
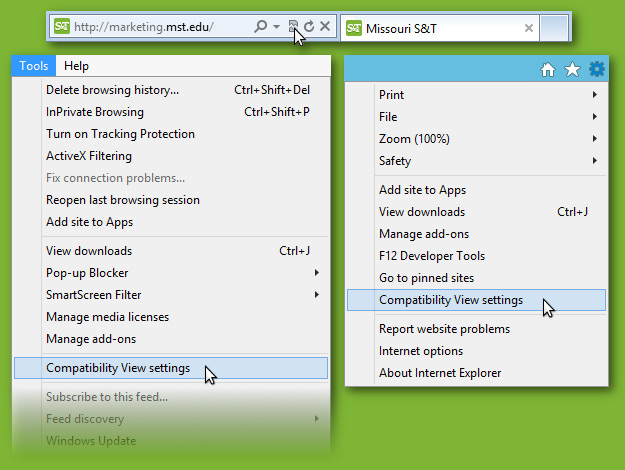
Your version of Internet Explorer is either running in "Compatibility View" or is too outdated to display this site. If you believe your version of Internet Explorer is up to date, please remove this site from Compatibility View by opening Tools > Compatibility View settings (IE11) or clicking the broken page icon in your address bar (IE9, IE10)

Missouri S&T Missouri S&T
- Future Students
- Current Students
- Faculty and Staff
- writingcenter.mst.edu
- Online Resources
- Writing Guides
- Counter Arguments
Writing and Communication Center
- 314 Curtis Laws Wilson Library, 400 W 14th St Rolla, MO 65409 United States
- (573) 341-4436
- [email protected]
Counter Argument
One way to strengthen your argument and demonstrate a comprehensive understanding of the issue you are discussing is to anticipate and address counter arguments, or objections. By considering opposing views, you show that you have thought things through, and you dispose of some of the reasons your audience might have for not accepting your argument. Ask yourself what someone who disagrees with you might say in response to each of the points you’ve made or about your position as a whole.
If you can’t immediately imagine another position, here are some strategies to try:
- Do some research. It may seem to you that no one could possibly disagree with the position you are taking, but someone probably has. Look around to see what stances people have and do take on the subject or argument you plan to make, so that you know what environment you are addressing.
- Talk with a friend or with your instructor. Another person may be able to play devil’s advocate and suggest counter arguments that haven’t occurred to you.
- Consider each of your supporting points individually. Even if you find it difficult to see why anyone would disagree with your central argument, you may be able to imagine more easily how someone could disagree with the individual parts of your argument. Then you can see which of these counter arguments are most worth considering. For example, if you argued “Cats make the best pets. This is because they are clean and independent,” you might imagine someone saying “Cats do not make the best pets. They are dirty and demanding.”
Once you have considered potential counter arguments, decide how you might respond to them: Will you concede that your opponent has a point but explain why your audience should nonetheless accept your argument? Or will you reject the counterargument and explain why it is mistaken? Either way, you will want to leave your reader with a sense that your argument is stronger than opposing arguments.
Two strategies are available to incorporate counter arguments into your essay:
Refutation:
Refutation seeks to disprove opposing arguments by pointing out their weaknesses. This approach is generally most effective if it is not hostile or sarcastic; with methodical, matter-of-fact language, identify the logical, theoretical, or factual flaws of the opposition.
For example, in an essay supporting the reintroduction of wolves into western farmlands, a writer might refute opponents by challenging the logic of their assumptions:
Although some farmers have expressed concern that wolves might pose a threat to the safety of sheep, cattle, or even small children, their fears are unfounded. Wolves fear humans even more than humans fear wolves and will trespass onto developed farmland only if desperate for food. The uninhabited wilderness that will become the wolves’ new home has such an abundance of food that there is virtually no chance that these shy animals will stray anywhere near humans.
Here, the writer acknowledges the opposing view (wolves will endanger livestock and children) and refutes it (the wolves will never be hungry enough to do so).
Accommodation:
Accommodation acknowledges the validity of the opposing view, but argues that other considerations outweigh it. In other words, this strategy turns the tables by agreeing (to some extent) with the opposition.
For example, the writer arguing for the reintroduction of wolves might accommodate the opposing view by writing:
Critics of the program have argued that reintroducing wolves is far too expensive a project to be considered seriously at this time. Although the reintroduction program is costly, it will only become more costly the longer it is put on hold. Furthermore, wolves will help control the population of pest animals in the area, saving farmers money on extermination costs. Finally, the preservation of an endangered species is worth far more to the environment and the ecological movement than the money that taxpayers would save if this wolf relocation initiative were to be abandoned.
This writer acknowledges the opposing position (the program is too expensive), agrees (yes, it is expensive), and then argues that despite the expense the program is worthwhile.
Some Final Hints
Don’t play dirty. When you summarize opposing arguments, be charitable. Present each argument fairly and objectively, rather than trying to make it look foolish. You want to convince your readers that you have carefully considered all sides of the issues and that you are not simply attacking or caricaturing your opponents.
Sometimes less is more. It is usually better to consider one or two serious counter arguments in some depth, rather than to address every counterargument.
Keep an open mind. Be sure that your reply is consistent with your original argument. Careful consideration of counter arguments can complicate or change your perspective on an issue. There’s nothing wrong with adopting a different perspective or changing your mind, but if you do, be sure to revise your thesis accordingly.
Table of Contents
Collaboration, information literacy, writing process, counterarguments – rebuttal – refutation.
- © 2023 by Roberto León - Georgia College & State University
Ignoring what your target audience thinks and feels about your argument isn't a recipe for success. Instead, engage in audience analysis : ask yourself, "How is your target audience likely to respond to your propositions? What counterarguments -- arguments about your argument -- will your target audience likely raise before considering your propositions?"

