AI Scene Description Feedback
- Overall how would you rate the usefulness of the description provided by this feature? Very High High Moderate Low Very Low
- Overall how would you rate the usefulness of the ability to describe any frame within our collection? Very High High Moderate Low Very Low
- How do you anticipate this feature will improve student outcomes?
- Please share any additional input you might have about this feature or future improvements

Language / Accessibility Settings
Browse topics, keyboard shortcuts.
Standards Details For:
Writing a Personal Narrative: Revising (Episode 6)
Grade Level
Also include, please take a moment to rate your experience with our new standards feature.
Retrieving matching standards
Embed Media
Audio language.
Videos are generally available for preview to non-members as short clips. Limited full-length titles are also available. Log In to view the full length title.

This episode offers tips for revising a draft of a personal narrative. Revisions help a writer fine-tune and strengthen their stories. Part of the "Writing a Personal Narrative" series.
Media Details
Runtime: 4 minutes 26 seconds
- Topic: Language Arts
- Subtopic: Composition (Writing) , English Grammar , Literacy
- Grade/Interest Level: 3 - 6
- Standards: Meets 2034 total
- Release Year: 2015
- Producer/Distributor: Teaching Without Frills
- Series: Writing a Personal Narrative
- Report a Problem
Related Media

Writing a Personal Narrative: Brainstorming (Episode 1)

Writing a Personal Narrative: Writing an Introduction (Episode 3)

Writing a Personal Narrative: Writing a Draft (Episode 4)

Writing a Personal Narrative: Planning and Pre-Writing (Episode 2)

Writing a Personal Narrative: Writing a Closing (Episode 5)

Writing a Personal Narrative: Editing (Episode 7)

Writing a Personal Narrative: Publishing (Episode 8)

Funding provided by the Department of Education

Administered by the National Association of the Deaf
- Features for Creative Writers
- Features for Work
- Features for Higher Education
- Features for Teachers
- Features for Non-Native Speakers
- Learn Blog Grammar Guide Community Events FAQ
- Grammar Guide
Telling the Story of Yourself: 6 Steps to Writing Personal Narratives

