- PRO Courses Guides New Tech Help Pro Expert Videos About wikiHow Pro Upgrade Sign In
- EDIT Edit this Article
- EXPLORE Tech Help Pro About Us Random Article Quizzes Request a New Article Community Dashboard This Or That Game Popular Categories Arts and Entertainment Artwork Books Movies Computers and Electronics Computers Phone Skills Technology Hacks Health Men's Health Mental Health Women's Health Relationships Dating Love Relationship Issues Hobbies and Crafts Crafts Drawing Games Education & Communication Communication Skills Personal Development Studying Personal Care and Style Fashion Hair Care Personal Hygiene Youth Personal Care School Stuff Dating All Categories Arts and Entertainment Finance and Business Home and Garden Relationship Quizzes Cars & Other Vehicles Food and Entertaining Personal Care and Style Sports and Fitness Computers and Electronics Health Pets and Animals Travel Education & Communication Hobbies and Crafts Philosophy and Religion Work World Family Life Holidays and Traditions Relationships Youth
- Browse Articles
- Learn Something New
- Quizzes Hot
- This Or That Game New
- Train Your Brain
- Explore More
- Support wikiHow
- About wikiHow
- Log in / Sign up
- Education and Communications
- College University and Postgraduate
- Academic Writing

How to Do Footnotes
Last Updated: February 9, 2024 Fact Checked
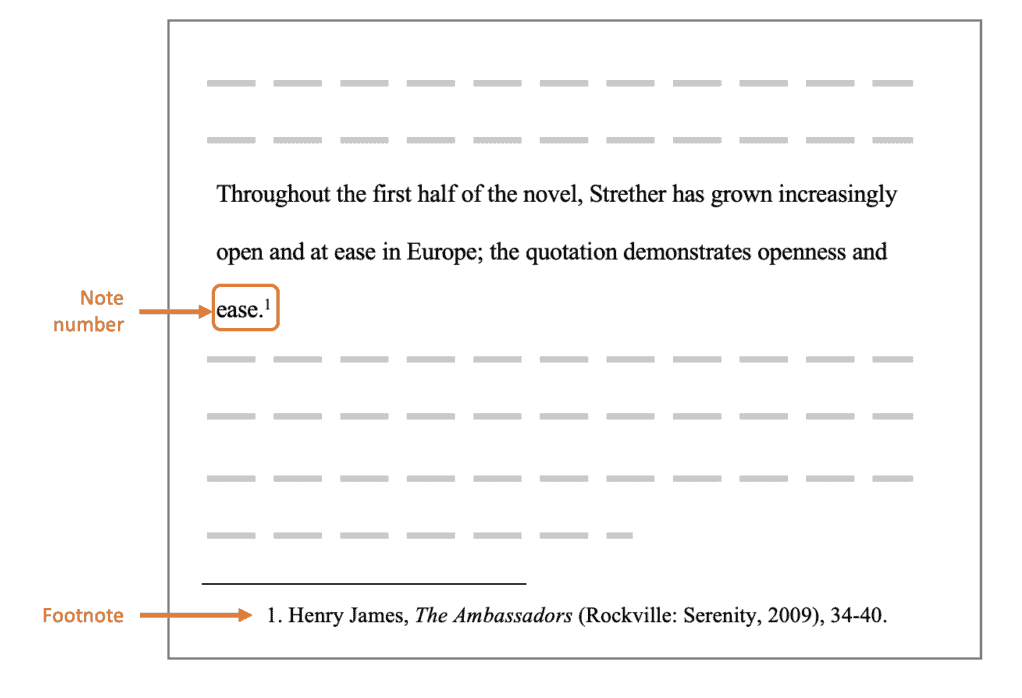
Sample Footnotes
Placing citations, supplementing text, expert interview, expert q&a.
This article was co-authored by Noah Taxis and by wikiHow staff writer, Jennifer Mueller, JD . Noah Taxis is an English Teacher based in San Francisco, California. He has taught as a credentialed teacher for over four years: first at Mountain View High School as a 9th- and 11th-grade English Teacher, then at UISA (Ukiah Independent Study Academy) as a Middle School Independent Study Teacher. He is now a high school English teacher at St. Ignatius College Preparatory School in San Francisco. He received an MA in Secondary Education and Teaching from Stanford University’s Graduate School of Education. He also received an MA in Comparative and World Literature from the University of Illinois Urbana-Champaign and a BA in International Literary & Visual Studies and English from Tufts University. There are 9 references cited in this article, which can be found at the bottom of the page. This article has been fact-checked, ensuring the accuracy of any cited facts and confirming the authority of its sources. This article has been viewed 1,372,598 times.
Footnotes are used generally in academic and professional writing to cite sources or add supplemental information to the main text of a paper. Academic citation styles, such as the Modern Language Association (MLA) and the American Psychological Association (APA), discourage the use of extensive footnotes. Others, such as Chicago style, require them. [1] X Research source

Tip: Footnotes are typically a smaller font size than the main text of your paper. Typically, you won't need to change the default size on the word processing app you're using to write your paper – it will do this automatically when you create a footnote.

- You'll typically only have one footnote per sentence. If you need more than one footnote, place the other footnote at the end of the sentence clause it relates to, outside the closing punctuation. The only exception is if the sentence is broken up by a long dash, in which case, the superscript number goes before the beginning of the dash. [4] X Trustworthy Source Purdue Online Writing Lab Trusted resource for writing and citation guidelines Go to source
Footnote Number in Line with Text: It is well known that patients who suffer from Crohn's and Colitis can have many debilitating symptoms. 1.
Superscripted Footnote Number: It is well known that patients who suffer from Crohn's and Colitis can have many debilitating symptoms. 1

- For some longer papers, such as doctoral theses, footnote numbers may start over with each chapter. If you're unsure if this is appropriate for your project, discuss it with your editor or advisor.
- Most word processing apps will maintain sequential numbering for you, provided you use the app's function for inserting footnotes, rather than trying to type the numbers manually.

- You typically have formatting options that allow you to choose numbers, letters, or other symbols to indicate footnotes. You can also change the size or placement of footnotes, although the default option is usually appropriate.

- For most style guides, the use of footnotes does not replace the need for a list of references at the end of your paper. Even if a full list of references isn't strictly required, it can help place your paper in context.

- For example, suppose you've paraphrased information from a book by Reginald Daily, titled Timeless wikiHow Examples: Through the Ages. If you were using Chicago style, your footnote citation would look something like this: Reginald Daily, Timeless wikiHow Examples: Through the Ages (Minneapolis: St. Olaf Press, 2010), 115.

- For example, suppose later on in your paper you need to cite Reginald Daily's wikiHow book again. Your shortened citation might look something like this: Daily, wikiHow Examples , 130.
Tip: Some citation styles recommend using the abbreviation "id." or "ibid." if you cite to the same source in footnotes immediately following. Others, notably the Chicago Manual of Style, require the use of a shortened citation instead.

- For example, suppose you have a sentence in your text comparing the conclusions in Reginald Daily's book with the observations in another book on the same topic. Your footnote might look something like this: Reginald Daily, Timeless wikiHow Examples: Through the Ages (Minneapolis: St. Olaf Press, 2010), 115; Mary Beth Miller, The wiki Revolution (New York: New Tech Press, 2018), 48.

- For example, if Miller's work reached a conclusion that was contrary to the conclusion Daily reached, your footnote might look something like this: Reginald Daily, Timeless wikiHow Examples: Through the Ages (Minneapolis: St. Olaf Press, 2010), 115; but see Mary Beth Miller, The wiki Revolution (New York: New Tech Press, 2018), 48.
- If you believe it would be helpful to your readers, you can add a brief parenthetical comment after the second source that explains why you included it.

- For example, suppose you want to include a brief explanation as to why you're citing Daily's book, despite the fact that it was published in 2010. Your footnote might look something like this: Reginald Daily, Timeless wikiHow Examples: Through the Ages (Minneapolis: St. Olaf Press, 2010), 115. Although published in 2010, Daily's work provides a jumping-off point for research in this area.

- For example, there may be a basic concept that is beyond the scope of your paper, but important for your readers to understand. You could add a footnote that says "For an explanation of the theory of relativity, see generally" followed by a source or list of sources.
- Typically, these types of footnotes provide your reader with information on something that is tangential to your paper but could be important to help your readers understand the topic as a whole or place your paper in context.

- Some style guides, such as MLA and APA, instruct that parenthetical statements should be included in the main text of your paper, rather than in footnotes. [15] X Trustworthy Source Purdue Online Writing Lab Trusted resource for writing and citation guidelines Go to source
Tip: Keep your footnotes as brief as possible, especially with supplemental footnotes. Don't stray too far off topic or go into a tangent that is only marginally related to the topic of your paper.

- These types of footnotes frequently accompany a quote from a source and may include a citation to the source. For example, if you quoted a source that discussed wikiHow, and you wanted to clarify, you might add a footnote that says "wikiHow examples are used to clarify text in situations where it would be helpful to have a visual cue. Reginald Daily, Timeless wikiHow Examples: Through the Ages (Minneapolis: St. Olaf Press, 2010), 115."

- For example, suppose you are writing a paper about the use of wikiHow articles as sources, and you include a study finding that wikiHow articles are more accurate than articles on major news sites about similar topics. You might add a footnote that says "Despite this fact, the vast majority of professors at public universities in the US do not accept wikiHow articles as sources for research papers."
- You can also use footnotes to make a witty remark, which can add humor and lightheartedness to your paper. However, these types of footnotes should be used extremely rarely, and only when appropriate to the subject matter.

- Before writing, confirm with your professor or organization what style guide you should be using to write your paper. Make sure your use of footnotes follows the rules for that style. Thanks Helpful 0 Not Helpful 0
- If a footnote includes both a citation and supplemental information, the citation usually comes first. Thanks Helpful 0 Not Helpful 0

You Might Also Like

Thanks for reading our article! If you’d like to learn more about academic writing, check out our in-depth interview with Noah Taxis .
- ↑ https://www.plagiarism.org/article/what-are-footnotes
- ↑ https://stpauls-mb.libguides.com/citations/footnotes
- ↑ https://www.library.georgetown.edu/tutorials/research-guides/turabian-footnote-guide
- ↑ https://owl.purdue.edu/owl/research_and_citation/mla_style/mla_formatting_and_style_guide/mla_endnotes_and_footnotes.html
- ↑ https://libguides.stonehill.edu/c.php?g=884839&p=6358739
- ↑ https://www.law.cornell.edu/citation/6-300
- ↑ https://libguides.utep.edu/c.php?g=429690&p=2930768
- ↑ https://jle.aals.org/cgi/viewcontent.cgi?article=1243&context=home
- ↑ https://libguides.liberty.edu/c.php?g=864199&p=6197236
About This Article

To use footnotes as citations, find a sentence you want to cite and insert a "1" at the end of it using the footnote setting in your word processor. Then, insert your citation next to the corresponding "1" at the bottom of the page, like "Reginald Daily, Timeless wikiHow Examples: Through the Ages (Minneapolis: St. Olaf Press, 2010), 115." When you're finished, move onto the next sentence you need to cite and repeat the process. To learn how to use footnotes to clarify information in your paper, read the article! Did this summary help you? Yes No
- Send fan mail to authors
Reader Success Stories
Ntando Malandela
Aug 29, 2017
Did this article help you?
Kevin Nesbit
Mar 24, 2017
Violet Black
May 21, 2017
Brandi Bumgardner
Dec 9, 2017

