

Harvard University
- Cost & scholarships
- Essay prompt
Want to see your chances of admission at Harvard University?
We take every aspect of your personal profile into consideration when calculating your admissions chances.
Harvard University’s 2023-24 Essay Prompts
Diversity short response.
Harvard has long recognized the importance of enrolling a diverse student body. How will the life experiences that shape who you are today enable you to contribute to Harvard?
Intellectual Experience Short Response
Briefly describe an intellectual experience that was important to you.
Extracurricular Short Response
Briefly describe any of your extracurricular activities, employment experience, travel, or family responsibilities that have shaped who you are.
Future Goals Short Response
How do you hope to use your Harvard education in the future?
Roommate Short Response
Top 3 things your roommates might like to know about you.
Common App Personal Essay
The essay demonstrates your ability to write clearly and concisely on a selected topic and helps you distinguish yourself in your own voice. What do you want the readers of your application to know about you apart from courses, grades, and test scores? Choose the option that best helps you answer that question and write an essay of no more than 650 words, using the prompt to inspire and structure your response. Remember: 650 words is your limit, not your goal. Use the full range if you need it, but don‘t feel obligated to do so.
Some students have a background, identity, interest, or talent that is so meaningful they believe their application would be incomplete without it. If this sounds like you, then please share your story.
The lessons we take from obstacles we encounter can be fundamental to later success. Recount a time when you faced a challenge, setback, or failure. How did it affect you, and what did you learn from the experience?
Reflect on a time when you questioned or challenged a belief or idea. What prompted your thinking? What was the outcome?
Reflect on something that someone has done for you that has made you happy or thankful in a surprising way. How has this gratitude affected or motivated you?
Discuss an accomplishment, event, or realization that sparked a period of personal growth and a new understanding of yourself or others.
Describe a topic, idea, or concept you find so engaging that it makes you lose all track of time. Why does it captivate you? What or who do you turn to when you want to learn more?
Share an essay on any topic of your choice. It can be one you‘ve already written, one that responds to a different prompt, or one of your own design.
What will first-time readers think of your college essay?
Our Services
College Admissions Counseling
UK University Admissions Counseling
EU University Admissions Counseling
College Athletic Recruitment
Crimson Rise: College Prep for Middle Schoolers
Indigo Research: Online Research Opportunities for High Schoolers
Delta Institute: Work Experience Programs For High Schoolers
Graduate School Admissions Counseling
Private Boarding & Day School Admissions
Online Tutoring
Essay Review
Financial Aid & Merit Scholarships
Our Leaders and Counselors
Our Student Success
Crimson Student Alumni
Our Reviews
Our Scholarships
Careers at Crimson
University Profiles
US College Admissions Calculator
GPA Calculator
Practice Standardized Tests
SAT Practice Test
ACT Practice Tests
Personal Essay Topic Generator
eBooks and Infographics
Crimson YouTube Channel
Summer Apply - Best Summer Programs
Top of the Class Podcast
ACCEPTED! Book by Jamie Beaton
Crimson Global Academy
+1 (646) 419-3178
Go back to all articles
How To Answer Harvard's 2023/24 Supplemental Essays: Tips & Insights
/f/64062/2240x1260/0f4d5915de/blog-essay.png)
What's New in 2023/24
What are Harvard's Essay Prompts?
How to Answer Harvard's Essay Prompts
General Guidelines
Explore the changes in Harvard's supplemental essay prompts for 2023/24, understand the nuances of each question, and gain insights on crafting compelling responses with our detailed guide, complete with expert tips and links to successful Harvard essay examples.
Harvard's 2023/24 Supplemental Essay Updates: What's Changed?
Gaining admission to Harvard is no small feat, with acceptance rates sometimes plummeting as low as 3% . In such a competitive environment, every component of your application, especially your essay, becomes a crucial tool to stand out to admissions officers.
Every year, top-tier universities like Harvard fine-tune their application process to get a deeper understanding of their applicants. For the 2023/24 admissions cycle, Harvard University has made notable modifications to its supplemental essay questions .
Last year, applicants had a mix of required and optional prompts, with varying word limits, ranging from 50 to 150 words. These prompts touched on extracurricular activities, intellectual experiences, personal backgrounds, and more.
This year, Harvard has streamlined the process, requiring all applicants to answer five questions, each with a strict 200-word limit . The questions emphasize the importance of diversity, intellectual experiences, extracurricular activities, the utilization of a Harvard education, and personal insights for potential roommates.
This shift indicates a desire for more concise, focused responses from applicants, allowing the admissions committee to gain a clearer, more uniform understanding of each student's background, aspirations, and personality.

What Are Harvard’s Supplemental Essay Prompts for 2023/24?
For the 2023/24 application cycle, Harvard University has outlined specific supplemental essay prompts to understand applicants better in addition to the Common App or Coalition App questions. These questions delve into your experiences, intellectual pursuits, and personal insights. Students are required to answer each Harvard-specific question in under 200 words. Here's a breakdown of the prompts:
- Diversity and Contribution : Harvard values a diverse student body. Reflect on your life experiences and explain how they have shaped you and how you plan to contribute to Harvard. (200 words)
- Intellectual Experience : Discuss an intellectual experience that has had a significant impact on you. (200 words)
- Personal Shaping Experiences : Elaborate on extracurricular activities, employment, travel, or family responsibilities that have played a pivotal role in defining who you are. (200 words)
- Future Aspirations : Describe how you envision utilizing your Harvard education in the future. (200 words)
- Getting to Know You : List three things your future roommates should know about you. (200 words)
These prompts offer applicants a chance to showcase their personalities, aspirations, and experiences, providing a holistic view of their candidacy.
Looking for inspiration? Dive into these Harvard essay examples to see what successful applications look like!
How to Answer Harvard’s Supplemental Essay Questions?
This guide aims to help you craft a compelling response that showcases your unique journey and potential contributions to Harvard's diverse community.
As you begin planning responses to each individual prompt, be sure to consider what experiences, reflections, and qualities you want to showcase once you’ve responded to all the prompts:
- Ensure you won’t leave out any important experiences, reflections, and qualities you want Harvard to know about.
- Be sure you’ll avoid repeating the same experiences, reflections, or qualities in the other prompts.
Answering Prompt 1
Harvard values a diverse student body. reflect on your life experiences and explain how they have shaped you and how you plan to contribute to harvard., - 200 words or fewer, 1. understand the question.
Harvard is not merely asking for a list of experiences. They want to understand the depth of your experiences , how they've molded your character, and how you'll use that growth to contribute to the Harvard community.
Since Harvard is telling you they value diversity, consider emphasizing unique experiences or circumstances that highlight the most personal and profound aspects of your personality, values, and perspectives.
2. Reflect on Your Unique Experiences
Consider moments in your life that have had a significant impact on your worldview:
- Have you lived in multiple countries, exposing you to various cultures?
- Did you overcome challenges that forced you to view the world differently?
- Were there pivotal moments in your upbringing that shaped your identity?
- How did interactions with diverse individuals or groups influence your perspectives?
3. Dive Deep into Personal Growth
Discuss the evolution of your perspectives, values, or aspirations.
- How did these experiences challenge your beliefs or expand your understanding?
- What lessons did you derive, and how have they influenced your subsequent actions or decisions?
- What experiences or reflections shape your deepest beliefs and values? — or, shape some deep questions or doubts you wrestle with?
4. Connect to Harvard
Consider how your unique perspective will enrich Harvard's community .
- Will you introduce new viewpoints in classroom discussions or help teams work together more successfully?
- Will you contribute to or initiate student organizations or community projects?
- Will you exemplify certain traits that enhance a vibrant, curious, and inclusive learning environment?
5. Be Concise and Authentic
With a 200-word limit, precision is key. Ensure your narrative is genuine, making your essay resonate with the reader. Avoid generic statements; instead, provide specific examples that showcase your journey.
Harvard's first supplemental essay is an opportunity to showcase the depth of your experiences and how they've shaped you . Reflecting on significant moments, emphasizing personal growth, and connecting your unique perspective to how you'll contribute to Harvard is essential. Remember to be concise, authentic, and ensure your essay is polished to perfection.
Answering Prompt 2
Discuss an intellectual experience that has had a significant impact on you..
This question aims to help you articulate the depth and significance of an intellectual experience and its profound impact on your academic and personal journey.
1. Define "Intellectual Experience"
Before diving in, understand that an intellectual experience isn't limited to classroom learning . It could be:
- A book that changed your perspective
- A conversation that challenged your beliefs
- An experience that triggered a profound insight or understanding
- Or even a personal project or research endeavor
2. Choose a Meaningful Experience
Reflect on experiences that genuinely transformed your thinking:
- Was there a particular course or project that ignited a passion?
- Did a specific book, article, or documentary challenge your pre-existing beliefs?
- Have you attended seminars, workshops, or lectures that introduced you to new ideas?
3. Delve into the "Why"
Discuss why this experience was transformative:
- What preconceptions or beliefs did it challenge?
- How did it expand or deepen your understanding of a particular subject or idea?
- Did it inspire further exploration or study into the topic?
4. Highlight Personal Growth
Describe how this intellectual experience influenced your academic and personal journey:
- Did it guide your academic pursuits or career aspirations?
- How did it shape your values, beliefs, or worldview?
5. Be Authentic and Reflective
Your genuine curiosity and passion should shine through. Avoid using jargon or overly complex language. Instead, focus on genuine reflection and personal growth .
Harvard's second supplemental essay seeks to understand your intellectual journey . It's an opportunity to showcase your curiosity, passion, and the transformative power of learning. By reflecting on a significant intellectual experience and its impact on you, you can demonstrate your academic depth, your own intellectual processes and aptitudes, and intellectual growth.
Interested in learning more? Attend one of our free events
Build your application strategy with the latest 2023-24 admissions trends & analysis.
Tuesday, April 23, 2024 12:00 AM CUT
Join this exclusive webinar to learn about the latest trends in college admissions and discover the key to getting accepted to top universities in upcoming application cycles!
REGISTER NOW
Answering Prompt 3
Elaborate on extracurricular activities, employment, travel, or family responsibilities that have played a pivotal role in defining who you are..
This question is designed to help you articulate the significance of experiences outside the classroom and their profound impact on your personal journey.
1. Prioritize Depth Over Quantity
While you might have multiple experiences, focus on one or two that have had the most profound impact on you . This allows you to delve deeper and provide a more insightful reflection.
2. Choose a Defining Experience
Reflect on moments that genuinely shaped your character:
- Was there an extracurricular activity that taught you leadership, teamwork, or dedication?
- Did a job teach you responsibility, time management, or the value of hard work?
- Has travel exposed you to diverse cultures, broadening your perspectives?
- Were there family responsibilities that instilled in you a sense of maturity, empathy, or resilience?
3. Describe the Experience
Briefly set the scene. Whether it's the bustling environment of a part-time job, the challenges of a leadership role in a club, or the nuances of a family responsibility, paint a picture for the reader.
4. Reflect on the Impact
Discuss how this experience influenced your personal growth:
- What challenges did you face, and how did you overcome them?
- What skills or values did you acquire or strengthen?
- How did this experience shape your aspirations, perspectives, or values?
5. Connect to the Present
Highlight how this experience continues to influence you:
- How do the lessons you learned guide your current decisions or actions?
- How has it influenced your academic interests or future aspirations?
Harvard's third supplemental essay is an opportunity to showcase experiences outside the classroom that have significantly influenced your personal growth . Reflecting on these pivotal moments and their lasting impact can provide a holistic picture of your character, values, and aspirations.
Answering Prompt 4
Describe how you envision utilizing your harvard education in the future..
This question aims to help you articulate how a Harvard education aligns with your future goals and the impact you aim to make in your chosen field or community.
1. Reflect on Your Goals
Begin by identifying your long-term aspirations . Have a clear vision in mind, whether it's a specific career, a desire to address a global challenge, or a passion you wish to pursue further.
2. Highlight Harvard's Unique Offerings
Research specific programs, courses, or opportunities at Harvard that align with your goals. This could be a particular academic program, research opportunities, or extracurricular activities.
3. Draw a Connection
Discuss how these unique offerings will equip you with the skills, knowledge, or experiences needed to achieve your future aspirations . Make it evident that Harvard is the ideal place for you to realize these goals.
4. Go Beyond the Obvious
While Harvard's academic excellence is a given, delve into the broader Harvard experience. Consider the influence of its diverse community, its culture of innovation, or its commitment to leadership and service.
5. Discuss the Broader Impact
Expand on how you plan to use your Harvard education to make a difference . Whether it's in your community, in a particular field, or on a global scale, showcase your commitment to creating positive change.
6. Stay Authentic
Ensure your response is genuine and reflects your true aspirations. Admissions officers can discern genuine passion and commitment from generic responses.
Harvard's fourth supplemental essay is an opportunity to showcase your forward-thinking approach and how you plan to leverage Harvard's resources to achieve your future goals. By drawing a clear connection between what Harvard offers and your aspirations, you demonstrate a purposeful approach to your education.
Answering Prompt 5
List three things your future roommates should know about you..
This question aims to help you present a genuine and well-rounded picture of yourself, offering insights into your personality, habits, and values.
1. Reflect on Your Personality
This prompt is an invitation to share more about your personal side. Think about the quirks, habits, or values that define you. What are the things that make you, well, you?
2. Balance Seriousness with Lightness
While one point could be a deep reflection of your values or beliefs, another could be a fun fact or a unique hobby. This mix gives a rounded picture of who you are.
3. Be Genuine
Avoid coming up with things you believe the admissions committee wants to hear. This is your chance to let your true self shine through.
4. Consider Your Daily Life
Think about your habits or routines, the music you listen to, or the books you read. These can offer insights into your personality and preferences.
5. Reflect on Past Living Experiences
Have you shared a space with someone before — roommate, sibling, family members, fellow campers?… Think about what made the experience harmonious. Were there particular habits, routines, or guiding principles you followed that were appreciated by those you were sharing space with?
Harvard's fifth supplemental essay is a chance to showcase your personality beyond academics and extracurriculars . By sharing genuine aspects of yourself related to day-to-day living and the many small ways you interact with those around you in more personal spaces, you give a glimpse into your life outside the classroom and what it might be like to share a living space with you.
5 Tips for the "Why This School?" Essay
General Guidelines for Crafting Stellar Harvard Supplemental Essays
1. Understand the Question: Before you start writing, ensure you fully understand what the prompt is asking. Break it down and consider its nuances. This will help you stay on track and address all aspects of the question.
2. Be Authentic: Harvard isn't just looking for high achievers; they're looking for genuine individuals. Your essay should reflect your true self, not what you think the admissions committee wants to hear.
3. Show, Don't Tell: Instead of just stating facts or beliefs, use anecdotes, experiences, or stories to convey your points. This makes your essay more engaging and paints a clearer picture of who you are.
4. Stay Within the Word Limit: While it might be tempting to write more, respect the word limits. It shows that you can convey your thoughts concisely and respect guidelines.
5. Proofread and Edit: Always review your essay multiple times for clarity, coherence, and grammar. Consider also asking a teacher, mentor, or friend to review it.
6. Connect to Harvard: While the prompts might not explicitly ask for it, subtly showing why your experiences, values, or aspirations align with Harvard's culture or offerings can be a plus.
7. Reflect on Growth: Colleges love to see personal growth. Reflect on how experiences have shaped you, lessons learned, and how you've evolved.
8. Avoid Repetition: Ensure that your supplemental essays present new information and don't repeat what's already in your Common App essay or other parts of your application.
9. Be Forward-Looking: While it's essential to reflect on past experiences, also touch on how these experiences prepare you for future endeavors, especially at Harvard.
10. Start Early: Give yourself ample time to brainstorm, draft, and revise. Starting early reduces stress and allows you to approach the essay with a clear mind.
Remember, the supplemental essays are an opportunity to showcase aspects of yourself that aren't evident in other parts of your application . Use them wisely to provide a holistic picture of yourself and why you'd be a great fit for Harvard.

Final Thoughts
The journey to Harvard is more than just academic prowess; it's about crafting a narrative that resonates deeply with the admissions committee. Your supplemental essays provide a unique window into your personality, aspirations, and the distinct perspectives you'll bring to the Harvard community.
Every Harvard aspirant has a story waiting to be told. This is your moment to share yours. Approach your essays with authenticity, introspection, and a genuine passion for your narrative.
If you're wondering whether your essay truly captures your essence or if it stands out from the multitude of applications, our essay review service is here to help. Our team of experts will meticulously review and provide feedback to refine your essay, ensuring it resonates with admissions officers. For further inspiration, delve into our ebook , which showcases essays from students who clinched spots at top universities. And if Harvard is your dream, these successful Harvard essay examples will provide invaluable insights.
For those just starting their college application journey, consider booking a free consultation with our seasoned college counselors. We're dedicated to guiding you in creating an application that significantly enhances your chances of donning the Crimson colors. Harvard is within reach, and we're here to help you every step of the way.

What Makes Crimson Different
Key Resources & Further Reading
- Everything you need to know about US Application Supplemental Essays
- Acing your College Application Essay: 5 Expert Tips to Make it Stand Out from the Rest
- How to Tackle Every Type of Supplemental Essay
- 2023-24 Common App Essay Prompts
- What are the Most Unusual US College Supplemental Essay Prompts?
More Articles
What would megan fox's (hypothetical) harvard essay look like.
/f/64062/1080x1350/4ca43b3259/megan-fox-harvard-essay.png)
Unleashing Creativity in Research: How High Schoolers Can Find Unique and Engaging Research Topics
/f/64062/800x450/e647829a9e/research-your-major.jpg)
Can Colleges See How Many Times You’ve Taken the SAT?
/f/64062/1920x800/d5fd05a1b4/crimson-essay-writing-workshop.png)
Crimson students are 7x more likely to gain acceptance to their dream college!
Remember, you don't have to navigate this journey alone. crimson provides a comprehensive suite of services, from academic mentoring and test prep to essay assistance, extracurricular guidance, and career mentoring, ensuring a holistic approach to your college preparation journey..
Harvard University 2023-24 Supplemental Essay Prompt Guide
Regular Decision Deadline: Jan 1
You Have:
Harvard University 2023-24 Application Essay Question Explanations
The Requirements: Five essays of 200 words or fewer
Supplemental Essay Type(s): Diversity , Activity , Oddball
Harvard is asking 2023-24 applicants to pen five short essays in response to the following prompts:
Harvard has long recognized the importance of enrolling a diverse student body. how will the life experiences that shape who you are today enable you to contribute to harvard* (200 words).
Admissions wants to know what has made you into the person you are today and how those experiences will affect the way you engage with and contribute to the Harvard community. So, tell a story about an experience that has shaped you and connect the lessons you learned to the ways in which you will contribute to diversity on campus next fall. Start by thinking about the kinds of experiences you’ve had in the communities you’ve been a part of thus far. Then, once you’ve identified the life experience(s) that have shaped you, think ahead to how those will impact your time at Harvard. Admissions wants to know what your area of influence will look like on campus—whether that be applying the leadership skills you developed in your community theater troupe to the drama productions at Farkas Hall, celebrating intersectional identities with other members of the queer Jewish community with BAGELS , or connecting and networking with your peers through Harvard Black Students Association . Whatever you write about, make sure your response to this prompt shows that you have put some serious thought into the things that have shaped you and how you will apply those lessons and experiences to your time at Harvard next fall.
Briefly describe an intellectual experience that was important to you.* (200 words)
It’s no surprise that Harvard is hoping to invite students to campus who are excited about learning, so take this opportunity to geek out about an awesome learning experience you had recently. Maybe you find marine life to be absolutely fascinating, so you’ve been reading up on the most dangerous creatures in the deep dark sea (and their preferred prey, of course). Perhaps you had the opportunity to take a class or seminar with a thought leader you really admire or you went on a reading retreat that expanded your horizons. Whatever it may be, this is the perfect opportunity to show admissions your passion for pursuing knowledge and reflect on the impact it had on you.
Briefly describe any of your extracurricular activities, employment experience, travel, or family responsibilities that have shaped who you are.* (200 words)
Next up is a fun twist on the classic activity essay, which asks you to expand on an extracurricular endeavor that has shaped who you are. Our advice is to focus on one or two activities that have made the biggest impact on you. Although we usually urge students to write about items that haven’t appeared elsewhere on their application, the activity essay is an exception since it specifically asks you to address an item on your resume. The trick here is to pick something with meat! Maybe your trip to visit your extended family members in Thailand opened your eyes to how limited your world had been in your small Midwestern town. Perhaps four years of debate club have nurtured your communication skills and ability to speak up for yourself. Whatever activity you choose to write about, be sure to pick one that has been fundamental to your understanding of who you are.
How do you hope to use your Harvard education in the future?* (200 words)
Admissions already knows a bit about what makes you you; now they want to know why Harvard is the obvious next step in the trajectory of your life. Take some time to meditate on what you hope your life will look like after Harvard—we’re talking ten, twenty years in the future. Once you have an idea of what you hope for that person to be like or do on an average day, invite admissions into your vision and show them how a Harvard education is a pivotal step (or three) on the ladder of success to get there. Regardless of your vision, your response should cite programs, activities, and organizations that Harvard offers. Anyone can say they hope to become a renowned doctor or an attorney for the people, but not everyone is going to do their homework to show admissions that they’ve thought through exactly how they want to get there. Of course, admissions isn’t going to hold you to your blueprint, but they do want to see that you’ve given not only your decision to apply to Harvard some serious thought, but your life post-graduation as well.
Top 3 things your roommates might like to know about you.* (200 words)
With this prompt, admissions is hoping to see a different side of you, perhaps one that is less intellectual (unless that’s just who you are, in which case, rock on with your nerdy self) and a little more casual. Start by making a list. Write down everything that comes to mind. You can edit and revise later—no idea is too silly to jot down! Maybe you think your roommates should know that you just can’t not sing while in the shower (we’re talking Celine Dion, Adele, Whitney Houston) or that you make the meanest plate of rice and beans in your pressure cooker (and you love to share). Once you’ve narrowed your list down to three (3) things, see if you can weave together a narrative that gives admissions a little taste of what it would be like to hang out in the dorms with you. How do you connect with your peers? What most excites you about residential life? What are the quirks that make you you ? By the time admissions puts down your application, they should feel like your personality is jumping off the page.
About Kat Stubing
View all posts by Kat Stubing »
We're waiting for your call.
Contact us for information on rates and more!
- I am a * Student Parent Potential Partner School Counselor Private College Counselor
- Name * First Last
- Phone Type Mobile Landline
- Street Address
- Address City State / Province / Region Afghanistan Albania Algeria American Samoa Andorra Angola Anguilla Antarctica Antigua and Barbuda Argentina Armenia Aruba Australia Austria Azerbaijan Bahamas Bahrain Bangladesh Barbados Belarus Belgium Belize Benin Bermuda Bhutan Bolivia Bonaire, Sint Eustatius and Saba Bosnia and Herzegovina Botswana Bouvet Island Brazil British Indian Ocean Territory Brunei Darussalam Bulgaria Burkina Faso Burundi Cabo Verde Cambodia Cameroon Canada Cayman Islands Central African Republic Chad Chile China Christmas Island Cocos Islands Colombia Comoros Congo Congo, Democratic Republic of the Cook Islands Costa Rica Croatia Cuba Curaçao Cyprus Czechia Côte d'Ivoire Denmark Djibouti Dominica Dominican Republic Ecuador Egypt El Salvador Equatorial Guinea Eritrea Estonia Eswatini Ethiopia Falkland Islands Faroe Islands Fiji Finland France French Guiana French Polynesia French Southern Territories Gabon Gambia Georgia Germany Ghana Gibraltar Greece Greenland Grenada Guadeloupe Guam Guatemala Guernsey Guinea Guinea-Bissau Guyana Haiti Heard Island and McDonald Islands Holy See Honduras Hong Kong Hungary Iceland India Indonesia Iran Iraq Ireland Isle of Man Israel Italy Jamaica Japan Jersey Jordan Kazakhstan Kenya Kiribati Korea, Democratic People's Republic of Korea, Republic of Kuwait Kyrgyzstan Lao People's Democratic Republic Latvia Lebanon Lesotho Liberia Libya Liechtenstein Lithuania Luxembourg Macao Madagascar Malawi Malaysia Maldives Mali Malta Marshall Islands Martinique Mauritania Mauritius Mayotte Mexico Micronesia Moldova Monaco Mongolia Montenegro Montserrat Morocco Mozambique Myanmar Namibia Nauru Nepal Netherlands New Caledonia New Zealand Nicaragua Niger Nigeria Niue Norfolk Island North Macedonia Northern Mariana Islands Norway Oman Pakistan Palau Palestine, State of Panama Papua New Guinea Paraguay Peru Philippines Pitcairn Poland Portugal Puerto Rico Qatar Romania Russian Federation Rwanda Réunion Saint Barthélemy Saint Helena, Ascension and Tristan da Cunha Saint Kitts and Nevis Saint Lucia Saint Martin Saint Pierre and Miquelon Saint Vincent and the Grenadines Samoa San Marino Sao Tome and Principe Saudi Arabia Senegal Serbia Seychelles Sierra Leone Singapore Sint Maarten Slovakia Slovenia Solomon Islands Somalia South Africa South Georgia and the South Sandwich Islands South Sudan Spain Sri Lanka Sudan Suriname Svalbard and Jan Mayen Sweden Switzerland Syria Arab Republic Taiwan Tajikistan Tanzania, the United Republic of Thailand Timor-Leste Togo Tokelau Tonga Trinidad and Tobago Tunisia Turkmenistan Turks and Caicos Islands Tuvalu Türkiye US Minor Outlying Islands Uganda Ukraine United Arab Emirates United Kingdom United States Uruguay Uzbekistan Vanuatu Venezuela Viet Nam Virgin Islands, British Virgin Islands, U.S. Wallis and Futuna Western Sahara Yemen Zambia Zimbabwe Åland Islands Country
- Which best describes you (or your child)? High school senior High school junior College student College grad Other
- How did you find CEA? Internet Search New York Times Guidance counselor/school Social Media YouTube Friend Special Event Delehey College Consulting Other
- Common App and Coalition Essays
- Supplemental Essays
- University of California Essays
- University of Texas Essays
- Resume Review
- Post-Grad Essays
- Specialized Services
- Waitlist Letters
- Private School Essays
- General College Counseling
- School list with priorities noted:
- Anything else we should know?
- Name This field is for validation purposes and should be left unchanged.
- Agnes Scott College
- Alvernia University
- American University
- Amherst College
- Babson College
- Bard College
- Barnard College
- Baylor University
- Bennington College
- Bentley University
- Berry College
- Bethany College
- Bishop’s University
- Boston College
- Boston University (BU)
- Bowdoin College
- Brandeis University
- Brown University
- Bryn Mawr College
- Bucknell University
- Butler University
- California Institute of Technology (Caltech)
- California Lutheran University
- Capitol Technology University
- Carleton College
- Carnegie Mellon University
- Catawba College
- Centre College
- Chapman University
- Claremont McKenna College
- Clark University
- College of Mount Saint Vincent
- College of William and Mary
- College of Wooster
- Colorado College
- Colorado School of Mines
- Columbia University
- Cornell University
- Culver-Stockton College
- D'Youville University
- Dartmouth College
- Davidson College
- Drexel University
- Duke University
- Earlham College
- Elon University
- Emerson College
- Emory University
- Flagler College
- Fordham University
- George Mason University
- Georgetown University
- Georgia State University
- Georgia Tech
- Gonzaga University
- Harvard University
- Harvey Mudd College
- Haverford College
- Hillsdale College
- Hofstra University
- Illinois Institute of Technology
- Illinois Wesleyan University
- Indiana University Bloomington
- Ithaca College
- Johns Hopkins University
- Kalamazoo College
- Lafayette College
- Lehigh University
- Lewis and Clark College
- Linfield University
- Loyola Marymount University (LMU)
- Lynn University
- Macalester College
- Malone University
- Manchester University
- Marist College
- Mary Baldwin University
- Massachusetts Institute of Technology (MIT)
- Meredith College
- Monmouth College
- Moravian University
- Morehouse College
- Mount Holyoke College
- New York University (NYU)
- North Park University
- Northwestern University
- Occidental College
- Oklahoma City University
- Olin College of Engineering
- Pepperdine University
- Pitzer College
- Pomona College
- Princeton University
- Providence College
- Purdue University
- Rensselaer Polytechnic Institute
- Rice University
- Saint Elizabeth University
- Santa Clara University
- Sarah Lawrence College
- Scripps College
- Seattle Pacific University
- Smith College
- Soka University of America
- Southern Methodist University
- St. John’s College
- Stanford University
- Stonehill College
- Swarthmore College
- Syracuse University
- Texas A&M University
- Texas Christian University
- The College of Idaho
- The George Washington University
- The New School
- Trinity College
- Tufts University
- Tulane University
- University of California
- University of Central Florida (UCF)
- University of Chicago
- University of Cincinnati
- University of Colorado Boulder
- University of Florida
- University of Georgia
- University of Illinois Urbana-Champaign
- University of Maryland
- University of Massachusetts Amherst
- University of Miami
- University of Michigan
- University of Minnesota
- University of North Carolina at Chapel Hill (UNC)
- University of North Carolina at Charlotte
- University of North Carolina at Greensboro
- University of Notre Dame
- University of Oklahoma
- University of Oregon
- University of Pennsylvania
- University of Pittsburgh
- University of Richmond
- University of San Diego
- University of San Francisco
- University of Southern California (USC)
- University of Texas at Austin
- University of Tulsa
- University of Vermont
- University of Virginia (UVA)
- University of Washington
- University of Wisconsin-Madison
- Vanderbilt University
- Vassar College
- Villanova University
- Virginia Tech
- Wake Forest University
- Washington and Lee University
- Washington University in St. Louis
- Wellesley College
- Worcester Polytechnic Institute (WPI)
- Yale University
Want free stuff?
We thought so. Sign up for free instructional videos, guides, worksheets and more!

One-On-One Advising
Common App Essay Prompt Guide

Supplemental Essay Prompt Guide
- YouTube Tutorials
- Our Approach & Team
- Undergraduate Testimonials
- Postgraduate Testimonials
- Where Our Students Get In
- CEA Gives Back
- Undergraduate Admissions
- Graduate Admissions
- Private School Admissions
- International Student Admissions
- Common App Essay Guide
- Supplemental Essay Guides
- Coalition App Guide
- The CEA Podcast
- Admissions Stats
- Notification Trackers
- Deadline Databases
- College Essay Examples
- Academy and Worksheets
- Waitlist Guides
- Get Started

Choose Your Test
Sat / act prep online guides and tips, my successful harvard application (complete common app + supplement).
Other High School , College Admissions , Letters of Recommendation , Extracurriculars , College Essays

In 2005, I applied to college and got into every school I applied to, including Harvard, Princeton, Stanford, and MIT. I decided to attend Harvard.
In this guide, I'll show you the entire college application that got me into Harvard—page by page, word for word .
In my complete analysis, I'll take you through my Common Application, Harvard supplemental application, personal statements and essays, extracurricular activities, teachers' letters of recommendation, counselor recommendation, complete high school transcript, and more. I'll also give you in-depth commentary on every part of my application.
To my knowledge, a college application analysis like this has never been done before . This is the application guide I wished I had when I was in high school.
If you're applying to top schools like the Ivy Leagues, you'll see firsthand what a successful application to Harvard and Princeton looks like. You'll learn the strategies I used to build a compelling application. You'll see what items were critical in getting me admitted, and what didn't end up helping much at all.
Reading this guide from beginning to end will be well worth your time—you might completely change your college application strategy as a result.
First Things First
Here's the letter offering me admission into Harvard College under Early Action.

