IELTS Mentor "IELTS Preparation & Sample Answer"
- Skip to content
- Jump to main navigation and login

Nav view search
- IELTS Sample
Vocabulary For Academic IELTS Writing Task 1 (part 1)

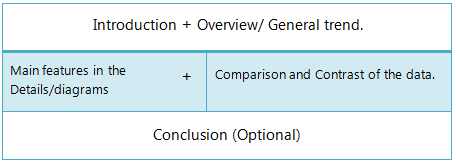
Introduction + Basic/ General Trends + Details Description + Summary (optional) .
Vocabulary for the introduction part:, general statement part:, vocabulary for the general trend part:, 1. in general... 2. in common... 3. generally speaking... 4. overall... 5. it is obvious... 6. as it is observed... 7. as a general trend... 8. as can be seen... 9. as an overall trend/ as overall trend... 10. as it is presented... 11. it can be clearly seen that... 12. at the first glance... 13. it is clear, 14. at the onset... 15. it is clear that... 16. a glance at the graph(s) reveals that..., the structure of the ielts academic writing task 1 (report writing):, introduction:, reporting details:, conclusion:.
Vocabulary to Start the Report Body:
1. as it is presented in the diagram(s)/ graph(s)/ pie chart(s)/ table... 2. as (it is) shown in the illustration... 3. as can be seen in the... 4. as the diagrams suggest... 5. according to the... 6. categorically speaking... 7. getting back to the details... 8. now, turning to the details... 9. the table data clearly shows that... 10. the diagram reveals that... 11. the data suggest that... 12. the graph gives the figure... 13. it is interesting to note that... 14. it is apparently seen that... 15. it is conspicuous that... 16. it is explicitly observed that... 17. it is obvious... 18. it is clear from the data... 19. it is worth noticing that... 20. it is crystal clear/ lucid that... 21. it can be clearly observed that... 22. it could be plainly viewed that... 23. it could be noticed that... 24. we can see that..., vocabulary to show the changes:.
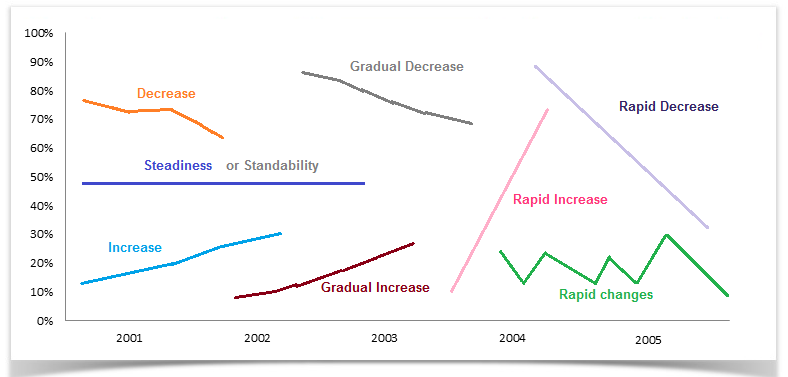
Vocabulary to represent changes in graphs:

Types of Changes/ Differences and Vocabulary to present them:
Dates, months & years related vocabulary and grammar: , percentage, portion and numbers:, words/ phrases of approximation - vocabulary:, what criteria would a band 9 graph response satisfy.

Next »» Graph Writing Vocabulary (Part 2)»
IELTS Materials
- IELTS Bar Graph
- IELTS Line Graph
- IELTS Table Chart
- IELTS Flow Chart
- IELTS Pie Chart
- IELTS Letter Writing
- IELTS Essay
- Academic Reading
Useful Links
- IELTS Secrets
- Band Score Calculator
- Exam Specific Tips
- Useful Websites
- IELTS Preparation Tips
- Academic Reading Tips
- Academic Writing Tips
- GT Writing Tips
- Listening Tips
- Speaking Tips
- IELTS Grammar Review
- IELTS Vocabulary
- IELTS Cue Cards
- IELTS Life Skills
- Letter Types

- Privacy Policy
- Cookie Policy
- Copyright Notice
- HTML Sitemap

IELTS Writing Task 1 Vocabulary (Complete List)
Finding and learning all the IELTS Writing Task 1 vocabulary you need can be exhausting.
But IELTS Academic Writing Task 1 vocabulary is actually the most valuable, as graphs appear in over 75% of Task 1 questions.
In this lesson, I’ll teach you all the words you need to describe any Task 1 graph accurately.

You’ll learn;
- basic vocabulary for graphs
- vocabulary to be more descriptive
- vocabulary for estimates
- vocabulary for predictions
- how examiners assess your vocabulary
Basic IELTS Writing Task 1 Vocabulary
As the British Council explains here , you mustn’t repeat the same words too often if you want a high Lexical Resource score.
This is why you’ll find so many IELTS Writing Task 1 vocabulary synonyms to describe the images below.
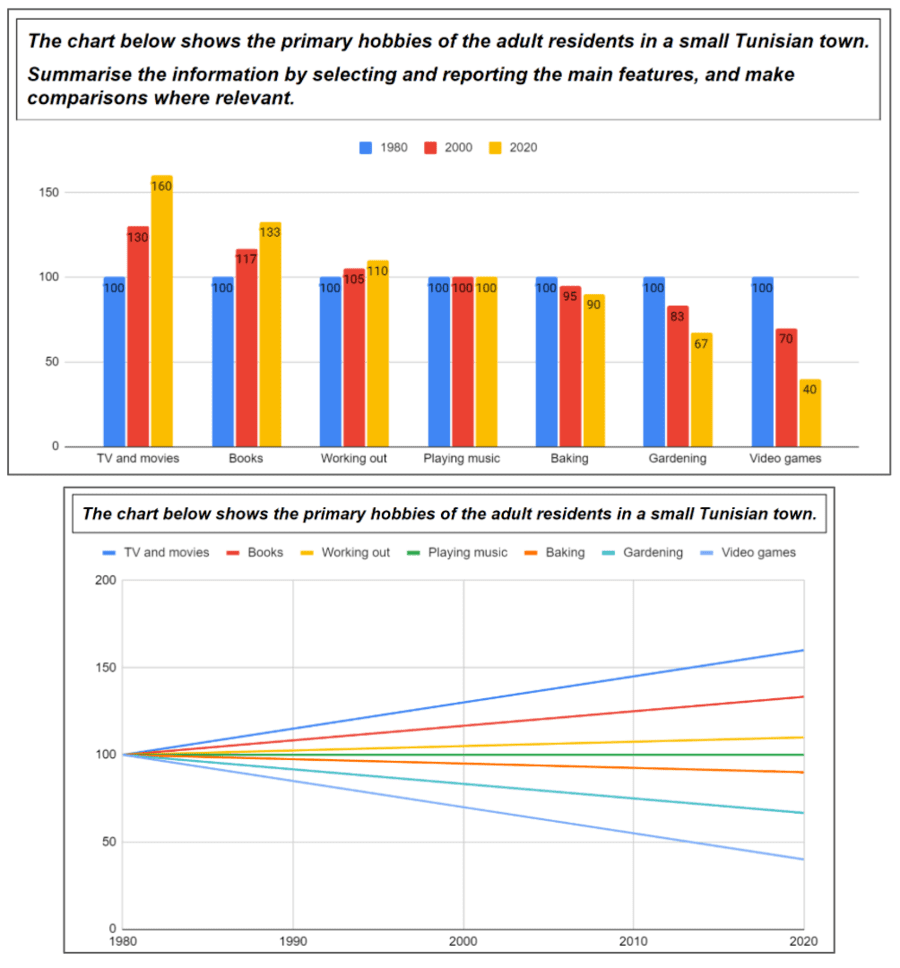
Increasing Categories
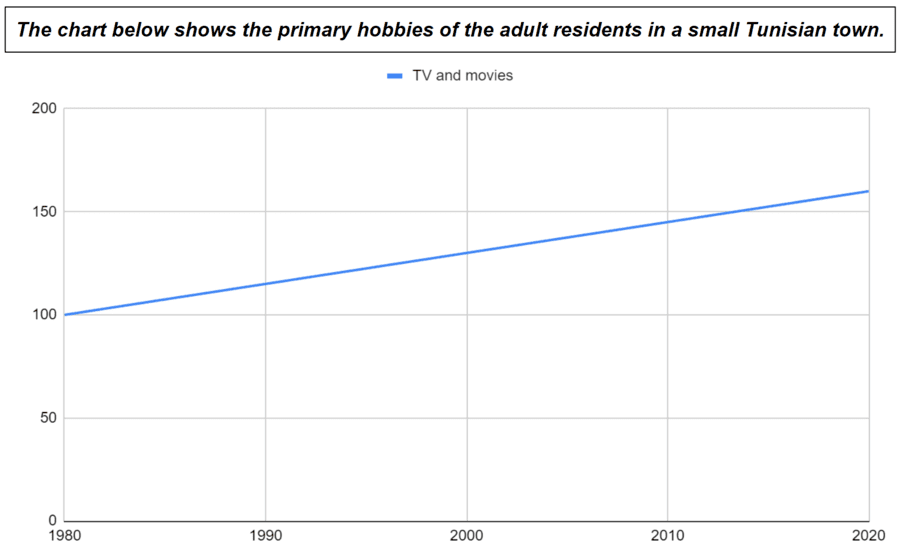
- The number of people watching TV and movies increased from 1980 to 2020.
- The number of people watching TV and movies grew from 1980 to 2020.
- The number of people watching TV and movies rose from 1980 to 2020.
- The number of people watching TV and movies climbed from 1980 to 2020.
- The number of people watching TV and movies went up from 1980 to 2020.
- From 1980 to 2020, there was an increase in the number of people watching TV and movies.
- From 1980 to 2020, there was a growth in the number of people watching TV and movies.
- From 1980 to 2020, there was a rise in the number of people watching TV and movies.
Decreasing Categories
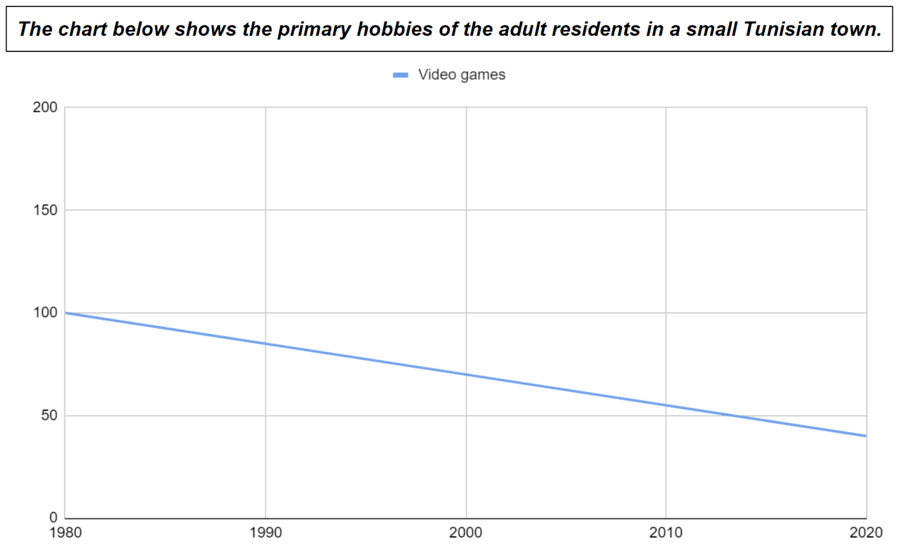
- The number of people playing video games decreased from 1980 to 2020.
- The number of people playing video games declined from 1980 to 2020.
- The number of people playing video games dropped from 1980 to 2020.
- The number of people playing video games fell from 1980 to 2020.
- The number of people playing video games went down from 1980 to 2020.
- From 1980 to 2020, there was a decrease in the number of people playing video games.
- From 1980 to 2020, there was a decline in the number of people playing video games.
- From 1980 to 2020, there was a drop in the number of people playing video games.
- From 1980 to 2020, there was a fall in the number of people playing video games.
Stable Categories
- The number of people playing music stayed at the same level from 1980 to 2020.
- The number of people playing music was constant from 1980 to 2020.
- The number of people playing music remained stable from 1980 to 2020.
- The number of people playing music remained unchanged from 1980 to 2020.
Fluctuating Categories

- The number of people studying fluctuated from 1980 to 2020.
- From 1980 to 2020, there were fluctuations in the number of people studying.
As the British Council explains, you must learn all of this vocabulary before your test if you need a high score.
Descriptive IELTS Writing Task 1 Vocabulary
Now that you know the basics, you need to learn adverbs and adjectives that that will allow you to be more descriptive.
But first, we must understand the difference between rate and amount .
Rate vs Amount
To help you understand, let’s look at these two images.

Even though both hills are 1 km high, we can see that they climb upwards at different rates .
The rate is how steep the hills are, and the amount is the 1 km climb.
You can see how this applies to a Task 1 question in the image below.

Don’t worry!
You don’t need to know the exact angle (∠) to describe the rate.
You’ll just describe the rate in a general way, using the adverbs and adjectives below.
Adverbs of Rate
Adjectives of Rate
Adverbs of amount
- dramatically
- substantially
- significantly
- considerably
Adjectives of amount
- substantial
- significant
- considerable
So why do we need to separate rate from amount ?
Because adverbs and adjectives of rate can only be used with some graphs.
We can only use them when we see the angle (∠) of the increase or decrease.
For example, the way the information is presented in the bar graph and line graph below allows us to see the angle (∠) of increase or decrease for each category.
However, the pie charts and table only show numbers, so no angles are visible.
Therefore, we can only use the adverbs and adjectives of rate with the bar graph and the line graph.
On the other hand, we can see the amount of change in all four questions above.
That means we can use adverbs and adjectives of amount with all chart types.
A side note that you might find interesting is that all four graphs above represent the same information.
Examples of Descriptive IELTS Writing Task 1 Vocabulary
Even though there are several suitable adverbs and adjectives in each of the descriptions below, we never use more than one.
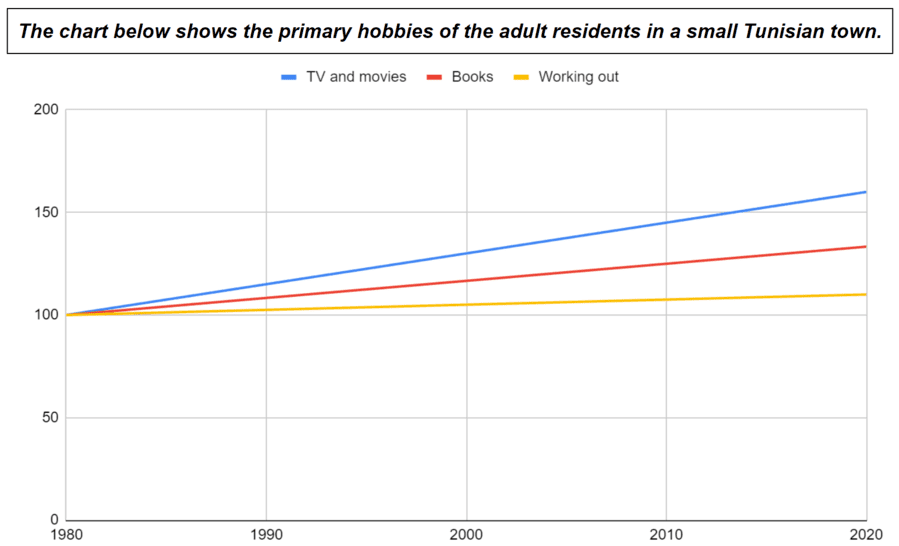
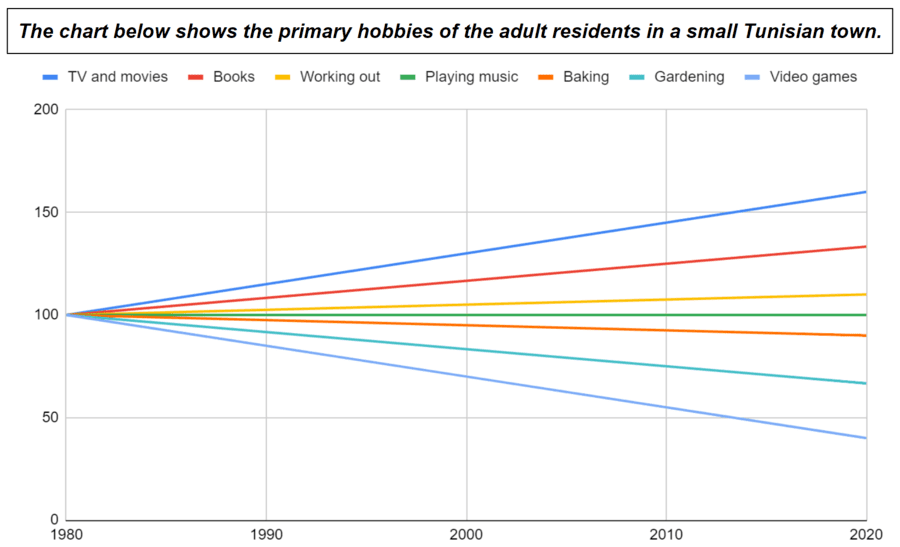
- The number of people watching TV and movies increased steeply/rapidly/dramatically/substantially/significantly/considerably from 1980 to 2020.
- From 1980 to 2020, there was a steep/rapid/dramatic/substantial/significant/considerable increase in the number of people watching TV and movies .
- The number of people reading books increased modestly/moderately from 1980 to 2020.
- From 1980 to 2020, there was a modest/moderate increase in the number of people reading books .
- The number of people working out increased gradually/slowly/slightly/marginally from 1980 to 2020.
- From 1980 to 2020, there was a gradual/slow/slight/marginal increase in the number of people working out .
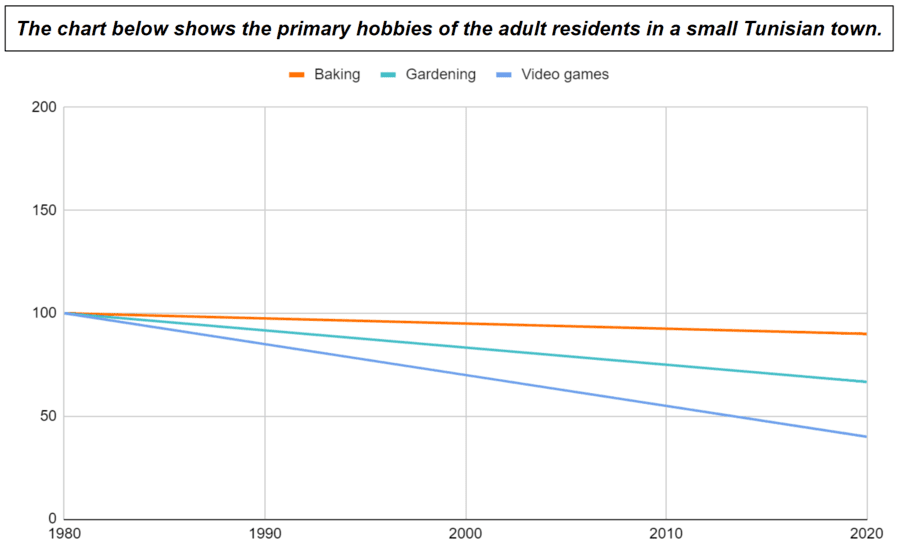
- The number of people baking decreased gradually/slowly/slightly/marginally from 1980 to 2020.
- From 1980 to 2020, there was a gradual/slow/slight/marginal decrease in the number of people baking .
- The number of people gardening decreased modestly/moderately from 1980 to 2020.
- From 1980 to 2020, there was a modest/moderate decrease in the number of people gardening .
- The number of people playing video games decreased steeply/rapidly/dramatically/substantially/significantly/considerably from 1980 to 2020.
- From 1980 to 2020, there was a steep/rapid/dramatic/substantial/significant/considerable decrease in the number of people playing video games .
Big or No Rate Changes in Categories
In the next set, we will look at adverbs and adjectives you can use when there’s a big change in the rate (suddenly/sharply/sudden/sharp) and adverbs and adjectives for when there is no change in the rate (steadily/consistently/steady/consistent).
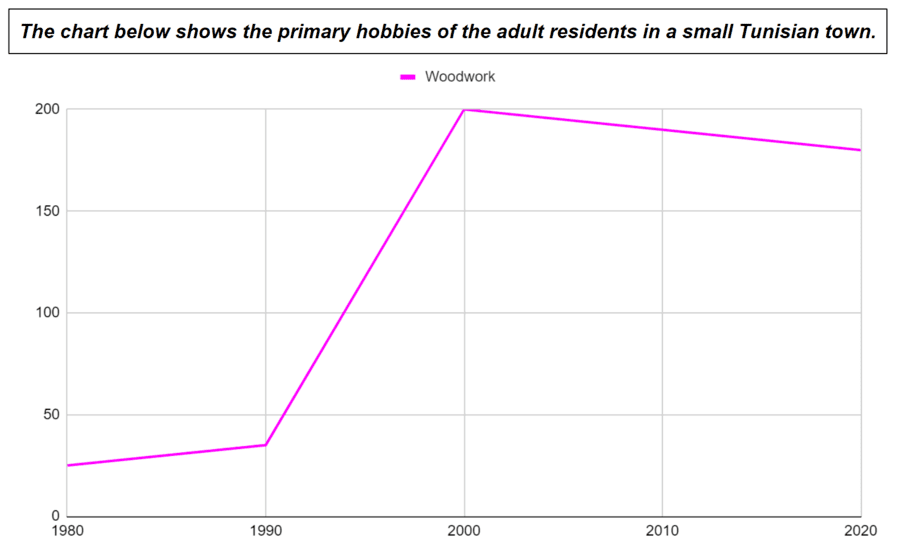
- The number of people doing woodwork increased by about 10 from 1980 to 1990 and suddenly/sharply increased to 200 people in 2000. After that, it steadily/consistently decreased until 2020.
- From 1980 to 1990, there was an increase of about 10 in the number of people doing woodwork, and there was a sudden/sharp increase to 200 people in 2000. After that, there was a steady/consistent decrease.
Stable Trends & Fluctuations
And now, adverbs and adjectives to describe stable trends and fluctuations.
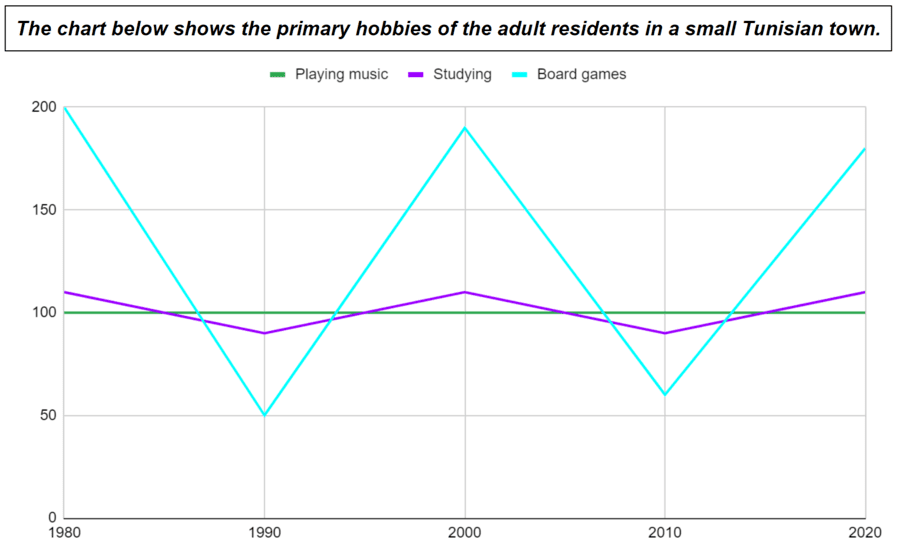
- The number of people playing music remained completely stable from 1980 to 2020.
- The number of people studying remained relatively stable from 1980 to 2020.
- The number of people studying fluctuated slightly from 1980 to 2020.
- From 1980 to 2020, there were slight fluctuations in the number of people studying .
- The number of people playing board games fluctuated wildly/considerably/substantially from 1980 to 2020.
- From 1980 to 2020, there were wild/considerable/substantial fluctuations in the number of people playing board games .
IELTS Writing Task 1 Vocabulary for Estimates
Sometimes, the questions will show you exact numbers, like in the table below.
For questions like this, just copy the number into your essay.

