Essay Writing Guide
Essay Writing

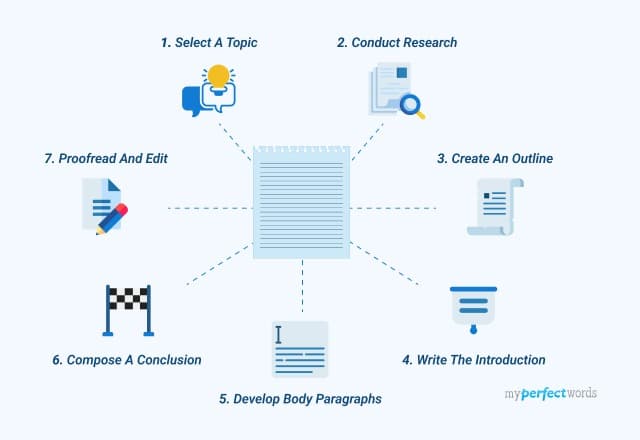
Learn How to Write An Essay in Simple Steps
13 min read

People also read
An Easy Guide to Writing an Essay
A Complete 500 Word Essay Writing Guide
A Catalog of 500+ Essay Topics for Students
Explore Different Types of Essays, their Purpose, and Sub-types
Essay Format: A Basic Guide With Examples
Learn How to Create a Perfect Essay Outline
How to Start an Essay- A Step-by-Step Guide
A Complete Essay Introduction Writing Guide With Examples
20+ Hook Examples to Grab Reader’s Attention
The Ultimate Guide to Writing Powerful Thesis Statement
20+ Thesis Statement Examples for Different Types of Essays?
How to Write a Topic Sentence: Purpose, Tips & Examples
Learn How to Write a Conclusion in Simple Steps
Transition Words For Essays - The Ultimate List
4 Types of Sentences - Definition & Examples
Writing Conventions - Definition, Tips & Examples
Essay Writing Problems - 5 Most Paralyzing Problems
How to Make an Essay Longer: 14 Easy Ways
How to Title an Essay - A Detailed Guide
1000 Word Essay - A Simple Guide With Examples
- 1. What is an Essay?
- 2. Steps to Write an Essay
- 3. How to Structure an Essay Paragraph?
- 4. Essay Example
- 5. Essay Writing Tips
An essay is a common type of writing and assignment that high-school and college students have to deal with. Essay writing can be a pretty daunting task, especially when you lack creative writing skills or don’t enjoy writing at all, or both.
Most of the students are not aware of the essential steps to write an essay. Read on and master how to write an essay on any topic that is well-researched, detailed, and tailored for an A grade.
What is an Essay?
Let's begin by learning the definition of an essay. So, what is an essay? An essay is a brief composition based on a certain topic or subject that students do as part of their schoolwork or university coursework.
Essays are one of the most common assignments handed out by colleges and institutions since they are an excellent tool for improving many essential skills including analytical thinking, research, creative skills, and so on.
Let's look at writing strategies that can help you get an A in your essay. Let's start at the beginning and work our way through these steps to write a good essay:
- Choose the Essay Type
- Choose an Interesting Topic
- Create an Essay Outline
- Write Your First Draft
- Write an Essay Introduction
- Develop a Thesis Statement
- Compose Body Paragraphs
- Write a Strong Conclusion
- Review Your Essay
Let's take a look at each step of learning how to create an excellent essay in depth.
Steps to Write an Essay
Here is the basic structure that you need to follow for writing an academic essay:
1. Choose the Essay Type
The first step is to choose the type of essay that you are writing. Choosing the right type of essay also plays an important role in the overall success of your paper.
Here are the basic types of papers in which academic essays can be divided.
- Narrative essay
- Persuasive essay
- Descriptive essay
- Analytical essay
- Argumentative essay
- Expository essay
Knowing the type of essay will eventually help you decide on the topic and the overall structure of your essay in the best possible way.
2. Choose an Interesting Topic
If you are given the topic, skip to the next step, create an outline and start the writing process.
If you are not given a topic, you have a little more work to do and choose your topic first.
The key to choosing a good topic is to think of what interests you and what you can relate to, the most.
Also, make sure that the topic you choose has sufficient research material available. Search either on the internet or in books for the topic you have chosen to write on.
You can also find a list of interesting essay topics that you can explore and choose the one to write your essay on.
3. Create an Essay Outline
Creating an outline is very important if you want to compose an impressive piece of paper. By putting all the ideas on the paper, you can easily see connections and links between ideas in a more clear manner.
If you don’t know how to write an essay outline, here are the following steps that you need to follow for structuring your essay properly.
- Write your topic at the top of the page
- List down all the main ideas
- Leave space under each idea
- In this space, list down smaller ideas that relates to the main idea
Following these steps for writing an essay outline will give you a complete idea of the themes required to be discussed in your paper.
4. Write your First Draft
Your first writing draft will help you do the following;
- Set the framework and structure of your essay.
- The way you will answer the main question.
- The kind of examples and evidence you will use in the essay.
- The way you will structure your argument
The first draft is not your final essay. Consider it your essay’s raw material that you can edit and proofread later.
5. Write an Essay Introduction
The introductory paragraph of an essay should be both attention-grabbing and informative.
To learn how to write an essay introduction, you first need all the necessary information required to tell the reader about the main idea of your essay.
A vague or boring introduction will give off the wrong impression, and your reader might decide not to read it any further.
Here are the steps in which you can start your essay introduction that is both interesting and informative.
- Use a hook sentence and add informative or shocking revelations.
- Provide background information and context on your topic
- Define the objective of your essay
- Provide an overview of the whole essay structure
6. Develop a Thesis Statement
A thesis statement defines the main purpose and claims of your essay. It is typically defined in one or two sentences and is added at the end of your introductory paragraph.
A perfect thesis statement has two parts. The first part states the topic and the latter states the main point of the essay.
Let's have a look at examples of thesis statements and distinguish between strong and weak thesis statements.
A: “The technological advancement has revolutionized human interaction, medical progress, scientific invention, and economic ventures but also manifested insecurities and privacy issues.”
B: “The Internet has assisted humans in numerous ways but also affected them.”
Without any doubt, A is a perfectly crafted thesis statement.
7. Compose Body Paragraphs
The body of an essay describes or explains your topic. Each idea that you write in the outline will be a separate paragraph within the body of the essay.
Since the body is made up of multiple paragraphs, it is important that they are consistent with one another.
Each body paragraph starts with a topic sentence. For those who don’t know what is a topic sentence , it is the first sentence that describes the main purpose of each paragraph. The topic sentence forms a transition between the body paragraphs.
Use transitions to introduce new paragraphs such as “firstly.. secondly... thirdly…, finally, moreover, furthermore, in addition”, etc.
It is a good idea to refer to the transition words for essays to introduce new paragraphs in an impressive manner.
The main aim of body paragraphs is to support your thesis by presenting evidence, facts and figures, statistics, quotes, examples, and other strong evidence.
Here are the tips that you should follow for writing each body paragraph.
- Write a clear topic sentence
- Provide solid evidence to support your argumen
- Provide examples
- Make sure the paragraph information is consistent
- Use transitions between paragraphs
- Conclude each paragraph by linking the evidence to your main point
8. Write a Strong Conclusion
The conclusion sums up the overall ideas and provides a final perspective on the topic. Concluding your essay holds the same importance as the introductory paragraph.
For writing a perfect essay conclusion , provide a futuristic overview, persuade your reader about your point of view and restate the thesis statement.
If you have no idea about how to write a conclusion for an essay, here are the key points that you should include.
- Draw connections between the arguments mentioned in the body section
- State the outcomes
- Show the relevance and significance of the thesis statement
- Mention the broader implications of the topic
Here is the information that you should avoid writing in a conclusion:
- Don’t introduce new ideas or arguments at this stage.
- Do not undermine your arguments
- Do not write phrases like 'in conclusion, or 'to conclude'
9. Review Your Essay
If you think that you are done with your essay after writing your conclusion, you are wrong. Before considering that your work is finished, you need to do some final touches.
Review your essay and make sure it follows the essay format properly. Double-check your essay instructions and make sure your essay is in the desired format.
Don’t forget to check your paper for grammar and spelling mistakes as well.
How to Structure an Essay Paragraph?
Here are the factors that are included in each body paragraph of the essay.
- A topic sentence is the first sentence of a paragraph. It sets the tone for the paragraph.
- Supporting sentences that help to explain the main idea and topic of the paragraph.
- Evidence that you have gathered with research, and supports your point of view.
- Analysis of the given evidence and a critical conclusion of the paragraph.
- A conclusion or a concluding sentence that sums up the entire paragraph.
All of these components make up a perfect paragraph for any essay.
Essay Example
The best practice is to learn from the essay examples written by expert writers to avoid common essay writing problems . The examples can help you know the purpose of each type of essay and how to write a perfect one.
Imitate their writing style, argument construction, and structure.
As you read, highlight the important parts of an essay to learn how they did it. Keep in mind that the length of an essay depends on the level and complexity of the topic.
Here is a well-written sample essay from one of our expert writers that you can have a look at.
Essay Writing Tips
Here are the expert tips that you should follow for writing a perfect essay.
- Start writing your essay early
- Remember the main question or idea in your mind.
- Brainstorm ideas
- Research your topic in-depth
- Break down the essay into different sections and do not try to finish it in a single sitting.
- Write and add the introduction and conclusion after finishing the essay.
- Use transition words to create a coherent flow between the paragraphs.
- Connect the evidence with the main idea carefully.
- Do not copy-paste the content.
- Ensure flawless grammar and punctuation.
- Cite the references properly.
- Edit and revise relentlessly.
- Put the essay away for a few days and check again.
Essay writing can be made easier if you follow a certain pattern and master the steps we have provided you with. Moreover, the tips given above will help you improve your essay-writing skills also.
Try practicing as much as you can and impress your teacher with a well-written essay.
Writing essays can be difficult but the fact is, you can’t escape academic writing no matter what.
This is where the best essay writing service like MyPerfectWords.com comes in to help students save their academic grades. We are an online essay and paper writing service that offers customer support to high school, college, and university students.
Here are the academic papers in which you can get help from expert writers here.
- College essays (narrative essays, persuasive essays, compare and contrast essays, etc.)
- Custom papers
- Book reviews/book report
- Case studies
- Research papers
- College papers
And much more. Besides, our writing services , we also offer free revision and plagiarism reports with each paper and make sure that the students get flawless work from us.
All you need to do is fill out the order form and leave the rest to us.
Frequently Asked Questions
What is an essay format.
The essay format is the set of guidelines that decide how your paper should be arranged. Formatting a paper includes following rules for its structure, title, and citations before you begin writing it.
When formatting this type of document there are certain things to focus on like making sure each paragraph has one main idea which leads into two more ideas in succession.
Remember not to let these paragraphs become too long because they can lose the reader's attention if they go over three pages long.
What are basic writing skills?
Here are the basic writing skills:
- Spelling and punctuation
- Good reading skills
- Knowledge of sentence and paragraph structure
- Understanding of different types of writing
- Great editing and rewriting skills
Other than these, there are a number of other writing skills.

Write Essay Within 60 Seconds!

Nova Allison is a Digital Content Strategist with over eight years of experience. Nova has also worked as a technical and scientific writer. She is majorly involved in developing and reviewing online content plans that engage and resonate with audiences. Nova has a passion for writing that engages and informs her readers.

Paper Due? Why Suffer? That’s our Job!
Keep reading
What is an Essay?
10 May, 2020
11 minutes read
Author: Tomas White
Well, beyond a jumble of words usually around 2,000 words or so - what is an essay, exactly? Whether you’re taking English, sociology, history, biology, art, or a speech class, it’s likely you’ll have to write an essay or two. So how is an essay different than a research paper or a review? Let’s find out!
Defining the Term – What is an Essay?
The essay is a written piece that is designed to present an idea, propose an argument, express the emotion or initiate debate. It is a tool that is used to present writer’s ideas in a non-fictional way. Multiple applications of this type of writing go way beyond, providing political manifestos and art criticism as well as personal observations and reflections of the author.

