Educational Leadership: What Is It and Why Is It Important?

When it comes to the success of students and positive outcomes for whole families and communities, educational leadership can play a critical role.
Communities and whole societies are changing at a rapid pace, creating a tremendous need for practical-minded leaders who can innovate new ways of learning and meet the needs of diverse communities. Whether in traditional school settings, nonprofit organizations, or large corporations, thoughtful and skillful educational professionals in leadership roles can make all the difference.
Take Danielle Keane, a principal in the South Bronx, who dedicated herself to making the school “a place that people wanted to be” when the 2021 school year began. Throughout the summer, she hosted small in-person middle school graduations and facilitated “homecoming” sessions twice a week where families could come back to the school building and hear about safety measures, scheduled comedy nights and literacy classes. She hosted a movie night in the park and a back-to-school carnival. And when school started, she welcomed back 90% of the school’s students to in-person learning, well over the city’s average.
Educational leaders like Keane can transform whole communities through their meaningful work.
If you’re looking to take on an educational leadership role, you must first envision what is involved. There are many key qualities and skills a leader must incorporate into the many situations of the workplace. Depending on your skillset, you will be eligible for different career paths, salary levels, and opportunities .
No matter which academic or career path you choose, there are few callings more rewarding than that of a leader in education. In this blog, you can learn:
- What is Educational Leadership?
- Why Educational Leadership is Important
- Educational Leadership Qualities
- Educational Leadership Skills
- The Top Considerations of an Educational Leader
- Equity and Educational Leadership
- Educational Leadership Jobs
- Educational Leadership Doctoral Programs: PhD vs. Ed.D.

What is educational leadership?
Educational leadership is built on the premise of constructing and applying knowledge in ways that make a positive difference. Through collaboration and communication, professionals in educational leadership work with diverse communities and build partnerships to promote positive outcomes by setting and meeting transformative goals.
While many educational leadership professionals have advanced degrees and can work in academic settings, they are practitioners who work in applied positions. By connecting theory to real-world projects and contexts, educational leaders take a comprehensive, evidence-based, relational approach to problem-solving.
Request Your Free EdD Program Guide
Why educational leadership is important
The impact of educational leadership is felt throughout schools, nonprofits, and private sector organizations.
School Principals
A recent study by The Wallace Foundation reported that effective school leaders make both a stronger and broader positive impact on the schools they lead than research had previously shown. The study:
- Estimates that replacing a school principal in the 25th percentile of effectiveness with one in the 75th percentile of effectiveness would result in approximately three months of additional math and reading learning gains each year for students in that school
- Suggests that the impact of an effective principal on student learning is nearly as great as the impact of an effective teacher
- Finds that the way school principals approach educational leadership has a direct relationship with school outcomes and test scores
Higher Education Administrators
Leaders of educational institutions stand to influence everything from curricular decisions to public perception of their campus. Studies have found that the approach higher educational leaders take in making various decisions can have a powerful ripple effect throughout their faculty members, students, and even the broader community. For example:
- Higher education leaders’ positive attitudes toward diversity and inclusion efforts cultivate greater awareness of bias among employees who are less likely to experience the negative impacts of bias, thereby increasing the likelihood of those employees endorsing inclusion efforts.
- Leadership was found to be the most crucial enabler of agility in higher education institutions.
- Higher education institutions whose leaders have implemented disability-related supports see significantly higher rates of student persistence among students with disabilities.
Nonprofit Leaders
Studies show that nonprofit organizations with poor leadership negatively affect the staff working with them, the clientele they serve, and even the public at-large. Poor leadership in the nonprofit sector erodes public trust .
Conversely, nonprofit executives who receive relevant training in the knowledge and skills they need in order to effectively lead an organization experience positive personal outcomes (such as their mindsets) and improve their organization’s practices. Likewise, nonprofit leaders who guide their organizations in accountability, communication, and advocacy can help bring about more positive public perceptions of nonprofit organizations.
Human Resources Directors
HR professionals with a post-grad education degree are especially skilled at strategic collaboration with diverse audiences and stakeholders and promoting change across diverse organizational settings. Those abilities can promote meaningful change in human resources roles.
Effective human resources directors can make a noticeable difference in company culture, employee morale, and even the bottom line. Check out just a few statistics from McKinsey on the benefit of good human resources professionals:
- Organizations with human resources departments that facilitate a positive employee experience are 1.3 times more likely to report that they outperformed their organizational goals.
- Companies with cultures that rank in the top-quartile of the McKinsey Organization Health Index post a return to shareholders that is 60 percent higher than median companies and a staggering 200 percent higher than companies that rank in the bottom quartile.
Educational leadership qualities
While anyone can strive to become a successful educational leader, there are some common qualities that are found in professionals who tend to gravitate toward educational leadership: compassion, vision, and perseverance.
The role of an educational leader is, at its core, a role that seeks to meet the needs of others. Rachael George, an elementary school principal, spoke to the role of compassion in educational leadership in “ Leading with Compassion ,” a blog post for the Association for Supervision and Curriculum Development (ASCD) in which she discusses the impact of two colleagues in leadership roles:
“Creating bonds and intentionally fostering relationships with your community is the foundation for academic achievement. As three educational leaders, we strive to show genuine love for those in our community. That deep care is likely one of the reasons why our students have been successful, with each of our schools blasting through average scores on state assessments.”
Leadership roles involve goals and metrics, but they’re also about culture, creating a sense of belonging, and empowering people through connection. People who naturally come by compassion and seek to cultivate it in their lives have one of the key qualities of educational leaders—and, as George’s example shows, an emphasis on compassionate care for others often leads to positive outcomes and impressive metrics, as well.
Successful educational leaders tend to be people who can evaluate past challenges and policies where they work and develop a better way forward . Not only that—they can see, or collaborate in seeing, what it will take to get to that future place. Their ability to imagine and creatively plan, for example, can directly correlate to student success .
Take a look at a few examples of visionary leadership in an academic setting, nonprofit organization, and the private sector:
- A 2020 study found a positive relationship between visionary leadership in school principals and teacher performance.
- Nonprofit leaders report that visionary leadership improves raising of funds as well as recruitment of volunteers.
- Visionary leadership is identified as one of five leadership styles that are components of an optimistic leadership style that can determine successful, future-driven leadership .
Perseverance
Educational leaders are faced with many challenges. They are often called upon when social and cultural issues arise , when injustice dominates current events, and when individuals and communities are suffering. Attempting to develop long-term fixes for systemic problems while responding to immediate, pressing needs can be a tightrope to walk.
That’s why perseverance matters so much for educational leaders. For example, DonorBox ranks “resilience and stamina” as the number one quality of a successful nonprofit founder :
Hardship is a daily reality for most nonprofit leaders. The Greater Good Science Center defines resilience skills as being able to minimize the impact of stress, which in turn helps us avoid burnout. Nonprofit founders need to be flexible, willing to adapt, and able to move forward despite setbacks— demonstrating persistence.
Educational leadership skills
Professionals who are trained in educational leadership are equipped with many of the top skills that employers are looking for in the modern workplace. Some of the most important educational leadership skills, which correlate with some of the most-wanted skills among recruiters, schools, and companies, are analytical thinking, collaboration, and leadership.
Analytical Thinking
The World Economic Forum named “analytical thinking and innovation” as the number one skill for 2025 in “The Future of Jobs Report 2020 .” As more and more data becomes available in every sector, from education to the corporate world, leaders with strong analytical thinking skills are more necessary than ever when it comes to asking the right questions of the data set before them.
Consider just a few examples of how analytical thinking has made a positive difference in organizations led by educational leaders :
- School administrators are applying analytical thinking to student data to improve their return on investment for technology purchases and to highlight best practices that lead to better student outcomes. For example, a charter school administrator analyzed data and discovered that one biology teacher specifically outperformed the other biology teachers in the school. So the leader designated that teacher as the biology mentor for all charter schools in their system.
- Human resources directors are cutting through their cognitive biases and experiencing new insights in existing company cultures as they apply analytical thinking in minimizing bias and increasing fairness.
- Community college administrators find that good data analysis helps them to make more informed decisions and present compelling evidence to key stakeholders.
Collaboration
Educational leaders often spend a great deal of time speaking to others—whether those they are serving, those who work within their organizations, or community partners. By collaborating with diverse audiences and stakeholders about organizational research, practices, and theories, educational leaders can make collaborative strategic plans that lead to positive outcomes.
Here are some examples of how educational leaders have fostered collaboration to create positive effects:
- Ten liberal arts colleges in Pennsylvania partner to facilitate faculty development, study abroad programs, and compliance and risk management.
- Community organizations in rural north central Wisconsin collaborated to serve over 1000 immigrant families and provide them with information about the COVID-19 pandemic in their preferred language.
- A school district, a pair of agencies serving homeless youth, and a group of local philanthropists in Texas repurposed an abandoned school into a shelter that serves approximately 4,000 unhoused students.
The top considerations of an educational leader
Professionals in educational leadership roles will perform a multitude of tasks based on their specific positions, which is to say that a superintendent’s day may look quite different from a human resource director’s day. But, if we peel back the layers just a bit, we’ll see that many of their decisions and approaches are likely shaped in similar ways and based in similar issues faced by educational leaders, including:
- How to answer questions of equity, ethics, and social justice
- What it looks like to bring about solutions to complex problems
- The way to make a positive difference in a community or culture
- How to make and measure a positive impact in a given setting, person, or group
Equity and educational leadership
One of the highest callings of educational leaders is fostering diversity, inclusion, and equity among the people they lead. As a practitioner, the role of the educational leadership professional is not one of theory or distance from real communities. As people who work with people, educational leadership professionals are embedded every day in real-world circumstances that deal with questions of social justice, ethics, and equity.
Educational leaders may pursue greater equity for the people they serve through community partnerships, advocacy, or educational opportunities.
Educational leadership jobs
Careers in educational leadership range from small schools to huge corporations. Educational leadership often refers to administrative positions in schools, school districts, and universities. Many educational leadership professionals work as principals or assistant principals, instructional coordinators, and academic deans. These individuals help to meet the needs of students, families, and teachers so that each person has the opportunity to reach their goals and experience positive outcomes.
But, as we’ve discussed, school settings are not the only place where educational leadership is important. Educational leadership is also put into practice in the corporate setting, such as in the case of human resources directors, chief learning officers, and trainers. In the nonprofit sector, educational leadership professionals work as program directors, executive directors, and community organizers. Educational leadership professionals who are interested in policy may work as education policy analysts for school systems, in think tanks, or for lobbying organizations.
Educational leadership doctoral programs: PhD vs. EdD
For those who are interested in educational leadership programs, there are several options. Some people will go with a masters degree, others a PhD, and others an EdD. While professionals with master’s degrees can have successful careers in educational leadership, those with doctorates will experience more open doors and greater potential for the careers they want.
