What Works In Schools : Sexual Health Education
CDC’s What Works In Schools Program improves the health and well-being of middle and high school students by:
- Improving health education,
- Connecting young people to the health services they need, and
- Making school environments safer and more supportive.

What is sexual health education?
Quality provides students with the knowledge and skills to help them be healthy and avoid human immunodeficiency virus (HIV), sexually transmitted infections (STI) and unintended pregnancy.
A quality sexual health education curriculum includes medically accurate, developmentally appropriate, and culturally relevant content and skills that target key behavioral outcomes and promote healthy sexual development. 1
The curriculum is age-appropriate and planned across grade levels to provide information about health risk behaviors and experiences.

Sexual health education should be consistent with scientific research and best practices; reflect the diversity of student experiences and identities; and align with school, family, and community priorities.
Quality sexual health education programs share many characteristics. 2-4 These programs:
- Are taught by well-qualified and highly-trained teachers and school staff
- Use strategies that are relevant and engaging for all students
- Address the health needs of all students, including the students identifying as lesbian, gay, bisexual, transgender, queer and questioning (LGBTQ)
- Connect students to sexual health and other health services at school or in the community
- Engage parents, families, and community partners in school programs
- Foster positive relationships between adolescents and important adults.
How can schools deliver sexual health education?
A school health education program that includes a quality sexual health education curriculum targets the development of functional knowledge and skills needed to promote healthy behaviors and avoid risks. It is important that sexual health education explicitly incorporate and reinforce skill development.
Giving students time to practice, assess, and reflect on skills taught in the curriculum helps move them toward independence, critical thinking, and problem solving to avoid STIs, HIV, and unintended pregnancy. 5
Quality sexual health education programs teach students how to: 1
- Analyze family, peer, and media influences that impact health
- Access valid and reliable health information, products, and services (e.g., STI/HIV testing)
- Communicate with family, peers, and teachers about issues that affect health
- Make informed and thoughtful decisions about their health
- Take responsibility for themselves and others to improve their health.
What are the benefits of delivering sexual health education to students?
Promoting and implementing well-designed sexual health education positively impacts student health in a variety of ways. Students who participate in these programs are more likely to: 6-11
- Delay initiation of sexual intercourse
- Have fewer sex partners
- Have fewer experiences of unprotected sex
- Increase their use of protection, specifically condoms
- Improve their academic performance.
In addition to providing knowledge and skills to address sexual behavior , quality sexual health education can be tailored to include information on high-risk substance use * , suicide prevention, and how to keep students from committing or being victims of violence—behaviors and experiences that place youth at risk for poor physical and mental health and poor academic outcomes.
*High-risk substance use is any use by adolescents of substances with a high risk of adverse outcomes (i.e., injury, criminal justice involvement, school dropout, loss of life). This includes misuse of prescription drugs, use of illicit drugs (i.e., cocaine, heroin, methamphetamines, inhalants, hallucinogens, or ecstasy), and use of injection drugs (i.e., drugs that have a high risk of infection of blood-borne diseases such as HIV and hepatitis).
What does delivering sexual health education look like in action?
To successfully put quality sexual health education into practice, schools need supportive policies, appropriate content, trained staff, and engaged parents and communities.
Schools can put these four elements in place to support sex ed.
- Implement policies that foster supportive environments for sexual health education.
- Use health content that is medically accurate, developmentally appropriate, culturally inclusive, and grounded in science.
- Equip staff with the knowledge and skills needed to deliver sexual health education.
- Engage parents and community partners.
Include enough time during professional development and training for teachers to practice and reflect on what they learned (essential knowledge and skills) to support their sexual health education instruction.
By law, if your school district or school is receiving federal HIV prevention funding, you will need an HIV Materials Review Panel (HIV MRP) to review all HIV-related educational and informational materials.
This review panel can include members from your School Health Advisory Councils, as shared expertise can strengthen material review and decision making.
For More Information
Learn more about delivering quality sexual health education in the Program Guidance .
Check out CDC’s tools and resources below to develop, select, or revise SHE curricula.
- Health Education Curriculum Analysis Tool (HECAT), Module 6: Sexual Health [PDF – 70 pages] . This module within CDC’s HECAT includes the knowledge, skills, and health behavior outcomes specifically aligned to sexual health education. School and community leaders can use this module to develop, select, or revise SHE curricula and instruction.
- Developing a Scope and Sequence for Sexual Health Education [PDF – 17 pages] .This resource provides an 11-step process to help schools outline the key sexual health topics and concepts (scope), and the logical progression of essential health knowledge, skills, and behaviors to be addressed at each grade level (sequence) from pre-kindergarten through the 12th grade. A developmental scope and sequence is essential to developing, selecting, or revising SHE curricula.
- Centers for Disease Control and Prevention. Health Education Curriculum Analysis Tool, 2021 , Atlanta: CDC; 2021.
- Goldfarb, E. S., & Lieberman, L. D. (2021). Three decades of research: The case for comprehensive sex education. Journal of Adolescent Health, 68(1), 13-27.
- Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (2016). Characteristics of an Effective Health Education Curriculum .
- Pampati, S., Johns, M. M., Szucs, L. E., Bishop, M. D., Mallory, A. B., Barrios, L. C., & Russell, S. T. (2021). Sexual and gender minority youth and sexual health education: A systematic mapping review of the literature. Journal of Adolescent Health , 68 (6), 1040-1052.
- Szucs, L. E., Demissie, Z., Steiner, R. J., Brener, N. D., Lindberg, L., Young, E., & Rasberry, C. N. (2023). Trends in the teaching of sexual and reproductive health topics and skills in required courses in secondary schools, in 38 US states between 2008 and 2018. Health Education Research , 38 (1), 84-94.
- Coyle, K., Anderson, P., Laris, B. A., Barrett, M., Unti, T., & Baumler, E. (2021). A group randomized trial evaluating high school FLASH, a comprehensive sexual health curriculum. Journal of Adolescent Health , 68 (4), 686-695.
- Marseille, E., Mirzazadeh, A., Biggs, M. A., Miller, A. P., Horvath, H., Lightfoot, M.,& Kahn, J. G. (2018). Effectiveness of school-based teen pregnancy prevention programs in the USA: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Prevention Science, 19(4), 468-489.
- Denford, S., Abraham, C., Campbell, R., & Busse, H. (2017). A comprehensive review of reviews of school-based interventions to improve sexual-health. Health psychology review, 11(1), 33-52.
- Chin HB, Sipe TA, Elder R. The effectiveness of group-based comprehensive risk-reduction and abstinence education interventions to prevent or reduce the risk of adolescent pregnancy, human immunodeficiency virus, and sexually transmitted infections: Two systematic reviews for the guide to community preventive services. Am J Prev Med 2012;42(3):272–94.
- Mavedzenge SN, Luecke E, Ross DA. Effective approaches for programming to reduce adolescent vulnerability to HIV infection, HIV risk, and HIV-related morbidity and mortality: A systematic review of systematic reviews. J Acquir Immune Defic Syndr 2014;66:S154–69.
To receive email updates about this page, enter your email address:
Exit Notification / Disclaimer Policy
- The Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC) cannot attest to the accuracy of a non-federal website.
- Linking to a non-federal website does not constitute an endorsement by CDC or any of its employees of the sponsors or the information and products presented on the website.
- You will be subject to the destination website's privacy policy when you follow the link.
- CDC is not responsible for Section 508 compliance (accessibility) on other federal or private website.
What is comprehensive sexuality education?
Comprehensive sexuality education ( CSE ) is a curriculum -based process of teaching and learning about the cognitive, emotional, physical, and social aspects of sexuality. It aims to equip children and young people with knowledge, skills, attitudes, and values that will empower them to: realize their health, well-being, and dignity; develop respectful social and sexual relationships; consider how their choices affect their own well-being and that of others; and understand and ensure the protection of their rights throughout their lives.
[Source: UNESCO. 2017. International technical guidance on sexuality education, pp.16-17.]
Depending on the country or region, CSE may go by other names. It may be referred to as ‘ life skills ’, ‘ family life ’, or ‘ HIV ’ education . It is sometimes called ‘holistic sexuality education’. It is important to confirm with ministries what they use to describe CSE, particularly as context-based terms can inform the most effective approach to take when partnering with and supporting these ministries.
- delivered in formal and non-formal settings , in school or out of school ;
- scientifically accurate , based on research, facts, and evidence;
- incremental , starting at an early age with foundational content and skills, with new information building upon previous learning, using a spiral-curriculum approach that returns to the same topics at a more advanced level each year;
- age- and developmentally appropriate , with content and skills growing in abstractness and explicitness with the age and developmental level of the learners; it also must accommodate developmental diversity, adapting for learners with cognitive and emotional development differences;
- curriculum-based , following a written curriculum that includes key teaching and learning objectives, and the delivery of clear content and skills in a structured way;
- comprehensive , and about much more than just sexual behaviours.
The comprehensive aspect of CSE refers to the breadth, depth, and consistency of topics, as opposed to one-off lessons or interventions. CSE addresses sexual and reproductive health issues, including, but not limited to:
- sexual and reproductive anatomy and physiology;
- puberty and menstruation;
- reproduction, contraception , pregnancy, and childbirth;
- STIs, including HIV and AIDS .
CSE also addresses the psychological, social, and emotional issues relating to these topics, including those that may be challenging in some social and cultural contexts. It supports learners’ empowerment by improving their analytical, communication, and other life skills for health and well-being in relation to:
- human rights,
- a healthy and respectful family life and interpersonal relationships,
- personal and shared values,
- cultural and social norms,
- gender equality,
- non-discrimination,
- sexual behaviour,
- gender-based and other violence,
- consent and bodily integrity,
- sexual abuse and harmful practices such as child , early, and forced marriage, and female genital mutilation/cutting.
Key values of CSE
CSE builds on and promotes universal human rights for all, including children and young people. It emphasizes all persons’ rights to health, education, information equality, and non-discrimination. It raises awareness among young people that they have their own rights, and that they must acknowledge and respect the rights of others, and advocate for those whose rights are violated.
Integrating a gender perspective throughout CSE curricula is integral to effective CSE programmes. CSE analyses how gender norms can influence inequality, and how inequality can affect the overall health and well-being of children and young people, as well as the efforts to prevent issues such as HIV, STIs, early and unintended pregnancies, and gender-based violence . CSE contributes to gender equality by building awareness of the centrality and diversity of gender identities and expressions in people’s lives; examining gender norms shaped by cultural, social and biological differences and similarities; and by encouraging the creation of respectful and equitable relationships based on empathy and understanding.
CSE must be delivered in the context of the range of values, beliefs, and experiences that exist even within a single culture. It enables learners to examine, understand, and challenge the ways in which cultural structures, norms, and behaviours affect their choices and relationships within a variety of settings.
CSE impacts whole cultures and communities, not simply individual learners. It can contribute to the development of a fair and compassionate society by empowering individuals and communities, promoting critical thinking skills, and strengthening young people’s sense of citizenship. It empowers young people to take responsibility for their own decisions and behaviours, and how they may affect others. It builds the skills and attitudes that enable young people to treat others with respect, acceptance, tolerance, and empathy, regardless of their ethnicity, race, social, economic, or immigration status, religion, disability, sexual orientation , gender identity or expression, or sex characteristics.
CSE teaches young people to reflect on the information around them in order to make informed decisions, communicate and negotiate effectively, and develop assertiveness rather than passivity or aggression. These skills foster the creation of respectful and healthy relationships with family members, peers, friends, and romantic or sexual partners.
[Source: UNESCO. 2017. International technical guidance on sexuality education, pp 16-17.]
‘ Sexuality ’ is defined as ‘a core dimension of being human which includes: the understanding of, and relationship to, the human body; emotional attachment and love; sex; gender; gender identity; sexual orientation; sexual intimacy; pleasure and reproduction. Sexuality is complex and includes biological, social, psychological, spiritual, religious, political, legal, historic, ethical and cultural dimensions that evolve over a lifespan’.
[Source: UNESCO. 2017. International technical guidance on sexuality education, p.17.]
The word ‘sexuality’ has different meanings in different languages and in different cultural contexts. Taking into account a number of variables and the diversity of meanings in different languages, the following aspects of sexuality need to be considered in the context of CSE:
- Sexuality refers to the individual and social meanings of interpersonal and sexual relationships, in addition to biological aspects. It is a subjective experience and a part of the human need for both intimacy and privacy.
- Simultaneously, sexuality is a social construct, most easily understood within the variability of beliefs, practices, behaviours and identities. ‘Sexuality is shaped at the level of individual practices and cultural values and norms’ (Weeks, 2011).
- Sexuality is linked to power. The ultimate boundary of power is the possibility of controlling one’s own body. CSE can address the relationship between sexuality, gender and power, and its political and social dimensions. This is particularly appropriate for older learners.