Jennifer Xue

Table of Contents
Why do we write personal narratives, 6 guidelines for writing personal narrative essays, inspiring personal narratives, examples of personal narrative essays, tell your story.
First off, you might be wondering: what is a personal narrative? In short, personal narratives are stories we tell about ourselves that focus on our growth, lessons learned, and reflections on our experiences.
From stories about inspirational figures we heard as children to any essay, article, or exercise where we're asked to express opinions on a situation, thing, or individual—personal narratives are everywhere.
According to Psychology Today, personal narratives allow authors to feel and release pains, while savouring moments of strength and resilience. Such emotions provide an avenue for both authors and readers to connect while supporting healing in the process.
That all sounds great. But when it comes to putting the words down on paper, we often end up with a list of experiences and no real structure to tie them together.
In this article, we'll discuss what a personal narrative essay is further, learn the 6 steps to writing one, and look at some examples of great personal narratives.
As readers, we're fascinated by memoirs, autobiographies, and long-form personal narrative articles, as they provide a glimpse into the authors' thought processes, ideas, and feelings. But you don't have to be writing your whole life story to create a personal narrative.
You might be a student writing an admissions essay , or be trying to tell your professional story in a cover letter. Regardless of your purpose, your narrative will focus on personal growth, reflections, and lessons.
Personal narratives help us connect with other people's stories due to their easy-to-digest format and because humans are empathising creatures.
We can better understand how others feel and think when we were told stories that allow us to see the world from their perspectives. The author's "I think" and "I feel" instantaneously become ours, as the brain doesn't know whether what we read is real or imaginary.
In her best-selling book Wired for Story, Lisa Cron explains that the human brain craves tales as it's hard-wired through evolution to learn what happens next. Since the brain doesn't know whether what you are reading is actual or not, we can register the moral of the story cognitively and affectively.
In academia, a narrative essay tells a story which is experiential, anecdotal, or personal. It allows the author to creatively express their thoughts, feelings, ideas, and opinions. Its length can be anywhere from a few paragraphs to hundreds of pages.
Outside of academia, personal narratives are known as a form of journalism or non-fiction works called "narrative journalism." Even highly prestigious publications like the New York Times and Time magazine have sections dedicated to personal narratives. The New Yorke is a magazine dedicated solely to this genre.
The New York Times holds personal narrative essay contests. The winners are selected because they:
had a clear narrative arc with a conflict and a main character who changed in some way. They artfully balanced the action of the story with reflection on what it meant to the writer. They took risks, like including dialogue or playing with punctuation, sentence structure and word choice to develop a strong voice. And, perhaps most important, they focused on a specific moment or theme – a conversation, a trip to the mall, a speech tournament, a hospital visit – instead of trying to sum up the writer’s life in 600 words.
In a nutshell, a personal narrative can cover any reflective and contemplative subject with a strong voice and a unique perspective, including uncommon private values. It's written in first person and the story encompasses a specific moment in time worthy of a discussion.
Writing a personal narrative essay involves both objectivity and subjectivity. You'll need to be objective enough to recognise the importance of an event or a situation to explore and write about. On the other hand, you must be subjective enough to inject private thoughts and feelings to make your point.
With personal narratives, you are both the muse and the creator – you have control over how your story is told. However, like any other type of writing, it comes with guidelines.
1. Write Your Personal Narrative as a Story
As a story, it must include an introduction, characters, plot, setting, climax, anti-climax (if any), and conclusion. Another way to approach it is by structuring it with an introduction, body, and conclusion. The introduction should set the tone, while the body should focus on the key point(s) you want to get across. The conclusion can tell the reader what lessons you have learned from the story you've just told.
2. Give Your Personal Narrative a Clear Purpose
Your narrative essay should reflect your unique perspective on life. This is a lot harder than it sounds. You need to establish your perspective, the key things you want your reader to take away, and your tone of voice. It's a good idea to have a set purpose in mind for the narrative before you start writing.
Let's say you want to write about how you manage depression without taking any medicine. This could go in any number of ways, but isolating a purpose will help you focus your writing and choose which stories to tell. Are you advocating for a holistic approach, or do you want to describe your emotional experience for people thinking of trying it?
Having this focus will allow you to put your own unique take on what you did (and didn't do, if applicable), what changed you, and the lessons learned along the way.
3. Show, Don't Tell
It's a narration, so the narrative should show readers what happened, instead of telling them. As well as being a storyteller, the author should take part as one of the characters. Keep this in mind when writing, as the way you shape your perspective can have a big impact on how your reader sees your overarching plot. Don't slip into just explaining everything that happened because it happened to you. Show your reader with action.
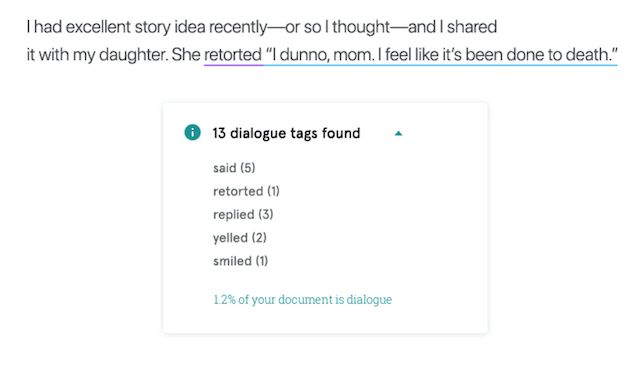
You can check for instances of telling rather than showing with ProWritingAid. For example, instead of:
"You never let me do anything!" I cried disdainfully.
"You never let me do anything!" To this day, my mother swears that the glare I levelled at her as I spat those words out could have soured milk.
Using ProWritingAid will help you find these instances in your manuscript and edit them without spending hours trawling through your work yourself.
4. Use "I," But Don't Overuse It
You, the author, take ownership of the story, so the first person pronoun "I" is used throughout. However, you shouldn't overuse it, as it'd make it sound too self-centred and redundant.
ProWritingAid can also help you here – the Style Report will tell you if you've started too many sentences with "I", and show you how to introduce more variation in your writing.
5. Pay Attention to Tenses
Tense is key to understanding. Personal narratives mostly tell the story of events that happened in the past, so many authors choose to use the past tense. This helps separate out your current, narrating voice and your past self who you are narrating. If you're writing in the present tense, make sure that you keep it consistent throughout.

