Module 2: Reading
Text: paraphrasing a thesis statement.
We’ve discussed the fact that every piece of writing has a thesis statement , a sentence that captures the main idea of the text. Some are explicit –stated directly in the text itself. Others are implicit –implied by the content but not written in one distinct sentence.
You’ll remember that the “How to Identify a Thesis Statement” video offered advice for locating a text’s thesis statement. Remember when it asks you to write 1 or 2 sentences that summarize the text? When you write that summary, without looking at the text itself, you’ve actually paraphrased the thesis statement.
Review this process by re-watching the video here.
Click here to download a transcript for this video
Paraphrasing is a skill that asks you to capture the idea of a text, without using any of the same words. This is harder to do than it might first appear. Like advanced reading skills, it takes practice to do well.
As you paraphrase, keep the following tips in mind:
- Paraphrases are roughly the same length as the original text . If the thesis sentence is a medium-length sentence, your paraphrase will also be a medium-length sentence (though it doesn’t have to have exactly the same number of words).
- Paraphrases use entirely distinct wording from the original text . Common small words like “the” and “and” are perfectly acceptable, of course, but try to use completely different nouns and verbs. If needed, you can quote short snippets, 1-2 words, if you feel the precise words are necessary.
- Paraphrases keep the same meaning and tone as the original text . Make sure that anyone reading your paraphrase would understand the same thing, as if they had read the original text you paraphrased.

Contribute!
Improve this page Learn More
- Text: Paraphrasing a Thesis Statement. Provided by : Lumen Learning. License : CC BY: Attribution
- How to Identify the Thesis Statement. Authored by : Martha Ann Kennedy. Located at : https://youtu.be/di1cQgc1akg . License : All Rights Reserved . License Terms : Standard YouTube License


- school Campus Bookshelves
- menu_book Bookshelves
- perm_media Learning Objects
- login Login
- how_to_reg Request Instructor Account
- hub Instructor Commons
- Download Page (PDF)
- Download Full Book (PDF)
- Periodic Table
- Physics Constants
- Scientific Calculator
- Reference & Cite
- Tools expand_more
- Readability
selected template will load here
This action is not available.

4.48: Text- Paraphrasing a Thesis Statement
- Last updated
- Save as PDF
- Page ID 59073
We’ve discussed the fact that every piece of writing has a thesis statement , a sentence that captures the main idea of the text. Some are explicit –stated directly in the text itself. Others are implicit –implied by the content but not written in one distinct sentence.
You’ll remember that the “How to Identify a Thesis Statement” video offered advice for locating a text’s thesis statement. Remember when it asks you to write 1 or 2 sentences that summarize the text? When you write that summary, without looking at the text itself, you’ve actually paraphrased the thesis statement.
Review this process by re-watching the video here.
An interactive or media element has been excluded from this version of the text. You can view it online here: http://pb.libretexts.org/braw/?p=218
Click here to download a transcript for this video
Paraphrasing is a skill that asks you to capture the idea of a text, without using any of the same words. This is harder to do than it might first appear. Like advanced reading skills, it takes practice to do well.
As you paraphrase, keep the following tips in mind:
- Paraphrases are roughly the same length as the original text . If the thesis sentence is a medium-length sentence, your paraphrase will also be a medium-length sentence (though it doesn’t have to have exactly the same number of words).
- Paraphrases use entirely distinct wording from the original text . Common small words like “the” and “and” are perfectly acceptable, of course, but try to use completely different nouns and verbs. If needed, you can quote short snippets, 1-2 words, if you feel the precise words are necessary.
- Paraphrases keep the same meaning and tone as the original text . Make sure that anyone reading your paraphrase would understand the same thing, as if they had read the original text you paraphrased.
- Text: Paraphrasing a Thesis Statement. Provided by : Lumen Learning. License : CC BY: Attribution
- How to Identify the Thesis Statement. Authored by : Martha Ann Kennedy. Located at : https://youtu.be/di1cQgc1akg . License : All Rights Reserved . License Terms : Standard YouTube License
- AI Content Shield
- AI KW Research
- AI Assistant
- SEO Optimizer
- AI KW Clustering
- Customer reviews
- The NLO Revolution
- Press Center
- Help Center
- Content Resources
- Facebook Group
How to Rephrase a Thesis Statement: An Effective Guide
Table of Contents
A thesis statement defines your argument and provides the reader with an insight into the paper. A restatement in the paper’s conclusion reminds your readers of what you have demonstrated in your body paragraphs. It also helps you bring your piece to a close. How to rephrase a thesis statement? This article is your definitive guide.
Thesis Statement: An Overview
A thesis statement is a vital part of the writing process that should not be overlooked. Thesis statements provide readers with a brief insight into a lengthy argument or research paper . They consist of a claim and evidence or examples to support the claim.
A thesis statement is an essential element of a research paper. Your thesis statement provides the framework of your argument by defining the purpose of your work and the significant points you wish to make. It also provides the reader with an easy-to-read overview of your work.
A thesis statement appears in the introductory paragraph of the research work. A thesis restatement, stated in the paper’s conclusion, reminds the readers of the writer’s point successfully proven in the body paragraphs. It differs from the thesis statement in the sentence structure and the wording.
How to rephrase a thesis statement?
A thesis restatement reformulates what your original thesis was. It makes the original thesis statement evident to the audience and shows that the argument stated is true. The following tips will guide you through rephrasing the thesis statement effectively.
1. Decide a suitable place for your restatement.
A thesis restatement most commonly comes at the beginning of the conclusion of your paper. However, there’s no rule for positioning a thesis restatement.
You do not have to restate your thesis in the conclusion’s first sentence/paragraph.
It might help if you write a draft of your conclusion and figure out if the position of your restatement is ideal. If not, figure out a suitable place and adjust your work.
2. Take advantage of what you’ve accomplished and make a more profound impact
When the reader reads the thesis restatement, they must have read through the body paragraphs and fully understand the paper’s purpose.
Use your thesis restatement to take a stand on your previously stated information firmly. Provide your reader with more profound meaning with your thesis restatement.
3. Make your reader understand why your argument is significant.
Your introduction has stated your thesis, which might not necessarily give the reader a reason to consider your topic substantial.
When you restate your thesis, in conclusion, use the fact that the reader has gone through the entire work as an advantage. Your thesis restatement should answer the ‘so what’ question with confidence. This would tell your reader why your argument is significant.
4. Avoid clichés.
In rephrasing your thesis statement, avoid using phrases such as “As stated earlier, In conclusion, As seen in this paper.” These overused phrases show a lack of originality.
They portray you as an uncreative individual to your reader. Use unique and creative starts to pass across a strong message to your reader.
5. State it confidently.
Confidently restate your thesis. Making apologetic statements show that you aren’t sure of your argument. This will weaken your conclusion and portray your paper as ‘irrelevant.’
Avoid using words that undermine your arguments like ‘It seems, It is possible that,’ unless your topic of discussion is just a possibility.
Tips for Making your Thesis Restatement Unique
Unlike what you think, a thesis restatement is not a blaring line in your conclusion. It’s more than a conclusion that highlights what your paper has conveyed. Therefore, it’s vital in a thesis restatement to give the reader a better understanding of what you’ve accomplished and why your argument is significant.
The following tips will help you craft a unique thesis restatement, different from the original.
1. Use different wordings and structure
Your thesis restatement must differ in wording and sentence structure from the original statement.
It will help if you replace essential concepts and words in the initial thesis with their synonyms. While changing the sentence structure, ensure that your readers will be able to comprehend it.
2. Change the tense.
The thesis statement in your introductory paragraph was probably written in the future tense, prompting the reader of what to expect.
When rephrasing your thesis statement, use past tense to demonstrate to readers what you have accomplished with your paper.
3. Split up the points
The original thesis statement in your introductory paragraph was probably concise if not one or two sentences. In your conclusion, try to make it longer.
Spread your points across some sentences or even a paragraph. The thesis statement will read differently and allow you to explicitly explain how you have proven your argument in the body paragraphs.

The thesis statement contains the main idea or point of your paper. Rephrasing your thesis statement reminds your readers of what you have accomplished with your paper.
It also gives them a better understanding of your argument better . This article has provided all the tips you need to rephrase a thesis statement effectively.

