Google Essay for Students and Teacher
500+ words essay on google.
Google is named after the mathematical word “googol,” described as the value represented by one followed by 100 zeros. Google is the leading Internet search engine; its main service provides customers with targeted search outcomes chosen from over 8 billion web pages. Both Stanford dropouts, Larry Page and Sergey Brin, developed Google search technology from a college project. Thus, an insight into Google Essay discusses how Google works and came into existence.

Google is undoubtedly today’s most famous and interesting business in the globe. It’s the mission, according to its corporate website, is to “organize the data of the world and make it widely available and helpful” (Google, 2010).
Google ranked first in the annual “Best companies” of Fortune Magazine, winning other top businesses in 2007 and 2008 for two successive years. His performance as a top employer is due to his inner corporate culture the most quoted reason. Google is the ultimate global company and is defined as a “fast-paced, high-energy working setting” (Google, 2010).
Because Google is focused on its “young” internet-savvy market, its employees ‘ average age is significantly smaller than most businesses. Google’s median age is 30 and the distribution of sex is 65% male and 35% female (Linkedin, 2010).
The dress code is “casual” and laid-back because it values skill and hard work, not appearance. Google has a very engaging culture of the business. Also, Google Mountain View’s headquarters, CA called Googleplex, is intended to have a “campus-like” feel in tune with its predominantly young new recruits at the college level (Google, 2010).
Get the huge list of more than 500 Essay Topics and Ideas

Google and Rivals
Microsoft and Yahoo both invest strongly in search technology and gain market share on an ongoing basis. 2. With few rivals like Yahoo and MSN, Google operates in an oligopoly sector.
Thus, Google may find it hard to maintain its customers with low differentiation within the consequence of the search engine. Also, Yahoo and MSN launch their own search engines and targeted marketing systems; Google is in a race to create fresh search instruments to attract customers and grow their marketing networks.
Click fraud mentioned by Google as one of the potential “concerns” that may influence its income. In reality, due to click fraud, Google confessed to frequently paying refunds.
In reality, due to click fraud, Google confessed to frequently paying refunds. Click fraud happens when an individual, automated script or computer program imitates a lawful user of a web browser clicking on an advertisement in order to generate an inappropriate charge per click in the online pay-per-click advertisement.
For instance, Network click fraud-you are hosting ads on your own private website from Google AdSense. Google charges you each time you click on your website’s ad. Its fraud if you sit on the desktop constantly clicking on the ad or writing a computer program that clicks on the ad constantly. Such fraud is simple for Google to spot, so smart network click fraudsters simulate distinct IP addresses, or install Trojan horses on pcs from other people to produce fake clicks.
Customize your course in 30 seconds
Which class are you in.

- Travelling Essay
- Picnic Essay
- Our Country Essay
- My Parents Essay
- Essay on Favourite Personality
- Essay on Memorable Day of My Life
- Essay on Knowledge is Power
- Essay on Gurpurab
- Essay on My Favourite Season
- Essay on Types of Sports
Leave a Reply Cancel reply
Your email address will not be published. Required fields are marked *
Download the App