6. Make Your Conclusion Satisfying
Satisfy your readers by giving them an unforgettable closing scene. The body of the narration should build up the plot to climax. This doesn't have to be something incredible or shocking, just something that helps give an interesting take on your story.
The takeaways or the lessons learned should be written without lecturing. Whenever possible, continue to show rather than tell. Don't say what you learned, narrate what you do differently now. This will help the moral of your story shine through without being too preachy.
GoodReads is a great starting point for selecting read-worthy personal narrative books. Here are five of my favourites.
Owl Moon by Jane Yolen
Jane Yolen, the author of 386 books, wrote this poetic story about a daughter and her father who went owling. Instead of learning about owls, Yolen invites readers to contemplate the meaning of gentleness and hope.
Night by Elie Wiesel
Elie Wiesel was a teenager when he and his family were sent to Auschwitz concentration camp in 1944. This Holocaust memoir has a strong message that such horrific events should never be repeated.
The Diary of a Young Girl by Anne Frank
This classic is a must-read by young and old alike. It's a remarkable diary by a 13-year-old Jewish girl who hid inside a secret annexe of an old building during the Nazi occupation of the Netherlands in 1942.
The Year of Magical Thinking by Joan Didion
This is a personal narrative written by a brave author renowned for her clarity, passion, and honesty. Didion shares how in December 2003, she lost her husband of 40 years to a massive heart attack and dealt with the acute illness of her only daughter. She speaks about grief, memories, illness, and hope.
Educated by Tara Westover
Author Tara Westover was raised by survivalist parents. She didn't go to school until 17 years of age, which later took her to Harvard and Cambridge. It's a story about the struggle for quest for knowledge and self-reinvention.
Narrative and personal narrative journalism are gaining more popularity these days. You can find distinguished personal narratives all over the web.
Curating the best of the best of personal narratives and narrative essays from all over the web. Some are award-winning articles.
Narratively
Long-form writing to celebrate humanity through storytelling. It publishes personal narrative essays written to provoke, inspire, and reflect, touching lesser-known and overlooked subjects.
Narrative Magazine
It publishes non,fiction narratives, poetry, and fiction. Among its contributors is Frank Conroy, the author of Stop-Time , a memoir that has never been out of print since 1967.
Thought Catalog
Aimed at Generation Z, it publishes personal narrative essays on self-improvement, family, friendship, romance, and others.
Personal narratives will continue to be popular as our brains are wired for stories. We love reading about others and telling stories of ourselves, as they bring satisfaction and a better understanding of the world around us.
Personal narratives make us better humans. Enjoy telling yours!