However, some questions don’t show the numbers like this, and you need to use the y-axis to estimate, such as in the line graph below.
For graphs like this, you can never be 100% sure what the number is.
To make sure we are correct, we use approximations.
You will find examples of these below.
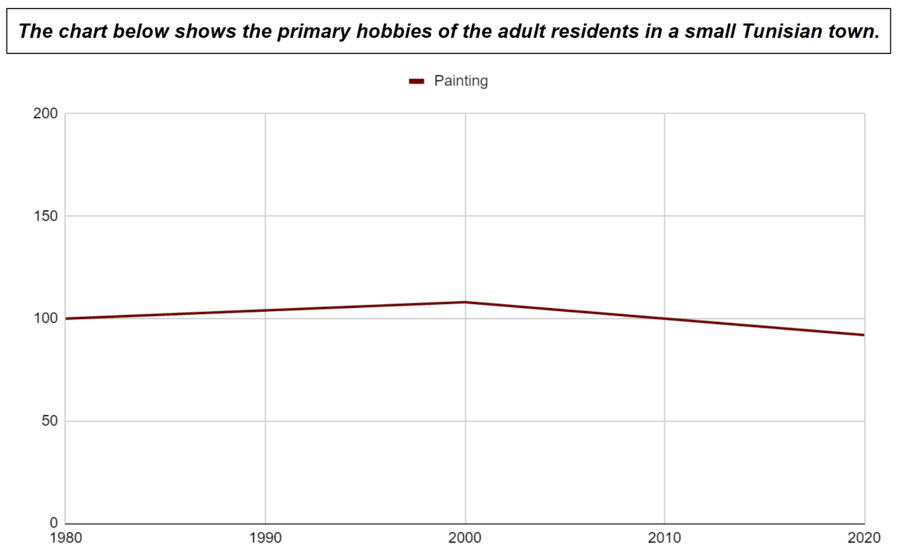
- The number of people painting in 1980 was approximately/roughly/about/around 100.
- The number of people painting in 2000 was approximately/roughly/about/around/just above/just over 100.
- The number of people painting in 2020 was approximately/roughly/about/around/almost/just below/just under/nearly 100.
You can see that some of these words were only used when ‘ painting ‘ was definitely above 100, some when ‘ painting ‘ was definitely below 100, and others can be used in all situations.
- Definitely above : just above, just over.
- Definitely below : almost, just below, just under, nearly .
- Above or below : approximately, roughly, about, around.
IELTS Writing Task 1 Vocabulary for Predictions
So far in this lesson, all of the data we looked at was in the past.
However, there are times when the question will contain future predictions, like in the chart below.
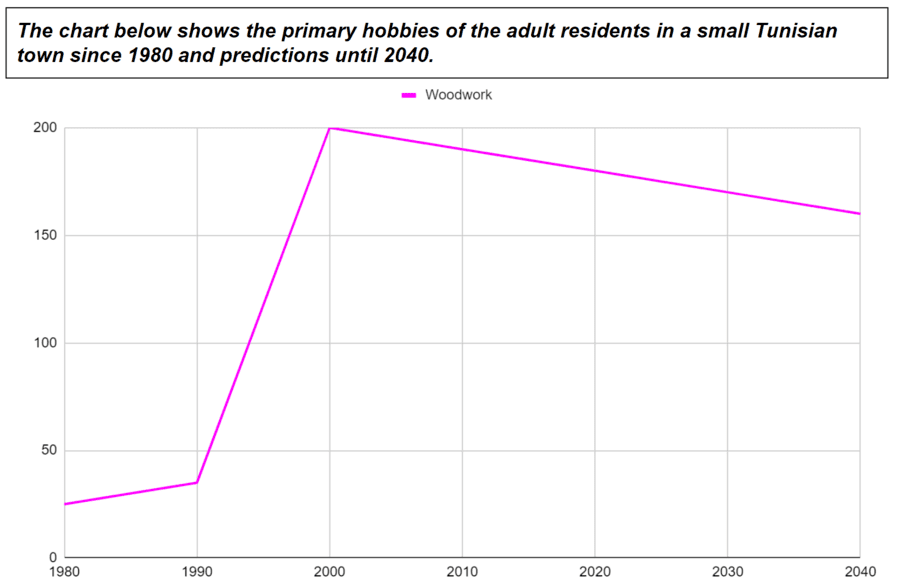
As there’s no guarantee that these predictions will come true, we cannot use grammar structures like ‘will’ or ‘going to’ to describe them.
Instead, we must use phrases like these;
- is expected to
- is forecast to
- is predicted to
- is projected to
- is shown to
Here’s an example;
- The number of people doing woodwork increased by about 10 from 1980 to 1990 and suddenly increased to 200 people in 2000. After that, it has steadily decreased, and this trend is predicted to continue until 2040.
How Examiners Assess Your IELTS Writing Task 1 Vocabulary
The examiner will assess your vocabulary based on the Lexical Resource band descriptor, which you can find here .
Here are the main things you need to know.
Clear Communication
Communicating clearly is the most essential aspect of your Lexical Resource band score.
To communicate clearly, every word in your answer needs to be used accurately.
But, you can only use a word accurately if you fully understand it.

This is why there are images and complete sentences to explain all the IELTS Writing Task 1 vocabulary in this lesson.
To help you improve your accuracy further, you will need to read texts that contain this type of language.
Good sources are the business sections of newspapers. Here are some examples;
- The Guardian
- Yahoo Finance
Accurate Spelling
If you make lots of spelling mistakes, you won’t get a high Lexical Resource score.
Some people are naturally good at spelling, and others need to work hard to remember.
If you often misspell words, please make sure to learn the correct spelling of all the IELTS Writing Task 1 vocabulary in this lesson or else it won’t improve your score.

Accurate collocations
Collocations are words that are often used together.
For example, common collocations for the word ‘ increase’ are;
- increase to
- increase from
- increase by
- increase until

This is why it’s crucial to learn phrases or whole sentences instead of learning individual words.
For example, if you only learn the word ‘ increase ‘, you won’t know the correct collocation for your IELTS test.
But if you learn the words ‘ it increased from ‘, you will use the correct collocation.
A range of topic-specific vocabulary
The great thing about Academic IELTS Task 1 is that there will probably be a chart in your question.
That means that all the IELTS Writing Task 1 vocabulary from this lesson will give you the topic-specific vocabulary you need.
Just be aware that it’s okay to use the same word two or three times in your essay.
So if the word ‘ increase ‘ is in your essay two or three times, that won’t bring down your score.
But you can’t use the word ‘ increase ‘ every single time, and that’s why you need to learn all the different ways to describe this type of trend.
Another thing you should be aware of is that the examiner will count the noun and the verb forms of a word as two different words.
For example, in the sentence below, the word ‘ increase’ is used as a noun and as a verb, so the examiner will recognize that these are different words.
There was an increase (noun) of about 10 people doing woodwork between 1980 and 1990, and it suddenly increased (verb) to roughly 200 people in 2000.
However, the IELTS Writing Task 1 vocabulary in this lesson is not the only vocabulary you’ll need for your answer.
You will also need vocabulary based on the categories in the question.
For example, one of the categories in today’s lesson was ‘ video games ‘, so you needed to know that ‘ playing video games ‘ was the appropriate term to use in the answer.
Make sure to continue improving your range of vocabulary with the strategy to improve Lexical Resource .
With all of the vocabulary you’ve learned in this lesson, your life will be much easier on test day. Make sure that you also learn the vocabulary you need for Task 1 map and Task 1 process questions.
If you need to revise any of the vocabulary, this video lesson will be helpful for you.
Next, make sure you understand the other IELTS band scores as well, so complete the Task Achievement lesson , the Coherence and Cohesion lesson and the grammar lesson for Academic IELTS Task 1.
The biggest hurdle for most IELTS candidates in Task 1 is writing effective overviews so you’ll need to complete my overview lesson as well and then follow my 5-Step Plan for writing your essay.
I also wanted to share two activities to help you practice IELTS Writing Task 1 vocabulary on the British Council and Cambridge websites.
Privacy Overview

IELTS Writing Task 1 Vocabulary – The Essential words for IELTS test-takers
In the realm of IELTS Writing Task 1 , a diverse and rich vocabulary is an indispensable tool that elevates the effectiveness and precision of your response. Through adept use of vocabulary, you can provide clear and concise introductions, overviews, and descriptions of the given data, facilitating a seamless progression in your response.
In this article, we provide you with an IELTS writing task 1 vocabulary list that encompasses introductions, overviews, and descriptions tailored to specific visual representations, allowing you to confidently convey information and establish a well-structured narrative. By employing this vocabulary effectively, you can not only communicate your understanding of the data but also exhibit the linguistic finesse required to excel in the IELTS Writing Task 1.

1. What is IELTS writing task 1?
IELTS Writing Task 1 is one of the two writing tasks in the International English Language Testing System (IELTS) exam, which is used to assess the English language proficiency of non-native English speakers. The IELTS exam is commonly required for study, work, or immigration purposes in English-speaking countries.
In IELTS Writing Task 1, test-takers are presented with visual information in the form of graphs, charts, diagrams, maps, or tables. The task requires candidates to write a descriptive report summarizing the main features of the visual information, identifying trends, and making comparisons if applicable. The purpose of this task is to assess the candidate’s ability to accurately and effectively convey information from visual data in written English.
Test-takers are expected to follow specific instructions , such as describing the data, highlighting significant points, and presenting the information in a coherent and organized manner. The response should be written in a formal and academic style, and the length of the response usually needs to be at least 150 words.
2. What is the importance of vocabulary in IELTS writing task 1?
Vocabulary plays a crucial role in IELTS Writing Task 1 for several reasons:
2.1. Accuracy and Clarity
Using a rich and precise vocabulary allows you to accurately convey the details and nuances of the visual information presented in the task. Clear and accurate descriptions demonstrate your ability to understand and interpret the data correctly.
2.2. Variety of Expressions
A strong vocabulary enables you to avoid repetition and express ideas in a more diverse and sophisticated manner. This variety enhances the overall quality of your response and helps you avoid using the same words or phrases repeatedly.
2.3. Coherence and Cohesion
Proper use of vocabulary helps in creating well-structured sentences and paragraphs, leading to a coherent and cohesive response. This makes your writing easier to follow and understand for the reader, including the examiner.
2.4. Range of Synonyms
Sometimes, the same concept can be expressed using different words or phrases. A broad vocabulary allows you to use synonyms effectively, making your writing more engaging and demonstrating your language proficiency.
2.5. Higher Band Score
IELTS examiners assess vocabulary usage to determine the depth and range of your language skills. Demonstrating a strong vocabulary can contribute to a higher band score in the IELTS Writing Task 1 assessment criteria.
2.6. Precision
Certain visual information requires precise vocabulary to accurately describe trends, comparisons, and other details. A strong vocabulary helps you avoid vague or general language, ensuring your response is precise and accurate.
2.7. Lexical Resource
IELTS examiners evaluate your “lexical resource,” which refers to your ability to use a wide range of vocabulary effectively. A diverse vocabulary demonstrates your ability to express yourself in various contexts and on different topics.
2.8. Improve Overall Impression
Well-chosen vocabulary can make your writing more engaging, polished, and professional. This can contribute to a positive overall impression, even if there are minor errors in grammar or structure.

3. IELTS Writing task 1 vocabulary
3.1. ielts writing task 1 vocabulary – introduction part.
In the introduction part of IELTS Writing Task 1, you aim to provide a concise overview of the visual information you will be describing. This introduction sets the context for your response and should include key details such as the type of graph or chart, the time frame or location if applicable, and a brief mention of the main trends or observations you will discuss in the subsequent paragraphs. Here is a list of IELTS Writing task 1 vocabulary and phrases that can be useful for the introduction part:
- The graph/chart/table/diagram presents: This phrase is commonly used to introduce the type of visual information you are describing.
- The given graph/chart/table illustrates: Similar to the first phrase, this signals the type of visual representation you will be discussing.
- Depicting: This word can be used as a synonym for “illustrating” or “presenting.”
- Data/Information is taken from: Use this to mention the source of the data, if provided.
- Over the period of: When discussing a timeframe, this phrase is helpful.
- Between [starting year] and [ending year]: Useful for indicating a specific time range.
- During the [specific time frame]: Another way to highlight the time period under consideration.
- In terms of [location]: When discussing data related to a particular place or location.
3.2. IELTS Writing task 1 vocabulary – Overview
In the overview part of IELTS Writing Task 1, you’re expected to provide a summary of the main trends, significant features, and key comparisons evident in the visual data. This summary should give the reader a clear understanding of the overall picture without delving into too much detail. Here is a list of IELTS Writing task 1 vocabulary and phrases that can be helpful for the overview section:
- Overall/In general: These words can be used to introduce your summary of the main trends.
- In summary/To sum up: These phrases signal that you are about to provide a concise overview.
- The most notable feature/trend is: Use this to highlight the most significant observation.
- The most striking aspect of the data is: Similar to the previous phrase, emphasizing a key point.
- It is clear from the data that: Indicating a strong observation or trend.
- Significant changes/developments include: Introducing important shifts in the data.
- The data reveals a pattern of: Indicating a recurring trend.
- A common trend across the data is: Highlighting something that appears consistently.
- The data demonstrates a clear correlation between: Showing a connection between two factors.
- There is a distinct difference between: For highlighting contrasts or variations.
- Compared to/In contrast to: Useful for discussing differences between data points.
- An interesting point to note is: Drawing attention to an intriguing aspect.
- While [X] showed [trend], [Y] exhibited [trend]: To present a comparison between two or more data sets.
- The data is characterized by: Describing the nature of the trends or patterns.
- It is worth mentioning that: Highlighting a noteworthy detail.
3.3. IELTS Writing task 1 vocabulary – Pie chart
When describing a pie chart in IELTS Writing Task 1, it’s important to use appropriate vocabulary and phrases to accurately convey the data and trends presented. Here’s a list of IELTS Writing task 1 vocabulary and phrases that can be helpful when describing a pie chart:
- The pie chart illustrates: Begin by introducing the type of chart and its purpose.
- The chart provides a breakdown of: Describe the purpose of the pie chart, which is to show the distribution of a whole.
- Divided into segments/sectors: Describe how the chart is organized.
- The data is represented in the form of a circle: Explain the basic structure of a pie chart.
- The segments represent different categories: Explain what each segment represents.
- The chart is divided into [number] main sections: Describe the number of segments.
- The largest segment/sector is: Start with the most prominent category.
- The smallest portion is: Mention the least significant category.
- The chart is dominated by: Use this phrase to indicate the category with the highest percentage.
- A significant proportion is allocated to: Describe a category that holds substantial value.
- The chart shows a clear hierarchy of: Explain the arrangement of segments based on size.
- The majority/plurality of the chart is taken up by: Indicate the most prevailing category.
- The chart presents a range of proportions for: Explain the distribution of values.
- The [category] accounts for [percentage]%: Provide specific percentage values.
- A substantial portion of the chart is dedicated to: Describe a category with a notable share.
- A small fraction/percentage is attributed to: Discuss a less significant category.
- Comparing the segments, it is evident that: Begin discussing comparisons between segments.
- The [category A] segment is [percentage] points larger/smaller than [category B]: Present a specific comparison between two categories.
- There is a noticeable contrast between : Highlight differences between categories.
- The differences in segment sizes are quite pronounced: Describe clear disparities.
3.4. IELTS Writing task 1 vocabulary – Line graph
When describing a line graph in IELTS Writing Task 1, you should use appropriate vocabulary and phrases to effectively convey the trends, fluctuations, and relationships shown in the graph. Here’s a list of IELTS Writing task 1 vocabulary and phrases that can be useful when describing a line graph:
- The line graph depicts : Begin by introducing the type of graph and its purpose.
- The graph provides a visual representation of : Describe the graph’s purpose, which is to show trends over time.
- The data is plotted on the graph over a period of : Mention the time frame covered by the graph.
- The graph displays changes in [variable] over time: Specify the variable being depicted.
- The x-axis represents [time unit], while the y-axis represents [variable]: Explain the axes of the graph.
- There are [number] lines on the graph, each representing a different [category]: Describe the number of lines and their purpose.
- The lines on the graph illustrate the trends for: Describe what each line represents.
- The graph charts the progression/regression of : Describe the overall movement shown in the graph.
- The lines on the graph fluctuate: Describe the variations in the lines.
- The graph documents the changes in [variable] over the [time period]: Explain the purpose of the graph concisely.
- The graph illustrates the correlation between [variable A] and [variable B]: Discuss the relationship between variables.
- Over the course of [time period], [variable] experienced fluctuations: Discuss the time-based variations.
- The [variable] remained relatively stable/uniform throughout [time period]: Discuss stability or lack of significant change.
- There was a gradual increase/decrease in [variable] over [time period]: Describe the rate of change.
- [Variable A] showed a sharp rise/fall between [time points]: Discuss sudden changes.
- A significant upturn/downturn is observed in the graph : Discuss a noticeable change.
- The lines intersected at [point] indicating: Discuss points of intersection or convergence.
- The graph highlights a consistent upward/downward trend: Describe the overall direction of the lines.
- The lines started to converge/diverge towards the end of the period: Discuss lines coming together or moving apart.
- [Variable A] exhibited a similar pattern to [variable B] over [time period]: Compare patterns between lines.
3.5. IELTS Writing task 1 vocabulary – Bar chart
When describing a bar chart in IELTS Writing Task 1, it’s important to use the right vocabulary and phrases to accurately communicate the data and comparisons presented. Here’s a list of IELTS Writing task 1 vocabulary and phrases that can be helpful when describing a bar chart:
- The bar chart illustrates: Start by introducing the type of chart and its purpose.
- The chart provides a breakdown of: Describe the chart’s purpose, which is to show comparisons between categories.
- The data is presented using vertical/horizontal bars: Explain the basic structure of the bar chart.
- The x-axis/y-axis represents [categories]: Describe the axes and what they represent.
- The bars represent different [categories]: Explain the purpose of the bars.
- The chart is divided into [number] main categories: Describe the number of categories.
- The longest/tallest bar represents: Start by discussing the most prominent category.
- The shortest/smallest bar is: Mention the least significant category.
- The chart is dominated by: Indicate the category with the highest value.
- A significant portion is allocated to: Describe a category with substantial value.
- The chart shows a clear hierarchy of: Explain the arrangement of categories based on size.
- The majority/plurality of the chart is occupied by: Discuss the most prevalent category.
- The chart presents a range of values for: Explain the distribution of values.
- The [category] bar accounts for [percentage]%: Provide specific percentage values.
- Comparing the bars, it is evident that: Begin discussing comparisons between categories.
- The [category A] bar is [height] units taller/shorter than the [category B] bar: Present a specific comparison.
- There is a noticeable contrast between: Highlight differences between categories.
- The differences in bar heights are quite pronounced: Describe clear disparities.
3.6. IELTS Writing task 1 vocabulary- Process
When describing a process in IELTS Writing Task 1, you need to use appropriate vocabulary and phrases to effectively explain the sequence of steps or stages. Here’s a list of IELTS Writing task 1 vocabulary and phrases that can be helpful when describing a process:
- The process diagram illustrates: Start by introducing the type of diagram and its purpose.
- The diagram depicts the steps involved in: Describe the diagram’s purpose, which is to show a sequence of actions.
- The diagram shows the various stages of: Explain what the diagram illustrates.
- The process is divided into [number] main steps/stages: Describe the number of stages.
- The diagram consists of [number] phases: Describe the number of phases.
- The first step/initial stage involves: Start by describing the beginning.
- The process begins with: Introduce the starting point.
- At the outset: Describe the starting stage.
- Following this/Next/After that: Indicate the sequence of steps.
- Subsequently: Indicate the order of actions.
- In the next stage/step: Continue describing the sequence.
- Moving on to the next phase: Transition to the following phase.
- The subsequent step involves: Continue the explanation.
- In the succeeding stages: Describe the steps that come after.
- The process then advances to: Move forward in the explanation.
- The subsequent steps are repeated: Discuss repetitions in the process.
- After several iterations: Describe repeated stages.
- This is followed by: Transition to the next action.
- At this point/At this stage: Discuss the current step.
- The final step/last stage concludes the process: Describe the end of the process.
3.7. IELTS Writing task 1 vocabulary – Diagram
When describing a diagram in IELTS Writing Task 1, you need to use appropriate vocabulary and phrases to effectively explain the various components, elements, and relationships shown in the diagram. Here’s a list of IELTS Writing task 1 vocabulary and phrases that can be helpful when describing a diagram:
- The diagram illustrates: Begin by introducing the type of diagram and its purpose.
- The diagram provides a visual representation of: Describe the diagram’s purpose and what it depicts.
- The diagram depicts the various components of: Explain what the diagram is showing.
- The different parts of the diagram are labeled as: Discuss labeling and identification.
- The diagram is divided into [number] main sections: Describe the number of sections or parts.
- The diagram consists of [number] key elements/components: Mention the number of elements.
- The diagram is organized into [number] main categories: Describe the organization of the diagram.
- The central element is: Start by discussing the central component.
- The diagram is centered around: Discuss the central focus of the diagram.
- The main components are connected by: Describe the connections or relationships.
- The elements are linked together in a [specific] manner: Discuss the nature of the connections.
- The diagram is labeled with [labels/annotations] indicating: Mention the labels or annotations.
- Starting from the [left/right/top/bottom]: Begin describing the diagram’s layout.
- The [element/component] is positioned [relative position]: Describe the placement of elements.
- The diagram presents a sequence of [steps/events]: Explain the sequence depicted.
- The [elements/components] are arranged in [specific] order: Discuss the order or arrangement.
- Each [element/component] is associated with: Describe the associations.
- The diagram indicates [relationship/interaction]: Explain the relationships between elements.
- Moving from [element] to [element]: Describe the movement or transition.
- The diagram portrays a [process/system]: Discuss the nature of the portrayal.
In summary, the provided list of IELTS Writing Task 1 vocabulary equips you with essential language tools to articulate accurate and comprehensive descriptions of various visual data. Mastering these terms empowers you to craft well-structured and coherent responses, showcasing your ability to effectively convey information and meet the requirements of the task. With this arsenal of vocabulary, you’re better poised to excel in presenting data concisely and proficiently in the IELTS Writing Task 1. In order to master the IELTS test, you can practice on the IELTS practice test !
- Ebooks & Courses
- Practice Tests
Academic IELTS Task 1 – Vocabulary for Task 1 Essays –
As with all parts of the IELTS exam, Academic IELTS Task 1 is assessed on four criteria. We looked at the first two, Task Achievement and Cohesion and Coherence, on the Task 1 overview page ( IELTS Academic Writing Task 1 ) and it’s now time to focus on Vocabulary.
This lesson includes:
1) Understanding the marking criteria
2) Key vocabulary for Academic IELTS Task 1:
- Adjectives & adverbs
- Verbs & nouns
Collocations
- Other useful phrases
- Percentages, proportions & approximations
3) A word list PDF to download.
Understanding the Marking Criteria
Before we start looking at the specific vocabulary you will need for your IELTS Task 1 essay, it’s essential that you understand how vocabulary is assessed. Vocabulary, also called Lexical Resource, carries 25% of the marks so, you need to know what the examiner is looking for.
We’re going to focus on Bands 6 - 8 as these are the levels most students are aiming for. Here are the official marking criteria for Vocabulary. Don’t worry if you don’t fully understand them. I explain the main points below. If you follow my guidance in this lesson, you’ll be able to meet these criteria and get a good score for IELTS Task 1.
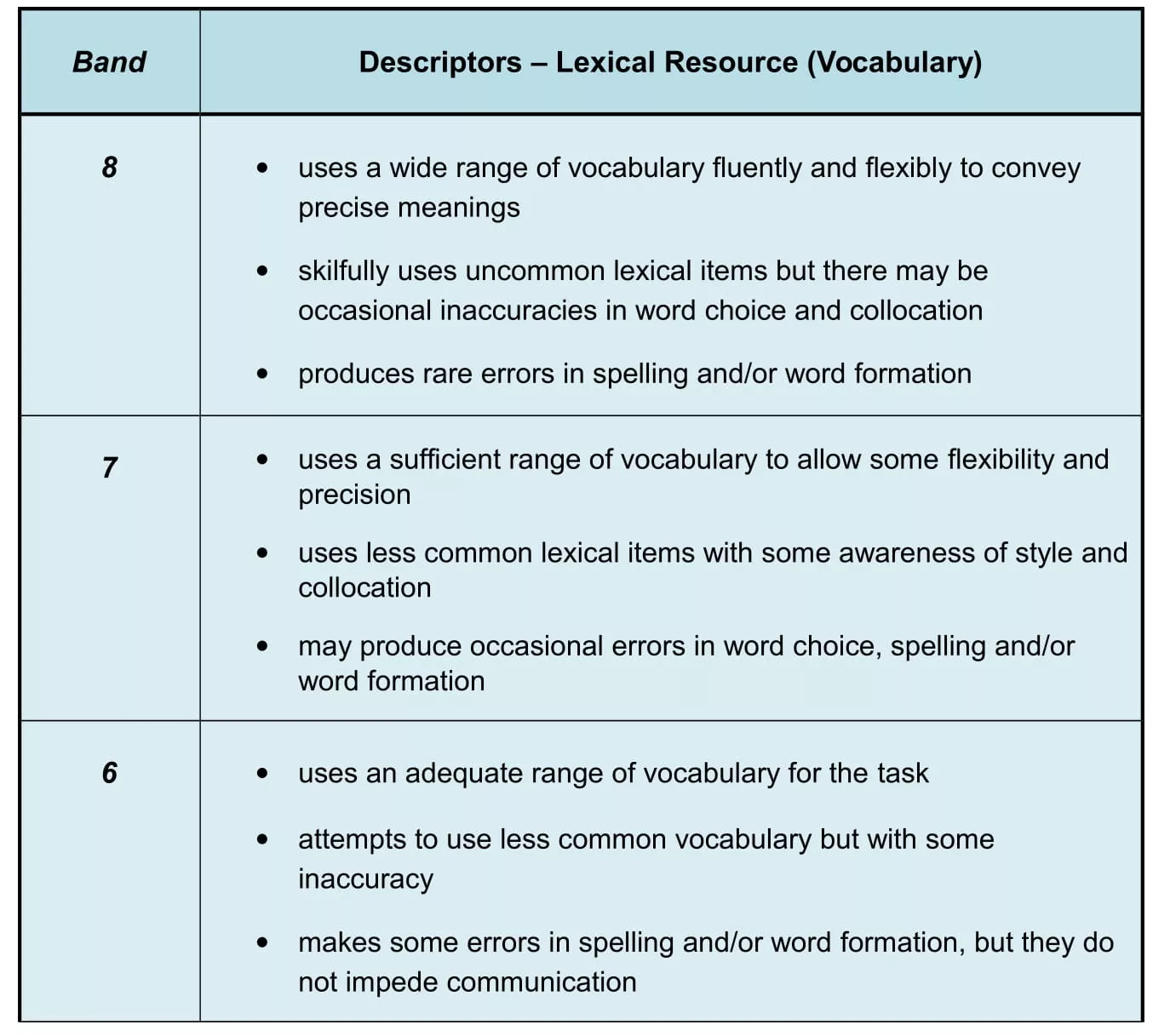
You can see a full table of all the band level marking criteria for Writing IELTS Task 1 by clicking this link – Task 1 Marking Criteria .
The marking criteria for vocabulary can be summed up in a single sentence:
- Vocabulary (Lexical Resource) is the ability to use a range of appropriate vocabulary and to use it correctly.
Of course, there’s more to it than that and there are three key things you need to do to get a high score for vocabulary. Correct spelling is obviously essential so I won’t say any more about this.
1) Use appropriate vocabulary
In your Task 1 essay, you will be describing data and this requires some very specific vocabulary that you might only use in this part of the exam. This is what the marking criteria are referring to when they mention ‘precise meanings’ and ‘less common lexical items/vocabulary’.
You’ll find lists of useful Task 1 specific words below.
2) Use vocabulary flexibly
You need to have a wide enough range of vocabulary that you can say the same thing in more than one way, that is, paraphrase. This is what the marking criteria mean by the phrase ‘allow some flexibility and precision’. You do this by using synonyms.
Paraphrasing also involves using different sentence structures, which I cover in the lesson on Grammar for Academic IELTS Task 1 .
3) Use collocations correctly
The marking criteria specifically mention the correct use of collocations as something you'll be assessed on.
A collocation is a combination of two or more words that sound correct to a native speaker when used together. The word combination often doesn’t work if you try to replace the first word with a synonym. For example, we say,
- heavy rain but not weighty rain
- fast food not quick food
- keen interest not eager interest
My advice here is to only use collocations you are 100% sure are correct. These are something to focus on when learning vocabulary and I include some Task 1 related examples in the word lists we’ll now focus on.
Key Vocabulary for Academic IELTS Task 1
Adjective & adverbs.
In your IELTS Task 1 essay, you are required to describe what you see in a chart, graph, table, map or a diagram, most especially, to record changes in the data. To do this, you will use describing words, that is, adjectives and adverbs.
- Adjectives are words that describe or modify nouns or pronouns.
- Adverbs are words that describe or modify verbs or adjectives.
Adverbs can generally be formed by adding ‘ly’ to the end of the adjective.
Here is a table of adjectives and adverbs relevant to Task 1 questions. Don’t try to learn them all. This is only a very short essay (min. 150 words) so you won’t be able to include much detail.
Learn 2 or 3 words for large changes and 2 or 3 for small or moderate changes .
Large Changes:
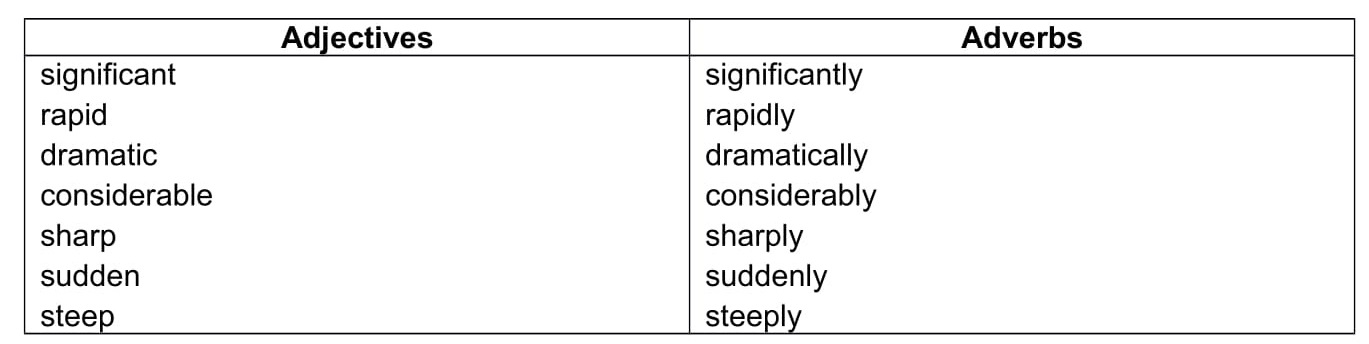
Small or Moderate Changes:
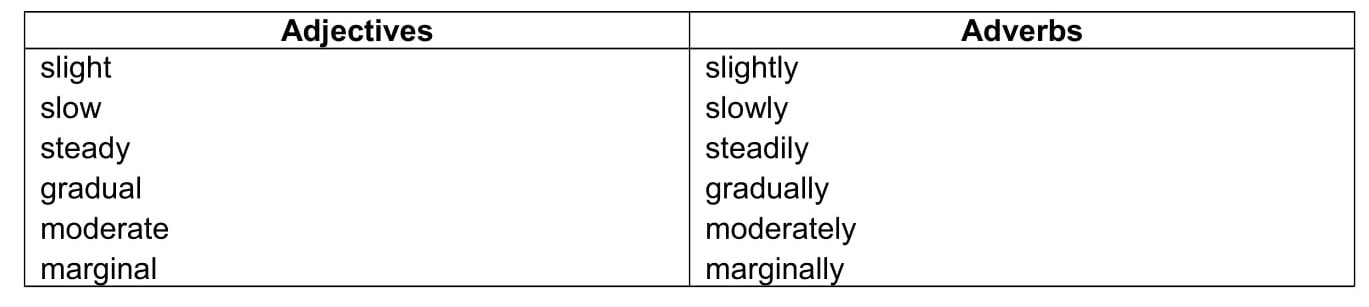
Verbs & Nouns
You will also need some specific verbs and nouns.
- Verbs are words that describe an action or state.
- Nouns are words that refer to a thing, a place, a person or a quality.
Many words have a verb form and a noun form as can be seen in the tables below.
For your essay, you should learn 2 or 3 words for upward movement , 2 or 3 for downward movement because you will probably have to write about changes in data.
Upward movement
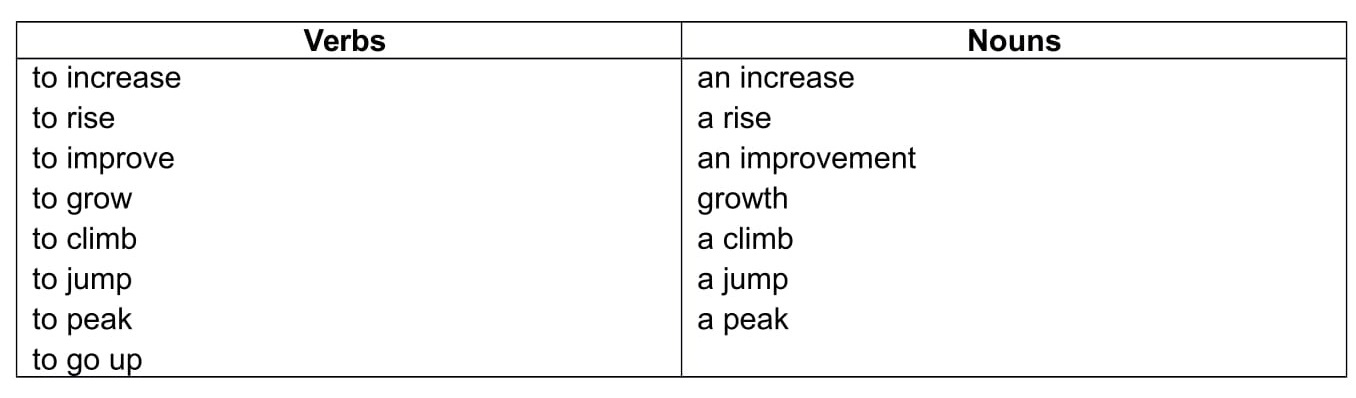
Downward movement
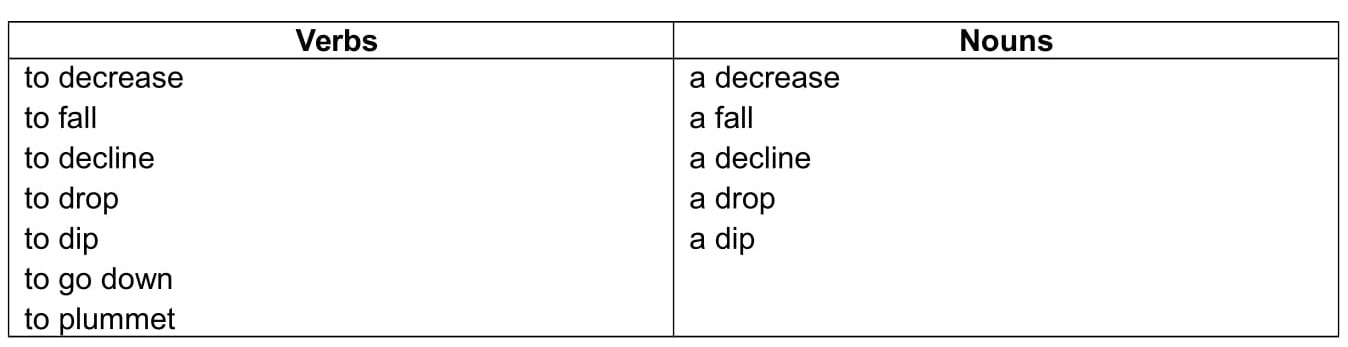
The following words can be used to describe both upward and downward movements .