An essay can be as short as 500 words, it can also be 5000 words or more. However, most essays fall somewhere around 1000 to 3000 words ; this word range provides the writer enough space to thoroughly develop an argument and work to convince the reader of the author’s perspective regarding a particular issue. The topics of essays are boundless: they can range from the best form of government to the benefits of eating peppermint leaves daily. As a professional provider of custom writing, our service has helped thousands of customers to turn in essays in various forms and disciplines.
Origins of the Essay
Over the course of more than six centuries essays were used to question assumptions, argue trivial opinions and to initiate global discussions. Let’s have a closer look into historical progress and various applications of this literary phenomenon to find out exactly what it is.
Today’s modern word “essay” can trace its roots back to the French “essayer” which translates closely to mean “to attempt” . This is an apt name for this writing form because the essay’s ultimate purpose is to attempt to convince the audience of something. An essay’s topic can range broadly and include everything from the best of Shakespeare’s plays to the joys of April.
The essay comes in many shapes and sizes; it can focus on a personal experience or a purely academic exploration of a topic. Essays are classified as a subjective writing form because while they include expository elements, they can rely on personal narratives to support the writer’s viewpoint. The essay genre includes a diverse array of academic writings ranging from literary criticism to meditations on the natural world. Most typically, the essay exists as a shorter writing form; essays are rarely the length of a novel. However, several historic examples, such as John Locke’s seminal work “An Essay Concerning Human Understanding” just shows that a well-organized essay can be as long as a novel.
The Essay in Literature
The essay enjoys a long and renowned history in literature. They first began gaining in popularity in the early 16 th century, and their popularity has continued today both with original writers and ghost writers. Many readers prefer this short form in which the writer seems to speak directly to the reader, presenting a particular claim and working to defend it through a variety of means. Not sure if you’ve ever read a great essay? You wouldn’t believe how many pieces of literature are actually nothing less than essays, or evolved into more complex structures from the essay. Check out this list of literary favorites:
- The Book of My Lives by Aleksandar Hemon
- Notes of a Native Son by James Baldwin
- Against Interpretation by Susan Sontag
- High-Tide in Tucson: Essays from Now and Never by Barbara Kingsolver
- Slouching Toward Bethlehem by Joan Didion
- Naked by David Sedaris
- Walden; or, Life in the Woods by Henry David Thoreau
Pretty much as long as writers have had something to say, they’ve created essays to communicate their viewpoint on pretty much any topic you can think of!

The Essay in Academics
Not only are students required to read a variety of essays during their academic education, but they will likely be required to write several different kinds of essays throughout their scholastic career. Don’t love to write? Then consider working with a ghost essay writer ! While all essays require an introduction, body paragraphs in support of the argumentative thesis statement, and a conclusion, academic essays can take several different formats in the way they approach a topic. Common essays required in high school, college, and post-graduate classes include:
Five paragraph essay
This is the most common type of a formal essay. The type of paper that students are usually exposed to when they first hear about the concept of the essay itself. It follows easy outline structure – an opening introduction paragraph; three body paragraphs to expand the thesis; and conclusion to sum it up.
Argumentative essay
These essays are commonly assigned to explore a controversial issue. The goal is to identify the major positions on either side and work to support the side the writer agrees with while refuting the opposing side’s potential arguments.
Compare and Contrast essay
This essay compares two items, such as two poems, and works to identify similarities and differences, discussing the strength and weaknesses of each. This essay can focus on more than just two items, however. The point of this essay is to reveal new connections the reader may not have considered previously.
Definition essay
This essay has a sole purpose – defining a term or a concept in as much detail as possible. Sounds pretty simple, right? Well, not quite. The most important part of the process is picking up the word. Before zooming it up under the microscope, make sure to choose something roomy so you can define it under multiple angles. The definition essay outline will reflect those angles and scopes.
Descriptive essay
Perhaps the most fun to write, this essay focuses on describing its subject using all five of the senses. The writer aims to fully describe the topic; for example, a descriptive essay could aim to describe the ocean to someone who’s never seen it or the job of a teacher. Descriptive essays rely heavily on detail and the paragraphs can be organized by sense.
Illustration essay
The purpose of this essay is to describe an idea, occasion or a concept with the help of clear and vocal examples. “Illustration” itself is handled in the body paragraphs section. Each of the statements, presented in the essay needs to be supported with several examples. Illustration essay helps the author to connect with his audience by breaking the barriers with real-life examples – clear and indisputable.
Informative Essay
Being one the basic essay types, the informative essay is as easy as it sounds from a technical standpoint. High school is where students usually encounter with informative essay first time. The purpose of this paper is to describe an idea, concept or any other abstract subject with the help of proper research and a generous amount of storytelling.
Narrative essay
This type of essay focuses on describing a certain event or experience, most often chronologically. It could be a historic event or an ordinary day or month in a regular person’s life. Narrative essay proclaims a free approach to writing it, therefore it does not always require conventional attributes, like the outline. The narrative itself typically unfolds through a personal lens, and is thus considered to be a subjective form of writing.
Persuasive essay
The purpose of the persuasive essay is to provide the audience with a 360-view on the concept idea or certain topic – to persuade the reader to adopt a certain viewpoint. The viewpoints can range widely from why visiting the dentist is important to why dogs make the best pets to why blue is the best color. Strong, persuasive language is a defining characteristic of this essay type.

The Essay in Art
Several other artistic mediums have adopted the essay as a means of communicating with their audience. In the visual arts, such as painting or sculpting, the rough sketches of the final product are sometimes deemed essays. Likewise, directors may opt to create a film essay which is similar to a documentary in that it offers a personal reflection on a relevant issue. Finally, photographers often create photographic essays in which they use a series of photographs to tell a story, similar to a narrative or a descriptive essay.
Drawing the line – question answered
“What is an Essay?” is quite a polarizing question. On one hand, it can easily be answered in a couple of words. On the other, it is surely the most profound and self-established type of content there ever was. Going back through the history of the last five-six centuries helps us understand where did it come from and how it is being applied ever since.
If you must write an essay, follow these five important steps to works towards earning the “A” you want:
- Understand and review the kind of essay you must write
- Brainstorm your argument
- Find research from reliable sources to support your perspective
- Cite all sources parenthetically within the paper and on the Works Cited page
- Follow all grammatical rules
Generally speaking, when you must write any type of essay, start sooner rather than later! Don’t procrastinate – give yourself time to develop your perspective and work on crafting a unique and original approach to the topic. Remember: it’s always a good idea to have another set of eyes (or three) look over your essay before handing in the final draft to your teacher or professor. Don’t trust your fellow classmates? Consider hiring an editor or a ghostwriter to help out!
If you are still unsure on whether you can cope with your task – you are in the right place to get help. HandMadeWriting is the perfect answer to the question “Who can write my essay?”

A life lesson in Romeo and Juliet taught by death
Due to human nature, we draw conclusions only when life gives us a lesson since the experience of others is not so effective and powerful. Therefore, when analyzing and sorting out common problems we face, we may trace a parallel with well-known book characters or real historical figures. Moreover, we often compare our situations with […]

Ethical Research Paper Topics
Writing a research paper on ethics is not an easy task, especially if you do not possess excellent writing skills and do not like to contemplate controversial questions. But an ethics course is obligatory in all higher education institutions, and students have to look for a way out and be creative. When you find an […]

Art Research Paper Topics
Students obtaining degrees in fine art and art & design programs most commonly need to write a paper on art topics. However, this subject is becoming more popular in educational institutions for expanding students’ horizons. Thus, both groups of receivers of education: those who are into arts and those who only get acquainted with art […]
Purdue Online Writing Lab Purdue OWL® College of Liberal Arts
Essay Writing

Welcome to the Purdue OWL
This page is brought to you by the OWL at Purdue University. When printing this page, you must include the entire legal notice.
Copyright ©1995-2018 by The Writing Lab & The OWL at Purdue and Purdue University. All rights reserved. This material may not be published, reproduced, broadcast, rewritten, or redistributed without permission. Use of this site constitutes acceptance of our terms and conditions of fair use.
The Modes of Discourse—Exposition, Description, Narration, Argumentation (EDNA)—are common paper assignments you may encounter in your writing classes. Although these genres have been criticized by some composition scholars, the Purdue OWL recognizes the wide spread use of these approaches and students’ need to understand and produce them.
This resource begins with a general description of essay writing and moves to a discussion of common essay genres students may encounter across the curriculum. The four genres of essays (description, narration, exposition, and argumentation) are common paper assignments you may encounter in your writing classes. Although these genres, also known as the modes of discourse, have been criticized by some composition scholars, the Purdue OWL recognizes the wide spread use of these genres and students’ need to understand and produce these types of essays. We hope these resources will help.
The essay is a commonly assigned form of writing that every student will encounter while in academia. Therefore, it is wise for the student to become capable and comfortable with this type of writing early on in her training.
Essays can be a rewarding and challenging type of writing and are often assigned either to be done in class, which requires previous planning and practice (and a bit of creativity) on the part of the student, or as homework, which likewise demands a certain amount of preparation. Many poorly crafted essays have been produced on account of a lack of preparation and confidence. However, students can avoid the discomfort often associated with essay writing by understanding some common genres.
Before delving into its various genres, let’s begin with a basic definition of the essay.
What is an essay?
Though the word essay has come to be understood as a type of writing in Modern English, its origins provide us with some useful insights. The word comes into the English language through the French influence on Middle English; tracing it back further, we find that the French form of the word comes from the Latin verb exigere , which means "to examine, test, or (literally) to drive out." Through the excavation of this ancient word, we are able to unearth the essence of the academic essay: to encourage students to test or examine their ideas concerning a particular topic.
Essays are shorter pieces of writing that often require the student to hone a number of skills such as close reading, analysis, comparison and contrast, persuasion, conciseness, clarity, and exposition. As is evidenced by this list of attributes, there is much to be gained by the student who strives to succeed at essay writing.
The purpose of an essay is to encourage students to develop ideas and concepts in their writing with the direction of little more than their own thoughts (it may be helpful to view the essay as the converse of a research paper). Therefore, essays are (by nature) concise and require clarity in purpose and direction. This means that there is no room for the student’s thoughts to wander or stray from his or her purpose; the writing must be deliberate and interesting.
This handout should help students become familiar and comfortable with the process of essay composition through the introduction of some common essay genres.
This handout includes a brief introduction to the following genres of essay writing:
- Expository essays
- Descriptive essays
- Narrative essays
- Argumentative (Persuasive) essays
How to Write an Essay Introduction (with Examples)

The introduction of an essay plays a critical role in engaging the reader and providing contextual information about the topic. It sets the stage for the rest of the essay, establishes the tone and style, and motivates the reader to continue reading.
Table of Contents
What is an essay introduction , what to include in an essay introduction, how to create an essay structure , step-by-step process for writing an essay introduction , how to write an introduction paragraph , how to write a hook for your essay , how to include background information , how to write a thesis statement .
- Argumentative Essay Introduction Example:
- Expository Essay Introduction Example
Literary Analysis Essay Introduction Example
Check and revise – checklist for essay introduction , key takeaways , frequently asked questions .
An introduction is the opening section of an essay, paper, or other written work. It introduces the topic and provides background information, context, and an overview of what the reader can expect from the rest of the work. 1 The key is to be concise and to the point, providing enough information to engage the reader without delving into excessive detail.
The essay introduction is crucial as it sets the tone for the entire piece and provides the reader with a roadmap of what to expect. Here are key elements to include in your essay introduction:
- Hook : Start with an attention-grabbing statement or question to engage the reader. This could be a surprising fact, a relevant quote, or a compelling anecdote.
- Background information : Provide context and background information to help the reader understand the topic. This can include historical information, definitions of key terms, or an overview of the current state of affairs related to your topic.
- Thesis statement : Clearly state your main argument or position on the topic. Your thesis should be concise and specific, providing a clear direction for your essay.
Before we get into how to write an essay introduction, we need to know how it is structured. The structure of an essay is crucial for organizing your thoughts and presenting them clearly and logically. It is divided as follows: 2
- Introduction: The introduction should grab the reader’s attention with a hook, provide context, and include a thesis statement that presents the main argument or purpose of the essay.
- Body: The body should consist of focused paragraphs that support your thesis statement using evidence and analysis. Each paragraph should concentrate on a single central idea or argument and provide evidence, examples, or analysis to back it up.
- Conclusion: The conclusion should summarize the main points and restate the thesis differently. End with a final statement that leaves a lasting impression on the reader. Avoid new information or arguments.