Write like a bestselling author
Love writing? ProWritingAid will help you improve the style, strength, and clarity of your stories.
Jennifer Xue is an award-winning e-book author with 2,500+ articles and 100+ e-books/reports published under her belt. She also taught 50+ college-level essay and paper writing classes. Her byline has appeared in Forbes, Fortune, Cosmopolitan, Esquire, Business.com, Business2Community, Addicted2Success, Good Men Project, and others. Her blog is JenniferXue.com. Follow her on Twitter @jenxuewrites].
Get started with ProWritingAid
Drop us a line or let's stay in touch via :
- PRO Courses Guides New Tech Help Pro Expert Videos About wikiHow Pro Upgrade Sign In
- EDIT Edit this Article
- EXPLORE Tech Help Pro About Us Random Article Quizzes Request a New Article Community Dashboard This Or That Game Popular Categories Arts and Entertainment Artwork Books Movies Computers and Electronics Computers Phone Skills Technology Hacks Health Men's Health Mental Health Women's Health Relationships Dating Love Relationship Issues Hobbies and Crafts Crafts Drawing Games Education & Communication Communication Skills Personal Development Studying Personal Care and Style Fashion Hair Care Personal Hygiene Youth Personal Care School Stuff Dating All Categories Arts and Entertainment Finance and Business Home and Garden Relationship Quizzes Cars & Other Vehicles Food and Entertaining Personal Care and Style Sports and Fitness Computers and Electronics Health Pets and Animals Travel Education & Communication Hobbies and Crafts Philosophy and Religion Work World Family Life Holidays and Traditions Relationships Youth
- Browse Articles
- Learn Something New
- Quizzes Hot
- This Or That Game New
- Train Your Brain
- Explore More
- Support wikiHow
- About wikiHow
- Log in / Sign up
- Education and Communications
- College University and Postgraduate
- Academic Writing
How to Write a Personal Narrative like a Pro (With Examples)
Last Updated: December 12, 2023 Fact Checked
Template and Sample Narrative
- Brainstorming
This article was co-authored by Grant Faulkner, MA . Grant Faulkner is the Executive Director of National Novel Writing Month (NaNoWriMo) and the co-founder of 100 Word Story, a literary magazine. Grant has published two books on writing and has been published in The New York Times and Writer’s Digest. He co-hosts Write-minded, a weekly podcast on writing and publishing, and has a M.A. in Creative Writing from San Francisco State University. There are 7 references cited in this article, which can be found at the bottom of the page. This article has been fact-checked, ensuring the accuracy of any cited facts and confirming the authority of its sources. This article has been viewed 861,084 times.
Personal narratives focus on a particular real life event that was pivotal or important for the writer. You may have to write a personal narrative as part of a college application or as an assignment for a class. To write a strong personal narrative, start by coming up with an engaging idea. Then, write the narrative with an opening hook and a detailed, organized structure. Always review and revise the personal narrative before handing it in so it is at its best.
Things You Should Know
- Center your narrative around an important moment in your life. For example, you might write about a time you had to make a hard decision or deal with a conflict.
- Move chronologically through the events you’re discussing. This will make your narrative easy to follow and draw your reader in.
- Finish with a moral takeaway or a life lesson. What did you learn from these events, and why is it important? How did they shape you as a person?

Brainstorming Ideas for the Narrative

- For example, you may write about your struggles with body image in high school and how you overcame them in adulthood. Or you may write about your disastrous 15th birthday party and how it affected your relationship with your mother.

- For example, you write a personal narrative about your complicated relationship with your birth mother. Or you may write about a conflict you have with a sport you play or a club you are a part of.

- For example, you may explore a theme like poverty by writing about your family’s struggle with money and finances. You may write about having to defer college applications to work at your parent’s business to make ends meet for your family.

- The Boys of My Youth by Jo Ann Beard
- Slouching Towards Bethlehem by Joan Didion
- Me Talk Pretty One Day by David Sedaris
- The Lives section of The New York Times
Writing the Personal Narrative

- For example, the first line in the personal narrative by Tony Gervino is attention grabbing: “I was 6 when my brother John leaned across the kitchen table and casually whispered that he had killed Santa Claus.” [5] X Research source

- For example, in Tony Gervino’s essay, he sets the scene by providing setting, character, and narrative voice: “It was July 1973, we were living in Scarsdale, N.Y., and he was four years older than I was, although that seemed like decades.”

- For example, you may start with an event in childhood with your older sister and then move forward in time to the present day, focusing on you and your older sister as adults.

- For example, you may describe the feeling of your mother’s famous lemon cake as “rich and zesty, with a special ingredient that to this day, I cannot identify.”

- For example, you may end a personal narrative about your complicated relationship with your troubled sister by ending on a recent memory where you both enjoyed each other’s company. You may leave the reader with a lesson you have learned about loving someone, even with all their messiness and baggage.

Polishing the Personal Narrative

- You can also try reading the narrative out loud to someone else so they can hear how it sounds. This can then make it easier for them to give you feedback.

- Be willing to accept feedback from others. Be open to constructive criticism as it will likely strengthen the narrative.

Community Q&A
You Might Also Like

- How to Write a Narrative Essay
- How to Write a Journal Entry
- How to Write an Epistolary Narrative
- How to Write an Autobiography
- ↑ https://www.indeed.com/career-advice/career-development/personal-narrative-examples
- ↑ https://www.byrdseed.com/writing-better-personal-narratives/
- ↑ https://grammar.yourdictionary.com/grammar-rules-and-tips/tips-for-writing-a-personal-narrative-essay.html
- ↑ https://www.nytimes.com/2011/07/17/magazine/lives-a-rats-tale.html
- ↑ https://open.lib.umn.edu/writingforsuccess/chapter/10-1-narration/
- ↑ https://writingcenter.unc.edu/tips-and-tools/reading-aloud/
- ↑ https://writingcenter.unc.edu/tips-and-tools/revising-drafts/
About This Article