Google Company Overview Essay
Google’s history, core activities, organizational structure.
Larry Page and Sergey Brin founded the Google Company while doing their Ph. D at the Stanford University (Battelle 2005). The two founders launched and incorporated the company as a private enterprise in 1998, and thereafter, they obtained their first public offering in 2004. By 2006, Google was fully established and the founders repositioned Google’s headquarters to Mountain View, California. Since then, Google has grown rapidly. Google has the largest market share of the search engines.
Google’s search engine has gained fame, and is used globally. Google also offers a social networking site called Google+. Gmail is one of the best and most efficient productivity software offered by Google and its usage expands on a daily process globally. Google has the largest market share in internet usage, social networking and cloud computing. An approximate of 80% of businesses uses Google products and services globally (Battelle 2005).
The Google Corporation manipulates more than one million data centre servers globally. There is an increasing demand for the services of handling servers worldwide and Google anticipates managing over one billion data centre servers in the near future. As at 7 October, 4:00pm, Google’s stock price dropped by 6.61 trading at $865.74 per share. This represented a 0.8% negative change from the previous sales. However, Google’s stock price head towards trading at $1000 per share in the near future.
Google is a technological company. Its key activities comprise of the search engine and online advertising. Google also deals with operating systems, hardware and software products. However, the main source of revenue for Google is the online advertising business. Google does an online business of selling and delivering products and services in more than 50 countries. Google has an enhanced mobile segment and home segment Motorola business.
Through the home segment, Google provides video entertainment services. The consumers ought to subscribe with Google to access digital television services. The mobile segment manufactures and sells electronics. Google has acquired and collaborated with many other technological companies to offer an infinite number of products and services.
Google uses a functional structure, where the top management team focuses on employing value-chain activity measures (Gibbs 2013). To ease the management of the operations, Google’s management team has subdivided the company into five departments as shown below.
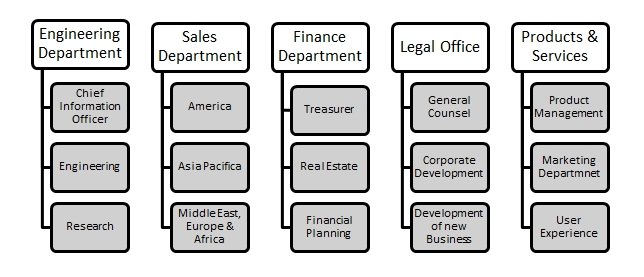
Each of the departmental heads reports directly to the executive management team, and the team reports to the board of directors. The small business units obtain a chance to innovate and invent things within the larger company. The multidivisional structure with small business units facilitates centralized planning for a large company as Google.
Vision and values
Google operates under a very high vision of systemizing the world’s information and making it readily accessible and useful (Miguel 2009). To attain the set mission, Google has adopted a culture of value for its employees. Google’s employees work very hard, under a very challenging environment, but they make fun out of the challenging environment.
Google is an amazing company that has overturned the lives of people. Gone are the days when researchers would spend hours in the library trying to fish out information from written books. Google has enhanced the entertainment industry, and shopping is just a click of a mouse. Google has changed people’s lives to the better as compared to the earlier days, and a world without Google is unimaginable.
Battelle, J 2005, ‘ The Birth of Google ’, Wired . Web.
Gibbs, S 2013, ‘ Google introduces the biggest algorithm change in three years ’, Guardian . Web.
Miguel, H 2009, ‘ Google to Offer Ads Based on Interests ’, The New York Times . Web.
- Chicago (A-D)
- Chicago (N-B)
IvyPanda. (2023, October 31). Google Company Overview. https://ivypanda.com/essays/google-company-overview/
"Google Company Overview." IvyPanda , 31 Oct. 2023, ivypanda.com/essays/google-company-overview/.
IvyPanda . (2023) 'Google Company Overview'. 31 October.
IvyPanda . 2023. "Google Company Overview." October 31, 2023. https://ivypanda.com/essays/google-company-overview/.
1. IvyPanda . "Google Company Overview." October 31, 2023. https://ivypanda.com/essays/google-company-overview/.
Bibliography
IvyPanda . "Google Company Overview." October 31, 2023. https://ivypanda.com/essays/google-company-overview/.
- Google Search Engine and Yahoo Search Engine
- The History and Growth of Google
- Google Does No Evil
- Google Company Analysis
- Google Company's Success
- Google Operations in China
- The Case of Google Inc
- Google Inc.'s Competitive Advantage and Future
- Google Inc.'s Current State of Affairs and Future Plans
- Google Corporation: Business Profile
- Pastis Restaurant, New York
- Allure Cruise Line Marketing Strategies and Positioning
- Vapiano Restaurant in Attracting Customers
- Oman's Oil Industry: Transportation and Logistics
- Marriot International, Inc. Analysis
Ultimate Guide to Writing Your College Essay
Tips for writing an effective college essay.
College admissions essays are an important part of your college application and gives you the chance to show colleges and universities your character and experiences. This guide will give you tips to write an effective college essay.
Want free help with your college essay?
UPchieve connects you with knowledgeable and friendly college advisors—online, 24/7, and completely free. Get 1:1 help brainstorming topics, outlining your essay, revising a draft, or editing grammar.
Writing a strong college admissions essay
Learn about the elements of a solid admissions essay.
Avoiding common admissions essay mistakes
Learn some of the most common mistakes made on college essays
Brainstorming tips for your college essay
Stuck on what to write your college essay about? Here are some exercises to help you get started.
How formal should the tone of your college essay be?
Learn how formal your college essay should be and get tips on how to bring out your natural voice.
Taking your college essay to the next level
Hear an admissions expert discuss the appropriate level of depth necessary in your college essay.
Student Stories
Student Story: Admissions essay about a formative experience
Get the perspective of a current college student on how he approached the admissions essay.
Student Story: Admissions essay about personal identity
Get the perspective of a current college student on how she approached the admissions essay.
Student Story: Admissions essay about community impact
Student story: admissions essay about a past mistake, how to write a college application essay, tips for writing an effective application essay, sample college essay 1 with feedback, sample college essay 2 with feedback.
This content is licensed by Khan Academy and is available for free at www.khanacademy.org.
Is Google Making Us Stupid?
What the Internet is doing to our brains
“Dave, stop. Stop, will you? Stop, Dave. Will you stop, Dave?” So the supercomputer HAL pleads with the implacable astronaut Dave Bowman in a famous and weirdly poignant scene toward the end of Stanley Kubrick’s 2001: A Space Odyssey . Bowman, having nearly been sent to a deep-space death by the malfunctioning machine, is calmly, coldly disconnecting the memory circuits that control its artificial “ brain. “Dave, my mind is going,” HAL says, forlornly. “I can feel it. I can feel it.”
I can feel it, too. Over the past few years I’ve had an uncomfortable sense that someone, or something, has been tinkering with my brain, remapping the neural circuitry, reprogramming the memory. My mind isn’t going—so far as I can tell—but it’s changing. I’m not thinking the way I used to think. I can feel it most strongly when I’m reading. Immersing myself in a book or a lengthy article used to be easy. My mind would get caught up in the narrative or the turns of the argument, and I’d spend hours strolling through long stretches of prose. That’s rarely the case anymore. Now my concentration often starts to drift after two or three pages. I get fidgety, lose the thread, begin looking for something else to do. I feel as if I’m always dragging my wayward brain back to the text. The deep reading that used to come naturally has become a struggle.
I think I know what’s going on. For more than a decade now, I’ve been spending a lot of time online, searching and surfing and sometimes adding to the great databases of the Internet. The Web has been a godsend to me as a writer. Research that once required days in the stacks or periodical rooms of libraries can now be done in minutes. A few Google searches, some quick clicks on hyperlinks, and I’ve got the telltale fact or pithy quote I was after. Even when I’m not working, I’m as likely as not to be foraging in the Web’s info-thickets—reading and writing e-mails, scanning headlines and blog posts, watching videos and listening to podcasts, or just tripping from link to link to link. (Unlike footnotes, to which they’re sometimes likened, hyperlinks don’t merely point to related works; they propel you toward them.)
For me, as for others, the Net is becoming a universal medium, the conduit for most of the information that flows through my eyes and ears and into my mind. The advantages of having immediate access to such an incredibly rich store of information are many, and they’ve been widely described and duly applauded. “The perfect recall of silicon memory,” Wired ’s Clive Thompson has written , “can be an enormous boon to thinking.” But that boon comes at a price. As the media theorist Marshall McLuhan pointed out in the 1960s, media are not just passive channels of information. They supply the stuff of thought, but they also shape the process of thought. And what the Net seems to be doing is chipping away my capacity for concentration and contemplation. My mind now expects to take in information the way the Net distributes it: in a swiftly moving stream of particles. Once I was a scuba diver in the sea of words. Now I zip along the surface like a guy on a Jet Ski.
I’m not the only one. When I mention my troubles with reading to friends and acquaintances—literary types, most of them—many say they’re having similar experiences. The more they use the Web, the more they have to fight to stay focused on long pieces of writing. Some of the bloggers I follow have also begun mentioning the phenomenon. Scott Karp, who writes a blog about online media , recently confessed that he has stopped reading books altogether. “I was a lit major in college, and used to be [a] voracious book reader,” he wrote. “What happened?” He speculates on the answer: “What if I do all my reading on the web not so much because the way I read has changed, i.e. I’m just seeking convenience, but because the way I THINK has changed?”
Bruce Friedman, who blogs regularly about the use of computers in medicine , also has described how the Internet has altered his mental habits. “I now have almost totally lost the ability to read and absorb a longish article on the web or in print,” he wrote earlier this year. A pathologist who has long been on the faculty of the University of Michigan Medical School, Friedman elaborated on his comment in a telephone conversation with me. His thinking, he said, has taken on a “staccato” quality, reflecting the way he quickly scans short passages of text from many sources online. “I can’t read War and Peace anymore,” he admitted. “I’ve lost the ability to do that. Even a blog post of more than three or four paragraphs is too much to absorb. I skim it.”
Anecdotes alone don’t prove much. And we still await the long-term neurological and psychological experiments that will provide a definitive picture of how Internet use affects cognition. But a recently published study of online research habits, conducted by scholars from University College London, suggests that we may well be in the midst of a sea change in the way we read and think. As part of the five-year research program, the scholars examined computer logs documenting the behavior of visitors to two popular research sites, one operated by the British Library and one by a U.K. educational consortium, that provide access to journal articles, e-books, and other sources of written information. They found that people using the sites exhibited “a form of skimming activity,” hopping from one source to another and rarely returning to any source they’d already visited. They typically read no more than one or two pages of an article or book before they would “bounce” out to another site. Sometimes they’d save a long article, but there’s no evidence that they ever went back and actually read it. The authors of the study report:
It is clear that users are not reading online in the traditional sense; indeed there are signs that new forms of “reading” are emerging as users “power browse” horizontally through titles, contents pages and abstracts going for quick wins. It almost seems that they go online to avoid reading in the traditional sense.
Thanks to the ubiquity of text on the Internet, not to mention the popularity of text-messaging on cell phones, we may well be reading more today than we did in the 1970s or 1980s, when television was our medium of choice. But it’s a different kind of reading, and behind it lies a different kind of thinking—perhaps even a new sense of the self. “We are not only what we read,” says Maryanne Wolf, a developmental psychologist at Tufts University and the author of Proust and the Squid: The Story and Science of the Reading Brain . “We are how we read.” Wolf worries that the style of reading promoted by the Net, a style that puts “efficiency” and “immediacy” above all else, may be weakening our capacity for the kind of deep reading that emerged when an earlier technology, the printing press, made long and complex works of prose commonplace. When we read online, she says, we tend to become “mere decoders of information.” Our ability to interpret text, to make the rich mental connections that form when we read deeply and without distraction, remains largely disengaged.
Reading, explains Wolf, is not an instinctive skill for human beings. It’s not etched into our genes the way speech is. We have to teach our minds how to translate the symbolic characters we see into the language we understand. And the media or other technologies we use in learning and practicing the craft of reading play an important part in shaping the neural circuits inside our brains. Experiments demonstrate that readers of ideograms, such as the Chinese, develop a mental circuitry for reading that is very different from the circuitry found in those of us whose written language employs an alphabet. The variations extend across many regions of the brain, including those that govern such essential cognitive functions as memory and the interpretation of visual and auditory stimuli. We can expect as well that the circuits woven by our use of the Net will be different from those woven by our reading of books and other printed works.
Sometime in 1882, Friedrich Nietzsche bought a typewriter—a Malling-Hansen Writing Ball, to be precise. His vision was failing, and keeping his eyes focused on a page had become exhausting and painful, often bringing on crushing headaches. He had been forced to curtail his writing, and he feared that he would soon have to give it up. The typewriter rescued him, at least for a time. Once he had mastered touch-typing, he was able to write with his eyes closed, using only the tips of his fingers. Words could once again flow from his mind to the page.
But the machine had a subtler effect on his work. One of Nietzsche’s friends, a composer, noticed a change in the style of his writing. His already terse prose had become even tighter, more telegraphic. “Perhaps you will through this instrument even take to a new idiom,” the friend wrote in a letter, noting that, in his own work, his “‘thoughts’ in music and language often depend on the quality of pen and paper.”
Recommended Reading
Living with a computer.