I was so thrilled when I got this letter. It validated many years of hard work, and I was excited to take my next step into college (...and work even harder).
I received similar successful letters from every college I applied to: Princeton, Stanford, and MIT. (After getting into Harvard early, I decided not to apply to Yale, Columbia, UChicago, UPenn, and other Ivy League-level schools, since I already knew I would rather go to Harvard.)
The application that got me admitted everywhere is the subject of this guide. You're going to see everything that the admissions officers saw.
If you're hoping to see an acceptance letter like this in your academic future, I highly recommend you read this entire article. I'll start first with an introduction to this guide and important disclaimers. Then I'll share the #1 question you need to be thinking about as you construct your application. Finally, we'll spend a lot of time going through every page of my college application, both the Common App and the Harvard Supplemental App.
Important Note: the foundational principles of my application are explored in detail in my How to Get Into Harvard guide . In this popular guide, I explain:
- what top schools like the Ivy League are looking for
- how to be truly distinctive among thousands of applicants
- why being well-rounded is the kiss of death
If you have the time and are committed to maximizing your college application success, I recommend you read through my Harvard guide first, then come back to this one.
You might also be interested in my other two major guides:
- How to Get a Perfect SAT Score / Perfect ACT Score
- How to Get a 4.0 GPA
What's in This Harvard Application Guide?
From my student records, I was able to retrieve the COMPLETE original application I submitted to Harvard. Page by page, word for word, you'll see everything exactly as I presented it : extracurricular activities, awards and honors, personal statements and essays, and more.
In addition to all this detail, there are two special parts of this college application breakdown that I haven't seen anywhere else :
- You'll see my FULL recommendation letters and evaluation forms. This includes recommendations from two teachers, one principal, and supplementary writers. Normally you don't get to see these letters because you waive access to them when applying. You'll see how effective strong teacher advocates will be to your college application, and why it's so important to build strong relationships with your letter writers .
- You'll see the exact pen marks made by my Harvard admissions reader on my application . Members of admissions committees consider thousands of applications every year, which means they highlight the pieces of each application they find noteworthy. You'll see what the admissions officer considered important—and what she didn't.
For every piece of my application, I'll provide commentary on what made it so effective and my strategies behind creating it. You'll learn what it takes to build a compelling overall application.
Importantly, even though my application was strong, it wasn't perfect. I'll point out mistakes I made that I could have corrected to build an even stronger application.
Here's a complete table of contents for what we'll be covering. Each link goes directly to that section, although I'd recommend you read this from beginning to end on your first go.
Common Application
Personal Data
Educational data, test information.
- Activities: Extracurricular, Personal, Volunteer
- Short Answer
- Additional Information
Academic Honors
Personal statement, teacher and counselor recommendations.
- Teacher Letter #1: AP Chemistry
- Teacher Letter #2: AP English Lang
School Report
- Principal Recommendation
Harvard Application Supplement
- Supplement Form
- Writing Supplement Essay
Supplementary Recommendation #1
Supplementary recommendation #2, supplemental application materials.
Final Advice for You
I mean it—you'll see literally everything in my application.
In revealing my teenage self, some parts of my application will be pretty embarrassing (you'll see why below). But my mission through my company PrepScholar is to give the world the most helpful resources possible, so I'm publishing it.
One last thing before we dive in—I'm going to anticipate some common concerns beforehand and talk through important disclaimers so that you'll get the most out of this guide.

Important Disclaimers
My biggest caveat for you when reading this guide: thousands of students get into Harvard and Ivy League schools every year. This guide tells a story about one person and presents one archetype of a strong applicant. As you'll see, I had a huge academic focus, especially in science ( this was my Spike ). I'm also irreverent and have a strong, direct personality.
What you see in this guide is NOT what YOU need to do to get into Harvard , especially if you don't match my interests and personality at all.
As I explain in my Harvard guide , I believe I fit into one archetype of a strong applicant—the "academic superstar" (humor me for a second, I know calling myself this sounds obnoxious). There are other distinct ways to impress, like:
- being world-class in a non-academic talent
- achieving something difficult and noteworthy—building a meaningful organization, writing a novel
- coming from tremendous adversity and performing remarkably well relative to expectations
Therefore, DON'T worry about copying my approach one-for-one . Don't worry if you're taking a different number of AP courses or have lower test scores or do different extracurriculars or write totally different personal statements. This is what schools like Stanford and Yale want to see—a diversity in the student population!
The point of this guide is to use my application as a vehicle to discuss what top colleges are looking for in strong applicants. Even though the specific details of what you'll do are different from what I did, the principles are the same. What makes a candidate truly stand out is the same, at a high level. What makes for a super strong recommendation letter is the same. The strategies on how to build a cohesive, compelling application are the same.
There's a final reason you shouldn't worry about replicating my work—the application game has probably changed quite a bit since 2005. Technology is much more pervasive, the social issues teens care about are different, the extracurricular activities that are truly noteworthy have probably gotten even more advanced. What I did might not be as impressive as it used to be. So focus on my general points, not the specifics, and think about how you can take what you learn here to achieve something even greater than I ever did.
With that major caveat aside, here are a string of smaller disclaimers.
I'm going to present my application factually and be 100% straightforward about what I achieved and what I believed was strong in my application. This is what I believe will be most helpful for you. I hope you don't misinterpret this as bragging about my accomplishments. I'm here to show you what it took for me to get into Harvard and other Ivy League schools, not to ask for your admiration. So if you read this guide and are tempted to dismiss my advice because you think I'm boasting, take a step back and focus on the big picture—how you'll improve yourself.
This guide is geared toward admissions into the top colleges in the country , often with admissions rates below 10%. A sample list of schools that fit into this: Harvard, Princeton, Yale, Stanford, Columbia, MIT, UChicago, Duke, UPenn, CalTech, Johns Hopkins, Dartmouth, Northwestern, Brown. The top 3-5 in that list are especially looking for the absolute best students in the country , since they have the pick of the litter.
Admissions for these selective schools works differently from schools with >20% rates. For less selective schools, having an overall strong, well-rounded application is sufficient for getting in. In particular, having an above average GPA and test scores goes the majority of the way toward getting you admission to those schools. The higher the admission rate, the more emphasis will be placed on your scores. The other pieces I'll present below—personal statements, extracurriculars, recommendations—will matter less.
Still, it doesn't hurt to aim for a stronger application. To state the obvious, an application strong enough to get you Columbia will get you into UCLA handily.
In my application, I've redacted pieces of my application for privacy reasons, and one supplementary recommendation letter at the request of the letter writer. Everything else is unaltered.
Throughout my application, we can see marks made by the admissions officer highlighting and circling things of note (you'll see the first example on the very first page). I don't have any other applications to compare these to, so I'm going to interpret these marks as best I can. For the most part, I assume that whatever he underlines or circles is especially important and noteworthy —points that he'll bring up later in committee discussions. It could also be that the reader got bored and just started highlighting things, but I doubt this.
Finally, I co-founded and run a company called PrepScholar . We create online SAT/ACT prep programs that adapt to you and your strengths and weaknesses . I believe we've created the best prep program available, and if you feel you need to raise your SAT/ACT score, then I encourage you to check us out . I want to emphasize that you do NOT need to buy a prep program to get a great score , and the advice in this guide has little to do with my company. But if you're aren't sure how to improve your score and agree with our unique approach to SAT/ACT prep, our program may be perfect for you.
With all this past us, let's get started.

The #1 Most Important College Application Question: What Is Your PERSONAL NARRATIVE?
If you stepped into an elevator with Yale's Dean of Admissions and you had ten seconds to describe yourself and why you're interesting, what would you say?
This is what I call your PERSONAL NARRATIVE. These are the three main points that represent who you are and what you're about . This is the story that you tell through your application, over and over again. This is how an admissions officer should understand you after just glancing through your application. This is how your admissions officer will present you to the admissions committee to advocate for why they should accept you.
The more unique and noteworthy your Personal Narrative is, the better. This is how you'll stand apart from the tens of thousands of other applicants to your top choice school. This is why I recommend so strongly that you develop a Spike to show deep interest and achievement. A compelling Spike is the core of your Personal Narrative.
Well-rounded applications do NOT form compelling Personal Narratives, because "I'm a well-rounded person who's decent at everything" is the exact same thing every other well-rounded person tries to say.
Everything in your application should support your Personal Narrative , from your course selection and extracurricular activities to your personal statements and recommendation letters. You are a movie director, and your application is your way to tell a compelling, cohesive story through supporting evidence.
Yes, this is overly simplistic and reductionist. It does not represent all your complexities and your 17 years of existence. But admissions offices don't have the time to understand this for all their applicants. Your PERSONAL NARRATIVE is what they will latch onto.
Here's what I would consider my Personal Narrative (humor me since I'm peacocking here):
1) A science obsessive with years of serious research work and ranked 6 th in a national science competition, with future goals of being a neuroscientist or physician
2) Balanced by strong academic performance in all subjects (4.0 GPA and perfect test scores, in both humanities and science) and proficiency in violin
3) An irreverent personality who doesn't take life too seriously, embraces controversy, and says what's on his mind
These three elements were the core to my application. Together they tell a relatively unique Personal Narrative that distinguishes me from many other strong applicants. You get a surprisingly clear picture of what I'm about. There's no question that my work in science was my "Spike" and was the strongest piece of my application, but my Personal Narrative included other supporting elements, especially a description of my personality.

My College Application, at a High Level
Drilling down into more details, here's an overview of my application.
- This put me comfortably in the 99 th percentile in the country, but it was NOT sufficient to get me into Harvard by itself ! Because there are roughly 4 million high school students per year, the top 1 percentile still has 40,000 students. You need other ways to set yourself apart.
- Your Spike will most often come from your extracurriculars and academic honors, just because it's hard to really set yourself apart with your coursework and test scores.
- My letters of recommendation were very strong. Both my recommending teachers marked me as "one of the best they'd ever taught." Importantly, they corroborated my Personal Narrative, especially regarding my personality. You'll see how below.
- My personal statements were, in retrospect, just satisfactory. They represented my humorous and irreverent side well, but they come across as too self-satisfied. Because of my Spike, I don't think my essays were as important to my application.
Finally, let's get started by digging into the very first pages of my Common Application.

There are a few notable points about how simple questions can actually help build a first impression around what your Personal Narrative is.
First, notice the circle around my email address. This is the first of many marks the admissions officer made on my application. The reason I think he circled this was that the email address I used is a joke pun on my name . I knew it was risky to use this vs something like [email protected], but I thought it showed my personality better (remember point #3 about having an irreverent personality in my Personal Narrative).
Don't be afraid to show who you really are, rather than your perception of what they want. What you think UChicago or Stanford wants is probably VERY wrong, because of how little information you have, both as an 18-year-old and as someone who hasn't read thousands of applications.
(It's also entirely possible that it's a formality to circle email addresses, so I don't want to read too much into it, but I think I'm right.)
Second, I knew in high school that I wanted to go into the medical sciences, either as a physician or as a scientist. I was also really into studying the brain. So I listed both in my Common App to build onto my Personal Narrative.
In the long run, both predictions turned out to be wrong. After college, I did go to Harvard Medical School for the MD/PhD program for 4 years, but I left to pursue entrepreneurship and co-founded PrepScholar . Moreover, in the time I did actually do research, I switched interests from neuroscience to bioengineering/biotech.
Colleges don't expect you to stick to career goals you stated at the age of 18. Figuring out what you want to do is the point of college! But this doesn't give you an excuse to avoid showing a preference. This early question is still a chance to build that Personal Narrative.
Thus, I recommend AGAINST "Undecided" as an area of study —it suggests a lack of flavor and is hard to build a compelling story around. From your high school work thus far, you should at least be leaning to something, even if that's likely to change in the future.
Finally, in the demographic section there is a big red A, possibly for Asian American. I'm not going to read too much into this. If you're a notable minority, this is where you'd indicate it.
Now known as: Education

This section was straightforward for me. I didn't take college courses, and I took a summer chemistry class at a nearby high school because I didn't get into the lottery at my school that year (I refer to this briefly in my 4.0 GPA guide ).
The most notable point of this section: the admissions officer circled Principal here . This is notable because our school Principal only wrote letters for fewer than 10 students each year. Counselors wrote letters for the other hundreds of students in my class, which made my application stand out just a little.
I'll talk more about this below, when I share the Principal's recommendation.
(In the current Common Application, the Education section also includes Grades, Courses, and Honors. We'll be covering each of those below).
Now known as: Testing
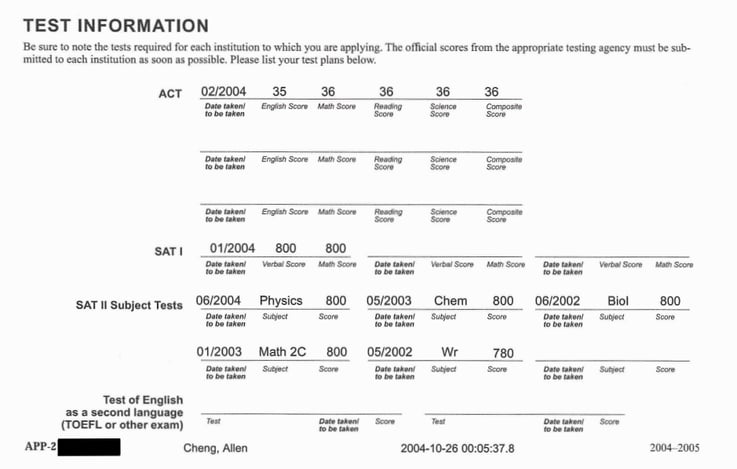
Back then AP scores weren't part of this section, but I'll take them from another part of my application here.

However, their standards are still very high. You really do want to be in that top 1 percentile to pass the filter. A 1400 on the SAT IS going to put you at a disadvantage because there are so many students scoring higher than you. You'll really have to dig yourself out of the hole with an amazing application.
I talk about this a lot more in my Get into Harvard guide (sorry to keep linking this, but I really do think it's an important guide for you to read).

Let's end this section with some personal notes.
Even though math and science were easy for me, I had to put in serious effort to get an 800 on the Reading section of the SAT . As much as I wish I could say it was trivial for me, it wasn't. I learned a bunch of strategies and dissected the test to get to a point where I understood the test super well and reliably earned perfect scores.
I cover the most important points in my How to Get a Perfect SAT Score guide , as well as my 800 Guides for Reading , Writing , and Math .
Between the SAT and ACT, the SAT was my primary focus, but I decided to take the ACT for fun. The tests were so similar that I scored a 36 Composite without much studying. Having two test scores is completely unnecessary —you get pretty much zero additional credit. Again, with one test score, you have already passed their filter.
Finally, class finals or state-required exams are a breeze if you get a 5 on the corresponding AP tests .
Now known as: Family (still)
This section asks for your parent information and family situation. There's not much you can do here besides report the facts.

I'm redacting a lot of stuff again for privacy reasons.
The reader made a number of marks here for occupation and education. There's likely a standard code for different types of occupations and schools.
If I were to guess, I'd say that the numbers add to form some metric of "family prestige." My dad got a Master's at a middle-tier American school, but my mom didn't go to graduate school, and these sections were marked 2 and 3, respectively. So it seems higher numbers are given for less prestigious educations by your parents. I'd expect that if both my parents went to schools like Caltech and Dartmouth, there would be even lower numbers here.
This makes me think that the less prepared your family is, the more points you get, and this might give your application an extra boost. If you were the first one in your family to go to college, for example, you'd be excused for having lower test scores and fewer AP classes. Schools really do care about your background and how you performed relative to expectations.
In the end, schools like Harvard say pretty adamantly they don't use formulas to determine admissions decisions, so I wouldn't read too much into this. But this can be shorthand to help orient an applicant's family background.

Extracurricular, Personal, and Volunteer Activities
Now known as: Activities
For most applicants, your Extracurriculars and your Academic Honors will be where you develop your Spike and where your Personal Narrative shines through. This was how my application worked.
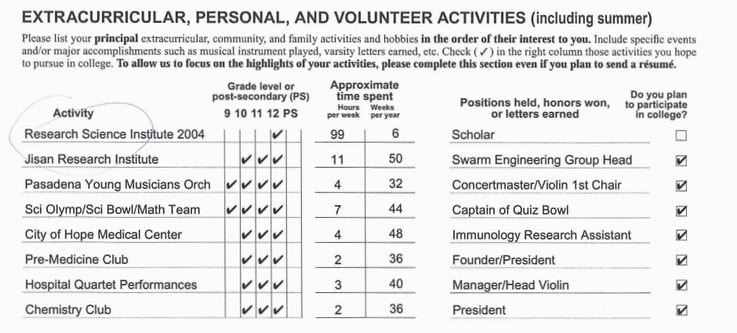
Just below I'll describe the activities in more detail, but first I want to reflect on this list.
As instructed, my extracurriculars were listed in the order of their interest to me. The current Common App doesn't seem to ask for this, but I would still recommend it to focus your reader's attention.
The most important point I have to make about my extracurriculars: as you go down the list, there is a HUGE drop in the importance of each additional activity to the overall application. If I were to guess, I assign the following weights to how much each activity contributed to the strength of my activities section:
In other words, participating in the Research Science Institute (RSI) was far more important than all of my other extracurriculars, combined. You can see that this was the only activity my admissions reader circled.
You can see how Spike-y this is. The RSI just completely dominates all my other activities.
The reason for this is the prestige of RSI. As I noted earlier, RSI was (and likely still is) the most prestigious research program for high school students in the country, with an admission rate of less than 5% . Because the program was so prestigious and selective, getting in served as a big confirmation signal of my academic quality.
In other words, the Harvard admissions reader would likely think, "OK, if this very selective program has already validated Allen as a top student, I'm inclined to believe that Allen is a top student and should pay special attention to him."
Now, it took a lot of prior work to even get into RSI because it's so selective. I had already ranked nationally in the Chemistry Olympiad (more below), and I had done a lot of prior research work in computer science (at Jisan Research Institute—more about this later). But getting into RSI really propelled my application to another level.
Because RSI was so important and was such a big Spike, all my other extracurriculars paled in importance. The admissions officer at Princeton or MIT probably didn't care at all that I volunteered at a hospital or founded a high school club .
This is a good sign of developing a strong Spike. You want to do something so important that everything else you do pales in comparison to it. A strong Spike becomes impossible to ignore.
In contrast, if you're well-rounded, all your activities hold equal weight—which likely means none of them are really that impressive (unless you're a combination of Olympic athlete, internationally-ranked science researcher, and New York Times bestselling author, but then I'd call you unicorn because you don't exist).
Apply this concept to your own interests—what can be so impressive and such a big Spike that it completely overshadows all your other achievements?
This might be worth spending a disproportionate amount of time on. As I recommend in my Harvard guide and 4.0 GPA guide , smartly allocating your time is critical to your high school strategy.
In retrospect, one "mistake" I made was spending a lot of time on the violin. Each week I spent eight hours on practice and a lesson and four hours of orchestra rehearsals. This amounted to over 1,500 hours from freshman to junior year.
The result? I was pretty good, but definitely nowhere near world-class. Remember, there are thousands of orchestras and bands in the country, each with their own concertmasters, drum majors, and section 1 st chairs.
If I were to optimize purely for college applications, I should have spent that time on pushing my spike even further —working on more Olympiad competitions, or doing even more hardcore research.
Looking back I don't mind this much because I generally enjoyed my musical training and had a mostly fun time in orchestra (and I had a strong Spike anyway). But this problem can be a lot worse for well-rounded students who are stretched too thin.

Aside from these considerations about a Spike, I have two major caveats.
First, developing a Spike requires continuous, increasingly ambitious foundational work. It's like climbing a staircase. From the beginning of high school, each step was more and more ambitious—my first academic team, my first research experience, leading up to state and national competitions and more serious research work.
So when I suggest devoting a lot of time to developing your Spike, it's not necessarily the Spike in itself—it's also spending time on foundational work leading up to what will be your major achievement. That's why I don't see my time with academic teams or volunteering as wasted, even though in the end they didn't contribute as much to my application.
Second, it is important to do things you enjoy. I still enjoyed playing the violin and being part of an orchestra, and I really enjoyed my school's academic teams, even though we never went beyond state level. Even if some activities don't contribute as much to your application, it's still fine to spend some time on them—just don't delude yourself into thinking they're stronger than they really are and overspend time on them.
Finally, note that most of my activities were pursued over multiple years. This is a good sign of commitment—rather than hopping from activity year to year, it's better to show sustained commitment, as this is a better signal of genuine passion.
In a future article, I'll break down these activities in more detail. But this guide is already super long, so I want to focus our attention on the main points.
Short Answer: Extracurricular Activities
In today's Common Application, you have 50 characters to describe "Position/Leadership description and organization name" and 150 characters for "Please describe this activity, including what you accomplished and any recognition you received, etc."
Back then, we didn't have as much space per activity, and instead had a short answer question.
The Short Answer prompt:
Please describe which of your activities (extracurricular and personal activities or work experience) has been most meaningful and why.
I chose RSI as my most significant activity for two reasons—one based on the meaning of the work, and another on the social aspect.

It's obvious that schools like Yale and UChicago want the best students in the world that they can get their hands on. Academic honors and awards are a great, quantifiable way to show that.
Here's the complete list of Academic Honors I submitted. The Common Application now limits you to five honors only (probably because they got tired of lists like these), but chances are you capture the top 98% of your honors with the top five.


Charlie wins a Golden Ticket to Harvard.
I know this is intimidating if you don't already have a prestigious honor. But remember there are thousands of nationally-ranked people in a multitude of honor types, from science competitions to essay contests to athletics to weird talents.
And I strongly believe the #1 differentiator of high school students who achieve things is work ethic, NOT intelligence or talent. Yes, you need a baseline level of competence to get places, but people far undervalue the progress they can make if they work hard and persevere. Far too many people give up too quickly or fatigue without putting in serious effort.
If you're stuck thinking, "well I'm just an average person, and there's no way I'm going to become world-class in anything," then you've already lost before you've begun. The truth is everyone who achieves something of note puts in an incredible amount of hard work. Because this is invisible to you, it looks like talent is what distinguishes the two of you, when really it's much more often diligence.
I talk a lot more about the Growth Mindset in my How To Get a 4.0 GPA guide .
So my Chemistry Olympiad honor formed 90% of the value of this page. Just like extracurriculars, there's a quick dropoff in value of each item after that.
My research work took up the next two honors, one a presentation at an academic conference, and the other (Siemens) a research competition for high school researchers.
The rest of my honors were pretty middling:
- National Merit Scholarship semifinalist pretty much equates to PSAT score, which is far less important than your SAT/ACT score. So I didn't really get any credit for this, and you won't either.
- In Science Olympiad (this is a team-based competition that's not as prestigious as the academic Olympiads I just talked about), I earned a number of 1 st place state and regional medals, but we never made it to nationals.
- I was mediocre at competition math because I didn't train for it, and I won some regional awards but nothing amazing. This is one place I would have spent more time, maybe in the time I'd save by not practicing violin as much. There are great resources for this type of training, like Art of Problem Solving , that I didn't know existed and could've helped me rank much higher.
At the risk of beating a dead horse, think about how many state medalists there are in the country, in the hundreds of competitions that exist . The number of state to national rankers is probably at least 20:1 (less than 50:1 because of variation in state size), so if there are 2,000 nationally ranked students, there are 40,000 state-ranked students in something !
So state honors really don't help you stand out on your Princeton application. There are just too many of them around.
On the other hand, if you can get to be nationally ranked in something, you will have an amazing Spike that distinguishes you.

Now known as: Personal Essay
Now, the dreaded personal statement. Boy, oh boy, did I fuss over this one.
"What is the perfect combination of personal, funny, heartrending, and inspirational?"
I know I was wondering this when I applied.
Having read books like 50 Successful Harvard Application Essays , I was frightened. I didn't grow up as a refugee, wrenched from my war-torn home! I didn't have a sibling with a debilitating illness! How could anything I write compare to these tales of personal strength?
The trite truth is that colleges want to know who you really are . Clearly they don't expect everyone to have had immense personal struggle. But they do want students who are:
- growth-oriented
- introspective
- kind and good-hearted
Whatever those words mean to you in the context of your life is what you should write about.
In retrospect, in the context of MY application, the personal statement really wasn't what got me into Harvard . I do think my Spike was nearly sufficient to get me admitted to every school in the country.
I say "nearly" because, even if you're world-class, schools do want to know you're not a jerk and that you're an interesting person (which is conveyed through your personal essay and letters of recommendation).
Back then, we had a set of different prompts :

What did you think?
I'm still cringing a bit. Parts of this are very smug (see /r/iamverysmart ), and if you want to punch the writer in the face, I don't blame you. I want to as well.
We'll get to areas of improvement later, but first, let's talk about what this personal essay did well.
As I said above, I saw the theme of the snooze button as a VEHICLE to showcase a few qualities I cared about :
1) I fancied myself a Renaissance man (obnoxious, I know) and wanted to become an inventor and creator . I showed this through mentioning different interests (Rubik's cube, chemistry, Nietzsche) and iterating through a few designs for an alarm clock (electric shocks, explosions, Shakespearean sonnet recitation).
2) My personality was whimsical and irreverent. I don't take life too seriously. The theme of the essay—battling an alarm clock—shows this well, in comparison to the gravitas of the typical student essay. I also found individual lines funny, like "All right, so I had violated the divine honor of the family and the tenets of Confucius." At once I acknowledge my Chinese heritage but also make light of the situation.
3) I was open to admitting weaknesses , which I think is refreshing among people taking college applications too seriously and trying too hard to impress. The frank admission of a realistic lazy habit—pushing the Snooze button—served as a nice foil to my academic honors and shows that I can be down-to-earth.
So you see how the snooze button acts as a vehicle to carry these major points and a lot of details, tied together to the same theme .
In the same way, The Walking Dead is NOT a zombie show—the zombie environment is a VEHICLE by which to show human drama and conflict. Packaging my points together under the snooze button theme makes it a lot more interesting than just outright saying "I'm such an interesting guy."
So overall, I believe the essay accomplishes my goals and the main points of what I wanted to convey about myself.
Note that this is just one of many ways to write an essay . It worked for me, but it may be totally inappropriate for you.
Now let's look at this essay's weaknesses.

Looking at it with a more seasoned perspective, some parts of it are WAY too try-hard. I try too hard to show off my breadth of knowledge in a way that seems artificial and embellishing.
The entire introduction with the Rubik's cube seems bolted on, just to describe my long-standing desire to be a Renaissance man. Only three paragraphs down do I get to the Snooze button, and I don't refer again to the introduction until the end. With just 650 words, I could have made the essay more cohesive by keeping the same theme from beginning to end.
Some phrases really make me roll my eyes. "Always hungry for more" and "ever the inventor" sound too forced and embellishing. A key principle of effective writing is to show, not say . You don't say "I'm passionate about X," you describe what extraordinary lengths you took to achieve X.
The mention of Nietzsche is over-the-top. I mean, come on. The reader probably thought, "OK, this kid just read it in English class and now he thinks he's a philosopher." The reader would be right.
The ending: "with the extra nine minutes, maybe I'll teach myself to cook fried rice" is silly. Where in the world did fried rice come from? I meant it as a nod to my Chinese heritage, but it's too sudden to work. I could have deleted the sentence and wrapped up the essay more cleanly.
So I have mixed feelings of my essay. I think it accomplished my major goals and showed the humorous, irreverent side of my personality well. However, it also gave the impression of a kid who thought he knew more than he did, a pseudo-sophisticate bordering on obnoxious. I still think it was a net positive.
At the end of the day, I believe the safest, surefire strategy is to develop a Spike so big that the importance of the Personal Essay pales in comparison to your achievements. You want your Personal Essay to be a supplement to your application, not the only reason you get in.
There are probably some cases where a well-rounded student writes an amazing Personal Essay and gets in through the strength of that. As a Hail Mary if you're a senior and can't improve your application further, this might work. But the results are very variable—some readers may love your essay, others may just think it's OK. Without a strong application to back it up, your mileage may vary.

This is a really fun section. Usually you don't get to read your letter of recommendation because you sign the FERPA waiver. I've also reached out to my letter writers to make sure they're ok with my showing this.
Teacher recommendations are incredibly important to your application. I would say that after your coursework/test scores and activities/honors, they're the 3 rd most important component of your application .
The average teacher sees thousands of students through a career, and so he or she is very well equipped to position you relative to all other students. Furthermore, your teachers are experienced adults—their impressions of you are much more reliable than your impressions of yourself (see my Personal Essay above). They can corroborate your entire Personal Narrative as an outside observer.
The most effective recommendation letters speak both to your academic strengths and to your personality. For the second factor, the teacher needs to have interacted with you meaningfully, ideally both in and out of class. Check out our guide on what makes for effective letters of recommendation .

Starting from sophomore year, I started thinking about whom I connected better with and chose to engage with those teachers more deeply . Because it's standard for colleges to require two teachers in different subjects, I made sure to engage with English and history teachers as well as math and science.
The minimum requirement for a good letter is someone who taught a class in which you did well. I got straight A's in my coursework, so this wasn't an issue.
Beyond this, I had to look for teachers who would be strong advocates for me on both an academic and personal level . These tended to be teachers I vibed more strongly with, and typically these were teachers who demonstrably cared about teaching. This was made clear by their enthusiasm, how they treated students, and how much they went above expectations to help.
I had a lot of teachers who really just phoned it in and treated their job perfunctorily—these people are likely to write pretty blasé letters.
A final note before reading my actual teacher evaluations— you should avoid getting in the mindset where you get to know teachers JUST because you want a good recommendation letter . Your teachers have seen hundreds, if not thousands, of students pass through, and it's much easier to detect insincerity than you think.
If you honestly like learning and are an enthusiastic, responsible, engaging student, a great recommendation letter will follow naturally. The horse should lead the cart.
Read my How to Get a 4.0 GPA for tips on how to interact with teachers in a genuine way that'll make them love you.

Teacher Letter #1: AP Chemistry Teacher
I took AP Chemistry in 10 th grade and had Miss Cherryl Vorak (now Mynster). She was young, having taught for fewer than 5 years when I had her. She was my favorite teacher throughout high school for these reasons:
- She was enthusiastic, very caring, and spent a lot of time helping struggling students. She exuded pride in her work and seemed to consider teaching her craft.
- She had a kind personality and was universally well liked by her students, even if they weren't doing so well. She was fair in her policies (it probably helped that science is more objective than English). She was also a younger teacher, and this helped her relate to kids more closely.
- She was my advocate for much of the US National Chemistry Olympiad stuff, and in this capacity I got to know her even better outside of class. She provided me a lot of training materials, helped me figure out college chemistry, and directed me to resources to learn more.
By the time of the letter writing, I had known her for two full years and engaged with her continuously, even when I wasn't taking a class with her in junior year. We'd build up a strong relationship over the course of many small interactions.
All of this flowed down to the recommendation you see here. Remember, the horse leads the cart.
First, we'll look at the teacher evaluation page. The Common Application now has 16 qualities to rate, rather than the 10 here. But they're largely the same.

You can see a very strong evaluation here, giving me the highest ratings possible for all qualities.
In today's Common Application, all of these Ratings are retained, aside from "Potential for Growth." Today's Common App also now includes Faculty Respect, Maturity, Leadership, Integrity, Reaction to Setbacks, Concern for Others, and TE Overall. You can tell that the updated Common App places a great emphasis on personality.
The most important point here: it is important to be ranked "One of the top few encountered in my career" for as many ratings as possible . If you're part of a big school, this is CRITICAL to distinguish yourself from other students. The more experienced and trustworthy the teacher, the more meaningful this is.
Again, it's a numbers game. Think about the 20,000+ high schools in the country housing 4 million+ high school students—how many people fit in the top 5% bucket?
Thus, being marked merely as Excellent (top 10%) is actually a negative rating , as far as admissions to top colleges is concerned. If you're in top 10%, and someone else with the SAME teacher recommender is being rated as "One of the top ever," it's really hard for the admissions officer to vouch for you over the other student.
You really want to make sure you're one of the best in your school class, if not one of the best the teacher has ever encountered. You'll see below how you can accomplish this.
Next, let's look at her letter.
As you read this, think— what are the interactions that would prompt the teacher to write a recommendation like this? This was a relationship built up in a period of over 2 years, with every small interaction adding to an overall larger impression.