To write a personal narrative, start by choosing a memorable moment, event, or conflict in your life that you want to write about. Then, use your personal narrative to describe your story, going chronologically through the events. Try to use a lot of sensory detail, like how things smelled, sounded, felt, and looked, so your readers can picture everything you're describing. At the end of your narrative, include a lesson you learned or something you took away from the experience. To learn how to brainstorm ideas for your personal narrative, read on! Did this summary help you? Yes No
- Send fan mail to authors
Reader Success Stories
Oct 7, 2016
Did this article help you?

Sheena Whytelaw
Nov 8, 2022
Sarah Harris
Jun 17, 2016
Tammy Wheeler
Oct 23, 2016
Christian Dilauro
Sep 14, 2020

Featured Articles

Trending Articles

Watch Articles

- Terms of Use
- Privacy Policy
- Do Not Sell or Share My Info
- Not Selling Info
Don’t miss out! Sign up for
wikiHow’s newsletter

Personal Narrative Writing Guide
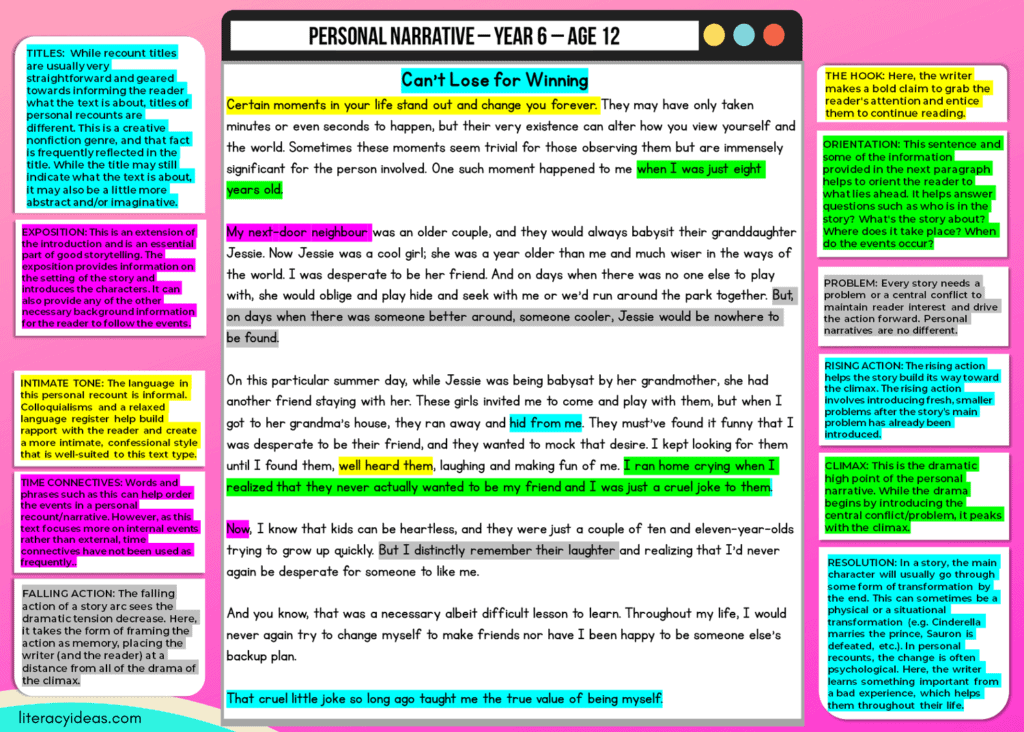
WHAT IS A PERSONAL NARRATIVE?

