposited to Zenodo under accession code 10653704 93 .
Tieman, D. et al. A chemical genetic roadmap to improved tomato flavor. Science 355 , 391–394 (2017).
Article ADS CAS PubMed Google Scholar
Plutowska, B. & Wardencki, W. Application of gas chromatography–olfactometry (GC–O) in analysis and quality assessment of alcoholic beverages – A review. Food Chem. 107 , 449–463 (2008).
Article CAS Google Scholar
Legin, A., Rudnitskaya, A., Seleznev, B. & Vlasov, Y. Electronic tongue for quality assessment of ethanol, vodka and eau-de-vie. Anal. Chim. Acta 534 , 129–135 (2005).
Loutfi, A., Coradeschi, S., Mani, G. K., Shankar, P. & Rayappan, J. B. B. Electronic noses for food quality: A review. J. Food Eng. 144 , 103–111 (2015).
Ahn, Y.-Y., Ahnert, S. E., Bagrow, J. P. & Barabási, A.-L. Flavor network and the principles of food pairing. Sci. Rep. 1 , 196 (2011).
Article CAS PubMed PubMed Central Google Scholar
Bartoshuk, L. M. & Klee, H. J. Better fruits and vegetables through sensory analysis. Curr. Biol. 23 , R374–R378 (2013).
Article CAS PubMed Google Scholar
Piggott, J. R. Design questions in sensory and consumer science. Food Qual. Prefer. 3293 , 217–220 (1995).
Article Google Scholar
Kermit, M. & Lengard, V. Assessing the performance of a sensory panel-panellist monitoring and tracking. J. Chemom. 19 , 154–161 (2005).
Cook, D. J., Hollowood, T. A., Linforth, R. S. T. & Taylor, A. J. Correlating instrumental measurements of texture and flavour release with human perception. Int. J. Food Sci. Technol. 40 , 631–641 (2005).
Chinchanachokchai, S., Thontirawong, P. & Chinchanachokchai, P. A tale of two recommender systems: The moderating role of consumer expertise on artificial intelligence based product recommendations. J. Retail. Consum. Serv. 61 , 1–12 (2021).
Ross, C. F. Sensory science at the human-machine interface. Trends Food Sci. Technol. 20 , 63–72 (2009).
Chambers, E. IV & Koppel, K. Associations of volatile compounds with sensory aroma and flavor: The complex nature of flavor. Molecules 18 , 4887–4905 (2013).
Pinu, F. R. Metabolomics—The new frontier in food safety and quality research. Food Res. Int. 72 , 80–81 (2015).
Danezis, G. P., Tsagkaris, A. S., Brusic, V. & Georgiou, C. A. Food authentication: state of the art and prospects. Curr. Opin. Food Sci. 10 , 22–31 (2016).
Shepherd, G. M. Smell images and the flavour system in the human brain. Nature 444 , 316–321 (2006).
Meilgaard, M. C. Prediction of flavor differences between beers from their chemical composition. J. Agric. Food Chem. 30 , 1009–1017 (1982).
Xu, L. et al. Widespread receptor-driven modulation in peripheral olfactory coding. Science 368 , eaaz5390 (2020).
Kupferschmidt, K. Following the flavor. Science 340 , 808–809 (2013).
Billesbølle, C. B. et al. Structural basis of odorant recognition by a human odorant receptor. Nature 615 , 742–749 (2023).
Article ADS PubMed PubMed Central Google Scholar
Smith, B. Perspective: Complexities of flavour. Nature 486 , S6–S6 (2012).
Pfister, P. et al. Odorant receptor inhibition is fundamental to odor encoding. Curr. Biol. 30 , 2574–2587 (2020).
Moskowitz, H. W., Kumaraiah, V., Sharma, K. N., Jacobs, H. L. & Sharma, S. D. Cross-cultural differences in simple taste preferences. Science 190 , 1217–1218 (1975).
Eriksson, N. et al. A genetic variant near olfactory receptor genes influences cilantro preference. Flavour 1 , 22 (2012).
Ferdenzi, C. et al. Variability of affective responses to odors: Culture, gender, and olfactory knowledge. Chem. Senses 38 , 175–186 (2013).
Article PubMed Google Scholar
Lawless, H. T. & Heymann, H. Sensory evaluation of food: Principles and practices. (Springer, New York, NY). https://doi.org/10.1007/978-1-4419-6488-5 (2010).
Colantonio, V. et al. Metabolomic selection for enhanced fruit flavor. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. 119 , e2115865119 (2022).
Fritz, F., Preissner, R. & Banerjee, P. VirtualTaste: a web server for the prediction of organoleptic properties of chemical compounds. Nucleic Acids Res 49 , W679–W684 (2021).