So then, what are the differences between a doctorate of education and PhD in education ? Before we get there, let’s note the similarities. Both degrees
- Are terminal degrees (the highest a student can go on that academic path)
- Focus on enhancing professional knowledge in various environments
- Make candidates more marketable and increase their salary potential
- Benefit graduates’ employers
- Prepare candidates for roles in administration, supervision, training, development, curriculum, instruction, and teaching
From that common ground, some differences emerge. Let’s take a look at what they are.
A PhD usually pursues a teaching career in academia and does first-hand research to help inform best practices. This allows candidates primary exploration of their field.
A PhD is likely to take on the role of an academic in higher education. PhD candidates are likely to publish original research in academic journals and present research papers at conferences.
An EdD program is designed to develop scholarly practitioners for applied positions in real-world settings. The research is oriented around making a local impact and developing a better understanding of a local context. An EdD will feature a substantial core curriculum in leading an organization, ethical leadership and social justice, and implementing organization change.
Because of its emphasis on real-world application, the EdD leads to more opportunities for its graduates. While PhD graduates will largely work in research and theory, which may limit the workplace opportunities for them, EdD graduates can apply their leadership knowledge in nearly any setting . It’s difficult to think of any workplace that wouldn’t benefit from visionary leadership, an emphasis on meaningful change and transformative partnerships. With an EdD, leaders can bring about impactful change in schools, nonprofits, government agencies, and businesses that support whole communities.
Become an effective educational leader with an EdD from Marymount University Online
Are you ready to foster strategic collaboration, empower meaningful change, and innovate in ways that make a direct, positive impact in schools, communities, or organizations? If so, an EdD from Marymount University Online may be an ideal fit for you.
The degree program is designed for working professionals who want to bring elevated skills to their current organizations or find new opportunities for leadership. With no GRE requirement and a path to completion that’s less than three years long, active professionals can prepare for educational leadership while maintaining their current personal and professional responsibilities.
Imagine your future in education administration, corporate leadership, nonprofit management, or policy analysis. You can take a step toward that future today. Prepare to use transformative leadership to promote change across diverse instructional and organizational settings. With our rigorous, practitioner-focused degree, you’ll be ready to effect change that matters.
Learn more about the EdD from Marymount University Online from our students .
Connect With Us
Complete the form to access our comprehensive program guide with more details about our:
- World-class faculty
- Application process
- Unique student support
An admissions advisor will be in touch to answer your questions and help determine if Marymount is right for you.
Complete The Form

Out-of-State Students
Clinical placement requirements are unique for each state. Please see our list of program offerings by state or contact us to determine whether our programs fulfill your state requirements.
CCNE Accreditation
The baccalaureate degree program in nursing at Marymount University is accredited by the Commission on Collegiate Nursing Education, 655 K Street, NW, Suite 750, Washington, DC 20001, 202-887-6791.
Requirements Not Met
To proceed with either the BSN to MSN FNP or the BSN to DNP FNP or the BSN to DNP PMHNP or the MSN PMHNP, you are required to have a bachelor’s degree and hold your RN license.
To proceed with either the PMC-FNP or the PMC-DNP or the PMC-PMHNP, you are required to have a master's degree and hold your RN license.
To proceed with the ABSN, you are required to have a bachelor's degree.
If you don’t meet these requirements but would still like further information, please contact us .
To proceed with the EdD in Educational Leadership and Organizational Leadership degree, you are required to have a master’s degree.
If you don’t meet this requirement but would still like further information, please contact us .
To proceed with the Doctor of Business Administration - Business Intelligence degree, you are required to have a master’s degree.
X Close Box
© 2024 Marymount University • All Rights Reserved • Privacy Policy • California Privacy Notice
- Schedule an Appointment
- Request Info
- Open supplemental data
- Reference Manager
- Simple TEXT file
People also looked at
Review article, strategy and strategic leadership in education: a scoping review.

- 1 Universidade Católica Portuguesa, Research Centre for Human Development, Porto, Portugal
- 2 Universidade de Évora, Évora, Portugal
Strategy and strategic leadership are critical issues for school leaders. However, strategy as a field of research has largely been overlooked within the educational leadership literature. Most of the theoretical and empirical work on strategy and strategic leadership over the past decades has been related to non-educational settings, and scholarship devoted to these issues in education is still minimal. The purpose of this scoping review was to provide a comprehensive overview of relevant research regarding strategy and strategic leadership, identifying any gaps in the literature that could inform future research agendas and evidence for practice. The scoping review is underpinned by the five-stage framework of Arksey and O’Malley . The results indicate that there is scarce literature about strategy and that timid steps have been made toward a more integrated and comprehensive model of strategic leadership. It is necessary to expand research into more complex, longitudinal, and explanatory ways due to a better understanding of these constructs.
Introduction
Strategy and strategic leadership are critical issues for school leaders ( Davies and Davies, 2006 ; Davies and Davies, 2010 ; Eacott, 2010a ; Eacott, 2011 ). However, strategy as a field of research has largely been overlooked in educational leadership literature ( Davies and Davies, 2006 ; Eacott, 2008a ; Eacott, 2008b ; Davies and Davies, 2010 ; Eacott, 2011 ). Most of the theoretical and empirical work on strategy and strategic leadership over the past decades has been related to non-educational settings, and scholarship devoted to these issues in education is still very limited ( Cheng, 2010 ; Eacott, 2011 ; Chan, 2018 ).
The concept of strategy appeared in educational management literature in the 1980s; however, little research was produced until the 1990s (cf. Eacott, 2008b ). Specific educational reforms led to large amounts of international literature mostly devoted to strategic planning ( Eacott, 2008a ; Eacott, 2008b ; Eacott, 2011 ). For a long period, the concept of strategy was incomplete and confusing. The word “strategy” was often used to characterize different kinds of actions, namely, to weight management activities, to describe a high range of leadership activities, to define planning, or to report to individual actions within an organization ( Eacott, 2008a ).
Strategy and strategic planning became synonymous ( Eacott, 2008b ). However, strategy and planning are different concepts, with the strategy being more than the pursuit of a plan ( Davies, 2003 , Davies, 2006 ; Eacott, 2008a ; Eacott, 2008b ; Quong and Walker, 2010 ). Both phases of plans’ design and plans’ implementation are related, and the quality of this second phase highly depends on planning’ quality ( Davies, 2006 ; Davies, 2007 ; Eacott, 2008a ; Eacott, 2008b ; Eacott, 2011 ; Meyers and VanGronigen, 2019 ). Planning and acting are related and must emerge from the strategy. As stated by Bell (2004) .
Planning based on a coherent strategy demands that the aims of the school are challenged, that both present and future environmental influences inform the development of the strategy, that there should be a clear and well-articulated vision of what the school should be like in the future and that planning should be long-term and holistic (p. 453).
Therefore, it is necessary to adopt a comprehensive and holistic framework of strategy, considering it as a way of intentionally thinking and acting by giving sense to a specific school vision or mission ( Davies, 2003 , 2006 ; Eacott, 2008a ; Eacott, 2008b ; Quong and Walker, 2010 ).
The works of Davies and colleagues ( Davies, 2003 ; Davies, 2004 ; Davies and Davies, 2004 ; Davies and Davies, 2006 ; Davies and Davies, 2010 ) and Eacott (2008a , 2008b) , Eacott (2010a , 2011) were essential and contributed to a shift in the rationale regarding strategy by highlighting a more integrative and alternate view. Davies and colleagues ( Davies, 2003 ; Davies, 2004 ; Davies and Davies, 2004 ; Davies and Davies, 2006 ; Davies and Davies, 2010 ) developed a comprehensive framework for strategically focused schools , comprising strategic processes, approaches, and leadership. In this model, the strategy is conceptualized as a framework for present and future actions, sustained by strategic thinking about medium to long term goals, and aligned to school vision or direction.
Strategic leadership assumes necessarily a relevant role in strategically focused schools. Eacott (2006) defines strategic leadership as “leadership strategies and behaviors relating to the initiation, development, implementation, monitoring, and evaluation of strategic actions within an educational institution, taking into consideration the unique context (past, present, and future) and availability of resources, physical, financial and human” (p. 1). Thereby, key elements of strategic leadership can be identified as one that: 1) acts in a proactive way to contextual changes; 2) leads school analysis and response to changing environment; 3) leads planning and action for school effectiveness and improvement in face of contextual challenges and; 4) leads monitoring and evaluation processes to inform decision making strategically ( Cheng, 2010 ). This brings to the arena a complex and dynamic view of strategic leadership as it is a complex social activity that considers important historical, economic, technological, cultural, social, and political influences and challenges ( Eacott, 2011 ).
Along with these authors, this paper advocates a more comprehensive and contextualized view of strategy and strategic leadership, where strategy is the core element of any leadership action in schools ( Davies and Davies, 2010 ; Eacott, 2011 ). Here, strategic leadership is not seen as a new theory, but an element of all educational leadership and management theories ( Davies and Davies, 2010 ). Even so, these concepts can inform and be informed by diverse leadership theories, a strategy-specific framework is needed in the educational field.
Considering all the above, strategy can be identified as a topic that is being researched in education, in the recent decades. Nonetheless, there is still scarce educational literature about this issue ( Davies and Davies, 2006 ; Davies and Davies, 2010 ; Cheng, 2010 ; Eacott, 2011 ; Chan, 2018 ). After 10 years of Eacott’s analysis of literature on strategy in education, it seems that this educational construct is being overlooked as there is still no consensual definition of strategy, different studies are supported in diverse conceptual frameworks and empirical studies about this topic are scarce ( Cheng, 2010 ; Eacott, 2011 ; Chan, 2018 ). Moreover, despite the interest of a multidisciplinary vision of strategy and strategic leadership, we agree with Eacott (2008b) about the need for a meaningful definition of strategy and strategic leadership in education, as it is a field with its specifications. Hence, research is needed for a clear definition of strategy, an integrated and complete framework for strategic action, a better identification of multiple dimensions of strategy and a comprehensive model of strategic leadership that has strategic thinking and action as core elements for schools improvement (e.g., Eacott, 2010a ; Hopkins et al., 2014 ; Reynolds et al., 2014 ; Harris et al., 2015 ; Bellei et al., 2016 ). This paper aims to contribute to the field offering a scoping review on strategy and strategic leadership in the educational field.
A clear idea of what strategy and strategic leadership mean and what theory or theories support it are of great importance for research and practice. This scoping review is an attempt to contribute to a strategy-specific theory by continuing to focus on ways to appropriately develop specific theories about strategy and strategic leadership in the educational field, particularly focusing on school contexts.
This study is a scoping review of the literature related to strategy and strategic leadership, which aims to map its specific aspects as considered in educational literature. Scoping reviews are used to present a broad overview of the evidence about a topic, irrespective of study quality, and are useful when examining emergent areas, to clarify key concepts or to identify gaps in research (e.g., Arksey and O’Malley, 2005 ; Peters et al., 2015 ; Tricco et al., 2016 ). Since in the current study we wanted to explore and categorize, but not evaluate, information available concerning specific aspects of strategy in educational literature, we recognize that scoping review methodology serves well this purpose.