A Personal Narrative recounts an event or experience from the writer’s life in story form and often in intimate detail. This text type not only relates to the events happening around the author but also often reveals the writer’s inner thoughts and emotions also.
A personal narrative can be understood as nonfiction storytelling based on the writer’s thoughts, feelings, and experiences. Told in the first person, the writer draws on their life events to construct a story.
Combining elements of nonfiction recount writing with introspection and the frequent use of literary devices more commonly associated with fiction and poetry, a personal narrative can be best understood as a type of creative nonfiction .
PERSONAL NARRATIVE VERSUS A PERSONAL RECOUNT: SO WHAT’S THE DIFFERENCE?
Personal narratives are also frequently referred to as personal recounts. They share much in common but are unique text types, so let’s explore how they compare and contrast.
When we first instruct our students to write stories based on the events of their own lives, they will inevitably write simple recounts. These recounts are based on retelling personal incidents of their lives but lack the depth we can typically expect to find in a personal narrative.
While personal narratives also recount events from the writer’s life, with greater emphasis placed on exploring the writer’s thoughts and feelings on these events rather than just what happened.
A personal narrative is a means for the writer to explore the meaning of the events in their life. It is, at its core, an introspective and creative endeavor that focuses as much on the interior life of the writer as it does on external events.

While the conclusion of a traditional recount usually provides some of the writer’s insights, in a personal narrative, these are woven throughout the text.
STRUCTURE AND FEATURES OF A PERSONAL NARRATIVE
Personal narrative structure.
ORIENTATION Explain the who, what, when, and where of the experience in your introduction to your audience.
FOCUS Mainly focus on meaningful events.
CHRONOLOGY Events are described in the sequence in which they occurred.
ORGANIZATION Relevant information is organized into paragraphs
INSIGHT & MEANING Include personal comments, opinions or interpretations of the experience or event in your personal narrative.
PERSONAL NARRATIVE FEATURES
TENSE The first and third person are used most frequently and recall is always written in the past tense. Present tense can be used for analysis and opinion.
NOUNS Use proper nouns to refer to specific people, places times and events
VOICE Both active and passive voice are used in recounts. Use these to express your emotions and thinking clearly.
CONNECTIVES Use conjunctions and connectives to link events and indicate time sequence in your personal narrative.
A COMPLETE TEACHING UNIT ON PERSONAL NARRATIVE WRITING

Teach your students to write AMAZING PERSONAL NARRATIVES using a proven model of research skills, writing strategies and engaging content. ALL CONTENT, RESOURCES AND ASSESSMENT TOOLS INCLUDED covering.
Download this COMPLETE 85 PAGE UNIT today. NO PREPARATION REQUIRED.
HOW LONG SHOULD A PERSONAL NARRATIVE BE?
The personal narrative is a modern text type and therefore has no traditionally defined optimum length, and we can find texts ranging from a couple of hundred words to a multi-volume series in this genre.
However, for our students, this text type can be thought of in terms of length as similar to an essay. Like an essay, the text needs to be long enough to comprehensively answer the question, prompt, or the event/experience the student is retelling.
David Sedaris, the American writer and one of the best-known writers of humorous personal narratives, has written many books that could accurately be classified in this genre.
While these full-length books are often built around a loose theme, each chapter could stand alone as a personal narrative essay in its own right, each built around a single identifiable experience or event.
As with an essay, the length of a personal narrative can be based on a variety of factors, including:
- Age and ability of the students
- Specifics of the question or writing prompt
- Any limitation imposed by a word count
- The complexity of the event/experience being written about.
Regardless of length, given its structural similarity with the essay, personal narratives usually follow a basic three-part structure.
HOW TO WRITE A PERSONAL NARRATIVE STEP-BY-STEP
We mentioned previously that this text type is relatively modern, so there aren’t many fixed rules concerning structure. That said, we can usually identify three distinct parts of a personal narrative corresponding to the three parts outlined in the hamburger essay or the 5-paragraph essay format. These are:

- The introduction
- The body paragraphs
- The conclusion
If you want an in-depth guide to this format, check out our comprehensive article here . But, for now, let’s take a brief look at the purpose of each section as it relates to a personal narrative.
WRITING THE INTRODUCTION OF A PERSONAL NARRATIVE