Here’s a step-by-step guide on how to write an essay introduction:
- Start with a Hook : Begin your introduction paragraph with an attention-grabbing statement, question, quote, or anecdote related to your topic. The hook should pique the reader’s interest and encourage them to continue reading.
- Provide Background Information : This helps the reader understand the relevance and importance of the topic.
- State Your Thesis Statement : The last sentence is the main argument or point of your essay. It should be clear, concise, and directly address the topic of your essay.
- Preview the Main Points : This gives the reader an idea of what to expect and how you will support your thesis.
- Keep it Concise and Clear : Avoid going into too much detail or including information not directly relevant to your topic.
- Revise : Revise your introduction after you’ve written the rest of your essay to ensure it aligns with your final argument.
Here’s an example of an essay introduction paragraph about the importance of education:
Education is often viewed as a fundamental human right and a key social and economic development driver. As Nelson Mandela once famously said, “Education is the most powerful weapon which you can use to change the world.” It is the key to unlocking a wide range of opportunities and benefits for individuals, societies, and nations. In today’s constantly evolving world, education has become even more critical. It has expanded beyond traditional classroom learning to include digital and remote learning, making education more accessible and convenient. This essay will delve into the importance of education in empowering individuals to achieve their dreams, improving societies by promoting social justice and equality, and driving economic growth by developing a skilled workforce and promoting innovation.
This introduction paragraph example includes a hook (the quote by Nelson Mandela), provides some background information on education, and states the thesis statement (the importance of education).
This is one of the key steps in how to write an essay introduction. Crafting a compelling hook is vital because it sets the tone for your entire essay and determines whether your readers will stay interested. A good hook draws the reader in and sets the stage for the rest of your essay.
- Avoid Dry Fact : Instead of simply stating a bland fact, try to make it engaging and relevant to your topic. For example, if you’re writing about the benefits of exercise, you could start with a startling statistic like, “Did you know that regular exercise can increase your lifespan by up to seven years?”
- Avoid Using a Dictionary Definition : While definitions can be informative, they’re not always the most captivating way to start an essay. Instead, try to use a quote, anecdote, or provocative question to pique the reader’s interest. For instance, if you’re writing about freedom, you could begin with a quote from a famous freedom fighter or philosopher.
- Do Not Just State a Fact That the Reader Already Knows : This ties back to the first point—your hook should surprise or intrigue the reader. For Here’s an introduction paragraph example, if you’re writing about climate change, you could start with a thought-provoking statement like, “Despite overwhelming evidence, many people still refuse to believe in the reality of climate change.”
Including background information in the introduction section of your essay is important to provide context and establish the relevance of your topic. When writing the background information, you can follow these steps:
- Start with a General Statement: Begin with a general statement about the topic and gradually narrow it down to your specific focus. For example, when discussing the impact of social media, you can begin by making a broad statement about social media and its widespread use in today’s society, as follows: “Social media has become an integral part of modern life, with billions of users worldwide.”
- Define Key Terms : Define any key terms or concepts that may be unfamiliar to your readers but are essential for understanding your argument.
- Provide Relevant Statistics: Use statistics or facts to highlight the significance of the issue you’re discussing. For instance, “According to a report by Statista, the number of social media users is expected to reach 4.41 billion by 2025.”
- Discuss the Evolution: Mention previous research or studies that have been conducted on the topic, especially those that are relevant to your argument. Mention key milestones or developments that have shaped its current impact. You can also outline some of the major effects of social media. For example, you can briefly describe how social media has evolved, including positives such as increased connectivity and issues like cyberbullying and privacy concerns.
- Transition to Your Thesis: Use the background information to lead into your thesis statement, which should clearly state the main argument or purpose of your essay. For example, “Given its pervasive influence, it is crucial to examine the impact of social media on mental health.”

A thesis statement is a concise summary of the main point or claim of an essay, research paper, or other type of academic writing. It appears near the end of the introduction. Here’s how to write a thesis statement:
- Identify the topic: Start by identifying the topic of your essay. For example, if your essay is about the importance of exercise for overall health, your topic is “exercise.”
- State your position: Next, state your position or claim about the topic. This is the main argument or point you want to make. For example, if you believe that regular exercise is crucial for maintaining good health, your position could be: “Regular exercise is essential for maintaining good health.”
- Support your position: Provide a brief overview of the reasons or evidence that support your position. These will be the main points of your essay. For example, if you’re writing an essay about the importance of exercise, you could mention the physical health benefits, mental health benefits, and the role of exercise in disease prevention.
- Make it specific: Ensure your thesis statement clearly states what you will discuss in your essay. For example, instead of saying, “Exercise is good for you,” you could say, “Regular exercise, including cardiovascular and strength training, can improve overall health and reduce the risk of chronic diseases.”
Examples of essay introduction
Here are examples of essay introductions for different types of essays:
Argumentative Essay Introduction Example:
Topic: Should the voting age be lowered to 16?
“The question of whether the voting age should be lowered to 16 has sparked nationwide debate. While some argue that 16-year-olds lack the requisite maturity and knowledge to make informed decisions, others argue that doing so would imbue young people with agency and give them a voice in shaping their future.”
Expository Essay Introduction Example
Topic: The benefits of regular exercise
“In today’s fast-paced world, the importance of regular exercise cannot be overstated. From improving physical health to boosting mental well-being, the benefits of exercise are numerous and far-reaching. This essay will examine the various advantages of regular exercise and provide tips on incorporating it into your daily routine.”
Text: “To Kill a Mockingbird” by Harper Lee
“Harper Lee’s novel, ‘To Kill a Mockingbird,’ is a timeless classic that explores themes of racism, injustice, and morality in the American South. Through the eyes of young Scout Finch, the reader is taken on a journey that challenges societal norms and forces characters to confront their prejudices. This essay will analyze the novel’s use of symbolism, character development, and narrative structure to uncover its deeper meaning and relevance to contemporary society.”
- Engaging and Relevant First Sentence : The opening sentence captures the reader’s attention and relates directly to the topic.
- Background Information : Enough background information is introduced to provide context for the thesis statement.
- Definition of Important Terms : Key terms or concepts that might be unfamiliar to the audience or are central to the argument are defined.
- Clear Thesis Statement : The thesis statement presents the main point or argument of the essay.
- Relevance to Main Body : Everything in the introduction directly relates to and sets up the discussion in the main body of the essay.

Writing a strong introduction is crucial for setting the tone and context of your essay. Here are the key takeaways for how to write essay introduction: 3
- Hook the Reader : Start with an engaging hook to grab the reader’s attention. This could be a compelling question, a surprising fact, a relevant quote, or an anecdote.
- Provide Background : Give a brief overview of the topic, setting the context and stage for the discussion.
- Thesis Statement : State your thesis, which is the main argument or point of your essay. It should be concise, clear, and specific.
- Preview the Structure : Outline the main points or arguments to help the reader understand the organization of your essay.
- Keep it Concise : Avoid including unnecessary details or information not directly related to your thesis.
- Revise and Edit : Revise your introduction to ensure clarity, coherence, and relevance. Check for grammar and spelling errors.
- Seek Feedback : Get feedback from peers or instructors to improve your introduction further.
The purpose of an essay introduction is to give an overview of the topic, context, and main ideas of the essay. It is meant to engage the reader, establish the tone for the rest of the essay, and introduce the thesis statement or central argument.
An essay introduction typically ranges from 5-10% of the total word count. For example, in a 1,000-word essay, the introduction would be roughly 50-100 words. However, the length can vary depending on the complexity of the topic and the overall length of the essay.
An essay introduction is critical in engaging the reader and providing contextual information about the topic. To ensure its effectiveness, consider incorporating these key elements: a compelling hook, background information, a clear thesis statement, an outline of the essay’s scope, a smooth transition to the body, and optional signposting sentences.
The process of writing an essay introduction is not necessarily straightforward, but there are several strategies that can be employed to achieve this end. When experiencing difficulty initiating the process, consider the following techniques: begin with an anecdote, a quotation, an image, a question, or a startling fact to pique the reader’s interest. It may also be helpful to consider the five W’s of journalism: who, what, when, where, why, and how. For instance, an anecdotal opening could be structured as follows: “As I ascended the stage, momentarily blinded by the intense lights, I could sense the weight of a hundred eyes upon me, anticipating my next move. The topic of discussion was climate change, a subject I was passionate about, and it was my first public speaking event. Little did I know , that pivotal moment would not only alter my perspective but also chart my life’s course.”
Crafting a compelling thesis statement for your introduction paragraph is crucial to grab your reader’s attention. To achieve this, avoid using overused phrases such as “In this paper, I will write about” or “I will focus on” as they lack originality. Instead, strive to engage your reader by substantiating your stance or proposition with a “so what” clause. While writing your thesis statement, aim to be precise, succinct, and clear in conveying your main argument.
To create an effective essay introduction, ensure it is clear, engaging, relevant, and contains a concise thesis statement. It should transition smoothly into the essay and be long enough to cover necessary points but not become overwhelming. Seek feedback from peers or instructors to assess its effectiveness.
References
- Cui, L. (2022). Unit 6 Essay Introduction. Building Academic Writing Skills .
- West, H., Malcolm, G., Keywood, S., & Hill, J. (2019). Writing a successful essay. Journal of Geography in Higher Education , 43 (4), 609-617.
- Beavers, M. E., Thoune, D. L., & McBeth, M. (2023). Bibliographic Essay: Reading, Researching, Teaching, and Writing with Hooks: A Queer Literacy Sponsorship. College English, 85(3), 230-242.
Paperpal is a comprehensive AI writing toolkit that helps students and researchers achieve 2x the writing in half the time. It leverages 21+ years of STM experience and insights from millions of research articles to provide in-depth academic writing, language editing, and submission readiness support to help you write better, faster.
Get accurate academic translations, rewriting support, grammar checks, vocabulary suggestions, and generative AI assistance that delivers human precision at machine speed. Try for free or upgrade to Paperpal Prime starting at US$19 a month to access premium features, including consistency, plagiarism, and 30+ submission readiness checks to help you succeed.
Experience the future of academic writing – Sign up to Paperpal and start writing for free!
Related Reads:
- What is an Argumentative Essay? How to Write It (With Examples)
- How to Paraphrase Research Papers Effectively
- How to Cite Social Media Sources in Academic Writing?
How Long Should a Chapter Be?
Similarity checks: the author’s guide to plagiarism and responsible writing, types of plagiarism and 6 tips to avoid it in your writing , you may also like, what are journal guidelines on using generative ai..., types of plagiarism and 6 tips to avoid..., similarity checks: the author’s guide to plagiarism and..., what is a master’s thesis: a guide for..., should you use ai tools like chatgpt for..., what are the benefits of generative ai for..., how to avoid plagiarism tips and advice for..., plagiarism checkers vs. ai content detection: navigating the..., plagiarism prevention: why you need a plagiarism check....
4 Examples of Academic Writing
#scribendiinc
Written by Scribendi
The best way to understand what effective academic writing looks like is to review academic writing examples.
Let's begin with four of the most common types of academic writing: research proposals, dissertations, abstracts, and academic articles. We'll be examining each type of writing and providing academic writing samples of each.
Whether you aim to earn funding for a passion project or are stymied by how to format an abstract, these academic writing examples will help you nail your next undertaking.
Academic Writing Example 1: Research Proposals
A research proposal is an outline of the proposed research of a PhD candidate, a private researcher, or someone hoping to obtain a research grant .
Your proposal should put your best foot forward: It details your intended research question and how it relates to existing research, makes an argument for why your research should be chosen for advancement or funding, and explains the deliverables you hope to achieve with your research.
A more detailed look at what proposal writing is and what goes into a research proposal may also be beneficial. Every proposal is different because every project is different. Proposal requirements also differ according to the university or funding agency that reviews the proposal.
Research Proposal Structure
A cover letter summarizing your proposal and showcasing why you should be chosen
An introduction or abstract
An explanation of the background, purpose, and significance of your research
A research plan or methodology that includes a timeline (a Gantt chart may be beneficial)
A projected budget, if applicable
Academic Writing Sample: Research Proposal Excerpt
Building on the work of the three foundational sociological theorists—Marx, Weber, and Durkheim—and Mark Traugott's theory of the "insurgent barricade," this proposed research will analyze the appearance, use, and disappearance of barricade warfare as an effective battle strategy.
Focusing on these three theorists, this research will determine which theory or theories best explain the life cycle of barricade warfare, focusing in particular on its disappearance. A brief but comprehensive history of barricade warfare will be provided in addition to the theoretical explanations of barricade warfare's utility.
Research Proposal Writing Tips
Before you format your proposal, contact your targeted university, private organization, or funding agency to confirm what they require for proposals. Then, try to follow this format as closely as possible.
Be detailed when outlining your goals and your funding needs. Connect the objectives of the research to the resources you're requesting.
Be realistic in what you ask for as far as resources—don't ask for more or less than you need, and show evidence to justify your choices.
Don't dedicate too much text in your proposal to describing past research. A summary of key points, arguments, theories, and how your research will build on them should suffice.
Remember that no matter how good your proposal is, it might be rejected. You're likely up against dozens or even hundreds of other candidates who have equally sound proposals. Don't be discouraged if this happens. See it as a learning opportunity for your next proposal.
Academic Writing Example 2: Dissertations
A dissertation is a body of writing that represents original research and is generally written as part of a PhD or master's program.
Typically, it builds on previous research in the field to make a significant contribution or advancement. You may benefit from more detailed information on what a dissertation is , how to write a dissertation , and how to edit a dissertation .
Dissertation Structure
Introduction/background and the significance of the study
Literature review
Methodology
Results/findings
Conclusion/contribution to the body of research
Academic Writing Sample: Dissertation Excerpt
There are two options for choosing a unit of analysis for this phenomenon: the social artifact (erected barricades) or the social interaction (the collaboration of insurgents engaged in barricade warfare). The best choice is social interaction.
Most individual occurrences of barricade warfare involve the construction of more than one barricade, and the number of barricades is not necessarily a valid indicator of the sociological magnitude of an insurgence. The most relevant choice is an insurgence, the event of a conflict involving barricade warfare.
Dissertation Writing Tips
Remember to bear in mind the significance of your study. It doesn't have to be paradigm shifting, but you want to infuse the dissertation with reminders of why your research is important.
Don't get bogged down in trying to show that your research is one of a kind or uniquely contributive to the body of research. It likely isn't, and it's more effective to show how you are building on previous research .
Remember to check with your college or university to ensure that you're formatting your dissertation according to the school's expectations.
Ask your advisor questions when you need to.
Be prepared to make alterations to your dissertation according to your thesis committee's suggestions. This doesn't mean you did a bad job—it just means there's room for improvement.
Academic Writing Example 3: Abstracts
The abstract is actually a component of other forms of academic writing, such as scholarly articles and dissertations. The abstract acts as a comprehensive outline of your paper in paragraph form.
Abstract Structure
Results
You may want to read more about what abstracts are and why they are important in preparing yourself for writing one.
Academic Writing Sample: Abstract
Barricade warfare has occurred across several spectra, but most notably, it occurred almost exclusively in a 300-year period between the 16th and 19th centuries. Each instance had an inciting incident, but a common thread was the culture of revolution: a revolutionary tradition based on the belief that injustice was being carried out and that, in this case, barricade insurgence was the way to resolve it.
This study uses the theories of Karl Marx and Emile Durkheim to analyze barricade warfare, its appearance, and its disappearance. Ultimately, neither theory can independently explain this phenomenon.
Marx offers a reasonable explanation for why barricade warfare may have died, but his theory is difficult to test empirically and fails to explain the absence of recurrences. Conversely, Durkheim's theory is much easier to observe and can explain why barricade warfare has not experienced a renaissance. However, he offered no reason as to why it died in the first place.
These two theoretical orientations complement each other nicely and, ultimately, neither can stand alone.
Notice that this abstract comes in at under 200 words (a common limit) but nevertheless covers the background of the study, how it was approached, and the results and conclusions of the research.
If you are struggling to meet a word count, check out 10 Academic Phrases Your Writing Doesn't Need .
Abstract Writing Tips
Be conscious of your word count. Stay under the limit.
Check with your school or target journal to make sure special formatting is not required.
Don't use abbreviations or citations in the abstract.
Don't simply restate your thesis or copy your introduction. Neither of these is an abstract.
Remember that your abstract often gives readers their first impressions of your work. Despite its short length, it deserves a lot of attention.
Academic Writing Example 4: Articles
Academic articles are pieces of writing intended for publication in academic journals or other scholarly sources. They may be original research studies, literature analyses, critiques , or other forms of scholarly writing.
Article Structure
Abstract and keywords
Introduction
Materials and methods
References and appendices
Academic Writing Sample: Article Excerpt
"Those great revolutionary barricades were places where heroes came together" (Hugo, 2008). This description by Victor Hugo of the 1832 June Rebellion in Paris comes from his seminal work of fiction, Les Miserables.
Although the account is fictionalized, it is deeply representative of what historian Mark Traugott (2010, p. 225) terms the "culture of revolution." This spirit of heroic response to social injustice swept across Europe during the second half of the millennium and was characterized in part by barricade warfare.
The phenomenon of the insurgent barricade has essentially disappeared, however, leaving no trace of its short-lived but intense epoch, and the question of why this happened remains a mystery. The theories of Karl Marx and Emile Durkheim, when taken together, provide a compelling explanation for the disappearance of barricade warfare, and the tenets of each theory will be examined to explain this phenomenon.
Article Writing Tips
Follow these detailed steps for writing an article and publishing it in a journal .
Make sure that you follow all of your target journal's guidelines.
Have a second set of educated eyes look over your article to correct typos, confusing language, and unclear arguments.
Don't be discouraged if your article is not chosen for publication. As with proposal writing, you are up against countless others with equally compelling research.
Don't be discouraged if the journal asks you to make changes to your article. This is common. It means they see value in your article, as well as room for improvement.
Whether you're applying for funding, earning an advanced degree, aiming to publish in a journal, or just trying to cram your 4,000-word study into a 150-word abstract, hopefully these academic writing examples have helped get your creative juices flowing.
Go out there and write! With these academic writing samples at your side, you are sure to model your academic writing appropriately.
Achieve Your Academic Goals
Hire an expert academic editor , or get a free sample, about the author.