Pam is an expert grammarian with years of experience teaching English, writing and ESL Grammar courses at the university level. She is enamored with all things language and fascinated with how we use words to shape our world.
Explore All Paraphrasing Tool Articles
Advanced & effective paraphrase simplify tool.
The paraphrase simplify tool is designed to paraphrase and simplify your text effectively. This tool can be used for in-depth…
- Paraphrasing Tool
What Is a Paraphrase Citation?
When you paraphrase, many people think you don’t have to give a citation. Understand that because you have used someone’s…
Paraphrasing Vs Summarizing: What’s the Difference?
Paraphrasing and summarizing are two similar activities, but they are not the same. To understand the difference between paraphrasing vs…
The Best Paraphrase Tools: A Review
When it comes to paraphrase tools, there are so many to choose. This is why we decided some paraphrase tool…
The Best Paraphrasing Hacks From Students Themselves
Did you have a tough concept that you had a lot of trouble understanding? Paraphrasing helps with that. But it…
What are the Best Paraphrasing Tool to Download
Paraphrasing is the process of rewriting or rephrase a sentence without changing its meaning. A paraphrasing tool allows you to…
📕 Studying HQ
How to rephrase a thesis statement to make it stronger, dr. wilson mn.
- August 3, 2022
After you have written your thesis statement, you might want to go back and revise it to make it sound more polished or professional. This process is called rephrasing and is challenging. In this article, we will give you some tips on how to rephrase your thesis statement so that it sounds its best.
What You'll Learn
Thesis Statement Structure
When you are ready to begin writing your paper, the first step is to rephrase your thesis statement so that it sounds better. This can be a difficult task, but it is worth the effort to make sure that your thesis statement is clear and concise. Here are some tips on how to rephrase your thesis statement so that it sounds better:

1. Break down your thesis statement into smaller parts. This will help you to focus on each individual component of your thesis statement and make sure that it is clear and concise. Here’s a simple thesis statement formula to use:
2. Make sure that each part of your thesis statement flows smoothly into the next. This will help to create a cohesive argument for your paper.
3. Use active voice when possible. Active voice makes your arguments sound more forceful and persuasive.
4. Avoid using jargon or overly technical language. Stick to using clear and simple language that can be understood by everyone.
5. Read your thesis statement aloud to yourself or have someone else read it aloud to you. This will help you to catch any errors or awkward phrasing that you may have missed.
By following these tips, you can be sure that your thesis statement will sound better and be easier for your readers to

Here’s How To Approach Nursing Research Paper Writing – Step By Step Guideline
Rephrasing A Thesis statement
Whether you’re writing an essay for school or a paper for publication, rephrasing your thesis statement is a great way to make it sound more polished and professional. Here are some tips on how to do it:
– First, break your thesis down into its component parts. What are the main points you’re trying to make? Identify the most important one, and rephrase it in a way that is both concise and clear.

– Next, look at each of the other points you’re making and see if there’s a way to express them more succinctly. Try to boil them down to their essence, and state them in a way that is both easy to understand and packs a punch.
– Finally, put it all together and take a look at your new thesis statement. If it sounds awkward or unclear, keep working at it until it sounds just right. With a little effort, you can end up with a much stronger statement that will make your essay that much more effective.
Check out the thesis statement generator

Rewording A Thesis Statement Tips
Are you working on a paper and feel like your thesis statement could be better? If so, don’t worry! It’s a common problem and there are some easy ways to fix it. Here are a few tips on how to rephrase a thesis statement to sound better:
1. Make sure your thesis is clear and concise. This is the most important thing to remember when rephrasing your thesis statement. It should be easy for your reader to understand what you’re trying to say.
2. Use strong language. Avoid phrases like “I think” or “I believe”. These make your thesis statement sound weaker. Instead, use language that is more definitive and confident.
3. Be specific. vague statements will make your thesis statement sound weak and uninteresting. Be as specific as possible to hold your reader’s attention and make them want to read more.
4. Use active voice. Passive voice can make your thesis statement sound dull and boring. Active voice is much more engaging and will make your reader want to continue reading.
5. Avoid clichés. Clichés are overused and tired phrases that don’t add anything new or interesting to your paper. Instead, try to
Here’s how to write a discussion post
Essay Writing Help from thestudycorp.com
If you’re looking for help with rephrasing your thesis statement, look no further than thestudycorp.com! We’ll show you how to take your original statement and improve upon it, making it sound stronger and more concise. Check out our blog post on the subject for more tips and tricks.
Start by filling this short order form order.studyinghq.com
And then follow the progressive flow.
Having an issue, chat with us here
Cathy, CS.
New Concept ? Let a subject expert write your paper for You
Have a subject expert write for you now, have a subject expert finish your paper for you, edit my paper for me, have an expert write your dissertation's chapter, popular topics.
Business StudyingHq Essay Topics and Ideas How to Guides Samples
- Nursing Solutions
- Study Guides
- Free Study Database for Essays
- Privacy Policy
- Writing Service
- Discounts / Offers
Study Hub:
- Studying Blog
- Topic Ideas
- How to Guides
- Business Studying
- Nursing Studying
- Literature and English Studying
Writing Tools
- Citation Generator
- Topic Generator
- Paraphrasing Tool
- Conclusion Maker
- Research Title Generator
- Thesis Statement Generator
- Summarizing Tool
- Terms and Conditions
- Confidentiality Policy
- Cookies Policy
- Refund and Revision Policy
Our samples and other types of content are meant for research and reference purposes only. We are strongly against plagiarism and academic dishonesty.
Contact Us:
📞 +15512677917
2012-2024 © studyinghq.com. All rights reserved