How to Trick People Into Saving Money

The Dark Psychology of Social Networks
“You are right,” Nietzsche replied, “our writing equipment takes part in the forming of our thoughts.” Under the sway of the machine, writes the German media scholar Friedrich A. Kittler , Nietzsche’s prose “changed from arguments to aphorisms, from thoughts to puns, from rhetoric to telegram style.”
The human brain is almost infinitely malleable. People used to think that our mental meshwork, the dense connections formed among the 100 billion or so neurons inside our skulls, was largely fixed by the time we reached adulthood. But brain researchers have discovered that that’s not the case. James Olds, a professor of neuroscience who directs the Krasnow Institute for Advanced Study at George Mason University, says that even the adult mind “is very plastic.” Nerve cells routinely break old connections and form new ones. “The brain,” according to Olds, “has the ability to reprogram itself on the fly, altering the way it functions.”
As we use what the sociologist Daniel Bell has called our “intellectual technologies”—the tools that extend our mental rather than our physical capacities—we inevitably begin to take on the qualities of those technologies. The mechanical clock, which came into common use in the 14th century, provides a compelling example. In Technics and Civilization , the historian and cultural critic Lewis Mumford described how the clock “disassociated time from human events and helped create the belief in an independent world of mathematically measurable sequences.” The “abstract framework of divided time” became “the point of reference for both action and thought.”
The clock’s methodical ticking helped bring into being the scientific mind and the scientific man. But it also took something away. As the late MIT computer scientist Joseph Weizenbaum observed in his 1976 book, Computer Power and Human Reason: From Judgment to Calculation , the conception of the world that emerged from the widespread use of timekeeping instruments “remains an impoverished version of the older one, for it rests on a rejection of those direct experiences that formed the basis for, and indeed constituted, the old reality.” In deciding when to eat, to work, to sleep, to rise, we stopped listening to our senses and started obeying the clock.
The process of adapting to new intellectual technologies is reflected in the changing metaphors we use to explain ourselves to ourselves. When the mechanical clock arrived, people began thinking of their brains as operating “like clockwork.” Today, in the age of software, we have come to think of them as operating “like computers.” But the changes, neuroscience tells us, go much deeper than metaphor. Thanks to our brain’s plasticity, the adaptation occurs also at a biological level.
The Internet promises to have particularly far-reaching effects on cognition. In a paper published in 1936 , the British mathematician Alan Turing proved that a digital computer, which at the time existed only as a theoretical machine, could be programmed to perform the function of any other information-processing device. And that’s what we’re seeing today. The Internet, an immeasurably powerful computing system, is subsuming most of our other intellectual technologies. It’s becoming our map and our clock, our printing press and our typewriter, our calculator and our telephone, and our radio and TV.
When the Net absorbs a medium, that medium is re-created in the Net’s image. It injects the medium’s content with hyperlinks, blinking ads, and other digital gewgaws, and it surrounds the content with the content of all the other media it has absorbed. A new e-mail message, for instance, may announce its arrival as we’re glancing over the latest headlines at a newspaper’s site. The result is to scatter our attention and diffuse our concentration.
The Net’s influence doesn’t end at the edges of a computer screen, either. As people’s minds become attuned to the crazy quilt of Internet media, traditional media have to adapt to the audience’s new expectations. Television programs add text crawls and pop-up ads, and magazines and newspapers shorten their articles, introduce capsule summaries, and crowd their pages with easy-to-browse info-snippets. When, in March of this year, The New York Times decided to devote the second and third pages of every edition to article abstracts , its design director, Tom Bodkin, explained that the “shortcuts” would give harried readers a quick “taste” of the day’s news, sparing them the “less efficient” method of actually turning the pages and reading the articles. Old media have little choice but to play by the new-media rules.
Never has a communications system played so many roles in our lives—or exerted such broad influence over our thoughts—as the Internet does today. Yet, for all that’s been written about the Net, there’s been little consideration of how, exactly, it’s reprogramming us. The Net’s intellectual ethic remains obscure.
About the same time that Nietzsche started using his typewriter, an earnest young man named Frederick Winslow Taylor carried a stopwatch into the Midvale Steel plant in Philadelphia and began a historic series of experiments aimed at improving the efficiency of the plant’s machinists. With the approval of Midvale’s owners, he recruited a group of factory hands, set them to work on various metalworking machines, and recorded and timed their every movement as well as the operations of the machines. By breaking down every job into a sequence of small, discrete steps and then testing different ways of performing each one, Taylor created a set of precise instructions—an “algorithm,” we might say today—for how each worker should work. Midvale’s employees grumbled about the strict new regime, claiming that it turned them into little more than automatons, but the factory’s productivity soared.
More than a hundred years after the invention of the steam engine, the Industrial Revolution had at last found its philosophy and its philosopher. Taylor’s tight industrial choreography—his “system,” as he liked to call it—was embraced by manufacturers throughout the country and, in time, around the world. Seeking maximum speed, maximum efficiency, and maximum output, factory owners used time-and-motion studies to organize their work and configure the jobs of their workers. The goal, as Taylor defined it in his celebrated 1911 treatise, The Principles of Scientific Management , was to identify and adopt, for every job, the “one best method” of work and thereby to effect “the gradual substitution of science for rule of thumb throughout the mechanic arts.” Once his system was applied to all acts of manual labor, Taylor assured his followers, it would bring about a restructuring not only of industry but of society, creating a utopia of perfect efficiency. “In the past the man has been first,” he declared; “in the future the system must be first.”
Taylor’s system is still very much with us; it remains the ethic of industrial manufacturing. And now, thanks to the growing power that computer engineers and software coders wield over our intellectual lives, Taylor’s ethic is beginning to govern the realm of the mind as well. The Internet is a machine designed for the efficient and automated collection, transmission, and manipulation of information, and its legions of programmers are intent on finding the “one best method”—the perfect algorithm—to carry out every mental movement of what we’ve come to describe as “knowledge work.”
Google’s headquarters, in Mountain View, California—the Googleplex—is the Internet’s high church, and the religion practiced inside its walls is Taylorism. Google, says its chief executive, Eric Schmidt, is “a company that’s founded around the science of measurement,” and it is striving to “systematize everything” it does. Drawing on the terabytes of behavioral data it collects through its search engine and other sites, it carries out thousands of experiments a day, according to the Harvard Business Review , and it uses the results to refine the algorithms that increasingly control how people find information and extract meaning from it. What Taylor did for the work of the hand, Google is doing for the work of the mind.
The company has declared that its mission is “to organize the world’s information and make it universally accessible and useful.” It seeks to develop “the perfect search engine,” which it defines as something that “understands exactly what you mean and gives you back exactly what you want.” In Google’s view, information is a kind of commodity, a utilitarian resource that can be mined and processed with industrial efficiency. The more pieces of information we can “access” and the faster we can extract their gist, the more productive we become as thinkers.
Where does it end? Sergey Brin and Larry Page, the gifted young men who founded Google while pursuing doctoral degrees in computer science at Stanford, speak frequently of their desire to turn their search engine into an artificial intelligence, a HAL-like machine that might be connected directly to our brains. “The ultimate search engine is something as smart as people—or smarter,” Page said in a speech a few years back. “For us, working on search is a way to work on artificial intelligence.” In a 2004 interview with Newsweek , Brin said, “Certainly if you had all the world’s information directly attached to your brain, or an artificial brain that was smarter than your brain, you’d be better off.” Last year, Page told a convention of scientists that Google is “really trying to build artificial intelligence and to do it on a large scale.”
Such an ambition is a natural one, even an admirable one, for a pair of math whizzes with vast quantities of cash at their disposal and a small army of computer scientists in their employ. A fundamentally scientific enterprise, Google is motivated by a desire to use technology, in Eric Schmidt’s words, “to solve problems that have never been solved before,” and artificial intelligence is the hardest problem out there. Why wouldn’t Brin and Page want to be the ones to crack it?
Still, their easy assumption that we’d all “be better off” if our brains were supplemented, or even replaced, by an artificial intelligence is unsettling. It suggests a belief that intelligence is the output of a mechanical process, a series of discrete steps that can be isolated, measured, and optimized. In Google’s world, the world we enter when we go online, there’s little place for the fuzziness of contemplation. Ambiguity is not an opening for insight but a bug to be fixed. The human brain is just an outdated computer that needs a faster processor and a bigger hard drive.
The idea that our minds should operate as high-speed data-processing machines is not only built into the workings of the Internet, it is the network’s reigning business model as well. The faster we surf across the Web—the more links we click and pages we view—the more opportunities Google and other companies gain to collect information about us and to feed us advertisements. Most of the proprietors of the commercial Internet have a financial stake in collecting the crumbs of data we leave behind as we flit from link to link—the more crumbs, the better. The last thing these companies want is to encourage leisurely reading or slow, concentrated thought. It’s in their economic interest to drive us to distraction.
Maybe I’m just a worrywart. Just as there’s a tendency to glorify technological progress, there’s a countertendency to expect the worst of every new tool or machine. In Plato’s Phaedrus , Socrates bemoaned the development of writing. He feared that, as people came to rely on the written word as a substitute for the knowledge they used to carry inside their heads, they would, in the words of one of the dialogue’s characters, “cease to exercise their memory and become forgetful.” And because they would be able to “receive a quantity of information without proper instruction,” they would “be thought very knowledgeable when they are for the most part quite ignorant.” They would be “filled with the conceit of wisdom instead of real wisdom.” Socrates wasn’t wrong—the new technology did often have the effects he feared—but he was shortsighted. He couldn’t foresee the many ways that writing and reading would serve to spread information, spur fresh ideas, and expand human knowledge (if not wisdom).
The arrival of Gutenberg’s printing press, in the 15th century, set off another round of teeth gnashing. The Italian humanist Hieronimo Squarciafico worried that the easy availability of books would lead to intellectual laziness, making men “less studious” and weakening their minds. Others argued that cheaply printed books and broadsheets would undermine religious authority, demean the work of scholars and scribes, and spread sedition and debauchery. As New York University professor Clay Shirky notes, “Most of the arguments made against the printing press were correct, even prescient.” But, again, the doomsayers were unable to imagine the myriad blessings that the printed word would deliver.
So, yes, you should be skeptical of my skepticism. Perhaps those who dismiss critics of the Internet as Luddites or nostalgists will be proved correct, and from our hyperactive, data-stoked minds will spring a golden age of intellectual discovery and universal wisdom. Then again, the Net isn’t the alphabet, and although it may replace the printing press, it produces something altogether different. The kind of deep reading that a sequence of printed pages promotes is valuable not just for the knowledge we acquire from the author’s words but for the intellectual vibrations those words set off within our own minds. In the quiet spaces opened up by the sustained, undistracted reading of a book, or by any other act of contemplation, for that matter, we make our own associations, draw our own inferences and analogies, foster our own ideas. Deep reading , as Maryanne Wolf argues, is indistinguishable from deep thinking.
If we lose those quiet spaces, or fill them up with “content,” we will sacrifice something important not only in our selves but in our culture. In a recent essay , the playwright Richard Foreman eloquently described what’s at stake:
I come from a tradition of Western culture, in which the ideal (my ideal) was the complex, dense and “cathedral-like” structure of the highly educated and articulate personality—a man or woman who carried inside themselves a personally constructed and unique version of the entire heritage of the West. [But now] I see within us all (myself included) the replacement of complex inner density with a new kind of self—evolving under the pressure of information overload and the technology of the “instantly available.”
As we are drained of our “inner repertory of dense cultural inheritance,” Foreman concluded, we risk turning into “‘pancake people’—spread wide and thin as we connect with that vast network of information accessed by the mere touch of a button.”
I’m haunted by that scene in 2001 . What makes it so poignant, and so weird, is the computer’s emotional response to the disassembly of its mind: its despair as one circuit after another goes dark, its childlike pleading with the astronaut—“I can feel it. I can feel it. I’m afraid”—and its final reversion to what can only be called a state of innocence. HAL’s outpouring of feeling contrasts with the emotionlessness that characterizes the human figures in the film, who go about their business with an almost robotic efficiency. Their thoughts and actions feel scripted, as if they’re following the steps of an algorithm. In the world of 2001 , people have become so machinelike that the most human character turns out to be a machine. That’s the essence of Kubrick’s dark prophecy: as we come to rely on computers to mediate our understanding of the world, it is our own intelligence that flattens into artificial intelligence.
When you buy a book using a link on this page, we receive a commission. Thank you for supporting The Atlantic .
From the garage to the Googleplex
The Google story begins in 1995 at Stanford University. Larry Page was considering Stanford for grad school and Sergey Brin, a student there, was assigned to show him around.
By some accounts, they disagreed about nearly everything during that first meeting, but by the following year they struck a partnership. Working from their dorm rooms, they built a search engine that used links to determine the importance of individual pages on the World Wide Web. They called this search engine Backrub.
Soon after, Backrub was renamed Google (phew). The name was a play on the mathematical expression for the number 1 followed by 100 zeros and aptly reflected Larry and Sergey's mission “to organize the world’s information and make it universally accessible and useful.”
Over the next few years, Google caught the attention of not only the academic community, but Silicon Valley investors as well. In August 1998, Sun co-founder Andy Bechtolsheim wrote Larry and Sergey a check for $100,000, and Google Inc. was officially born. With this investment, the newly incorporated team made the upgrade from the dorms to their first office: a garage in suburban Menlo Park, California, owned by Susan Wojcicki (employee #16 and former CEO of YouTube). Clunky desktop computers, a ping pong table, and bright blue carpet set the scene for those early days and late nights. (The tradition of keeping things colorful continues to this day.)
Even in the beginning, things were unconventional: from Google’s initial server (made of Lego) to the first “Doodle” in 1998: a stick figure in the logo announcing to site visitors that the entire staff was playing hooky at the Burning Man Festival. “Don't be evil” captured the spirit of our intentionally unconventional methods. In the years that followed, the company expanded rapidly — hiring engineers, building a sales team, and introducing the first company dog, Yoshka . Google outgrew the garage and eventually moved to its current headquarters (a.k.a.“The Googleplex”) in Mountain View, California. The spirit of doing things differently made the move. So did Yoshka.
The relentless search for better answers continues to be at the core of everything we do. Today, Google makes hundreds of products used by billions of people across the globe, from YouTube and Android to Gmail and, of course, Google Search. Although we’ve ditched the Lego servers and added just a few more company dogs, our passion for building technology for everyone has stayed with us — from the dorm room, to the garage, and to this very day.
I tried the new Google. Its answers are worse.
Google’s ai-‘supercharged’ search generative experience, or sge, sometimes makes up facts, misinterprets questions and picks low-quality sources — even after nearly 11 months of public testing..