Scribendi's in-house editors work with writers from all over the globe to perfect their writing. They know that no piece of writing is complete without a professional edit, and they love to see a good piece of writing transformed into a great one. Scribendi's in-house editors are unrivaled in both experience and education, having collectively edited millions of words and obtained numerous degrees. They love consuming caffeinated beverages, reading books of various genres, and relaxing in quiet, dimly lit spaces.
Have You Read?
"The Complete Beginner's Guide to Academic Writing"
Related Posts


10 Academic Phrases Your Writing Doesn't Need

21 Legit Research Databases for Free Journal Articles in 2022

Grant Writing Basics
Upload your file(s) so we can calculate your word count, or enter your word count manually.
We will also recommend a service based on the file(s) you upload.
English is not my first language. I need English editing and proofreading so that I sound like a native speaker.
I need to have my journal article, dissertation, or term paper edited and proofread, or I need help with an admissions essay or proposal.
I have a novel, manuscript, play, or ebook. I need editing, copy editing, proofreading, a critique of my work, or a query package.
I need editing and proofreading for my white papers, reports, manuals, press releases, marketing materials, and other business documents.
I need to have my essay, project, assignment, or term paper edited and proofread.
I want to sound professional and to get hired. I have a resume, letter, email, or personal document that I need to have edited and proofread.
Prices include your personal % discount.
Prices include % sales tax ( ).

- Essay Editor
Essay - What it Is and How to Write it With an AI Aithor

Writing concise and persuasive texts is a skill required in many professional settings. One of the ways we learn this skill is by writing essays. However, essays require lots of preparation and research, so they can be hard to write, especially if you struggle to understand how to make your essay better.
In this article, you’ll learn what an essay is and how to use the Aithor AI essay generator for writing essays.
Revolutionize your writing process: our AI rewrite tool is here to help
What is an essay?
In a broad sense, an essay is a genre of writing that allows its author to explore a certain topic in detail. The main goal of an essay is to present certain facts and opinions to its readers, provoke thought, engage them in discussion around the issue at hand, and sometimes even convince them of the author’s point of view.
To do this, essays always follow a set structure consisting of:
- the introduction , where the author introduces readers to the topic of the essay and to the main argument the essay is set to prove,
- the body , where the author develops the main idea of the essay, expanding on its topic and providing reasoning to prove the main argument,
- the conclusion , where the author summarizes the entire text and once again states the initial argument.
Due to this complex structure, essay authors have to research the topic of their future essays and create detailed plans to communicate their points across. This can become an issue for many students who often have to write essays on subjects they aren’t closely familiar with.
Thankfully, it is now possible to use AI to help write essays with a strong premise and reasoning. Let’s find out how you can utilize essay generator Aithor to create essays for your academic purposes.
How to write an essay with AI essay generator Aithor
Aithor.com is an AI essay generator created specifically to provide aid to students with their essay assignments. There are multiple ways AI can be used to create perfect texts on any given topic. Here is an overview of how AI can help with each stage of writing a perfect essay.
1. Identifying the thesis statement
A thesis statement is a brief summary of an essay that contains the main argument you are going to refer to throughout the whole text. Your essay writing process should always start with identifying a proper thesis statement as it will influence your line of reasoning and analysis.
AI generators can prove a great assistance in this stage of essay writing. By simply typing in the broader topic of your essay, you can get a list of a dozen potential thesis statements offering different outlooks on the issue at hand. The only thing you will need to do is choose the one that resonates with you the most.
2. Gathering sources
Without learning about the background of an issue, it’s impossible to write a comprehensive essay. That’s when AI for writing essays can provide much-needed assistance.
The essay generator Aithor can sort through a large database of academic literature in mere seconds and find sources that can be used in your essay. This saves a tremendous amount of time, allowing you to focus on studying the subject instead of wasting your time on manual searching.
3. Meeting word count requirement
When you write an essay assignment, you often have to meet a certain word count requirement. However, this can prove hard when you feel like you’ve already exhausted the topic.
The good news is, that it’s easy to learn how to get AI to write an essay addition. Simply scan the text of your essay and find the parts you think need to be a bit longer. Then you can prompt an essay generator to continue writing a specific part of your essay, which can help you achieve the required word count.
4. Asking for examples
If you’re unsure of how your essay should look, you can use AI-generated essays as an example. AI generators are good at creating template texts illustrating how to write specific texts. It can also help you decide how you want to approach your analysis and present your arguments effectively.
5. Avoiding plagiarism
The essay generator Aithor has access to a vast database of texts and can check your essay for any accidental plagiarism. In addition, Aithor can help you reference your sources properly and per specific academic standards, which is also important to avoid triggering anti-plagiarism systems.
6. Enhancing your grammar
Like any other written text, an essay shouldn’t include any grammar or stylistic mistakes, or you may end up with a lower grade than you hoped for.
AI can provide good feedback to improve the quality of your essay and correct any mistakes. This is particularly important for students who spend a long amount of time on their essays as they might become so engrossed in their writing that they fail to notice any errors.
Conclusion: How to Write it With an AI Aithor
AI essay generators like Aithor.com have become a great help when it comes to essay writing. From helping students conduct research to checking for grammar mistakes, AI tools can significantly improve the quality of students’ work. Knowing how to make your essay better with AI is crucial in the fast-paced world of academic studies, so make sure to explore all the ways of using AI for writing essays.
Recent articles
Artificial intelligence: evolution of essay writing.
We live in the age when each new year brings more innovations than the previous one. One of the most debated topics of recent time is AI writing software. Not only did users get a handy helper for composing emails, but a tireless machine for writing pages of text on a variety of topics. It’s only natural that students who often have to write long essays as homework started using it too. This article will dissect how artificial intelligence will change the future essays and if AI generation tool ...
Definition Essay - Writing Guide, Examples and Tips
If you don’t know how to write a definition essay, but the task has been given already, there’s no sense in making panic. Here you can find a few useful tips and recommendations on how to prepare a proper writing piece. A Definition Essay: what is it? A definition essay refers to a type of academic writing, assigned during high school and college studying. It includes not only a definition of some issue or concept but a complicated analysis of the selected phenomenon. In general, it helps to ...
Elevate your articles with a click: discover our AI rewriting tool subscription

Teaching Connections
Advancing discussions about teaching, who’s afraid of academic writing a reflective essay on dispelling anxiety and fear in an academic writing course.
WONG Jock Onn Centre for English Language Communication (CELC)
Jock Onn considers how educators can apply an ethics of care in their teaching, as he takes us through survey findings on students’ perspectives towards academic writing, particularly the emotions they associate with this activity and the challenges they face.

Photo by Brooke Cagle on Unsplash
I had previously spent many semesters in my teaching practice developing methods that I thought would help students excel in academic writing. It did not matter to me at the time that student feedback told me that my coursework was demanding; I took it to mean that I was on the right track (Wong, 2023a). It was only in recent years that I realised the need to show more care in my teaching (Wong, 2023b). Last year, amazingly, for the first time, the word ‘care’ appeared in my student feedback. A student wrote, “Dr Wong displays care for his students…” Realising the importance of care, I decided to find out why students need care and conducted a simple Google survey (entitled “Attitudes Towards Academic Writing”) last semester with my three classes. I asked them to make known the emotions they associate with academic writing, write qualitative comments on their answers, and tell me what challenges they face. I received 41 responses, and the survey yielded some tentative but interesting findings.
The survey asked, “Which of the following emotions do you associate with academic writing?” As shown in Table 1, over 50% of the students associated academic writing with fear and anxiety. Slightly over a quarter associated it with a rather positive feeling (26.8%) and only a very small percentage (4.9%) associated it with something very positive. The fact that over half of the respondents associated academic writing with fear (53.7%) and anxiety (63.4%) was a surprise to me. Fortunately, less than 10% hated academic writing.