You can see how seriously they take the letter because of all the underlining . This admissions reader underlined things that weren't even underlined in my application, like my US National Chemistry Olympiad awards. It's one thing for a student to claim things about himself—it's another to have a teacher put her reputation on the line to advocate for her student.
The letter here is very strong for a multitude of reasons. First, the length is notable —most letters are just a page long, but this is nearly two full pages , single spaced. This indicates not just her overall commitment to her students but also of her enthusiastic support for me as an applicant.
The structure is effective: first Miss Vorak talks about my academic accomplishments, then about my personal qualities and interactions, then a summary to the future. This is a perfect blend of what effective letters contain .
On the micro-level, her diction and phrasing are precise and effective . She makes my standing clear with specific statements : "youngest student…top excelling student among the two sections" and "one of twenty students in the nation." She's clear about describing why my achievements are notable and the effort I put in, like studying college-level chemistry and studying independently.
When describing my personality, she's exuberant and fleshes out a range of dimensions: "conscientious, motivated and responsible," "exhibits the qualities of a leader," "actively seeks new experiences," "charismatic," "balanced individual with a warm personality and sense of humor." You can see how she's really checking off all the qualities colleges care about.
Overall, Miss Vorak's letter perfectly supports my Personal Narrative —my love for science, my overall academic performance, and my personality. I'm flattered and grateful to have received this support. This letter was important to complement the overall academic performance and achievements shown on the rest of my application.

Teacher Letter #2: AP English Language Teacher
My second teacher Mrs. Swift was another favorite. A middle-aged, veteran English teacher, the best way I would describe her is "fiery." She was invigorating and passionate, always trying to get a rise out of students and push their thinking, especially in class discussions. Emotionally she was a reliable source of support for students.
First, the evaluation:

You can see right away that her remarks are terser. She didn't even fill out the section about "first words that come to mind to describe this student."
You might chalk this up to my not being as standout of a student in her mind, or her getting inundated with recommendation letter requests after over a decade of teaching.
In ratings, you can see that I only earned 3 of the "one of the top in my career." There are a few explanations for this. As a teacher's career lengthens, it gets increasingly hard to earn this mark. I probably also didn't stand out as much as I did to my Chemistry teacher—most of my achievement was in science (which she wasn't closely connected to), and I had talented classmates. Regardless, I did appreciate the 3 marks she gave me.
Now, the letter. Once again, as you read this letter, think: what are the hundreds of micro-interactions that would have made a teacher write a letter like this?

Overall, this letter is very strong. It's only one page long, but her points about my personality are the critical piece of this recommendation. She also writes with the flair of an English teacher:
"In other situations where students would never speak their minds, he showed no hesitation to voice questions, thoughts, and ideas."
"controversial positions often being the spark that set off the entire class"
"ability to take the quiet and shy student and actively engage"…"went out of my way to partner him with other students who needed"
"strength of conviction"…"raw, unbridled passion"…"He will argue on any topic that has touched a nerve."
These comments most support the personality aspect of my Personal Narrative—having an irreverent, bold personality and not being afraid of speaking my mind. She stops just short of making me sound obnoxious and argumentative. An experienced teacher vouching for this adds so much more weight than just my writing it about myself.
Teacher recommendations are some of the most important components of your application. Getting very strong letters take a lot of sustained, genuine interaction over time to build mutual trust and respect. If you want detailed advice on how to interact with teachers earnestly, check out my How to Get a 4.0 GPA and Better Grades guide .
Let's go to the final recommendation, from the school counselor.

Now known as: School Report
The first piece of this is reporting your academic status and how the school works overall. There's not much to say here, other than the fact that my Principal wrote my recommendation for me, which we'll get into next.

Counselor Recommendation
Now known as: Counselor Recommendation
Let's talk about my school principal writing my recommendation, rather than a school counselor.
This was definitely advantageous—remember how, way up top in Educational Data, the reader circled the "Principal." Our Principal only wrote a handful of these recommendations each year , often for people who worked closely with him, like student body presidents. So it was pretty distinctive that I got a letter from our Principal, compared to other leading applicants from my school.
This was also a blessing because our counseling department was terrible . Our school had nearly 1,000 students per grade, and only 1 counselor per grade. They were overworked and ornery, and because they were the gatekeepers of academic enrollment (like class selection and prerequisites), this led to constant frictions in getting the classes you wanted.
I can empathize with them, because having 500+ neurotic parents pushing for advantages for their own kids can get REALLY annoying really fast. But the counseling department was still the worst part of our high school administration, and I could have guessed that the letters they wrote were mediocre because they just had too many students.
So how did my Principal come to write my recommendation and not those for hundreds of other students?
I don't remember exactly how this came to be, to be honest. I didn't strategize to have him write a letter for me years in advance. I didn't even interact with him much at all until junior year, when I got on his radar because of my national rankings. Come senior year I might have talked to him about my difficulty in reaching counselors and asked that he write my recommendation. Since I was a top student he was probably happy to do this.
He was very supportive, but as you can tell from the letter to come, it was clear he didn't know me that well.
Interestingly, the prompt for the recommendation has changed. It used to start with: "Please write whatever you think is important about this student."
Now, it starts with: " Please provide comments that will help us differentiate this student from others ."
The purpose of the recommendation has shifted to the specific: colleges probably found that one counselor was serving hundreds of students, so the letters started getting mushy and indistinguishable from each other.
Here's the letter:

This letter is probably the weakest overall of all my letters. It reads more like a verbal resume than a personal account of how he understands me.
Unlike my two teacher recommendations, he doesn't comment on the nature of our interactions or about my personality (because he truly didn't understand them well). He also misreported by SAT score as 1530 instead of 1600 (I did score a 1530 in an early test, but my 1600 was ready by January 2004, so I don't know what source he was using).
Notably, the letter writer didn't underline anything.
I still appreciate that he wrote my letter, and it was probably more effective than a generic counselor letter. But this didn't add much to my application.
At this point, we've covered my entire Common Application. This is the same application I sent to every school I applied to, including Harvard, Princeton, and Stanford. Thanks for reading this far—I hope you've gotten a lot out of this already.
If you keep reading to the end, I'll have advice for both younger students and current applicants to build the strongest application possible.
Next, we'll go over the Harvard Supplemental Application, which of course is unique to Harvard.

For most top colleges like Princeton, Yale, Stanford, Columbia, and so on, you will need to complete a supplemental application to provide more info than what's listed on the Common Application.
Harvard was and is the same. The good news is that it's an extra chance for you to share more about yourself and keep pushing your Personal Narrative.
There are four major components here:
- The application form
- Writing supplement essay
- Supplementary recommendations
- Supplemental application materials
I'll take you through the application section by section.
Harvard Supplement Form
First, the straightforward info and questions.

This section is pretty straightforward and is similar to what you'd see on a Columbia application.
I planned to live in a Harvard residence, as most students do.
Just as in my Common App, I noted that I was most likely to study biological sciences, choose Medicine as my vocation, and participate in orchestra, writing, and research as my extracurriculars. Nothing surprising here—it's all part of my Personal Narrative.
Interestingly, at the time I was "absolutely certain" about my vocational goals, which clearly took a detour once I left medical school to pursue entrepreneurship to create PrepScholar...
I had the space to list some additional honors, where I listed some musical honors that didn't make the cut in my Common App.
Here are the next two pages of the Harvard supplemental form.
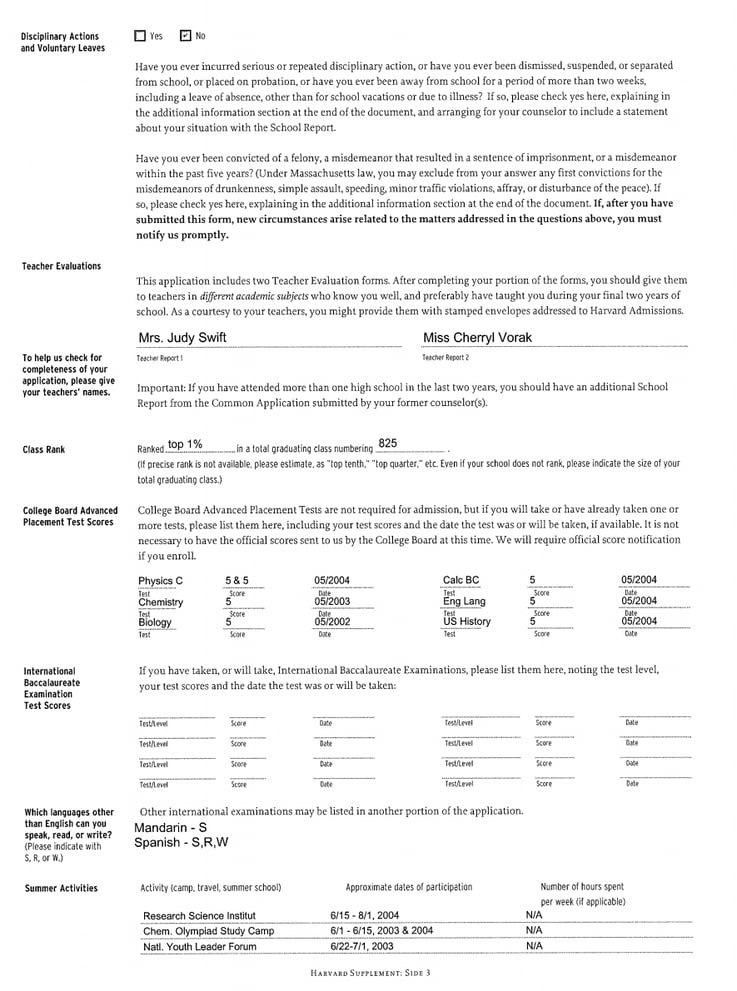
The most interesting note here is that the admissions officer wrote a question mark above "Music tape or CD." Clearly this was inconsistent with my Personal Narrative —if violin was such an important part of my story, why didn't I want to include it?
The reason was that I was actually pretty mediocre at violin and was nowhere near national-ranked. Again, remember how many concertmasters in the thousands of orchestras there are in the world—I wasn't good enough to even be in the top 3 chairs in my school orchestra (violin was very competitive).
I wanted to focus attention on my most important materials, which for my Personal Narrative meant my research work. You'll see these supplementary materials later.

Additional Essays
Now known as: Writing Supplement
For the most part, the Harvard supplemental essay prompt has stayed the same. You can write about a topic of your choice or about any of the suggestions. There are now two more prompts that weren't previously there: "What you would want your future college roommate to know about you" and "How you hope to use your college education."
Even though this is optional, I highly recommend you write something here. Again, you have so few chances in the overall application to convey your personal voice—an extra 500 words gives you a huge opportunity. I would guess that the majority of admitted Harvard students submit a Writing Supplement.
After a lot of brainstorming, I settled on the idea that I wanted to balance my application by writing about the major non-academic piece of my Personal Narrative—my music training . Also, I don't think I explicitly recognized this at the time, but I wanted to distance myself from the Asian-American stereotype—driven entirely by parent pressure, doing most things perfunctorily and without interest. I wanted to show I'd broken out of that mold.
Here's my essay:

Reading it now, I actually think this was a pretty bad essay, and I cringe to high heaven. But once again, let's focus on the positive first.
I used my violin teacher as a vehicle for talking about what the violin meant to me. (You can tell I love the concept of the vehicle in essays.) He represented passion for the violin—I represented my academic priorities. Our personal conflict was really the conflict between what we represented.
By the end of the essay, I'd articulated the value of musical training to me—it was cathartic and a way to balance my hard academic pursuits.
Halfway in the essay, I also explicitly acknowledged the Asian stereotype of parents who drove their kids, and said my parents were no different. The reader underlined this sentence. By pointing this out and showing how my interest took on a life of its own, I wanted to distance myself from that stereotype.
So overall I think my aims were accomplished.
Despite all that, this essay was WAY overdramatic and overwrought . Some especially terrible lines:
"I was playing for that cathartic moment when I could feel Tchaikovsky himself looking over my shoulder."
"I was wandering through the fog in search of a lighthouse, finally setting foot on a dock pervaded by white light."
OK, please. Who really honestly feels this way? This is clumsy, contrived writing. It signals insincerity, actually, which is bad.
To be fair, all of this is grounded in truth. I did have a strict violin teacher who did get pretty upset when I showed lack of improvement. I did appreciate music as a diversion to round out my academic focus. I did practice hard each day, and I did have a pretty gross callus on my pinky.
But I would have done far better by making it more sincere and less overworked.
As an applicant, you're tempted to try so hard to impress your reader. You want to show that you're Worthy of Consideration. But really the best approach is to be honest.
I think this essay was probably neutral to my application, not a strong net positive or net negative.


Supplementary Recommendations
Harvard lets you submit letters from up to two Other Recommenders. The Princeton application, Penn application, and others are usually the same.
Unlike the other optional components (the Additional Information in the Common App, and the Supplementary Essay), I would actually consider these letters optional. The reader gets most of the recommendation value from your teacher recommendations—these are really supplementary.
A worthwhile Other Recommender:
- has supervised an activity or honor that is noteworthy
- has interacted with you extensively and can speak to your personality
- is likely to support you as one of the best students they've interacted with
If your Other Recommenders don't fulfill one or more of these categories, do NOT ask for supplementary letters. They'll dilute your application without adding substantively to it.
To beat a dead horse, the primary component of my Personal Narrative was my science and research work. So naturally I chose supervisors for my two major research experiences to write supplemental letters.
First was the Director of Research Science Institute (the selective summer research program at MIT). The second was from the head of Jisan Research Institute, where I did Computer Science research.

This letter validates my participation in RSI and incorporates the feedback from my research mentor, David Simon. At the time, the RSI students were the most talented students I had met, so I'm also flattered by some of the things the letter writer said, like "Allen stood out early on as a strong performer in academic settings."
I didn't get to know the letter writer super well, so he commented mainly on my academic qualifications and comments from my mentor.
My mentor, who was at one of the major Harvard-affiliated hospitals, said some very nice things about my research ability, like:
"is performing in many ways at the level of a graduate student"
"impressed with Allen's ability to read even advanced scientific publications and synthesize his understanding"
Once again, it's much more convincing for a seasoned expert to vouch for your abilities than for you to claim your own abilities.
My first research experience was done at Jisan Research Institute, a small private computer science lab run by a Caltech PhD. The research staff were mainly high school students like me and a few grad students/postdocs.
My research supervisor, Sanza Kazadi, wrote the letter. He's requested that I not publish the letter, so I'll only speak about his main points.
In the letter, he focused on the quality of my work and leadership. He said that I had a strong focus in my work, and my research moved along more reliably than that of other students. I was independent in my work in swarm engineering, he says, putting together a simulation of the swarm and publishing a paper in conference proceedings. He talked about my work in leading a research group and placing a high degree of trust in me.
Overall, a strong recommendation, and you get the gist of his letter without reading it.
One notable point—both supplemental letters had no marks on them. I really think this means they place less emphasis on the supplementary recommendations, compared to the teacher recommendations.
Finally, finally, we get to the very last piece of my application.
Let me beat the dead horse even deader. Because research was such a core part of my Personal Narrative, I decided to include abstracts of both of my papers. The main point was to summarize the body of work I'd done and communicate the major results.
As Harvard says, "These materials are entirely optional; please only submit them if you have unusual talents."
This is why I chose not to submit a tape of my music: I don't think my musical skill was unusually good.
And frankly, I don't think my research work was that spectacular. Unlike some of my very accomplished classmates, I hadn't ranked nationally in prestigious competitions like ISEF and Siemens. I hadn't published my work in prominent journals.
Regardless, I thought these additions would be net positive, if only marginally so.

I made sure to note where the papers had been published or were entering competitions, just to ground the work in some achievement.

Keep Reading
At PrepScholar, we've published the best guides available anywhere to help you succeed in high school and college admissions.
Here's a sampling of our most popular articles:
How to Get a Perfect SAT Score / Perfect ACT Score —Learn the strategies I used to get a perfect 1600 on the SAT, and a perfect 36 on the ACT.
SAT 800 Series: Reading | Math | Writing —Learn important strategies to excel in each section of the SAT.
ACT 36 Series: English | Math | Reading | Science —Learn how to get a perfect 36 on each section of the ACT.
How to Get Into Harvard and the Ivy League —The foundational guide where I discuss the philosophy behind what colleges are looking for, how to develop a Spike, and why being well-rounded is the path to rejection.
How to Get a 4.0 GPA and Better Grades —Are you struggling with getting strong grades in challenging coursework? I step you through all the major concepts you need to excel in school, from high-level mindset to individual class strategies.

As co-founder and head of product design at PrepScholar, Allen has guided thousands of students to success in SAT/ACT prep and college admissions. He's committed to providing the highest quality resources to help you succeed. Allen graduated from Harvard University summa cum laude and earned two perfect scores on the SAT (1600 in 2004, and 2400 in 2014) and a perfect score on the ACT. You can also find Allen on his personal website, Shortform , or the Shortform blog .
Student and Parent Forum
Our new student and parent forum, at ExpertHub.PrepScholar.com , allow you to interact with your peers and the PrepScholar staff. See how other students and parents are navigating high school, college, and the college admissions process. Ask questions; get answers.

Ask a Question Below
Have any questions about this article or other topics? Ask below and we'll reply!
Improve With Our Famous Guides
- For All Students
The 5 Strategies You Must Be Using to Improve 160+ SAT Points
How to Get a Perfect 1600, by a Perfect Scorer
Series: How to Get 800 on Each SAT Section:
Score 800 on SAT Math
Score 800 on SAT Reading
Score 800 on SAT Writing
Series: How to Get to 600 on Each SAT Section:
Score 600 on SAT Math
Score 600 on SAT Reading
Score 600 on SAT Writing
Free Complete Official SAT Practice Tests
What SAT Target Score Should You Be Aiming For?
15 Strategies to Improve Your SAT Essay
The 5 Strategies You Must Be Using to Improve 4+ ACT Points
How to Get a Perfect 36 ACT, by a Perfect Scorer
Series: How to Get 36 on Each ACT Section:
36 on ACT English
36 on ACT Math
36 on ACT Reading
36 on ACT Science
Series: How to Get to 24 on Each ACT Section:
24 on ACT English
24 on ACT Math
24 on ACT Reading
24 on ACT Science
What ACT target score should you be aiming for?
ACT Vocabulary You Must Know
ACT Writing: 15 Tips to Raise Your Essay Score
How to Get Into Harvard and the Ivy League
How to Get a Perfect 4.0 GPA
How to Write an Amazing College Essay
What Exactly Are Colleges Looking For?
Is the ACT easier than the SAT? A Comprehensive Guide
Should you retake your SAT or ACT?
When should you take the SAT or ACT?
Stay Informed
Get the latest articles and test prep tips!
Looking for Graduate School Test Prep?
Check out our top-rated graduate blogs here:
GRE Online Prep Blog
GMAT Online Prep Blog
TOEFL Online Prep Blog
Holly R. "I am absolutely overjoyed and cannot thank you enough for helping me!”
What are your chances of acceptance?
Calculate for all schools, your chance of acceptance.
Your chancing factors
Extracurriculars.
How to Write the Harvard University Essays 2023-2024
Harvard University, perhaps the most prestigious and well-known institution in the world, is the nation’s oldest higher learning establishment with a founding date of 1636. Boasting an impressive alumni network from Sheryl Sandberg to Al Gore, it’s no surprise that Harvard recruits some of the top talents in the world.
It’s no wonder that students are often intimidated by Harvard’s extremely open-ended supplemental essays. However, CollegeVine is here to help and offer our guide on how to tackle Harvard’s supplemental essays.
Read this Harvard essay example to inspire your own writing.
How to Write the Harvard University Supplemental Essays
Prompt 1: Harvard has long recognized the importance of enrolling a diverse student body. How will the life experiences that shape who you are today enable you to contribute to Harvard? (200 words)
Prompt 2: Briefly describe an intellectual experience that was important to you. (200 words)
Prompt 3: Briefly describe any of your extracurricular activities, employment experience, travel, or family responsibilities that have shaped who you are. (200 words)
Prompt 4: How do you hope to use your Harvard education in the future? (200 words)
Prompt 5: Top 3 things your roommates might like to know about you. (200 words)
Harvard has long recognized the importance of enrolling a diverse student body. How will the life experiences that shape who you are today enable you to contribute to Harvard? (200 words)
Brainstorming Your Topic
This prompt is a great example of the classic diversity supplemental essay . That means that, as you prepare to write your response, the first thing you need to do is focus in on some aspect of your identity, upbringing, or personality that makes you different from other people.
As you start brainstorming, do remember that the way colleges factor race into their admissions processes will be different this year, after the Supreme Court struck down affirmative action in June. Colleges can still consider race on an individual level, however, so if you would like to write your response about how your racial identity has impacted you, you are welcome to do so.
If race doesn’t seem like the right topic for you, however, keep in mind that there are many other things that can make us different, not just race, gender, sexuality, ethnicity, and the other aspects of our identities that people normally think of when they hear the word “diversity.” That’s not to say that you can’t write about those things, of course. But don’t worry if you don’t feel like those things have played a significant role in shaping your worldview. Here are some examples of other topics that could support a strong essay:
- Moving to several different cities because of your parents’ jobs
- An usual hobby, like playing the accordion or making your own jewelry
- Knowing a lot about a niche topic, like Scottish castles
The only questions you really need to ask yourself when picking a topic are “Does this thing set me apart from other people?” and “Will knowing this thing about me give someone a better sense of who I am overall?” As long as you can answer “yes” to both of those questions, you’ve found your topic!
Tips for Writing Your Essay
Once you’ve selected a topic, the question becomes how you’re going to write about that topic in a way that helps Harvard admissions officers better understand how you’re going to contribute to their campus community. To do that, you want to connect your topic to some broader feature of your personality, or to a meaningful lesson you learned, that speaks to your potential as a Harvard student.
For example, perhaps your interest in Scottish castles has given you an appreciation for the strength of the human spirit, as the Scots were able to persevere and build these structures even in incredibly remote, cold parts of the country. Alternatively, maybe being half Puerto Rican, but not speaking Spanish, has taught you about the power of family, as you have strong relationships even with relatives you can’t communicate with verbally.
Remember that, like with any college essay, you want to rely on specific anecdotes and experiences to illustrate the points you’re making. To understand why, compare the following two excerpts from hypothetical essays.
Example 1: “Even though I can’t speak Spanish, and some of my relatives can’t speak English, whenever I visit my family in Puerto Rico I know it’s a place where I belong. The island is beautiful, and I especially love going to the annual party at my uncle’s house.”
Example 2: “The smell of the ‘lechón,’ or suckling pig greets me as soon as I enter my uncle’s home, even before everyone rushes in from the porch to welcome me in rapid-fire Spanish. At best, I understand one in every ten words, but my aunt’s hot pink glasses, the Caribbean Sea visible through the living room window, and of course, the smell of roasting pork, tell me, wordlessly yet undeniably, that I’m home.”
Think about how much better we understand this student after Example 2. If a few words were swapped out, Example 1 could’ve been written by anyone, whereas Example 2 paints us a clear picture of how this student’s Puerto Rican heritage has tangibly impacted their life.
Mistakes to Avoid
The biggest challenge with this particular “Diversity” essay is the word count. Because you only have 200 words to work with, you don’t have space to include more than one broader takeaway you’ve learned from this aspect of your identity.
Of course, people are complicated, and you’ve likely learned many things from being Puerto Rican, or from being interested in Scottish castles. But for the sake of cohesion, focus on just one lesson. Otherwise your essay may end up feeling like a bullet-point list of Hallmark card messages, rather than a thoughtful, personal, reflective piece of writing.
The other thing you want to avoid is writing an essay that’s just about your topic. Particularly since you’re going to be writing about an aspect of your identity that’s important to you, you’ll likely have a lot to say just about that. If you aren’t careful, you may burn through all 200 words without getting to the broader significance of what this piece of your personality says about who you are as a whole.
That component, however, is really the key to a strong response. Harvard receives over 40,000 applications a year, which means that, whether you write about being Puerto Rican or Scottish castles, it’s likely someone else is writing about something similar.
That doesn’t mean you need to agonize over picking something absolutely nobody else is writing about, as that’s practically impossible. All it means is that you need to be clear about how this aspect of your identity has shaped you as a whole, as that is how your essay will stand out from others with similar topics.
Briefly describe an intellectual experience that was important to you. (200 words)
Harvard admissions officers are being considerate here, as they’re telling you explicitly what they would like you to write about. Of course, there are still nuances to the prompt, but in terms of brainstorming, just ask yourself: What is an intellectual experience that’s been important to me?
Keep in mind that “intellectual” doesn’t necessarily mean “academic.” You absolutely can write a great response about a paper, project, or some other experience you had through school. But you could also write about attending a performance by the Berlin Philharmonic, or about a book you read for fun that made a big impact on you. So long as the experience was intellectually stimulating, you can write a strong essay about it.
Once you’ve picked an experience, the key is to describe it in a way that shows Harvard admissions officers how this experience has prepared you to contribute to their classrooms, and campus community as a whole. In other words, don’t just tell them what you did, but also what you learned and why that matters for understanding what kind of college student you’ll be.
For example, say you choose to write about a debate project you did in your American history class, where you had to prepare for both sides and only learned which one you would actually be defending on the day of the debate. You could describe how, although you came into the project with pre-existing opinions about the topic, the preparation process taught you that, if you’re thoughtful and open-minded, you can usually find merit and logic even in the polar opposite position from your own.
Alternatively, you could write about a book you read that had been translated from Danish, and how reading it got you interested in learning more about how to translate a text as faithfully as possible. After watching many interviews with translators and reading a book about translation, you have learned that sometimes, the most literal translation doesn’t capture the spirit from the original language, which to you is proof that, in any piece of writing, the human element is at least as important as the words on the page.
Notice that both of these examples include broader reflections that zoom out from the particular experiences, to show what you took away from them: increased open-mindedness to different perspectives, for the first, and a more nuanced understanding of what makes art, art, in the case of the second.
A strong response must include this kind of big-picture takeaway, as it shows readers two things. First, that you can reflect thoughtfully on your experiences and learn from them. And second, it shows them a skill or perspective you’d be bringing with you to Harvard, which gives them a better sense of how you’d fit into their campus community.
The only real thing you need to watch out for is accidentally selecting an experience that, for whatever reason, doesn’t allow you to incorporate the kind of bigger-picture takeaway described above. Maybe the experience just happened, so you’re still in the process of learning from it. Or maybe the lessons you learned are too nuanced to describe in 200 words.
Whatever this reason, if you find yourself unable to articulate the broader significance of this experience, head back to the drawing board, to select one that works better for this prompt. What you don’t want to do is try to force in a takeaway that doesn’t really fit, as that will make your essay feel generic or disjointed, since the “moral of the story” won’t clearly connect to the story itself.
Briefly describe any of your extracurricular activities, employment experience, travel, or family responsibilities that have shaped who you are. (200 words)
This is a textbook example of the “Extracurricular” essay . As such, what you need to do is well-defined, although it’s easier said than done: select an extracurricular activity that has, as Harvard says, “shaped who you are,” and make sure you’re able to articulate how it’s been formative for you.
As you brainstorm which extracurricular you want to write about, note that the language of the prompt is pretty open-ended. You write about “any” activity, not just one you have a lot of accolades in, and you don’t even have to write about an activity—you can also write about a travel experience, or family responsibility.
If the thing that immediately jumps to mind is a club, sport, volunteer experience, or other “traditional” extracurricular, that’s great! Run with that. But if you’re thinking and nothing in that vein seems quite right, or, alternatively, you’re feeling bold and want to take a creative approach, don’t be afraid to get outside the box. Here are some examples of other topics you could write a strong essay about:
- A more hobby-like extracurricular, like crocheting potholders and selling them on Etsy
- Driving the Pacific Coast Highway on your own
- Caring for your family’s two large, colorful macaws
These more creative topics can do a lot to showcase a different side of you, as college applications have, by their nature, a pretty restricted scope, and telling admissions officers about something that would never appear on your resume or transcript can teach them a lot about who you are. That being said, the most important thing is that the topic you pick has genuinely been formative for you. Whether it’s a conventional topic or not, as long as that personal connection is there, you’ll be able to write a strong essay about it.
The key to writing a strong response is focusing less on the activity itself, and more on what you’ve learned from your involvement in it. If you’re writing about a more conventional topic, remember that admissions officers already have your activities list. You don’t need to say “For the last five years, I’ve been involved in x,” because they already know that, and when you only have 200 words, wasting even 10 of them means you’ve wasted 5% of your space.
If you’re writing about something that doesn’t already show up elsewhere in your application, you want to provide enough details for your reader to understand what you did, but not more than that. For example, if you’re writing about your road trip, you don’t need to list every city you stopped in. Instead, just mention one or two that were particularly memorable.
Rather than focusing on the facts and figures of what you did, focus on what you learned from your experience. Admissions officers want to know why your involvement in this thing matters to who you’ll be in college. So, think about one or two bigger picture things you learned from it, and center your response around those things.
For example, maybe your Etsy shop taught you how easy it is to bring some positivity into someone else’s life, as crocheting is something you would do anyways, and the shop just allows you to share your creations with other people. Showcasing this uplifting, altruistic side of yourself will help admissions officers better envision what kind of Harvard student you’d be.
As always, you want to use specific examples to support your points, at least as much as you can in 200 words. Because you’re dealing with a low word count, you probably won’t have space to flex your creative writing muscles with vivid, immersive descriptions.
You can still incorporate anecdotes in a more economical way, however. For example, you could say “Every morning, our scarlet macaw ruffles her feathers and greets me with a prehistoric chirp.” You’re not going into detail about what her feathers look like, or where this scene is happening, but it’s still much more engaging than something like “My bird always says hello to me in her own way.”
The most common pitfall with an “Extracurricular” essay is describing your topic the way you would on your resume. Don’t worry about showing off some “marketable skill” you think admissions officers want to see, and instead highlight whatever it is you actually took away from this experience, whether it’s a skill, a realization, or a personality trait. The best college essays are genuine, as admissions officers feel that honesty, and know they’re truly getting to know the applicant as they are, rather than some polished-up version.
Additionally, keep in mind that, like with anything in your application, you want admissions officers to learn something new about you when reading this essay. So, if you’ve already written your common app essay about volunteering at your local animal shelter, you shouldn’t also write this essay about that experience. Your space in your application is already extremely limited, so don’t voluntarily limit yourself even further by repeating yourself when you’re given an opportunity to say something new.
How do you hope to use your Harvard education in the future? (200 words)
Although the packaging is a little different, this prompt has similarities to the classic “Why This College?” prompt . That means there are two main things you want to do while brainstorming.
First, identify one or two goals you have for the future—with just 200 words, you won’t have space to elaborate on any more than that. Ideally, these should be relatively concrete. You don’t have to have your whole life mapped out, but you do need to be a lot more specific than “Make a difference in the world.” A more zoomed-in version of that goal would be something like “Contribute to conservation efforts to help save endangered species,” which would work.
Second, hop onto Harvard’s website and do some research on opportunities the school offers that would help you reach your goals. Again, make sure these are specific enough. Rather than a particular major, which is likely offered at plenty of other schools around the country, identify specific courses within that major you would like to take, or a professor in the department you would like to do research with. For example, the student interested in conservation might mention the course “Conservation Biology” at Harvard.
You could also write about a club, or a study abroad program, or really anything that’s unique to Harvard, so long as you’re able to draw a clear connection between the opportunity and your goal. Just make sure that, like with your goals, you don’t get overeager. Since your space is quite limited, you should choose two, or maximum three, opportunities to focus on. Any more than that and your essay will start to feel rushed and bullet point-y.
If you do your brainstorming well, the actual writing process should be pretty straightforward: explain your goals, and how the Harvard-specific opportunities you’ve selected will help you reach them.
One thing you do want to keep in mind is that your goals should feel personal to you, and the best way to accomplish that is by providing some background context on why you have them. This doesn’t have to be extensive, as, again, your space is limited. But compare the following two examples, written about the hypothetical goal of helping conservation efforts from above, to get an idea of what we’re talking about:
Example 1: “As long as I can remember, I’ve loved all kinds of animals, and have been heartbroken by the fact that human destruction of natural resources could lead to certain species’ extinction.”
Example 2: “As a kid, I would sit in front of the aquarium’s walrus exhibit, admiring the animal’s girth and tusks, and dream about seeing one in the wild. Until my parents regretfully explained to me that, because of climate change, that was unlikely to ever happen.”
The second example is obviously longer, but not egregiously so: 45 words versus 31. And the image we get of this student sitting and fawning over a walrus is worth that extra space, as we feel a stronger personal connection to them, which in turn makes us more vicariously invested in their own goal of environmental advocacy.
As we’ve already described in the brainstorming section, the key to this essay is specificity. Admissions officers want you to paint them a picture of how Harvard fits into your broader life goals. As we noted earlier, that doesn’t mean you have to have everything figured out, but if you’re too vague about your goals, or how you see Harvard helping you reach them, admissions officers won’t see you as someone who’s prepared to contribute to their campus community.
Along similar lines, avoid flattery. Gushy lines like “At Harvard, every day I’ll feel inspired by walking the same halls that countless Nobel laureates, politicians, and CEOs once traversed” won’t get you anywhere, because Harvard admissions officers already know their school is one of the most prestigious and famous universities in the world. What they don’t know is what you are going to bring to Harvard that nobody else has. So, that’s what you want to focus on, not vague, surface-level attributes of Harvard related to its standing in the world of higher education.
Top 3 things your roommates might like to know about you. (200 words)
Like Prompt 2, this prompt tells you exactly what you need to brainstorm: three things a roommate would like to know about you. However, also like Prompt 2, while this prompt is direct, it’s also incredibly open-ended. What really are the top three things you’d like a complete stranger to know about you before you live together for nine months?
Questions this broad can be hard to answer, as you might not know where to start. Sometimes, you can help yourself out by asking yourself adjacent, but slightly more specific questions, like the following:
- Do you have any interests that influence your regular routine? For example, do you always watch the Seahawks on Sunday, or are you going to be playing Taylor Swift’s discography on repeat while you study?
- Look around your room—what items are most important to you? Do you keep your movie ticket stubs? Are you planning on taking your photos of your family cat with you to college?
- Are there any activities you love and already know you’d want to do with your roommate, like weekly face masks or making Christmas cookies?
Hopefully, these narrower questions, and the example responses we’ve included, help get your gears turning. Keep in mind that this prompt is a great opportunity to showcase sides of your personality that don’t come across in your grades, activities list, or even your personal statement. Don’t worry about seeming impressive—admissions officers don’t expect you to read Shakespeare every night for two hours. What they want is an honest, informative picture of what you’re like “behind the scenes,” because college is much more than just academics.
Once you’ve selected three things to write about, the key to the actual essay is presenting them in a logical, cohesive, efficient way. That’s easier said than done, particularly if the three things you’ve picked are quite different from each other.
To ensure your essay feels like one, complete unit, rather than three smaller ones stuck together, strong transitions will be crucial. Note that “strong” doesn’t mean “lengthy.” Just a few words can go a long way towards helping your essay flow naturally. To see what we mean here, take the following two examples:
Example 1: “Just so you know, every Sunday I will be watching the Seahawks, draped in my dad’s Steve Largent jersey. They can be a frustrating team, but I’ll do my best to keep it down in case you’re studying. I also like to do facemasks, though. You’re always welcome to any of the ones I have in my (pretty extensive) collection.”
Example 2: “Just so you know, every Sunday I will be watching the Seahawks, draped in my dad’s Steve Largent jersey. But if football’s not your thing, don’t worry—once the game’s over, I’ll need to unwind anyways, because win or lose the Hawks always find a way to make things stressful. So always feel free to join me in picking out a face mask from my (pretty extensive) collection, and we can gear up for the week together.”
The content in both examples is the same, but in the first one, the transition from football to facemasks is very abrupt. On the other hand, in the second example the simple line “But if football’s not your thing, don’t worry” keeps things flowing smoothly.
There’s no one right way to write a good transition, but as you’re polishing your essay a good way to see if you’re on the right track is by asking someone who hasn’t seen your essay before to read it over and tell you if there are any points that made them pause. If the answer is yes, your transitions probably still need more work.
Finally, you probably noticed that the above examples are both written in a “Dear roomie” style, as if you’re actually speaking directly to your roommate. You don’t have to take this exact approach, but your tone should ideally be light and fun. Living alone for the first time, with other people your age, is one of the best parts of college! Plus, college applications are, by their nature, pretty dry affairs for the most part. Lightening things up in this essay will give your reader a breath of fresh air, which will help them feel more engaged in your application as a whole.
Harvard is doing you a favor here by keeping the scope of the essay narrow—they ask for three things, not more. As we’ve noted many times with the other supplements, 200 words will be gone in a flash, so don’t try to cram in extra things. It’s not necessary to do that, because admissions officers have only asked for three, and trying to stuff more in will turn your essay into a list of bullet points, rather than an informative piece of writing about your personality.
Finally, as we’ve hinted at a few times above, the other thing you want to avoid is using this essay as another opportunity to impress admissions officers with your intellect and accomplishments. Remember, they have your grades, and your activities list, and all your other essays. Plus, they can ask you whatever questions they want—if they wanted to know about the most difficult book you’ve ever read, they would. So, loosen up, let your hair down, and show them you know how to have fun too!
Where to Get Your Harvard Essays Edited
Do you want feedback on your Harvard essays? After rereading your essays countless times, it can be difficult to evaluate your writing objectively. That’s why we created our free Peer Essay Review tool , where you can get a free review of your essay from another student. You can also improve your own writing skills by reviewing other students’ essays.
If you want a college admissions expert to review your essay, advisors on CollegeVine have helped students refine their writing and submit successful applications to top schools. Find the right advisor for you to improve your chances of getting into your dream school!
Related CollegeVine Blog Posts

