Democracy Essay for Students and Children
500+ words essay on democracy.
Democracy is known as the finest form of government. Why so? Because in a democracy, the people of the country choose their government. They enjoy certain rights which are very essential for any human being to live freely and happily. There are various democratic countries in the world , but India is the largest one. Democracy has withstood the test of time, and while other forms have the government has failed, democracy stood strong. It has time and again proved its importance and impact.


Significance of a Democracy
Democracy is very important for human development . When people have free will to live freely, they will be happier. Moreover, we have seen how other forms of government have turned out to be. Citizens are not that happy and prosperous in a monarchy or anarchy.
Furthermore, democracy lets people have equal rights. This ensures that equality prevails all over the country. Subsequently, it also gives them duties. These duties make them better citizens and are also important for their overall development.
Most importantly, in a democracy, the people form the government. So, this selection of the government by the citizens gives everyone a chance to work for their country. It allows the law to prevail efficiently as the rules are made by people whom they have selected.
In addition, democracy allows people of various religions and cultures to exist peacefully. It makes them live in harmony with one another. People of democracy are more tolerant and accepting of each other’s differences. This is very important for any country to be happy and prosper.
Get the huge list of more than 500 Essay Topics and Ideas
India: A Democratic Country
India is known to be the largest democracy all over the world. After the rule of the British ended in 1947 , India adopted democracy. In India, all the citizens who are above the age of 18 get the right to vote. It does not discriminate on the basis of caste, creed, gender, color, or more.

Although India is the largest democracy it still has a long way to go. The country faces a lot of problems which do not let it efficiently function as a democracy. The caste system is still prevalent which hampers with the socialist principle of democracy. Moreover, communalism is also on the rise. This interferes with the secular aspect of the country. All these differences need to be set aside to ensure the happiness and prosperity of the citizens.
In short, democracy in India is still better than that in most of the countries. Nonetheless, there is a lot of room for improvement which we must focus on. The government must implement stringent laws to ensure no discrimination takes place. In addition, awareness programs must be held to make citizens aware of their rights and duties.
Customize your course in 30 seconds
Which class are you in.

- Travelling Essay
- Picnic Essay
- Our Country Essay
- My Parents Essay
- Essay on Favourite Personality
- Essay on Memorable Day of My Life
- Essay on Knowledge is Power
- Essay on Gurpurab
- Essay on My Favourite Season
- Essay on Types of Sports
Leave a Reply Cancel reply
Your email address will not be published. Required fields are marked *
Download the App

What Is Democracy? Definition and Examples
- B.S., Texas A&M University
A democracy is a form of government that empowers the people to exercise political control, limits the power of the head of state, provides for the separation of powers between governmental entities, and ensures the protection of natural rights and civil liberties . In practice, democracy takes many different forms. Along with the two most common types of democracies—direct and representative—variants such as participatory, liberal, parliamentary, pluralist, constitutional, and socialist democracies can be found in use today.
Key Takeaways: Democracy
- Democracy, literally meaning “rule by the people,” empowers individuals to exercise political control over the form and functions of their government.
- While democracies come in several forms, they all feature competitive elections, freedom of expression , and protection of individual civil liberties and human rights.
- In most democracies, the needs and wishes of the people are represented by elected lawmakers who are charged with writing and voting on laws and setting policy.
- When creating laws and policies, the elected representatives in a democracy strive to balance conflicting demands and obligations to maximize freedom and protect individual rights.
Despite the prominence in the headlines of non-democratic, authoritarian states like China, Russia, North Korea, and Iran, democracy remains the world’s most commonly practiced form of government. In 2018, for example, a total of 96 out of 167 countries (57%) with populations of at least 500,000 were democracies of some type. Statics show that the percentage of democracies among the world’s governments has been increasing since the mid-1970s, currently standing just short of its post- World War II high of 58% in 2016.
Democracy Definition
Meaning “rule by the people,” democracy is a system of government that not only allows but requires the participation of the people in the political process to function properly. U.S. President Abraham Lincoln , in his famed 1863 Gettysburg Address may have best-defined democracy as a “…government of the people, by the people, for the people…”
Semantically, the term democracy comes from the Greek words for “people” (dēmos) and “rule” (karatos). However, achieving and preserving a government by the people—a “popular” government—is far more complicated than the concept’s semantic simplicity might imply. In creating the legal framework under which the democracy will function, typically a constitution, several crucial political and practical questions must be answered.
Is “rule by the people” even appropriate for the given state? Do the inherent freedoms of a democracy justify dealing with its complex bureaucracy and electoral processes, or would the streamlined predictability of a monarchy , for example, be preferable?
Assuming a preference for democracy, which residents of the country, state, or town should enjoy the political status of full citizenship? Simply stated, who are the “people” in the “government by the people” equation? In the United States, for example, the constitutionally established doctrine of birthright citizenship provides that any person born on U.S. soil automatically becomes a U.S. citizen. Other democracies are more restrictive in bestowing full citizenship.
Which people within the democracy should be empowered to participate in it? Assuming that only adults are allowed to fully participate in the political process, should all adults be included? For example, until the enactment of the 19th Amendment in 1920, women in the United States were not allowed to vote in national elections. A democracy that excludes too many of the governed from taking part in what is supposed to be their government runs the risk of becoming an aristocracy—government by a small, privileged ruling class—or an oligarchy —government by an elite, typically wealthy, few.
If, as one of the foundational principles of democracy holds, the majority rules, what will a “proper” majority be? A majority of all citizens or a majority of citizens who vote only? When issues, as they inevitably will, divide the people, should the wishes of the majority always prevail, or should, as in the case of the American Civil Rights Movement , minorities be empowered to overcome majority rule? Most importantly, what legal or legislative mechanisms should be created to prevent the democracy from becoming a victim of what one of America’s Founding Fathers , James Madison , called “the tyranny of the majority?”
Finally, how likely is it that a majority of the people will continue to believe that democracy is the best form of government for them? For a democracy to survive it must retain the substantial support of both the people and the leaders they choose. History has shown that democracy is a particularly fragile institution. In fact, of the 120 new democracies that have emerged around the world since 1960, nearly half have resulted in failed states or have been replaced by other, typically more authoritarian forms of government. It is therefore essential that democracies be designed to respond quickly and appropriately to the internal and external factors that will inevitably threaten them.
Democratic Principles
While their opinions vary, a consensus of political scientists agree that most democracies are based on six foundational elements:
- Popular sovereignty: The principle that the government is created and maintained by the consent of the people through their elected representatives.
- An Electoral System: Since according to the principle of popular sovereignty, the people are the source of all political power, a clearly defined system of conducting free and fair elections is essential.
- Public Participation: Democracies rarely survive without the active participation of the people. Health democracies enable and encourage the people to take part in their political and civic processes.
- Separation of Powers: Based on a suspicion of power concentrated in a single individual—like a king—or group, the constitutions of most democracies provide that political powers be separated and shared among the various governmental entities.
- Human Rights: Along with their constitutionally enumerated rights freedoms, democracies protect the human rights of all citizens. In this context, human rights are those rights considered inherent to all human beings, regardless of nationality, sex, national or ethnic origin, color, religion, language, or any other considerations.
- A Rule of Law: Also called due process of law , the rule of law is the principle that all citizens are accountable to laws that are publicly created and equitably enforced in a manner consistent with human rights by an independent judicial system.
Types of Democracy
Throughout history, more types of democracy have been identified than there are countries in the world. According to social and political philosopher Jean-Paul Gagnon, more than 2,234 adjectives have been used to describe democracy. While many scholars refer to direct and representative as the most common of these, several other types of democracies can be found around the world today. While direct democracy is unique, most other recognized types of democracy are variants of representative democracy. These various types of democracy are generally descriptive of the particular values emphasized by the representative democracies that employ them.
Originated in Ancient Greece during the 5th century BCE, direct democracy , sometimes called “pure democracy,” is considered the oldest non-authoritarian form of government. In a direct democracy, all laws and public policy decisions are made directly by a majority vote of the people, rather than by the votes of their elected representatives.
Functionally possible only in small states, Switzerland is the only example of a direct democracy applied on a national level today. While Switzerland is no longer a true direct democracy, any law passed by the popularly elected national parliament can be vetoed by a direct vote of the public. Citizens can also change the constitution through direct votes on amendments. In the United States, examples of direct democracy can be found in state-level recall elections and lawmaking ballot initiatives .
Representative
Also called indirect democracy, representative democracy is a system of government in which all eligible citizens elect officials to pass laws and formulate public policy on their behalf. These elected officials are expected to represent the needs and viewpoints of the people in deciding the best course of action for the nation, state, or other jurisdiction as a whole.
As the most commonly found type of democracy in use today, almost 60% of all countries employ some form of representative democracy including the United States, the United Kingdom, and France.
Participatory
In a participatory democracy, the people vote directly on policy while their elected representatives are responsible for implementing those policies. Participatory democracies rely on the citizens in setting the direction of the state and the operation of its political systems. While the two forms of government share similar ideals, participatory democracies tend to encourage a higher, more direct form of citizen participation than traditional representative democracies.
While there are no countries specifically classified as participatory democracies, most representative democracies employ citizen participation as a tool for social and political reform. In the United States, for example, so-called “grassroots” citizen participation causes such as the Civil Rights Movement of the 1960s have led elected officials to enact laws implementing sweeping social, legal, and political policy changes.
Liberal democracy is loosely defined as a form of representative democracy that emphasizes the principles of classical liberalism —an ideology advocating the protection of individual civil liberties and economic freedom by limiting the power of the government. Liberal democracies employ a constitution, either statutorily codified, as in the United States or uncodified, as in the United Kingdom, to define the powers of the government, provide for a separation of those powers, and enshrine the social contract .
Liberal democracies may take the form of a constitutional republic , like the United States, or a constitutional monarchy , such as the United Kingdom, Canada, and Australia.
Parliamentary
In a parliamentary democracy, the people directly elect representatives to a legislative parliament . Similar to the U.S. Congress , the parliament directly represents the people in making necessary laws and policy decisions for the country.
In parliamentary democracies such as the United Kingdom, Canada, and Japan, the head of government is a prime minister, who is first elected to parliament by the people, then elected prime minister by a vote of the parliament. However, the prime minister remains a member of the parliament and thus plays an active role in the legislative process of creating and passing laws. Parliamentary democracies are typically a feature of a constitutional monarch, a system of government in which the head of state is a queen or king whose power is limited by a constitution.
In a pluralist democracy, no single group dominates politics. Instead, organized groups within the people compete to influence public policy. In political science, the term pluralism expresses the ideology that influence should be spread among different interest groups, rather than held by a single elite group as in an aristocracy. Compared to participatory democracies, in which individuals take part in influencing political decisions, in a pluralist democracy, individuals work through groups formed around common causes hoping to win the support of elected leaders.
In this context, the pluralist democracy assumes that the government and the society as a whole benefit from a diversity of viewpoints. Examples of pluralist democracy can be seen in the impact special interest groups, such as the National Organization for Women , have had on American politics.
Constitutional
While the exact definition continues to be debated by political scientists, constitutional democracy is generally defined as a system of government based on popular sovereignty and a rule of law in which the structures, powers, and limits of government are established by a constitution. Constitutions are intended to restrict the power of the government, typically by separating those powers between the various branches of government, as in the United States’ constitution’s system of federalism . In a constitutional democracy, the constitution is considered to be the “ supreme law of the land .”
Democratic socialism is broadly defined as a system of government based on a socialist economy , in which most property and means of production are collectively, rather than individually, controlled by a constitutionally established political hierarchy—the government. Social democracy embraces government regulation of business and industry as a means of furthering economic growth while preventing income inequality .
While there are no purely socialist governments in the world today, elements of democratic socialism can be seen in Sweden’s provision of free universal health care, education, and sweeping social welfare programs.
Is America a Democracy
While the word “democracy” does not appear in the United States Constitution, the document provides the basic elements of representative democracy: an electoral system based on majority rule, separation of powers, and a dependence on a rule of law. Also, America’s Founding Fathers used the word often when debating the form and function of the Constitution.
However, a long-running debate over whether the United States is a democracy or a republic continues today. According to a growing number of political scientists and constitutional scholars, it is both—a “democratic republic.”
Similar to democracy, a republic is a form of government in which the country is governed by the elected representatives of the people. However, since the people do not govern the state themselves, but do so through their representatives, a republic is distinguished from direct democracy.
Professor Eugene Volokh of the UCLA School of Law argues that the governments of democratic republics embrace the principles shared by both republics and democracies. To illustrate his point, Volokh notes that in the United States, many decisions on local and state levels are made by the people through the process of direct democracy, while as in a republic, most decisions at the national level are made by democratically elected representatives.
Brief History
Archeological evidence suggests that disorganized practices at least resembling democracy existed in some parts of the world during prehistoric times, However, the concept of democracy as a form of populist civic engagement emerged during the 5th century BCE in the form of the political system used in some of the city-states of Ancient Greece , most notably Athens . At that time, and for the next several centuries, tribes or city-states remained small enough that if democracy was practiced at all, it took the form of direct democracy. As city-states grew into larger, more heavily populated sovereign nation-states or countries, direct democracy became unwieldy and slowly gave way to representative democracy. This massive change necessitated an entirely new set of political institutions such as legislatures, parliaments, and political parties all designed according to the size and cultural character of the city or country to be governed.
Until the 17th century, most legislatures consisted only of the entire body of citizens, as in Greece, or representatives selected from among a tiny oligarchy or an elite hereditary aristocracy. This began to change during the English Civil Wars from 1642 to 1651 when members of the radical Puritan reformation movement demanded expanded representation in Parliament and the universal right to vote for all male citizens. By the middle 1700s, as the power of the British Parliament grew, the first political parties—the Whigs and Tories—emerged. It soon became obvious that laws could not be passed or taxes levied without the support of the Whig or Tory party representatives in Parliament.
While the developments in the British Parliament showed the feasibility of a representative form of government, the first truly representative democracies emerged during the 1780s in the British colonies of North America and took its modern form with the formal adoption of the Constitution of the United States of America on March 4, 1789.
Sources and Further Reference
- Desilver, Drew. “Despite global concerns about democracy, more than half of countries are democratic.” Pew Research Center , May 14, 2019, https://www.pewresearch.org/fact-tank/2019/05/14/more-than-half-of-countries-are-democratic/.
- Kapstein, Ethan B., and Converse, Nathan. “The Fate of Young Democracies.” Cambridge University Press, 2008, ISBN 9780511817809.
- Diamond, Larry. “Democracy in Decline?” Johns Hopkins University Press, October 1, 2015, ISBN-10 1421418185.
- Gagnon, Jean-Paul. “2,234 Descriptions of Democracy: An Update to Democracy's Ontological Pluralism.” Democratic Theory, vol. 5, no. 1, 2018.
- Volokh, Eugene. “Is the United States of America a republic or a democracy?” The Washington Post , May 13, 2015, https://www.washingtonpost.com/news/volokh-conspiracy/wp/2015/05/13/is-the-united-states-of-america-a-republic-or-a-democracy/.
- Reasons to Keep the Electoral College
- Republic vs. Democracy: What Is the Difference?
- Key Election Terms for Students
- Democracy Promotion as Foreign Policy
- 7 Points to Know About Ancient Greek Government
- What Is Federalism? Definition and How It Works in the US
- Democracy Then and Now
- Overview of United States Government and Politics
- Direct Democracy: Definition, Examples, Pros and Cons
- Is Iraq a Democracy?
- The Three Branches of US Government
- Representative Democracy: Definition, Pros, and Cons
- Understanding the Ballot Initiative Process
- The Powers of Congress
- About the Legislative Branch of U.S. Government
- Basic Structure of the US Government

- school Campus Bookshelves
- menu_book Bookshelves
- perm_media Learning Objects
- login Login
- how_to_reg Request Instructor Account
- hub Instructor Commons
- Download Page (PDF)
- Download Full Book (PDF)
- Periodic Table
- Physics Constants
- Scientific Calculator
- Reference & Cite
- Tools expand_more
- Readability
selected template will load here
This action is not available.

1.1: Introduction - What is Democracy?
- Last updated
- Save as PDF
- Page ID 183377

Democracy may be a word familiar to most, but it is a concept still misunderstood and misused at a time when dictators, single-party regimes, and military coup leaders alike assert popular support by claiming the mantle of democracy. Yet the power of the democratic idea has prevailed through a long and turbulent history, and democratic government, despite continuing challenges, continues to evolve and flourish throughout the world.
Democracy, which derives from the Greek word "demos," or "people," is defined, basically, as government in which the supreme power is vested in the people. In some forms, democracy can be exercised directly by the people; in large societies, it is by the people through their elected agents. Or, in the memorable phrase of President Abraham Lincoln, democracy is government "of the people, by the people, and for the people."
Freedom and democracy are often used interchangeably, but the two are not synonymous. Democracy is indeed a set of ideas and principles about freedom, but it also consists of practices and procedures that have been molded through a long, often tortuous history. Democracy is the institutionalization of freedom.

Talk to our experts
1800-120-456-456
- Democracy Essay for Students in English

Essay on Democracy
Introduction.
Democracy is mainly a Greek word which means people and their rules, here peoples have the to select their own government as per their choice. Greece was the first democratic country in the world. India is a democratic country where people select their government of their own choice, also people have the rights to do the work of their choice. There are two types of democracy: direct and representative and hybrid or semi-direct democracy. There are many decisions which are made under democracies. People enjoy few rights which are very essential for human beings to live happily.
Our country has the largest democracy. In a democracy, each person has equal rights to fight for development. After the independence, India has adopted democracy, where the people vote those who are above 18 years of age, but these votes do not vary by any caste; people from every caste have equal rights to select their government. Democracy, also called as a rule of the majority, means whatever the majority of people decide, it has to be followed or implemented, the representative winning with the most number of votes will have the power. We can say the place where literacy people are more there shows the success of the democracy even lack of consciousness is also dangerous in a democracy. Democracy is associated with higher human accumulation and higher economic freedom. Democracy is closely tied with the economic source of growth like education and quality of life as well as health care. The constituent assembly in India was adopted by Dr B.R. Ambedkar on 26 th November 1949 and became sovereign democratic after its constitution came into effect on 26 January 1950.
What are the Challenges:
There are many challenges for democracy like- corruption here, many political leaders and officers who don’t do work with integrity everywhere they demand bribes, resulting in the lack of trust on the citizens which affects the country very badly. Anti-social elements- which are seen during elections where people are given bribes and they are forced to vote for a particular candidate. Caste and community- where a large number of people give importance to their caste and community, therefore, the political party also selects the candidate on the majority caste. We see wherever the particular caste people win the elections whether they do good for the society or not, and in some cases, good leaders lose because of less count of the vote.
India is considered to be the largest democracy around the globe, with a population of 1.3 billion. Even though being the biggest democratic nation, India still has a long way to becoming the best democratic system. The caste system still prevails in some parts, which hurts the socialist principle of democracy. Communalism is on the rise throughout the globe and also in India, which interferes with the secular principle of democracy. All these differences need to be set aside to ensure a thriving democracy.
Principles of Democracy:
There are mainly five principles like- republic, socialist, sovereign, democratic and secular, with all these quality political parties will contest for elections. There will be many bribes given to the needy person who require food, money, shelter and ask them to vote whom they want. But we can say that democracy in India is still better than the other countries.
Basically, any country needs democracy for development and better functioning of the government. In some countries, freedom of political expression, freedom of speech, freedom of the press, are considered to ensure that voters are well informed, enabling them to vote according to their own interests.
Let us Discuss These Five Principles in Further Detail
Sovereign: In short, being sovereign or sovereignty means the independent authority of a state. The country has the authority to make all the decisions whether it be on internal issues or external issues, without the interference of any third party.
Socialist: Being socialist means the country (and the Govt.), always works for the welfare of the people, who live in that country. There should be many bribes offered to the needy person, basic requirements of them should be fulfilled by any means. No one should starve in such a country.
Secular: There will be no such thing as a state religion, the country does not make any bias on the basis of religion. Every religion must be the same in front of the law, no discrimination on the basis of someone’s religion is tolerated. Everyone is allowed to practice and propagate any religion, they can change their religion at any time.
Republic: In a republic form of Government, the head of the state is elected, directly or indirectly by the people and is not a hereditary monarch. This elected head is also there for a fixed tenure. In India, the head of the state is the president, who is indirectly elected and has a fixed term of office (5 years).
Democratic: By a democratic form of government, means the country’s government is elected by the people via the process of voting. All the adult citizens in the country have the right to vote to elect the government they want, only if they meet a certain age limit of voting.
Merits of Democracy:
better government forms because it is more accountable and in the interest of the people.
improves the quality of decision making and enhances the dignity of the citizens.
provide a method to deal with differences and conflicts.
A democratic system of government is a form of government in which supreme power is vested in the people and exercised by them directly or indirectly through a system of representation usually involving periodic free elections. It permits citizens to participate in making laws and public policies by choosing their leaders, therefore citizens should be educated so that they can select the right candidate for the ruling government. Also, there are some concerns regarding democracy- leaders always keep changing in democracy with the interest of citizens and on the count of votes which leads to instability. It is all about political competition and power, no scope for morality.
Factors Affect Democracy:
capital and civil society
economic development
modernization
Norway and Iceland are the best democratic countries in the world. India is standing at fifty-one position.
India is a parliamentary democratic republic where the President is head of the state and Prime minister is head of the government. The guiding principles of democracy such as protected rights and freedoms, free and fair elections, accountability and transparency of government officials, citizens have a responsibility to uphold and support their principles. Democracy was first practised in the 6 th century BCE, in the city-state of Athens. One basic principle of democracy is that people are the source of all the political power, in a democracy people rule themselves and also respect given to diverse groups of citizens, so democracy is required to select the government of their own interest and make the nation developed by electing good leaders.

FAQs on Democracy Essay for Students in English
1. What are the Features of Democracy?
Features of Democracy are as follows
Equality: Democracy provides equal rights to everyone, regardless of their gender, caste, colour, religion or creed.
Individual Freedom: Everybody has the right to do anything they want until it does not affect another person’s liberty.
Majority Rules: In a democracy, things are decided by the majority rule, if the majority agrees to something, it will be done.
Free Election: Everyone has the right to vote or to become a candidate to fight the elections.
2. Define Democracy?
Democracy means where people have the right to choose the rulers and also people have freedom to express views, freedom to organise and freedom to protest. Protesting and showing Dissent is a major part of a healthy democracy. Democracy is the most successful and popular form of government throughout the globe.
Democracy holds a special place in India, also India is still the largest democracy in existence around the world.
3. What are the Benefits of Democracy?
Let us discuss some of the benefits received by the use of democracy to form a government. Benefits of democracy are:
It is more accountable
Improves the quality of decision as the decision is taken after a long time of discussion and consultation.
It provides a better method to deal with differences and conflicts.
It safeguards the fundamental rights of people and brings a sense of equality and freedom.
It works for the welfare of both the people and the state.
4. Which country is the largest democracy in the World?
India is considered the largest democracy, all around the world. India decided to have a democratic Govt. from the very first day of its independence after the rule of the British. In India, everyone above the age of 18 years can go to vote to select the Government, without any kind of discrimination on the basis of caste, colour, religion, gender or more. But India, even being the largest democracy, still has a long way to become perfect.
5. Write about the five principles of Democracy?
There are five key principles that are followed in a democracy. These Five Principles of Democracy of India are - secular, sovereign, republic, socialist, and democratic. These five principles have to be respected by every political party, participating in the general elections in India. The party which got the most votes forms the government which represents the democratic principle. No discrimination is done on the basis of religion which represents the secular nature of democracy. The govt. formed after the election has to work for the welfare of common people which shows socialism in play.

