19+ Reasons College Should be Free (Pros and Cons)

Imagine owing more money than you can even think of, right after you finish school. Sounds like a nightmare, doesn't it?
Well, for millions of people, this isn't just a bad dream—it's reality. In the United States, the total student loan debt has reached a mind-blowing $1.7 trillion! That's trillion, with a 'T'.
It's like buying about 340,000 really fancy houses or going on a lifetime supply of vacations but instead, it's money owed by students.
College is free in some places in the world, and even in some U.S. States. But most college costs tens or hundreds-of-thousands of dollars. 3 main reasons supporters think college should be free are: the rising cost of tuition, increasing equality, and the social benefits from a more educated populace.
Should college be free? You might think, "Sure, who doesn't like free stuff?" But it's not as simple as that. The price and experience of college is a social construct that can be really hard to change.
We'll explore how college got so expensive in the first place, what people are saying about making it free, and examples from places that have already tried it.

The Rising Cost of College Tuition
Once Upon a Time: A Glimpse of the Past
Believe it or not, attending college was once a much more affordable dream for many Americans. If we set our time-travel dials to the 1970s, the average annual tuition cost at a four-year public university was approximately $358—yes, you read that right!
When we adjust for inflation, that would be around $2,200 today. Now contrast this with the modern price tag: according to the Education Data Initiative , the average cost of tuition as of 2023 was $9,678 for in-state students and a whopping $27,091 for out-of-state students at public universities. For private universities, the annual average shot up to around $38,768.
Rocketing to New Heights: What's Driving the Cost?
The burning question is, why have these numbers skyrocketed? Multiple factors come into play.
First and foremost, colleges and universities have expanded their amenities and facilities. Students these days are often welcomed with state-of-the-art gyms, luxe dorms, and even gourmet dining options. While these add-ons certainly make college life more appealing, they also hike up the overall cost.
Another culprit is the administrative bloat. The number of non-teaching staff at many institutions has grown significantly. From 1975 to 2005, the number of administrators and managerial employees in higher education institutions more than doubled, according to the Department of Education. Their salaries, benefits, and offices add another layer of expense that is often passed on to students.
State funding—or rather, the lack of it—also shares the blame. For decades, state governments have been reducing their contributions to public higher education. A report from the Center on Budget and Policy Priorities revealed that between 2008 and 2018, state funding for two- and four-year colleges was slashed by nearly $7 billion after adjusting for inflation.
The Heavy Price of Loans: A Debt-Fueled Future
The rising costs inevitably lead students and families to the daunting world of student loans. It doesn't matter if you are a trained skillsperson or a white-collar businessman , college is expensive and loans don't pay themselves.
As of 2023, about 45.3 million Americans are shackled with student loan debt , which has crossed the staggering $1.77 trillion mark.
To give you a clearer picture: the average borrower from the Class of 2021 graduated with approximately $29,100 in student loan debt. And 54% of the 2021 Class held this debt.
But what does this debt mean in real-life terms? Imagine you're a 22-year-old fresh out of college with that average debt. Even if you manage to land a job right away, a good chunk of your paycheck will go to loan payments for years to come. For some, this means delaying major life milestones like buying a house, getting married, or starting a family.
So, clearly, something needs to be done. Let's get into the specific reasons some people believe college should be free. Later, we'll talk about the various debates around free college tuition.
Economic Reasons for Free College
- Increased Access to Higher Education : Making college free would mean more people could go to college without the fear of financial burden, increasing accessibility for low and middle-income families.
- Higher Earning Potential : College graduates, on average, earn more than those with just a high school diploma. This means they contribute more in taxes over their lifetimes.
- Reduced Student Loan Debt : A large portion of the U.S. population is struggling with student loan debt, which has economic repercussions like delaying the ability to buy a home or start a family.
- Boosts Economy : A better-educated workforce can contribute more effectively to the economy, leading to faster growth and increased innovation.
- Less Reliance on Social Programs : People with higher education are less likely to rely on social programs like food stamps and unemployment benefits, saving the government money in the long run.
- Global Competitiveness : To compete globally, a country needs a well-educated workforce. Free college could be a step toward that goal.
- Reduced Unemployment : Higher education often leads to higher employability and can help in reducing overall unemployment rates.
Social Reasons for Free College
- Social Mobility : Access to higher education is key for upward social mobility. Free college can level the playing field for students from disadvantaged backgrounds.
- Increased Civic Engagement : Studies have shown that college graduates are more likely to vote, volunteer, and engage in civic activities.
- Equality : Making college free can help close the racial, gender, and socio-economic gaps in higher education attendance and graduation rates.
- Better Health : Higher education is correlated with better health outcomes, including longer life expectancy and better mental health.
- Diversity : Free college can lead to a more diverse workforce, as more people from various backgrounds have the opportunity to attend college and enter fields they might otherwise not have considered.
- Educational Freedom : Students might feel freer to pursue degrees in the humanities, arts, or social sciences, instead of opting for degrees that they perceive will "pay off" more quickly to cover their student loan debts.
Moral and Philosophical Reasons for Free College
- Right to Education : Some argue that, like K-12 education, higher education is a right and should be available to all, irrespective of income.
- Public Good : Education is often cited as a public good that benefits society as a whole, not just the individual receiving the education.
- Human Capital : In the knowledge economy, human capital is one of the most valuable resources. Free college can be seen as an investment in a country's human capital.
Practical Reasons for Free College
- Simplification of Financial Aid : A free college system could potentially simplify the complicated financial aid system, making it easier for students to apply and receive support.
- Teacher Recruitment : If college is free, the teaching profession might attract more qualified candidates who are currently deterred by the prospect of low salaries combined with high student debt.
- Encourages Lifelong Learning : Without the barrier of cost, adults and older citizens might be more inclined to return to school to upskill or change careers, fostering a culture of lifelong learning.
Debates Around Free College
The idea of making college free has sparked passionate arguments, both for and against. On the one hand, proponents argue that free college can transform society, making it more equitable and prosperous. Detractors, however, counter that it's not as simple or as financially viable as it sounds.
The Pros: Where Supporters Stand
Equality and Access : Advocates often point out that free college would make higher education accessible to everyone, regardless of their financial background. Data from the Pell Institute shows that in 2016, only 11% of low-income students graduated with a bachelor's degree within six years, compared to 58% of their higher-income peers.
Economic Upliftment : Free college could be an investment in human capital, leading to a more skilled workforce. According to Georgetown University's Center on Education and the Workforce, 65% of all jobs in the American economy will require education beyond high school by 2027.
Reducing the Debt Burden : With student loan debt surpassing $1.77 trillion, supporters argue that free college could alleviate this massive financial strain affecting millions of Americans.
The Cons: Where Critics Stand
Cost to Taxpayers : One of the most common arguments against free college is the cost. Critics point out that somebody has to pay for it, and that "somebody" is often the taxpayer. According to the National Bureau of Economic Research, free public college would cost around $79 billion a year .
Quality Concerns : Some worry that making college free could lead to overcrowded classes and reduced educational quality. Already, according to the National Student Clearinghouse Research Center , only about 60% of college students complete their bachelor's degrees within six years.
Fairness Question : Critics argue that free college could be seen as a subsidy for wealthier families who can already afford tuition, thereby increasing income inequality rather than reducing it.
The Middle Ground: Compromise Solutions
Some experts propose middle-ground solutions like income-based repayment plans or free community college as a stepping stone.
For instance, Tennessee's free community college program, Tennessee Promise , has seen considerable success since its inception in 2014. The program has increased college enrollment among high school graduates by 4.6%.
International Examples: What Can We Learn?
Several countries like Germany, Norway, and Finland offer free higher education and have seen positive societal impacts.
In Germany, where tuition is free for undergraduate students, the percentage of young people who attend university is higher than the U.S. However, critics note that these countries often have higher tax rates to fund such programs.
Public Opinion: What Do People Think?
Interestingly, public opinion is shifting in favor of free college. A 2023 poll from The Campaign for Free College Tuition showed that 70-81% of voters in the U.S. support making public colleges and universities tuition-free. The numbers are even higher among younger demographics, suggesting that the idea is gaining traction.
Economic Benefits of Free College
More money in your pocket: higher wages.
Let's start with something everyone can understand: money. If you graduate from college, you're likely to earn more money than someone who didn't.
In 2022, the Bureau of Labor Statistics reported that the average weekly earnings for someone with a bachelor's degree were about $1,334, while someone with just a high school diploma earned around $899. That's a big difference! Over a lifetime, college graduates could earn up to $1 million more than those who only finished high school.
Bye-Bye, Student Loans!
Imagine not having to worry about paying back a big student loan every month. Wouldn't that be great?
According to data, around 45 million Americans owe a massive $1.7 trillion in student loans. That's trillion with a "T"! These loans can stick around for years, making it hard for people to buy homes, start families, or even just enjoy life without a mountain of debt hanging over them. Free college would mean that students wouldn't start their adult lives deep in the hole.
A Bigger, Better Economy
When people earn more, they also spend more. And when they spend more, the whole economy gets a boost.
The more you earn, the more you pay in taxes, which means more money for public projects and services like roads, schools, and hospitals. Remember that study from Georgetown University's Center on Education and the Workforce says that by 2027, about 65% of all jobs will require some form of higher education? That means we need a workforce that's ready for those jobs.
Less Stress on Social Services
People with college degrees are less likely to need things like unemployment benefits or food stamps.