- The expectations that govern sexual behaviour differ widely across and within cultures. Certain behaviours are seen as acceptable and desirable, while others are considered unacceptable. This does not mean that these behaviours do not occur, or that they should be excluded from discussion within the context of sexuality education.
- Sexuality is present throughout life, manifesting in different ways and interacting with physical, emotional and cognitive maturation. Education is a major tool for promoting sexual well-being and preparing children and young people for healthy and responsible relationships at the different stages of their lives.
[Source: UNESCO. 2017. International technical guidance on sexuality education, p. 17.]
When viewed holistically and positively:
- Sexual health is about well-being, not merely the absence of disease.
- Sexual health involves respect, safety and freedom from discrimination and violence.
- Sexual health depends on the fulfilment of certain human rights.
- Sexual health is relevant throughout the individual’s lifespan, not only to those in the reproductive years, but also to both the young and the elderly.
- Sexual health is expressed through diverse sexualities and forms of sexual expression.
- Sexual health is critically influenced by gender norms, roles, expectations and power dynamics.
- Sexual health needs to be understood within specific social, economic and political contexts.
- Characteristics of effective CSE programmes
Sex Education Resources
Here you can find relevant research as well as tools, templates and sample documents for each phase of the toolkit.
Displaying 36 resources
Addressing Sexual Health in Schools: Policy Considerations
This resource provides an overview of key policy components for sexual health education in schools. It includes sample policies and other resources pertaining to parental notification and involvement, curriculum selection and materials review, professional development, the role of external agencies and more.
Best Practices for Family Engagement
Best Practices for Family Engagement provides tips on how to engage parents and guardians before, during and after sex education implementation.
Brochure for School District Engagement
Eyes Open Iowa created a high-level brochure to introduce school districts to the project, purpose, student need, and resources available which can help clarify the CSE opportunity and pathway to success.
Capacity Assessment and Planning Tool (CAPT)
The Capacity Assessment and Planning Tool (CAPT) aids in determining how ready a school district is to engage in sex education efforts. This can be adapted to respond to a specific state or regional context.
Common Core Standards for English Language and Mathematics
Because the majority of states have voluntarily adopted the Common Core Standards for mathematics and English language arts/literacy (ELA), some WISE grantee partners have aligned their sexuality curriculum with the ELA components.
Comprehensive Sex Education and Academic Success: Effective Programs Foster Student Achievement
This fact sheet provides a summary of recent research highlighting the connections between sex education and academic success.
Curriculum Selection Tool
This curriculum selection tool lists a variety of criteria to consider including curriculum, training and TA availability and cost, alignment with standards and best practices, etc.
Division of Adolescent and School Health (DASH)
DASH supports 19 state and 17 local education agencies to support schools and school districts in implementing exemplary sexual health education, increase adolescent access to sexual health services and establish safe and supportive environments for students and staff.
Florida's Sexual Health Education Community Outreach Toolkit
This Tool Kit was created to provide valuable information, innovative ideas, and strategies for community members to build awareness and support for policies and programs that improve sexual health outcomes among youth.
Georgia State and Regional Sex Education Policy Overview
School districts and teachers may not be aware of current sex education policies and education codes that govern sex education. Creating a simple, accessible handout with the key policies and codes can ensure stakeholders understand what is mandated and where opportunities for tailoring to local contexts exist. GCAPP created a state-level overview and regional fact sheets to allow regions to compare their policies with the state policy.
Health Education Curriculum Analysis Tool
The Health Education Curriculum Analysis Tool (HECAT) can help school districts, schools, and others conduct a clear, complete, and consistent analysis of health education curricula based on the National Health Education Standards and CDC’s Characteristics of Effective Health Education Curricula.
How Schools Work and How to Work with Schools
This publication, produced by the National Association of State Boards of Education (NASBE), provides a summary of the federal, state and local educational systems of governance, outlines key tips for engaging and partnering with schools and answers frequently asked questions about education.
Implementation Planning Worksheet
The Implementation Planning Worksheet assists school district staff in planning who will be delivering sex education and when.
Making Adaptations to Evidence-Based Pregnancy and STD/HIV Prevention Programs
ETR offers adaptation kits which contain practical tools and resources to guide adolescent reproductive health practitioners in making effective adaptations and maintaining fidelity to program core components. The adaptation kits were developed to provide clarity on how each program was designed, its core components, and the types of adaptations that are considered safe and those that should be avoided.
Memorandum of Understanding
This memorandum of understanding template outlines potential roles and responsibilities of the partners involved in sex education implementation efforts. Not only does an MOU clarify expectations, but also helps to institutionalize efforts so that agreements can continue even if a key stakeholder changes positions.
National Health Education Standards
The National Health Education Standards provide a framework to help teachers, administrators, and policymakers promote health-enhancing behaviors among students in grade levels Pre-K through 12. The framework, consisting of eight health education standards, includes performance indicators that can be applied to a variety of health topics.
National Sexuality Education Standards Curricula Mapping Tools
By mapping state or local standards and/or programs and curricula to the National Sexuality Education Standards, school professionals can identify which topics are currently covered in sex education class by grade level and which are not.
National Sexuality Education Standards, Second Edition (2020)
The goal of the National Sex Education Standards: Core Content and Skills, K–12 (Second Edition) is to provide clear, consistent, and straightforward guidance on the essential, minimum, core content and skills needed for sex education that is age-appropriate for students in grades K–12 to be effective. The National Sexuality Education Standards were developed and align to the National Health Education Standards.
North Carolina Parent Opinion Survey of Public School Sexuality Education
SHIFT NC created a report to document the findings from their parent survey. They used the positive reactions from parents about inclusion of sex education in schools to substantiate their efforts and allay school district leadership fears.
Parent Opinion Survey Questions
Georgia Campaign for Adolescent Power and Potential (GCAPP), a WISE lead partner, developed a parent survey to find out what parents wanted their students to learn.
Pipeline Tracking Tool
This spreadsheet can be helpful in tracking status of potential partner school districts.
Preliminary Assessment
Based on a similar tool developed by SHIFT NC, this preliminary assessment provides an early gauge of whether or not a school district shows promise.
Sample School District Stakeholder Message Development
Georgia Campaign for Adolescent Power & Potential (GCAPP), a WISE lead partner, developed a simple tool to document the various needs of key constituency groups. This sample shows the different school district stakeholders they engaged and how they tailored their message to distinct stakeholder needs. GCAPP staff would reference this document before conversations with these key stakeholders to ensure they were connecting their efforts to each stakeholder’s needs during every interaction.
Sample Table Showing Curriculum Mapped to Education Code
ETR Associates mapped two curricula -- Making Healthy Choices and P ositive Prevention -- to mandated HIV and CSE education codes to determine alignment between curricula and policy. This table provides an example of what mapping and alignment looks like in practice.
School Health Advisory Council
This sample presentation discusses the role and function of School Health Advisory Councils (SHACs) as well as tips for successful recruitment and retention of SHAC members.
School Health Policies and Practices Study (SHPPS)
SHPPS is a national survey periodically conducted to assess school health policies and practices at the state, district, school, and classroom levels.
School Health Profiles
The School Health Profiles are a system of surveys assessing school health policies and practices in states, large urban school districts, territories, and tribal governments. Profiles are conducted biennially by education and health agencies among middle and high school principals and lead health education teachers.
Sex and HIV Education Programs For Youth: Their Impact and Important Characteristics
This research summarizes sex and HIV education programs and hones in on 17 characteristics of programs that led to behavior change.
State Education Data Profiles
This database provides access to statewide information on education system characteristics (e.g., number of students, schools, teachers), finances, assessments and selected demographics. Cross-state comparison tools are also available.
State Policies in Brief, Sex and HIV Education
The Guttmacher Institute’s State Policies in Brief provide state-by-state information on key issues affecting sexual and reproductive health and rights. The publications are updated monthly to reflect the most recent legislative, administrative, and judicial actions. The Sex and HIV Education brief summarizes state-level sex and HIV education policies, as well as specific content requirements, based on a review of state laws, regulations and other legally binding policies
State Profiles
SIECUS State Profiles is a state-by-state resource that describes sexuality education and abstinence-only-until-marriage programs in each state. Each state profile includes a summary of state laws and policies related to sexuality education. It also includes information about a variety of federal funding programs that support sexuality education and/or abstinence-only-until-marriage programs as well as how much money each state is receiving from each federal program (if applicable) and a summary of how it is being used.
State School Health Policy Database
The NASBE State School Health Policy Database contains brief descriptions of laws, legal codes, rules, regulations, administrative orders, mandates, standards, resolutions, and other written means of exercising authority. It also includes guidance documents and other non-binding materials that provide a more detailed picture of a state’s school health policies and activities. Hyperlinks to full written policies are provided whenever possible. The database is searchable by state, topic, and keyword.
Technical Assistance Action Plan
This Technical Assistance Action Plan is a tool to assist in the process of moving from planning to action. The planning tables below can help bridge the gap between the roll-out plan and the provision of needed technical assistance. Tables may be adapted to serve individual districts, as needed.
Tool to Assess the Characteristics of Effective Sex and STD/HIV Programs
Based on the Sex and HIV Education Programs for Youth: Their Impact and Important Characteristics research, this tool is designed to assess, select, improve, or design a sex or STD/HIV education program.
WISE Toolkit
This PDF of the WISE Toolkit includes content related to the each of the four phases and corresponding steps.
Youth Risk Behavior Surveillance System (YRBSS)
The YRBSS monitors six priority health-risk behaviors among youth and young adults including sexual behaviors that contribute to unintended pregnancy and STDs/HIV, alcohol and other drug use as well as violence. Annual and trend data is available.
This is the first edition of the National Sexuality Education Standards. To access the second edition, please click here .
The goal of the National Sexuality Education Standards : Core Content and Skills , K–12 is to provide clear, consistent and straightforward guidance on the essential minimum, core content for sexuality education that is developmentally and age-appropriate for students in grades K–12.
Specifically, the National Sexuality Education Standards were developed to address the inconsistent implementation of sexuality education nationwide and the limited time allocated to teaching the topic. The National Sexuality Education Standards :
• Outline what, based on research and extensive professional expertise, are the minimum, essential content and skills for sexuality education K–12 given student needs, limited teacher preparation and typically available time and resources. • Assist schools in designing and delivering sexuality education K–12 that is planned, sequential and part of a comprehensive school health education approach. • Provide a clear rationale for teaching sexuality education content and skills at different grade levels that is evidence-informed, age-appropriate and theory driven. • Support schools in improving academic performance by addressing a content area that is both highly relevant to students and directly related to high school graduation rates. • Present sexual development as a normal, natural, healthy part of human development that should be a part of every health education curriculum. • Offer clear, concise recommendations for school personnel on what is age-appropriate to teach students at different grade levels. • Translate an emerging body of research related to school-based sexuality education so that it can be put into practice in the classroom.
The Standards are presented both by topic and by grade level.
Download a PDF of The National Sexuality Education Standards here.
SIGN UP FOR EMAIL UPDATES
Interested in receiving the latest updates from SIECUS? Join our email list today.

Stay up to date with the latest news
An official website of the United States government
The .gov means it’s official. Federal government websites often end in .gov or .mil. Before sharing sensitive information, make sure you’re on a federal government site.
The site is secure. The https:// ensures that you are connecting to the official website and that any information you provide is encrypted and transmitted securely.
- Publications
- Account settings
Preview improvements coming to the PMC website in October 2024. Learn More or Try it out now .
- Advanced Search
- Journal List
- Int J Environ Res Public Health

Sex Education in the Spotlight: What Is Working? Systematic Review
Associated data.
The data presented in this study are available from the corresponding author on reasonable request.
Adolescence, a period of physical, social, cognitive and emotional development, represents a target population for sexual health promotion and education when it comes to achieving the 2030 Agenda goals for sustainable and equitable societies. The aim of this study is to provide an overview of what is known about the dissemination and effectiveness of sex education programs and thereby to inform better public policy making in this area. Methodology : We carried out a systematic review based on international scientific literature, in which only peer-reviewed papers were included. To identify reviews, we carried out an electronic search of the Cochrane Database Reviews, ERIC, Web of Science, PubMed, Medline, Scopus and PsycINFO. This paper provides a narrative review of reviews of the literature from 2015 to 2020. Results : 20 reviews met the inclusion criteria (10 in school settings, 9 using digital platforms and 1 blended learning program): they focused mainly on reducing risk behaviors (e.g., VIH/STIs and unwanted pregnancies), whilst obviating themes such as desire and pleasure, which were not included in outcome evaluations. The reviews with the lowest risk of bias are those carried out in school settings and are the ones that most question the effectiveness of sex education programs. Whilst the reviews of digital platforms and blended learning show greater effectiveness in terms of promoting sexual and reproductive health in adolescents (ASRH), they nevertheless also include greater risks of bias. Conclusion : A more rigorous assessment of the effectiveness of sexual education programs is necessary, especially regarding the opportunities offered by new technologies, which may lead to more cost-effective interventions than with in-person programs. Moreover, blended learning programs offer a promising way forward, as they combine the best of face-to-face and digital interventions, and may provide an excellent tool in the new context of the COVID-19 pandemic.