In this study, Arksey and O’Malley (2005) five-stage framework for scoping reviews, complemented by the guidelines of other authors ( Levac et al., 2010 ; Colquhoun et al., 2014 ; Peters et al., 2015 ; Khalil et al., 2016 ), was employed. The five stages of Arksey and O’Malley’s framework are 1) identifying the initial research questions, 2) identifying relevant studies, 3) study selection, 4) charting the data, and 5) collating, summarizing and reporting the results. In the sections below, the process of this scoping review is presented.
Identifying the Initial Research Questions
The focus of this review was to explore key aspects of strategy and strategic leadership in educational literature. The primary question that guided this research was: What is known about strategy and strategic leadership in schools? This question was subdivided into the following questions: How should strategy and strategic leadership in schools be defined? What are the main characteristics of strategic leadership in schools? What key variables are related to strategy and strategic leadership in schools?
Identifying Relevant Studies
As suggested by Arksey and O’Malley (2005) , keywords for the search were defined, and databases were selected. Key concepts and search terms were developed to capture literature related to strategy and strategic leadership in schools, considering international perspectives. The linked descriptive key search algorithm that was developed to guide the search is outlined in Table 1 .

TABLE 1 . Key search algorithm.
Considering scoping review characteristics, time and resources available, inclusion and exclusion criteria were developed. Papers related to strategy and strategic leadership, published between 1990 and 2019, were included. Educational literature has reported the concepts of strategy and strategic leadership since the 1980s ( Eacott, 2008a ; 2008b ). However, it gained expansion between 1990 and 2000 with studies flourishing mostly about strategic planning ( Eacott, 2008b ). Previous research argues that strategy is more than planning, taking note of the need to distinguish the concepts. Considering our focus on strategy and strategic leadership, studies about strategic planning were excluded as well as papers specifically related to other theories of leadership than strategic leadership. A full list of inclusion and exclusion criteria is outlined in Table 2 .

TABLE 2 . Inclusion and exclusion criteria.
The following six electronic databases were searched to identify peer-reviewed literature: ERIC, Education Source, Academic Search Complete, Science Direct, Emerland, and Web of Science. Additionally, a manual search of the reference lists of identified articles was undertaken, and Google Scholar was utilized to identify any other primary sources. The review of the literature was completed over 2 months, ending in August 2019.
Study Selection
The process of studies’ selection followed the Preferred Reporting of Items for Systematic Reviews and Meta-Analyses (PRISMA) Statement ( Moher et al., 2009 ). Figure 1 illustrates the process of article selection.
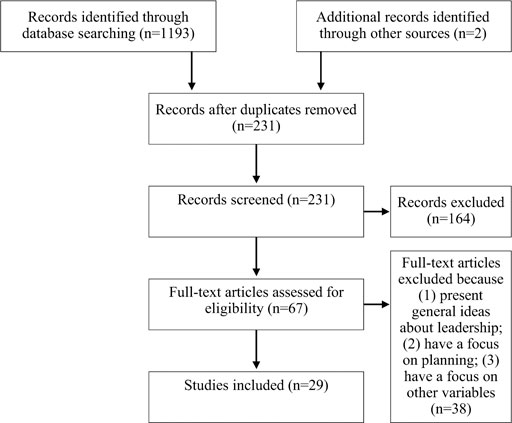
FIGURE 1 . PRISMA chart outlining the study selection process.
With the key search descriptors, 1,193 articles were identified. A further number of articles were identified using Google Scholar. However, a large number of articles were removed from the search, as they were duplicated in databases, and 231 studies were identified as being relevant.
The next phases of studies’ selection were guided by the inclusion and exclusion criteria presented above. A screening of the titles, keywords, and abstracts revealed a large number of irrelevant articles, particularly those related to strategic planning (e.g., Agi, 2017 ) and with general ideas about leadership (e.g., Corral and Gámez, 2010 ). Only 67 studies were selected for full-text access and analyses.
Full-text versions of the 67 articles were obtained, with each article being reviewed and confirmed as appropriate. This process provided an opportunity to identify any further additional relevant literature from a review of the reference lists of each article (backward reference search; n = 2). Ultimately, both with database search and backward reference search, a total of 29 articles were included to be analyzed in the scoping review, considering inclusion and exclusion criteria. During this process of study selection, several studies were excluded. As in the previous phase, examples of excluded papers include studies related to strategic planning where the focus is on the planning processes (e.g., Bennett et al., 2000 ; Al-Zboon and Hasan, 2012 ; Schlebusch and Mokhatle, 2016 ) or with general ideas about leadership (e.g., FitzGerald and Quiñones, 2018 ). Additionally, articles that were primarily associated with other topics or related to specific leadership theories (e.g., instructional leadership, transformational leadership) and that only referred briefly to strategic leadership were excluded (e.g., Bandur, 2012 ; Malin and Hackmann, 2017 ). Despite the interest of all these topics for strategic action, we were interested specifically in the concepts of strategy, strategic leadership, and its specifications in educational literature.
Data Charting and Collation
The fourth stage of Arksey and O’Malley (2005) scoping review framework consists of charting the selected articles. Summaries were developed for each article related to the author, year, location of the study, participants, study methods, and a brief synthesis of study results related to our research questions. Details of included studies are provided in the table available in Supplementary Appendix S1 .

Summarising and Reporting Findings
The fifth and final stage of Arksey and O’Malley (2005) scoping review framework summarises and reports findings as presented in the next section. All the 29 articles were studied carefully and a content analysis was taken to answer research questions. Research questions guided summaries and synthesis of literature content.
In this section, results are presented first with a brief description of the origin and nature of the studies, and then as answering research questions previously defined.
This scoping review yielded 29 articles, specifically devoted to strategy and strategic leadership in education, from eleven different countries (cf. Figure 2 ). The United Kingdom and Australia have the highest numbers of papers. There is a notable dispersion of literature in terms of geographical distribution.
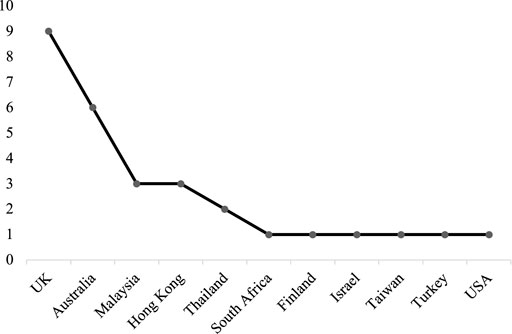
FIGURE 2 . Number of papers per country.
A large number of these articles were published by Brent Davies and colleagues ( N = 9) and Scott Eacott ( N = 6). Without question, these authors have influenced and shaped the theoretical grounding about strategy and strategic leadership in educational literature. While Davies and colleagues have contributed to design a framework of strategy and strategic leadership, influencing the emergence of other studies related to these topics, Eacott provided an essential contribution by exploring, systematizing, and problematizing the existing literature about these same issues. The other authors have published between one and two papers about these topics.
Seventeen papers are of conceptual or theoretical nature, and twelve are empirical research papers (quantitative methods–7; qualitative methods–4; mixed methods–1). The conceptual/theoretical papers analyze the concepts of strategy and strategic leadership, present a framework for strategic leadership, and discuss implications for leaders’ actions. The majority of empirical studies are related to the skills, characteristics, and actions of strategic leaders. Other empirical studies explore relations between strategic leadership and other variables, such as collaboration, culture of teaching, organizational learning, and school effectiveness.
How should Strategy and Strategic Leadership in Schools be Defined?
The concept of strategy is relatively new in educational literature and, in great part, related to school planning. In this scoping review, a more integrated and comprehensive view is adopted ( Davies, 2003 ; Davies, 2006 ; Eacott, 2008a ; Eacott, 2008b ; Quong and Walker, 2010 ). Davies (2003) defined strategy as a specific pattern of decisions and actions taken to achieve an organization’s goals (p. 295). This concept of strategy entails some specific aspects, mainly that strategy implies a broader view incorporating data about a specific situation or context ( Davies, 2003 ; Dimmock and Walker, 2004 ; Davies, 2006 ; Davies, 2007 ). It is a broad organizational-wide perspective , supported by a vision and direction setting , that conceals longer-term views with short ones ( Davies, 2003 ; Dimmock and Walker, 2004 ; Davies, 2006 ; Davies, 2007 ). It can be seen as a template for short-term action . However, it deals mostly with medium-and longer-term views of three-to 5-year perspectives ( Davies, 2003 ; Davies, 2006 ; Davies, 2007 ). In this sense, a strategy is much more a perspective or a way of thinking that frames strategically successful schools ( Davies, 2003 ; Davies and Davies, 2005 ; Davies, 2006 ; Davies and Davies, 2010 ).
Eacott (2008a) has argued that strategy in the educational leadership context is a field of practice and application that is of a multidisciplinary or interdisciplinary nature. More than a single definition of strategy, what is needed is a conceptual understanding and articulation of its fundamental features, which removes the need to answer, “what is a strategy?” Understanding strategy as choosing a direction within a given context, through leadership, and articulating that direction through management practices ( Eacott, 2008a , p. 356) brings to the arena diverse elements of strategy from both leadership and management. From this alternative point of view, a strategy may be seen as leadership ( Eacott, 2010a ). More than an answer to “what is a strategy?”, it is crucial to understand “when and how does the strategy exist?” ( Eacott, 2010a ), removing the focus on leaders’ behaviors and actions per se to cultural, social, and political relationships ( Eacott, 2011 ). Hence, research strategy and strategic leadership oblige by acknowledging the broader educational, societal, and political contexts ( Dimmock and Walker, 2004 ; Eacott, 2010a ; Eacott, 2010b ; Eacott, 2011 ).
Strategic leadership is a critical component of school development ( Davies and Davies, 2006 ). However, to define leadership is challenging considering the amount of extensive, diverse literature about this issue. Instead of presenting a new categorization about leadership, the authors most devoted to strategic leadership consider it as a key dimension of any activity of leadership ( Davies and Davies, 2004 ; Davies and Davies, 2006 ; Eacott, 2010a ; Eacott, 2010b ; Eacott, 2011 ). Barron et al. (1995) stressed the idea of change. As mentioned by the authors, implementation of strategic leadership means change: change in thinking, change in the way schools are organized, change in management styles, change in the distribution of power, change in teacher education programs, and change in roles of all participants ( Barron et al., 1995 , p. 180). Strategic leadership is about creating a vision, setting the direction of the school over the medium-to longer-term and translating it into action ( Davies and Davies, 2010 ; Eacott, 2011 ). In that sense, strategic leadership is a new way of thinking ( Barron et al., 1995 ) that determines a dynamic and iterative process of functioning in schools ( Eacott, 2008b ).