Only about 2% of people with a bachelor's degree rely on food stamps , compared to 12% of those with only a high school diploma. By making college free, we're actually saving money in the long run because fewer people would need to use these kinds of social services.
Businesses Love It, Too!
You might be surprised to hear this, but a lot of businesses actually like the idea of free college. Why? Because they want workers who are skilled and educated.
Companies often spend a lot of money on training new employees. If more people had access to college, businesses could save on these costs and get employees who are ready to hit the ground running.
A Snowball Effect: More Benefits Down the Road
Making college free could have a snowball effect. That means one good thing leads to another, and another.
For example, if more people can go to college, that could lead to more entrepreneurs starting new businesses. Those new businesses would create more jobs. And guess what? More jobs mean a stronger economy!
Investing in Our Future
In the end, free college isn't just a nice idea; it's a smart investment in our country's future. It's like planting a seed. You water it, take care of it, and watch it grow. Over time, that small seed turns into a tree that provides shade, fruit, and even cleaner air.
Just like that tree, the benefits of free college could grow and touch many parts of our lives, making the country a better place for everyone.
Social Benefits of Free College
More than just money: the bigger picture.
When we talk about free college, it's easy to focus on dollars and cents. But what about the stuff that's harder to put a price tag on? We're talking about the good things that can happen in our communities and society if more people could go to college without worrying about the cost. Let's dive in!
Leveling the Playing Field: Greater Equality
First up is equality. Right now, your chances of going to college often depend on how much money your family has. That's not fair, is it? Free college could be a game-changer. It would give everybody a fair shot at getting a higher education, no matter where they come from.
Breaking the Chain: Ending the Cycle of Poverty
Education is like a key that can unlock a better future. For many people, it's a way out of poverty. When you're educated, you're more likely to get a good job, which means you're less likely to struggle with money. And guess what? That goodness doesn't stop with you. When you do better, your kids are more likely to do better, too. It's a cycle, but a good one!
A Smarter Society: Better Decision-Making
When people are educated, they make better decisions. That includes everything from picking the right foods to eat to understanding complex issues like climate change or social justice. An educated public is better at making choices that benefit everyone. This is crucial, especially when it comes to voting for our leaders.
Healthier Lives: A Boost for Public Health
Did you know that people with higher levels of education tend to live healthier lives? Yep, it's true! According to the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC), adults with a bachelor's degree or higher are less likely to smoke and more likely to exercise compared to those with less education. If more people could go to college, we could end up with a healthier nation.
Strengthening Communities: More Civic Engagement
Here's another cool benefit: educated people are more likely to be involved in their communities. They're more likely to volunteer, attend public meetings, and even join local organizations. A study by the College Board Research found that 40% of adults with a bachelor's degree volunteered, compared to only 19% of high school graduates.
Happier Lives: Boosting Mental Health
Last but not least, let's talk about happiness. Education can lead to better mental health. When people have good jobs and stable lives, they're less likely to suffer from stress and anxiety. And who doesn't want to be happier?
A Society We All Want to Live In
Free college can do more than just help individuals; it can help all of us. From making society more equal and smarter to improving public health and even boosting our spirits, the social benefits of free college could make our country a better place to live for everyone.
Examples of Places Where College is Free or Subsidized
First off, let's get something straight: free or very affordable college isn't just a pie-in-the-sky dream. It's real, and it's happening in different parts of the world. Some places even have it right here in the United States! Let's take a closer look at these examples to see what we can learn.
A Taste of Tennessee: Free Community College
Let's start close to home with Tennessee. Yup, you heard right! In Tennessee, they have a program called the Tennessee Promise. High school graduates can go to community college for two years without paying a cent in tuition.
Guess what? Since this program started in 2014, college enrollment shot up by 4.6%, according to a study in the Journal of Policy Analysis and Management.
New York's Excelsior Program
New York State offers the Excelsior Scholarship, a program that makes public colleges tuition-free for families earning less than $125,000 a year. However, there's a catch: after graduating, students must live and work in New York for the same number of years they received the scholarship. If not, the scholarship turns into a loan.
Across the Pond: Germany's Example
Let's hop over the ocean to Germany, where tuition for undergraduate students is free at public universities. That even goes for international students! And it's not like these are second-rate schools. Some German universities are ranked among the top in the world.
The Nordic Model: Sweden, Norway, and Finland
Heading north, countries like Sweden, Norway, and Finland also offer free higher education. Students only pay a small administrative fee each semester, which is usually less than $100. These countries believe that everyone has the right to education, regardless of their bank balance.
The South American Surprise: Argentina and Brazil
Now, let's fly across the globe to South America. Countries like Argentina and Brazil offer free or very low-cost higher education. In Brazil, the best universities are actually the public ones, and they're free! However, it's super competitive to get in.
The Catch: Higher Taxes and Competitive Entry
Now, it's important to note that free college often comes with its own set of challenges. For example, countries that offer free tuition usually have higher taxes. Plus, getting into these colleges can be super tough because so many people want to go.
Lessons We Can Learn
So, what can we take away from all this? First, free or low-cost college is totally doable. Second, each place has its own way of making it work, whether it's through higher taxes, tough entrance exams, or special rules like staying in the state after graduation.
A World of Possibilities
As you can see, the idea of free or subsidized college isn't just a pipe dream; it's a reality in many places. These examples show that there are different paths to the same goal: making higher education accessible to everyone.
How Can College Education be Free?
We've talked a lot about why free college is a good idea. But now comes the million-dollar question: How do we actually make it happen? Don't worry; people have been thinking hard about this, and there are some pretty cool ideas out there.
Tax the Super Rich: A Popular Suggestion
One idea that's getting a lot of attention is taxing the super-rich. That means the government would take a little extra money from people who have a whole lot of it and use that to pay for free college.
For example, Senator Elizabeth Warren proposed a 2% annual tax on households with a net worth between $50 million and $1 billion. According to estimates, this could raise around $2.75 trillion over 10 years. That's more than enough to make public colleges free and even help with other things like healthcare!
Closing Tax Loopholes: Every Penny Counts
You might not know this, but there are all sorts of ways people and companies can avoid paying taxes. These are called "tax loopholes," and they can add up to a lot of money. Closing these loopholes could free up extra funds that could be used for education.
Cutting Wasteful Spending: Trim the Fat
Another idea is to look at where the government is already spending money and see if any of it could be better used for education. Maybe there are programs that aren't really working or areas where the government is spending more than it needs to. By "trimming the fat," we could find the money for free college without raising taxes.
Partnerships with Private Companies
What if businesses chipped in to help make college free? Some companies already offer scholarships or have programs to help their employees go back to school. Expanding these partnerships could be a win-win: companies get educated workers, and students get to go to college for free or at a lower cost.
State and Federal Programs
Making college free doesn't have to be something that only the federal government does. States can get in on the action too! In fact, some states like Tennessee and New York have already started their own programs. The federal government could help by matching the money states put in, making it easier for them to offer free or reduced tuition.
Sliding Scale Tuition: Pay What You Can
Here's another idea: what if the cost of college was based on how much your family can afford? Some colleges are already doing this. They look at your family's income and then decide how much you should pay. That way, people who can afford to pay more do, and those who can't, pay less or nothing at all.
Multiple Roads to the Same Destination
As you can see, there's no one-size-fits-all solution to making college free. But that's a good thing! It means we have lots of options to explore. The most important thing is to get started. After all, the best way to make free college a reality is to take the first step, no matter how small.
Whew! We've covered a lot of ground, haven't we? From the rising cost of college tuition to the debates and benefits, all the way to real-life examples and ways to make it happen—free college is a big topic! But when you connect all the dots, one thing becomes super clear: the time for free college is now.
Imagine a world where everybody has an equal shot at higher education. A world where your future isn't decided by the size of your bank account, but by your hard work, talent, and dreams. Sounds pretty great, right? And guess what? It's totally possible. Countries around the world are already doing it, and some places in the United States are giving it a shot, too.
And let's not forget the ripple effect of free college. It's not just good for students; it's good for everyone! From boosting the economy and leveling the social playing field to creating a smarter, healthier, and happier society—free college could be the key to solving a lot of our problems.
Of course, making college free won't be easy. There are challenges to face and questions to answer. How will we pay for it? How will it affect the quality of education? These are important questions, and we'll need smart, creative solutions to answer them. But the good news is, we've got options, lots of them!
Like any big journey, the road to free college starts with a single step. Maybe that step is talking to your friends and family about why it's a good idea. Or maybe it's writing to your local politicians to tell them why it's important. Whatever that first step is for you, now's the time to take it.
The idea of free college has been around for a while, but it's never been more important than it is today. With the cost of tuition soaring and the benefits clearer than ever, there's no reason to wait. So let's roll up our sleeves, put our heads together, and make free college a reality for everyone. Because the best investment we can make is in our future.
Related posts:
- 25 Reasons Homework Should Be Banned (Busywork Arguments)
- 47+ Social Problem Examples (Issues In Society)
- 37+ Instructional Strategies (Examples + Quizzes)
- 12+ School Uniform Pros and Cons (For and Against Debate)
- 109+ SWOT Analysis Examples (Definition + Quiz)
Reference this article:
About The Author