Have you heard about the new Google ? They “ supercharged ” it with artificial intelligence. Somehow, that also made it dumber.
With the regular old Google, I can ask, “What’s Mark Zuckerberg’s net worth?” and a reasonable answer pops up: “169.8 billion USD.”
Now let’s ask the same question with the “experimental” new version of Google search. Its AI responds: Zuckerberg’s net worth is “$46.24 per hour, or $96,169 per year. This is equivalent to $8,014 per month, $1,849 per week, and $230.6 million per day.”
Um, none of those numbers add up.
Google acting dumb matters because its AI is headed to your searches sooner or later . The company has already been testing this new Google — dubbed Search Generative Experience, or SGE — with volunteers for nearly 11 months, and recently started showing AI answers in the main Google results even for people who have not opted in to the test .
Should you trust that AI?
The new Google can do some useful things. But as you’ll see, it sometimes also makes up facts, misinterprets questions, delivers out-of-date information and just generally blathers on. Even worse, researchers are finding the AI often elevates lower-quality sites as reliable sources of information.
Normally, I wouldn’t review a product that isn’t finished. But this test of Google’s future has been going on for nearly a year, and the choices being made now will influence how billions of people get information. At stake is also a core idea behind the current AI frenzy: that the tech can replace the need to research things ourselves by just giving us answers. If a company with the money and computing power of Google can’t make it work, who can?
SGE merges the search engine you know with the capabilities of a chatbot. On top of traditional results, SGE writes out direct answers to queries, interspersed with links to dig deeper.
Geoffrey A. Fowler

