The Five Pillars of Islam Analytical Essay
The Muslim religion is based on Five Pillars of Islam. These are basic values and principles which influence the notion, actions and morals of the faith.
Every Muslim adherent is bound by the Five Pillars of Islam to uphold his or her devotion to the Islamic faith. Devout Muslims are required toask for forgiveness for their wrongdoings in order to secure their place in heaven or Jannah . The five tenets of Islam guide the faithful not to waver in their obedience to Allah.
Muslims maintain deep honor for the existence of God, who they believe exists in all the aspects of their life. The religion harbors a profound belief that every individual has a unique natural destiny that is presented to a person by God, thus it is He whogives something to a human. This implies that everything that Muslims own belongs to God.
The first tenet of Islam is Shahada . Shahada means Allah who is the most superior God. He reaches out to the faithful Muslim through Muhammad (Henderson 63-64). This term invokedby Muslims is a constant reminder that only Allah should be worshipped.Moreover, He is the supreme deity with the ability and liberty to act at will.
This status lends credence to His commandments stated in the Koran. Shahada impliesthat the Christian principleswhich recognize God as the most powerful entity are false.All other religious powers, such as pantheism, are equally obsolete. Muslims believe that Prophet Muhammad is holy because, through him, Allah communicated significant revelationsto the faithful (Khan 13-14).
The second Islamic pillar is Salat or prayer. This tenet involves profession of wrongdoings. The profession process begins with the cleansing of oneself and spirit. Prayer is undertaken five times every day, from dawn to dusk.
There are five prayers that fallunder Salat are Fajr, Shurooq, Asr, Dhuhr, Isha and Maghrib. The prayer which Muslims say at sunset is referred to as the Maghrib while Isha comes later in the evening. All the prayers act as a constant reminder of the significance of Allah and his omnipresence among and within the Muslim faithful.
The third pillar is fasting or Saum . Fasting is a significant tenet of the Islamic faith, which puts all the faithful at the same level of the sacrifice as those who do not have food. The month of Ramadan witnesses Muslims of all the social stratasacrifice the basic need and food. Saum is to help Muslims to seek answers for their questionsfrom Allah. In most cases, the fasting process does not involve any form of ingestion or sexual activity during the daytime hours of the holy month (Henderson 62-67).
The fourth pillar is Charity or Zakat. Giving alms is an important facet of the Islamic faith. Muslims advocate and practice philanthropy. Charity benefits the underprivileged members of the society and enables the donor to make tremendous steps towards devoutness and obedience to Allah as He believes in generosity. Muslims consider donations as a way of appreciating God’s help. The final Pillar of Islam is Pilgrimage or Hajj .
The Muslim pilgrimage is normally held in Mecca where all thefinancially stable faithful tender their financial sacrifice as a way of appreciating God’s love and blessing. Muslims are required by the Koran to set the pilgrimage date during the first two weeks of the final month of a lunar year. The Five Pillars of Islam are used to emphasize unity among the faithful and act in one voice (Khan 12-14).
In general, all the Five Pillars of Islam dictate the activities and operations of the members of the religion. Shahada and Pilgrimage facets are eminently based on individual actions, although the first Islamic tenet requires community service or appreciation of Umma to some extent.
The remaining pillars, such as prayers, fasting and giving away alms, are a manifestation of Allah’s love andinclusiveness. The pillars inspire activities undertaken in unity by the faithful to improve the status of the less fortunate followers. The community features prominently in relatively all the aspects of the Islamic religious conviction. Through the Five Pillars, Muslims believe in and strive to present their religion in the form of a complete culture rather than just a spiritual entity.

Works Cited
Henderson, Shirley . Journey to Allah. Ebony , 65.4 (2010): 62-67. Print.
Khan, Daisy. The Five Pillars of Islam. Appleseeds , 6.3 (2003): 12-14. Print.
- Chicago (A-D)
- Chicago (N-B)
IvyPanda. (2023, October 31). The Five Pillars of Islam. https://ivypanda.com/essays/the-five-pillars-of-islam/
"The Five Pillars of Islam." IvyPanda , 31 Oct. 2023, ivypanda.com/essays/the-five-pillars-of-islam/.
IvyPanda . (2023) 'The Five Pillars of Islam'. 31 October.
IvyPanda . 2023. "The Five Pillars of Islam." October 31, 2023. https://ivypanda.com/essays/the-five-pillars-of-islam/.
1. IvyPanda . "The Five Pillars of Islam." October 31, 2023. https://ivypanda.com/essays/the-five-pillars-of-islam/.
Bibliography
IvyPanda . "The Five Pillars of Islam." October 31, 2023. https://ivypanda.com/essays/the-five-pillars-of-islam/.
- A Christian Organization Serving in an Islamic Context
- The Five Pillars of Islam: Foundation of Muslim Life
- Islamic Worldview Analysis and Comparison With Christianity
- Islamic Faith and Ritual Practice
- Different Styles in World Music
- The Warrior Hero: Heroic Attributes of Rustem
- The Koran in the Middle East History
- A Christian Perspective of Health Care
- Interpretation of the Koran
- CIA Director George Tenet's Ethical Obligations
- Zen Buddhism and Oneida Community
- Judaism, Islam and Christianity: Differences and Similarities
- Buddhism & Hinduism: Comparisons and Contractions
- Buddhism and Hinduism
- Sikhism: Religion and Theology
Five Pillars of Islam
- Important Principles
- Prayer Salat
- Prophets of Islam
- Ramadan and Eid Al Fitr
- Hajj and Eid Al Adha
- M.Ed., Loyola University–Maryland
- B.S., Child Development, Oregon State University
The “five pillars of Islam” are religious duties that provide a framework for a Muslim’s life. These duties are performed regularly and encompass duties to God, to personal spiritual growth, to care for the poor, self-discipline, and sacrifice.