1. Introduction
Adolescence is a period of transition, growth, exploration and opportunities that the World Health Organization defines as referring to individuals between 10 years and 19 years of age [ 1 ]. During this life phase, adolescents undergo physical, psychological and sexual maturation and tend to develop an increased interest in sex and relationships, with positive relationships becoming strongly linked to sexual and reproductive health as well as overall wellbeing [ 2 ]. Sexual health is understood as a state of wellness comprising physical, emotional, mental, and social dimensions [ 3 ]: it represents one of the necessary requirements to achieve the general objective of sustainable and equitable societies in terms of the 2030 Agenda [ 4 ], which advocates the need for a sexual education that is anchored in a gender- and human rights-oriented perspective.
In high-income countries, sexual debut usually occurs during adolescence [ 5 ], though research suggests that sexual initiation is increasingly occurring at earlier ages [ 6 ]. Adolescents have to deal with the results of unhealthy sexual behaviors, including unplanned pregnancies and sexually transmitted infections [ 7 ], as well as experiences of sexual violence [ 8 , 9 ]. Adolescents are aware that they need more knowledge in order to enjoy healthy relationships [ 10 ], yet do not receive enough of the kind of information from parents or other formal sources that would allow them to develop a more positive, respectful experience of sexuality and sexual relationships [ 11 ].
Sexual education can be defined as any combination of learning experiences aimed at facilitating voluntary behavior conducive to sexual health. Sex education during adolescence has centered on the delivery of content (abstinence-only vs. comprehensive instruction) by teachers, parents, health professionals or community educators, and on the context (within school and beyond) of such delivery [ 12 ]. As regards content, the proponents of abstinence-only programs aim to help young adults avoid unintended pregnancies and sexually transmitted diseases (STDs), working on the assumption that while contraceptive use merely reduces the risk, abstinence will eliminate it entirely [ 13 ]. Nevertheless, an overwhelming majority of studies in this field have shown that programs advocating abstinence-only-until-marriage (AOUM) are neither effective in delaying sexual debut nor in changing other sexual risk behaviors [ 14 , 15 ], and participants in abstinence-only sex education programs consider that these had only a low impact in their lives [ 16 ]. On the other hand, holistic and comprehensive approaches to sex education go beyond risk behaviors and acknowledge other important aspects, as for example love, relationships, pleasure, sexuality, desire, gender diversity and rights, in accordance with internationally established guidelines [ 17 ], and with the 2030 Agenda [ 4 ]. Comprehensive Sexuality Education (CSE) “plays a central role in the preparation of young people for a safe, productive, fulfilling life” (p. 12) [ 17 ] and adolescents who receive comprehensive sex education are more likely to delay their sexual debut, as well as to use contraception during sexual initiation [ 18 ]. Comprehensive sexual education initiatives thereby promote sexual health in a way that involves not only the biological aspects of sexuality but also its psychological and emotional aspects, allowing young people to have enjoyable and safe sexual experiences.
With regard to context, sexual education may occur in different settings. School settings are key sites for implementing sexual education and for promoting adolescent sexual health [ 19 ], but today internet is becoming an increasingly important source of information and advice on these topics [ 20 ]. Access to the internet by adolescents is almost universal in high-income countries. The ubiquity and accessibility of digital platforms result in adolescents spending a great deal of time on the internet, and the search for information is the primary purpose of health-related internet use [ 21 ]. At the same time, this widespread use of technology by young people offers interesting possibilities for sexual health education programs, given the ease of access, availability, low cost, and the possibility of participating remotely [ 22 ]. The topics that young people search for online include information on everyday health-related issues, physical well-being and sexual health [ 23 ]. The majority of internet users of all ages in the US (80%) search online for health information including sexual health information [ 24 ], and among adolescents social media platforms are the most frequent means of obtaining information about health, especially regarding sexuality [ 25 ].
Thanks to the ubiquity and popularity of technologies, digital media interventions for sexual education offer a promising way forward, both via the internet (eHealth) and via mobile phones (mHealth, a specific way of promoting eHealth), given the privacy and anonymity they afford, especially for young people. Digital interventions in school—both inside and outside the classroom—offer interesting possibilities, because of their greater flexibility with regard to a variety of learning needs and benefits in comparison with traditional, face-to-face interventions, and because they offer ample opportunities for customization, interactivity as well as a safe, controlled, and familiar environment for transmitting sexual health knowledge and skills [ 26 ]. As Garzón-Orjuela et al. [ 27 ] argues, contemporary adolescents’ needs are mediated by their digital and technological environment, making it important to adapt interventions in the light of these realities. Online searches for sexual health information are likely to become increasingly important for young people with diminishing access to information from schools or health care providers in the midst of the lockdowns and widespread school closures during the COVID-19 pandemic [ 28 ], with more than two million deaths and 94 million people infected around the world [ 29 ]. Specifically, blended learning programs, consisting of internet-based educational interventions complemented by face-to-face interventions, may prove a significant addition to regular secondary school sex education programs [ 30 , 31 ]. Blended learning programs can be especially helpful in promoting sexual and reproductive health in the context of the COVID-19 pandemic, which is challenging the way we have so far approached formal education, with its focus on face to face interventions, given the need, now more than ever, to “develop and disseminate online sex education curricula, and ensure the availability of both in-person and online instruction in response to school closures caused by the pandemic” [ 28 ].
The present study sets out to research the dissemination and effectiveness in different settings (school, digital and blended learning) of sex education programs that promote healthy and positive relationships and the reduction of risk behaviors, so as to make current sexual health interventions more effective [ 32 ]. Numerous researchers have carried out trials and systematic reviews so as to evaluate the effectiveness of school-based sexual health and relationship education [ 19 , 27 , 33 , 34 , 35 ], as well as that of digital platform programs [ 36 , 37 , 38 , 39 ]. However, there has not been a review that is representative of the literature as a whole. Furthermore, in the reviews that have been carried out, differing aims and inclusion criteria have led to differences in the sampling of available primary studies [ 19 ]. As Garzón-Orjuela et al. [ 27 ] asserts, the field of adolescent sex education is continuously evolving and in need of evaluation and improvement. Better assessments are necessary in order to clarify whether they offer a viable and effective strategy for influencing adolescents, especially with respect to improved ASRH behaviors. Hence, given the need for an up-to-date revision so as to consider more recent emerging evidence in this field, in this study we carry out a review of reviews that includes reviews of interventions both in school settings and via digital platforms, as well as, for the first time, those that combine both formats (blended learning).
The decision to conduct a review of reviews (RoR), assessing the quality and summarizing the findings of existing systematic reviews, rather than working directly with primary intervention studies, addresses the need to include as wide a range of topics covered within the field of sex education as possible [ 40 ]. As Schackleton et al. [ 35 ] (p. 383) point out, in order to provide overviews of research evidence that are relevant to policy making, it is important “to bring together evidence on different forms of intervention and on different outcomes because it is useful for policy makers to know what is the range of approaches previously evaluated and whether these have consistent effects across different outcomes.” Carrying out and publicly sharing reviews of reviews such as the present study constitutes one way of better providing practitioners with evidence they can then carry over into their interventions [ 32 ].
2. Methodology
(1) To systematically review existing reviews of Sex Education (SE) of school-based (face-to-face), digital platforms and blended learning programs for adolescent populations in high-income countries.
(2) To summarize evidence relating to effectiveness.

2.2. Methods
The review is structured in accordance with the PRISMA checklist (Preferred Reporting Items for Systematic Reviews and Meta-Analysis) (see Figure A1 ), and the systematic review protocol has previously been published on the PROSPERO International Prospective Registry of Technical Reviews (CRD42021224537).
2.3. Search Strategy
This systematic review is based on international scientific literature and only peer- reviewed papers have been included. Only meta-analyses (publications that combine results from different studies) and systematic reviews (literature reviews that synthesize high-quality research evidence) were used for this review. Findings from reviews of reviews were not analyzed. To identify reviews, we electronically searched the Cochrane Database Reviews, ERIC, Web of Science, PubMed, Medline, Scopus and PsycINFO. After the list was completed the duplicated papers were automatically removed. Two reviewers working independently applied inclusion criteria in screening citations by titles, abstracts, and keywords to identify records for full-text review. A third reviewer reconciled any disagreement. The same procedure was carried out in screening the full text of studies selected after the title and abstract screening phase. Two reviewers then examined the full text of each article to determine which satisfied inclusion criteria. Data extraction was carried out independently by the first and second reviewer. The extracted data included specific details about the interventions, populations, study methods and outcomes significant to the review question and objective. Any discrepancies were discussed until consensus was reached. Search terms are included in Table A1 .
This RoR included the reviews published since 2015, when the United Nations decided on new Global Sustainable Development Goals, until December 2020. The 2030 Agenda for Sustainable Development [ 4 ] takes into account the relevance of Sexual Health to achieve peace and prosperity.
2.4. Inclusion Criteria
We extracted data using a “Population, Intervention, Comparison, Outcome” structure, PICO [ 41 ].
Population: Reviews of interventions targeting adolescents (aged 10–19 years), school-setting, digital platforms or blended learning education were eligible for inclusion. Reviews in which studies of interventions targeted youth and adults were eligible if the primary studies included people between the ages of 10–19 years.
Intervention: Reviews of interventions developed in school-setting (school-based), digital (digital platforms) or blended learning programs were included. Interventions based on multiple settings or targeted multiple health-related issues were only considered for inclusion if any primary studies were linked to school-based, digital or blended learning interventions, as well as targeting Sexual and Reproductive Health (SRH).
Comparison groups: Randomized controlled trials (RCTs) and studies using a quasi-experimental design (including non-randomized trials—nRCTs). Single group, pre- and post-test research designs, group exposed to sexual education (SE) program (school-based, digital platforms or blended learning) compared with non-exposed control group or another intervention.
Outcomes: Primary outcomes: (1) Sexual behavior and (2) Health and social outcomes related to sexual health. Secondary outcomes: (1) Knowledge and understanding of sexual health and relationship issues and (2) Attitudes, values and skills.
2.5. Exclusion Criteria
Reviews were excluded if:
- Their primary focus was adult people and adolescents were not included.
- Their primary focus was sexual-health screening, sexual abuse or assault or prevention of sexual abuse or rape.
- The studies targeted specific populations (e.g., pre-pubertal children, children with developmental disorders, migrant and refugee, or sexual minorities).
- The interventions focused on low- and middle-income countries or if high income countries were not included in the study.
- Recipients were professionals, teachers, parents or a combination of the latter.
2.6. Risk of Bias and Assessment of Study Quality
Review quality was assessed by the first author using the AMSTAR II checklist [ 42 ]. This is an updating and adaptation of AMSTAR [ 43 , 44 ] which allows a more detailed assessment of systematic reviews that include randomized or non-randomized studies of healthcare interventions, or both. It consists of a 16-item tool (including 5 critical domains) assessing the quality of a review’s design, its search strategy, inclusion and exclusion criteria, quality assessment of included studies, methods used to combine the findings, likelihood of publication bias and statements of conflict of interest. The maximum quality score is 16.
2.7. Data Synthesis
After manually coding the papers and extracting relevant data, we used a narrative/descriptive approach for data synthesis to summarize characteristics of the studies included. Considering the heterogeneity of outcomes, their measures and research designs, meta-analysis of all the studies included was not carried out. Two researchers were involved in data synthesis. Discrepancies were resolved through discussion, and a third researcher was consulted to resolve any remaining discrepancies. For the classification of the information and presentation of the effects of the interventions reported, data was separated (school setting, digital platforms or blended learning) and structured around population, intervention, comparison, and outcome. To address the main review questions, data was synthesized in two phases. Phase 1 addressed the first question, the description of sex education/sexual health interventions. Phase 2 addressed the second question, the effectiveness and benefit of the interventions; studies with a low risk of bias were highlighted, so as to strengthen the reliability of findings (AMSTAR II) [ 42 ].
3.1. Results of Search
Our searches yielded 1476 unique citations. After excluding 776 records based on title and abstract screening, we reviewed 217 full-text articles for eligibility, of which 20 ultimately met inclusion criteria, and proceeded to data extraction. Of the 197 studies that we excluded after full-text review, 82 were carried out in low- and middle-income countries, 47 targeted exclusively adults, 56 dealt with minority groups, and 12 targeted exclusively pre-teen students.
3.2. Risk of Bias in Included Studies
According to the AMSTAR II quality assessment tool’s developers [ 42 ] scores may range from 1 to 16: in this case only 2 reviews scored 16 out of 16: 1 in a school setting [ 45 ], and 1 on a digital platform [ 46 ]. 6 of the 20 systematic reviews were of high quality: 5 in school settings [ 45 , 47 , 48 , 49 , 50 ], and 1 in digital platforms [ 46 ]; there was one study of medium quality in a school setting [ 51 ]. The remaining studies were of low or very low quality (N = 13). It is possible that low quality reviews may not provide reliable evidence, so those scoring in low and critically low quality should be regarded skeptically.