SGE is a response to the reality that some people, including me, are starting to turn to AI like ChatGPT for more complex questions or when we don’t feel like reading a bunch of different sites. Onely , a search optimization firm, estimates that using SGE can make a user’s overall research journey 10 to 20 times shorter by assembling pros and cons, prices and other information into one place.
An all-knowing answer bot sounds useful given our shrinking attention spans. But Google has a lot to work out. We expect searches to be fast, yet Google’s AI answers take a painful second or two to generate. Google has to balance the already fragile economy of the web, where its AI answers can steal traffic from publishers who do the expensive and hard work of actually researching things.
And most of all, the new Google has to deliver on the promise that it can consistently and correctly answer our questions. That’s where I focused my testing — and kept finding examples where the AI-supercharged Google did worse than its predecessor.
Putting Google’s AI answers to the test
Often when you’re Googling, what you really want is a short bit of information or a link. On a day-to-day basis, the new Google is often annoying because its AI is so darned chatty.
A goofy example: “What do Transformers eat?”
The AI answer told me that fictional robots don’t really need to eat or drink, though they need some kind of fuel. Meanwhile, old Google had the one-word answer I was looking for: Energon. (It’s a kind of magical fuel.) You got that answer from new Google only by scrolling down the page.
This doesn’t just happen with alien robots. When SE Ranking, a firm dedicated to search engine optimization, tested SGE with 100,000 keyword queries, it found the average answer it generated was 3,485 characters — or roughly a third as long as this column. One of Google’s challenges is figuring out when its AI is better off just keeping quiet; sometimes, SGE asks you to press a “generate” button before it will write out an answer.
Most of all, when we search, we expect correct information. Google claims SGE has a leg up on ChatGPT because its knowledge is up-to-date.
Yet I found the new Google still struggled with recent affairs. Three days after the most recent Academy Awards, I searched for “Oscars 2024.” It told me the Oscars were still to come and listed some nominees.
And nothing undermined my trust in Google’s AI answers more than watching it confidently make stuff up.
That includes facts about yours truly. I asked it about an award-winning series I wrote for The Washington Post, and it attributed it to some stranger — and then gave a link to some other website.
Then there was the time SGE all too happily made up information about something that doesn’t even exist. I asked about a San Francisco restaurant called Danny’s Dan Dan Noodles, and it told me it has “crazy wait times” and described its food.
The problem is that this is an imaginary shop I named after my favorite Chinese dish. Google’s AI had no problem inventing information about it.
So-called hallucinations about real and fake topics are a known problem with current AI. A disclaimer above SGE results says, “Generative AI is experimental,” but that doesn’t solve the problem. Google needs to figure out how to say “I don’t know” when it isn’t confident.
Suspect sources
To give us answers to everything, Google’s AI has to decide which sources are reliable. I’m not very confident about its judgment.
Remember our bonkers result on Zuckerberg’s net worth? A professional researcher — and also regular old Google — might suggest checking the billionaires list from Forbes . Google’s AI answer relied on a very weird ZipRecruiter page for “Mark Zuckerberg Jobs,” a thing that does not exist.
In my tests, suspect sources were a pattern. At the suggestion of Onely, I asked the new Google which was more reliable: Apple iPhones or Samsung phones. As a longtime reviewer, I could tell you lots of good sources of information on this, including professional journalists and repair organizations like iFixit.
Instead, the AI cites random views of people pulled from social media. Beyond the limited usefulness of a single Reddit user’s experience, how does Google know that it wasn’t a fake review posted by the phonemaker?
“Google SGE plays by a different set of rules compared to the traditional search engine we know today,” said Tomek Rudzki, Onely’s head of research and development.
SEO firms have been trying to do quantitative studies of SGE’s values, though they’re limited by Google’s requirements on test accounts. But they’ve found a similar pattern in the disconnect between the sites that the old and new Google link to. The SEO software company Authoritas tested searches with a thousand shopping terms in late March, and found that 77 percent of the time, the domain of the No. 1 traditional search result showed up nowhere in the AI-written answer.
And in its study of 100,000 keyword searches, SE Ranking found that the question-and-answer service Quora is the most-linked source by SGE; LinkedIn and Reddit were fifth and sixth. How often would those sources be acceptable on an eighth-grade term paper?
On searches about tech topics — including lots of “how to” questions — SE Ranking found the most-linked domain was simplilearn.com . I’d never heard of it before; the site describes itself as an “online bootcamp.”
“This trend not only diminishes the quality of search results but also reduces traffic and revenue for many small businesses, including affiliate websites,” says SE Ranking’s head of SEO, Anastasia Kotsiubynska.
A work in progress
Google says SGE is an opt-in experiment. But Google already blew past its expected end last December, and it hasn’t offered any update on when it will come to search for everyone. It’s possible that Google doesn’t think SGE is accurate or fast or profitable enough and that it will end up changing it dramatically.
They are wise to go slow, even if it makes Google look as though it’s behind in the AI race. The rival search engine Bing from Microsoft made a similar AI overhaul in February 2023, but its AI is still best known for going off the rails .
In an interview, Elizabeth Reid, a Google vice president leading SGE, characterized it as a work in progress.
“We’re really focused on ensuring we get the experience really right. There are a lot of different factors on this — things like latency, accuracy, helpfulness,” Reid said. “What we’ve been finding as we’re iterating and learning is that it’s pretty nuanced.” In other words, there are times the AI is helpful and other times it’s not — and Google is still trying to figure out where to draw the line.
When I shared the examples in this column, Reid told me that SGE’s hallucination rates are “very low” and have decreased “meaningfully” since SGE’s May launch, though she declined to be specific.
“I don’t want to minimize it — it is a challenge with the technology” and something “we’re really working on,” Reid said. Putting links right next to the AI answers, she added, is important to enable people to check the facts for themselves.
Here’s a proposal: Because Google acknowledges correct facts are a problem, it ought to disclose its own data on accuracy before it brings SGE to a broader audience. With billions of searches daily, even 0.001 percent can add up to a lot of wrong information.
Another area of Google’s focus is “trying to help ensure that we get to the core of the question as quickly as possible, and then give additional elaboration,” Reid said.
As for citing low-quality sources, Google disputed the outside research on SGE, saying it is based on searches that are more limited than what Google sees in practice. But it declined to share data of its own.
Reid said SGE doesn’t have a different standard than old Google. “We do see more diversity of sources that are coming forth. But the aim is really to continue to put high-quality content at the top,” she said.
Choosing who to believe is hard enough for humans. What makes Google think its current AI tech, known as LLMs, or large language models, is up to the task?
“They’re not perfect,” Reid said. “We want to take this thoughtful approach because the brand of trust that people have with Google is really important.”
The future of our information depends on it.
Help Desk: Making tech work for you
Help Desk is a destination built for readers looking to better understand and take control of the technology used in everyday life.
Take control: Sign up for The Tech Friend newsletter to get straight talk and advice on how to make your tech a force for good.
Tech tips to make your life easier: 10 tips and tricks to customize iOS 16 | 5 tips to make your gadget batteries last longer | How to get back control of a hacked social media account | How to avoid falling for and spreading misinformation online
Data and Privacy: A guide to every privacy setting you should change now . We have gone through the settings for the most popular (and problematic) services to give you recommendations. Google | Amazon | Facebook | Venmo | Apple | Android
Ask a question: Send the Help Desk your personal technology questions .
- The best tech to have in a natural disaster April 5, 2024 The best tech to have in a natural disaster April 5, 2024
- This $400 toothbrush is peak AI mania April 5, 2024 This $400 toothbrush is peak AI mania April 5, 2024
- Elon Musk’s X restores free blue check marks. Here’s what it means. April 4, 2024 Elon Musk’s X restores free blue check marks. Here’s what it means. April 4, 2024

- Personal Support
- Business Support
- Get a Quote
- Contact Press
- Partner Programs
- Submit Vulnerability
- About Malwarebytes
- News & Press
- MyAccount sign in: manage your personal or Teams subscription >
- Cloud Console sign in: manage your cloud business products >
- Partner Portal sign in: management for Resellers and MSPs >

Google Chrome gets ‘Device Bound Session Credentials’ to stop cookie theft
Google has announced the introduction of Device Bound Session Credentials (DBSC) to secure Chrome users against cookie theft.
In January we reported how hackers found a way to gain unauthorized access to Google accounts, bypassing multi-factor authentication (MFA) , by stealing authentication cookies with info-stealer malware. An authentication cookie is added to a web browser after a user proves who they are by logging in. It tells a website that a user has already logged in , so they aren’t asked for their username and password over and over again. A cybercriminal with an authentication cookie for a website doesn’t need a password, because the website thinks they’ve already logged in. It doesn’t even matter if the owner of the account changes their password.
At the time, Google said it would take action:
“We routinely upgrade our defenses against such techniques and to secure users who fall victim to malware. In this instance, Google has taken action to secure any compromised accounts detected.”
However, some info stealers reportedly updated their methods to counter Google’s fraud detection measures.
The idea that malware could steal authentication cookies and send them to a criminal did not sit well with Google. In its announcement it explains that, “because of the way cookies and operating systems interact, primarily on desktop operating systems, Chrome and other browsers cannot protect them against malware that has the same level of access as the browser itself.”
So it turned to another solution. And if the simplicity of the solution is any indication for its effectiveness, then this should be a good one.
It works by using cryptography to limit the use of an authentication cookie to the device that first created it. When a user visits a website and starts a session, the browser creates two cryptographic keys—one public, one private. The private key is stored on the device in a way that is hard to export, and the public key is given to the website. The website uses the public key to verify that the browser using the authentication cookie has the private key. In order to use a stolen cookie, a thief would also need to steal the private key, so the more robust the “hard to export” bit gets, the safer your cookies will be.
Google stated in its announcement that it thinks this will substantially reduce the success rate of cookie theft malware. This would force attackers to act locally on a device, which makes on-device detection and cleanup more effective, both for anti-malware software as well as for enterprise managed devices.
As such, Device Bound Session Credentials fits in well with Google’s strategy to phase out third-party cookies .
Development of the project is done in the open at Github with the goal of DBSC becoming an open web standard. The goal is to have a fully working trial ready by the end of 2024. Google says that identity providers such as Okta, and browsers such as Microsoft Edge, have expressed interest in DBSC as they want to secure their users against cookie theft.
We don’t just report on threats—we remove them
Cybersecurity risks should never spread beyond a headline. Keep threats off your devices by downloading Malwarebytes today .
SHARE THIS ARTICLE

RELATED ARTICLES

60% of small businesses are concerned about cybersecurity threats
April 7, 2024 - In a recent US Chamber of Commerce poll, small businesses identified cybersecurity as their biggest concern.

Cookie consent choices are just being ignored by some websites
April 5, 2024 - Resaerchers found that 90% of websites were in violation of one or more privacy regulations concerning cookie consent.

Jackson County hit by ransomware, declares state of emergency
April 4, 2024 - Jackson County has suffered "significant disruptions within its IT systems," and its offices are closed.

Google patches critical vulnerability for Androids with Qualcomm chips
April 3, 2024 - Google has issued patches for 28 security vulnerabilities, including a critical patch for Androids with Qualcomm chips.
Trusted Advisor now available for Mac, iOS, and Android
April 2, 2024 - Our Trusted Advisor dashboard provides an easy-to-understand assessment of your device’s security.
ABOUT THE AUTHOR
Was a Microsoft MVP in consumer security for 12 years running. Can speak four languages. Smells of rich mahogany and leather-bound books.