Finally, you will need a couple of phrases to describe situations that show little or no change .
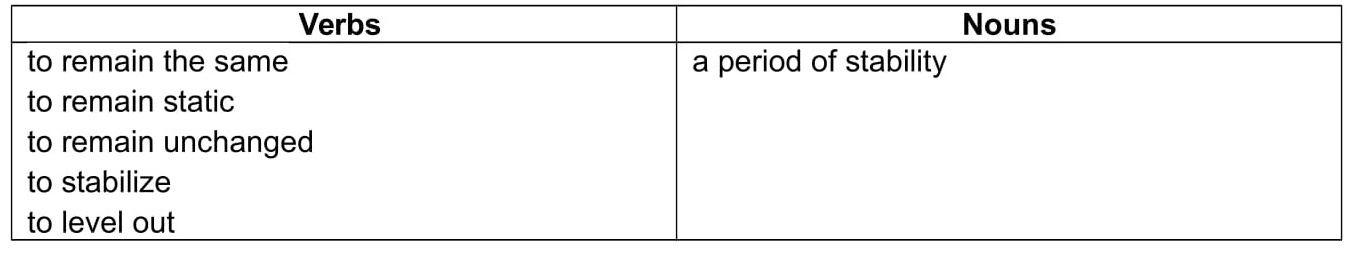
Remember to use the appropriate verb tenses in your essay.
Many of the words in these lists can be formed into collations that are ideal for expressing change.
There are two ways that you can create them:
- Verb + Adverb
- Adjective + Noun
Here are some examples:
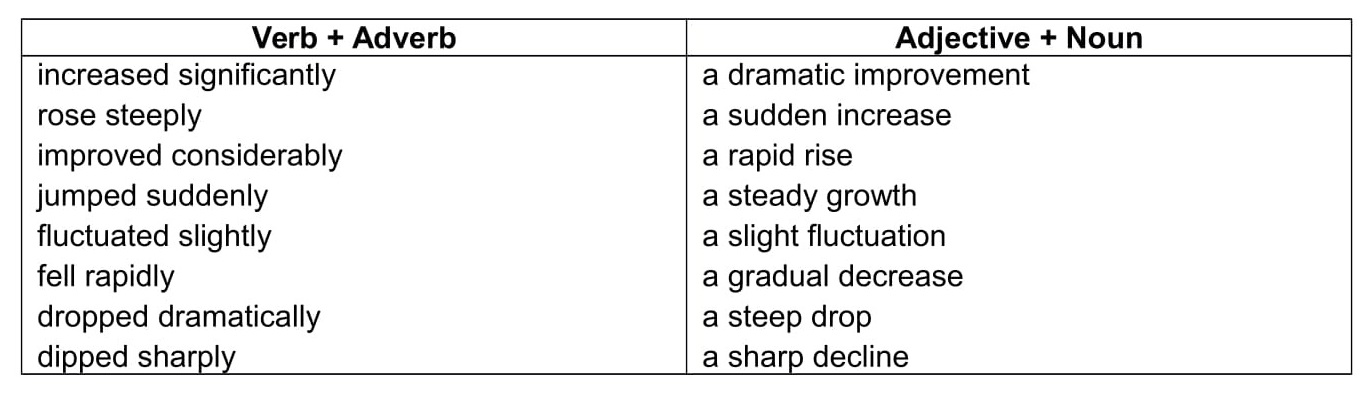
Again, don’t try to learn them all. Just pick a couple that you feel comfortable using.
The following sentences illustrate how you might use some of this vocabulary in an IELTS Task 1 essay.
1) The price of houses went into sharp decline between 1980 and 1985 but increased significantly from 1986 to 1990.
2) Over the whole time period, there was a steady growth in the number of women choosing to study part-time but for men, the level fluctuated .
Other Useful Phrases
Here are a few more phrases that you may find useful.

Percentages, Proportions & Approximations
All chart, graphs and table in IELTS Task 1 questions contain numerical data. You will gain marks if you are able to vary your language when you present this numerical data in your essay. Using approximations and proportions are an ideal way to do this, so we’ll start with these as they are useful for all types of IELTS Task 1 essay questions.
Approximations

Often, numerical data is expressed as percentages and you can use approximations to present this form of data in a different way. Here are some examples:
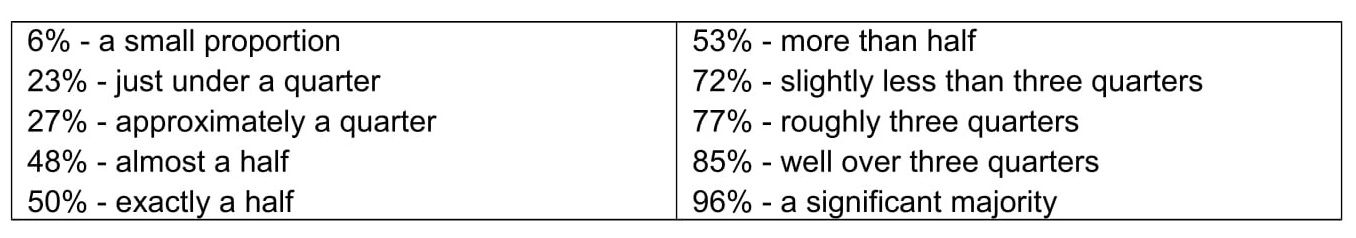
I’ve created a PDF of these word lists. Download it here: Task 1 Vocabulary PDF
You now have more than enough vocabulary to write a high-scoring Academic IELTS Task 1 essay. Use the lists when you practice writing Task 1 essays. You'll soon become familiar with the vocabulary and this will help you to choose which words and phrases to learn fully and memorise.
You’ll also find some useful vocabulary for making comparisons on this page:
Grammar for Academic Task 1 Essays
And, there’s a lot more help with Task 1 in the lessons in the menu below.
Want to watch and listen to this lesson?
Click on this video.
Would you prefer to share this page with others by linking to it?
- Click on the HTML link code below.
- Copy and paste it, adding a note of your own, into your blog, a Web page, forums, a blog comment, your Facebook account, or anywhere that someone would find this page valuable.
Like this page?
Ielts task 1 ( academic) – all lessons.
IELTS Academic Writing – A summary of the test including important facts, test format & assessment.
Academic Writing Task 1 – The format, the 7 question types & sample questions, assessment & marking criteria. All the key information you need to know.
Understanding Task 1 Questions – How to quickly and easily analyse and understand IELTS Writing Task 2 questions.
How To Plan a Task 1 Essay – Discover 3 reasons why you must plan, the 4 simple steps of essay planning and learn a simple 4 part essay structure.
Vocabulary for Task 1 Essays – Learn key vocabulary for a high-scoring essay. Word lists & a downloadable PDF.
Grammar for Task 1 Essays – Essential grammar for Task 1 Academic essays including, verb tenses, key sentence structures, articles & prepositions.
The 7 Question Types:
Click the links below for a step-by-step lesson on each type of Task 1 question.
- Table Chart
- Process Diagram
- Multiple Graphs
- IELTS Writing
- Academic Task 1 Vocabulary
- Back To Top
* New * Grammar For IELTS Ebooks

$9.99 each Full Set Just $ 23.97
Find Out More >>
IELTS Courses

Full details...

IELTS Writing Ebook

Discount Offer
$7 each Full Set Just $ 21

Find out more >>
Testimonials
“I am very excited to have found such fabulous and detailed content. I commend your good work.” Jose M.
“Thanks for the amazing videos. These are ‘to the point’, short videos, beautifully explained with practical examples." Adari J.
"Hi Jacky, I bought a listening book from you this morning. You know what? I’m 100% satisfied. It’s super helpful. If I’d had the chance to read this book 7 years ago, my job would be very different now." Loi H.
"Hi Jacky, I recently got my IELTS results and I was pleased to discover that I got an 8.5 score. I'm firmly convinced your website and your videos played a strategic role in my preparation. I was able to improve my writing skills thanks to the effective method you provide. I also only relied on your tips regarding the reading section and I was able to get a 9! Thank you very much." Giano
“After listening to your videos, I knew I had to ditch every other IELTS tutor I'd been listening to. Your explanations are clear and easy to understand. Anyways, I took the test a few weeks ago and my result came back: Speaking 7, listening 9, Reading 8.5 and Writing 7 with an average band score of 8. Thanks, IELTS Jacky." Laide Z.
Contact
About Me
Site Map
Privacy Policy
Disclaimer
IELTS changes lives.
Let's work together so it changes yours too.
Copyright © 2024 IELT Jacky
All Right Reserved
IELTS is a registered trademark of the University of Cambridge, the British Council, and IDP Education Australia. This site and its owners are not affiliated, approved or endorsed by the University of Cambridge ESOL, the British Council, and IDP Education Australia.

Press ESC to close

IELTS Academic/ General Writing Task 1: Complete Guide for Vocabulary and Grammar
Grammar and vocabulary are the dynamic duos of IELTS academic writing tasks. Every component assesses your ability to write/ speak grammatically correct sentences and to use contextual vocabulary . In the writing task 1, grammar and vocabulary play an important role. Let us see how!
IELTS Academic Writing Task 1 Marking Criteria
As suggested by many experts, understanding the exam format and the marking criteria makes your preparation a lot easier and not to mention, organised.
In the writing task 1, you will be asked to write a letter in 150 words. It could be formal, informal or semi-formal. You shouldn’t spend more than 20 minutes writing this letter and must take care that you do not write less than 150 words.
If your word count exceeds 10-15 words, it is acceptable. However, you must not keep on writing as the second task needs more time.
The Marking Criteria are Fairly Detailed for Writing Task 1:
- Grammatical range and accuracy
- Task achievement
- Lexical resource
- Coherence and cohesion
Here you can see that grammar accounts for 25% of the marks in your IELTS writing task 1 topic. Furthermore, your grammar is assessed in two things:
- Ability to write grammatically accurate sentences.
- Ability to use a wide range of grammar structures.
Accuracy of Grammar
Examiners look for how many ‘error-free’ sentences you have written. Therefore, you need to make sure each sentence has no errors. Even a small mistake like an article in the wrong place or misplaced plural counts towards this.
As a result, it is vital that you check your work after you finish writing. Always try to leave yourself two minutes in the end to proofread your work. Simple errors, which could be fixed with a quick check, select and report or modify, will really damage your marks in this area.
Range of Grammar
A good academic writing task answer will have a range of appropriate structures and tenses. Many students try to insert complex sentences and tenses into their answers. This isn’t a good strategy. It will make your answers look unnatural and can result in you making mistakes.
A good answer uses complex sentences (such as conditional and relative clauses) that flow naturally.
Grammar for IELTS General Writing Task 1
Grammar is often the area that students struggle with the most, as it can easily bring a student’s scores down. The most important thing you have to do for any IELTS writing task 1 is to answer the question. For general training task 1 questions you always have to write a letter.
You will notice that the question below states that you should write about why you are writing to your friend and then gives four bullet points for you to mention. These are the five main things you must write about and you should write about these five things and these five things only.
More Detail
Now that you have your five main points you simply split your letter into five main paragraphs and deal with each main point in a separate paragraph.
In each paragraph, you should make it very clear which point you are writing about in order to make it obvious to the examiner. You can do this by including keywords from the question, or even better, synonyms or paraphrases of those keywords.
Grammar for IELTS Academic Writing Task 1
Students taking the IELTS academic test need to write a report on a data set, pie chart, map, or process. You must write 150 words or more. Task 1 is worth 1/3 of your total mark on the Writing test.
The most important thing is that you can demonstrate that you can clearly communicate in English. The key to doing well is to know exactly what the examiners want and give it to them.
Using the appropriate tenses in IELTS writing task 1 is essential if you want to get a high band score.
The key is to look at the title of the pie chart and the information contained on both axes to establish what time frame is used. This will help you establish what tense you should use.
- If the time is one point in the past, for example, in January 1990, then we should use the past tense.
- If it has projections for the future, for example, in 2045, we use future tenses.
- If there is no time, we use the present simple.
Below is a range of tenses that could be used in task 1. Remember, the tense you use will depend on the information displayed in the graph.
Present Perfect
We use this tense generally to talk about an action that happened at an unspecified time before now. The exact time period is not important.
In writing task 1, we use this tense to talk about changes in data that have happened over a period of time.
The price of oil has fallen by $5 a barrel every week since July.
Present Perfect Continuous
We use this tense to show that something started in the past and has continued up until now.
Oil prices have been decreasing since July.
Future Perfect
We use this tense to state that something will be finished by a particular time in the future.
The price of oil will have reached $300 a barrel by 2020.
Simple Past
Use this tense to talk about an action that started and finished at a specific time in the past.
The price of oil fell from $150 in Jan 2014 to $50 in Jan 2015.
Vocabulary for Academic Writing Task 1
Using contextual vocabulary is an important aspect of writing task 1.
Describing Trends
In IELTS writing task 1 you may have to describe trends. This may come up in a line graph, bar chart or comparing more than one chart.
Also Read: How to Write Education Essays for IELTS Writing Task 2? A Guide For Writing Test
Possible Vocabulary to Describe Trends:
- Significant
- Considerable
Possible Vocabulary to Denote Action:
- Fluctuation
Possible verbs:
Possible vocabulary to modify:.
- Dramatically
- Significantly
- Considerably
Describing Increases and Decreases
When describing any of the charts in IELTS writing task 1, you might have to describe increases and decreases. There are three main ways you can describe increases and decreases.
Noun Phrase + Verb + Adverb
The price of the property fell sharply
The percentage of homes dropped dramatically.
There + Be + Noun + In + Noun Phrase
There was a fall in literacy levels.
There has been an increase in the cost of coffee.
Using Fractions
The price of oil halved in less than a year.
The price of oil has halved since July.
By July, the price of oil has halved.
Making Comparisons
IELTS writing task 1 will often require you to make comparisons between data sources, groups and times. Here are five grammatical structures you can use to make comparisons.
More/ Few/ Less + Noun + Than
Overall, more people preferred public transport than taxis.
Of one Syllable -er + Than
A higher number of people preferred public transport than taxis.
Summarising
IELTS writing task 1 is essentially a summarising task. Your overview paragraph should contain two or three sentences summarizing the main features of the graph. In order to help you do this, here are some short phrases.
- To summarise, the most marked change is….
- Overall, it is clear….
- Overall, the majority/minority….
- In sum, the most noticeable trend is….
- Don’t say ‘to conclude’. This is only for discursive essays.
Approximations, Percentages and Fractions
In many of the IELTS writing task 1 questions, you will have to deal with percentages. This is a good opportunity to express these percentages in a different way. A way of varying this language is to express them as fractions or proportions.
Remember that you should vary your language as much as possible in order to score high in the ‘lexical resource’ part of the test.
For instance, use approximations. E.g. 49% can be expressed as “nearly a half”.
Below is a range of expressions that can be used to express percentages:
- 73%- nearly three quarters
- 51%- just over a half
- 49%- just under a half
- 32%- nearly a third
- 3%- a tiny fraction
- 50%- exactly a half
- 26%- roughly one quarter
- 49%- around a half
- 24%- almost a quarter
- 77%- approximately three quarters
Proportions
- 70%- a large proportion
- 71%- a significant majority
- 15% a small minority
- 3%- an insignificant minority
IELTS writing task 1 is a comparatively short task but judges a number of skills. Therefore it is important to focus on the details very minutely. Grammar and Vocabulary are like the building blocks of your writing and as such, need attention. If your sentence is constructed in a grammatically correct way and you use relevant vocabulary your score will definitely get the much-needed boost!
Also Read: Difference Between IDP and British Council: Which is Better for the IELTS Test?