In their model of strategic leadership, Davies and Davies (2006) consider that leadership must be based on strategic intelligence, summarised as three types of wisdom: 1) people wisdom, which includes participation and sharing information with others, developing creative thinking and motivation, and developing capabilities and competencies within the school; 2) contextual wisdom, which comprises understanding and developing school culture, sharing values and beliefs, developing networks, and understanding external environment; and 3) procedural wisdom, which consists of the continuous cycle of learning, aligning, timing and acting. This model also includes strategic processes and strategic approaches that authors define as the centre of this cycle ( Davies and Davies, 2006 , p. 136).
To deeply understand strategic leadership, it is necessary to explore strategic processes and approaches that leaders take ( Davies and Davies, 2010 ). In this sense, strategic leadership, strategic processes, and strategic approaches are key elements for sustainable and successful schools, which are found to be strategically focused. Davies (2006) designed a model for a strategically focused school that may be defined as one that is educationally effective in the short-term but also has a clear framework and processes to translate core moral purpose and vision into an excellent educational provision that is challenging and sustainable in the medium-to long-term (p.11). This model incorporates 1) strategic processes (conceptualization, engagement, articulation, and implementation), 2) strategic approaches (strategic planning, emergent strategy, decentralized strategy, and strategic intent), and 3) strategic leadership (organizational abilities and personal characteristics). Based on these different dimensions, strategically focused schools have built-in sustainability, develop set strategic measures to assess their success, are restless, are networked, use multi-approach planning processes, build the strategic architecture of the school, are strategically opportunistic, deploy strategy in timing and abandonment and sustain strategic leadership ( Davies, 2004 , pp.22–26).
What Are the Main Characteristics of Strategic Leadership in Schools?
Davies (2003) , Davies and Davies (2005) , Davies and Davies (2006) , Davies and Davies (2010) discuss what strategic leaders do (organizational abilities) and what characteristics strategic leaders display (personal characteristics). The key activities of strategic leaders, or organizational abilities, are 1) create a vision and setting a direction, 2) translate strategy into action, 3) influence and develop staff to deliver the strategy, 4) balance the strategic and the operational, 5) determine effective intervention points ( what, how, when, what not to do and what to give up ), 6) develop strategic capabilities, and 7) define measures of success ( Davies and Davies, 2006 ; Davies and Davies, 2010 ). The main characteristics that strategic leaders display, or their characteristics, are 1) dissatisfaction or restlessness with the present, 2) absorptive capacity, 3) adaptive capacity, and 4) wisdom.
Two specific studies explored the strategic leadership characteristics of Malaysian leaders ( Ali, 2012 ; Ali, 2018 ), considering the above-mentioned model as a framework. For Malaysian Quality National Primary School Leaders, the results supported three organizational capabilities (strategic orientation, translation, and alignment) and three individual characteristics of strategic leadership (dissatisfaction or restlessness with the present, absorptive capacity, and adaptive capacity). For Malaysian vocational college educational leaders, the results were consistent with seven distinct practices of strategic leadership, such as strategic orientation, strategic alignment, strategic intervention, restlessness, absorptive capacity, adaptive capacity, and leadership wisdom.
Other studies were also focused on the characteristics of strategic leadership with different populations and countries. Chatchawaphun et al. (2016) identified the principles, attributes, and skills of the strategic leadership of secondary school administrators from Thailand. The principles identified within the sample of principals included appropriate values, modern visionary, future focusing strategy, empirical evidence focus, intention toward accomplishment, decency, and making relationships. The attributes found were strategic learning, strategic thinking, and value push up. The skills were learning, interpretation, forecasting, planning, challenge, and decision making. Chan (2018) explored strategic leadership practices performed by Hong Kong school leaders of early childhood education and identified effective planning and management, reflective and flexible thinking, and networking and professional development as variables. Eacott (2010c) investigated the strategic role of Australian public primary school principals concerning the leader characteristics of tenure (referring to the time in years in their current substantive position) and functional track (referring to the time in years spent at different levels of the organizational hierarchy). These demographic variables have moderating effects on the strategic leadership and management of participants. These five studies seem to be outstanding contributions to solidify a framework of strategic leadership and to test it with different populations in different countries.
Additionally, Quong and Walker (2010) present seven principles for effective and successful strategic leaders. Strategic leaders are future-oriented and have a future strategy, their practices are evidence-based and research-led, they get things done, open new horizons, are fit to lead, make good partners and do the “next” right thing—these seven principles of action seem related to the proposal of Davies and colleagues. Both authors highlighted visions for the future, future long-term plans, and plans’ translation into action as important characteristics of strategic leaders.
One other dimension that is being explored in research relates to ethics. Several authors assert that insufficient attention and research have been given to aspects related to moral or ethical leadership among school leaders ( Glanz, 2010 ; Quong and Walker, 2010 ; Kangaslahti, 2012 ). The seventh principle of the Quong and Walker (2010) model of strategic leadership is that leaders do the “next” right thing. This relates to the ethical dimension of leadership, meaning that strategic leaders recognize the importance of ethical behaviors and act accordingly. For some authors, ethics in strategic leadership is a critical issue for researchers and practitioners that needs to be taken into consideration ( Glanz, 2010 ; Quong and Walker, 2010 ). Glanz (2010) underlined social justice and caring perspectives as required to frame strategic initiatives. Kangaslahti (2012) analyzed the strategic dilemmas that leaders face in educational settings (e.g., top-down strategy vs. bottom-up strategy process; leadership by authority vs. staff empowerment; focus on administration vs. focus on pedagogy; secret planning and decision making vs. open, transparent organization; the well-being of pupils vs. well-being of staff) and how they can be tackled by dilemma reconciliation. Chen (2008) , in case study research, explored the conflicts that school administrators have confronted in facilitating school reform in Taiwan. The author identified four themes related to strategic leadership in coping with the conflicts accompanying this school reform: 1) educational values, 2) timeframe for change, 3) capacity building, and 4) community involvement. These studies reinforce the idea that school improvement and success seem to be influenced by the way leaders think strategically and deal with conflicts or dilemmas. Researchers need to design ethical frameworks or models from which practitioners can think ethically about their strategic initiatives and their dilemmas or conflicts ( Chen, 2008 ; Glanz, 2010 ; Kangaslahti, 2012 ).
Despite the critical contribution of Davies’ models ( Davies, 2003 ; Davies, 2004 ; Davies and Davies, 2006 ; Davies and Davies, 2010 ) and subsequent works, Eacott (2010a) questions the production of lists of behaviors and traits. This is likely one of the main differences between Davies’ and Eacott’s contributions in this field. While Davies and colleagues include organizational abilities and personal characteristics in their model of strategic leadership, Eacott (2010a , 2010b) emphasizes the broader context where strategy occurs. These ideas, however, are not contradictory but complementary in the comprehension of strategy as leadership in education since both authors present a comprehensive and integrated model of strategic leadership. Even though Davies and colleagues present some specific characteristics of leaders, these characteristics are incorporated into a large model for strategy in schools.
What Are Other Key Variables Related to Strategy and Strategic Leadership in Schools?
Other studies investigated the relationship between strategic leadership and other key variables, such as collaboration ( Ismail et al., 2018 ), the culture of teaching ( Khumalo, 2018 ), organizational learning ( Aydin et al., 2015 ) and school effectiveness ( Prasertcharoensuk and Tang, 2017 ).
One descriptive survey study presented teacher collaboration as a mediator of strategic leadership and teaching quality ( Ismail et al., 2018 ). The authors argue that school leaders who demonstrate strategic leadership practices can lead to the creation of collaborative practices among teachers and thus help to improve the professional standards among them, namely, teaching quality ( Ismail et al., 2018 ). One cross-sectional study identified positive and significant relations among the variables of strategic leadership actions and organizational learning. Transforming, political, and ethical leadership actions were identified as significant predictors of organizational learning. However, managing actions were not found to be a significant predictor ( Aydin et al., 2015 ). One other study establishes that strategic leadership practices promote a teaching culture defined as the commitment through quality teaching for learning outcomes ( Khumalo, 2018 ). These three studies provide essential highlights of the relevance of strategic leadership for school improvement and quality. Nonetheless, it is interesting to note that in a research survey that examined the effect of leadership factors of administrators on school effectiveness, the authors concluded that the direct, indirect, and overall effects of the administrators’ strategic leadership had no significant impact on school effectiveness ( Prasertcharoensuk and Tang, 2017 ). These studies introduce important questions that need to be explored both related to strategy and strategic leadership features and its relations and impacts on relevant school variables. Such studies stimulate researchers to explore these and other factors that relate to strategic leadership.
The knowledge about strategy and strategic leadership is still incomplete and confusing ( Eacott, 2008a ; Eacott, 2008b ). From the 29 studies selected, divergent data and multiple concepts of strategy can be identified which reinforces the confusion about these issues. Some integrative clarification is still needed about the concepts of strategy and strategic leadership as about its core features. In this section, it is intended to contribute to the clarification and integration of the concepts considering the studies selected.
The emergence of politics and reforms related to school autonomy and responsibility in terms of efficacy and accountability brings the concept of strategy to the educational literature ( Eacott, 2008b ; Cheng, 2010 ). It first appeared in the 1980s but gained momentum between 1990 and 2000. However, the main focus of the literature was on strategic planning based upon mechanistic or technical-rational models of strategy. Authors have criticized the conceptualization of strategy as a way for elaborating a specific plan of action for schools ( Davies, 2003 ; Davies, 2006 ; Eacott, 2008a ; Eacott, 2008b ; Quong and Walker, 2010 ). These same authors adopted a more comprehensive and holistic model of strategy. The concepts have been developed from a more rational and mechanistic view related to planning processes to a more comprehensive and complex view of strategy and leadership that take into consideration a situated and contextual framework. Considering the contribution of these studies, strategy incorporates three core dimensions, articulated with a schoolwide perspective 1) Vision, mission and direction (e.g., Davies, 2003 ; Dimmock and Walker, 2004 ; Davies, 2006 ; Davies and Davies, 2006 ; Davies, 2007 ; Eacott, 2008a ) 2) Intentional thinking (e.g., Barron et al., 1995 ; Davies, 2003 ; Davies and Davies, 2005 ; Davies, 2006 ; Davies and Davies, 2010 ): and; 3) Articulated decision-making and action (e.g., Davies, 2003 ; Dimmock and Walker, 2004 ; Davies and Davies, 2006 ; Davies, 2006 ; Davies, 2007 ; Eacott, 2008a ; Eacott, 2010a ; Eacott, 2010b ; Eacott, 2011 ).
Strategic leaders have an important role in strategy but, even considering this comprehensive and holistic concept of strategy, research poses the question of what are the main characteristics of strategic leaders in schools? From the literature reviewed, specific abilities, behaviors, and other characteristics may be identified. Looking for an integrated picture of strategic leadership, Table 3 represents the main contributions of the studies selected.