In Arabic, “arkan” (pillars) provide structure and hold something steadily in place. They provide support, and all must be present for the framework to balance steadily. The articles of faith provide a foundation, answering the question of “what do Muslims believe?” The Five Pillars of Islam help Muslims to structure their lives around that foundation, answering the question of “how do Muslims affirm their faith in daily life?”
Islamic teachings about the Five Pillars of Islam are found in the Quran and the Hadith. In the Quran, they are not outlined in a neat bullet-pointed list, but are rather dispersed throughout the Quran and emphasized in importance through repetition.
The Prophet Muhammad did mention the five pillars of Islam in an authentic narration ( hadith ):
“Islam has been built upon five [pillars]: testifying that there is no diety but Allah and that Muhammad is the Messenger of Allah, performing the prayers, paying the zakah, making the pilgrimage to the House, and fasting in Ramadan” (Hadith Bukhari, Muslim).
Shahaadah (Profession of Faith)
The first act of worship that every Muslim performs is a confirmation of faith, known as the shahaadah . The word shahaadah literally means “to bear witness,” so by professing faith verbally, one is bearing witness to the truth of Islam’s message and its most fundamental teachings. The shahaadah is repeated by Muslims several times each day, both individually and in daily prayer, and it is a frequently-written phrase in Arabic calligraphy .
People who want to convert to Islam do so by simply reciting the shahaadah aloud, preferably in front of two witnesses. There is no other requirement or prerequisite ceremony for embracing Islam. Muslims also strive to say or hear these words as their last, before they die.
Salaat (Prayer)
Daily prayer is a touchstone in a Muslim’s life. In Islam, prayer is directly to Allah alone, directly, without any intermediary or intercessor. Muslims take time out five times each day to direct their hearts towards worship. The movements of prayer – standing, bowing, sitting, and prostrating – represent humility before the Creator. Words of prayer include words of praise and thanks to Allah, verses from the Quran, and personal supplications.
Zakat (Almsgiving)
In the Quran, giving in charity to the poor is often mentioned hand-in-hand with daily prayer. It is central to a Muslim’s core belief that everything we have comes from Allah, and is not ours to hoard or covet. We should feel blessed for everything we have and must be willing to share with those less fortunate. Charity at any time is recommended, but there is also a set percentage required for those who reach a certain minimum net worth.
Sawm (Fasting)
Many communities observe fasting as a way to purify the heart, mind, and body. In Islam, fasting helps us to empathize with those less fortunate, helps us to reprioritize our lives, and brings us closer to Allah in strengthened faith. Muslims may fast throughout the year, but all adult Muslims of sound body and mind must fast during the month of Ramadan each year. The Islamic fast lasts from dawn to sunset each day, during which time no food or drink of any kind is consumed. Muslims also spend the time in additional worship, refrain from bad talk and gossip, and share in friendship and in charity with others.
Hajj (Pilgrimage)
Unlike the other “pillars” of Islam, which are performed on a daily or annual basis, the pilgrimage is required to be done only once in a lifetime. Such is the impact of the experience and the hardship that it entails. The Hajj pilgrimage occurs during a certain set month every year, lasts for several days, and is only required of those Muslims who are physically and financially able to make the journey.
- All About Ramadan, Islam's Holy Month
- The Architecture and History of the Kaaba
- Shahaadah: Declaration of Faith: Pillar of Islam
- The 5 Muslim Daily Prayer Times and What They Mean
- Key Differences Between Shia and Sunni Muslims
- What Is Iftar During Ramadan?
- The Stages of Hajj, the Islamic Pilgrimage to Mecca (Makkah)
- Prophet Ibrahim (Abraham)
- Why Do Muslims End Prayers with "Ameen"?