Contributors
Threat Center

Select your language
Strong Taiwan Quake Kills 9, Injures Hundreds
The earthquake was the most powerful to hit the island in 25 years. Dozens of people remained trapped, and many buildings were damaged, with the worst centered in the city of Hualien.
- Share full article
![the google essay [object Object]](https://static01.nyt.com/images/2024/04/03/multimedia/03taiwan-quake-briefing-carousel-add-bvzm/03taiwan-quake-briefing-carousel-add-bvzm-square640.jpg?quality=75&auto=webp)
- Hualien, Taiwan A landslide after the quake. Lam Yik Fei for The New York Times
- New Taipei City, Taiwan Books flew off shelves as a home shook. @Abalamindo via Storyful
- Taipei, Taiwan Passengers waiting at a train station as some services were suspended. Chiang Ying-Ying/Associated Press
- Hualien, Taiwan People are rescued from a building that had partially collapsed. TVBS via Associated Press
- Hualien, Taiwan Firefighters rescuing trapped residents from a building. CTI News via Reuters
- Taipei, Taiwan Students evacuated to a school courtyard after the earthquake. Lam Yik Fei for The New York Times
- Guishan Island, Taiwan Rocks tumbling down one side of an island popular for hiking. Lavine Lin via Reuters
- Hualien, Taiwan A building leaned to one side after the quake. Randy Yang via Associated Press
- Ishigaki, Okinawa, Japan Watching news on a rooftop of a hotel after a tsunami warning. Chang W. Lee/The New York Times
- Hualien, Taiwan Motorbikes damaged in the quake. TVBS via Associated Press
- New Taipei City, Taiwan Damage in an apartment Fabian Hamacher/Reuters
- New Taipei City, Taiwan Water cascading down a building during the quake. Wang via Reuters
Meaghan Tobin and Victoria Kim
Here’s what you need to know about the earthquake.
Taiwan was rocked Wednesday morning by the island’s strongest earthquake in a quarter century, a magnitude 7.4 tremor that killed at least nine people, injured more than 800 others and trapped dozens of people.
The heaviest damage was in Hualien County on the island’s east coast, a sleepy, scenic area prone to earthquakes. Footage from the aftermath showed a 10-story building there partially collapsed and leaning heavily to one side, from which residents emerged through windows and climbed down ladders, assisted by rescuers. Three hikers were killed after being hit by falling rocks on a hiking trail in Taroko National Park, according to the county government.
By late afternoon, officials said rescue efforts were underway to try to rescue 127 people who were trapped, many of them on hiking trails in Hualien.
One building in Changhua County, on the island’s west coast, collapsed entirely. The quake was felt throughout Taiwan and set off at least nine landslides, sending rocks tumbling onto Suhua Highway in Hualien, according to local media reports. Rail services were halted at one point across the island.
The earthquake, with an epicenter off Taiwan’s east coast, struck during the morning commute, shortly before 8 a.m. Taiwanese authorities said by 3 p.m., more than 100 aftershocks, many of them stronger than magnitude 5, had rumbled through the area.
In the capital, Taipei, buildings shook for over a minute from the initial quake. Taiwan is at the intersection of the Philippine Sea tectonic plate and the Eurasian plate, making it vulnerable to seismic activity. Hualien sits on multiple active faults, and 17 people died in a quake there in 2018.
Here is the latest:
The earthquake hit Taiwan as many people there were preparing to travel for Tomb Sweeping Day, a holiday across the Chinese-speaking world when people mourn the dead and make offerings at their graves. Officials warned the public to stay away from visiting tombs in mountain areas as a precaution, especially because rain was forecast in the coming days.
TSMC, the world’s biggest maker of advanced semiconductors, briefly evacuated workers from its factories but said a few hours later that they were returning to work. Chip production is highly precise, and even short shutdowns can cost millions of dollars.
Christopher Buckley
Lai Ching-te, Taiwan’s vice president, who is also its president-elect, visited the city of Hualien this afternoon to assess the destruction and the rescue efforts, a government announcement said. Mr. Lai, who will become president in May, said the most urgent tasks were rescuing trapped residents and providing medical care. Next, Mr. Lai said, public services must be restored, including transportation, water and power. He said Taiwan Railway’s eastern line could be reopened by Thursday night.
Meaghan Tobin
Taiwan’s fire department has updated its figures, reporting that nine people have died and 934 others have been injured in the quake. Fifty-six people in Hualien County remain trapped.
Shake intensity
Taiwan’s fire department reports that nine people have died and 882 others have been injured in Taiwan. In Hualien County, 131 people remain trapped.
Agnes Chang
Footage shows rocks tumbling down one side of Guishan Island, a popular spot for hiking known as Turtle Island, off the northeast coast of Taiwan. Officials said no fishermen or tourists were injured after the landslide.