Counterargument Definition
C ounterargument refers to an argument given in response to another argument that takes an alternative approach to the issue at hand.
C ounterargument may also be known as rebuttal or refutation .
Related Concepts: Audience Awareness ; Authority (in Speech and Writing) ; Critical Literacy ; Ethos ; Openness ; Researching Your Audience
Guide to Counterarguments in Writing Studies
Counterarguments are a topic of study in Writing Studies as
- Rhetors engage in rhetorical reasoning : They analyze the rebuttals their target audiences may have to their claims , interpretations , propositions, and proposals
- Rhetors may develop counterarguments by questioning a rhetor’s backing , data , qualifiers, and/or warrants
- Rhetors begin arguments with sincere summaries of counterarguments
- a strategy of Organization .
Learning about the placement of counterarguments in Toulmin Argument , Arisotelian Argument , and Rogerian Argument will help you understand when you need to introduce counterarguments and how thoroughly you need to address them.
Why Do Counterarguments Matter?
If your goal is clarity and persuasion, you cannot ignore what your target audience thinks, feels, and does about the argument. To communicate successfully with audiences, rhetors need to engage in audience analysis : they need to understand the arguments against their argument that the audience may hold.
Imagine that you are scrolling through your social media feed when you see a post from an old friend. As you read, you immediately feel that your friend’s post doesn’t make sense. “They can’t possibly believe that!” you tell yourself. You quickly reply “I’m not sure I agree. Why do you believe that?” Your friend then posts a link to an article and tells you to see for yourself.
There are many ways to analyze your friend’s social media post or the professor’s article your friend shared. You might, for example, evaluate the professor’s article by using the CRAAP Test or by conducting a rhetorical analysis of their aims and ethos . After engaging in these prewriting heuristics to get a better sense of what your friend knows and feels about the topic at hand, you may feel more prepared to respond to their arguments and also sense how they might react to your post.

Toulmin Counterarguments
There’s more than one way to counter an argument.
In Toulmin Argument , a counterargument can be made against the writer’s claim by questioning their backing , data , qualifiers, and/or warrants . For example, let’s say we wrote the following argument:
“Social media is bad for you (claim) because it always (qualifier) promotes an unrealistic standard of beauty (backing). In this article, researchers found that most images were photoshopped (data). Standards should be realistic; if they are not, those standards are bad (warrant).”
Besides noting we might have a series of logical fallacies here, counterarguments and dissociations can be made against each of these parts:
- Against the qualifier: Social media does not always promote unrealistic standards.
- Against the backing : Social media presents but does not promote unrealistic standards.
- Against the data : This article focuses on Instagram; these findings are not applicable to Twitter.
- Against the warrant : How we approach standards matters more than the standards themselves; standards do not need to be realistic, but rather we need to be realistic about how we approach standards.
In generating and considering counterarguments and conditions of rebuttal, it is important to consider how we approach alternative views. Alternative viewpoints are opportunities not only to strengthen and contrast our own arguments with those of others; alternative viewpoints are also opportunities to nuance and develop our own arguments.
Let us continue to look at our social media argument and potential counterarguments. We might prepare responses to each of these potential counterarguments, anticipating the ways in which our audience might try to shift how we frame this situation. However, we might also concede that some of these counterarguments actually have good points.
For example, we might still believe that social media is bad, but perhaps we also need to consider more about
- What factors make it worse (nuance the qualifier)?
- Whether or not social media is a neutral tool or whether algorithms take advantage of our baser instincts (nuance the backing )
- Whether this applies to all social media or whether we want to focus on just one social media platform (nuance the data )
- How should we approach social standards (nuance the warrant )?
Identifying counterarguments can help us strengthen our arguments by helping us recognize the complexity of the issue at hand.