- Doors of Jannah
- Introduction and Resource Guide to Islam
- Definition of Jannah in Islam
- Lesson Plans for Eid al Adha, an Islamic Celebration
- Zakat: the Charitable Practice of Islamic Almsgiving
- The Importance of the "Hadith" for Muslims
- Friday Prayer in Islam
- Evidence Islam is Truth
- The Benefits of Islam
- Beliefs of Islam
- How to Convert to Islam
- Worship and Practice
- The Hereafter
- Stories of New Muslims
- Comparative Religion
- The Holy Quran
- The Prophet Muhammad
- Current Issues
- Islamic History
- Systems in Islam
Evidence Islam is Truth 159 articles
- The Scientific Miracles of the Holy Quran 15 articles
- The Scientific Miracles of the Prophet Muhammad Sayings 2 articles
- Muhammad in the Bible and Other Scriptures 4 articles
- The Authenticity and Preservation of the Holy Quran 21 articles
- Evidence of Muhammad’s Prophethood 29 articles
- Logical Proofs 45 articles
- The Existence of God 62 articles
The Benefits of Islam 62 articles
- The Door to Eternal Paradise 3 articles
- Salvation from Hellfire 1 articles
- True Happiness and Inner Peace 28 articles
- Forgiveness for All Previous Sins 1 articles
- Benefits to Society 15 articles
- Benefits to Science and Civilization 7 articles
- What Others Say about Islam, Muhammad, and the Quran 7 articles
Beliefs of Islam 211 articles
- What is Islam 21 articles
- The Six Pillars of Faith and Other Islamic Beliefs 49 articles
- About God 63 articles
- The Purpose of Life 22 articles
- Stories of the Prophets 64 articles
How to Convert to Islam 13 articles
- How to Convert to Islam and Become a Muslim 13 articles
Worship and Practice 115 articles
- The Five Pillars of Islam and Other Acts of Worship 49 articles
- Islamic Morals and Practices 66 articles
The Hereafter 35 articles
- Paradise 8 articles
- Hellfire 9 articles
- The Journey after Death 12 articles
- The Day of Judgement and Its Signs 9 articles
Stories of New Muslims 277 articles
- Men 98 articles
- Women 132 articles
- Priests and Religious Figures 20 articles
- Personalities 32 articles
Comparative Religion 160 articles
- Jesus 59 articles
- The Bible 21 articles
- Christianity 26 articles
- Mary 10 articles
- Judaism 20 articles
- Hinduism 5 articles
- Buddhism 2 articles
- Sikhism 2 articles
- Scientology 2 articles
- Tolerance in Islam 6 articles
- Uncommon Faiths 17 articles
The Holy Quran 234 articles
- The Authenticity and Preservation of the Holy Quran 26 articles
- Structure and Attributes of the Quran 17 articles
- Selected Topics from the Quran 25 articles
- A Summary of the Quranic Chapters 123 articles
- Essential Verses in the Quran 28 articles
The Prophet Muhammad 124 articles
- Pearls from His Sayings 19 articles
- His Characteristics 22 articles
- His Biography 19 articles
- Evidence of His Prophethood 29 articles
- About His Sayings 15 articles
- Stories of His Companions 22 articles
Current Issues 92 articles
- Human Rights 14 articles
- Jihad and Terrorism 2 articles
- Women 39 articles
- Islam and Non-Muslims 23 articles
- Sects Attributed to Islam 14 articles
Islamic History 25 articles
- In Brief 15 articles
- In Detail 10 articles
Systems in Islam 77 articles
- Family 18 articles
- Politics 3 articles
- Economy 11 articles
- Justice 6 articles
- Crime and Punishment 7 articles
- Health and Nutrition 19 articles
- The Environment 13 articles
- Islamic Songs (Nasheed)
- New Muslims
- Short Videos About Islam
Evidence Islam is Truth 122 videos
- The Scientific Miracles of the Holy Quran 17 videos
- The Scientific Miracles of the Prophet Muhammad Sayings 2 videos
- Muhammad in the Bible and Other Scriptures 2 videos
- The Authenticity and Preservation of the Holy Quran 25 videos
- Evidence of Muhammad’s Prophethood 6 videos
- Logical Proofs 33 videos
- The Existence of God 38 videos
The Benefits of Islam 102 videos
- The Door to Eternal Paradise 3 videos
- Salvation from Hellfire 6 videos
- True Happiness and Inner Peace 36 videos
- Benefits to Society 39 videos
- Benefits to Science and Civilization 13 videos
- What Others Say about Islam, Muhammad, and the Quran 6 videos
Beliefs of Islam 176 videos
- What is Islam 43 videos
- The Six Pillars of Faith and Other Islamic Beliefs 37 videos
- About God 53 videos
- The Purpose of Life 24 videos
- Stories of the Prophets 15 videos
How to Convert to Islam 8 videos
- How to Convert to Islam and Become a Muslim 8 videos
Worship and Practice 16 videos
- The Five Pillars of Islam and Other Acts of Worship 7 videos
- Islamic Morals and Practices 8 videos
The Hereafter 17 videos
- Paradise 3 videos
- Hellfire 2 videos
- The Journey after Death 5 videos
- The Day of Judgement and Its Signs 8 videos
Stories of New Muslims 235 videos
- Men 180 videos
- Women 34 videos
- Priests and Religious Figures 5 videos
- Personalities 18 videos
Comparative Religion 123 videos
- Jesus 65 videos
- The Bible 20 videos
- Christianity 27 videos
- Mary 2 videos
- Judaism 6 videos
- Tolerance in Islam 9 videos

The Holy Quran 51 videos
- The Scientific Miracles of the Holy Quran 9 videos
- The Authenticity and Preservation of the Holy Quran 31 videos
- Jewels from the Quran 7 videos
- A Summary of the Meanings of Its Verses 1 videos
The Prophet Muhammad 71 videos
- Pearls from His Sayings 2 videos
- His Characteristics 32 videos
- His Biography 21 videos
- Evidence of His Prophethood 9 videos
- About His Sayings 1 videos
- Stories of His Companions 5 videos
Current Issues 64 videos
- Human Rights 14 videos
- Jihad and Terrorism 30 videos
- Women 20 videos
- Islam and Non-Muslims 10 videos
Islamic History 21 videos
- In Brief 3 videos
- In Detail 18 videos
Systems in Islam 25 videos
- Family 4 videos
- Politics 1 videos
- Economy 2 videos
- Justice 13 videos
- Crime and Punishment 2 videos
- Health and Nutrition 3 videos
Islamic Songs (Nasheed) 14 videos
- NBN Band 1 videos
- Zain Bhikha 1 videos
- Ahmad Bukhatir 2 videos
- Yusuf Islam (Cat Stevens) 2 videos
- Kamal Uddin 2 videos
- Labbayk 1 videos
- TalkIslam 2 videos
New Muslims 148 videos
- Merits of Islam 8 videos
- Islamic Beliefs 11 videos
- Acts of Worship 27 videos
- Islamic Lifestyle, Morals and Practices 23 videos
- The Holy Quran 11 videos
- Prophet Muhammad 32 videos
- Social Interaction 22 videos
- Increasing faith 23 videos
Short Videos About Islam 26 videos
- Islam in 3 Minutes 18 videos
- Understanding Islam By Yusuf Estes 8 videos
Islam at a Glance
- Intro E-books
- The Five Pillars of Islam and Other Acts of Worship
The Fifth Pillar of Islam: The Pilgrimage (Hajj)
Description: the merits and various rites performed in hajj, the fifth of the five obligatory fundamental muslim practices..