One Comment
Thank you for such structural and wonderful information, this might help a lot, and the aspirants can find rich information here, may you also suggest some grammar books?
Leave a Reply Cancel reply

Share Article:
About the Author
Indulekha prabha.
My name is Indulekha Prabha. I am an English teacher and a content writer by profession. When I'm not working you can find me writing fiction, reading poetry and painting.
You might also like

Recent IELTS Writing Task 1 Exam Question: Letter Of Complaint To A Hotel

Recent IELTS Writing task 1 Exam Question: Bar Chart On Work Performance

Recent IELTS Writing Task 1 Exam Question – Map of a town
Other stories, how to write education essays for ielts writing task 2 a guide for writing test, how to write advantages & disadvantages essay questions in ielts writing task 2.
- Skip to main content
IELTS Podcast
Pass IELTS with expert help.
IELTS Writing Task 1 Vocabulary List With Examples
In this tutorial, we discuss IELTS Academic Writing Task 1 Vocabulary with examples of them in sentences.
Find out why writing ‘this means’ could be the key to a better score, how to better introduce an overview – and the keywords in the question that you should ALWAYS change!
What is IELTS Writing Task 1?
IELTS Writing Task 1 is part of the International English Language Testing System (IELTS) exam. You need to write in a formal, academic style of English.
There is a visual, such as a map, chart, table, or process diagram, and you will write a report based on the information presented.
The report should be at least 150 words in length and there are two main things that you need to do:
- Describe the main trends, patterns, or features shown in the diagram.
- Make comparisons between the data.
Therefore, Writing Task 1 is designed to test your ability to present information clearly and accurately, as well as to show you understand the main idea (this is an overview).
Why is vocabulary so important for IELTS Writing Task 1 and how do you improve your answer?
1. word choice affects the clarity of an essay.
Word choice can affect the clarity and complexity of an essay. To score well on task achievement as well as coherence and cohesion, you must communicate clearly.
For a band 7 or above, most phrases in your answer need to be used accurately. Too many complex words can make your writing confusing and difficult to understand.
Good paraphrasing is also important, below we have detailed the three ways you can paraphrase and a good essay will include all of them.
2. Vocabulary helps express complex ideas clearly
By knowing the right words to use, you will be able to communicate complex ideas effectively. This will help you achieve a higher band score on the IELTS Writing Task 1 exam since clarity (coherence) is one of the 4 elements scored by examiners.
3. High-level vocabulary helps to achieve a high IELTS score
By memorising more complex phrases and using them accurately in their writing, students can improve their Lexical Resource band score. Here’s a great example:
For an overview, many students write something like, ‘Overall, sales of bottled water increased during the period studied while customers bought less soda’
The word ‘Overall’ signals an overview. That’s fine, but try this! Overall, what stands out from the diagram is that…
Overall, what stands out from the diagram is that sales of bottled water increased during the period studied while consumers bought less soda.’
It’s a much more complex sentence and shows off more than one tense in a sentence which is hard to do accurately. This trick works for pretty much any task 1 diagram.
4. Vocabulary is needed to construct complex sentences
Using a range of adverbs and adjectives allows for more descriptive sentences while understanding how prepositions work can help improve sentence structure and clarity.
Your sentences need to be grammatically accurate as well as complex.
The easiest way to improve your grammar score is to practice using useful complex phrases that you can prepare in advance (lots of examples below!).
5. Vocabulary is needed to paraphrase the question – change these keywords.
Vocabulary, or lexis, plays a significant role in IELTS Writing Task 1, as it is responsible for 25% of the final task 1 grade.
A lot of students will lose marks by basically repeating the question in the first sentence of their answer.
An easy way around this is to memorise your three keywords: Illustrates, depicts, and presents which all mean ‘shows’.
Then start with, The diagram illustrates ….
If the question says ‘the diagram shows’ but it is a line graph, then say ‘The line graph illustrates’
If the question says ‘The bar graph illustrates’ then you write ‘The diagram depicts’.
Change the word for ‘diagram’ and the word for ‘shows’ to start your answer well with good paraphrasing.
TOP TIP – Never change a fixed expression!!
A lot of students try to do this, and it’s always a disaster..
For example. Marnie learned the phrase ‘Turning to the details’ for introducing a new paragraph in a task 1 essay. She couldn’t remember it exactly in the test and so she wrote, ‘Around the detail’ which sounded right to her but doesn’t make any sense.
Fixed expressions mean just that – don’t try to paraphrase any part of a fixed expression. Learn and use them accurately or write something more simple.
How to build a better vocabulary list for IELTS Writing Task 1
1. adjective/noun and verb/adverb examples.
To really show off your vocabulary in the test, make sure you use at least TWO adjective/noun and verb/adverb examples.
- In the second year, there was a slight increase in sales of coffee . Slight increase is an adjective/noun combination.
- However, in the third year, sales dropped dramatically. Dropped dramatically is a verb/adverb phrase.
Not all combinations work well together, so be sure to look at a lot of examples and choose your favourites.
Dropped slightly, dropped suddenly, dropped dramatically, dropped significantly, A significant increase, a marginal increase, a steady increase, a dramatic increase all work well.
2. Word lists and collocations
Word lists are collections of words that can be used to express a particular idea or concept in an IELTS Task 1 essay.
These word lists can be formed into collocations, words that typically go together. For example, “increased significantly” could be used as part of a collocation with “price” or “number” .
The price increased significantly in the second year.
However, you couldn’t say ‘people increased significantly’ as this doesn’t collocate naturally. You would have to write ‘the number of people buying soda increased significantly’
To improve your collocation skills:
- Identify words that are commonly used together, such as ‘increase’ and ‘from’.
- Make a list of commonly used collocations for each word you identified. For example, for ‘increase’, your list could include phrases such as increase to, increase from, increase by and increase until.
- Practice using these collocations in writing and speaking exercises to help build your vocabulary for IELTS Writing Task 1.
- Identify the keywords in the topic sentence of your essay and add them to a vocabulary list. For example, price and sales, in the USA.
- Look for verb and noun forms, as well as adverbs and adjectives that can be used to avoid repetition in your essay. For the price you could use, It was priced at, sales price, cost. For sales you could use sold, total sales, and the amount sold. For the USA you could use America, The US, and American customers. Note these next to the question before you start writing your answer so you don’t forget to use them.
- Research any unfamiliar words or phrases you come across so you can better understand their meanings if you see them again in another essay.
4. Get better at paraphrasing
Did you know there are three main ways to paraphrase in the IELTS test?
- Synonyms – we saw a few examples above, remember to switch up illustrates, depicts and presents.
- Change the form of the word. Sometimes, words like ‘sales’ are hard to find a synonym for. Changing the form counts as paraphrasing! Sold, was sold, selling, and total sales are all acceptable examples of paraphrasing.
- Reference! This, that, which, it. If you’re struggling to think of a synonym or another word form, reference. For example, In 2005, coffee was the most popular beverage of the three studied. By 2008, however, it was the third most popular product. We are using ‘it’ as a way to paraphrase ‘coffee’. Use a dictionary or online resources such as Merriam-Webster Dictionary or Thesaurus Online to find relevant synonyms for each word on your list if necessary; this will help ensure that all of your phrases are accurate and suitable for use in an academic setting such as IELTS Writing Task 1.
A comprehensive list of IELTS Writing Task 1 vocabulary
Here is a list of vocabulary that may be useful for IELTS Writing Task 1, along with some example sentences:
- Describe : to give a detailed account of something. “The data describes the changes in the number of visitors to the park over the past 2 years.”
- Show : to present or display something “The table shows the average monthly temperatures in London for the past year.”
- Present : to make something available or visible “The chart presents data on the number of international students studying at four universities in the USA.”
- Illustrate : to represent or show something in a visual way “The diagram illustrates the water purification process of how water at a treatment plant.”
- Depict : to represent or describe something in a visual way “The graph depicts changes in the price of oil over the past 35 years.”
- Reveal : to make something known or visible that was previously unknown or hidden “The data reveals a strong correlation between the amount of exercise a person does and their overall health.”
- Indicate : to show or point out something “ The chart indicates that there has been a steady increase in the number of Japanese tourists visiting the island in recent years.”
- Demonstrate : to show or prove something through evidence or an example “The data demonstrates a clear relationship between the amount of time spent studying and test performance.”
- Display : to show or present something in a way that is visible to others “The table displays the results of the survey, showing the percentage of residents who agreed with each statement.”
- Trend Analysis: the process of identifying and describing trends in data or events ” The trend analysis of the data illustrates that there has been a steady increase in the number of students using public transportation in the city over the past eight years.”
- Decline: to reduce or lessen in amount, intensity, or degree. “House prices in Smalltown went into a sharp decline between 1980 and 1985 but increased significantly from 1986 to 1990.”
- Fluctuated: rise and fall irregularly in number or amount. “Over the whole time period studied, there was a steady growth in the number of women choosing to study part-time but for men, the figures fluctuated.”
- Difference: to be distinct or different in some way. “The difference in temperature between the two cities is quite significant. In the coastal city, the average temperature in August is 28 degrees celsius, while in the inland city, the average temperature is 34 degrees Celsius.”
- Decrease in: to reduce or become smaller in size, amount, or degree. ” The bar chart illustrates a decrease in the number of reported accidents in the supermarket warehouse over the past six months. In January, there were 50 accidents reported, but by June, this number had fallen to 30.”
- Little or no change in data: means that the data remains relatively constant or unchanged over a period of time. “The data shows that there was little or no change in the number of people using the city’s tool-sharing program over the past year. In 2020, the average number of daily program participants was 50, and in 2021, it remained at around the same level at 52.”
- Increase to: This collocation means that something has increased in amount or number. “The population of the country has increased to 35 million people since 2019.”
- Increase from : indicates an increase from a previous amount or number, usually over a period of time. “The population of the country has increased from 24 million people ten years ago to 26 million today.”
- Increase by: This collocation indicates that something has increased by a certain amount or percentage since its last measurement or estimate was made. “The population of Fiji has increased by three per cent since last year’s census results were announced.”
- TOP TIP – Try to use ‘This means’: Use this phrase to indicate that you are making comparisons. For example, “ This means that potatoes were higher than sales of other food products. or This means that it had increased by 34%.”
FAQ (Frequently Asked Questions)
Some of these questions were already covered in this blog post but I will still list them here (because not everyone carefully reads every paragraph) so here’s the TL;DR version
What is IELTS Writing Task 1 Vocabulary?
It’s vocabulary that can be useful in the Academic IELTS exam. It includes adjectives, adverbs, verbs, collocations and other useful phrases that can help students better express their ideas in the test.
What kind of vocabulary is used in the IELTS Writing Task 1?
In IELTS Writing Task 1, vocabulary is assessed on two levels: static and dynamic. Static vocabulary refers to words or phrases that do not change over time, such as “shop” or “house”.
Dynamic vocabulary refers to words or phrases that change over time, such as “increase” or “decrease”.
Both types of vocabulary are used in the IELTS writing test and can be found in graphs, charts, tables and other diagrams.
The marking scheme for lexis accounts for 25% of your overall score on the writing test so it’s important to have a good grasp of both types of vocabulary when preparing for the exam.
How can I use the IELTS Writing Task 1 Vocabulary?
- Familiarize yourself with the IELTS Writing Task 1 Vocabulary, by reviewing the list of words and their definitions.
- Practice using this vocabulary in mock IELTS Writing tests, to add variety to your responses and improve your score.
- Paraphrase words like ‘small’ and ‘large’ and use a mix of verb/adverb and adjective/noun phrases.
- Use these words every time you practice mock IELTS Writing tests so that they become part of your natural vocabulary for Task 1 writing.
What are the different types of graphs used in the IELTS Writing Task 1?
The types of graphs used in the IELTS Writing Task 1 include
- Diagrams (pie charts, bar graphs, line graphs, tables or a combination of the above.
- Maps – these can be both in the past, a past/present, present/future or a combination of the above
- Process Diagrams: Process diagrams show how something works from start to finish (e .g., from customer order through the production line) or a cyclical process.
What are the common mistakes to avoid while using IELTS Writing Task 1 Vocabulary?
Common mistakes to avoid while using IELTS Writing Task 1 Vocabulary include:
- Repeating the same words too often – if a word is hard to find a synonym for, remember, change the form or use referencing.
- Not using words that imply more or less, such as “increase” or “decrease”
- Trying to paraphrase a fixed expression.
More Writing Task 1 Tutorials
- How to get band 9 in Task 1
- 5-step plan for Task 1
- How to paraphrase in Task 1
- Academic task 1 marking criteria
- Five essential writing skills for Task 1
- What tense to use in Task 1
- How to describe percentages
- Vocabulary to describe a map
- Academic task 1 sample essays and answers
- Task 1 sample charts and graph questions
- Academic Task 1 sample diagram questions
- How to score well on a bar chart question in writing task 1
- IELTS academic task 1 sample question
- IELTS academic task 1 sample question – bar chart showing interest
- IELTS Academic writing task 1 question – pie chart showing usage
- Skip to primary navigation
- Skip to main content
- Skip to primary sidebar
- Skip to footer

IELTS Advantage
IELTS Preparation Courses
IELTS Writing Task 1: Everything You Need to Know
Ielts writing task 1 in 6 simple steps.

Academic Writing Task 1 Strategy
- Understand how the test is marked. Knowing the marking criteria will allow you to give the examiner exactly what they need.
- Paraphrase the question. It is best to paraphrase the question in the first paragraph. You can do this by using synonyms.
- Write the overview. To write your overview , pick 3 or 4 of the main features and write about them generally without referencing any data.
- Support the main features. In a new paragraph, support the key features with the data in the information given to you.
- Check your work. Check your report for spelling and grammar mistakes. Make sure that the data you mentioned is also accurate!

Essential Writing Task 1 Skills
- How to Write an Overview Paragraph
- How to Paraphrase
- How to Write a Complex Sentence
- How Many Words?
- Task 1 Charts Checklist
- Task 1 Tips
- The Danger of Synonyms
- 6 Common Mistakes
- Paragraphing and Editing
Writing Task 1 Full Lessons
- Writing Academic Task 1 in 5 Easy Steps
- Charts Lesson
- Maps Lesson
- Multiple Charts/Graphs
- Process Lesson

Academic Task 1 Sample Answers

- Bar Chart Sample Essay (Cars in Asia)
- Process- Cement and Concrete Production
- Pie Chart (Italy and Yemen Populations)
- Process Question
- Bar Chart Question (UK Telephone Usage)
- Line Graph (US Consumption of Energy)
- Bar Chart Sample Answer (International Students)
General Training Writing Task 1

General Training Writing Task 1 in 5 Simple Steps
- Understand how the test is marked. Knowing the marking criteria is the best way of giving the examiner exactly what they need and nothing else.
- Decide whether the letter is formal or informal. This part is easy. If the question asks you to write to a ‘friend’, it should be an informal letter. If the question asks you to write to anyone else, it should be a formal letter. It is that simple!
- Discuss each bullet point from the question. Make sure to take a new paragraph for each bullet point. This will make your letter easy to read and understand.
- Sign off your letter. Don’t overcomplicate this part. Include a sign-off suitable to your letter’s tone and write your name beneath.
- Check your work. Make sure your letter doesn’t contain any grammar or vocabulary mistakes.
- Letter Writing Tips
- How to Write an Informal Letter
- How to Write a Formal Letter
General Training Essential Writing Task 1 Skills
- Task 1 General Training Writing Strategy
- Task 1 General Training Writing Guide
Sample Answers
- Formal and informal sample letters.
Writing Task 1 Essential Information
- People doing the Academic test will write a report on a data set, map, or process. People doing General Training will write a letter.
- You must write 150 words or more.
- You should spend around 20 minutes on this part of the test.
- Task 1 is worth 1/3 of your total mark on the Writing test.
- You will be assessed in four areas: Task Achievement (25%) Coherence and Cohesion (25%) Lexical Resource (25%) Grammatical Range and Accuracy (25%)
- The most important thing is that you can demonstrate that you can clearly communicate in English.
- The key to doing well is to know exactly what the examiners want and give it to them.
- Grammar and Vocabulary Guide

- Top 10 Grammar Mistakes

IELTS Writing Task 1 FAQs
How can i improve my writing.
You will find all the resources you need on our Writing Task 1 page. Click the link below:
Writing Task 1
If you need serious help or personalised feedback, you should check out our online course. There is a waiting list, but you can add your name here:
How can I get a Band 7, 8 or 9?
The answer to this question is different for every individual IELTS student, as it depends on a number of factors, including your work ethic, English skills and exam strategy. You'll find a guide to answering this question in this article
If you need serious help with improving your IELTS scores, you should check out our online writing course. There is a waiting list, but you can add your name by clicking the link below:
Can you correct my writing?
Please click the link below and it will give you all the information you need about our writing correction service:
Writing Correction Service
Do you have any sample answers?
Yes, you will find them at the link below:
Task 1 Sample Answers
Will using 'high level' or 'academic' words help me improve my score?
Probably not.
Read my recent article about IELTS vocabulary here:
5 Things You Need to Know about IELTS Vocabulary
How many paragraphs should I write?
Introduction
You can put the overview at the end if you'd like.
Can I use idioms?
No, you should typically avoid using idioms in Writing Task 1.
The only time this is acceptable is if you are taking the General Training test and must write an informal letter.
Should I write a conclusion for Task 1 Academic?
No. A conclusion is a summary of YOUR ideas and your opinion. Task 1 is simply reporting what you see, so there shouldn't be any of your ideas or your opinion.
Instead of a conclusion, you should write an overview.
The reason lots of people get confused about this is that some teachers, books and even one British Council website call the overview a 'conclusion'. It's not a conclusion, it's an overview.
Finally, it does not matter where you put the overview paragraph. We teach our students to put it after the introduction, but it is also fine to have it as your final paragraph.
How many words should I write?
You must write at least 150 words in Writing Task 1 (yes, the examiners will count them!)
I would suggest that you aim to write around 160-170 words for Task 1. Aiming for 20-30 words more than the required amount makes you more likely to reach the word limit without setting an unrealistic goal.
Will I lose marks if I don't write enough words?
Yes. If you don't write the required number of words, you will lose marks in 'Task Achievement' for not answering the question fully. Read more here .
Can I use contractions?
No, should not use contractions when you are writing an academic essay or formal letter. However, it is fine to use contractions in an informal letter.
When should I write formally?
There are a few signposts that indicate when you should write formally or informally. Watch our video lesson to find out what they are:
IELTS Writing Task 1 General Training: Formal or Informal Letters?
IELTS Preparation with Liz: Free IELTS Tips and Lessons, 2024
- Test Information FAQ
- Band Scores
- IELTS Candidate Success Tips
- Computer IELTS: Pros & Cons
- How to Prepare
- Useful Links & Resources
- Recommended Books
- Writing Task 1
- Writing Task 2
- Speaking Part 1 Topics
- Speaking Part 2 Topics
- Speaking Part 3 Topics
- 100 Essay Questions
- On The Day Tips
- Top Results
- Advanced IELTS
IELTS Writing Task 1 Tips, Model Answers & More
Useful IELTS writing task 1 tips, answers, lessons & videos for success achieving a high score. This page contains all the information and help you need to do well. Learn about the IELTS marking criteria, paragraphing, vocabulary and much more. This page has tips for Academic writing task 1 and GT writing task 1 (see bottom of page).
IELTS Writing Task 1 Information
- IELTS recommend you spend no more than 20 mins on writing task 1. However, the time is yours to manage as you wish.
- You should write over 150 words.
- IELTS writing task 1 is worth only about 33% of your total writing marks.
- Task Achievement (25%)
- Coherence & Cohesion (25%)
- Vocabulary (25%)
- Grammar (25%)
- : IELTS Writing Task 1 Band Scores
- Academic writing task 1 is a report on a chart (bar chart, line graph, pie chart, table, map, diagram/process). See below for practice charts, model answers, tips etc.
- General Training writing task 1 is a letter only. GT letter writing tips can be found towards the bottom of this page. Click here for Information about GT Writing Differences. There are tips for letter writing, further down this page.
- All words will be counted and all numbers count as one word. See this page: How Words are Counted
- For more information about IELTS test rules, tips etc, see this page: IELTS Test 1 FAQ
IELTS Writing Task 1 Practice Charts
A collection of useful IELTS writing task 1 practice samples to develop your writing at home.
IELTS Charts for Practice : Academic Test Only
- Academic students may get bar charts, tables, line graphs, pie charts, maps and diagrams (processes).
IELTS Letters for Practice : GT Test Only
- GT students will only be given letters for task 1. GT students can find more tips lower down this page.
IELTS Writing Task 1 Tips & Free Videos
Free IELTS writing task 1 tips and videos for the right techniques and understanding the test more clearly.
- Essential Tips : How to Prepare for Writing Task 1
- Tips : How Many Words Should you Write?
- Tips: What tense to use in writing task 1?
- Tips : Penalty for Under the Word Count
- Video : How to Describe a Bar Chart with model answer
- Video : Map Language: 1
- Video: Conclusion or Overview Tips
- Video : Vocabulary for Accurate Data
- Video : How many Paragraphs
- Video : Official Writing Answer Sheet Tips
- Video : Line Graph 4 Main Sentences
- Video : Line Graph How to Write a Complex Sentence
IELTS Bar Chart Video
Learn how to describe a bar chart in IELTS writing task 1. You can find a model answer for this lesson here: Model Answer .
Writing Task 1 Model Answers
IELTS model answers for charts, graphs, diagrams, maps and tables.. Each sample answer is estimated band score 9.
- Diagram Model Answer
- Bar Chart & Pie Charts Model Answer
- Table Model Answer
- Map Model Answer
- Line Graph Model Answer
- Bar Chart Model Answer
- Pie Chart Model Answer
- Bar Chart of Age Groups Model Answer
- Table Future Form Model Answer
- Line Graph & Bar Chart Model Answer
- Practise at Home: IELTS Sample Practice Charts
IELTS Writing Task 1 Practice Lessons
IELTS writing task 1 free practice lessons to help you develop skills and understand about the requirements of task 1 academic. More lessons will be added over time.
- Table & Pie Charts
- IELTS Diagram Rain Water
- Two Line Graphs: Exercise & Model
- IELTS Diagram Paragraphs and Organisation
- IELTS Life Cycle Diagram: Model & Gap Fill
- Bar Chart of Change over Time
- IELTS Line Graph Gap Fill Exercise
- IELTS Diagrams: Practice Exercise
- IELTS Line Graph: Vocabulary List
- IELTS Line Graph: How to Describe Guidelines
- IELTS Line Graph: Exercise & Model
- Task 1 Introduction Paragraph Practice
- IELTS Map: Comparison Exercise
- IELTS Two Charts Practice: Pie Chart & Bar Chart
- IELTS Bar Chart: Practice Exercise
- IELTS Diagram Water Supply
- Grammar Accuracy: Practice & Tips
- IELTS Bar Chart: Introduction & Overview Practice
- IELTS Pie Chart: How to Describe a Pie Chart Step by Step
- IELTS Diagram: Introduction & Overview Practice
- Introduction Paragraph: Common Errors
- IELTS Bar Chart Sample Answer
IELTS General Training Letter
The following links are for IELTS candidates who are preparing for the General Training Writing Test. Your task will be asked to write a letter. You will not be writing a report as in the Academic Test. Use the links below to help you prepare:
10 Essential Tips for IELTS Letter Writing
How to Improve your IELTS GT Letter
Differences between GT & Academic Writing
General training model letters and practice exercises:
- Apology Letter: Model Answers Formal & Informal
- Amendment Letter: Model Answer 2017
- Complaint Letter: Model Answer
- Complaint Letter: Error Correction
- Letter to a Friend: Model Answer
- Invitation Letter: Model Answer
………………
FREE SUBSCRIBE: Get New Lessons & Posts by Email
Type your email…
Advanced IELTS Lessons & E-books

Recent Lessons
50% discount advanced ielts lessons & e-books final day, answers to age group bar chart lesson, ielts bar chart of age groups 2024, 50% discount: advanced ielts lessons & e-books, ielts topic: urban planning, ielts listening transcripts: when and how to use them.