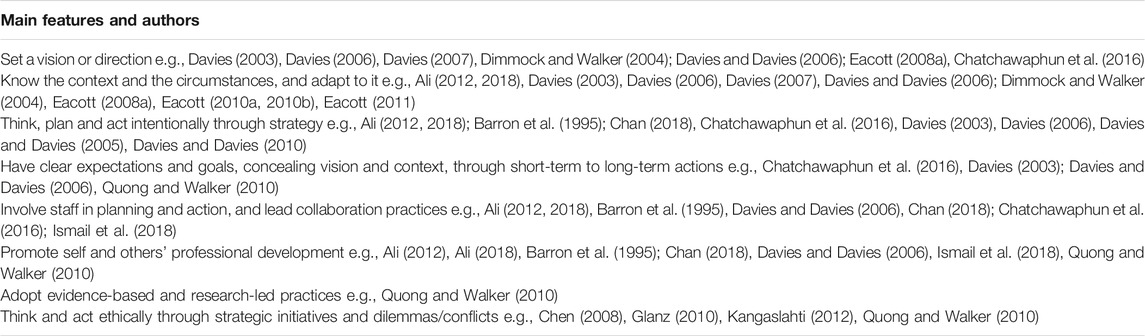
TABLE 3 . Strategic leadership: Main features.
Despite the contribution of these studies to deep knowledge about strategic leadership, the discussion here considers whether it is worthwhile to produce lists of behaviors and traits for strategic leaders in the absence of an integrated model that acknowledges the broader educational, societal and political context ( Dimmock and Walker, 2004 ; Eacott, 2010a ; Eacott, 2010b ; Eacott, 2011 ). Eacott (2011) argues that strategy, as constructed through analysis, is decontextualized and dehumanized and essentially a vacuous concept with limited utility to the practice that it seeks to explain (p. 426). Without a comprehensive and contextual model of strategy and strategic leadership, supported by research, the topics may still be overlooked and misunderstood. With this in mind, Figure 3 attempts to represent the core dimensions of strategy from a comprehensive perspective.
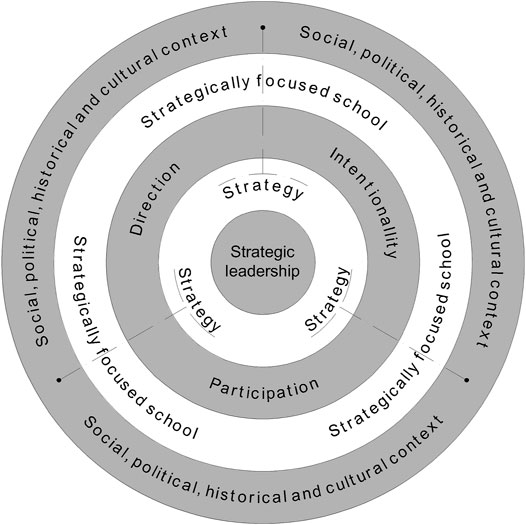
FIGURE 3 . Strategy and core dimensions from a comprehensive perspective.
As this is a scoping review, we tried to display a general view of the literature that can serve as a basis for a specific strategy theory in education and to more in-depth studies related to strategy and strategic leadership in schools. Nevertheless, we need to identify some methodological limitations of this study. As a scoping review, methods and reporting need improvement ( Tricco et al., 2018 ) and we are aware of this circumstance. Also, our search strategy may have overlooked some existing studies, since grey documents (e.g., reports) and studies from diverse languages than English were not included, that can misrepresent important data. Besides, inclusion criteria focused only on studies specifically devoted to strategy (not strategic planning) and strategic leadership (no other theories of leadership), but we acknowledge important contributions from this specific literature that were excluded. Finally, in our study there is no comparative analysis between the western and eastern/oriental contexts. However, we are aware that these contexts really differ and a context-specific reflection on strategy and strategic leadership in education would be useful. More research is needed to overcome the limitations mentioned.
Besides, the pandemic COVID19 brought new challenges in education, and particularly, to leaders. This study occurred before the pandemic and this condition was not acknowledged. However, much has changed in education as a consequence of the pandemic control measures, these changes vary from country to country, and schools’ strategies have changed for sure. Future research needs to explore strategy and strategic leadership in education considering a new era post pandemic.
With this scoping review, the authors aimed to contribute to enduring theories about strategy and strategic leadership in education. From our findings, it appears that this issue is being little explored. Despite the important contributions of authors cited in this scoping review ( Aydin et al., 2015 ; Chatchawaphun et al., 2016 ; Prasertcharoensuk and Tang, 2017 ; Ali, 2018 ; Chan, 2018 ; Ismail et al., 2018 ; Khumalo, 2018 ), minor advances seem to have been made after 2010. This is intriguing taking into account the leaders’ role in the third wave of educational reform, where strategic leadership pursues a new vision and new aims for education due to maximizing learning opportunities for students through “ triplisation in education’ (i.e., as an integrative process of globalization, localization and individualization in education)” ( Cheng, 2010 , p. 48). It was expected that research moved from rational planning models towards a more complex view of strategy in education ( Eacott, 2011 ). This review brings the idea that some timid and situated steps have been made.
Since the important review by Eacott, published in 2008, a step forward was made in the distinction between strategy and planning. Despite the significant number of papers about planning that were found during this review, the majority were published before 2008 (e.g., Nebgen, 1990 ; Broadhead et al., 1998 ; Bennett et al., 2000 ; Beach and Lindahl, 2004 ; Bell, 2004 ). Also, most of the papers selected adopt a more integrative, comprehensive, and complex view of strategy and strategic leadership (e.g., Eacott, 2010a ; Eacott, 2010b ; Davies and Davies, 2010 ; Eacott, 2011 ; Ali, 2012 ; Ali, 2018 ; Chan, 2018 ). More than identifying the “best of” strategy and strategic leadership, alternative models understand strategy as a way of thinking ( Davies and Davies, 2010 ) and a work in progress ( Eacott, 2011 ).
This also resonates with the educational literature about loosely coupled systems . There is evidence that loosely coupled educational organizations continue to exist and that resistance to change is a characteristic of school organizations ( Hautala et al., 2018 ). Strategic leadership gains relevance since leaders need to consider how to manage their loose and tight configurations and, hence, reinforce simultaneous personal and organizational dimensions related to school improvement. It is time to expand the research into more complex, longitudinal, and explanatory ways due to a better understanding of the constructs. This scoping review was an attempt to contribute to this endeavor by integrating and systematizing educational literature about strategy and strategic leadership.
Author Contributions
MC-collected and analyzed data, write the paper IC, JV, and JA-guided the research process and reviewed the paper.
Conflict of Interest
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Publisher’s Note
All claims expressed in this article are solely those of the authors and do not necessarily represent those of their affiliated organizations, or those of the publisher, the editors and the reviewers. Any product that may be evaluated in this article, or claim that may be made by its manufacturer, is not guaranteed or endorsed by the publisher.
Acknowledgments
The authors are grateful to the Fundação para a Ciência e Tecnologia (FCT) for the support to this publication (Ref. UIDB/04872/2020).
Supplementary Material
The Supplementary Material for this article can be found online at: https://www.frontiersin.org/articles/10.3389/feduc.2021.706608/full#supplementary-material
Agi, U. (2017). School Development Planning: A Strategic Tool for Secondary School Improvement in Rivers State, Nigeria. J. Int. Soc. Teach. Educ. 21 (1), 88–99.
Google Scholar
Al-Zboon, W., and Hasan, M. (2012). Strategic School Planning in Jordan. Education 132 (4), 809–825.
Arksey, H., and O'Malley, L. (2005). Scoping Studies: Towards a Methodological Framework. Int. J. Soc. Res. Methodol. 8 (1), 19–32. doi:10.1080/1364557032000119616
CrossRef Full Text | Google Scholar
Aydin, M., Guclu, N., and Pisapia, J. (2015). The Relationship between School Principals’ Strategic Leadership Actions and Organizational Learning. Am. J. Educ. Stud. 7 (1), 5–25.
Bandur, A. (2012). School‐based Management Developments: Challenges and Impacts. J. Educ. Admin 50 (6), 845–873. doi:10.1108/09578231211264711
Barron, B., Henderson, M., and Newman, P. (1995). Strategic Leadership: A Theoretical and Operational Definition. J. Instructional Psychol. 22, 178–181.
Beach, R. H., and Lindahl, R. (2004). A Critical Review of Strategic Planning: Panacea for Public Education?. J. Sch. Leadersh. 14 (2), 211–234. doi:10.1177/105268460401400205
Bell, L. (2004). Strategic Planning in Primary Schools. Manag. Educ. 18 (4), 33–36. doi:10.1177/08920206040180040701
Bellei, C., Vanni, X., Valenzuela, J. P., and Contreras, D. (2016). School Improvement Trajectories: An Empirical Typology. Sch. Effectiveness Sch. Improvement 27 (3), 275–292. doi:10.1080/09243453.2015.1083038
Bennett, Megan Crawford, Rosalind L, N., Crawford, M., Levačić, R., Glover, D., and Earley, P. (2000). The Reality of School Development Planning in the Effective Primary School: Technicist or Guiding Plan? Sch. Leadersh. Manag. 20 (3), 333–351. doi:10.1080/13632430050128354
Broadhead, P., Hodgson, J., Cuckle, P., and Dunford, J. (1998). School Development Planning: Moving from the Amorphous to the Dimensional and Making it Your Own. Res. Pap. Educ. 13 (1), 3–18. doi:10.1080/0267152980130102
Chan, C. W. (2018). Leading Today's Kindergartens. Educ. Manag. Adm. Leadersh. 46 (4), 679–691. doi:10.1177/1741143217694892
Chatchawaphun, P., Julsuwan, S., and Srisa-ard, B. (2016). Development of Program to Enhance Strategic Leadership of Secondary School Administrators. Ies 9 (10), 34–46. doi:10.5539/ies.v9n10p34
Chen, P. (2008). Strategic Leadership and School Reform in Taiwan. Sch. Effectiveness Sch. Improvement 19 (3), 293–318. doi:10.1080/09243450802332119
Cheng, Y. (2010). A Topology of Three-Wave Models of Strategic Leadership in Education. Int. Stud. Educ. Adm. 38 (1), 35–54.
Colquhoun, H. L., Levac, D., O'Brien, K. K., Straus, S., Tricco, A. C., Perrier, L., et al. (2014). Scoping Reviews: Time for Clarity in Definition, Methods, and Reporting. J. Clin. Epidemiol. , 67(12), 1291–1294. doi:10.1016/j.jclinepi.2014.03.013
Corral Granados, A., and Granados Gámez, G. (2010). Sustainability and Triple Bottom Line: Key Issues for Successful Spanish School Principals. Intl Jnl Educ. Mgt. , 24(6), 467–477.doi:10.1108/09513541011067656
Davies, B. (2004), Developing the Strategically Focused School, Sch. Leadersh. Manag. , 24(1), 11–27. doi:10.1080/1363243042000172796
Davies, B., and Davies, B. J. (2005). Strategic Leadership Reconsidered. Leadersh. Pol. Schools , 4(3), 241–260. doi:10.1080/15700760500244819
Davies, B., and Davies, B. (2010). The Nature and Dimensions of Strategic Leadership. Int. Stud. Educ. Adm. , 38(1), 5–21.