Free Personality Test

Free Memory Test

Free IQ Test

PracticalPie.com is a participant in the Amazon Associates Program. As an Amazon Associate we earn from qualifying purchases.
Follow Us On:
Youtube Facebook Instagram X/Twitter
Psychology Resources
Developmental
Personality
Relationships
Psychologists
Serial Killers
Psychology Tests
Personality Quiz
Memory Test
Depression test
Type A/B Personality Test
© PracticalPsychology. All rights reserved
Privacy Policy | Terms of Use
College Should Be Free Persuasive Essay Example
Did you know that around 43.2 Million people suffer from College Debt, and all of that amount together comes up to over 1.59 Trillion? It has been highly debated for many years whether college students shouldn't have to pay to go to school in the United States and many Bills have been introduced to initiate Colleges going free. College Tuition should be free. Free college would reduce student debt, providing free college tuition gives an opportunity for everyone to go to college, and the economy and society would benefit from tuition free colleges.
College should be Free because then the people who go won't have to pay off their college debt for the next couple of decades.“Student loan debt significantly impacts one's ability to purchase a home. When Equifax asked in 2015 millennial renters why they did not buy a home, 55.7% of respondents listed “student loan debt/not enough money saved” as the top reason.” (Williams, 1). This text states that the college debt is holding them back from the important things like, buying a house and keeping up their rent because they just aren’t able to afford or keep up the money while dealing with college debt. “When students graduate with debt, they will likely continue to add to their debt with interest. As such, it can take many years before they manage to dig themselves out of debt that only seems to keep growing. In the meantime, this delays spending on such things as buying a house or a car.” (www.uopeople.edu, 1) This quote shows that even after they graduate, they are stuck with these hard bills to pay off that only increase when they don't have the money to pay them which puts off important things and stuff they need to survive like, rent and food their focus is stuck on getting rid of this large amount of debt they have accumulated.So not only will we save Americans from a lifetime of debt, there are many other benefits as well.
College Tuition should be free because it provides everyone with an equal opportunity to receive a good college education. “Free college tuition programs have proved effective in helping mitigate the system’s current inequities by increasing college enrollment, lowering dependence on student loan debt, and improving completion rates, especially among students of color and lower-income students who are often the first in their family to attend college.” (Winograd, Lubin, 1) From what this quote states it is said that without college tuition not only do the everyday people who have been going can keep going but would show more people of color and people who come from low income and less fortunate families are able to go which leaves them with better education and better opportunities for their future. It also states that more students are graduating from college because they now have had the opportunity to go. “Students—including many older students juggling work and family responsibilities—recognize that higher education is a key to opportunity, and that has fueled a substantial increase in college enrollment rates in recent years. But unfortunately, for millions of other students, our higher education system isn't delivering what they need, or deserve. In part because of the rising costs of college, too many students are unable to enroll or complete high-quality degrees.” (www.ed.gov, 1) This is basically saying that costs are rising, and many people in America use college as their opportunity and maybe their only opportunity to not have to struggle with money and can get the job they need to support themselves and their families, but it's becoming increasingly harder because of the ever so costly college tuition rates. since everyone would have an equal chance at a college education they can get better jobs and will be less of a burden on society and the government, leading to less government programs and homelessness
Free College would benefit the Economy and Society. “the U.S. economy will have a shortfall of 5 million college-educated workers by 2020. This gap is unsurprising. By 2020, 65 percent of all jobs will require bachelor’s or associate’s degrees or some other education beyond high school, particularly in the fastest growing occupations—science, technology, engineering, mathematics, health care, and community service.” (Bergeron, Martin, 1) It is explained in this quote that some jobs that need a higher education than just high school are becoming so needed that people being able to have the chance to get them would really boost the economy. “By nearly any measure, college graduates outperform their peers who have only completed their high school degree. For example, the average graduate is 24 percent more likely to be employed and average earnings among graduates are $32,000 higher annually and $1 million higher over a lifetime.” (aplu.org, 1) This quote gives light to the fact that with a better education and job opportunities, we can all make more money and be able to support ourselves and society. On the other hand some claim that while helping society we still need to find the money to pay the costs associated with college and universities.
Free College is a bad idea because the money still has to come from somewhere. “The estimated cost of Bernie Sanders’s free college program is $47 billion per year and has states paying 33% of the cost, or $15.5 billion. [25] According to David H. Feldman, Ph.D., and Robert B. Archibald, Ph.D., both Professors of Economics at William & Mary College, “This will require tax increases, or it will force states to move existing resources into higher education and away from other state priorities like health care, prisons, roads, and K-12 education.” Part of their concerns are not valid because many of those services are funded via the state's homeowners who pay their property taxes. “Free college is free for the student, but the money to cover the cost must come from somewhere. As mentioned earlier, this money could come from the defense budget, which is fine until there is a war, and the U.S. needs this money. It would also come from taxes, which means that Americans would be forced to pay more so that college can be free.” Another point made was that part of the US defense budget would be used, in fact the bill was presented to potentially use this budget in 2017 and was never seen to pass.
I believe that the larger significance of having college free and getting rid of tuition would greatly benefit American society, It will give financially disadvantaged students a chance to move up the social ladder and afford them the same opportunities that their more financially fortunate peers are given, This will give a chance for everyone to be truly equal in society and gives chances to those who need to support themselves and their families. The takeaway for the readers is seeing the benefit this would have to society as a whole and they should start to support free college tuition in America.
https://edsource.org/2020/tuition-free-college-is-critical-to-our-economy/641232
aplu.org/projects-and-initiatives/college-costs-tuition-and-financial-aid/publicuvalues/societal-benefits.html
https://www.forbes.com/sites/wesleywhistle/2021/03/30/the-impact-of-free-community-college/?sh=c8c11d54bdfe
https://www.americanprogress.org/article/strengthening-our-economy-through-college-for-all/
https://theintercept.com/2017/09/18/the-senates-military-spending-increase-alone-is-enough-to-make-public-college-free/
https://www.ablison.com/important-pros-and-cons-of-free-education/
https://www.procon.org/headlines/free-college-top-3-pros-and-cons/
https://www.collegeraptor.com/find-colleges/articles/affordability-college-cost/pros-cons-tuition-free-college/
https://www.investopedia.com/articles/personal-finance/100515/10-ways-student-debt-can-destroy-your-life.asp.
Related Samples
- Reflection Paper On Fear Of Failure
- Mental Health Counseling Essay Example
- Persuasive Essay on Learwood Middle School Shouldn't Enforce a Dress Code Policy
- Paying College Athletes Essay Research Paper
- Is College Worth the Time and Money?
- Using Zoom in Online Teaching Essay Example
- Essay Sample: Homework Help Students in a Future
- Masters of Foreign Language Teaching Program: Reflective Essay Example
- Intro to Bitcoin: The Ideal Currency for the Elite
- At-Risk Youth in Santa Barbara County High Schools Essay Example
Didn't find the perfect sample?

You can order a custom paper by our expert writers
- Entertainment
- Environment
- Information Science and Technology
- Social Issues
Home Essay Samples Education College Tuition
Why College Should Be Free: Analysis of Arguments and Counterarguments
Table of contents, the access to education argument, the economic benefits argument, the counterarguments, the societal investment argument, the conclusion.
*minimum deadline
Cite this Essay
To export a reference to this article please select a referencing style below

- Primary Education
- Higher Education
- Extracurricular Activities
- Segregation in Schools
Related Essays
Need writing help?
You can always rely on us no matter what type of paper you need
*No hidden charges
100% Unique Essays
Absolutely Confidential
Money Back Guarantee
By clicking “Send Essay”, you agree to our Terms of service and Privacy statement. We will occasionally send you account related emails
You can also get a UNIQUE essay on this or any other topic
Thank you! We’ll contact you as soon as possible.
Home — Essay Samples — Education — College Education — Should College Education Be Free: Persuasive Paper
Should College Education Be Free: Persuasive Paper
- Categories: College Education
About this sample

Words: 661 |
Published: Mar 6, 2024
Words: 661 | Page: 1 | 4 min read
Introduction

Cite this Essay
Let us write you an essay from scratch
- 450+ experts on 30 subjects ready to help
- Custom essay delivered in as few as 3 hours
Get high-quality help

Prof Ernest (PhD)
Verified writer
- Expert in: Education

+ 120 experts online
By clicking “Check Writers’ Offers”, you agree to our terms of service and privacy policy . We’ll occasionally send you promo and account related email
No need to pay just yet!
Related Essays
3 pages / 1214 words
1 pages / 598 words
1 pages / 472 words
1 pages / 533 words
Remember! This is just a sample.
You can get your custom paper by one of our expert writers.
121 writers online
Still can’t find what you need?
Browse our vast selection of original essay samples, each expertly formatted and styled
Related Essays on College Education
In the United States, the choice between attending a community college or a four-year university is a significant decision for many individuals pursuing higher education. While both options offer valuable educational [...]
For generations, the pursuit of higher education has been regarded as an almost unassailable pathway to success. However, in the 21st century, the landscape of success and career achievement is undergoing a transformation. This [...]
Higher education is valuable for individuals and society as a whole. It enhances personal growth, improves career prospects, and fosters a well-rounded society. Baum, S., & Ma, J. (2016). Trends in College Pricing 2016. The [...]
Choosing the right educational path is a pivotal moment in an individual's life, with far-reaching implications for their future career and personal growth. The decision often boils down to two main options: trade school and [...]
As Matshona Dhliwayo once said, “Money doesn’t grow on trees, but grows on intelligent minds.” The idea of whether college should be free has been a controversial and widely debated topic. Imagine living in an old, [...]
In today's rapidly evolving world, the importance of a college education has never been more crucial. As technology advances and the job market becomes increasingly competitive, a college degree has become a necessity for [...]
Related Topics
By clicking “Send”, you agree to our Terms of service and Privacy statement . We will occasionally send you account related emails.
Where do you want us to send this sample?
By clicking “Continue”, you agree to our terms of service and privacy policy.
Be careful. This essay is not unique
This essay was donated by a student and is likely to have been used and submitted before
Download this Sample
Free samples may contain mistakes and not unique parts
Sorry, we could not paraphrase this essay. Our professional writers can rewrite it and get you a unique paper.
Please check your inbox.
We can write you a custom essay that will follow your exact instructions and meet the deadlines. Let's fix your grades together!
Get Your Personalized Essay in 3 Hours or Less!
We use cookies to personalyze your web-site experience. By continuing we’ll assume you board with our cookie policy .
- Instructions Followed To The Letter
- Deadlines Met At Every Stage
- Unique And Plagiarism Free

- Knowledge Base
- Popular Essay Topics
Why College Should be Free Essay
- Author StudySaurus
- Category Popular Essay Topics
Disclaimer: This paper has been submitted by a student. This is not a sample of the work written by professional academic writers.
Any opinions, findings, conclusions or recommendations expressed in this work are those of the authors and do not necessarily reflect the views of StudySaurus.
Topic: Should a college or university education be tuition free essay
College tuition fees have been on the rise in the last couple of years. Now many jobs require a college degree which makes it hard for those without higher education. The higher somebody goes in their education the easier it is to get almost any job they want. College education has become a necessity in today’s society and rising tuition fees are putting a college education out of reach for some students. The first two years of college should be provided and funded by the U.S. government because it will encourage students to achieve their college education without looking at college as such a financial obstacle.
Today the cost of attending a public university or community college is so high that most students simply cannot afford it. As a result, the federal government continues to offer financial aid and Pell grants to lower-income families. Student loans are also available and are known as the most dominant source of financial aid. “During the 2012-2013 school year alone, about 10 million college students took out loans and in 2015, the total amount of student loan debt in America was estimated to be about $1.3 trillion.” This just goes to show that even though some students are getting financial aid help to go to school, there is always a fee to pay out of pocket.
Should College be free Essay
Today’s society more and more jobs are requiring specific technical requirements or a college degree. Free college would expand higher educational benefits such as jobs and higher pay as opposed to those with little to no college background. Recovery magazine believes “By 2020, 65 percent of all jobs in the economy will require post-secondary education and training beyond high school.” (Carnavale, Smith, Strohl. pg 3) free college tuition will give so many students an equal opportunity to achieve their goals no matter if it’s just an associates degree or a doctoral degree. Achieving a college degree can not only be a life long achievement but can better their future and open doors to better job opportunities.
Of course, not everyone agrees with free college. Some argue that calling something free doesn’t make it free. Public education is funded by taxpayers and free college means higher taxes. With college tuition being so-called “free” it will attract students who are unfit for the college environment and will eventually drop out which means taxes will go up for taxpayers whether they have kids attending college or not. Some agree that college should not be free since some students will be unmotivated, lazy or unconcerned about their education. Students who are going to college are going to get their profession and will eventually be able to pay off their student debts. General taxpayers believe if a student’s desire is to attend college, then they will do whatever it takes to receive financial aid assistance. With college not being free, this is no way means students can’t receive financial aid help such as scholarships, federal Pell grand or even student loans. Overall it is important to make students understand their responsibilities in life and its wrong to place the burden of paying for their free education on the general population.