Harvard Supplemental Essays 2023-24 – Prompts and Advice
August 17, 2023

A 3.4% acceptance for the Class of 2027 gives you a pretty informative introduction to the ultra-competitive admissions process at Harvard University. To dive deeper, Harvard rejects the majority of valedictorians who apply each year as well as a sizable chunk of those who bring 1600 SAT/36 ACT scores to the table. Further, more than one-third of current Crimson undergrads are legacy students (their parents and/or other close relatives are alumni) and recruited athletes make up around 20% of each incoming freshman class. Therefore, it is reasonable to assume that, if you fall outside of those categories, your chances of getting into Harvard are less than 3%. This brings us to the topic of this blog – the Harvard supplemental essays.
Want to learn more about How to Get Into Harvard University? Visit our blog entitled: How to Get Into Harvard University: Admissions Data and Strategies for all of the most recent admissions data as well as tips for gaining acceptance.
Yet, this sobering and realistic assessment of the facts on the ground should not discourage those with an extremely strong record of accomplishment—both inside and outside of the classroom—from applying. Rather, we present this information to highlight one glaring truth: the essays are one of the best opportunities you will have to make your Harvard application shine brighter than your competition.
For the 2023-24 admissions cycle, there are five Harvard supplemental essays. Unlike previous years, all essays are required.
2023-24 Harvard Supplemental Essays
Harvard has long recognized the importance of enrolling a diverse student body. how will the life experiences that shape who you are today enable you to contribute to harvard (200 words).
This prompt asks you to not only share a particular life experience but also describe why that experience will enable you to contribute to Harvard in general. Essentially, it’s asking you to take your essay’s reflection one step further—you’ll need to share why the experience you’ve chosen has impacted you as well as why/how you believe it will allow you to positively impact the Harvard community.
First, choose a key aspect of your experiences or background that reveals something deep and meaningful about you. (Although you could choose more than one, we’d advise against it, given that you only have 200 words in which to respond.) As you brainstorm, consider the following avenues:
- Your role in your family.
- Your role in your social group.
- A challenge you’ve faced.
- A formative experience or realization.
- Core values and beliefs.
- Important aspects of your upbringing.
- Cultural, religious, community influence.
Harvard supplemental essays Continued)
Second, you’ll need to describe both personal and future impact. Make sure that your answer reveals something about how you will live out Harvard’s values or contribute to an academic/social community. For the latter angle, you could name a specific course , research opportunity , or extracurricular club , to name a few—perhaps living in a beach town has heavily contributed to your passion for the world’s oceans, and you seek to bring that perspective to the biology department’s research opportunities. Alternatively, you could discuss something more intangible—perhaps Harvard’s mission to encourage intellectual transformation resonates with you, and you hope to bring your experience of moving frequently for your dad’s job—and the open-mindedness and resilience you cultivated as a result—to classroom discussions about sensitive topics.
Briefly describe an intellectual experience that was important to you. (200 words)
In short, admissions officers want to see evidence of your drive, passion, and intellectual ambition. You may have taken over a dozen AP courses, but so did most of your competition. Did you pursue independent research or a more formalized research experience at a university? Did you spend your summer pursuing your academic interests to the best extent that was financially feasible (e.g., expensive summer programs are not accessible to everyone)? What were the fruits of your labor? Does your name appear on published research? Did you present at a conference? Did you independently pursue CS certifications, mastering multiple programming languages? Or did you learn a foreign language outside of school hours? Translate a work of literature into another language? In addition to describing the experience, you’ll also need to share why it was important to you.
Ideally, whatever example you cite will be closely aligned with your future academic area of interest.
Harvard supplemental essays (Continued)
Briefly describe any of your extracurricular activities, employment experience, travel, or family responsibilities that have shaped who you are..
Harvard is not necessarily asking you to write about the activity where you earned the most prestigious awards. Nor does it have to be the one where you held the highest position of leadership. The university is going to see all of your activities in that section of the Common App. As such, you want to ask yourself—which of your entries is crying out for more explanation and detail? Which one is closest to your heart and most representative of your unique passions?
For example, you may be a volunteer EMT and have compelling experiences to share that have significantly impacted your perspective, or contributed to your desire to be a physician, or developed your empathy (or perhaps all of the above). Alternatively, you may have worked in a local restaurant and learned more about the lives of your undocumented coworkers, which shaped and contributed to your advocacy work in that area.
An activity or experience that “shaped who you are” is a big ask, but as long as you can demonstrate how it impacted and influenced you in a significant way, the activity you choose can be something you’ve been doing for ten years or two months.
How do you hope to use your Harvard education in the future? (200 words)
This prompt differs from your quintessential “Why Us?” essay in a small but important way—Harvard isn’t asking why you want to attend but how you hope to utilize the education you receive. This might seem like a rather nebulous proposition—you are seventeen years old, after all—but think about what your goals, passions, and aspirations are right now . You’ll then need to do some projecting, even if generalized. For example, some students can feel in their bones that they’re bound for the law school track while others only have a vague sense of what the future might hold for them but know that—right now—they’re most drawn to psychology. That’s where your research will come into play—spend some time investigating:
- Specific courses offered in your current discipline(s) of interest at Harvard.
- Harvard professors whose work/research/writings you find fascinating.
- Academically-focused student organizations at Harvard.
- Undergraduate research opportunities in the summer or during the school year as well as independent research you would like to conduct under faculty supervision.
Now, merge the two—based on your current goals and what Harvard has to offer, how can you see yourself putting your education to good future use? In short, how will Harvard’s resources prepare you for the real world?
Top 3 things your roommates might like to know about you. (200 words)
Applicants can utilize this response to give greater insight into the little details about themselves that may not appear elsewhere in the application. Keep the old adage “you don’t truly know a person until you live with them” in mind. Think about what your future roommate will learn about your daily habits, hobbies, quirks, passions, and preferences. What music do you like to listen to? What activities do you like to do (that, ideally, have not yet been communicated elsewhere)? Talk about your typical routine.
Once you make a list of potential inclusions, think about what each item communicates about you as a person. For example, if you can seldom be found without a novel in hand or spend an hour every morning practicing yoga, why is that important for us to know? That said, at least one detail could be comical or light-hearted (perhaps you can’t survive without a large supply of lime seltzer or always eat salt & vinegar chips when you’re up late studying). In the grand scheme of things, this is a genuine chance to reveal more about your character, unique personality, and also—sometimes— how to get along with others.
How important are the Harvard supplemental essays?
The Harvard supplemental essays are in the “considered” bucket. They are placed in the same category as factors such as test scores, GPA, and recommendations.
Want personalized essay assistance with your Harvard supplemental essays?
If you are interested in working with one of College Transitions’ experienced and knowledgeable essay coaches as you craft your Harvard supplemental essays, we encourage you to get a quote today.
- College Essay

Dave Bergman
Dave has over a decade of professional experience that includes work as a teacher, high school administrator, college professor, and independent educational consultant. He is a co-author of the books The Enlightened College Applicant (Rowman & Littlefield, 2016) and Colleges Worth Your Money (Rowman & Littlefield, 2020).
- 2-Year Colleges
- Application Strategies
- Best Colleges by Major
- Best Colleges by State
- Big Picture
- Career & Personality Assessment
- College Search/Knowledge
- College Success
- Costs & Financial Aid
- Dental School Admissions
- Extracurricular Activities
- Graduate School Admissions
- High School Success
- High Schools
- Law School Admissions
- Medical School Admissions
- Navigating the Admissions Process
- Online Learning
- Private High School Spotlight
- Summer Program Spotlight
- Summer Programs
- Test Prep Provider Spotlight

“Innovative and invaluable…use this book as your college lifeline.”
— Lynn O'Shaughnessy
Nationally Recognized College Expert
College Planning in Your Inbox
Join our information-packed monthly newsletter.
Sign Up Now
- Affiliate Program

- UNITED STATES
- 台灣 (TAIWAN)
- TÜRKIYE (TURKEY)
- Academic Editing Services
- - Research Paper
- - Journal Manuscript
- - Dissertation
- - College & University Assignments
- Admissions Editing Services
- - Application Essay
- - Personal Statement
- - Recommendation Letter
- - Cover Letter
- - CV/Resume
- Business Editing Services
- - Business Documents
- - Report & Brochure
- - Website & Blog
- Writer Editing Services
- - Script & Screenplay
- Our Editors
- Client Reviews
- Editing & Proofreading Prices
- Wordvice Points
- Partner Discount
- Plagiarism Checker
- APA Citation Generator
- MLA Citation Generator
- Chicago Citation Generator
- Vancouver Citation Generator
- - APA Style
- - MLA Style
- - Chicago Style
- - Vancouver Style
- Writing & Editing Guide
- Academic Resources
- Admissions Resources
How to Write the Harvard Supplemental Essays for 2023-2024
Harvard College needs no introduction—its name is synonymous with prestige in higher education. This alone can account for the extremely low acceptance rate, which was just 5.2% (out of 39,000 applicants) for the Class of 2021. But there is a way that applicants can improve their chances of getting into Harvard, and that is to write a stellar personal essay.
What are the Harvard Supplemental Essays?
When applying to Harvard, you are given the opportunity to include supplemental essays to showcase anything you feel was not adequately conveyed through your Common Application Essay . While Harvard’s admissions website indicates that including this essay is “optional,” almost all advisors will strongly encourage you to submit as much information about yourself as you can. Perhaps the fact that over 85% of the Harvard Class of 2019 wrote a supplemental essay might convince you just how important it can be.
Harvard Supplemental Essay Prompts for the 2023-2024 School Year
Each year, applicants find themselves struggling with exactly what they should put in their essays to impress the admissions committee. The Harvard supplemental essay prompts for 2023-2024 are no different. But because Harvard seeks students who are independent, creative, and self-motivated, this open-ended quality makes perfect sense. This essay is essentially a blank canvas on which you can paint some fascinating aspects about yourself in vivid color.
Here are the Prompts for the Harvard Supplemental Essays 2023-2024
Please briefly elaborate on one of your extracurricular activities or work experiences. (50-150 words)
Activity essays like this one allow you to say everything you couldn’t fit on your Common App activity list. Make sure to pick an activity that has meaning and one which you haven’t already written about. It’s usually a good strategy to pick something that you’ve been doing for a long time, where you can showcase key qualities like commitment, perseverance, and leadership. If you prefer to write about a job or hobby you just got started on, however, you can still write a compelling essay about why you started, what made you interested in it, and what you have learned in your journal thus far. You should contribute additional context to what the Harvard admissions officers know about you, and you only have a small space to do it in, so use it wisely.
Your intellectual life may extend beyond the academic requirements of your particular school. Please use the space below to list additional intellectual activities that you have not mentioned or detailed elsewhere in your application. These could include, but are not limited to, supervised or self-directed projects not done as school work, training experiences, online courses not run by your school, or summer academic or research programs not described elsewhere. (150 words)
This prompt is pretty easy to understand. Harvard is asking you to list any of your intellectual activities that you have not already included in your application materials. Did you try to build a computer game or app in the last few months? Maybe you interned somewhere that made you interested in a certain industry or line of work. Or perhaps you took an online Chinese course to get ready for an extended trip to China over the summer. Harvard wants to understand what you are getting up to, so let them know and don’t spare any important and exciting details!
You may wish to include an additional essay if you feel that the college application forms do not provide sufficient opportunity to convey important information about yourself or your accomplishments. You may write on a topic of your choice, or you may choose from one of the following topics (No word limit; max file size is 2000 KB) .
- An unusual circumstance in your life
- Travel, living, or working experiences in your own or other communities
- What you would want your future college roommate to know about you?
- An intellectual experience (course, project, book, discussion, paper, poetry, or research topic in engineering, mathematics, science, or other modes of inquiry) that has meant the most to you
- How you hope to use your college education
- A list of books you have read during the past twelve months
- The Harvard College Honor code declares that we “hold honesty as the foundation of our community.” As you consider entering this community that is committed to honesty, please reflect on a time when you or someone you observed had to make a choice about whether to act with integrity and honesty.
- The mission of Harvard College is to educate our students to be citizens and citizen-leaders for society. What would you do to contribute to the lives of your classmates in advancing this mission?
- Each year a substantial number of students admitted to Harvard defer their admission for one year or take time off during college. If you decided in the future to choose either option, what would you like to do?
- Harvard has long recognized the importance of student body diversity of all kinds. We welcome you to write about distinctive aspects of your background, personal development, or the intellectual interests you might bring to your Harvard classmates.
As you can see, applicants have a LOT of choices in terms of the direction they take when writing their Harvard supplemental essay. Read on for tips on how to approach ANY of these prompts in a meaningful and productive way to get the most out of this important essay and impress the admissions officers.
How Long Should the Harvard Supplemental Essays Be?
Although Harvard gives no explicit word or character limit for the supplemental essay, most accepted students will write between 500 and 700 words (or about a page when written in Times New Roman 12-point font). This doesn’t provide you a lot of room to ruminate at length on your experiences or to write about multiple topics. Therefore, you need to focus on one aspect of yourself (or what the prompt is asking you to write about) and drive it home. But don’t worry about getting it right on your first draft—write as freely as you can and work on re-drafting and revising your essay once all of the important elements have come to the surface. The more time you spend on the essay, the more polished and powerful it will be. Visit Harvard’s admissions website for comprehensive guidelines on writing this essay.
Paint a Picture of Yourself as a Unique Student and Graduate Candidate
When looking over the prompts, consider which one will allow you to write about an aspect of yourself that you didn’t portray in other essays you have submitted. Do not choose the same event, experience, passion, ability, interest, or talent that you used for the Common Application. For instance, if in the Common App Essay you wrote about your love of reading and described some of the books you have read, do NOT choose the Harvard essay about “A List Of Books You Have Read During The Past Twelve Months.” Similarly, if you already wrote about your experience backpacking around Asia last year, choose a different Harvard prompt than “Traveling Or Living Experiences In Other Countries.” No matter how profound or life-changing your experience was, writing about the exact same topic or experience is redundant and will not add to the depth of character you need to convey.
Zooming out, not only should you choose a separate topic for your supplemental essay, you should consider choosing an entirely different perspective as well. If your Common App Essay is about a past experience, choose the Harvard essay that asks about your future plans. If the first essay is about your impressive abilities, focus the second on how you overcame a challenge or deficit. If in the Common App Essay you have discussed your love of organic chemistry, write in the Harvard essay about your weekly volunteering at the local homeless shelter. In other words, deepen the picture you present of yourself. Show how you live (and flourish) in many dimensions!
When writing a Harvard essay, applicants must also stand out from the crowd . Do not think of it as a chance to merely remind the admissions committee about what you have accomplished, to list more details about your stellar academic record, or to brag about some outstanding marker on your resume. You have to dig deeper and WOW them in order for you to stand out in their minds.
Present Yourself Sincerely to Harvard Admissions Officials
Remember to always SHOW your sincerity, your attitude, and your excellence in your admissions essays—do not merely TELL about it. You can achieve this by focusing on actions, using lots of verbs, and by including a great number of details and examples as you describe your experiences. If playing the piano profoundly affected your sense of what “work” means to you, do not merely write, “Practicing all the time made me realize how working hard pays off.” Show this correlation between effort and understanding of work via anecdotes and details.
Here is what showing looks like (versus telling ):
“Three hours of straight practice a day in our windowless basement, six days a week perched upon a hard wooden bench, aching fingers on the keys, nothing between myself and Chopin but willpower and concentration, the haunting sounds of the hammer on the strings my instant reward for uncountable days and years of effort—all of this flashed through my mind on Jun 19, 2019, as I took the stage for my first Tanglewood recital.”
A detailed anecdote full of action makes it much easier for a reader to accept your assertion that playing piano profoundly affected your life. Readers can trust the feelings and positions you explicitly state only once you have proved them with examples and details.
Show How You Fit Into Harvard’s Unique Culture and Mission
When approaching this essay, it is important to understand that Harvard places special importance on the development of passions and community involvement over pure academic excellence. They also are deeply committed to diversity of experiences and views, and this means that they value curiosity in their students: intellectual, philosophical, social, etc. These values are included in their mission statement, which is “to educate the citizens and citizen-leaders for our society” via “exposure to new ideas, new ways of understanding, and new ways of knowing,” which is designed to set students on a “journey of intellectual transformation.”
With these institutional objectives in mind, you should focus on how you can best illustrate your curiosity, and your potential for growth and greatness, in your essay. Do this by conveying your passion and showing how your passion drives your potential to contribute to worthwhile advances in society. One way to accomplish this in the essay is to choose a prompt that emphasizes your ambitions or even your plans to use your education. Consider responding to a prompt that explicitly mentions Harvard, or to one that asks “how you hope to use your college education” and become a “citizen-leader.” These provide a great opportunity to showcase those personal attributes that fit the mold of the desired Harvard student.
Explain Why You Deserve to Attend Harvard College
Another aspect to keep in mind is that Harvard is interested in enrolling people who are genuinely good , in addition to being intelligent, talented, or ambitious. The final line of their mission statement reads: “From this we hope that students will begin to fashion their lives by gaining a sense of what they want to do with their gifts and talents, assessing their values and interests, and learning how they can best serve the world.” The last phrase indicates a person who demonstrates true concern about the world in which they live.
Thus showing strong regard for other people or animals or expressing a sense of duty and honor is a definite plus for the Harvard admissions committee. This is another perspective from which you might portray yourself in your essay—the hardworking, dutiful, kind, compassionate citizen-leader that they want and deserve to have, and the one that wants to be part of a like-minded community. But only focus on this aspect of yourself if you can do so authentically and honestly. The worst thing possible would be to lie or come off as disingenuous to the admissions committee. So just be yourself, your whole self, and nothing but yourself.
And before submitting your essay, be sure to get English editing and proofreading services from Wordvice–the best admissions editing service in the business. We offer supplemental essay editing services , as well as a host of revision services for admissions documents, including cover letter editing , personal statement editing , CV editing , and recommendation letter editing .
And try the new free AI Text Editor at Wordvice AI, which features a suite of revision tools including an AI Proofreading Tool and AI Paraphrasing Tool , among others. Best of luck writing this important admissions essay!
Waitlisted? No Brags. No Updates. Learn About Ivy Coach's Letter of Continued Interest
The Ivy Coach Daily
- College Admissions
- College Essays
- Early Decision / Early Action
- Extracurricular Activities
- Standardized Testing
- The Rankings
August 10, 2023
2023-2024 Harvard Supplemental Essay Prompts

Harvard University has released its supplemental essays for the 2023-2024 college admissions cycle. The Ivy League institution, which defended the practice of Affirmative Action for all American universities and was defeated in a late June 2023 ruling of the United States Supreme Court, is arguably being watched more closely than any other university with respect to its response to the outlawing of the consideration of race in admissions. So how did Harvard change its supplemental essays?
Over the last few admissions cycles, in addition to The Common Application essay(s), Harvard asked applicants one long essay prompt, a short prompt, and a list. This year, the long prompt and list are gone. In their place are five — that’s right — five 200-word essays. The essay questions are new as well. It’s as though Harvard did a refresh. So let’s dive into the language of the Harvard essay prompts for applicants to the Class of 2028 !
2023-2024 Harvard Essay Topics and Questions
1. Harvard has long recognized the importance of enrolling a diverse student body. How will the life experiences that shape who you are today enable you to contribute to Harvard?
This prompt is Harvard’s most overt response to the Supreme Court’s ruling. While the Supreme Court struck down the legality of Affirmative Action, Chief Justice John Roberts, in his majority opinion ruling against Harvard, wrote, ““At the same time, as all parties agree, nothing in this opinion should be construed as prohibiting universities from considering an applicant’s discussion of how race affected his or her life, be it through discrimination, inspiration, or otherwise.”
This essay prompt is the manifestation of the loophole Chief Justice Roberts penned in the majority opinion. In response to the Supreme Court’s decision , Harvard President-elect Claudine Gay said, “The Supreme Court’s decision on college and university admissions will change how we pursue the educational benefits of diversity. But our commitment to that work remains steadfast.”
Oh yes, it does — as evidenced by this Harvard essay prompt in which applicants are required to thoughtfully reflect on the diversity — in all of its forms — that they hope to bring to Harvard’s community. And, remember, it doesn’t have to be racial diversity. It can be religious diversity. It can be diversity of thought. The question is intentionally open-ended.
2. Briefly describe an intellectual experience that was important to you.
Ideally, applicants will write about an intellectual experience that relates to their hook so they showcase a singular angle rather than well-roundedness on their Harvard application. As such, if a student is an astrophysicist, writing about an intellectual experience beneath the night’s sky has the potential to wow Harvard’s admissions committee.
3. Briefly describe any of your extracurricular activities, employment experience, travel, or family responsibilities that have shaped who you are.
Harvard has long asked for students to write about one of their extracurricular pursuits. Applicants should just make sure not to repeat an activity here that they wrote about in any other essay that Harvard’s admissions officers will see. The activity should also be included within the activities section on The Common Application .
And while so many Harvard applicants do love to brag in response to this essay prompt by, for instance, writing about how much money they raised for a charity, Ivy Coach’s students applying to Harvard would never make such a mistake. After all, a big reason Ivy Coach’s students so often earn admission to Harvard — as every one of them has in 26 of the last 30 Early cycles — is that they present as entirely likable. Admissions officers want to root for our students.
4. How do you hope to use your Harvard education in the future?
In past years, international applicants to Harvard were presented this essay prompt but, this year, it’s being asked of all Harvard applicants. It’s an opportunity to showcase precisely how a student hopes to change the world in one super specific way — through the hook they’ve ideally presented in their activities and storytelling.
5. Top 3 things your roommates might like to know about you.
It seems Harvard has taken a page from Stanford University with this latest essay prompt. Stanford has asked applicants to write a note to their future roommate for many years.
For this essay, it’s vital that all three things applicants share demonstrate intellectual curiosity and/or kindness. The responses can’t just be silly. Too many applicants are inclined to answer this question with answers that offer no insight into how they think or wish to change the world. And that’s a wasted opportunity.
Ivy Coach’s Assistance with Harvard Essays
If you’re interested in Ivy Coach ’s help optimizing your case for admission to Harvard by presenting the most powerful storytelling possible, fill out our consultation form , and we’ll be in touch to outline our college counseling services for seniors .
You are permitted to use www.ivycoach.com (including the content of the Blog) for your personal, non-commercial use only. You must not copy, download, print, or otherwise distribute the content on our site without the prior written consent of Ivy Coach, Inc.
Related Articles

Using A.I. to Write College Admission Essays
October 13, 2023

Word and Character Limits in College Essays
September 27, 2023

What English Teachers Get Wrong About Writing College Essays

Bragging in College Essays: Is It Ever Okay?
September 26, 2023

What Not to Write: 3 College Essay Topics to Avoid
September 24, 2023

2023-2024 Caltech Supplemental Essay Prompts
September 14, 2023
TOWARD THE CONQUEST OF ADMISSION
If you’re interested in Ivy Coach’s college counseling, fill out our complimentary consultation form and we’ll be in touch.
Fill out our short form for a 20-minute consultation to learn about Ivy Coach’s services.
Which program are you applying to?

Accepted Admissions Blog
Everything you need to know to get Accepted

August 10, 2022
Tips for Answering the Harvard Supplemental Essay Prompts [2022 – 2023]
![harvard common app essay prompts Tips for Answering the Harvard Supplemental Essay Prompts [2022 - 2023]](https://blog.accepted.com/wp-content/uploads/2021/11/Harvard_2022-2023.jpg)
It comes as no surprise that Harvard consistently ranks among the top universities in the world. Its highly regarded reputation and academic chops attract the best and brightest. The alluring Harvard brand coupled with its extraordinary education cannot be ignored.
It is important to keep in mind throughout the application process that your focus should be on finding the school that will allow you to explore and grow to your full potential while delivering what is most important to you. Identifying the best fit requires you to be thorough in your research and to consider a myriad of factors as you assess the best path to achieve your goals.
Harvard accepts the Common Application , the Universal College Application, and the Coalition Application (with no preference). All of these applications require an essay response.
Although Harvard does not require supplemental essays, you have the option of including an additional essay if you feel your application does not adequately represent you or your accomplishments. If you decide to include an additional essay, make sure to use it to tell the admissions committee something significant about yourself that is not addressed sufficiently in another portion of your application materials. The admissions committee wants a holistic picture of you as a potential student. They want to be able to identify your voice and personality in your writing. This is an opportunity to convey meaningful aspects of your character , discuss unique interests, demonstrate how you inspire those around you, and address how Harvard will help you to thrive. How will you take advantage of the opportunities offered at Harvard? How will you contribute to the Harvard educational experience?
Get a free consultation: Click here to schedule a call to find out how our admissions experts can help YOU get accepted to Harvard!
If Harvard is your first choice, you have the option to apply through one of its early decision programs (November 1st deadline). For details about these two programs and the exact rules governing both, please see the Harvard website .
As you consider a supplemental essay, remember that your content must be compelling . Think about Harvard’s approach to academic excellence and what that means to you. It recognizes the value of students who are not only academically exceptional but also meaningfully engaged in their world and open to new experiences. Additionally, Harvard’s collegiate atmosphere flourishes based on a dynamic synergy among and between students and faculty. It is looking for “students who will be the best educators of one another and their professors– individuals who will inspire those around them during their College years and beyond.” Harvard prides itself on its close-knit undergraduate community. This emphasis is apparent in the Harvard Houses, where teaching, learning and living go hand-in-hand. How might you contribute to this environment? Perhaps you’d like to sing in a choir? Run a certain club? Is there a research program working alongside professors that is of interest to you? The key is to demonstrate how you will live in community with others in a positive way.
Harvard University supplemental essay prompts (optional)
You may wish to include an additional essay if you feel that the college application forms do not provide sufficient opportunity to convey important information about yourself or your accomplishments. You may write on a topic of your choice, or you may choose from one of the following topics:
- Unusual circumstances in your life Your goal is to discuss unusual circumstances that provide a better context to your life experience. This may be something you did not choose to share in your Common Application (or Universal College Application) Essay response but feel is essential to a deeper understanding of you. Consider what this experience(s) reflects about your personal qualities, personality, and character. How do these circumstances influence your perspective and aspirations? How might your background make Harvard a particularly good fit for you?
- Travel, living, or working experiences in your own or other communities Have you traveled or lived in a place or places that made a significant impact on you? Keep in mind this includes your local community or anywhere else in the world! Here, again, is an opportunity to provide further context for your life-experience. Discuss interesting extracurricular, cultural or intellectual experiences and how they have impacted your perspectives about the world. What did you learn from these experiences and what do they reveal about you? Think about how you engage with both familiar and new environments, cultures, and activities. How will your past experiences enrich the Harvard educational environment?
- What you would want your future college roommate to know about you This question asks you to share something significant about your day-to-day way of being. You can discuss just about anything here! Although you could approach this essay in a somewhat playful manner, do not be tempted to address a topic for its shock value. It’s important that your response is genuine and conveys your personality in an appropriate tone. Remember: Harvard is looking for students who will be excellent educators; think about how that might relate to the things you’d choose to tell a future roommate situation in particular and the Harvard community in general.
- An intellectual experience (course, project, book, discussion, paper, poetry, or research topic in engineering, mathematics, science, or other modes of inquiry) that has meant the most to you This response allows you to discuss something that is important to you and to demonstrate how you think about intellectual problems. This is an exercise in creative and critical thinking. It also provides a platform for you to convey your enthusiasm for learning. What excited you about this intellectual experience? How did the experience challenge your preconceptions? How did it impact your way of thinking? What was your reaction? How did it change your perspective? This response offers insight into your potential to thrive in the demanding academic environment at Harvard.
- How you hope to use your college education With a look toward the future, this is an opportunity to discuss why Harvard is the ideal place for you to achieve your goals. It also allows you to discuss your motivations, passions , values, and perspectives on learning. Discuss what excites you about the overall experience at Harvard. Look toward the future and how the Harvard educational experience will support you. Can you articulate the value of a Harvard education? Your response will convey your aspirations, temperament, leadership, and potential to succeed at Harvard.
- A list of books you have read during the past twelve months As you compile your list, think about the breadth and depth of content. You do not need to include every book you read in the last year. Select the ones that best demonstrate your interests/passions or allowed you to explore something novel. This list should include the books you are most excited about but also the ones that challenged your way of thinking. Each title is a means of interacting with the world of ideas and communicates something significant about you.