Tuwani, R., Wadhwa, S. & Bagler, G. BitterSweet: Building machine learning models for predicting the bitter and sweet taste of small molecules. Sci. Rep. 9 , 1–13 (2019).
Dagan-Wiener, A. et al. Bitter or not? BitterPredict, a tool for predicting taste from chemical structure. Sci. Rep. 7 , 1–13 (2017).
Pallante, L. et al. Toward a general and interpretable umami taste predictor using a multi-objective machine learning approach. Sci. Rep. 12 , 1–11 (2022).
Malavolta, M. et al. A survey on computational taste predictors. Eur. Food Res. Technol. 248 , 2215–2235 (2022).
Lee, B. K. et al. A principal odor map unifies diverse tasks in olfactory perception. Science 381 , 999–1006 (2023).
Mayhew, E. J. et al. Transport features predict if a molecule is odorous. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. 119 , e2116576119 (2022).
Niu, Y. et al. Sensory evaluation of the synergism among ester odorants in light aroma-type liquor by odor threshold, aroma intensity and flash GC electronic nose. Food Res. Int. 113 , 102–114 (2018).
Yu, P., Low, M. Y. & Zhou, W. Design of experiments and regression modelling in food flavour and sensory analysis: A review. Trends Food Sci. Technol. 71 , 202–215 (2018).
Oladokun, O. et al. The impact of hop bitter acid and polyphenol profiles on the perceived bitterness of beer. Food Chem. 205 , 212–220 (2016).
Linforth, R., Cabannes, M., Hewson, L., Yang, N. & Taylor, A. Effect of fat content on flavor delivery during consumption: An in vivo model. J. Agric. Food Chem. 58 , 6905–6911 (2010).
Guo, S., Na Jom, K. & Ge, Y. Influence of roasting condition on flavor profile of sunflower seeds: A flavoromics approach. Sci. Rep. 9 , 11295 (2019).
Ren, Q. et al. The changes of microbial community and flavor compound in the fermentation process of Chinese rice wine using Fagopyrum tataricum grain as feedstock. Sci. Rep. 9 , 3365 (2019).
Hastie, T., Friedman, J. & Tibshirani, R. The Elements of Statistical Learning. (Springer, New York, NY). https://doi.org/10.1007/978-0-387-21606-5 (2001).
Dietz, C., Cook, D., Huismann, M., Wilson, C. & Ford, R. The multisensory perception of hop essential oil: a review. J. Inst. Brew. 126 , 320–342 (2020).
CAS Google Scholar
Roncoroni, Miguel & Verstrepen, Kevin Joan. Belgian Beer: Tested and Tasted. (Lannoo, 2018).
Meilgaard, M. Flavor chemistry of beer: Part II: Flavor and threshold of 239 aroma volatiles. in (1975).
Bokulich, N. A. & Bamforth, C. W. The microbiology of malting and brewing. Microbiol. Mol. Biol. Rev. MMBR 77 , 157–172 (2013).
Dzialo, M. C., Park, R., Steensels, J., Lievens, B. & Verstrepen, K. J. Physiology, ecology and industrial applications of aroma formation in yeast. FEMS Microbiol. Rev. 41 , S95–S128 (2017).
Article PubMed PubMed Central Google Scholar
Datta, A. et al. Computer-aided food engineering. Nat. Food 3 , 894–904 (2022).
American Society of Brewing Chemists. Beer Methods. (American Society of Brewing Chemists, St. Paul, MN, U.S.A.).
Olaniran, A. O., Hiralal, L., Mokoena, M. P. & Pillay, B. Flavour-active volatile compounds in beer: production, regulation and control. J. Inst. Brew. 123 , 13–23 (2017).
Verstrepen, K. J. et al. Flavor-active esters: Adding fruitiness to beer. J. Biosci. Bioeng. 96 , 110–118 (2003).
Meilgaard, M. C. Flavour chemistry of beer. part I: flavour interaction between principal volatiles. Master Brew. Assoc. Am. Tech. Q 12 , 107–117 (1975).
Briggs, D. E., Boulton, C. A., Brookes, P. A. & Stevens, R. Brewing 227–254. (Woodhead Publishing). https://doi.org/10.1533/9781855739062.227 (2004).
Bossaert, S., Crauwels, S., De Rouck, G. & Lievens, B. The power of sour - A review: Old traditions, new opportunities. BrewingScience 72 , 78–88 (2019).
Google Scholar
Verstrepen, K. J. et al. Flavor active esters: Adding fruitiness to beer. J. Biosci. Bioeng. 96 , 110–118 (2003).
Snauwaert, I. et al. Microbial diversity and metabolite composition of Belgian red-brown acidic ales. Int. J. Food Microbiol. 221 , 1–11 (2016).
Spitaels, F. et al. The microbial diversity of traditional spontaneously fermented lambic beer. PLoS ONE 9 , e95384 (2014).