Was this material helpful?
Related essays, about studysaurus, community. knowledge. success..
StudySaurus is run by two uni-students that still get a kick out of learning new things. We hope to share these experiences with you.
Ideas , concepts , tutorials, essay papers – everything we would’ve liked to have known, seen or heard during our high-school & UNI years, we want to bring to YOU.
Privacy & Cookies Policy Terms and Conditions DMCA Request
Have a language expert improve your writing
Run a free plagiarism check in 10 minutes, generate accurate citations for free.
- Knowledge Base
- How to write an argumentative essay | Examples & tips
How to Write an Argumentative Essay | Examples & Tips
Published on July 24, 2020 by Jack Caulfield . Revised on July 23, 2023.
An argumentative essay expresses an extended argument for a particular thesis statement . The author takes a clearly defined stance on their subject and builds up an evidence-based case for it.
Instantly correct all language mistakes in your text
Upload your document to correct all your mistakes in minutes

Table of contents
When do you write an argumentative essay, approaches to argumentative essays, introducing your argument, the body: developing your argument, concluding your argument, other interesting articles, frequently asked questions about argumentative essays.
You might be assigned an argumentative essay as a writing exercise in high school or in a composition class. The prompt will often ask you to argue for one of two positions, and may include terms like “argue” or “argument.” It will frequently take the form of a question.
The prompt may also be more open-ended in terms of the possible arguments you could make.
Argumentative writing at college level
At university, the vast majority of essays or papers you write will involve some form of argumentation. For example, both rhetorical analysis and literary analysis essays involve making arguments about texts.
In this context, you won’t necessarily be told to write an argumentative essay—but making an evidence-based argument is an essential goal of most academic writing, and this should be your default approach unless you’re told otherwise.
Examples of argumentative essay prompts
At a university level, all the prompts below imply an argumentative essay as the appropriate response.
Your research should lead you to develop a specific position on the topic. The essay then argues for that position and aims to convince the reader by presenting your evidence, evaluation and analysis.
- Don’t just list all the effects you can think of.
- Do develop a focused argument about the overall effect and why it matters, backed up by evidence from sources.
- Don’t just provide a selection of data on the measures’ effectiveness.
- Do build up your own argument about which kinds of measures have been most or least effective, and why.
- Don’t just analyze a random selection of doppelgänger characters.
- Do form an argument about specific texts, comparing and contrasting how they express their thematic concerns through doppelgänger characters.
Receive feedback on language, structure, and formatting
Professional editors proofread and edit your paper by focusing on:
- Academic style
- Vague sentences
- Style consistency
See an example

An argumentative essay should be objective in its approach; your arguments should rely on logic and evidence, not on exaggeration or appeals to emotion.
There are many possible approaches to argumentative essays, but there are two common models that can help you start outlining your arguments: The Toulmin model and the Rogerian model.
Toulmin arguments
The Toulmin model consists of four steps, which may be repeated as many times as necessary for the argument:
- Make a claim
- Provide the grounds (evidence) for the claim
- Explain the warrant (how the grounds support the claim)
- Discuss possible rebuttals to the claim, identifying the limits of the argument and showing that you have considered alternative perspectives
The Toulmin model is a common approach in academic essays. You don’t have to use these specific terms (grounds, warrants, rebuttals), but establishing a clear connection between your claims and the evidence supporting them is crucial in an argumentative essay.
Say you’re making an argument about the effectiveness of workplace anti-discrimination measures. You might:
- Claim that unconscious bias training does not have the desired results, and resources would be better spent on other approaches
- Cite data to support your claim
- Explain how the data indicates that the method is ineffective
- Anticipate objections to your claim based on other data, indicating whether these objections are valid, and if not, why not.
Rogerian arguments
The Rogerian model also consists of four steps you might repeat throughout your essay:
- Discuss what the opposing position gets right and why people might hold this position
- Highlight the problems with this position
- Present your own position , showing how it addresses these problems
- Suggest a possible compromise —what elements of your position would proponents of the opposing position benefit from adopting?
This model builds up a clear picture of both sides of an argument and seeks a compromise. It is particularly useful when people tend to disagree strongly on the issue discussed, allowing you to approach opposing arguments in good faith.
Say you want to argue that the internet has had a positive impact on education. You might:
- Acknowledge that students rely too much on websites like Wikipedia
- Argue that teachers view Wikipedia as more unreliable than it really is
- Suggest that Wikipedia’s system of citations can actually teach students about referencing
- Suggest critical engagement with Wikipedia as a possible assignment for teachers who are skeptical of its usefulness.
You don’t necessarily have to pick one of these models—you may even use elements of both in different parts of your essay—but it’s worth considering them if you struggle to structure your arguments.
Regardless of which approach you take, your essay should always be structured using an introduction , a body , and a conclusion .
Like other academic essays, an argumentative essay begins with an introduction . The introduction serves to capture the reader’s interest, provide background information, present your thesis statement , and (in longer essays) to summarize the structure of the body.
Hover over different parts of the example below to see how a typical introduction works.
The spread of the internet has had a world-changing effect, not least on the world of education. The use of the internet in academic contexts is on the rise, and its role in learning is hotly debated. For many teachers who did not grow up with this technology, its effects seem alarming and potentially harmful. This concern, while understandable, is misguided. The negatives of internet use are outweighed by its critical benefits for students and educators—as a uniquely comprehensive and accessible information source; a means of exposure to and engagement with different perspectives; and a highly flexible learning environment.
The body of an argumentative essay is where you develop your arguments in detail. Here you’ll present evidence, analysis, and reasoning to convince the reader that your thesis statement is true.
In the standard five-paragraph format for short essays, the body takes up three of your five paragraphs. In longer essays, it will be more paragraphs, and might be divided into sections with headings.
Each paragraph covers its own topic, introduced with a topic sentence . Each of these topics must contribute to your overall argument; don’t include irrelevant information.
This example paragraph takes a Rogerian approach: It first acknowledges the merits of the opposing position and then highlights problems with that position.
Hover over different parts of the example to see how a body paragraph is constructed.
A common frustration for teachers is students’ use of Wikipedia as a source in their writing. Its prevalence among students is not exaggerated; a survey found that the vast majority of the students surveyed used Wikipedia (Head & Eisenberg, 2010). An article in The Guardian stresses a common objection to its use: “a reliance on Wikipedia can discourage students from engaging with genuine academic writing” (Coomer, 2013). Teachers are clearly not mistaken in viewing Wikipedia usage as ubiquitous among their students; but the claim that it discourages engagement with academic sources requires further investigation. This point is treated as self-evident by many teachers, but Wikipedia itself explicitly encourages students to look into other sources. Its articles often provide references to academic publications and include warning notes where citations are missing; the site’s own guidelines for research make clear that it should be used as a starting point, emphasizing that users should always “read the references and check whether they really do support what the article says” (“Wikipedia:Researching with Wikipedia,” 2020). Indeed, for many students, Wikipedia is their first encounter with the concepts of citation and referencing. The use of Wikipedia therefore has a positive side that merits deeper consideration than it often receives.
An argumentative essay ends with a conclusion that summarizes and reflects on the arguments made in the body.
No new arguments or evidence appear here, but in longer essays you may discuss the strengths and weaknesses of your argument and suggest topics for future research. In all conclusions, you should stress the relevance and importance of your argument.
Hover over the following example to see the typical elements of a conclusion.
The internet has had a major positive impact on the world of education; occasional pitfalls aside, its value is evident in numerous applications. The future of teaching lies in the possibilities the internet opens up for communication, research, and interactivity. As the popularity of distance learning shows, students value the flexibility and accessibility offered by digital education, and educators should fully embrace these advantages. The internet’s dangers, real and imaginary, have been documented exhaustively by skeptics, but the internet is here to stay; it is time to focus seriously on its potential for good.
If you want to know more about AI tools , college essays , or fallacies make sure to check out some of our other articles with explanations and examples or go directly to our tools!
- Ad hominem fallacy
- Post hoc fallacy
- Appeal to authority fallacy
- False cause fallacy
- Sunk cost fallacy
College essays
- Choosing Essay Topic
- Write a College Essay
- Write a Diversity Essay
- College Essay Format & Structure
- Comparing and Contrasting in an Essay
(AI) Tools
- Grammar Checker
- Paraphrasing Tool
- Text Summarizer
- AI Detector
- Plagiarism Checker
- Citation Generator
An argumentative essay tends to be a longer essay involving independent research, and aims to make an original argument about a topic. Its thesis statement makes a contentious claim that must be supported in an objective, evidence-based way.
An expository essay also aims to be objective, but it doesn’t have to make an original argument. Rather, it aims to explain something (e.g., a process or idea) in a clear, concise way. Expository essays are often shorter assignments and rely less on research.
At college level, you must properly cite your sources in all essays , research papers , and other academic texts (except exams and in-class exercises).
Add a citation whenever you quote , paraphrase , or summarize information or ideas from a source. You should also give full source details in a bibliography or reference list at the end of your text.
The exact format of your citations depends on which citation style you are instructed to use. The most common styles are APA , MLA , and Chicago .
The majority of the essays written at university are some sort of argumentative essay . Unless otherwise specified, you can assume that the goal of any essay you’re asked to write is argumentative: To convince the reader of your position using evidence and reasoning.
In composition classes you might be given assignments that specifically test your ability to write an argumentative essay. Look out for prompts including instructions like “argue,” “assess,” or “discuss” to see if this is the goal.
Cite this Scribbr article
If you want to cite this source, you can copy and paste the citation or click the “Cite this Scribbr article” button to automatically add the citation to our free Citation Generator.
Caulfield, J. (2023, July 23). How to Write an Argumentative Essay | Examples & Tips. Scribbr. Retrieved April 11, 2024, from https://www.scribbr.com/academic-essay/argumentative-essay/
Is this article helpful?

Jack Caulfield
Other students also liked, how to write a thesis statement | 4 steps & examples, how to write topic sentences | 4 steps, examples & purpose, how to write an expository essay, "i thought ai proofreading was useless but..".
I've been using Scribbr for years now and I know it's a service that won't disappoint. It does a good job spotting mistakes”