Neoclassical Argument – Aristotelian Argument
Learn how to compose a counterargument passage or section.
While Toulmin Argument focuses on the nuts and bolts of argumentation, a counterargument can also act as an entire section of an Aristotelian Argument . This section typically comes after you have presented your own lines of argument and evidence .
This section typically consists of two rhetorical moves :
Examples of Counterarguments
By introducing counterarguments, we show we are aware of alternative viewpoints— other definitions, explanations, meanings, solutions, etc. We want to show that we are good listeners and aren’t committing the strawman fallacy . We also concede some of the alternative viewpoints that we find most persuasive. By making concessions, we can show that we are reasonable ( ethos ) and that we are listening . Rogerian Argument is an example of building listening more fully into our writing.
Using our social media example, we might write:
I recognize that in many ways social media is only as good as the content that people upload to it. As Professor X argues, social media amplifies both the good and the bad of human nature.
Once we’ve shown that we understand and recognize good arguments when we see them, we put forward our response to the counterclaim. In our response, we do not simply dismiss alternative viewpoints, but provide our own backing, data, and warrants to show that we, in fact, have the more compelling position.
To counter Professor X’s argument, we might write:
At the same time, there are clear instances where social media amplifies the bad over the good by design. While content matters, the design of social media is only as good as the people who created it.
Through conceding and countering, we can show that we recognize others’ good points and clarify where we stand in relation to others’ arguments.
Counterarguments and Organization
Learn when and how to weave counterarguments into your texts.

As we write, it is also important to consider the extent to which we will respond to counterarguments. If we focus too much on counterarguments, we run the risk of downplaying our own contributions. If we focus too little on counterarguments, we run the risk of seeming aloof and unaware of reality. Ideally, we will be somewhere in between these two extremes.
There are many places to respond to counterarguments in our writing. Where you place your counterarguments will depend on the rhetorical situation (ex: audience , purpose, subject ), your rhetorical stance (how you want to present yourself), and your sense of kairos . Here are some common choices based on a combination of these rhetorical situation factors:
- If a counterargument is well-established for your audience, you may want to respond to that counterargument earlier in your essay, clearing the field and creating space for you to make your own arguments. An essay about gun rights, for example, would need to make it clear very quickly that it is adding something new to this old debate. Doing so shows your audience that you are very aware of their needs.
- If a counterargument is especially well-established for your audience and you simply want to prove that it is incorrect rather than discuss another solution, you might respond to it point by point, structuring your whole essay as an extended refutation. Fact-checking and commentary articles often make this move. Responding point by point shows that you take the other’s point of view seriously.
- If you are discussing something relatively unknown or new to your audience (such as a problem with black mold in your dormitory), you might save your response for after you have made your points. Including alternative viewpoints even here shows that you are aware of the situation and have nothing to hide.
Whichever you choose, remember that counterarguments are opportunities to ethically engage with alternative viewpoints and your audience.
The following questions can guide you as you begin to think about counterarguments:
- What is your argument ? What alternative positions might exist as counterarguments to your argument?
- How can considering counterarguments strengthen your argument?
- Given possible counterarguments, what points might you reconsider or concede?
- To what extent might you respond to counterarguments in your essay so that they can create and respond to the rhetorical situation ?
- Where might you place your counterarguments in your essay?
- What might including counterarguments do for your ethos ?
Recommended Resources
- Sweetland Center for Writing (n.d.). “ How Do I Incorporate a Counterargument? ” University of Michigan.
- The Writing Center (n.d.) “ All About Counterarguments .” George Mason University.
- Lachner, N. (n.d.). “ Counterarguments .” University of Nevada Reno, University Writing and Speaking Center.
- Jeffrey, R. (n.d.). “ Questions for Thinking about Counterarguments .” In M. Gagich and E. Zickel, A Guide to Rhetoric, Genre, and Success in First-Year Writing.
- Kause, S. (2011). “ On the Other Hand: The Role of Antithetical Writing in First Year Composition Courses .” Writing Spaces Vol. 2.
- Burton, G. “ Refutatio .” Silvae Rhetoricae.
Toulmin, S. (1958). The Uses of Argument. Cambridge University Press.
Perelman, C. and Olbrechts-Tyteca, L. (1971). “The Dissociation of Concepts”; “The Interaction of Arguments,” in The New Rhetoric: A Treatise on Argumentation (pp. 411-459, 460-508), University of Notre Dame Press.
Mozafari, C. (2018). “Crafting Counterarguments,” in Fearless Writing: Rhetoric, Inquiry, Argument (pp. 333-337), MacMillian Learning