Blanco, C. A., Andrés-Iglesias, C. & Montero, O. Low-alcohol Beers: Flavor Compounds, Defects, and Improvement Strategies. Crit. Rev. Food Sci. Nutr. 56 , 1379–1388 (2016).
Jackowski, M. & Trusek, A. Non-Alcohol. beer Prod. – Overv. 20 , 32–38 (2018).
Takoi, K. et al. The contribution of geraniol metabolism to the citrus flavour of beer: Synergy of geraniol and β-citronellol under coexistence with excess linalool. J. Inst. Brew. 116 , 251–260 (2010).
Kroeze, J. H. & Bartoshuk, L. M. Bitterness suppression as revealed by split-tongue taste stimulation in humans. Physiol. Behav. 35 , 779–783 (1985).
Mennella, J. A. et al. A spoonful of sugar helps the medicine go down”: Bitter masking bysucrose among children and adults. Chem. Senses 40 , 17–25 (2015).
Wietstock, P., Kunz, T., Perreira, F. & Methner, F.-J. Metal chelation behavior of hop acids in buffered model systems. BrewingScience 69 , 56–63 (2016).
Sancho, D., Blanco, C. A., Caballero, I. & Pascual, A. Free iron in pale, dark and alcohol-free commercial lager beers. J. Sci. Food Agric. 91 , 1142–1147 (2011).
Rodrigues, H. & Parr, W. V. Contribution of cross-cultural studies to understanding wine appreciation: A review. Food Res. Int. 115 , 251–258 (2019).
Korneva, E. & Blockeel, H. Towards better evaluation of multi-target regression models. in ECML PKDD 2020 Workshops (eds. Koprinska, I. et al.) 353–362 (Springer International Publishing, Cham, 2020). https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-030-65965-3_23 .
Gastón Ares. Mathematical and Statistical Methods in Food Science and Technology. (Wiley, 2013).
Grinsztajn, L., Oyallon, E. & Varoquaux, G. Why do tree-based models still outperform deep learning on tabular data? Preprint at http://arxiv.org/abs/2207.08815 (2022).
Gries, S. T. Statistics for Linguistics with R: A Practical Introduction. in Statistics for Linguistics with R (De Gruyter Mouton, 2021). https://doi.org/10.1515/9783110718256 .
Lundberg, S. M. et al. From local explanations to global understanding with explainable AI for trees. Nat. Mach. Intell. 2 , 56–67 (2020).
Ickes, C. M. & Cadwallader, K. R. Effects of ethanol on flavor perception in alcoholic beverages. Chemosens. Percept. 10 , 119–134 (2017).
Kato, M. et al. Influence of high molecular weight polypeptides on the mouthfeel of commercial beer. J. Inst. Brew. 127 , 27–40 (2021).
Wauters, R. et al. Novel Saccharomyces cerevisiae variants slow down the accumulation of staling aldehydes and improve beer shelf-life. Food Chem. 398 , 1–11 (2023).
Li, H., Jia, S. & Zhang, W. Rapid determination of low-level sulfur compounds in beer by headspace gas chromatography with a pulsed flame photometric detector. J. Am. Soc. Brew. Chem. 66 , 188–191 (2008).
Dercksen, A., Laurens, J., Torline, P., Axcell, B. C. & Rohwer, E. Quantitative analysis of volatile sulfur compounds in beer using a membrane extraction interface. J. Am. Soc. Brew. Chem. 54 , 228–233 (1996).
Molnar, C. Interpretable Machine Learning: A Guide for Making Black-Box Models Interpretable. (2020).
Zhao, Q. & Hastie, T. Causal interpretations of black-box models. J. Bus. Econ. Stat. Publ. Am. Stat. Assoc. 39 , 272–281 (2019).
Article MathSciNet Google Scholar
Hastie, T., Tibshirani, R. & Friedman, J. The Elements of Statistical Learning. (Springer, 2019).
Labrado, D. et al. Identification by NMR of key compounds present in beer distillates and residual phases after dealcoholization by vacuum distillation. J. Sci. Food Agric. 100 , 3971–3978 (2020).
Lusk, L. T., Kay, S. B., Porubcan, A. & Ryder, D. S. Key olfactory cues for beer oxidation. J. Am. Soc. Brew. Chem. 70 , 257–261 (2012).
Gonzalez Viejo, C., Torrico, D. D., Dunshea, F. R. & Fuentes, S. Development of artificial neural network models to assess beer acceptability based on sensory properties using a robotic pourer: A comparative model approach to achieve an artificial intelligence system. Beverages 5 , 33 (2019).
Gonzalez Viejo, C., Fuentes, S., Torrico, D. D., Godbole, A. & Dunshea, F. R. Chemical characterization of aromas in beer and their effect on consumers liking. Food Chem. 293 , 479–485 (2019).