8 Effective Strategies to Write Argumentative Essays
In a bustling university town, there lived a student named Alex. Popular for creativity and wit, one challenge seemed insurmountable for Alex– the dreaded argumentative essay!
One gloomy afternoon, as the rain tapped against the window pane, Alex sat at his cluttered desk, staring at a blank document on the computer screen. The assignment loomed large: a 350-600-word argumentative essay on a topic of their choice . With a sigh, he decided to seek help of mentor, Professor Mitchell, who was known for his passion for writing.
Entering Professor Mitchell’s office was like stepping into a treasure of knowledge. Bookshelves lined every wall, faint aroma of old manuscripts in the air and sticky notes over the wall. Alex took a deep breath and knocked on his door.
“Ah, Alex,” Professor Mitchell greeted with a warm smile. “What brings you here today?”
Alex confessed his struggles with the argumentative essay. After hearing his concerns, Professor Mitchell said, “Ah, the argumentative essay! Don’t worry, Let’s take a look at it together.” As he guided Alex to the corner shelf, Alex asked,
Table of Contents
“What is an Argumentative Essay?”
The professor replied, “An argumentative essay is a type of academic writing that presents a clear argument or a firm position on a contentious issue. Unlike other forms of essays, such as descriptive or narrative essays, these essays require you to take a stance, present evidence, and convince your audience of the validity of your viewpoint with supporting evidence. A well-crafted argumentative essay relies on concrete facts and supporting evidence rather than merely expressing the author’s personal opinions . Furthermore, these essays demand comprehensive research on the chosen topic and typically follows a structured format consisting of three primary sections: an introductory paragraph, three body paragraphs, and a concluding paragraph.”
He continued, “Argumentative essays are written in a wide range of subject areas, reflecting their applicability across disciplines. They are written in different subject areas like literature and philosophy, history, science and technology, political science, psychology, economics and so on.
Alex asked,
“When is an Argumentative Essay Written?”
The professor answered, “Argumentative essays are often assigned in academic settings, but they can also be written for various other purposes, such as editorials, opinion pieces, or blog posts. Some situations to write argumentative essays include:
1. Academic assignments
In school or college, teachers may assign argumentative essays as part of coursework. It help students to develop critical thinking and persuasive writing skills .
2. Debates and discussions
Argumentative essays can serve as the basis for debates or discussions in academic or competitive settings. Moreover, they provide a structured way to present and defend your viewpoint.
3. Opinion pieces
Newspapers, magazines, and online publications often feature opinion pieces that present an argument on a current issue or topic to influence public opinion.
4. Policy proposals
In government and policy-related fields, argumentative essays are used to propose and defend specific policy changes or solutions to societal problems.
5. Persuasive speeches
Before delivering a persuasive speech, it’s common to prepare an argumentative essay as a foundation for your presentation.
Regardless of the context, an argumentative essay should present a clear thesis statement , provide evidence and reasoning to support your position, address counterarguments, and conclude with a compelling summary of your main points. The goal is to persuade readers or listeners to accept your viewpoint or at least consider it seriously.”
Handing over a book, the professor continued, “Take a look on the elements or structure of an argumentative essay.”
Elements of an Argumentative Essay
An argumentative essay comprises five essential components:
Claim in argumentative writing is the central argument or viewpoint that the writer aims to establish and defend throughout the essay. A claim must assert your position on an issue and must be arguable. It can guide the entire argument.
2. Evidence
Evidence must consist of factual information, data, examples, or expert opinions that support the claim. Also, it lends credibility by strengthening the writer’s position.
3. Counterarguments
Presenting a counterclaim demonstrates fairness and awareness of alternative perspectives.
4. Rebuttal
After presenting the counterclaim, the writer refutes it by offering counterarguments or providing evidence that weakens the opposing viewpoint. It shows that the writer has considered multiple perspectives and is prepared to defend their position.
The format of an argumentative essay typically follows the structure to ensure clarity and effectiveness in presenting an argument.
How to Write An Argumentative Essay
Here’s a step-by-step guide on how to write an argumentative essay:
1. Introduction
- Begin with a compelling sentence or question to grab the reader’s attention.
- Provide context for the issue, including relevant facts, statistics, or historical background.
- Provide a concise thesis statement to present your position on the topic.
2. Body Paragraphs (usually three or more)
- Start each paragraph with a clear and focused topic sentence that relates to your thesis statement.
- Furthermore, provide evidence and explain the facts, statistics, examples, expert opinions, and quotations from credible sources that supports your thesis.
- Use transition sentences to smoothly move from one point to the next.
3. Counterargument and Rebuttal
- Acknowledge opposing viewpoints or potential objections to your argument.
- Also, address these counterarguments with evidence and explain why they do not weaken your position.
4. Conclusion
- Restate your thesis statement and summarize the key points you’ve made in the body of the essay.
- Leave the reader with a final thought, call to action, or broader implication related to the topic.
5. Citations and References
- Properly cite all the sources you use in your essay using a consistent citation style.
- Also, include a bibliography or works cited at the end of your essay.
6. Formatting and Style
- Follow any specific formatting guidelines provided by your instructor or institution.
- Use a professional and academic tone in your writing and edit your essay to avoid content, spelling and grammar mistakes .
Remember that the specific requirements for formatting an argumentative essay may vary depending on your instructor’s guidelines or the citation style you’re using (e.g., APA, MLA, Chicago). Always check the assignment instructions or style guide for any additional requirements or variations in formatting.
Did you understand what Prof. Mitchell explained Alex? Check it now!
Fill the Details to Check Your Score

Prof. Mitchell continued, “An argumentative essay can adopt various approaches when dealing with opposing perspectives. It may offer a balanced presentation of both sides, providing equal weight to each, or it may advocate more strongly for one side while still acknowledging the existence of opposing views.” As Alex listened carefully to the Professor’s thoughts, his eyes fell on a page with examples of argumentative essay.
Example of an Argumentative Essay
Alex picked the book and read the example. It helped him to understand the concept. Furthermore, he could now connect better to the elements and steps of the essay which Prof. Mitchell had mentioned earlier. Aren’t you keen to know how an argumentative essay should be like? Here is an example of a well-crafted argumentative essay , which was read by Alex. After Alex finished reading the example, the professor turned the page and continued, “Check this page to know the importance of writing an argumentative essay in developing skills of an individual.”
Importance of an Argumentative Essay
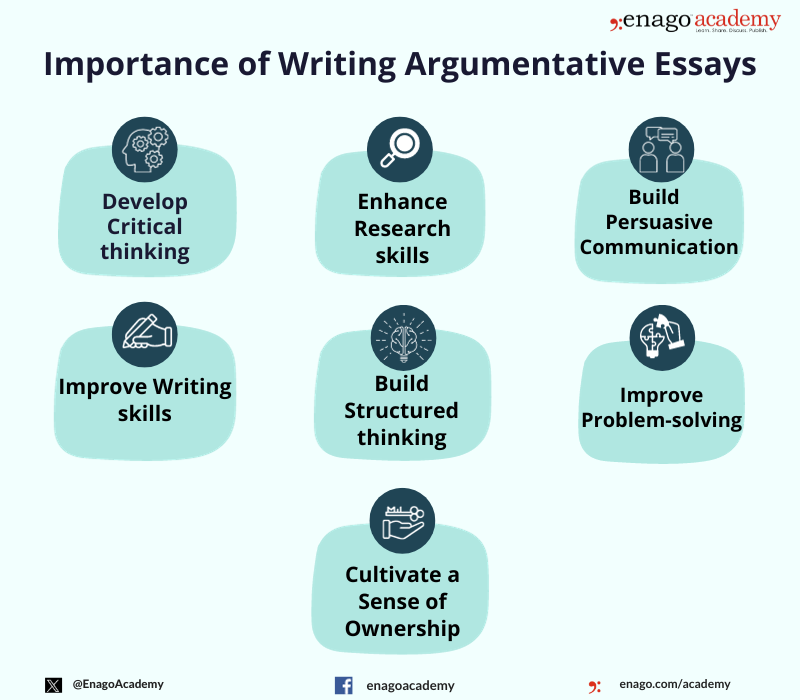
After understanding the benefits, Alex was convinced by the ability of the argumentative essays in advocating one’s beliefs and favor the author’s position. Alex asked,
“How are argumentative essays different from the other types?”
Prof. Mitchell answered, “Argumentative essays differ from other types of essays primarily in their purpose, structure, and approach in presenting information. Unlike expository essays, argumentative essays persuade the reader to adopt a particular point of view or take a specific action on a controversial issue. Furthermore, they differ from descriptive essays by not focusing vividly on describing a topic. Also, they are less engaging through storytelling as compared to the narrative essays.
Alex said, “Given the direct and persuasive nature of argumentative essays, can you suggest some strategies to write an effective argumentative essay?
Turning the pages of the book, Prof. Mitchell replied, “Sure! You can check this infographic to get some tips for writing an argumentative essay.”
Effective Strategies to Write an Argumentative Essay

As days turned into weeks, Alex diligently worked on his essay. He researched, gathered evidence, and refined his thesis. It was a long and challenging journey, filled with countless drafts and revisions.
Finally, the day arrived when Alex submitted their essay. As he clicked the “Submit” button, a sense of accomplishment washed over him. He realized that the argumentative essay, while challenging, had improved his critical thinking and transformed him into a more confident writer. Furthermore, Alex received feedback from his professor, a mix of praise and constructive criticism. It was a humbling experience, a reminder that every journey has its obstacles and opportunities for growth.
Frequently Asked Questions
An argumentative essay can be written as follows- 1. Choose a Topic 2. Research and Collect Evidences 3. Develop a Clear Thesis Statement 4. Outline Your Essay- Introduction, Body Paragraphs and Conclusion 5. Revise and Edit 6. Format and Cite Sources 7. Final Review
One must choose a clear, concise and specific statement as a claim. It must be debatable and establish your position. Avoid using ambiguous or unclear while making a claim. To strengthen your claim, address potential counterarguments or opposing viewpoints. Additionally, use persuasive language and rhetoric to make your claim more compelling
Starting an argument essay effectively is crucial to engage your readers and establish the context for your argument. Here’s how you can start an argument essay are: 1. Begin With an Engaging Hook 2. Provide Background Information 3. Present Your Thesis Statement 4. Briefly Outline Your Main 5. Establish Your Credibility
The key features of an argumentative essay are: 1. Clear and Specific Thesis Statement 2. Credible Evidence 3. Counterarguments 4. Structured Body Paragraph 5. Logical Flow 6. Use of Persuasive Techniques 7. Formal Language
An argumentative essay typically consists of the following main parts or sections: 1. Introduction 2. Body Paragraphs 3. Counterargument and Rebuttal 4. Conclusion 5. References (if applicable)
The main purpose of an argumentative essay is to persuade the reader to accept or agree with a particular viewpoint or position on a controversial or debatable topic. In other words, the primary goal of an argumentative essay is to convince the audience that the author's argument or thesis statement is valid, logical, and well-supported by evidence and reasoning.
Great article! The topic is simplified well! Keep up the good work
Rate this article Cancel Reply
Your email address will not be published.