Thesis Statements
What this handout is about.
This handout describes what a thesis statement is, how thesis statements work in your writing, and how you can craft or refine one for your draft.
Introduction
Writing in college often takes the form of persuasion—convincing others that you have an interesting, logical point of view on the subject you are studying. Persuasion is a skill you practice regularly in your daily life. You persuade your roommate to clean up, your parents to let you borrow the car, your friend to vote for your favorite candidate or policy. In college, course assignments often ask you to make a persuasive case in writing. You are asked to convince your reader of your point of view. This form of persuasion, often called academic argument, follows a predictable pattern in writing. After a brief introduction of your topic, you state your point of view on the topic directly and often in one sentence. This sentence is the thesis statement, and it serves as a summary of the argument you’ll make in the rest of your paper.
What is a thesis statement?
A thesis statement:
- tells the reader how you will interpret the significance of the subject matter under discussion.
- is a road map for the paper; in other words, it tells the reader what to expect from the rest of the paper.
- directly answers the question asked of you. A thesis is an interpretation of a question or subject, not the subject itself. The subject, or topic, of an essay might be World War II or Moby Dick; a thesis must then offer a way to understand the war or the novel.
- makes a claim that others might dispute.
- is usually a single sentence near the beginning of your paper (most often, at the end of the first paragraph) that presents your argument to the reader. The rest of the paper, the body of the essay, gathers and organizes evidence that will persuade the reader of the logic of your interpretation.
If your assignment asks you to take a position or develop a claim about a subject, you may need to convey that position or claim in a thesis statement near the beginning of your draft. The assignment may not explicitly state that you need a thesis statement because your instructor may assume you will include one. When in doubt, ask your instructor if the assignment requires a thesis statement. When an assignment asks you to analyze, to interpret, to compare and contrast, to demonstrate cause and effect, or to take a stand on an issue, it is likely that you are being asked to develop a thesis and to support it persuasively. (Check out our handout on understanding assignments for more information.)
How do I create a thesis?
A thesis is the result of a lengthy thinking process. Formulating a thesis is not the first thing you do after reading an essay assignment. Before you develop an argument on any topic, you have to collect and organize evidence, look for possible relationships between known facts (such as surprising contrasts or similarities), and think about the significance of these relationships. Once you do this thinking, you will probably have a “working thesis” that presents a basic or main idea and an argument that you think you can support with evidence. Both the argument and your thesis are likely to need adjustment along the way.
Writers use all kinds of techniques to stimulate their thinking and to help them clarify relationships or comprehend the broader significance of a topic and arrive at a thesis statement. For more ideas on how to get started, see our handout on brainstorming .
How do I know if my thesis is strong?
If there’s time, run it by your instructor or make an appointment at the Writing Center to get some feedback. Even if you do not have time to get advice elsewhere, you can do some thesis evaluation of your own. When reviewing your first draft and its working thesis, ask yourself the following :
- Do I answer the question? Re-reading the question prompt after constructing a working thesis can help you fix an argument that misses the focus of the question. If the prompt isn’t phrased as a question, try to rephrase it. For example, “Discuss the effect of X on Y” can be rephrased as “What is the effect of X on Y?”
- Have I taken a position that others might challenge or oppose? If your thesis simply states facts that no one would, or even could, disagree with, it’s possible that you are simply providing a summary, rather than making an argument.
- Is my thesis statement specific enough? Thesis statements that are too vague often do not have a strong argument. If your thesis contains words like “good” or “successful,” see if you could be more specific: why is something “good”; what specifically makes something “successful”?
- Does my thesis pass the “So what?” test? If a reader’s first response is likely to be “So what?” then you need to clarify, to forge a relationship, or to connect to a larger issue.
- Does my essay support my thesis specifically and without wandering? If your thesis and the body of your essay do not seem to go together, one of them has to change. It’s okay to change your working thesis to reflect things you have figured out in the course of writing your paper. Remember, always reassess and revise your writing as necessary.
- Does my thesis pass the “how and why?” test? If a reader’s first response is “how?” or “why?” your thesis may be too open-ended and lack guidance for the reader. See what you can add to give the reader a better take on your position right from the beginning.
Suppose you are taking a course on contemporary communication, and the instructor hands out the following essay assignment: “Discuss the impact of social media on public awareness.” Looking back at your notes, you might start with this working thesis:
Social media impacts public awareness in both positive and negative ways.
You can use the questions above to help you revise this general statement into a stronger thesis.
- Do I answer the question? You can analyze this if you rephrase “discuss the impact” as “what is the impact?” This way, you can see that you’ve answered the question only very generally with the vague “positive and negative ways.”
- Have I taken a position that others might challenge or oppose? Not likely. Only people who maintain that social media has a solely positive or solely negative impact could disagree.
- Is my thesis statement specific enough? No. What are the positive effects? What are the negative effects?
- Does my thesis pass the “how and why?” test? No. Why are they positive? How are they positive? What are their causes? Why are they negative? How are they negative? What are their causes?
- Does my thesis pass the “So what?” test? No. Why should anyone care about the positive and/or negative impact of social media?
After thinking about your answers to these questions, you decide to focus on the one impact you feel strongly about and have strong evidence for:
Because not every voice on social media is reliable, people have become much more critical consumers of information, and thus, more informed voters.
This version is a much stronger thesis! It answers the question, takes a specific position that others can challenge, and it gives a sense of why it matters.
Let’s try another. Suppose your literature professor hands out the following assignment in a class on the American novel: Write an analysis of some aspect of Mark Twain’s novel Huckleberry Finn. “This will be easy,” you think. “I loved Huckleberry Finn!” You grab a pad of paper and write:
Mark Twain’s Huckleberry Finn is a great American novel.
You begin to analyze your thesis:
- Do I answer the question? No. The prompt asks you to analyze some aspect of the novel. Your working thesis is a statement of general appreciation for the entire novel.
Think about aspects of the novel that are important to its structure or meaning—for example, the role of storytelling, the contrasting scenes between the shore and the river, or the relationships between adults and children. Now you write:
In Huckleberry Finn, Mark Twain develops a contrast between life on the river and life on the shore.
- Do I answer the question? Yes!
- Have I taken a position that others might challenge or oppose? Not really. This contrast is well-known and accepted.
- Is my thesis statement specific enough? It’s getting there–you have highlighted an important aspect of the novel for investigation. However, it’s still not clear what your analysis will reveal.
- Does my thesis pass the “how and why?” test? Not yet. Compare scenes from the book and see what you discover. Free write, make lists, jot down Huck’s actions and reactions and anything else that seems interesting.
- Does my thesis pass the “So what?” test? What’s the point of this contrast? What does it signify?”
After examining the evidence and considering your own insights, you write:
Through its contrasting river and shore scenes, Twain’s Huckleberry Finn suggests that to find the true expression of American democratic ideals, one must leave “civilized” society and go back to nature.
This final thesis statement presents an interpretation of a literary work based on an analysis of its content. Of course, for the essay itself to be successful, you must now present evidence from the novel that will convince the reader of your interpretation.
Works consulted
We consulted these works while writing this handout. This is not a comprehensive list of resources on the handout’s topic, and we encourage you to do your own research to find additional publications. Please do not use this list as a model for the format of your own reference list, as it may not match the citation style you are using. For guidance on formatting citations, please see the UNC Libraries citation tutorial . We revise these tips periodically and welcome feedback.
Anson, Chris M., and Robert A. Schwegler. 2010. The Longman Handbook for Writers and Readers , 6th ed. New York: Longman.
Lunsford, Andrea A. 2015. The St. Martin’s Handbook , 8th ed. Boston: Bedford/St Martin’s.
Ramage, John D., John C. Bean, and June Johnson. 2018. The Allyn & Bacon Guide to Writing , 8th ed. New York: Pearson.
Ruszkiewicz, John J., Christy Friend, Daniel Seward, and Maxine Hairston. 2010. The Scott, Foresman Handbook for Writers , 9th ed. Boston: Pearson Education.
You may reproduce it for non-commercial use if you use the entire handout and attribute the source: The Writing Center, University of North Carolina at Chapel Hill
Make a Gift
We use cookies and similar technologies to improve your website experience and help us understand how you use our website. By continuing to use this website, you consent to the usage of cookies. Learn more about our Privacy Statement and Cookie Policy .
- Our Mission
- Code of Conduct
- The Consultants
- Hours and Locations
- Apply to Become a Consultant
- Make an Appointment
- Face-to-Face Appointments
- Zoom Appointments
- Written Feedback Appointments
- Support for Writers with Disabilities
- Policies and Restrictions
- Upcoming Workshops
- Class Workshops
- Meet the Consultants
- Writing Guides and Tools
- Schedule an appointment! Login or Register
- Graduate Students
- ESOL Students
Thesis Statements
A thesis statement is:.
- The statement of the author’s position on a topic or subject.
- Clear, concise, and goes beyond fact or observation to become an idea that needs to be supported (arguable).
- Often a statement of tension, where the author refutes or complicates an existing assumption or claim (counterargument).
- Often answers WHY or HOW questions related to the topic at hand.
A thesis statement is NOT:
- A statement of fact or observation (no matter how astute the observation).
- A statement of personal conviction or opinion.
- A generalization or overly broad claim.
For the writer, the thesis statement:
- Helps the writer determine the essay’s real focus. What are you trying to say with the evidence presented? A thesis provides a theory to be tested by evidence.
- Serves as a planning tool. The component parts of the thesis often correspond with the essay’s topic sentences.
For the reader, the thesis statement:
- Serves as a “map” to guide the reader through the paper. In the same way the thesis helps you organize your paper, the thesis helps organize the reader’s thinking. Once a solid thesis is presented, the reader will understand that all of the evidence presented is in service of proving the thesis.
- Creates a reason to keep reading. The reader will want to discover the support behind the thesis.
If you are having trouble writing a thesis...
...ask yourself a genuine, difficult question about the topic (usually a “how” or “why” question), and state your response, even if you are not sure why you want to give that answer. Your response may very well be a workable thesis, and the pursuit of proving that answer may reveal to you more about your sources of evidence.
...think of a strong statement or observation you have made about the subject beginning with the words “In this essay, I will...” Then ask yourself why this observation is important, or “So What?” 1 Answer the question with “I believe this is because...” In the draft stage you might phrase a working thesis as the following:
In this essay, I plan to explain how Mark Twain’s Adventures of Huckleberry Finn contrasts his river and shore scenes. I believe Twain is telling us that in order to find America’s true democratic ideals one must leave “civilized” society (the shore) and go back to nature (the river).
Then revise out the “I” statements. A revised version of this thesis might look like this:
Through its contrasting river and shore scenes, Mark Twain’s Adventure’s of Huckleberry Finn suggests that to find the true expression of American democratic ideals, one must leave “civilized” society and go back to nature.
Writing in the Disciplines
Keep in mind that thesis statements vary depending on the purpose of the assignment (or type of essay), and also by discipline. Here are a few notes on the thesis statements and the purpose of writing in a few different disciplines. 2
English: “A thesis is an interpretive argument about a text or an aspect of a text. An interpretive argument is defined as one that makes a reasonable but contestable claim about a text; in other words, it is an opinion about a text that can be supported with textual evidence."
Sciences (Biology): “A well-written scientific paper explains the scientist’s motivation for doing an experiment, the experimental design and execution, and the meaning of the results... The last sentences of the introduction should be a statement of objectives and a statement of hypotheses.”
Business: “When you write in business courses, you will usually write for a specific audience. Your goal will be to communicate in a straight-forward manner and with a clear purpose." 3
History: “In historical writing, a thesis explains the words or deeds of people in the past. It shows cause and effect; it answers the question why?... A thesis must change a reader’s mind to be of value. If it presents only facts or an obvious finding, it will merely confirm what the reader already believes.”
1. This strategy comes from Writing Analytically by Jill Stephen and David Rosenwasser.
2. The following statements on writing in the disciplines have been borrowed from the Writing Guides found at the Writing Across the Curriculum website at http://wac.gmu.edu/guides/GMU%20guides.html .
3. From A Writer’s Reference, 6th Edition, with Writing in the Disciplines, by Diana Hacker.

The Writing Center
4400 University Drive, 2G8 Fairfax, VA 22030
- Johnson Center, Room 227E
- +1-703-993-1200
- [email protected]
Quick Links
- Register with us
© Copyright 2024 George Mason University . All Rights Reserved. Privacy Statement | Accessibility
What are your chances of acceptance?
Calculate for all schools, your chance of acceptance.
Your chancing factors
Extracurriculars.
How to Write a Strong Thesis Statement: 4 Steps + Examples