- Table of Contents
- Random Entry
- Chronological
- Editorial Information
- About the SEP
- Editorial Board
- How to Cite the SEP
- Special Characters
- Advanced Tools
- Support the SEP
- PDFs for SEP Friends
- Make a Donation
- SEPIA for Libraries
- Entry Contents
Bibliography
Academic tools.
- Friends PDF Preview
- Author and Citation Info
- Back to Top
Normative democratic theory deals with the moral foundations of democracy and democratic institutions, as well as the moral duties of democratic representatives and citizens. It is distinct from descriptive and explanatory democratic theory, which aim to describe and explain how democracy and democratic institutions function. Normative democracy theory aims to provide an account of when and why democracy is morally desirable as well as moral principles for guiding the design of democratic institutions and the actions of citizens and representatives. Of course, normative democratic theory is inherently interdisciplinary and must draw on the results of political science, sociology, psychology, and economics in order to give concrete moral guidance.
This brief outline of normative democratic theory focuses attention on seven related issues. First, it proposes a definition of democracy. Second, it outlines different approaches to the question of why democracy is morally valuable at all. Third, it discusses the issue of whether and when democratic institutions have authority and different conceptions of the limits of democratic authority. Fourth, it explores the question of what it is reasonable to demand of citizens in large democratic societies. This issue is central to the evaluation of normative democratic theories. A large body of opinion has it that most classical normative democratic theory is incompatible with what we can reasonably expect from citizens. Fifth, it surveys different accounts of the proper characterization of equality in the processes of representation and the moral norms of representation. Sixth, it discusses the relationship between central findings in social choice theory and democracy. Seventh, it discusses the question of who should be included in the group that makes democratic decisions.
1. Democracy Defined
2.1.1.1 the production of relatively good laws and policies: responsiveness theories, 2.1.1.2 the production of relatively good laws and policies: epistemic theories, 2.1.1.3 character-based arguments, 2.1.2 instrumental arguments against democracy, 2.1.3 grounds for instrumentalism, 2.2.1 liberty, 2.2.2 democracy as public justification, 2.2.3 equality, 3.1 instrumentalist conceptions of democratic authority, 3.2.1 democracy as collective self-rule, 3.2.2 freedom and democratic authority, 3.2.3 equality and authority, 3.3.1 internal limits to democratic authority, 3.3.2 the problem of persistent minorities, 3.3.3 external limits to democratic authority, 4.1 the problem of democratic participation, 4.2.1 elite theory of democracy, 4.2.2 interest group pluralism, 4.2.3 neo-liberalism.
- 4.2.4. The self-interest assumption
4.2.5 The Division of Democratic Labor
4.3.1 the duty to vote, 4.3.2 principled disobedience of the law, 4.3.3 accommodate disagreement through compromise and consensus, 5.1 what sort of representative system is best, 5.2 the ethics of representation, 6. social choice and democracy, 7. the boundary problem: constituting the demos, other internet resources, related entries.
The term “democracy”, as we will use it in this entry, refers very generally to a method of collective decision making characterized by a kind of equality among the participants at an essential stage of the decision-making process. Four aspects of this definition should be noted. First, democracy concerns collective decision making, by which we mean decisions that are made for groups and are meant to be binding on all the members of the group. Second, we intend for this definition to cover many different kinds of groups and decision-making procedures that may be called democratic. So there can be democracy in families, voluntary organizations, economic firms, as well as states and transnational and global organizations. The definition is also consistent with different electoral systems, for example first-past-the-post voting and proportional representation. Third, the definition is not intended to carry any normative weight. It is compatible with this definition of democracy that it is not desirable to have democracy in some particular context. So the definition of democracy does not settle any normative questions. Fourth, the equality required by the definition of democracy may be more or less deep. It may be the mere formal equality of one-person one-vote in an election for representatives to a parliament where there is competition among candidates for the position. Or it may be more robust, including substantive equality in the processes of deliberation and coalition building leading up to the vote. “Democracy” may refer to any of these political arrangements. It may involve direct referenda of the members of a society in deciding on the laws and policies of the society or it may involve the participation of those members in selecting representatives to make the decisions.
The function of normative democratic theory is not to settle questions of definition but to determine which, if any, of the forms democracy may take are morally desirable and when and how. To evaluate different moral justifications of democracy, we must decide on the merits of the different principles and conceptions of human beings and society from which they proceed.
2. The Justification of Democracy
In this section, we examine different views concerning the justification of democracy. Proposed justifications of democracy identify values or reasons that support democracy over alternative forms of decision-making, such as oligarchy or dictatorship. It is important to distinguish views concerning the justification of democracy from views concerning the authority of democracy, which we examine in section 3 . Attempts to establish democratic authority identify values or reasons in virtue of which subjects have a duty to obey democratic decisions. Justification and authority can come apart (Simmons 2001: ch. 7)—it is possible to hold that the balance of values or reasons supports democracy over alternative forms of decision-making while denying that subjects have a duty to obey democratic decisions.
We can evaluate the justification of democracy along at least two different dimensions: instrumentally, by reference to the outcomes of using it compared with other methods of political decision; or intrinsically, by reference to values that are inherent in the method.
2.1 Instrumentalism
2.1.1 instrumental arguments in favor of democracy.
Two kinds of in instrumental benefits are commonly attributed to democracy: (1) the production of relatively good laws and policies and (2) improvements in the characters of the participants.
It is often argued that democratic decision-making best protects subjects’ rights or interests because it is more responsive to their judgments or preferences than competing forms of government. John Stuart Mill, for example, argues that since democracy gives each subject a share of political power, democracy forces decision-makers to take into account the rights and interests of a wider range of subjects than are taken into account under aristocracy or monarchy (Mill 1861: ch. 3). There is some evidence that as groups are included in the democratic process, their interests are better advanced by the political system. For example, when African Americans regained the right to vote in the United States in 1965, they were able to secure many more benefits from the state than previously (Wright 2013). Economists argue that democracy promotes economic growth (Acemoglu et al. 2019). Several contemporary authors defend versions of this instrumental argument by pointing to the robust empirical correlation between well-functioning democratic institutions and the strong protection of core liberal rights, such as rights to a fair trial, bodily integrity, freedom of association, and freedom of expression (Gaus 1996: ch. 13; Christiano 2011; Gaus 2011: ch. 22).
A related instrumental argument for democracy is provided by Amartya Sen, who argues that
no substantial famine has ever occurred in any independent country with a democratic form of government and a relatively free press. (Sen 1999: 152)
The basis of this argument is that politicians in a multiparty democracy with free elections and a free press have incentives to respond to the expressions of needs of the poor.
Epistemic justifications of democracy argue that, under the right conditions, democracy is generally more reliable than alternative methods at producing political decisions that are correct according to procedure-independent standards. While there are many different explanations for the reliability of democratic decision-making, we outline three of the most prominent explanations here: (1) Condorcet’s Jury Theorem, (2) the effects of cognitive diversity, and (3) information gathering and sharing.
The most prominent explanation for democracy’s epistemic reliability rests on Condorcet’s Jury Theorem (CJT), a mathematical theorem developed by eighteenth-century mathematician the Marquis de Condorcet that builds on the so-called “law of large numbers”. CJT states that, when certain assumptions hold, the probability that a majority of voters support the correct decision increases and approaches one as the number of voters increases. The assumptions are (Condorcet 1785):
- each voter is more likely than not to identify the correct decision (the competence assumption );
- voters vote for what they believe is the correct decision (the sincerity assumption );
- votes are statistically independent of one another (the independence assumption ).
While Condorcet’s original proof was restricted to decisions with only two choices, more recent work argues that CJT can be extended to decisions with three or more choices (List & Goodin 2001). The use of CJT to explain democracy’s reliability is often thought to originate with Jean-Jacques Rousseau’s claim that
[i]f, when a sufficiently informed populace deliberates, the citizens were to have no communication among themselves, the general will would always result from the large number of small differences, and the deliberation would always be good. (Rousseau 1762: Book III, ch. IV)
Contemporary theorists continue to rely on CJT, or variants of it, to justify democracy (Barry 1965; Cohen 1986; Grofman and Feld 1988; Goodin & Spiekermann 2019).
The appeal of CJT for epistemic democrats derives from the fact that, if its underlying assumptions are satisfied, decisions produced by even moderately-sized electorates are almost certain to be correct. For example, if the assumptions of CJT hold for an electorate of 10,000 voters, and if each voter is 51 percent likely to identify the correct decision of two options, then the probability that a majority will select the correct decision is 99.97 percent. The formal mathematics of CJT are not subject to dispute. However, critics of CJT-based arguments for democracy argue that the assumptions underlying CJT are rarely, if ever, satisfied in actual democracies (see Black 1963: 159–65; Ladha 1992; Estlund 1997b; 2008: ch. XII; Anderson 2006). First, many have remarked that voters’ opinions are not independent of each other. Indeed, the democratic process seems to emphasize persuasion and coalition building. Second, the theorem does not seem to apply to cases in which the information that voters have access to, and on the basis of which they make their judgments, is segmented in various ways. Segmentation occurs when some sectors of the society do not have the relevant information while others do have it. Modern societies and politics seem to instantiate this kind of segmentation in terms of class, race, ethnic groupings, religion, occupational position, geographical place and so on. Finally, all voters approach issues they have to make decisions on with strong ideological biases that undermine the claim that each voter is bringing a kind of independent observation on the nature of the common good to the vote.
Advocates of CJT-based justifications of democracy generally respond to these sorts of criticisms by attempting to develop variations of CJT with weaker assumptions. These assumptions are more easily satisfied in democracies and so the revised theorems may show that even moderately-sized electorates are almost certain to produce correct decisions (Grofman & Feld 1988; Austen-Smith 1992; Austen-Smith & Banks 1996).
A second common epistemic justification for democracy—which is often traced to Aristotle ( Politics , Book II, Ch. 11; see Waldron 1995)—argues that democratic procedures are best able to exploit the underlying cognitive diversity of large groups of citizens to solve collective problems. Since democracy brings a lot of people into the process of decision making, it can take advantage of many sources of information and perspectives in assessing proposed laws and policies. More recently, Hélène Landemore (2013) has drawn on the “diversity-trumps-ability” theorem of Scott Page and Lu Hong (Hong & Page 2004; Page 2007)—which states that a random collection of agents drawn from a large set of limited-ability agents typically outperforms a collection of the very best agents from that same set—to argue that democracy can be expected to produce better decisions than rule by experts. Both Page and Hong’s original theorem and Landemore’s use of it to justify democracy are subject to dispute (see Quirk 2014; Brennan 2014; Thompson 2014; Bajaj 2014).
A third common epistemic justification for democracy relies on the idea that democratic decision-making tends to be more informed than other forms of decision-making about the interests of citizens and the causal mechanisms necessary to advance those interests. John Dewey argues that democracy involves “a consultation and a discussion which uncovers social needs and troubles”. Even if experts know how best to solve collective problems, they need input from the masses to correct their biases tell them where the problems lie (Dewey 1927 [2012: 154–155]; see also Anderson 2006; Knight & Johnson 2011).
Many have endorsed democracy on the grounds that democracy has beneficial effects on the characters of subjects. Many agree with Mill and Rousseau that democracy tends to make people stand up for themselves more than other forms of rule do because it makes collective decisions depend on their input more than monarchy or aristocracy do. Hence, in democratic societies individuals are encouraged to be more autonomous. Relatedly, by giving citizens a share of control over political-decision-making, democracy cultivates citizens with active and productive characters rather than passive characters. In addition, it has been argued that democracy tends to get people to think carefully and rationally more than other forms of rule because it makes a difference to political outcomes whether they do or not. Finally, some argue that democracy tends to enhance the moral qualities of citizens. When they participate in making decisions, they have to listen to others, they are called upon to justify themselves to others and they are forced to think in part in terms of the interests of others. Some have argued that when people find themselves in this kind of circumstance, they can be expected genuinely to think in terms of the common good and justice. Hence, some have argued that democratic processes tend to enhance the autonomy, rationality, activity, and morality of participants. Since these beneficial effects are thought to be worthwhile in themselves, they count in favor of democracy and against other forms of rule (Mill 1861 [1991: 74]; Elster 1986 [2003: 152]; Hannon 2020).
Some argue in addition that the above effects on character tend to enhance the quality of legislation as well. A society of autonomous, rational, active, and moral decision-makers is more likely to produce good legislation than a society ruled by a self-centered person or a small group of persons who rule over slavish and unreflective subjects. Of course, the soundness of any of the above arguments depends on the truth of the causal theories of the consequences of different institutions.
Not all instrumental arguments favor democracy. Plato argues that democracy is inferior to various forms of monarchy, aristocracy and even oligarchy on the grounds that democracy tends to undermine the expertise necessary to the proper governance of societies (Plato 1974, Book VI). Most people do not have the kinds of intellectual talents that enable them to think well about the difficult issues that politics involves. But in order to win office or get a piece of legislation passed, politicians must appeal to these people’s sense of what is right or not right. Hence, the state will be guided by very poorly worked out ideas that experts in manipulation and mass appeal use to help themselves win office. Plato argues instead that the state should be ruled by philosopher-kings who have the wisdom and moral character required for good rule. He thus defends a version of what David Estlund calls “epistocracy”, a form of oligarchy that involves rule by experts (Estlund 2003).
Mill defends a form of epistocracy that is sometimes referred to as the “plural voting” scheme (1861: ch. 4). While all rational adults get at least one vote under this scheme, some citizens get a greater number of votes based on satisfying some measure of political expertise. While Mill identifies the relevant measure of expertise in terms of formal education, the plural voting scheme is consistent with other measures. This scheme might be thought to combine the instrumental value of political expertise with the intrinsic value of broad inclusion.
One objection to any form of epistocracy—the demographic objection —holds that any criterion of expertise is likely to select demographically homogeneous individuals who are be biased in ways that undermine their ability to produce political outcomes that promote the general welfare (Estlund 2003).
Hobbes argues that democracy is inferior to monarchy because democracy fosters destabilizing dissension among subjects (Hobbes 1651: chap. XIX). On his view, individual citizens and even politicians are apt not to have a sense of responsibility for the quality of legislation because no one makes a significant difference to the outcomes of decision making. As a consequence, citizens’ concerns are not focused on politics and politicians succeed only by making loud and manipulative appeals to citizens in order to gain more power, but all lack incentives to consider views that are genuinely for the common good. Hence the sense of lack of responsibility for outcomes undermines politicians’ concern for the common good and inclines them to make sectarian and divisive appeals to citizens.
Many contemporary theorists expand on these Platonic and Hobbesian criticisms. A good deal of empirical data shows that citizens of large-scale democracies are ill-informed and apathetic about politics. This makes room for special interests to control the behavior of politicians and use the state for their own limited purposes all the while spreading the costs to everyone. Moreover, there is empirical evidence that democratic citizens often engage in motivated reasoning that unconsciously aims to affirm their existing political identities rather than arrive at correct judgments (Lord, Ross, & Lepper 1979; Bartels 2002; Kahan 2013; Achen & Bartels 2016). Some theorists argue that these considerations justify abandoning democracy altogether, while modest versions of these arguments have been used to justify modification of democratic institutions (Caplan 2007; Somin 2013; Brennan 2016). Relatedly, some theorists argue that rather than having beneficial effects on the characters of subjects as Mill and others argue, democracy actually has deleterious effects on the subjects’ characters and relationships (Brennan 2016: ch. 3).
Pure instrumentalists argue that these instrumental arguments for and against the democratic process are the only bases on which to evaluate the justification of democracy or compare it with other forms of political decision-making. There are a number of different kinds of argument for pure instrumentalism. One kind of argument proceeds from a more general moral theory. For example, classical utilitarianism has no room in its monistic axiology for the intrinsic values of fairness and liberty or the intrinsic importance of an egalitarian distribution of political power. Its sole concern with maximizing utility—understood as pleasure or desire satisfaction—guarantees that it can provide only instrumental arguments for and against democracy.
But one need not be a thoroughgoing utilitarian to argue for instrumentalism in democratic theory. There are arguments in favor of instrumentalism that pertain directly to the question of democracy and collective decision making generally. One argument states that political power involves the exercise of power of some over others. And it argues that the exercise of power of one person over another can only be justified by reference to the protection of the interests or rights of the person over whom power is exercised. Thus no distribution of political power could ever be justified except by reference to the quality of outcomes of the decision making process (Arneson 1993 [2002: 96–97]; 2003; 2004; 2009). Another sort of argument for instrumentalism proceeds negatively, attempting to show that the non-instrumental values most commonly used in attempted justifications for democracy do not actually justify democracy, and that an instrumental justification for democracy is therefore the only available sort of justification (Wall 2007).
Other arguments question the coherence of the idea of intrinsically fair collective decision making processes. For instance, social choice theory questions the idea that there can be a fair decision making function that transforms a set of individual preferences into a rational collective preference. The core objection is that no general rule satisfying reasonable constraints can be devised that can transform any set of individual preferences into a rational social preference. And this is taken to show that democratic procedures cannot be intrinsically fair (Riker 1982: 116). Ronald Dworkin argues that the idea of equality, which is for him at the root of social justice, cannot be given a coherent and plausible interpretation when it comes to the distribution of political power among members of the society. The relation of politicians to citizens inevitably gives rise to inequality; the process of democratic deliberation inevitably gives those with superior argument making abilities and greater willingness to participate more influence and therefore more power, than others, so equality of political power cannot be intrinsically fair or just (Dworkin 2000). In later work, Dworkin has pulled back from this originally thoroughgoing instrumentalism (Dworkin 1996).
2.2 Non-instrumentalism
Few theorists deny that political institutions must be at least in part evaluated in terms of the outcomes of having those institutions. Some argue in addition, that some forms of decision making are morally desirable independent of the consequences of having them. A variety of different approaches have been used to show that democracy has this kind of intrinsic value.
One prominent justification for democracy appeals to the value of liberty. According to one version of the view, democracy is grounded in the idea that each ought to be master of his or her life. Each person’s life is deeply affected by the larger social, legal and cultural environment in which he or she lives. Only when each person has an equal voice and vote in the process of collective decision-making will each have equal control over this larger environment. Thinkers such as Carol Gould conclude that only when some kind of democracy is implemented, will individuals have a chance at self-government (Gould 1988: 45–85). Since individuals have a right of self-government, they have a right to democratic participation. The idea is that the right of self-government gives one a right, within limits, to do wrong. Just as an individual has a right to make some bad decisions for himself or herself, so a group of individuals have a right to make bad or unjust decisions for themselves regarding those activities they share.
One major difficulty with this line of argument is that it appears to require that the basic rule of decision-making be consensus or unanimity. If each person must freely choose the outcomes that bind him or her then those who oppose the decision are not self-governing. They live in an environment imposed on them by others. So only when all agree to a decision are they freely adopting the decision (Wolff 1970: ch. 2). The trouble is that there is rarely agreement on major issues in politics. Indeed, it appears that one of the main reasons for having political decision making procedures is that they can settle matters despite disagreement.
One liberty-based argument that might seem to escape this worry appeals to an irreducibly collective right to self-determination. It is often argued that political communities have a right as a community to organize themselves politically in accordance with their values, principles, or commitments. Some argue that the right to collective self-determination requires democratic institutions that give citizens collective control over their political and legal structure (Cassese 1995). However, many argue democratic institutions are sufficient but not necessary to realize the right to collective self-determination because political communities might exercise this right to implement non-democratic institutions (Altman & Wellman 2009; Stilz 2016).
Another non-instrumental justification of democracy appeals to the ideal of public justification. The idea behind this approach is that laws and policies are legitimate to the extent that they are publicly justified to the citizens of the community. Public justification is justification to each citizen as a result of free and reasoned debate among equals.
Jürgen Habermas’s discourse theory of deliberative democracy has been highly influential in the development of this approach. Habermas analyses the form and function of modern legal systems through the lens of his theory of communicative action. This analysis yields the Democratic Principle:
[O]nly those statutes may claim legitimacy that can meet with the assent of all citizens in a discursive process of legislation that in turn has been legally constituted. (Habermas 1992 [1996: 110])
Habermas advances a conception of democratic legitimacy according to which law is legitimate only if it results from a free and inclusive democratic process of “opinion and will-formation”. What might such a process look like in a complex and differentiated society? Habermas answers by advancing a “two-track” model that understands democratic legitimation in terms of the relationship between institutionalized deliberative bodies (e.g legislatures, agencies, courts) and informal communication in the public sphere, which is “wild”, and not centrally coordinated.
One possible objection to this view is that free and inclusive democratic procedures are insufficient to satisfy the demand for deliberative consensus embodied in the Democratic Principle. This demand is unlikely to be satisfied in diverse societies, since deep disagreements about which laws ought to be enacted is likely to remain after the relevant process of opinion and will-formation. The Democratic Principle might thus be thought to embody an overly idealistic conception of democratic legitimacy (Estlund 2008: ch.10). Another possible worry is that the Discourse Principle is not a genuine moral principle, but a principle that embodies the felicity conditions of practical discourse. As such, the Discourse Principle cannot ground a conception of democratic legitimacy that yields robust moral prescriptions (Forst 2016).
Drawing on Habermas and John Rawls, among others, Joshua Cohen (1996 [2003]) develops a conception of democracy in which citizens justify laws and policies on the basis of mutually acceptable reasons. Democracy, properly understood, is the context in which individuals freely engage in a process of reasoned discussion and deliberation on an equal footing. The ideas of freedom and equality provide guidelines for structuring democratic institutions.
The aim of Cohen’s conception of democracy as public justification is reasoned consensus among citizens. But a serious problem arises when we ask about what happens when disagreement remains. Two possible replies have been suggested. It has been urged that forms of consensus weaker than full consensus are sufficient for public justification and that the weaker varieties are achievable in many societies. For instance, there may be consensus on the list of reasons that are acceptable publicly but disagreement on the weight of the different reasons. Or there may be agreement on general reasons abstractly understood but disagreement about particular interpretations of those reasons. What would have to be shown here is that such weak consensus is achievable in many societies and that the disagreements that remain are not incompatible with the ideal of public justification.
The basic principle seems to be the principle of reasonableness according to which reasonable persons will only offer principles for the regulation of their society that other reasonable persons can reasonably accept. One only offers principles that others, who restrain themselves in the same way, can accept. Such a principle implies a kind of principle of restraint which requires that reasonable persons avoid proposing laws and policies on the basis of controversial moral or philosophical principles. When individuals offer proposals for the regulation of their society, they ought not to appeal to the whole truth as they see it but only to that part of the whole truth that others can reasonably accept. To put the matter in the way Rawls puts it: political society must be regulated by principles on which there is an overlapping consensus (Rawls 2005: Lecture IV). This is meant to obviate the need for a complete consensus on the principles that regulate society.
However, it is hard to see how this approach avoids the need for a complete consensus, which is highly unlikely to occur in any even moderately diverse society. The reason for this is that it is not clear why it is any less of an imposition on me when I propose legislation or policies for the society that I must restrain myself to considerations that other reasonable people accept than it is an imposition on others when I attempt to pass legislation on the basis of reasons they reasonably reject. For if I do restrain myself in this way, then the society I live in will not live up to the standards that I believe are essential to evaluating the society. I must then live in and support a society that does not accord with my conception of how it ought to be organized. It is not clear why this is any less of a loss of control over society than for those who must live in a society that is partly regulated by principles they do not accept. If one is a problem, then so is the other, and complete consensus is the only solution (Christiano 2009).
Many democratic theorists have argued that democracy is a way of treating persons as equals when there is good reason to impose some kind of organization on their shared lives but they disagree about how best to do it. Peter Singer argues that when people insist on different ways of arranging matters properly, each person in a sense claims a right to be dictator over their shared lives (Singer 1973: 30–41). But these claims to dictatorship cannot all hold up. Democracy embodies a kind of peaceful and fair compromise among these conflicting claims to rule. Each compromises equally on what he claims as long as the others do, resulting in each having an equal say over decision making. In effect, democratic decision making respects each person’s point of view on matters of common concern by giving each an equal say about what to do in cases of disagreement (Singer 1973; Waldron 1999: chap. 5).
What if people disagree on the democratic method or on the particular form democracy is to take? Are we to decide these latter questions by means of a higher order procedure? And if there is disagreement on the higher order procedure, must we also democratically decide that question? The view seems to lead to an infinite regress.
An alternative way of justifying democracy on the basis of equality is to ground democracy in public equality. Public equality is a principle of equality which ensures that people can see that they are being treated as equals. This view arises from three ideas. First, there is the basic egalitarian idea that people’s interests ought to be equally advanced, or at least that they ought to have equal opportunities to advance them. Second, human beings generally have highly fallible and biased understandings of their own and other people’s interests. Third, persons have fundamental interests in being able to see that they are being treated as equals. Public equality is an egalitarian principle that can be seen to be realized among persons despite the dramatically incomplete forms of knowledge people have. It is not all of justice, but it is essential that the principle be realized in a pluralistic society.
Democracy is a uniquely publicly egalitarian way to make collective decisions when there is substantial disagreement and conflict of interest among persons about how to shape the society they share. Each can see that the only plausible way of overcoming persistent disagreement over how to shape the society they all live in, while still publicly treating all persons as equals in the face of bias and fallibility, is to give each person an equal say in the process of shaping that society. Thus, democracy is necessary to the realization of public equality in a political society. Within the framework determined by this publicly realized equality, persons are permitted to attempt to bring about their more particular ideas about justice and the common good that they think are right.
The idea of public equality also grounds limits to democratic decision making. The thought is that a society cannot democratically decide to abolish the democratic rights of some of its members. Public equality also requires that basic liberal and civil rights be respected as well, by the democratic process and so serves as a limit to democratic decision making (Christiano 2008; Valentini 2013).
A number of worries attend this kind of view. First, it is generally thought that majority rule is required for treating persons as equals in collective decision making. This is because only majority rule is neutral towards alternatives in decision making. Unanimity tends to favor the status quo as do various forms of supermajority rule. But if this is so, the above view raises the twin dangers of majority tyranny and of persistent minorities, i.e., groups of persons who find themselves always losing in majority decisions. Surely these latter phenomena must be incompatible with public equality. Second, the kind of view defended above is susceptible to the worry that political equality is not a coherent ideal in any modern state with a complex division of labor and the need for representation. This last worry will be discussed in more detail in the next sections on democratic citizenship and legislative representation. The first worry will be discussed more in the discussion on the limits to democratic authority.
A related approach grounds democracy in the ideal of relational equality . A concern with relational equality is a concern for
human relationships that are, in certain crucial respects at least, unstructured by differences of rank, power, or status. (Scheffler 2010: 225)
Niko Kolodny argues that democratic institutions are an essential component of relational equality (Kolodny 2014a,b). One line of Kolodny’s argument holds that political decisions involve the use of coercive force. Inequalities in the power to use force undermine equal social status at least in part because the power to use force is “the power that usually determines the distribution of other powers” (Kolodny 2014b: 307). Individuals who have superior power to use force on others have a superior social status. An egalitarian distribution of political power is thus essential for realizing social equality. And only democratic institutions provide an egalitarian distribution of political power. We will discuss the relationship between relational equality and democracy further when we discuss the authority of democracy in Part 3 below.
3. The Authority of Democracy
Since democracy is a collective decision process, the question naturally arises about whether there is any duty of citizens to obey democratic decisions when they disagree with it.
There are three main concepts of the legitimate authority of the state. First, a state has legitimate authority to the extent that it is morally justified in coercively imposing its rule on the members. Legitimate authority on this account has no direct implications concerning the obligations or duties that citizens may hold toward that state. It simply says that if the state is morally justified in doing what it does, then it has legitimate authority. Second, a state has legitimate authority to the extent that its directives generate duties in citizens to obey. The duties of the citizens need not be owed to the state but they are real duties to obey. The third is that the state has a right to rule that is correlated with the citizens’ duty to it to obey it. This is the strongest notion of authority and it seems to be the core idea behind the legitimacy of the state. The idea is that when citizens disagree about law and policy it is important to be able to answer the question, who has the right to choose?
Instrumental arguments for democracy give some reason for why one ought to respect the democracy when one disagrees with its decisions. There may be many instrumental considerations that play a role in deciding on the question of whether one ought to obey. And these instrumental considerations are pretty much the same whether one is considering obedience to democracy or some other form of rule.
There is one instrumentalist approach which is quite unique to democracy and that seems to ground a strong conception of democratic authority. That is the epistemic approach inspired by the Condorcet Jury Theorem, which we discussed in section 2.1.1.2 above. There, we discussed a number of difficulties with the application of the Condorcet Jury Theorem to the case of voting in elections and referenda in large-scale democracies, including lack of independence, informational segmentation, and the existence of ideological biases.
One further worry about the Jury Theorem’s epistemic conceptions of authority is that it would prove too much since it undermines the common practice of the loyal opposition in democracies. If the background conditions of the Jury Theorem are met, a large-scale democracy majority is practically certain to produce the right decisions. On what basis can citizens in a political minority rationally hold on to their competing views? The members of the minority have a powerful reason for shifting their allegiance to the majority position, since each has very good reason to think that the majority is right. The epistemic conception of authority based on the Jury Theorem thus threatens to be objectionably authoritarian, since it looks like it demands not only obedience of action but obedience of thought as well. Even in scientific communities the fact that a majority of scientists favor a particular view does not make the minority scientists think that they are wrong, though it does perhaps give them pause (Goodin 2003: ch. 7).
Some theories of democratic authority combine instrumental and non-instrumental considerations. David Estlund argues that democratic procedures have legitimate authority because they are better than random and epistemically the best of the political systems that are acceptable to all reasonable citizens (Estlund 2008). They must be better than random because, otherwise, why wouldn’t we use a fair random procedure like a lottery or coin flip? Democratic authority must have an epistemic element. And the justification of democratic procedure must be acceptable to all reasonable citizens in order to respect their freedom and equality. Estlund’s conception of democratic authority—which he calls “epistemic proceduralism”— thus combines the ideal of public justification with a concern for the tendency of democracies to produce good decisions.
3.2 Intrinsic Conceptions of Democratic Authority
Some theorists argue that there is a special relation between democracy and legitimate authority grounded in the value of collective self-rule. John Locke argues that when a person consents to the creation of a political society, they necessarily consent to the use of majority rule in deciding how the political society is to be organized (Locke 1690: sec. 96). Locke thinks that majority rule is the natural decision rule when there is disagreement. He argues that a society is a kind of collective body that must move in the direction of the greater force. One way to understand this argument is as follows. If we think of each member of society as an equal and if we think that there is likely to be disagreement beyond the question of whether to join society or not, then we must accept majority rule as the appropriate decision rule. This interpretation of the greater force argument assumes that the expression “greater force” is to be understood in terms of the equal worth of each person’s interests and rights, so the society must go in the direction in which the greater number of persons wants it to go.
Locke thinks that a people, which is formed by individuals who consent to be members, could choose a monarchy by means of majority rule and so this argument by itself does not give us an argument for democracy. But Locke refers back to this argument when he defends the requirement of representative institutions for deciding when property may be regulated and taxes levied. He argues that a person must consent to the regulation or taxation of his property by the state. But he says that this requirement of consent is satisfied when a majority of the representatives of property holders consent to the regulation and taxation of property (Locke, 1690: sec. 140). This does seem to be moving towards a genuinely democratic conception of legitimate authority.
Rousseau argues that when individuals consent to form a political community, they agree to put themselves under the direction of the “general will” (Rousseau 1762). The general will is not a mere aggregation of individuals’ private wills. It is, rather, the will of the political community as a whole. And since the general will can only emerge as the product of a properly organized democratic procedure, individuals consent to put themselves under the direction of a properly organized democratic procedure. On one interpretation of Rousseau, democratic procedures are properly organized only when they (1) define rights that apply equally to all, (2) via a procedure that considers everyone’s interests equally, and (3) everyone who is coerced to obey the laws has a voice in that procedure.
There are at least two ways of understanding the idea of the general will. On what might be called the constitutive interpretation, the general will is constituted by the results of a properly organized democratic procedure. That is, the results of a properly organized democratic procedure are the general will in virtue of the fact that they emerge from a properly organized democratic procedure, and not because they reflect some procedure-independent truth about the common good. On what might be called the epistemic interpretation, the results of a properly organized democratic procedure are the way of tracking the procedure-independent truth about the common good. As we discussed in section 3.1 , Rousseau is often interpreted as appealing to Condorcet’s Jury Theorem to support the epistemic credentials of a properly organized democratic procedure.
Anna Stilz develops an account of democratic authority that appeals to the value of “freedom as independence” (Stilz 2009). Freedom as independence is freedom from being subject to the will of another. In order not to be subject to the will of others, individuals need property rights and a protected sphere of autonomy to pursue one’s plans. Drawing on Kant, Stilz argues that attempts by particular individuals, no matter how conscientious, to define and secure rights to property and autonomy in a state of nature will be inconsistent with freedom as independence. Such attempts unilaterally impose new obligations on others through acts of private will in the face of competing claims. But even if individuals in a state of nature do agree to a resolution of their competing claims, they are dependent on the will of others to honor this agreement. Stilz thus argues that justice must be administered by an authoritative legal system which can coercively impose one set of objective rules—rules we must respect even when we disagree—to adjudicate our conflicting claims. But if such a system is to be consistent with the freedom of subjects, it cannot be imposed by the private wills of rulers. The solution, Stilz argues, lies in Rousseau’s idea of the general will. When subjects obey the general will, they are not obeying the private will of any individual; they are obeying a will that arises from all and applies to all.
One worry with this account is that those who oppose democratically-enacted laws or policies can complain that those laws or policies are imposed against their will. Perhaps they are not subject to the will of a particular individual, but they are subject to the will of a majority. This might be thought to constitute a significant threat to individuals’ freedom as independence. Another worry, which Stilz’s view arguably inherits from Rousseau, is that the conditions for the general will to emerge are so demanding that the view implies that no state that exists or has existed has legitimate political authority. Stilz’s view might thus be thought to entail what A.J. Simmons calls “a posteriori anarchism” (Simmons 2001).
Another approach to democratic authority asserts that failing to obey the decisions of a democratic assembly amounts to treating one’s fellow citizens as inferiors (Christiano 2008: ch. 6). In the face of disagreement about substantive law and policy, democracy realizes a kind of public equality by giving each individual an equal say in determining which laws or policies will be enacted. Citizens who skirt laws made by suitably egalitarian procedures act contrary to the equal right of all citizens to have a say in making laws. Those who refuse to pay taxes or respect property laws on the grounds that they are unjust are affirming a superior right to that of others in determining how the shared aspects of social life ought to be arranged. Thus, they violate the duty to treat others publicly as equals. And there is reason to think this duty must normally have some pre-eminence. Public equality is the most important form of equality and democracy is required by public equality. The other forms of equality in play in substantive disputes about law and policy are ones about which people can have reasonable disagreements (within limits specified by the principle of public equality). Citizens thus have obligations to abide by the democratic process even if their favored conceptions of justice or equality are passed by in the decision making process.
Daniel Viehoff develops an egalitarian conception of democratic authority based on the ideal of relational equality (Viehoff 2014; see section 2.2.3 above for more on relational equality). Viehoff argues that relational equality is threatened by “subjection” in a relationship, which occurs when individuals have significantly different power over how they interact with and relate to one another. According to Viehoff, obeying the outcomes of egalitarian democratic procedures is necessary and sufficient for citizens to achieve coordination on common rules without subjection. It is sufficient because democratic procedures distribute decision-making power equally, which ensures that coordination is not determined by unequal power advantages. It is necessary because parties must set aside the considerations of greater and lesser power to realize non-subjection in their relationship.
Fabienne Peter develops a fairness-based conception of democratic authority that incorporates epistemic considerations (Peter 2008; 2009). Drawing on insights from proceduralist epistemology, Peter’s “pure epistemic proceduralism” holds that suitably egalitarian democratic decisions are binding at least in part because they result from a fair procedure of knowledge-production. This account differs from Estlund’s epistemic proceduralism (see section 5.1 above) because it does not condition the authority of democratic procedures on their ability to produce decisions that track the procedure-independent truth. Rather, the authority of democratic procedures is grounded in their fairness. And it differs from pure procedural accounts because the relevant notion of fairness is fairness in knowledge-production.
3.3 Limits to the Authority of Democracy
What are the limits to democratic authority? A limit to democratic authority is a principle violation of which defeats democratic authority. When the principle is violated by the democratic assembly, the assembly loses its authority in that instance or the moral weight of the authority is overridden. A number of different views have been offered on this issue. We can distinguish between internal and external limits to democratic authority. An internal limit arises from the constitutive requirements of the democratic process or from the principles that ground democracy. An external limit arises from principles that are independent of the values or requirements that ground democracy.
External limits to democratic authority are rebutting limits, which are principles that weigh against—and may sometimes outweigh the principles that ground democracy. So in a particular case, an individual may see that there are reasons to obey the assembly and some reasons against obeying the assembly and in the case at hand the reasons against obedience outweigh the reasons in favor of obedience. Internal limits to democratic authority are undercutting limits. These limits function not by weighing against the considerations in favor of authority, they undercut the considerations in favor of authority altogether; they simply short circuit the authority. When an undercutting limit is in play, it is not as if the principles which ground the limit outweigh the reasons for obeying the democratic assembly, it is rather that the reasons for obeying the democratic assembly are undermined altogether; they cease to exist or at least they are severely weakened.
Some have argued that the democratic process ought to be limited to decisions that are not incompatible with the proper functioning of the democratic process. So they argue that the democratic process may not legitimately take away the political rights of its citizens in good standing. It may not take away rights that are necessary to the democratic process such as freedom of association or freedom of speech. But these limits do not extend beyond the requirements for proper democratic functioning. They do not protect non political artistic speech or freedom of association in the case of non political activities (Ely 1980: chap. 4).
Another kind of internal limit is a limit that arises from the principles that underpin democracy. And the presence of this limit would seem to be necessary to making sense of the first limit because in order for the first limit to be morally important we need to know why a democracy ought to protect the democratic process.
Locke gives an account of the internal limits of democracy in his idea that there are certain things to which a citizen may not consent (Locke 1690: ch. XI). She may not consent to arbitrary rule or the violation of fundamental rights including democratic and liberal rights. Since consent is the basis of democratic authority for Locke, this account provides an explanation of the idea behind the first internal limit, that democracy may not be suspended by democratic means but it goes beyond that limit to suggest that rights that are not essentially connected with the exercise of the franchise may also not be violated because one may not consent to their violation.
More recently, Ronald Dworkin has defended an account of the limits of democratic authority (Dworkin 1996). He argues that democracy is justified by appeal to a principle of self-government. He argues that self-government cannot be realized unless all citizens are treated as full members of the political community, because, otherwise, they are not able to identify as members of the community. Among the conditions of full membership, he argues, are rights to be treated as equals and rights to have one’s moral independence respected. These principles support robust requirements of non-discrimination and of basic liberal rights.
The conception of democratic authority that grounds it in public equality also provides an account of the limits of that authority (Christiano 2008: ch. 6). Since democracy is founded in public equality, it may not violate public equality in any of its decisions. The basic idea is that overt violation of public equality by a democratic assembly undermines the claim that the democratic assembly embodies public equality. Democracy’s embodiment of public equality is conditional on its protecting public equality. To the extent that liberal rights are grounded in public equality and the provision of an economic minimum is also so grounded, this suggests that democratic rights and liberal rights and rights to an economic minimum create a limit to democratic authority. This account also provides a deep grounding for the kinds of limits to democratic authority defended in the first internal limit and it goes beyond these to the extent that protection of rights that are not connected with the exercise of the franchise is also necessary to public equality.
This account of the authority of democracy also provides some help with a vexing problem of democratic theory. This problem is the difficulty of persistent minorities. There is a persistent minority in a democratic society when that minority always loses in the voting. This is always a possibility in democracies because of the use of majority rule. If the society is divided into two or more highly unified voting blocks in which the members of each group votes in the same ways as all the other members of that group, then the group in the minority will find itself always on the losing end of the votes. This problem has plagued some societies, particularly those with indigenous peoples who live within developed societies. Though this problem is often connected with majority tyranny it is distinct from the problem of majority tyranny because it may be the case that the majority attempts to treat the minority well, in accordance with its conception of good treatment. It is just that the minority never agrees with the majority on what constitutes proper treatment. Being a persistent minority can be highly oppressive even if the majority does not try to act oppressively. This can be understood with the help of the very ideas that underpin democracy. Persons have interests in being able to correct for the cognitive biases of others and to be able to make the world in such a way that it makes sense to them. These interests are set back for a persistent minority since they never get their way.
The conception of democracy as grounded in public equality can shed light on this problem. It can say that the existence of a persistent minority violates public equality (Christiano 2008: chap. 7). In effect, a society in which there is a persistent minority is one in which that minority is being treated publicly as an inferior because it is clear that its fundamental interests are being set back. Hence to the extent that violations of public equality undercut the authority of a democratic assembly, the existence of a persistent minority undermines the authority of the democracy at least with respect to the minority. This suggests that certain institutions ought to be constructed so that the minority is not persistent.
One natural kind of limit to democratic authority is the external kind of limit. Here the idea is that there are certain considerations that favor democratic decision making and there are certain values that are independent of democracy that may be at issue in democratic decisions. For example, many theories recognize core liberal rights—such as rights to property, bodily integrity, and freedom of thought and expression—as external limits to democratic authority. Locke is often interpreted as arguing that individuals have natural rights to property in themselves and the external world that democratic laws must respect in order to have legitimate authority (Locke 1690).
Some views may assert that there are only external limits to democratic authority. But it is possible to think that there are both internal and external limits. Such an issue may arise in decisions to go to war, for example. In such decisions, one may have a duty to obey the decision of the democratic assembly on the grounds that this is how one treats one’s fellow citizens as equals but one may also have a duty to oppose the war on the grounds that the war is an unjust aggression against other people. To the extent that this consideration is sufficiently serious it may outweigh the considerations of equality that underpin democratic authority. Thus one may have an overall duty not to obey in this context. Issues of foreign policy in general seem to give rise to possible external limits to democracy.
4. The Demands of Democratic Participation
In this section, we examine the demands of participation in large-scale democracies. We begin by examining a core challenge to the idea that democratic citizens are capable of governing a large and complex society. We then explore different proposed solutions to the core challenge. Finally, we examine the moral duties of democratic citizens in large-scale democracies in light of the core challenge.
A vexing problem of democratic theory has been to determine whether ordinary citizens are up to the task of governing a large and complex society. There are three distinct problems here:
- Plato argued that some people are more intelligent and informed about political matters than others and have a superior moral character, and that those persons ought to rule ( The Republic , Book VI)
- Others have argued that a society must have a division of labor. If everyone were engaged in the complex and difficult task of politics, little time or energy would be left for the other essential tasks of a society. Conversely, if we expect most people to engage in other difficult and complex tasks, how can we expect them to have the time and resources sufficient to devote themselves intelligently to politics?
- Since individuals have so little impact on the outcomes of political decision making in large societies, they have little sense of responsibility for the outcomes. Some have argued that it is not rational to vote since the chances that an individual’s vote will a decide the outcome of an election (i.e., will determine whether a candidate gets elected or not) are nearly indistinguishable from zero. For example, one widely accepted estimate puts the odds of an individual casting the deciding vote in a United States presidential election at 1 in 100 million. Many estimates put the odds much lower. Worse still, Anthony Downs has argued that almost all of those who do vote have little reason to become informed about how best to vote (Downs 1957: ch.13). On the assumption that citizens reason and behave roughly according to the Downsian model, either the society must in fact be run by a relatively small group of people with minimal input from the rest or it will be very poorly run. As we can see these criticisms are echoes of the sorts of criticisms Plato and Hobbes made.
These observations pose challenges for any robustly egalitarian or deliberative conception of democracy. Without the ability to participate intelligently in politics one cannot use one’s votes to advance one’s aims nor can one be said to participate in a process of reasoned deliberation among equals. So, either equality of political power implies a kind of self-defeating equal participation of citizens in politics or a reasonable division of labor seems to undermine equality of power. And either substantial participation of citizens in public deliberation entails the relative neglect of other tasks or the proper functioning of the other sectors of the society requires that most people do not participate intelligently in public deliberation.
4.2 Proposed Solutions to the Problem of Democratic Participation
Some modern theorists of democracy, called elite theorists, have argued against any robustly egalitarian or deliberative forms of democracy in light of the problem of democratic participation. They argue that high levels of citizen participation tend to produce bad legislation designed by demagogues to appeal to poorly informed and overly emotional citizens. They look upon the alleged uninformedness of citizens evidenced in many empirical studies in the 1950s and 1960s as perfectly reasonable and predictable. Indeed they regard the alleged apathy of citizens in modern states as highly desirable social phenomena.
Political leaders are to avoid divisive and emotionally charged issues and make policy and law with little regard for the fickle and diffuse demands made by ordinary citizens. Citizens participate by voting but since they know very little they are not effectively the ruling part of the society. The process of election is usually just a fairly peaceful way of maintaining or changing those who rule (Schumpeter 1942 [1950: 269]).
On Schumpeter’s view, however, citizens do have a role to play in avoiding serious disasters. When politicians act in ways that nearly anyone can see is problematic, the citizens can throw the bums out.
So the elite theory of democracy does seem compatible with some of the instrumentalist arguments given above but it is strongly opposed to the intrinsic arguments from liberty, public justification and equality. To be sure, there can be an elite deliberative democracy wherein elites deliberate, perhaps even out of sight of the population at large, on how to run the society.
A view akin to the elite theory but less pessimistic about citizens’ political agency and competence argues that a well-functioning representative democracy can function as a kind of “defensible epistocracy” (Landa & Pevnick 2020). This view holds that, under the right conditions, elected officials can be expected to exercise political power more responsibly than citizens in a direct democracy because each official is far more likely to cast the deciding vote in legislative assemblies (the “pivotality effect”) and officials have more incentive to exercise power with due regard for the general welfare (the “accountability effect”). Moreover, under the right conditions, representative democracy allows individuals to assess the competence of candidates for office and to select candidates who are best able to help the community pursue its commitments.
One approach that is in part motivated by the problem of democratic citizenship but which attempts to preserve some elements of equality against the elitist criticism is the interest group pluralist account of politics. Robert Dahl’s early statement of the view is very powerful.
In a rough sense, the essence of all competitive politics is bribery of the electorate by politicians… The farmer… supports a candidate committed to high price supports, the businessman…supports an advocate of low corporation taxes… the consumer…votes for candidates opposed to a sales tax. (Dahl 1959: 69)
In this conception of the democratic process, each citizen is a member of an interest group with narrowly defined interests that are closely connected to their everyday lives. On these subjects citizens are supposed to be quite well informed and interested in having an influence. Or at least, elites from each of the interest groups that are relatively close in perspective to the ordinary members are the principal agents in the process. On this account, democracy is not rule by the majority but rather rule by coalitions of minorities. Policy and law in a democratic society are decided by means of bargaining among the different groups.