Gilbert, J. L. et al. Identifying breeding priorities for blueberry flavor using biochemical, sensory, and genotype by environment analyses. PLOS ONE 10 , 1–21 (2015).
Goulet, C. et al. Role of an esterase in flavor volatile variation within the tomato clade. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. 109 , 19009–19014 (2012).
Article ADS CAS PubMed PubMed Central Google Scholar
Borisov, V. et al. Deep Neural Networks and Tabular Data: A Survey. IEEE Trans. Neural Netw. Learn. Syst. 1–21 https://doi.org/10.1109/TNNLS.2022.3229161 (2022).
Statista. Statista Consumer Market Outlook: Beer - Worldwide.
Seitz, H. K. & Stickel, F. Molecular mechanisms of alcoholmediated carcinogenesis. Nat. Rev. Cancer 7 , 599–612 (2007).
Voordeckers, K. et al. Ethanol exposure increases mutation rate through error-prone polymerases. Nat. Commun. 11 , 3664 (2020).
Goelen, T. et al. Bacterial phylogeny predicts volatile organic compound composition and olfactory response of an aphid parasitoid. Oikos 129 , 1415–1428 (2020).
Article ADS Google Scholar
Reher, T. et al. Evaluation of hop (Humulus lupulus) as a repellent for the management of Drosophila suzukii. Crop Prot. 124 , 104839 (2019).
Stein, S. E. An integrated method for spectrum extraction and compound identification from gas chromatography/mass spectrometry data. J. Am. Soc. Mass Spectrom. 10 , 770–781 (1999).
American Society of Brewing Chemists. Sensory Analysis Methods. (American Society of Brewing Chemists, St. Paul, MN, U.S.A., 1992).
McAuley, J., Leskovec, J. & Jurafsky, D. Learning Attitudes and Attributes from Multi-Aspect Reviews. Preprint at https://doi.org/10.48550/arXiv.1210.3926 (2012).
Meilgaard, M. C., Carr, B. T. & Carr, B. T. Sensory Evaluation Techniques. (CRC Press, Boca Raton). https://doi.org/10.1201/b16452 (2014).
Schreurs, M. et al. Data from: Predicting and improving complex beer flavor through machine learning. Zenodo https://doi.org/10.5281/zenodo.10653704 (2024).
Download references
Acknowledgements
We thank all lab members for their discussions and thank all tasting panel members for their contributions. Special thanks go out to Dr. Karin Voordeckers for her tremendous help in proofreading and improving the manuscript. M.S. was supported by a Baillet-Latour fellowship, L.C. acknowledges financial support from KU Leuven (C16/17/006), F.A.T. was supported by a PhD fellowship from FWO (1S08821N). Research in the lab of K.J.V. is supported by KU Leuven, FWO, VIB, VLAIO and the Brewing Science Serves Health Fund. Research in the lab of T.W. is supported by FWO (G.0A51.15) and KU Leuven (C16/17/006).
Author information
These authors contributed equally: Michiel Schreurs, Supinya Piampongsant, Miguel Roncoroni.
Authors and Affiliations
VIB—KU Leuven Center for Microbiology, Gaston Geenslaan 1, B-3001, Leuven, Belgium
Michiel Schreurs, Supinya Piampongsant, Miguel Roncoroni, Lloyd Cool, Beatriz Herrera-Malaver, Florian A. Theßeling & Kevin J. Verstrepen
CMPG Laboratory of Genetics and Genomics, KU Leuven, Gaston Geenslaan 1, B-3001, Leuven, Belgium
Leuven Institute for Beer Research (LIBR), Gaston Geenslaan 1, B-3001, Leuven, Belgium
Laboratory of Socioecology and Social Evolution, KU Leuven, Naamsestraat 59, B-3000, Leuven, Belgium
Lloyd Cool, Christophe Vanderaa & Tom Wenseleers
VIB Bioinformatics Core, VIB, Rijvisschestraat 120, B-9052, Ghent, Belgium
Łukasz Kreft & Alexander Botzki
AB InBev SA/NV, Brouwerijplein 1, B-3000, Leuven, Belgium
Philippe Malcorps & Luk Daenen
You can also search for this author in PubMed Google Scholar
Contributions
S.P., M.S. and K.J.V. conceived the experiments. S.P., M.S. and K.J.V. designed the experiments. S.P., M.S., M.R., B.H. and F.A.T. performed the experiments. S.P., M.S., L.C., C.V., L.K., A.B., P.M., L.D., T.W. and K.J.V. contributed analysis ideas. S.P., M.S., L.C., C.V., T.W. and K.J.V. analyzed the data. All authors contributed to writing the manuscript.
Corresponding author
Correspondence to Kevin J. Verstrepen .
Ethics declarations
Competing interests.