The introduction of a personal narrative performs several functions.
1: It hooks the Reader
The first job of the introduction is to ‘hook’ the reader. If we can’t catch the reader’s interest initially, there will be no middle or end for the reader. A strong hook is needed at the very outset, and it can take several forms.
Some effective hooks to open a personal narrative with include:
- A bold claim
- An interesting anecdote
- A fascinating fact or revealing statistic
- A compelling quotation
Whichever technique the student chooses to open their narrative with, they should ensure it is relevant to the subject matter explored, whether it focuses on external or internal events or experiences or a mixture of both.
2: It orients the Reader
Like many other nonfiction and fiction text types, the opening paragraph (or paragraphs) will also orient the reader by answering some basic questions such as:
- What is the text about?
- Who is in this story?
- Where is it set?
- When do the events or experiences occur?
While it may also hint at why these events or experiences matter, a detailed answer to the why of a personal narrative may be saved for the text’s conclusion.
This section of the personal narrative can also be thought of as The Exposition .
3: It Sets the Tone
The introduction reveals not only what the text will be about but also how the writer (and, by extension, the reader) will treat the topic. This is the tone.
For example, a more sombre tone has been established where the language used is serious and formal. In this instance, the reader will adopt a more serious approach to the work.
On the other hand, if the treatment of the event or experience is humorous, this will be apparent in the language choices the writer makes and the mood they establish. Going forward, the reader can reasonably expect to be amused by what’s to come in the text.
THE BODY PARAGRAPHS OF A PERSONAL NARRATIVE
The body paragraphs of a personal narrative comprise the bulk of the text.
As with any type of recount, this section will generally focus on the chronological retelling of an event or experience.
However, there is another significant difference between this type of recount and the other types.’ The root of this difference can be found in the word ‘narrative’.
While the body paragraphs of a personal narrative can make use of some of the defining characteristics of more traditional types of recount, if the introduction acts as the exposition of the setting and character of the story, the body paragraphs move the text along its story arc.
Though we will cover the main elements briefly, structuring a story is an art in itself and if you want to find out more about it, check out our detailed article on the subject here.
Also, if you want to learn more about the structure of general recounts, find out more here .
While we’ve seen that the introduction of a personal narrative corresponds to a story’s exposition, the following elements of a story arc can be found in the text’s body.
1: The Problem
The problem or conflict is an essential ingredient in any story worth the name. It creates the story’s focal point, ignites the reader’s interest, and drives the story forward. In a personal narrative, this problem can be internal or external, however, there is often an emphasis placed on how the issues affect the writer psychologically. 2: The Rising Action
As the narrative develops, the dramatic tension will tend to increase. The main problem will intensify, or the writer may introduce additional more minor problems to amp things up. 3: The Climax
This is where the story reaches its dramatic high point. In the case of a personal narrative where the conflict or problem is psychological, this drama and its climax may play out internally.
WRITING THE CONCLUSION OF YOUR PERSONAL NARRATIVE ESSAY

This third and final section of the personal narrative performs a slightly different function to a regular essay’s conclusion.
While the conclusions of most nonfiction text types focus on restating a central thesis and/or providing a summary of arguments, the conclusion in a personal narrative follows a story’s final section more closely.
That is, it usually contains the story’s falling action and resolution.
Let’s take a quick look at each.
1: The Falling Action
The story arc dips in dramatic tension after the dramatic high point of the climax. As personal narratives often focus on ‘internal’ events, this ‘action’ can also occur internally. 2: Resolution
The resolution marks the end of the story, and in this text type, it usually involves some personal change in circumstances or transformation. It can also take the form of a lesson learned or new knowledge attained.
TIPS FOR WRITING A GREAT PERSONAL NARRATIVE ESSAY
- Begin with a clear and compelling story: Your personal narrative essay should focus on a significant event or experience in your life that you want to share with the reader.
- Write in the first person perspective: Use “I” statements to describe your experiences and thoughts and take us inside your mind.
- Be descriptive: To bring your story to life, use descriptive language to paint a picture of the sights, sounds, and emotions of your experience.
- Focus on what matters the most: Tell a powerful story with just a few key details. When writing your personal narrative, focus on the most impactful events and thoughts that help convey your message.
- Emphasize the impact the experience had upon you: Leave the reader with a clear understanding of the impact that the experience had on your life.
- Be true to yourself: Ensure your personal narrative essay is honest and genuine in your descriptions and reflections.
- Deliver a powerful ending: The conclusion should summarize the major points of your essay and leave the reader with a lasting impression.
- Review and Revise: Don’t be afraid to proofread your essay several times to ensure it is the best it can be.