This approach is conceivably compatible with the more egalitarian approach to democracy. This is because it attempts to reconcile equality with collective decision making by limiting the tasks of citizens to ones which they are able to perform reasonably well. It is not particularly compatible with the deliberative public justification approach because it takes the democratic process to be concerned essentially with bargaining among the different interest groups where the preferences are not subject to further debate in the society as a whole.
A third approach inspired by the problem of participation may be called the neo-liberal approach to politics favored by public choice theorists such as James Buchanan & Gordon Tullock (1962). Against elite theories, they contend that elites and their allies will tend to expand the powers of government and bureaucracy for their own interests and that this expansion will occur at the expense of a largely inattentive public. For this reason, they argue for severe restrictions on the powers of elites. They argue against the interest group pluralist theorists that the problem of participation occurs within interest groups more or less as much as among the citizenry at large. Only powerful economic interests are likely to succeed in organizing to influence the government and they will do so largely for their own benefit. Since economic elites will advance their own interests in politics while spreading the costs to others, policies will tend to be more costly (because imposed on everyone in society) than they are beneficial (because they benefit only the elites in the interest group.)
Neo-liberals infer that one ought to transfer many of the current functions of the state to the market and limit the state to the enforcement of basic property rights and liberties. These can be more easily understood and brought under the control of ordinary citizens.
But the neo-liberal account of democracy must answer to two large worries. First, citizens in modern societies have more ambitious conceptions of social justice and the common good than are realizable by the minimal state. The neo-liberal account thus implies a very serious curtailment of democracy of its own. More evidence is needed to support the contention that these aspirations cannot be achieved by the modern state. Second, the neo-liberal approach ignores the problem of large private concentrations of wealth and power that are capable of pushing small states around for their own benefit and imposing their wills on populations without their consent.
Somin (2013) also argues that government be significantly reduced in size so that citizens have a lesser knowledge burden to carry. But he calls for government decentralization so that citizens can vote with their feet in favor of or against competing units of government, in effect creating a kind of market in governments among which citizens can choose.
4.2.4 The self-interest assumption
A considerable amount of the literature in political science and the economic theory of the state are grounded in the assumption that individuals act primarily and perhaps even exclusively in their self-interest narrowly construed. The problem of participation and the accounts of the democratic process described above are in large part dependent on this assumption. When the preferences of voters are not assumed to be self-interested the calculations of the value of participation change. For example, if a person is a motivated utilitarian, the small chance of making a difference is coupled with a huge accumulated return to many people if there is a significant difference between alternatives. It may be worth it in this case to become reasonably well informed (Parfit 1984: 74). Even more weakly altruistic moral preferences could make a big difference to the rationality of becoming informed, for example if one had a preference to comply with perceived civic duty to vote responsibly (see section 4.3.1 for discussion of the duty to vote). Any moral preference can be formulated in consistent utility functions.
Moreover, defenders of deliberative democracy often claim that concerns for the common good and justice are not merely given prior to politics but that they can evolve and improve through the process of discussion and debate in politics (Elster 1986 [2003]; Gutmann & Thompson 2004; Cohen 1989 [2009]). They assert that much debate and discussion in politics would not be intelligible were it not for the fact that citizens are willing to engage in open minded discussion with those who have distinct morally informed points of view. Empirical evidence suggests that individuals are motivated by moral considerations in politics in addition to their interests (Mansbridge 1990).
Public deliberation in any large-scale democracy will occur within a complex and differentiated “deliberative system”, a
wide variety of institutions, associations, and sites of contestation accomplish political work. (Mansbridge et. al. 2012)
Moreover, the deliberative system of a complex democracy will be characterized by a division of democratic labor , with different parts of the system making different contributions to the overall system. The question arises: what is the appropriate role for a citizen in this division of labor? Philosophically, we should ask two questions. What ought citizens have knowledge about in order to fulfill their role? What standards ought citizens’ beliefs live up to in order to be adequately supported? One promising view is that citizens must think about what ends the society ought to aim at and leave the question of how to achieve those aims to experts (Christiano 1996: ch 5). The rationale for this division of labor is that expertise is not as fundamental to the choice of aims as it is to the development of legislation and policy. Citizens are capable in their everyday lives of understanding and cultivating deep understandings of values and of their interests. And if citizens genuinely do choose the aims and others faithfully pursue the means to achieving those aims, then citizens are in the driver’s seat in society and they can play this role as equals.
To be sure, citizens need to know who to vote for and whether those they vote for are genuinely advancing their aims. This would appear to require some basic knowledge of about how best to achieve their political aims. How is this possible without extensive knowledge? In addition, there is empirical evidence that those who are better informed have more influence on representatives (Erikson 2015). So, if this task requires some kind of knowledge to do well, how can this be compatible with equality?
One promising response is that ordinary citizens do not need individually to have a lot of knowledge of social science and particular facts in order to make political decisions based on such knowledge. Recent research in cognitive science indicates the individuals use “cognitive shortcuts” to save on time in acquiring information about the world they live in (Lupia & McCubbins 1998). This use of shortcuts is common and essential throughout economic and political life. In political life, we see part of the rationale for the many intermediate institutions between government and citizens (Downs 1957: 221–229). Citizens save time by making use of institutions such as the press, unions and other interest group associations, political parties, and opinion leaders to get information about politics. They also rely on interactions in the workplace as well as conversations with friends and families. Political parties can connect ordinary citizens in various ways to expertise because each one contains a division of labor within them that mirrors that in the state. Experts in parties have incentives to make their expertise intelligible to other members (Christiano 2012). In addition, under favorable conditions, political parties stimulate the development of citizens’ normative perspectives and facilitate a healthy public competition of political justifications based on those perspectives (White & Ypi 2016).
People are dependent on social networks in other ways in a democracy. People receive “free” information (which they do not deliberately seek out) about politics and law in school, through their jobs, in discussion with friends, colleagues and family and incidentally through the media. And this can form a better or worse basis on which to pursue other information. Institutions can make a difference to the stream of free information individuals receive. Education can be distributed in a more or less egalitarian way. The circumstances of work can provide more or less free information about politics and law. People who have jobs with a significant amount of power such as lawyers, business persons, government officials will be beneficiaries of very high quality free information. They need to know about law and politics to do their jobs properly. Those who hold low skilled and non-unionized jobs will receive much less free information about politics at work. To the extent that we can alter the economic division of labor by for example giving more place to unions or having greater worker participation, we might be able to reduce inequalities of information among citizens.
4.3 The Moral Duties of Democratic Citizens
What are the moral duties of democratic citizens in complex democracies? In this section, we discuss three important democratic duties: (1) the duty to vote, (2) the duty to promote justice through principled disobedience of the law, and (3) duties to accommodate disagreement through compromise and consensus.
It is often thought that democratic citizens have a moral duty to vote in elections. But this is not obvious. Individual votes are a causally insignificant contribution to the democratic process. In large-scale democracies, the chance that any particular citizen’s vote will decide the outcome of an election is minuscule. What moral reason do democratic citizens have to participate in politics even though they’re almost certain not to make the difference to who gets elected? Why shouldn’t they seek to promote the good or justice in other ways?
Parfit develops an act-utilitarian answer to this question (Parfit 1984: 73–75). Act-utilitarians hold that morally right actions maximize the total expected sum of the utilities of all persons in the society. Parfit argues that voting might nonetheless maximize expected utility if one candidate is significantly superior to the other(s). If we add the benefits to each member of the society of having the superior candidate win, we get a very large difference in value. So when we multiply that value by the probability of casting the deciding vote, which is often thought to be about 1/100,000,000 in a United States presidential election, we might still get a reasonably high expected value. When we subtract the cost to the voter and others of voting, which is often quite low, from this number, we may still have a good reason to vote.
One worry with Parfit’s view is that it faces a version of what Jason Brennan calls “the particularity problem” (Brennan 2011). This is the problem of explaining why citizens ought to promote value through political participation as opposed to through non-political acts. Voting is just one way of promoting overall utility; we need to know the expected utility of the different acts they might perform instead. Even if the argument above is correct, it might be the case that many individuals maximize expected utility by not voting and doing something even more beneficial with their time.
Alex Guerrero argues that citizens have moral reasons to vote because candidates who win by a larger proportion of votes can claim a greater “normative mandate” to govern (Guerrero 2010). Still each individual vote makes only a tiny contribution to the proportion of votes a candidate receives. So, we might doubt the strength of the reason to vote that Guerrero identifies.
Some theorists argue that individuals have a moral duty to vote in order to absolve themselves of complicity in state injustices (Beerbohm 2012; Zakaras 2018). All states commit injustices—they make and enforce unjust laws, wage unjust wars, and much else. And citizens of large-scale democracies have a kind of standing responsibility, by paying taxes and obeying laws, for their state’s injustices of which they must actively absolve themselves The complicity account argues that citizens avoid shared responsibility for their state’s injustices if they oppose those injustices through voting and of public advocacy (Beerbohm 2012).
One worry is that it is unclear why voting and publicly advocating against injustice should be thought to absolve responsibility that is established by paying taxes and obeying laws. Another worry is that one’s concern to oppose injustice should derive from a more direct concern for the wrongs suffered by victims of injustice rather than a concern with keeping one’s hands clean.
One sort of account that avoids this worry grounds the moral duty to vote in the importance of doing one’s fair share of the demands of political justice consistent with public equality. The demands of creating and sustaining just institutions distribute fairly among all citizens (Maskivker 2019). If one fails to do one’s fair share of these demands, then one fails to show due regard for the eventual victims of injustice. Furthermore, voting provides citizens with a mechanism for doing their fair shares of the demands of making their institutions just in a way that is consistent with respecting the public equality of fellow citizens. By showing up and casting a vote, citizens can contribute to the collective achievement of justice while maintaining equal decision-making power with fellow citizens.
Civil disobedience has long been recognized as a central mechanism through which democratic citizens may legitimately promote political justice in their society. According to the standard view, civil disobedience is a public, non-violent and conscientious breach of law that aims to change laws or government policies. People who engage in civil disobedience are willing to accept the legal consequences of their actions in order to show fidelity to the law (Bedau 1961; Rawls 1971: ch. 55). The standard definition of civil disobedience has been subjected to challenge. For example, some argue that the private acts in which the disobedient seeks to evade legal consequences can count as instances of civil disobedience (Raz 1979; Brownlee 2004, 2007, 2012).
Perhaps the most common way of justifying civil disobedience argues that the same considerations that ground the pro tanto duty to obey the law sometimes make it appropriate to engage in civil disobedience of the law (see, e.g., Rawls 1971: ch. 57; Sabl 2001; Markovits 2005; Smith 2011). For example, Rawls argues that while citizens of a “nearly just” society have a pro tanto duty to obey its laws in virtue of it being nearly just, civil disobedience can be justified as a way of making the relevant society more just (Rawls 1971: ch. 57). Similarly, Daniel Markovits argues that members of a society with suitably egalitarian and inclusive democratic procedures have a general duty to obey its laws because they are produced by procedures that are suitably egalitarian and inclusive, but that civil disobedience can be justified as a way of making the relevant procedures more egalitarian or inclusive (Markovits 2005).
It is easy to see why this constitutes an attractive way of justifying civil disobedience, since it justifies it by appeal to the same values that ground the pro tanto duty to obey the law. On the other hand, as Simmons notes, if there is no general duty to obey the law, there would seem to be no presumption in favor of obedience and thus no special need for a justification of civil disobedience; obedience and disobedience would stand equally in need of justification (Simmons 2007: ch 4).
Advocates of the standard approach generally assume that only civil disobedience can be justified in this way. However, some argue civil disobedience does not enjoy a special normative presumption over uncivil disobedience. The core idea that insofar as the values that ground a pro tanto duty to obey the law—for example, justice or democratic equality—are sometimes best served by civil disobedience of the law, they are sometimes best served by covert, evasive, anonymous, or even violent disobedience of the law (Delmas 2018; Lai 2019; Pasternak 2018).
Disagreement about what laws, policies, or principles ought to be implemented is a persistent feature of democratic societies. It is often argued that citizens and officials have duties to moderate their political activity in order to accommodate the competing views of fellow citizens or officials. Two duties of accommodation are widely discussed in the literature: duties of compromise and duties of public justification.
A compromise can be understood as an agreement between parties to advance laws or policies that all regard as suboptimal because they disagree about which laws or policies are optimal (May 2005). While it is widely accepted that there are sometimes compelling instrumental reasons to compromise, whether there are intrinsic moral reasons to compromise is more controversial. Some defend intrinsic reasons to compromise based on democratic values like inclusion, mutual respect, and reciprocity (Gutmann and Thompson 2014; Wendt 2016; Weinstock 2013). However, Simon May argues that such arguments fail and that all reasons to compromise are pragmatic (May 2005).
Advocates of the public justification approach to democracy (see section 2.2.2 ) often argue that democratic citizens and officials have individual moral duties of public justification. John Rawls argues for a “duty of civility” that requires citizens and officials to be prepared to give mutually acceptable justifications for important laws when voting and engaged in public advocacy. Given the inevitability of disagreement about comprehensive moral and philosophical truth in free democracies, the duty of civility requires citizens to appeal to a reasonable “political” conception of justice that can be the object of an “overlapping consensus” between different comprehensive doctrines. While different theorists motivate duties of public justification in different ways, many appeal to the need for exercises of coercive political authority to respect citizens’ freedom and equality.
5. Democratic Representation
Representation is an essential part of the division of labor of large-scale democracies. In this section, we examine two moral questions concerning representation. First, what sort of representative system is best? Second, by what moral principles are representatives bound?
A number of debates have centered on the question of what kinds of representative systems are best for a democratic society. What choice we make here will depend heavily on our underlying moral justification of democracy, our conception of citizenship as well as on our empirical understanding of political institutions and how they function. The most basic types of formal political representation available are single member district representation, proportional representation and group representation. In addition, many societies have opted for multicameral legislative institutions. In some cases, combinations of the above forms have been tried.
Single member district representation returns single representatives of geographically defined areas containing roughly equal populations to the legislature and is prominent in the United States, the United Kingdom, and India, among other places. The most common form of proportional representation is party list proportional representation. In a simple form of such a scheme, a number of parties compete for election to a legislature that is not divided into geographical districts. Parties acquire seats in the legislature as a proportion of the total number of votes they receive in the voting population as a whole. Group representation occurs when the society is divided into non-geographically defined groups such as ethnic or linguistic groups or even functional groups such as workers, farmers and capitalists and returns representatives to a legislature from each of them.
Many have argued in favor of single member district legislation on the grounds that it has appeared to them to lead to more stable government than other forms of representation. The thought is that proportional representation tends to fragment the citizenry into opposing homogeneous camps that rigidly adhere to their party lines and that are continually vying for control over the government. Since there are many parties and they are unwilling to compromise with each other, governments formed from coalitions of parties tend to fall apart rather quickly. The post war experience of governments in Italy appears to confirm this hypothesis. Single member district representation, in contrast, is said to enhance the stability of governments by virtue of its favoring a two party system of government. Each election cycle then determines which party is to stay in power for some length of time.
Charles Beitz argues that single member district representation encourages moderation in party programs offered for citizens to consider (Beitz 1989: ch. 7). This results from the tendency of this kind of representation towards two party systems. In a two party system with majority rule, it is argued, each party must appeal to the median voter in the political spectrum. Hence, they must moderate their programs to appeal to the median voter. Furthermore, they encourage compromise among groups since they must try to appeal to a lot of other groups in order to become part of one of the two leading parties. These tendencies encourage moderation and compromise in citizens to the extent that political parties, and interest groups, hold these qualities up as necessary to functioning well in a democracy.
In criticism, advocates of proportional and group representation have argued that single member district representation tends to muffle the voices and ignore the interests of minority groups in the society (Mill 1861; Christiano 1996). Minority interests and views tend to be articulated in background negotiations and in ways that muffle their distinctiveness. Furthermore, representatives of minority interests and views often have a difficult time getting elected at all in single member district systems so it has been charged that minority views and interests are often systematically underrepresented. Sometimes these problems are dealt with by redrawing the boundaries of districts in a way that ensures greater minority representation. The efforts are invariably quite controversial since there is considerable disagreement about the criteria for apportionment.
In proportional representation, by contrast, representatives of different groups are seated in the legislature in proportion to citizens’ choices. Minorities need not make their demands conform to the basic dichotomy of views and interests that characterize single member district systems so their views are more articulated and distinctive as well as better represented.
Advocates of group representation, like Iris Marion Young, have argued that some historically disenfranchised groups may still not do very well under proportional representation (Young 1990: ch. 6). They may not be able to organize and articulate their views as easily as other groups. Also, minority groups can still be systematically defeated in the legislature and their interests may be consistently set back even if they do have some representation. For these groups, some have argued that the only way to protect their interests is legally to ensure that they have adequate and even disproportionate representation.
One worry about group representation is that it tends to freeze some aspects of the agenda that might be better left to the choice of citizens. For instance, consider a population that is divided into linguistic groups for a long time. And suppose that only some citizens continue to think of linguistic conflict as important. In the circumstances a group representation scheme may tend to be biased in an arbitrary way that favors the views or interests of those who do think of linguistic conflict as important.
What moral norms apply to representatives carrying out their official duties? We can get a better handle on possible answers by introducing Hannah Pitkin’s famous distinction between trustees and delegates (Pitkin 1967). Representatives who act as trustees rely on their own independent judgments in carrying out their duties. Norms of trusteeship are supported in recognition that, given a natural division of democratic labor, officials are in a much better position to make well-reasoned and well-informed political decisions than ordinary citizens.
Representatives who act as delegates defer to the judgments of their citizens. These norms might be thought to reflect the value of democratic accountability. Because the people authorize representatives to govern, it is natural to think that representatives are accountable to the people to enact their judgments. If representatives are not accountable in this way, citizens lose democratic control over their representatives’ actions.
Which norms should win out when they conflict? Pitkin argues that the answer varies by context. This seems plausible. For example, if we take the view that citizens primarily have the role of determining the aims of the society, we might think that representatives ought to be delegates with regard to the aims, but trustees with regard to the ways of realizing the aims (Christiano 1996). See Suzanne Dovi’s discussion of representation for a deeper and more nuanced discussion of these issues.
Kenneth Arrow’s impossibility theorem is thought by some to provide a major set of difficulties for democratic theory (Arrow 1951). William Riker, Russell Hardin, and others have thought that the impossibility theorem shows that there are deep problems with democratic ideals (Riker 1982; Hardin 1999). Neither of these thinkers are opposed to democracy itself, they both think that there are good instrumental reasons for having democracy.
The basic results of social choice theory are laid out in detail elsewhere in the encyclopedia (List 2013). Here we will simply articulate the basic result and an illustration. The question of Arrowian social choice theory is: how do we determine a social preference for a society overall on the basis of the set of the individual preferences of the members? Arrow shows that a social choice function that satisfies a number of plausible constraints cannot be defined when there are three or more alternatives to be chosen by the group. He lays out a number of conditions to be imposed on a social choice function. Unlimited domain : The social choice function must be able to give us a social preference no matter what the preferences of the individuals over alternatives are. Non dictatorship : the social choice function must not select the preference of one particular member regardless of others’ preferences. Transitivity and completeness : The individual preferences orderings must be transitive and complete orderings and the social preference derived from them must be transitive and complete. Independence of irrelevant alternatives : the social preference between two alternatives must be the result only of the individual orderings between those two alternatives. Pareto condition : if all the members prefer an alternative x over y , then x must be ranked above y in the social preference. The theorem says that no social choice function over more than two alternatives can satisfy all of these conditions.
A useful illustration of this idea involves an extension of majority rule to cases of more than two alternatives. The Condorcet rule says that an alternative x wins when, for every other alternative, a majority prefers x over that alternative. For example, suppose we have three persons A , B and C and three alternatives x , y and z . A prefers x over y , y over z ; B prefers y over z and z over x ; C prefers x over z and z over y . In this case, x is the Condorcet winner since it beats y , and it beats z . The problem with this plausible sounding rule is the case of a majority cycle. Suppose you have three persons A , B and C , and three alternatives, x , y and z . In the case in which A prefers x over y and y over z , while B prefers y over z and z over x , and C prefers z over x and x over y , the Condorcet rule will yield a social preference of x over y , y over z and z over x . One can see here that the Condorcet rule satisfies all the conditions except transitivity of social preference. One way to avoid intransitivity is to restrict the domain of preferences from which the social preference arises. Another is to introduce cardinal information that compares the how much people prefer alternatives (violating independence). Another might be to make one person a dictator. So, this case nicely illustrates that one cannot satisfy all of the constraints simultaneously.
Riker argues that the theorem shows that the idea that the popular will can be the governing element in a society is false. If an existence condition for a popular will is a restricted set of preferences the question naturally arises as to whether such a condition is always or normally met in a moderately complex society. We might wonder whether a highly pluralistic society with a very complex division of labor is likely to satisfy the restricted preference set condition necessary to avoid cycles or other pathologies of social choice. Some have argued that we have empirical evidence to the effect that modern societies do normally satisfy such conditions (Mackie 2003). Others have argued that this seems unlikely (Riker 1982; Ingham 2019). This is not merely a defense of unlimited domain. It is a defense of the thesis that normally the collections of preferences in modern societies are not likely to have the properties that enable them to avoid cycles.
The fairness critique from social choice theory is based on the idea that when a voting process meets requirements of fairness, the fairness of the process and the preferences may not generate determinate outcomes. If cycles are pervasive, the outcomes of democratic processes may be determined by clever strategies and not by the fairness of the procedures (Riker 1982). Three remarks are in order here. First, it is compatible with the process being completely fair that the outcomes of the process are indeterminate. After all, coin flips are fair. Second, there is some question as to how prominent the cycles are. Third, one might think that if the conditions which enable opposing sides to strategize effectively are themselves roughly equal, then the concerns for fairness are fully met. If resources for persuasion and organization are distributed in an egalitarian way, perhaps the fairness account is vindicated after all. This point can be made more compelling when we consider Sean Ingham’s account of political equality. He includes intensity of preference in his account of fairness. This is a departure from the Arrowian approach, but it is in many ways a realistic one. The idea is that majorities have equal control over policy areas when they are able to get what they want with the same amount of intensity of preferences. And equality holds generally when all groups of the same size have the same control (Ingham 2019). There remains an extreme case in which all majorities have equal intensity of preference and are caught in a majority cycle. But the chances of this happening are very slim, even if the chances of majority cycles more generally are not as small. Even if there are a lot of majority cycles, if the issues are resolved in such a way that those majorities that have most at stake in the conflict are the ones that get their way, then we can have fairness in a quite robust sense even while having pervasive majority cycles.
If democratic societies allow members to participate as equals in collective decision making, a natural question arises: who has the right to participate in making collective decisions? We can ask this question within a particular jurisdiction (ought all adults have the right to participation? Ought children have the right to participation? Ought all residents have such rights?). But we can also ask what the extent of the jurisdiction ought to be. How many of the people in the world ought to be included in the collective decision-making? An easy, though slightly misleading, way of asking this question is, what ought the physical boundaries of a particular institution of collective decision-making be? We see partially democratic societies within the confines of the modern nation-state. But we might ask, why should we restrict the set of persons who participate in making decisions of the modern state just to those who happen to be the physical inhabitants of those states? Surely there are many other persons affected by decisions made by democratic states aside from those persons. For example, activities in one society A can pollute another society B . Why shouldn’t the members of B have a say in the decisions regarding the polluting activities in A ? And there can be many other effects that activities in A can have on B .
Some have suggested that the boundaries of a state ought to be determined through a principle of national self-determination. We identify a nation as an ongoing group of persons who share certain cultural, historical and political norms and who identify with each other and with a piece of land. Then we determine the boundaries of the territory by appeal to the size of the group of people and the land they cherish (Miller 1995; Song 2012). This is an appealing idea in many ways: shared nationality breeds a willingness to share the sacrifices that arise from collective decision making; it generates a sense of at-homeness for people. But it is hard to use as a general principle for dividing land among persons when one of the central facts for many societies is that a diversity of nations, ethnic groups and cultures co-mingle on the very same land.
Is there a democratic solution to the boundary problem? A number of ideas have been suggested. The first idea is that the people ought to decide what the boundaries are. But this suggestion, while it may be a pragmatic resolution to the problem, seems to beg the question about who the members are and who are not (Whelan 1983).
A second theoretical solution that has some democratic credentials is to invoke the principle that all who are subjected to decision making, in the sense of who are coerced or have duties imposed upon them, ought to have a say in the decision making (Abizadeh 2008). This principle is plausible enough, but it doesn’t get at enough cases. The pollution case above is not a case of subjection.
A third proposed theoretical solution is the all-affected principle. One formulation is “all affected persons ought to have a say in the decisions that affect them”. This does suggest that when the activities in one state affect those of another state, the people of the other state ought to have a say in those activities. Some have thought that this principle tends to lead to a kind of politically cosmopolitan principle in support of world government (Goodin 2007).
But the all-affected principle is conceptually quite uncertain and morally deeply problematic, and it provides very little, if anything, in the way of a solution to the boundary problem.
First, “having a say” is not clear. Does it require having a vote in collective decision-making? Or is it also satisfied by a person’s being able to modify another’s action by negotiating with them, as we see when there is bargaining over an externality? This latter version would undermine the idea that the all-affected principle has direct implications for the boundary problem. When the United States permits activities that produce acid rain in Canada, Canada can negotiate with the United States to lessen the production of acid rain and/or to compensate Canada for the harm. As long as there is a fair and effective system of negotiation, this would seem to satisfy the all-affected principle without giving Canadians a vote in American politics or Americans a vote in Canadian politics.
Second, it is not clear what “being affected” means. One, does a person being affected just mean that there is a change in the person’s situation or must the effect involve the setting back of one’s preferences, or interests, or legitimate interests, or exercise of one’s capacities or one’s good? Two, are one’s interests affected by a decision only when they are advanced or set back relative to some baseline (either the present state of affairs or some morally defined baseline like what you have promised me), or am I affected by decisions that could be to my advantage or disadvantage but end up making no difference? For example, if I am drowning in a pool and you are deciding whether to save me or go buy yourself a candy bar, am I affected by your buying the candy bar? If I am not affected when no change occurs, then who is affected by a decision often depends on who participates in the decision and we have no solution to the problem of inclusion. If I am affected, then the principle has some quite extraordinary implications. Now it turns out that impoverished persons in South Asia are affected by my buying a candy bar, since I could have sent the money to them (Goodin 2007).
The all-affected principle is a merely suggestive and rhetorically effective phrase. It is a conversation starter and a list of topics to be discussed, not a genuine principle. For example, if I must include everyone possibly affected by my decision for every decision I make, I will not be able to make many decisions and my decision making will no longer enable me to give a shape to my own life and my relations with others. My life becomes fragmented and lacks integrity (Williams 1973). An analog of this problem would arise for political societies, presumably. Each society would have to include a variety of different persons in each decision. It is hard to see how any society could take on any particular character if this is the case.
A more plausible principle that encompasses some of the suggestions of the all-affected principle is that a framework of institutions should be set up so that people have power to advance and protect their legitimate interests in life.
But if we understand the principle in this way, it is not clear that it helps us much with the boundary problem. First of all, there are different ways in which people can be said to possess power over their lives. One kind of power is the power to participate as an equal in a collective decision-making process. Another kind is to be able to advance one’s interests in a decentralized process like a market or a system of agreement making like international law. Recalling our pollution problem above, we could give the state of which they are members power to negotiate with the polluting state terms that are mutually agreeable. Only the power to participate as an equal in collective decision-making involves the boundaries of collective decision-making.
Another solution to the boundary problem is a conservative one. The basic idea is to keep the boundaries of states roughly as they are except if there is a pressing need to change them. Trying to alter the boundaries of political societies is a recipe for serious conflict because there is no institution that has the legitimacy or power actually to resolve problems at an international level and there is likely to be a lot of disagreement on how to do it. States as we know them, are by far the most powerful political entities in the international system. They have developed more effective practices of accountability of power than any other entity in the system. They have created unified societies with highly interdependent populations. Finally, states and the individuals in them can be made accountable to some degree to other individuals and states through the process of negotiation and international law making. The origin of these boundaries may be arbitrary, but it is not, for all that, irrelevant. To be sure, there are clear cases where borders can be changed. One source of pressing need is serious injustice within a country. Another might be the existence of permanent minorities that are sectionally defined. Here, we ask only how to revise boundaries and the basis of such revision is that it is a remedy for serious injustice (Buchanan 1991).
- Abizadeh, Arash, 2008, “Democratic Theory and Border Coercion: No Right to Unilaterally Control Your Own Borders”, Political Theory , 36(1): 37–65. doi:10.1177/0090591707310090
- Acemoglu, Daron, Suresh Naidu, Pascual Restrepo, and James A. Robinson, 2019, “Democracy Does Cause Growth”, Journal of Political Economy , 127(1): 47–100. doi:10.1086/700936
- Achen, Christopher H. and Larry M. Bartels, 2016, Democracy for Realists: Why Elections Do Not Produce Responsive Government (Princeton Studies in Political Behavior), Princeton: Princeton University Press.
- Altman, Andrew and Christopher Heath Wellman, 2009, A Liberal Theory of International Justice , Oxford: Oxford University Press. doi:10.1093/acprof:oso/9780199564415.001.0001
- Anderson, Elizabeth, 2006, “The Epistemology of Democracy”, Episteme , 3(1–2): 8–22. doi:10.3366/epi.2006.3.1-2.8
- Aristotle, Politics: Writings from the Complete Works , Jonathan Barnes (ed.), Princeton: Princeton University Press, 2016.
- Arneson, Richard J., 1993 [2003], “Democratic Rights at National and Workplace Levels”, in The Idea of Democracy , David Copp, Jean Hampton, and John Roember, 118–138, 143–147; reprinted as “Democracy at the National Level” in Christiano 2003: 95–115.
- –––, 2003, “Defending the Purely Instrumental Account of Democratic Legitimacy”, Journal of Political Philosophy , 11(1): 122–132. doi:10.1111/1467-9760.00170
- –––, 2004, “Democracy Is Not Intrinsically Just”, in Justice and Democracy , Keith Dowding, Robert E. Goodin, and Carole Pateman (eds.), Cambridge: Cambridge University Press, 40–58. doi:10.1017/CBO9780511490217.003
- –––, 2009, “The Supposed Right to a Democratic Say”, in Contemporary Debates in Political Philosophy , Thomas Christiano and John Christman (eds.), Oxford, UK: Wiley-Blackwell, 195–212. doi:10.1002/9781444310399.ch11
- Arrow, Kenneth J., 1951, Social Choice and Individual Values , New Haven, CT: Yale University Press.
- Austen-Smith, David, 1992, “Strategic Models of Talk in Political Decision Making”, International Political Science Review , 13(1): 45–58. doi:10.1177/019251219201300104
- Austen-Smith, David and Jeffrey S. Banks, 1996, “Information Aggregation, Rationality, and the Condorcet Jury Theorem”, American Political Science Review , 90(1): 34–45. doi:10.2307/2082796
- Bajaj, Sameer, 2014, “Review of Democratic Reason: Politics, Collective Intelligence, and the Rule of the Many , by Hélène Landemore”, Ethics , 124(2): 426–431. doi:10.1086/673507
- Barry, Brian, 1965, Political Argument , London: Routledge & Kegan Paul.
- Bartels, Larry M., 2002, “Beyond the Running Tally: Partisan Bias in Political Perceptions”, Political Behavior , 24(2): 117–150. doi:10.1023/A:1021226224601
- Bedau, Hugo A., 1961, “On Civil Disobedience”, Journal of Philosophy , 58(21): 653–665. doi:10.2307/2023542
- Beerbohm, Eric Anthony, 2012, In Our Name: The Ethics of Democracy , Princeton: Princeton University Press.
- Beitz, Charles R., 1989, Political Equality: An Essay on Democratic Theory , Princeton: Princeton University Press.
- Black, Duncan, 1963, The Theory of Committees and Elections , second edition, Cambridge: Cambridge University Press.
- Brennan, Jason, 2011, The Ethics of Voting , Princeton: Princeton University Press.
- –––, 2014, “How Smart Is Democracy? You Can’t Answer That Question a Priori”, Critical Review , 26(1–2): 33–58. doi:10.1080/08913811.2014.907040
- –––, 2016, Against Democracy , Princeton: Princeton University Press.
- Brownlee, Kimberley, 2004, “Features of a Paradigm Case of Civil Disobedience”, Res Publica , 10(4): 337–351. doi:10.1007/s11158-004-2326-6
- –––, 2007, “The Communicative Aspects of Civil Disobedience and Lawful Punishment”, Criminal Law and Philosophy , 1(2): 179–192. doi:10.1007/s11572-006-9015-9
- –––, 2012, Conscience and Conviction: The Case for Civil Disobedience , Oxford: Oxford University Press. doi:10.1093/acprof:oso/9780199592944.001.0001
- Buchanan, Allen, 1991, Secession: The Morality of Political Divorce from Fort Sumter to Lithuania to Quebec , Boulder, CO: Westview Press.
- Buchanan, James and Gordon Tullock, 1962, The Calculus of Consent: Logical Foundations of Constitutional Democracy , Ann Arbor, MI: University of Michigan Press.
- Caplan, Bryan, 2007, The Myth of the Rational Voter: Why Democracies Choose Bad Policies , Princeton: Princeton University Press.
- Cassese, Antonio, 1995, Self-Determination of Peoples: A Legal Reappraisal , Cambridge: Cambridge University Press.
- Christiano, Thomas, 1996, The Rule of the Many: Fundamental Issues in Democratic Theory , Boulder, CO: Westview Press.
- ––– (ed.), 2003, Philosophy and Democracy: An Anthology , Oxford: Oxford University Press.
- –––, 2004, “The Authority of Democracy”, Journal of Political Philosophy , 12(3): 266–290. doi:10.1111/j.1467-9760.2004.00200.x
- –––, 2006, “A Democratic Theory of Territory and Some Puzzles about Global Democracy”, Journal of Social Philosophy , 37(1): 81–107. doi:10.1111/j.1467-9833.2006.00304.x
- –––, 2008, The Constitution of Equality: Democratic Authority and Its Limits , Oxford: Oxford University Press. doi:10.1093/acprof:oso/9780198297475.001.0001
- –––, 2009, “Must Democracy Be Reasonable?”, Canadian Journal of Philosophy , 39(1): 1–34. doi:10.1353/cjp.0.0037
- –––, 2011, “An Instrumental Argument for a Human Right to Democracy: An Instrumental Argument for a Human Right to Democracy”, Philosophy & Public Affairs , 39(2): 142–176. doi:10.1111/j.1088-4963.2011.01204.x
- –––, 2012, “Rational Deliberation among Experts and Citizens”, in Parkinson and Mansbridge 2012: 27–51. doi:10.1017/CBO9781139178914.003
- –––, 2015, “Self-Determination and the Human Right to Democracy”, in Philosophical Foundations of Human Rights , Rowan Cruft, S. Matthew Liao, and Massimo Renzo (eds.), Oxford: Oxford University Press, 459–480. doi:10.1093/acprof:oso/9780199688623.003.0026
- Cohen, Joshua, 1986, “An Epistemic Conception of Democracy”, Ethics , 97(1): 26–38. doi:10.1086/292815
- –––, 1989 [2009], “Deliberation and Democratic Legitimacy”, in The Good Polity: Normative Analysis of the State , Alan Hamlin and Philip Pettit (eds.), Oxford: Basil Blackwell, 17–34; reprinted in Philosophy, Politics, Democracy: Selected Essays , Cambridge, MA: Harvard University Press, 16–37.
- –––, 1996 [2003], “Procedure and Substance in Deliberative Democracy”, in Democracy and Difference: Contesting the Boundaries of the Political , Seyla Benhabib (ed.), Princeton: Princeton University Press, 95–119; reprinted in Christiano 2003: 17–38.
- Condorcet, Marquis de, 1785, Essai sur l’application de l’analyse à la probabilité des décisions rendues àla pluralité des voix , Paris; reprinted Cambridge: Cambridge University Press, 2014. DOI: 10.1017/CBO9781139923972
- Dahl, Robert A., 1959, A Preface to Democratic Theory , Chicago: University of Chicago Press.
- Delmas, Candice, 2018, A Duty to Resist: When Disobedience Should Be Uncivil , Oxford: Oxford University Press. doi:10.1093/oso/9780190872199.001.0001
- Dewey, John, 1927 [2012], The Public and Its Problems: An Essay in Political Inquiry , New York: Henry Holt; reprinted, Melvin L. Rogers (ed.), University Park, PA: Pennsylvania State University, 2012.
- Downs, Anthony, 1957, An Economic Theory of Democracy , New York: Harper and Row.
- Doyle, Michael W., 2011, Liberal Peace: Selected Essays , New York: Routledge. doi:10.4324/9780203804933
- Dworkin, Ronald, 1996, Freedom’s Law: The Moral Reading of the American Constitution , Cambridge, MA: Harvard University Press.
- –––, 2000, Sovereign Virtue: The Theory and Practice of Equality , Cambridge, MA: Harvard University Press.
- Elster, Jon, 1986 [2003], “The Market and the Forum: Three Varieties of Political Theory”, in Foundations of Scoial Choice Theory , Jon Elster and Aanund Hyllund (eds.), Cambridge: Cambridge University Press, 103–132; reprinted in Christiano 2003: 138–158.
- Ely, John Hart, 1980, Democracy and Distrust: A Theory of Judicial Review , Cambridge, MA: Harvard University Press.
- Erikson, Robert S., 2015, “Income Inequality and Policy Responsiveness “, Annual Review of Political Science , 18: 11–29. doi:10.1146/annurev-polisci-020614-094706
- Estlund, David, 1997a [2003], “Beyond Fairness and Deliberation: The Epistemic Dimension of Democratic Authority”, in Deliberative Democracy: Essays on Reason and Politics , James Bohman and William Rehg (eds.), Cambridge, MA: MIT Press, 173–204; reprinted in Christiano 2003: 69–91.
- –––, 1997b, “The Epistemic Dimension of Democratic Authority”:, The Modern Schoolman , 74(4): 259–276. doi:10.5840/schoolman199774424
- –––, 2003, “Why Not Epistocracy”, in Desire, Identity, and Existence: Essays in Honor of T.M. Penner , Naomi Reshotko (ed.), Kelowna, BC: Academic Printing and Publishing, 53–69.
- –––, 2006, “Democracy and the Real Speech Situation”, in Deliberative Democracy and Its Discontents , Samantha Besson and José Luis Martí (eds.), London: Routledge, 75–92.
- –––, 2008, Democratic Authority: A Philosophical Framework , Princeton: Princeton University Press.
- Estlund, David M., Jeremy Waldron, Bernard Grofman, and Scott L. Feld, 1989, “Democratic Theory and the Public Interest: Condorcet and Rousseau Revisited”, American Political Science Review , 83(4): 1317–1340. doi:10.2307/1961672
- Farber, Henry S. and Joanne Gowa, 1995, “Polities and Peace”, International Security , 20(2): 123–146. doi:10.2307/2539231
- Forst, Rainer, 2016, “The Justification of Basic Rights: A Discourse-Theoretical Approach”, Netherlands Journal of Legal Philosophy , 45(3): 7–28. doi:10.5553/NJLP/221307132016045003002
- Gartzke, Erik, 2007, “The Capitalist Peace”, American Journal of Political Science , 51(1): 166–91.
- Gaus, Gerald F., 1996, Justificatory Liberalism: An Essay on Epistemology and Political Theory , New York: Oxford University Press.
- –––, 2011, The Order of Public Reason: A Theory of Freedom and Morality in a Diverse and Bounded World , Cambridge: Cambridge University Press. doi:10.1017/CBO9780511780844
- Goodin, Robert E., 2003, Reflective Democracy , Oxford: Oxford University Press. doi:10.1093/0199256179.001.0001
- –––, 2007, “Enfranchising All Affected Interests, and Its Alternatives”, Philosophy & Public Affairs , 35(1): 40–68. doi:10.1111/j.1088-4963.2007.00098.x
- Goodin, Robert E. and Kai Spiekermann, 2019, An Epistemic Theory of Democracy , Oxford: Oxford University Press. doi:10.1093/oso/9780198823452.001.0001
- Gould, Carol C., 1988, Rethinking Democracy: Freedom and Social Cooperation in Politics, Economics and Society , New York: Cambridge University Press.
- Grofman, Bernard and Scott L. Feld, 1988, “Rousseau’s General Will: A Condorcetian Perspective”, American Political Science Review , 82(2): 567–576. doi:10.2307/1957401
- Guerrero, Alexander A., 2010, “The Paradox of Voting and the Ethics of Political Representation”, Philosophy & Public Affairs , 38(3): 272–306. doi:10.1111/j.1088-4963.2010.01188.x
- Gutmann, Amy and Dennis Thompson, 2004, Why Deliberative Democracy? , Princeton: Princeton University Press.
- –––, 2014, The Spirit of Compromise: Why Governing Demands It and Campaigning Undermines It: Why Governing Demands It and Campaigning Undermines It , Princeton: Princeton University Press.
- Habermas, Jürgen, 1992 [1996], Faktizität und Geltung. Beiträge zur Diksurstheorie des Rechts und des demokratischen Rechtsstaats , Frankfurt am Main: Suhrkamp Verlag. Translated as Between Facts and Norms: Contributions to a Discourse Theory of Law and Democracy , William Rehg (trans.), Cambridge, MA: MIT Press, 1996.
- Hannon, Michael, 2020, “Empathetic Understanding and Deliberative Democracy”, Philosophy and Phenomenological Research , 101(3): 591–611. doi:10.1111/phpr.12624
- Hardin, Russell, 1999, Liberalism, Constitutionalism, and Democracy , Oxford: Oxford University Press. doi:10.1093/0198290845.001.0001
- Hayek, Friedrich A., 1960, The Constitution of Liberty , Chicago, IL: University of Chicago Press.
- Hobbes, Thomas, 1651, Leviathan , London; reprinted, C.B. MacPherson (ed.), Harmondsworth: Penguin Books, 1968.
- Hong, Lu and Scott E. Page, 2004, “Groups of Diverse Problem Solvers Can Outperform Groups of High-Ability Problem Solvers”, Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences , 101(46): 16385–16389. doi:10.1073/pnas.0403723101
- Hume, David, 1748, “Of the Original Contract”; reprinted in Hume’s Ethical Writings: Selections from David Hume , Alasdair MacIntyre (ed.), Notre Dame: University of Notre Dame Press, 1965.
- Ingham, Sean, 2019, Rule by Multiple Majorities: A New Theory of Popular Control , Cambridge: Cambridge University Press. doi:10.1017/9781108683821
- Kahan, Dan M., 2013, “Ideology, Motivated Reasoning, and Cognitive Reflection”, Judgment and Decision Making , 8(4): 407–424
- Kant, Immanuel, 1795, Zum ewigen Frieden: Ein philosophischer Entwurf , Königsberg: Friedrich Nicolovius. Translated as “Toward Perpetual Peace” in Immanuel Kant: Practical Philosophy , Mary J. Gregor (trans./ed.), Cambridge: Cambridge University Press, 1996, pp. 311–352.
- Knight, Jack and James Johnson, 2011, The Priority of Democracy: Political Consequences of Pragmatism , Princeton: Princeton University Press.
- Kolodny, Niko, 2014a, “Rule Over None I: What Justifies Democracy?”, Philosophy & Public Affairs , 42(3): 195–229. doi:10.1111/papa.12035
- –––, 2014b, “Rule Over None II: Social Equality and the Justification of Democracy”, Philosophy & Public Affairs , 42(4): 287–336. doi:10.1111/papa.12037
- Ladha, Krishna K., 1992, “The Condorcet Jury Theorem, Free Speech, and Correlated Votes”, American Journal of Political Science , 36(3): 617–634. doi:10.2307/2111584
- Lai, Ten-Herng., 2019, “Justifying Uncivil Disobedience”, in Oxford Studies in Political Philosophy, Volume 5 , David Sobel, Peter Vallentyne, and Steven Wall (eds.), Oxford: Oxford University Press, 90–114. doi:10.1093/oso/9780198841425.003.0004
- Landa, Dimitri and Ryan Pevnick, 2020, “Representative Democracy as Defensible Epistocracy”, American Political Science Review , 114(1): 1–13. doi:10.1017/S0003055419000509
- Landemore, Hélène, 2013, Democratic Reason: Politics, Collective Intelligence, and the Rule of the Many , Princeton: Princeton University Press.
- Layne, Christopher, 1994, “Kant or Cant: The Myth of the Democratic Peace”, International Security , 19(2): 5–49. doi:10.2307/2539195
- Levy, Jack S. and William R. Thompson, 2010, Causes of War , Malden, MA: Wiley- Blackwell.
- List, Christian, 2013, “Social Choice Theory”, in Stanford Encyclopedia of Philosophy , (Winter 2013 Edition), Edward N. Zalta (ed.), URL = < https://plato.stanford.edu/archives/win2013/entries/social-choice/ >
- List, Christian and Robert E. Goodin, 2001, “Epistemic Democracy: Generalizing the Condorcet Jury Theorem”, Journal of Political Philosophy , 9(3): 277–306. doi:10.1111/1467-9760.00128
- Locke, John, 1690, Second Treatise on Civil Government , London; reprinted C.B. MacPherson (ed.), Indianapolis, IN: Hackett, 1980.
- Lord, Charles G., Lee Ross, and Mark R. Lepper, 1979, “Biased Assimilation and Attitude Polarization: The Effects of Prior Theories on Subsequently Considered Evidence.”, Journal of Personality and Social Psychology , 37(11): 2098–2109. doi:10.1037/0022-3514.37.11.2098
- Lupia Arthur and Matthew D. McCubbins, 1998, The Democratic Dilemma: Can Citizens Learn What They Need To Know? , Cambridge: Cambridge University Press.
- Mackie, Gerry, 2003, Democracy Defended , Cambridge: Cambridge University Press. doi:10.1017/CBO9780511490293
- Madison, James, Alexander Hamilton, and John Jay, 1787–1788, The Federalist Papers , New York; reprinted Isaac Kramnick (ed.), Harmondsworth, UK: Penguin Books, 1987. [ Federalist Papers available online ]
- Mansbridge, Jane J. (ed.), 1990, Beyond Self-Interest , Chicago: University of Chicago Press.
- Mansbridge, Jane, James Bohman, Simone Chambers, Thomas Christiano, Archon Fung, John Parkinson, Dennis F. Thompson, and Mark E. Warren, 2012, “A Systemic Approach to Deliberative Democracy”, in Parkinson and Mansbridge2003: 1–26. doi:10.1017/CBO9781139178914.002
- Markovits, Daniel, 2005, “Democratic Disobedience”, Yale Law Journal , 114(8): 1897–1952.
- Maskivker, Julia, 2019, The Duty to Vote , Oxford: Oxford University Press. doi:10.1093/oso/9780190066062.001.0001
- May, Simon Cabulea, 2005, “Principled Compromise and the Abortion Controversy”, Philosophy & Public Affairs , 33(4): 317–348. doi:10.1111/j.1088-4963.2005.00035.x
- Mill, John Stuart, 1861 [1991], Considerations on Representative Government , London: Parker, Son, and Bourn; reprinted Buffalo, NY: Prometheus Books, 1991.
- Miller, David, 1995, On Nationality , Oxford: Clarendon Press.
- Nozick, Robert, 1974, Anarchy, State and Utopia , New York: Basic Books.
- Page, Scott E., 2007, The Difference: How the Power of Diversity Creates Better Groups, Firms, Schools, and Societies , Princeton: Princeton University Press.
- Parfit, Derek, 1984, Reasons and Persons , Oxford: Oxford University Press. doi:10.1093/019824908X.001.0001
- Parkinson, John and Jane Mansbridge (eds.), 2012, Deliberative Systems: Deliberative Democracy at the Large Scale , Cambridge: Cambridge University Press. doi:10.1017/CBO9781139178914
- Pasternak, Avia, 2018, “Political Rioting: A Moral Assessment”, Philosophy & Public Affairs , 46(4): 384–418. doi:10.1111/papa.12132
- Peter, Fabienne, 2008, “Pure Epistemic Proceduralism”, Episteme , 5(1): 33–55. doi:10.3366/E1742360008000221
- –––, 2009, Democratic Legitimacy , New York: Routledge.
- Pevnick, Ryan, 2020, “The Failure of Instrumental Arguments for a Human Right to Democracy”, Journal of Political Philosophy , 28(1): 27–50. doi:10.1111/jopp.12197
- Pitkin, Hanna Fenichel, 1967, The Concept of Representation , Berkeley, CA: University of California.
- Plato, The Republic , revised/trans. by Lee, D., Harmondsworth: Penguin Books, 1974, 2 nd edition.
- Quirk, Paul J., 2014, “Making It up on Volume: Are Larger Groups Really Smarter?”, Critical Review , 26(1–2): 129–150. doi:10.1080/08913811.2014.907046
- Rawls, John, 1971, A Theory of Justice , Cambridge, MA: Harvard University Press.
- –––, 2005, Political Liberalism , New York: Columbia University Press, expanded edition.
- Ray, James Lee, 1995, Democracy and International Conflict: An Evaluation of the Democratic Peace Proposition , Columbia, SC: University of South Carolina Press.
- Raz, Joseph, 1979, The Authority of Law: Essays on Law and Morality , Oxford: Clarendon Press.
- Riker, William H., 1982, Liberalism Against Populism: A Confrontation Between the Theory of Democracy and the Theory of Social Choice , San Francisco, CA: W. H. Freeman.
- Rosenblum, Nancy L., 2008, On the Side of the Angels: An Appreciation of Parties and Partisanship , Princeton: Princeton University Press.
- Rousseau, David L., Christopher Gelpi, Dan Reiter, and Paul K. Huth, 1996, “Assessing the Dyadic Nature of the Democratic Peace, 1918–88”, American Political Science Review , 90(3): 512–533. doi:10.2307/2082606
- Rousseau, Jean-Jacques, 1762, Du contrat social; ou Principes du droit politique , Amsterdam. Translated as The Social Contract , Charles Frankel (trans.), New York: Hafner Publishing Co., 1947.
- Russett, Bruce M., 1993, Grasping the Democratic Peace: Principles for a Post–Cold War World , Princeton: Princeton University Press.
- Russett, Bruce M. and Harvey Starr, 2003, “From Democratic Peace to Kantian Peace: Democracy and Conflict in the International System”, in Handbook of War Studies II , Manus I. Midlarsky (ed.), Ann Arbor, MI: University of Michigan Press, 93–128.
- Sabl, Andrew, 2001, “Looking Forward to Justice: Rawlsian Civil Disobedience and Its Non-Rawlsian Lessons”, Journal of Political Philosophy , 9(3): 307–330. doi:10.1111/1467-9760.00129
- Scheffler, Samuel, 2010, Equality and Tradition: Questions of Value in Moral and Political Theory , New York: Oxford University Press.
- Schumpeter, Joseph A., 1942 [1950], Capitalism, Socialism and Democracy , New York: Harper and Row; second edition 1947; third edition 1950.
- Sen, Amartya, 1999, Development as Freedom , New York: Knopf.
- Simmons, A. John, 2001, Justification and Legitimacy: Essays on Rights and Obligations , Cambridge: Cambridge University Press. doi:10.1017/CBO9780511625152
- –––, 2007, Political Philosophy , Oxford: Oxford University Press.
- Singer, Peter, 1973, Democracy and Disobedience , Oxford: Clarendon Press.
- Smith, William, 2011, “Civil Disobedience and the Public Sphere”, Journal of Political Philosophy , 19(2): 145–166. doi:10.1111/j.1467-9760.2010.00365.x
- Somin, Ilya, 2013, Democracy and Political Ignorance: Why Smaller Government is Smarter , Stanford, CA: Stanford University Press.
- Song, Sarah, 2012, “The Boundary Problem in Democratic Theory: Why the Demos Should Be Bounded by the State”, International Theory , 4(1): 39–68. doi:10.1017/S1752971911000248
- Stilz, Anna, 2009, Liberal Loyalty: Freedom, Obligation, and the State , Princeton: Princeton University Press.
- –––, 2016, “The Value of Self-Determination”, in Oxford Studies in Political Philosophy, Volume 2 , David Sobel, Peter Vallentyne, and Steven Wall (eds.), Oxford: Oxford University Press, ch. 8. doi:10.1093/acprof:oso/9780198759621.003.0005
- Thompson, Abigail, 2014, “Does Diversity Trump Ability?” Notices of the AMS , 61(9): 1024–1030. [ Thompson 2014 available online ]
- Valentini, Laura, 2013, “Justice, Disagreement and Democracy”, British Journal of Political Science , 43(1): 177–199. doi:10.1017/S0007123412000294
- Viehoff, Daniel, 2014, “Democratic Equality and Political Authority”, Philosophy & Public Affairs , 42(4): 337–375. doi:10.1111/papa.12036
- Waldron, Jeremy, 1995, “The Wisdom of the Multitude: Some Reflections on Book 3, Chapter 11 of Aristotle’s Politics ”, Political Theory , 23(4): 563–584. doi:10.1177/0090591795023004001
- –––, 1999, Law and Disagreement , Oxford: Clarendon Press.
- Wall, Steven, 2007, “Democracy and Equality”, The Philosophical Quarterly , 57(228): 416–438. doi:10.1111/j.1467-9213.2007.495.x
- Weart, Spencer R., 1998, Never at War: Why Democracies Will Never Fight One Another , New Haven, CT: Yale University Press.
- Wendt, Fabian, 2016, Compromise, Peace and Public Justification: Political Morality Beyond Justice , London: Palgrave Macmillon. doi:10.1007/978-3-319-28877-2
- Weinstock, Daniel, 2013, “On the Possibility of Principled Moral Compromise”, Critical Review of International Social and Political Philosophy , 16(4): 537–556. doi:10.1080/13698230.2013.810392
- Whelan, Frederick G., 1983, “Prologue: Democratic Theory and the Boundary Problem”, Nomos 25: Liberal Democracy , J. Roland Pennock and John W. Chapman (eds.), American Society for Political and Legal Philosophy, 13–47.
- White, Jonathan and Lea Ypi, 2016, The Meaning of Partisanship , Oxford: Oxford University Press. doi:10.1093/acprof:oso/9780199684175.001.0001
- Williams, B., 1973, “A Critique of Utilitarianism”, in Utilitarianism: For and Against , with J.J.C. Smart, Cambridge: Cambridge University Press.
- Wolff, Robert Paul, 1970, In Defense of Anarchism , New York, NY: Harper and Row.
- Wright, Gavin, 2013, Sharing the Prize: The Economics of the Civil Rights Revolution in the American South , Cambridge, MA: Harvard University Press.
- Young, Iris Marion, 1990, Justice and the Politics of Difference , Princeton: Princeton University Press.
- Zakaras, Alex, 2018, “Complicity and Coercion: Toward and Ethics of Political Participation”, in Oxford Studies in Political Philosophy (Volume 4), David Sobel, Peter Vallentyne, and Steven Wall (eds.), Oxford: Oxford University Press, ch. 8.
How to cite this entry . Preview the PDF version of this entry at the Friends of the SEP Society . Look up topics and thinkers related to this entry at the Internet Philosophy Ontology Project (InPhO). Enhanced bibliography for this entry at PhilPapers , with links to its database.
- [Please contact the author with suggestions]
authority | citizenship | civil disobedience | constitutionalism | egalitarianism | equality | Hobbes, Thomas | justice | justification, political: public | legitimacy, political | liberty: positive and negative | Locke, John | Mill, John Stuart | Plato | -->pluralism --> | political obligation | publicity | public reason | Rawls, John | representation, political | rights | Rousseau, Jean Jacques | rule of law and procedural fairness | voting
Copyright © 2022 by Tom Christiano < thomasc @ u . arizona . edu > Sameer Bajaj < sameer . bajaj1 @ gmail . com >
- Accessibility
Support SEP
Mirror sites.
View this site from another server:
- Info about mirror sites
The Stanford Encyclopedia of Philosophy is copyright © 2024 by The Metaphysics Research Lab , Department of Philosophy, Stanford University
Library of Congress Catalog Data: ISSN 1095-5054