Featured Articles

Trending Articles

Watch Articles

- Terms of Use
- Privacy Policy
- Do Not Sell or Share My Info
- Not Selling Info
wikiHow Tech Help Pro:
Level up your tech skills and stay ahead of the curve
- Skip to main content
- Skip to secondary menu
- Skip to primary sidebar
- Skip to footer
Erin Wright Writing
Writing-Related Software Tutorials
What Are Footnotes and How to Use Them
By Erin Wright

What Are Footnotes?
Footnotes are supplementary pieces of information that support your writing. If you’re following The Chicago Manual of Style (Chicago style, which is the best style guide for general business content), supplementary information includes works cited, suggestions for further research, commentary, quotations, copyright statements, or a combination of any of the above. 1
If you’re following the Publication Manual of the American Psychological Association (APA style) or MLA style from the Modern Language Association, works cited typically appear in the reference list or bibliography; so, footnotes are reserved for commentary, suggestions for further research, or copyright statements. 2
Work cited example based on Chicago style:
1. Lynne Truss, Eats, Shoots & Leaves (New York: Gotham Books, 2003), 89.
Commentary example:
2. This study excluded Groups D and E; therefore, it should not be considered exhaustive.
Suggestion for further research example:
3. Visit www.erinwrightwriting.com for more information about ampersands.
Where Should Footnotes Appear in Formal Documents?
Footnotes usually appear at the bottom of the page. Each footnote is preceded by a number that also appears as a superscript after the corresponding material on that page. Chicago style allows you to use symbols, such as the asterisk or the dagger, instead of numbers if you only have a few footnotes. 3
If you’re following APA style or MLA style, footnotes can appear at the foot of the page or all together at the end of the document. 4 (In Chicago style and MLA style, notes placed at the end of articles, chapters, or books are called endnotes. 5 ) Unlike Chicago style, APA style and MLA style don’t recommend using symbols as footnote identifiers. 6
Where Should Footnotes Appear in General Business Writing?
If you’re publishing less formal content online, such as a blog post or a how-to article, there’s no rule that says you can’t put footnotes at the end of individual sections. I like to call them “floating footnotes” because they float where they’re most needed instead of languishing at the end of a page or document.
In fact, floating footnotes can be more helpful than traditional footnotes for viewers who only need to read a few sections of your content. Floating footnotes can also benefit viewers who don’t want to scroll all the way to the end of a long webpage or ebook.
However, reserve floating footnotes for longer pieces so your content doesn’t become disjointed. If your blog post or article is only a couple of screen lengths, tradition footnotes should work just fine. You can see an example of a floating footnote in the second-to-last section of Three Ways to Add Currency Symbols in Microsoft Word .
Three Tips for Writing Footnotes
1. If your supplementary information is longer than a paragraph, consider using an appendix instead of a footnote.
2. If you’re following Chicago style and your footnotes are taking up too much page space, consider using endnotes instead.
3. Avoid unnecessary footnotes: if they don’t cite your sources or improve your readers’ understanding of the topic, they’re probably not necessary.
Check out these related posts on the differences between bibliographies and reference pages and how to insert footnotes and endnotes in Microsoft Word .
And of course, here are my footnotes for this blog post:
1. The Chicago Manual of Style , 17th ed. (Chicago: University of Chicago Press, 2017), 14.19, 14.37–40.
2. Publication Manual of the American Psychological Association, 7th ed. (Washington, DC: American Psychological Association, 2020), 2.13; MLA Handbook , 9th ed. (New York; Modern Language Association, 2021), 7.1-7.2.
3. The Chicago Manual of Style , 14.25.
4. Publication Manual of the American Psychological Association , 2.13; MLA Handbook , 7.3.
5. The Chicago Manual of Style , 14.43; MLA Handbook , 7.3.
6. Publication Manual of the American Psychological Association , 2.13; MLA Handbook , 7.3.
Updated January 25, 2022
- Microsoft Word Tutorials
- Adobe Acrobat Tutorials
- PowerPoint Tutorials
- Writing Tips
- Editing Tips
- Writing-Related Resources
How to Use Footnotes in Research Papers
edfuentesg / Getty Images
- An Introduction to Punctuation
- Ph.D., Rhetoric and English, University of Georgia
- M.A., Modern English and American Literature, University of Leicester
- B.A., English, State University of New York
A footnote is a reference, explanation, or comment 1 placed below the main text on a printed page. Footnotes are identified in the text by a numeral or a symbol .
In research papers and reports , footnotes commonly acknowledge the sources of facts and quotations that appear in the text.
" Footnotes are the mark of a scholar," says Bryan A. Garner. "Overabundant, overflowing footnotes are the mark of an insecure scholar — often one who gets lost in the byways of analysis and who wants to show off" ( Garner's Modern American Usage , 2009).
Examples and Observations
- " Footnotes: vices . In a work containing many long footnotes, it may be difficult to fit them onto the pages they pertain to, especially in an illustrated work."
- " Content footnotes supplement or simplify substantive information in the text; they should not include complicated, irrelevant, or nonessential information..." " Copyright permission footnotes acknowledge the source of lengthy quotations, scale and test items, and figures and tables that have been reprinted or adapted."
- Content Footnotes "What, after all, is a content footnote but material that one is either too lazy to integrate into the text or too reverent to discard? Reading a piece of prose that constantly dissolves into extended footnotes is profoundly disheartening. Hence my rule of thumb for footnotes is exactly the same as that for parentheses . One should regard them as symbols of failure. I hardly need to add that in this vale of tears failure is sometimes unavoidable."
- Footnote Forms All notes have the same general form: 1. Adrian Johns. The Nature of the Book: Print and Knowledge in the Making (Chicago: University of Chicago Press, 1998), 623. If you cite the same text again, you can shorten subsequent notes: 5. Johns. Nature of the Book , 384-85.
- The Disadvantages of Footnotes "More than one recent critic has pointed out that footnotes interrupt a narrative . References detract from the illusion of veracity and immediacy . . . . (Noel Coward made the same point more memorably when he remarked that having to read a footnote resembles having to go downstairs to answer the door while in the midst of making love.)"
- Belloc on Footnotes "[L]et a man put his foot-notes in very small print indeed at the end of a volume, and, if necessary, let him give specimens rather than a complete list. For instance, let a man who writes history as it should be written — with all the physical details in evidence, the weather, the dress, colors, everything — write on for the pleasure of his reader and not for his critic. But let him take sections here and there, and in an appendix show the critic how it is being done. Let him keep his notes and challenge criticism. I think he will be secure. He will not be secure from the anger of those who cannot write clearly, let alone vividly, and who have never in their lives been able to resurrect the past, but he will be secure from their destructive effect."
- The Lighter Side of Footnotes "A footnote is like running downstairs to answer the doorbell on your wedding night."
1 "The footnote has figured prominently in the fictions of such leading contemporary novelists as Nicholson Baker 2 , David Foster Wallace 3 , and Dave Eggers. These writers have largely revived the digressive function of the footnote." (L. Douglas and A. George, Sense and Nonsensibility: Lampoons of Learning and Literature . Simon and Schuster, 2004)
2 "[T]he great scholarly or anecdotal footnotes of Lecky, Gibbon, or Boswell, written by the author of the book himself to supplement, or even correct over several later editions, what he says in the primary text, are reassurances that the pursuit of truth doesn't have clear outer boundaries: it doesn't end with the book; restatement and self-disagreement and the enveloping sea of referenced authorities all continue. Footnotes are the finer-suckered surfaces that allow tentacular paragraphs to hold fast to the wider reality of the library." (Nicholson Baker, The Mezzanine . Weidenfeld and Nicholson, 1988)
3 "One of the odd pleasures in reading the work of the late David Foster Wallace is the opportunity to escape from the main text to explore epic footnotes , always rendered at the bottoms of pages in thickets of tiny type." (Roy Peter Clark, The Glamour of Grammar . Little, Brown, 2010)
- Hilaire Belloc, On , 1923
- Chicago Manual of Style , University of Chicago Press, 2003
- Anthony Grafton, The Footnote: A Curious History . Harvard University Press, 1999.
- Publication Manual of the American Psychological Association , 6th ed., 2010.
- Paul Robinson, "The Philosophy of Punctuation." Opera, Sex, and Other Vital Matters . University of Chicago Press, 2002.
- Kate Turabian, A Manual for Writers of Research Papers, Theses, and Dissertations , 7th ed. University of Chicago Press, 2007 .
- What Are Endnotes, Why Are They Needed, and How Are They Used?
- Formatting Papers in Chicago Style
- Top 10 Reference Works for Writers and Editors
- Definition of Appendix in a Book or Written Work
- Turabian Style Guide With Examples
- Margin (Composition Format) Definition
- What Is a Style Guide and Which One Do You Need?
- 140 Key Copyediting Terms and What They Mean
- Documentation in Reports and Research Papers
- What Is a Citation?
- Justification (Typesetting and Composition)
- What Is a Senior Thesis?
- What are Ellipsis Points?
- Examples of Epigraphs in English
- Definition and Examples of Title Case and Headline Style
- How to Write a Research Paper That Earns an A

- Foundations
- Write Paper
Search form
- Experiments
- Anthropology
- Self-Esteem
- Social Anxiety

- Research Paper >
How to Write Footnotes
Information on how to write footnotes and endnotes. Footnotes, a type of citation format, are most often used for history and philosophy papers. As such, scientists rarely encounter it, but it is still useful to know how to follow the practice.
This article is a part of the guide:
- Outline Examples
- Example of a Paper
- Write a Hypothesis
- Introduction
Browse Full Outline
- 1 Write a Research Paper
- 2 Writing a Paper
- 3.1 Write an Outline
- 3.2 Outline Examples
- 4.1 Thesis Statement
- 4.2 Write a Hypothesis
- 5.2 Abstract
- 5.3 Introduction
- 5.4 Methods
- 5.5 Results
- 5.6 Discussion
- 5.7 Conclusion
- 5.8 Bibliography
- 6.1 Table of Contents
- 6.2 Acknowledgements
- 6.3 Appendix
- 7.1 In Text Citations
- 7.2 Footnotes
- 7.3.1 Floating Blocks
- 7.4 Example of a Paper
- 7.5 Example of a Paper 2
- 7.6.1 Citations
- 7.7.1 Writing Style
- 7.7.2 Citations
- 8.1.1 Sham Peer Review
- 8.1.2 Advantages
- 8.1.3 Disadvantages
- 8.2 Publication Bias
- 8.3.1 Journal Rejection
- 9.1 Article Writing
- 9.2 Ideas for Topics
Many biology journals, for example, prefer footnotes because they allow annotation of the in-text citation on the same page.
Whilst footnotes are a little more cumbersome than the 'author/date' system, they are useful where sources require elaboration and short explanatory notes.

What is a Footnote
The footnote takes the form of a superscripted number, just after a paraphrased piece of information. Subsequently, a cross-reference to this number is inserted at the bottom of the same page.
In fact, for dissertations and theses, many writers use footnotes to keep track of their citations , adding a short note of what exactly each one adds to the paper.
Once the paper is complete, the writer converts them to endnotes at the end or every chapter, or even removes them all together, and uses a standard APA or MLA bibliography instead.