What’s Covered:
What is the purpose of a thesis statement, writing a good thesis statement: 4 steps, common pitfalls to avoid, where to get your essay edited for free.
When you set out to write an essay, there has to be some kind of point to it, right? Otherwise, your essay would just be a big jumble of word salad that makes absolutely no sense. An essay needs a central point that ties into everything else. That main point is called a thesis statement, and it’s the core of any essay or research paper.
You may hear about Master degree candidates writing a thesis, and that is an entire paper–not to be confused with the thesis statement, which is typically one sentence that contains your paper’s focus.
Read on to learn more about thesis statements and how to write them. We’ve also included some solid examples for you to reference.
Typically the last sentence of your introductory paragraph, the thesis statement serves as the roadmap for your essay. When your reader gets to the thesis statement, they should have a clear outline of your main point, as well as the information you’ll be presenting in order to either prove or support your point.
The thesis statement should not be confused for a topic sentence , which is the first sentence of every paragraph in your essay. If you need help writing topic sentences, numerous resources are available. Topic sentences should go along with your thesis statement, though.
Since the thesis statement is the most important sentence of your entire essay or paper, it’s imperative that you get this part right. Otherwise, your paper will not have a good flow and will seem disjointed. That’s why it’s vital not to rush through developing one. It’s a methodical process with steps that you need to follow in order to create the best thesis statement possible.
Step 1: Decide what kind of paper you’re writing
When you’re assigned an essay, there are several different types you may get. Argumentative essays are designed to get the reader to agree with you on a topic. Informative or expository essays present information to the reader. Analytical essays offer up a point and then expand on it by analyzing relevant information. Thesis statements can look and sound different based on the type of paper you’re writing. For example:
- Argumentative: The United States needs a viable third political party to decrease bipartisanship, increase options, and help reduce corruption in government.
- Informative: The Libertarian party has thrown off elections before by gaining enough support in states to get on the ballot and by taking away crucial votes from candidates.
- Analytical: An analysis of past presidential elections shows that while third party votes may have been the minority, they did affect the outcome of the elections in 2020, 2016, and beyond.
Step 2: Figure out what point you want to make
Once you know what type of paper you’re writing, you then need to figure out the point you want to make with your thesis statement, and subsequently, your paper. In other words, you need to decide to answer a question about something, such as:
- What impact did reality TV have on American society?
- How has the musical Hamilton affected perception of American history?
- Why do I want to major in [chosen major here]?
If you have an argumentative essay, then you will be writing about an opinion. To make it easier, you may want to choose an opinion that you feel passionate about so that you’re writing about something that interests you. For example, if you have an interest in preserving the environment, you may want to choose a topic that relates to that.
If you’re writing your college essay and they ask why you want to attend that school, you may want to have a main point and back it up with information, something along the lines of:
“Attending Harvard University would benefit me both academically and professionally, as it would give me a strong knowledge base upon which to build my career, develop my network, and hopefully give me an advantage in my chosen field.”
Step 3: Determine what information you’ll use to back up your point
Once you have the point you want to make, you need to figure out how you plan to back it up throughout the rest of your essay. Without this information, it will be hard to either prove or argue the main point of your thesis statement. If you decide to write about the Hamilton example, you may decide to address any falsehoods that the writer put into the musical, such as:
“The musical Hamilton, while accurate in many ways, leaves out key parts of American history, presents a nationalist view of founding fathers, and downplays the racism of the times.”
Once you’ve written your initial working thesis statement, you’ll then need to get information to back that up. For example, the musical completely leaves out Benjamin Franklin, portrays the founding fathers in a nationalist way that is too complimentary, and shows Hamilton as a staunch abolitionist despite the fact that his family likely did own slaves.
Step 4: Revise and refine your thesis statement before you start writing
Read through your thesis statement several times before you begin to compose your full essay. You need to make sure the statement is ironclad, since it is the foundation of the entire paper. Edit it or have a peer review it for you to make sure everything makes sense and that you feel like you can truly write a paper on the topic. Once you’ve done that, you can then begin writing your paper.
When writing a thesis statement, there are some common pitfalls you should avoid so that your paper can be as solid as possible. Make sure you always edit the thesis statement before you do anything else. You also want to ensure that the thesis statement is clear and concise. Don’t make your reader hunt for your point. Finally, put your thesis statement at the end of the first paragraph and have your introduction flow toward that statement. Your reader will expect to find your statement in its traditional spot.
If you’re having trouble getting started, or need some guidance on your essay, there are tools available that can help you. CollegeVine offers a free peer essay review tool where one of your peers can read through your essay and provide you with valuable feedback. Getting essay feedback from a peer can help you wow your instructor or college admissions officer with an impactful essay that effectively illustrates your point.

Related CollegeVine Blog Posts


Conclusions
A conclusion is usually the last paragraph of an essay. It’s as important as the introduction and the body paragraphs because it reinforces the essay’s topic and purpose. Think of a conclusion as a cool down after a rigorous workout. You can’t abruptly end an intense workout, but rather, you must lightly stretch to let your muscles rest and recover properly. The same idea applies to your conclusion. You can’t suddenly stop writing in the middle of your essay, so this paragraph gradually brings your paper to a close. Below are some tips to help you conclude your essay on a high note.
Breakdown of Conclusions
The conclusion is your last chance to reflect on the importance of what you have written. You may want to refer to your introduction for ideas because the two paragraphs tend to mirror each other. Often, a conclusion has three parts. Many writers like to repeat their argument in the conclusion’s first sentence. Afterwards, they consider the larger significance of their topic, explaining what they have learned and sharing it with their audience. The last sentence brings everything together, concluding the essay with one final takeaway.
Topic Sentence
Many writers rephrase the key aspects of their thesis statement in the topic sentence of the conclusion. The goal is to remind the audience of the essay’s overall argument.
Reflective sentences
It’s best to reflect on the larger significance of your topic in at least two sentences. This is where you get to explain what you have learned and share your newfound knowledge with your audience. You also want to comment on why your topic is important without analyzing it further.
Final sentence
The final sentence brings your essay to a close. You can sum up the major points of your essay into one last takeaway, leaving your audience with something to think about.
Example Conclusion and Discussion
The literary elements of imagery, characters, and conflict within “The Fall of the House of Usher” allow Edgar Allan Poe to explore the gothic concept that suffering can be handed down from parent to child. The fears of the parents become the fears of the children. When keeping a secret becomes an obsession, the urgency spreads like a disease, infecting all in the family and even their environment. Isolation from the world spawns a toxic mixture of resentment and codependency, which is a terrible price to pay for a preserved reputation. When a solution becomes a punishment, the entire family will crumble and fall.
The topic sentence (located in the first sentence) rephrases the major parts of a typical thesis statement, the topic, purpose, and organization.
The reflective sentences (the second, third, and fourth sentences) explain what was learned and share this information with the audience. Notice that each reflective sentence comments on the topic’s larger significance, leading up to one final takeaway.
The final sentence (the fifth sentence) brings the essay’s main points together to make one last observation about the topic, giving the audience some food for thought.

What to Remember When Writing a Conclusion
Paragraph length.
Similar to an introduction, the conclusion is usually shorter than a body paragraph. Typically, the minimum paragraph length for a college-level essay is five to seven sentences. Remember, a conclusion is only meant to wrap up your essay, so it doesn’t need to be very long.
Paragraph Content
A conclusion should not bring up any new ideas; it’s a place for you to finalize your thoughts and remind your readers of your essay’s topic and purpose. The conclusion is an opportunity to leave a strong, lasting impression on your audience. In some ways, it’s similar to closing a door while also opening a window. You close the door on your topic, wrapping up your final thoughts on the matter. However, at the same time, you open a window, allowing your audience to look at your topic from a new perspective and leaving them with something to think about long after they have finished reading your paper.
Page last updated July 6, 2023.
Reference management. Clean and simple.
How to write a thesis statement + examples

What is a thesis statement?
Is a thesis statement a question, how do you write a good thesis statement, how do i know if my thesis statement is good, examples of thesis statements, helpful resources on how to write a thesis statement, frequently asked questions about writing a thesis statement, related articles.
A thesis statement is the main argument of your paper or thesis.
The thesis statement is one of the most important elements of any piece of academic writing . It is a brief statement of your paper’s main argument. Essentially, you are stating what you will be writing about.
You can see your thesis statement as an answer to a question. While it also contains the question, it should really give an answer to the question with new information and not just restate or reiterate it.
Your thesis statement is part of your introduction. Learn more about how to write a good thesis introduction in our introduction guide .
A thesis statement is not a question. A statement must be arguable and provable through evidence and analysis. While your thesis might stem from a research question, it should be in the form of a statement.
Tip: A thesis statement is typically 1-2 sentences. For a longer project like a thesis, the statement may be several sentences or a paragraph.
A good thesis statement needs to do the following:
- Condense the main idea of your thesis into one or two sentences.
- Answer your project’s main research question.
- Clearly state your position in relation to the topic .
- Make an argument that requires support or evidence.
Once you have written down a thesis statement, check if it fulfills the following criteria:
- Your statement needs to be provable by evidence. As an argument, a thesis statement needs to be debatable.
- Your statement needs to be precise. Do not give away too much information in the thesis statement and do not load it with unnecessary information.
- Your statement cannot say that one solution is simply right or simply wrong as a matter of fact. You should draw upon verified facts to persuade the reader of your solution, but you cannot just declare something as right or wrong.
As previously mentioned, your thesis statement should answer a question.
If the question is:
What do you think the City of New York should do to reduce traffic congestion?
A good thesis statement restates the question and answers it:
In this paper, I will argue that the City of New York should focus on providing exclusive lanes for public transport and adaptive traffic signals to reduce traffic congestion by the year 2035.
Here is another example. If the question is:
How can we end poverty?
A good thesis statement should give more than one solution to the problem in question:
In this paper, I will argue that introducing universal basic income can help reduce poverty and positively impact the way we work.
- The Writing Center of the University of North Carolina has a list of questions to ask to see if your thesis is strong .
A thesis statement is part of the introduction of your paper. It is usually found in the first or second paragraph to let the reader know your research purpose from the beginning.
In general, a thesis statement should have one or two sentences. But the length really depends on the overall length of your project. Take a look at our guide about the length of thesis statements for more insight on this topic.
Here is a list of Thesis Statement Examples that will help you understand better how to write them.
Every good essay should include a thesis statement as part of its introduction, no matter the academic level. Of course, if you are a high school student you are not expected to have the same type of thesis as a PhD student.
Here is a great YouTube tutorial showing How To Write An Essay: Thesis Statements .