By the People: Essays on Democracy
Harvard Kennedy School faculty explore aspects of democracy in their own words—from increasing civic participation and decreasing extreme partisanship to strengthening democratic institutions and making them more fair.
Winter 2020
By Archon Fung , Nancy Gibbs , Tarek Masoud , Julia Minson , Cornell William Brooks , Jane Mansbridge , Arthur Brooks , Pippa Norris , Benjamin Schneer

The basic terms of democratic governance are shifting before our eyes, and we don’t know what the future holds. Some fear the rise of hateful populism and the collapse of democratic norms and practices. Others see opportunities for marginalized people and groups to exercise greater voice and influence. At the Kennedy School, we are striving to produce ideas and insights to meet these great uncertainties and to help make democratic governance successful in the future. In the pages that follow, you can read about the varied ways our faculty members think about facets of democracy and democratic institutions and making democracy better in practice.
Explore essays on democracy
Archon fung: we voted, nancy gibbs: truth and trust, tarek masoud: a fragile state, julia minson: just listen, cornell william brooks: democracy behind bars, jane mansbridge: a teachable skill, arthur brooks: healthy competition, pippa norris: kicking the sandcastle, benjamin schneer: drawing a line.
Get smart & reliable public policy insights right in your inbox.
Democracy Essay
Democracy is derived from the Greek word demos or people. It is defined as a government in which the supreme power is vested in the people. Democracy is exercised directly by the people; in large societies, it is by the people through their elected agents. In the phrase of President Abraham Lincoln, democracy is the “Government of the people, by the people, and for the people.” There are various democratic countries, but India has the largest democracy in the world. This Democracy Essay will help you know all about India’s democracy. Students can also get a list of CBSE Essays on different topics to boost their essay-writing skills.
500+ Words Democracy Essay
India is a very large country full of diversities – linguistically, culturally and religiously. At the time of independence, it was economically underdeveloped. There were enormous regional disparities, widespread poverty, illiteracy, unemployment, and a shortage of almost all public welfare means. Since independence, India has been functioning as a responsible democracy. The same has been appreciated by the international community. It has successfully adapted to challenging situations. There have been free and fair periodic elections for all political offices, from the panchayats to the President. There has been a smooth transfer of political power from one political party or set of political parties to others, both at national and state levels, on many occasions.
India: A Democratic Country
Democracy is of two, i.e. direct and representative. In a direct democracy, all citizens, without the intermediary of elected or appointed officials, can participate in making public decisions. Such a system is only practical with relatively small numbers of people in a community organisation or tribal council. Whereas in representative democracy, every citizen has the right to vote for their representative. People elect their representatives to all levels, from Panchayats, Municipal Boards, State Assemblies and Parliament. In India, we have a representative democracy.
Democracy is a form of government in which rulers elected by the people take all the major decisions. Elections offer a choice and fair opportunity to the people to change the current rulers. This choice and opportunity are available to all people on an equal basis. The exercise of this choice leads to a government limited by basic rules of the constitution and citizens’ rights.
Democracy is the Best Form of Government
A democratic government is a better government because it is a more accountable form of government. Democracy provides a method to deal with differences and conflicts. Thus, democracy improves the quality of decision-making. The advantage of a democracy is that mistakes cannot be hidden for long. There is a space for public discussion, and there is room for correction. Either the rulers have to change their decisions, or the rulers can be changed. Democracy offers better chances of a good decision. It respects people’s own wishes and allows different kinds of people to live together. Even when it fails to do some of these things, it allows a way of correcting its mistakes and offers more dignity to all citizens. That is why democracy is considered the best form of government.
Students must have found this “Democracy Essay” useful for improving their essay writing skills. They can get the study material and the latest update on CBSE/ICSE/State Board/Competitive Exams, at BYJU’S.
Leave a Comment Cancel reply
Your Mobile number and Email id will not be published. Required fields are marked *
Request OTP on Voice Call
Post My Comment
- Share Share
Register with BYJU'S & Download Free PDFs
Register with byju's & watch live videos.