- By Imam Mufti
- Published on 13 Feb 2006
- Last modified on 25 Jun 2019
- Printed: 3,113
- Viewed: 337,801 (daily average: 51)
- Rating: 3.2 out of 5
- Rated by: 155
- Emailed: 108
- Commented on: 24
- Play article audio
_001.jpg)
Pilgrimage is viewed as a particularly meritorious activity. Pilgrimage serves as a penance - the ultimate forgiveness for sins, devotion, and intense spirituality. The pilgrimage to Mecca, the most sacred city in Islam, is required of all physically and financially able Muslims once in their life. The pilgrimage rite begins a few months after Ramadan, on the 8th day of the last month of the Islamic year of Dhul-Hijjah, and ends on the 13th day. Mecca is the center towards which the Muslims converge once a year, meet and refresh in themselves the faith that all Muslims are equal and deserve the love and sympathy of others, irrespective of their race or ethnic origin. The racial harmony fostered by Hajj is perhaps best captured by Malcolm X on his historic pilgrimage:
"Every one of the thousands at the airport, about to leave for Jeddah, was dressed this way. You could be a king or a peasant and no one would know. Some powerful personages, who were discreetly pointed out to me, had on the same thing I had on. Once thus dressed, we all had begun intermittently calling out "Labbayka! (Allahumma) Labbayka!" (At your service, O Lord!) Packed in the plane were white, black, brown, red, and yellow people, blue eyes and blond hair, and my kinky red hair - all together, brothers! All honoring the same God, all in turn giving equal honor to each other . . .
That is when I first began to reappraise the ‘white man’. It was when I first began to perceive that ‘white man’, as commonly used, means complexion only secondarily; primarily it described attitudes and actions. In America, ‘white man’ meant specific attitudes and actions toward the black man, and toward all other non-white men. But in the Muslim world, I had seen that men with white complexions were more genuinely brotherly than anyone else had ever been. That morning was the start of a radical alteration in my whole outlook about ‘white’ men.
There were tens of thousands of pilgrims, from all over the world. They were of all colors, from blue-eyed blonds to black-skinned Africans. But we were all participating in the same ritual displaying a spirit of unity and brotherhood that my experiences in America had led me to believe never could exist between the white and the non-white... America needs to understand Islam, because this is the one religion that erases from its society the race problem. Throughout my travels in the Muslim world, I have met, talked to, and even eaten with people who in America would have been considered white - but the ‘white’ attitude was removed from their minds by the religion of Islam. I have never before seen sincere and true brotherhood practiced by all colors together, irrespective of their color."
Thus the pilgrimage unites the Muslims of the world into one international fraternity. More than two million persons perform the Hajj each year, and the rite serves as a unifying force in Islam by bringing followers of diverse backgrounds together in worship. In some Muslim societies, once a believer has made the pilgrimage, he is often labeled with the title ‘hajji’ ; this, however, is a cultural, rather than religious custom. Finally, the Hajj is a manifestation of the belief in the unity of God - all the pilgrims worship and obey the commands of the One God.
At certain stations on the caravan routes to Mecca, or when the pilgrim passes the point nearest to those stations, the pilgrim enters the state of purity known as ihram . In this state, the certain ‘normal’ actions of the day and night become impermissible for the pilgrims, such as covering the head, clipping the fingernails, and wearing normal clothing in regards to men. Males remove their clothing and don the garments specific to this state of ihram , two white seamless sheets that are wrapped around the body. All this increases the reverence and sanctity of the pilgrimage, the city of Mecca, and month of Dhul-Hijjah. There are 5 stations, one on the coastal plains northwest of Mecca towards Egypt and one south towards Yemen, while three lie north or eastwards towards Medina, Iraq and Najd. The simple garb signifies the equality of all humanity in God’s sight, and the removal of all worldly affections. After entering the state of ihram, the pilgrim proceeds to Mecca and awaits the start of the Hajj. On the 7th of Dhul-Hijjah the pilgrim is reminded of his duties, and the rituals commence on the 8th of the month. The pilgrim visits the holy places outside Mecca - Arafah, Muzdalifah, and Minaa - prays, sacrifices an animal in commemoration of Abraham’s sacrifice, throws pebbles at specific pillars at Minaa, and shortens or shaves his head. The rituals also involve walking seven times around the sacred sanctuary, or Kaaba , in Mecca, and ambulating, walking and running, seven times between the two small hills of Mt. Safaa and Mt. Marwah. Discussing the historical or spiritual significance of each rite is beyond the scope of this introductory article.
Apart from Hajj, the "minor pilgrimage" or umrah is undertaken by Muslims during the rest of the year. Performing the umrah does not fulfill the obligation of Hajj. It is similar to the major and obligatory Islamic pilgrimage (hajj), and pilgrims have the choice of performing the umrah separately or in combination with the Hajj. As in the Hajj, the pilgrim begins the umrah by assuming the state of ihram . They enter Mecca and circle the sacred shrine of the Kaaba seven times. He may then touch the Black Stone, if he can, pray behind the Maqam Ibrahim, drink the holy water of the Zamzam spring. The ambulation between the hills of Safa and Marwah seven times and the shortening or shaving of the head complete the umrah .