- U.S. Locations
- UMGC Europe
- Learn Online
- Find Answers
- 855-655-8682
- Current Students
Essay Conclusions
Explore more of umgc.
- Writing Resources
Contact The Effective Writing Center
E-mail: writingcenter@umgc.edu
Learn about the elements of a successful essay conclusion.
The conclusion is a very important part of your essay. Although it is sometimes treated as a roundup of all of the bits that didn’t fit into the paper earlier, it deserves better treatment than that! It's the last thing the reader will see, so it tends to stick in the reader's memory. It's also a great place to remind the reader exactly why your topic is important. A conclusion is more than just "the last paragraph"—it's a working part of the paper. This is the place to push your reader to think about the consequences of your topic for the wider world or for the reader's own life!
A good conclusion should do a few things:
Restate your thesis
Synthesize or summarize your major points
Make the context of your argument clear
Restating Your Thesis
You've already spent time and energy crafting a solid thesis statement for your introduction, and if you've done your job right, your whole paper focuses on that thesis statement. That's why it's so important to address the thesis in your conclusion! Many writers choose to begin the conclusion by restating the thesis, but you can put your thesis into the conclusion anywhere—the first sentence of the paragraph, the last sentence, or in between. Here are a few tips for rephrasing your thesis:
Remind the reader that you've proven this thesis over the course of your paper. For example, if you're arguing that your readers should get their pets from animal shelters rather than pet stores, you might say, "If you were considering that puppy in the pet-shop window, remember that your purchase will support 'puppy mills' instead of rescuing a needy dog, and consider selecting your new friend at your local animal shelter." This example gives the reader not only the thesis of the paper, but a reminder of the most powerful point in the argument!
Revise the thesis statement so that it reflects the relationship you've developed with the reader during the paper. For example, if you've written a paper that targets parents of young children, you can find a way to phrase your thesis to capitalize on that—maybe by beginning your thesis statement with, "As a parent of a young child…"
Don’t repeat your thesis word for word—make sure that your new statement is an independent, fresh sentence!
Summary or Synthesis
This section of the conclusion might come before the thesis statement or after it. Your conclusion should remind the reader of what your paper actually says! The best conclusion will include a synthesis, not just a summary—instead of a mere list of your major points, the best conclusion will draw those points together and relate them to one another so that your reader can apply the information given in the essay. Here are a couple of ways to do that:
Give a list of the major arguments for your thesis (usually, these are the topic sentences of the parts of your essay).
Explain how these parts are connected. For example, in the animal-shelter essay, you might point out that adopting a shelter dog helps more animals because your adoption fee supports the shelter, which makes your choice more socially responsible.
One of the most important functions of the conclusion is to provide context for your argument. Your reader may finish your essay without a problem and understand your argument without understanding why that argument is important. Your introduction might point out the reason your topic matters, but your conclusion should also tackle this questions. Here are some strategies for making your reader see why the topic is important:
Tell the reader what you want him or her to do. Is your essay a call to action? If so, remind the reader of what he/she should do. If not, remember that asking the reader to think a certain way is an action in itself. (In the above examples, the essay asks the reader to adopt a shelter dog—a specific action.)
Explain why this topic is timely or important. For example, the animal-shelter essay might end with a statistic about the number of pets in shelters waiting for adoption.
Remind the readers of why the topic matters to them personally. For example, it doesn’t matter much if you believe in the mission of animal shelters, if you're not planning to get a dog; however, once you're looking for a dog, it is much more important. The conclusion of this essay might say, "Since you’re in the market for a dog, you have a major decision to make: where to get one." This will remind the reader that the argument is personally important!
Conclusion paragraphs
No cost tutoring services
Online degrees at UMGC
Our helpful admissions advisors can help you choose an academic program to fit your career goals, estimate your transfer credits, and develop a plan for your education costs that fits your budget. If you’re a current UMGC student, please visit the Help Center .
Personal Information
Contact information, additional information.
By submitting this form, you acknowledge that you intend to sign this form electronically and that your electronic signature is the equivalent of a handwritten signature, with all the same legal and binding effect. You are giving your express written consent without obligation for UMGC to contact you regarding our educational programs and services using e-mail, phone, or text, including automated technology for calls and/or texts to the mobile number(s) provided. For more details, including how to opt out, read our privacy policy or contact an admissions advisor .
Please wait, your form is being submitted.
By using our website you agree to our use of cookies. Learn more about how we use cookies by reading our Privacy Policy .
Free Paraphrasing Tool
Try our other writing services

Avoid plagiarism in your paraphrased text
People are in love with our paraphrasing tool.
No Signup Needed
You don’t have to register or sign up. Insert your text and get started right away.

The Paraphraser is Ad-Free
Don’t wait for ads or distractions. The paraphrasing tool is ad-free!