Click Below to Learn:
- IELTS Test Information
Copyright Notice
Copyright © Elizabeth Ferguson, 2014 – 2024
All rights reserved.
Privacy Policy & Disclaimer
- Click here: Privacy Policy
- Click here: Disclaimer
Return to top of page
Copyright © 2024 · Prose on Genesis Framework · WordPress · Log in

IELTS Writing - Academic Task 1 - Vocabulary
The following words and phrases will help you describe trends:
Sample sentences
- There was a substantial increase in the value of stocks on March 15th.
- House prices rose dramatically in July.
- The number of tourists visiting New York fell sharply in October.
- The percentage of students walking to school continued to rise gradually over the ten year period from 2000-2010.
- There was a sharp increase in employee turnover after the strike.
- Interest in environmental issues has risen steadily over the last 10 years.
More useful words and phrases
- Percent – the word percent comes after a number Examples: More than 25% of the students are from Brazil. More than 25 percent of the students come from Brazil.
- Percentage - The word percentage comes after words like the, a, this and that. Often, it is preceded by an adjective. Examples: A small percentage of residents have lived in the building for more than 20 years. The percentage of students who live on campus has fallen sharply since the fire.
- For numbers up to ten, write the numbers in words. For numbers over 10, you can write the numbers in numbers. Examples: Five percent of the employees were late this month. More than 50 percent of the students handed in their assignments late after the long weekend.
- If the sentence starts with a number, always write it in words. Examples: Wrong: 25 students were from China. Right: Twenty-five students were from China.
Take note of the following prepositions which you will need to describe dates, numbers and comparisons:
Dates In December, In 2005, From 2001-2010, By 1998, Between 1965-1969
Numbers Increase of 25% Decreased by 10% Fell from 200 in July to 150 in August
Comparison Compared to Compared with Relative to

1. IELTS BASICS
- IELTS Overview
- Types of Exams
- Registration
- Test Administration
2. FREE IELTS SAMPLES
- IELTS Speaking Topics
- IELTS Speaking Topics 2
- IELTS Speaking Samples
- IELTS Letter Topics 1
- IELTS Letter Topics 2
- IELTS Letter Topics 3
- Sample IELTS Letters
- IELTS Essay Topics
- Sample IELTS Essays
3. IELTS SKILLS
Ielts reading.
- Reading Overview
- General & Academic
- IELTS Reading Tips
IELTS Listening
- Listening Overview
- IELTS Listening Tips
IELTS Speaking
- Speaking Overview
- IELTS Speaking Tips
IELTS Writing
- Writing Overview
- Academic Writing
- Academic Task 1 - Charts
- Academic Task 1 - Vocabulary
- General Writing
- IELTS Letter Writing Tips
- Key Expressions for Letters
- IELTS Essay Writing Tips
- Key Expressions for Essays
Support Skills
- Pronunciation
4. IELTS RESOURCES
- IELTS Books
- In-Class IELTS Training
- Online IELTS Training
- Training Abroad
- Free IELTS Videos

Writing task 1 academic vocabulary
How to use ielts vocabulary accurately when describing data..
Updated: July 2023
In IELTS writing task 1, vocabulary accounts for 25% of your marks. Being able to use a wide variety of vocabulary accurately will help your score. I did a post on this before about using specific vocabulary in the academic task 1 writing section click here to see that post.
In this post, I want to review this vocabulary and there is an exercise for practice based on a line graph. Notice that the line graph is dynamic, which means it changes over time. This vocabulary can also be used with static data, which doesn’t change over time.
Common IELTS academic task 1 vocabulary.
Note that some of these words can change tense such as past tense, present tense, and gerunds (-ing form) Always analyse the task first to make sure you know what tense to use. So obviously if the task shows dates in the past then you would use the past tense.
represents / representing / represented accounts for / accounting for / accounted for is made up of the number of + countable noun / the amount of + uncountable noun the proportion of/ the figure for/ figures for Is equal to that of… (comparing equal figures) consists of / consisted of comprised / comprises / comprising constitutes / constituted / constituting amounts to / amounting to / amounted to numbered / numbers / numbering totalled / totals / totalling according to / regarding the graph / chart / data / diagram by the end of the period / by the end of the timeframe
More details in this lesson here-> click here to see it
Using the vocabulary in context.
1. The figure for car imports to the UK comprised just over one-fifth (21%). 2. Figures for computer sales in France amounted to 59%. 3. The figure for the employment rate in Spain represented 26%. 4. The amount of rice exported from Vietnam accounted for just under half (49%). 5. The proportion of semiconductor imports to the EU totalled 64%. 6. The number of car imports to Germany consisted of 31% by the end of the timeframe . 7. The total number of doughnuts sold was equal to that of cupcake sales at approximately 41%. 8. According to the graph , almost half of the population is made up of people under the age of 50. 9. The figure for employment rates in the public sector constituted just under 40% by the end of the period. 10. The proportion of people that ate at fast-food restaurants showed a sharp decline in 2019. 11. According to the chart, students that studied math represents just over 23% with science accounting for around 19%. 12. Regarding the pie chart, the figure for tobacco sales saw a significant decrease in 2021, comprising the lowest income of all.
Practice exercise

Source: Cambridge IELTS 15 book page 49
Study the line chart above and using the vocabulary from the example sentences fill in the gaps below. More than one answer is possible. The first one has been done.
1. The figure for visitors staying on cruise ships represented half a million by 2011.
2. The total _________ ___ visitors __________ ____ 3.5 million by the end of ____ __________ .
3. The ___________ of visitors who stayed on an island saw a levelling off from 2013 to 2015.
4. _____________ to the graph, total visitor numbers saw a significant increase throughout the __________.
5. ______________ those who stayed on cruise ships, this __________ witnessed some fluctuations from 2010 to 2013.
6. By the _______ ____ the period , the_________ for visitors who stayed on cruise ships __________ ____ 2 million.
7. The _____________ of visitors staying on an island _____________ 1.5 million by the _______ of the ___________ .
8. Overall, total visitor ___________ saw a substantial climb throughout the given period _______________ ____ 3.5 million visitors by 2017.
9. By mid 2015, visitors that stayed on an island were _______ _____ _______ _____ those who stayed on cruise ships at just under 1.5million.
Click the blue button below to check the answers. These are my ideas, answers may vary
2. The total number of visitors accounted for 3.5 million by the end of the period .
3. The proportion of visitors who stayed on an island saw a levelling off from 2013 to 2015.
4. According to the graph, total visitor numbers saw a significant increase throughout the timeframe.
5. Regarding those who stayed on cruise ships, this figure witnessed some fluctuations from 2010 to 2013.
6. By the end of the period , the figure for visitors who stayed on cruise ships amounted to 2 million.
7. The proportion of visitors staying on an island numbered 1.5 million by the end of the timeframe .
8. Overall, total visitor numbers saw a substantial climb throughout the given period amounting to 3.5 million visitors by 2017.
9. By mid-2015, visitors that stayed on an island were equal to that of those who stayed on cruise ships at just under 1.5 million.
Any questions? leave a comment below.. also check out the correction service at this link if you need professional corrections.
Leave a Comment Cancel reply
Vocabulary for IELTS writing task 1
Being able to use appropriate vocabularies, presenting the main trend, comparing & contrasting data and presenting the logical flow of the graph ensure a high band score in your Academic IELTS writing task 1
- Post author By City IELTS
- Post date 16th April 2020