Parts of This Article
Add a comment
- Country: Select Country Afghanistan Albania Antarctica Algeria American Samoa Andorra Angola Antigua and Barbuda Azerbaijan Argentina Australia Austria Bahamas Bahrain Bangladesh Armenia Barbados Belgium Bermuda Bhutan Bolivia, Plurinational State of Bosnia and Herzegovina Botswana Bouvet Island Brazil Belize British Indian Ocean Territory Solomon Islands Virgin Islands, British Brunei Darussalam Bulgaria Myanmar Burundi Belarus Cambodia Cameroon Canada Cape Verde Cayman Islands Central African Republic Sri Lanka Chad Chile China Taiwan, Province of China Christmas Island Cocos (Keeling) Islands Colombia Comoros Mayotte Congo Congo, the Democratic Republic of the Cook Islands Costa Rica Croatia Cuba Cyprus Czechia Benin Denmark Dominica Dominican Republic Ecuador El Salvador Equatorial Guinea Ethiopia Eritrea Estonia Faroe Islands Falkland Islands (Malvinas) South Georgia and the South Sandwich Islands Fiji Finland Åland Islands France French Guiana French Polynesia French Southern Territories Djibouti Gabon Georgia Gambia Palestine Germany Ghana Gibraltar Kiribati Greece Greenland Grenada Guadeloupe Guam Guatemala Guinea Guyana Haiti Heard Island and McDonald Islands Holy See (Vatican City State) Honduras Hong Kong Hungary Iceland India Indonesia Iran, Islamic Republic of Iraq Ireland Israel Italy Côte d'Ivoire Jamaica Japan Kazakhstan Jordan Kenya Korea, Democratic People's Republic of Korea, Republic of Kuwait Kyrgyzstan Lao People's Democratic Republic Lebanon Lesotho Latvia Liberia Libya Liechtenstein Lithuania Luxembourg Macao Madagascar Malawi Malaysia Maldives Mali Malta Martinique Mauritania Mauritius Mexico Monaco Mongolia Moldova, Republic of Montenegro Montserrat Morocco Mozambique Oman Namibia Nauru Nepal Netherlands Curaçao Aruba Sint Maarten (Dutch part) Bonaire, Sint Eustatius and Saba New Caledonia Vanuatu New Zealand Nicaragua Niger Nigeria Niue Norfolk Island Norway Northern Mariana Islands United States Minor Outlying Islands Micronesia, Federated States of Marshall Islands Palau Pakistan Panama Papua New Guinea Paraguay Peru Philippines Pitcairn Poland Portugal Guinea-Bissau Timor-Leste Puerto Rico Qatar Réunion Romania Russian Federation Rwanda Saint Barthélemy Saint Helena, Ascension and Tristan da Cunha Saint Kitts and Nevis Anguilla Saint Lucia Saint Martin (French part) Saint Pierre and Miquelon Saint Vincent and the Grenadines San Marino Sao Tome and Principe Saudi Arabia Senegal Serbia Seychelles Sierra Leone Singapore Slovakia Viet Nam Slovenia Somalia South Africa Zimbabwe Spain South Sudan Sudan Western Sahara Suriname Svalbard and Jan Mayen Eswatini Sweden Switzerland Syrian Arab Republic Tajikistan Thailand Togo Tokelau Tonga Trinidad and Tobago United Arab Emirates Tunisia Turkey Turkmenistan Turks and Caicos Islands Tuvalu Uganda Ukraine North Macedonia Egypt United Kingdom Guernsey Jersey Isle of Man Tanzania, United Republic of United States Virgin Islands, U.S. Burkina Faso Uruguay Uzbekistan Venezuela, Bolivarian Republic of Wallis and Futuna Samoa Yemen Zambia
(Not shown to the public)
Your comment will be reviewed and should be published within 24 hours.
Fields marked with an asterisk (*) are required.
Other Articles in the Same Category
Other videos in the same category.

Article Categories
Video categories, most viewed, editor’s pick, list contents, most popular, your favorites.
Your favorites list is empty. You may add articles to this list using the article tools.
Your History
Retrieve Your Password
Forgot your password? No problem. Just let us know your email address and we will email you a password reset link that will allow you to choose a new one.
Registration
Why register? This web site has several customizations made specifically for you, such as: your favorites, your history, marking articles you have previously viewed, listing articles published since your last visit, changing font size, and more. These features are based on cookies and will work correctly only when you use the same computer. To enable these features from any computer, you should login while browsing this site.
The field(s) below are optional

- school Campus Bookshelves
- menu_book Bookshelves
- perm_media Learning Objects
- login Login
- how_to_reg Request Instructor Account
- hub Instructor Commons
- Download Page (PDF)
- Download Full Book (PDF)
- Periodic Table
- Physics Constants
- Scientific Calculator
- Reference & Cite
- Tools expand_more
- Readability
selected template will load here
This action is not available.