3.3. Reviews Included
Key information regarding the 20 reviews included is shown in Table A2 and Table A3 .
3.3.1. Setting
Ten studies (50%) dealt with school-based interventions [ 45 , 47 , 48 , 49 , 50 , 51 , 52 , 53 , 54 , 55 ], 9 (45%) referred to online interventions [ 46 , 56 , 57 , 58 , 59 , 60 , 61 , 62 , 63 ] and 1 (5%) was a review of blended learning programs [ 64 ]. In total 491 studies were included in the 20 reviews covered by the present RoR. The 10 reviews of school setting interventions include a total of 266 studies (54%), the 9 reviews of online interventions cover a total of 216 (44%) studies, and the only review of blended learning interventions includes a total of 9 studies (2%). All studies were conducted in high-income economies following the World Bank classification [ 65 ], including US samples in 16 of the 20 studies, although there are two studies in which the country of the sample is not identified [ 51 , 52 ]. Most of the studies evaluating interventions in school settings also include developing countries (low- and middle-income economies) [ 45 , 47 , 50 , 52 , 53 , 55 ], as is also the case in three reviews of online interventions [ 46 , 61 , 62 ] (see Table A2 ).
3.3.2. Population
The targeted age for reviews in school settings, as shown in Table A2 , is the period of adolescence, from 10 to 19 years of age, though one of the studies covers ages from 7 to 19 years [ 53 ]. All the online studies also include young adults (20–24 years old), alongside the adolescent sample [ 46 , 56 , 57 , 59 , 60 , 61 , 62 , 63 ], whilst the review by DeSmet et al. [ 58 ] extends the upper limit to 29 years of age. Along with the sample of adolescents and young adults, the blended learning studies review also incorporates adults of over 25 years of age [ 64 ].
3.3.3. Interventions/Types of Study
All the studies included in this review of reviews used randomized controlled trials (RCTs), non-randomized controlled trials (non-RCT), and a quasi-experimental design or a pre-test/post-test design to examine program effects.
3.3.4. Outcomes
The term “sexual outcomes” refers to the attitudes, behaviors, and experiences of adolescents consequent to their sex education [ 14 ] (p. 1), and an extensive range of variables was included (see Table A2 ): knowledge (e.g., knowledge of contraceptive effectiveness or effective method use); attitudes (e.g., about sex and reproductive health); beliefs (e.g., self-efficacy); skills (e.g., condom skills); intentions/motivation (e.g., use of birth control methods; condom use); behaviors (e.g., sexual debut; condom use; contraception use; intercourse; initiation of sexual activity) and; other outcomes related to sexual behavior (e.g., pregnancy prevalence; number of partners; rates of sexually transmissible infections (STIs); cervical screening; appreciation of sexual diversity; dating and intimate partner violence prevention; sexual violence).
3.3.5. Country of Review
Of the 10 reviews of interventions in school settings, the authors are from the USA in 7 reviews [ 47 , 48 , 49 , 50 , 53 , 54 , 55 ], from the United Kingdom in 1 [ 45 ], from Australia in 1 [ 51 ], and from Thailand in 1 [ 52 ]. Of the 9 reviews of interventions in digital settings, the authors are from the United States in 3 reviews [ 59 , 60 , 63 ], from the United Kingdom in 2 [ 46 , 56 ], from Australia in 1 [ 62 ], from Belgium in 1 [ 58 ], from France in 1 [ 61 ] and from Turkey in 1 [ 57 ]. The authors of the blended learning review are from the USA [ 64 ].
3.3.6. Year of Last Paper Included
The studies cited in the reviews that met the inclusion criteria for this review were published over a wide range of years (between 1981–2019), although only one [ 61 ], with articles published up to and including 2019 was published later than 2017. Of these, 3 were carried out in school settings [ 49 , 51 , 53 ], and 1 on digital platforms [ 46 ].
3.3.7. Search Tools
All reviews include more than 2 tools to carry out the search, in a range of 3–12, and in 7 of them the review of gray literature was included.
3.3.8. Multicenter Studies and Number of Studies Included
All reviews from school settings are multicenter, except that of Mirzazadeh et al. [ 49 ], which includes only one North American sample. The same is true for the blended learning review [ 64 ] and for the reviews of digital platforms, except for the reviews by Bailey et al. [ 56 ], L´Engle et al. [ 60 ], and Widman et al. [ 63 ]. Regarding the number of countries included in the reviews, the range in the school-setting reviews is from 1 to 11, in digital platforms reviews from 1 to 16, and in the only review of blended learning, 3. As for the range of studies included, in the reviews in school setting the range is between 8 and 80, in digital platforms, between 5 and 60, and in the only review of reviews of blended learning 9 studies were included.
3.3.9. Number of Reviews Covered That Include Meta-Analysis
As for the number of reviews that carry out a meta-analysis, there are 8 in total: 4 in school settings [ 45 , 48 , 49 , 55 ] and 4 on digital platforms [ 43 , 46 , 56 , 58 ], while in the only review of blended learning there is no meta- analysis.
3.4. Effectiveness
3.4.1. school settings.
Half of the reviews conclude that interventions are not effective in promoting healthy sexual behaviors and/or reducing risks [ 45 , 47 , 48 , 49 , 50 ]. These reviews are of high quality and with a reduced risk of bias (see Table A4 ), so that the results are highly reliable, even though in most of the studies cited the risk of bias was judged to be high and the quality of evidence was low or very low. These reviews include those of the Marseille et al. [ 48 ] and Mirzazadeh et al. [ 49 ] team, who in two studies—each led by one of the two authors—analyze, on the one hand, the effectiveness of school-based teen pregnancy prevention programs [ 48 ], and, on the other hand, the effectiveness of school-based programs prevent HIV and other sexually transmitted infections in North America [ 49 ]. The results of the studies question the usefulness of interventions carried out in schools to prevent both unwanted pregnancies and the incidence of HIV and other sexual transmitted infections in adolescents in North America. In addition to these results, those of Lopez et al. [ 47 ] focus on analyzing the effectiveness of programs implemented in schools to promote the use of contraceptive methods and conclude that many trials reported contraceptive use as an outcome but did not take into consideration whether contraceptive methods and their relative effectiveness were part of the content. For its part, the review by Mason-Jones et al. [ 45 ] also concludes that the educational programs covered had no significant effect as regards the prevalence of HIV or other STIs (herpes simplex virus, moderate evidence and syphilis, low evidence), nor was there any apparent effect in terms of the number of pregnancies at the end of the trial (moderate evidence). Finally, the review by Oringanje et al. [ 50 ] finds only limited evidence for program effects on biological measures, and inconsistent results for behavioral (secondary) outcomes across trials and concludes that it was only the interventions which combined education and contraception promotion (multiple interventions) that led to a significant reduction in unintended pregnancies over the medium- and long-term follow-up period.
In contrast to these negative results in terms of the effectiveness of the programs implemented in the school environment (identified in 5 of the 10 reviews included), 3 of the 10 reviews concluded that the programs evaluated were mostly effective in promoting knowledge, attitudes and/or in reducing risk behaviors [ 51 , 52 , 53 ] whilst programs were effective in terms of some of the primary outcomes in the reviews by Haberland et al., [ 54 ], and Peterson et al. [ 55 ]. However, these data must be taken with caution since the level of bias in these reviews—excepting that of Kedzior et al. [ 51 ] with a medium quality level—is at a low or critically low-quality level. In the review by Chokprajakchad et al. [ 52 ], 22 programs reviewed were effective in changing targeted adolescent psychosocial and/or behavioral outcomes, in 12 of 17 studies evaluating delay in the initiation of sexual intercourse, the programs were effective and many of the reviewed studies demonstrated impacts on short-term outcomes, such as knowledge, attitudes, perception and intention. The review by Goldfarb et al. [ 53 ] identifies changes in appreciation of sexual diversity, dating and intimate partner violence prevention, healthy relationships, child sex abuse prevention and additional outcomes. According to the review by Kedzior et al. [ 51 ], focused on studies promoting social connectedness with regard to sexual and reproductive sexual health, the programs reviewed improved condom use, delayed initiation of sex, and reduced pregnancy rates. Additionally, in this review, program effectiveness was influenced by ethnicity and gender: greater improvements in condom use were often reported among African American students. For its part, in the study by Peterson et al. [ 55 ] the meta-analysis of three randomized trials provided some evidence that school-environment interventions may contribute to a later sexual debut while their narrative synthesis of other outcomes offered only mixed results.
Finally, the review by Haberland et al. [ 54 ], which focused on studies analyzing whether addressing gender and power in sexuality education curricula is associated with better outcomes, concluded that where interventions addressed gender or power (N = 10/22) there was a fivefold greater likelihood of effectiveness than in those that did not.
3.4.2. Online Platforms
The reviews included show a very diverse panorama of digital platforms used to carry out educational interventions (e.g., websites, social media, gaming, apps or text messaging and mailing), which makes it difficult to compare the results. Of the 9 reviews of studies included, only one—in which the effects of TCCMD (Targeted Client Communication delivered via Mobile Devices) are evaluated [ 46 ]—meets the quality criteria according to the AMSTAR II quality assessment tool [ 42 ] (see Table A4 ); the rest include biases that limit the reliability of the results so that these must be taken with caution. In the studies reviewed by Palmer et al. [ 46 ] among adolescents nine programs were delivered only via text messages; four programs used text messages in combination with other media (for example, emails, multimedia messaging, or voice calls); and one program used only voice calls.
When compared with more conventional approaches, interventions that use TCCMD may increase sexual health knowledge (low certainty evidence), and may modestly increase contraception use (low certainty evidence) while the effect on condom use remains unclear given the very low certainty evidence. Additionally, when compared with digital non-targeted communication, the effects TCCMD on sexual health knowledge, condom and contraceptive use are also unclear, again given the very low-certainty evidence. The review finds evidence of a modest beneficial intervention effect on contraceptive use among adolescent (and adult) populations, but that there was insufficient evidence to demonstrate that this translated into a reduction in contraception.
Most of the reviews included refer to changes to a greater or lesser extent [ 56 , 57 , 59 , 60 , 62 , 63 ], while no changes determined by the intervention were identified in the study by DeSmet et al. [ 58 ]. Finally, the review by Martin et al. [ 61 ] does not include details about changes as a result of the programs.
The review by L´Engle et al. [ 60 ] assesses mHealth mobile phone interventions for ASRH (almost all of which were carried out via SMS platforms, with the notable exception of only four of the programs covered which used other media formats instead of or as well as SMS). The interventions reviewed set out to foster positive and preventive SRH behaviors, augment take-up and continued use of contraception, support medication adherence for HIV-positive young people, support teenage parents, and encourage use of health screening and treatment services. Results from the studies covered in the review offer support for diverse uses of mobile phones in order to help further ASRH. The health promotion programs that made use of text messaging demonstrated robust acceptability and relevance for young people globally and contributed to improved SRH awareness, less unprotected sex, and more testing for STIs. However, the review also found that improved reporting on essential mHealth criteria is necessary in order to understand, replicate, and scale up mHealth interventions. Holstrom’s [ 59 ] review, focused on evaluations of internet-based sexual health interventions, finds that these were associated with greater sexual health knowledge and awareness, lower rates of unprotected sex and higher rates of condom use, as well as increased STI testing. Moreover, the review explores young people’s continuing use of and trust in internet as a source of information about sexual health, as well as the particular themes that interest them. Specifically, the study finds that young people want to know not only about STIs, but also about sexual pleasure, about how to talk with partners about their sexual desires, as well as about techniques to better pleasure their partners.
The review by Widman et al. [ 63 ] reveals a significant weighted mean effect of technology-based interventions on condom use and abstinence, the effects of which were not affected by age, gender, country, intervention, dose, interactivity, or program tailoring. The effects were more significant when evaluated with short-term (one to five months) follow-ups than with longer term (over six months) ones. Moreover, digital programs were more effective than control programs in contributing to sexual health knowledge and safer sex norms and attitudes. This meta-analysis, drawing on fifteen years of research into youth-oriented digital interventions, is clear evidence of their ability to contribute to safer sex behavior and awareness. In the review by Wadham et al. [ 62 ] the majority of studies used a web-based platform for their programs (16 out of 25). These web-based programs varied between complex, bespoke multimedia interventions to more simplified educational modules. Five studies employed SMS platforms both via mobile phone messaging and web-based instant message services. Three of the programs used social networking sites, either for live chat purposes or alongside a web-based platform. Several studies showed that variety in terms of media and platforms was associated with stronger positive responses among participants and improved outcomes. Eleven of the twenty-five studies focused specifically on HIV prevention, with seven finding a statistically significant effect of the program with regard to knowledge levels about prevention of HIV and other STIs, as well as about general sexual health knowledge. However, only twenty percent of the programs that assessed intended use of condoms reported significant effects due to the intervention.