Counselling
Want a daily email of lesson plans that span all subjects and age groups?
Democracy - a short introduction.
1,615,838 Views
34,035 Questions Answered
Let’s Begin…
There are many forms of government in the world. One of the most common forms is democracy. In this lesson you will see what it takes to make a democracy work and why it gives its people so many freedoms and protections.
About TED-Ed Best of Web
TED-Ed Best of Web are exceptional, user-created lessons that are carefully selected by volunteer teachers and TED-Ed staff.
Meet The Creators
- Video created by MinuteVideos
- Lesson Plan created by Craig Zimmer
Find anything you save across the site in your account
E. B. White on “The Meaning of Democracy”

By The New Yorker

This piece originally appeared in the Notes and Comment section of the July 3, 1943, issue of The New Yorker. “ The 40s: The Story of a Decade ,” an anthology of New Yorker articles, stories, and poems, will be released on Tuesday.
We received a letter from the Writers’ War Board the other day asking for a statement on “The Meaning of Democracy.” It presumably is our duty to comply with such a request, and it is certainly our pleasure. Surely the Board knows what democracy is. It is the line that forms on the right. It is the don’t in don’t shove. It is the hole in the stuffed shirt through which the sawdust slowly trickles; it is the dent in the high hat. Democracy is the recurrent suspicion that more than half of the people are right more than half of the time. It is the feeling of privacy in the voting booths, the feeling of communion in the libraries, the feeling of vitality everywhere. Democracy is a letter to the editor. Democracy is the score at the beginning of the ninth. It is an idea which hasn’t been disproved yet, a song the words of which have not gone bad. It’s the mustard on the hot dog and the cream in the rationed coffee. Democracy is a request from a War Board, in the middle of a morning in the middle of a war, wanting to know what democracy is. — E. B. White
Books & Fiction
By signing up, you agree to our User Agreement and Privacy Policy & Cookie Statement . This site is protected by reCAPTCHA and the Google Privacy Policy and Terms of Service apply.