The death toll has risen to nine, according to Taiwan government statistics.
Meaghan Tobin, Siyi Zhao
Officials in Taiwan warned residents to not visit their relatives' tombs, especially in the mountains, this weekend during the holiday, known as Ching Ming, meant to honor them. There had already been 100 aftershocks and the forecast called for rain, which could make travel conditions on damaged roads more treacherous.
Crews are working to reach people trapped on blocked roads. As of 1 p.m. local time, roads were impassable due to damage and fallen rock in 19 places, according to the Ministry of Transportation. At least 77 people remain trapped. A bridge before Daqingshui Tunnel appeared to have completely collapsed.
Taiwan’s worst rail disaster in decades — a train derailment in 2021 that killed 49 people — took place on the first day of the Tomb Sweeping holiday period that year, in the same region as the earthquake.
The earthquake hit Taiwan as many people here were preparing to travel for Tomb Sweeping Day, or Ching Ming, a day across the Chinese-speaking world when people mourn their dead, especially by making offerings at their graves. Now those plans will be disrupted for many Taiwanese.
The holiday weekend would typically see a spike in travel as people visit family across Taiwan. Currently, both rail transport and highways are blocked in parts of Hualien, said Transport Minister Wang Guo-cai. Work is underway to restore rail transportation in Hualien, and two-way traffic is expected to be restored at noon on Thursday, he said.
Taiwan’s preparedness has evolved in response to past quakes.
Taiwan’s earthquake preparedness has evolved over the past few decades in response to some of the island’s largest and most destructive quakes .
In the years after a 7.6 magnitude earthquake in central Taiwan killed nearly 2,500 people in 1999, the authorities established an urban search-and-rescue team and opened several emergency medical operation centers, among other measures .
And in 2018, after a quake in the eastern coastal city of Hualien killed 17 people and caused several buildings to partially collapse, the government ordered a wave of building inspections .
Taiwan has also been improving its early warning system for earthquakes since the 1980s. And two years ago, it rolled out new building codes that, among other things, require owners of vulnerable buildings to install ad-hoc structural reinforcements.
So how well prepared was Taiwan when a 7.4 magnitude quake struck near Hualien on Wednesday morning, killing at least seven people and injuring hundreds more?
Across the island, one building collapsed entirely, 15 others were in a state of partial collapse and another 67 were damaged, the island’s fire department said on Wednesday afternoon . Structural engineers could not immediately be reached for comment to assess that damage, or the extent to which building codes and other regulations might have either contributed to it or prevented worse destruction.
As for search-and-rescue preparedness, Taiwan is generally in very good shape, said Steve Glassey, an expert in disaster response who lives in New Zealand.
“ The skill sets, the capabilities, the equipment, the training is second to none,” said Dr. Glassey, who worked with Taipei’s urban search-and-rescue team during the response to a devastating 2011 earthquake in Christchurch, New Zealand. “They’re a very sharp operation.”
But even the best urban search-and-rescue team will be stretched thin if an earthquake causes multiple buildings to collapse, Dr. Glassey said.
Taiwan has options for requesting international help with search-and-rescue efforts. It could directly ask another country, or countries, to send personnel. And if multiple teams were to get involved, it could ask the United Nations to help coordinate them, as it did after the 1999 earthquake.
Pierre Peron, a spokesman for the United Nations, said on Wednesday afternoon that no such request had yet been made as a result of the latest earthquake.
Meaghan Tobin contributed reporting.
At least seven people have died and 736 have been injured as a result of the earthquake, according to Taiwan’s fire department. Another 77 people remained trapped in Hualien County, many of them on hiking trails. Search and rescue operations are underway, said the fire department.
Aftershocks of magnitudes between 6.5 and 7 were likely to occur over the next three or four days, said Wu Chien-fu, director of the Taiwanese Central Weather Administration’s Seismology Center, at a news conference.
As of 2 p.m., 711 people had been injured across Taiwan, the fire department said, and 77 people in Hualien County remained trapped. The four who were known to have died were in Hualien.
Victoria Kim
Hualien County is a quiet and scenic tourist destination.
Hualien County on Taiwan’s east coast is a scenic, sleepy tourist area tucked away from the island’s urban centers, with a famous gorge and aquamarine waters. It also happens to sit on several active faults , making it prone to earthquakes.
The county has a population of about 300,000, according to the 2020 census, about a third of whom live in the coastal city of Hualien, the county seat. It is one of the most sparsely populated parts of Taiwan. About three hours by train from the capital, Taipei, the city describes itself as the first place on the island that’s touched by the sun.
Hualien County is home to Taroko National Park, one of Taiwan’s most popular scenic areas. Visitors come to explore the Taroko Gorge, a striated marble canyon carved by the Liwu River, which cuts through mountains that rise steeply from the coast. The city of Hualien is a popular destination as a gateway to the national park.
According to the state-owned Central News Agency, three hikers were trapped on a trail near the entrance to the gorge on Wednesday, after the quake sent rocks falling. Two of them were found dead, the news agency said. Administrators said many roads within the park had been cut off by the earthquake, potentially trapping hikers, according to the report.
Earthquakes have rattled Hualien with some regularity. In 2018, 17 people were killed and hundreds of others injured when a magnitude 6.5 quake struck just before midnight, its epicenter a short distance northeast of the city of Hualien.
Many of the victims in that quake were in a 12-story building that was severely tilted, the first four floors of which were largely crushed, according to news reports from the time. The next year, the area was shaken by a 6.1-magnitude earthquake that injured 17 people.
The area has some of the highest concentrations of Taiwan’s aboriginal population, with several of the island’s Indigenous tribes calling the county home .
The county government in Hualien released a list of people that had been hospitalized with injuries, which stood at 118 people as of midday Wednesday.
Across Taiwan, one building fell down entirely, in Changhua County on the west coast, and 15 buildings partially collapsed, Taiwan’s fire department said. Another 67 buildings were damaged. One of the partially collapsed structures was a warehouse in New Taipei City where four people were rescued, according to Taiwan’s Central News Agency. Another 12 were rescued at a separate New Taipei City building where the foundation sank into the ground.
Peggy Jiang, who manages The Good Kid, a children’s bookstore down the street from the partially collapsed Uranus Building in Hualien, said it was a good thing they had yet to open when the quake struck. The area is now blocked off by police and rescue vehicles. “Most people in Hualien are used to earthquakes,” she said. “But this one was particularly scary, many people ran in the street immediately afterward.”
Lin Jung, 36, who manages a shop selling sneakers in Hualien, said he had been at home getting ready to take his 16-month-old baby to a medical appointment when the earthquake struck. He said it felt at first like a series of small shocks, then “suddenly it turned to an intense earthquake shaking up and down.” The glass cover of a ceiling lamp fell and shattered. “All I could do was protect my baby.”
Chris Buckley , Paul Mozur , Meaghan Tobin and John Yoon
The earthquake damaged buildings and a highway in Hualien.
The magnitude 7.4 earthquake that struck Taiwan on Wednesday damaged many buildings and a major highway in Hualien, a city on the eastern coast, and it knocked out power as it rocked the island.
Across Taiwan, the quake and its aftershocks caused one building to completely collapse and 15 others to partially collapse, according to Taiwan’s fire department. Sixty-seven other buildings sustained damage.
Two tall buildings in Hualien that sustained particularly extensive damage were at the center of the rescue efforts there. Most damage across the city was not life-threatening, said Huang Hsuan-wan, a reporter for a local news site.
Where buildings were reported damaged in Hualien City
“A lot of roads were blocked off. There are a lot of walls toppled over onto cars,” Derik du Plessis, 44, a South African resident of Hualien, said shortly after the earthquake. He described people rushing around the city to check on their houses and pick up their children. One of his friends lost her house, he said.
One of the damaged buildings in Hualien, a 10-story structure called the Uranus Building that housed a mix of homes and shops, was tilted over and appeared to be on the verge of collapse. Many of its residents managed to flee, but some were missing, said Sunny Wang, a journalist based in the city. Rescuers were trying to reach the basement, concerned that people might be trapped there.
Photographs of the initial damage in Hualien showed another building, a five-story structure, leaning to one side, with crushed motorcycles visible at the ground-floor level. Bricks had fallen off another high-rise, leaving cracks and holes in the walls.
The quake also set off at least nine landslides on Suhua Highway in Hualien, according to Taiwan’s Central News Agency, which said part of the road had collapsed.
Taiwan’s fire department said four people had been killed in the earthquake.
Across Taiwan, 40 flights have been canceled or delayed because of the earthquake, according to Taiwan’s Central Emergency Operation Center.
President Tsai Ing-wen visited Taiwan’s national emergency response center this morning, where she was briefed about the response efforts underway by members of the ministries of defense, transportation, economic affairs and agriculture, as well as the fire department.
A look at Taiwan’s strongest earthquakes.
The magnitude 7.4 earthquake that hit Taiwan on Wednesday morning was the strongest in 25 years, the island’s Central Weather Administration said.
At least four people died after the quake struck off Taiwan’s east coast, officials said.
Here’s a look back at some of the major earthquakes in modern Taiwanese history:
Taichung, 1935
Taiwan’s deadliest quake registered a magnitude of 7.1 and struck near the island’s west coast in April 1935, killing more than 3,200 people, according to the Central Weather Administration. More than 12,000 others were injured and more than 50,000 homes were destroyed or damaged.
Tainan, 1941
A magnitude 7.3 earthquake in December 1941, which struck southwestern Taiwan, caused several hundred deaths, the United States Geological Survey said.
Chi-Chi, 1999
A 7.6 magnitude earthquake in central Taiwan killed nearly 2,500 people in September 1999. The quake, which struck about 90 miles south-southwest of Taipei, was the second-deadliest in the island’s history, according to the U.S.G.S. and the Central Weather Administration. More than 10,000 people were injured and more than 100,000 homes were destroyed or damaged.
Yujing, 2016
A 6.4 magnitude earthquake in February 2016 caused a 17-story apartment complex in southwestern Taiwan to collapse, killing at least 114 people . The U.S.G.S. later said that 90 earthquakes of that scale or greater had occurred within 250 kilometers, or 155 miles, of that quake’s location over the previous 100 years.
Advertisement
Free Text Summarizer
Try our other writing services

Want to be 100% sure your summary is plagiarism-free?
Make your life easier with the free summarizer tool.
Academic research
Speed up your academic research by extracting key points.
Every day use
Reduce your reading time by summarizing long blocks of text within seconds.
Easily condense transcripts of long meetings into concise bullet points.
Difficult text
Simplify hard-to-read paragraphs, sentences or complete articles with 1 click.

Why use this summarizer?
- 100% free: Generate unlimited summaries without paying a penny
- Accurate: Get a reliable and trustworthy summary of your original text without any errors
- No signup: Use it without giving up any personal data
- Secure: No summary data is stored, guaranteeing your privacy
- Speed: Get an accurate summary within seconds, thanks to AI
- Flexible: Adjust summary length to get more (or less) detailed summaries
How to use this summarizer
1. insert, paste or download your text, 2. pick the way you want to summarize, 3. adjust your summary length, 4. get your summary in seconds.
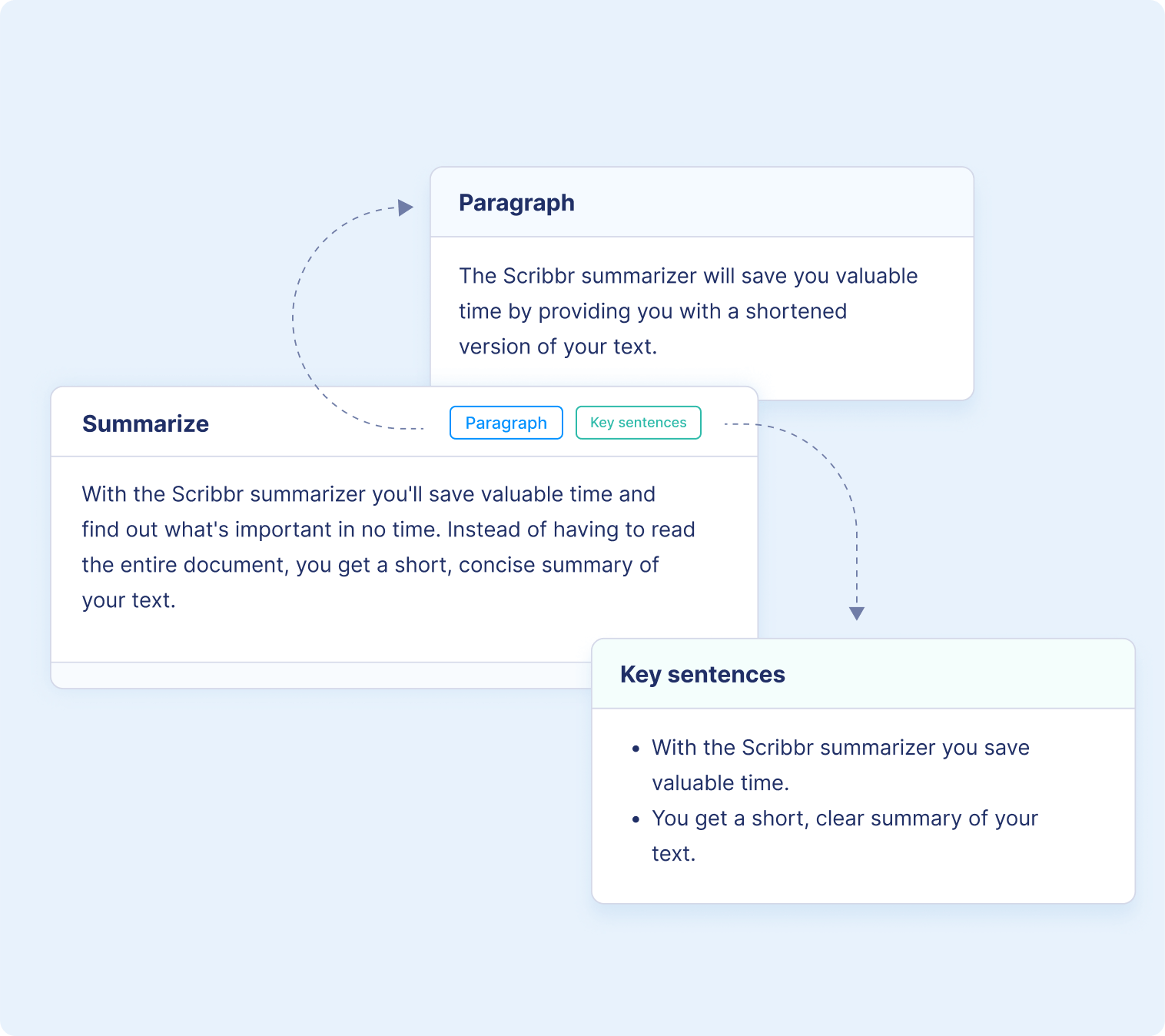
2 ways of summarizing your text
1. key sentences.
Extracts the key points of your text and turns them into digestible bullet points
2. Concise paragraphs
Summarizes your text in a concise paragraph
Summarize your text today
Want to make sure your summary doesn’t contain any plagiarism, ask our team.
Want to contact us directly? No problem. We are always here for you.
- Email [email protected]
- Start live chat
- Call +1 (510) 822-8066
- WhatsApp +31 20 261 6040