Davies, B. (2007). Developing Sustainable Leadership. Manag. Educ. , 21(3), 4–9. doi:10.1177/0892020607079984
Davies, B. J., and Davies, B.(2004), Strategic Leadership, Sch. Leadersh. Manag. , 24(1), 29–38. doi:10.1080/1363243042000172804
Davies, B. J., and Davies, B. (2006). Developing a Model for Strategic Leadership in Schools. Educ. Manag. Adm. Leadersh. , 34(1), 121–139. doi:10.1177/1741143206059542
Davies, B. (2006). Processes Not Plans Are the Key to Strategic Development. Manag. Educ. , 20(2), 11–15. doi:10.1177/089202060602000204
Davies, B. (2003). Rethinking Strategy and Strategic Leadership in Schools. Educ. Manag. Adm. , 31(3), 295–312. doi:10.1177/0263211x03031003006
Dimmock, C., and Walker, A. (2004). A New Approach to Strategic Leadership: Learning‐centredness, Connectivity and Cultural Context in School Design, Sch. Leadersh. Manag. , 24(1), 39–56. doi:10.1080/1363243042000172813
Eacott, S. (2006). Strategy: An Educational Leadership Imperative, Perspect. Educ. Leadersh. , 16(6), 1–12.
Eacott, S. (2008b). An Analysis of Contemporary Literature on Strategy in Education. Int. J. Leadersh. Educ. , 11(3), 257–280. doi:10.1080/13603120701462111
Eacott, S. (2010b). Lacking a Shared Vision: Practitioners and the Literature on the Topic of Strategy. J. Sch. Leadersh. , 20, 425–444. doi:10.1177/105268461002000403
Eacott, S. (2011) Leadership Strategies: Re-conceptualising Strategy for Educational Leadership. Sch. Leadersh. Manag. , 31 (1), 35–46. doi:10.1080/13632434.2010.540559
Eacott, S. (2010a). Strategy as Leadership: an Alternate Perspective to the Construct of Strategy. Int. Stud. Educ. Adm. , 38(1), 55–65.
Eacott, S. (2008a). Strategy in Educational Leadership: In Search of unity, J. Educ. Admin. , 46(3), 353–375. doi:10.1108/09578230810869284
Eacott, S. (2010c). Tenure, Functional Track and Strategic Leadership. Intl Jnl Educ. Mg.t , 24(5), 448–458. doi:10.1108/09513541011056009
FitzGerald, A. M., and Quiñones, S. (2018). The Community School Coordinator: Leader and Professional Capital Builder. Jpcc , 3(4), 272–286. doi:10.1108/JPCC-02-2018-0008
Glanz, J. (2010). Justice and Caring: Power, Politics, and Ethics in Strategic Leadership. Int. Stud. Educ. Adm. , 38(1), 66–86.
Harris, A., Adams, D., Jones, M. S., and Muniandy, V. (2015). System Effectiveness and Improvement: The Importance of Theory and Context. Sch. Effectiveness Sch. Improvement , 26(1), 1–3. doi:10.1080/09243453.2014.987980
Hautala, T., Helander, J., and Korhonen, V. (2018). Loose and Tight Coupling in Educational Organizations - an Integrative Literature Review. Jea , 56(2), 236–255. doi:10.1108/JEA-03-2017-0027
Hopkins, D., Stringfield, S., Harris, A., Stoll, L., and Mackay, T. (2014). School and System Improvement: A Narrative State-Of-The-Art Review. Sch. Effectiveness Sch. Improvement , 25(2), 257–281. doi:10.1080/09243453.2014.885452
Ismail, S. N., Kanesan, A., Kanesan, A. G., and Muhammad, F. 2018). Teacher Collaboration as a Mediator for Strategic Leadership and Teaching Quality. Int. J. Instruction , 11(4), 485–498. doi:10.12973/iji.2018.11430a
Kangaslahti, J. (2012). Mapping the Strategic Leadership Practices and Dilemmas of a Municipal Educational Organization. Euromentor J. - Stud. about Educ. , 4, 9–17.
Khalil, H., Peters, M., Godfrey, C. M., McInerney, P., Soares, C. B., and Parker, D., (2016). An Evidence-Based Approach to Scoping Reviews. Worldviews Evid. Based Nurs. , 13(2), 118–123. doi:10.1111/wvn.12144
PubMed Abstract | CrossRef Full Text | Google Scholar
Khumalo, S. (2018). Promoting Teacher Commitment through the Culture of Teaching through Strategic Leadership Practices. Gend. Behav. , 16(3), 12167 -12177.
Levac, D., Colquhoun, H., and O'Brien, K. K. (2010). Scoping Studies: Advancing the Methodology. Implement Sci. , 5(1), 69–9. http://www.biomedcentral.com/content/pdf/1748-5908-5-69.pdf . doi:10.1186/1748-5908-5-69
Malin, J. R., and Hackmann, D. (2017). Urban High School Principals' Promotion of College-And-Career Readiness. Jea , 55(6), 606–623. doi:10.1108/JEA-05-2016-0054
Meyers, C. V., and VanGronigen, B. A. (2019). A Lack of Authentic School Improvement Plan Development, J. Educ. Admin , 57(3), 261–278. doi:10.1108/JEA-09-2018-0154
Mohd Ali, H. b., and Zulkipli, I. B. (2019). Validating a Model of Strategic Leadership Practices for Malaysian Vocational College Educational Leaders. Ejtd 43, 21–38. doi:10.1108/EJTD-03-2017-0022
Mohd Ali, H. (2012). The Quest for Strategic Malaysian Quality National Primary School Leaders. Intl Jnl Educ. Mgt. , 26 (1), 83–98. doi:10.1108/09513541211194392
Moher, D., Liberati, A., Tetzlaff, J., and Altman, D. G. (2009) Preferred Reporting Items for Systematic Reviews and Meta-Analyses: the PRISMA Statement. BMJ , 339, b2535–269. doi:10.1136/bmj.b2535
Nebgen, M. K. (1990). Strategic Planning: Achieving the Goals of Organization Development. J. Staff Dev. , 11(1), 28–31.doi:10.1108/eum0000000001151
Peters, M., Godfrey, C., McInerney, P., Soares, C., Khalil, H., and Parker, D., (2015). Methodology for JBI Scoping Reviews . The Joanna Briggs Institute reviewers’ manual . Adelaide, South Australia: The Joanna Briggs Institute .
Prasertcharoensuk, T., and Tang, K. N. (2017). The Effect of Strategic Leadership Factors of Administrators on School Effectiveness under the Office of Maha Sarakham Primary Educational Service Area 3. Kasetsart J. Soc. Sci. , 38(3), 316–323. doi:10.1016/j.kjss.2016.09.001
Quong, T., and Walker, A. (2010). Seven Principles of Strategic Leadership. Int. Stud. Educ. Adm. , 38(1), 22–34.
Reynolds, D., Sammons, P., De Fraine, B., Van Damme, J., Townsend, T., Teddlie, C., et al. (2014). Educational Effectiveness Research (EER): A State-Of-The-Art Review. Sch. Effectiveness Sch. Improvement , 25(2), 197–230. doi:10.1080/09243453.2014.885450
Schlebusch, G., and Mokhatle, M. (2016) Strategic Planning as a Management Tool for School Principals in Rural Schools in the Motheo District. Int. J. Educ. Sci. , 13(3), 342–348. doi:10.1080/09751122.2016.11890470
Tricco, A. C., Lillie, E., Zarin, W., O'Brien, K., Colquhoun, H., Kastner, M., et al. (2016). A Scoping Review on the Conduct and Reporting of Scoping Reviews. BMC Med. Res. Methodol. , 16(15), 15–10. doi:10.1186/s12874-016-0116-4
Tricco, A. C., Lillie, E., Zarin, W., O'Brien, K. K., Colquhoun, H., Levac, D., et al. 2018). PRISMA Extension for Scoping Reviews (PRISMA-ScR): Checklist and Explanation. Ann. Intern. Med. , 169(7), 467–473. doi:10.7326/M18-0850
Keywords: strategy, strategic leadership, school leadership, scoping review, education
Citation: Carvalho M, Cabral I, Verdasca JL and Alves JM (2021) Strategy and Strategic Leadership in Education: A Scoping Review. Front. Educ. 6:706608. doi: 10.3389/feduc.2021.706608
Received: 07 May 2021; Accepted: 23 September 2021; Published: 15 October 2021.
Reviewed by:
Copyright © 2021 Carvalho, Cabral, Verdasca and Alves. This is an open-access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License (CC BY). The use, distribution or reproduction in other forums is permitted, provided the original author(s) and the copyright owner(s) are credited and that the original publication in this journal is cited, in accordance with accepted academic practice. No use, distribution or reproduction is permitted which does not comply with these terms.
*Correspondence: Marisa Carvalho, [email protected]
Educational Leadership and Management Reflective Essay
My new skills about educational management and leadership, reference list.
Schools and colleges bring teachers, parents, and students together (Fitzgerald, 2009). Each of these groups has its unique goals and objectives. Every school leader should employ the best strategies in order to mentor these stakeholders.
School leadership is a complex practice aimed at guiding teachers and learners. Educational leadership is one of the best practices towards improving the performance of different learners.
I have gained new skills as a school leader. My first understanding is that the quality of school leadership determines the performance of every learning institution. This explains why every person should apply the best educational leadership skills. Every institution requires the best leaders in order to attain its goals.
The best leaders will ensure their institutions provide quality education to their learners. Leadership should promote “performance, openness, mentorship, and teamwork” (Day, Gronn, & Salas, 2004, p. 874).
I will use this knowledge in order to become a successful educational leader. Every educational leader should focus on the best goals (Cranston & Ehrich, 2009).
Creating Teams
The first concept towards better educational leadership is creating cohesive teams. According to Bush (2007, p. 396), “a team is a group of individuals whose mission is to achieve a set of common goals or solve the problems affecting them”.
Every team member is committed to the targeted goals or objectives. A team will succeed if it has a good mentor or leader. A motivated team will achieve its goals much easier. The class readings have also explored some of the best practices towards better educational leadership.
Leaders should use different teams in order to achieve their goals (Sheard & Kakabadse, 2004). This practice will ensure every team achieves its educational goals (National College of School Leadership, 2009).
Team Leadership
Team leadership is a dynamic approach that ensures every learner achieves his or her academic goals. The readings have widened my skills as a team leader in an academic environment. The application of proper leadership ensures every team achieves its goals.
Every team leader should be competent and self-determined (Mayrowetz, 2008). I am also planning to become a professional team leader.