Enago Academy's Most Popular Articles

- AI in Academia
- Trending Now
Using AI for Journal Selection — Simplifying your academic publishing journey in the smart way
Strategic journal selection plays a pivotal role in maximizing the impact of one’s scholarly work.…

- Career Corner
Recognizing the signs: A guide to overcoming academic burnout
As the sun set over the campus, casting long shadows through the library windows, Alex…

- Diversity and Inclusion
Reassessing the Lab Environment to Create an Equitable and Inclusive Space
The pursuit of scientific discovery has long been fueled by diverse minds and perspectives. Yet…

Simplifying the Literature Review Journey — A comparative analysis of 6 AI summarization tools
Imagine having to skim through and read mountains of research papers and books, only to…

- Publishing Research
- Reporting Research
How to Optimize Your Research Process: A step-by-step guide
For researchers across disciplines, the path to uncovering novel findings and insights is often filled…
How to Improve Lab Report Writing: Best practices to follow with and without…
Digital Citations: A comprehensive guide to citing of websites in APA, MLA, and CMOS…
Choosing the Right Analytical Approach: Thematic analysis vs. content analysis for…

Sign-up to read more
Subscribe for free to get unrestricted access to all our resources on research writing and academic publishing including:
- 2000+ blog articles
- 50+ Webinars
- 10+ Expert podcasts
- 50+ Infographics
- 10+ Checklists
- Research Guides
We hate spam too. We promise to protect your privacy and never spam you.
I am looking for Editing/ Proofreading services for my manuscript Tentative date of next journal submission:

What should universities' stance be on AI tools in research and academic writing?
New User? Start here.
Why College Education Should Be Free? : Argumentative Essay

Table of Contents
College education should be free to ensure that all individuals have equal access to higher education, regardless of their financial background. A highly educated population is essential for economic growth and development, and making college education free would help to create a more skilled and educated workforce. By removing the financial burden of tuition fees, students could focus on their studies and pursue their desired career paths without worrying about debt. Making college education free would also promote equality and social mobility, providing opportunities for individuals from all backgrounds to access higher education and improve their economic situation. Investing in education is investing in the future, and making college education free would provide a strong foundation for the development of the country.
Top Reasons Why College Education Should Be Free?
Access to Education: Making college education free would provide greater access to higher education for individuals who cannot afford the high cost of tuition fees. This would help to increase the number of students enrolled in college and would provide them with the opportunity to gain the skills and knowledge necessary to pursue their desired careers.
Reducing Financial Burden: College education is a significant financial burden for many families. Making it free would eliminate the financial strain on families and students, enabling them to focus on their education rather than worrying about the cost of tuition fees.
Economic Growth: A highly-educated population is essential for economic growth and development. By making college education free, more individuals would be able to pursue higher education and contribute to the development of the economy.
Increasing Social Mobility: Education is an important factor in increasing social mobility. Making college education free would help to level the playing field and provide greater opportunities for individuals from lower-income families to access higher education and improve their economic situation.
Reducing Student Debt: Student debt is a significant problem for many students. Making college education free would reduce the need for students to take out loans to finance their education, reducing the burden of debt on graduates.
Promoting Equality: Education is a fundamental right and should be accessible to all. Making college education free would help to promote equality by providing individuals from all backgrounds with the opportunity to access higher education.
Investment in the Future: Investing in education is investing in the future. Making college education free would provide a strong foundation for the development of the country, ensuring that the workforce is highly educated and skilled.
Building a Knowledge-based Society: A knowledge-based society is one that values education and places a high priority on learning. Making college education free would help to build a society that values education and promotes lifelong learning.
Providing a Competitive Edge: In today’s global economy, having a highly-educated workforce is essential for competitiveness. Making college education free would provide a competitive edge by ensuring that the workforce is highly skilled and educated.
Fulfilling Social Responsibility: As a society, we have a responsibility to ensure that everyone has access to education. Making college education free would fulfill our social responsibility by providing greater access to higher education for all.
Pros: Should College Be Free?
There are several potential pros to making college free:
- Increased Access to Education: By making college free, more individuals may be able to attend college who would otherwise not have been able to afford it. This could potentially increase the number of people with higher education degrees, which could have a positive impact on society.
- Reduced Student Debt: One of the biggest challenges facing college graduates today is the burden of student loan debt. By making college free, students would not have to take out loans to pay for tuition and other expenses, potentially reducing the overall amount of debt they carry.
- Increased Economic Growth: A more educated workforce could potentially lead to increased economic growth and innovation. This could benefit society as a whole by improving productivity and creating new job opportunities.
- More Equal Opportunities: A free college education could help level the playing field for students from low-income backgrounds who may not have the same opportunities as their more affluent peers. This could lead to greater social mobility and a more equitable society.
- Improved Workforce Skills: With a free college education, students may be more likely to pursue degrees in fields that are in high demand, such as science, technology, engineering, and mathematics (STEM). This could help ensure that the workforce has the skills needed to compete in a global economy.
Cons: Why College Should Not Be Free?
There are several arguments that can be made against the idea of making college education completely free:
- Cost: Implementing a free college education policy would be expensive and require significant funding from taxpayers. This could be a burden on those who do not have children attending college and may not see the direct benefits of the policy.
- Quality: Making college free may lead to a decrease in the quality of education. Colleges may not have the funds to maintain facilities or hire the best professors, which could ultimately hurt the education students receive.
- Value: If college education is made completely free, it may be devalued in the eyes of society. This could result in fewer students seeing the value in obtaining a college degree, which could ultimately hurt the job market and the economy as a whole.
- Alternative routes: Not all students need a traditional college education to succeed in their careers. There are alternative routes such as trade schools, vocational programs, and entrepreneurship that can be just as effective, if not more so, than a traditional college education.
- Equity: Making college free may not address the root causes of educational inequality. While it may provide financial relief to some students, it may not address other factors such as access to quality K-12 education, which can have a significant impact on a student’s ability to succeed in college.
Overall, while the idea of a free college education may seem appealing, there are significant drawbacks that must be considered before implementing such a policy.
Which Universities are Offering Free College?
There are a number of universities that offer free college education or tuition-free programs. However, it’s important to note that the definition of “free college” can vary depending on the specific program or university, and in some cases, there may still be fees or other expenses associated with attending these schools. Here are a few examples of universities that offer some form of free college education:
- Cooper Union: This private college in New York City offers a full-tuition scholarship to every admitted student, regardless of their financial need.
- Alice Lloyd College: This private college in Kentucky offers a free tuition program to students who come from one of the 108 counties in the central Appalachian region.
- Berea College: This private college in Kentucky covers the full cost of tuition for all students, and also provides additional financial support for books, room and board, and other expenses.
- College of the Ozarks: This private college in Missouri offers a tuition-free education to all students, who work on campus to cover the cost of their education.
- Curtis Institute of Music: This private music conservatory in Philadelphia offers a full-tuition scholarship to all admitted students.
- Webb Institute: This private college in New York offers a full-tuition scholarship to all admitted students, as well as a stipend for room and board.
It’s important to do your own research to find out which colleges and universities offer free college education, as the programs and requirements can vary widely. For personalized assistance in navigating the complexities of college admissions and exploring options like free education programs, you can also consider reaching out to college essay writing service .
How To Reduce Your College Costs Now?
Reducing college costs is a concern for many students and their families. Here are some tips on how to reduce your college costs:
- Apply for Financial Aid: Filling out the Free Application for Federal Student Aid (FAFSA) can help you get access to grants, scholarships, work-study, and other financial aid options that can reduce your college costs. Make sure to submit your FAFSA on time and provide all the necessary information.
- Look for Scholarships: Scholarships are a great way to reduce your college costs. There are many scholarships available for different categories of students, such as academic merit, athletic ability, community service, and other factors. Research and apply for scholarships that fit your qualifications and interests.
- Consider Community College: Starting at a community college and then transferring to a four-year college can save you a lot of money in tuition and fees. Community colleges often offer lower tuition rates and have transfer agreements with four-year colleges that can help you save money and time.
- Choose In-State Public Colleges: Attending an in-state public college can significantly reduce your college costs compared to out-of-state public colleges and private colleges. In-state tuition rates are often much lower than out-of-state tuition rates.
- Reduce Living Expenses: Living expenses such as room and board, transportation, and personal expenses can add up quickly. Look for ways to reduce your living expenses by living off-campus, cooking your meals, using public transportation, and other cost-saving measures.
- Take Advantage of Tax Benefits: There are tax credits and deductions available for college expenses, such as the American Opportunity Tax Credit and the Lifetime Learning Credit. Consult a tax professional or use tax software to see if you qualify for these benefits.
- Work Part-Time: Working part-time while attending college can help you earn money to pay for your college expenses. Look for on-campus jobs or jobs that are flexible with your class schedule.
By following these tips, you can reduce your college costs and save money while pursuing your education.
What are the Publicly Funded College Tuition Programs?
Publicly funded college tuition programs are initiatives put in place by state and federal governments to make college education more affordable and accessible for students. These programs provide financial assistance to eligible students to cover the cost of tuition fees, and in some cases, other expenses such as books and living costs.
Here are some examples of publicly funded college tuition programs:
- Pell Grants: These are grants awarded by the federal government to low-income undergraduate students to help cover the cost of tuition, fees, and other educational expenses.
- State-sponsored scholarship programs: Many states offer scholarships to students who meet certain eligibility criteria, such as academic achievement, financial need, or residency.
- State-sponsored tuition waivers: Some states provide tuition waivers to students who meet certain eligibility criteria, such as military veterans, dependents of deceased or disabled veterans, or students pursuing certain majors or careers.
- Free college programs: Some states, such as New York and Oregon, have implemented free college programs that cover the cost of tuition for eligible students.
- Community college initiatives: Several states have launched initiatives to provide free or reduced-cost tuition for community college students, such as Tennessee’s Tennessee Promise program.
Overall, these publicly funded college tuition programs are designed to make college education more accessible to all students, regardless of their financial background or other circumstances.
Providing free college education has several benefits. Firstly, it ensures equal opportunities for all students regardless of their socio-economic background. Students from low-income families or marginalized communities who may not be able to afford tuition fees can get access to quality education. This will lead to a more educated and skilled workforce, which is crucial for economic growth and development. Secondly, it would reduce the burden of student loan debt on graduates, allowing them to focus on their careers and contribute to the economy. Lastly, a free college education can also lead to a more educated and informed society, promoting social mobility and reducing income inequality. Overall, a free college education can have far-reaching positive impacts on individuals and society as a whole.
Frequently Asked Questions Search By Students
Q.1: why education should be free for all.
Ans: Education is one of the most powerful tools for personal and societal development. It helps individuals acquire the knowledge, skills, and values necessary to lead a fulfilling life and contribute to their communities. However, not everyone has equal access to education due to financial barriers. Education should be free for all because it is a fundamental human right and a public good that benefits individuals and society as a whole. By providing free education, we can ensure that everyone has the opportunity to learn and improve their lives, regardless of their economic background. It also promotes social mobility, reduces inequality, and boosts economic growth by creating a more skilled and productive workforce. Ultimately, free education is a wise investment in our future, as it enables individuals to reach their full potential and build a better world for all.
Q.2: Why education is compulsory for everyone?
Ans: Education is considered to be one of the fundamental necessities of human life. It is an essential component of human development and plays a crucial role in shaping individuals and societies. Education is compulsory for everyone because it provides numerous benefits to individuals, communities, and countries.
Firstly, education enhances the intellectual capacity of individuals. It enables individuals to develop analytical and critical thinking skills, allowing them to make informed decisions and solve complex problems. Education also helps individuals to understand the world around them, broaden their perspectives, and develop a sense of curiosity and creativity.
Secondly, education is a tool for social and economic mobility. It provides individuals with the skills and knowledge required to participate in the workforce, earn a decent income, and contribute to the development of their communities. Education also helps individuals to gain social recognition and respect, which can lead to better social and economic opportunities.
Thirdly, education promotes social cohesion and reduces social inequalities. Education can create a common ground for individuals from different backgrounds, cultures, and religions to come together, share their experiences, and learn from each other. Education also helps to reduce poverty, crime, and social exclusion, which are major challenges faced by societies.
Q.3: Why my education should be funded?
Ans: Investing in education is one of the most valuable and strategic investments a society can make. Education is the foundation of economic development, innovation, and personal growth. Funding education not only benefits the individual student, but it also creates a ripple effect that benefits society as a whole.
Firstly, education provides individuals with the knowledge and skills they need to succeed in today’s complex world. Students learn to think critically, analyze data, and communicate effectively, which are essential skills in virtually any profession. Moreover, higher education prepares students for the workforce and improves their chances of securing a well-paying job. This leads to higher income, a better standard of living, and greater economic stability for individuals and their families.
Secondly, education fosters innovation and drives economic growth. Education provides students with the necessary skills and knowledge to invent, design, and create new products and technologies. These advancements lead to increased productivity, job creation, and economic growth. Additionally, funding education leads to a more educated and skilled workforce, which attracts businesses and investment to a region and spurs economic development.
Thirdly, funding education is a smart long-term investment in society’s future. Education creates an educated, informed, and responsible citizenry, which is critical for a functioning democracy. Furthermore, an educated population is better equipped to address the pressing social and environmental challenges of our time.
Some Free Argumentative Essay Examples-
Why Do I Deserve A Scholarship- Essay Writing Tips And Examples
Why Abortion Should Be Legal Essay: Argumentative Essay