K.J.V. is affiliated with bar.on. The other authors declare no competing interests.
Peer review
Peer review information.
Nature Communications thanks Florian Bauer, Andrew John Macintosh and the other, anonymous, reviewer(s) for their contribution to the peer review of this work. A peer review file is available.
Additional information
Publisher’s note Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Supplementary information
Supplementary information, peer review file, description of additional supplementary files, supplementary data 1, supplementary data 2, supplementary data 3, supplementary data 4, supplementary data 5, supplementary data 6, supplementary data 7, reporting summary, source data, source data, rights and permissions.
Open Access This article is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License, which permits use, sharing, adaptation, distribution and reproduction in any medium or format, as long as you give appropriate credit to the original author(s) and the source, provide a link to the Creative Commons licence, and indicate if changes were made. The images or other third party material in this article are included in the article’s Creative Commons licence, unless indicated otherwise in a credit line to the material. If material is not included in the article’s Creative Commons licence and your intended use is not permitted by statutory regulation or exceeds the permitted use, you will need to obtain permission directly from the copyright holder. To view a copy of this licence, visit http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/ .
Reprints and permissions
About this article
Cite this article.
Schreurs, M., Piampongsant, S., Roncoroni, M. et al. Predicting and improving complex beer flavor through machine learning. Nat Commun 15 , 2368 (2024). https://doi.org/10.1038/s41467-024-46346-0
Download citation
Received : 30 October 2023
Accepted : 21 February 2024
Published : 26 March 2024
DOI : https://doi.org/10.1038/s41467-024-46346-0
Share this article
Anyone you share the following link with will be able to read this content:
Sorry, a shareable link is not currently available for this article.
Provided by the Springer Nature SharedIt content-sharing initiative
By submitting a comment you agree to abide by our Terms and Community Guidelines . If you find something abusive or that does not comply with our terms or guidelines please flag it as inappropriate.
Quick links
- Explore articles by subject
- Guide to authors
- Editorial policies
Sign up for the Nature Briefing: Translational Research newsletter — top stories in biotechnology, drug discovery and pharma.
See More About
Select your interests.
Customize your JAMA Network experience by selecting one or more topics from the list below.
- Academic Medicine
- Acid Base, Electrolytes, Fluids
- Allergy and Clinical Immunology
- American Indian or Alaska Natives
- Anesthesiology
- Anticoagulation
- Art and Images in Psychiatry
- Artificial Intelligence
- Assisted Reproduction
- Bleeding and Transfusion
- Caring for the Critically Ill Patient
- Challenges in Clinical Electrocardiography
- Climate and Health
- Climate Change
- Clinical Challenge
- Clinical Decision Support
- Clinical Implications of Basic Neuroscience
- Clinical Pharmacy and Pharmacology
- Complementary and Alternative Medicine
- Consensus Statements
- Coronavirus (COVID-19)
- Critical Care Medicine
- Cultural Competency
- Dental Medicine
- Dermatology
- Diabetes and Endocrinology
- Diagnostic Test Interpretation
- Drug Development
- Electronic Health Records
- Emergency Medicine
- End of Life, Hospice, Palliative Care
- Environmental Health
- Equity, Diversity, and Inclusion
- Facial Plastic Surgery
- Gastroenterology and Hepatology
- Genetics and Genomics
- Genomics and Precision Health
- Global Health
- Guide to Statistics and Methods
- Hair Disorders
- Health Care Delivery Models
- Health Care Economics, Insurance, Payment
- Health Care Quality
- Health Care Reform
- Health Care Safety
- Health Care Workforce
- Health Disparities
- Health Inequities
- Health Policy
- Health Systems Science
- History of Medicine
- Hypertension
- Images in Neurology
- Implementation Science
- Infectious Diseases
- Innovations in Health Care Delivery
- JAMA Infographic
- Law and Medicine
- Leading Change
- Less is More
- LGBTQIA Medicine
- Lifestyle Behaviors
- Medical Coding
- Medical Devices and Equipment
- Medical Education
- Medical Education and Training
- Medical Journals and Publishing
- Mobile Health and Telemedicine
- Narrative Medicine
- Neuroscience and Psychiatry
- Notable Notes
- Nutrition, Obesity, Exercise
- Obstetrics and Gynecology
- Occupational Health
- Ophthalmology
- Orthopedics
- Otolaryngology
- Pain Medicine
- Palliative Care
- Pathology and Laboratory Medicine
- Patient Care
- Patient Information
- Performance Improvement
- Performance Measures
- Perioperative Care and Consultation
- Pharmacoeconomics
- Pharmacoepidemiology
- Pharmacogenetics
- Pharmacy and Clinical Pharmacology
- Physical Medicine and Rehabilitation
- Physical Therapy
- Physician Leadership
- Population Health
- Primary Care
- Professional Well-being
- Professionalism
- Psychiatry and Behavioral Health