The review by Bailey et al. [ 56 ] (p. 5) assesses interactive digital interventions (IDIs), defined as “digital media programs that provide health information and tailored decision support, behavioral-change support and/or emotional support” and focuses on the sexual well-being of young people between the ages of thirteen and twenty four in the United Kingdom. IDIs have significant though small effects on self-efficacy and sexual behavior, although there is not sufficient evidence to ascertain the effects on biological outcomes or other longer-term impacts. When comparing IDIs with in-person sexual health programs, the former demonstrate significant, moderate positive effects on sexual health knowledge, significant small effects on intention but no demonstrable effects on self-efficacy. The review by Celik et al. [ 57 ] looks at digital programs (the majority internet- and computer-based with only six making use of mobile phone-based applications) and sets out to understand their effectiveness in changing adolescents’ health behaviors. Findings from the studies ( n = 9) suggest that the digital interventions carried out with the adolescents generally had a positive effect on health-promoting behaviors. However, in another study focused on fostering HIV prevention [ 66 ], there was a statistically significant increase in health-promoting behavior in only one of the four studies reviewed.
In the review by DeSmet et al. [ 58 ], no significant behavioral changes as a result of the interventions for sexual health promotion using serious digital games are identified, although the interventions did have significant though small positive effects on outcomes. The fact that so few studies both met the inclusion criteria and also analyzed behavioral effects suggests the need to further investigate the effectiveness of this kind of game-based approach.
Finally, in the review by Martin et al. [ 61 ] 60 studies were covered, detailing a total of 37 interventions, though only 23 of the reviews included effectiveness results. A majority of the interventions were delivered via websites ( n = 20) while online social networks were the second most favored medium ( n = 13), mostly via Facebook ( n = 8). The programs under review favored online interaction, principally amongst peers ( n = 23) but also with professionals ( n = 16). The review concludes that ASHR programs promoting these kinds of online participation interventions have demonstrated feasibility, practical interest, and attractiveness, though their effectiveness has yet to be determined, given that they are still in the early stages of design and evaluation.
3.4.3. Blended Learning
In the only blended learning review included in our study [ 64 ], the authors conclude that blended learning approaches are being successfully applied in ASHR interventions, including in school-based programs, and have led to positive behavioral and psychosocial changes. However, these results should be treated with caution as the review does not follow the guidelines recommended in the AMSTAR II quality assessment tool [ 44 ] (see Table A4 ) and only includes nine studies.
4. Discussion
The present review of reviews assesses, for the first time jointly to our knowledge, the effectiveness of sexual education programs for the adolescent population (ASRH) developed in school settings, digital platforms and blended learning. Of the twenty reviews included (comprising a total of 491 programs, mostly from the USA), ten correspond to reviews of programs implemented in school settings, nine to those dealing with interventions via digital platforms and only one deals with studies relating to blended learning. Twelve (60%) of the reviews included (6 out of 10 in school settings, 5 out of 9 on digital platforms, and the only blended learning review) have been published in the last 3 years (between 2018 and 2020). Thus, the present study constitutes the most up-to-date and recent review of reviews incorporating several contemporary studies not covered by earlier reviews [ 19 , 27 , 33 , 35 , 36 , 37 , 38 , 39 ].
4.1. Interventions Reviewed
The interventions included in the reviews covered by our study were largely focused on reducing risk behaviors (e.g., VIH/STIs and unwanted pregnancies), and envisaging sex as a problem behavior. Programs reviewed often focused on the physical and biological aspects of sex, including pregnancy, STIs, frequency of sexual intercourse, use of condom, and reducing adolescents´ number of sexual partners. One exception is Golfard’s et al. [ 53 ] review about comprehensive sex education, which is centered on healthy relationships and sexual diversity, though it also makes reference to prevention of violence (dating and intimate partner violence prevention and sex abuse prevention). However, Golfard’s et al.’s [ 53 ] rejects more than 80% of the studies initially reviewed because they were focused solely on pregnancy and disease prevention. In the reviews of interventions on digital platforms and via blended learning all the outcomes focused on behaviors related to sexual health (focused on the prevention of risk behaviors), and in several cases also addressed perceived satisfaction and usability. These results are in line with other studies that confirm the over-attention given to risk behaviors, to the detriment of other more positive aspects of sexuality [ 67 , 68 ]. Teachers continue to perceive their responsibility as combating sexual risk, whilst viewing young people as immature and oversexualized [ 69 ], even as adolescents themselves express a preference for sex education with less emphasis on strictly negative sexual outcomes [ 16 ], and more emphasis on peer education [ 70 ].
As for more positive views of sexuality, only on rare occasions do interventions address issues such as sexual pleasure, desire and healthy relationships. Desire and pleasure were not included in the outcome evaluations for school settings, nor for digital and blended learning programs included in this review: again this is in line with the position of other authors cited in the present study, who advocate the need to also embrace the more positive aspects of sexuality [ 53 , 56 ]. Specifically, Bailey and colleagues [ 56 ] (p. 73) suggest as “optimal outcomes” social and emotional well-being in sexual health. Young people want to know about more than STIs, they also “want information about sexual pleasure, how to communicate with partners about what they want sexually and specific techniques to better pleasure their partners” [ 59 ] (p. 282). Similarly, Kedzior et al. [ 51 ] also argue for the need to move beyond a risk-aversion approach and towards one that places more emphasis on positive adolescent sexual and reproductive health.
Pleasure and desire are largely absent within sex and relationship education [ 71 ] and, when they are included, they are often proposed as part of a discourse on safe practice, where pleasure continues to be equated with danger [ 72 ]. The persistent absence of a “discourse of desire” in sex education [ 73 , 74 ] is especially problematic for women, for whom desire is still mediated by (positive) male attention, and for whom pleasure is derived from being found desirable and not from sexual self-expression or from their own desires [ 75 ]. Receiving sexualized attention from men makes women “feel good” by increasing their self-esteem and self-confidence [ 76 ]. However, it is still men who decide what is sexy and what is not, based on the attention they pay to women “girl watching”, [ 77 ] (p. 386), which leads the latter to self-objectify [ 78 ] with all the attendant negative consequences for their overall and sexual health [ 79 ]. In fact, women experience “pushes” and “pulls” [ 80 ] (p.393) with regard to sexualized culture. In one sense, the sexualization of culture has placed women in the position of subjects who desire, not just that of subjects who are desired, but at the same time it becomes a form of regulation in which young women are forced to assume the current sexualized ideal [ 81 , 82 ] in order to position themselves as “modern, liberated and feminine,” and avoid being seen as “outdated or prudish” [ 83 ] (p. 16). Koepsel [ 84 ] provides a holistic definition of pleasure as well as clear recommendations for how educators can overcome these deficits by incorporating pleasure into their existing curricula. At present, sexual education is still largely centered on questions of public health, and there is as yet no consensus on criteria for defining sexual well-being and other aspects of positive sexuality [ 85 ]. Patterson et al. [ 86 ] argue for the need to mandate “comprehensive, positive, inclusive and skills-based learning” to enhance people´s ability to develop healthy positive relationships throughout their lives.
The absence of desire and pleasure in the outcomes of the evaluated reviews is connected with the absence of gender-related outcomes. Only one of the reviews addresses the issue of gender and power in sexuality programs [ 54 ], illustrating how their inclusion can bring about a five-fold increase in the effectiveness of risk behavior prevention. Nonetheless, men are far less likely than women to sign up for a sexuality course, and as a result of masculine ideologies many young males experience negative attitudes towards sex education [ 87 ]. To date we still have little idea as to what are the “active ingredients” that can contribute to successfully encouraging men to challenge gender inequalities, male privilege and harmful or restrictive masculinities so as to help improve sexual and reproductive health for all [ 88 ] (p.16). Schmidt et al.’s [ 89 ] review looks at 10 evidence-based sexual education programs in schools: the majority discuss sexually transmitted diseases and unplanned pregnancy, abstinence, and contraceptive use, while very few address components related to healthy dating relationships, discussion of interpersonal violence or an understanding of gender roles.
The International Guidance on Sexuality Education [ 90 ], and the International Technical Guidance on Sexuality Education [ 17 ] promote the delivery of sexual education within a framework of human rights and gender equality to support children and adolescents in questioning social and cultural norms. The year 2020 marked the anniversaries of several path breaking policies, laws and events for women’s rights: the 100th anniversary of women´s suffrage in the United States; the 25th anniversary of the Beijing Platform for Action, a global roadmap for women´s empowerment; and, the 20th anniversary of the United Nations Security Council Resolution for a Women, Peace and Security agenda. Although there have been important advances in recent years in research relating to the inclusion of gender equality and human rights interventions in ASRH policies and programming still “fundamental gaps remain” [ 40 ] (p.14). Gender equality, and to an even greater extent human rights, have had very little presence in sexual and reproductive health programs and policies, and there is a pressing need to do more to address these issues systematically. Specifically, issues such as abortion and female genital mutilation, with clear repercussions in terms of gender equality and human rights, are rarely dealt with [ 40 ].
Furthermore, sexual education that privileges heterosexuality reinforces hegemonic attributes of femininity and masculinity, and ignores identities that distance themselves from these patterns. Our collective heteronormative legacy marginalizes and harms LGB families [ 91 ] and LGBTQ+-related information about healthy relationships is largely absent from sexual and reproductive health programs [ 92 ]. Students want a more LGBTQ+ inclusive curriculum [ 92 ]: in the present RoR one review [ 53 ] addresses the issue of non-heteronormative identity in sexuality programs with significant results; and other authors are exploring promising initiatives which are also challenging this lack of inclusivity [ 93 ] and rectifying heterosexual bias [ 94 ]. However, unfortunately, the underlying neoliberal focus of the majority of contemporary sexuality education militates to assimilate LGBTQ+ people into existing economic and social normative frameworks rather than helping disrupt them [ 95 ].
4.2. Effectiveness
This present review of reviews shows a variety of types of sexual health promotion initiatives across the three settings (school-based, digital and blended learning), with inconsistent results. The reviews with lower risk of bias are those carried out in school settings and those that are most critical regarding the effectiveness of programs promoting ASRH, both in the prevention of pregnancies and of HIV/STIs. Reviews dealing with digital platforms and blended learning show greater effectiveness in terms of promoting adolescent sexual health: however, these are also the studies that incorporate the highest risks of bias. Specifically, in digital platforms programs the great variety of alternatives makes comparability difficult. Moreover, these programs, along with blended learning, are in a more incipient state of evaluation, compared to school-setting evaluations, and present greater risks of lower quality than reviews in school settings.
The results of the present RoR are in line with those of previous RoRs [ 19 , 32 ]. The review of reviews by Denford et al.s´ [ 19 ] RoR covered 37 reviews up to 2016 and summarized 224 primary randomized controlled trials: whilst it concludes that school-based programs addressing risky sexual behavior can be effective, its reviews of exclusively school-based studies offer mixed results as to effectiveness in relation to attitudes, skills and behavioral change. Some of those studies report positive effects while others find there are no effects, if not even negative effects, in terms of the aforementioned outcomes [ 19 ]. As regards pregnancy, programs appear to be effective at increasing awareness regarding STIs and contraception but overall the findings suggest that the impact of these interventions on attitudes, behaviors and skills variables are mixed, with some studies leading to improvements whilst others show no change. Moreover, the fact that community-based programs were also taken into consideration might have led to the effectiveness of school-based programs being exaggerated [ 19 ].
However, although in our RoR the higher quality/lower bias studies—in keeping with the findings of previous reviews [ 19 , 33 ]—fail to show a clear pattern of effectiveness, the interventions could nevertheless be generating changes as Denford et al. [ 19 ] suggest, though not in the measured outcomes, bearing in mind the low incidence of sexual intercourse and pregnancy in school-going adolescents.
With regard to school settings, Peterson et al. [ 55 ] conclude that further, more rigorous evidence is necessary to evaluate the extent to which interventions addressing school-related factors are effective and to help better understand the mechanisms by which they may contribute to improving adolescent sexual health. With regard to digital platform programs, Wadham et al. [ 62 ] (p. 101) argue that “although new media has the capacity to expand efficiencies and coverage, the technology itself does not guarantee success.” An interesting observation in their review was that interventions which were either web-based adaptations of prior prevention programs, or were theory-based or had been developed from models of behavioral change appeared effective independently of the chosen digital media mode. However, digital programs are still in the early stages of design and evaluation, especially in terms of the effects of peer interaction and often diverge from existing theoretical models [ 61 ] (p. 13). The expert opinion-based proposal of the European Society for Sexual Medicine [ 96 ] argues that e-sexual health education can contribute to improving the sexual health of the population it seems the future of CSHE is moving towards smartphone apps [ 97 ].