Brevity - Say More with Less

Clarity (in Speech and Writing)

Coherence - How to Achieve Coherence in Writing

Flow - How to Create Flow in Writing

Inclusivity - Inclusive Language

The Elements of Style - The DNA of Powerful Writing

Suggested Edits
- Please select the purpose of your message. * - Corrections, Typos, or Edits Technical Support/Problems using the site Advertising with Writing Commons Copyright Issues I am contacting you about something else
- Your full name
- Your email address *
- Page URL needing edits *
- Email This field is for validation purposes and should be left unchanged.
Other Topics:

Citation - Definition - Introduction to Citation in Academic & Professional Writing
- Joseph M. Moxley
Explore the different ways to cite sources in academic and professional writing, including in-text (Parenthetical), numerical, and note citations.

Collaboration - What is the Role of Collaboration in Academic & Professional Writing?
Collaboration refers to the act of working with others or AI to solve problems, coauthor texts, and develop products and services. Collaboration is a highly prized workplace competency in academic...

Genre may reference a type of writing, art, or musical composition; socially-agreed upon expectations about how writers and speakers should respond to particular rhetorical situations; the cultural values; the epistemological assumptions...

Grammar refers to the rules that inform how people and discourse communities use language (e.g., written or spoken English, body language, or visual language) to communicate. Learn about the rhetorical...

Information Literacy - Discerning Quality Information from Noise
Information Literacy refers to the competencies associated with locating, evaluating, using, and archiving information. In order to thrive, much less survive in a global information economy — an economy where information functions as a...

Mindset refers to a person or community’s way of feeling, thinking, and acting about a topic. The mindsets you hold, consciously or subconsciously, shape how you feel, think, and act–and...

Rhetoric: Exploring Its Definition and Impact on Modern Communication
Learn about rhetoric and rhetorical practices (e.g., rhetorical analysis, rhetorical reasoning, rhetorical situation, and rhetorical stance) so that you can strategically manage how you compose and subsequently produce a text...

Style, most simply, refers to how you say something as opposed to what you say. The style of your writing matters because audiences are unlikely to read your work or...

The Writing Process - Research on Composing
The writing process refers to everything you do in order to complete a writing project. Over the last six decades, researchers have studied and theorized about how writers go about...

Writing Studies
Writing studies refers to an interdisciplinary community of scholars and researchers who study writing. Writing studies also refers to an academic, interdisciplinary discipline – a subject of study. Students in...
Featured Articles

Academic Writing – How to Write for the Academic Community

Professional Writing – How to Write for the Professional World

Authority – How to Establish Credibility in Speech & Writing

counter Meme Templates
Bad counter.

Counter Strike

Zero counter

counter-terrorist looking at the computer

Kung Fu Panda counterpt

Donald Trump correcting Kim Jong-Un

Mods. Pin him down and twist his nuts counter-clockwise.

Goku prowler.

Player counters yellow card from referee with Uno reverse card

Counterfeit Karen

Force Of Will

csgo facepalm


Counterpoint I'm in charge and I order you to be quiet

counter-strike

Full Counter

pora na CSa

Bomb has been planted - Counter Strike

counter strike

Sieg Geon! / Sieg Zeon! / ジークジオン!

Counter strike thumbs up

time for cs

counterstrike

Counter Strike Camping

doomguy counter

Counter Terrorist

cat pushing thing off counter

counter-terrorist talking to you

airline ticket counter

Kitten at counter Cat Cafe Bangkok Thailand

Counter Argument Classic Meme

heisenberg haircut

fake apple laptop

Dancing T CS GO

Batman vs the riddler

Counter Strike global offensive

Full counter

BackStabbers_Official Nuh uh pass

Your jordans are fake

Arguemental Counter GIF
- Arguemental Counter
Related GIFs
- #danganronpa
- #Hajime-Hinata
- #Critical-Role
25 Counterargument Examples