- Public Health
- Pulmonary Medicine
- Regulatory Agencies
- Reproductive Health
- Research, Methods, Statistics
- Resuscitation
- Rheumatology
- Risk Management
- Scientific Discovery and the Future of Medicine
- Shared Decision Making and Communication
- Sleep Medicine
- Sports Medicine
- Stem Cell Transplantation
- Substance Use and Addiction Medicine
- Surgical Innovation
- Surgical Pearls
- Teachable Moment
- Technology and Finance
- The Art of JAMA
- The Arts and Medicine
- The Rational Clinical Examination
- Tobacco and e-Cigarettes
- Translational Medicine
- Trauma and Injury
- Treatment Adherence
- Ultrasonography
- Users' Guide to the Medical Literature
- Vaccination
- Venous Thromboembolism
- Veterans Health
- Women's Health
- Workflow and Process
- Wound Care, Infection, Healing
Others Also Liked
- Download PDF
- X Facebook More LinkedIn
Pitkin RM , Branagan MA , Burmeister LF. Accuracy of Data in Abstracts of Published Research Articles. JAMA. 1999;281(12):1110–1111. doi:10.1001/jama.281.12.1110
Manage citations:
© 2024
- Permissions
Accuracy of Data in Abstracts of Published Research Articles
Author Affiliations: Obstetrics & Gynecology , Los Angeles, Calif (Dr Pitkin); Chest , Northbrook, Ill (Ms Branagan); and Department of Preventive Medicine, University of Iowa, Iowa City (Dr Burmeister).
Context The section of a research article most likely to be read is the abstract, and therefore it is particularly important that the abstract reflect the article faithfully.
Objective To assess abstracts accompanying research articles published in 6 medical journals with respect to whether data in the abstract could be verified in the article itself.
Design Analysis of simple random samples of 44 articles and their accompanying abstracts published during 1 year (July 1, 1996-June 30, 1997) in each of 5 major general medical journals ( Annals of Internal Medicine , BMJ , JAMA, Lancet , and New England Journal of Medicine ) and a consecutive sample of 44 articles published during 15 months (July 1, 1996-August 15, 1997) in the CMAJ .
Main Outcome Measure Abstracts were considered deficient if they contained data that were either inconsistent with corresponding data in the article's body (including tables and figures) or not found in the body at all.
Results The proportion of deficient abstracts varied widely (18%-68%) and to a statistically significant degree ( P <.001) among the 6 journals studied.
Conclusions Data in the abstract that are inconsistent with or absent from the article's body are common, even in large-circulation general medical journals.
The abstract accompanying a research article, because it is often the only part of the article that will be read, should reflect fully and accurately the work reported. We observed in 1 medical specialty journal that a quarter or more of manuscripts returned after revision contained data in the abstract that could not be verified in the body of the paper. 1 If this problem were to persist in published articles, then a potential for misinterpretation would exist. In the present study, we surveyed research articles and their accompanying abstracts published recently in 6 medical journals to verify data in the abstract by relating them to corresponding data in the body of the report.
Articles studied included simple random samples of reports of original research (including meta-analyses but not other types of reviews) appearing in 5 medical journals between July 1, 1996, and June 30, 1997 ( Annals of Internal Medicine , BMJ , JAMA, Lancet , and New England Journal of Medicine ); all articles appearing in a sixth journal CMAJ ( Canadian Medical Association Journal ), between July 1, 1996, and August 15, 1997, were also studied. Additional inclusion criteria were (1) the article was accompanied by an abstract and (2) the article occupied at least 2 full journal pages.
To estimate the sample sizes, we used some preliminary observations 1 that 25% to 50% of articles published in 2 of the journals studied contained 1 or more deficiencies in abstracts. We assumed this rate would range from 10% to 40% across the 6 journals studied and that α was .05 and power was 0.8, yielding a projected sample size of 44 from each journal. From each of the 5 journals that published more than 44 research articles in the 2 volumes studied (July 1, 1996-June 30, 1997), we selected a computer-generated simple random sample of 44. From the CMAJ , we analyzed a consecutive cohort of all 44 articles published from July 1, 1996, through August 15, 1997.
For each selected article, the abstract was scrutinized by 1 of 3 examiners who identified each datum or other piece of information in the abstract and then sought to relate it to its source in the body of the article, including tables and figures. Two types of discrepancies were sought: (1) data given differently in the abstract and the body and (2) data given in the abstract but not in the body. If either was identified, the abstract was considered deficient. Discrepancies attributable to rounding were not considered to be deficiencies as long as the rounding was done appropriately, and the rounded value appeared in the abstract and the more detailed value in the body.