However, “despite clear and compelling evidence for the benefits of high-quality curriculum-based CSE, few children and young people receive preparation for their lives that empowers them to take control and make informed decisions about their sexuality and relationships freely and responsibly” [ 17 ] (p. 12), and during “the current public health crisis, the sexual and reproductive health of adolescents and young adults must not be overlooked, as it is integral to both their and the larger society’s well-being” [ 28 ] (p. 9). In the light of these challenges, Coyle et al.’s [ 64 ] suggestion that the blended learning model may end up achieving a far more dominant role in the future of sexual education acquires even more relevance.
4.3. Limitations
This study represents the first review of reviews, as far as we are aware, in which the effectiveness of sex education programs in different settings (school-based, digital and blended learning) is evaluated, using a rich methodology and providing interesting conclusions. However, the present review of reviews is not without its limitations.
While systematic reviews and reviews of reviews can offer a way synthesizing large amounts of data, the great heterogeneity and diversity of measured outcomes make it difficult to establish a synthesis of the results, even more so in cases where it is not possible to apply meta-analysis. Furthermore, the quality of reviews of reviews is limited by that of the reviews they include and RoRs do not necessarily represent the leading edge research in the field.
In addition, although we searched for a wide range of keywords on the most commonly used databases in the field of health (namely ERIC, Web of Science, PubMed, and PsycINFO) to identify relevant papers, it is possible that the choice of keywords and database may have resulted in our omitting some relevant studies. Moreover, our review has focused on articles in international journals published in English, allowing us access to the most rigorous peer-reviewed studies and to those with greater international diffusion, given that English is the most frequently used language in the scientific environment: notwithstanding, this has also limited the scope of our review by precluding research published in other languages and contexts. Nor have documents that could have been found in the gray literature been included, given that only peer-reviewed studies have been considered for inclusion.
It is worth remembering moreover that most of the data on the outcomes of the studies included are self-reported, with mention of only occasional biological outcomes, which may limit the reliability of the effectiveness results. This represents another interesting reflection on the way in which the evaluation of the effectiveness of programs on sexual education is being carried out, and alerts us to the need for change.
Finally, it should be noted that this review of reviews is focused on adolescents from high-income countries, and our results show that studies carried out in the United States are largely overrepresented, since it is the country that provides the highest number of samples, especially in school settings: this may give rise to bias when it comes to generalizing from these results. Once again, this raises another necessary reflection on the capitalization that studies focused on American samples are having in the construction of the body of scientific knowledge on sexual and reproductive behavior, when in reality sexuality is conditioned by socio-economic variables that require a far-more multicultural and world-centric approach.
5. Conclusions
This review of reviews is the first to assess jointly the effectiveness of school-based, digital and blended learning interventions in ASRH in high-income countries. The effectiveness of the sex education programs reviewed mostly focused on the reduction of risky behaviors (e.g., STI or unwanted pregnancies) as public health outcomes; however, pleasure, desire and healthy relationships are outcomes that are mostly conspicuous by their absence in the reviews we have covered. Nonetheless, the broad range of studies included in this RoR, with their diversity of settings and methods, populations and objectives, precludes any easily drawn comparisons or conclusions. The inconsistent results and the high risk of bias reduce the conclusiveness of this review, so a more rigorous assessment of the effectivity of sexual education programs is pending and action needs to be taken to guarantee better and more rigorous evaluations, with sufficient human and financial resources. Schools and organizations need technical assistance to build the capacity for rigorous program planning, implementation and evaluation [ 98 ]. To this end, there are already examples of interesting proposals, such as that of the Working to Institutionalize Sex Education (WISE) Initiative, a privately funded effort to help public school districts develop and deliver comprehensive sexuality programs in the USA [ 99 ].
The extent of the risks of bias identified in the reviews and studies covered by this RoR points to an important conclusion, allowing us to highlight the precariousness that characterizes the evaluation of sexual education programs and the consequent undermining of public policy oriented to promoting ASRH. Public policies that promote ASRH are of vital importance when it comes to minimizing risks related to sexual behavior, and maximizing healthy relations and sexual well-being for the youngest members of our society.
Above all it is important to recognize the opportunities afforded by new technologies, so ubiquitous in the lives of young people, since they allow for programs that are far more cost-effective than traditional, in-person interventions. Finally, blended learning programs are perhaps even more promising, given their combination of the best of face-to-face and digital interventions, meaning they provide an excellent educative tool in the new context of the COVID-19 pandemic, and may even become the dominant teaching model in the future.

Flow diagram Preferred reporting items for systematic reviews and meta-analysis, PRISMA).
Search Terms Used.
Description of studies.
Characteristics and main results of the studies included.
Evaluation of the studies included (AMSTAR II).
1 1. Did the research questions and inclusion criteria for the review include the components of PCIO?; 2. Did the report of the review contain an explicit statement that the review methods were established prior to the conduct of the review and did the report justify any significant deviations from the protocol?; 3. Did the review authors explain their selection of the study designs for inclusion in the review?; 4. Did the review authors use a comprehensive literature search strategy?; 5. Did the review authors perform study selection in duplicate?; 6. Did the review authors perform data extraction in duplicate?; 7. Did the review authors provide a list of excluded studies and justify the exclusions?; 8. Did the review authors describe the included studies in adequate detail?; 9. Did the review authors use a satisfactory technique for assessing the risk of bias (RoB) in individual studies that were included in the review?; 10. Did the review authors report on the sources of funding for the studies included in the review?; 11. If meta-analysis was performed, did the review authors use appropriate methods for statistical combination of results?; 12. If meta-analysis was performed, did the review authors assess the potential impact of RoB in individual studies on the results of the meta-analysis or other evidence synthesis?; 13. Did the review authors account for RoB in primary studies when interpreting/discussing the results of the review?; 14. Did the review authors provide a satisfactory explanation for, and discussion of, any heterogeneity observed in the results of the review?; 15. If they performed quantitative synthesis did the review authors carry out an adequate investigation of publication bias (small study bias) and discuss its likely impact on the results of the review?; 16. Did the review authors report any potential sources of conflict of interest, including any funding they received for conducting the review? 2 H = Hight; M = Media; C = Low; CL = Critically Low. N = No; Y = Yes.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, M.L.-F. and R.M.-R.; methodology, M.L.-F.; R.M.-R.; Y.R.-C. and M.V.C.-F.; formal analysis, M.L.-F.; R.M.-R.; Y.R.-C. and M.V.C.-F.; investigation, M.L.-F.; R.M.-R.; Y.R.-C. and M.V.C.-F.; writing—original draft preparation, M.L.-F. and R.M.-R.; writing—review and editing, M.L.-F.; R.M.-R., and Y.R.-C. and.; supervision, M.L.-F.; R.M.-R.; Y.R.-C. and M.V.C.-F. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
This research received no external funding.
Institutional Review Board Statement
Not applicable.
Informed Consent Statement
Data availability statement, conflicts of interest.
The authors declare that they have no conflicts of interest.
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.

Comprehensive sexuality education: For healthy, informed and empowered learners

Did you know that only 37% of young people in sub-Saharan Africa can demonstrate comprehensive knowledge about HIV prevention and transmission? And two out of three girls in many countries lack the knowledge they need as they enter puberty and begin menstruating? Early marriage and early and unintended pregnancy are global concerns for girls’ health and education: in East and Southern Africa pregnancy rates range 15-25%, some of the highest in the world. These are some of the reasons why quality comprehensive sexuality education (CSE) is essential for learners’ health, knowledge and empowerment.
What is comprehensive sexuality education or CSE?
Comprehensive sexuality education - or the many other ways this may be referred to - is a curriculum-based process of teaching and learning about the cognitive, emotional, physical and social aspects of sexuality. It aims to equip children and young people with knowledge, skills, attitudes and values that empowers them to realize their health, well-being and dignity; develop respectful social and sexual relationships; consider how their choices affect their own well-being and that of others; and understand and ensure the protection of their rights throughout their lives.
CSE presents sexuality with a positive approach, emphasizing values such as respect, inclusion, non-discrimination, equality, empathy, responsibility and reciprocity. It reinforces healthy and positive values about bodies, puberty, relationships, sex and family life.
How can CSE transform young people’s lives?
Too many young people receive confusing and conflicting information about puberty, relationships, love and sex, as they make the transition from childhood to adulthood. A growing number of studies show that young people are turning to the digital environment as a key source of information about sexuality.
Applying a learner-centered approach, CSE is adapted to the age and developmental stage of the learner. Learners in lower grades are introduced to simple concepts such as family, respect and kindness, while older learners get to tackle more complex concepts such as gender-based violence, sexual consent, HIV testing, and pregnancy.
When delivered well and combined with access to necessary sexual and reproductive health services, CSE empowers young people to make informed decisions about relationships and sexuality and navigate a world where gender-based violence, gender inequality, early and unintended pregnancies, HIV and other sexually transmitted infections still pose serious risks to their health and well-being. It also helps to keep children safe from abuse by teaching them about their bodies and how to change practices that lead girls to become pregnant before they are ready.
Equally, a lack of high-quality, age-appropriate sexuality and relationship education may leave children and young people vulnerable to harmful sexual behaviours and sexual exploitation.
What does the evidence say about CSE?
The evidence on the impact of CSE is clear:
- Sexuality education has positive effects, including increasing young people’s knowledge and improving their attitudes related to sexual and reproductive health and behaviors.
- Sexuality education leads to learners delaying the age of sexual initiation, increasing the use of condoms and other contraceptives when they are sexually active, increasing their knowledge about their bodies and relationships, decreasing their risk-taking, and decreasing the frequency of unprotected sex.
- Programmes that promote abstinence as the only option have been found to be ineffective in delaying sexual initiation, reducing the frequency of sex or reducing the number of sexual partners. To achieve positive change and reduce early or unintended pregnancies, education about sexuality, reproductive health and contraception must be wide-ranging.
- CSE is five times more likely to be successful in preventing unintended pregnancy and sexually transmitted infections when it pays explicit attention to the topics of gender and power
- Parents and family members are a primary source of information, values formation, care and support for children. Sexuality education has the most impact when school-based programmes are complemented with the involvement of parents and teachers, training institutes and youth-friendly services .
How does UNESCO work to advance learners' health and education?
Countries have increasingly acknowledged the importance of equipping young people with the knowledge, skills and attitudes to develop and sustain positive, healthy relationships and protect themselves from unsafe situations.
UNESCO believes that with CSE, young people learn to treat each other with respect and dignity from an early age and gain skills for better decision making, communications, and critical analysis. They learn they can talk to an adult they trust when they are confused about their bodies, relationships and values. They learn to think about what is right and safe for them and how to avoid coercion, sexually transmitted infections including HIV, and early and unintended pregnancy, and where to go for help. They learn to identify what violence against children and women looks like, including sexual violence, and to understand injustice based on gender. They learn to uphold universal values of equality, love and kindness.
In its International Technical Guidance on Sexuality Education , UNESCO and other UN partners have laid out pathways for quality CSE to promote health and well-being, respect for human rights and gender equality, and empower children and young people to lead healthy, safe and productive lives. An online toolkit was developed by UNESCO to facilitate the design and implementation of CSE programmes at national level, as well as at local and school level. A tool for the review and assessment of national sexuality education programmes is also available. Governments, development partners or civil society organizations will find this useful. Guidance for delivering CSE in out-of-school settings is also available.
Through its flagship programme, Our rights, Our lives, Our future (O3) , UNESCO has reached over 30 million learners in 33 countries across sub-Saharan Africa with life skills and sexuality education, in safer learning environments. O3 Plus is now also reaching and supporting learners in higher education institutions.
To strengthen coordination among the UN community, development partners and civil society, UNESCO is co-convening the Global partnership forum on CSE together with UNFPA. With over 65 organizations in its fold, the partnership forum provides a structured platform for intensified collaboration, exchange of information and good practices, research, youth advocacy and leadership, and evidence-based policies and programmes.
Good quality CSE delivery demands up to date research and evidence to inform policy and implementation . UNESCO regularly conducts reviews of national policies and programmes – a report found that while 85% of countries have policies that are supportive of sexuality education, significant gaps remain between policy and curricula reviewed. Research on the quality of sexuality education has also been undertaken, including on CSE and persons with disabilities in Asia and East and Southern Africa .
How are young people and CSE faring in the digital space?
More young people than ever before are turning to digital spaces for information on bodies, relationships and sexuality, interested in the privacy and anonymity the online world can offer. UNESCO found that, in a year, 71% of youth aged 15-24 sought sexuality education and information online.
With the rapid expansion in digital information and education, the sexuality education landscape is changing . Children and young people are increasingly exposed to a broad range of content online some of which may be incomplete, poorly informed or harmful.
UNESCO and its Institute of Information Technologies in Education (IITE) work with young people and content creators to develop digital sexuality education tools that are of good quality, relevant and include appropriate content. More research and investment are needed to understand the effectiveness and impact of digital sexuality education, and how it can complement curriculum-based initiatives. Part of the solution is enabling young people themselves to take the lead on this, as they are no longer passive consumers and are thinking in sophisticated ways about digital technology.