A counterargument is a response, rebuttal, or refutation of an argument with your own argument. Its purpose is to oppose and disprove a theory that someone else has put forward.
We use counterarguments extensively in debates as well as argumentative essay writing.
When teaching essay writing, I teach my students to always present counterarguments to their opponents’ points of view. This helps them to strengthen their own argument and demonstrate awareness of potential rebuttals.
Below are some methods, with examples, that could be used – be it in essay writing, debates, or any other communication genre.
Counterargument Examples
1. empirical challenges.
An empirical challenge is, simply, a rebuttal that challenges the facts presented by the opponent, showing that their facts are wrong and yours are right.
To undermine your opponent’s set of facts, it will be your job to present facts that show that the opponent’s supposed facts are wrong, perhaps due to misreading data or cherry-picking.
Then, you would need to present concrete information, data, or evidence that negates the claim or conclusion of an opponent’s argument.
The core strength of empirical challenges is in their reliance on hard facts and numbers, which are difficult to refute without equally credible opposing data.
Example of Empirical Challenge: If your opponent argues that global warming isn’t a serious issue, an empirical challenge would be to provide scientific data or research studies showing the increase in global temperatures and the harmful effects.
See Also: Empirical Evidence Examples
2. Challenging the Relevance
Challenging the relevance means questioning whether your opponent’s argument or perspective is applicable to the discussion at hand.
This sort of counter-argument seeks to destabilize your opponent’s view by showing that, while their facts or arguments might be sound in isolation, they do not bear any relation to, or are unfit for, the topic at hand, making them irrelevant.
The power of relevance challenge lays in its ability to destabilize your opponent’s argument without needing to directly dispute the truth of their claims.
Example of Challenging the Relevance: You will often find this argument when comparing the usefulness of various research methodologies for a research project. Multiple research methods may be valid, but there’s likely one that’s best for any given study.
See Also: Relevance Examples
3. Reductio ad absurdum
Reductio ad absurdum is a latin term that means reducing to the absurd . This method involves demonstrating the absurdity of an opponent’s argument by showing its illogical or extreme consequences.
The goal is to show that if the argument were valid, it would inevitably lead to senseless or ridiculous outcomes.
The application of reductio ad absurdum is especially effective in debates or discussions where flawed logic or hyperbolic statements are used to influence the audience’s opinion, as it discredits the credibility of the other person’s argument.
Example of Reductio ad absurdum : Consider a scenario where someone argues for the total removal of all regulations on vehicle speed to improve the efficiency of transportation. You can counter this argument through reductio ad absurdum by stating, “By that logic, let’s allow cars to travel at 200 miles per hour down residential streets. After all, it would make the mail delivery much faster!” It becomes evident that permitting extremely high speeds could lead to dangerous conditions and potential for disastrous accidents.
4. Pointing Out Logical Fallacies
The strategy of pointing out logical fallacies involves identifying and highlighting flaws in your opponent’s reasoning.
In a debate or discussion, logical fallacies are often subtle errors that lead to invalid conclusions or arguments.
By identifying these fallacies, you avoid being swayed by flawed reasoning and instead promote cognizant, logical thought.
Successful use of this strategy requires a good understanding of the different kinds of logical fallacies , such as straw man fallacies, ad hominem attacks, and appeals to ignorance.
Example of Pointing Out Logical Fallacies: Consider an argument where your opponent asserts, “All cats I’ve ever seen have been aloof, so all cats must be aloof.” This is a hasty generalization fallacy, where a conclusion about all members of a group is drawn from inadequate sample size.
5. Counterexamples
A counterexample is an example that opposes or contradicts an argument or theory proposed by another.
The use of a counterexample is a practical and powerful means of rebutting an argument or theory that has been presented as absolute or universally applicable.
When you provide a singular example that contradicts your opponent’s proposed theory, it demonstrates the theory isn’t universally true and therefore, weakens their argument.
However, this tactic requires sound knowledge and a good command of subject matter to be able to identify and present valid exceptions.
Example of Counterexamples: Consider an argument where someone states that “Mammals can’t lay eggs.” A solid counterexample would be the platypus, a mammal that does lay eggs. This single example is sufficient to contradict the universal claim.
6. Using Hypotheticals
Hypothetical situations, in essence, are imagined scenarios used to refute your opponent’s point of view. It’s, in essence, an example that is plausible, but not real.
Using hypotheticals assists in clarifying the ramifications of a particular argument, policy, or theory. When a hypothetical scenario effectively illustrates the flaws or shortcomings of your opponent’s viewpoint, it can completely unsettle their position.
However, care must be taken to frame the hypotheticals reasonably and realistically, lest they distort the argument or derail the conversation.
Example of Using Hypotheticals: If someone argues that raising the minimum wage will lead to job loss, you could counter with a hypothetical that if businesses paid their employees more, those employees would have more spending power, bolstering the economy and creating more jobs.
7. Comparison and Contrast
Comparison and contrast entails directly comparing your argument to your opponent’s, showing the strength of your perspective and the weakness of the opponent’s.
This tool allows you to support your arguments or disprove your opponent’s by using existing examples or situations that illustrate your point clearly.
The technique relies heavily on the logical thinking of comparing two or more entities in a manner that is informative, convincing, and significant to the argument.
Example of Comparison and Contrast: Let’s say, for instance, you are arguing against privatization of public utilities. You could compare the rates and services of private utilities to those of public ones showing that private companies often charge more for the same services, thereby supporting your argument against privatization.
See More: Compare and Contrast Examples
8. Challenging Biases
Challenging biases involves questioning the objectivity of your opponent’s argument by pointing out the predispositions that may influence their perspective.
Biases can greatly affect the validity and reliability of an argument because they can skew the interpretation of information and hinder fair judgement.
By challenging biases, you can expose the partiality in your opponent’s argument, thereby diminishing its credibility and persuasiveness.
However, it’s important to respectfully and tactfully challenge biases to prevent the discussion from turning into a personal attack.
Example of Challenging Biases: If your opponent is a staunch supporter of a political party and they provide an argument that solely favors this party, you could challenge their bias by questioning whether their support for the party is unduly influencing their viewpoint, hence the need for them to consider the opposing perspectives.
See More: List of Different Biases
9. Ethical Dispute
Ethical disputes involve challenging your opponent’s argument based on moral values or principles.
Ethics play a crucial role in shaping people’s beliefs, attitudes, and actions. Therefore, ethical disputes can serve as powerful counterarguments, especially in debates concerning sensitive or controversial topics.
If your opponent’s position contradicts generally accepted ethical norms or values, you can point this out to weaken their argument.
Just remember, ethics can occasionally be subjective and personal, so it’s important to approach ethical disputes with sensitivity and respect.
Example of Ethical Dispute: If your opponent supports factory farming based on economic benefits, you could challenge their argument by pointing out the ethical issues related to animal welfare and the environment.
10. Challenging the Source
Challenging the source is a tactic used to question the credibility or reliability of the information used by your opponent in their argument.
This technique focuses on examining the origin of the evidence presented, probing whether the source is credible, trusted, and free from bias.
To do this, I recommend using this media literacy framework .
If the source used by your opponent is flawed, biased or unreliable, their argument loses credibility, making your position stronger.
Example of Challenging the Source: If your opponent uses an obscure blog as their primary source of their argument on a scientific topic, you could challenge the source by questioning its credibility and offering information from reputable scientific journals instead.
See More: Good Sources for Essay Writing
A Full List of Methods for Counterargument
- Empirical challenges
- Challenging the relevance
- Reductio ad absurdum
- Pointing out logical fallacies
- Counterexamples
- Using hypotheticals
- Comparison and contrast
- Challenging biases
- Ethical dispute
- Challenging the source
- Questioning assumptions
- Slippery slope argument
- Challenging a false dichtomy
- Historical Precedent
- Anecdotal Evidence
- Challenging the Definition
- Socratic Questioning
- Highlighting Unintended Consequences
- Appeal to Emotion
- Challenging the Frame
- Highlighting Inconsistencies
- Challenging Completeness
- Temporal Challenge
- Offering alternative explanations
- Exposing oversimplifications
- Appeal to authority
Counterargument is an essential skill for debaters and essay writers. You need to be able to know and understand strategies for countering the arguments of your opponents to position your argument in the best light possible. To do this, we have to vectors of attack: First, you can undermine their arguments and demonstrate the flaws. Second, you can present your argument as stronger.
The key, however, is to ensure your arguments are as airtight and foolproof as possible to prevent effective rebuttals to your own counterarguments!