Full lesson on useful words for effectively writing IELTS writing task 1. Also know the format , words to describe the trends, contrast or comparison. You are strongly recommended to go through the entire lesson.
Vocabulary for Academic IELTS Writing Task 1 (part 1)
Academic IELTS Writing Task 1 question requires you to use several vocabularies to present the data given in a pie/ bar/ line/ mixed graph or to describe a process or a flow chart. Being able to use appropriate vocabularies, presenting the main trend, comparing & contrasting data and presenting the logical flow of the graph ensure a high band score in your Academic IELTS writing task 1.
This vocabulary section aims to help you learn all the vocabularies, phrases and words you need to know and use in your Academic writing task 1 to achieve a higher band score. The examiner will use four criteria to score your response: task achievement, coherence and cohesion, lexical resource, & grammatical range and accuracy. Since lexical resource will determine 25% of your score in Task 1, you have to enrich your vocabulary to hit a high band score. To demonstrate that you have a great lexical resource, you need to:
» Use correct synonyms in your writing. » Use a range of vocabulary. » Do not repeat words and phrases from the exam question unless there is no alternative. » Use less common vocabulary. » Do not use the same word more than once/twice. » Use precise and accurate words in a sentence.
It is advisable that you learn synonyms and use them accurately in your writing in order to give the impression that you can use a good range of vocabulary.
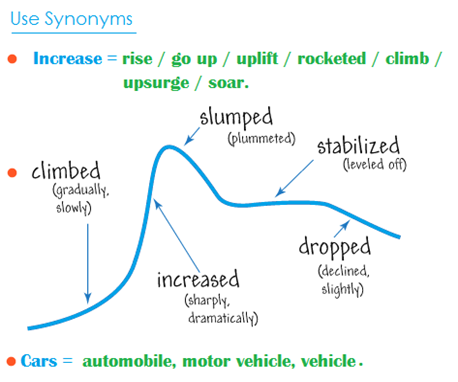
The general format for writing academic writing task 1 is as follows:
Introduction + Basic/ General Trends + Details Description + Summary (optional) .
Each part has a specific format and therefore being equipped with the necessary vocabulary will help you answer the task 1 efficiently and will save a great deal of time.
Vocabulary for the Introduction Part:
Example:
1. The diagram shows employment rates among adults in four European countries from 1925 to 1985.
2. The given pie charts represent the proportion of male and female employees in 6 broad categories, dividing into manual and non-manual occupations in Australia, between 2010 and 2015.
3. The chart gives information about consumer expenditures on six products in four countries namely Germany, Italy, Britain and France.
4. The supplied bar graph compares the number of male and female graduates in three developing countries while the table data presents the overall literacy rate in these countries.
5. The bar graph and the table data depict the water consumption in different sectors in five regions.
6. The bar graph enumerates the money spent on different research projects while the column graph demonstrates the fund sources over a decade, commencing from 1981.
7. The line graph delineates the proportion of male and female employees in three different sectors in Australia between 2010 and 2015.
Note that, some writers prefer “The line graph demonstrates…” format instead of “The given line graph demonstrates…” . However, if you write “The given/ provided/ presented….” it would be correct as well.
1. For a single graph use ‘s’ after the verb, like – gives data on, shows/ presents etc. However, if there are multiple graphs, DO NOT use ‘s’ after the verb.
2. If there are multiple graphs and each one presents a different type of data, you can write which graph presents what type of data and use ‘while’ to show a connection. For example -‘The given bar graph shows the amount spent on fast food items in 2009 in the UK while the pie chart presents a comparison of people’s ages who spent more on fast food.
3. Your introduction should be quite impressive as it makes the first impression to the examiner. It either makes or breaks your overall score.
4. For multiple graphs and/ or table(s), you can write what they present in combination instead of saying which each graph depicts. For example, “The two pie charts and the column graph in combination depicts a picture of the crime in Australia from 2005 to 2015 and the percentages of young offenders during this period.”
Caution: Never copy word for word from the question. If you do, you would be penalised. Always paraphrase the introduction in your own words.
General Statement Part:
The General statement is the first sentence (or two) you write in your reporting. It should always deal with:
What + Where + When.
Example: The diagram presents information on the percentages of teachers who have expressed their views about the different problems they face when dealing with children in three Australian schools from 2001 to 2005.
What = the percentages of teachers… Where = three Australian schools… When = from 2001 to 2005…
A good General statement should always have these parts.
Vocabulary for the General Trend Part:
In general, In common, Generally speaking, Overall, It is obvious, As is observed, As a general trend, As can be seen, As an overall trend, As is presented, It can be clearly seen that, At the first glance, it is clear, At the onset, it is clear that, A glance at the graphs reveals that…
1. In general, the employment opportunities increased till 1970 and then declined throughout the next decade.
2. As is observed, the figures for imprisonment in the five mentioned countries show no overall pattern, rather shows the considerable fluctuations from country to country.
3. Generally speaking, citizens in the USA had a far better life standard than that of remaining countries.
4. As can be seen, the highest number of passengers used the London Underground station at 8:00 in the morning and at 6:00 in the evening.
4. Generally speaking, more men were engaged in managerial positions in 1987 than that of women in New York this year.
5. As an overall trend, the number of crimes reported increased fairly rapidly until the mid-seventies, remained constant for five years and finally, dropped to 20 cases a week after 1982.
6. At a first glance, it is clear that more percentages of native university pupils violated regulations and rules than the foreign students did during this period.
7. At the onset, it is clear that drinking in public and drink driving were the most common reasons for US citizens to be arrested in 2014.
8. Overall, the leisure hours enjoyed by males, regardless of their employment status, was much higher than that of women.
The structure of the IELTS Academic Writing Task 1 (Report Writing):
Introduction:
Introduction ( never copy word for word from the question ) + Overview/ General trend ( what the diagrams indicate at a first glance ).
Reporting Details:
Main features in the Details + Comparison and Contrast of the data. (Do not give all the figures.) + Most striking features of the graph.
Conclusion:
Conclusion (General statement + Implications, significant comments) [The conclusion part is optional.]
Tips: 1. Write introduction and General trend in the same paragraph. Some students prefer to write the ‘General Trend’ in a separate paragraph and many teachers suggest the both to be written in a single paragraph. Unless you have a really good reason to write the general trend in the second paragraph, try to write them both in the first paragraph. However, this is just a suggestion, not a requirement.
2. Your ‘Introduction (general statement + overall trend/ general trend) should have 75 – 80 words.
3. DO NOT give numbers, percentages or quantity in your general trend. Rather give the most striking feature of the graph that could be easily understood at a glance. Thus it is suggested to AVOID –
“A glance at the graphs reveals that 70% male were employed in 2001 while 40 thousand women in this year had jobs.” And use a format /comparison like the following: “A glance at the graphs reveals that more men were employed than their female counterpart in 2001 and almost two-third females were jobless in the same year. “
Vocabulary to Start the Report Body:
Just after you finish writing your ‘Introduction’ (i.e. General Statement + General overview/ trend), you are expected to start a new paragraph to describe the main features of the diagrams. This second paragraph is called the ‘Body Paragraph / Report Body”. You can have a single body paragraph/ report body or up to 3, (not more than 3 in any case) depending on the number of graphs provided in the question and the type of these graphs. There are certain phrases you can use to start your body paragraph and following is a list of such phrases —
1. As is presented in the diagram(s)/ graph(s)/ pie chart(s)/ table… 2. As (is) shown in the illustration… 3. As can be seen in the… 4. As the diagrams suggest… 5. According to the… 6. Categorically speaking… 7. Getting back to the details… 8. Now, turning to the details… 9. The table data clearly shows that… 10. The diagram reveals that… 11. The data suggest that… 12. The graph gives the figure… 13. It is interesting to note that… 14. It is apparently seen that… 15. It is conspicuous that… 16. It is explicitly observed that… 17. It is obvious… 18. It is clear from the data… 19. It is worth noticing that… 20. It is crystal clear/ lucid that… 21. It can be clearly observed that… 22. It could be plainly viewed that… 23. It could be noticed that… 24. We can see that…
Vocabulary to show the changes:
1. The overall sale of the company increased by 20% at the end of the year.
2. The expenditure of the office remained constant for the last 6 months but the profit rose by almost 25%.
3. There was a 15% drop in the ratio of student enrolment in this University.
4. The population of the country remained almost the same as it was 2 years ago.
5. The population of these two cities increase significantly in the last two decades and it is expected that it will remain stable during the next 5 years.
Tips: 1. Use ‘improve’ / ‘an improvement’ to describe a situation like economic condition or employment status. To denote numbers use other verbs/nouns like increase.
2. Do not use the same word/ phrase over and over again. In fact, you should not use a noun or verb form to describe a trend/change more than twice; once is better!
3. To achieve a high band score you need to use a variety of vocabulary as well as sentence formations.
Vocabulary to represent changes in graphs:
1. The economic inflation of the country increased sharply by 20% in 2008.
2. There was a sharp drop in the industrial production in the year 2009.
3. The demand for new houses dramatically increased in 2002.
4. The population of the country dramatically increased in the last decade.
5. The price of the oil moderately increased during the last quarter but as a consequence, the price of daily necessity rapidly went up.
Vocabulary to represent frequent changes in graphs:
1. The price of the goods fluctuated during the first three months in 2017.
2. The graph shows the oscillations of the price from 1998 to 2002.
3. The passenger number in this station oscillates throughout the day and in early morning and evening, it remains busy.
4. The changes of car production in Japan show a palpitation for the second quarter of the year.
5. The number of students in debate clubs fluctuated in different months of the year and rapid ups and downs could be observed in the last three months of this year.
Tips: 1. 4. DO NOT try to present every single data presented in a graph. Rather pick 5-7 most significant and important trends/ changes and show their comparisons and contrasts.
2. The question asks you to write a report and summarise the data presented in graphs(s). This is why you need to show the comparisons, contrasts, show the highest and lowest points and most striking features in your answer, not every piece of data presented in the diagram(s).
Types of Changes/ Differences and Vocabulary to present them:
Great change / huge difference:
Adjectives Adverbs
Overwhelming Overwhelmingly Substantial Substantially Enormous Enormously
Big change / Big difference:
Significant Significantly Considerable Considerably
Medium change / Moderate difference:
Somewhat Somewhat Moderate Moderately
Minor change / Small difference:
Fractional Fractionally Marginal Marginally Slight Slightly
Dates, Months & Years related vocabulary and grammar:
» From 1990 to 2000, Commencing from 1980, Between 1995 and 2005, After 2012. » By 1995, In 1998, In February, Over the period, During the period, During 2011. » In the first half of the year, For the first quarter, The last quarter of the year,
During the first decade. » In the 80s, In the 1980s, During the next 6 months, In the mid-70s, Next 10 years, Previous year, Next year, Between 1980 – 1990. » Within a time span of ten years, within five years. » Next month, Next quarter, Next year, Previous month, Previous year. » Since, Then, From.
Percentage, Portion and Numbers related vocabulary and grammar:
Percentages: 10% increase, 25 percent decrease, increased by 15%, dropped by 10 per cent, fall at 50%, reached to 75%, tripled, doubled, one-fourth, three-quarters, half, double fold, treble, 5 times higher, 3 timers lower, declined to about 49%, stood exactly at 43%.
Fractions: 4% = A tiny fraction. 24% = Almost a quarter. 25% Exactly a quarter. 26% = Roughly one quarter. 32% Nearly one-third, nearly a third. 49% = Around a half, just under a half. 50% Exactly a half. 51% = Just over a half. 73% = Nearly three quarters. 77% = Approximately three quarter, more than three-quarter. 79% = Well over three quarters.
Proportions: 2% = A tiny portion, a very small proportion. 4% = An insignificant minority, an insignificant proportion. 16% = A small minority, a small portion. 70% = A large proportion. 72% = A significant majority, A significant proportion.89% = A very large proportion. 89% = A very large proportion.
Words/ Phrases of Approximation – Vocabulary:
» Approximately » Nearly » Roughly » Almost » About » Around » More or less » Just over » Just under » Just around » Just about » Just below » A little more than » A little less than.
What criteria would a band 9 graph response satisfy?
Task Achievement: A) Fully satisfies all the requirements of the task. B) Clearly presents a fully developed response.
What will be assessed by the examiner? a) How appropriately, accurately and relevantly you fulfil your task requirements. b) How accurately you write your report and how appropriately you present the data (compare/ contrast/ show the most striking trends/ features/ data.)
Coherence and Cohesion: A) Uses cohesion in such a way that it attracts no attention. B) Skillfully manages paragraphing.
What will be assessed by the examiner? a) No misinterpretation and presentation of data and trend. b) How well you organise your paragraphs. c) Overall clarity and fluency of your report and message. d) How well you have organised and liked the information, data and ideas in your writing. e) Logical sequencing and appropriate use of linking devices between and within your sentences.
1. Do not incorporate more than 3-4 paragraphs. 2. Do not use a single paragraph to describe everything. 3. The conclusion part is optional. If you think that you have already written more than 170 words and have nothing to say, you can skip the conclusion.
Lexical Resource: A) Uses a wide range of vocabulary with very natural and sophisticated control of lexical features. B) Rare minor errors occur only as ‘slips’.
What will be assessed by the examiner? a) The range of vocabulary you have used in your writing. b) How accurately and appropriately you have used words/ phrases while presenting the graph(s) as a report. Tips: Do NOT use words/ phrases that are already given in the question. Do so only if there is no alternative word(s)/ phrase(s) to convey the same meaning/idea.
Grammatical Range and Accuracy: A) Uses a wide range of structures with full flexibility and accuracy. B) Rare minor errors occur only as ‘slips’.
Tips: Do not use the same sentence structure and data comparison/ contrasting style over and over again. Bring a variety in your writing to show that you can formulate different sentence structures without making any grammatical mistakes.
Vocabulary For Academic IELTS Writing Task 1 (part 2)
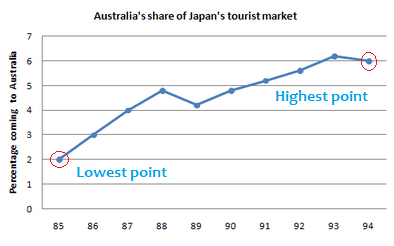
Vocabulary to represent highest and lowest points in graphs:
Example:
1. The price of the oil reached a peak amounting $20 in February and again touched the lowest point amounting only $10 in July. 2. Student enrollment in foreign Universities and Colleges increased dramatically hitting a peak of over 20 thousand in 2004. 3. The highest number of books was sold in July while it was lowest in December. 4. The oil price reached a pick in 2003 while it was lowest in 2006. 5. The selling volume of the DVD hit a pick with 2 million copies sold in a month but after just three months it reached the bottom with only 20 thousand sold in a month.
Vocabulary to show fluctuations/ups and downs/ rise and fall in Verb forms:
Be erratic Rise and fall erratically Changes sporadically Rise and fall irregularly Changes Intermittently
Date, month & year related Vocabulary and Grammatical rules:
Between …(year/ month)… and …(year/ month)… From …(year/ month/ day/date)… to …(year/ month/day/date)… In …(year/ month)… On …(day/ day of the week/ a date)… At ……, In ……, By …… During … (year)… Over the period/ over the century/ later half of the year/ the year… Over the next/ past/ previous …….. days/ weeks/ months/ years/ decades…
Presenting Percentages:
You can present a percentage data in one of the three different ways. It is suggested that you use all these formats in your report writing instead of repeating the same style to show percentages in your writing.
% = In percentage / in % . (20%, 25 percentage, ten per cent etc.) % = In proportion. (two out of five, every student out of three etc. ) % = In fraction. (one-third, two-fifth, a quarter etc.)
Vocabulary to show how many times…
» Exactly the same. » Roughly the same » Practically the same » Twice » Thrice » Four times » Five times …………… » Ten times …………… » Hundred times.
Vocabulary to show how much changed…
» Halved » Equalled » Doubled » Trebled / tripled » Quadrupled (fourfold /four times) » Pentadrupled (fivefold /five times) » Hexadrupled (sixfold /six times) » Septupled (sevenfold /seven times) » Octupled (Eightfold/eight times) » Nonupled (Ninefold/ nine times) …………….. Centupled (hundredfold/ hundred times)
Vocabulary to represent comparison in graphs:
Example:
1. The number of high-level women executives is well beneath than the number of male executives in this organisation, where approximately 2000 people work in executive levels.
2. About 1000 people died in the highway car accident in 2003 which is well above than the statistics of all other years.
3. The number of domestic violence cases was just below 500 in March which is just a little over than the previous months.
4. The average rainfall in London in 2014 was just above than the average of two other cities.
5. The salaries of male executives in three out of four companies were well above than the salaries of female executives in 1998.
Expressions to focus on an item in the graph:
Use the following expression to focus on an item in the graph.
» With regards to » In the case of » As for » Turning to » When it comes to ….. it/ they ….. » Where … is/are concerned,…… » Regarding
Compare and contrast:
Useful Vocabulary to make Comparison and Contrast:
» Similarly, In a similar fashion, In the same way, Same as, As much as, Meanwhile.
» However, On the contrary, on the other hand, in contrast.
Make sure you the appropriate comparative and superlative form of the words when you make a comparison. Here is a basic overview of the comparative and superlative forms to help you remember what you already know.
One Syllable Adjectives with one syllable form their comparatives and superlatives form. In your academic writing task 1, you will often use such comparison and contrast related words.
cheap » cheaper » cheapest || large » larger » largest || bright » brighter » brightest etc.
Exceptions: good » better » best || bad » worse » worst etc.
1. The fast food items in uptown restaurants were comparatively cheaper than that of city restaurants.
2. The largest proportion of water was used in the agriculture sector in most of the Asian countries while the European countries used the highest percentage of water for industrial purposes.
3. The price of the book in store A is cheaper than the price of store B.
4. The temperature decreased further and that made the weather condition worse.
5. The temperature was better in the mid-April but in mid-July, it became worse.
Two Syllables Some adjectives with two syllables form their comparatives and superlatives: pretty » prettier » prettiest || happy » happier » happiest etc.
1. Customers were happier than now, according to the survey, as the price was cheaper in 1992.
2. The overall production level of this company made the authority happier as it was doubled in the last quarter of the year.
But many form their comparatives and superlatives using ‘ more ‘: striking » more striking » most striking || common » more common » most common || clever » more clever/cleverer » most clever/cleverest etc.
Three or more Syllables All adjectives with three or more syllables form their comparatives and superlatives using ‘more’ & ‘most’: attractive » more attractive » most attractive || profitable » more profitable » most profitable || expensive » more expensive » most expensive.
Examples: 1. Custom-made cars was more expensive in 2014 than it is now.
2. The factory offered more attractive overtime rates and that motivated more employees to work for extra times.
Vocabulary to present Linkers: However, On the other hand, Similarly, On the contrary, Meanwhile, In contrast, By comparison.
Vocabulary to show that something/a trend is similar or the same:
Use the following vocabularies if both subjects are the same/ identical:
… Identical to/ Identical with … … Equal to with … … Exactly the same … … The same as … … Precisely the same … … Absolutely the same … … just the same as …
Use the following vocabularies if both subjects are not identical but similar:
… Almost the same as … … Nearly the same as … … Practically the same as … … Almost identical/ similar … … About the same as …
Way to show that something/a trend is just the reverse/opposite:
» The reverse is the case… » It is quite the opposite/ reverse…
Rules of Time Preposition use:
‘In’
»» Use preposition ‘in’ when you talk about years, months, decades, centuries, seasons.
Example: Years= in 1998, in 2015 etc. Months= in January, in December etc. Decades= in the nineties, in the seventies etc. Centuries= in the 19th century, in the 14th century, in the 1980s etc. Seasons= in summer, in winter, in autumn etc.
»» Use preposition ‘in’ to talk about past or future.
Example: Past time= in 1980, in the past, in 1235, in the ice age, in the seventies, in the last century etc. Future time = in 2030, in the future, in the next century etc.
»» Use preposition ‘in’ when you talk about a long period.
Example: in the ice age, in the industrial age, in iron age etc.
‘On’
»» Use preposition ‘on’ when you talk about days (days of the weeks or special days).
Example: Days of the week= on Sunday, on Friday, on Tuesday. Special days= on New Year’s Day, on your birthday, on Independence Day, on holiday, on wedding day etc.
»» Use preposition ‘on’ when you talk about dates.
Example: on July 4th, on 21st January 2015, on 5th May etc.
»» Use preposition ‘on’ when you talk about times (like morning/ afternoon/ evening/ night) of a day.
Example: on Friday morning, on Saturday afternoon, on Sunday evening, on Monday evening etc.
However, notice the below list that shows a further use of preposition ‘in’ and ‘on’ for periods of the days versus periods. This is often confusing and mistakenly used by IELTS candidates. Look at those, notice the use and memorise it.
‘At’
»» Use preposition ‘at’ when you need to express an exact time.
Example: At eight o’clock, at 10: 45 am, at two p.m, at nine o’clock.
»» Use preposition ‘at’ when you talk about meal times
Example: At breakfast time, at lunchtime, at dinner time etc.
»» Use preposition ‘at’ when you talk about weekends, holiday periods, or the night time.
Example: At the weekend, at Christmas, at Easter, at night etc.
Words to make a comparison / contrast:
A bit/ slightly/ a little/ only just/ approximately/ about/ almost/ precisely/ quite/ nearly/ considerably/ a huge/ a great deal/ quite a lot/ completely/ exactly…
Example: » This year population growth of the country is slightly larger than the previous year. » This year population grown is almost twice than 2007. » Sale of the company has increased quite a lot this year.
Using Appropriate Prepositions: You must use the correct preposition in the IELTS writing task 1 to get a high score. Be accurate about the uses of to, by, of, off, in, on, for etc.
Examples: » Papers are sold by the ream. » Oranges are purchased and sold by the dozen. » Students enrollment in the University has increased by 2% this year. » Eggs are counted in dozens. » Rice is measured in kg. » He is junior to me by 4 years. » The employees are paid per week in this factory. » All these products are made of glasses.
Vocabulary – Using the appropriate “Prepositions”: » It started at …, The sale started at $20…, It peaked at … » It reached at/to …, It reached the lowest point /nadir at … »It increased to 80 from 58. It decreased from 10 to 3. »There was a drop of six units. It dropped by 3 units. »It declined by 15%. There was a 10% drop in the next three years.
Formal and Informal expressions and words:
Few more informal expressions with their formal versions are given below. Since IELTS is a formal test, your writing should be formal as well. Using informal words or expressions should be avoided. Some of the informal words are so frequently used that it would be tough for you to eliminate them from your writing. However, we would suggest you make a habit of using formal words and expressions instead- for your performance and band score’s sake.
Vocabulary For Academic IELTS Writing Task 1 (part 3)
Following are the vocabularies for Academic IELTS Writing Task 1 grouped as Noun, Verb, Adjective, Adverb, and Phrase to help you improve your vocabulary and understanding of the usages of these while describing a graph.
A growth: There was a growth in the earning of the people of the city at the end of the year. An increase: Between the noon and evening, there was an increase in the temperature of the coast area and this was probably because of the availability of the sunlight at that time. A rise: A rise of the listener in the morning can be observed from the bar graph. An improvement: The data show that there was an improvement in traffic condition between 11:00 am till 3:00 pm. A progress: There was a progress in the law and order of the city during the end of the last year.
Rapid Increase:
A surge: From the presented information, it is clear that there was a surge in the number of voters in 1990 compared to the data given for the previous years.
A rapid increase/ a rapid growth/ a rapid improvement: There was a rapid growth in the stock value of the company ABC during the December of the last year.
N.B: Following adjectives can be used before the above nouns to show a rapid growth/ increase of something:
Rapid, Sudden, Steady, Noticeable, Mentionable, Tremendous, huge, enormous, massive, vast, gigantic, monumental, incredible, fabulous, great etc.
(The above list is the words which are actually adjective and can be used before nouns to show the big changes)
A/ The peak: Visitors number reached a peak in 2008 and it exceeded 2 million. Top/ highest/ maximum: The oil prices reached the top/ highest in 1981 during the war.
N.B: Some of the words to present the highest/ top of something are given below:
Apex, pyramid, zenith, acme, obelisk, climax, needle, spire, vertex, summit, tower, most, greatest, max, tops, peak, height, crown…
A fluctuation: There was a fluctuation of the passenger numbers who used the railway transportation during the year 2003 to 2004. A variation: A variation on the shopping habit of teenagers can be observed from the data. A disparately/ dissimilarity/ an inconsistency: The medicine tested among the rabbits shows an inconsistency of the effect it had.
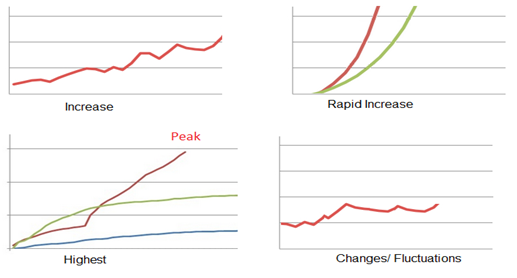
Steadiness:
Stability: The data from the line graph show a stability of the price in the retail market from January till June for the given year. A plateau: As is presented in the line graph, there was a plateau of the oil price from 1985 to 1990.
A fall: There was a fall in the price of the energy bulbs in 2010 which was less than $5. A decline: A decline occurred after June and the production reached to 200/day for the next three months. A decrease: After the initial four years, the company’s share price increased, and there was a decrease in the bearish market.
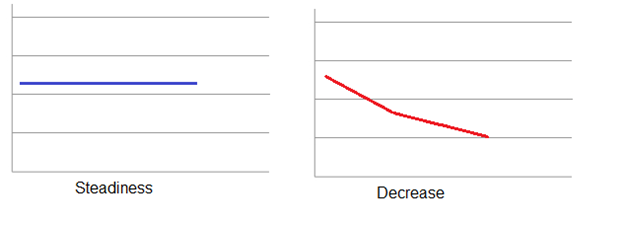
Using ‘Nouns’ and ‘Verbs’ to describe trends in a graph:
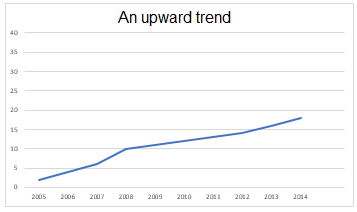
Verbs Nouns
» Increased (to) An increase » Rose (to) A rise » Climbed (to) An upward trend » Went up (to) A growth
» Surge A surge » Boomed (to) A boom / a dramatic increase.
» Decreased (to) A decrease » Declined (to) A decline » Fell (to) A fall » Reduce (to) A reduction » Dipped (to) » Dropped (to) A drop » Went down (to) A downward trend
» Plunge » Slumped (to) A slum / a dramatic fall. » Plummeted (to)
» Remained stable (at) » Remained static (at) » Remained steady (at) » Stayed constant (at) » Levelled out (at) A level out » Did not change No change » Remained unchanged No change » Maintained the same level » Plateaued (at) A plateau
» Fluctuated (around) A fluctuation » Oscillated An oscillation
» Peaked (at) The peak/ apex/ zenith/ summit/ the highest point
» Bottomed (at) The lowest point/ the bottom/ bottommost point
Use ‘adjective/adverb’ to indicate the movement of a trend.
Examples: 1. There has been a slight increase in the unemployment rate in 1979 at which point it stood at 12%. 2. The price of gold dropped rapidly over the next three years.
Use ‘adjective’ to modify the ‘Noun’ form of a trend and use ‘adverb’ to modify the ‘verb’ form of a trend.
Greater or Higher?
We usually use ‘greater’ when we compare two numbers, and ‘higher’ while comparing two percentages or ratio. Reversely, ‘smaller or fewer’ could be used to compare two numbers and ‘lower’ to compare two percentages or ratios. The following table would make it clear —
1. The number of male doctors in this city was greater than the number of female doctors. 2. The number of European programmers who attended the seminar was fewer than the number of Asian programmers. 3. The percentage of male doctors in this city was higher than the percentage of female doctors. 4. During 2010, the inflow of illegal immigrants was lower than that of 2012. 5. the birth rate in Japan in 2014 was higher than the birth rate in 2015.
Vocabulary to compare to what extent / to (/by) what degree something is greater/higher than the other.
» Overwhelmingly, Substantially, Significantly. Considerably. » Moderately, Markedly. » Hardly, Barely, Slightly, Fractionally, Marginally.
Vocabulary to show the sequence:
» Subsequently, Respectively, Consecutively, Sequentially. » Previous, Next, First, Second, Third, Finally, Former, Latter. Tips: “The market shares of HTC, Huawei, Samsung, Apple and Nokia in 2010 were 12%, 7%, 20%, 16% and 4% globally.” This above sentence makes it ambiguous to understand which mobile brand had what percentage of market share. If there are more than 2 values/ figures, you should always use ‘consecutively/ sequentially/ respectively ‘. Using either of these words would eliminate any doubt about the above sentence as it will clearly state that the percentages of market shares mentioned here would match the mobile brands sequentially (i.e. first one for the first brand, the second one for the second brand and so on.)
“The market shares of HTC, Huawei, Samsung, Apple and Nokia in 2010 were 12%, 7%, 20%, 16% and 4% respectively in the global market.”
Note: You do not need to use ‘consecutively/ sequentially/ respectively’ if there are only two values to write.
Vocabulary to show transitions:
Vocabulary to describe different types of data/trends in a paragraph while showing a smooth and accurate transition is quite important. Following word(s)/ phrase(s) would help you do so in an excellent way…
» Then » Afterwards » Following that » Followed by » Next » Subsequently » Former » Latter » After » Previous » Prior to » Simultaneously » During » While » Finally.
Few More Vocabularies:
Few more useful vocabulary to use in your report writing:
» Stood at » A marked increase » Steep » Gradual » Hike » Drastic » Declivity » Acclivity » Prevalent » Plummet
Useful phrases for describing graphs:
» To level off » To reach a plateau » To hit the highest point » To stay constant » To flatten out » To show some fluctuation » To hit the lowest point » Compared to » Compared with » Relative to
Vocabulary For Academic IELTS Writing Task 1 (part 4)
You will often need to use ‘adjectives’ and ‘adverbs’ to indicate the speed of changes in the trend (called ‘Degree of Speed) in your answer. Following is a list of vocabularies that will help you present the quick changes quite effectively.
Adjectives: » Rapid, Quick, Sharp, Swift, Sudden, Wild. » Steady, Gradual, Moderate » Slow, Gentle.
Adverbs: » Rapidly, Quickly, Sharply, Swiftly, Suddenly, Wildly. » Steadily, Gradually, Moderately » Slowly, Gently.
A different set of vocabulary to represent the ‘Degree of Trend’ would also be handy to summarise data presented in a graph. Both ‘adjective’ and ‘adverb’ form of this vocabulary list is given below. Use ‘adjectives’ to modify a ‘Noun’, while ‘adverbs’ should be used to modify a ‘verb’.
Adjectives: » Significant, Huge, Enormous, Steep, Substantial, Considerable, Marked, Dramatic, Abrupt. » Moderate, Slight. » Minimum (singular), Minima (plural)
Adverbs: » Significantly, Hugely, Enormously, Steeply, Substantially, Considerably, Markedly, Dramatically, Abruptly. » Moderately, Slightly. » Minimally
Vocabulary to describe a Map:
IELTS Map Example 1: The map below is of the town of Garlsdon. A new supermarket (S) is planned for the town. The map shows two possible sites for the supermarket. Summarise the information by selecting and reporting the main features, and make comparisons where relevant.
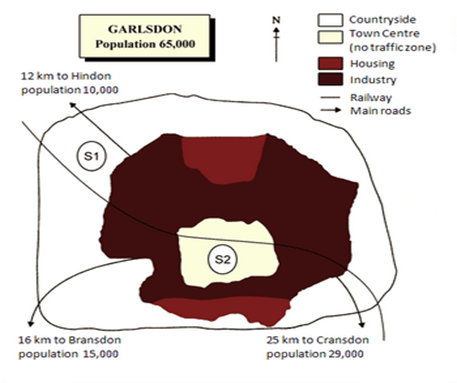
IELTS Map Example 2: The two maps below show an island, before and after the construction of some tourist facilities. Summarise the information by selecting and reporting the main features, and make comparisons where relevant.
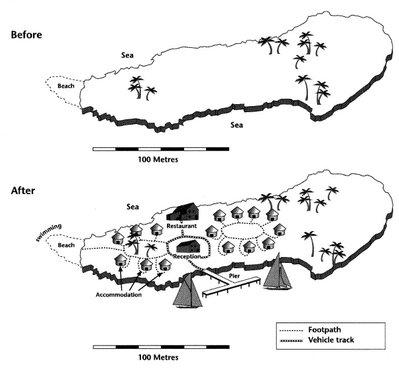
» Horizontal, Vertical. » Circle, Square, Rectangle. » Across, Across from. » Under, Over, Inside, Beside, On top of, Adjacent, Opposite, Next to. » Along, Through, As far as. » Midpoint, Halfway, In the middle. » Intersection, Overlapping. » Exterior. » Parallel to, Parallel, Perpendicular to. » Edge, Diagonal. » In front of the, Behind the. » To the right, To the left. » On the right-hand side, On the left-hand side. » North, South, East, West. » Northern, Southern, Eastern, Western. » To the north, To the East… » Where. » In which, To which, From which. » Built, Erected, Replaced. » Situated, Located. » Changed to/ Converted/ Gave way to/ Became. » While in 2001, it was ……, later, it was converted to ……
Vocabulary to describe a Process Diagram:
In Introduction: The diagram/ picture/ flow chart depicts/ illustrates/ describes the proces of/ how…. While Describing the Process: A) First/ Firstly, Second/ Secondly, Third/Thirdly …… Next/ After that/ Then, Following that/Followed by, Subsequently/ Subsequent to that, Finally/ Lastly… B) Where/ From where/ After which/ After that/ Afterward… C) When/ As soon as/ Immediately, Just after that… D) At the beginning, In the end, Just after the beginning, Just before the end…
To denote the end of a step: A) After this step/ stage/ process… B) Once this stage/ step is completed… To donate what a Step involves: A) The phase/ step/ stage involved…
To denote the repetition of a cycle/ process: A) The cycle/ process then repeat itself. B) The cycle/ process is then repeated.
Vocabulary to describe Predictions:
Some graphs and diagrams not only list down the data that represent something from the past or the present time but also gives a prediction of the future. For instance, a line graph might present the population of a country from 1950 to 2050, over a hundred years. If you are taking the IELTS exam in 2017, you need to describe the population of this country till 2016 using the past tense. For the population figure in 2017, you will use the present tense. Finally, the population from 2018 till 2050 is a prediction and hence you should be using the future tense while describing it in your writing. Moreover, you need to use certain vocabularies to represent such future data/ predictions. Following is a list of such vocabularies to help you accurately describe any predicted data —
It is predicted/ estimated/ projected/ forecasted/ expected/ anticipated that……… will ……….. Is /are predicted/ estimated/ projected/ forecasted/ expected/ anticipated to ………… It gives prediction/ estimation/ projection/ forecast of ………. It …… will ……… ……. Will have ……. by ……. (year/month/decade)…….
Vocabulary to show the value/ incorporate data/ figure:.
You should not write down every piece of data/figure that is given in the diagram in your report writing and doing so would actually hurt your band score. You are expected to mainly show the following in your report writing: —
- Comparison of data/trend
- Contrast of data/trend
- Most significant figures/data/information/ trend (typically 4-6)
- The highest point
- The lowest point
- The overall scenario.
- However, to compare/contrast data or to show a significant change/trend you will need to show a figure that you will use as the base. For example, The British spent over eighty thousand Pounds on average which was twice than the spending of Americans and approximately quadruple than that of Irish. Here, over 80 thousand pounds is the base figure.
Following is a list of vocabulary to use to show such figures in your report writing:
- Is/ was/ were: The percentage of foreign students was exactly ten in 2001 in this university and it rose three times in ten years.
- Stand at/ Stood at: The percentages of males and females who opined that they should be allowed to get married at 21 stood at 14 and 16 in 1990 but witnessed a noticeable decline in 2010.
- Exactly & As high as: The sale in March was exactly 400 and went up as high as 1100 in June.
- Using (): In summer, the number of refrigerators sold (154) was far greater than the refrigerators sold (63) in winter.
- Which: 1. From January to March the death case rose three times which was only 23 between October and December. 2. The temperature, which was 21 degrees C in March, climbed to 39 degrees C in mid-July. Makes up: In the first decade, the population remained steady, which made up 2.8 million approximately, but it doubled in the next 30 years. Constitutes: The initial expenditure, which constituted 280 USD, climbed rapidly and reached the peak during 2014. Accounts for: 1. In June 2016. The number of Asian students enrolment in this university accounted for 45 which is estimated to be almost double in the next year. 2. The number of infected people, which accounts for nine, is markedly lower than the number of infected patients in the last month, which accounted for forty.
Vocabulary to write the Conclusion part:
- To draw the conclusion: In conclusion / To conclude / On the whole. To Summarize: In short / In brief / To sum up / In summary.
- However, according to some teachers and examiners, a more appropriate ways of drawing the conclusion of your graph writing should start with the words/ phrases:
Generally, Generally speaking, All in all, From the graphs, it is quite evident that.
- Examples: 1. In conclusion, third world countries have improved their production sectors like garments, over the last 10 years whereas the first world countries have improved their technology and research sectors during the same period.
- 2. In brief, the overall sale of the company has improved in the last 5 years except 2005 when the sale reduced significantly due to retrenchment.
- 3. All in all, the process of building an IC is a complex one and involves more than eight steps to complete including the testing phase.
- 4. It is quite evident that the women employment progressed remarkably in the last decade and in some employment sectors women are well ahead of men.
- 5. To conclude, weather forecasting is a complex process and a great deal of technology is used to prepare and broadcast the reliable weather forecasting.
- Tip: ‘ In a nutshell ‘ is not a formal expression and this is why you should not use it in your IELTS Writing.
Vocabulary For Academic IELTS Writing Task 1 (part 5)
Uncommon vocabulary to use in your Report Writing:
Everybody uses some common vocabularies to describe a diagram and to write a report. For instance, there would be hardly anyone who does not use the words ‘increase, decrease, fall, higher, fluctuate, climb, decline, quickly increase, sharply decrease, and those are really obvious words used by most of the IETLS candidates. If you too use these overused words and phrases, you would not be able to give an impression that your range of vocabulary is stronger and richer than others. This article “Vocabulary For Academic IELTS Writing Task 1 (part 5)” solely focuses on introducing you to a nice set of words and vocabulary that you can use in your Academic IELTS Task 1 to achieve a high band score:
» Illustration : can replace – “diagram, chart.” » As the diagrams suggest : can replace – “As can be seen, According to the diagrams. » Illustrate : can replace – “describe, show, present data on.” » Trifling : can replace – “small, insignificant.” » Delineate : can replace – “show, present, describe.” » From this graph, it is quite evident that : can replace – “In conclusion, In summary, In general.” » The most possible ground : can replace – “the most common reason.” » Elaborate : can replace – “describe, explain.” » Nadir : can replace – “the lowest point.” » Apex/ Vertex : can replace – “the highest point.” » Soared : can replace – ” sharply increased.” » Skyrocketed : can replace – ” very quickly increased. » Frantically : can replace – “very quickly, very rapidly.” » Slumped : can replace – “quickly dropped.” » Plummeted : can replace – “quickly dropped.” » Surged : can replace – “went up, climbed, increased.” » Deteriorate : can replace – “fall.” » Dip : can replace – “fall, decline.” » Dive : can replace – “fall, drop.” » Go into free-fall : can replace – “fall, drop, decline, decrease.” » Plummet, plunge, slum : can replace – “fall, drop, decline.” » Take a nosedive : can replace – “reduce, drop, fall, decline.” » Slide : can replace – “drop, fall.” » Decade : can replace – “ten years.” » Projected : can replace – “predicted, forecasted, estimated.” » Overwhelmingly : can replace – “greatly, significantly.” » Hardly : can replace – “barely, merely, » At the onset it is clear : can replace – “As can be seen from the graph.” » Indicate : can replace – “point out.” » All in all : can replace – “In summary, in conclusion.” » Obtain : can replace – “get.” » Commence : can replace – “start”. » In the interim : can replace – “in the meantime.” » Correct : can replace – “right”. » Inexpensive : can replace – “cheap.” » Depict : can replace – “show.” » Plateaued : can replace – “remained the same.” » Oscillate/ Vacillate/ Palpipate : can replace – “fluctuate.” » Declivity : can replace – “drop, fall, decrease”. » Acclivity : can replace – “An upward slope, an upward trend, increase.” » A steep fall : can replace – “A quick fall”.
Vocabulary to ensure high band score in IELTS Graph writing:
Few more useful vocabulary to ensure high band score in IELTS Graph writing:
Meaning: Reach a state of little or no change after a period of activity or progress, levelled out. Example: The share price of the ACME company have plateaued out.
Meaning: Submerge, lower plunge, sink. Example: The employee satisfaction score then dipped in 2005 and remained at this level for the next three years.
Meaning: Decrease, decline, deteriorate. Example: The number of passengers then slumped and reached to only 2500 compared to four thousand in the previous year.
Meaning: Sheer, sharp, abrupt, perpendicular. Example: The steep decline of the heavy drinkers contributed to the enhanced life expectancy in this country.
- Substantial
Meaning: Notable, considerable, significant, marked Example: A substantial number of these diploma holders did not finish their tertiary education.
Meaning: Significant, notable, noteworthy, remarkable, considerable, substantial. Example: The dramatic rise of the car use has polluted the air.
Meaning: Step by step, slow but continuous, uniform, successive, progressive, steady, regular, even, consistent. Example: The participation of women in these sectors gradually improved and in 2015, more than 38% women were employed in these job sectors.
Meaning: Reduce, decrease, plummet, plunge, slump, shrink, fall off, lessen. Example: Investment in clean energy declined in the third world countries in 2005 while it actually doubled in most of the first world countries.
- An upward trend
Meaning: The tendency of being higher, something that goes upward. Example: An upward trend in the number of club members was visible from 2005 to 2007 after which it actually dropped.
- Respectively
Meaning: Consecutively, sequentially. Example: Car theft cases in Denmark, Sweden, UK and Japan were respectively 240, 210, 354 and 189 in January 2018.
- Consecutively
Meaning: Sequentially, progressively. Example: While the daily fast food consumption per person in the UK was 50 grams, it was 61, 32 and 25 grams in the USA, Sweden and China consecutively .
Meaning: The highest point, peak, vertex, pinnacle, summit, top. Example: The price then increased noticeably and reached the apex in 2017.
Meaning: Ascent, climb, rise. Example: The activity of the car ownership in Europe further developed and reached to 57% in 2011.
Meaning: A downward slope, decline, decrease. Example: The declivity on the number of female members in 2011 was almost double than that of the previous year.
- Remained stable
Meaning: Remained constant, did not change. Example: The ratio of highly skilled professionals in the former country increased significantly but remained stable in the later one.
Meaning: Plunge, fall, decline, slump, nosedive, drop, decrease. Example: The ratio of unemployed youth, who have vocational education, plummeted in 2005 than that of two years earlier.
Meaning: Common, general, usual, prevailing, widespread, endemic, rampant. Example: The prevalence of the trend could be better understood if we compare the data with that of the last twenty years.
Meaning: To remain stable/ intact, to come to a stop. Example: The old hospital stood at the same position as it was five decades earlier but the free-space in front of it was converted to a car parking area.
Meaning: Identify, itemise, list, summarise, recite, specify, quote, relate. Example: The illustration enumerates how Australian Bureau of Meteorology collects up-to-the-minute information on the weather.
Meaning: Completely, hurriedly, abruptly. Example: The technological advancement has radically changed the way employees used to work in their offices.
- Positive development
Meaning: Improvement, progress, stay forward, increase, grow, rise. Example: The increasing number of female executives in the company is considered a positive development .
Meaning: Following, next, successive, succeeding. Example: Despite a hike at the beginning of the year, the oil price steadily declined in the subsequent months until June 2017.
Meaning: Start, begin, set in motion, open, initiate, inaugurate. Example: The construction of the road was commenced at the beginning of 2001 and ended in 2003.
Meaning: Slump, plummet, shrink, fall off, decline, decrease, drop, reduce. Example: Employers’ contribution to the fee for skill development courses has plunged to a great extent in the last decade, as the graph suggests.
Meaning: Increase, went higher, jump. Example: Duration of watching TV as a leisure activity surged among the elder people in Australia after 1998.
Meaning: Fall, descent, plummet, plunge, nosedive, drop. Example: Consumption of word resources in some Asian countries, on the contrary, has dived after 2014.
Meaning: Swift, sudden, instantaneous, hurried, startling, unanticipated, unexpected, rapid, speedy. Example: The abrupt rise of the population in the early 21st century is contrasting to that of the beginning of the 18th century, as the data suggests.
Meaning: Correlative, corresponding, parallel, reciprocal. Example: The academic performance and professional efficiency are somewhat relative to each other despite the presence of many other variables, according to the survey outcome.
Meaning: Tolerable, adequate, moderate, fair, satisfactory, acceptable. Example: The wheat export then witnessed a modest decline and it affected the revenue earned in 2015.
Meaning: Disparity, inequality, dissimilarity, difference, variety, diversification. Example: It can be inferred from the given data that variations in the pH values are sometimes detrimental.
Meaning: Explain, make clear, clarify, throw/shed light on, explicate, annotate. Example: The line chart elucidates how much waste was recycled in the UK between 1990 and 2015.
Meaning: Untangle, clear up, disentangle, explain, straighten out, separate out. Example: The data unravel the fact that the crime rate increases in the later decades despite some stringent initiatives from the law-enforcers.
»» Make sure you know all of these words/ phrases and can use them while writing a report/ describing a graph.
- Cam 13 IELTS Reading Vocabulary Cam 13 Test 1 Passage 1 Cam 13 Test 1 Passage 2 … Read more
- Cam 15 IELTS Reading Vocabulary Cam 15 Test 1 Passage 1 Cam 15 Test 1 Passage 2 … Read more
- Vocabulary IELTS Reading RA01IE04 Improve your IELTS reading by learning Vocabulary that is most commonly used in reading papers
- Vocabulary for IELTS Reading – List RA01IE03 Improve your IELTS reading by knowing the most relevant reading related English words.
- Vocabulary List RA01IE02 IELTS Reading You should know the meaning of following words/phrases for being able to … Read more
- Vocabulary List IEAC033R IELTS Reading Test 9 You should know the meaning of following words/phrases for being able to … Read more
- Vocabulary List IEAC034R IELTS Reading Test 9 IELTS Vocabular IEAC034R Reading Test 9 Translated By Google Translator.There may be some … Read more
- Vocabulary List IEAC033R IELTS Reading Test 2 Important Note: Translated By google translator, there may be some errors.You should … Read more
- Vocabulary List IEAC033R IELTS Reading Test 1 IELTS Vocabulary for Reading Important Note: Translated By google translator, there may … Read more
Share this:
- Tags IELTS coaching centre , ielts essays , ielts institute , Ielts malerkotla , ielts writing task 1
WhatsApp us
IELTS Writing Process Diagram Vocabulary for Task 1
On IELTS Writing Task 1, you’ll need to describe a graphic. Sometimes, this can be a type of chart . Other times, it will be a process diagram. So how do you know what process diagram vocabulary IELTS examiners are looking for? That’s where Magoosh comes in!
In this post, we’ll look at words and phrases you can use to describe processes on IELTS Academic Writing Task 1 . (And for additional tips on IELTS vocabulary, check out our collection of the best IELTS Writing tips and Task 1 Language and Vocabulary guide !)
What is a Process Diagram on the IELTS?
A process diagram is an illustration that shows you how something is done. It could be anything from the creation of a product to the recycling cycle (as in this IELTS Task 1 process example !)
Generally, you’ll find two types of process questions. The first is a manufacturing process: something that humans do. The second is a natural process: something that occurs in nature.
Within your essay, you won’t need to come up with deep insights or hypotheses about the diagram that you’re looking at. Instead, you’ll simply need to follow the prompt, describing what you see. This can be surprisingly complex, so practice is crucial.
No matter what type of process the prompt asks you to write about, you can use the same kinds of process vocabulary IELTS words and phrases in your response!
Process Diagram Vocabulary for IELTS
Words to describe the type of diagram.
- Distributes
- Human-produced
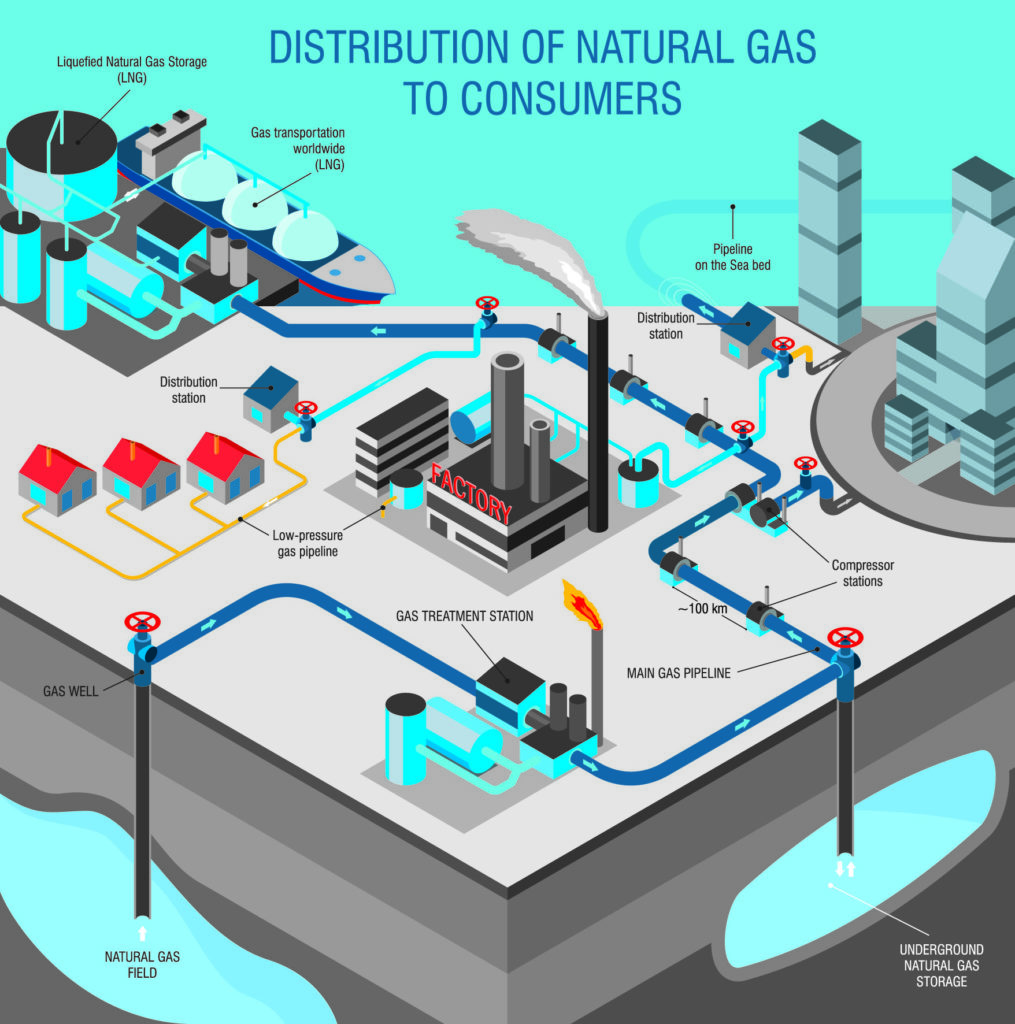
This diagram illustrates the man-made process that a company uses to distribute natural gas to consumers. Overall, this seven-step , linear process illustrates which types of consumers the company prioritizes.
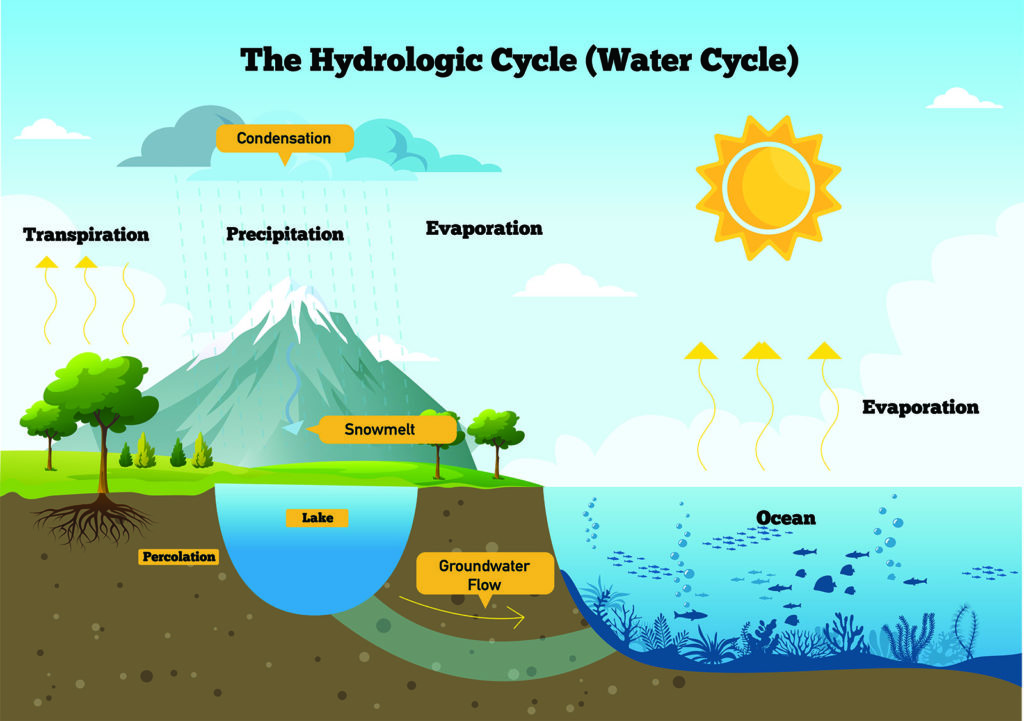
This diagram depicts the natural hydrological cycle process by which water moves through the environment. This cyclical process involves steps , such as evaporation, condensation, and precipitation.
Words to Describe the Steps in the Process
- First/firstly
- Second/secondly
- After/afterwards/once
- Subsequently
- Finally/lastly
Process Diagram Vocabulary IELTS Examples
First , the product begins in the design stage . Following this , prototyping and 3D printing occur. Next , the product moves to the production stage .
In the first step of this process, three things happen simultaneously. Light, water and carbon dioxide all enter the chloroplast. Once this has happened, the water enters the thylakoid and carbon dioxide becomes part of the Calvin cycle in the second step . Subsequently , in the third step , the chloroplast produces oxygen and sugar.
Words to Describe a Cycle or Repetition
- Continues indefinitely
- Repetitious