Automatically Inserting Footnotes
The reason that footnotes are still popular in some fields is that most word processing programs now include a function that makes it very easy to include footnotes in any paper.
In Microsoft Word, clicking Insert > Reference > Footnote allows you to insert footnotes automatically, and automatically numbers them. This function is so useful, that even if you cut and paste, and swap information around, it automatically adjusts the footnotes.
This is why it is an excellent resource for keeping track of your sources during the course of a research paper .
How to Write Footnotes - Protocols
If you are using footnotes, the common convention is to insert a full citation, including author, year and the title of the book, followed by the page number. Afterwards, the surname of the author and the page number is sufficient.
Older journals often use the word ibid, to show that a footnote uses the same source as the previous one, but this has become much rarer.
- Psychology 101
- Flags and Countries
- Capitals and Countries
Martyn Shuttleworth (Nov 21, 2009). How to Write Footnotes. Retrieved Apr 07, 2024 from Explorable.com: https://explorable.com/how-to-write-footnotes
You Are Allowed To Copy The Text
The text in this article is licensed under the Creative Commons-License Attribution 4.0 International (CC BY 4.0) .
This means you're free to copy, share and adapt any parts (or all) of the text in the article, as long as you give appropriate credit and provide a link/reference to this page.
That is it. You don't need our permission to copy the article; just include a link/reference back to this page. You can use it freely (with some kind of link), and we're also okay with people reprinting in publications like books, blogs, newsletters, course-material, papers, wikipedia and presentations (with clear attribution).
Want to stay up to date? Follow us!
Check out the official book.
Learn how to construct, style and format an Academic paper and take your skills to the next level.

(also available as ebook )
Save this course for later
Don't have time for it all now? No problem, save it as a course and come back to it later.
Footer bottom
- Privacy Policy

- Subscribe to our RSS Feed
- Like us on Facebook
- Follow us on Twitter
Home / Guides / Citation Guides / MLA Format / How to use footnotes in MLA
How to use footnotes in MLA
Sometimes when writing a paper, you have additional information that you want to include, but it won’t work well in the main text of your paper. This additional information also may not work as a parenthetical citation. In those cases, you can use footnotes in MLA Style. (Note that this article is for MLA. If you are curious about footnotes in APA style, see APA footnotes .)
What is a footnote?
A footnote is additional information that is added at the bottom of the page and indicated with a superscript number. Writers choose to add a footnote when the information would be distracting if it appeared in the main text. You may choose to add a footnote when you want to clarify a point or justify a point of view. Footnotes can also be used if you want to show another line of argument on the topic, or you want to show the differences between your work and others.
While MLA format does allow for footnotes, writers are encouraged to use footnotes sparingly.
How to use footnotes
There are two types of footnotes: bibliographical and content.
Bibliographical notes
Bibliographical notes add additional sources relevant to your thesis. Use these types of notes when your references are too long and citing all of them would interrupt your text. In the note you can cite a long string of sources. You can also use bibliographical notes to make comments on your sources and to identify areas of further research. Keep in mind, however, that references to a few authors’ names can also be put into a parenthetical citation in the text.
MLA style recommends that you use bibliographic notes sparingly.
Content footnotes
Content footnotes offer information or commentary that doesn’t fit in your main text or offer a further explanation of the topic. Content footnotes also allow you to add background information that may be interesting to your readers or refer to other sources with more detail than in bibliographic notes.
Like bibliographic notes, MLA recommends that content notes should be used sparingly.
Endnotes vs. footnotes
The difference between a footnote and an endnote is its placement in the paper. Footnotes appear at the bottom of the same page where they are referenced. Endnotes appear all together at the end of the paper in a list labeled Note(s) or Endnote(s). Endnotes are listed before the Works Cited page. You should ask your professors what style of notes are required in their classes.
Footnote format
Footnotes are formatted with superscript numbers that usually appear at the end of the sentence after the punctuation. You can also use a footnote in the middle of the sentence by placing the number directly after a punctuation mark. If you use a footnote in a sentence that has a dash, make sure the footnote number is placed before the dash. Footnotes should be numbered sequentially throughout the paper. Do not start over again at number 1 on each page.
The footnote citation at the bottom of the page should have the number, and it should also be in superscript. For the note itself, use the same font as the rest of your paper but in a smaller size. For example, if your paper is written in 12 pt. font, then your footnote should be in 10 pt. font. If you use a source in a footnote, you also need to include it in the Works Cited list at the end of your paper.
- Works Cited
Magyarody, Katherine. “‘Sacred Ties of Brotherhood’: The Social Mediation of Imperial Ideology in The Last of the Mohicans and Canadian Crusoes .” Nineteenth-Century Literature , vol. 71, no. 3, 2016, pp. 315–342. JSTOR , www.jstor.org/stable/26377183.
MLA Handbook . 9th ed., Modern Language Association of America, 2021.
Published October 27, 2020. Updated July 18, 2021.
By Catherine Sigler. Catherine has a Ph.D. in English Education and has taught college-level writing for 15 years.
MLA Formatting Guide
MLA Formatting
- Annotated Bibliography
- Bibliography
- Block Quotes
- et al Usage
- In-text Citations
- Paraphrasing
- Page Numbers
- Sample Paper
- MLA 8 Updates
- MLA 9 Updates
- View MLA Guide
Citation Examples
- Book Chapter
- Journal Article
- Magazine Article
- Newspaper Article
- Website (no author)
- View all MLA Examples
How useful was this post?
Click on a star to rate it!
We are sorry that this post was not useful for you!
Let us improve this post!
Tell us how we can improve this post?
To use endnotes in your paper, you need to follow the guidelines provided below:
General points
Use superscript Arabic numerals to number the endnote citations in the text. You can use your word processor’s notes feature so that the numbering is generated automatically.
Do not use the ibid abbreviation in endnotes.
The title of the endnote page at the end of your paper can be “Notes” or “Endnotes.”
If you want to add any citations within the note, include the page numbers in parentheses at the end of the sentence or at a natural breaking point.
Endnotes in the text
Place endnote indicators after any punctuation marks as in the examples below:
The work was compared with the literature study. 1
As Vivekananda said, “Education is the manifestation of divinity already in man.” 2
However, if you have a dash, place endnote indicator before the dash.
Drawing to the point mentioned by Shakespeare 3 —a dramatist, poet, and actor—we conclude that true love persists till the end of the doom’s day.
Other points
Multiple endnotes within a sentence are allowed. However, place them wisely to ensure clarity.
An endnote citation can appear in the middle of a sentence if the sentence warrants that placement for clarity, but insert the endnote in the least distracting (but unambiguous) place.
While MLA only uses endnotes in its publications, notes may be styled as footnotes or as endnotes.
MLA Citation Examples
Writing Tools
Citation Generators
Other Citation Styles
Plagiarism Checker
Upload a paper to check for plagiarism against billions of sources and get advanced writing suggestions for clarity and style.
Get Started
What Are Footnotes and How Do You Use Them?
#scribendiinc
Written by Scribendi
While reading a book or article, have you ever noticed little numbers placed at the ends of some sentences?
These numbers usually appear as superscripts and correspond with numbers placed at the bottom of the page, next to which appears further information that is both necessary and supplementary. Sometimes this information will come in the form of citations, but sometimes it will simply present additional notes about the topic at hand.
These citations and explanations are called "footnotes" (because they appear in the footer of the page). Take a look at the example below to see where footnotes appear on a page:

We've outlined how to use footnotes below. Check it out!
1. What Are Footnotes?
2. footnotes vs. endnotes, 2.1 should i use footnotes or endnotes, 3. how to do footnote citations, 3.1 in-text citations, 3.2 footnotes, 4. how to use footnotes in essays, 4.1 style guides, 4.1.1 modern language association (mla), 4.1.2 american psychological association (apa), 4.1.3 chicago manual of style (cms), 5. technical guide to using footnotes, 5.1 how to add footnotes in microsoft word, 5.2 how to add footnotes in google docs, 6. final tips and tricks .
Footnotes are notes that are placed at the end of a page and used to reference parts of the text (generally using superscript numbers). Writers use footnotes for several purposes, including citations , parenthetical information, outside sources, copyright permissions, background information, and more.
Now that you understand what footnotes are, you might be wondering: why use them? The truth is, long explanatory notes can be difficult for readers to trudge through (especially when they occur in the middle of a paper). Providing this information is necessary, but doing so in the main text can disrupt the flow of the writing.
Imagine if every time an author wanted to provide a citation, the entire citation had to be written out at the end of the sentence, like this (Anthony Grafton, The Footnote: A Curious History [Cambridge, MA: Harvard University Press, 1999] 221). Books would become much longer and reading would be much more tedious. That's why footnotes are so useful: they let authors provide the required information without disrupting the flow of ideas.
While footnotes are a great resource for sharing information without clogging up the writing, it's important to note that certain style guides restrict when footnotes can be used. We'll get into that soon!
Unsure how to edit your paper? Contact the Scribendi team for professional proofreading .
Authors can also use endnotes to avoid disrupting their writing with extraneous information. Both serve similar purposes; the main difference lies in their location in your text. Here's a closer look at how both footnotes and endnotes work.
- Identified in the main text with a small superscript number
- Used for citations, parenthetical information, outside sources, copyright permissions, background information, and more
- Provide the correlating notes at the bottom of the same page
- Identified in the main text with a small superscript number (like footnotes)
- Used for citations, parenthetical information, outside sources, copyright permissions, background information, and more (like footnotes)
- Found collectively at the end of an article, chapter, or document (unlike footnotes)
When deciding whether to use footnotes or endnotes , authors must consider three main factors:
- The style guide being used (as some require either footnotes or endnotes)
- The number of notes being included (as having too many footnotes on each page can be distracting)
- Which option will be more convenient for the reader
To make a footnote citation, label the area of your text that you need to reference with a number (if it's your first footnote, start with "1."). At the bottom of the page, include this number with the citation. When readers see the number in the text, they know they can find the source by looking for the corresponding footnote.
Here's an example of a quoted piece of text using in-text citations vs. footnotes.
"Like the high whine of the dentist's drill, the low rumble of the footnote on the historian's page reassures" ( The Footnote: A Curious History [Cambridge, MA: Harvard University Press], 1999. pg. 1).
"Like the high whine of the dentist's drill, the low rumble of the footnote on the historian's page reassures." 1
[Text continues]
Bottom of the page:
1. The Footnote: A Curious History [Cambridge, MA: Harvard University Press], 1999. pg. 1
The exact format of your footnote depends on the style guide you're following. Here are some of the most common style guides for writing papers, as well as the footnote rules for each one.
Of the major style guides, The Chicago Manual of Style (CMS) uses footnotes most often. However, footnotes are occasionally employed in other style guides as well. The main difference is that, while CMS uses footnotes for citation purposes, the Modern Language Association (MLA) and the American Psychological Association (APA) generally rely on them for the provision of additional information.
While MLA style discourages the use of long footnotes or endnotes, the style guide does permit their use for directing readers to other pertinent information on a relevant subject.
The guide recommends that superscript numbers within the text are placed outside any punctuation that might be present (i.e., after a period if the note is at the end of a sentence and after a comma if the note is at the end of a clause). The exception to this is that the superscript numbers should be placed before dashes.
- When a footnote must be placed at the end of a clause, 1 add the number after the comma.
- When a footnote must be placed at the end of a sentence, add the number after the period. 2
- Numbers denoting footnotes should always appear after punctuation, with the exception of one piece of punctuation 3 —the dash.
4.1.2 American Psychological Association (APA)
Like MLA, APA discourages the use of footnotes unless absolutely necessary. Even then, the guide recommends that footnotes only be used to provide content notes (such as providing brief, supplemental information about the text or directing readers to additional information) and to denote copyright permissions. The rules regarding placement of the in-text numbers is the same in APA as in MLA.
4.1.3 The Chicago Manual of Style (CMS)
Of the three main style guides described here, CMS relies on footnotes the most. While CMS does allow the author–date system of in-text referencing (i.e., providing the author's name and the date of publication in parentheses at the end of the phrase, clause, or sentence that references the work), it also offers a citation style in which footnotes or endnotes are employed. In both cases, bibliographies are also required. Whether an author should use the author–date system or footnotes is often decided by the author's professor, journal, or publisher.
As an example, if footnotes are used, the following format should be adhered to when referencing a book in CMS:
Let Us Revise Your Reference Material to Any Style Guide
Try our academic proofreading service , or get a free sample.
To use footnotes in your own book, essay, or article, you must first decide on the most appropriate and logical placement of your footnotes in the text. Add numbers according to your chosen style guide, and be sure to add the numbers directly after the phrase, clause, or sentence to which the corresponding footnote refers.
Most online writing programs (such as Microsoft Word and Google Docs) come with easy-to-use tools for inserting footnotes. Here are step-by-step guides to using footnotes in both these programs.
5.2 How to Add Footnotes in Microsoft Word
Here's how to use footnotes in Microsoft Word 2021:
- Click on the place in the text where you want the first footnote to appear.
- Under the References tab, you'll see the following symbol: AB.1. Beneath this symbol is a button with the words, "Insert Footnote." Click it to create your first footnote.
- After you click that button, two numbers should appear: one number should appear in the main text, and the corresponding number should appear at the bottom of the page.
- Write your citation or additional information next to the number that appears in the footer. Format the information according to the rules of your style guide.
- You can easily return to your place in the text by clicking the number at the beginning of the footnote.
Congrats! You've created your first footnote. You can also adjust the footnote settings (like the numbering) by clicking the arrow beside the Footnotes group. It's really that easy!
Here's how to use footnotes on Google Docs:
- Under the Insert tab, click on "Footnotes."
All you really have to do to create footnotes is click a button—it couldn't be easier!
6. Final Tips and Tricks
To improve your writing and avoid cluttering the page, you should use footnotes sparingly and only to provide helpful additions or citations. As previously noted, this information may be considered supplementary, which is why it's best to place it away from the main portion of your writing.
When creating your footnotes, always keep reader convenience in mind, and remember that the footnotes are there to convey helpful information. If your footnotes are excessive or unnecessary, readers are likely to become annoyed—they may even be distracted from the main points of your writing.
Now that you're no longer asking "What are footnotes?" and you know how to use them according to various style guides, footnotes can become a great asset to you as a writer. Be sure to follow the recommendations above, as well as those of your preferred style guide, to ensure that you're using footnotes to their best effect. Don't forget—if you ever need help with writing, our academic articles are here for you!
If you need professional proofreading , let Scribendi perfect your writing.
Image source: Daria Nepriakhina/Stocksnap.io
Polish Your Writing with Professional Proofreading
About the author.