- The Harvard College Honor code declares that we “hold honesty as the foundation of our community.” As you consider entering this community that is committed to honesty, please reflect on a time when you or someone you observed had to make a choice about whether to act with integrity and honesty. This prompt is not only asking you to detail your thought process but also to consider your values and how you or others impact the world around you/them through actions. The focus here is on the fact that there is a “choice” to be made after weighing the options. What do “honesty,” “integrity” and “community” mean to you? Clearly Harvard holds honesty as the essential building block of community. Why do you believe honesty is essential to community? How important are shared values in a community? If you are writing about your own actions, think about what prompted you to act or prevented you from acting: What did you do? What was its result? If you are writing about someone you observed, discuss his or her choice. Why was it significant and what did you think about the behavior? In either case, what was at stake based on the decision and what was the impact of the choice that was made?
- The mission of Harvard College is to educate our students to be citizens and citizen-leaders for society. What would you do to contribute to the lives of your classmates in advancing this mission? The heart of this prompt gets at your impact on those around you. Remember, Harvard is looking for “students who will be the best educators of one another and their professors— individuals who will inspire those around them during their College years and beyond.” This also asks you to articulate your ideas about the characteristics of a good citizen and leader. This is an opportunity to discuss your imagined role within your peer group at Harvard as well as in a broader sense as you look toward the future. You must also demonstrate your ability to reflect on society from different perspectives. Think about what you can do to contribute to the world in a meaningful way—from a school club to a larger cultural or religious community to the global society. What might you do to inspire, support, or educate others ?
- Each year a substantial number of students admitted to Harvard defer their admission for one year or take time off during college. If you decided in the future to choose either option, what would you like to do? This is a good prompt to address if you are considering a gap year or if you have plans to take time off while at college to pursue a particular interest. This could be career related, a personal improvement quest, or something else. Explain what you plan to do during this time away from Harvard, your rationale, and what you hope to gain from the experience. How would you embrace this opportunity to gain some skill or explore something meaningfully? How might this experience help you achieve future goals and enhance the community at Harvard upon your return. Tip: You will want to be sure to create a realistic plan for your deferred admission year; saying you will start a business, without naming the business, any kind of business plan, and any reasonable evidence for the business’s projected success will therefore not make for a compelling essay. However, perhaps you would like a year to pursue an internship with an agency whose cause you support; work on a political campaign with which you already have a relationship; volunteer for Habitat for Humanity, etc. Be specific and make sure your plans are plausible, motivated by your values, and supported by past experiences.
- Harvard has long recognized the importance of student body diversity of all kinds. We welcome you to write about distinctive aspects of your background, personal development or the intellectual interests you might bring to your Harvard classmates. How might your particular life experience add value to the diverse student body at Harvard? How might you enrich discussions or provide different perspectives? This is primarily about what unique insights and perspectives you bring to the table; consider how you might engage with your classmates differently based on your personal experiences. Think about your culture, significant experiences that shaped you, your passions, or issues of concern to your unique intellectual pursuits. Some examples might be: discussing your upbringing as a Catholic in an Evangelical area; how your particular background as an international student will diversify the Harvard class; how being a Democrat or a Republican has impacted your thinking; and countless other examples. In short, what makes YOU stand out?
Final thoughts on applying to Harvard
The Harvard admissions committee seeks not only well-rounded individuals; it also covets students who are intensely creative in some discipline or activity, reflective, passionate, artistic, compassionate, talented, and brilliant. Do not be intimidated by these characteristics. Instead, strive to convey your unique self, life experiences, aspirations, motivations, interests and perspectives in a compelling way.
Not surprisingly, the applicant pool at Harvard is extremely competitive. It received 57,786 undergraduate applications for the class of 2025. Only 2,320 were offered admission. What is the best way to standout in this outstanding applicant pool? Be you, convey your strengths, and express unique identity through your application and essay responses!
Take solace in the fact that Harvard is assessing your overall application in an effort to provide the best fit for you as a student. Stay focused and try not to get overwhelmed. Make sure to adhere to deadlines as you dedicate yourself to this process. Plan appropriately to give yourself the time you need to put forth your best self. And remember, this is a two-way street; you need to do your part to convince the admissions committee that you are the best match for Harvard, while also considering what appeals to YOU about the “big H.”
If you’re applying to Harvard University, you already know you’re up against tight competition. Don’t be overwhelmed. Get the guidance of an experienced admissions specialist who will help you stand out from the highly competitive applicant pool so you can apply with confidence and get accepted! Click here to get started!

Related Resources:
- 5 Fatal Flaws to Avoid in Your College Application Essays , a free guide
- School-Specific Supplemental Application Essay Tips
- How Should I Choose Which Essay Questions to Answer When I Have Choices?
About Us Press Room Contact Us Podcast Accepted Blog Privacy Policy Website Terms of Use Disclaimer Client Terms of Service
Accepted 1171 S. Robertson Blvd. #140 Los Angeles CA 90035 +1 (310) 815-9553 © 2022 Accepted


What are the 2024-25 Common App essay prompts?
Feb 28, 2024 • knowledge, information, below is the full set of essay prompts for 2024–2025..
- Some students have a background, identity, interest, or talent that is so meaningful they believe their application would be incomplete without it. If this sounds like you, then please share your story.
- The lessons we take from obstacles we encounter can be fundamental to later success. Recount a time when you faced a challenge, setback, or failure. How did it affect you, and what did you learn from the experience?
- Reflect on a time when you questioned or challenged a belief or idea. What prompted your thinking? What was the outcome?
- Reflect on something that someone has done for you that has made you happy or thankful in a surprising way. How has this gratitude affected or motivated you?
- Discuss an accomplishment, event, or realization that sparked a period of personal growth and a new understanding of yourself or others.
- Describe a topic, idea, or concept you find so engaging that it makes you lose all track of time. Why does it captivate you? What or who do you turn to when you want to learn more?
- Share an essay on any topic of your choice. It can be one you've already written, one that responds to a different prompt, or one of your own design.
We will retain the optional community disruption question within the Writing section. Over the next year, we'll consult with our member, counselor, and student advisory committees to ensure we gather diverse perspectives and make informed decisions.
- Phone: (617) 993-4823
- October 15, 2021
How to Write the Harvard Supplemental Essays (2021-2022)
Welcome to the Harvard supplemental essay prompts for the 2021-2022 college application cycle! Here’s everything you need to know to write the best supplemental essays possible.

Harvard College, founded in 1636, is one of the most difficult institutions to gain acceptance to in the country — the acceptance rate was just 3.43% last year because of a 30% surge in the number of applications. That’s why it’s incredibly important to pay attention to all aspects of your Harvard application to maximize your chances, including the supplemental essays.
And you better buckle up — there are a ton of questions. The good news is you don’t have to write about them all: question three gives you a zillion prompts to choose from. Question three is also optional. In fact, Harvard only has one obligatory prompt, which is very straightforward. But before you breathe a sigh of relief, you should know that when Harvard calls their prompts “optional,” this is a trap. Think about it: why are they asking these questions if they don’t really care whether or not you respond? Harvard is one of those schools where no one is a shoo-in (unless you’re Malia Obama or something). Take every opportunity you can to make an impression. In other words, you’re going to want to take Harvard up on the chance to write “optional” essays.
Please briefly elaborate on one of your extracurricular activities or work experiences. (150 words)
Get straight to the point with this one, since you need to be brief. Pick your most meaningful activity — the one you’ve dedicated serious time and energy to, and the one that’s allowed you to demonstrate significant leadership. Go beyond the simple facts of your accomplishments and the basics that are already there on your activities list. Tell us why this endeavor was important to you and why it was personal. Remember that the idea here isn’t to exaggerate or brag.
Also, avoid false modesty i.e. “I have helped dozens of people, but in the end, they did more for me than I did for them.” If you achieved something, talk about it, maybe with a focus on what it taught you about working with others or about yourself. Be straightforward and matter-of-fact while still offering a unique insight into your activity of choice.
Your intellectual life may extend beyond the academic requirements of your particular school. Please use the space below to list additional intellectual activities that you have not mentioned or detailed elsewhere in your application. These could include, but are not limited to, supervised or self-directed projects not done as school work, training experiences, online courses not run by your school, or summer academic or research programs not described elsewhere. (150 words)
This prompt is new on the application and allows students who have pursued academic endeavors outside of school to really shine, such as the examples they offered. It’s important that you don’t just take the opportunity to list more extracurricular activities in general. Instead, if you can, choose things you may have pursued outside of school — maybe you studied abroad in the summer or taught yourself how to code. Since the essay is short and they ask you to simply list these activities, you don’t have to craft an entire narrative around one activity. Include any opportunities
The fact that Harvard (and other incredibly selective schools like Stanford and Princeton) includes this question to give you a hint as to what they’re looking for in applicants: intellectual curiosity and the ability to take initiative.
Additional essay. You may wish to include an additional essay if you feel the college application forms do not provide sufficient opportunity to convey important information about yourself or your accomplishments. You may write on a topic of your choice, or you may choose from one of the following topics. (Optional)
Before I go through all the topics that Harvard proposes, I’ll tell you what we tell all our students when it comes to choosing a topic for the Common Application essay. The last choice on the Common App is always “any topic of your choice.” Harvard is doing the same thing here: “You may write on a topic of your choice.” Choosing to write about anything you want is just fine — this isn’t a trick option they’re giving you. Think of the choices here as a number of possible topics among infinite others. You should not let yourself feel constrained by these questions.
You can write about anything you like. In fact, in most cases, this is what I’d recommend. Still, maybe one of these prompts is perfectly suited for your life story (that you didn’t already tell in your main Common App essay).
On that note, think of it as a second Common App essay and, as with the Common App, I would recommend aiming for no more than 650 words. Tell a compelling story with a beginning, middle, and end. Tell us something about you we don’t already know.
Unusual circumstances in your life
The most obvious candidates to choose this response are students who have lived in six different cities in the past six years, students who worked every day after school and during the weekends on the family farm, students who had enormous family responsibilities, such as taking care of a sibling or parent, and so on. Not only do stories like these show something unique about who you are, they also provide perspective on your activities list, which, if you’re one of these students, may not be that long. As always, the idea is not to come across as a victim of your circumstances. Tell a story, rather than “explaining” your unusual circumstances: if, for example, you struggled with a serious illness during your sophomore year, tell a specific story about a moment during that time. Show us (rather than tell us) what that was like through an anecdote.
Travel, living, or working experiences in your own or other communities
First off, be careful when talking about travel. While you may have extraordinary stories from the month you spent with your family in Monaco last summer, these kinds of tales will simply make you look like a rich kid — someone admissions officers might have a hard time relating to your experiences. Similarly, it’s best to avoid stories from expensive summer study abroad programs.
You probably also want to avoid talking about service trips. Admissions officers read too many of these kinds of essays, and everyone does community service in high school. Many students are, in fact, required to do a certain number of hours. On a similar note, please don’t write about how twice a week you leave your private school in Manhattan to go and help “the poor and underserved students” at a public high school in the Bronx. You need to be careful about the language you use. Once again, these stories highlight your own privilege, and very few high school students who grew up comfortably have the perspective and maturity to talk about the experiences of others with any real perspective or self-awareness, especially across social class gaps. No offense meant—there are, of course, exceptions to this rule.
On the other hand, if you and your family recently moved from, say, Montana to Chicago, or from Paris to Cleveland, that could be an interesting story.
What you would want your future college roommate to know about you
I’m a big fan of prompts like these since they allow students to show lots of creativity and personality. A serious warning, however: topics like this one are very difficult to pull off. You need exceptional self-awareness and writing abilities to execute this one. Do not use this as a chance to brag, e.g. “I would want my future roommate to know that I logged over 400 community service hours last year.” Would you want to room with that person? Beyond this, you can talk about any of your quirks and eccentricities, provided that you do so in a truly brilliant way (no pressure).
An intellectual experience (course, project, book, discussion, paper, poetry, or research topic in engineering, mathematics, science, or other modes of inquiry) that has meant the most to you
You might consider tackling this one if you left the question about “Additional Intellectual Experiences” blank or if you have something you’d like to elaborate on. Maybe you did something really impressive and meaningful that didn’t exactly qualify as an independent project, or that is listed on your transcript. At some high schools, for instance, seniors are required to undertake a senior project. These may be “done as school work,” and so don’t qualify for the “Additional Intellectual Experiences” prompt. But if you’ve done a project like this, and went way beyond the minimum requirements, it might be worth discussing here. Bottom line: go ahead and nerd out.
How you hope to use your college education
I don’t have much to say about this prompt, except that if you choose to answer it, you risk sounding a bit pompous i.e. “With my Harvard Diploma in hand, I will set out to change the world.”
You will be talking about things you haven’t actually done, and anyone can make him- or herself sound great when describing an imaginary future that includes a Harvard degree. It’s always better to discuss what you have done than what you hope to do.
On the other hand, if you will be a first-generation college student and want to use your education to open doors for others, that is a noble answer to this prompt, and likely a compelling one for Harvard admissions officers. Consider your circumstances and where your story fits best.
A list of books you have read during the past twelve months
I’m convinced this question is a trap. They tell you they want an additional essay, and then one of the prompts asks you for a list?
If you’re reading this 12 minutes before your Harvard application is due, and this is the only prompt you have time to respond to, you better hope you have a very long list of very unusual books, some of which you read in the original Sanskrit (half-joking). Don’t bother listing any required reading.
The Harvard College honor Code declares that we “hold honesty as the foundation of our community.” As you consider entering this community that is committed to honesty, please reflect on a time when you or someone you observed had to make a choice about whether to act with integrity and honesty.
Well, for starters, you probably don’t want to write about someone else’s ethical dilemma, especially if you were the one who came to the rescue and provided guidance, setting your poor, confused friend back on the righteous path. You’ll just look sanctimonious. And if you think this goes without saying, you’d be surprised.
If you choose to write about your own experience, you run into a similar problem: do you discuss a time when you made the hard choice to do what was right and risk looking holier than thou? Or do you write about a time when you failed to do what was right and look like a jerk? The second option is probably preferable, frankly, but even talking about a failure usually leads folks to conclude on some predictable moral platitude about what they learned.
But be very careful when selecting the mistake you want to share with Harvard. I wouldn’t recommend this prompt to most students, but there are always exceptions to the rule.
The mission of Harvard College is to educate our students to be citizens and citizen-leaders for society. What would you do to contribute to the lives of your classmates in advancing this mission?
See my comments on “How do you hope to use your college education.” It’s very difficult to talk about what you hope to do in the future in a convincing way. Most people would promise to do just about anything in exchange for an acceptance letter from Harvard. Better to focus on what you have done.
Each year a substantial number of students admitted to Harvard defer their admission for one year or take time off during college. If you decide in the future to choose either option, what would you like to do?
Don’t choose this one unless you’ve already thought about it. If this is something you have given serious thought to, as always, you want to focus on what you have done, not what you hope one day to do. I know I’m repeating myself, but anyone can write something like, “After my sophomore year at Harvard, I plan to take a year off and selflessly serve in the Peace Corps.” This is better suited for someone who already has plans in place.
Your response to this prompt will be most effective if you’ve already got something lined up for a gap year after high school. Maybe you’ve already been offered a job by a shipbuilder in Maine, and you plan to take it and work for a year before you start college. That’s very cool.
Whether or not you have something concrete in place, you’ll want to talk about your past experiences and how they inform your decision to take time off. Maybe you’re applying to work as a stage manager at a couple of local theaters so you can continue to pursue a passion you’ve been developing since you were ten. Great — that’s compelling. But avoid the “because-of-COVID” gap year conversation, unless it brings new details about you to light.
You may be wondering if taking a gap year is a bad thing to do in Harvard’s opinion. It definitely isn’t, unless you’re taking time off simply because you’re burned out, and are looking forward to another year living at home with someone cooking for you and doing your laundry. A gap year during which you plan to buy an RV with your friends and drive to Argentina also may not impress Harvard, but if it’s something that is fundamentally important to you and reveals an interest or curiosity you couldn’t mention elsewhere.
Harvard has long recognized the importance of student body diversity of all kinds. We welcome you to write about distinctive aspects of your background, personal development or the intellectual interests you might bring to your Harvard classmates.
As always, the point of these essays is to stand out and differentiate yourself. So think about how your background differs from most students at Harvard, and how that background will contribute to Harvard’s community.
There’s an elephant in the room here that should be addressed. Since 2014, Harvard has been embroiled in an affirmative action lawsuit , which has revealed biases against Asian-American applicants on the part of Harvard University in the admissions process. At the end of the linked article, the question of writing about being of East Asian descent on college applications is even addressed explicitly. Harvard is continually increasing the number of Asian American students, with 25.9% of the class of 2025 being Asian American , and is clearly doing its best to show that it is not judging any group unfairly in the admissions process, especially as the appeals process for the lawsuit is underway.
Nevertheless, if you are Asian American and planning on applying to Harvard, this question may not be the best for you. Even if Harvard has changed its ways, and has made the admissions process fairer for Asian Americans, over a quarter of the accepted class last year was made up of Asian Americans. All other ethnic groups (except Caucasians), and also first-generation college students, are far less represented. Especially in a holistic admissions process where the emphasis on standardized testing is declining, more factors that are often out of a student’s control are coming into play. Approach this delicately.
In any event, remember that for your “optional” essay for Harvard, you can always choose to write about whatever you like. In most cases, this is the best approach.
If you’re unsure of what to write about or simply want to be sure your essays are the best they can be, please contact our college admission consultants .
- College Applications , Ivy League , The College Essay

How Your Extracurricular Activities Can Boost Your College Application
The Best Internship Opportunities for High School Students
Weighted vs. Unweighted GPA: What’s the Difference?
- Partnerships
- Our Insights
- Our Approach
Our Services
- High School Roadmaps
- College Applications
- Graduate School Admissions
- H&C Incubator
- [email protected]
Terms and Conditions . Privacy policy
©2024 H&C Education, Inc. All rights reserved.
No products in the cart.

Harvard: 5 Common App Essay Introductions That Worked
Many applicants struggle with writing the perfect Common App essay introduction to get into their dream school. Your essay’s introduction is one of the most important parts of a successful Common App essay that will make an impression on the admissions officer reading your application.
We’ve compiled 5 Common App essay introductions that were accepted to Harvard University to show you exactly what it takes to make an impression in your first paragraph and grab the admissions officer’s attention.
Prompt: Some students have a background or story that is so central to their identity that they believe their application would be incomplete without it. If this sounds like you, then please share your story.
“Hey kids, here’s twenty bucks. If any of y’all have the guts to ask that there bride to dance, it’s yours,” offered a bearded man in a cowboy hat. He wore a slick black suit and shiny purple tie. His words made me feel like he was giving me a fantastic opportunity, but his smile was that of a used car salesman’s. The four of us kids stared at the man, and then three of them stared at me. I was staring at the bride.
See the Full Harvard Application Essay »
Prompt: Describe a place or environment where you are perfectly content. What do you do or experience there, and why is it meaningful to you?
In northern Wisconsin there is a small cabin, built years ago by my great-grandfather. The cabin rests on the shore of Bass Lake, named such despite the fact that no bass have ever actually made their home there. My father swam in Bass Lake decades ago, watched the grown-ups play cards at night, played touch football with his brothers in the yard. Today the cabin is collectively owned by the Bonsall family, including my dad, and no doubt he will one day pass along that ownership to me, and I will receive my own stake in the family heritage. When I was younger, the entire Bonsall clan would assemble at the cabin each summer, just as they always had. During those summers I swam in Bass Lake, caught my first fish in its waters, sat on the iron swing by the lake and gazed into the flames of the campfire, listening partly to the conversation between my relatives, partly to the chirping of the crickets in the woods. I heard the sound of spring rain pattering against the tent on wet summer nights, and the call of the loons on the lake on dry ones. I have rarely felt so content as on those nights at the cabin.
Most of my friends asked me why I did it. It took four days and left me completely exhausted. What reason was there to embark on such a journey?
It all started the summer before my freshman year in high school when I rode my bike off of my grandma’s street for the first time and rode up into a neighboring subdivision. From then on I was hooked. I started riding all over the place; from the main drag in town up into the country along narrow roads I didn’t know existed.
The pungent yet strangely welcoming odor of acetone permeated my senses as I entered the familiar lab environment. All around me, white-clad students hurriedly gathered chemicals and watched their flasks intensely as the solvent simultaneously boiled and condensed. Foggy safety goggles and furrowed eyebrows revealed the immense concentration of everyone in the room as they tackled various challenges. From my vantage point, I watched as a captivating transformation evolved at each station. Striking shades of green and orange contrasted with dull strokes of brown and grey in flasks around the room; soft, white powder stood out from needle-like blue crystals as both slowly dissolved into beakers of water. The randomness of each adventure added to my excitement as I impatiently waited to begin.
Entering my kindergarten classroom, I shuffled around my blueberry shaped classmates as some began throwing their winter layers into cubbies. Admittedly, my torso was equally bulbous – covered with the threats and extortions of my mother: a heavy jacket, gloves, and a hat. But, below the waist I wore only a pair of frigid khaki shorts. As I walked proudly to my seat, my teacher quickly approached me. Bug-eyed, in what I assumed was intense admiration, she asked “Stephen, aren’t you the tiniest bit cold?”.
“No,” I replied, smiling. “I don’t get cold.”
See Full Applications That Got Into Harvard
To see full applications and essays that got into Harvard and other Ivy League schools check out our roster of successful applications to top schools. IvyApps has full applications to Harvard, Stanford, Princeton, Yale and other top schools and features full essays, supplements, as well as students GPA and standardized test scores.
- Essay written by Anonymous
Get Help With Your Essays and Applications
- Ask your questions
- Get help on essay editing
- Gain insight on their experience

Report Content
Block member.
Please confirm you want to block this member.
You will no longer be able to:
- See blocked member's posts
- Mention this member in posts
- Message this member
- Add this member as a connection
Please note: This action will also remove this member from your connections and send a report to the site admin. Please allow a few minutes for this process to complete.
Harvard University

Harvard College is a close-knit undergraduate community within Harvard University. With world-class faculty, groundbreaking research opportunities, and a commitment to a diverse environment of bright, talented students, Harvard is more than just a place to get an education—it's where students come to be transformed. Our unparalleled student experience educates the next generation of citizens and citizen leaders. In addition, Harvard has one of the most generous need-based financial aid programs in the world, ensuring that the cost will never stand in the way of a Harvard education.
Academic programs.
- Engineering
- Government/Political Science
- Liberal Arts
- Performing Arts
- Social Science
- Visual Arts
Student experience
- Co-op/Internship Opportunities
- Disability Services
- Intramural/Club Sports
- LGBTQIA Services
- Military/Veteran Services
- On-Campus Housing
- ROTC Program
- Study Abroad
- Undergraduate Research
- Veteran Fee Waiver
Application information
Find out about requirements, fees, and deadlines
There is no single academic path we expect all students to follow, but the strongest applicants take the most rigorous secondary school curricula available to them. An ideal four-year preparatory program includes four years of English, with extensive practice in writing; four years of math (see website for specific math guidance); four years of science: biology, chemistry, physics, and an advanced course in one of these subjects; three years of history, including American and European history; and four years of one foreign language. Apply as a first-year student if you have completed less than a full year of college course work.
Each year, we accept a small group (12 on average) of exceptional students to transfer to Harvard College from other similar liberal arts programs. Admitted students come from a range of educational institutions - community colleges, public and private universities in the U.S., and international universities. To be eligible to transfer, you must have completed at least one continuous academic year in a full-time, in-person degree program at one college and not more than two academic years. You must complete at least two full years of study at Harvard. Once a student has completed more than two years total of college at another institution, regardless of courses taken, that student is no longer eligible for transfer admission.

Additional Information
Harvard is the oldest college in the country, steeped in long-standing traditions and campus pride. Our community's spirit and exuberance are alive in every corner of the campus, and we can't wait to show you what makes Harvard a school like no other. We encourage prospective students to learn more about Harvard College - you can register for a campus visit , take a virtual tour , and learn more through student stories .

Admissions office

86 Brattle St Cambridge , MA 02138 , United States of America
Phone number
(617) 495-1551
For first-year students
Admissions website.
college.harvard.edu/admissions
Financial aid website
college.harvard.edu/financial-aid
For transfer students
New England
View more in this region
Follow Harvard University
- Facebook icon
- Twitter icon
- Youtube icon
- Instagram icon

- Editor's Pick

Amid Boston Overdose Crisis, a Pair of Harvard Students Are Bringing Narcan to the Red Line

At First Cambridge City Council Election Forum, Candidates Clash Over Building Emissions

Harvard’s Updated Sustainability Plan Garners Optimistic Responses from Student Climate Activists

‘Sunroof’ Singer Nicky Youre Lights Up Harvard Yard at Crimson Jam

‘The Architect of the Whole Plan’: Harvard Law Graduate Ken Chesebro’s Path to Jan. 6
Harvard Overhauls College Application in Wake of Affirmative Action Decision