Students also gave qualitative comments on why they experienced fear and anxiety in academic writing. Some indicated that they had insufficient linguistic knowledge, including the vocabulary and skills to write academically. A few even claimed that they did not know what academic writing entails. Other respondents indicated a lack of confidence. For example, a student wrote that knowing that their work is being graded caused anxiety. Several students attributed their anxiety to uncertainty and a lack of confidence in academic writing. In some cases, fear or anxiety was a result of bad experiences in junior college (JC). A student recounted their JC experience, when they had to produce an essay in three hours, causing their brain and hand to hurt.
The survey further asked respondents to tick the problems they face in academic writing from a list. Table 2 shows that the top three problems students face in academic writing have to do with not knowing what constitutes academic writing, not having enough ideas, and sentence cohesion . More than half of the students said that they did not know how to write academically (58.5%) and did not have enough ideas for writing (51.2%). Also, over 30% of respondents had problems with the introduction (‘don’t know how to start’) (36.6%), and grammar (34.1%).
Table 2 Problems that students face (in decreasing order of importance)

Anxiety is said to be “one of the critical individual affective factors in the process of learning a second language or a foreign language” (He et al., 2021, p. 1). Presumably, the same could be said of the process of learning academic writing. Anxiety, as studies suggest, is linked to “avoidance of the feared situation and loss of motivation to perform”, which could adversely affect retention (England et al., 2017, p. 2/17). Student anxiety and fear can ultimately affect language performance (Soriano & Co, 2022, p. 450). Thus, dispelling anxiety and fear among students is a pedagogic imperative.
To dispel anxiety and fear, one would benefit from understanding what they mean. I believe most of us do. However, two co-authors offer an interesting perspective. According to Kastrup and Mallow (2016), fear “deals with things of which there is good reason to be afraid”, whereas anxiety means “being scared of something that is not intrinsically fearful” (pp. 3-1). Although Kastrup and Mallow (2016) speak in the context of science, their definitions seem to make general sense. As educators, we recognise that while some student concerns are practical in nature (e.g., they do not know the rules), others seem to be psychological. The solution to practical concerns could be addressed in a more straightforward fashion by using sound teaching methods; however, psychological barriers may require a different approach.
My proposed way of addressing the psychological challenge is to replace the bad experiences with pleasant ones. As Cook (2021) puts it, teachers “must provide instructor presence by providing a positive education experience for students” and give them “a sense of belonging” (p. 136). The teacher can achieve this by creating a positive learning experience through an ethic of care (Noddings, 2012). The teacher can display “empathic concern” (Patel, 2023) by acknowledging student perspectives in class, using inclusive languages, encouraging open communication, and accommodating student needs (p. 64). The teacher can create “a safe learning environment” by establishing “rules of engagement” and encouraging students to “explain their answers” in class without labelling the answers as “wrong” or “incorrect” (Teo, 2023, p. 79). After all, “harsh criticisms” can impede learning (Soriano & Co, 2022, p. 452), whereas positive feedback can alleviate anxiety (He et al., 2021). A student recently gave feedback that I often asked them whether they understood what I had taught, and this suggests that checking for understanding regularly is reassuring. To this end, the teacher could use ungraded quizzes, which do not cause student anxiety (England et al., 2017). There are many other things a teacher could do in this vein to help address such psychological learning barriers (Harvard Medical School, 2017; Abigail, 2019).
To maximise student learning, the teacher plays a big role, a role much bigger than I had previously thought—the teacher has a responsibility to dispel fear and anxiety among students. I agree with Kastrup and Mallow (2016) that it is the teachers “who most affect the anxiety (or lack thereof) of the students” (pp. 3-12). I would now say that what makes an excellent teacher is not just the use of time-tested teaching methods but also a capacity to care (Wong, 2023b). Thus, for me, the obvious way forward is to ‘integrate care in higher education’ by ‘teaching with heart’ (Holles, 2023, p. 18).
Abigail, H. (2019, March 5). Tips to beat back writing anxiety . Retrieved from IUPUI University Writing Center Blog: https://liberalarts.iupui.edu/programs/uwc/tips-to-beat-back-writing-anxiety/
Cook, M. (2021). Students’ perceptions of interactions from instructor presence, cognitive presence, and social presence in online lessons. International Journal of TESOL Studies (Special Issue “ELT in the Time of the Coronavirus 2020”, Part 3), 3 (1), 134-161. https://doi.org/10.46451/ijts.2021.03.03
England, B. J., Brigati, J. R., & Schussler, E. E. (2017, August 3). Student anxiety in introductory biology classrooms: Perceptions about active learning and persistence in the major. PLoS One, 12 (8), e0182506. http://dx.doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0182506
Harvard Medical School. (2017, October 13). Write your anxieties away . Retrieved from Harvard Health Blog: https://www.health.harvard.edu/blog/write-your-anxieties-away-2017101312551
He, X., Zhou, D., & Zhang, X. (2021, July-September). An empirical study on Chinese University students’ English Language classroom anxiety with the idiodynamic approach. Sage Open, 11 (3), 1-14. https://doi.org/10.1177/21582440211037676
Holles, C. (2023). Faculty-student interaction and well-being: The call for care. International Journal of TESOL Studies, 5 (3), 7-20. https://doi.org/10.58304/ijts.20230302
Kastrup, H., & Mallow, J. V. (2016). Student Attitudes, Student Anxieties, and How to Address Them: A Handbook for Science Teachers. Morgan & Claypool Publishers. https://dx.doi.org/10.1088/978-1-6817-4265-6
Noddings, N. (2012). The caring relation in teaching. Oxford Review of Education, 38 (6), 771-81. http://dx.doi.org/10.1080/03054985.2012.745047
Patel, S. N. (2023). Empathetic and dialogic interactions: Modelling intellectual Empathy and communicating care. International Journal of TESOL Studies, 3 , 51-70. https://doi.org/10.58304/ijts.20230305
Soriano, R. M., & Co, A. G. (2022, March). Voices from within: Students’ lived experiences on English language anxiety. International Journal of Evaluation and Research in Education, 11 (1), 449-58. http://dx.doi.org/10.11591/ijere.v11i1.21898
Teo, C. (2023). Beyond academic grades: Reflections on my care for university students’ holistic development in Singapore. International Journal of TESOL Studies, 5 (3), 71-83. https://doi.org/10.58304/ijts.20230306
Wong, J. (2023a, March 29). When angels fall: The plight of an ambitious educator. Teaching Connections: Advancing Discussions about Teaching . Retrieved from https://blog.nus.edu.sg/teachingconnections/2023/03/29/when-angels-fall-the-plight-of-an-ambitious-educator/
Wong, J. (2023b). What completes an excellent teacher? Care in higher education English language teaching. International Journal of TESOL Studies2, 5 (3), 1-6. https://doi.org/10.58304/ijts.20230301


Microsoft 365 Life Hacks > Writing > Prose vs. poetry: what’s the difference?
Prose vs. poetry: what’s the difference?
Both prose and poetry are forms of writing; however, many people don’t fully understand the differences between the two. Learn the difference between prose versus poetry to expand your knowledge of common writing styles.

Have you ever read a beautifully written, heartfelt passage, but weren’t sure if it was considered a poem or prose? People often use the terms ‘prose’ and ‘poetry’ interchangeably, even though they’re two different forms of writing.
What is prose?
Prose is writing that doesn’t follow any meters or rhyming schemes. In fact, everyday writing is considered prose! Books, short stories, essays, and any sort of writing that doesn’t follow a specific structure is considered prose.

Get the most out of your documents with Word
Elevate your writing and collaborate with others - anywhere, anytime
Types of prose
There are a few different types of prose: Fictional prose, nonfictional prose, heroic prose, and prose poetry.
Fictional prose
Prose fiction is when an author tells a story that isn’t based on true events. The Great Gatsby by F. Scott Fitzgerald is a great example of fictional prose.
Nonfictional prose
Non-fictional prose is when an author writes about real events. For example, newspapers or memoirs are examples of non-fiction prose. When Breath Becomes Air by Paul Kalanithi is a memoir that is considered non-fiction prose.
Heroic prose
Heroic prose is a story that is passed down orally, but it can also be written down. This form of prose isn’t as common as fictional prose, nonfictional prose, or prose poetry. Heroic prose includes parables, myths, and fables. The Odyssey by Homer is an example of heroic prose.
Prose poetry
Prose poetry is a form of writing that uses literary devices such as imagery, symbols, or alliteration. Prose poetry can be both fiction and non-fiction, and it is characterized by its poetic qualities expressed in prose form, but not necessarily by the absence of line breaks or rhyming scheme .
Here’s a sample of prose poetry from Amy Lowell’s Bath:
“The day is fresh-washed and fair, and there is a smell of tulips and narcissus in the air. The sunshine pours in at the bath-room window and bores through the water in the bath-tub in lathes and planes of greenish-white. It cleaves the water into flaws like a jewel, and cracks it to bright light.” You may have notice that Lowell does incorporate a rhyme in her poem—both white and light rhyme—but the poem itself doesn’t follow a specific rhyming scheme.
What is poetry?
There are many different forms of poetry out there, but in general, poetry focuses on rhythm. Poems also incorporate structure, patterns, and rhyming schemes. Some popular forms of poetry include:
- Lyric poetry
Here is an example from a famous poem titled I’m nobody! Who are you? by Emily Dickinson:
“How dreary to be somebody! How public like a frog To tell one’s name the livelong day To an admiring bog!”
The fundamental differences between poetry and prose
Prose is a straightforward form of writing that follows natural flow of language and doesn’t use line breaks. Poetry, on the other hand, often uses structure such as rhyme, rhythm, and intentional line breaks. While not all poems have to rhyme , it’s a signature of the form and many do.
If you’re interested in learning more about poetry, see how you can write a narrative poem or use punctuation in poetry .
Get started with Microsoft 365
It’s the Office you know, plus the tools to help you work better together, so you can get more done—anytime, anywhere.
Topics in this article
More articles like this one.

What is independent publishing?
Avoid the hassle of shopping your book around to publishing houses. Publish your book independently and understand the benefits it provides for your as an author.

What are literary tropes?
Engage your audience with literary tropes. Learn about different types of literary tropes, like metaphors and oxymorons, to elevate your writing.

What are genre tropes?
Your favorite genres are filled with unifying tropes that can define them or are meant to be subverted.

What is literary fiction?
Define literary fiction and learn what sets it apart from genre fiction.

Everything you need to achieve more in less time
Get powerful productivity and security apps with Microsoft 365

Explore Other Categories
How To Write A Research Paper
Find Sources For A Research Paper

How to Find Sources For a Research Paper | A Guide
10 min read
Published on: Mar 26, 2024
Last updated on: Mar 25, 2024