Scribendi's in-house editors work with writers from all over the globe to perfect their writing. They know that no piece of writing is complete without a professional edit, and they love to see a good piece of writing transformed into a great one. Scribendi's in-house editors are unrivaled in both experience and education, having collectively edited millions of words and obtained numerous degrees. They love consuming caffeinated beverages, reading books of various genres, and relaxing in quiet, dimly lit spaces.
Have You Read?
"The Complete Beginner's Guide to Academic Writing"
Related Posts

How to Cite a Website (and Achieve True Unagi)

How to Create a Bibliography Using Word

Turabian Style: How to Use It
Upload your file(s) so we can calculate your word count, or enter your word count manually.
We will also recommend a service based on the file(s) you upload.
English is not my first language. I need English editing and proofreading so that I sound like a native speaker.
I need to have my journal article, dissertation, or term paper edited and proofread, or I need help with an admissions essay or proposal.
I have a novel, manuscript, play, or ebook. I need editing, copy editing, proofreading, a critique of my work, or a query package.
I need editing and proofreading for my white papers, reports, manuals, press releases, marketing materials, and other business documents.
I need to have my essay, project, assignment, or term paper edited and proofread.
I want to sound professional and to get hired. I have a resume, letter, email, or personal document that I need to have edited and proofread.
Prices include your personal % discount.
Prices include % sales tax ( ).

Generate accurate APA citations for free
- Knowledge Base
- APA Style 7th edition
- APA Footnotes | Format & Examples
APA Footnotes | Format & Examples
Published on June 7, 2022 by Eoghan Ryan . Revised on January 17, 2024.
To cite sources in APA Style , you must use APA in-text citations , not notes.
However, you can use footnotes in APA to:
- Give additional information
- Provide copyright attribution
Footnotes can appear at the bottom of relevant pages, or they can be grouped together and placed on a separate page at the end of the text.
Instantly correct all language mistakes in your text
Upload your document to correct all your mistakes in minutes

Table of contents
Formatting footnotes in apa, content footnotes, copyright footnotes, frequently asked questions about apa footnotes.
Footnotes use superscript numbers and should appear in consecutive order. Footnote numbers typically appear at the end of a sentence or clause, after the period or other punctuation.
However, there are exceptions:
- If a footnote relates to text in parentheses, the footnote number should also appear inside the parentheses.
- If the footnote relates to material offset by a dash , the footnote number should come before the dash, rather than after.
Don’t repeat footnotes. If you need to refer to an earlier note again, write “see Footnote 3” or similar in the text or in parentheses.
Footnotes can appear either at the bottom of the relevant page, or at the end of the paper on a separate footnotes page. You can choose which approach to use.
Footnotes at the bottom of the page
You can use your word processor to automatically insert footnotes at the bottom of the page. This will ensure that each superscript number in the text corresponds to the correct footnote. It will also separate them from the main text.
Footnotes at the bottom of a page should be single-spaced.
There should be a single space between the superscript number and the footnote text.

Footnotes page at the end of the paper
When placing footnotes at the end of a text in APA, place them on a separate footnotes page, after the reference page .

The title of the page, “Footnotes,” should be centered and bold.
Indent the first line of each footnote and place a single space between the superscript number and the footnote text. Like most text in an APA format paper, footnotes at the end of the text should be double-spaced.
Footnotes should be presented in the order their numbers appear in the text.
Are your APA in-text citations flawless?
The AI-powered APA Citation Checker points out every error, tells you exactly what’s wrong, and explains how to fix it. Say goodbye to losing marks on your assignment!
Get started!

You can use content footnotes in APA to provide additional information to readers. For example, you might clarify a specific point or direct the reader to sources that contain more detail on a related topic.
As APA doesn’t encourage the use of footnotes, you should keep these notes as brief as possible. They should not exceed one paragraph. You can consider including longer material in an APA appendix instead.
If you include copyright material that exceeds fair use guidelines (like an extended passage from a book, or test or scale items), you may need to obtain permission from the copyright holder. You can use footnotes in APA to acknowledge this permission.
If you receive permission to reproduce an image or infographic, include this copyright note in the relevant caption, not in a footnote.
APA Style requires you to use APA in-text citations , not footnotes, to cite sources .
However, you can use APA footnotes sparingly for two purposes:
- Giving additional information
- Providing copyright attribution
APA footnotes use superscript numbers and should appear in numerical order. You can place footnotes at the bottom of the relevant pages, or on a separate footnotes page at the end:
- For footnotes at the bottom of the page, you can use your word processor to automatically insert footnotes .
- For footnotes at the end of the text in APA, place them on a separate page entitled “Footnotes,” after the r eference page . Indent the first line of each footnote, and double-space them.
For both approaches, place a space between the superscript number and the footnote text.
To insert a footnote automatically in a Word document:
- Click on the point in the text where the footnote should appear
- Select the “References” tab at the top and then click on “Insert Footnote”
- Type the text you want into the footnote that appears at the bottom of the page
Cite this Scribbr article
If you want to cite this source, you can copy and paste the citation or click the “Cite this Scribbr article” button to automatically add the citation to our free Citation Generator.
Ryan, E. (2024, January 17). APA Footnotes | Format & Examples. Scribbr. Retrieved April 2, 2024, from https://www.scribbr.com/apa-style/apa-footnotes/
Is this article helpful?