By Mary Norris

By Amy Woolard

By W. S. Di Piero
share this!
March 26, 2024
This article has been reviewed according to Science X's editorial process and policies . Editors have highlighted the following attributes while ensuring the content's credibility:
fact-checked
trusted source
Essays on democracy draw attention to critical threats, explore safeguards ahead of Jan. 6
by Tracy DeStazio, University of Notre Dame

Following the events of Jan. 6, 2021—when a violent mob stormed the U.S. Capitol building in an effort to interrupt the certification process of the 2020 presidential election—experts began to question how to protect the next presidential election from a similar threat. To that end, University of Notre Dame political scientists have partnered with preeminent scholars of democracy from across the country to produce a set of recommendations to strengthen and safeguard democracy in America.
The University's Rooney Center for the Study of American Democracy established the January 6th, 2025, Project in an effort to understand the social, political, psychological and demographic factors that led to that troublesome day in the capital.
By pursuing research, teaching and public engagement , the project offers insight into how American democracy got to this point and how to strengthen and protect it, while emphasizing how to prepare for a similar attack many deem imminent on Jan. 6, 2025, when Congress seeks to certify the 2024 presidential election results. The project includes 34 members who represent various disciplines and leading universities—10 of whom hail from Notre Dame's faculty.
Matthew E.K. Hall, director of the Rooney Center, said one of the project's first goals was to create a collection of essays written by its members to be included in a special issue of The ANNALS of the American Academy of Political and Social Science , which was published this month. These essays aim to draw attention to the vulnerabilities in our democratic system and the threats building against it, and to create consensus on ways to remedy both problems.
The authors set out to tackle the following tough questions, but from different perspectives: How serious are the threats to our democracy, how did we get to this point, and what can we do to fix the situation? The 14 essays are broken down into categories, falling under the headings of "'Us' Versus 'Them,'" "Dangerous Ideas" and "Undermining Democratic Institutions." With most pieces being co-authored by faculty from multiple institutions, the collection offers a collaborative approach to evaluating what led America to this crisis and how to avert it.
David Campbell, director of the Notre Dame Democracy Initiative and the Packey J. Dee Professor of American Democracy in the Department of Political Science, described the project as "an example of how Notre Dame can be a national leader on the issue of preserving American democracy. Not only do we have top scholars working on the issue, but we can provide a forum for a community of scholars across many leading universities. Maintaining democracy will require all hands on deck."
In the collection's introduction, Hall explained the backdrop of what led America to this point and why these essays help acknowledge the challenges we are facing as a nation.
"We are basically living through a revival of fascist politics in the U.S.," Hall wrote, "where politicians are using divisive rhetoric to separate us into an 'us' versus 'them' paradigm—left versus right, white versus Black, rich versus poor, urban versus rural, religious versus secular—the divisions go on and on."
Hall estimated that between 25 and 30% of Americans have consistently endorsed some fascist ideas such as racial oppression, conspiracy theories and authoritarianism. "Ordinarily, this consistent minority is held in check by the democratic process," Hall explained.
"These candidates don't even get nominated for major political positions because their co-partisan allies don't want to lose the general election.
"But when our politics become this intensely polarized, most partisans will support their party no matter who is nominated," he continued. "As a result, politicians pushing these fascist ideas can gain power by taking over one political party and then exploiting the polarization to win elections. Once taking power, they will likely manipulate the electoral process to remain in power."
Consequently, Hall said, fascist leaders are able to exploit these social divisions to break down basic social norms and shared understandings about American politics. This pushes huge swaths of society toward accepting dangerous ideas that would normally be rejected, such as expanded executive power, intense animosity toward political opponents, a wavering support for free speech, and political candidates who deny election losses.
This weakened support for democratic norms enables attacks on our democratic institutions, such as ignoring court rulings, enacting voter suppression laws and—most shockingly (as in the case of Jan. 6)—openly subverting elections.
With the political situation as dire as many feel it to be, the January 6th, 2025, Project's essays outline a few practical steps that can be taken to strengthen and safeguard democracy in America.
For example, Hall said, as the nation moves forward into this next election year, American voters have to stay focused on the "deliberate denial of reality" on the part of some politicians so that they can discern the difference between lies, truths and just plain distractions.
"The more we lose touch with basic facts and accept misinformation, conspiracies and contradictory claims as the norm in our society," he said, "the more vulnerable we are to losing our democracy.
"Even more importantly, we have to be willing to sacrifice short-term political gains in order to preserve the long-term stability of our democracy. That might mean holding your nose to vote for candidates that you would not otherwise support."
Hall added that Americans must redouble their devotion to democratic principles such as open elections and free speech, and states should adopt institutional reforms that remove partisans from the electoral process (for example, employing nonpartisan election commissions). He also noted the importance of paying close attention to efforts that divide groups of Americans, especially those that portray outgroup members as evil or less than human.
The members of the project hope that by honestly acknowledging the challenges our nation is facing, understanding the mistakes that were made and recognizing the vulnerabilities in our system that led us to this situation—and by resolving to fix these issues—we can pull our country's political system back from the edge of the cliff before it's too late.
"The public needs to take these critical threats seriously and we're hoping that these essays draw attention to them, and help to build consensus about the underlying problems in our politics and potential remedies," Hall concluded.
Democracy is one of several University-wide initiatives emerging from Notre Dame's recently released Strategic Framework . The Democracy Initiative will further establish Notre Dame as a global leader in the study of democracy, a convenor for conversations about and actions to preserve democracy, and a model for the formation of civically engaged citizens and public servants.
Provided by University of Notre Dame
Explore further
Feedback to editors

Romania center explores world's most powerful laser
14 hours ago
A cosmic 'speed camera' just revealed the staggering speed of neutron star jets in a world first
Mar 30, 2024
Saturday Citations: 100-year-old milk, hot qubits and another banger from the Event Horizon Telescope project

Curiosity rover searches for new clues about Mars' ancient water

Study says since 1979 climate change has made heat waves last longer, spike hotter, hurt more people

Scientist taps into lobsters' unusual habits to conquer the more than 120-year quest to farm them
Mar 29, 2024

Blind people can hear and feel April's total solar eclipse with new technology

Mapping the best route for a spacecraft traveling beyond the sun's sphere of influence
Researchers outline new approach in search for dark matter through future DUNE research project

Researchers reveal evolutionary path of important proteins
Relevant physicsforums posts, interesting anecdotes in the history of physics.
10 hours ago
Cover songs versus the original track, which ones are better?
13 hours ago
The new Shogun show
History of railroad safety - spotlight on current derailments.
Mar 27, 2024
Metal, Rock, Instrumental Rock and Fusion
Who should have been the 4th laureate in the nobel prize in physics.
Mar 25, 2024
More from Art, Music, History, and Linguistics
Related Stories

Political rhetoric changes views on democratic principles, study finds
Oct 25, 2023

'On the brink of a new civil war': Survey highlights fragility of American democracy, stark partisan divides
Nov 3, 2022
The majority of Americans do not support anti-democratic behavior, even when elected officials do: Study
Mar 18, 2024

Preventing another 'Jan. 6' starts by changing how elections are certified, experts say
Mar 20, 2024

Report: Political violence threatens health of US democracy
Nov 7, 2023

Democratic backslide a threat to free elections globally: Report
Mar 7, 2024
Recommended for you
Your emotional reaction to climate change may impact the policies you support, study finds


Value-added tax data could help countries prepare better for crises

New study suggests that while social media changes over decades, conversation dynamics stay the same

World Happiness Report: Why we might be measuring happiness wrong

Advanced statistical analysis highlights the role of interaction between US Supreme Court judges
Let us know if there is a problem with our content.
Use this form if you have come across a typo, inaccuracy or would like to send an edit request for the content on this page. For general inquiries, please use our contact form . For general feedback, use the public comments section below (please adhere to guidelines ).
Please select the most appropriate category to facilitate processing of your request
Thank you for taking time to provide your feedback to the editors.
Your feedback is important to us. However, we do not guarantee individual replies due to the high volume of messages.
E-mail the story
Your email address is used only to let the recipient know who sent the email. Neither your address nor the recipient's address will be used for any other purpose. The information you enter will appear in your e-mail message and is not retained by Phys.org in any form.
Newsletter sign up
Get weekly and/or daily updates delivered to your inbox. You can unsubscribe at any time and we'll never share your details to third parties.
More information Privacy policy
Donate and enjoy an ad-free experience
We keep our content available to everyone. Consider supporting Science X's mission by getting a premium account.
E-mail newsletter
- More from M-W
- To save this word, you'll need to log in. Log In
Definition of democracy
Frequently asked questions.
Is the United States a democracy or a republic?
The United States is both a democracy and a republic. Democracies and republics are both forms of government in which supreme power resides in the citizens. The word republic refers specifically to a government in which those citizens elect representatives who govern according to the law. The word democracy can refer to this same kind of representational government, or it can refer instead to what is also called a direct democracy , in which the citizens themselves participate in the act of governing directly.
What is the basic meaning of democracy ?
The word democracy most often refers to a form of government in which people choose leaders by voting.
What is a democratic system of government?
A democratic system of government is a form of government in which supreme power is vested in the people and exercised by them directly or indirectly through a system of representation usually involving periodic free elections.
- self-government
Examples of democracy in a Sentence
These examples are programmatically compiled from various online sources to illustrate current usage of the word 'democracy.' Any opinions expressed in the examples do not represent those of Merriam-Webster or its editors. Send us feedback about these examples.
Word History
borrowed from Middle French democracie, democratie, borrowed from Late Latin dēmocratia, borrowed from Greek dēmokratía, from dēmo- demo- + -kratia -cracy
1539, in the meaning defined at sense 1a
Phrases Containing democracy
- pure democracy
- social democracy
Articles Related to democracy

'Gaslighting,' 'Woke,' 'Democracy,' and...
'Gaslighting,' 'Woke,' 'Democracy,' and Other Top Lookups
We know you're going to look these up

Democracy or Republic: What's the...
Democracy or Republic: What's the difference?
A case can be made for either

Forms of Government Quiz
How do people take and hold power?
Dictionary Entries Near democracy
Cite this entry.
“Democracy.” Merriam-Webster.com Dictionary , Merriam-Webster, https://www.merriam-webster.com/dictionary/democracy. Accessed 31 Mar. 2024.
Kids Definition
Kids definition of democracy.
from early French democratie "democracy," from Latin democratia (same meaning), from Greek demokratia "democracy," from dēmos "people, the masses" and -kratia "rule, government," from kratos "strength, power, authority" — related to epidemic
Legal Definition
Legal definition of democracy, more from merriam-webster on democracy.
Nglish: Translation of democracy for Spanish Speakers
Britannica English: Translation of democracy for Arabic Speakers
Britannica.com: Encyclopedia article about democracy
Subscribe to America's largest dictionary and get thousands more definitions and advanced search—ad free!

Can you solve 4 words at once?
Word of the day.
See Definitions and Examples »
Get Word of the Day daily email!
Popular in Grammar & Usage
The tangled history of 'it's' and 'its', more commonly misspelled words, commonly misspelled words, how to use em dashes (—), en dashes (–) , and hyphens (-), absent letters that are heard anyway, popular in wordplay, the words of the week - mar. 29, 9 superb owl words, 10 words for lesser-known games and sports, your favorite band is in the dictionary, games & quizzes.


Essay on Democracy in India in English for Children and Students

Table of Contents
Essay on Democracy in India: India is the largest democracy in the world. Ruled by various kings and emperors and colonized by the Europeans for centuries, India became a democratic nation post its independence in 1947. Thereafter, the citizens of India were given the right to vote and elect their leaders. The second most populous country and the seventh-largest country by area, India is the largest democracy in the world. Indian democratic government was formed after the nation attained independence in 1947. The parliamentary and state assembly elections are held every 5 years to elect the Central and state governments.
Fill Out the Form for Expert Academic Guidance!
Please indicate your interest Live Classes Books Test Series Self Learning
Verify OTP Code (required)
I agree to the terms and conditions and privacy policy .
Fill complete details
Target Exam ---
India’s democracy is built on the idea of political equality. This means that all citizens are treated the same under the law, regardless of their religion, caste, creed, race, or any other differences. As a result, every Indian citizen has the same political rights and opportunities.
Long and Short Essay on Democracy in India in English
Here are long and short essays on Democracy in India in English to help you with the topic in your exams/school assignments. You can select any Democracy in India essay as per your need:
Essay on Democracy in India Essay 200 words
Democracy is a system of government that allows the citizens to cast a vote and elect a government of their choice. India became a democratic state after its independence from British rule in 1947. It is the largest democratic nation in the world.
Democracy in India gives its citizens the right to vote irrespective of their caste, colour, creed, religion and gender. It has five democratic principles – sovereign, socialist, secular, democratic, and republic.
Various political parties stand for elections at the state and national levels periodically. They propagate about the tasks accomplished in their previous tenure and also share their future plans with the people. Every citizen of India, above the age of 18 years has the right to vote. The government is making continuous efforts to encourage more and more people to cast their votes. People must know everything about the candidates standing for the elections and vote for the most deserving one for good governance.
India is known to have a successful democratic system. However, certain loopholes need to be worked on. Among other things, the government must work on eliminating poverty, illiteracy, communalism, gender discrimination, and casteism in order to ensure democracy in the true sense.

Essay on Democracy in India Essay 300 words
Democracy is said to be the best form of government. It allows every citizen of the country to vote and choose their leaders irrespective of their caste, colour, creed, religion, or gender. The government is elected by the common people of the country and it won’t be wrong to say that it is their wisdom and awareness that determines the success or failure of the government.
Many countries have a democratic system. However, India is the largest democracy in the world. It runs on five democratic principles: sovereign, socialist, secular, democratic, and republic. India was declared a democratic nation after it attained freedom from British colonial rule in 1947. Not only the largest, but Indian democracy is also known to be one of the most successful ones.
India has a federal form of democracy with a government at the center responsible to the parliament and state governments equally accountable for their legislative assemblies. Elections are held at regular intervals in the county, and several parties compete to get to the center and make their place in the states. People are encouraged to exercise their right to vote to elect the most deserving candidate, though caste is also a big factor in Indian politics.
Campaigns are carried out by different political parties to emphasize the work they have done for the development of people as well as their future agenda to benefit people.
Democracy in India does not only means providing the right to vote but also ensuring social and economic equality. While the democratic system of the country has received worldwide appreciation, many areas require improvement so that democracy can be formed in true sense. The government must work on eradicating illiteracy, poverty, communalism, casteism, and gender discrimination.
Essay on Democracy in India Essay 400 words
Democracy is government by the people, the people, and the people. The citizens in a democratic nation enjoy the right to vote and elect their government.
India is the largest democracy in the world. After being ruled by the Mughals, Mauryas, British and various other rulers for centuries, India finally became a democratic state after its independence in 1947. The people of the country, who had suffered at the hands of foreign powers, finally got the right to choose their own ministers by casting vote. Democracy in India is not limited to just providing the right to vote to its citizens, it is also working towards social and economic equality.
Democracy in India works on five democratic principles. These are:
- Sovereign: This means free from the interference or control of any foreign power.
- Socialist: This means providing social and economic equality to all the citizens.
- Secular: This means freedom to practice any religion or reject all.
- Democratic: This means the government of India is elected by its citizens.
- Republic: This means the head of the country is not a hereditary king or queen.
Working of Democracy in India
Every Indian citizen, above 18 years of age can exercise the right to vote in India. There is no discrimination based on a person’s caste, creed, religion, gender, or education when providing the right to vote.
Candidates from several national and regional parties, including Indian National Congress (INC), Bharatiya Janta Party (BJP), Communist Party of India (CPI), Communist Party of India -Marxist (CPI -M), All India Trinamool Congress (TMC) and Bahujan Samaj Party (BSP) fight for the elections. Candidates evaluate their work during the last tenure of these parties or their representatives and also the promises made by them in order to decide whom to vote.
Scope for Improvement:
There is a lot of scope for improvement in the Indian democracy. Steps must be taken to:
- Eradicate poverty
- Promote literacy
- Encourage people to vote
- Educate people on choosing the right candidate
- Encourage intelligent and educated people to take up leadership roles
- Eradicate communalism
- Ensure impartial and responsible media
- Monitor the working of the elected members
- Form responsible opposition
Though democracy in India has been appreciated worldwide for its working there is still a lot of scope for improvement. The aforementioned steps must be taken to ensure smooth functioning of democracy in the country.
Essay on Democracy in India Essay 500 words
A democratic nation is one where the citizens have the right to elect their government. It is sometimes also said to be the “rule of the majority”. Several countries around the world run democratic governments, but India takes pride in being the largest democracy.
History of Democracy in India
India had been ruled by several rulers from Mughals to Mauryas. Each of them had its own style of governing the people. It was only after the country got independence from the colonial rule of the Britishers in 1947 that it became a democratic nation. It was then that the people of India, who had suffered tyranny at the hands of the British, attained the right to vote and elect their government for the first time.
Democratic Principles of India
Sovereign refers to an entity free from any foreign power’s control. The citizens of India enjoy sovereign power to elect their ministers.
Socialism means providing social and economic equality to all the citizens of India irrespective of their caste, colour, creed, gender, and religion.
Secular means the freedom to practice the religion of one’s choice. There is no official state religion in the country.
This means the government of India is elected by its citizens. The right to vote is given to all Indian citizens without any discrimination.
The head of the country is not a hereditary king or queen. An electoral college elects him.
The Working of Democracy in India
Every citizen of India above the age of 18 years has the right to vote. The Constitution does not discriminate against anyone on the basis of their caste, colour, creed, gender, religion, or education.
There are seven national parties in the country, namely, Indian National Congress (INC), Bharatiya Janta Party (BJP), Communist Party of India (CPI), Communist Party of India -Marxist (CPI-M), Nationalist Congress Party (NCP), All India Trinamool Congress (TMC) and Bahujan Samaj Party (BSP). Besides these, a number of regional parties fight the elections to state legislatures. Elections are held periodically, and people exercise their right to vote to elect their representatives. The government is continually making efforts to encourage more and more people to use their right to vote to choose good governance.
Democracy in India is not merely about giving people the right to vote but ensuring equality in all the spheres of life.
Hindrances in the Working of Democracy in India
While the elections have been happening at the right time and a systematic approach is followed to conduct the same ever since the concept of democracy came into being in India there are many hindrances in the smooth functioning of democracy in the country. These include illiteracy, gender discrimination, poverty, cultural disparity, political influence, casteism, and communalism. All these factors adversely affect democracy in India.
While democracy in India has been appreciated worldwide, there are still miles to go. Factors such as illiteracy, poverty, gender discrimination and communalism that impact the working of democracy in India need to be eradicated in order to allow the citizens to enjoy democracy in true sense.

Essay on Democracy in India Essay 600 words
Democracy in India was formed after the nation was freed from British rule in 1947. It led to the birth of the world’s largest democracy. Under the effective leadership of the Indian National Congress, the people of India attained the right to vote and elect their government.
There are a total of seven national parties in the country – Indian National Congress (INC), Nationalist Congress Party (NCP), Bharatiya Janta Party (BJP), Communist Party of India (CPI), Communist Party of India -Marxist (CPI-M), All India Trinamool Congress (TMC) and Bahujan Samaj Party (BSP). Apart from these, many regional parties come forward for elections to state legislatures. Elections to the parliament and state assemblies are held every 5 years.
Here are the Democratic Principles of India:
Sovereign means independent – free from interference or control of any foreign power. The country has a government directly elected by the citizens of the country. Indian citizens have the sovereign power to elect their leaders by elections conducted for the parliament, local bodies, and the state legislature.
Socialist means social and economic equality for all the country’s citizens. Democratic socialism means attaining socialistic goals by way of evolutionary, democratic, and non-violent means. The government is making continual efforts to lessen economic inequality by decreasing the concentration of wealth.
This means the right and freedom to choose one’s religion. In India, one has the right to practise any religion or reject them all. The Government of India respects all religions and does not have any official state religion. It does not disgrace or promote any religion.
This means the government of the country is elected democratically by its citizens. The people of the country have the right to elect its government at all the levels (Union, State and local) by way of universal adult franchise, also known as ‘one man, one vote.’ The right to vote is given without any discrimination on the basis of the colour, caste, creed, religion, gender, or education. Not just political, the people of India also enjoy social and economic democracy.
The head of the state here is not a heredity king or queen but an elected person. The ceremonial head of the state, that is, the President of India, is elected by an electoral college for a period of five years, while executive powers are vested in the Prime Minister.
Challenges Faced by Indian Democracy
While the constitution promises a democratic state and the people of India have been entitled to all the rights a person should enjoy in a democratic state, there are a lot of factors that impact its democracy and pose a challenge to it. Here is a look at these factors:
Illiteracy among people is one of the biggest challenges the Indian democracy has faced since its inception. Education enables people to exercise their right to vote wisely.
The political parties usually manipulate people belonging to the poor and backward classes. They are often bribed to acquire their vote.
Apart from these, casteism, gender discrimination, communalism, religious fundamentalism, political violence, and corruption are among other factors that are a challenge to democracy in India.
Democracy in India has received appreciation from world over. The right to vote to every citizen of the country has been given without any discrimination on the basis of their caste, colour, creed, religion, gender, or education. However, the country’s huge cultural, religious, and linguistic diversity is a major challenge for its democracy. The differences sought to be created out of it are a cause of serious concern. There is a need to curb these divisive tendencies in order to ensure the smooth functioning of democracy in India.
Essay on Democracy in India FAQs
What is a short paragraph about indian democracy.
Indian democracy ensures equal rights for all citizens and operates on the principle of fairness and inclusion, allowing people to elect their leaders and have a say in the country's governance.
What is democracy 250 words?
Democracy is a system of government where people choose their leaders through voting. It values equality, freedom, and participation, allowing citizens to voice their opinions and make decisions collectively.
How do you write a democracy essay?
To write a democracy essay, begin with an introduction explaining democracy's principles, discuss its importance and challenges in the main body, and conclude by emphasizing its role in shaping a just society.
What is Indian democracy essay?
An essay on Indian democracy explores how India's diverse population participates in governance, emphasizing the importance of equality, diversity, and representation in its democratic system.
What is democracy short speech?
Democracy is a system where people have a voice in their government. It promotes fairness, freedom, and cooperation among citizens for a better society.
Related content
Talk to our academic expert!
Language --- English Hindi Marathi Tamil Telugu Malayalam
Get access to free Mock Test and Master Class
Register to Get Free Mock Test and Study Material
Offer Ends in 5:00
Read our research on: Abortion | Podcasts | Election 2024
Regions & Countries
What can improve democracy, ideas from people in 24 countries, in their own words.

This Pew Research Center analysis on views of how to improve democracy uses data from nationally representative surveys conducted in 24 countries across North America, Europe, the Middle East, the Asia-Pacific region, sub-Saharan Africa and Latin America. All responses are weighted to be representative of the adult population in each country.
For non-U.S. data, this analysis draws on nationally representative surveys of 27,285 adults conducted from Feb. 20 to May 22, 2023. All surveys were conducted over the phone with adults in Canada, France, Germany, Greece, Italy, Japan, the Netherlands, South Korea, Spain, Sweden and the United Kingdom. Surveys were conducted face-to-face with adults in Argentina, Brazil, Hungary, India, Indonesia, Israel, Kenya, Mexico, Nigeria, Poland and South Africa. In Australia, we used a mixed-mode probability-based online panel. Read more about international survey methodology .
In the U.S., we surveyed 3,576 adults from March 20 to March 26, 2023. Everyone who took part in this survey is a member of the Center’s American Trends Panel (ATP), an online survey panel that is recruited through national, random sampling of residential addresses. This way, nearly all U.S. adults have a chance of selection. The survey is weighted to be representative of the U.S. adult population by gender, race, ethnicity, partisan affiliation, education and other categories. Read more about the ATP’s methodology .
Researchers examined random samples of English responses, machine-translated non-English responses, and non-English responses translated by a professional translation firm to develop a codebook for the main topics mentioned across the 24 countries. The codebook was iteratively improved via practice coding and calculations of intercoder reliability until a final selection of 17 substantive codes was formally adopted. (For more on the codebook, refer to Appendix C .)
To apply the codebook to the full collection of open-ended responses, a team of Pew Research Center coders and professional translators were trained to code English and non-English responses. Coders in both groups coded random samples and were evaluated for consistency and accuracy. They were asked to independently code responses only after reaching an acceptable threshold for intercoder reliability. (For more on the coding methodology, refer to Appendix A .)
There is some variation in whether and how people responded to our open-ended question. In each country surveyed, some respondents said that they did not understand the question, did not know how to answer or did not want to answer. This share of adults ranged from 4% in Spain to 47% in the U.S.
In some countries, people also tended to mention fewer things that would improve democracy in their country relative to people surveyed elsewhere. For example, across the 24 countries surveyed, a median of 73% mentioned only one topic in our codebook (e.g., politicians). The share in South Korea is much higher, with 92% suggesting only one area of improvement when describing what they think would improve democracy. In comparison, about a quarter or more mention two areas of improvement in France, Spain, Sweden and the U.S.
These differences help explain why the share giving a particular answer in certain publics may appear much lower than others, even if it is the top- ranked suggestion for improving democracy. To give a specific example, 10% of respondents in Poland mention politicians, while 18% do so in South Africa – yet the topic is ranked second in Poland and third in South Africa. Given this discrepancy, researchers have chosen to highlight not only the share of the public that mentions a given topic but also its relative ranking among all topics coded, both in text and in graphics.
Here is the question used for this report , along with coded responses for each country, and the survey methodology .
Open-ended responses highlighted in the text of this report were chosen to represent the key themes researchers identified. They have been edited for clarity and, in some cases, translated into English by a professional firm. Some responses have also been shortened for brevity.
Pew Research Center surveys have long found that people in many countries are dissatisfied with their democracy and want major changes to their political systems – and this year is no exception . But high and growing rates of discontent certainly raise the question: What do people think could fix things?

We set out to answer this by asking more than 30,000 respondents in 24 countries an open-ended question: “What do you think would help improve the way democracy in your country is working?” While the second- and third-most mentioned priorities vary greatly, across most countries surveyed, there is one clear top answer: Democracy can be improved with better or different politicians.
People want politicians who are more responsive to their needs and who are more competent and honest, among other factors. People also focus on questions of descriptive representation – the importance of having politicians with certain characteristics such as a specific race, religion or gender.
Respondents also think citizens can improve their own democracy. Across most of the 24 countries surveyed, issues of public participation and of different behavior from the people themselves are a top-five priority.
Other topics that come up regularly include:
- Economic reform , especially reforms that will enhance job creation.
- Government reform , including implementing term limits, adjusting the balance of power between institutions and other factors.
We explore these topics and the others we coded in the following chapters:
- Politicians, changing leadership and political parties ( Chapter 1 )
- Government reform, special interests and the media ( Chapter 2 )
- Economic and policy changes ( Chapter 3 )
- Citizen behavior and individual rights and equality ( Chapter 4 )
- Electoral reform and direct democracy ( Chapter 5 )
- Rule of law, safety and the judicial system ( Chapter 6 )
You can also read people’s answers in their own words in our interactive data essay and quote sorter: “How People in 24 Countries Think Democracy Can Improve.” Many responses in the quote sorter and throughout this report appear in translation; for selected quotes in their original language, visit this spreadsheet .
The survey was conducted from Feb. 20 to May 22, 2023, in 24 countries and 36 different languages. Below, we highlight some key themes, drawn from the open-ended responses and the 17 rigorously coded substantive topics.
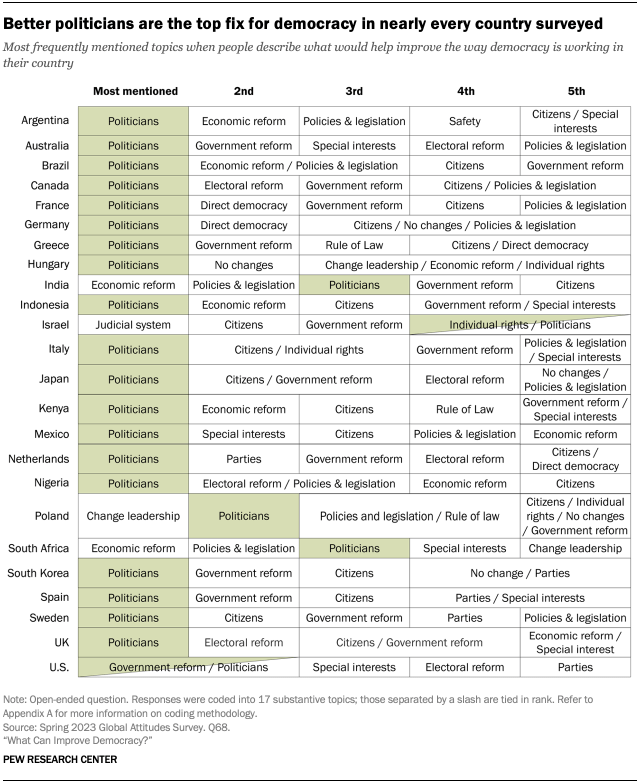
How politicians can improve
In almost every country surveyed, changes to politicians are the most commonly mentioned way to improve democracy. People broadly call for three types of improvements: better representation , increased competence and a higher level of responsiveness . They also call for politicians to be less corrupt or less influenced by special interests.
Representation
“Bringing in more diverse voices, rather than mostly wealthy White men.” Woman, 30, Australia
First, people want to see politicians from different groups in society – though which groups people want represented run the gamut. In Japan, for example, one woman said democracy would improve if there were “more diversity and more women parliamentarians.” In Kenya, having leaders “from all tribes” is seen as a way to make democracy work better. People also call for younger voices and politicians from “poor backgrounds,” among other groups. The opposing views of two American respondents, though, highlight why satisfying everyone is difficult:
“Most politicians in office right now are rich, Christian and old. Their overwhelmingly Christian views lead to laws and decisions that not only limit personal freedoms like abortion and gay marriage, but also discriminate against minority religions and their practices.”
– Man, 23, U.S.
“We need to stop worrying about putting people in positions because of their race, ethnicity or gender. What happened to being put in a position because they are the best person for that position?”
– Man, 64, U.S.
“Our politicians should have an education corresponding to their subject or field.” Woman, 72, Germany
Second, people want higher-caliber politicians. This includes a desire to see more technical expertise and traits such as morality, honesty, a “stronger backbone” or “more common sense.”
Sometimes, people simply want politicians with “no criminal records” – something mentioned explicitly by a South Korean man and echoed by respondents in the United States, India and Israel, among other places.
Responsiveness
“Make democracy promote more of the people’s voice. The people’s voice is the great strength for leadership.” Man, 27, Indonesia
Third, people want their politicians to hear them and respond to their needs and wishes, and for politicians to keep their promises. One man in the United Kingdom said, “If leaders would listen more to the local communities and do their jobs as members of Parliament, that would really help democracy in this country. It seems like once they’re elected, they just play lip service to the role.”
Special interests and corruption
Concerns about special interests and corruption are common in certain countries, including Mexico, the U.S. and Australia. One Mexican woman said, “Politicians should listen more to the Mexican people, not buy people off using money or groceries.” Others complained about politicians “pillaging” the country and enriching themselves by keeping tax money.
Calls for systemic reform
For some, the political system itself needs to change in order for democracy to work better. Changing the governmental structure is one of the top five topics coded in most countries surveyed – and it’s tied for the most mentioned issue in the U.S., along with politicians. These reforms include adjusting the balance of power between institutions, implementing term limits, and more.
Some also see the need to reform the electoral system in their country; others want more direct democracy through referenda or public forums. Judicial system reform is a priority for some, especially in Israel. (In Israel, the survey was conducted amid large-scale protests against a proposed law that would limit the power of the Supreme Court, but prior to the Oct. 7 Hamas attack and the court’s rejection of the law in January .)
Government reform
The U.S. stands out as the only country surveyed where reforming the government is the top concern (tied with politicians). Americans mention very specific proposals such as giving the District of Columbia and Puerto Rico statehood, increasing the size of the House of the Representatives to allow one representative per 100,000 people, requiring a supermajority for all spending bills, eliminating the filibuster, and more.
Term limits for elected officials are a particularly popular reform in the U.S. Americans call for them to prevent “career politicians,” as in the case of one woman who said, “I think we need to limit the number of years politicians can serve. No one should be able to serve as a politician for 40+ years like Joe Biden. I don’t have anything against him. I just think that we need limits. We have too many people who have served for too long and have little or nothing to show for it.” Term limits for Supreme Court justices are also top of mind for many Americans when it comes to judicial system reform.
Electoral reform
“There are many parts of the UK where it’s obvious who will get elected. My vote doesn’t count where I live because the Conservative Party wins every time. Effectively it means that the majority is not represented by the government. With proportional representation, everybody’s vote would count.” Man, 62, UK
The electoral system is among the top targets for change in some countries. In Canada, Nigeria and the UK, changing how elections work is the second-most mentioned topic of the 17 substantive codes – and it falls in the top five in Australia, Japan, the Netherlands and the U.S.
Suggested changes vary across countries and include switching from first-past-the-post to a proportional voting system, having a fixed date for elections, lowering the voting age, returning to hand-counted paper ballots, voting directly for candidates rather than parties, and more.
Direct democracy
Calls for direct democracy are prevalent in several European countries – even ranking second in France and Germany. One French woman said, “There should be more referenda, they should ask the opinion of the people more, and it should be respected.”
In the broadest sense, people want a “direct voting system” or for “people to have the vote, not middlemen elected officials.” More narrowly, they also mention specific topics they would like referenda for, including rejoining the European Union in the UK; “abortion, retirement and euthanasia” in France; “all legislation which harms the justice system” in Israel; asylum policy, nitrogen policy and local affairs in the Netherlands; “when and where the country goes to war” in Australia; “gay marriage, marijuana legalization and bail reform” in the U.S.; “nuclear power, sexuality, NATO and the EU” in Sweden; and who should be prime minister in Japan. (The survey was conducted prior to Sweden joining NATO in March 2024.)
The judicial system
Of the systemic reforms suggested, few bring up changes to the judicial system in most countries. Only in Israel, where the topic ranked first at the time of the survey, does judicial system reform appear in the top 10 coded issues. Israelis approach this issue from vastly different perspectives. For instance, some want to curtail the Supreme Court’s influence over government decisions, while others want to preserve its independence, as in these two examples:
“Finish the legislation that will limit the enormous and generally unreasonable power of the Supreme Court in Israel!”
– Man, 64, Israel
“Do everything to keep the last word of the High Court on any social and moral issue.”
– Man, 31, Israel
Is the grass always greener?
Notably, some respondents propose the exact reform that those in another country would like to do away with.
For example, while some people in countries without mandatory voting think it could be useful to implement, there are respondents in Australia – where voting is compulsory – who want it to end. People without mandatory voting see it as a way to force everyone to have a say: “We have to get everyone out to vote. Everyone complains. Voting should be mandatory. Everyone has to vote and have a say,” said a Canadian woman. But the flip side one Australian expressed was, “Eliminate compulsory voting. The votes of people who do not care about a result voids the vote of somebody who does.”
The ideal number of parties in government is another topic that brings about opposing suggestions. In the Netherlands, which has a relatively large number of parties, altering the party system is the second-most mentioned way to improve democracy. Dutch respondents differed on terms of the maximum number of parties they want to see (“a three-party system,” “four or five parties at most,” “a maximum of seven parties,” etc.) but the tenor is broadly similar: Too many parties is leading to fragmentation, polarization and division. Elsewhere, however, some squarely attribute polarization to a system with too few parties. In the U.S., a man noted, “The most egregious problem is that a two-party system cannot ever hope to be representative of its people as the will of any group cannot be captured in a binary system: The result will be increased polarization between the Democratic and Republican parties.”
Even in countries with more than two parties, like Canada and the UK, there can be a sense that only two are viable. A Canadian man said, “We need to have a free election with more than two parties.”