The proportions of articles containing deficiencies were compared across journals by χ 2 analysis. On the basis of normal approximation, 95% confidence intervals (CIs) were calculated for each proportion. We also performed a validation study by randomly selecting (using another computer-generated random number sequence) 7 of each set of 44 articles and having these examined by a second (and different) examiner.
Table 1 contains the proportions of deficient abstracts and 95% CIs for each journal, tabulated considering the abstract as the unit, as well as the types of deficiencies found in the 6 journals. The proportion of deficient abstracts ranged from a low of 18% to a high of 68%. Inconsistency between abstract and body was generally more common than omitted data (ie, data in the abstract not found in the body). A substantial proportion of deficient abstracts contained both kinds of defects (25/104; 24%).
In the validation study, 38 of the 42 paired comparisons were concordant with respect to identification of deficiencies. The κ value for agreement between the 2 evaluators was 0.81 ( z = 5.22; P <.001).
The frequency with which we found abstracts to be inaccurate, in the sense of containing information not verifiable in the article's main body (including tables and figures, as well as text) was surprisingly large, ranging from 18% to 68% in the 6 journals surveyed. The more common type of the 2 deficiencies was inconsistency between data in the abstract and those in the body. Giving data or other information in the abstract but not in the body was somewhat less common. These findings are all the more surprising considering that the journals studied are all prominent and highly regarded general medical publications whose editors were founding members of the International Committee of Medical Journal Editors, a respected standard-setting body. These journals have full-time professional staffs who can be presumed to devote a good deal of time and energy to editorial and production processes.
Many of the discrepancies identified were quite minor and not likely to cause serious misinterpretation. For example, 1 abstract 2 reported the population to consist of "42 consecutive patients," whereas the body indicated it to be "44 consecutive patients of which 42 agreed to participate." Sometimes, however, discrepancies were more serious; for example, 1 abstract 3 gave the estimated 15-year survival as 48%, whereas the body of the text indicated it to be 58%.
The specific question we asked in this study—Can the data and other information in the abstract be verified in the body of the article?—does not seem to have been examined before. Previous studies 4 , 5 of abstract quality generally involved overall or global assessment. Most of the recent literature on abstracts has concerned structured abstracts, introduced in 1987 6 with the goal of making abstracts more informative. Several investigations 7 - 9 indicated that structured abstracts are actually better in quality, more informative, more readable, and a more efficient use of readers' time. Structured abstracts may well offer all of these advantages, but there is little reason to expect them to reduce the types of deficiencies assessed in this study. Indeed, if structured abstracts are more informative (ie, if they provide more information), they might be more likely to be subject to deficiencies we assessed. In the present study, we could not discern any relationship between various structured formats and the deficiencies assessed.
It is important to acknowledge that we addressed only 1 aspect of abstract accuracy in asking if what is in the abstract is consistent with the body of the article. There is another, at least equally important question: Is the important information in the article found in the abstract? Our study was not designed to address this question.
We found previously 1 that providing authors with specific instructions about abstract accuracy when they are revising manuscripts is ineffective in preventing the types of defects assessed in this study. If it is important that abstracts be as accurate as possible—and it can hardly be argued otherwise—and if authors cannot be counted on to provide this level of accuracy, the responsibility must be taken by journals' editorial staffs. As part of the copyediting process, the abstract needs to be scrutinized painstakingly on a line-by-line or even word-by-word basis and each bit of information verified individually and specifically.
- Register for email alerts with links to free full-text articles
- Access PDFs of free articles
- Manage your interests
- Save searches and receive search alerts

IMAGES
VIDEO
COMMENTS
Read the latest Research articles from Scientific Reports
published on Yelp.com in the restaurant industry. The results from this validation show that our ... the 2010 Pew Research report, the millennial is defined as having been born between 1977 and 1992 (Norén, L. 2011). The reviewers of the millennial generation have a high power of influence on the audience that thinks and acts like them. ...
Return articles published in. e.g., J Biol Chem or Nature. Return articles dated between — e.g., 1996. Saved to My library. Done Remove article. My ... Articles Case law. New! Supercharge your PDF reading: Follow references, skim outline, jump to figures. Stand on the shoulders of giants EN. Languages. English Español Català Čeština Dansk ...
Explore the latest full-text research PDFs, articles, conference papers, preprints and more on PEER-REVIEWED JOURNALS. Find methods information, sources, references or conduct a literature review ...
To examine the knowledge, attitudes, and practices (KAP) of caregivers of children with Kawasaki disease toward Kawasaki disease. Miaomiao Zhao, Jiaxin Ye, Luping Chen, Yitong Yang, Meng Zhao, Mingzhu Yang and Zhaoling Shi. BMC Public Health 2024 24 :899. Research Published on: 26 March 2024. Full Text.
Journal Top 100 - 2022. This collection highlights our most downloaded* research papers published in 2022. Featuring authors from around the world, these papers highlight valuable research from an ...