Eoghan Ryan
Other students also liked, beginner's guide to apa in-text citation, apa format for academic papers and essays, creating apa reference entries, "i thought ai proofreading was useless but..".
I've been using Scribbr for years now and I know it's a service that won't disappoint. It does a good job spotting mistakes”
Footnotes in a Paper: How to Use Them Effectively in Your Writing
Discover the best way to use footnotes in a paper. Get expert tips on how to efficiently and effectively use footnotes in academic papers.
Footnotes in a paper can be a valuable tool in providing a way to supplement our writing with additional information, citations, and explanations without disrupting the flow of the main text. However, many writers may be unsure of when and how to use footnotes effectively. In this article, we will explore the importance and usage of footnotes in academic writing, and provide practical tips for incorporating footnotes into your own writing. Whether you are a seasoned academic writer or just starting out, understanding how to use footnotes can help you increase the clarity and credibility of your writing.
What Are Footnotes?
Footnotes are a useful tool in academic writing that allows for the inclusion of additional information or comments in a document or text. Typically denoted by a small number or symbol in the main text, footnotes in a paper appear at the bottom of the page and can serve a variety of purposes. For example, footnotes can be used to clarify a point, provide background information, or give credit to a source that is not directly quoted or referenced in the main text. They are also helpful in avoiding disruptions to the flow of the main text, particularly when lengthy citations or explanations are required. In short, footnotes provide readers with additional information or references related to specific sections of the text, making them a valuable tool for researchers.
How to Write a Footnote
To write a footnote for a paper, follow these general steps:
- Determine what information needs to be included in the footnote. This may include the author’s name, the title of the source, the publication date, the publisher, and the page number(s) you are referencing.
- Place the footnote number or symbol at the end of the sentence or clause that requires the footnote. The footnote number or symbol should be placed after the punctuation, such as a period or comma.
- Write the footnote itself at the bottom of the page. The first line of the footnote should be indented, and the subsequent lines should be flush with the left margin.
- Format the footnote according to the citation style you are using (e.g. MLA, APA , Chicago). Each citation style has specific rules for how footnotes should be formatted, so consult the appropriate style guide for details.
- If you are using a word processing program, such as Microsoft Word, you can use the “Insert Footnote” function to automatically insert footnotes and format them correctly.
Difference Between Footnotes and Endnotes
The main difference between footnotes and endnotes is their placement within a document. Footnotes appear at the bottom of the page on which they are referenced, while endnotes appear at the end of a document, chapter, or section.
Here are some other differences between footnotes and endnotes:
Chicago Style Footnotes
Chicago-style footnotes are a common citation style used in research papers. In this format, footnotes are used to provide information about a source within the text. There are two types of Chicago-style footnotes: short form and long form. Short form citations include only the basic details of a source if a full bibliography is provided, while long form citations include a full citation the first time a source is cited, with subsequent citations using the short form.
Here is an example of a Chicago-style footnote using the short form:
“The concept of social capital has been widely discussed in recent years, with Putnam’s Bowling Alone¹ being one of the most influential works in the field.” At the bottom of the page, the corresponding footnote would appear as: ¹ Putnam, Bowling Alone, 26.
Note that the author’s last name is listed first, followed by the abbreviated title of the work (in this case, “Bowling Alone”), and the page number where the information was found.
Here is a Chicago-style footnote using the short form example:
First reference: John Smith, The History of Chicago (Chicago: University of Chicago Press, 2005), 25. Subsequent reference: Smith, The History of Chicago, 30.
Here is an example of a Chicago footnote in text:
“According to Smith, the notion of human rights can be traced back to ancient Greek philosophy.¹”² Bottom of page: ¹John Smith, The Origins of Human Rights (New York: Oxford University Press, 2021), 15. ²Smith, Origins of Human Rights, 22.
Learn how to make citations in Chicago style in our blog “ Chicago Style Citation Made Easy: Formatting and Examples “.
APA Style Footnotes
APA format generally uses parenthetical in-text citations instead of footnotes. However, there are two exceptions to this rule: content footnotes and copyright attribution. Content footnotes provide additional information on a single topic that does not fit coherently in the text, while copyright attribution footnotes are used when a writer uses a lengthy quotation or other copyrighted material, such as a stock photograph. Footnotes are formatted similarly to Chicago style, with sequential superscript numbers coming after the passage and the corresponding footnote at the bottom of the page.
Here’s an example of an APA-style footnote for supplementary information:
In-text: According to recent studies, the COVID-19 vaccine is highly effective in preventing infection and transmission of the virus.¹ Footnote: ¹For more information on the studies cited, see Smith et al. (2021) and Jones et al. (2022).
Learn how to make citations in APA style in our blog “ How to Make Citations using APA Formatting: A Guide “.
MLA Style Footnotes
MLA (Modern Language Association) style does not typically use footnotes. Instead, in-text citations are used to indicate the source of information or quotations. However, if footnotes are required for a specific publication or assignment, the following guidelines can be followed:
Placement: Footnotes should be placed at the bottom of the page on which the reference appears.
Numbering: Footnotes should be numbered consecutively throughout the paper using Arabic numerals. The number should be placed after any punctuation marks, such as periods or commas.
Formatting: Footnotes should be single-spaced and in a smaller font size than the main text.
Content: Footnotes should include bibliographic information for the source being cited, as well as any additional information necessary to clarify the reference. For example, a footnote for a book might include the author, title, publisher, and year of publication, while a footnote for a website might include the URL and date of access.
Example of MLA Style Footnote for a book:
John Doe, The History of Art (New York: Penguin Books, 2000), 24. Example of MLA Style Footnote for a website: “The Benefits of Exercise,” National Institutes of Health, accessed May 15, 2023, https://www.nih.gov/health-information/benefits-exercise .
A MLA Style footnote text example:
Text: According to a recent study, the use of social media can have negative effects on mental health (Johnson 36).² Footnote citation: ² Johnson, Sarah. “The Impact of Social Media on Mental Health.” Journal of Health Psychology, vol. 22, no. 1, 2018, pp. 35-44.
Learn how to make citations in MLA style in our blog “ A Writer’s Guide to MLA Format: How to Get It Right “.
Improve your papers’ impact and visibility through quality visual communication
Mind the Graph is an innovative platform that provides a wide range of tools to help scientists improve their papers’ impact and visibility through quality visual communication. With Mind the Graph, scientists can easily create graphical abstracts, posters, and other visual aids that can effectively communicate their research findings to a wider audience.

Subscribe to our newsletter
Exclusive high quality content about effective visual communication in science.
Content tags

How to Format Your Research Paper
- APA 7 Paper Format
- MLA Paper Format
- Chicago Paper Format
How to Create Footnotes
- Hanging Indents
- Ask a Librarian
What Are They
Footnotes are short numbered notes that are placed at the bottom of the page in an essay or article. They are used for a variety of reasons including, citing materials, providing notes on a source or topic, and to acknowledge copyright status.
Although you will find footnotes in many journal articles, they are not typically required in APA or MLA formatted essays. They are most heavily used when applying the CMOS style.
For information on footnotes in the Publication Manual of the American Psychological Association see section 2.13 "Footnotes.". For information on using footnotes with MLA see the " Using Notes in MLA Style " article from the MLA Style Center . For information on footnotes in The Chicago Manual of Style see Chapter 14 "Notes and Bibliography."
Using Google Docs:
- Cómo incorporar notas al calce en Google Docs Vea éste video en español.
Using Microsoft Word:
- Cómo incorporar notas al calce en Microsoft Word Vea éste video en español.
- << Previous: Chicago Paper Format
- Next: Hanging Indents >>
- Last Updated: Mar 29, 2024 2:49 PM
- URL: https://necc.mass.libguides.com/formatting
To cite this LibGuide use the following templates:
APA : Northern Essex Community College Library. (Date updated). Title of page . Title of LibGuide. URL
MLA : Northern Essex Community College Library. "Title of Page." Title of LibGuide, Date updated, URL.
Purdue Online Writing Lab Purdue OWL® College of Liberal Arts
General Format

Welcome to the Purdue OWL
This page is brought to you by the OWL at Purdue University. When printing this page, you must include the entire legal notice.
Copyright ©1995-2018 by The Writing Lab & The OWL at Purdue and Purdue University. All rights reserved. This material may not be published, reproduced, broadcast, rewritten, or redistributed without permission. Use of this site constitutes acceptance of our terms and conditions of fair use.
This section contains information on The Chicago Manual of Style (CMOS) method of document formatting and citation. These resources follow The Chicago Manual of Style (17th edition), which was issued in 2017.
Since The Chicago Manual of Style (CMOS) is primarily intended as a style guide for published works rather than class papers, these guidelines will be supplemented with information from, Kate L. Turabian’s Manual for Writers of Research Papers, Theses, and Dissertations (8th ed.), which is largely based on CMOS with some slight alterations.
To see a side-by-side comparison of the three most widely used citation styles, including a chart of all CMOS citation guidelines, see the Citation Style Chart.
Please use the example at the bottom of this page to cite the Purdue OWL in CMOS.
A Note on Citations
Unlike many citation styles, CMOS gives writers two different methods for documenting sources: the Author-Date System and the Notes-Bibliography (NB) System. As its name suggests, Author-Date uses parenthetical citations in the text to reference the source's author's last name and the year of publication. Each parenthetical citation corresponds to an entry on a References page that concludes the document. In these regards, Author-Date is very similar to, for instance, APA style.
By contrast, NB uses numbered footnotes in the text to direct the reader to a shortened citation at the bottom of the page. This corresponds to a fuller citation on a Bibliography page that concludes the document. Though the general principles of citation are the same here, the citations themselves are formatted differently from the way they appear in Author-Date.
If you are using CMOS for school or work, don't forget to ensure that you're using your organization's preferred citation method. For examples of these two different styles in action, see our CMOS sample papers:
Author-Date Sample Paper
NB Sample Paper
General CMOS Guidelines
- Text should be consistently double-spaced, except for block quotations, notes, bibliography entries, table titles, and figure captions.
- A prose quotation of five or more lines, or more than 100 words, should be blocked.
- CMOS recommends blocking two or more lines of poetry.
- A blocked quotation does not get enclosed in quotation marks.
- A blocked quotation must always begin a new line.
- Blocked quotations should be indented with the word processor’s indention tool.
- Page numbers begin in the header of the first page of text with Arabic number 1.
- For CMOS and Turabian’s recommendations, see “Headings,” below.
Supplemental Turabian Style Guidelines
- Margins should be set at no less than 1”.
- Typeface should be something readable, such as Times New Roman or Courier.
- Font size should be no less than 10 pt. (preferably, 12 pt.).
Major Paper Sections
- The title should be centered a third of the way down the page.
- Your name, class information, and the date should follow several lines later.
- For subtitles, end the title line with a colon and place the subtitle on the line below the title.
- Double-space each line of the title page.

CMOS Title Page
- Different practices apply for theses and dissertations (see Kate L. Turabian’s A Manual for Writers of Research Papers, Theses, ad Dissertations [8 th ed.].
- Titles mentioned in the text, notes, or bibliography are capitalized “headline-style,” meaning first words of titles and subtitles and any important words thereafter should be capitalized.
- Book and periodical titles (titles of larger works) should be italicized.
- Article and chapter titles (titles of shorter works) should be enclosed in double quotation marks.
- The titles of most poems should be enclosed in double quotation marks, but the titles of very long poems should be italicized.
- Titles of plays should be italicized.
- For example, use lowercase terms to describe periods, except in the case of proper nouns (e.g., “the colonial period,” vs. “the Victorian era”).
- A prose quotation of five or more lines should be “blocked.” The block quotation should match the surrounding text, and it takes no quotation marks. To offset the block quote from surrounding text, indent the entire quotation using the word processor’s indentation tool. It is also possible to offset the block quotation by using a different or smaller font than the surrounding text.
- Label the first page of your back matter, your comprehensive list of sources, “Bibliography” (for Notes and Bibliography style) or “References” (for Author-Date style).
- Leave two blank lines between “Bibliography” or “References” and your first entry.
- Leave one blank line between remaining entries.
- List entries in letter-by-letter alphabetical order according to the first word in each entry, be that the author's name or the title of the piece..
- For two to three authors, write out all names.
- For four to ten authors, write out all names in the bibliography but only the first author’s name plus “et al.” in notes and parenthetical citations.
- When a source has no identifiable author, cite it by its title, both on the references page and in shortened form (up to four keywords from that title) in parenthetical citations throughout the text.
- Write out publishers’ names in full.
- Do not use access dates unless publication dates are unavailable.
- If you cannot ascertain the publication date of a printed work, use the abbreviation “n.d.”
- Provide DOIs instead of URLs whenever possible.
- If no DOI is available, provide a URL.
- If you cannot name a specific page number when called for, you have other options: section (sec.), equation (eq.), volume (vol.), or note (n.).