Frequently asked questions
Yes, it can. The AI has been trained on a big dataset, so technical or complex data won’t be a problem for the text summarizer .
The text summarizer is accessible on both desktop and mobile.
This text summarizer can condense long text within seconds.
At the moment, a maximum of 600 words can be summarized at once, within a few seconds. Want to summarize more? Just paste another block of text. There’s no limit on how much text you can summarize with our text summarizer .
The text summarizer can give you a longer or shorter summary, depending on your wishes. Want a more detailed summary? Just adjust the summary length at the top.

IMAGES
VIDEO
COMMENTS
500+ Words Essay on Google. Google is named after the mathematical word "googol," described as the value represented by one followed by 100 zeros. Google is the leading Internet search engine; its main service provides customers with targeted search outcomes chosen from over 8 billion web pages.
Background. Google came into existence more than 20 years ago on the 4th of September 1998. Google was created by two friends named Larry Page and Sergey Brin. They found Google when they were completing their Ph.D. at the Stanford University in California. The headquarters of Google is located in California, United States.
Google has become an essential tool for students of all levels, from primary school to graduate studies. In this essay, we will explore the advantages of Google for students, including its powerful search engine, free productivity tools, and collaborative features.
How to Write a Thesis Statement | 4 Steps & Examples. Published on January 11, 2019 by Shona McCombes.Revised on August 15, 2023 by Eoghan Ryan. A thesis statement is a sentence that sums up the central point of your paper or essay.It usually comes near the end of your introduction.. Your thesis will look a bit different depending on the type of essay you're writing.
The essay writing process consists of three main stages: Preparation: Decide on your topic, do your research, and create an essay outline. Writing: Set out your argument in the introduction, develop it with evidence in the main body, and wrap it up with a conclusion. Revision: Check your essay on the content, organization, grammar, spelling ...
Example of a Great Essay | Explanations, Tips & Tricks. Published on February 9, 2015 by Shane Bryson . Revised on July 23, 2023 by Shona McCombes. This example guides you through the structure of an essay. It shows how to build an effective introduction, focused paragraphs, clear transitions between ideas, and a strong conclusion.
Google essay writing may be challenging for some students, as it requires extensive research. At the same time, essays on Google are interesting and engaging assignments that allow students to learn more about the company and its products. Such papers can cover various issues, from technology to corporate culture.
Google's history. Larry Page and Sergey Brin founded the Google Company while doing their Ph. D at the Stanford University (Battelle 2005). The two founders launched and incorporated the company as a private enterprise in 1998, and thereafter, they obtained their first public offering in 2004. By 2006, Google was fully established and the ...
Sample College Essay 2 with Feedback. This content is licensed by Khan Academy and is available for free at www.khanacademy.org. College essays are an important part of your college application and give you the chance to show colleges and universities your personality. This guide will give you tips on how to write an effective college essay.
Google's headquarters, in Mountain View, California—the Googleplex—is the Internet's high church, and the religion practiced inside its walls is Taylorism. ... In a recent essay, the ...
Short Essay on Google 200 Words in English. The 200 words short essay mentioned below is suitable for kids and children up to 6th standard. The essay is written to guide the children with their school works-assignments and comprehension exercises. Google is a global search engine optimizer that overturned the world's way of functioning.
Google Scholar provides a simple way to broadly search for scholarly literature. Search across a wide variety of disciplines and sources: articles, theses, books, abstracts and court opinions.
Create and edit web-based documents, spreadsheets, and presentations. Store documents online and access them from any computer.
Get expert help from Scribbr's academic editors, who will proofread and edit your essay, paper, or dissertation to perfection. Proofreading Services. ... Time-saving templates that you can download and edit in Word or Google Docs. Our mission? Help you achieve your academic goals.
Use QuillBot's free online grammar checker tool to perfect your writing by reviewing your text for grammar, spelling, and punctuation errors. Whenever you need to review your writing or grammar check sentences, QuillBot is here to help make the editing process painless. QuillBot's free online sentence corrector helps you avoid mistakes and ...
In August 1998, Sun co-founder Andy Bechtolsheim wrote Larry and Sergey a check for $100,000, and Google Inc. was officially born. With this investment, the newly incorporated team made the upgrade from the dorms to their first office: a garage in suburban Menlo Park, California, owned by Susan Wojcicki (employee #16 and former CEO of YouTube).
Essays not only test a student's understanding of a subject but also help develop critical thinking, analytical skills, and the ability to articulate ideas effectively. However, writing an exceptional essay is not always an easy task. It requires a blend of creativity, research, and proper structuring.
You can unlock unlimited credits, unlimited autocomplete, unlimited sources, and more for $14 per month. Conclusions. Overall, EssayGenius and JotBot were the best AI tools I tested. I was ...
QuillBot's AI-powered paraphrasing tool will enhance your writing. Your words matter, and our paraphrasing tool is designed to ensure you use the right ones. With unlimited Custom modes and 8 predefined modes, Paraphraser lets you rephrase text countless ways. Our product will improve your fluency while also ensuring you have the appropriate ...
We recommend using an essay tracker spreadsheet to help you visualize and organize the following: Deadlines and number of essays needed; Prompt overlap, allowing you to write one essay for similar prompts; You can build your own essay tracker using our free Google Sheets template. College essay tracker template. Choose a unique topic
April 1, 2024. In recent months, Google has raced to settle a backlog of lawsuits ahead of major antitrust showdowns with the Justice Department later this year. On Monday, the company resolved ...
This is equivalent to $8,014 per month, $1,849 per week, and $230.6 million per day.". Um, none of those numbers add up. Google acting dumb matters because its AI is headed to your searches ...
Google has announced the introduction of Device Bound Session Credentials (DBSC) to secure Chrome users against cookie theft.. In January we reported how hackers found a way to gain unauthorized access to Google accounts, bypassing multi-factor authentication (MFA), by stealing authentication cookies with info-stealer malware.An authentication cookie is added to a web browser after a user ...
Former President Donald Trump on Friday posted a video that featured an image of President Joe Biden tied up in the back of a pickup truck.
An essay is a focused piece of writing that explains, argues, describes, or narrates. In high school, you may have to write many different types of essays to develop your writing skills. Academic essays at college level are usually argumentative: you develop a clear thesis about your topic and make a case for your position using evidence ...
At least seven people have died and 736 have been injured as a result of the earthquake, according to Taiwan's fire department. Another 77 people remained trapped in Hualien County, many of them ...
100% free: Generate unlimited summaries without paying a penny Accurate: Get a reliable and trustworthy summary of your original text without any errors No signup: Use it without giving up any personal data Secure: No summary data is stored, guaranteeing your privacy Speed: Get an accurate summary within seconds, thanks to AI Flexible: Adjust summary length to get more (or less) detailed summaries