8.5: Five Pillars of Islam
- Last updated
- Save as PDF
- Page ID 226346
- Lumen Learning
Five Pillars of Islam
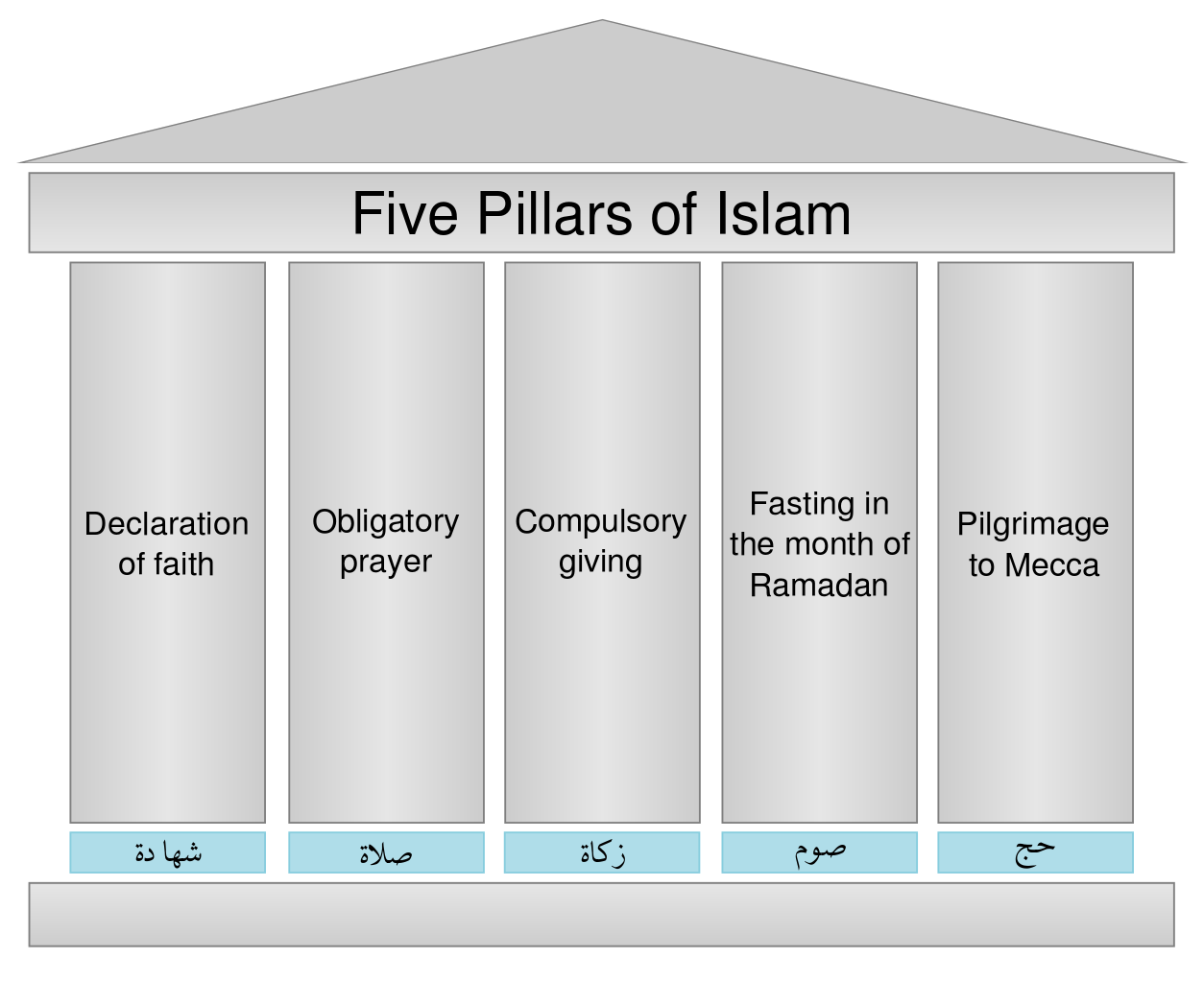
The Pillars of Islam are five basic acts in Islam, considered obligatory for all believers. The Quran presents them as a framework for worship and a sign of commitment to the faith. They are:
- Shahadah (creed)
- Daily prayers (salat)
- Almsgiving (zakah)
- Fasting during Ramadan
- Pilgrimage to Mecca (hajj) at least once in a lifetime
The Shia and Sunni sects both agree on the essential details for the performance of these acts.
Ritual prayers, called Ṣalāh or Ṣalāt, must be performed five times a day. Salah is intended to focus the mind on God, and is seen as a personal communication with him that expresses gratitude and worship. Salah is compulsory but flexibility in the specifics is allowed depending on circumstances. The prayers are recited in the Arabic language, and consist of verses from the Qur’an.
A mosque is a place of worship for Muslims, who often refer to it by its Arabic name, masjid. The word mosque in English refers to all types of buildings dedicated to Islamic worship, although there is a distinction in Arabic between the smaller, privately owned mosque and the larger, “collective” mosque. Although the primary purpose of the mosque is to serve as a place of prayer, it is also important to the Muslim community as a place to meet and study. Modern mosques have evolved greatly from the early designs of the 7th century, and contain a variety of architectural elements such as minarets.
Alms-giving
“Zakāt” (“alms”) is giving a fixed portion of accumulated wealth by those who can afford it to help the poor or needy and for those employed to collect Zakat; also, for bringing hearts together, freeing captives, for those in debt (or bonded labour) and for the (stranded) traveller. It is considered a religious obligation (as opposed to voluntary charity) that the well-off owe to the needy because their wealth is seen as a “trust from God’s bounty.” Conservative estimates of annual Zakat are estimated to be 15 times global humanitarian aid contributions. The amount of zakat to be paid on capital assets (e.g. money) is 2.5% (1/40), for people who are not poor. The Qur’an and the hadith also urge a Muslim to give even more as an act of voluntary alms-giving called ṣadaqah.
Fasting (ṣawm) from food and drink (among other things) must be performed from dawn to dusk during the month of Ramadhan. The fast is to encourage a feeling of nearness to God, and during it, Muslims should express their gratitude for and dependence on him, atone for their past sins, and think of the needy. Sawm is not obligatory for several groups for whom it would constitute an undue burden. For others, flexibility is allowed depending on circumstances, but missed fasts usually must be made up quickly.