Chris Drew (PhD)
Dr. Chris Drew is the founder of the Helpful Professor. He holds a PhD in education and has published over 20 articles in scholarly journals. He is the former editor of the Journal of Learning Development in Higher Education. [Image Descriptor: Photo of Chris]
- Chris Drew (PhD) https://helpfulprofessor.com/author/chris-drew-phd/ 5 Top Tips for Succeeding at University
- Chris Drew (PhD) https://helpfulprofessor.com/author/chris-drew-phd/ 50 Durable Goods Examples
- Chris Drew (PhD) https://helpfulprofessor.com/author/chris-drew-phd/ 100 Consumer Goods Examples
- Chris Drew (PhD) https://helpfulprofessor.com/author/chris-drew-phd/ 30 Globalization Pros and Cons
Leave a Comment Cancel Reply
Your email address will not be published. Required fields are marked *
Consider the following thesis for a short paper that analyzes different approaches to stopping climate change:
Climate activism that focuses on personal actions such as recycling obscures the need for systemic change that will be required to slow carbon emissions.
The author of this thesis is promising to make the case that personal actions not only will not solve the climate problem but may actually make the problem more difficult to solve. In order to make a convincing argument, the author will need to consider how thoughtful people might disagree with this claim. In this case, the author might anticipate the following counterarguments:
- By encouraging personal actions, climate activists may raise awareness of the problem and encourage people to support larger systemic change.
- Personal actions on a global level would actually make a difference.
- Personal actions may not make a difference, but they will not obscure the need for systemic solutions.
- Personal actions cannot be put into one category and must be differentiated.
In order to make a convincing argument, the author of this essay may need to address these potential counterarguments. But you don’t need to address every possible counterargument. Rather, you should engage counterarguments when doing so allows you to strengthen your own argument by explaining how it holds up in relation to other arguments.
How to address counterarguments
Once you have considered the potential counterarguments, you will need to figure out how to address them in your essay. In general, to address a counterargument, you’ll need to take the following steps.
- State the counterargument and explain why a reasonable reader could raise that counterargument.
- Counter the counterargument. How you grapple with a counterargument will depend on what you think it means for your argument. You may explain why your argument is still convincing, even in light of this other position. You may point to a flaw in the counterargument. You may concede that the counterargument gets something right but then explain why it does not undermine your argument. You may explain why the counterargument is not relevant. You may refine your own argument in response to the counterargument.
- Consider the language you are using to address the counterargument. Words like but or however signal to the reader that you are refuting the counterargument. Words like nevertheless or still signal to the reader that your argument is not diminished by the counterargument.
Here’s an example of a paragraph in which a counterargument is raised and addressed.
Image version