People also read
How to Write a Research Paper Step by Step
How to Write a Proposal For a Research Paper in 10 Steps
A Comprehensive Guide to Creating a Research Paper Outline
Types of Research - Methodologies and Characteristics
300+ Engaging Research Paper Topics to Get You Started
Interesting Psychology Research Topics & Ideas
Qualitative Research - Types, Methods & Examples
Understanding Quantitative Research - Definition, Types, Examples, And More
Research Paper Example - Examples for Different Formats
How To Start A Research Paper - Steps With Examples
How to Write an Abstract That Captivates Your Readers
How To Write a Literature Review for a Research Paper | Steps & Examples
Types of Qualitative Research Methods - An Overview
Understanding Qualitative vs. Quantitative Research - A Complete Guide
How to Cite a Research Paper in Different Citation Styles
Easy Sociology Research Topics for Your Next Project
200+ Outstanding History Research Paper Topics With Expert Tips
How To Write a Hypothesis in a Research Paper | Steps & Examples
How to Write an Introduction for a Research Paper - A Step-by-Step Guide
How to Write a Good Research Paper Title
How to Write a Conclusion for a Research Paper in 3 Simple Steps
How to Write an Abstract For a Research Paper with Examples
How To Write a Thesis For a Research Paper Step by Step
How to Write a Discussion For a Research Paper | Objectives, Steps & Examples
How to Write the Results Section of a Research Paper - Structure and Tips
How to Write a Problem Statement for a Research Paper in 6 Steps
How To Write The Methods Section of a Research Paper Step-by-Step
Share this article
Research papers are an essential part of academic life, but one of the most challenging aspects can be finding credible sources to support your arguments.
With the vast amount of information available online, it's easy to feel overwhelmed. However, by following some simple steps, you can streamline the process of finding reliable sources for your research paper .
In this guide, we'll break down the process into easy-to-follow steps to help you find the best sources for your paper.
On This Page On This Page -->
Step 1: Define Your Topic and Research Questions
Before you venture into your quest for sources, it's essential to have a clear understanding of your research topic and the specific questions you aim to address. Define the scope of your paper and identify keywords and key concepts that will guide your search for relevant sources.
Step 2: Utilize Academic Databases
Academic databases are treasure troves of scholarly articles, research papers, and academic journals covering a wide range of subjects. Institutions often provide access to these databases through their libraries. Some popular academic databases include:
- IEEE Xplore
- Google Scholar
These databases allow you to search for peer-reviewed articles and academic papers related to your topic.
Use advanced search features to narrow down your results based on publication date, author, and keywords .
Academic Resources Classified by Discipline
Here's a breakdown of prominent databases categorized by academic discipline:
Step 3: Explore Library Catalogs
Your university or local library's catalog is another valuable resource for finding sources. Library catalogs contain books, periodicals, and other materials that may not be available online.
Use the catalog's search function to locate relevant books, journals, and other materials that can contribute to your research.
Step 4: Consult Bibliographies and References
When you find a relevant source, take note of its bibliography or make a list of sources for the research paper. These lists often contain citations to other works that may be useful for your research.
By exploring the references cited in a particular source, you can uncover additional resources and expand your understanding of the topic.
Step 5: Boolean Operators for Effective Searches
Boolean operators are words or symbols used to refine search queries by defining the relationships between search terms. The three primary operators include "AND," which narrows searches by requiring all terms to be present; "OR," which broadens searches by including either term or both; and "NOT," which excludes specific terms to refine results further.
Most databases provide advanced search features for seamless application of Boolean logic.
Step 6: Consider Primary Sources
Depending on your research topic, primary sources such as interviews, surveys, archival documents, and original data sets can provide valuable insights and support for your arguments.
Primary sources offer firsthand accounts and original perspectives on historical events, social phenomena, and scientific discoveries.
Step 7: Evaluate the Credibility of Sources
Not all sources are created equal, and it's crucial to evaluate the credibility and reliability of the information you encounter.
Consider the author's credentials, the publication venue, and whether the source is peer-reviewed. Look for evidence of bias or conflicts of interest that may undermine the source's credibility.
Step 8: Keep Track of Your Sources
As you gather sources for your research paper, maintain a systematic record of the materials you consult. Keep track of bibliographic information, including author names, publication dates, titles, and page numbers . This information will be invaluable when citing your sources and creating a bibliography or works cited page.
Other Online Sources
In addition to academic databases and library catalogs, exploring popular online sources can provide valuable insights and perspectives on your research topic. Here are some types of online sources you can consider:
Websites hosted by reputable organizations, institutions, and experts (such as the New York Times) can offer valuable information and analysis on a wide range of topics. Look for websites belonging to universities, research institutions, government agencies, and established non-profit organizations.
Crowdsourced Encyclopedias like Wikipedia
While Wikipedia can provide a broad overview of a topic and lead you to other sources, it's essential to verify the information found there with more authoritative sources.
Use Wikipedia as a starting point for your research, but rely on peer-reviewed journal articles and academic sources for in-depth analysis and evidence.
Tips for Assessing the Credibility of Online Sources
When using online sources, it's important to exercise caution and critically evaluate the credibility and reliability of the information you find. Here are some tips for assessing the credibility of online sources:
- Check the Domain Extension: Look for websites with domain extensions that indicate credibility. URLs ending in .edu are educational resources, while URLs ending in .gov are government-related resources. These sites often provide reliable and authoritative information.
- Look for DOIs (Digital Object Identifiers): DOIs are unique alphanumeric strings assigned to scholarly articles and indicate that the article has been published in a peer-reviewed, scientific journal. Finding a DOI can help you assess the scholarly rigor of the source.
- Evaluate the Authorship and Credentials: Consider the qualifications and expertise of the author or organization behind the website or blog. Look for information about the author's credentials, affiliations, and expertise in the subject matter.
- Consider the Currency and Relevance: Assess how up-to-date the information is and whether it aligns with the scope and focus of your research. Look for recent publications and timely analyses that reflect current trends and developments in the field.
Wrapping it up!
Finding sources for your research paper may seem like a challenge, but by following these steps, you can locate credible sources to support your arguments and enhance the quality of your paper.
By approaching the research process systematically and critically evaluating the information you encounter, you can produce a well-researched and compelling research paper.
If you are struggling with finding credible sources or have time constraints, do not hesitate to seek writing help for your research papers . CollegeEssay.org has professional writers ready to assist you.
Connect with our essay writing service now and receive expert guidance and support to elevate your research paper to the next level.
Cathy A. (Law)
For more than five years now, Cathy has been one of our most hardworking authors on the platform. With a Masters degree in mass communication, she knows the ins and outs of professional writing. Clients often leave her glowing reviews for being an amazing writer who takes her work very seriously.
Paper Due? Why Suffer? That’s our Job!

Keep reading

- Privacy Policy
- Cookies Policy
- Terms of Use
- Refunds & Cancellations
- Our Writers
- Success Stories
- Our Guarantees
- Affiliate Program
- Referral Program
- AI Essay Writer
Disclaimer: All client orders are completed by our team of highly qualified human writers. The essays and papers provided by us are not to be used for submission but rather as learning models only.
Is a robot writing your kids’ essays? We asked educators to weigh in on the growing role of AI in classrooms.
Educators weigh in on the growing role of ai and chatgpt in classrooms..

Remember writing essays in high school? Chances are you had to look up stuff in an encyclopedia — an actual one, not Wikipedia — or else connect to AOL via a modem bigger than your parents’ Taurus station wagon.
Now, of course, there’s artificial intelligence. According to new research from Pew, about 1 in 5 US teens who’ve heard of ChatGPT have used it for schoolwork. Kids in upper grades are more apt to have used the chatbot: About a quarter of 11th- and 12th-graders who know about ChatGPT have tried it.
For the uninitiated, ChatGPT arrived on the scene in late 2022, and educators continue to grapple with the ethics surrounding its growing popularity. Essentially, it generates free, human-like responses based on commands. (I’m sure this sentence will look antiquated in about six months, like when people described the internet as the “information superhighway.”)
Advertisement
I used ChatGPT to plug in this prompt: “Write an essay on ‘The Scarlet Letter.’” Within moments, ChatGPT created an essay as thorough as anything I’d labored over in AP English.
Is this cheating? Is it just part of our strange new world? I talked to several educators about what they’re seeing in classrooms and how they’re monitoring it. Before you berate your child over how you wrote essays with a No. 2 pencil, here are some things to consider.
Adapting to new technology isn’t immoral. “We have to recalibrate our sense of what’s acceptable. There was a time when every teacher said: ‘Oh, it’s cheating to use Wikipedia.’ And guess what? We got used to it, we decided it’s reputable enough, and we cite Wikipedia all the time,” says Noah Giansiracusa, an associate math professor at Bentley University who hosts the podcast “ AI in Academia: Navigating the Future .”
“There’s a calibration period where a technology is new and untested. It’s good to be cautious and to treat it with trepidation. Then, over time, the norms kind of adapt,” he says — just like new-fangled graphing calculators or the internet in days of yore.
“I think the current conversation around AI should not be centered on an issue with plagiarism. It should be centered on how AI will alter methods for learning and expressing oneself. ‘Catching’ students who use fully AI-generated products ... implies a ‘gotcha’ atmosphere,” says Jim Nagle, a history teacher at Bedford High School. “Since AI is already a huge part of our day-to-day lives, it’s no surprise our students are making it a part of their academic tool kit. Teachers and students should be at the forefront of discussions about responsible and ethical use.”

Teachers and parents could use AI to think about education at a higher level. Really, learning is about more than regurgitating information — or it should be, anyway. But regurgitation is what AI does best.
“If our system is just for students to write a bunch of essays and then grade the results? Something’s missing. We need to really talk about their purpose and what they’re getting out of this, and maybe think about different forms of assignments and grading,” Giansiracusa says.
After all, while AI aggregates and organizes ideas, the quality of its responses depends on the users’ prompts. Instead of recoiling from it, use it as a conversation-starter.
“What parents and teachers can do is to start the conversation with kids: ‘What are we trying to learn here? Is it even something that ChatGPT could answer? Why did your assignment not convince you that you need to do this thinking on your own when a tool can do it for you?’” says Houman Harouni , a lecturer on education at the Harvard Graduate School of Education.
Harouni urges parents to read an essay written by ChatGPT alongside their student. Was it good? What could be done better? Did it feel like a short cut?
“What they’re going to remember is that you had that conversation with them; that someone thought, at some point in their lives, that taking a shortcut is not the best way ... especially if you do it with the tool right in front of you, because you have something real to talk about,” he says.
Harouni hopes teachers think about its implications, too. Consider math: So much grunt work has been eliminated by calculators and computers. Yet kids are still tested as in days of old, when perhaps they could expand their learning to be assessed in ways that are more personal and human-centric, leaving the rote stuff to AI.
“We could take this moment of confusion and loss of certainty seriously, at least in some small pockets, and start thinking about what a different kind of school would look like. Five years from now, we might have the beginnings of some very interesting exploration. Five years from now, you and I might be talking about schools wherein teaching and learning is happening in a very self-directed way, in a way that’s more based on … igniting the kid’s interest and seeing where they go and supporting them to go deeper and to go wider,” Harouni says.
Teachers have the chance to offer assignments with more intentionality.
“Really think about the purpose of the assignments. Don’t just think of the outcome and the deliverable: ‘I need a student to produce a document.’ Why are we getting students to write? Why are we doing all these things in the first place? If teachers are more mindful, and maybe parents can also be more mindful, I think it pushes us away from this dangerous trap of thinking about in terms of ‘cheating,’ which, to me, is a really slippery path,” Giansiracusa says.
AI can boost confidence and reduce procrastination. Sometimes, a robot can do something better than a human, such as writing a dreaded resume and cover letter. And that’s OK; it’s useful, even.
“Often, students avoid applying to internships because they’re just overwhelmed at the thought of writing a cover letter, or they’re afraid their resume isn’t good enough. I think that tools like this can help them feel more confident. They may be more likely to do it sooner and have more organized and better applications,” says Kristin Casasanto, director of post-graduate planning at Olin College of Engineering.
Casasanto says that AI is also useful for de-stressing during interview prep.
“Students can use generative AI to plug in a job description and say, ‘Come up with a list of interview questions based on the job description,’ which will give them an idea of what may be asked, and they can even then say, ‘Here’s my resume. Give me answers to these questions based on my skills and experience.’ They’re going to really build their confidence around that,” Casasanto says.
Plus, when students use AI for basics, it frees up more time to meet with career counselors about substantive issues.
“It will help us as far as scalability. … Career services staff can then utilize our personal time in much more meaningful ways with students,” Casasanto says.
We need to remember: These kids grew up during a pandemic. We can’t expect kids to resist technology when they’ve been forced to learn in new ways since COVID hit.
“Now we’re seeing pandemic-era high school students come into college. They’ve been channeled through Google Classroom their whole career,” says Katherine Jewell, a history professor at Fitchburg State University.
“They need to have technology management and information literacy built into the curriculum,” Jewell says.
Jewell recently graded a paper on the history of college sports. It was obvious which papers were written by AI: They didn’t address the question. In her syllabus, Jewell defines plagiarism as “any attempt by a student to represent the work of another, including computers, as their own.”
This means that AI qualifies, but she also has an open mind, given students’ circumstances.
“My students want to do the right thing, for the most part. They don’t want to get away with stuff. I understand why they turned to these tools; I really do. I try to reassure them that I’m here to help them learn systems. I’m focusing much more on the learning process. I incentivize them to improve, and I acknowledge: ‘You don’t know how to do this the first time out of the gate,’” Jewell says. “I try to incentivize them so that they’re improving their confidence in their abilities, so they don’t feel the need to turn to these tools.”
Understand the forces that make kids resort to AI in the first place . Clubs, sports, homework: Kids are busy and under pressure. Why not do what’s easy?
“Kids are so overscheduled in their day-to-day lives. I think there’s so much enormous pressure on these kids, whether it’s self-inflicted, parent-inflicted, or school-culture inflicted. It’s on them to maximize their schedule. They’ve learned that AI can be a way to take an assignment that would take five hours and cut it down to one,” says a teacher at a competitive high school outside Boston who asked to remain anonymous.
Recently, this teacher says, “I got papers back that were just so robotic and so cold. I had to tell [students]: ‘I understand that you tried to use a tool to help you. I’m not going to penalize you, but what I am going to penalize you for is that you didn’t actually answer the prompt.”
Afterward, more students felt safe to come forward to say they’d used AI. This teacher hopes that age restrictions become implemented for these programs, similar to apps such as Snapchat. Educationally and developmentally, they say, high-schoolers are still finding their voice — a voice that could be easily thwarted by a robot.
“Part of high school writing is to figure out who you are, and what is your voice as a writer. And I think, developmentally, that takes all of high school to figure out,” they say.
And AI can’t replicate voice and personality — for now, at least.
Kara Baskin can be reached at [email protected] . Follow her @kcbaskin .
Have a language expert improve your writing
Run a free plagiarism check in 10 minutes, generate accurate citations for free.
- Knowledge Base
- Academic writing
- A step-by-step guide to the writing process
The Writing Process | 5 Steps with Examples & Tips
Published on April 24, 2020 by Jack Caulfield . Revised on December 8, 2023.