A foundation for life and love
- Safe, seen and included: report on school-based sexuality education
- International Technical Guidance on Sexuality Education
- Safe, seen and included: inclusion and diversity within sexuality education; briefing note
- Comprehensive sexuality education (CSE) country profiles
- Evidence gaps and research needs in comprehensive sexuality education: technical brief
- The journey towards comprehensive sexuality education: global status report
- Definition of Sustainable Development Goal (SDG) thematic indicator 4.7.2: Percentage of schools that provided life skills-based HIV and sexuality education within the previous academic year
- From ideas to action: addressing barriers to comprehensive sexuality education in the classroom
- Facing the facts: the case for comprehensive sexuality education
- UNESCO strategy on education for health and well-being
- UNESCO Health and education resource centre
- Campaign: A foundation for life and love
- UNESCO’s work on health and education
Related items
- Health education
- Sex education
Internet Explorer Alert
It appears you are using Internet Explorer as your web browser. Please note, Internet Explorer is no longer up-to-date and can cause problems in how this website functions This site functions best using the latest versions of any of the following browsers: Edge, Firefox, Chrome, Opera, or Safari . You can find the latest versions of these browsers at https://browsehappy.com
- Publications
- HealthyChildren.org
Shopping cart
Order Subtotal
Your cart is empty.
Looks like you haven't added anything to your cart.
- Career Resources
- Philanthropy
- About the AAP
- The Role of the Pediatrician in the Promotion of Healthy, Active Living
- How Can You Support Patients in Healthy, Active Living? Check Out Updated Report
- Helping Kids Build Healthy Active Lives: AAP Policy Explained
- Climate Change & Children’s Health: AAP Policy Explained
- News Releases
- Policy Collections
- The State of Children in 2020
- Healthy Children
- Secure Families
- Strong Communities
- A Leading Nation for Youth
- Transition Plan: Advancing Child Health in the Biden-Harris Administration
- Health Care Access & Coverage
- Immigrant Child Health
- Gun Violence Prevention
- Tobacco & E-Cigarettes
- Child Nutrition
- Assault Weapons Bans
- Childhood Immunizations
- E-Cigarette and Tobacco Products
- Children’s Health Care Coverage Fact Sheets
- Opioid Fact Sheets
- Advocacy Training Modules
- Subspecialty Advocacy Report
- AAP Washington Office Internship
- Online Courses
- Live and Virtual Activities
- National Conference and Exhibition
- Prep®- Pediatric Review and Education Programs
- Journals and Publications
- NRP LMS Login
- Patient Care
- Practice Management
- AAP Committees
- AAP Councils
- AAP Sections
- Volunteer Network
- Join a Chapter
- Chapter Websites
- Chapter Executive Directors
- District Map
- Create Account
- Early Relational Health
- Early Childhood Health & Development
- Safe Storage of Firearms
- Promoting Firearm Injury Prevention
- Mental Health Education & Training
- Practice Tools & Resources
- Policies on Mental Health
- Mental Health Resources for Families
The Importance of Access to Comprehensive Sex Education
Comprehensive sex education is a critical component of sexual and reproductive health care.
Developing a healthy sexuality is a core developmental milestone for child and adolescent health.
Youth need developmentally appropriate information about their sexuality and how it relates to their bodies, community, culture, society, mental health, and relationships with family, peers, and romantic partners.
AAP supports broad access to comprehensive sex education, wherein all children and adolescents have access to developmentally appropriate, evidence-based education that provides the knowledge they need to:
- Develop a safe and positive view of sexuality.
- Build healthy relationships.
- Make informed, safe, positive choices about their sexuality and sexual health.
Comprehensive sex education involves teaching about all aspects of human sexuality, including:
- Cyber solicitation/bullying.
- Healthy sexual development.
- Body image.
- Sexual orientation.
- Gender identity.
- Pleasure from sex.
- Sexual abuse.
- Sexual behavior.
- Sexual reproduction.
- Sexually transmitted infections (STIs).
- Abstinence.
- Contraception.
- Interpersonal relationships.
- Reproductive coercion.
- Reproductive rights.
- Reproductive responsibilities.
Comprehensive sex education programs have several common elements:
- Utilize evidence-based, medically accurate curriculum that can be adapted for youth with disabilities.
- Employ developmentally appropriate information, learning strategies, teaching methods, and materials.
- Human development , including anatomy, puberty, body image, sexual orientation, and gender identity.
- Relationships , including families, peers, dating, marriage, and raising children.
- Personal skills , including values, decision making, communication, assertiveness, negotiation, and help-seeking.
- Sexual behavior , including abstinence, masturbation, shared sexual behavior, pleasure from esx, and sexual dysfunction across the lifespan.
- Sexual health , including contraception, pregnancy, prenatal care, abortion, STIs, HIV and AIDS, sexual abuse, assault, and violence.
- Society and culture , including gender roles, diversity, and the intersection of sexuality and the law, religion, media, and the arts.
- Create an opportunity for youth to question, explore, and assess both personal and societal attitudes around gender and sexuality.
- Focus on personal practices, skills, and behaviors for healthy relationships, including an explicit focus on communication, consent, refusal skills/accepting rejection, violence prevention, personal safety, decision making, and bystander intervention.
- Help youth exercise responsibility in sexual relationships.
- Include information on how to come forward if a student is being sexually abused.
- Address education from a trauma-informed, culturally responsive approach that bridges mental, emotional, and relational health.
Comprehensive sex education should occur across the developmental spectrum, beginning at early ages and continuing throughout childhood and adolescence :
- Sex education is most effective when it begins before the initiation of sexual activity.
- Young children can understand concepts related to bodies, gender, and relationships.
- Sex education programs should build an early foundation and scaffold learning with developmentally appropriate content across grade levels.
- AAP Policy outlines considerations for providing developmentally appropriate sex education throughout early childhood, middle childhood, adolescence, and young adulthood.
Most adolescents report receiving some type of formal sex education before age 18. While sex education is typically associated with schools, comprehensive sex education can be delivered in several complementary settings:
- Schools can implement comprehensive sex education curriculum across all grade levels
- The Sexuality Information and Education Council of the United States (SIECUS) provides guidelines for providing developmentally appropriate comprehensive sex education across grades K-12.
- Pediatric health clinicians and other health care providers are uniquely positioned to provide longitudinal sex education to children, adolescents, and young adults.
- Bright Futures: Guidelines for Health Supervision of Infants, Children, and Adolescents outlines clinical considerations for providing comprehensive sex education at all developmental stages, as a part of preventive health care.
- Research suggests that community-based organizations should be included as a source for comprehensive sexual health promotion.
- Faith-based communities have developed sex education curricula for their congregations or local chapters that emphasize the moral and ethical aspects of sexuality and decision-making.
- Parents and caregivers can serve as the primary sex educators for their children, by teaching fundamental lessons about bodies, development, gender, and relationships.
- Many factors impact the sex education that youth receive at home, including parent/caregiver knowledge, skills, comfort, culture, beliefs, and social norms.
- Virtual sex education can take away feelings of embarrassment or stigma and can allow for more youth to access high quality sex education.
Comprehensive sex education provides children and adolescents with the information that they need to:
- Understand their body, gender identity, and sexuality.
- Build and maintain healthy and safe relationships.
- Engage in healthy communication and decision-making around sex.
- Practice healthy sexual behavior.
- Understand and access care to support their sexual and reproductive health.
Comprehensive sex education programs have demonstrated success in reducing rates of sexual activity, sexual risk behaviors, STIs, and adolescent pregnancy and delaying sexual activity. Many systematic reviews of the literature have indicated that comprehensive sex education promotes healthy sexual behaviors:
- Reduced sexual activity.
- Reduced number of sexual partners.
- Reduced frequency of unprotected sex.
- Increased condom use.
- Increased contraceptive use.
However, comprehensive sex education curriculum goes beyond risk-reduction, by covering a broader range of content that has been shown to support social-emotional learning, positive communication skills, and development of healthy relationships.
A 2021 review of the literature found that comprehensive sex education programs that use a positive, affirming, and inclusive approach to human sexuality are associated with concrete benefits across 5 key domains:
Benefits of comprehensive sex education programs
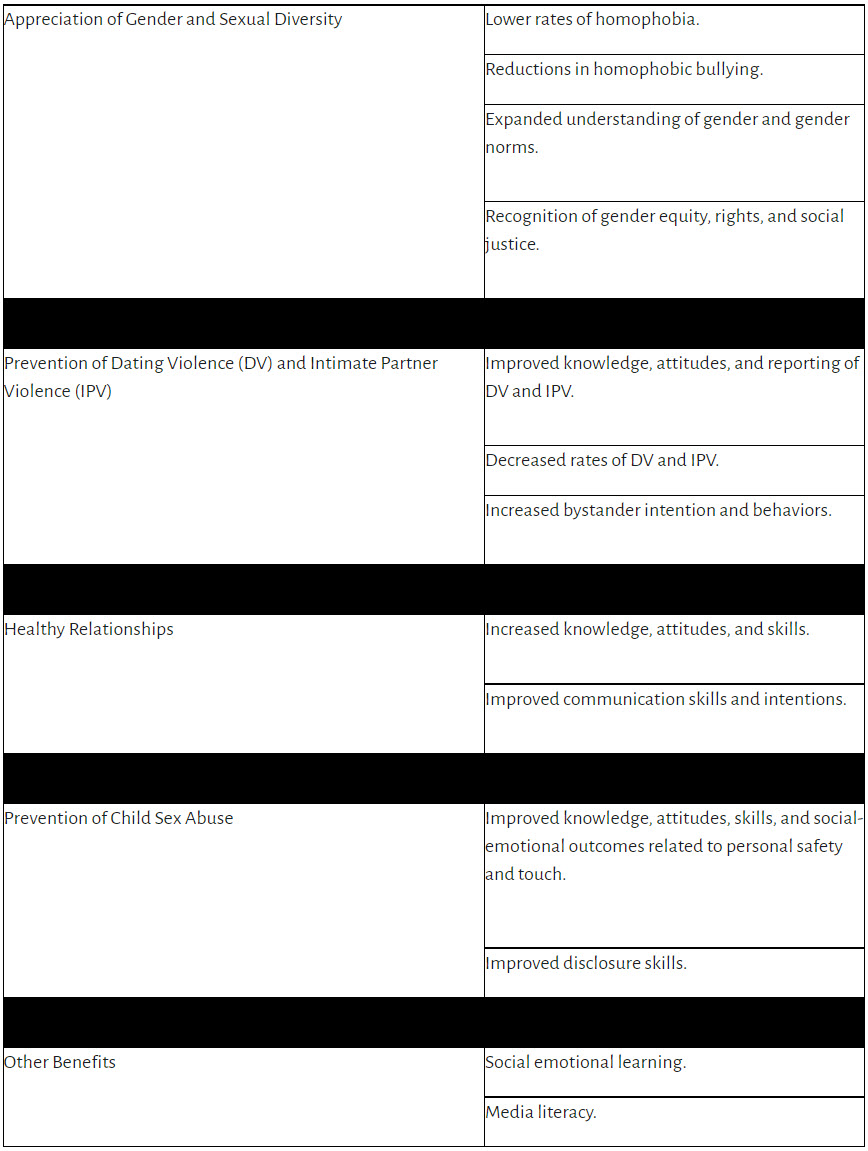
When children and adolescents lack access to comprehensive sex education, they do not get the information they need to make informed, healthy decisions about their lives, relationships, and behaviors.
Several trends in sexual health in the US highlight the need for comprehensive sex education for all youth.
Education about condom and contraceptive use is needed:
- 55% of US high school students report having sexual intercourse by age 18 .
- Self-reported condom use has decreased significantly among high school students.
- Only 9% of sexually active high school students report using both a condom for STI-prevention and a more effective form of birth control to prevent pregnancy .
STI prevention is needed:
- Adolescents and young adults are disproportionately impacted by STIs.
- Cases of chlamydia, gonorrhea, and syphilis are rising rapidly among young people.
- When left untreated , these infections can lead to infertility, adverse pregnancy and birth outcomes, and increased risk of acquiring new STIs.
- Youth need comprehensive, unbiased information about STI prevention, including human papillomavirus (HPV) .
Continued prevention of unintended pregnancy is needed:
- Overall US birth rates among adolescent mothers have declined over the last 3 decades.
- There are significant geographic disparities in adolescent pregnancy rates, with higher rates of pregnancy in rural counties and in southern and southwestern states.
- Social drivers of health and systemic inequities have caused racial and ethnic disparities in adolescent pregnancy rates.
- Eliminating disparities in adolescent pregnancy and birth rates can increase health equity, improve health and life outcomes, and reduce the economic impact of adolescent parenting.
Misinformation about sexual health is easily available online:
- Internet use is nearly universal among US children and adolescents.
- Adolescents report seeking sexual health information online .
- Sexual health websites that adolescents visit can contain inaccurate information .