This cyclical process technically begins when a new product is produced, though it can continue to loop indefinitely .
While the linear process is technically complete after Delivery (Step 7), the diagram depicts this as a repetitious , or cyclical , process. This is likely because the need for additional goods will recur , and so the cycle of the delivery process could theoretically continue indefinitely .
Verbs to Know for Describing a Process
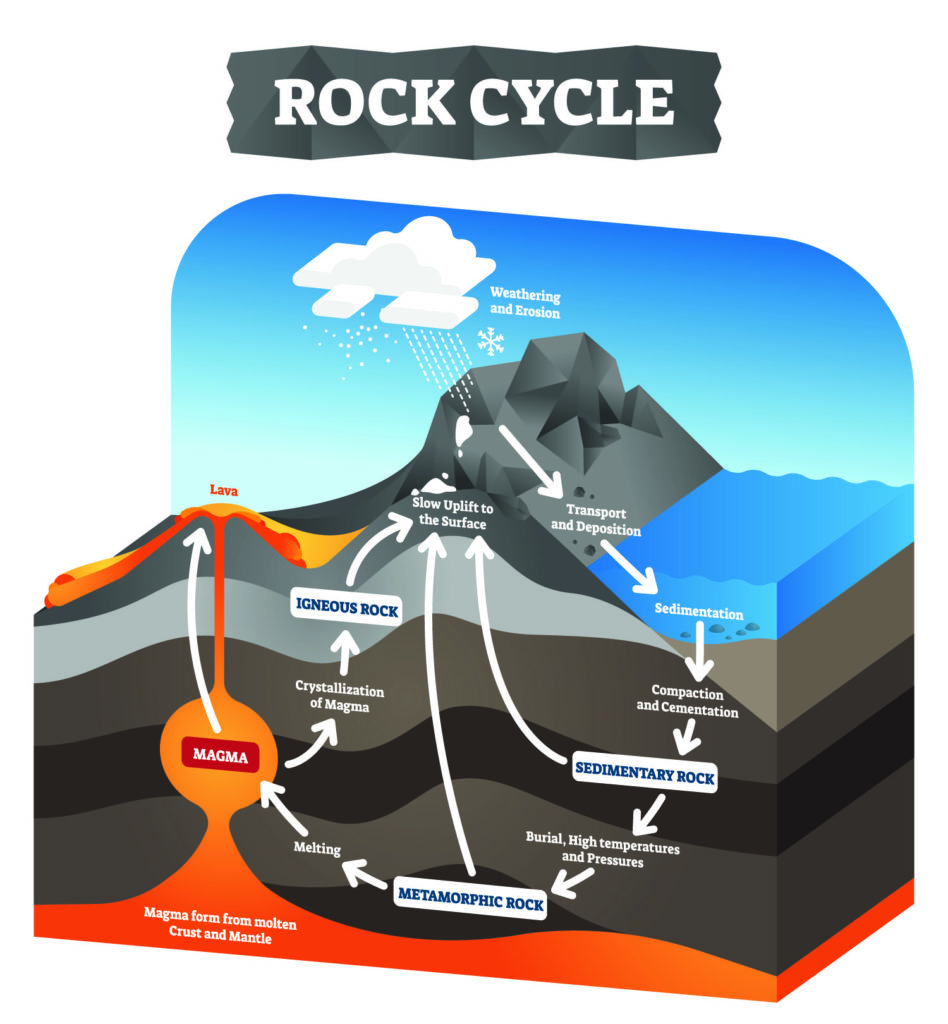
The rock cycle process begins with weathering and erosion. It then continues with transport and deposition. The process ends with melting rock in magma.
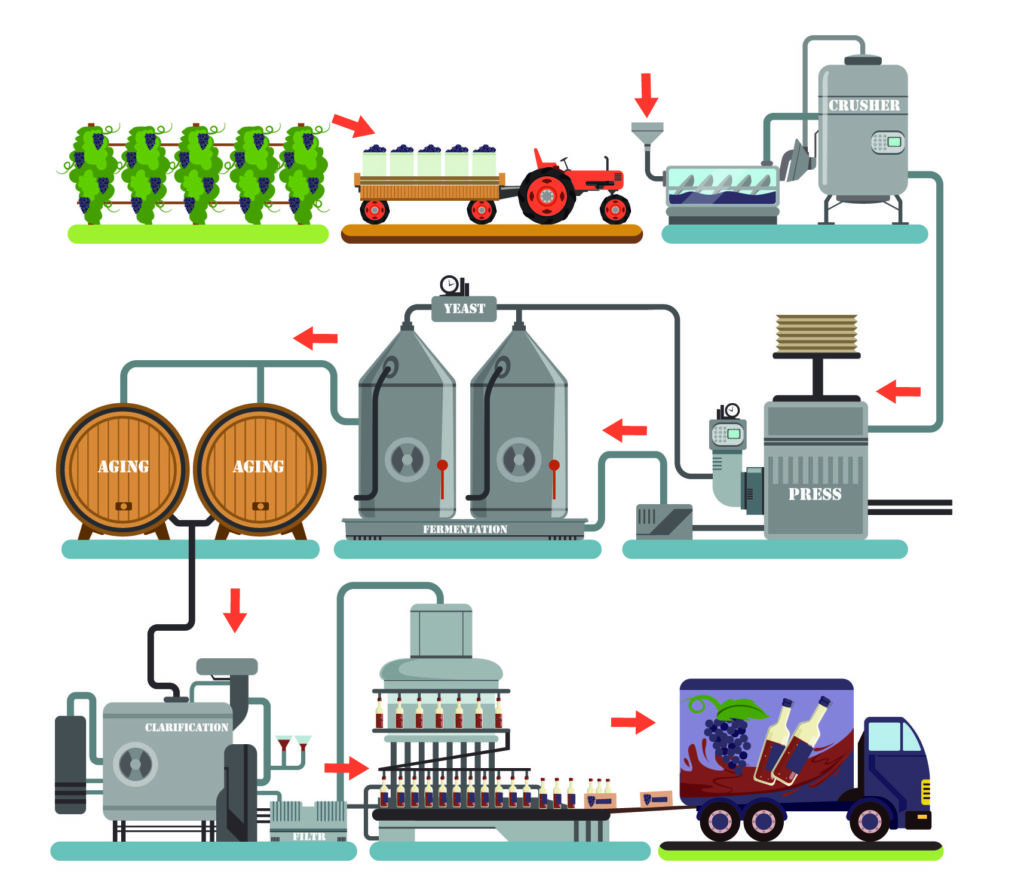
Clarification follows the pressing stage. The cycle then ends as the wine is bottled and shipped.

Eliot Friesen-Meyers is the Senior Curriculum Manager for Magoosh IELTS and TOEFL. He attended Goshen College (B.A.), New York University (M.A.), and Harvard University (M.T.S.), gaining experience and skills in curriculum development, ESOL instruction, online teaching and learning, and IELTS and TOEFL test prep education. Eliot’s teaching career started with Literacy Americorps in Pittsburgh, Pennsylvania, and later, taught ESL programs at Northeastern University, University of California-Irvine, and Harold Washington College. Eliot was also a speaker at the 2019 TESOL International Conference . With over 10 years of experience, he understands the challenges students face and loves helping them overcome those challenges. Come join Eliot on Youtube , Facebook , and Instagram . Recent blog posts Complete Guide to IELTS Writing Task 1 Complete Guide to IELTS Writing Task 2
View all posts
More from Magoosh

Leave a Reply Cancel reply
Your email address will not be published. Required fields are marked *

Search Discipline, Institutes or Program
Latest IELTS Writing Vocabulary Task 1 : A Complete List
by CANAM Group
- By: CANAM Group
- Updated On: Aug 09,2023 04:17 PM IST
Vocabulary is an important part of IELTS writing task 1. Read this blog to know how to attempt IELTS writing task 1, its vocabulary, the best tips to follow and many more. The writing section is one of the four sections of IELTS. To succeed in the same, one should know IELTS Writing Vocabulary. Both task 1 and task 2 of the writing section demands that the aspirant has a good hold on vocabulary. Read the blog to know more about the IELTS writing vocabulary, how to attempt writing task 1, tips for scoring well and many more.
Table of Contents
- • What is IELTS Writing Task 1?
- • 5 Common Mistakes in IELTS Writing Task 1
- • IELTS Writing Task 1: Preparation Strategy
- • IELTS Writing Task 1 Vocabulary
What is IELTS Writing Task 1?
Assessment criteria, 5 common mistakes in ielts writing task 1, ielts writing task 1: preparation strategy, ielts writing task 1 vocabulary, linking words, listing words, providing examples, highlighting key features, consequences, causes and reason, trends words, comparison words, approximation and fraction.
Have questions? we have all the answers. Find out all the information you need about this program, student visa, work permit, and more.
The best way to prepare for IELTS Writing Task 1 is by practicing old papers and improving where you lack.
Get great articles direct to your inbox
The latest news, articles, and resources, sent straight to your inbox every month.
Popular Universities to Study Abroad
World class education waiting for you.

Navitas Group - Australian College of Applied Professions (ACAP) - Melbourne Campus
Victoria, Australia • 12 Programmes
Tuition Fee : AUD 26500-27000 / year

University of New Brunswick - Saint John Campus
New Brunswick, Canada • 53 Programmes
Tuition Fee : CAD 16500-22500 / year

University of South Wales - Cardiff Campus
Wales, UK • 47 Programmes
Tuition Fee : GBP 13000-14000 / year
Shorelight Group - University of Massachusetts - Boston
Massachusetts, USA • 68 Programmes
Tuition Fee : USD 35000-36000 / year

Canadian Tourism College
British Columbia, Canada • 4 Programmes
Tuition Fee : CAD 18500-24500 / year

Lakehead University - Thunder Bay Campus
Ontario, Canada • 195 Programmes
Tuition Fee : CAD 28500-38000 / year

New Zealand Skills and Education College (NZSE) - Auckland CBD Campus
Auckland, New Zealand • 7 Programmes
Tuition Fee : NZD 18000-18500 / year

Northeastern University - Vancouver Campus
British Columbia, Canada • 3 Programmes
Tuition Fee : CAD 0-0 / year
Latest at CANAM
Events, webinar, college / university visits and more.

Canadian Universities & Colleges Admissions Fair & Workshop
Study in Canada • Event
- Study in Canada
Amritsar • 10:30AM
9th April to 19th April • 10:30 AM to 5:00 PM

Canada Application Day-2024
Study in Canada • Application Days
Ahmedabad • 11:00AM

University Visit - University of Guelph & University of Guelph Humber
Study in Canada • University Visit
New Delhi • 03:00PM
Top countries destinations
Popular university and colleges for Studying abroad.
- Study in Australia
- Study in New Zealand
- Study in UK
- Study in USA
Bond University Queensland
Central queensland university - rockhampton, north campus queensland, charles sturt university - wagga wagga campus new south wales, deakin university - geelong waurn ponds campus victoria, engineering institute of technology - perth campus western australia, griffith university - nathan campus queensland, james cook university - cairns campus queensland, la trobe university - bendigo campus victoria, lci melbourne - art & design school victoria, university canada west british columbia, university of windsor ontario, dalhousie university nova scotia, carleton university ontario, cape breton university nova scotia, university of ottawa ontario, university of saskatchewan saskatchewan, university of regina saskatchewan, university of guelph ontario, ara institute of canterbury - city campus southland, aspire 2 international - auckland campus auckland, auckland university of technology - city campus auckland, eastern institute of technology - hawke bay campus hawke's bay, manukau institute of technology -manukau campus auckland, massey university - auckland campus auckland, nelson marlborough institute of technology (nmit) - nelson campus southland, new zealand institute of business & technology (nzibt) auckland, the university of waikato - hamilton campus hamilton, university of warwick england, de montfort university england, university of west london england, university of strathclyde scotland, aston university england, university of bath england, university of liverpool england, durham university england, newcastle university england, kent state university ohio, san jose state university california, wright state university ohio, clark university massachusetts, rowan university new jersey, arkansas state university arkansas, university of wisconsin milwaukee wisconsin, southern illinois university edwardsville illinois, university of findlay ohio, popular english language proficiency exams.
IELTS is an English language proficiency test required for studying...
IELTS eligibility
IELTS Exam Type
IELTS Exam Dates
IELTS Test Centres
The skill and capability to communicate efficiently and effectively is the...
PTE Exam Pattern
PTE Exam Registration
PTE Exam Fee
PTE Exam Centres
TOEFL is a well-known English language test that is accepted...
TOEFL Exam Pattern
TOEFL Exam Registration
TOEFL Exam Fee
TOEFL Exam Centres
The CAEL exam is used to assess a student's level of English...
CAEL Exam Pattern
CAEL Exam Registration
CAEL Exam Fee
CAEL Exam Centres
The skill and capability to communicate efficiently
Duolingo English Test Exam Pattern
Duolingo English Test Exam Registration
Duolingo English Test Exam Fee
Duolingo English Test Exam Centres
The Canadian company Paragon Testing Enterprises, a division...
CELPIP Exam Pattern
CELPIP Exam Registration
CELPIP Exam Fee
CELPIP Exam Centres
IELTS Online
- Live Classes

Blogs and Articles
Curated content to keep you updated on the latest education trends, news and more.
An Introduction To Studying In Australia
Updated on • Apr 01,2024 05:56 PM IST • Australia
20 Common IELTS Essay Topics for Writing Task 2
Updated on • Apr 01,2024 05:46 PM IST • IELTS
Why Study in Ireland
Updated on • Apr 01,2024 04:30 PM IST • Ireland
Study in New Zealand without IELTS
Updated on • Mar 30,2024 05:35 PM IST • New Zealand
Masters in Psychology in Canada: Best Universities, Eligibility, Documents, Admissions Process and Scholarships
Updated on • Mar 29,2024 11:47 AM IST • Study in Canada
Guide to Student Housing in Nova Scotia
Updated on • Mar 29,2024 10:49 AM IST • Study in Canada
Masters in Geology in Canada: Colleges, Courses, and Fees
Updated on • Mar 28,2024 11:32 AM IST • Study in Canada
MBA in New Zealand: Universities, Eligibility, Types, Documents and Job Opportunities
Updated on • Mar 27,2024 05:13 PM IST • New Zealand
New Zealand IELTS Band Requirements
Updated on • Mar 20,2024 05:09 PM IST • New Zealand
Project Management Courses in Canada: Eligibility, Cost, Universities and more
Updated on • Mar 19,2024 03:09 PM IST • Courses in Canada
Study Loan for Canada : A Complete Guide
Updated on • Mar 18,2024 05:23 PM IST • Education Loans
Intakes in Germany for International Students
Updated on • Mar 18,2024 04:48 PM IST • Germany
Colleges in Edmonton Canada for International Students
Updated on • Mar 18,2024 04:10 PM IST • Colleges in Canada
How to Apply for Student Loans to Study Abroad?
Updated on • Mar 18,2024 01:14 PM IST • Study Abroad
Master's in Mechanical Engineering in Germany: Programs, Eligibility, & More
Updated on • Mar 18,2024 11:26 AM IST • Germany
Spring Intake in the USA 2025: Universities & Preparation Timeline
Updated on • Mar 16,2024 11:32 AM IST • USA
Best universities in UK for MS in Computer Science
Updated on • Mar 15,2024 01:28 PM IST • UK
Universities in Leeds (UK) for International Students
Updated on • Mar 15,2024 11:51 AM IST • UK
Exams Required to Study in UK
Updated on • Mar 15,2024 11:13 AM IST • UK
MBBS in Australia: Top Universities, Syllabus, Cost of Study, Eligibility, Scholarships & Jobs
Updated on • Mar 15,2024 10:14 AM IST • Australia
Related Blogs and Articles
A little effort to provide an authentic and reliable content for keen readers!!
Updated on • 01-04-2024 • IELTS
Minimum IELTS Scores to Study in New Zealand Universities
Updated on • 08-03-2024 • IELTS
Describe a place you would like to visit - IELTS Cue Card
Updated on • 07-03-2024 • IELTS
PTE vs IELTS : Know the Difference and Which is Easier?
Updated on • 06-03-2024 • IELTS
Most Common IELTS Writing Topic
Updated on • 21-02-2024 • IELTS
What is a good score for IELTS?
Updated on • 20-02-2024 • IELTS
Describe a Live Sports Match That You Have Watched - IELTS CUE Card
Updated on • 17-02-2024 • IELTS
IELTS Speaking Part 1: Shopping
Updated on • 07-02-2024 • IELTS
IELTS Technology Vocabulary
Updated on • 03-02-2024 • IELTS
IELTS Speaking Vocabulary- Travel and Tourism
Updated on • 02-02-2024 • IELTS
IELTS Speaking Vocabulary- Food and Nutrition
Difference between IELTS and TOEFL
Updated on • 30-01-2024 • IELTS
Universities in Canada accepting IELTS 6 & 6.5 Band for Masters
Updated on • 20-01-2024 • IELTS
IELTS Reading Practice Tests 2024: Reading Passage and Sample Questions
Updated on • 13-01-2024 • IELTS
IELTS Letter Writing Topics 2024
Canada IELTS band requirements 2024
Updated on • 12-01-2024 • IELTS
IELTS Exam Dates 2024 in India
Animal Minds Parrot Alex Reading Answers - IELTS Reading Practice
Updated on • 02-01-2024 • IELTS
Adam's Wine IELTS Reading Answers Explained
Updated on • 29-12-2023 • IELTS
Describe a Person Who Solved a Problem in a Smart Way - IELTS Cue Card
Updated on • 27-12-2023 • IELTS
Request for call back successful
Someone from our team will get back to you within 24 hours.
Your information has been received

Contact via Whatsapp
Please provide the following details & we will get back to you at the soonest.
Whatsapp request successful!
Someone from our team will get back to you on Whatsapp within 24 hours.
Call Team Canam
1800 137 8055 or
Request Call Back
Please provide the following details so that we can reach out to you.
Request for call back successful!
Canam Virtual Counselling
405-406, 4th Floor, Kanchenjunga Building, 18, Barakhamba Road, New Delhi 110001 India
Select mode of communication

Join Virtual Counseling via Zoom

Schedule an Online Appointment
Request for Zoom Session
Please provide the following details to help us fix you a zoom session.
Please provide the date and time that works best for you.
Start your journey to study abroad
Please fill in the information and we will get back to you with more information.