The two steps are marked with counterargument and “counter” to the counterargument: COUNTERARGUMENT/ But some experts argue that it’s important for individuals to take action to mitigate climate change. In “All That Performative Environmentalism Adds Up,” Annie Lowery argues that personal actions to fight climate change, such as reducing household trash or installing solar panels, matter because change in social behavior can lead to changes in laws. [1]
COUNTER TO THE COUNTERARGUMENT/ While Lowery may be correct that individual actions can lead to collective action, this focus on individual action can allow corporations to receive positive publicity while continuing to burn fossil fuels at dangerous rates.
Where to address counterarguments
There is no one right place for a counterargument—where you raise a particular counterargument will depend on how it fits in with the rest of your argument. The most common spots are the following:
- Before your conclusion This is a common and effective spot for a counterargument because it’s a chance to address anything that you think a reader might still be concerned about after you’ve made your main argument. Don’t put a counterargument in your conclusion, however. At that point, you won’t have the space to address it, and readers may come away confused—or less convinced by your argument.
- Before your thesis Often, your thesis will actually be a counterargument to someone else’s argument. In other words, you will be making your argument because someone else has made an argument that you disagree with. In those cases, you may want to offer that counterargument before you state your thesis to show your readers what’s at stake—someone else has made an unconvincing argument, and you are now going to make a better one.
- After your introduction In some cases, you may want to respond to a counterargument early in your essay, before you get too far into your argument. This is a good option when you think readers may need to understand why the counterargument is not as strong as your argument before you can even launch your own ideas. You might do this in the paragraph right after your thesis.
- Anywhere that makes sense As you draft an essay, you should always keep your readers in mind and think about where a thoughtful reader might disagree with you or raise an objection to an assertion or interpretation of evidence that you are offering. In those spots, you can introduce that potential objection and explain why it does not change your argument. If you think it does affect your argument, you can acknowledge that and explain why your argument is still strong.
[1] Annie Lowery, “All that Performative Environmentalism Adds Up.” The Atlantic . August 31, 2020. https://www.theatlantic.com/ideas/archive/2020/08/your-tote-bag-can-mak…
- picture_as_pdf Counterargument
- Entertainment
Erik Kazakov
Giphy clips.