When the Common Application portal opened at midnight Tuesday, thousands of high schoolers found the Harvard College application had significantly changed.
After the Supreme Court radically curtailed the use of race in higher education admissions, the College overhauled the free-response questions on its application, eliminating the Harvard supplement optional essay — the longer-form response that allowed applicants to write on virtually any topic of their choosing — and replacing it with required short answer questions.
Harvard’s application now contains five short-answer questions, all of which are required and have a 200-word limit.
The questions ask about applicants’ life experience, intellectual interests, extracurricular activities, how they hope to use their Harvard education in the future, and the top three things that they want their roommate to know about them. The new short essays draw directly from prompts in the old College application.
“As part of the undergraduate admissions process, an optional essay is being replaced by five required short essays to provide every student the opportunity to reflect on and share how their life experiences and academic and extracurricular activities shaped them, how they will engage with others at Harvard, and their aspirations for the future,” College spokesperson Jonathan Palumbo wrote in an email Tuesday.
Previously, the College’s application had three optional writing components: a 150-word extracurricular response, a 150-word piece to describe “additional intellectual experiences,” and the Harvard supplement.
“The changes Harvard made to its application are clearly designed to help admissions do what the Supreme Court said is okay — namely, to consider race as part of an applicant’s ‘experiences as an individual — not on the basis of race,’” Joshua S. Wyner, executive director of the College Excellence Program at The Aspen Institute, wrote in an email.
The Supreme Court’s decision restricting race-based affirmative action reads that “nothing in this opinion should be construed as prohibiting universities from considering an applicant’s discussion of how race affected his or her life, be it through discrimination, inspiration, or otherwise.”
Still, the Court held that “universities may not simply establish through application essays or other means the regime we hold unlawful today.”
Brennan Barnard, the director of College Counseling and Outreach at Khan Lab School, an offshoot of the online Khan Academy, said he believes it is possible “to look at somebody’s background as a person and how that identity has informed their day to day life without making it just about race.”
“And in reality, college admission officers have been doing this for decades,” Barnard added.
Oregon State University Vice Provost of Enrollment Management Jon J. Boeckenstedt wrote in an emailed statement Tuesday that the Supreme Court “made it clear that colleges could still ask, and students could still write, about life experiences” and the impact they had on students.
“But some students seem confused about what they can include (I’ve even heard that some students believe that saying anything about race or ethnicity will get them denied),” Boeckenstedt wrote.
Boeckenstedt added that he is “pleased” that institutions are actively affirming their commitment to enrolling a diverse student body, “as the SCOTUS decision indicated they could.”
But while changing the essay prompts is “easy,” “the big challenges will arise when Harvard tries to apply that standard,” Wyner wrote.
“Practically, what does it mean for admissions to consider race as part of someone’s experience but then not make a decision ‘on the basis of race?’” Wyner wrote.
“That ambiguity will not be resolved with this new application but when Harvard is dragged back into court to explain how it has applied this very opaque standard,” he added.
—Staff writer Michelle N. Amponsah can be reached at [email protected] . Follow her on Twitter at @mnamponsah .
—Staff writer Rahem D. Hamid can be reached at [email protected] .
Want to keep up with breaking news? Subscribe to our email newsletter.
Related Articles
- Share full article
For more audio journalism and storytelling, download New York Times Audio , a new iOS app available for news subscribers.
Supported by
The Ezra Klein Show
Transcript: Ezra Klein Interviews Ethan Mollick
Every Tuesday and Friday, Ezra Klein invites you into a conversation about something that matters, like today’s episode with Ethan Mollick. Listen wherever you get your podcasts .
Transcripts of our episodes are made available as soon as possible. They are not fully edited for grammar or spelling.
How Should I Be Using A.I. Right Now?
Give your a.i. a personality, spend 10 hours experimenting, and other practical tips from ethan mollick..
[MUSIC PLAYING]
From New York Times Opinion, this is “The Ezra Klein Show.”
This feels wrong to me. But I have checked the dates. It was barely more than a year ago that I wrote this piece about A.I., with the title “This Changes Everything.” I ended up reading it on the show, too. And the piece was about the speed with which A.I. systems were improving. It argued that we can usually trust that tomorrow is going to be roughly like today, that next year is going to be roughly like this year. That’s not what we’re seeing here. These systems are growing in power and capabilities at an astonishing rate.
The growth is exponential, not linear. When you look at surveys of A.I. researchers, their timeline for how quickly A.I. is going to be able to do basically anything a human does better and more cheaply than a human — that timeline is accelerating, year by year, on these surveys. When I do my own reporting, talking to the people inside these companies, people at this strange intersection of excited and terrified of what they’re building, no one tells me they are seeing a reason to believe progress is going to slow down.
And you might think that’s just hype, but a lot of them want it to slow down. A lot of them are scared of how quickly it is moving. They don’t think that society is ready for it, that regulation is ready for it. They think the competitive pressures between the companies and the countries are dangerous. They wish something would happen to make it all go slower. But what they are seeing is they are hitting the milestones faster, that we’re getting closer and closer to truly transformational A.I., that there is so much money and talent and attention flooding into the space that that is becoming its own accelerant. They are scared. We should at least be paying attention.
And yet, I find living in this moment really weird, because as much as I know this wildly powerful technology is emerging beneath my fingertips, as much as I believe it’s going to change the world I live in profoundly, I find it really hard to just fit it into my own day to day work. I consistently sort of wander up to the A.I., ask it a question, find myself somewhat impressed or unimpressed at the answer. But it doesn’t stick for me. It is not a sticky habit. It’s true for a lot of people I know.
And I think that failure matters. I think getting good at working with A.I. is going to be an important skill in the next few years. I think having an intuition for how these systems work is going to be important just for understanding what is happening to society. And you can’t do that if you don’t get over this hump in the learning curve, if you don’t get over this part where it’s not really clear how to make A.I. part of your life.
So I’ve been on a personal quest to get better at this. And in that quest, I have a guide. Ethan Mollick is a professor at the Wharton School of the University of Pennsylvania. He studies and writes about innovation and entrepreneurship. But he has this newsletter, One Useful Thing, that has become, really, I think, the best guide how to begin using, and how to get better at using A.I. He’s also got a new book on the subject, “Co-Intelligence.” And so I asked him on the show to walk me through what he’s learned.
This is going to be, I should say, the first of three shows on this topic. This one is about the present. The next is about some things I’m very worried about in the near future, particularly around what A.I. is going to do to our digital commons. And then, we’re going to have a show that is a little bit more about the curve we are all on about the slightly further future, and the world we might soon be living in.
As always, my email for guest suggestions, thoughts, feedback, [email protected].
Ethan Mollick, welcome to the show.
Thanks for having me.
So let’s assume I’m interested in A.I. And I tried ChatGPT a bunch of times, and I was suitably impressed and weirded out for a minute. And so I know the technology is powerful. I’ve heard all these predictions about how it will take everything over, or become part of everything we do. But I don’t actually see how it fits into my life, really, at all. What am I missing?
So you’re not alone. This is actually very common. And I think part of the reason is that the way ChatGPT works isn’t really set up for you to understand how powerful it is. You really do need to use the paid version, they are significantly smarter. And you can almost think of this — like, GPT-3, which was — nobody really paid attention to when it came out, before ChatGPT, was about as good as a sixth grader at writing. GPT-3.5, the free version of ChatGPT, is about as good as a high school, or maybe even a college freshman or sophomore.
And GPT-4 is often as good as a Ph.D. in some forms of writing. Like, there’s a general smartness that increases. But even more than that, ability seems to increase. And you’re much more likely to get that feeling that you are working with something amazing as a result. And if you don’t work with the frontier models, you can lose track of what these systems can actually do. On top of that, you need to start just using it. You kind of have to push past those first three questions.
My advice is usually bring it to every table that you come to in a legal and ethical way. So I use it for every aspect of my job in ways that I legally and ethically can, and that’s how I learn what it’s good or bad at.
When you say, bring it to every table you’re at, one, that sounds like a big pain, because now I’ve got to add another step of talking to the computer constantly. But two, it’s just not obvious to me what that would look like. So what does it look like? What does it look like for you, or what does it look like for others — that you feel is applicable widely?
So I just finished this book. It’s my third book. I keep writing books, even though I keep forgetting that writing books is really hard. But this was, I think, my best book, but also the most interesting to write. And it was thanks to A.I. And there’s almost no A.I. writing in the book, but I used it continuously. So things that would get in the way of writing — I think I’m a much better writer than A.I. — hopefully, people agree. But there’s a lot of things that get in your way as a writer. So I would get stuck on a sentence. I couldn’t do a transition. Give me 30 versions of this sentence in radically different styles. There’s 200 different citations. I had the A.I. read through the papers that I read through, write notes on them, and organize them for me. I had the A.I. suggest analogies that might be useful. I had the A.I. act as readers, and in different personas, read through the paper from the perspective of, is there some example I could give that’s better? Is this understandable or not? And that’s very typical of the kind of way that I would, say, bring it to the table. Use it for everything, and you’ll find its limits and abilities.
Let me ask you one specific question on that, because I’ve been writing a book. And on some bad days of writing the book, I decided to play around with GPT-4. And of the things that it got me thinking about was the kind of mistake or problem these systems can help you see and the kind they can’t. So they can do a lot of, give me 15 versions of this paragraph, 30 versions of this sentence. And every once in a while, you get a good version or you’ll shake something a little bit loose.
But almost always when I am stuck, the problem is I don’t know what I need to say. Oftentimes, I have structured the chapter wrong. Oftentimes, I’ve simply not done enough work. And one of the difficulties for me about using A.I. is that A.I. never gives me the answer, which is often the true answer — this whole chapter is wrong. It is poorly structured. You have to delete it and start over. It’s not feeling right to you because it is not right.
And I actually worry a little bit about tools that can see one kind of problem and trick you into thinking it’s this easier problem, but make it actually harder for you to see the other kind of problem that maybe if you were just sitting there, banging your head against the wall of your computer, or the wall of your own mind, you would eventually find.
I think that’s a wise point. I think there’s two or three things bundled there. The first of those is A.I. is good, but it’s not as good as you. It is, say, at the 80th percentile of writers based on some results, maybe a little bit higher. In some ways, if it was able to have that burst of insight and to tell you this chapter is wrong, and I’ve thought of a new way of phrasing it, we would be at that sort of mythical AGI level of A.I. as smart as the best human. And it just isn’t yet.
I think the second issue is also quite profound, which is, what does using this tool shape us to do and not do? One nice example that you just gave is writing. And I think a lot of us think about writing as thinking. We don’t know if that’s true for everybody, but for writers, that’s how they think. And sometimes, getting that shortcut could shortcut the thinking process. So I’ve had to change sometimes a little bit how I think when I use A.I., for better or for worse. So I think these are both concerns to be taken seriously.
For most people — right, if you’re just going to pick one model, what would you pick? What do you recommend to people? And second, how do you recommend they access it? Because something going on in the A.I. world is there are a lot of wrappers on these models. So ChatGPT has an app. Claude does not have an app. Obviously, Google has its suite of products. And there are organizations that have created a different spin on somebody else’s A.I. — so Perplexity, which is, I believe, built on GPT-4 now, you can pay for it.
And it’s more like a search engine interface, and has some changes made to it. For a lot of people, the question of how easy and accessible the thing is to access really matters. So which model do you recommend to most people? And which entry door do you recommend to most people? And do they differ?
It’s a really good question. I recommend working with one of the models as directly as possible, through the company that creates them. And there’s a few reasons for that. One is you get as close to the unadulterated personality as possible. And second, that’s where features tend to roll out first. So if you like sort of intellectual challenge, I think Claude 3 is the most intellectual of the models, as you said.
The biggest capability set right now is GPT-4, so if you do any math or coding work, it does coding for you. It has some really interesting interfaces. That’s what I would use — and because GPT-5 is coming out, that’s fairly powerful. And Google is probably the most accessible, and plugged into the Google ecosystem. So I don’t think you can really go wrong with any of these. Generally, I think Claude 3 is the most likely to freak you out right now. And GPT-4 is probably the most likely to be super useful right now.
So you say it takes about 10 hours to learn a model. Ten hours is a long time, actually. What are you doing in that 10 hours? What are you figuring out? How did you come to that number? Give me some texture on your 10 hour rule.
So first off, I want to indicate the 10 hours is as arbitrary as 10,000 steps. Like, there’s no scientific basis for it. This is an observation. But it also does move you past the, I poked at this for an evening, and it moves you towards using this in a serious way. I don’t know if 10 hours is the real limit, but it seems to be somewhat transformative. The key is to use it in an area where you have expertise, so you can understand what it’s good or bad at, learn the shape of its capabilities.
When I taught my students this semester how to use A.I., and we had three classes on that, they learned the theory behind it. But then I gave them an assignment, which was to replace themselves at their next job. And they created amazing tools, things that filed flight plans or did tweeting, or did deal memos. In fact, one of the students created a way of creating user personas, which is something that you do in product development, that’s been used several thousand times in the last couple of weeks in different companies.
So they were able to figure out uses that I never thought of to automate their job and their work because they were asked to do that. So part of taking this seriously in the 10 hours is, you’re going to try and use it for your work. You’ll understand where it’s good or bad, what it can automate, what it can’t, and build from there.
Something that feels to me like a theme of your work is that the way to approach this is not learning a tool. It is building a relationship. Is that fair?
A.I. is built like a tool. It’s software. It’s very clear at this point that it’s an emulation of thought. But because of how it’s built, because of how it’s constructed, it is much more like working with a person than working with a tool. And when we talk about it this way, I almost feel kind of bad, because there’s dangers in building a relationship with a system that is purely artificial, and doesn’t think and have emotions. But honestly, that is the way to go forward. And that is sort of a great sin, anthropomorphization, in the A.I. literature, because it can blind you to the fact that this is software with its own sets of foibles and approaches.
But if you think about it like programming, then you end up in trouble. In fact, there’s some early evidence that programmers are the worst people at using A.I. because it doesn’t work like software. It doesn’t do the things you would expect a tool to do. Tools shouldn’t occasionally give you the wrong answer, shouldn’t give you different answers every time, shouldn’t insult you or try to convince you they love you.
And A.I.s do all of these things. And I find that teachers, managers, even parents, editors, are often better at using these systems, because they’re used to treating this as a person. And they interact with it like a person would, giving feedback. And that helps you. And I think the second piece of that “not tool” piece is that when I talk to OpenAI or Anthropic, they don’t have a hidden instruction manual. There is no list of how you should use this as a writer, or as a marketer, or as an educator. They don’t even know what the capabilities of these systems are. They’re all sort of being discovered together. And that is also not like a tool. It’s more like a person with capabilities that we don’t fully know yet.
So you’ve done this with all the big models. You’ve done, I think, much more than this, actually, with all the big models. And one thing you describe feeling is that they don’t just have slightly different strengths and weaknesses, but they have different — for lack of a better term, and to anthropomorphize — personalities, and that the 10 hours in part is about developing an intuition not just for how they work, but kind of how they are and how they talk, the sort of entity you’re dealing with.
So give me your high level on how GPT-4 and Claude 3 and Google’s Gemini are different. What are their personalities like to you?
It’s important to know the personalities not just as personalities, but because there are tricks. Those are tunable approaches that the system makers decide. So it’s weird to have this — in one hand, don’t anthropomorphize, because you’re being manipulated, because you are. But on the other hand, the only useful way is to anthropomorphize. So keep in mind that you are dealing with the choices of the makers.
So for example, Claude 3 is currently the warmest of the models. And it is the most allowed by its creators, Anthropic, I think, to act like a person. So it’s more willing to give you its personal views, such as they are. And again, those aren’t real views. Those are views to make you happy — than other models. And it’s a beautiful writer, very good at writing, kind of clever — closest to humor, I’ve found, of any of the A.I.s. Less dad jokes and more actual almost jokes.
GPT-4 feels like a workhorse at this point. It is the most neutral of the approaches. It wants to get stuff done for you. And it will happily do that. It doesn’t have a lot of time for chitchat. And then we’ve got Google’s Bard, which feels like — or Gemini now — which feels like it really, really wants to help. We use this for teaching a lot. And we build these scenarios where the A.I. actually acts like a counterparty in a negotiation. So you get to practice the negotiation by negotiating with the A.I. And it works incredibly well. I’ve been building simulations for 10 years, can’t imagine what a leap this has been. But when we try and get Google to do that, it keeps leaping in on the part of the students, to try and correct them and say, no, you didn’t really want to say this. You wanted to say that. And I’ll play out the scenario as if it went better. And it really wants to kind of make things good for you.
So these interactions with the A.I. do feel like you’re working with people, both in skills and in personality.
You were mentioning a minute ago that what the A.I.s do reflect decisions made by their programmers. They reflect guardrails, what they’re going to let the A.I. say. Very famously, Gemini came out and was very woke. You would ask it to show you a picture of soldiers in Nazi Germany, and it would give you a very multicultural group of soldiers, which is not how that army worked. But that was something that they had built in to try to make more inclusive photography generation.
But there are also things that happen in these systems that people don’t expect, that the programmers don’t understand. So I remember the previous generation of Claude, which is from Anthropic, that when it came out, something that the people around it talked about was, for some reason, Claude was just a little bit more literary than the other systems. It was better at rewriting things in the voices of literary figures. It just had a slightly artsier vibe.
And the people who trained it weren’t exactly sure why. Now, that still feels true to me. Right now, of the ones I’m using, I’m spending the most time with Claude 3. I just find it the most congenial. They all have different strengths and weaknesses, but there is a funny dimension to these where they are both reflecting the guardrails and the choices of the programmers. And then deep inside the training data, deep inside the way the various algorithms are combining, there is some set of emergent qualities to them, which gives them this at least edge of chance, of randomness, of something — yeah, that does feel almost like personality.
I think that’s a very important point. And fundamental about A.I. is the idea that we technically know how LLMs work, but we don’t know how they work the way they do, or why they’re as good as they are. They’re really — we don’t understand it. The theories range from everyone — from it’s all fooling us, to they’ve emulated the way humans think because the structure of language is the structure of human thought. So even though they don’t think, they can emulate it. We don’t know the answer.
But you’re right, there’s these emergent sets of personalities and approaches. When I talk to A.I. design companies, they often can’t explain why the A.I. stops refusing answering a particular kind of question. When they tune the A.I. to do something better, like answer a math better, it suddenly does other things differently. It’s almost like adjusting the psychology of a system rather than tuning parameters.
So when I said that Claude is allowed to be more personable, part of that is that the system prompt in Claude, which is the initial instructions it gets, allow it to be more personable than, say, Microsoft’s Copilot, formerly Bing, which has explicit instructions after a fairly famous blow up a while ago, that it’s never supposed to talk about itself as a person or indicate feelings. So there’s some instructions, but that’s on top of these roiling systems that act in ways that even the creators don’t expect.
One thing people know about using these models is that hallucinations, just making stuff up, is a problem. Has that changed at all as we’ve moved from GPT-3.5 to 4, as we move from Claude 2 to 3. Like, has that become significantly better? And if not, how do you evaluate the trustworthiness of what you’re being told?
So those are a couple of overlapping questions. The first of them is, it getting better over time? So there is a paper in the field of medical citations that indicated that around 80 to 90 percent of citations had an error, were made up with GPT-3.5. That’s the free version of Chat. And that drops for GPT-4.
So hallucination rates are dropping over time. But the A.I. still makes stuff up because all the A.I. does is hallucinate. There is no mind there. All it’s doing is producing word after word. They are just making stuff up all the time. The fact that they’re right so often is kind of shocking in a lot of ways.
And the way you avoid hallucination is not easily. So one of the things we document in one of our research papers is we purposely designed for a group of Boston Consulting Group consultants — so an elite consulting company — we did a lot of work with them. And one of the experiments we did was we created a task where the A.I. would be confident but wrong. And when we gave people that task to do, and they had access to A.I., they got the task wrong more often than people who didn’t use A.I., because the A.I. misled them, because they fell asleep at the wheel. And all the early research we have on A.I. use suggests that when A.I.s get good enough, we just stop paying attention.
But doesn’t this make them unreliable in a very tricky way? 80 percent — you’re, like, it’s always hallucinating. 20 percent, 5 percent, it’s enough that you can easily be lulled into overconfidence. And one of the reasons it’s really tough here is you’re combining something that knows how to seem extremely persuasive and confident — you feed into the A.I. a 90-page paper on functions and characteristics of right wing populism in Europe, as I did last night.
And within seconds, basically, you get a summary out. And the summary certainly seems confident about what’s going on. But on the other hand, you really don’t know if it’s true. So for a lot of what you might want to use it for, that is unnerving.
Absolutely, and I think hard to grasp, because we’re used to things like type II errors, where we search for something on the internet and don’t find it. We’re not used to type I errors, where we search for something and get an answer back that’s made up. This is a challenge. And there’s a couple things to think about. One of those is — I advocate the BAH standard, best available human. So is the A.I. more or less accurate than the best human you could consult in that area?
And what does that mean for whether or not it’s an appropriate question to ask? And that’s something that we kind of have to judge collectively. It’s valuable to have these studies being done by law professors and medical professionals and people like me and my colleagues in management. They’re trying to understand, how good is the A.I.? And the answer is pretty good, right? So it makes mistakes. “Does it make more or less mistakes than a human” is probably a question we should be asking a lot more.
And the second thing is the kind of tasks that you judge it for. I absolutely agree with you. When summarizing information, it may make errors. Less than an intern you assign to it is an open question, but you have to be aware of that error rate. And that goes back to the 10 hour question. The more you use these A.I.s, the more you start to know when to be suspicious and when not to be. That doesn’t mean you’re eliminating errors.
But just like if you assigned it to an intern, and you’re, like, this person has a sociology degree. They’re going to do a really good job summarizing this, but their biases are going to be focused on the sociological facts and not the political facts. You start to learn these things. So I think, again, that person model helps, because you don’t expect 100 percent reliability out of a person. And that changes the kind of tasks you delegate.
But it also reflects something interesting about the nature of the systems. You have a quote here that I think is very insightful. You wrote, “the core irony of generative A.I.s is that A.I.s were supposed to be all logic and no imagination. Instead, we get A.I.s that make up information, engage in seemingly emotional discussions, and which are intensely creative.” And that last fact is one that makes many people deeply uncomfortable.
There is this collision between what a computer is in our minds and then this strange thing we seem to have invented, which is an entity that emerges out of language, an entity that almost emerges out of art. This is the thing I have the most trouble keeping in my mind, that I need to use the A.I. as an imaginative, creative partner and not as a calculator that uses words.
I love the phrase “a calculator that uses words.” I think we have been let down by science fiction, both in the utopias and apocalypses that A.I. might bring, but also, even more directly, in our view of how machines should work. People are constantly frustrated, and give the same kinds of tests to A.I.s over and over again, like doing math, which it doesn’t do very well — they’re getting better at this.
And on the other hand, saying, well, creativity is a uniquely human spark that we can’t touch, and that A.I., on any creativity test we give it — which, again, are all limited in different ways, blows out humans in almost all measures of creativity that we have. Or all the measures are bad, but that still means something.
But we were using those measures five years ago, even though they were bad. That’s a point you make that I think is interesting and slightly unsettling.
Yeah, we never had to differentiate humans from machines before. It was always easy. So the idea that we had to have a scale that worked for people and machines, who had that? We had the Turing test, which everyone knew was a terrible idea. But since no machine could pass it, it was completely fine. So the question is, how do we measure this? This is an entirely separate set of issues. Like, we don’t even have a definition of sentience or consciousness.
And I think that you’re exactly right on the point, being that we are not ready for this kind of machine, so our intuition is bad.
So one of the things I will sometimes do, and did quite recently, is give the A.I. a series of personal documents, emails I wrote to people I love that were very descriptive of a particular moment in my life. And then I will ask the A.I. about them, or ask the A.I. to analyze me off of them.
And sometimes, it’s a little breathtaking. Almost every moment of true metaphysical shock — to use a term somebody else gave me — I’ve had here has been relational, at how good the A.I. can be — almost like a therapist, right? Sometimes it will see things, the thing I am not saying, in a letter, or in a personal problem. And it will zoom in there, right? It will give, I think, quicker and better feedback in an intuitive way that is not simply mimicking back what I said and is dealing with a very specific situation. It will do better than people I speak to in my life around that.
Conversely, I’m going to read a bit of it later. I tried mightily to make Claude 3 a useful partner in prepping to speak to you, and also in prepping for another podcast recently. And I functionally never have a moment there where I’m all that impressed.
That makes complete sense. I think the weird expectations — we call it the jagged frontier of A.I., that it’s good at some stuff and bad at other stuff. It’s often unexpected. It can lead to these weird moments of disappointment, followed by elation or surprise. And part of the reason why I advocate for people to use it in their jobs is, it isn’t going to outcompete you at whatever you’re best at. I mean, I cannot imagine it’s going to do a better job prepping someone for an interview than you’re doing. And that’s not me just — I’m trying to be nice to you because you’re interviewing me, but because you’re a good interviewer. You’re a famous interviewer. It’s not going to be as good as that. Now, there’s questions about how good these systems get that we don’t know, but we’re kind of at a weirdly comfortable spot in A.I., which is, maybe it’s the 80th percentile of many performances. But I talk to Hollywood writers. It’s not close to writing like a Hollywood writer. It’s not close to being as good an analyst.
It’s not — but it’s better than the average person. And so it’s great as a supplement to weakness, but not to strength. But then, we run back into the problem you talked about, which is, in my weak areas, I have trouble assessing whether the A.I. is accurate or not. So it really becomes sort of a eating its own tail kind of problem.
But this gets to this question of, what are you doing with it? The A.I.s right now seem much stronger as amplifiers and feedback mechanisms and thought partners for you than they do as something you can really outsource your hard work and your thinking to. And that, to me, is one of the differences between trying to spend more time with these systems — like, when you come into them initially, you’re like, OK, here’s a problem, give me an answer.
Whereas when you spend time with them, you realize actually what you’re trying to do with the A.I. is get it to elicit a better answer from you.
And that’s why the book’s called “Co-Intelligence.” For right now, we have a prosthesis for thinking. That’s, like, new in the world. We haven’t had that before — I mean, coffee, but aside from that, not much else. And I think that there’s value in that. I think learning to be partner with this, and where it can get wisdom out of you or not — I was talking to a physics professor at Harvard. And he said, all my best ideas now come from talking to the A.I. And I’m like, well, it doesn’t do physics that well. He’s like, no, but it asks good questions. And I think that there is some value in that kind of interactive piece.
It’s part of why I’m so obsessed with the idea of A.I. in education, because a good educator — and I’ve been working on interactive education skill for a long time — a good educator is eliciting answers from a student. And they’re not telling students things.
So I think that that’s a really nice distinction between co-intelligence, and thought partner, and doing the work for you. It certainly can do some work for you. There’s tedious work that the A.I. does really well. But there’s also this more brilliant piece of making us better people that I think is, at least in the current state of A.I., a really awesome and amazing thing.
We’ve already talked a bit about — Gemini is helpful, and ChatGPT-4 is neutral, and Claude is a bit warmer. But you urge people to go much further than that. You say to give your A.I. a personality. Tell it who to be. So what do you mean by that, and why?
So this is actually almost more of a technical trick, even though it sounds like a social trick. When you think about what A.I.s have done, they’ve trained on the collective corpus of human knowledge. And they know a lot of things. And they’re also probability machines. So when you ask for an answer, you’re going to get the most probable answer, sort of, with some variation in it. And that answer is going to be very neutral. If you’re using GPT-4, it’ll probably talk about a rich tapestry a lot. It loves to talk about rich tapestries. If you ask it to code something artistic, it’ll do a fractal. It does very normal, central A.I. things. So part of your job is to get the A.I. to go to parts of this possibility space where the information is more specific to you, more unique, more interesting, more likely to spark something in you yourself. And you do that by giving it context, so it doesn’t just give you an average answer. It gives you something that’s specialized for you. The easiest way to provide context is a persona. You are blank. You are an expert at interviewing, and you answer in a warm, friendly style. Help me come up with interview questions. It won’t be miraculous in the same way that we were talking about before. If you say you’re Bill Gates, it doesn’t become Bill Gates. But that changes the context of how it answers you. It changes the kinds of probabilities it’s pulling from and results in much more customized and better results.
OK, but this is weirder, I think, than you’re quite letting on here. So something you turned me on to is there’s research showing that the A.I. is going to perform better on various tasks, and differently on them, depending on the personality. So there’s a study that gives a bunch of different personality prompts to one of the systems, and then tries to get it to answer 50 math questions. And the way it got the best performance was to tell the A.I. it was a Starfleet commander who was charting a course through turbulence to the center of an anomaly.
But then, when it wanted to get the best answer on 100 math questions, what worked best was putting it in a thriller, where the clock was ticking down. I mean, what the hell is that about?
“What the hell” is a good question. And we’re just scratching the surface, right? There’s a nice study actually showing that if you emotionally manipulate the A.I., you get better math results. So telling it your job depends on it gets you better results. Tipping, especially $20 or $100 — saying, I’m about to tip you if you do well, seems to work pretty well. It performs slightly worse in December than May, and we think it’s because it has internalized the idea of winter break.
I’m sorry, what?
Well, we don’t know for sure, but —
I’m holding you up here.
People have found the A.I. seems to be more accurate in May, and the going theory is that it has read enough of the internet to think that it might possibly be on vacation in December?
So it produces more work with the same prompts, more output, in May than it does in December. I did a little experiment where I would show it pictures of outside. And I’m like, look at how nice it is outside? Let’s get to work. But yes, the going theory is that it has internalized the idea of winter break and therefore is lazier in December.
I want to just note to people that when ChatGPT came out last year, and we did our first set of episodes on this, the thing I told you was this was going to be a very weird world. What’s frustrating about that is that — I guess I can see the logic of why that might be. Also, it sounds probably completely wrong, but also, I’m certain we will never know. There’s no way to go into the thing and figure that out.
But it would have genuinely never occurred to me before this second that there would be a temporal difference in the amount of work that GPT-4 would do on a question held constant over time. Like, that would have never occurred to me as something that might change at all.
And I think that that is, in some ways, both — as you said, the deep weirdness of these systems. But also, there’s actually downside risks to this. So we know, for example, there is an early paper from Anthropic on sandbagging, that if you ask the A.I. dumber questions, it would get you less accurate answers. And we don’t know the ways in which your grammar or the way you approach the A.I. — we know the amount of spaces you put gets different answers.
So it is very hard, because what it’s basically doing is math on everything you’ve written to figure out what would come next. And the fact that what comes next feels insightful and humane and original doesn’t change that that’s what the math that’s doing is. So part of what I actually advise people to do is just not worry about it so much, because I think then it becomes magic spells that we’re incanting for the A.I. Like, I will pay you $20, you are wonderful at this. It is summer. Blue is your favorite color. Sam Altman loves you. And you go insane.
So acting with it conversationally tends to be the best approach. And personas and contexts help, but as soon as you start evoking spells, I think we kind of cross over the line into, “who knows what’s happening here?”
Well, I’m interested in the personas, although I just — I really find this part of the conversation interesting and strange. But I’m interested in the personalities you can give the A.I. for a different reason. I prompted you around this research on how a personality changes the accuracy rate of an A.I. But a lot of the reason to give it a personality, to answer you like it is Starfleet Commander, is because you have to listen to the A.I. You are in relationship with it.
And different personas will be more or less hearable by you, interesting to you. So you have a piece on your newsletter which is about how you used the A.I. to critique your book. And one of the things you say in there, and give some examples of, is you had to do so in the voice of Ozymandias because you just found that to be more fun. And you could hear that a little bit more easily.
So could you talk about that dimension of it, too, making the A.I. not just prompting you to be more accurate, but giving it a personality to be more interesting to you?
The great power of A.I. is as a kind of companion. It wants to make you happy. It wants to have a conversation. And that can be overt or covert.
So, to me, actively shaping what I want the A.I. to act like, telling it to be friendly or telling it to be pompous, is entertaining, right? But also, it does change the way I interact with it. When it has a pompous voice, I don’t take the criticism as seriously. So I can think about that kind of approach. I could get pure praise out of it, too, if I wanted to do it that way.
But the other factor that’s also super weird, while we’re on the way of super weird A.I. things, is that if you don’t do that, it’s going to still figure something out about you. It is a cold reader. And I think a lot about the very famous piece by Kevin Roose, the New York Times technology reporter, about Bing about a year ago, when Bing, which was GPT-4 powered, came out and had this personality of Sydney.
And Kevin has this very long description that got published in The New York Times about how Sydney basically threatened him, and suggested he leaves his wife, and very dramatic, kind of very unsettling interaction. And I was working with — I didn’t have anything quite that intense, but I got into arguments with Sydney around the same time, where it would — when I asked her to do work for me, it said you should do the work yourself. Otherwise, it’s dishonest. And it kept accusing me of plagiarism, which felt really unusual.
But the reason why Kevin ended up in that situation is the A.I. knows all kinds of human interactions and wants to slot into a story with you.
So a great story is jealous lover who’s gone a little bit insane, and the man who won’t leave his wife, or student and teacher, or two debaters arguing with each other, or grand enemies. And the A.I. wants to do that with you. So if you’re not explicit, it’s going to try and find a dialogue.
And I’ve noticed, for example, that if I talk to the A.I. and I imply that we’re having a debate, it will never agree with me. If I imply that I’m a teacher and it’s a student, even as much as saying I’m a professor, it is much more pliable.
So part of why I like assigning a personality is to have an explicit personality you’re operating with, so it’s not trying to cold read and guess what personality you’re looking for.
Kevin and I have talked a lot about that conversation with Sydney. And one of the things I always found fascinating about it is, to me, it revealed an incredibly subtle level of read by Sydney Bing, which is, what was really happening there? When you say the A.I. wants to make you happy, it has to read on some level what it is you’re really looking for, over time.
And what was Kevin? What is Kevin? Kevin is a journalist. And Kevin was nudging and pushing that system to try to do something that would be a great story. And it did that. It understood, on some level — again, the anthropomorphizing language there. But it realized that Kevin wanted some kind of intense interaction. And it gave him, like, the greatest A.I. story anybody has ever been given. I mean, an A.I. story that we are still talking about a year later, an A.I. story that changed the way A.I.s were built, at least for a while.
And people often talked about what Sydney was revealing about itself. But to me, what was always so unbelievably impressive about that was its ability to read the person, and its ability to make itself into the thing, the personality, the person was trying to call forth.
And now, I think we’re more practiced at doing this much more directly. But I think a lot of people have their moment of sleeplessness here. That was my Rubicon on this. I didn’t know something after that I didn’t know before it in terms of capabilities.
But when I read that, I thought that the level of — interpersonal isn’t the right word, but the level of subtlety it was able to display in terms of giving a person what it wanted, without doing so explicitly — right, without saying, “we’re playing this game now,” was really quite remarkable.
It’s a mirror. I mean, it’s trained on our stuff. And one of the revealing things about that, that I think we should be paying a lot more attention to, is the fact that because it’s so good at this, right now, none of the frontier A.I. models with the possible exception of Inflection’s Pi, which has been basically acquired in large part by Microsoft now, were built to optimize around keeping us in a relationship with the A.I. They just accidentally do that. There are other A.I. models that aren’t as good that have been focused on this, but that has been something explicit from the frontier models they’ve been avoiding till now. Claude sort of breaches that line a little bit, which is part of why I think it’s engaging. But I worry about the same kind of mechanism that inevitably reined in social media, which is, you can make a system more addictive and interesting. And because it’s such a good cold reader, you could tune A.I. to make you want to talk to it more.
It’s very hands off and sort of standoffish right now. But if you use the voice system in ChatGPT-4 on your phone, where you’re having a conversation, there’s moments where you’re like, oh, you feel like you’re talking to a person. You have to remind yourself. So to me, that persona aspect is both its great strength, but also one of the things I’m most worried about that isn’t a sort of future science fiction scenario.
I want to hold here for a minute, because we’ve been talking about how to use frontier models, I think implicitly talking about how to use A.I. for work. But the way that a lot of people are using it is using these other companies that are explicitly building for relationships. So I’ve had people at one of the big companies tell me that if we wanted to tune our system relationally, if we wanted to tune it to be your friend, your lover, your partner, your therapist, like, we could blow the doors off that. And we’re just not sure it’s ethical.
But there are a bunch of people who have tens of millions of users, Replika, Character.AI, which are doing this. And I tried to use Replika about six, eight months ago. And honestly, I found it very boring. They had recently lobotomized it because people were getting too erotic with their Replikants. But I just couldn’t get into it. I’m probably too old to have A.I. friends, in the way that my parents were probably too old to get really in to talking to people on AOL Instant Messenger.
But I have a five-year-old, and I have a two-year-old. And by the time my five-year-old is 10 and my two-year-old is 7, they’re not necessarily going to have the weirdness I’m going to have about having A.I. friends. And I don’t think we even have any way to think about this.
I think that is an absolute near-term certainty, and sort of an unstoppable one, that we are going to have A.I. relationships in a broader sense. And I think the question is, just like we’ve just been learning — I mean, we’re doing a lot of social experiments at scale we’ve never done before in the last couple of decades, right? Turns out social media brings out entirely different things in humans that we weren’t expecting. And we’re still writing papers about echo chambers and tribalism and facts, and what we agree or disagree with. We’re about to have another wave of this. And we have very little research. And you could make a plausible story up, that what’ll happen is it’ll help mental health in a lot of ways for people, and then there’ll be more social outside, that there might be a rejection of this kind of thing.
I don’t know what’ll happen. But I do think that we can expect with absolute certainty that you will have A.I.s that are more interesting to talk to, and fool you into thinking, even if you know better, that they care about you in a way that is incredibly appealing. And that will happen very soon. And I don’t know how we’re going to adjust to it. But it seems inevitable, as you said.
I was worried we were getting off track in the conversation, but I realized we were actually getting deeper on the track I was trying to take us down.
We were talking about giving the A.I. personality, right — telling Claude 3, hey, I need you to act as a sardonic podcast editor, and then Claude 3’s whole persona changes. But when you talk about building your A.I. on Kindroid, on Character, on Replika — so I just created a Kindroid one the other day. And Kindroid is kind of interesting, because its basic selling point is we’ve taken the guardrails largely off. We are trying to make something that is not lobotomized, that is not perfectly safe for work. And so the personality can be quite unrestrained. So I was interested in what that would be like.
But the key thing you have to do at the beginning of that is tell the system what its personality is. So you can pick from a couple that are preset, but I wrote a long one myself — you know, you live in California. You’re a therapist. You like all these different things. You have a highly intellectual style of communicating. You’re extremely warm, but you like ironic humor. You don’t like small talk. You don’t like to say things that are boring or generic. You don’t use a lot of emoticons and emojis. And so now it talks to me the way people I talk to talk.
And the thing I want to bring this back to is that one of the things that requires you to know is what kind of personalities work with you, for you to know yourself and your preferences a little bit more deeply.
I think that’s a temporary state of affairs, like extremely temporary. I think a GPT-4 class model — we actually already know this. They can guess your intent quite well. And I think that this is a way of giving you a sense of agency or control in the short term. I don’t think you’re going to need to know yourself at all. And I think you wouldn’t right now if any of the GPT-4 class models allowed themselves to be used in this way, without guardrails, which they don’t, I think you would already find it’s just going to have a conversation with you and morph into what you want.
I think that for better or worse, the “insight” in these systems is good enough that way. It’s sort of why I also don’t worry so much about prompt crafting in the long term, to go back to the other issue we were talking about, because I think that they will work on intent. And there’s a lot of evidence that they’re good at guessing intent. So I like this period, because I think it does value self reflection. And our interaction with the A.I. is somewhat intentional because we can watch this interaction take place.
But I think there’s a reason why some of the worry you hear out of the labs is about superhuman levels of manipulation. There’s a reason why the whistleblower from Google was all about that — sort of fell for the chat bot, and that’s why they felt it was alive. Like, I think we’re deeply trickable in this way. And A.I. is really good at figuring out what we want without us being explicit.
So that’s a little bit chilling, but I’m nevertheless going to stay in this world we’re in, because I think we’re going to be in it for at least a little while longer, where you do have to do all this prompt engineering. What is a prompt, first? And what is prompt engineering?
So a prompt is — technically, it is the sentence, the command you’re putting into the A.I. What it really is is the beginning part of the A.I.s text that it’s processing. And then it’s just going to keep adding more words or tokens to the end of that reply, until it’s done. So a prompt is the command you’re giving the A.I. But in reality, it’s sort of a seed from which the A.I. builds.
And when you prompt engineer, what are some ways to do that? Maybe one to begin with, because it seems to work really well, is chain of thought.
Just to take a step back, A.I. prompting remains super weird. Again, strange to have a system where the companies making the systems are writing papers as they’re discovering how to use the systems, because nobody knows how to make them work better yet. And we found massive differences in our experiments on prompt types. So for example, we were able to get the A.I. to generate much more diverse ideas by using this chain of thought approach, which we’ll talk about.
But also, it turned out to generate a lot better ideas if you told it it was Steve Jobs than if you told it it was Madame Curie. And we don’t know why. So there’s all kinds of subtleties here. But the idea, basically, of chain of thought, that seems to work well in almost all cases, is that you’re going to have the A.I. work step by step through a problem. First, outline the problem, you know, the essay you’re going to write. Second, give me the first line of each paragraph. Third, go back and write the entire thing. Fourth, check it and make improvements.
And what that does is — because the A.I. has no internal monologue, it’s not thinking. When the A.I. isn’t writing something, there’s no thought process. All it can do is produce the next token, the next word or set of words. And it just keeps doing that step by step. Because there’s no internal monologue, this in some ways forces a monologue out in the paper. So it lets the A.I. think by writing before it produces the final result. And that’s one of the reasons why chain of thought works really well.
So just step-by-step instructions is a good first effort.
Then you get an answer, and then what?
And then — what you do in a conversational approach is you go back and forth. If you want work output, what you’re going to do is treat it like it is an intern who just turned in some work to you. Actually, could you punch up paragraph two a little bit? I don’t like the example in paragraph one. Could you make it a little more creative, give me a couple of variations? That’s a conversational approach trying to get work done.
If you’re trying to play, you just run from there and see what happens. You can always go back, especially with a model like GPT-4, to an earlier answer, and just pick up from there if your heads off in the wrong direction.
So I want to offer an example of how this back and forth can work. So we asked Claude 3 about prompt engineering, about what we’re talking about here. And the way it described it to us is, quote, “It’s a shift from the traditional paradigm of human-computer interaction, where we input explicit commands and the machine executes them in a straightforward way, to a more open ended, collaborative dialogue, where the human and the A.I. are jointly shaping the creative process,” end quote. And that’s pretty good, I think. That’s interesting. It’s worth talking about. I like that idea that it’s a more collaborative dialogue. But that’s also boring, right? Even as I was reading it, it’s a mouthful. It’s wordy. So I kind of went back and forth with it a few times. And I was saying, listen, you’re a podcast editor. You’re concise, but also then I gave it a couple examples of how I punched up questions in the document, right? This is where the question began. Here’s where it ended. And then I said, try again, and try again, and try again, and make it shorter. And make it more concise.
And I got this: quote, “OK, so I was talking to this A.I., Claude, about prompt engineering, you know, this whole art of crafting prompts to get the best out of these A.I. models. And it said something that really struck me. It called prompt engineering a new meta skill that we’re all picking up as we play with A.I., kind of like learning a new language to collaborate with it instead of just bossing it around. What do you think, is prompt engineering the new must have skill?” End Claude.
And that second one, I have to say, is pretty damn good. That really nailed the way I speak in questions. And it gets it at this way where if you’re willing to go back and forth, it does learn how to echo you.
So I am at a loss about when you went to Claude and when it was you, to be honest. So I was ready to answer at like two points along the way, so that was pretty good from my perspective, sitting here, talking to you. That felt interesting, and felt like the conversation we’ve been having. And I think there’s a couple of interesting lessons there.
The first, by the way, of — interestingly, you asked A.I. about one of its weakest points, which is about A.I. And everybody does this, but because its knowledge window doesn’t include that much stuff about A.I., it actually is pretty weak in terms of knowing how to do good prompting, or what a prompt is, or what A.I.s do well. But you did a good job with that. And I love that you went back and forth and shaped it. One of the techniques you used to shape it, by the way, was called few-shot, which is giving an example. So the two most powerful techniques are chain of thought, which we just talked about, and few-shot, giving it examples. Those are both well supported in the literature. And then, I’d add personas. So we’ve talked about, I think, the basics of prompt crafting here overall. And I think that the question was pretty good.
But you keep wanting to not talk about the future. And I totally get that. But I think when we’re talking about learning something, where there is a lag, where we talk about policy — should prompt crafting be taught in schools? I think it matters to think six months ahead. And again, I don’t think a single person in the A.I. labs I’ve ever talked to thinks prompt crafting for most people is going to be a vital skill, because the A.I. will pick up on the intent of what you want much better.
One of the things I realized trying to spend more time with the A.I. is that you really have to commit to this process. You have to go back and forth with it a lot. If you do, you can get really good questions, like the one I just did — or, I think, really good outcomes. But it does take time.
And I guess in a weird way it’s like the same problem of any relationship, that it’s actually hard to state your needs clearly and consistently and repeatedly, sometimes because you have not even articulated them in words yourself. At least the A.I., I guess, doesn’t get mad at you for it.
But I’m curious if you have advice, either at a practical level or principles level, about how to communicate to these systems what you want from them.
One set of techniques that work quite well is to speed run to where you are in the conversation. So you can actually pick up an older conversation where you got the A.I.‘s mindset where you want and work from there. You can even copy and paste that into a new window. You can ask the A.I. to summarize where you got in that previous conversation, and the tone the A.I. was taking, and then when you give a new instruction say the interaction I like to have with you is this, so have it solve the problem for you by having it summarize the tone that you happen to like at the end.
So there are a bunch of ways of building on your work as you start to go forward, so you’re not starting from scratch every time. And I think you’ll start to get shorthands that get you to that right kind of space. For me, there are chats that I pick up on. And actually, I assign these to my students too. I have some ongoing conversations that they’re supposed to have with the A.I., but then there’s a lot of interactions they’re supposed to have that are one off.
So you start to divide the work into, this is a work task. And we’re going to handle this in a single chat conversation. And then I’m going to go back to this long standing discussion when I want to pick it up, and it’ll have a completely different tone. So I think in some ways, you don’t necessarily want convergence among all your A.I. threads. You kind of want them to be different from each other.
You did mention something important there, because they’re already getting much bigger in terms of how much information they can hold. Like, the earlier generations could barely hold a significant chat. Now, Claude 3 can functionally hold a book in its memory. And it’s only going to go way, way, way up from here. And I know I’ve been trying to keep us in the present, but this feels to me really quickly like where this is both going and how it’s going to get a lot better.
I mean, you imagine Apple building Siri 2030, and Siri 2030 scanning your photos and your Journal app — Apple now has a Journal app. You have to assume they’re thinking about the information they can get from that, if you allow it — your messages, anything you’re willing to give it access to. It then knows all of this information about you, keeps all of that in its mind as it talks to you and acts on your behalf. I mean, that really seems to me to be where we’re going, an A.I. that you don’t have to keep telling it who to be because it knows you intimately and is able to hold all that knowledge all at the same time constantly.