Good academic writing requires effective planning, drafting, and revision.
The writing process looks different for everyone, but there are five basic steps that will help you structure your time when writing any kind of text.
Receive feedback on language, structure, and formatting
Professional editors proofread and edit your paper by focusing on:
- Academic style
- Vague sentences
- Style consistency
See an example

Table of contents
Step 1: prewriting, step 2: planning and outlining, step 3: writing a first draft, step 4: redrafting and revising, step 5: editing and proofreading, other interesting articles, frequently asked questions about the writing process.
Before you start writing, you need to decide exactly what you’ll write about and do the necessary research.
Coming up with a topic
If you have to come up with your own topic for an assignment, think of what you’ve covered in class— is there a particular area that intrigued, interested, or even confused you? Topics that left you with additional questions are perfect, as these are questions you can explore in your writing.
The scope depends on what type of text you’re writing—for example, an essay or a research paper will be less in-depth than a dissertation topic . Don’t pick anything too ambitious to cover within the word count, or too limited for you to find much to say.
Narrow down your idea to a specific argument or question. For example, an appropriate topic for an essay might be narrowed down like this:
Doing the research
Once you know your topic, it’s time to search for relevant sources and gather the information you need. This process varies according to your field of study and the scope of the assignment. It might involve:
- Searching for primary and secondary sources .
- Reading the relevant texts closely (e.g. for literary analysis ).
- Collecting data using relevant research methods (e.g. experiments , interviews or surveys )
From a writing perspective, the important thing is to take plenty of notes while you do the research. Keep track of the titles, authors, publication dates, and relevant quotations from your sources; the data you gathered; and your initial analysis or interpretation of the questions you’re addressing.
Here's why students love Scribbr's proofreading services
Discover proofreading & editing
Especially in academic writing , it’s important to use a logical structure to convey information effectively. It’s far better to plan this out in advance than to try to work out your structure once you’ve already begun writing.
Creating an essay outline is a useful way to plan out your structure before you start writing. This should help you work out the main ideas you want to focus on and how you’ll organize them. The outline doesn’t have to be final—it’s okay if your structure changes throughout the writing process.
Use bullet points or numbering to make your structure clear at a glance. Even for a short text that won’t use headings, it’s useful to summarize what you’ll discuss in each paragraph.
An outline for a literary analysis essay might look something like this:
- Describe the theatricality of Austen’s works
- Outline the role theater plays in Mansfield Park
- Introduce the research question: How does Austen use theater to express the characters’ morality in Mansfield Park ?
- Discuss Austen’s depiction of the performance at the end of the first volume
- Discuss how Sir Bertram reacts to the acting scheme
- Introduce Austen’s use of stage direction–like details during dialogue
- Explore how these are deployed to show the characters’ self-absorption
- Discuss Austen’s description of Maria and Julia’s relationship as polite but affectionless
- Compare Mrs. Norris’s self-conceit as charitable despite her idleness
- Summarize the three themes: The acting scheme, stage directions, and the performance of morals
- Answer the research question
- Indicate areas for further study
Once you have a clear idea of your structure, it’s time to produce a full first draft.
This process can be quite non-linear. For example, it’s reasonable to begin writing with the main body of the text, saving the introduction for later once you have a clearer idea of the text you’re introducing.
To give structure to your writing, use your outline as a framework. Make sure that each paragraph has a clear central focus that relates to your overall argument.
Hover over the parts of the example, from a literary analysis essay on Mansfield Park , to see how a paragraph is constructed.
The character of Mrs. Norris provides another example of the performance of morals in Mansfield Park . Early in the novel, she is described in scathing terms as one who knows “how to dictate liberality to others: but her love of money was equal to her love of directing” (p. 7). This hypocrisy does not interfere with her self-conceit as “the most liberal-minded sister and aunt in the world” (p. 7). Mrs. Norris is strongly concerned with appearing charitable, but unwilling to make any personal sacrifices to accomplish this. Instead, she stage-manages the charitable actions of others, never acknowledging that her schemes do not put her own time or money on the line. In this way, Austen again shows us a character whose morally upright behavior is fundamentally a performance—for whom the goal of doing good is less important than the goal of seeming good.
When you move onto a different topic, start a new paragraph. Use appropriate transition words and phrases to show the connections between your ideas.
The goal at this stage is to get a draft completed, not to make everything perfect as you go along. Once you have a full draft in front of you, you’ll have a clearer idea of where improvement is needed.
Give yourself a first draft deadline that leaves you a reasonable length of time to revise, edit, and proofread before the final deadline. For a longer text like a dissertation, you and your supervisor might agree on deadlines for individual chapters.
Now it’s time to look critically at your first draft and find potential areas for improvement. Redrafting means substantially adding or removing content, while revising involves making changes to structure and reformulating arguments.
Evaluating the first draft
It can be difficult to look objectively at your own writing. Your perspective might be positively or negatively biased—especially if you try to assess your work shortly after finishing it.
It’s best to leave your work alone for at least a day or two after completing the first draft. Come back after a break to evaluate it with fresh eyes; you’ll spot things you wouldn’t have otherwise.
When evaluating your writing at this stage, you’re mainly looking for larger issues such as changes to your arguments or structure. Starting with bigger concerns saves you time—there’s no point perfecting the grammar of something you end up cutting out anyway.
Right now, you’re looking for:
- Arguments that are unclear or illogical.
- Areas where information would be better presented in a different order.
- Passages where additional information or explanation is needed.
- Passages that are irrelevant to your overall argument.
For example, in our paper on Mansfield Park , we might realize the argument would be stronger with more direct consideration of the protagonist Fanny Price, and decide to try to find space for this in paragraph IV.
For some assignments, you’ll receive feedback on your first draft from a supervisor or peer. Be sure to pay close attention to what they tell you, as their advice will usually give you a clearer sense of which aspects of your text need improvement.
Redrafting and revising
Once you’ve decided where changes are needed, make the big changes first, as these are likely to have knock-on effects on the rest. Depending on what your text needs, this step might involve:
- Making changes to your overall argument.
- Reordering the text.
- Cutting parts of the text.
- Adding new text.
You can go back and forth between writing, redrafting and revising several times until you have a final draft that you’re happy with.
Think about what changes you can realistically accomplish in the time you have. If you are running low on time, you don’t want to leave your text in a messy state halfway through redrafting, so make sure to prioritize the most important changes.
Check for common mistakes
Use the best grammar checker available to check for common mistakes in your text.
Fix mistakes for free
Editing focuses on local concerns like clarity and sentence structure. Proofreading involves reading the text closely to remove typos and ensure stylistic consistency. You can check all your drafts and texts in minutes with an AI proofreader .
Editing for grammar and clarity
When editing, you want to ensure your text is clear, concise, and grammatically correct. You’re looking out for:
- Grammatical errors.
- Ambiguous phrasings.
- Redundancy and repetition .
In your initial draft, it’s common to end up with a lot of sentences that are poorly formulated. Look critically at where your meaning could be conveyed in a more effective way or in fewer words, and watch out for common sentence structure mistakes like run-on sentences and sentence fragments:
- Austen’s style is frequently humorous, her characters are often described as “witty.” Although this is less true of Mansfield Park .
- Austen’s style is frequently humorous. Her characters are often described as “witty,” although this is less true of Mansfield Park .
To make your sentences run smoothly, you can always use a paraphrasing tool to rewrite them in a clearer way.
Proofreading for small mistakes and typos
When proofreading, first look out for typos in your text:
- Spelling errors.
- Missing words.
- Confused word choices .
- Punctuation errors .
- Missing or excess spaces.
Use a grammar checker , but be sure to do another manual check after. Read through your text line by line, watching out for problem areas highlighted by the software but also for any other issues it might have missed.
For example, in the following phrase we notice several errors:
- Mary Crawfords character is a complicate one and her relationships with Fanny and Edmund undergoes several transformations through out the novel.
- Mary Crawford’s character is a complicated one, and her relationships with both Fanny and Edmund undergo several transformations throughout the novel.
Proofreading for stylistic consistency
There are several issues in academic writing where you can choose between multiple different standards. For example:
- Whether you use the serial comma .
- Whether you use American or British spellings and punctuation (you can use a punctuation checker for this).
- Where you use numerals vs. words for numbers.
- How you capitalize your titles and headings.
Unless you’re given specific guidance on these issues, it’s your choice which standards you follow. The important thing is to consistently follow one standard for each issue. For example, don’t use a mixture of American and British spellings in your paper.
Additionally, you will probably be provided with specific guidelines for issues related to format (how your text is presented on the page) and citations (how you acknowledge your sources). Always follow these instructions carefully.
If you want to know more about AI for academic writing, AI tools, or fallacies make sure to check out some of our other articles with explanations and examples or go directly to our tools!
- Ad hominem fallacy
- Post hoc fallacy
- Appeal to authority fallacy
- False cause fallacy
- Sunk cost fallacy
- Deep learning
- Generative AI
- Machine learning
- Reinforcement learning
- Supervised vs. unsupervised learning
(AI) Tools
- Grammar Checker
- Paraphrasing Tool
- Text Summarizer
- AI Detector
- Plagiarism Checker
- Citation Generator
Revising, proofreading, and editing are different stages of the writing process .
- Revising is making structural and logical changes to your text—reformulating arguments and reordering information.
- Editing refers to making more local changes to things like sentence structure and phrasing to make sure your meaning is conveyed clearly and concisely.
- Proofreading involves looking at the text closely, line by line, to spot any typos and issues with consistency and correct them.
Whether you’re publishing a blog, submitting a research paper , or even just writing an important email, there are a few techniques you can use to make sure it’s error-free:
- Take a break : Set your work aside for at least a few hours so that you can look at it with fresh eyes.
- Proofread a printout : Staring at a screen for too long can cause fatigue – sit down with a pen and paper to check the final version.
- Use digital shortcuts : Take note of any recurring mistakes (for example, misspelling a particular word, switching between US and UK English , or inconsistently capitalizing a term), and use Find and Replace to fix it throughout the document.
If you want to be confident that an important text is error-free, it might be worth choosing a professional proofreading service instead.
If you’ve gone over the word limit set for your assignment, shorten your sentences and cut repetition and redundancy during the editing process. If you use a lot of long quotes , consider shortening them to just the essentials.
If you need to remove a lot of words, you may have to cut certain passages. Remember that everything in the text should be there to support your argument; look for any information that’s not essential to your point and remove it.
To make this process easier and faster, you can use a paraphrasing tool . With this tool, you can rewrite your text to make it simpler and shorter. If that’s not enough, you can copy-paste your paraphrased text into the summarizer . This tool will distill your text to its core message.
Cite this Scribbr article
If you want to cite this source, you can copy and paste the citation or click the “Cite this Scribbr article” button to automatically add the citation to our free Citation Generator.
Caulfield, J. (2023, December 08). The Writing Process | 5 Steps with Examples & Tips. Scribbr. Retrieved March 28, 2024, from https://www.scribbr.com/academic-writing/writing-process/
Is this article helpful?

Jack Caulfield
Other students also liked, how to create a structured research paper outline | example, quick guide to proofreading | what, why and how to proofread, academic paragraph structure | step-by-step guide & examples, what is your plagiarism score.
- Share full article
Advertisement
Supported by
Guest Essay
A.I.-Generated Garbage Is Polluting Our Culture

By Erik Hoel
Mr. Hoel is a neuroscientist and novelist and the author of The Intrinsic Perspective newsletter.
Increasingly, mounds of synthetic A.I.-generated outputs drift across our feeds and our searches. The stakes go far beyond what’s on our screens. The entire culture is becoming affected by A.I.’s runoff, an insidious creep into our most important institutions.
Consider science. Right after the blockbuster release of GPT-4, the latest artificial intelligence model from OpenAI and one of the most advanced in existence, the language of scientific research began to mutate. Especially within the field of A.I. itself.