Team leaders should be ready to promote cohesiveness and improve the level of communication. Team leadership is “the ability to solve every problem affecting a given group” (Hall, 2002, p. 730).
Distributed and Middle Leadership
Distributed leadership remains a major practice in many learning institutions. This leadership approach helps every manager devolve his or her responsibilities across the institution. This leadership approach follows a top-down strategy.
This leadership approach is effective because it improves the level of academic performance (Johnson, 2003). The class materials have also informed me about the importance of middle leadership. Middle leaders examine every aspect of their learning institutions.
The leader “promotes enquiry, professional development, and curriculum” (Sheard & Kakabadse, 2004, p. 102). This leader also encourages his students and teachers to establish new teams.
The leaders sustain the best networks in order to achieve their goals. I have understood why every educational leader should use the best leadership styles.
I have gained new skills from the learning process. I am planning to use these skills in my future professional practice. A good educational leader supports every teacher or learner (Gunter & Fitzgerald, 2007).
Every manager should portray the best organisational behaviours. Different leadership models such as transformational and transactional practices will ensure every learner is contented with the learning environment. I will always use these practices in order to create the best teams.
Bush, T. (2007). Educational leadership and management: theory, policy, and practice. South African Journal of Education, 27 (3), 391-406.
Cranston, N., & Ehrich, L. (2009). Senior management teams in schools: Understanding their dynamics, enhancing their effectiveness. Leading and Managing, 15 (1), 14-25.
Day, D., Gronn, P., & Salas, E. (2004). Leadership capacity in teams. The Leadership Quarterly, 15 (6), 857-880.
Fitzgerald, T. (2009). The Tyranny of Bureaucracy: Continuing challenges of Leading and Managing . Educational management administration and Leadership, 37 (1), 51-65.
Gunter, H., & Fitzgerald, T. (2007). Leading learning and leading teachers: Challenges for schools in the 21st Century. Leading and Managing, 13 (1), 1-15.
Hall, V. (2002). From teamwork to team-work in education. In K. Leithwood & P. Hallinger (Eds.), Second international handbook of educational leadership and administration. Part 2 (pp. 697-733). London: Kluwer Academic Publishers.
Johnson, N. (2003). Working in Teams . Web.
Mayrowetz, D. (2008). Making sense of distributed leadership: Exploring the multiple usages of the concept in the field. Educational Administration Quarterly, 44 (3), 424-435.
National College of School Leadership. (2009). School leadership: Federations and distributed leadership . Web.
Sheard, G., & Kakabadse, A. (2004). A process perspective on leadership and team development. Journal of Management Development, 23 (1), 7-106.
- Chicago (A-D)
- Chicago (N-B)
IvyPanda. (2023, December 20). Educational Leadership and Management. https://ivypanda.com/essays/educational-leadership-and-management/
"Educational Leadership and Management." IvyPanda , 20 Dec. 2023, ivypanda.com/essays/educational-leadership-and-management/.
IvyPanda . (2023) 'Educational Leadership and Management'. 20 December.
IvyPanda . 2023. "Educational Leadership and Management." December 20, 2023. https://ivypanda.com/essays/educational-leadership-and-management/.
1. IvyPanda . "Educational Leadership and Management." December 20, 2023. https://ivypanda.com/essays/educational-leadership-and-management/.
Bibliography
IvyPanda . "Educational Leadership and Management." December 20, 2023. https://ivypanda.com/essays/educational-leadership-and-management/.
- Importance of Mentorship in Nursing
- The Concept of Mentoring
- Distributed and Distance Learning Systems
- Importance of distributed teams
- Drawbacks and Disadvantages of Distributed Computing
- Mentor Texts: Different Writing Techniques Usage
- Marketing Mentor Framing Strategies
- Expectancy Theory of Learning and Its Features
- Mentoring Model in Educational Process
- Mentoring and Coaching Experience
- Reform of Education in California
- Designing Educational Spaces: A Birth-To-Eighteen-Year-Old Training for a Rich Parent
- The Best Education Strategies and Design in Academic and Professional Life
- The Usefulness of Educational Research
- Impact of education reduction
Academia.edu no longer supports Internet Explorer.
To browse Academia.edu and the wider internet faster and more securely, please take a few seconds to upgrade your browser .
Enter the email address you signed up with and we'll email you a reset link.
- We're Hiring!
- Help Center

Educational Leadership Reflective Essay

Related Papers
Business Horizons
Seokhwa Yun , Hank Sims
Central Asian Journal of Literature, Philosophy and Culture
Central Asian Studies
the paper examines the issues of effective leadership in different organizations. The authors describe and analyze elements of situational leadership and consider the relationship between personal characteristics of a person and his/her leadership abilities. The authors give illustrative examples of leadership qualities in different historical persons.
Ale Kuea Ioane
This paper offers a comprehensive analysis and description of the contextual factors affecting Motufoua Secondary School (MSS) and its leadership, outlining and explaining the contextual elements that have a potential impact. Furthermore, it discusses the current leadership responses and proposes a "model of application" for implementing transformational leadership as a tool to address these contextual factors. Ultimately, the paper concludes that the theory of transformational leadership is well-suited for effecting change and improvement in light of these challenges.
Journal of Business Studies Quarterly
Jim A McCleskey
In order to advance our knowledge of leadership, it is necessary to understand where the study of leadership has been. McCleskey (2014) argued that the study of leadership spans more than 100 years. This manuscript describes three seminal leadership theories and their development. Analysis of a sampling of recent articles in each theory is included. The manuscript also discusses the concept of leadership development in light of those three seminal theories and offers suggestions for moving forward both the academic study of leadership and the practical application of research findings on the field.
Subin Paily
Aman Pillay
Thomas Jefferson University Digital Commons
Larry M . Starr
In two parts this paper examines how leadership is understood, taught, and anticipated to be learned in undergraduate, graduate, and executive education programs. Part 1 https://jdc.jefferson.edu/jscpsfp/4/ introduces the challenges of defining leadership then presents three taxonomies or themes representing the prevailing leadership models, theories, and practices. I then introduce a fourth theme derived from a broader understanding of context, particularly differences between challenges that are complicated and complex. This informs an expanded context-definition of leadership for which examples of leadership characteristics and proficiencies from a complex systems perspective are presented. Part 2 is presented as a separate essay. It discusses the assumptions, expectations and relationships among learners, instructors, context, and content from which teaching and learning approaches have emerged. Pedagogy is most common, andragogy is increasingly appropriate for the changing demographics of higher education, and heutagogy is urged for adult learners in higher levels, particularly doctoral and applied executive leadership learning programs. I then describe leadership curricula and using a woven strands metaphor I propose courses appropriate for undergraduate, master, and doctoral leadership programs.
isara solutions
International Res Jour Managt Socio Human
In modern days rapid changes are being observed in the environment, it’s a challenge for everyone, both to common men as well as professionals. In this developing culture it is difficult to match up with the changing situation. A change in economy, politics, and market, new technology makes people to open their boundaries to practice the change and accept the changing environment. In the business these changes pressure the manager to face the changing environment and keep it with. To overcome those changes managers can constitute toward SITUATIONAL LEADERSHIP. In most simple words situational leadership means effective management to solving problems effectively as per the situation changes by implementing of specific approach.
Artur Victoria
The choice of style of leadership must attention about what the leader thinks about his power and authority on human nature. The leader assumes that people can basically self-address, where appropriate together to produce motivation. Leadership is a question of how to be... . We spent a good part of our lives learning how to do things, but in the end is the individual quality and character that define the great leaders. As for leaders, thrive through the efforts of people who lead. The basic task of a leader is to train a workforce highly productive and motivated. The leader has to overcome challenges to achieve a cohesive community that is well structured within and outside your organization which would invest in relationships and convey a vision to establish a communication between the workforce and an assorted market. The leader is one who worries about what is around you, near or far, inside or outside the organization, and that the true leader understands that the worker and not compromise the performance of the organization. The leader has to be circular in relations in the organization, as people want to join the cause because of the effects brought by its attitudes. The leader should propose a common framework of exit and enter a higher sphere where people realize they are being observed and valued by their ideas. Leadership is an interpersonal influence exercised in a situation and directed through the process of communication for the achievement of specific objectives.
RELATED TOPICS
- We're Hiring!
- Help Center
- Find new research papers in:
- Health Sciences
- Earth Sciences
- Cognitive Science
- Mathematics
- Computer Science
- Academia ©2024
- +44 (0)1782 491098
- Request information
- MSc Management
- MSc Management with Marketing
- MSc Management with Sustainability
- MSc Management with Data Analytics
- MSc Computer Science
- MSc Computer Science with Data Analytics
- MSc Computer Science with Artificial Intelligence
- MA Education
- MA International Education
- MA Education Leadership and Management
- MA Early Childhood Education
- MA Education Technology
- MPH Global Health
- MPH with Leadership
- On-campus courses
- Start application
- Complete existing application
- Admission requirements
- Start dates
Why is leadership important in education?

Educational leadership encompasses principles that focus on academic success but also on academic management through collaborating with parents, students, and teachers. In fact, effective leadership is highly dependent on the ability to delegate to other academic staff and to empower students to take responsibility in understanding the best ways for them to learn.
The ongoing global pandemic has confronted academic leaders with numerous challenges. Lockdowns and social distancing have meant that online learning has become the norm, but has made practical, hands-on learning difficult. This has affected all subjects throughout the academic year, but some have been harder hit than others: in the sciences, which experienced restrictions on time in the lab for research and experiments; and in the arts, as drama is a subject which, by its nature, requires contact with many people. Both teachers and students have had to apply adaptive strategies to the restrictions.
The International Journal on Lifelong Education and Leadership published a paper in 2020 entitled Navigating Emotional Waters in Schools: Becoming an Emotionally Adaptable Leader. The paper acknowledges the emotional impact of a crisis such as the pandemic on all staff members and the importance of emotional intelligence in leadership roles. It highlights the multifaceted approach that times of flux demand including skills in transformational leadership, complexity leadership, crisis management, cutback management, and resiliency. That’s a lot of leadership skills and professional development required in a short space of time and the effect of the pandemic on the future of education has yet to be measured. The paper offers a framework for becoming an emotionally adaptable leader with short-term and long-term strategic plans.
In the United Kingdom, the Leadership Foundation for Higher Education merged with The Equality Challenge Unit and the Higher Education Academy to form Advance HE in 2018. The Leadership Foundation Fellowship is no longer being offered, however, Advanced HE has focused on offering resources such as online workshops for leaders in higher education across the world. These sessions complemented the Final Capstone Report as part of the Creating Socially Distanced Campuses and Education Project. Four overarching themes were explored:
- Leadership: Inspiring a collective commitment and achieving focus with kindness, care, and compassion.
- Communication: With both staff and students (including supporting staff development needs).
- Partnership: ‘Working with’ rather than just ‘doing for’ students.