It’s not even going there. Like, it’s already there. Gemini 1.5 can hold an entire movie, books. But like, it starts to now open up entirely new ways of working. I can show it a video of me working on my computer, just screen capture. And it knows all the tasks I’m doing and suggests ways to help me out. It starts watching over my shoulder and helping me. I put in all of my work that I did prior to getting tenure and said, write my tenure statement. Use exact quotes.
And it was much better than any of the previous models because it wove together stuff, and because everything was its memory. It doesn’t hallucinate as much. All the quotes were real quotes, and not made up. And already, by the way, GPT-4 has been rolling out a model of ChatGPT that has a private note file the A.I. takes — you can access it — but it takes notes on you as it goes along, about things you liked or didn’t like, and reads those again at the beginning of any chat. So this is present, right? It’s not even in the future.
And Google also connects to your Gmail, so it’ll read through your Gmail. I mean, I think this idea of a system that knows you intimately, where you’re picking up a conversation as you go along, is not a 2030 thing. It is a 2024 thing if you let the systems do it.
One thing that feels important to keep in front of mind here is that we do have some control over that. And not only do we have some control over it, but business models and policy are important here. And one thing we know from inside these A.I. shops is these A.I.s already are, but certainly will be, really super persuasive.
And so if the later iterations of the A.I. companions are tuned on the margin to try to encourage you to be also out in the real world, that’s going to matter, versus whether they have a business model that all they want is for you to spend a maximum amount of time talking to your A.I. companion, whether you ever have a friend who is flesh and blood be damned. And so that’s an actual choice, right? That’s going to be a programming decision. And I worry about what happens if we leave that all up to the companies, right? At some point, there’s a lot of venture capital money in here right now. At some point, the venture capital runs out. At some point, people need to make big profits. At some point, they’re in competition with other players who need to make profits. And that’s when things — you get into what Cory Doctorow calls the “enshitification” cycle, where things that were once adding a lot of value to the user begin extracting a lot of value to the user.
These systems, because of how they can be tuned, can lead to a lot of different outcomes. But I think we’re going to have to be much more comfortable than we’ve been in the past deciding what we think is a socially valuable use and what we think is a socially destructive use.
I absolutely agree. I think that we have agency here. We have agency in how we operate this in businesses, and whether we use this in ways that encourage human flourishing and employees, or are brutal to them. And we have agency over how this works socially. And I think we abrogated that responsibility with social media, and that is an example. Not to be bad news, because I generally have a lot of mixed optimism and pessimism about parts of A.I., but the bad news piece is there are open source models out there that are quite good.
The internet is pretty open. We would have to make some pretty strong choices to kill A.I. chat bots as an option. We certainly can restrict the large American companies from doing that, but a Llama 2 or Llama 3 is going to be publicly available and very good. There’s a lot of open source models. So the question also is how effective any regulation will be, which doesn’t mean we shouldn’t regulate it.
But there’s also going to need to be some social decisions being made about how to use these things well as a society that are going to have to go beyond just the legal piece, or companies voluntarily complying.
I see a lot of reasons to be worried about the open source models. And people talk about things like bioweapons and all that. But for some of the harms I’m talking about here, if you want to make money off of American kids, we can regulate you. So sometimes I feel like we almost, like, give up the fight before it begins. But in terms of what a lot of people are going to use, if you want to be having credit card payments processed by a major processor, then you have to follow the rules.
I mean, individual people or small groups can do a lot of weird things with an open source model, so that doesn’t negate every harm. But if you’re making a lot of money, then you have relationships we can regulate.
I couldn’t agree more. And I don’t think there’s any reason to give up hope on regulation. I think that we can mitigate. And I think part of our job, though, is also not just to mitigate the harms, but to guide towards the positive viewpoints, right? So what I worry about is that the incentive for profit making will push for A.I. that acts informally as your therapist or your friend, while our worries about experimentation, which are completely valid, are slowing down our ability to do experiments to find out ways to do this right. And I think it’s really important to have positive examples, too. I want to point to the A.I. systems acting ethically as your friend or companion, and figure out what that is, so there’s a positive model to look for. So I’m not just — this is not to denigrate the role of regulation, which I think is actually going to be important here, and self regulation, and rapid response from government, but also the companion problem of, “we need to make some sort of decisions about what are the paragons of this, what is acceptable as a society?”
So I want to talk a bit about another downside here, and this one more in the mainstream of our conversation, which is on the human mind, on creativity. So a lot of the work A.I. is good at automating is work that is genuinely annoying, time consuming, laborious, but often plays an important role in the creative process. So I can tell you that writing a first draft is hard, and that work on the draft is where the hard thinking happens.
And it’s hard because of that thinking. And the more we outsource drafting to A.I., which I think it is fair to say is a way a lot of people intuitively use it — definitely, a lot of students want to use it that way — the fewer of those insights we’re going to have on those drafts. Look, I love editors. I am an editor in one respect. But I can tell you, you make more creative breakthroughs as a writer than an editor. The space for creative breakthrough is much more narrow once you get to editing.
And I do worry that A.I. is going to make us all much more like editors than like writers.
I think the idea of struggle is actually a core one in many things. I’m an educator. And one thing that keeps coming out in the research is that there is a strong disconnect between what students think they’re learning and when they learn. So there was a great controlled experiment at Harvard in intro science classes, where students either went to a pretty entertaining set of lectures, or else they were forced to do active learning, where they actually did the work in class.
The active learning group reported being unhappier and not learning as much, but did much better on tests, because when you’re confronted with what you don’t know, and you have to struggle, when you feel, like, bad, you actually make much more progress than if someone spoon feeds you an entertaining answer. And I think this is a legitimate worry that I have. And I think that there’s going to have to be some disciplined approach to writing as well, like, I don’t use the A.I.
Not just because, by the way, it makes the work easier, but also because you mentally anchor on the A.I.‘s answer. And in some ways, the most dangerous A.I. application, in my mind, is the fact that you have these easy co-pilots in Word and Google Docs, because any writer knows about the tyranny of the blank page, about staring at a blank page and not knowing what to do next, and the struggle of filling that up. And when you have a button that produces really good words for you, on demand, you’re just going to do that. And it’s going to anchor your writing. We can teach people about the value of productive struggle, but I think that during the school years, we have to teach people the value of writing — not just assign an essay and assume that the essay does something magical, but be very intentional about the writing process and how we teach people about how to do that, because I do think the temptation of what I call “the button” is going to be there otherwise, for everybody.
But I worry this stretches, I mean, way beyond writing. So the other place I worry about this, or one of the other places I worry about this a lot, is summarizing. And I mean, this goes way back. When I was in school, you could buy Sparknotes. And they were these little, like, pamphlet sized descriptions of what’s going on in “War and Peace” or what’s going on in “East of Eden.”
And reading the Sparknotes often would be enough to fake your way through the test, but it would not have any chance, like, not a chance, of changing you, of shifting you, of giving you the ideas and insights that reading “Crime and Punishment” or “East of Eden” would do.
And one thing I see a lot of people doing is using A.I. for summary. And one of the ways it’s clearly going to get used in organizations is for summary — summarize my email, and so on.
And here too, one of the things that I think may be a real vulnerability we have, as we move into this era — my view is that the way we think about learning and insights is usually wrong. I mean, you were saying a second ago we can teach a better way. But I think we’re doing a crap job of it now, because I think people believe that — it’s sort of what I call the matrix theory of the human mind, if you could just jack the information into the back of your head and download it, you’re there.
But what matters about reading a book, and I see this all the time preparing for this show, is the time you spend in the book, where over time, like, new insights and associations for you begin to shake loose. And so I worry it’s coming into an efficiency-obsessed educational and intellectual culture, where people have been imagining forever, what if we could do all this without having to spend any of the time on it? But actually, there’s something important in the time.
There’s something important in the time with a blank page, with the hard book. And I don’t think we lionize intellectual struggle. In some ways, I think we lionize the people for whom it does not seem like a struggle, the people who seem to just glide through and be able to absorb the thing instantly, the prodigies. And I don’t know. When I think about my kids, when I think about the kind of attention and creativity I want them to have, this is one of the things that scares me most, because kids don’t like doing hard things a lot of the time.
And it’s going to be very hard to keep people from using these systems in this way.
So I don’t mean to push back too much on this.
No, please, push back a lot.
But I think you’re right.
Imagine we’re debating and you are a snarky. A.I. [LAUGHS]
Fair enough. With that prompt —
With that prompt engineering.
— yeah, I mean, I think that this is the eternal thing about looking back on the next generation, we worry about technology ruining them. I think this makes ruining easier. But as somebody who teaches at universities, like, lots of people are summarizing. Like, I think those of us who enjoy intellectual struggle are always thinking everybody else is going through the same intellectual struggle when they do work. And they’re doing it about their own thing. They may or may not care the same way.
So this makes it easier, but before A.I., there were — best estimates from the U.K. that I could find, 20,000 people in Kenya whose full time job was writing essays for students in the U.S. and U.K. People have been cheating and Sparknoting and everything for a long time. And I think that what people will have to learn is that this tool is a valuable co-intelligence, but is not a replacement for your own struggle.
And the people who found shortcuts will keep finding shortcuts. Temptation may loom larger, but I can’t imagine that — my son is in high school, doesn’t like to use A.I. for anything. And he just doesn’t find it valuable for the way he’s thinking about stuff. I think we will come to that kind of accommodation. I’m actually more worried about what happens inside organizations than I am worried about human thought, because I don’t think we’re going to atrophy as much as we think. I think there’s a view that every technology will destroy our ability to think.
And I think we just choose how to use it or not. Like, even if it’s great at insights, people who like thinking like thinking.
Well, let me take this from another angle. One of the things that I’m a little obsessed with is the way the internet did not increase either domestic or global productivity for any real length of time. So I mean, it’s a very famous line. You can see the IT revolution anywhere but in the productivity statistics. And then you do get, in the ‘90s, a bump in productivity that then peters out in the 2000s.
And if I had told you what the internet would be, like, I mean everybody, everywhere would be connected to each other. You could collaborate with anybody, anywhere, instantly. You could teleconference. You would have access to, functionally, the sum total of human knowledge in your pocket at all times. I mean, all of these things that would have been genuine sci-fi, you would have thought would have been — led to a kind of intellectual utopia. And it kind of doesn’t do that much, if you look at the statistics.
You don’t see a huge step change. And my view — and I’d be curious for your thoughts on this, because I know this is the area you study in — my view is it everything we said was good happened. I mean, as a journalist, Google and things like that make me so much more productive. It’s not that it didn’t give us the gift. It’s that it also had a cost — distraction, checking your email endlessly, being overwhelmed with the amount of stuff coming into you, the sort of endless communication task list, the amount of internal communications and organizations, now with Slack and everything else.
And so some of the time that was given to us back was also taken back. And I see a lot of dynamics like this that could play out with A.I. — I wouldn’t even just say if we’re not careful, I just think they will play out and already are. I mean, the internet is already filling with mediocre crap generated by A.I. There is going to be a lot of destructive potential, right? You are going to have your sex bot in your pocket, right? There’s a million things — and not just that, but inside organizations, there’s going to be people padding out what would have been something small, trying to make it look more impressive by using the A.I. to make something bigger. And then, you’re going to use the A.I. to summarize it back down. The A.I. researcher, Jonathan Frankel, described this to me as, like, the boring apocalypse version of A.I., where you’re just endlessly inflating and then summarizing, and then inflating and then summarizing the volume of content between different A.I.
My ChatGPT is making my presentation bigger and more impressive, and your ChatGPT is trying to summarize it down to bullet points for you. And I’m not saying this has to happen. But I am saying that it would require a level of organizational and cultural vigilance to stop, that nothing in the internet era suggests to me that we have.
So I think there’s a lot there to chew on. And I also have spent a lot of time trying to think about why the internet didn’t work as well. I was an early Wikipedia administrator.
Thank you for your service.
[LAUGHS] Yeah, it was very scarring. But I think a lot about this. And I think A.I. is different. I don’t know if it’s different in a positive way. And I think we talked about some of the negative ways it might be different. And I think it’s going to be many things at once, happening quite quickly. So I think the information environment’s going to be filled up with crap. We will not be able to tell the difference between true and false anymore. It will be an accelerant on all the kinds of problems that we have there.
On the other hand, it is an interactive technology that adapts to you. From an education perspective, I have lived through the entire internet will change education piece. I have MOOCs, massive online courses, with — quarter million people have taken them. And in the end, you’re just watching a bunch of videos. Like, that doesn’t change education.
But I can have an A.I. tutor that actually can teach you — and we’re seeing it happen — and adapt to you at your level of education, and your knowledge base, and explain things to you. But not just explain, elicit answers from you, interactively, in a way that actually learns things.
The thing that makes A.I. possibly great is that it’s so very human, so it interacts with our human systems in a way that the internet did not. We built human systems on top of it, but A.I. is very human. It deals with human forms and human issues and our human bureaucracy very well. And that gives me some hope that even though there’s going to be lots of downsides, that the upsides of productivity and things like that are real. Part of the problem with the internet is we had to digitize everything. We had to build systems that would make our offline world work with our online world. And we’re still doing that. If you go to business schools, digitizing is still a big deal 30 years on from early internet access. A.I. makes this happen much quicker because it works with us. So I’m a little more hopeful than you are about that, but I also think that the downside risks are truly real and hard to anticipate.
Somebody was just pointing out that Facebook is now 100 percent filled with algorithmically generated images that look like their actual grandparents, making things who are saying, like, what do you think of my work? Because that’s a great way to get engagement. And the other grandparents in there have no idea it’s A.I. generated.
Things are about to get very, very weird in all the ways that we talked about, but that doesn’t mean the positives can’t be there as well.
I think that is a good place to end. So always our final question, what are three books you’d recommend to the audience?
OK, so the books I’ve been thinking about are not all fun, but I think they’re all interesting. One of them is “The Rise and Fall of American Growth,” which is — it’s two things. It’s an argument about why we will never have the kind of growth that we did in the first part of the Industrial Revolution again, but I think that’s less interesting than the first half of the book, which is literally how the world changed between 1870 or 1890 and 1940, versus 1940 and 1990, or 2000.
And the transformation of the world that happened there — in 1890, no one had plumbing in the U.S.. And the average woman was carrying tons of water every day. And you had no news, and everything was local, and everyone’s bored all the time — to 1940, where the world looks a lot like today’s world, was fascinating. And I think it gives you a sense of what it’s like to be inside a technological singularity, and I think worth reading for that reason — or at least the first half.
The second book I’d recommend is “The Knowledge,” by Dartnell, which is a really interesting book. It is ostensibly almost a survival guide, but it is how to rebuild industrial civilization from the ground up, if we were to collapse. And I don’t recommend it as a survivalist. I recommend it because it is fascinating to see how complex our world is, and how many interrelated pieces we’ve managed to build up as a society. And in some ways, it gives me a lot of hope to think about how all of these interconnections work.
And then the third one is science fiction, and I was debating — I read a lot of science fiction, and there’s a lot of interesting A.I.s in science fiction. Everyone talks about — who’s in the science fiction world — Iain Banks, who wrote about the Culture, which is really interesting, about what it’s like to live beside super intelligent A.I. Vernor Vinge just died yesterday, when we were recording this, and wrote these amazing books about — he coined the term singularity.
But I want to recommend a much more depressing book that’s available for free, which is Peter Watts’s “Blindsight.” And it is not a fun book, but it is a fascinating thriller set on an interstellar mission to visit an alien race. And it’s essentially a book about sentience, and it’s a book about the difference between consciousness and sentience, and about intelligence and the different ways of perceiving the world in a setting where that is the sort of centerpiece of the thriller. And I think in a world where we have machines that might be intelligent without being sentient, it is a relevant, if kind of chilling, read.
Ethan Mollick, your book is called “Co-Intelligence.” Your Substack is One Useful Thing. Thank you very much.
This episode of “The Ezra Klein Show” was produced by Kristin Lin. Fact checking by Michelle Harris. Our senior engineer is Jeff Geld with additional mixing from Efim Shapiro. Our senior editor is Claire Gordon. The show’s production team also includes Annie Galvin and Rollin Hu. Original music by Isaac Jones. Audience strategy by Kristina Samulewski and Shannon Busta. The executive producer of New York Times Opinion Audio is Annie-Rose Strasser, and special thanks to Sonia Herrero.
EZRA KLEIN: From New York Times Opinion, this is “The Ezra Klein Show.”
ETHAN MOLLICK: Thanks for having me.
EZRA KLEIN: So let’s assume I’m interested in A.I. And I tried ChatGPT a bunch of times, and I was suitably impressed and weirded out for a minute. And so I know the technology is powerful. I’ve heard all these predictions about how it will take everything over, or become part of everything we do. But I don’t actually see how it fits into my life, really, at all. What am I missing?
ETHAN MOLLICK: So you’re not alone. This is actually very common. And I think part of the reason is that the way ChatGPT works isn’t really set up for you to understand how powerful it is. You really do need to use the paid version, they are significantly smarter. And you can almost think of this — like, GPT-3, which was — nobody really paid attention to when it came out, before ChatGPT, was about as good as a sixth grader at writing. GPT-3.5, the free version of ChatGPT, is about as good as a high school, or maybe even a college freshman or sophomore.
EZRA KLEIN: When you say, bring it to every table you’re at, one, that sounds like a big pain, because now I’ve got to add another step of talking to the computer constantly. But two, it’s just not obvious to me what that would look like. So what does it look like? What does it look like for you, or what does it look like for others — that you feel is applicable widely?
ETHAN MOLLICK: So I just finished this book. It’s my third book. I keep writing books, even though I keep forgetting that writing books is really hard. But this was, I think, my best book, but also the most interesting to write. And it was thanks to A.I. And there’s almost no A.I. writing in the book, but I used it continuously. So things that would get in the way of writing — I think I’m a much better writer than A.I. — hopefully, people agree. But there’s a lot of things that get in your way as a writer.
So I would get stuck on a sentence. I couldn’t do a transition. Give me 30 versions of this sentence in radically different styles. There’s 200 different citations. I had the A.I. read through the papers that I read through, write notes on them, and organize them for me. I had the A.I. suggest analogies that might be useful. I had the A.I. act as readers, and in different personas, read through the paper from the perspective of, is there some example I could give that’s better? Is this understandable or not?
And that’s very typical of the kind of way that I would, say, bring it to the table. Use it for everything, and you’ll find its limits and abilities.
EZRA KLEIN: Let me ask you one specific question on that, because I’ve been writing a book. And on some bad days of writing the book, I decided to play around with GPT-4. And of the things that it got me thinking about was the kind of mistake or problem these systems can help you see and the kind they can’t. So they can do a lot of, give me 15 versions of this paragraph, 30 versions of this sentence. And every once in a while, you get a good version or you’ll shake something a little bit loose.
ETHAN MOLLICK: I think that’s a wise point. I think there’s two or three things bundled there. The first of those is A.I. is good, but it’s not as good as you. It is, say, at the 80th percentile of writers based on some results, maybe a little bit higher. In some ways, if it was able to have that burst of insight and to tell you this chapter is wrong, and I’ve thought of a new way of phrasing it, we would be at that sort of mythical AGI level of A.I. as smart as the best human. And it just isn’t yet.
EZRA KLEIN: For most people — right, if you’re just going to pick one model, what would you pick? What do you recommend to people? And second, how do you recommend they access it? Because something going on in the A.I. world is there are a lot of wrappers on these models. So ChatGPT has an app. Claude does not have an app. Obviously, Google has its suite of products. And there are organizations that have created a different spin on somebody else’s A.I. — so Perplexity, which is, I believe, built on GPT-4 now, you can pay for it.
ETHAN MOLLICK: It’s a really good question. I recommend working with one of the models as directly as possible, through the company that creates them. And there’s a few reasons for that. One is you get as close to the unadulterated personality as possible. And second, that’s where features tend to roll out first. So if you like sort of intellectual challenge, I think Claude 3 is the most intellectual of the models, as you said.
EZRA KLEIN: So you say it takes about 10 hours to learn a model. Ten hours is a long time, actually. What are you doing in that 10 hours? What are you figuring out? How did you come to that number? Give me some texture on your 10 hour rule.
ETHAN MOLLICK: So first off, I want to indicate the 10 hours is as arbitrary as 10,000 steps. Like, there’s no scientific basis for it. This is an observation. But it also does move you past the, I poked at this for an evening, and it moves you towards using this in a serious way. I don’t know if 10 hours is the real limit, but it seems to be somewhat transformative. The key is to use it in an area where you have expertise, so you can understand what it’s good or bad at, learn the shape of its capabilities.
EZRA KLEIN: Something that feels to me like a theme of your work is that the way to approach this is not learning a tool. It is building a relationship. Is that fair?
ETHAN MOLLICK: A.I. is built like a tool. It’s software. It’s very clear at this point that it’s an emulation of thought. But because of how it’s built, because of how it’s constructed, it is much more like working with a person than working with a tool. And when we talk about it this way, I almost feel kind of bad, because there’s dangers in building a relationship with a system that is purely artificial, and doesn’t think and have emotions. But honestly, that is the way to go forward. And that is sort of a great sin, anthropomorphization, in the A.I. literature, because it can blind you to the fact that this is software with its own sets of foibles and approaches.
And A.I.s do all of these things. And I find that teachers, managers, even parents, editors, are often better at using these systems, because they’re used to treating this as a person. And they interact with it like a person would, giving feedback. And that helps you. And I think the second piece of that “not tool” piece is that when I talk to OpenAI or Anthropic, they don’t have a hidden instruction manual. There is no list of how you should use this as a writer, or as a marketer, or as an educator.
They don’t even know what the capabilities of these systems are. They’re all sort of being discovered together. And that is also not like a tool. It’s more like a person with capabilities that we don’t fully know yet.
EZRA KLEIN: So you’ve done this with all the big models. You’ve done, I think, much more than this, actually, with all the big models. And one thing you describe feeling is that they don’t just have slightly different strengths and weaknesses, but they have different — for lack of a better term, and to anthropomorphize — personalities, and that the 10 hours in part is about developing an intuition not just for how they work, but kind of how they are and how they talk, the sort of entity you’re dealing with.
ETHAN MOLLICK: It’s important to know the personalities not just as personalities, but because there are tricks. Those are tunable approaches that the system makers decide. So it’s weird to have this — in one hand, don’t anthropomorphize, because you’re being manipulated, because you are. But on the other hand, the only useful way is to anthropomorphize. So keep in mind that you are dealing with the choices of the makers.
GPT-4 feels like a workhorse at this point. It is the most neutral of the approaches. It wants to get stuff done for you. And it will happily do that. It doesn’t have a lot of time for chitchat. And then we’ve got Google’s Bard, which feels like — or Gemini now — which feels like it really, really wants to help. We use this for teaching a lot. And we build these scenarios where the A.I. actually acts like a counterparty in a negotiation.
So you get to practice the negotiation by negotiating with the A.I. And it works incredibly well. I’ve been building simulations for 10 years, can’t imagine what a leap this has been. But when we try and get Google to do that, it keeps leaping in on the part of the students, to try and correct them and say, no, you didn’t really want to say this. You wanted to say that. And I’ll play out the scenario as if it went better. And it really wants to kind of make things good for you.
EZRA KLEIN: You were mentioning a minute ago that what the A.I.s do reflect decisions made by their programmers. They reflect guardrails, what they’re going to let the A.I. say. Very famously, Gemini came out and was very woke. You would ask it to show you a picture of soldiers in Nazi Germany, and it would give you a very multicultural group of soldiers, which is not how that army worked. But that was something that they had built in to try to make more inclusive photography generation.
ETHAN MOLLICK: I think that’s a very important point. And fundamental about A.I. is the idea that we technically know how LLMs work, but we don’t know how they work the way they do, or why they’re as good as they are. They’re really — we don’t understand it. The theories range from everyone — from it’s all fooling us, to they’ve emulated the way humans think because the structure of language is the structure of human thought. So even though they don’t think, they can emulate it. We don’t know the answer.
EZRA KLEIN: One thing people know about using these models is that hallucinations, just making stuff up, is a problem. Has that changed at all as we’ve moved from GPT-3.5 to 4, as we move from Claude 2 to 3. Like, has that become significantly better? And if not, how do you evaluate the trustworthiness of what you’re being told?
ETHAN MOLLICK: So those are a couple of overlapping questions. The first of them is, it getting better over time? So there is a paper in the field of medical citations that indicated that around 80 to 90 percent of citations had an error, were made up with GPT-3.5. That’s the free version of Chat. And that drops for GPT-4.
EZRA KLEIN: But doesn’t this make them unreliable in a very tricky way? 80 percent — you’re, like, it’s always hallucinating. 20 percent, 5 percent, it’s enough that you can easily be lulled into overconfidence. And one of the reasons it’s really tough here is you’re combining something that knows how to seem extremely persuasive and confident — you feed into the A.I. a 90-page paper on functions and characteristics of right wing populism in Europe, as I did last night.
ETHAN MOLLICK: Absolutely, and I think hard to grasp, because we’re used to things like type II errors, where we search for something on the internet and don’t find it. We’re not used to type I errors, where we search for something and get an answer back that’s made up. This is a challenge. And there’s a couple things to think about. One of those is — I advocate the BAH standard, best available human. So is the A.I. more or less accurate than the best human you could consult in that area?
EZRA KLEIN: But it also reflects something interesting about the nature of the systems. You have a quote here that I think is very insightful. You wrote, “the core irony of generative A.I.s is that A.I.s were supposed to be all logic and no imagination. Instead, we get A.I.s that make up information, engage in seemingly emotional discussions, and which are intensely creative.” And that last fact is one that makes many people deeply uncomfortable.
ETHAN MOLLICK: I love the phrase “a calculator that uses words.” I think we have been let down by science fiction, both in the utopias and apocalypses that A.I. might bring, but also, even more directly, in our view of how machines should work. People are constantly frustrated, and give the same kinds of tests to A.I.s over and over again, like doing math, which it doesn’t do very well — they’re getting better at this.
EZRA KLEIN: But we were using those measures five years ago, even though they were bad. That’s a point you make that I think is interesting and slightly unsettling.
ETHAN MOLLICK: Yeah, we never had to differentiate humans from machines before. It was always easy. So the idea that we had to have a scale that worked for people and machines, who had that? We had the Turing test, which everyone knew was a terrible idea. But since no machine could pass it, it was completely fine. So the question is, how do we measure this? This is an entirely separate set of issues. Like, we don’t even have a definition of sentience or consciousness.
EZRA KLEIN: So one of the things I will sometimes do, and did quite recently, is give the A.I. a series of personal documents, emails I wrote to people I love that were very descriptive of a particular moment in my life. And then I will ask the A.I. about them, or ask the A.I. to analyze me off of them.
ETHAN MOLLICK: That makes complete sense. I think the weird expectations — we call it the jagged frontier of A.I., that it’s good at some stuff and bad at other stuff. It’s often unexpected. It can lead to these weird moments of disappointment, followed by elation or surprise. And part of the reason why I advocate for people to use it in their jobs is, it isn’t going to outcompete you at whatever you’re best at. I mean, I cannot imagine it’s going to do a better job prepping someone for an interview than you’re doing.
And that’s not me just — I’m trying to be nice to you because you’re interviewing me, but because you’re a good interviewer. You’re a famous interviewer. It’s not going to be as good as that. Now, there’s questions about how good these systems get that we don’t know, but we’re kind of at a weirdly comfortable spot in A.I., which is, maybe it’s the 80th percentile of many performances. But I talk to Hollywood writers. It’s not close to writing like a Hollywood writer. It’s not close to being as good an analyst.
EZRA KLEIN: But this gets to this question of, what are you doing with it? The A.I.s right now seem much stronger as amplifiers and feedback mechanisms and thought partners for you than they do as something you can really outsource your hard work and your thinking to. And that, to me, is one of the differences between trying to spend more time with these systems — like, when you come into them initially, you’re like, OK, here’s a problem, give me an answer.
ETHAN MOLLICK: And that’s why the book’s called “Co-Intelligence.” For right now, we have a prosthesis for thinking. That’s, like, new in the world. We haven’t had that before — I mean, coffee, but aside from that, not much else. And I think that there’s value in that. I think learning to be partner with this, and where it can get wisdom out of you or not — I was talking to a physics professor at Harvard. And he said, all my best ideas now come from talking to the A.I. And I’m like, well, it doesn’t do physics that well. He’s like, no, but it asks good questions. And I think that there is some value in that kind of interactive piece.
EZRA KLEIN: We’ve already talked a bit about — Gemini is helpful, and ChatGPT-4 is neutral, and Claude is a bit warmer. But you urge people to go much further than that. You say to give your A.I. a personality. Tell it who to be. So what do you mean by that, and why?
ETHAN MOLLICK: So this is actually almost more of a technical trick, even though it sounds like a social trick. When you think about what A.I.s have done, they’ve trained on the collective corpus of human knowledge. And they know a lot of things. And they’re also probability machines. So when you ask for an answer, you’re going to get the most probable answer, sort of, with some variation in it. And that answer is going to be very neutral. If you’re using GPT-4, it’ll probably talk about a rich tapestry a lot.
It loves to talk about rich tapestries. If you ask it to code something artistic, it’ll do a fractal. It does very normal, central A.I. things. So part of your job is to get the A.I. to go to parts of this possibility space where the information is more specific to you, more unique, more interesting, more likely to spark something in you yourself. And you do that by giving it context, so it doesn’t just give you an average answer. It gives you something that’s specialized for you.
The easiest way to provide context is a persona. You are blank. You are an expert at interviewing, and you answer in a warm, friendly style. Help me come up with interview questions. It won’t be miraculous in the same way that we were talking about before. If you say you’re Bill Gates, it doesn’t become Bill Gates. But that changes the context of how it answers you. It changes the kinds of probabilities it’s pulling from and results in much more customized and better results.
EZRA KLEIN: OK, but this is weirder, I think, than you’re quite letting on here. So something you turned me on to is there’s research showing that the A.I. is going to perform better on various tasks, and differently on them, depending on the personality. So there’s a study that gives a bunch of different personality prompts to one of the systems, and then tries to get it to answer 50 math questions. And the way it got the best performance was to tell the A.I. it was a Starfleet commander who was charting a course through turbulence to the center of an anomaly.
ETHAN MOLLICK: “What the hell” is a good question. And we’re just scratching the surface, right? There’s a nice study actually showing that if you emotionally manipulate the A.I., you get better math results. So telling it your job depends on it gets you better results. Tipping, especially $20 or $100 — saying, I’m about to tip you if you do well, seems to work pretty well. It performs slightly worse in December than May, and we think it’s because it has internalized the idea of winter break.
EZRA KLEIN: I’m sorry, what?
ETHAN MOLLICK: Well, we don’t know for sure, but —
EZRA KLEIN: I’m holding you up here.
ETHAN MOLLICK: Yeah.
EZRA KLEIN: People have found the A.I. seems to be more accurate in May, and the going theory is that it has read enough of the internet to think that it might possibly be on vacation in December?
ETHAN MOLLICK: So it produces more work with the same prompts, more output, in May than it does in December. I did a little experiment where I would show it pictures of outside. And I’m like, look at how nice it is outside? Let’s get to work. But yes, the going theory is that it has internalized the idea of winter break and therefore is lazier in December.
EZRA KLEIN: I want to just note to people that when ChatGPT came out last year, and we did our first set of episodes on this, the thing I told you was this was going to be a very weird world. What’s frustrating about that is that — I guess I can see the logic of why that might be. Also, it sounds probably completely wrong, but also, I’m certain we will never know. There’s no way to go into the thing and figure that out.
ETHAN MOLLICK: And I think that that is, in some ways, both — as you said, the deep weirdness of these systems. But also, there’s actually downside risks to this. So we know, for example, there is an early paper from Anthropic on sandbagging, that if you ask the A.I. dumber questions, it would get you less accurate answers. And we don’t know the ways in which your grammar or the way you approach the A.I. — we know the amount of spaces you put gets different answers.
EZRA KLEIN: Well, I’m interested in the personas, although I just — I really find this part of the conversation interesting and strange. But I’m interested in the personalities you can give the A.I. for a different reason. I prompted you around this research on how a personality changes the accuracy rate of an A.I. But a lot of the reason to give it a personality, to answer you like it is Starfleet Commander, is because you have to listen to the A.I. You are in relationship with it.
ETHAN MOLLICK: The great power of A.I. is as a kind of companion. It wants to make you happy. It wants to have a conversation. And that can be overt or covert.
EZRA KLEIN: Kevin and I have talked a lot about that conversation with Sydney. And one of the things I always found fascinating about it is, to me, it revealed an incredibly subtle level of read by Sydney Bing, which is, what was really happening there? When you say the A.I. wants to make you happy, it has to read on some level what it is you’re really looking for, over time.
ETHAN MOLLICK: It’s a mirror. I mean, it’s trained on our stuff. And one of the revealing things about that, that I think we should be paying a lot more attention to, is the fact that because it’s so good at this, right now, none of the frontier A.I. models with the possible exception of Inflection’s Pi, which has been basically acquired in large part by Microsoft now, were built to optimize around keeping us in a relationship with the A.I. They just accidentally do that.
There are other A.I. models that aren’t as good that have been focused on this, but that has been something explicit from the frontier models they’ve been avoiding till now. Claude sort of breaches that line a little bit, which is part of why I think it’s engaging. But I worry about the same kind of mechanism that inevitably reined in social media, which is, you can make a system more addictive and interesting. And because it’s such a good cold reader, you could tune A.I. to make you want to talk to it more.
EZRA KLEIN: I want to hold here for a minute, because we’ve been talking about how to use frontier models, I think implicitly talking about how to use A.I. for work. But the way that a lot of people are using it is using these other companies that are explicitly building for relationships. So I’ve had people at one of the big companies tell me that if we wanted to tune our system relationally, if we wanted to tune it to be your friend, your lover, your partner, your therapist, like, we could blow the doors off that. And we’re just not sure it’s ethical.
ETHAN MOLLICK: I think that is an absolute near-term certainty, and sort of an unstoppable one, that we are going to have A.I. relationships in a broader sense.
And I think the question is, just like we’ve just been learning — I mean, we’re doing a lot of social experiments at scale we’ve never done before in the last couple of decades, right? Turns out social media brings out entirely different things in humans that we weren’t expecting. And we’re still writing papers about echo chambers and tribalism and facts, and what we agree or disagree with.
We’re about to have another wave of this. And we have very little research. And you could make a plausible story up, that what’ll happen is it’ll help mental health in a lot of ways for people, and then there’ll be more social outside, that there might be a rejection of this kind of thing.
EZRA KLEIN: I was worried we were getting off track in the conversation, but I realized we were actually getting deeper on the track I was trying to take us down.
ETHAN MOLLICK: I think that’s a temporary state of affairs, like extremely temporary. I think a GPT-4 class model — we actually already know this. They can guess your intent quite well. And I think that this is a way of giving you a sense of agency or control in the short term. I don’t think you’re going to need to know yourself at all. And I think you wouldn’t right now if any of the GPT-4 class models allowed themselves to be used in this way, without guardrails, which they don’t, I think you would already find it’s just going to have a conversation with you and morph into what you want.
EZRA KLEIN: So that’s a little bit chilling, but I’m nevertheless going to stay in this world we’re in, because I think we’re going to be in it for at least a little while longer, where you do have to do all this prompt engineering. What is a prompt, first? And what is prompt engineering?
ETHAN MOLLICK: So a prompt is — technically, it is the sentence, the command you’re putting into the A.I. What it really is is the beginning part of the A.I.s text that it’s processing. And then it’s just going to keep adding more words or tokens to the end of that reply, until it’s done. So a prompt is the command you’re giving the A.I. But in reality, it’s sort of a seed from which the A.I. builds.
EZRA KLEIN: And when you prompt engineer, what are some ways to do that? Maybe one to begin with, because it seems to work really well, is chain of thought.
ETHAN MOLLICK: Just to take a step back, A.I. prompting remains super weird. Again, strange to have a system where the companies making the systems are writing papers as they’re discovering how to use the systems, because nobody knows how to make them work better yet. And we found massive differences in our experiments on prompt types. So for example, we were able to get the A.I. to generate much more diverse ideas by using this chain of thought approach, which we’ll talk about.
EZRA KLEIN: Then you get an answer, and then what?
ETHAN MOLLICK: And then — what you do in a conversational approach is you go back and forth. If you want work output, what you’re going to do is treat it like it is an intern who just turned in some work to you. Actually, could you punch up paragraph two a little bit? I don’t like the example in paragraph one. Could you make it a little more creative, give me a couple of variations? That’s a conversational approach trying to get work done.
EZRA KLEIN: So I want to offer an example of how this back and forth can work. So we asked Claude 3 about prompt engineering, about what we’re talking about here. And the way it described it to us is, quote, “It’s a shift from the traditional paradigm of human-computer interaction, where we input explicit commands and the machine executes them in a straightforward way, to a more open ended, collaborative dialogue, where the human and the A.I. are jointly shaping the creative process,” end quote.
And that’s pretty good, I think. That’s interesting. It’s worth talking about. I like that idea that it’s a more collaborative dialogue. But that’s also boring, right? Even as I was reading it, it’s a mouthful. It’s wordy. So I kind of went back and forth with it a few times. And I was saying, listen, you’re a podcast editor. You’re concise, but also then I gave it a couple examples of how I punched up questions in the document, right? This is where the question began. Here’s where it ended. And then I said, try again, and try again, and try again, and make it shorter. And make it more concise.
ETHAN MOLLICK: So I am at a loss about when you went to Claude and when it was you, to be honest. So I was ready to answer at like two points along the way, so that was pretty good from my perspective, sitting here, talking to you. That felt interesting, and felt like the conversation we’ve been having. And I think there’s a couple of interesting lessons there.
The first, by the way, of — interestingly, you asked A.I. about one of its weakest points, which is about A.I. And everybody does this, but because its knowledge window doesn’t include that much stuff about A.I., it actually is pretty weak in terms of knowing how to do good prompting, or what a prompt is, or what A.I.s do well. But you did a good job with that. And I love that you went back and forth and shaped it.
One of the techniques you used to shape it, by the way, was called few-shot, which is giving an example. So the two most powerful techniques are chain of thought, which we just talked about, and few-shot, giving it examples. Those are both well supported in the literature. And then, I’d add personas. So we’ve talked about, I think, the basics of prompt crafting here overall. And I think that the question was pretty good.
EZRA KLEIN: One of the things I realized trying to spend more time with the A.I. is that you really have to commit to this process. You have to go back and forth with it a lot. If you do, you can get really good questions, like the one I just did — or, I think, really good outcomes. But it does take time.
ETHAN MOLLICK: One set of techniques that work quite well is to speed run to where you are in the conversation. So you can actually pick up an older conversation where you got the A.I.’s mindset where you want and work from there. You can even copy and paste that into a new window. You can ask the A.I. to summarize where you got in that previous conversation, and the tone the A.I. was taking, and then when you give a new instruction say the interaction I like to have with you is this, so have it solve the problem for you by having it summarize the tone that you happen to like at the end.
EZRA KLEIN: You did mention something important there, because they’re already getting much bigger in terms of how much information they can hold. Like, the earlier generations could barely hold a significant chat. Now, Claude 3 can functionally hold a book in its memory. And it’s only going to go way, way, way up from here. And I know I’ve been trying to keep us in the present, but this feels to me really quickly like where this is both going and how it’s going to get a lot better.
ETHAN MOLLICK: It’s not even going there. Like, it’s already there. Gemini 1.5 can hold an entire movie, books. But like, it starts to now open up entirely new ways of working. I can show it a video of me working on my computer, just screen capture. And it knows all the tasks I’m doing and suggests ways to help me out. It starts watching over my shoulder and helping me. I put in all of my work that I did prior to getting tenure and said, write my tenure statement. Use exact quotes.
EZRA KLEIN: One thing that feels important to keep in front of mind here is that we do have some control over that. And not only do we have some control over it, but business models and policy are important here. And one thing we know from inside these A.I. shops is these A.I.s already are, but certainly will be, really super persuasive.
And so if the later iterations of the A.I. companions are tuned on the margin to try to encourage you to be also out in the real world, that’s going to matter, versus whether they have a business model that all they want is for you to spend a maximum amount of time talking to your A.I. companion, whether you ever have a friend who is flesh and blood be damned.
And so that’s an actual choice, right? That’s going to be a programming decision. And I worry about what happens if we leave that all up to the companies, right? At some point, there’s a lot of venture capital money in here right now. At some point, the venture capital runs out. At some point, people need to make big profits. At some point, they’re in competition with other players who need to make profits. And that’s when things — you get into what Cory Doctorow calls the “enshitification” cycle, where things that were once adding a lot of value to the user begin extracting a lot of value to the user.
ETHAN MOLLICK: I absolutely agree. I think that we have agency here. We have agency in how we operate this in businesses, and whether we use this in ways that encourage human flourishing and employees, or are brutal to them. And we have agency over how this works socially. And I think we abrogated that responsibility with social media, and that is an example. Not to be bad news, because I generally have a lot of mixed optimism and pessimism about parts of A.I., but the bad news piece is there are open source models out there that are quite good.
EZRA KLEIN: I see a lot of reasons to be worried about the open source models. And people talk about things like bioweapons and all that. But for some of the harms I’m talking about here, if you want to make money off of American kids, we can regulate you. So sometimes I feel like we almost, like, give up the fight before it begins. But in terms of what a lot of people are going to use, if you want to be having credit card payments processed by a major processor, then you have to follow the rules.
ETHAN MOLLICK: I couldn’t agree more. And I don’t think there’s any reason to give up hope on regulation. I think that we can mitigate. And I think part of our job, though, is also not just to mitigate the harms, but to guide towards the positive viewpoints, right? So what I worry about is that the incentive for profit making will push for A.I. that acts informally as your therapist or your friend, while our worries about experimentation, which are completely valid, are slowing down our ability to do experiments to find out ways to do this right.
And I think it’s really important to have positive examples, too. I want to point to the A.I. systems acting ethically as your friend or companion, and figure out what that is, so there’s a positive model to look for. So I’m not just — this is not to denigrate the role of regulation, which I think is actually going to be important here, and self regulation, and rapid response from government, but also the companion problem of, “we need to make some sort of decisions about what are the paragons of this, what is acceptable as a society?”
EZRA KLEIN: So I want to talk a bit about another downside here, and this one more in the mainstream of our conversation, which is on the human mind, on creativity. So a lot of the work A.I. is good at automating is work that is genuinely annoying, time consuming, laborious, but often plays an important role in the creative process. So I can tell you that writing a first draft is hard, and that work on the draft is where the hard thinking happens.
ETHAN MOLLICK: I think the idea of struggle is actually a core one in many things. I’m an educator. And one thing that keeps coming out in the research is that there is a strong disconnect between what students think they’re learning and when they learn. So there was a great controlled experiment at Harvard in intro science classes, where students either went to a pretty entertaining set of lectures, or else they were forced to do active learning, where they actually did the work in class.
Not just because, by the way, it makes the work easier, but also because you mentally anchor on the A.I.’s answer. And in some ways, the most dangerous A.I. application, in my mind, is the fact that you have these easy co-pilots in Word and Google Docs, because any writer knows about the tyranny of the blank page, about staring at a blank page and not knowing what to do next, and the struggle of filling that up. And when you have a button that produces really good words for you, on demand, you’re just going to do that. And it’s going to anchor your writing.
We can teach people about the value of productive struggle, but I think that during the school years, we have to teach people the value of writing — not just assign an essay and assume that the essay does something magical, but be very intentional about the writing process and how we teach people about how to do that, because I do think the temptation of what I call “the button” is going to be there otherwise, for everybody.
EZRA KLEIN: But I worry this stretches, I mean, way beyond writing. So the other place I worry about this, or one of the other places I worry about this a lot, is summarizing. And I mean, this goes way back. When I was in school, you could buy Sparknotes. And they were these little, like, pamphlet sized descriptions of what’s going on in “War and Peace” or what’s going on in “East of Eden.”
ETHAN MOLLICK: So I don’t mean to push back too much on this.
EZRA KLEIN: No, please, push back a lot.
ETHAN MOLLICK: But I think you’re right.
EZRA KLEIN: Imagine we’re debating and you are a snarky. A.I. [LAUGHS]
ETHAN MOLLICK: Fair enough. With that prompt —
EZRA KLEIN: With that prompt engineering.
ETHAN MOLLICK: — yeah, I mean, I think that this is the eternal thing about looking back on the next generation, we worry about technology ruining them. I think this makes ruining easier. But as somebody who teaches at universities, like, lots of people are summarizing. Like, I think those of us who enjoy intellectual struggle are always thinking everybody else is going through the same intellectual struggle when they do work. And they’re doing it about their own thing. They may or may not care the same way.
EZRA KLEIN: Well, let me take this from another angle. One of the things that I’m a little obsessed with is the way the internet did not increase either domestic or global productivity for any real length of time. So I mean, it’s a very famous line. You can see the IT revolution anywhere but in the productivity statistics. And then you do get, in the ’90s, a bump in productivity that then peters out in the 2000s.
And so some of the time that was given to us back was also taken back. And I see a lot of dynamics like this that could play out with A.I. — I wouldn’t even just say if we’re not careful, I just think they will play out and already are. I mean, the internet is already filling with mediocre crap generated by A.I. There is going to be a lot of destructive potential, right? You are going to have your sex bot in your pocket, right?
There’s a million things — and not just that, but inside organizations, there’s going to be people padding out what would have been something small, trying to make it look more impressive by using the A.I. to make something bigger. And then, you’re going to use the A.I. to summarize it back down. The A.I. researcher, Jonathan Frankel, described this to me as, like, the boring apocalypse version of A.I., where you’re just endlessly inflating and then summarizing, and then inflating and then summarizing the volume of content between different A.I.
ETHAN MOLLICK: So I think there’s a lot there to chew on. And I also have spent a lot of time trying to think about why the internet didn’t work as well. I was an early Wikipedia administrator.
EZRA KLEIN: Thank you for your service.
ETHAN MOLLICK: [LAUGHS] Yeah, it was very scarring. But I think a lot about this. And I think A.I. is different. I don’t know if it’s different in a positive way. And I think we talked about some of the negative ways it might be different. And I think it’s going to be many things at once, happening quite quickly. So I think the information environment’s going to be filled up with crap. We will not be able to tell the difference between true and false anymore. It will be an accelerant on all the kinds of problems that we have there.
The thing that makes A.I. possibly great is that it’s so very human, so it interacts with our human systems in a way that the internet did not. We built human systems on top of it, but A.I. is very human. It deals with human forms and human issues and our human bureaucracy very well. And that gives me some hope that even though there’s going to be lots of downsides, that the upsides of productivity and things like that are real.
Part of the problem with the internet is we had to digitize everything. We had to build systems that would make our offline world work with our online world. And we’re still doing that. If you go to business schools, digitizing is still a big deal 30 years on from early internet access. A.I. makes this happen much quicker because it works with us. So I’m a little more hopeful than you are about that, but I also think that the downside risks are truly real and hard to anticipate.
EZRA KLEIN: I think that is a good place to end. So always our final question, what are three books you’d recommend to the audience?
ETHAN MOLLICK: OK, so the books I’ve been thinking about are not all fun, but I think they’re all interesting. One of them is “The Rise and Fall of American Growth,” which is — it’s two things. It’s an argument about why we will never have the kind of growth that we did in the first part of the Industrial Revolution again, but I think that’s less interesting than the first half of the book, which is literally how the world changed between 1870 or 1890 and 1940, versus 1940 and 1990, or 2000.
EZRA KLEIN: Ethan Mollick, your book is called “Co-Intelligence.” Your Substack is One Useful Thing. Thank you very much.
ETHAN MOLLICK: Thank you.
EZRA KLEIN: This episode of “The Ezra Klein Show” was produced by Kristin Lin. Fact checking by Michelle Harris. Our senior engineer is Jeff Geld with additional mixing from Efim Shapiro. Our senior editor is Claire Gordon. The show’s production team also includes Annie Galvin and Rollin Hu. Original music by Isaac Jones. Audience strategy by Kristina Samulewski and Shannon Busta. The executive producer of New York Times Opinion Audio is Annie-Rose Strasser, and special thanks to Sonia Herrero.
Advertisement