Adjectives associated with A.I.-generated text have increased in peer reviews of scientific papers about A.I.
Frequency of adjectives per one million words
Commendable

A study published this month examined scientists’ peer reviews — researchers’ official pronouncements on others’ work that form the bedrock of scientific progress — across a number of high-profile and prestigious scientific conferences studying A.I. At one such conference, those peer reviews used the word “meticulous” more than 34 times as often as reviews did the previous year. Use of “commendable” was around 10 times as frequent, and “intricate,” 11 times. Other major conferences showed similar patterns.
Such phrasings are, of course, some of the favorite buzzwords of modern large language models like ChatGPT. In other words, significant numbers of researchers at A.I. conferences were caught handing their peer review of others’ work over to A.I. — or, at minimum, writing them with lots of A.I. assistance. And the closer to the deadline the submitted reviews were received, the more A.I. usage was found in them.
If this makes you uncomfortable — especially given A.I.’s current unreliability — or if you think that maybe it shouldn’t be A.I.s reviewing science but the scientists themselves, those feelings highlight the paradox at the core of this technology: It’s unclear what the ethical line is between scam and regular usage. Some A.I.-generated scams are easy to identify, like the medical journal paper featuring a cartoon rat sporting enormous genitalia. Many others are more insidious, like the mislabeled and hallucinated regulatory pathway described in that same paper — a paper that was peer reviewed as well (perhaps, one might speculate, by another A.I.?).
What about when A.I. is used in one of its intended ways — to assist with writing? Recently, there was an uproar when it became obvious that simple searches of scientific databases returned phrases like “As an A.I. language model” in places where authors relying on A.I. had forgotten to cover their tracks. If the same authors had simply deleted those accidental watermarks, would their use of A.I. to write their papers have been fine?
What’s going on in science is a microcosm of a much bigger problem. Post on social media? Any viral post on X now almost certainly includes A.I.-generated replies, from summaries of the original post to reactions written in ChatGPT’s bland Wikipedia-voice, all to farm for follows. Instagram is filling up with A.I.-generated models, Spotify with A.I.-generated songs. Publish a book? Soon after, on Amazon there will often appear A.I.-generated “workbooks” for sale that supposedly accompany your book (which are incorrect in their content; I know because this happened to me). Top Google search results are now often A.I.-generated images or articles. Major media outlets like Sports Illustrated have been creating A.I.-generated articles attributed to equally fake author profiles. Marketers who sell search engine optimization methods openly brag about using A.I. to create thousands of spammed articles to steal traffic from competitors.
Then there is the growing use of generative A.I. to scale the creation of cheap synthetic videos for children on YouTube. Some example outputs are Lovecraftian horrors, like music videos about parrots in which the birds have eyes within eyes, beaks within beaks, morphing unfathomably while singing in an artificial voice, “The parrot in the tree says hello, hello!” The narratives make no sense, characters appear and disappear randomly, and basic facts like the names of shapes are wrong. After I identified a number of such suspicious channels on my newsletter, The Intrinsic Perspective, Wired found evidence of generative A.I. use in the production pipelines of some accounts with hundreds of thousands or even millions of subscribers.
As a neuroscientist, this worries me. Isn’t it possible that human culture contains within it cognitive micronutrients — things like cohesive sentences, narrations and character continuity — that developing brains need? Einstein supposedly said : “If you want your children to be intelligent, read them fairy tales. If you want them to be very intelligent, read them more fairy tales.” But what happens when a toddler is consuming mostly A.I.-generated dream-slop? We find ourselves in the midst of a vast developmental experiment.
There’s so much synthetic garbage on the internet now that A.I. companies and researchers are themselves worried, not about the health of the culture, but about what’s going to happen with their models. As A.I. capabilities ramped up in 2022, I wrote on the risk of culture’s becoming so inundated with A.I. creations that when future A.I.s are trained, the previous A.I. output will leak into the training set, leading to a future of copies of copies of copies, as content became ever more stereotyped and predictable. In 2023 researchers introduced a technical term for how this risk affected A.I. training: model collapse . In a way, we and these companies are in the same boat, paddling through the same sludge streaming into our cultural ocean.
With that unpleasant analogy in mind, it’s worth looking to what is arguably the clearest historical analogy for our current situation: the environmental movement and climate change. For just as companies and individuals were driven to pollute by the inexorable economics of it, so, too, is A.I.’s cultural pollution driven by a rational decision to fill the internet’s voracious appetite for content as cheaply as possible. While environmental problems are nowhere near solved, there has been undeniable progress that has kept our cities mostly free of smog and our lakes mostly free of sewage. How?
Before any specific policy solution was the acknowledgment that environmental pollution was a problem in need of outside legislation. Influential to this view was a perspective developed in 1968 by Garrett Hardin, a biologist and ecologist. Dr. Hardin emphasized that the problem of pollution was driven by people acting in their own interest, and that therefore “we are locked into a system of ‘fouling our own nest,’ so long as we behave only as independent, rational, free-enterprisers.” He summed up the problem as a “tragedy of the commons.” This framing was instrumental for the environmental movement, which would come to rely on government regulation to do what companies alone could or would not.
Once again we find ourselves enacting a tragedy of the commons: short-term economic self-interest encourages using cheap A.I. content to maximize clicks and views, which in turn pollutes our culture and even weakens our grasp on reality. And so far, major A.I. companies are refusing to pursue advanced ways to identify A.I.’s handiwork — which they could do by adding subtle statistical patterns hidden in word use or in the pixels of images.
A common justification for inaction is that human editors can always fiddle around with whatever patterns are implemented if they know enough. Yet many of the issues we’re experiencing are not caused by motivated and technically skilled malicious actors; they’re caused mostly by regular users’ not adhering to a line of ethical use so fine as to be nigh nonexistent. Most would be uninterested in advanced countermeasures to statistical patterns enforced into outputs that should, ideally, mark them as A.I.-generated.
That’s why the independent researchers were able to detect A.I. outputs in the peer review system with surprisingly high accuracy: They actually tried. Similarly, right now teachers across the nation have created home-brewed output-side detection methods , like adding in hidden requests for patterns of word use to essay prompts that appear only when copy-pasted.
In particular, A.I. companies appear opposed to any patterns baked into their output that can improve A.I.-detection efforts to reasonable levels, perhaps because they fear that enforcing such patterns might interfere with the model’s performance by constraining its outputs too much — although there is no current evidence this is a risk. Despite public pledges to develop more advanced watermarking, it’s increasingly clear that the companies are dragging their feet because it goes against the A.I. industry’s bottom line to have detectable products.
To deal with this corporate refusal to act we need the equivalent of a Clean Air Act: a Clean Internet Act. Perhaps the simplest solution would be to legislatively force advanced watermarking intrinsic to generated outputs, like patterns not easily removable. Just as the 20th century required extensive interventions to protect the shared environment, the 21st century is going to require extensive interventions to protect a different, but equally critical, common resource, one we haven’t noticed up until now since it was never under threat: our shared human culture.
Erik Hoel is a neuroscientist, a novelist and the author of The Intrinsic Perspective newsletter.
The Times is committed to publishing a diversity of letters to the editor. We’d like to hear what you think about this or any of our articles. Here are some tips . And here’s our email: [email protected] .
Follow the New York Times Opinion section on Facebook , Instagram , TikTok , WhatsApp , X and Threads .

IMAGES
VIDEO
COMMENTS
Essay writing process. The writing process of preparation, writing, and revisions applies to every essay or paper, but the time and effort spent on each stage depends on the type of essay.. For example, if you've been assigned a five-paragraph expository essay for a high school class, you'll probably spend the most time on the writing stage; for a college-level argumentative essay, on the ...
Analytical Essays. As the name of this type of essay might suggest, it is an essay which is used to analyse something. This could be a piece of writing, a movie or anything else. The idea is that the analytical essay will look at what it is analysing from various viewpoints allowing the reader to form their own opinion.
Write your topic at the top of the page. List down all the main ideas. Leave space under each idea. In this space, list down smaller ideas that relates to the main idea. Following these steps for writing an essay outline will give you a complete idea of the themes required to be discussed in your paper. 4.
8 Types of Essays. To decide which essay style best suits your needs as a writer, check out the list below: 1. Expository essay: An expository essay, also known as a definition essay, is the most basic type of essay. Expository essays aim only to explain an idea or define a concept, without making an argument.
The essay is a written piece that is designed to present an idea, propose an argument, express the emotion or initiate debate. It is a tool that is used to present writer's ideas in a non-fictional way. Multiple applications of this type of writing go way beyond, providing political manifestos and art criticism as well as personal ...
Parts of an essay. An impactful, well-structured essay comes down to three important parts: the introduction, body, and conclusion. 1. The introduction sets the stage for your essay and is typically a paragraph long. It should grab the reader's attention and give them a clear idea of what your essay will be about.
An essay is a written composition that presents and supports a particular idea, argument, or point of view. It's a way to express your thoughts, share information, and persuade others to see things from your perspective. Essays come in various forms, such as argumentative, persuasive, expository, and descriptive, each serving a unique purpose.
Essay Writing. This resource begins with a general description of essay writing and moves to a discussion of common essay genres students may encounter across the curriculum. The four genres of essays (description, narration, exposition, and argumentation) are common paper assignments you may encounter in your writing classes.
Here's an example: The invention of the airplane by the Wright Brothers in 1903 revolutionized transportation and paved the way for modern aviation. It represents a monumental achievement in human history that forever changed the course of human civilization. 3. Create an essay outline.
Writing an essay is an essential part of school at any level. Become an essay expert with these essay examples to prepare you on your academic journey.
essay, an analytic, interpretative, or critical literary composition usually much shorter and less systematic and formal than a dissertation or thesis and usually dealing with its subject from a limited and often personal point of view. Some early treatises—such as those of Cicero on the pleasantness of old age or on the art of "divination ...
Writing a strong introduction is crucial for setting the tone and context of your essay. Here are the key takeaways for how to write essay introduction: 3. Hook the Reader: Start with an engaging hook to grab the reader's attention. This could be a compelling question, a surprising fact, a relevant quote, or an anecdote.
The basic structure of an essay always consists of an introduction, a body, and a conclusion. But for many students, the most difficult part of structuring an essay is deciding how to organize information within the body. This article provides useful templates and tips to help you outline your essay, make decisions about your structure, and ...
- The Writing Process: These features show all the steps taken to write a paper, allowing you to follow it from initial idea to published article. - Into the Essay: Excerpts from actual papers show the ideas from the chapters in action because you learn to write best by getting examples rather than instructions.
Essays of Michel de Montaigne. An essay is, generally, a piece of writing that gives the author's own argument, but the definition is vague, overlapping with those of a letter, a paper, an article, a pamphlet, and a short story.Essays have been sub-classified as formal and informal: formal essays are characterized by "serious purpose, dignity, logical organization, length," whereas the ...
4. State a definition essay thesis. It plays a great role in the whole work, concentrating both the author and the readers on the matter. The thesis reflects the main key points, supporting the definition of the selected concept. 5. Figure out the structure and outline of the work.
Academic Writing Example 4: Articles. Academic articles are pieces of writing intended for publication in academic journals or other scholarly sources. They may be original research studies, literature analyses, critiques, or other forms of scholarly writing. Article Structure. Title. Abstract and keywords. Introduction. Materials and methods ...
1. Identifying the thesis statement. A thesis statement is a brief summary of an essay that contains the main argument you are going to refer to throughout the whole text. Your essay writing process should always start with identifying a proper thesis statement as it will influence your line of reasoning and analysis.
An essay outline is a way of planning the structure of your essay before you start writing. It involves writing quick summary sentences or phrases for every point you will cover in each paragraph, giving you a picture of how your argument will unfold. You'll sometimes be asked to submit an essay outline as a separate assignment before you ...
Table 2 shows that the top three problems students face in academic writing have to do with not knowing what constitutes academic writing, not having enough ideas, and sentence cohesion. More than half of the students said that they did not know how to write academically (58.5%) and did not have enough ideas for writing (51.2%).
Prose is a straightforward form of writing that follows natural flow of language and doesn't use line breaks. Poetry, on the other hand, often uses structure such as rhyme, rhythm, and intentional line breaks. While not all poems have to rhyme, it's a signature of the form and many do. If you're interested in learning more about poetry ...
Overall, EssayGenius and JotBot were the best AI tools I tested. I was impressed by EssayGenius's ability to research the topic on its own and JotBot's mimicry of my own writing style. They do ...
Step 1: Define Your Topic and Research Questions. Before you venture into your quest for sources, it's essential to have a clear understanding of your research topic and the specific questions you aim to address. Define the scope of your paper and identify keywords and key concepts that will guide your search for relevant sources.
Table of contents. Step 1: Hook your reader. Step 2: Give background information. Step 3: Present your thesis statement. Step 4: Map your essay's structure. Step 5: Check and revise. More examples of essay introductions. Other interesting articles. Frequently asked questions about the essay introduction.
If you have questions about your submission, please write to us at [email protected] and provide the email address you used for submission. We invite students to write public-facing letters ...
Remember writing essays in high school? Chances are you had to look up stuff in an encyclopedia — an actual one, not Wikipedia — or else connect to AOL via a modem bigger than your parents ...
Table of contents. Step 1: Prewriting. Step 2: Planning and outlining. Step 3: Writing a first draft. Step 4: Redrafting and revising. Step 5: Editing and proofreading. Other interesting articles. Frequently asked questions about the writing process.
A.I.-Generated Garbage Is Polluting Our Culture. Mr. Hoel is a neuroscientist and novelist and the author of The Intrinsic Perspective newsletter. Increasingly, mounds of synthetic A.I.-generated ...