Multi-lingual
Use our paraphraser for texts in different languages.
What's a paraphrasing tool?
This AI-powered paraphraser lets you rewrite text in your own words. Use it to paraphrase articles, essays, and other pieces of text. You can also use it to rephrase sentences and find synonyms for individual words. And the best part? It’s all 100% free!
What's paraphrasing?
Paraphrasing involves expressing someone else’s ideas or thoughts in your own words while maintaining the original meaning. Paraphrasing tools can help you quickly reword text by replacing certain words with synonyms or restructuring sentences. They can also make your text more concise, clear, and suitable for a specific audience. Paraphrasing is an essential skill in academic writing and professional communication.
Why use this paraphrasing tool?
- Save time: Gone are the days when you had to reword sentences yourself; now you can rewrite a text or a complete text with one click.
- Improve your writing: Your writing will always be clear and easy to understand. Automatically ensure consistent language throughout.
- Preserve original meaning: Paraphrase without fear of losing the point of your text.
- No annoying ads: We care about the user experience, so we don’t run any ads.
- Accurate: Reliable and grammatically correct paraphrasing.
- No sign-up required: We don’t need your data for you to use our paraphrasing tool.
- Super simple to use: A simple interface even your grandma could use.
- It’s 100% free: No hidden costs, just unlimited use of a free paraphrasing tool.
Features of the paraphrasing tool
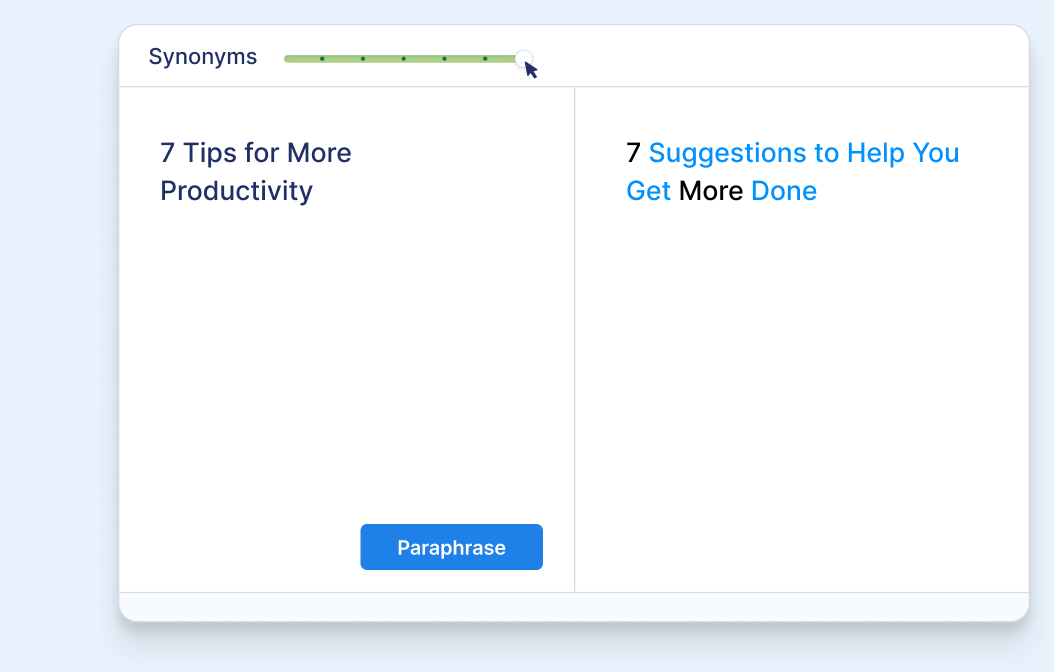
Rephrase individual sentences
With the Scribbr Paraphrasing Tool, you can easily reformulate individual sentences.
- Write varied headlines
- Rephrase the subject line of an email
- Create unique image captions
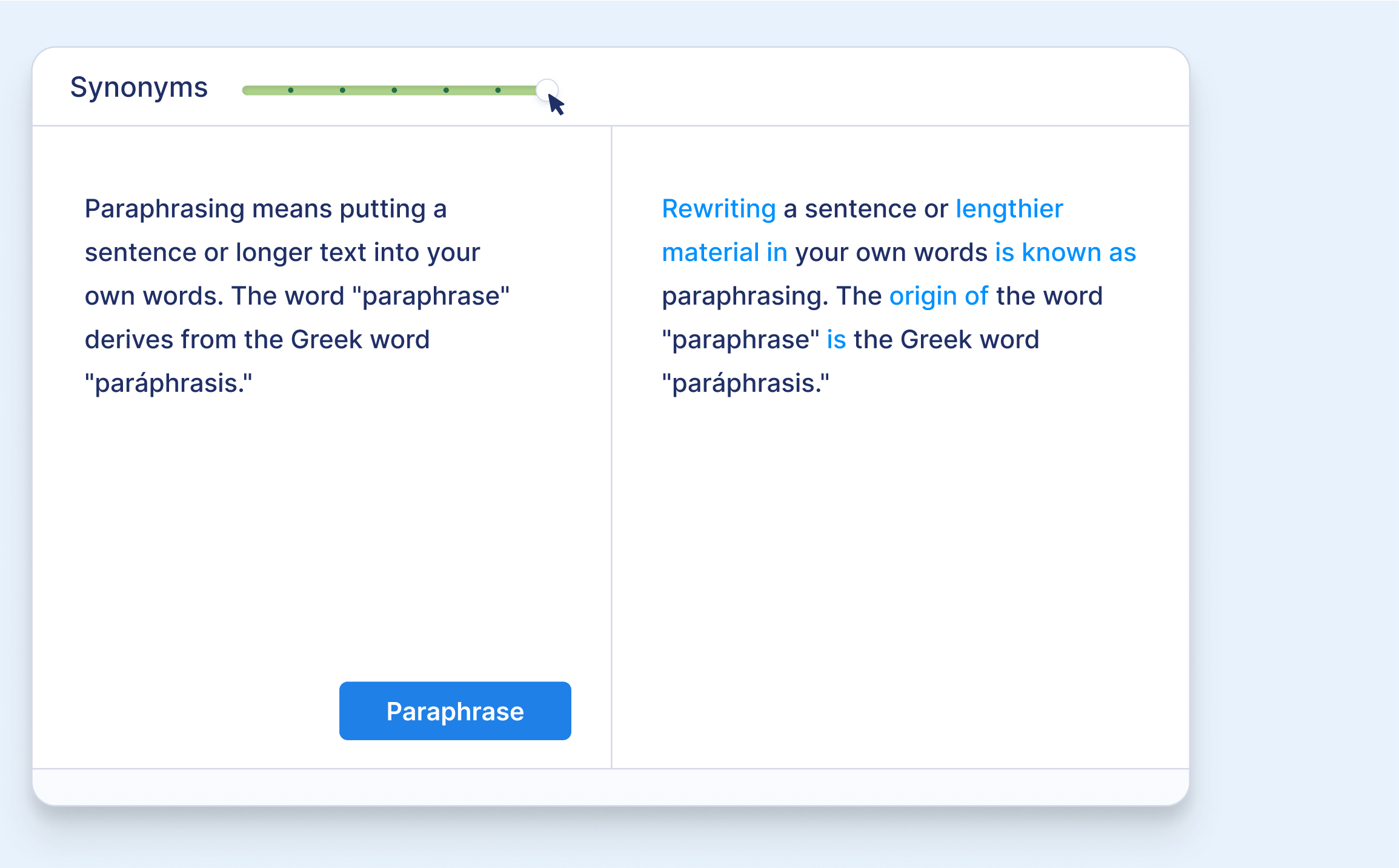
Paraphrase a whole text
Our paraphraser can also help with longer passages (up to 125 words per input). Upload your document or copy your text into the input field.
With one click, you can reformulate the entire text.
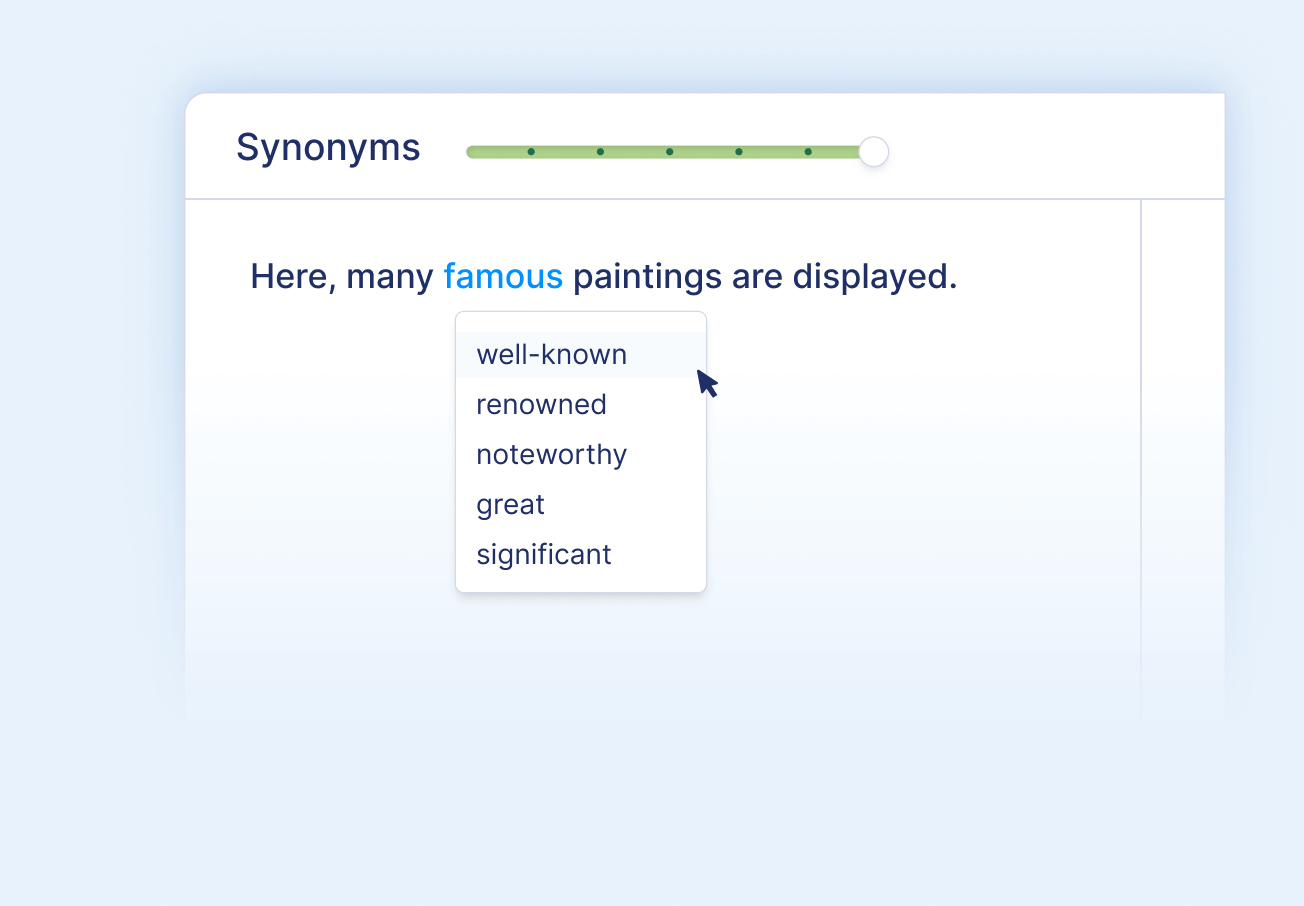
Find synonyms with ease
Simply click on any word to open the interactive thesaurus.
- Choose from a list of suggested synonyms
- Find the synonym with the most appropriate meaning
- Replace the word with a single click

Paraphrase in two ways
- Standard: Offers a compromise between modifying and preserving the meaning of the original text
- Fluency: Improves language and corrects grammatical mistakes.

Upload different types of documents
Upload any Microsoft Word document, Google Doc, or PDF into the paraphrasing tool.
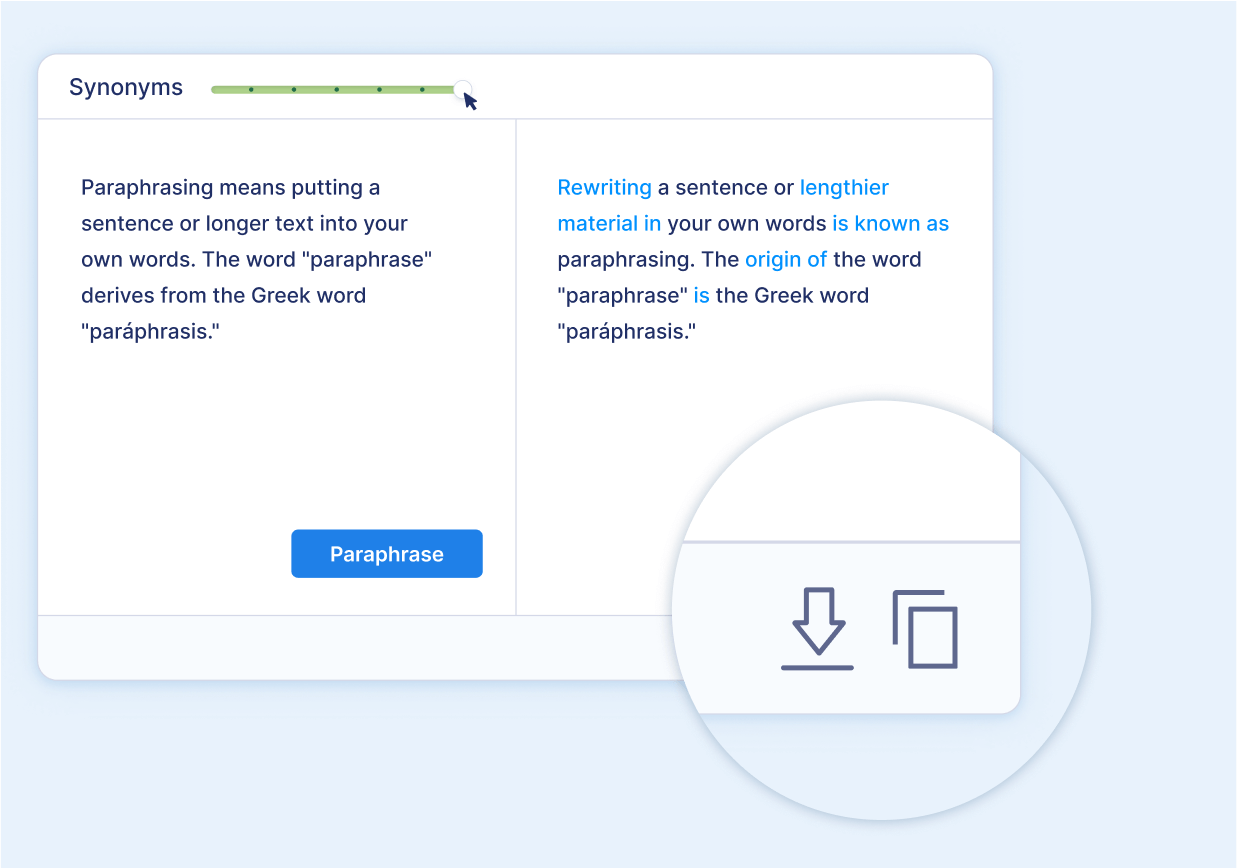
Download or copy your results
After you’re done, you can easily download or copy your text to use somewhere else.