Search programs matching your eligibility criteria
Don’t know where you fit the best? Take these 3 steps and find out what’s best for you or you can contact us and we will get back to you within 24 hours.
- 1 Education Background
- 2 Preference
- 3 Test Score
What is your country of Education?
What is your highest level of Education?
Your Highest Qualification
What is your most recent overall grade?
Grading Scheme
Grading Average
Which country are you interested in?
Which level of study are you interested in?
Which discipline or field of study are you interested in?
Which English proficiency test have you taken?
If not taken yet, enter predicted score
What standardized tests have you taken within the last 5 years?
How would you like to connect?

Please fill in the information to get free access to Canam's awarded intelligent course search platform.

- IELTS General Writing Task 1: Advanced vocabulary for letters
One of the marking criteria for Writing Task is vocabulary - the variety of words and expressions that you use. For a score of 7 and above, it is necessary to include advanced words and less common expressions in the letter. It is also important to start and finish the letter correctly.
How to start a letter
The writing style (formal / informal) defines the words that you use to start and finish the letter: There are two types of formal letters: You write to an organization (you don’t know who you are addressing to) You write to the head, teacher, tenant and you know the name of the person you are addressing to. In formal / semi-formal letters, after the greeting, we always write the purpose of the letter:
I am writing to inform you that ... I am writing to ask/inquire ... I am writing with regard to ... I am writing in connection with ... I am writing with reference to ... I would like to express my concern about ...
In informal letter after the greeting we write:
Apologies for not writing for so long, but I’ve been really busy … It’s been a long time since we saw each other. I’m just writing to let you know that …
The body of the letter
Each letter has its own purpose: complaint, request, recommendation / advice. Therefore, we select constructions and expressions that correspond to the particular purpose of the letter:
ASK FOR INFORMATION
I would be grateful if you could ... I would be grateful if you could inform me ... Could you please tell me if ... I wonder if you could tell me ... I would like you to ... I need to ask your advice about ...
I'm writing to express my dissatisfaction about ... I am writing you to express my dissatisfaction about the poor service provided by your airline. I am writing to express my dissatisfaction about the hotel room that is booked for my stay.
I'm very grateful for ... I'd like to thank you very much for ... I very much appreciated ...
I'm very sorry that/about ... Please forgive me for ... I'd like to apologize about ... Please accept my apologies about ...
If I were you, I’d … You should … You ought to … Why don’t you …
Would you like me to … I think it would be great if you … If you like, I’ll …
Useful phrases to finish the letter
Thank you very much for your attention. I hope the situation will be resolved soon. I look forward to hearing from you. Thank you very much for your cooperation. If you require any further information, please do not hesitate to contact me.
Hope to hear from you very soon. Keep in touch! If you need to know anything else, just get in touch with me as soon as you can. Thanks a lot for your help and I hope to hear from you soon.
Formal letter of complaint
Introduction:
I am writing to express my disappointment regarding the … (level of service at your hotel/restaurant/ level of customer service at your hotel during my visit last month). I am writing to express my dissatisfaction with the … (standard of accommodation at your hotel). I am writing to complain about the fact that … (there is no heating in our house).
Explain the problem:
Unfortunately, … (the heater is out of order) We are / I am extremely unhappy about this situation. This is making our lives uncomfortable. The best solution would be for me to return the wrong items to you. I request my money be refunded.
Conclusion:
I look forward to hearing from you soon.
- You are here:
- Prepare for IELTS
- IELTS Writing
- How to check IELTS Results
- IELTS Academic and IELTS General: differences and similarities
- Computer delivered IELTS
- IELTS Band Scores and English levels comparison chart
- IELTS Exam: Test structure and Format
- Essay Structure
- Detailed Analysis
- Academic Task 1
- Academic Task 2
- IELTS Vocabulary
- IELTS Listening
- IELTS Reading
- IELTS Speaking
- IELTS Writing Course
- Punctuation Guide
- Teacher Training: How to Teach IELTS
- Teacher Training: IELTS Writing for Teachers
- IELTS Training Sessions for Teachers
- Master IELTS General: Letters
- A Beginner’s Guide to IELTS
- Common Grammar Mistakes [for IELTS Writing Candidates]
Writing Correction Service
- Free IELTS Resources
- Practice Speaking Test
Select Page
How to Use More Advanced Vocabulary for Task 1 [IELTS Writing]
Posted by David S. Wills | Oct 11, 2017 | IELTS Tips , Writing | 2
Getting a high band score in the IELTS writing exam seems impossible to some students, but it’s not. In fact, there are a few things you need to do to boost your chances: learn to structure your writing , increase your vocabulary , and understand the question . Another way is to use more advanced vocabulary for task 1.
Why Use More Advanced Vocabulary for Task 1?
In the IELTS writing exam, you need to prove to the examiner that you have a good grasp of the language, and so using “increase” and “decrease” just isn’t enough. It sounds boring and doesn’t show you really know how to explain the data. Instead, you should use some lesser known words and phrases to highlight your expanded vocabulary. Moreover, you should use words that are accurate to the trends you are describing.
How to Use More Accurate Language?
Firstly, you need to know a wide range of useful IELTS vocabulary for task 1. Learn words like “soar” and “rocket,” as well as “substantially” and “modestly.” Then you need to figure out how to use them correctly . It is not enough just to guess when and how to use them. Your language should be accurate to the data you describe. Finally, practice word order to ensure you mix verbs, nouns, adjectives, and adverbs correctly.
A Lesson in Advanced Vocabulary Use
This PPT explains how to use better and more accurate language in the IELTS writing task 1. If you have any questions about it, leave a comment below and I will try to reply quickly.
About The Author
David S. Wills
David S. Wills is the author of Scientologist! William S. Burroughs and the 'Weird Cult' and the founder/editor of Beatdom literary journal. He lives and works in rural Cambodia and loves to travel. He has worked as an IELTS tutor since 2010, has completed both TEFL and CELTA courses, and has a certificate from Cambridge for Teaching Writing. David has worked in many different countries, and for several years designed a writing course for the University of Worcester. In 2018, he wrote the popular IELTS handbook, Grammar for IELTS Writing and he has since written two other books about IELTS. His other IELTS website is called IELTS Teaching.
Related Posts
Age and Work [IELTS Speaking and Writing]
August 9, 2021
Describe your Ideal Home
December 2, 2022
Describe a Piece of Art [IELTS Speaking]
September 3, 2020
How to Write an IELTS Essay [Task 2]
March 30, 2019
Hello David, how are things over there. I loved this class! Where can I find the answers for the test?
Oh wow, I forgot to include them.
1. overall / steadily upwards / modest / rocketed / climb
2. dropped / slightly / slipping / downwards / spectacular
Leave a reply Cancel reply
Your email address will not be published. Required fields are marked *
This site uses Akismet to reduce spam. Learn how your comment data is processed .
Download my IELTS Books
Recent Posts
- Past Simple vs Past Perfect
- Complex Sentences
- How to Score Band 9 [Video Lesson]
- Taxing Fast Food: Model IELTS Essay
- Airport Vocabulary
Recent Comments
- Daisey Lachut on IELTS Discussion Essays [Discuss Both Views/Sides]
- David S. Wills on Describe a Historical Period
- Siavash on Describe a Historical Period
- fabliha on IELTS Speaking Partners
- tufail khan on IELTS Discussion Essays [Discuss Both Views/Sides]
- Lesson Plans
- Model Essays
- TED Video Lessons
- Weekly Roundup
- Login Candidate Login Branch Login Node Login
Register for IELTS
Ielts map vocabulary for writing task 1.

The International English Language Testing System (IELTS) is the most important test for individuals planning to study, work, or migrate to an English-speaking country. The IELTS test has four sections ( Listening , Reading , Writing and Speaking ), out of which the Academic Writing task includes questions based on visual data like charts, graphs, diagrams, and sometimes maps. Therefore familiarity with specific IELTS Vocabulary related to these types of questions is important to approach questions. In this blog, we will focus on the IELTS map vocabulary to help you score higher in your IELTS Writing task 1.

What are map questions in the IELTS Writing task 1?
In the IELTS Writing Task 1, map questions require you to describe and compare maps. These maps might show a place at different times (past, present, future) or two different plans or proposals for the same place. Your task is to report the main features and make comparisons where relevant.
Here are some common types of map questions you might have to answer:
- Changes over time: These questions show maps of the same place at different times. You’ll need to describe how the area has changed over the years.
- Two different plans: Sometimes, the question might show two different proposals for a development project in the same area. You must compare and contrast these plans.
- Describing a place: You might be given a single map and asked to describe its main features. This is less common but still a possibility.
When answering these questions, focus on:
- Layout and structure: Organise your description. Typically, you should start with an overall description of the maps before moving into specific details
- Comparative language: Use words and phrases that compare and contrast, like “similarly,” “in contrast,” “unlike,” “whereas,” etc
- Descriptive vocabulary: Use a range of vocabulary to describe locations, directions, and changes (e.g., north of, adjacent to, transformed into, replaced by)
- Accuracy: Be precise in your descriptions. Misinterpreting the map can lead to a lower score
- Variety in grammar: Employ a range of grammatical structures to show your proficiency in English
Practicing with different types of map questions can help you become more comfortable with this task and improve your skills in describing and comparing spatial information.
Top 30 IELTS map vocabulary
Here are the 30 useful IELTS map vocabulary words and phrases. These are often useful in describing changes, locations, and features on maps, which is a common task in the IELTS exam .
Sample of IELTS map question
Here is an example of an IELTS map question for your reference, you can consider practicing a few questions like these to score higher in your IELTS test .
Hope this blog helps you understand all about the IELTS map questions and it is always a good idea to expand your IELTS map vocabulary to score higher in your IELTS Writing task 1 map question.
If you want to know more about the IELTS test, you can get in touch with your nearest IDP IELTS test centre . Our team of IELTS experts will guide you with your queries.
Read more insightful articles:
- Top tools to improve written english
- Similarities and differences between IELTS writing task 1 and 2
- Grammar mistakes to avoid in IELTS writing
Helpful resources
- IELTS preparation videos
- IELTS preparation guide
- Join IELTS webinar Series
Book your IELTS test

Book your IELTS test today
Ielts on computer.

Book IELTS on computer
Related blogs.
Tips to score high on your computer-delivered IELTS
The International English language testing system (IELTS) test is the most popular test and is preferred by people who are planning to study, work or migrate to an English-speaking country.
Most affordable universities in the USA
Studying in the USA offers a unique and enriching educational experience for students from around the world.
Pie chart vocabulary for IELTS Writing task 1
When preparing for the International English Language Testing System (IELTS) Writing Task 1, it's important to familiarise yourself with specific vocabulary related to pie charts, a common type of question in this section.
Password Changed successfully
As literacy lags nationwide, Purdue researcher highlights ways to enhance reading and writing in young children
Written By: Rebecca Hoffa, [email protected]

A text message from a friend. A product label at the grocery store. A street sign. Even in the most basic elements of day-to-day life, reading is everywhere.
Cammie McBride , professor in the Purdue University Department of Human Development and Family Science and associate dean for research in the College of Health and Human Sciences , has dedicated her career to taking a global approach toward understanding how children learn to read, exploring literacy across English and Chinese languages, among others.
“Children need to learn to read and write because it helps us navigate our environments,” McBride said. “If we can’t read, that’s more difficult. If you look worldwide, illiteracy is correlated with gross domestic product and the learning of a country’s people.”

Cammie McBride
From contributing to a massive open online course (MOOC) titled “Teaching Struggling Readers Around the World” to developing new resources and screening capabilities, McBride’s developmental psychology approach toward literacy ranges from cognitive linguistics, or how the brain processes language, to the relationships among parents, children and teachers and how those influence reading and writing.
McBride also serves as a co-lead on a $1.5 million grant to strengthen literacy preparation for Indiana teachers using science-based methods.
“My whole career, I’ve tried to look at how children read in different aspects,” McBride said. “I’m really interested in: Does reading develop from birth or before birth even? There are lots of aspects that go into reading that start at the very beginning. I’ve always been interested in those developmental models.”
McBride noted that one of her most interesting research findings has been enhancing understanding of a new cognitive-linguistic skill that has a direct impact for reading in Chinese as well as vocabulary in English, Dutch and other languages. The task requires children to put together morphemes, or the smallest unit of meaning in language, in ways that make sense. For example, if a teacher or parent gave the example that the sun going down in the sky is called a sunset and then asked the child what the moon going down in the sky would be called, the expectation would be the child would answer “moonset.” They’re putting together smaller units in ways that make sense.
“I think this task is really useful because we can test vocabulary to improve vocabulary, but this is another way, which is a focus on morphemes and how they come together,” McBride said. “If you understand how to put these together to make new aspects of meaning, you tend to be a better reader in Chinese, but also, this is a really good way to test for kids’ vocabulary development over time in every language. It’s a fun task — kids love to do that.”
McBride uses cognitive-linguistic skills like the example above in her research to understand methods for assessing children’s literacy and training teachers and families in what children need to learn to read. In order to read, McBride explained children must develop both oral language, such as vocabulary and forming sentences, as well as an understanding of print, such as understanding letters and their sounds. She explained that assessing children’s literacy skills early is important to keep them on track in their reading and writing development.
“These cognitive-linguistic skills are things we use in assessment and training,” McBride said. “Most 3- and 4-year-olds cannot read, and it would be weird to try to test them with reading materials before they can read, but you need to catch them quickly so that they don’t have a sense of failure and are always trying to catch up. If you test them at 3, 4 or 5 on cognitive-linguistic skills, this often can be a good way to determine if they’re at risk for reading difficulties and then give them some tools to help them improve.”
McBride mentioned dialogic reading is an effective tool parents can use to build up their child’s language skills. Rather than simply reading a book and looking at the pictures or testing the child on knowledge presented in the book, dialogic reading turns the process of reading into a conversation. Parents can ask open-ended questions, such as what the child thinks will happen next or if they’ve ever had a similar situation happen to them. The goal is to encourage two-sided communication.
If the child is struggling with reading, McBride’s go-to piece of advice is giving them more practice. While the same learning methods still can be effective with students who have a learning disorder, such as dyslexia, they may need to put more time and energy into practicing the reading process. McBride suggested literacy-based video games as a great tool to help children master literacy skills they may be struggling with. The important thing to keep in mind is to avoid burning the child out on reading.
“Keep it light because the other part of reading besides oral language and print is motivation,” McBride said. “You don’t want to get kids to feel like they’re being tested early; you want them to get interested themselves.”
After various nationwide setbacks toward literacy resulting from the COVID-19 pandemic, McBride is currently looking to take her research one step further by making literacy tests, which screen for children’s risks for reading problems and often are expensive and require a licensed educational psychologist to administer, more accessible. Her most recent work is focusing on the development of affordable online tests for children and families — a significant step in continuing to improve children’s reading preparation.
“If we want to understand if children are maybe at risk for reading and writing problems early, it’s good to have tests that can help us to determine that,” McBride said.

IMAGES
VIDEO
COMMENTS
This vocabulary section aims to help you learn all the vocabularies, phrases and words you need to know and use in your Academic writing task 1 to achieve a higher band score. The examiner will use four criteria to score your response: task achievement, coherence and cohesion, lexical resource, & grammatical range and accuracy.
But IELTS Academic Writing Task 1 vocabulary is actually the most valuable, as graphs appear in over 75% of Task 1 questions. In this lesson, I'll teach you all the words you need to describe any Task 1 graph accurately. You'll learn; basic vocabulary for graphs. vocabulary to be more descriptive.
This IELTS writing task 1 vocabulary list serves as a guide to enhance your proficiency in describing various types of visual data, such as graphs, charts, diagrams, maps, and processes. By utilizing the appropriate terminology and phrases, you can seamlessly navigate the intricacies of presenting trends, comparisons, and distributions.
This article will help you improve your score for IELTS Writing Task 1 vocabulary and grammar. Firstly, you should know that the IELTS writing test marking scheme is divided into four parts: Therefore, grammar accounts for 25% of the marks in your writing test. You are assessed on two things:
IELTS Writing Task 1 Language: Why Grammar and Vocabulary Matter. On your IELTS essays, grammar and vocabulary make a difference in your band descriptor—a huge difference, in fact! Out of the four categories you'll be marked on, Grammatical Range and Accuracy and Lexical Resource account for half of your score overall.
We looked at the first two, Task Achievement and Cohesion and Coherence, on the Task 1 overview page ( IELTS Academic Writing Task 1) and it's now time to focus on Vocabulary. This lesson includes: 1) Understanding the marking criteria. 2) Key vocabulary for Academic IELTS Task 1: Adjectives & adverbs. Verbs & nouns.
Vocabulary for Academic Writing Task 1. Using contextual vocabulary is an important aspect of writing task 1. Describing Trends. In IELTS writing task 1 you may have to describe trends. This may come up in a line graph, bar chart or comparing more than one chart.
How to build a better vocabulary list for IELTS Writing Task 1. 1. Adjective/noun and verb/adverb examples. To really show off your vocabulary in the test, make sure you use at least TWO adjective/noun and verb/adverb examples. In the second year, there was a slight increase in sales of coffee.
People doing the Academic test will write a report on a data set, map, or process. People doing General Training will write a letter. You must write 150 words or more. You should spend around 20 minutes on this part of the test. Task 1 is worth 1/3 of your total mark on the Writing test.
Useful IELTS writing task 1 tips, answers, lessons & videos for success achieving a high score. This page contains all the information and help you need to do well. Learn about the IELTS marking criteria, paragraphing, vocabulary and much more. This page has tips for Academic writing task 1 and GT writing task 1 (see bottom of page).
To get a high score in IELTS writing task 1 academic you need to have a good range of grammar and vocabulary. In this lesson, we will look at specific vocabulary that can be used in various ways. The words are: number, total, comprised, the proportion of, amounted to, accounted for, period and figure. Try the exercises at the end of the lesson ...
Eliot Friesen. on. April 7, 2021. in. IELTS Academic Writing Task 1. When you sit down for the Academic IELTS Writing Task 1 on test day, you'll see one or two visuals, such as a chart, diagram, or graph. You'll then write a report to give information based on key features of these visuals. Overall, you have 20 minutes to write 150 words.
For numbers up to ten, write the numbers in words. For numbers over 10, you can write the numbers in numbers. Examples: Five percent of the employees were late this month. More than 50 percent of the students handed in their assignments late after the long weekend. If the sentence starts with a number, always write it in words.
IELTS Academic Writing Task 1 vocabulary pdf Useful Language and Vocabulary (IELTS Academic Writing Task 1) Make sure you know at least 3 of these words from each category from the tables below AND that you are able to use them accurately in a sentence. Also, be aware that whilst many of the words have similar meanings they are not exactly the ...
In IELTS writing task 1, vocabulary accounts for 25% of your marks. Being able to use a wide variety of vocabulary accurately will help your score. I did a post on this before about using specific vocabulary in the academic task 1 writing section click here to see that post. In this post, I want to review this vocabulary and there is an ...
Vocabulary for Academic IELTS Writing Task 1 (part 1) Academic IELTS Writing Task 1 question requires you to use several vocabularies to present the data given in a pie/ bar/ line/ mixed graph or to describe a process or a flow chart. Being able to use appropriate vocabularies, presenting the main trend, comparing & contrasting data and ...
This vocabulary section aims to help you learn all the vocabularies, phrases and words you need to know and use in your Academic writing task 1 to achieve a higher band score. The examiner will use four criteria to score your response: task achievement, coherence and cohesion, lexical resource, and grammatical range and accuracy.
Process Vocabulary IELTS Examples. This diagram illustrates the man-made process that a company uses to distribute natural gas to consumers. Overall, this seven-step, linear process illustrates which types of consumers the company prioritizes. This diagram depicts the natural hydrological cycle process by which water moves through the environment.
5 Common Mistakes in IELTS Writing Task 1. Following are the five most common mistakes student make while attempting IELTS Writing Task 1: • Vague overview: Overview is an important part of the IELTS Writing Task 1. It is a 2-3 line paragraph that is to be written about the graph, chart etc. It should not contain any data but the main ...
IELTS Academic Writing Task 1 Vocabulary - words and phrases for IELTS graphs: Line graphs, Bar charts, Tables, Pie charts. Words and phrases for IELTS graphs for band 7.0-9.0. Suitable for: Line graphs. Bar charts. Tables. Pie charts. You don't need to memorize every single word. Choose the ones that you want to use in your answers and those ...
IELTS General Writing Task 1: Advanced vocabulary for letters. One of the marking criteria for Writing Task is vocabulary - the variety of words and expressions that you use. For a score of 7 and above, it is necessary to include advanced words and less common expressions in the letter. It is also important to start and finish the letter correctly.
Firstly, you need to know a wide range of useful IELTS vocabulary for task 1. Learn words like "soar" and "rocket," as well as "substantially" and "modestly.". Then you need to figure out how to use them correctly. It is not enough just to guess when and how to use them. Your language should be accurate to the data you describe.
Descriptive vocabulary: Use a range of vocabulary to describe locations, directions, and changes (e.g., north of, adjacent to, transformed into, replaced by) Accuracy: Be precise in your descriptions. Misinterpreting the map can lead to a lower score. Variety in grammar: Employ a range of grammatical structures to show your proficiency in English.
Vocabulary: Includes words and phrases that are used within disciplines including: (1) words and phrases with subject-specific meanings that differ from meanings used in everyday life (e., table); (2) general academic vocabulary used across disciplines (e., compare, analyze, evaluate); and (3) subject- specific words defined for use in the ...
The task requires children to put together morphemes, or the smallest unit of meaning in language, in ways that make sense. For example, if a teacher or parent gave the example that the sun going down in the sky is called a sunset and then asked the child what the moon going down in the sky would be called, the expectation would be the child ...