Teaching Resources
Use our resources and tools to improve your student’s writing skills through proven teaching strategies.
PERSONAL NARRATIVE TEACHING STRATEGIES AND ACTIVITIES
PERSONAL NARRATIVE PRACTICE EXERCISE: ACTIVITY 1
- Organise your students into small groups of four or five
- Provide each group with a selection of personal recounts
- Can the students identify how each sample text attempts to hook the reader in the opening paragraph?
- How effectively does the introduction of each text orient the reader?
- What is the tone of the text? How has this tone been created?
PERSONAL NARRATIVE PRACTICE EXERCISE: ACTIVITY 2
In their groups, with their sample personal narrative texts, ask students to identify how the writer deals with each element as listed below and discuss how effectively they have done so.
- The Problem
- The Rising Action
PERSONAL NARRATIVE PRACTICE EXERCISE: ACTIVITY 3
Now students understand how to structure and write each stage of their personal narrative, encourage them to spend some time brainstorming events and experiences from their lives that could serve as the topic for their writing.
When they have chosen a suitable topic, instruct them to begin planning the writing of their text using the categories listed above. They might even wish to create a simple graphic organizer to help.
For example:
Introduction
- What is the opening hook?
Body Paragraphs
- What is the central problem?
- What happens in the rising action?
- How does the climax play out?
- What happens in the falling action?
- What is the resolution of the story?
Once students have their narrative adequately planned, it’s time to get them writing earnestly to put all that theory into practice.
PERSONAL NARRATIVE WRITING TEMPLATE / GRAPHIC ORGANIZER

PERSONAL NARRATIVE WRITING EXAMPLES
VIDEO TUTORIAL ON PERSONAL NARRATIVE WRITING

NARRATIVE WRITING CHECKLIST BUNDLE

RELEVANT ARTICLES

How to Write a Recount Text (And Improve your Writing Skills)

How to Write a Historical Recount Text

5 Easy Recount Writing Lesson Plans students love.

15 Awesome Recount & Personal Narrative Topics

Explore our Teaching Unit on PERSONAL NARRATIVES

VIDEO
COMMENTS
In this video, you will learn how to revise your personal narrative story. We will discuss how to add, change, or remove parts of your story to make it even ...
In this video, you will learn how to write a closing or conclusion for your personal narrative story. We will discuss different strategies like rephrasing yo...
This episode offers tips for revising a draft of a personal narrative. Revisions help a writer fine-tune and strengthen their stories. Part of the "Writing a Personal Narrative" series.
However, like any other type of writing, it comes with guidelines. 1. Write Your Personal Narrative as a Story. As a story, it must include an introduction, characters, plot, setting, climax, anti-climax (if any), and conclusion. Another way to approach it is by structuring it with an introduction, body, and conclusion.
Forbes. Learn how to write a personal narrative from start to finish! This series is called Personal Narrative Writing for Kids. In this series, you will learn how to brainstorm, plan, write a draft, edit, revise, and ultimately publish your personal narratives! All the videos include teacher models to guide students as they write and share ...
5 Personal Narrative Examples. We’ve discussed the definition of a personal narrative and the steps to writing one. Now, let’s review a handful of examples. Me Talk Pretty One Day by David Sedaris. Me Talk Pretty One Day is both the name of a personal narrative and a best-selling collection of essays published in 2000 by David Sedaris. The ...
Show the narrative to others. Ask a friend, peer, classmate, or family member to read the narrative. Pose questions to them about the style, tone, and flow of the narrative. Ask them if the narrative feels personal, detailed, and engaging. [10] Be willing to accept feedback from others.
3. Apply strong narrative techniques. Just because you’re writing about a personal experience doesn’t exempt you from using strong storytelling techniques. Continue to apply important writing advice, such as: Show, don’t tell. Use strong verbs. Remove unnecessary filler words. 4. Avoid overusing the pronoun “I.”.
A personal narrative is a means for the writer to explore the meaning of the events in their life. It is, at its core, an introspective and creative endeavor that focuses as much on the interior life of the writer as it does on external events. While the conclusion of a traditional recount usually provides some of the writer’s insights, in a ...
In this video, you will learn how to write a draft for your personal narrative story. We will write the important events in order, using transition words and...