Powered by AI
The paraphrasing tool uses natural language processing to rewrite any text you give it. This way, you can paraphrase any text within seconds.
Avoid accidental plagiarism
Want to make sure your document is plagiarism-free? In addition to our paraphrasing tool, which will help you rephrase sentences, quotations, or paragraphs correctly, you can also use our anti-plagiarism software to make sure your document is unique and not plagiarized.
Scribbr’s anti-plagiarism software enables you to:
- Detect plagiarism more accurately than other tools
- Ensure that your paraphrased text is valid
- Highlight the sources that are most similar to your text
Start for free
How does this paraphrasing tool work?
1. put your text into the paraphraser, 2. select your method of paraphrasing, 3. select the quantity of synonyms you want, 4. edit your text where needed, who can use this paraphrasing tool.

Paraphrasing tools can help students to understand texts and improve the quality of their writing.
Create original lesson plans, presentations, or other educational materials.

Researchers
Explain complex concepts or ideas to a wider audience.
Journalists
Quickly and easily rephrase text to avoid repetitive language.

Copywriters
By using a paraphrasing tool, you can quickly and easily rework existing content to create something new and unique.

Bloggers can rewrite existing content to make it their own.

Writers who need to rewrite content, such as adapting an article for a different context or writing content for a different audience.

A paraphrasing tool lets you quickly rewrite your original content for each medium, ensuring you reach the right audience on each platform.
The all-purpose paraphrasing tool
The Scribbr Paraphrasing Tool is the perfect assistant in a variety of contexts.

Brainstorming
Writer’s block? Use our paraphraser to get some inspiration.

Professional communication
Produce creative headings for your blog posts or PowerPoint slides.
Academic writing
Paraphrase sources smoothly in your thesis or research paper.

Social media
Craft memorable captions and content for your social media posts.
Paraphrase text online, for free
The Scribbr Paraphrasing Tool lets you rewrite as many sentences as you want—for free.
Write with 100% confidence 👉
Ask our team.
Want to contact us directly? No problem. We are always here for you.
- Email [email protected]
- Start live chat
- Call +1 (510) 822-8066
- WhatsApp +31 20 261 6040

Frequently asked questions
The act of putting someone else’s ideas or words into your own words is called paraphrasing, rephrasing, or rewording. Even though they are often used interchangeably, the terms can mean slightly different things:
Paraphrasing is restating someone else’s ideas or words in your own words while retaining their meaning. Paraphrasing changes sentence structure, word choice, and sentence length to convey the same meaning.
Rephrasing may involve more substantial changes to the original text, including changing the order of sentences or the overall structure of the text.
Rewording is changing individual words in a text without changing its meaning or structure, often using synonyms.
It can. One of the two methods of paraphrasing is called “Fluency.” This will improve the language and fix grammatical errors in the text you’re paraphrasing.
Paraphrasing and using a paraphrasing tool aren’t cheating. It’s a great tool for saving time and coming up with new ways to express yourself in writing. However, always be sure to credit your sources. Avoid plagiarism.
If you don’t properly cite text paraphrased from another source, you’re plagiarizing. If you use someone else’s text and paraphrase it, you need to credit the original source. You can do that by using citations. There are different styles, like APA, MLA, Harvard, and Chicago. Find more information about citing sources here.
Paraphrasing without crediting the original author is a form of plagiarism , because you’re presenting someone else’s ideas as if they were your own.
However, paraphrasing is not plagiarism if you correctly cite the source . This means including an in-text citation and a full reference, formatted according to your required citation style .
As well as citing, make sure that any paraphrased text is completely rewritten in your own words.
Plagiarism means using someone else’s words or ideas and passing them off as your own. Paraphrasing means putting someone else’s ideas in your own words.
So when does paraphrasing count as plagiarism?
- Paraphrasing is plagiarism if you don’t properly credit the original author.
- Paraphrasing is plagiarism if your text is too close to the original wording (even if you cite the source). If you directly copy a sentence or phrase, you should quote it instead.
- Paraphrasing is not plagiarism if you put the author’s ideas completely in your own words and properly cite the source .
Try our services
- Plagiarism check
- AI Check New
- Get premium
Featured in
Paraphrase variations in 18 writing modes.
Your words and thoughts matter, and we’ve designed our paraphrase tool to ensure find the best words to match your expression. Just paste or start writing your text in our input box above, and our best in class AI will help you to generate the best paraphrases from your original writing.
Write 10x faster with keywords in Compose mode
Who has time for writer’s block? Our Composer can help you write 10x faster by enabling you to create paragraphs from keywords instantly for articles, cover letters, essays, and more than 500 other types of writing in 100+ Languages. This way you can focus more on your final work rather than your first draft.
Check plagiarism in 50+ languages
None of us wants to accidentally plagiarize, especially when we spend so much time getting our ideas on paper and refining them. Be sure that your text is unique and 100% FREE of plagiarism by using our plagiarism checker for 50+ languages.
Rephrasely uses state-of-the-art AI to paraphrase and compose in more than 100+ languages
Rephrasely uses state-of-the-art AI to produce variations of your text in more than 100+ languages for each of the eighteen (12 free and 6 premium) styles that we offer. By doing this, we are able to offer more value and variety than any other service.
Billed every month
- Unlimited paraphrasing in 20 styles
- Up to 500 paragraphs/month
- Up to 100 plagiarism checks/month
- More powerful paraphrasing for all modes and languages
$59.88 billed every 12 months
- Unlimited paragraph generating
- Unlimited plagiarism checks
Thesis Statement Generator
Frequently asked questions, how can i write thesis statement .
The first step to writing a thesis statement is to identify the topic. Once you know the topic and you have done your research, you have a better idea of the direction your paper is going in. Next, you need to make an outline of your paper. This will allow you to focus on what you need to include. It will also help you stay organized and on track. Once you have an outline, you can start writing your thesis statement.
A good thesis statement is concise, clear, and concise. It should state your main argument and give the reader an idea of what the paper will be about. It should be clear and to the point. It should grab the reader’s attention and make them want to read the rest of your paper. Once you have written your thesis statement, you can start writing the rest of your paper!
What are 5 examples of thesis statement ?
A thesis statement is an important part of an essay because it explains the purpose of the entire essay. It should be concise and clear, but it doesn’t need to be long. It can be one sentence or a few sentences, and it should usually be placed at the beginning of the essay. A strong thesis statement will make it clear to the reader what the essay is about and will help to keep the essay organized. It should also be interesting enough to catch the reader’s attention and get them interested in the rest of the essay. A good thesis statement should be able to summarize the essay without giving away the main points. It should be able to intrigue the reader and make them want to read more. A good thesis statement should also be able to explain the purpose of the essay and help the reader to understand what the author is trying to say.
Why is it important that you write thesis statement ?
Writing a thesis statement is an essential skill that every writer should have. A thesis statement is a concise summary of the main idea of an essay or other form of writing. It lets the reader know what to expect and provides a framework for the writer to use as they create the piece. It should be clear, direct, and focused. It should also be specific enough to allow for the writer's interpretation, but not so specific that it limits the scope of the piece.
A good thesis statement will help you create an engaging, informative, and/or persuasive piece of writing that is clear and easy to understand. It should set the tone for the piece, tell the reader what you're going to talk about, and why you're talking about it, and it should make them want to keep reading. It should be structured in such a way that it flows naturally from beginning to end. A thesis statement should be a good starting point for your writing and act as a guide to ensure that you stay on topic and deliver what you promised.
Who benefits from writing thesis statement ?
You must be clear about what you are writing about, and why you are writing it. Your thesis statement will help you to formulate your central argument and point of view. It will also help you to determine which sources you will use to support your claims, and in what order you will use them. The thesis statement is the foundation of your essay, and it is important that you take the time to write a strong one.
Where can I learn more about how to improve my thesis statement ?
One way to improve your thesis statement is to use a mind map to list the main points that you want to cover in your paper. Then, you can use the map to organize and refine your thoughts so that your thesis statement is clear and concise. Finally, once you have a solid thesis statement, you can use it to write an outline for your paper. This outline will help you stay on track as you write your paper, and it will help you organize the information in a way that is easy for the reader to follow.
What are some resources for writing thesis statement ?
A thesis statement is one that provides a brief overview of the topic and the angle you plan to take while writing the whole essay. If you’re stuck on the idea, here are some ideas you can use to write a thesis statement.
Observe other people’s arguments or statements on the topic. Which points do you agree with? What do you think is missing from the discussion?
You can also try answering the question in different ways. You can use first-person, second-person, third-person, or you can use a hypothetical. This will help you form a strong thesis statement.
Think of the most important question or question you want to address. This is the best place to start your discussion. Once you have this question in mind, you can narrow down the topic to a specific angle. This will help you write a more persuasive argument.
Take a look at your essay outline. If you have an outline, it should include the thesis statement you’re trying to prove. This will give you another perspective on how to address the topic.
Lastly, you can also try Googling your topic and see what comes up. If you find other people also writing about it, you can get some inspiration from them
What are some tips for writing thesis statement ?
A thesis statement is the most important sentence in any essay, because it tells the reader exactly what you will be discussing and how you will be approaching it. Since the thesis statement is such an important part of any essay, here are some tips for writing a strong one:
Be specific. Your thesis statement should be clear and concise, stating exactly what you plan to discuss and how you plan to do it. Don’t be too broad or too vague.
Use your own words. Don’t just repeat what your professor or textbook says. Use your own voice and put your own spin on it.
Don’t be too general. Don’t just say, “This essay will discuss…”. Instead, be specific about what you will be discussing.
Don’t be too specific. Don’t make your thesis statement so specific that it limits the overall scope of your essay.
Be original. Don’t just copy and paste something you found online. Write your own thesis statement, using your own words.
Make sure it’s cohesive. Your thesis statement should flow naturally and smoothly into the rest of your essay. It should serve as an introduction to the main body of your essay.
How can I make sure my thesis statement is successful ?
A good way to ensure your thesis statement is effective is to make it absolutely clear, with no ambiguity or room for misinterpretation. Thus, you need to be as straightforward as possible in your wording. Don’t use language that’s complicated, or that could have multiple meanings. Be crystal clear in your wording, and don’t leave any room for argument.
What are some common mistakes people make when writing thesis statement ?
Writing the thesis statement early on in the process is a mistake because it’s important to understand the evidence you’re going to use to support your argument. You can’t write a thesis statement until you’ve done your research. It’s a common misconception that you can just look at the assigned readings and formulate your thesis statement.
What you need to do is look at the readings and then do your own research. This will help you to better understand the subject and allow you to create a thesis statement that supports your position.
How can I avoid making mistakes when writing thesis statement ?
The most common mistakes people make when writing thesis statements are focusing too much on the topic, and not enough on what they want to prove or find. In a thesis statement, you want to focus on what you want to prove, and not get caught up in the details of what you’re talking about. This is why it’s important to use general language when making your thesis statement.
When writing a thesis, focus more on showing how you want to prove your point, than what you’re trying to prove. For example, the topic of a paper might be: “The effect of sleep deprivation on motor control.” A strong thesis statement may look like this: “Sleep deprivation negatively impacts motor control.” The first statement is too broad, and doesn’t give the reader any information about what to expect from the paper. The second thesis statement is more focused and gives the reader an idea of what the paper might be about.
What are some things I should keep in mind when writing thesis statement ?
Your thesis statement should be the most significant point of your essay. It should stand out, and it should be very clear. Don’t beat around the bush and don’t make readers guess what your essay is about. Make it apparent what you are going to talk about and why it’s important.
Your thesis statement should be concise and clear. It should have only one main point and should not be more than three sentences. Your essay may have more subtopics, but they should all lead to the main point.
Your thesis statement should be unique. Don’t use the same old clichés, and don’t make common and generic statements. Instead, provide insight and stand out from the crowd.
Is there anything else I should know about writing thesis statement ?
If you are having trouble coming up with a thesis statement, there is a simple trick to help you get started. When people face a new challenge, they often think of the worst-case scenario, and this can be helpful when writing a thesis statement. Think of the worst possible argument against your thesis statement. For example, if your thesis statement is that recycling is important, what is the worst argument against that statement? In this example, the worst argument against recycling is that it is too expensive.
By knowing what the worst argument against your thesis statement is, you can prepare to counter that argument in your essay. By writing your thesis statement last, you can make sure that you address all arguments against your position in your essay, and knowing what the worst argument is will help you do that. So next time you are having trouble coming up with a thesis statement, think of the worst argument against your position, and you will be well on your way to writing a great essay.