For many respondents, fixing democracy begins with the people
Citizens – both their quality and their participation in politics – come up regularly as an area that requires improvement for democracy to work better. In most countries, the issue is in the top five. And in Israel, Sweden, Italy and Japan, citizens are the second-most mentioned topic of the 17 coded. (In this analysis, “citizens” refers to all inhabitants of each country, not just the legal residents.)
In general, respondents see three ways citizens can improve: being more informed, participating more and generally being better people.
Being more informed
“More awareness and more information. We have highly separated classes. There are generations who have never read a newspaper. One cannot be fully democratic if one is not aware.” Man, 86, Italy
First, citizens being more informed is seen as crucial. Respondents argue that informed citizens are able to vote more responsibly and avoid being misled by surface-level political quips or misinformation.
In the Netherlands, for example, where the survey predated the electoral success of Geert Wilders’ right-wing populist Party for Freedom (PVV), one woman noted that citizens need “education, and openness, maybe. There are a lot of people who vote Geert Wilders because of his one-liners, and they don’t think beyond those. They haven’t learned to think beyond what’s right in front of them.” (For more information on how we classify populist parties, refer to Appendix E .)
Participating more
“Each and every one of us must go to the polls and make our own decisions.” Woman, 76, Japan
Second, some respondents want people in their country to be more involved in politics – whether that be turning out to vote, protesting at key moments or just caring more about politics or other issues. They hold the notion that if people participate, they will be less apathetic and less likely to complain, and their voices will be represented more fully. One woman in Sweden noted, “I would like to see more involvement from different groups of people: younger people, people with different backgrounds, people from minority groups.”
Being better people
“People should walk around rationally, respecting each other, dialoguing and respecting people’s cultures.” Woman, 29, Brazil
Third, the character of citizens comes up regularly – respondents’ requests for their countrymen range from “care more about others” to “love God and neighbor completely” to asking that they be “better critical thinkers,” among myriad other things. Still, some calls for improved citizen behavior contradict each other, as in the case of two Australian women who differ over how citizens should think about assimilation:
“We need to be more caring and thoughtful about people who come to the country. We need to be more tolerant and absorb them in our community.”
– Woman, 75, Australia
“We need to stop worrying that we are going to offend other nationalities and their traditions. We should be able to say ‘Merry Christmas’ instead of ‘happy holidays,’ and Christmas celebrations should be held in schools without worrying about offending others in our so-called ‘democratic society.’”
– Woman, 70, Australia
It’s difficult to please everyone
One challenge is that people in the same country may offer the exact opposite solutions. For example, in the UK, some people want politicians to make more money; others, less. In the U.S., while changes to the electoral system rank as one of the public’s top solutions for fixing democracy, some want to make it significantly easier to vote by methods like automatically registering citizens or making it easier to vote by mail. Others want to end these practices or even eliminate touch-screen voting machines.
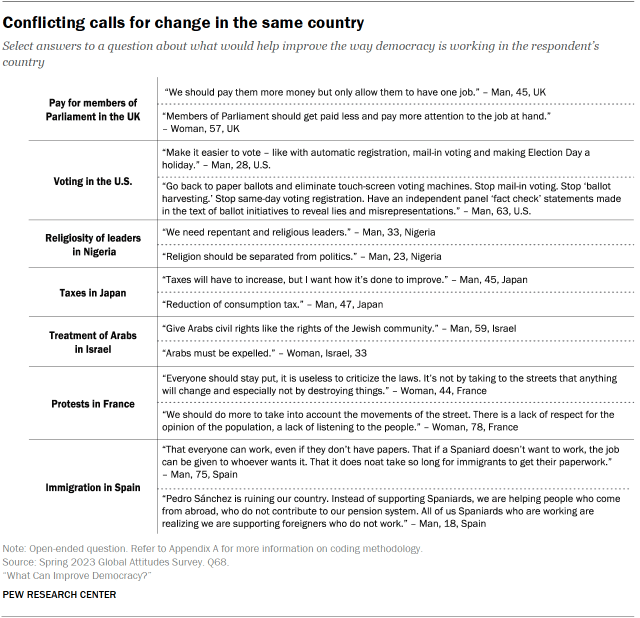
Economic reform and basic needs
People in several countries, mostly in the middle-income nations surveyed (Argentina, Brazil, India, Indonesia, Kenya, Mexico, Nigeria and South Africa) stand out for the emphasis they place on economic reform as a means to improve democracy. In India and South Africa, for example, the issue ranks first among the 17 substantive topics coded; in Argentina, Brazil, Indonesia and Kenya, it ranks second. These calls include a focus on creating jobs , curbing inflation , changing government spending priorities and more.
“When education, roads, hospitals and adequate water are made available, then I can say democracy will improve.” Man, 30, Nigeria
Sometimes, people draw a causal link between the economy and democracy, suggesting that improvements to the former would improve the latter. For example, one woman in Indonesia said, “Improve the economic conditions to ensure democracy goes well.” People also insinuated that having basic needs met is a precursor to their democracy functioning. One South African man noted that democracy in his country would work better if the government “created more employment for the youth, fixed the roads and gave us water. They must also fix the electricity problem.” A man in India said, “There’s a need for development in democracy.”
Indeed, specific policies and legislation – particularly improvements to infrastructure like roads, hospitals, water, electricity and schools – are the second-most mentioned topic in Brazil, India, Nigeria and South Africa. Some respondents offer laundry lists of policies that need attention, such as one Brazilian woman who called for “improving health care, controlling drug use, more security for the population, and improving the situation of people on the streets.”
Priority differences in high- and middle-income countries
Beyond economic reform , other changes to living conditions also receive more emphasis in some middle-income countries surveyed:
- In South Africa and Nigeria, both middle-income countries, mentions of economic reform tend to reference jobs . In other, high-income countries, calls for economic change generally refer to other economic issues like inflation and government spending priorities.
- When bringing up the issue of money in politics, respondents in middle-income countries generally cite corruption more than those in high-income countries. Those in high-income countries tend to bring up special interests more broadly.
- People in middle-income countries also focus more on issues related to public safety – including reducing crime and supporting law enforcement – than those in high-income countries.
- For their part, people in the 16 high-income countries surveyed tend to focus more on political party reform, direct democracy, government reform and media reform than those in the eight middle-income nations.
No changes and no solutions – or at least no democratic ones
“Democracy is fine because you have the freedom to express yourself without being persecuted, especially in politics.” Man, 26, Argentina
People sometimes say there are no changes that can make democracy in their country work better. These responses include broadly positive views of the status quo such as, “I am very happy to live in a country with democracy.” An Indian man responded simply, “Everything is going well in India.” Some respondents even compare their system favorably to others, as one Australian man said: “I think it currently works pretty well, far better than, say, the U.S. or UK, Poland or Israel.”
“Our current system is broken and I’m not sure what, if anything, can fix it at this point.” Woman, 41, U.S
But some are more pessimistic. They have the sense that “no matter what I do, nothing will change.” A Brazilian man said, “It is difficult to make it better. Brazil is too complicated.”
And some see no better options. In Hungary – where “no changes” was the second-most cited topic of the 17 coded – one man referenced Winston Churchill’s quote about democracy, saying, “Democracy is the worst form of government, not counting all the others that man has tried from time to time.”
In many countries, a sizable share offer no response at all – saying that they do not know or refusing to answer. This includes around a third or more of those in Indonesia, Japan and the U.S. In most countries, those who did not answer the question tended to have lower levels of formal education than those who offered a substantive solution. And in some places – including the U.S. – they were also more likely to be women than men.
Few call for ending democracy altogether
Despite considerable discontent with democracy , few people suggest changing to a non-democratic system. Those who do call for a new system offer options like a military junta, a theocracy or an autocracy as possible new systems.
Related: Who likes authoritarianism, and how do they want to change their government?
Road map for this research project
One other way to think about what people believe will help improve their democracy is to focus on three themes: basic needs that can be addressed, improvements to the system and complete overhauls of the system. We explore these themes in our interactive data essay and quote sorter: “How People in 24 Countries Think Democracy Can Improve.”
You can also explore people’s responses in their own words, with the option to filter by country and code by navigating over to the quote sorter .
In the chapters that follow, we discuss 15 of our coded themes in detail. We analyze how people spoke about them, as well as how responses varied across and within countries. We chose to emphasize the relative frequency, or rank order , in which people mentioned these different topics. For more about this choice, as well as details about our coding procedure and methodology , refer to Appendix A .
Explore the chapters of this report:
Why this report focuses on topic rank order in addition to percentages
There is some variation in whether and how people responded to our open-ended question. In each country surveyed, some respondents said that they did not understand the question, did not know how to answer or did not want to answer. This share of adults ranged from 4% in Spain to 47% in the U.S.
These differences help explain why the share giving a particular answer in certain publics may appear much lower than others, even if the topic is the top mentioned suggestion for improving democracy. To give a specific example, 10% in Poland mention politicians while 18% say the same in South Africa, but the topic is ranked second in Poland and third in South Africa. Given this, researchers have chosen to highlight not only the share of the public who mention a given topic but also its relative ranking among the topics coded, both in the text and in graphics.
Sign up for our Global newsletter
Delivered twice a month
Report Materials
Table of contents, freedom, elections, voice: how people in australia and the uk define democracy, global public opinion in an era of democratic anxiety, most people in advanced economies think their own government respects personal freedoms, more people globally see racial, ethnic discrimination as a serious problem in the u.s. than in their own society, citizens in advanced economies want significant changes to their political systems, most popular.
About Pew Research Center Pew Research Center is a nonpartisan fact tank that informs the public about the issues, attitudes and trends shaping the world. It conducts public opinion polling, demographic research, media content analysis and other empirical social science research. Pew Research Center does not take policy positions. It is a subsidiary of The Pew Charitable Trusts .
- Search Menu
- Browse content in Arts and Humanities
- Browse content in Archaeology
- Anglo-Saxon and Medieval Archaeology
- Archaeological Methodology and Techniques
- Archaeology by Region
- Archaeology of Religion
- Archaeology of Trade and Exchange
- Biblical Archaeology
- Contemporary and Public Archaeology
- Environmental Archaeology
- Historical Archaeology
- History and Theory of Archaeology
- Industrial Archaeology
- Landscape Archaeology
- Mortuary Archaeology
- Prehistoric Archaeology
- Underwater Archaeology
- Urban Archaeology
- Zooarchaeology
- Browse content in Architecture
- Architectural Structure and Design
- History of Architecture
- Residential and Domestic Buildings
- Theory of Architecture
- Browse content in Art
- Art Subjects and Themes
- History of Art
- Industrial and Commercial Art
- Theory of Art
- Biographical Studies
- Byzantine Studies
- Browse content in Classical Studies
- Classical History
- Classical Philosophy
- Classical Mythology
- Classical Literature
- Classical Reception
- Classical Art and Architecture
- Classical Oratory and Rhetoric
- Greek and Roman Epigraphy
- Greek and Roman Law
- Greek and Roman Archaeology
- Greek and Roman Papyrology
- Late Antiquity
- Religion in the Ancient World
- Digital Humanities
- Browse content in History
- Colonialism and Imperialism
- Diplomatic History
- Environmental History
- Genealogy, Heraldry, Names, and Honours
- Genocide and Ethnic Cleansing
- Historical Geography
- History by Period
- History of Agriculture
- History of Education
- History of Emotions
- History of Gender and Sexuality
- Industrial History
- Intellectual History
- International History
- Labour History
- Legal and Constitutional History
- Local and Family History
- Maritime History
- Military History
- National Liberation and Post-Colonialism
- Oral History
- Political History
- Public History
- Regional and National History
- Revolutions and Rebellions
- Slavery and Abolition of Slavery
- Social and Cultural History
- Theory, Methods, and Historiography
- Urban History
- World History
- Browse content in Language Teaching and Learning
- Language Learning (Specific Skills)
- Language Teaching Theory and Methods
- Browse content in Linguistics
- Applied Linguistics
- Cognitive Linguistics
- Computational Linguistics
- Forensic Linguistics
- Grammar, Syntax and Morphology
- Historical and Diachronic Linguistics
- History of English
- Language Acquisition
- Language Variation
- Language Families
- Language Evolution
- Language Reference
- Lexicography
- Linguistic Theories
- Linguistic Typology
- Linguistic Anthropology
- Phonetics and Phonology
- Psycholinguistics
- Sociolinguistics
- Translation and Interpretation
- Writing Systems
- Browse content in Literature
- Bibliography
- Children's Literature Studies
- Literary Studies (Asian)
- Literary Studies (European)
- Literary Studies (Eco-criticism)
- Literary Studies (Modernism)
- Literary Studies (Romanticism)
- Literary Studies (American)
- Literary Studies - World
- Literary Studies (1500 to 1800)
- Literary Studies (19th Century)
- Literary Studies (20th Century onwards)
- Literary Studies (African American Literature)
- Literary Studies (British and Irish)
- Literary Studies (Early and Medieval)
- Literary Studies (Fiction, Novelists, and Prose Writers)
- Literary Studies (Gender Studies)
- Literary Studies (Graphic Novels)
- Literary Studies (History of the Book)
- Literary Studies (Plays and Playwrights)
- Literary Studies (Poetry and Poets)
- Literary Studies (Postcolonial Literature)
- Literary Studies (Queer Studies)
- Literary Studies (Science Fiction)
- Literary Studies (Travel Literature)
- Literary Studies (War Literature)
- Literary Studies (Women's Writing)
- Literary Theory and Cultural Studies
- Mythology and Folklore
- Shakespeare Studies and Criticism
- Browse content in Media Studies
- Browse content in Music
- Applied Music
- Dance and Music
- Ethics in Music
- Ethnomusicology
- Gender and Sexuality in Music
- Medicine and Music
- Music Cultures
- Music and Religion
- Music and Culture
- Music and Media
- Music Education and Pedagogy
- Music Theory and Analysis
- Musical Scores, Lyrics, and Libretti
- Musical Structures, Styles, and Techniques
- Musicology and Music History
- Performance Practice and Studies
- Race and Ethnicity in Music
- Sound Studies
- Browse content in Performing Arts
- Browse content in Philosophy
- Aesthetics and Philosophy of Art
- Epistemology
- Feminist Philosophy
- History of Western Philosophy
- Metaphysics
- Moral Philosophy
- Non-Western Philosophy
- Philosophy of Science
- Philosophy of Action
- Philosophy of Law
- Philosophy of Religion
- Philosophy of Language
- Philosophy of Mind
- Philosophy of Perception
- Philosophy of Mathematics and Logic
- Practical Ethics
- Social and Political Philosophy
- Browse content in Religion
- Biblical Studies
- Christianity
- East Asian Religions
- History of Religion
- Judaism and Jewish Studies
- Qumran Studies
- Religion and Education
- Religion and Health
- Religion and Politics
- Religion and Science
- Religion and Law
- Religion and Art, Literature, and Music
- Religious Studies
- Browse content in Society and Culture
- Cookery, Food, and Drink
- Cultural Studies
- Customs and Traditions
- Ethical Issues and Debates
- Hobbies, Games, Arts and Crafts
- Lifestyle, Home, and Garden
- Natural world, Country Life, and Pets
- Popular Beliefs and Controversial Knowledge
- Sports and Outdoor Recreation
- Technology and Society
- Travel and Holiday
- Visual Culture
- Browse content in Law
- Arbitration
- Browse content in Company and Commercial Law
- Commercial Law
- Company Law
- Browse content in Comparative Law
- Systems of Law
- Competition Law
- Browse content in Constitutional and Administrative Law
- Government Powers
- Judicial Review
- Local Government Law
- Military and Defence Law
- Parliamentary and Legislative Practice
- Construction Law
- Contract Law
- Browse content in Criminal Law
- Criminal Procedure
- Criminal Evidence Law
- Sentencing and Punishment
- Employment and Labour Law
- Environment and Energy Law
- Browse content in Financial Law
- Banking Law
- Insolvency Law
- History of Law
- Human Rights and Immigration
- Intellectual Property Law
- Browse content in International Law
- Private International Law and Conflict of Laws
- Public International Law
- IT and Communications Law
- Jurisprudence and Philosophy of Law
- Law and Politics
- Law and Society
- Browse content in Legal System and Practice
- Courts and Procedure
- Legal Skills and Practice
- Primary Sources of Law
- Regulation of Legal Profession
- Medical and Healthcare Law
- Browse content in Policing
- Criminal Investigation and Detection
- Police and Security Services
- Police Procedure and Law
- Police Regional Planning
- Browse content in Property Law
- Personal Property Law
- Study and Revision
- Terrorism and National Security Law
- Browse content in Trusts Law
- Wills and Probate or Succession
- Browse content in Medicine and Health
- Browse content in Allied Health Professions
- Arts Therapies
- Clinical Science
- Dietetics and Nutrition
- Occupational Therapy
- Operating Department Practice
- Physiotherapy
- Radiography
- Speech and Language Therapy
- Browse content in Anaesthetics
- General Anaesthesia
- Neuroanaesthesia
- Browse content in Clinical Medicine
- Acute Medicine
- Cardiovascular Medicine
- Clinical Genetics
- Clinical Pharmacology and Therapeutics
- Dermatology
- Endocrinology and Diabetes
- Gastroenterology
- Genito-urinary Medicine
- Geriatric Medicine
- Infectious Diseases
- Medical Oncology
- Medical Toxicology
- Pain Medicine
- Palliative Medicine
- Rehabilitation Medicine
- Respiratory Medicine and Pulmonology
- Rheumatology
- Sleep Medicine
- Sports and Exercise Medicine
- Clinical Neuroscience
- Community Medical Services
- Critical Care
- Emergency Medicine
- Forensic Medicine
- Haematology
- History of Medicine
- Browse content in Medical Dentistry
- Oral and Maxillofacial Surgery
- Paediatric Dentistry
- Restorative Dentistry and Orthodontics
- Surgical Dentistry
- Medical Ethics
- Browse content in Medical Skills
- Clinical Skills
- Communication Skills
- Nursing Skills
- Surgical Skills
- Medical Statistics and Methodology
- Browse content in Neurology
- Clinical Neurophysiology
- Neuropathology
- Nursing Studies
- Browse content in Obstetrics and Gynaecology
- Gynaecology
- Occupational Medicine
- Ophthalmology
- Otolaryngology (ENT)
- Browse content in Paediatrics
- Neonatology
- Browse content in Pathology
- Chemical Pathology
- Clinical Cytogenetics and Molecular Genetics
- Histopathology
- Medical Microbiology and Virology
- Patient Education and Information
- Browse content in Pharmacology
- Psychopharmacology
- Browse content in Popular Health
- Caring for Others
- Complementary and Alternative Medicine
- Self-help and Personal Development
- Browse content in Preclinical Medicine
- Cell Biology
- Molecular Biology and Genetics
- Reproduction, Growth and Development
- Primary Care
- Professional Development in Medicine
- Browse content in Psychiatry
- Addiction Medicine
- Child and Adolescent Psychiatry
- Forensic Psychiatry
- Learning Disabilities
- Old Age Psychiatry
- Psychotherapy
- Browse content in Public Health and Epidemiology
- Epidemiology
- Public Health
- Browse content in Radiology
- Clinical Radiology
- Interventional Radiology
- Nuclear Medicine
- Radiation Oncology
- Reproductive Medicine
- Browse content in Surgery
- Cardiothoracic Surgery
- Gastro-intestinal and Colorectal Surgery
- General Surgery
- Neurosurgery
- Paediatric Surgery
- Peri-operative Care
- Plastic and Reconstructive Surgery
- Surgical Oncology
- Transplant Surgery
- Trauma and Orthopaedic Surgery
- Vascular Surgery
- Browse content in Science and Mathematics
- Browse content in Biological Sciences
- Aquatic Biology
- Biochemistry
- Bioinformatics and Computational Biology
- Developmental Biology
- Ecology and Conservation
- Evolutionary Biology
- Genetics and Genomics
- Microbiology
- Molecular and Cell Biology
- Natural History
- Plant Sciences and Forestry
- Research Methods in Life Sciences
- Structural Biology
- Systems Biology
- Zoology and Animal Sciences
- Browse content in Chemistry
- Analytical Chemistry
- Computational Chemistry
- Crystallography
- Environmental Chemistry
- Industrial Chemistry
- Inorganic Chemistry
- Materials Chemistry
- Medicinal Chemistry
- Mineralogy and Gems
- Organic Chemistry
- Physical Chemistry
- Polymer Chemistry
- Study and Communication Skills in Chemistry
- Theoretical Chemistry
- Browse content in Computer Science
- Artificial Intelligence
- Computer Architecture and Logic Design
- Game Studies
- Human-Computer Interaction
- Mathematical Theory of Computation
- Programming Languages
- Software Engineering
- Systems Analysis and Design
- Virtual Reality
- Browse content in Computing
- Business Applications
- Computer Security
- Computer Games
- Computer Networking and Communications
- Digital Lifestyle
- Graphical and Digital Media Applications
- Operating Systems
- Browse content in Earth Sciences and Geography
- Atmospheric Sciences
- Environmental Geography
- Geology and the Lithosphere
- Maps and Map-making
- Meteorology and Climatology
- Oceanography and Hydrology
- Palaeontology
- Physical Geography and Topography
- Regional Geography
- Soil Science
- Urban Geography
- Browse content in Engineering and Technology
- Agriculture and Farming
- Biological Engineering
- Civil Engineering, Surveying, and Building
- Electronics and Communications Engineering
- Energy Technology
- Engineering (General)
- Environmental Science, Engineering, and Technology
- History of Engineering and Technology
- Mechanical Engineering and Materials
- Technology of Industrial Chemistry
- Transport Technology and Trades
- Browse content in Environmental Science
- Applied Ecology (Environmental Science)
- Conservation of the Environment (Environmental Science)
- Environmental Sustainability
- Environmentalist Thought and Ideology (Environmental Science)
- Management of Land and Natural Resources (Environmental Science)
- Natural Disasters (Environmental Science)
- Nuclear Issues (Environmental Science)
- Pollution and Threats to the Environment (Environmental Science)
- Social Impact of Environmental Issues (Environmental Science)
- History of Science and Technology
- Browse content in Materials Science
- Ceramics and Glasses
- Composite Materials
- Metals, Alloying, and Corrosion
- Nanotechnology
- Browse content in Mathematics
- Applied Mathematics
- Biomathematics and Statistics
- History of Mathematics
- Mathematical Education
- Mathematical Finance
- Mathematical Analysis
- Numerical and Computational Mathematics
- Probability and Statistics
- Pure Mathematics
- Browse content in Neuroscience
- Cognition and Behavioural Neuroscience
- Development of the Nervous System
- Disorders of the Nervous System
- History of Neuroscience
- Invertebrate Neurobiology
- Molecular and Cellular Systems
- Neuroendocrinology and Autonomic Nervous System
- Neuroscientific Techniques
- Sensory and Motor Systems
- Browse content in Physics
- Astronomy and Astrophysics
- Atomic, Molecular, and Optical Physics
- Biological and Medical Physics
- Classical Mechanics
- Computational Physics
- Condensed Matter Physics
- Electromagnetism, Optics, and Acoustics
- History of Physics
- Mathematical and Statistical Physics
- Measurement Science
- Nuclear Physics
- Particles and Fields
- Plasma Physics
- Quantum Physics
- Relativity and Gravitation
- Semiconductor and Mesoscopic Physics
- Browse content in Psychology
- Affective Sciences
- Clinical Psychology
- Cognitive Neuroscience
- Cognitive Psychology
- Criminal and Forensic Psychology
- Developmental Psychology
- Educational Psychology
- Evolutionary Psychology
- Health Psychology
- History and Systems in Psychology
- Music Psychology
- Neuropsychology
- Organizational Psychology
- Psychological Assessment and Testing
- Psychology of Human-Technology Interaction
- Psychology Professional Development and Training
- Research Methods in Psychology
- Social Psychology
- Browse content in Social Sciences
- Browse content in Anthropology
- Anthropology of Religion
- Human Evolution
- Medical Anthropology
- Physical Anthropology
- Regional Anthropology
- Social and Cultural Anthropology
- Theory and Practice of Anthropology
- Browse content in Business and Management
- Business Strategy
- Business History
- Business Ethics
- Business and Government
- Business and Technology
- Business and the Environment
- Comparative Management
- Corporate Governance
- Corporate Social Responsibility
- Entrepreneurship
- Health Management
- Human Resource Management
- Industrial and Employment Relations
- Industry Studies
- Information and Communication Technologies
- International Business
- Knowledge Management
- Management and Management Techniques
- Operations Management
- Organizational Theory and Behaviour
- Pensions and Pension Management
- Public and Nonprofit Management
- Strategic Management
- Supply Chain Management
- Browse content in Criminology and Criminal Justice
- Criminal Justice
- Criminology
- Forms of Crime
- International and Comparative Criminology
- Youth Violence and Juvenile Justice
- Development Studies
- Browse content in Economics
- Agricultural, Environmental, and Natural Resource Economics
- Asian Economics
- Behavioural Finance
- Behavioural Economics and Neuroeconomics
- Econometrics and Mathematical Economics
- Economic Systems
- Economic Methodology
- Economic History
- Economic Development and Growth
- Financial Markets
- Financial Institutions and Services
- General Economics and Teaching
- Health, Education, and Welfare
- History of Economic Thought
- International Economics
- Labour and Demographic Economics
- Law and Economics
- Macroeconomics and Monetary Economics
- Microeconomics
- Public Economics
- Urban, Rural, and Regional Economics
- Welfare Economics
- Browse content in Education
- Adult Education and Continuous Learning
- Care and Counselling of Students
- Early Childhood and Elementary Education
- Educational Equipment and Technology
- Educational Strategies and Policy
- Higher and Further Education
- Organization and Management of Education
- Philosophy and Theory of Education
- Schools Studies
- Secondary Education
- Teaching of a Specific Subject
- Teaching of Specific Groups and Special Educational Needs
- Teaching Skills and Techniques
- Browse content in Environment
- Applied Ecology (Social Science)
- Climate Change
- Conservation of the Environment (Social Science)
- Environmentalist Thought and Ideology (Social Science)
- Natural Disasters (Environment)
- Social Impact of Environmental Issues (Social Science)
- Browse content in Human Geography
- Cultural Geography
- Economic Geography
- Political Geography
- Browse content in Interdisciplinary Studies
- Communication Studies
- Museums, Libraries, and Information Sciences
- Browse content in Politics
- African Politics
- Asian Politics
- Chinese Politics
- Comparative Politics
- Conflict Politics
- Elections and Electoral Studies
- Environmental Politics
- European Union
- Foreign Policy
- Gender and Politics
- Human Rights and Politics
- Indian Politics
- International Relations
- International Organization (Politics)
- International Political Economy
- Irish Politics
- Latin American Politics
- Middle Eastern Politics
- Political Methodology
- Political Communication
- Political Philosophy
- Political Sociology
- Political Theory
- Political Behaviour
- Political Economy
- Political Institutions
- Politics and Law
- Public Administration
- Public Policy
- Quantitative Political Methodology
- Regional Political Studies
- Russian Politics
- Security Studies
- State and Local Government
- UK Politics
- US Politics
- Browse content in Regional and Area Studies
- African Studies
- Asian Studies
- East Asian Studies
- Japanese Studies
- Latin American Studies
- Middle Eastern Studies
- Native American Studies
- Scottish Studies
- Browse content in Research and Information
- Research Methods
- Browse content in Social Work
- Addictions and Substance Misuse
- Adoption and Fostering
- Care of the Elderly
- Child and Adolescent Social Work
- Couple and Family Social Work
- Developmental and Physical Disabilities Social Work
- Direct Practice and Clinical Social Work
- Emergency Services
- Human Behaviour and the Social Environment
- International and Global Issues in Social Work
- Mental and Behavioural Health
- Social Justice and Human Rights
- Social Policy and Advocacy
- Social Work and Crime and Justice
- Social Work Macro Practice
- Social Work Practice Settings
- Social Work Research and Evidence-based Practice
- Welfare and Benefit Systems
- Browse content in Sociology
- Childhood Studies
- Community Development
- Comparative and Historical Sociology
- Economic Sociology
- Gender and Sexuality
- Gerontology and Ageing
- Health, Illness, and Medicine
- Marriage and the Family
- Migration Studies
- Occupations, Professions, and Work
- Organizations
- Population and Demography
- Race and Ethnicity
- Social Theory
- Social Movements and Social Change
- Social Research and Statistics
- Social Stratification, Inequality, and Mobility
- Sociology of Religion
- Sociology of Education
- Sport and Leisure
- Urban and Rural Studies
- Browse content in Warfare and Defence
- Defence Strategy, Planning, and Research
- Land Forces and Warfare
- Military Administration
- Military Life and Institutions
- Naval Forces and Warfare
- Other Warfare and Defence Issues
- Peace Studies and Conflict Resolution
- Weapons and Equipment