CMOS Bibliography Page
- Note numbers should begin with “1” and follow consecutively throughout a given paper.
- Note numbers are superscripted.
- Note numbers should be placed at the end of the clause or sentence to which they refer and should be placed after all punctuation, except for the dash.
- Note numbers are full-sized, not raised, and followed by a period (superscripting note numbers in the notes themselves is also acceptable).
- In parenthetical citation, separate documentation from brief commentary with a semicolon.
- Do not repeat the hundreds digit in a page range if it does not change from the beginning to the end of the range.
For more information on footnotes, please see CMOS NB Sample Paper .
While The Chicago Manual of Style does not include a prescribed system for formatting headings and subheads, it makes several recommendations.
- Maintain consistency and parallel structure in headings and subheads.
- Use headline-style for purposes of capitalization.
- Subheadings should begin on a new line.
- Subheadings can be distinguished by font-size.
- Ensure that each level of hierarchy is clear and consistent.
- Levels of subheads can be differentiated by type style, use of boldface or italics, and placement on the page, usually either centered or flush left.
- Use no more than three levels of hierarchy.
- Avoid ending subheadings with periods.
Turabian has an optional system of five heading levels.
Turabian Subheading Plan
Here is an example of the five-level heading system:

CMOS Headings
Tables and Figures
- Position tables and figures as soon as possible after they are first referenced. If necessary, present them after the paragraph in which they are described.
- For figures, include a caption, or short explanation of the figure or illustration, directly after the figure number.
- Cite a source as you would for parenthetical citation, and include full information in an entry on your Bibliography or References page.
- Acknowledge reproduced or adapted sources appropriately (i.e., photo by; data adapted from; map by...).
- If a table includes data not acquired by the author of the text, include an unnumbered footnote. Introduce the note by the word Source(s) followed by a colon, then include the full source information, and end the note with a period.
How to Cite the Purdue OWL in CMOS
On the new OWL site, contributors’ names and the last edited date are no longer listed at the top of every page. This means that most citations will now begin with the title of the resource, rather than the contributors' names.
Footnote or Endnote (N):
Corresponding Bibliographical Entry (B):
“Title of Resource.” List the OWL as Publishing Organization/Web Site Name . http://Web address for OWL resource.
“General Format.” The Purdue OWL. https://owl.english.purdue.edu/owl/resource/717/02/.
Author Date In-text Citation:
("General Format" 2017).
Author Date References Page Citation:
Year of Publication. “Title of Resource.” List the OWL as Publishing Organization/Web Site Name . http://Web address for OWL resource.
2017. “General Format.” The Purdue OWL . https://owl.english.purdue.edu/owl/resource/717/02.
Quill And Fox
Best Design Studio

Amber Robertson
Amber Robertson is the founder of Quill and Fox. A creative writing studio that helps people find their voice and share their stories. Amber is also a published author, with her first book slated for release in 2020. She loves spending time with her family and friends, reading, writing, and traveling. When Amber was younger, she loved to write short stories and plays. But somewhere along the way, she lost touch with her creativity. It wasn’t until she became a mom that she realized how important it was to share her stories—both the good and the bad—with the people she loves most. That’s when Quill and Fox was born. Amber is passionate about helping others find their voice and share their stories. She believes that every person has a story worth telling, and it’s her mission to help them tell it in a way that is authentic and true to themselves

What are Footnotes in a Paper? A Comprehensive Guide
Table of Contents
If you are a student or academic, you have likely come across footnotes in your research papers or essays. But what exactly are footnotes, and why are they important?
Definition of Footnotes in a Paper
Footnotes are notes placed at the bottom of a page in a document that provide additional information or clarification about a particular point in the text. They are often used in academic writing to give credit to sources, provide context to the reader, or expand on a concept.
Importance of Using Footnotes in a Paper
Using footnotes in your paper has several benefits. First, they allow you to give credit to sources and avoid plagiarism. By including a footnote citation for a source, you are acknowledging the original author’s work and avoiding potential legal issues.
Second, footnotes can provide additional context or background information on a particular topic. If you are writing about a complex concept or historical event, a footnote can provide the reader with more information that they may find helpful.
Finally, footnotes can help you maintain a professional and scholarly tone in your writing. By using footnotes to cite sources and provide additional information, you are demonstrating your expertise and attention to detail.
Footnotes serve several purposes in a paper, including providing additional information, giving credit to sources, and clarifying confusing or complex concepts.
To Provide Additional Information
One of the primary purposes of footnotes in a paper is to provide additional information that would otherwise disrupt the flow of the main text. For example, if you are writing about a historical event and want to include a specific date or detail, you can include it in a footnote rather than interrupting the main narrative.
Footnotes can also be used to provide background information on a particular topic. If you are discussing a complex concept or theory, a footnote can provide the reader with more information that they may find helpful.
To Give Credit to Sources
Another common use of footnotes is to give credit to sources. When you use someone else’s work in your paper, whether it is a direct quote or a paraphrase, you need to cite the source to avoid plagiarism.
By including a footnote citation for a source, you are acknowledging the original author’s work and giving the reader a way to find the source if they want to learn more.
Stay tuned to read the next two sections.
Types of Footnotes in a Paper

When it comes to footnotes in a paper, there are several different types that you may encounter. Understanding the different types of footnotes and how to use them can help you create a professional and effective paper.
Content Footnotes
Content footnotes are used to provide additional information or clarification about a particular point in the text. They can be used to define a term, provide a source for a statistic, or give more detail about a historical event.
Copyright Footnotes
Copyright footnotes are used to indicate that a particular piece of content is protected by copyright law. If you are using a copyrighted image, for example, you may include a copyright footnote to indicate that you have obtained the necessary permissions to use the image.
Citation Footnotes
Citation footnotes are used to give credit to sources. When you use someone else’s work in your paper, whether it is a direct quote or a paraphrase, you need to cite the source to avoid plagiarism. Citation footnotes typically include information such as the author’s name, the title of the work, and the page number.
How to Use Footnotes in a Paper
Using footnotes in a paper may seem straightforward, but there are some important guidelines to follow to ensure that your paper is professional and effective.
Placement of Footnotes
Footnotes should be placed at the bottom of the page where the text appears. If you are using Microsoft Word, you can use the “Insert Footnote” function to automatically create a footnote at the bottom of the page.
Formatting of Footnotes
Footnotes should be formatted consistently throughout your paper. They should be single-spaced with a space between each footnote. The font size should be the same as the main text, and the footnote number should be superscripted.
Numbering of Footnotes
Footnotes should be numbered sequentially throughout your paper. Each footnote should have a unique number, and the number should appear at the beginning of the footnote. If you need to reference a footnote later in your paper, you can use the footnote number to indicate which footnote you are referring to.
Common Mistakes to Avoid When Using Footnotes in a Paper
While footnotes can be a valuable tool in your writing, there are several common mistakes that you should avoid when using them.
Overuse of Footnotes
One of the most significant mistakes you can make when using footnotes is to overuse them. While footnotes can provide valuable information, using too many can be distracting and disrupt the flow of your writing.
As a general rule, footnotes should be used sparingly and only when necessary. If you find that you are using more than a few footnotes per page, you may want to consider whether the information would be better incorporated into the main text.
Inconsistent Formatting
Another mistake to avoid when using footnotes is inconsistent formatting. If your footnotes are formatted differently throughout your paper, it can be confusing for the reader and make it difficult to follow the information.
Make sure that you use a consistent format for all of your footnotes, including the font, size, spacing, and placement on the page. This will help ensure that your paper looks professional and is easy to read.
Failure to Properly Cite Sources
Finally, one of the most critical mistakes to avoid when using footnotes is failing to properly cite your sources. Whenever you use someone else’s work in your paper, whether it is a direct quote or a paraphrase, you need to cite the source.
Make sure that you are using the correct citation style for your paper, and that you are including all of the necessary information in your footnote citation. This will help ensure that you are giving credit to your sources and avoiding plagiarism.
In conclusion, footnotes are an essential tool in academic writing that can help you provide additional information, give credit to sources, and maintain a professional tone in your writing. When using footnotes in your paper, it is important to avoid common mistakes like overuse, inconsistent formatting, and failure to properly cite sources.
By using footnotes effectively and avoiding these mistakes, you can create a well-crafted paper that demonstrates your expertise and attention to detail.
How-To Geek
How to use footnotes and endnotes in microsoft word.
Whether you use Microsoft Word for personal or professional writing, sometimes you may want to add supplemental notes to sections of your work.
Quick Links
What are footnotes and endnotes, how to insert footnotes and endnotes, how to configure footnotes and endnotes in word 2016, how to cross-reference footnotes and endnotes in word 2016.
Whether you use Microsoft Word for personal or professional writing, sometimes you may want to add supplemental notes to sections of your work. Maybe you want to make a side comment on one of your arguments, or you need to cite another author's work without distracting from the main text. Luckily, Word has useful tools for adding footnotes and endnotes to your writing.
We're using Microsoft Word 2016, but Word has supported footnotes and endnotes since at least Word 2007. Depending on the version of Word you're using, the menus we walk through in this guide may look a little different. But don't worry---the features and functions are the same.
Footnotes and endnotes are both ways of adding extra bits of information to your writing outside of the main text. Think of them like verbal asides, only in writing. You can use footnotes and endnotes to add side comments to your work or to cite other publications like books, articles, or websites. The only difference between footnotes and endnotes is where they appear in your document.
As the name suggests, footnotes are attached to the bottom of the page containing the sentence they correspond to. Endnotes, on the other hand, are added to the end of a section or document. Which one you should use in your writing depends on your personal preference or---if you're writing for school or work---your organization's publication standards.
Fire up Microsoft Word, and then open the document to which you'd like to add footnotes (or create a new document if you're just getting started). Switch to the "References" tab on Word's Ribbon.
Here, you'll find a bunch of useful features for annotating your text, including tools for inserting a table of contents, adding citations, and generating a bibliography . The second group on this tab contains the footnote and endnote features we want.
To add a footnote, place your insertion point in your text where you want the footnote to appear, and then click the "Insert Footnote" button.
Word adds a small superscript number where you placed the insertion point.
And then immediately shifts focus to the footnote pane and places the insertion point at your new footnote, so you can start typing it right away.
Footnotes appear at the bottom of the page beneath a short horizontal line. Each time you add a footnote on this page, another number will be added to the list.
Once you've added your footnotes, you can hover your cursor over each sentence's reference marker to see a preview of the footnote within the text.
You can also quickly tab between footnotes in both the main text and the footnote list at the bottom of the page by clicking the "Next Footnote" button in the navigation bar.
Or, click the dropdown menu arrow on the "Next Footnote" button to select a different navigation option. You can choose to go to the previous footnote or navigate to the next or previous endnote.
The steps for inserting endnotes are essentially the same. Place your insertion point where you'd to annotate, and then click the "Insert Endnote" button on the "References" tab of Word's Ribbon.
Just like with footnotes, Word attaches a superscript number containing an endnote. But this time, the list of notes it generates appears at the end of the current section or the end of the document (you can customize where they appear, and we'll talk more about that in a bit).
Word has basic default settings for footnotes and endnotes, but you can adjust these settings at any time from the menu on the References tab.
Click the arrow in the lower right corner of the "Footnotes" menu.
This brings up a Footnote and Endnote window where you can customize the location, appearance, and format of all your footnotes and endnotes.
Change the Location of Footnotes and Endnotes
By default, Word puts footnotes at the bottom of the page and endnotes at the end of the document, but you can change where these notes appear.
Under "Location" in the Footnote and Endnote menu, find the "Footnotes" option (it should be selected by default when you first open the menu). Open the dropdown menu to the right of that option and you can change your footnote location to either the bottom of the page or below the text. If you choose the latter option, Word places your footnotes immediately after the main body of text instead of at the bottom of the page.
To change the default location of endnotes, select the "Endnotes" option, and then open the dropdown menu to its right. There, you can change endnote placement to the end of the current section or the end of the document.
Convert Footnotes to Endnotes (and Vice Versa)
Another option is to convert all of your footnotes to endnotes or vice versa. Instead of changing each one individually, this option lets you change them all at once. If you're working on a document with a lot of notes, this option can come in handy.
Under the "Location" section of the Footnote and Endnote menu, click the "Convert" button.
The Convert Notes dialog box pops up, giving you three options: 1) Convert All Footnotes to Endnotes, 2) Convert All Endnotes to Footnotes, and 3) Swap Footnotes and Endnotes. Select the option you want, and then click the "OK" button.
Change the Layout of Footnotes and Endnotes
By default, Word creates footnote and endnote lists with the same layout as the page on which they appear. However, you can adjust this from the Footnote and Endnote window by clicking the "Columns" dropdown menu and selecting the number of columns you'd like to use.
You can set your footnotes and endnotes to display in up to four different columns on the page.
Customize the Format of Footnotes and Endnotes
Word also lets you choose from several options for formatting how your footnotes and endnotes are numbered. It's generally a good idea to choose a different numbering system for each note type, especially if you're using a combination of footnotes and endnotes in the same document. This helps you and your reader quickly distinguish between the two at a glance.
In the Format section, click the dropdown arrow to the right of the "Number Format" option. Select your desired number format.
You can also label your notes with a custom symbol instead of a standard numbering system. Next to the Custom Mark option, click the "Symbol" button.
The Symbol menu will open. Select the symbol you'd like to use to label your notes, and then click the "OK" button.
Your selected icon should appear in the "Custom Mark" box, and Word will now use this symbol to label your notes.
By default, Word numbers footnotes and endnotes in individual series starting at "1" (or a, i, I, etc.) and continuing throughout the document. However, you can customize both the starting point and continuity of your notes.
If you want your footnotes or endnotes to start somewhere other than the first number in the series (for example, 2 instead of 1), click the arrows in the "Start At" dropdown box to increase or decrease the beginning value. One example of where this might be useful is if you're writing a book that contains endnotes and you're saving each chapter as a separate Word document. You could configure each chapter's document to start numbering endnotes where the last chapter left off.
To change the continuity of your numbering series, click the dropdown menu arrow next to the "Numbering" option.
You'll see three options for numbering your footnotes and endnotes: Continuous, Restart Each Section, and Restart Each Page. If you want your footnotes and endnotes to be numbered continuously from the beginning of your document to the end, select the "Continuous" option. If you'd prefer to have your notes numbered by chapter or section, select the "Restart Each Section" option. Or select "Restart Each Page" to number your notes by page.
Apply Your Changes to the Document
After configuring the above options, you'll need to select how you want your changes applied to your document. At the bottom of the menu, click the dropdown menu arrow next to the "Apply Changes To" option.
If you want your changes to apply to every page and section of your document, select the "Whole Document" option. Or select "This Section" to apply changes only to the section of the document you're currently in. (Note that this option will not appear if you have no section breaks in your document.)
Once you're satisfied with your settings, click the "Apply" button in the bottom right of the menu.
You can also insert a new footnote using your selected settings by clicking the "Insert" button in the lower left corner of the menu.
If you want to use the same footnote or endnote more than once throughout your text, there's an easy way to do it without having to insert the same thing over and over again.
Place your insertion point where you want a reference inserted into the text. On the References tab, click the "Cross-Reference" button.
In the Cross-Reference window, choose either "Footnote" or "Endnote" from the "Reference Type" dropdown menu.
Next, click the "Insert Reference To" dropdown menu.
The "Footnote Number" option inserts the number of the footnote in regular text, while the "Footnote Number (Formatted)" option inserts the number of the footnote in superscript. The "Page Number" option inserts the number of the referenced page instead of the footnote number. The "Above/Below" option inserts either the word "Above" or "Below" depending on where the original footnote appears in relation to the cross-reference. Select your desired option.
Word lets you create hyperlinks between cross-references so you can easily find the same footnote everywhere it appears in your document. The "Insert as Hyperlink" option is checked by default, so you can click any cross-reference and automatically be taken to the part of the document containing the original footnote. We recommend leaving this option checked, but you can uncheck it if you prefer.
Under the "For Which Footnote" option, select the footnote you'd like to cross-reference, and then click the "Insert" button at the bottom of the menu.