Search Millions of Research Papers. This fulltext search index includes over 35 million research articles and other scholarly documents preserved in the Internet Archive. The collection spans from digitized copies of eighteenth century journals through the latest Open Access conference proceedings and preprints crawled from the World Wide Web.
Journals. Explore our growing collection of Open Access journals. Early Journal Content, articles published prior to the last 95 years in the United States, or prior to the last 143 years if initially published internationally, are freely available to all. Even more content is available when you register to read - millions of articles from nearly 2,000 journals
Advanced. Journal List. PubMed Central ® (PMC) is a free full-text archive of biomedical and life sciences journal literature at the U.S. National Institutes of Health's National Library of Medicine (NIH/NLM)
With 160+ million publication pages, 25+ million researchers and 1+ million questions, this is where everyone can access science. You can use AND, OR, NOT, "" and () to specify your search ...
Explore the latest full-text research PDFs, articles, conference papers, preprints and more on RESEARCH TOPICS. Find methods information, sources, references or conduct a literature review on ...
View PDF SARS-CoV-2, influenza A/B and respiratory syncytial virus positivity and association with influenza-like illness and self-reported symptoms, over the 2022/23 winter season in the UK: a longitudinal surveillance cohort ... Content type: Research article Published on: 12 March 2024. View Full Text
A total of 89.6% of the participants without any advanced colorectal neoplasia (colorectal cancer or advanced precancerous lesions) identified on colonoscopy had a negative cfDNA blood-based test ...
Recently published articles from subdisciplines of psychology covered by more than 90 APA Journals™ publications. For additional free resources (such as article summaries, podcasts, and more), please visit the Highlights in Psychological Research page. Moving While Black: Intergroup Attitudes Influence Judgments of Speed (PDF, 71KB) Journal ...
The findings of this research revealed that flexibility, cost-effectiveness, electronic research availability, ease of connection to the Internet, and well-designed class interface were students' positive experiences. The students' negative experiences were caused by delayed feedback from instructors, unavailable technical support from ...
Download PDF Abstract: In this work, we discuss building performant Multimodal Large Language Models (MLLMs). In particular, we study the importance of various architecture components and data choices. Through careful and comprehensive ablations of the image encoder, the vision language connector, and various pre-training data choices, we identified several crucial design lessons.
Amachine learning algorithm can identify which patients would derive more benefit from cognitive behavioral therapy (CBT) versus counseling for depression, suggests research in this Journal of Consulting and Clinical Psychology (Vol. 88, No. 1) article. Researchers retrospectively explored data from 1,085 patients in the United Kingdom treated ...
The CLOC study is a prospective study of a two-stage area proba-bility sample of 1,532 married individuals from the Detroit Standard Metropolitan Statistical Area. The husband in each household was 65 years of age or older (see Carr et al., 2000, for a complete report). Of those individuals who were selected for participation in the CLOC study ...
Explore the latest full-text research PDFs, articles, conference papers, preprints and more on MARKETING RESEARCH. ... With more than 150 papers published in 2022, the Web of Science (WOS ...
This article provides an overview of writing for publication in peer-reviewed journals. While the main focus is on writing a research article, it also provides guidance on factors influencing journal selection, including journal scope, intended audience for the findings, open access requirements, and journal citation metrics.
FUNDING: The work is based on research conducted by the Southern California Evidence-based Practice Center under contract to the Agency for Healthcare Research and Quality (AHRQ), Rockville, MD (Contract 75Q80120D00009). The Patient-Centered Outcomes Research Institute (PCORI) funded the research (PCORI Publication No. 2023-SR-03). The findings and conclusions in this manuscript are those of ...
This study reviews the literature published on job crafting using bibliometric techniques. It utilizes the papers published on the topic from 1990 to 2023, retrieved from the Scopus database. The purpose of the paper is to draw the intellectual, conceptual and social structure of the field of research on job crafting.
In a 2017-2018 study, 1 1.3% of US parents reported that their children consumed melatonin in the past 30 days, and sales more than doubled between 2017 and 2020. 2 In the US, melatonin is considered a dietary supplement, is not regulated by the US Food and Drug Administration, and requires no prescription, raising particular concern because the amount of melatonin present in over-the-counter ...
The perception and appreciation of food flavor depends on many interacting chemical compounds and external factors, and therefore proves challenging to understand and predict. Here, we combine ...
Additional inclusion criteria were (1) the article was accompanied by an abstract and (2) the article occupied at least 2 full journal pages. To estimate the sample sizes, we used some preliminary observations 1 that 25% to 50% of articles published in 2 of the journals studied contained 1 or more deficiencies in abstracts. We assumed this rate ...
Abstract. the abstract in any scientific research publication should brief and straight forward. The abstract must emphasize the key findings of the work and its general significance. The abstract ...