Democracy: A Very Short Introduction
Author webpage
- Cite Icon Cite
- Permissions Icon Permissions
Democracy: A Very Short Introduction shows the distinction between the shared concept of democracy and different conceptions or instances of democracy. The key idea of democracy is that those governed—the demos —have a say in the government. However, until the 19th century, different conceptions of democracy did not extend to democratic society, resulting in the exclusion of many groups and individuals. The ideas of social and political thinkers including Plato, Aristotle, J. S. Mill, Marx, Rawls, and Sen provide the intellectual history of democracy. This VSI explores past and present forms of democratic government and considers traditional and inclusive historical approaches to democracy.
Signed in as
Institutional accounts.
- GoogleCrawler [DO NOT DELETE]
- Google Scholar Indexing
Personal account
- Sign in with email/username & password
- Get email alerts
- Save searches
- Purchase content
- Activate your purchase/trial code
Institutional access
- Sign in with a library card Sign in with username/password Recommend to your librarian
- Institutional account management
- Get help with access
Access to content on Oxford Academic is often provided through institutional subscriptions and purchases. If you are a member of an institution with an active account, you may be able to access content in one of the following ways:
IP based access
Typically, access is provided across an institutional network to a range of IP addresses. This authentication occurs automatically, and it is not possible to sign out of an IP authenticated account.
Sign in through your institution
Choose this option to get remote access when outside your institution. Shibboleth/Open Athens technology is used to provide single sign-on between your institution’s website and Oxford Academic.
- Click Sign in through your institution.
- Select your institution from the list provided, which will take you to your institution's website to sign in.
- When on the institution site, please use the credentials provided by your institution. Do not use an Oxford Academic personal account.
- Following successful sign in, you will be returned to Oxford Academic.
If your institution is not listed or you cannot sign in to your institution’s website, please contact your librarian or administrator.
Sign in with a library card
Enter your library card number to sign in. If you cannot sign in, please contact your librarian.
Society Members
Society member access to a journal is achieved in one of the following ways:
Sign in through society site
Many societies offer single sign-on between the society website and Oxford Academic. If you see ‘Sign in through society site’ in the sign in pane within a journal:
- Click Sign in through society site.
- When on the society site, please use the credentials provided by that society. Do not use an Oxford Academic personal account.
If you do not have a society account or have forgotten your username or password, please contact your society.
Sign in using a personal account
Some societies use Oxford Academic personal accounts to provide access to their members. See below.
A personal account can be used to get email alerts, save searches, purchase content, and activate subscriptions.
Some societies use Oxford Academic personal accounts to provide access to their members.
Viewing your signed in accounts
Click the account icon in the top right to:
- View your signed in personal account and access account management features.
- View the institutional accounts that are providing access.
Signed in but can't access content
Oxford Academic is home to a wide variety of products. The institutional subscription may not cover the content that you are trying to access. If you believe you should have access to that content, please contact your librarian.
For librarians and administrators, your personal account also provides access to institutional account management. Here you will find options to view and activate subscriptions, manage institutional settings and access options, access usage statistics, and more.
Our books are available by subscription or purchase to libraries and institutions.
External resource
- In the OUP print catalogue
- About Oxford Academic
- Publish journals with us
- University press partners
- What we publish
- New features
- Open access
- Rights and permissions
- Accessibility
- Advertising
- Media enquiries
- Oxford University Press
- Oxford Languages
- University of Oxford
Oxford University Press is a department of the University of Oxford. It furthers the University's objective of excellence in research, scholarship, and education by publishing worldwide
- Copyright © 2024 Oxford University Press
- Cookie settings
- Cookie policy
- Privacy policy
- Legal notice
This Feature Is Available To Subscribers Only
Sign In or Create an Account
This PDF is available to Subscribers Only
For full access to this pdf, sign in to an existing account, or purchase an annual subscription.
- Share full article
Advertisement
Supported by
Guest Essay
The One Idea That Could Save American Democracy

By Astra Taylor and Leah Hunt-Hendrix
Ms. Taylor and Ms. Hunt-Hendrix are political organizers and the authors of the book “Solidarity: The Past, Present, and Future of a World-Changing Idea.”
These days, we often hear that democracy is on the ballot. And there’s a truth to that: Winning elections is critical, especially as liberal and progressive forces try to fend off radical right-wing movements. But the democratic crisis that our society faces will not be solved by voting alone. We need to do more than defeat Donald Trump and his allies — we need to make cultivating solidarity a national priority.
For years, solidarity’s strongest associations have been with the left and the labor movement — a term invoked at protests and on picket lines. But its roots are much deeper, and its potential implications far more profound, than we typically assume. Though we rarely speak about it as such, solidarity is a concept as fundamental to democracy as its better-known cousins: equality, freedom and justice. Solidarity is simultaneously a bond that holds society together and a force that propels it forward. After all, when people feel connected, they are more willing to work together, to share resources and to have one another’s backs. Solidarity weaves us into a larger and more resilient “we” through the precious and powerful sense that even though we are different, our lives and our fates are connected.
We have both spent years working as organizers and activists . If our experience has taught us anything, it is that a sense of connection and mutualism is rarely spontaneous. It must be nurtured and sustained. Without robust and effective organizations and institutions to cultivate and maintain solidarity, it weakens and democracy falters. We become more atomized and isolated, suspicious and susceptible to misinformation, more disengaged and cynical, and easily pitted against one another.
Democracy’s opponents know this. That’s why they invest huge amounts of energy and resources to sabotage transformative, democratic solidarity and to nurture exclusionary and reactionary forms of group identity. Enraged at a decade of social movements and the long-overdue revival of organized labor, right-wing strategists and their corporate backers have redoubled their efforts to divide and conquer the American public, inflaming group resentments in order to restore traditional social hierarchies and ensure that plutocrats maintain their hold on wealth and power. In white papers, stump speeches and podcasts, conservative ideologues have laid out their vision for capturing the state and using it as a tool to remake our country in their image.
If we do not prioritize solidarity, this dangerous and anti-democratic project will succeed. Far more than just a slogan or hashtag, solidarity can orient us toward a future worth fighting for, providing the basis of a credible and galvanizing plan for democratic renewal. Instead of the 20th-century ideal of a welfare state, we should try to imagine a solidarity state.
We urgently need a countervision of what government can and should be, and how public resources and infrastructure can be deployed to foster social connection and repair the social fabric so that democracy can have a chance not just to limp along, but to flourish. Solidarity, here, is both a goal worth reaching toward and the method of building the power to achieve it. It is both means and ends, the forging of social bonds so that we can become strong enough to shift policy together.
Historically, the question of solidarity has been raised during volatile junctures like the one we are living through. Contemporary conceptions of solidarity first took form after the democratic revolutions of the 18th century and over the course of the Industrial Revolution. As kings were deposed and the church’s role as a moral authority waned, philosophers and citizens wondered how society could cohere without a monarch or god. What could bind people in a secular, pluralistic age?
The 19th-century thinkers who began seriously contemplating and writing about the idea of solidarity often used the image of the human body, where different parts work in tandem. Most famously, the French sociologist Émile Durkheim put solidarity at the center of his inquiry, arguing that as society increased in complexity, social bonds between people would strengthen, each person playing a specialized role while connected to a larger whole. Solidarity and social cohesion, he argued, would be the natural result of increasing social and economic interdependence. But as Durkheim himself would eventually recognize, the industrial economy that he initially imagined would generate solidarity would actually serve to weaken its fragile ties, fostering what he called anomie, the corrosive hopelessness that accompanied growing inequality.
In the United States, solidarity never achieved the same intellectual cachet as in Europe. Since this nation’s founding, the concept has generally been neglected, and the practice actively suppressed and even criminalized. Attempts to forge cross-racial solidarity have met with violent suppression time and again, and labor organizing, effectively outlawed until the New Deal era, still occupies hostile legal ground. Decades of market-friendly policies, promoted by Republicans and Democrats alike, have undermined solidarity in ways both subtle and overt, from encouraging us to see ourselves as individual consumers rather than citizens to fostering individualism and competition over collectivity and cooperation.
As our profit-driven economy has made us more insecure and atomized — and more susceptible to authoritarian appeals — the far right has seized its opportunity. A furious backlash now rises to cut down the shoots of solidarity that sprung up as a result of recent movements pushing for economic, racial, environmental and gender justice. In response, programs that encourage diversity and inclusion are being targeted by billionaire investors, while small acts of solidarity — like helping someone get an abortion or bailing protesters out of jail — have been criminalized.
Awaiting the return of Mr. Trump, the Heritage Foundation has mapped out a plan to remake government and society, using the full power of the state to roll back what it calls “the Great Awokening” and restore a Judeo-Christian, capitalist “culture of life” and “blessedness.” “Woke” has been turned into a pejorative so that the word can be wielded to tarnish and break the solidarity that people have only just begun to experience.
Our vision of a solidarity state offers a pointed rejoinder to this project. Social democrats and socialists have been right to emphasize the need for redistribution and robust public investment in goods and services. We must restructure our economy so that it works for the many and not the few. But unlike conservatives — think, for example, of Margaret Thatcher, the prime minister of Britain who in 1981 said, “Economics are the method; the object is to change the heart and soul” — liberals and leftists have tended to downplay the role of policy in shaping public sensibilities. This is a mistake.
Laws and social programs not only shape material outcomes; they also shape us, informing public perceptions and preferences, and generating what scholars call policy feedback loops. There is no neutral state to aspire to. Policies can either foster solidarity and help repair the divides that separate us or deepen the fissures.
Today, the American welfare state too often does the latter. As sociologists including Suzanne Mettler and Matthew Desmond have detailed, lower-income people tend to be stigmatized for needing assistance, while more-affluent citizens reap a range of benefits that are comparatively invisible, mainly through tax credits and tax breaks. Both arrangements — the highly visible and stigmatized aid to the poor and the more invisible and socially acceptable aid to the affluent — serve to foster resentment and obscure how we are all dependent on the state in various ways.
Instead of treating citizens as passive and isolated recipients of services delivered from on high, a solidarity state would experiment with creative ways of fostering connection and participation at every opportunity for more Americans. What if we had basic guarantees that were universal rather than means-tested programs that distinguish between the deserving and undeserving, stigmatizing some and setting groups apart? What if, following the model of a widely admired program in Canada, the government aided groups of private citizens who want to sponsor and subsidize migrants and refugees? What if public schools, post offices, transit systems, parks, public utilities and jobs programs were explicitly designed to facilitate social connection and solidarity in addition to providing essential support and services?
We’ll get there only if we take up the challenge of building solidarity from wherever we happen to sit. Both means and end, solidarity can be a source of power, built through the day-to-day work of organizing, and our shared purpose. Solidarity is the essential and too often missing ingredient of today’s most important political project: not just saving democracy but creating an egalitarian, multiracial society that can guarantee each of us a dignified life.
Astra Taylor and Leah Hunt-Hendrix are political organizers and the authors of the book “Solidarity: The Past, Present, and Future of a World-Changing Idea.”
The Times is committed to publishing a diversity of letters to the editor. We’d like to hear what you think about this or any of our articles. Here are some tips . And here’s our email: [email protected] .
Follow the New York Times Opinion section on Facebook , Instagram , TikTok , WhatsApp , X and Threads .
Biden is announcing a new rule to protect consumers who purchase short-term health insurance plans
President Joe Biden on Thursday announced new steps to protect consumers who buy short-term health insurance plans that critics say amount to junk.
A new rule finalized by the Democratic president’s administration will limit these plans to just three months. And the plans can only be renewed for a maximum of four months, instead of up to the three years that were allowed under Biden’s predecessor, Republican Donald Trump .
The Biden administration is also requiring short-term plans to provide consumers with clear explanations of the limits of their benefits.
The White House said the rule is part of Biden’s efforts to reduce costs for consumers, which he has been promoting extensively as he seeks reelection in November.
“The president really believes the American people do not want to be taken for suckers and junk insurance takes them for suckers,” Neera Tanden, Biden’s domestic policy adviser, said during a call the White House arranged to discuss the rule with reporters.
Short-term insurance is meant to be temporary, providing a safety net for consumers as they transition between jobs, for example, or retire before they are eligible for Medicare.
But short-terms plans — critics call them “junk insurance” — too often mislead consumers into thinking they were buying comprehensive health coverage, Tanden said. Consumers would later be surprised to learn when they tried to use the insurance that their benefits were capped or certain coverages were not provided.
Tanden said Trump and other Republican-elected officials undermined the Affordable Care Act by allowing insurance companies to exploit loopholes and sell short-term plans that often leave consumers surprised when confronted by thousands of dollars in medical bills.
The ACA was signed into law in 2010 by President Barack Obama. Biden and his administration have spent this week marking the 14th anniversary of the landmark law's enactment .
Short-term plans were expanded in 2018 during the Trump administration as a cheaper alternative to the Affordable Care Act’s costlier comprehensive insurance. Trump, who had promised to repeal and replace the law, has praised short-term plans as “much less expensive health care at a much lower price.”
In 2020, a divided federal appeals court upheld the Trump administration’s expansion of short-term health insurance plans.
The U.S. Court of Appeals for the District of Columbia Circuit said the Trump administration had the legal authority to increase the duration of the health plans from three to 12 months, with the option of renewing them for 36 months. The plans do not have to cover people with preexisting conditions or provide basic benefits like prescription drugs.


GOP billionaires v democracy: they know what they’re getting into this time
Posted: March 31, 2024 | Last updated: March 31, 2024
GOP billionaires who sought alternatives to Trump are coming back into the fold, and the Trump campaign is hoping to receive some big donations soon. This time around, the donor class ‘cannot make the argument that they don’t know what they’re getting into’, says Sheelah Kolhatkar, staff writer at The New Yorker. Faced with the choice of losing some wealth to preserve democracy, many of the ultra-wealthy seem to be leaning towards their personal short-term financial interests. ‘They put up the walls and protect what they’ve hoarded for themselves.’
More for You
A Federal Judge Made a Rare TV Appearance to Condemn Trump's Comments About Judge Juan Merchan
How to get rid of stink bugs, according to an entomologist
The Best Beach in Every State
Nate Berkus And Jeremiah Brent's Simple Tip For Making Any Home Smell Amazing
4 Chain Restaurants With The Absolute Best Chicken Pot Pie And 4 With The Worst
Netflix Drama: 25 Gripping Series That Will Keep You on the Edge of Your Seat
8 Used Cars That Have Been Recalled To Stay Away From
How to Get Rid of Ants in Your House and Yard
18 Things the Police Cannot Do if You Are Arrested
Manon Fiorot transported to hospital following win in UFC Atlantic City main event
The one food you should eat in every state
States with the Most Foxes in America
Lost cities hidden for thousands of years discovered under forest
The world’s most remote island open to tourists no longer takes five nights to get to
29 Activities to Avoid After 75
Vampire Frenzy: 16 Addictive Series That Suck Viewers into Their World
Can You Eat Potatoes with Sprouts?
17 Most Stolen Items in the US – What You Should Know
12 Japanese Cars That Aren’t Worth the Cost
Forget planks — you only need 10 minutes and a pair of dumbbells to build a stronger core

IMAGES
VIDEO
COMMENTS
Democracy is a system of government in which power is vested in the people and exercised by them directly or through freely elected representatives. The term is derived from the Greek 'demokratia,' which was coined in the 5th century BCE to denote the political systems of some Greek city-states, notably Athens.
People of democracy are more tolerant and accepting of each other's differences. This is very important for any country to be happy and prosper. Get the huge list of more than 500 Essay Topics and Ideas. India: A Democratic Country. India is known to be the largest democracy all over the world. After the rule of the British ended in 1947 ...
Sample Essay on Democracy (250 to 300 words) As Abraham Lincoln once said, "democracy is the government of the people, by the people and for the people.". There is undeniably no doubt that the core of democracies lies in making people the ultimate decision-makers. With time, the simple definition of democracy has evolved to include other ...
Published on January 29, 2021. A democracy is a form of government that empowers the people to exercise political control, limits the power of the head of state, provides for the separation of powers between governmental entities, and ensures the protection of natural rights and civil liberties. In practice, democracy takes many different forms.
Democracy is a system of government in which laws, policies, leadership, and major undertakings of a state or other polity are directly or indirectly decided by the "people," a group historically constituted by only a minority of the population (e.g., all free adult males in ancient Athens or all sufficiently propertied adult males in 19th-century Britain) but generally understood since ...
Liberal democracy, in theory at least, provides a mechanism for some form of rule by proportionate representation, with citizens empowered to bring about change through participation and persuade the powerful to act for the greater good. The cure for the ills of democracy is more democracy. But democracy is a process, not a state.
democracy, Form of government in which supreme power is vested in the people and exercised by them directly or indirectly through a system of representation usually involving periodic free elections.In a direct democracy, the public participates in government directly (as in some ancient Greek city-states, some New England town meetings, and some cantons in modern Switzerland).
Democracy is indeed a set of ideas and principles about freedom, but it also consists of practices and procedures that have been molded through a long, often tortuous history. Democracy is the institutionalization of freedom. Figure 1.1.2 1.1. 2: Civilized debate and due process of law are at the core of democratic practice.
Essay on Democracy. Introduction. Democracy is mainly a Greek word which means people and their rules, here peoples have the to select their own government as per their choice. Greece was the first democratic country in the world. ... Sovereign: In short, being sovereign or sovereignty means the independent authority of a state. The country has ...
Democracy Defined. The term "democracy", as we will use it in this entry, refers very generally to a method of collective decision making characterized by a kind of equality among the participants at an essential stage of the decision-making process. Four aspects of this definition should be noted.
Structure, Types, Countries. Democracy is a type of political structure, doctrine, or system of government under which policies, laws, leadership, as well as the major undertakings of a State are directly or indirectly decided and elected by the people of that particular country. In this short article, we will understand what democracy is, what ...
Democracy (from Ancient Greek: δημοκρατία, romanized : dēmokratía, dēmos 'people' and kratos 'rule') [1] is a system of government in which state power is vested in the people or the general population of a state. [2] Under a minimalist definition of democracy, rulers are elected through competitive elections while more expansive ...
At the Kennedy School, we are striving to produce ideas and insights to meet these great uncertainties and to help make democratic governance successful in the future. In the pages that follow, you can read about the varied ways our faculty members think about facets of democracy and democratic institutions and making democracy better in practice.
Democracy Essay. Democracy is derived from the Greek word demos or people. It is defined as a government in which the supreme power is vested in the people. Democracy is exercised directly by the people; in large societies, it is by the people through their elected agents. In the phrase of President Abraham Lincoln, democracy is the ...
Meet The Creators. Video created by MinuteVideos. Lesson Plan created by Craig Zimmer. There are many forms of government in the world. One of the most common forms is democracy. In this lesson you will see what it takes to make a democracy work and why it gives its people so many freedoms and protections.
Democracy has had diverse meanings. Indeed, the meaning of 'people' is itself socially determined. In ancient Athens, where the idea of democracy arguably was born, the word 'demos' originally meant district or land, and significant social groups were excluded from political participation, notably women, slaves and foreigners.
Abstract. Democracy: A Very Short Introduction is a short account of the history of the doctrine and practice of democracy, from ancient Greece and Rome through the American, French, and Russian revolutions, and of the usages and practices associated with it in the modern world. Considering the diverse range of interpretations of 'democracy', it looks at the controversies about such issues ...
Paragraph on Democracy. Democracy is mainly all about the government of the people, by the people, and for the people. This means the type of government in which all the power resides in the hands of the people. There was a time when the country was ruled by a dictatorship. When talking about dictatorship, the first name that strikes our mind ...
Democracy is a request from a War Board, in the middle of a morning in the middle of a war, wanting to know what democracy is. ... Short stories and poems, plus author interviews, profiles, and ...
With the political situation as dire as many feel it to be, the January 6th, 2025, Project's essays outline a few practical steps that can be taken to strengthen and safeguard democracy in America.
democracy: [noun] a government in which the supreme power is vested in the people and exercised by them directly or indirectly through a system of representation usually involving periodically held free elections.
Essay on Democracy in India Essay 200 words. Democracy is a system of government that allows the citizens to cast a vote and elect a government of their choice. India became a democratic state after its independence from British rule in 1947. It is the largest democratic nation in the world. Democracy in India gives its citizens the right to ...
One other way to think about what people believe will help improve their democracy is to focus on three themes: basic needs that can be addressed, improvements to the system and complete overhauls of the system. We explore these themes in our interactive data essay and quote sorter: "How People in 24 Countries Think Democracy Can Improve."
Abstract. Democracy: A Very Short Introduction shows the distinction between the shared concept of democracy and different conceptions or instances of democracy. The key idea of democracy is that those governed—the demos—have a say in the government.However, until the 19th century, different conceptions of democracy did not extend to democratic society, resulting in the exclusion of many ...
Ms. Taylor and Ms. Hunt-Hendrix are political organizers and the authors of the book "Solidarity: The Past, Present, and Future of a World-Changing Idea." These days, we often hear that ...
Add articles to your saved list and come back to them any time. If you want to understand the pathology of Donald Trump's politics - the violent nihilism that is at the core of his identity in ...
When the Supreme Court ended affirmative action in higher education, it left the college essay as one of few places where race can play a role in admissions decisions. For many students of color ...
Short-term insurance is meant to be temporary, providing a safety net for consumers as they transition between jobs, for example, or retire before they are eligible for Medicare. Share this ...
Faced with the choice of losing some wealth to preserve democracy, many of the ultra-wealthy seem to be leaning towards their personal short-term financial interests. 'They put up the walls and ...