IMAGES
COMMENTS
Explore. counter argument. GIFs. GIPHY is the platform that animates your world. Find the GIFs, Clips, and Stickers that make your conversations more positive, more expressive, and more you.
GIPHY is the platform that animates your world. Find the GIFs, Clips, and Stickers that make your conversations more positive, more expressive, and more you.
GIPHY is the platform that animates your world. Find the GIFs, Clips, and Stickers that make your conversations more positive, more expressive, and more you.
The perfect Argument Anger When Someone Counters My Argument Animated GIF for your conversation. Discover and Share the best GIFs on Tenor. Tenor.com has been translated based on your browser's language setting.
Discover and Share the best GIFs on Tenor. The perfect Danganronpa Hajime Hinata Danganronpa2 Animated GIF for your conversation. Discover and Share the best GIFs on Tenor. ... Counter Argument. anime. Share URL. Embed. Details File Size: 1722KB Duration: 1.400 sec Dimensions: 498x278 Created: 5/3/2020, 3:41:48 AM. Related GIFs. #himikoyumeno ...
Make Counter Argument Classic Meme memes or upload your own images to make custom memes. Create. Make a Meme Make a GIF Make a Chart Make a Demotivational s. ... browse all the GIF Templates or upload and save your own animated template using the GIF Maker. Do you have a wacky AI that can write memes for me? Funny you ask. Why yes, we do. Here ...
Here is a popular argument for 'GIF' Since the G in 'GIF' stands for 'Graphic', with a hard 'G', the acronym should also be pronounced with a hard 'G' Counter Argument:
With Tenor, maker of GIF Keyboard, add popular Argument animated GIFs to your conversations. Share the best GIFs now >>>
Make sure you introduce your counter argument using phrases like "It is argued that" or "It may seem as if". In general, you should present a counter argument towards the end of your thesis but prior to your conclusion. This gives you a chance to express your key points in advance of the counter argument and provide a rebuttal for your ...
Counter Argument. One way to strengthen your argument and demonstrate a comprehensive understanding of the issue you are discussing is to anticipate and address counter arguments, or objections. By considering opposing views, you show that you have thought things through, and you dispose of some of the reasons your audience might have for not ...
GIFs of John Oliver "GIFs" is officially pronounced with a hard "J" Advertisement Coins. 0 coins. Premium Powerups Explore Gaming. Valheim Genshin Impact Minecraft Pokimane Halo Infinite Call of Duty: Warzone Path of Exile Hollow Knight: Silksong Escape from Tarkov Watch Dogs: Legion. Sports. NFL ...
Counterargument. When you write an academic essay, you make an argument: you propose a thesis and offer some reasoning, using evidence, that suggests why the thesis is true. When you counter-argue, you consider a possible argument against your thesis or some aspect of your reasoning. This is a good way to test your ideas when drafting, while ...
How to actually write and implement a counter-argument: Identify or explain opposing viewpoints. Use phrases like "on the other hand..." or "it is often perceived that..." or "critics may argue..." or "although..." or "some people may think" or (invoking the viewpoint of an expert/group) "according to...". Summarize ...
Guide to Counterarguments in Writing Studies. Counterarguments are a topic of study in Writing Studies as . a form of invention. Rhetors engage in rhetorical reasoning: They analyze the rebuttals their target audiences may have to their claims, interpretations, propositions, and proposals; a part of Toulmin Argument. Rhetors may develop counterarguments by questioning a rhetor's backing ...
Make a Meme Make a GIF Make a Chart Make a Demotivational counter Meme Templates. Search. NSFW GIFs Only. Bad Counter. Add Caption. Counter Strike . Add Caption. Zero counter. ... Counter Argument Classic Meme. Add Caption. heisenberg haircut. Add Caption. fake apple laptop. Add Caption. Batman vs the riddler. Add Caption. Dancing T CS GO ...
A counterargument is the argument on the opposite side of the writer's argument or thesis. It is the point of view they are directly arguing against and attempting to prove as inaccurate. To ...
Details File Size: 12942KB Duration: 13.600 sec Dimensions: 498x379 Created: 6/10/2021, 9:30:56 PM
Counterargument Examples. 1. Empirical Challenges. An empirical challenge is, simply, a rebuttal that challenges the facts presented by the opponent, showing that their facts are wrong and yours are right. To undermine your opponent's set of facts, it will be your job to present facts that show that the opponent's supposed facts are wrong ...
The most common spots are the following: Before your conclusion. This is a common and effective spot for a counterargument because it's a chance to address anything that you think a reader might still be concerned about after you've made your main argument. Don't put a counterargument in your conclusion, however.
Counter argument against the idea that the acronym "GIF" has to be pronounced with a hard "g" because it stands for graphics. ... The creators of the format pronounced GIF as "Jif" with a soft "G" /ˈdʒɪf/ as in "gin". Steve Wilhite says that the intended pronunciation deliberately echoes the American peanut butter brand, ...
Find the GIFs, Clips, and Stickers that make your conversations more positive, more expressive, and more you. GIPHY is the platform that animates your world. Find the GIFs, Clips, and Stickers that make your conversations more positive, more expressive, and more you. ... argument 1,108 GIFs. Sort. Filter. 1 channels. Erik Kazakov. alukaaard ...
When writing your counterargument paragraph, you should respond to that other position. In your paragraph: Identify the opposing argument. Respond to it by discussing the reasons the argument is incomplete, weak, unsound, or illogical. Provide examples or evidence to show why the opposing argument is unsound, or provide explanations of how the ...
Open & share this gif argument, mfw, counter, with everyone you know. The GIF dimensions 500 x 281px was uploaded by anonymous user. Download most popular gifs on GIFER