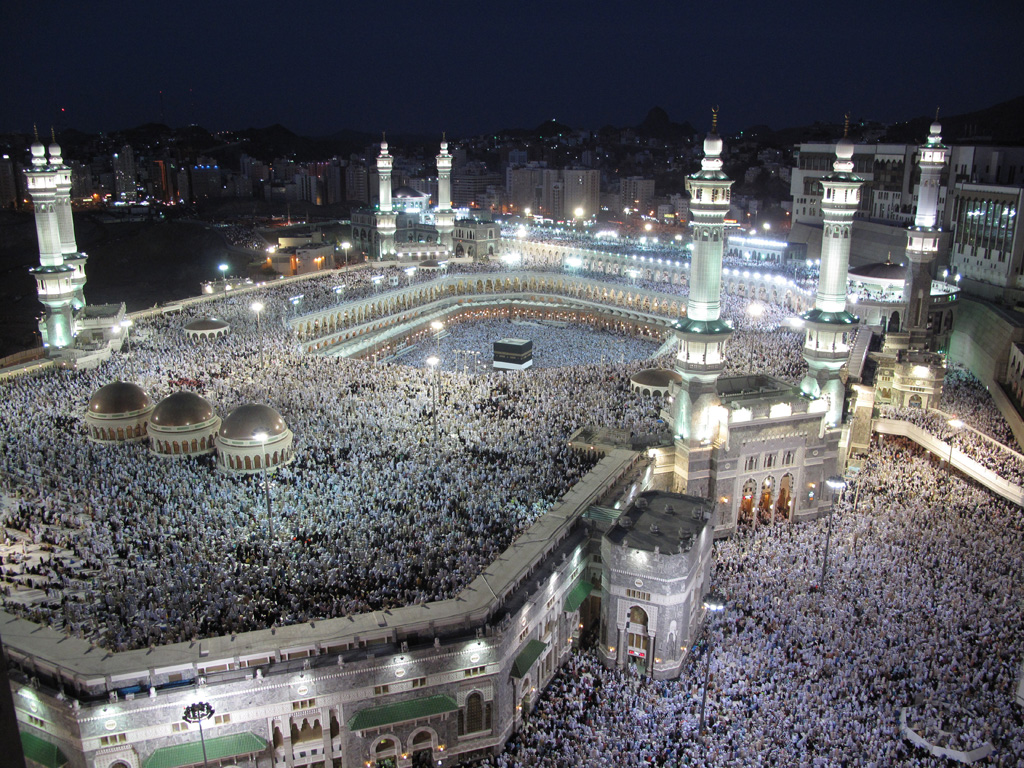

The pilgrimage, called the ḥajj, has to be done during the Islamic month of Dhu al-Hijjah in the city of Mecca. Every able-bodied Muslim who can afford it must make the pilgrimage to Mecca at least once in his or her lifetime. Rituals of the Hajj include:
- Walking seven times around the Kaaba
- Walking seven times between Mount Safa and Mount Marwah recounting the steps of Abraham’s wife, while she was looking for water in the desert before Mecca developed into a settlement
- Spending a day in the desert at Mina and then a day in the desert in Arafat praying and worshiping God and following the foot steps of Abraham
- Symbolically stoning the Devil in Mina recounting Abraham’s actions (45)
Contributors and Attributions
- Islam. Authored by : Wikipedia for Schools. Located at : en.Wikipedia.org/wiki/Islam. License : CC BY-SA: Attribution-ShareAlike

The Five Pillars of Islam
Almost as soon as the Arab armies of Islam conquered new lands, they began erecting mosques and palaces, as well as commissioning other works of art as expressions of their faith and culture. Connected to this, many aspects of religious practice in Islam also emerged and were codified. The religious practice of Islam, which literally means to submit to God, is based on tenets that are known as the Five Pillars ( arkan ), to which all members of the Islamic community ( u mma ) should adhere.

Shahada (photo: Mustafa and Aziza , CC BY-SA 2.0)
1. The profession of faith (the shahada )
The profession of faith (the shahada ) is the most fundamental expression of Is lamic beliefs. It sim ply states that “There is no God but God and Muhammad is his prophet.” It underscores the monotheistic nature of Islam. It is an extremely popular phrase in Arabic calligraphy and appears in numerous manuscripts and religious buildings.

Prayer Rug with Coupled Columns, early 18th century, wool (warp, weft and pile), symmetrically knotted pile, attributed to Turkey, probably Ladik, Konya, 172.7 x 121.9 cm ( The Metropolitan Museum of Art )
2. Daily prayers ( salat )
Muslims are expected to pray five times a day. This does not mean that they need to attend a mosque to pray; rather, the salat , or the daily prayer, should be recited five times a day. Muslims can pray anywhere; however, they are meant to pray towards Mecca . The faithful are meant to pray by bowing several times while standing and then kneel and touch the ground or prayer mat with their foreheads, as a symbol of their reverence and submission to Allah. On Friday, many Muslims attend the mosque near mid-day to pray and to listen to a sermon ( khutba ).
3. Alms-giving ( zakat )
The giving of alms is the third pillar. Although not defined in the Qu’ran , Muslims believe that they are meant to share their wealth with those less fortunate in their community of believers.
4. Fasting during Ramadan ( saum )
During the holy month of Ramadan (the ninth month in the Islamic calendar), Muslims are expected to fast from dawn to dusk. While there are exceptions made for the sick, elderly, and pregnant, all are expected to refrain from eating and drinking during daylight hours.