- Wellbeing: Mental and physical health and wellbeing for students and staff.
What is transformational leadership?
Transformational leadership is a type of leadership, the rise in prominence of which is generally credited to Bernard Bass who wrote a book of the same name with Ronald E. Riggio. It is defined as a leadership approach that causes change in individuals and social systems. Ideally, it inspires such positive change in the followers of effective leaders that it catalyses them into becoming leaders too.
Academic leadership has taken cues from transformational leadership in recent years as it has been shown to successfully engage all stakeholders (teachers, parents, students, and administrators) in decision-making and learning outcomes. This is in contrast with transmissional leadership which focuses on conveying information without inviting participation.
Bass notes that authentic leadership that is also transformational is grounded in a moral foundation based on four components:
- Idealised influence
- Inspirational motivation
- Intellectual stimulation
- Individualised consideration
Transformational leadership depends upon:
- The moral character of the leader
- The ethical values embedded in the leader’s vision, articulation, and programme (which followers either embrace or reject)
- The morality of the processes of social ethical choice and action that leaders and followers engage in and collectively pursue
The 2009 paper Transformational Leadership in the Classroom: Fostering Student Learning, Student Participation, and Teacher Credibility cites two other papers that demonstrate the successes of transformational leadership:
“Subordinates of transformational leaders have less role conflict, higher task performance, and higher satisfaction with a task than subordinates with non-transformational leaders (Howell & Frost, 1989) and show more helping as well as compliance (Den Hartog, De Hoogh, & Keegan, 2007).”
Transactional leadership is another leadership style popularised by Bass. This is one of the more hierarchical forms of leadership that is dependent on the formal authority of the leader within the academic department. It involves motivating and directing followers mainly by appealing to their own self-interest and uses a system of reward and punishment.
The future of educational leadership
The pandemic has tested the managerial styles and structures of school leadership. A recent TES (Teaching Education Supplement) article entitled “Teachers most likely to quit over poor management” stated that top-down pressure on school leaders is putting education recovery at risk. Over a third (34%) of respondents to a survey said that management issues in their schools would be most likely to drive them to quit the profession aside from pay, workload, and working conditions. Almost half (49%) of independent school teachers surveyed said that problems with management was the factor most likely to mean they would think about leaving the teaching profession behind.
Academia has been forced to learn quickly about effective leadership during crisis events. Any shortfalls in leadership competencies become glaringly obvious in crisis and can no longer go unnoticed. The paper Resilience, Reorientation, and Reinvention: School Leadership During the Early Months of the Covid-19 Pandemic draws learnings from other crisis events such as the actions of school principals after the 2011 earthquake in Christchurch, New Zealand. The authors interviewed 55 educators from 43 school organisations from around the world, but predominantly in the USA for the paper. Their findings were that a values-driven approach resulted in actionable responses to the Covid-19 pandemic. Key to these responses were the values of relationship, connectivity, collective wisdom, collaboration, empathy, and adaptive risk-taking.
Lead the way with a master’s in education
A master’s in education can play a key role in your professional development, whether you hold a position in the higher education sector or the school system.
Providing a course that allows you to deepen your knowledge of the challenges facing pedagogy today and develop your critical thinking, the 100% online MA Education Leadership Management from Keele University will help to progress your career.

Quick Links
- Accessibility statement


ESSAY SAUCE
FOR STUDENTS : ALL THE INGREDIENTS OF A GOOD ESSAY
Essay: Educational leadership
Essay details and download:.
- Subject area(s): Leadership essays
- Reading time: 2 minutes
- Price: Free download
- Published: 10 October 2015*
- File format: Text
- Words: 305 (approx)
- Number of pages: 2 (approx)
Text preview of this essay:
This page of the essay has 305 words. Download the full version above.
Today the world has focused on leadership, because all the problems which emerge in the changing circumstances of the world are due to weak or poor leadership style. So, leadership plays a vital role in the lives of people. Similarly in the educational system, the role of head teacher as a leader has its critical importance. Current study is about the relationship between the leadership styles and job satisfaction level of higher Secondary School Teachers. For proficient management of an organization, human resources are its paramount essentials. competent leaders and subordinates give a lot to attain organizational goals. Positive relationship between teachers and head’s performance is necessary for raising educational principles (Khan et al. 2009). During the past decade, schools have undertaken fundamental changes in areas such as curriculum development, teaching techniques, teachers’ roles, and learning strategies. These changes have been brought about a shift in the philosophy that dominated the realm of educational leadership.
As Leithwood (1994) indicated, the form of instructional leadership corresponded well to the period of the 1980s and the 1990s because it met the opportunity of the public and the decision-makers’ expectations from the figure head. However, the changes undertaken during the 1990s could not be dealt with, when the head was functioning as an instructional leader. The concept of transformational leadership steadily moved to the center of the discussion as school heads were expected to bring the imaginative leadership to the institution’a task that was not taken care of, by instructional leaders. Leithwood and Jantzi (1990) showed that school heads that succeeded in their job have used a broad variety of mechanisms to motivate and activate their staff to bring about the changes in their school culture. A variety of leadership styles are used by the leaders but most frequently used styles are autocratic leadership style and democratic leadership style.
...(download the rest of the essay above)
About this essay:
If you use part of this page in your own work, you need to provide a citation, as follows:
Essay Sauce, Educational leadership . Available from:<https://www.essaysauce.com/leadership-essays/essay-educational-leadership/> [Accessed 07-04-24].
These Leadership essays have been submitted to us by students in order to help you with your studies.
* This essay may have been previously published on Essay.uk.com at an earlier date.
Essay Categories:
- Accounting essays
- Architecture essays
- Business essays
- Computer science essays
- Criminology essays
- Economics essays
- Education essays
- Engineering essays
- English language essays
- Environmental studies essays
- Essay examples
- Finance essays
- Geography essays
- Health essays
- History essays
- Hospitality and tourism essays
- Human rights essays
- Information technology essays
- International relations
- Leadership essays
- Linguistics essays
- Literature essays
- Management essays
- Marketing essays
- Mathematics essays
- Media essays
- Medicine essays
- Military essays
- Miscellaneous essays
- Music Essays
- Nursing essays
- Philosophy essays
- Photography and arts essays
- Politics essays
- Project management essays
- Psychology essays
- Religious studies and theology essays
- Sample essays
- Science essays
- Social work essays
- Sociology essays
- Sports essays
- Types of essay
- Zoology essays

COMMENTS
Visionary Leadership is a Critical Element Essential for Exemplary Educational Leadership Visionary leadership is a critical component for successful principals. Before beginning the process of becoming an elementary principal, I did not realize the importance of having a strong vision. During our interview with the
When it comes to the success of students and positive outcomes for whole families and communities, educational leadership can play a critical role. Communities and whole societies are changing at a rapid pace, creating a tremendous need for practical-minded leaders who can innovate new ways of learning and meet the needs of diverse communities.
The role of leadership in shaping the future of education. Academy of Educational Leadership Journal, 27(1), 1-2. 3. Technology plays an increasingly important role in education. Educational leaders should embrace technology and use it to improve teaching and learning, streamline administrative processes, and
The educational leader is a reflective practitioner, change agent, and catalyst for. improvement. Above all of these roles, however, the educational leader is a. servant; he/she is there to provide and implement a vision that will help the. students, parents, and staff in the school community. The administrator, as a.
The chronology of educational leadership and management. The origins and development of educational management as a distinct discipline have been chronicled by Hughes (1985), Hughes and Bush (1991), Bush (1999), Glatter (1999) and Bolam (2004). It began in the United States in the early part of this century.
Strategy and strategic leadership are critical issues for school leaders. However, strategy as a field of research has largely been overlooked within the educational leadership literature. Most of the theoretical and empirical work on strategy and strategic leadership over the past decades has been related to non-educational settings, and scholarship devoted to these issues in education is ...
Download. Educational leadership is an important process that requires the cooperation of educational administrators, teachers, students, and parents. The purpose of educational leadership is to enhance and improve the education quality and the education system which affects the student's performance and academic success.
Educational Leadership and Management Reflective Essay. Schools and colleges bring teachers, parents, and students together (Fitzgerald, 2009). Each of these groups has its unique goals and objectives. Every school leader should employ the best strategies in order to mentor these stakeholders.
sum of the ideals that we are currently studying and use them to effectively lead a school. 2. I believe that I have the necessary attributes of a building leader and look forward to. serving as a mentor, budget officer, and communicator. The Educational Leadership Constituent Council (ELCC) standards have to be a.
Educational Leadership Reflective Essay Joshua S. Grover Spring, 2012 Introduction Responsibility: perhaps no better word describes what a leader faces as he or she manages an organization. As future leaders are cultivated and preened for future positions, it is necessary and vital to instill upon them the importance of such a position.
Leadership: Inspiring a collective commitment and achieving focus with kindness, care, and compassion. Communication: With both staff and students (including supporting staff development needs). Partnership: 'Working with' rather than just 'doing for' students. Wellbeing: Mental and physical health and wellbeing for students and staff.
Educational Leadership. An analysis of research on educational leadership acknowledges the importance of the principal in the elementary and secondary school setting. As a leader, the principal's role has developed from one of a managerial position to one of an instructional leader who also manages. Cheney and Davis (2011) note that "The ...
Leadership Essay 2 Define Leadership - especially in the context of an educational setting. "Leadership is the art of getting someone else to do something you want done because he wants to do it. — Dwight D. Eisenhower Eisenhower's definition of leadership is veraciously on the mark, particularly in the context of an educational setting.
This page of the essay has 305 words. Download the full version above. Today the world has focused on leadership, because all the problems which emerge in the changing circumstances of the world are due to weak or poor leadership style. So, leadership plays a vital role in the lives of people. Similarly in the educational system, the role of ...
The Importance Of Leadership And Management For Education. This essay sample was donated by a student to help the academic community. Papers provided by EduBirdie writers usually outdo students' samples. Since the early 1990's there has been a significant shift in the direction of Education and in particular, the recognition of the difference ...
Educational Leadership Theories Essay. Leadership has a major role to play in education in the 21st century. To be an effective academic leader, in today's world, it is vitally important that educational leaders possess a good understanding of how true leadership is best demonstrated in the impartation of knowledge.
Abstract. The role of a leader is invaluable in setting the tone of the environment and the vision for the school. There are so many parts to leadership, that continual learning will be necessary for any successful school leader. A school leader plays many roles including: a reflective practitioner, a change agent, an educational improvement ...
The Importance Of Leadership In Education. 1465 Words3 Pages. Recommended: benefits of cooperative learning in the classroom. Education is a very important aspect in the life of a child. The level of success a student has in the classroom is greatly influenced by their teachers. Students, as well as their parents, depend on the teachers to ...
The visionary leader promotes the ownership of the vision. to all the stakeholders and communicates with them on the success and the. failures of the goals. The three critical elements for effective leadership discussed demonstrate. the high expectations for educational administrators and those expectations. 15.