IMAGES
VIDEO
COMMENTS
A key part of understanding a thesis statement of a text is being able to express it in your own words. This paraphrase of a thesis is a key component in summarizing a reading accurately. The following "How to Identify a Thesis Statement" video offers advice for locating a text's thesis statement. It asks you to write one or two sentences ...
The thesis is the author's reason for writing. The word thesis is a Greek word meaning position. The thesis statement is the controlling idea. It is the point the writer wants to make. It is not necessarily in the beginning of an essay. It is not even necessarily physically present. It might be implied.
Paraphrases are roughly the same length as the original text. If the thesis sentence is a medium-length sentence, your paraphrase will also be a medium-length sentence (though it doesn't have to have exactly the same number of words). Paraphrases use entirely distinct wording from the original text. Common small words like "the" and ...
The thesis statement is essential in any academic essay or research paper for two main reasons: It gives your writing direction and focus. It gives the reader a concise summary of your main point. Without a clear thesis statement, an essay can end up rambling and unfocused, leaving your reader unsure of exactly what you want to say.
The following tips will guide you through rephrasing the thesis statement effectively. 1. Decide a suitable place for your restatement. A thesis restatement most commonly comes at the beginning of the conclusion of your paper. However, there's no rule for positioning a thesis restatement.
Here's a simple thesis statement formula to use: 2. Make sure that each part of your thesis statement flows smoothly into the next. This will help to create a cohesive argument for your paper. 3. Use active voice when possible. Active voice makes your arguments sound more forceful and persuasive. 4.
A key part of understanding a thesis statement of a text is being able to express it in your own words. This paraphrase of a thesis is a key component in summarizing a reading accurately. The following "How to Identify a Thesis Statement" video offers advice for locating a text's thesis statement.
Step 2: Write your initial answer. After some initial research, you can formulate a tentative answer to this question. At this stage it can be simple, and it should guide the research process and writing process. The internet has had more of a positive than a negative effect on education.
A thesis statement: tells the reader how you will interpret the significance of the subject matter under discussion. is a road map for the paper; in other words, it tells the reader what to expect from the rest of the paper. directly answers the question asked of you. A thesis is an interpretation of a question or subject, not the subject itself.
Keep in mind that thesis statements vary depending on the purpose of the assignment (or type of essay), and also by discipline. Here are a few notes on the thesis statements and the purpose of writing in a few different disciplines. 2. English: "A thesis is an interpretive argument about a text or an aspect of a text. An interpretive argument ...
is a complete sentence that expresses an opinion or an idea about a topic that can be supported or more fully developed in the body of the essay. summarizes the whole essay in one sentence and promises or reflects the essay's main purpose or "so what". provides the structure or unifying framework for the scope, focus, and direction of the ...
The thesis statement is the one sentence that encapsulates the result of your thinking, as it offers your main insight or argument in condensed form. A basic thesis statement has two main parts: Topic: What you're writing about. Angle: What your main idea is about that topic.
Step 4: Revise and refine your thesis statement before you start writing. Read through your thesis statement several times before you begin to compose your full essay. You need to make sure the statement is ironclad, since it is the foundation of the entire paper. Edit it or have a peer review it for you to make sure everything makes sense and ...
Step 1: Return to your thesis. To begin your conclusion, signal that the essay is coming to an end by returning to your overall argument. Don't just repeat your thesis statement —instead, try to rephrase your argument in a way that shows how it has been developed since the introduction. Example: Returning to the thesis.
The topic sentence (located in the first sentence) rephrases the major parts of a typical thesis statement, the topic, purpose, and organization. The reflective sentences (the second, third, and fourth sentences) explain what was learned and share this information with the audience. Notice that each reflective sentence comments on the topic's ...
It is a brief statement of your paper's main argument. Essentially, you are stating what you will be writing about. Organize your papers in one place. Try Paperpile. No credit card needed. Get 30 days free. You can see your thesis statement as an answer to a question. While it also contains the question, it should really give an answer to the ...
The conclusion is a very important part of your essay. Although it is sometimes treated as a roundup of all of the bits that didn't fit into the paper earlier, it deserves better treatment than that! It's the last thing the reader will see, so it tends to stick in the reader's memory. It's also a great place to remind the reader exactly why ...
Paraphrase text online, for free. The Scribbr Paraphrasing Tool lets you rewrite as many sentences as you want—for free. Rephrase as many texts as you want. No registration needed. Suitable for individual sentences or whole paragraphs. For school, university, or work.
A thesis statement is an important part of an essay because it explains the purpose of the entire essay. It should be concise and clear, but it doesn't need to be long. It can be one sentence or a few sentences, and it should usually be placed at the beginning of the essay.