Footnotes for white papers 101
Footnotes are an essential ingredient of a persuasive white paper..
It’s not difficult to write down your views.
It’s much harder to find compelling evidence to back up those views.

Footnotes help build your argument and prove that you did your homework.
But most writers have never thought much about footnotes since, well, college.
To help you use footnotes effectively, here are answers to some frequently asked questions about them.
Q: How can I tell when I need a footnote?
Whenever you define a term , find a source for your definition. Example: “PII is any information that can link an account number to a specific person.”
Whenever you give a number, date, or statistic , back it up with a reliable source. Example: “Since 2000, more than 200 million accounts have been exposed in security breaches in the U.S. alone.”
Whenever you state a controversial view , include a reference to help quiet the doubts that arise in the reader’s mind. Example: “By now, the cloud is perfectly secure for any enterprise.”
Note how all three examples look questionable without any sources. Each one would be much stronger with a footnote that gave a precise reference.
Q: Which are better: footnotes or endnotes?
As you know, a footnote falls at the bottom of a page, while an endnote is placed at the end of a document. This small detail makes a big difference.
Footnotes provide immediate credibility. Many readers glance down the page to see them, so they tend to be noticed. Footnotes look scholarly and suggest that a document is well-researched.
Endnotes are more tidy, since they do not break up the reading experience of a page. But fewer people flip back to see them, so endnotes tend to add less authority to a document.
It’s your choice which format you use.
For a longer discussion of this question, see my article here .
Q: How much text can I legally quote in a white paper?
You’re generally safe to quote a sentence or two from any published source like a newspaper, magazine, blog or company website, as long as you give proper credit.
Some say that you can legally use 200 or 300 words from any source. But this isn’t carved in stone.
According to the U.S. Copyright Office, “there is no formula to ensure that a predetermined percentage or amount of a work—or specific number of words, lines, pages, copies—may be used without permission.” [1]
Copyright material can be quoted for comment, education, parody, reporting, or research under “fair use” provisions.
Here is the key question to ask: Am I costing someone money to quote what I want from their material?
Here’s a thought experiment. Suppose someone wrote a book called 10 Dumb Things IT Managers Do to Undermine Their Careers .
If you come along and quote one of their 10 points, along with the full title and publisher, you likely won’t hurt sales of that book. You could even say you helped promote it.
But if you copy all 10 points with a fair chunk of text under each item, that’s giving away too much of someone else’s content.
The author and publisher could well argue that you hurt sales and cost them money.
To be practical, no one sues anyone else unless there’s a great deal of money at stake. Just be reasonable, and you shouldn’t have any legal problems.
Q: When do I need permission to quote from another document?
Some publishers that produce premium newsletters, market research, or other original material want you to ask permission before you quote anything from them.
Some industry analysts like Gartner try to enforce this policy.
If you simply want to quote one factoid that was already widely reported by other websites or publications, you can likely skip getting permission.
But if you grab all the best insights from a report priced at $3,995 and put them into your own white paper, the publisher may get pretty annoyed.
Can you blame them?
Once again, ask yourself the key question: Am I costing someone money to quote what I want from their material?
If you do want to quote from a high-priced report, always consider asking permission from the publisher. You can usually find contact information at the front of the report.
Q: How should I format my footnotes?
Here are two down-to-earth principles for formatting footnotes in a white paper:
- A footnote must provide enough detail for an interested reader to find that source if they wish.
- Footnote formats must be consistent within any white paper, and ideally across all white papers from a company.
Most white paper sponsors and readers will not notice much beyond these basics. You simply want your footnotes to be clear, accurate and complete.
For example, here is the format I use for footnotes in my white papers:
X: Author Name, “Title of Book or Article”, Publication (for articles), Publisher, date, page
To avoid any confusion, I give dates with the day first as in “13 March 2016” in the way more popular in Europe. Even if someone has never seen this format in their life, it’s abundantly clear.
Q: How can I cite a webpage?
If your source is a blog or website, you can append a URL to a footnote to show where and when you found the document online. For example:
retrieved 20 March 2016 from www.domain.com/page.html
Q: Where can I find out more about footnotes?
If you want to venture deeper, there are several styles for academic footnotes, including:
- APA (American Psychological Association) , often used in social sciences
- Chicago , often used in history and economics
- MLA (Modern Language Association) , often used in liberal arts and literature.
Don’t worry: The differences between them are immaterial to any B2B white paper readers.
But if you happen to be writing a white paper for academics, they may well notice. In this case, pick one footnote style and stick to it carefully, or have an academic review your formatting before you publish.
[1]: “More Information on Fair Use,” U.S. Copyright Office, retrieved 27 February 2016 from http://copyright.gov/fair-use/more-info.html
How do you use footnotes in white papers? Which type and style do you prefer? Please leave your comments below.
Want to hear whenever there’s a fresh article on this site? Subscribe here to stay in the know on long-form content . From time to time, we’ll also send you word about some great new resource or training. And you can unsubscribe any time.

About Gordon Graham
Worked on 320+ white papers for clients from Silicon Valley to Switzerland, on everything from choosing enterprise software to designing virtual worlds for kids, for clients from tiny startups to 3M, Google, and Verizon. Wrote White Papers for Dummies which earned 60+ 5-star ratings on Amazon. Won 16 awards from the Society for Technical Communication. Named AWAI 2019 Copywriter of the Year.
If you liked this post...

White papers and… the Greek gods?!