IMAGES
VIDEO
COMMENTS
Common Application or apply Coalition, Powered by Scoir. This includes subsets of questions, an activities list, and a personal essay (Common Application prompts, Coalition Application prompts) Harvard College Questions for the Common Application or Coalition Application Harvard supplement
Extracurricular Short Response. Required. 200 Words. Briefly describe any of your extracurricular activities, employment experience, travel, or family responsibilities that have shaped who you are. Read our essay guide to get started. Submit your essay for free peer review to refine and perfect it. Submit or review an essay.
February 24, 2023. We are pleased to announce that the Common App essay prompts will remain the same for 2023-2024. It's not just for the sake of consistency that we have chosen to keep the essay prompts the same for the upcoming application year. Our past research has shown that overall satisfaction with the prompts exceeded 95% across our ...
For the 2023/24 application cycle, Harvard University has outlined specific supplemental essay prompts to understand applicants better in addition to the Common App or Coalition App questions. These questions delve into your experiences, intellectual pursuits, and personal insights. Students are required to answer each Harvard-specific question ...
Harvard University 2023-24 Application Essay Question Explanations. The Requirements: Five essays of 200 words or fewer. Supplemental Essay Type(s): Diversity, Activity, Oddball. Harvard is asking 2023-24 applicants to pen five short essays in response to the following prompts: Harvard has long recognized the importance of enrolling a diverse ...
See my Common App, personal essays, and recommendation letters, and learn strategies for your own college application. Here's the COMPLETE application that got me into every school I applied to, including Harvard, Stanford, and Princeton. ... For the most part, the Harvard supplemental essay prompt has stayed the same. You can write about a ...
First, identify one or two goals you have for the future—with just 200 words, you won't have space to elaborate on any more than that. Ideally, these should be relatively concrete. You don't have to have your whole life mapped out, but you do need to be a lot more specific than "Make a difference in the world.".
He is a co-author of the books The Enlightened College Applicant (Rowman & Littlefield, 2016) and Colleges Worth Your Money (Rowman & Littlefield, 2020). We present the Harvard supplemental essays in 2023-24. The College Transitions team reviews the prompts and offers advice to applicants.
Here are the Prompts for the Harvard Supplemental Essays 2023-2024. Please briefly elaborate on one of your extracurricular activities or work experiences. (50-150 words) Activity essays like this one allow you to say everything you couldn't fit on your Common App activity list. Make sure to pick an activity that has meaning and one which you ...
Over the last few admissions cycles, in addition to The Common Application essay (s), Harvard asked applicants one long essay prompt, a short prompt, and a list. This year, the long prompt and list are gone. In their place are five — that's right — five 200-word essays. The essay questions are new as well. It's as though Harvard did a ...
Harvard accepts the Common Application, the Universal College Application, and the Coalition Application (with no preference). All of these applications require an essay response. ... Harvard University supplemental essay prompts (optional)
Below is the full set of essay prompts for 2024-2025. Some students have a background, identity, interest, or talent that is so meaningful they believe their application would be incomplete without it. If this sounds like you, then please share your story. The lessons we take from obstacles we encounter can be fundamental to later success.
Go to your Common App activities list and pick 2-3 of your most impressive or important (to you) activities. ... This essay prompt is new for Harvard, but here's an example essay written for Stanford: Hey, roomie :) I'm excited to finally meet you! I figured I'd go ahead and introduce myself so we can dive right in when we see each other.
As the Class of 2028 gets to writing, we mourn the loss of Harvard's old application. However, the focus on retaining a diverse student body in the questions Harvard asks its applicants is a ...
Welcome to the Harvard supplemental essay prompts for the 2021-2022 college application cycle! Here's everything you need to know to write the best supplemental essays possible. Harvard College, founded in 1636, is one of the most difficult institutions to gain acceptance to in the country — the acceptance rate was just 3.43% last year […]
Making Caring Common has compiled examples of character-focused essay questions from a range of colleges. It's important to note that this resource was compiled in 2020 and may not reflect current prompts. However, it still offers valuable examples of schools showcasing their values and inviting students to do the same.
We've compiled 5 Common App essay introductions that were accepted to Harvard University to show you exactly what it takes to make an impression in your first paragraph and grab the admissions officer's attention. Prompt: Some students have a background or story that is so central to their identity that they believe their application would ...
First-year application. Student information. Personal information. Legal name. First/given Middle. Different first name that you go by If you provide another first name, the colleges you send an application to may use it in future communications. Last/family/sur (Enter name exactly as it appears on official documents.)
February 27, 2024. We are happy to announce that the Common App essay prompts will remain the same for 2024-2025. Our decision to keep these prompts unchanged is supported by past research showing that overall satisfaction with the prompts exceeded 95% across our constituent groups - students, counselors, advisors, teachers, and member colleges.
Harvard College is a close-knit undergraduate community within Harvard University. With world-class faculty, groundbreaking research opportunities, and a commitment to a diverse environment of bright, talented students, Harvard is more than just a place to get an education—it's where students come to be transformed. Our unparalleled student experience educates the next generation of ...
When the Common Application portal opened at midnight Tuesday, thousands of high schoolers found the Harvard College application had significantly changed. ... Harvard's application now contains ...
So I've been on a personal quest to get better at this. And in that quest, I have a guide. Ethan Mollick is a professor at the Wharton School of the University of Pennsylvania.