Hi, I am Mark, a Literature writer by profession. Fueled by a lifelong passion for Literature, story, and creative expression, I went on to get a PhD in creative writing. Over all these years, my passion has helped me manage a publication of my write ups in prominent websites and e-magazines. I have also been working part-time as a writing expert for myassignmenthelp.com for 5+ years now. It’s fun to guide students on academic write ups and bag those top grades like a pro. Apart from my professional life, I am a big-time foodie and travel enthusiast in my personal life. So, when I am not working, I am probably travelling places to try regional delicacies and sharing my experiences with people through my blog.
Related Post

How to write an essay
- Essay format
Essay structure
- Essay structure guide
- Essay outline
- Essay title
- Essay introduction
- Paragraph structure
- Topic sentence
- Transition sentences
- Essay conclusion
- How to make an essay longer
- Short essay
- 150 words essay
- 200 word essay
- 250 word essay
- How many pages is 1000 words essay
- 1400 word essay
- 2000 word essay
- 5 paragraph essay
- 10 page essay
- 100 page essay
Essay topics
How to revise an essay, essay hooks.
Writing Get your essay and assignment written from scratch by PhD expert
Rewriting: Paraphrase or rewrite your friend's essay with similar meaning at reduced cost
Editing: Proofread your work by experts and improve grade at Lowest cost
Enter phone no. to receive critical updates and urgent messages !
Please upload all relevant files for quick & complete assistance.
Get original papers written according to your instructions and save time for what matters most.
What are your chances of acceptance?
Calculate for all schools, your chance of acceptance.
Your chancing factors
Extracurriculars.
52 Argumentative Essay Ideas that are Actually Interesting
What’s covered:, how to pick a good argumentative essay topic, elements of a strong argumentative essay, argumentative essay idea example topics.
Are you having writer’s block? Coming up with an essay topic can be the hardest part of the process. You have very likely encountered argumentative essay writing in high school and have been asked to write your own. If you’re having trouble finding a topic, we’ve created a list of 52 essay ideas to help jumpstart your brainstorming process! In addition, this post will cover strategies for picking a topic and how to make your argument a strong one. Ultimately, the goal is to convince your reader.
An argumentative essay tasks the writer with presenting an assertion and bolstering that assertion with proper research. You’ll present the claim’s authenticity. This means that whatever argument you’re making must be empirically true! Writing an argumentative essay without any evidence will leave you stranded without any facts to back up your claim. When choosing your essay topic, begin by thinking about themes that have been researched before. Readers will be more engaged with an argument that is supported by data.
This isn’t to say that your argumentative essay topic has to be as well-known, like “Gravity: Does it Exist?” but it shouldn’t be so obscure that there isn’t ample evidence. Finding a topic with multiple sources confirming its validity will help you support your thesis throughout your essay. If upon review of these articles you begin to doubt their worth due to small sample sizes, biased funding sources, or scientific disintegrity, don’t be afraid to move on to a different topic. Your ultimate goal should be proving to your audience that your argument is true because the data supports it.
The hardest essays to write are the ones that you don’t care about. If you don’t care about your topic, why should someone else? Topics that are more personal to the reader are immediately more thoughtful and meaningful because the author’s passion shines through. If you are free to choose an argumentative essay topic, find a topic where the papers you read and cite are fun to read. It’s much easier to write when the passion is already inside of you!
However, you won’t always have the choice to pick your topic. You may receive an assignment to write an argumentative essay that you feel is boring. There is still value in writing an argumentative essay on a topic that may not be of interest to you. It will push you to study a new topic, and broaden your ability to write on a variety of topics. Getting good at proving a point thoroughly and effectively will help you to both understand different fields more completely and increase your comfort with scientific writing.
Convincing Thesis Statement
It’s important to remember the general essay structure: an introduction paragraph with a thesis statement, body paragraphs, and a conclusion. A strong thesis statement will set your essay up for success. What is it? A succinct, concise, and pithy sentence found in your first paragraph that summarizes your main point. Pour over this statement to ensure that you can set up your reader to understand your essay. You should also restate your thesis throughout your essay to keep your reader focused on your point.
Ample Research
A typical argumentative essay prompt may look like this: “What has been the most important invention of the 21st century? Support your claim with evidence.” This question is open-ended and gives you flexibility. But that also means it requires research to prove your point convincingly. The strongest essays weave scientific quotes and results into your writing. You can use recent articles, primary sources, or news sources. Maybe you even cite your own research. Remember, this process takes time, so be sure you set aside enough time to dive deep into your topic.
Clear Structure
If the reader can’t follow your argument, all your research could be for nothing! Structure is key to persuading your audience. Below are two common argumentative essay structures that you can use to organize your essays.
The Toulmin argument and the Rogerian argument each contain the four sections mentioned above but executes them in different ways. Be sure to familiarize yourself with both essay structures so that your essay is the most effective it can be.
The Toulmin argument has a straightforward presentation. You begin with your assertion, your thesis statement. You then list the evidence that supports your point and why these are valid sources. The bulk of your essay should be explaining how your sources support your claim. You then end your essay by acknowledging and discussing the problems or flaws that readers may find in your presentation. Then, you should list the solutions to these and alternative perspectives and prove your argument is stronger.
The Rogerian argument has a more complex structure. You begin with a discussion of what opposing sides do right and the validity of their arguments. This is effective because it allows you to piece apart your opponent’s argument. The next section contains your position on the questions. In this section, it is important to list problems with your opponent’s argument that your argument fixes. This way, your position feels much stronger. Your essay ends with suggesting a possible compromise between the two sides. A combination of the two sides could be the most effective solution.
- Is the death penalty effective?
- Is our election process fair?
- Is the electoral college outdated?
- Should we have lower taxes?
- How many Supreme Court Justices should there be?
- Should there be different term limits for elected officials?
- Should the drinking age be lowered?
- Does religion cause war?
- Should the country legalize marijuana?
- Should the country have tighter gun control laws?
- Should men get paternity leave?
- Should maternity leave be longer?
- Should smoking be banned?
- Should the government have a say in our diet?
- Should birth control be free?
- Should we increase access to condoms for teens?
- Should abortion be legal?
- Do school uniforms help educational attainment?
- Are kids better or worse students than they were ten years ago?
- Should students be allowed to cheat?
- Is school too long?
- Does school start too early?
- Are there benefits to attending a single-sex school?
- Is summer break still relevant?
- Is college too expensive?
Art / Culture
- How can you reform copyright law?
- What was the best decade for music?
- Do video games cause students to be more violent?
- Should content online be more harshly regulated?
- Should graffiti be considered art or vandalism?
- Should schools ban books?
- How important is art education?
- Should music be taught in school?
- Are music-sharing services helpful to artists?
- What is the best way to teach science in a religious school?
- Should fracking be legal?
- Should parents be allowed to modify their unborn children?
- Should vaccinations be required for attending school?
- Are GMOs helpful or harmful?
- Are we too dependent on our phones?
- Should everyone have internet access?
- Should internet access be free?
- Should the police force be required to wear body cams?
- Should social media companies be allowed to collect data from their users?
- How has the internet impacted human society?
- Should self-driving cars be allowed on the streets?
- Should athletes be held to high moral standards?
- Are professional athletes paid too much?
- Should the U.S. have more professional sports teams?
- Should sports be separated by gender?
- Should college athletes be paid?
- What are the best ways to increase safety in sports?
Where to Get More Argumentative Essay Topic Ideas
If you need more help brainstorming topics, especially those that are personalized to your interests, you can use CollegeVine’s free AI tutor, Ivy . Ivy can help you come up with original argumentative essay ideas, and she can also help with the rest of your homework, from math to languages.
Related CollegeVine Blog Posts

- Share full article
Advertisement
Supported by
Guest Essay
Is This the End of Academic Freedom?