Quick tip: How to layer information for multiple audiences

Quick tip: Don’t say “once every xx seconds…”
Yes, you are right on two counts: footnotes are essential to give a paper credibility, and I haven’t used footnotes in any paper since…well, college. I will keep this in mind when writing and doing my research.
Thank you for this clear coverage about using footnotes in white papers. Using the European data format is interesting. Appreciate it!
What’s your opinion on using hyperlinks in the white paper, as you did for the Question to find out more about footnotes? In that case, would we still need footnotes?
Leave a Comment Cancel Reply
This site is protected by reCAPTCHA and the Google Privacy Policy and Terms of Service apply.
Need a great white paper?
Log in using your username and password
- Search More Search for this keyword Advanced search
- Latest content
- Current issue
- Hosted content
- BMJ Journals More You are viewing from: Google Indexer
You are here
- Online First
- Predicting treatment response in ASUC: do we measure systemic severity, organ response or both?
- Article Text
- Article info
- Citation Tools
- Rapid Responses
- Article metrics
- Pernille D Ovesen 1 ,
- Johan Fredrik Kristoffer Fremberg Ilvemark 1 ,
- http://orcid.org/0000-0002-4928-4708 Rune Wilkens 2 , 3 ,
- Casper Steenholdt 1 ,
- http://orcid.org/0000-0003-3230-7966 Jakob Seidelin 1 , 4
- 1 Department of Gastroenterology and Hepatology , Herlev Hospital , Herlev , Denmark
- 2 Digestive Disease Center , Copenhagen University Hospital - Bispebjerrg , Copenhagen , Denmark
- 3 Copenhagen Intestinal Ultrasound , Copenhagen , Denmark
- 4 Department of Clinical Science , University of Copenhagen Faculty of Health and Medical Sciences , Kobenhavn , Denmark
- Correspondence to Professor Jakob Seidelin, Department of Gastroenterology and Hepatology, Herlev Hospital, Herlev 2730, Denmark; jakob.benedict.seidelin{at}regionh.dk
https://doi.org/10.1136/gutjnl-2023-331793
Statistics from Altmetric.com
Request permissions.
If you wish to reuse any or all of this article please use the link below which will take you to the Copyright Clearance Center’s RightsLink service. You will be able to get a quick price and instant permission to reuse the content in many different ways.
- ULCERATIVE COLITIS
- CLINICAL DECISION MAKING
- ULTRASONOGRAPHY
- SURGERY FOR IBD
We would like to congratulate Adams et al on the paper addressing the important issue regarding the development of prognostic clinical indexes for patients with acute severe ulcerative colitis (ASUC) leading to the development of the ADMIT-ASC score. 1
Although we acknowledge the initiative, the development of a static prognostic index might be reconsidered with the increased availability and use of noninvasive and real-time cross-sectional imaging.
Recently, we investigated the use of intestinal ultrasound (IUS) to measure early changes in the sigmoid bowel wall thickness (BWT) as an indicator of intravenous corticosteroid (CS) response in patients admitted with ASUC. A >20% reduction in BWT after 48 hours predicted CS response within 7 days (p<0.0001 for pMayo response, p=0.006 for no need of rescue therapy) and was superior to CRP, albumin or pMayo response at 48 hours in multivariate analysis. 2
With C-reactive protein (CRP), albumin and endoscopic severity scores being major components of the ADMIT-ASC score, we set out to apply this score to our cohort and indeed we did find a good correlation with CS-response across the different ADMIT-ASC scores between the Ilvemark cohort and the Adams cohort (r=0.95; p<0.03) with a CS-non-response of 60% in patients with ADMIT-ASC≥3 (see figure 1 ). However, no relationship was found between change in delta BWT (ie, dBWT) after 48 hours and the ADMIT-ASC score (see figure 2 ; r=0.02; p=0.30), giving the impression that dBWT and ADMIT-ASC are independent yet highly well performing prognostic markers of ASUC outcome assessing different aspects of the condition.
- Download figure
- Open in new tab
- Download powerpoint
Correlation plot between ADMIT-ASC and SUCCESS when applied to ADMIT-ASC (p<0.03). ♦ADMIT-ASC 0; ■ AMIT-ASC 1; ▲ADMIT-ASC 2; ●, ADMIT-ASC 3+4. CS, corticosteroid.
‘The greater the severity, the greater the risk of colectomy and fail of treatment’ is an old and intuitive thought. Recently, Grupta et al reaffirmed this thought in their latest review article on the topic, referring to data like the important work by Seow et al back in 2009, showing that UC severity scores correlated negatively with infliximab response and the classic work by Truelove and Witts showing higher risk of colectomy with increasing signs of systemic inflammation. 3–5 Given the components of the ADMIT-ASC score, it could be considered to be a severity score highly weighing the amount of systemic inflammatory burden by including CRP, albumin and endoscopic activity, which along the previous findings mentioned above could explain its efficacy in predicting outcome in ASUC. On the other hand, IUS parameters are solely probing the level of organ inflammation and the change in BWT, that is, dBWT, in the initial phase of treatment thus specifically assessing organ response to treatment.
There seems to have been a gradual change in the ASUC population over time with more severely affected and toxic patients in the early studies towards a slightly higher proportion of patients with lower Truelove-Witts scores being admitted for intravenous CS treatment in more recent populations, including the population in recent study from La Jolla, California, USA, as well as our study and the cohorts studied by Adams et al . 1 2 5 6 We, therefore, suggest that a more granular prognostic assessment of ASUC patients would require both a systemic severity score like the ADMIT-ASC score and an organ response score like dBWT to better detect and react to patients at high risk of need of rescue therapy or surgery.
Responding to CS during admission for ASUC is no guarantee for long-term remission. While the colectomy rate has fallen after the introduction of rescue therapy, the 1-year relapse-free rate in CS responders remains as low as 58% in a recent cohort. 7 8 It is presently unknown whether inflammation severity scores or measures of organ response predict long-term treatment failure. However, identification of these unstable post-ASUC patients may require markers based on deeper characterisation of the immunopathology behind differences in disease behaviour.
Ethics statements
Patient consent for publication.
Consent obtained directly from patient(s).
Ethics approval
- Mohsen W , et al
- Ilvemark JFKF ,
- Wilkens R ,
- Thielsen P , et al
- Chapman TP , et al
- Irwin SP , et al
- TRUELOVE SC ,
- Hemperly A ,
- Truong S , et al
- Salameh R ,
- Kirchgesner J ,
- Allez M , et al
- Radojicic Z ,
- Nedeljkovic-Protic M , et al
Twitter @RuneWilkens, @jakobseidelin
Contributors PDO: study concept and design; acquisition of data; analysis and interpretation of data; drafting of the manuscript; critical revision of the manuscript for important intellectual content; statistical analysis. JFKFI: acquisition of data, critical revision of the manuscript for important intellectual content; statistical analysis. RW: critical revision of the manuscript for important intellectual content. CS: critical revision of the manuscript for important intellectual content. JS: study concept and design; acquisition of data; analysis and interpretation of data; drafting of the manuscript; critical revision of the manuscript for important intellectual content; statistical analysis; obtained funding; study supervision.
Funding The authors have not declared a specific grant for this research from any funding agency in the public, commercial or not-for-profit sectors.
Competing interests JFKFI has received research grants from Takeda, Janssen, Abbvie, ParaTech, the Danish Research Council, and the Capital Region of Denmark. RW has received grants/personal fees from Janssen, Takeda, Pfizer, Abbvie and Alimentiv. CS has served as speaker and advisory board member for MSD and Janssen. JS has received research grants from Takeda, Janssen, the Danish Research Council and the Capital Region Denmark and is national coordinator of studies from AbbVie, Arena Pharmaceuticals, Ely Lilly and Boehringer Ingelheim.
Provenance and peer review Not commissioned; externally peer reviewed.
Read the full text or download the PDF:

IMAGES
VIDEO
COMMENTS
1. Use the same font for footnotes as the rest of the paper. Generally, you should use the same font for your entire paper rather than using several different fonts. The default font on your word processing app is usually fine. [2] Tip: Footnotes are typically a smaller font size than the main text of your paper.
Published on March 28, 2022 by Jack Caulfield . Revised on June 7, 2022. Footnotes are notes placed at the bottom of the page in a piece of academic writing and indicated in the text with superscript numbers (or sometimes letters or other symbols). You can insert footnotes automatically in Word or Google Docs.
Footnotes should be placed at the bottom of the page on which the corresponding callout is referenced. Alternatively, a footnotes page could be created to follow the reference page. When formatting footnotes in the latter manner, center and bold the label "Footnotes" then record each footnote as a double-spaced and indented paragraph.
Short note example. 2. Woolf, "Modern Fiction," 11. The guidelines for use of short and full notes can vary across different fields and institutions. Sometimes you might be required to use a full note for every citation, or to use a short note every time as long as all sources appear in the Chicago style bibliography.
How to Write a Footnote Citation in MLA. Place footnotes at the bottom of the page in their own special section. Follow the same numerical order on the page. Firstly, start each note with the superscript number that corresponds with the in-text citation. Then, remember that bibliographical notes provide citations similar to the works cited and ...
Elaborating on ideas. Providing additional examples that don't fit into the main text. Footnotes appear at the bottom of the relevant page, while endnotes appear at the end of the paper, just before the Works Cited list. MLA allows the use of either type, but stick to one or the other. Any sources you cite in your footnotes or endnotes must ...
Note that when a long dash appears in the text, the footnote/endnote number appears before the dash:. For years, scholars have failed to address this point 8 —a fact that suggests their cowardice more than their carelessness.. Do not use asterisks (*), angle brackets (>), or other symbols for note references. The list of endnotes and footnotes (either of which, for papers submitted for ...
Footnotes usually appear at the bottom of the page. Each footnote is preceded by a number that also appears as a superscript after the corresponding material on that page. Chicago style allows you to use symbols, such as the asterisk or the dagger, instead of numbers if you only have a few footnotes. 3. If you're following APA style or MLA ...
Copy the exact words from the original source. 2. Place quotation marks (") at the beginning and end of the quoted text. 3. Insert the superscript number at the end of the sentence containing the quote. If more than one author is quoted within a sentence, insert a footnote next to each author's name.
How to format footnotes correctly: Always use the footnotes function. The callout should be in superscript, like this. 1. The callout should come after the punctuation, like this. 2. If there's a dash 3 —the callout comes before the punctuation, not after. All callouts should appear in numerical order, like this. 4.
A footnote is a reference, explanation, or comment 1 placed below the main text on a printed page. Footnotes are identified in the text by a numeral or a symbol . In research papers and reports, footnotes commonly acknowledge the sources of facts and quotations that appear in the text. " Footnotes are the mark of a scholar," says Bryan A. Garner.
What is a Footnote. The footnote takes the form of a superscripted number, just after a paraphrased piece of information. Subsequently, a cross-reference to this number is inserted at the bottom of the same page.. In fact, for dissertations and theses, many writers use footnotes to keep track of their citations, adding a short note of what exactly each one adds to the paper.
If you use a footnote in a sentence that has a dash, make sure the footnote number is placed before the dash. Footnotes should be numbered sequentially throughout the paper. Do not start over again at number 1 on each page. The footnote citation at the bottom of the page should have the number, and it should also be in superscript.
Congrats! You've created your first footnote. You can also adjust the footnote settings (like the numbering) by clicking the arrow beside the Footnotes group. It's really that easy! 5.2 How to Add Footnotes in Google Docs. Here's how to use footnotes on Google Docs: Click on the place in the text where you want the first footnote to appear.
APA footnotes use superscript numbers and should appear in numerical order. You can place footnotes at the bottom of the relevant pages, or on a separate footnotes page at the end: For footnotes at the bottom of the page, you can use your word processor to automatically insert footnotes.; For footnotes at the end of the text in APA, place them on a separate page entitled "Footnotes," after ...
Footnotes are a useful tool in academic writing that allows for the inclusion of additional information or comments in a document or text. Typically denoted by a small number or symbol in the main text, footnotes in a paper appear at the bottom of the page and can serve a variety of purposes. For example, footnotes can be used to clarify a ...
For information on footnotes in the Publication Manual of the American Psychological Association see section 2.13 "Footnotes.". For information on using footnotes with MLA see the "Using Notes in MLA Style" article from the MLA Style Center. For information on footnotes in The Chicago Manual of Style see Chapter 14 "Notes and Bibliography."
Do not repeat the hundreds digit in a page range if it does not change from the beginning to the end of the range. For more information on footnotes, please see CMOS NB Sample Paper. Headings. While The Chicago Manual of Style does not include a prescribed system for formatting headings and subheads, it makes several recommendations.
Footnotes are notes placed at the bottom of a page in a document that provide additional information or clarification about a particular point in the text. They are often used in academic writing to give credit to sources, provide context to the reader, or expand on a concept. Importance of Using Footnotes in a Paper.
Placement of superscript footnote numbers follow these rules: Format like this, 1 following any punctuation except a dash. The footnote number precedes a dash 2 -- like so. Place the footnote number (if it applies only to material within the parentheses 3) like this. Example.
Place your insertion point where you want a reference inserted into the text. On the References tab, click the "Cross-Reference" button. In the Cross-Reference window, choose either "Footnote" or "Endnote" from the "Reference Type" dropdown menu. Next, click the "Insert Reference To" dropdown menu.
Footnotes help your white paper convey more authority than a simple blog post or opinion piece. Footnotes help build your argument and prove that you did your homework. But most writers have never thought much about footnotes since, well, college. To help you use footnotes effectively, here are answers to some frequently asked questions about them.
We would like to congratulate Adams et al on the paper addressing the important issue regarding the development of prognostic clinical indexes for patients with acute severe ulcerative colitis (ASUC) leading to the development of the ADMIT-ASC score.1 Although we acknowledge the initiative, the development of a static prognostic index might be reconsidered with the increased availability and ...