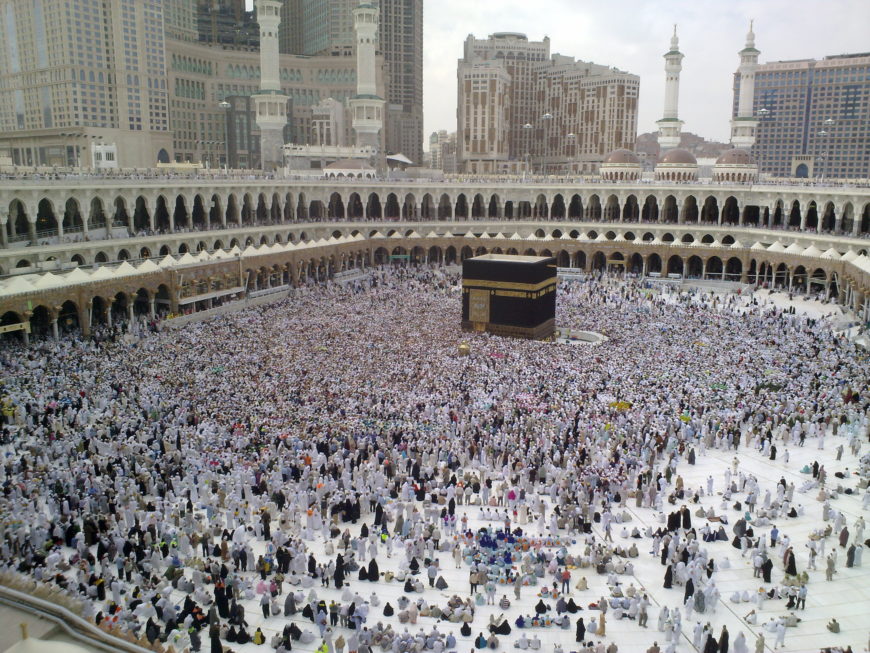

Last day of Hajj. All pilgrims leaving Mina, many already in Mecca for farewell circumambulation of Kaaba (photo: Omar Chatriwala , CC BY-SA 4.0 )
5. Hajj or pilgrimage to Mecca
All Muslims, who are able, are required to make the pilgrimage to Mecca and the surrounding holy sites at least once in their lives. Pilgrimage focuses on visiting the Kaaba and walking around it seven times. Pilgrimage occurs in the twelfth month of the Islamic Calendar.
Additional resources
More from Smarthistory on Hajj.
More Hajj stories from the Asian Art Museum.
More stories of the modern pilgrimage from the British Museum.
Smarthistory images for teaching and learning:
[flickr_tags user_id=”82032880@N00″ tags=”IslamIntro,”]
More Smarthistory images…
Cite this page
Your donations help make art history free and accessible to everyone!

IMAGES
VIDEO
COMMENTS
The second Islamic pillar is Salat or prayer. This tenet involves profession of wrongdoings. The profession process begins with the cleansing of oneself and spirit. Prayer is undertaken five times every day, from dawn to dusk. There are five prayers that fallunder Salat are Fajr, Shurooq, Asr, Dhuhr, Isha and Maghrib.
On Friday, many Muslims attend a mosque near midday to pray and to listen to a sermon ( khutba ). 3. Alms-giving ( zakat) The giving of alms is the third pillar. Although not defined in the Qu’ran, Muslims believe that they are meant to share their wealth with those less fortunate in their community of believers. 4.
Overview of the Five Pillars of Islam. Pillars of Sunni Islam. First pillar: Shahada (Declaration of Faith) Second Pillar: Salah (Prayer) Third Pillar: Zakat (Almsgiving) Fourth Pillar: Sawm (Fasting) Fifth Pillar: Hajj (Pilgrimage) Pillars of Shia Islam. Twelvers.
The “five pillars of Islam” are religious duties that provide a framework for a Muslim’s life. These duties are performed regularly and encompass duties to God, to personal spiritual growth, to care for the poor, self-discipline, and sacrifice. In Arabic, “arkan” (pillars) provide structure and hold something steadily in place.
Description: The merits and various rites performed in Hajj, the fifth of the five obligatory fundamental Muslim practices. The Hajj (pilgrimage to Mecca) is the fifth of the fundamental Muslim practices and institutions known as the five pillars of Islam. Pilgrimage is not undertaken in Islam to the shrines of saints, to monasteries for help ...
There are five key practices that all Muslims are obligated to fulfil throughout their lifetime. These practices are referred to as pillars because they form the foundation of Muslim life. The five pillars of Islam are Shahada, Salah, Zakat, Sawm, and Hajj.
These acts of worship, often called the "Five Pillars of Islam,” are based in the Qur’an and Sunnah and interpreted by the ‘ulama in the first three centuries of Islam. The Five Pillars are: the shahadah, salat, zakat, sawm, and Hajj. These grounding commitments shape the lives and practices of Muslims throughout the world, including in ...
The Pillars of Islam are five basic acts in Islam, considered obligatory for all believers. The Quran presents them as a framework for worship and a sign of commitment to the faith. They are: Shahadah (creed) Daily prayers (salat) Almsgiving (zakah) Fasting during Ramadan. Pilgrimage to Mecca (hajj) at least once in a lifetime.
5. Hajj or pilgrimage to Mecca. All Muslims, who are able, are required to make the pilgrimage to Mecca and the surrounding holy sites at least once in their lives. Pilgrimage focuses on visiting the Kaaba and walking around it seven times. Pilgrimage occurs in the twelfth month of the Islamic Calendar.