By Paula Chakravartty and Vasuki Nesiah
Dr. Chakravartty is a professor of media, communication and culture at New York University, where Dr. Nesiah is a professor of practice in human rights and international law.
At New York University, the spring semester began with a poetry reading. Students and faculty gathered in the atrium of Bobst Library. At that time, about 26,000 Palestinians had already been killed in Israel’s horrific war on Gaza; the reading was a collective act of bearing witness.
The last poem read aloud was titled “If I Must Die.” It was written, hauntingly, by a Palestinian poet and academic named Refaat Alareer who was killed weeks earlier by an Israeli airstrike. The poem ends: “If I must die, let it bring hope — let it be a tale.”
Soon after those lines were recited, the university administration shut the reading down . Afterward, we learned that students and faculty members were called into disciplinary meetings for participating in this apparently “disruptive” act; written warnings were issued.
We have both taught at N.Y.U. for over a decade and believe we are in a moment of unparalleled repression. Over the past six months, since the start of Israel’s war on Gaza, we have seen the university administration fail to adequately protect dissent on campus, actively squelching it instead. We believe what we are witnessing in response to student, staff and faculty opposition to the war violates the very foundations of academic freedom.
While N.Y.U. says that it remains committed to free expression on campus and that its rules about and approach to protest activity haven’t changed, students and faculty members in solidarity with the Palestinian people have found the campus environment alarmingly constrained.
About a week after Hamas’s attacks in October, the Grand Staircase in the Kimmel student center, a storied site of student protests , closed indefinitely; it has yet to reopen fully. A graduate student employee was reprimanded for putting up fliers in support of Palestinians on the student’s office door and ultimately took them down; that person is not the only N.Y.U. student to face some form of disciplinary consequence for pro-Palestinian speech or action. A resolution calling for the university to reaffirm protection of pro-Palestinian speech and civic activity on campus, passed by the elected Student Government Assembly in December, has apparently been stuck in a procedural black hole since.
The New York Police Department has become a pervasive presence on campus, with over 6,000 hours of officer presence added after the war broke out. Hundreds of faculty members have signed onto an open letter condemning the university’s “culture of fear about campus speech and activism.”
Such draconian interventions are direct threats to academic freedom.
At universities across the country, any criticism of Israel’s policies, expressions of solidarity with Palestinians, organized calls for a cease-fire or even pedagogy on the recent history of the land have all emerged as perilous speech. In a letter to university presidents in November, the A.C.L.U. expressed concern about “impermissible chilling of free speech and association on campus” in relation to pro-Palestinian student groups and views; since then, the atmosphere at colleges has become downright McCarthyite .
The donors, trustees, administrators and third parties who oppose pro-Palestinian speech seem to equate any criticism of the State of Israel — an occupying power under international law and one accused of committing war crimes — with antisemitism. To them, the norms of free speech are inherently problematic, and a broad definition of antisemitism is a tool for censorship . Outside funding has poured into horrifying doxxing and harassment campaigns. Pro-Israel surveillance groups like Canary Mission and CAMERA relentlessly target individuals and groups deemed antisemitic or critical of Israel. Ominous threats follow faculty and students for just expressing their opinions or living out their values.
To be clear, we abhor all expressions of antisemitism and wholeheartedly reject any role for antisemitism on our campuses. Equally, we believe that conflating criticism of Israel or Zionism with antisemitism is dangerous. Equating the criticism of any nation with inherent racism endangers basic democratic freedoms on and off campus. As the A.C.L.U. wrote in its November statement, a university “cannot fulfill its mission as a forum for vigorous debate” if it polices the views of faculty members and students, however much any of us may disagree with them or find them offensive.
In a wave of crackdowns on pro-Palestinian speech nationwide, students have had scholarships revoked, job offers pulled and student groups suspended. At Columbia, protesters have reported being sprayed by what they said was skunk, a chemical weapon used by the Israeli military; at Northwestern, two Black students faced criminal charges , later dropped, for publishing a pro-Palestinian newspaper parody; at Cornell, students were arrested during a peaceful protest . In a shocking episode of violence last fall, three Palestinian students , two of them wearing kaffiyehs, were shot while walking near the University of Vermont.
Many more cases of student repression on campuses are unfolding.
Academic freedom, as defined by the American Association of University Professors in the mid-20th century , provides protection for the pursuit of knowledge by faculty members, whose job is to educate, learn and research both inside and outside the academy. Not only does this resonate with the Constitution’s free speech protections ; international human rights law also affirms the centrality of academic freedom to the right to education and the institutional autonomy of educational institutions.
Across the United States, attacks on free speech are on the rise . In recent years, right-wing groups opposed to the teaching of critical race theory have tried to undermine these principles through measures including restrictions on the discussion of history and structural racism in curriculums, heightened scrutiny of lectures and courses that are seen to promote dissent and disciplinary procedures against academics who work on these topics.
What people may not realize is that speech critical of Israel’s occupation and apartheid policies has long been censored, posing persistent challenges to those of us who uphold academic freedom. Well before Oct. 7, speech and action at N.Y.U. in support of Palestinians faced intense and undue scrutiny.
Our students are heeding Refaat Alareer’s call to bear witness. They are speaking out — writing statements, organizing protests and responding to a plausible threat of genocide with idealism and conviction. As faculty members, we believe that college should be a time when students are encouraged to ask big questions about justice and the future of humanity and to pursue answers however disquieting to the powerful.
Universities must be places where students have access to specialized knowledge that shapes contemporary debates, where faculty members are encouraged to be public intellectuals, even when, or perhaps especially when, they are expressing dissenting opinions speaking truth to power. Classrooms must allow for contextual learning, where rapidly mutating current events are put into a longer historical timeline.
This is a high-stakes moment. A century ago, attacks on open discussion of European antisemitism, the criminalization of dissent and the denial of Jewish histories of oppression and dispossession helped create the conditions for the Holocaust. One crucial “never again” lesson from that period is that the thought police can be dangerous. They can render vulnerable communities targets of oppression. They can convince the world that some lives are not as valuable as others, justifying mass slaughter.
It is no wonder that students across the country are protesting an unpopular and brutal war that, besides Israel, only the United States is capable of stopping. It is extraordinary that the very institutions that ought to safeguard their exercise of free speech are instead escalating surveillance and policing, working on ever more restrictive student conduct rules and essentially risking the death of academic freedom.
From the Vietnam War to apartheid South Africa, universities have been important places for open discussion and disagreement about government policies, the historical record, structural racism and settler colonialism. They have also long served as sites of protest. If the university cannot serve as an arena for such freedoms, the possibilities of democratic life inside and outside the university gates are not only impoverished but under threat of extinction.
Paula Chakravartty is a professor of media, communication and culture at New York University, where Vasuki Nesiah is a professor of practice in human rights and international law. Both are members of the executive committee of the N.Y.U. chapter of the American Association of University Professors and members of N.Y.U.’s Faculty for Justice in Palestine.
The Times is committed to publishing a diversity of letters to the editor. We’d like to hear what you think about this or any of our articles. Here are some tips . And here’s our email: [email protected] .
Follow the New York Times Opinion section on Facebook , Instagram , TikTok , WhatsApp , X and Threads .

IMAGES
VIDEO
COMMENTS
The push for tuition-free higher education comes amid a broader enrollment crisis in the United States. Total undergraduate enrollment fell by 6.6 percent from 2019 to 2021, according to the ...
This essay argues that college education should be free for all students based on the benefits of higher education for individuals, society, and the economy. It cites statistics, examples, and arguments to support its position and challenges the common objections to free college.
Free college programs can help students afford college, increase graduation rates, and boost the economy, but they also have drawbacks and limitations. Learn about the types, arguments, and impacts of free college programs from both sides of the debate.
The author reviews his own randomized trial of free college in Milwaukee and other studies on financial aid programs. He argues that free college increases graduation rates, especially for two-year colleges, and supports the Biden and CP proposals.
College is free in some places in the world, and even in some U.S. States. But most college costs tens or hundreds-of-thousands of dollars. 3 main reasons supporters think college should be free are: the rising cost of tuition, increasing equality, and the social benefits from a more educated populace.
College should be Free because then the people who go won't have to pay off their college debt for the next couple of decades."Student loan debt significantly impacts one's ability to purchase a home. When Equifax asked in 2015 millennial renters why they did not buy a home, 55.7% of respondents listed "student loan debt/not enough money ...
The Argument for Tuition-Free College. Soaring tuitions and student loan debt are placing higher education beyond the reach of many American students. It's time to make college free and accessible to all. In 1862, President Abraham Lincoln signed the Land Grant College Act into law, laying the groundwork for the largest system of publicly ...
The average cost of tuition and fees at an in-state public college is over $10,000 per year — an increase of more than 200 percent since 1988, when the average was $3,190; at a private college ...
As the pursuit of a college degree becomes increasingly expensive, the question of whether college should be free has gained prominence in discussions about accessibility, equity, and the future of education. This essay explores the reasons why college education should be free and addresses counterarguments that challenge this proposal.
Conclusion. In conclusion, making college education free is a compelling proposition that can yield significant economic, social, and intellectual benefits. By eliminating tuition fees, we can empower individuals, promote social equality, and invest in human capital. It is crucial to consider the long-term gains of free education and address ...
An argumentative essay attempts to convince a reader to agree with a particular argument (the writer's thesis statement). The writer takes a firm stand one way or another on a topic and then uses hard evidence to support that stance. An argumentative essay seeks to prove to the reader that one argument —the writer's argument— is the ...
Persuasive Essay On Why College Should Be Free 960 Words | 4 Pages. College should be free For students going to college is a life changing factor. College education is a necessity for all society. When students go to college, they will develop their knowledge very well and they will know what's good and bad for their life.
The question of whether college education should be free in the United States has been a subject of ongoing debate. Proponents argue that free college would increase accessibility and reduce the burden of student debt, while opponents raise concerns about the cost, potential devaluation of degrees, and the impact on the economy.
Should College be free Essay. Today's society more and more jobs are requiring specific technical requirements or a college degree. Free college would expand higher educational benefits such as jobs and higher pay as opposed to those with little to no college background. Recovery magazine believes "By 2020, 65 percent of all jobs in the ...
An argumentative essay should be objective in its approach; your arguments should rely on logic and evidence, not on exaggeration or appeals to emotion. There are many possible approaches to argumentative essays, but there are two common models that can help you start outlining your arguments: The Toulmin model and the Rogerian model.
An argumentative essay comprises five essential components: 1. Claim. Claim in argumentative writing is the central argument or viewpoint that the writer aims to establish and defend throughout the essay. A claim must assert your position on an issue and must be arguable. It can guide the entire argument.
1. First evidential support of your reason (known as confirmatio) 2. Second evidential support of your reason, then third, and so on. B. Summarize your first reason again and tie it together with evidential support. III. Second reason, etc. A. Continue to list your reasons in the same format as the first.
This should be removed since argumentative essays focus on facts and data to support an argument, not the author's own opinion or experiences. ... get travel perks and free gear, and can use their time in college as a way to capture the attention of professional recruiters. No other college students receive anywhere near as much from their ...
An argumentative essay sample that supports the idea of free college education for every student. The essay explains the benefits of free education for students, the economy, and the society, and the challenges of making it happen. It cites sources from various articles and experts to support its claims.
College education should be free to ensure that all individuals have equal access to higher education, regardless of their financial background. ... Some Free Argumentative Essay Examples-Why Do I Deserve A Scholarship- Essay Writing Tips And Examples. Why Abortion Should Be Legal Essay: Argumentative Essay. Mark. View all posts.
If you are free to choose an argumentative essay topic, find a topic where the papers you read and cite are fun to read. It's much easier to write when the passion is already inside of you! However, you won't always have the choice to pick your topic. You may receive an assignment to write an argumentative essay that you feel is boring.
The models for writing an argumentative essay are the classical model, the Rogerian model, and the Toulmin model. To make sure that you write a good argumentative essay, read the different types of examples mentioned in this blog. 1. Good Argumentative Essay Examples.
While N.Y.U. says that it remains committed to free expression on campus and that its rules about and approach to protest activity haven't changed, students and faculty members in solidarity ...