Prevention of sex abuse, dating violence, and unhealthy relationships is needed:
- Child sexual abuse is common: 25% of girls and 8% of boys experience sexual abuse during childhood .
- Youth who experience sexual abuse have long-term impacts on their physical, mental, and behavioral health.
- 1 in 11 female and 1 in 14 male students report physical DV in the last year .
- 1 in 8 female and 1 in 26 male students report sexual DV in the last year .
- Youth who experience DV have higher rates of anxiety, depression, substance use, antisocial behaviors, and suicide risk.
The quality and content of sex education in US schools varies widely.
There is significant variation in the quality of sex education taught in US schools, leading to disparities in attitudes, health information, and outcomes. The majority of sex education programs in the US tend to focus on public health goals of decreasing unintended pregnancies and preventing STIs, via individual behavior change.
There are three primary categories of sex educational programs taught in the US :
- Abstinence-only education , which teaches that abstinence is expected until marriage and typically excludes information around the utility of contraception or condoms to prevent pregnancy and STIs.
- Abstinence-plus education , which promotes abstinence but includes information on contraception and condoms.
- Comprehensive sex education , which provides medically accurate, age-appropriate information around development, sexual behavior (including abstinence), healthy relationships, life and communication skills, sexual orientation, and gender identity.
State laws impact the curriculum covered in sex education programs. According to a report from the Guttmacher Institute :
- 26 US states and Washington DC mandate sex education and HIV education.
- 18 states require that sex education content be medically accurate.
- 39 states require that sex education programs provide information on abstinence.
- 20 states require that sex education programs provide information on contraception.
US states have varying requirements on sex education content related to sexual orientation :
- 10 states require sex education curriculum to include affirming content on LGBTQ2S+ identities or discussion of sexual health for youth who are LGBTQ2S+.
- 7 states have sex education curricular requirements that discriminate against individuals who are LGBTQ2S+.Youth who live in these states may face additional barriers to accessing sexual health information.
Abstinence-only sex education programs do not meet the needs of children and adolescents.
While abstinence is 100% effective in preventing pregnancy and STIs, research has conclusively shown that abstinence-only sex education programs do not support healthy sexual development in youth.
Abstinence-only programs are ineffective in reaching their stated goals, as evidenced by the data below:
- Abstinence-only programs are unsuccessful in delaying sex until marriage .
- Abstinence-only sex education programs do not impact the rates of pregnancy, STIs, or HIV in adolescents .
- Youth who take a “virginity pledge” as part of abstinence-only education programs have the same rates of premarital sex as their peers who do not take pledges, but are less likely to use contraceptives .
- US states that emphasize abstinence-only education have higher rates of adolescent pregnancy and birth .
Abstinence-only programs can harm the healthy sexual and mental development of youth by:
- Withholding information or providing inaccurate information about sexuality and sexual behavior .
- Contributing to fear, shame, and stigma around sexual behaviors .
- Not sharing information on contraception and barrier protection or overstating the risks of contraception .
- Utilizing heteronormative framing and stigma or discrimination against students who are LGBTQ2S+ .
- Reinforcing harmful gender stereotypes .
- Ignoring the needs of youth who are already sexually active by withholding education around contraception and STI prevention.
Abstinence-plus sex education programs focus solely on decreasing unintended pregnancy and STIs.
Abstinence-plus sex education programs promote abstinence until marriage. However, these programs also provide information on contraception and condom use to prevent unintended pregnancy and STIs.
Research has demonstrated that abstinence-plus programs have an impact on sexual behavior and safety, including:
- HIV prevention.
- Increase in condom use .
- Reduction in number of sexual partners .
- Delay in initiation of sexual behavior .
While these programs add another layer of education, they do not address the broader spectrum of sexuality, gender identity, and relationship skills, thus withholding critical information and skill-building that can impact healthy sexual development.
AAP and other national medical and public health associations support comprehensive sex education for youth.
Given the evidence outlined above, AAP and other national medical organizations oppose abstinence-only education and endorse comprehensive sex education that includes both abstinence promotion and provision of accurate information about contraception, STIs, and sexuality.
National medical and public health organizations supporting comprehensive sex education include:
- American Academy of Pediatrics .
- American Academy of Family Physicians.
- American College of Obstetricians and Gynecologists .
- American Medical Association .
- American Public Health Association .
- Society for Adolescent Health and Medicine .
Pediatric clinics provide a unique opportunity for comprehensive sex education.
Pediatric health clinicians typically have longitudinal care relationships with their patients and families, and thus have unique opportunities to address comprehensive sex education across all stages of development.
The clinical visit can serve as a useful adjunct to support comprehensive sex education provided in schools, or to fill gaps in knowledge for youth who are exposed to abstinence-only or abstinence-plus curricula.
AAP policy and Bright Futures: Guidelines for Health Supervision of Infants, Children, and Adolescents provide recommendations for comprehensive sex education in clinical settings, including:
- Encouraging parent-child discussions on sexuality, contraception, and internet/media use.
- Understanding diverse experiences and beliefs related to sexuality and sex education and meeting the unique needs of individual patients and families.
- Including discussions around healthy relationships, dating violence, and intimate partner violence in clinical care.
- Discussing methods of contraception and STI/HPV prevention prior to onset of sexual intercourse.
- Providing proactive and developmentally appropriate sex education to all youth, including children and adolescents with special health care needs.
Perspective

Karen Torres, Youth activist
There were two cardboard bears, and a person explained that one bear wears a bikini to the beach and the other bear wears shorts – that is the closest thing I ever got to sex ed throughout my entire K-12 education. I often think about that bear lesson because it was the day our institutions failed to teach me anything about my body, relationships, consent, and self-advocacy, which became even more evident after I was sexually assaulted at 16 years old. My story is not unique, I know that many young people have been through similar traumas, but many of us were also subjected to days, months, and years of silence and embarrassment because we were never given the knowledge to know how to spot abuse or the language to ask for help. Comprehensive sex ed is so much more than people make it out to be, it teaches about sex but also about different types of experiences, how to respect one another, how to communicate in uncomfortable situations, how to ask for help and an insurmountable amount of other valuable lessons.
From these lessons, people become well-rounded, people become more empathetic to other experiences, and people become better. I believe comprehensive sex ed is vital to all people and would eventually work as a part to build more compassionate communities.
Many US children and adolescents do not receive comprehensive sex education; and rates of formal sex education have declined significantly in recent decades.
Barriers to accessing comprehensive sex education include:
Misinformation, stigma, and fear of negative reactions:
- Misinformation and stigma about the content of sex education curriculum has been the primary barrier to equitable access to comprehensive sex education in schools for decades .
- Despite widespread parental support for sex education in schools, fears of negative public/parent reactions have led school administrators to limit youth access to the information they need to make healthy decisions about their sexuality for nearly a half-century.
- In recent years, misinformation campaigns have spread false information about the framing and content of comprehensive sex education programs, causing debates and polarization at school board meetings .
- Nearly half of sex education teachers report that concerns about parent, student, or administrator responses are a barrier to provision of comprehensive sex education.
- Opponents of comprehensive sex education often express concern that this education will lead youth to have sex; however, research has demonstrated that this is not the case . Instead, comprehensive sex ed is associated with delays in initiation of sexual behavior, reduced frequency of sexual intercourse, a reduction in number of partners, and an increase in condom use.
- Some populations of youth lack access to comprehensive sex education due to a societal belief that they are asexual, in need of protection, or don’t need to learn about sex. This barrier particularly impacts youth with disabilities or special health care needs .
- Sex ed curricula in some schools perpetuate gender/sex stereotypes, which could contribute to negative gender stereotypes and negative attitudes towards sex .
Inconsistencies in school-based sex education:
- There is significant variation in the content of sex education taught in schools in the US, and many programs that carry the same label (eg, “abstinence-plus”) vary widely in curriculum.
- While decisions about sex education curriculum are made at the state level, the federal government has provided funding to support abstinence-only education for decades , which incentivizes schools to use these programs.
- Since 1996, more than $2 billion in federal funds have been spent to support abstinence-only sex education in schools.
- 34 US states require schools to use abstinence-only curriculum or emphasize abstinence as the main way to avoid pregnancy and STIs.
- Only 16 US states require instruction on condoms or contraception.
- It is not standard to include information on how to come forward if a student is being sexually abused, and many schools do not have a process for disclosures made.
- Because of this, abstinence-only programs are commonly used in US schools, despite overwhelming evidence that they are ineffective in delaying sexual behavior until marriage, and withhold critical information that youth need for healthy sexual and relationship development.
Need for resources and training:
- Integration of comprehensive sex education into school curriculum requires financial resources to strengthen and expand evidence-based programs.
- Successful implementation of comprehensive sex education requires a trained workforce of teachers who can address the curriculum in age-appropriate ways for students in all grade-levels.
- Education, training, and technical assistance are needed to support pediatric health clinicians in addressing comprehensive sex education in clinical settings, as a complement to school-based education.
Lack of diversity and cultural awareness in curricula:
- A history of systemic racism, discrimination, and long-standing health, social and systemic inequities have created racial and ethnic disparities in access to sexual health services and representation in sex education materials. The legacy of intergenerational trauma in the medical system should be acknowledged in sex education curricula.
- Sex education curriculum is often centered on a white audience, and does not address or reflect the role of systemic racism in sexuality and development .
- Traditional abstinence-focused sex education programs have a heteronormative focus and do not address the unique needs of youth who are LGBTQ2S+ .
- Sex education programs often do not address reproductive body diversity, the needs of those with differences in sex development, and those who identify as intersex .
- Sex education programs often do not reflect the unique needs of youth with disabilities or special health care needs .
- Sex education programs are often not tailored to meet the religious considerations of faith communities.
- There is a need for sex education programs designed to help youth navigate sexual health and development in the context of their own culture and community .
Disparities in access to comprehensive sex education.
The barriers listed above limit access to comprehensive sex education in schools and communities. While these barriers impact youth across the US, there are some populations who are less likely to have access to comprehensive to sex education.
Youth who are LGBTQ2S+:
- Only 8% of students who are LGBTQ2S+ report having received sexual education that was inclusive .
- Students who are LGBTQ2S+ are 50% more likely than their peers who are heterosexual to report that sex education in their schools was not useful to them .
- Only 13% of youth who are bisexual+ and 10% of youth who are transgender and gender expansive report receiving sex education in schools that felt personally relevant.
- Only 20% of youth who are Black and LGBTQ2S+ and 13% of youth who are Latinx and LGBTQ2S+ report receiving sex education in schools that felt personally relevant.
- Only 10 US states require affirming content on LGBTQ2S+ relationships in sex education curriculum.
Youth with disabilities or special health care needs:
- Youth with disabilities or special health care needs have a particular need for comprehensive sex education, as these youth are less likely to learn about sex or sexuality form their parents , healthcare providers , or peer groups .
- In a national survey, only half of youth with disabilities report that they have participated in sex education .
- Typical sex education may not be sufficient for youth with Autism Spectrum Disorder, and special methods and curricula are necessary to match their needs .
- Lack the desire or maturity for romantic or sexual relationships.
- Are not subject to sexual abuse.
- Do not need sex education.
- Only 3 states explicitly include youth with disabilities within their sex education requirements.
Youth from historically underserved communities:
- Students who are Black in the US are more likely than students who are white to receive abstinence-only sex education , despite significant support from parents and students who are Black for comprehensive sex education.
- Youth who are Black and female are less likely than peers who are white to receive education about where to obtain birth control prior to initiating sexual activity.
- Youth who are Black and male and Hispanic are less likely than their peers who are white to receive formal education on STI prevention or contraception prior to initiating sexual activity.
- Youth who are Hispanic and female are less likely to receive instruction about waiting to have sex than youth of other ethnicities.
- Tribal health educators report challenges in identifying culturally relevant sex education curriculum for youth who are American Indian/Alaska Native.
- In a 2019 study, youth who were LGBTQ2S+ and Black, Latinx, or Asian reported receiving inadequate sex education due to feeling unrepresented, unsupported, stigmatized, or bullied.
- In survey research, many young adults who are Asian American report that they received inadequate sex education in school.
Youth from rural communities:
- Adolescents who live in rural communities have faced disproportionate declines in formal sex education over the past two decades, compared with peers in urban/suburban areas.
- Students who live in rural communities report that the sex education curriculum in their schools does not serve their needs .
Youth from communities and schools that are low-income:
- Data has shown an association between schools that are low-resource and lower adolescent sexual health knowledge, due to a combination of fewer school resources and higher poverty rates/associated unmet health needs in the student body.
- Youth with family incomes above 200% of the federal poverty line are more likely to receive education about STI prevention, contraception, and “saying no to sex,” than their peers below 200% of the poverty line.
Youth who receive sex education in some religious settings:
- Most adolescents who identify as female and who attended church-based sex education programs report instructions on waiting until marriage for sex, while few report receiving education about birth control.
- Young people who received sex education in religious schools report that education focused on the risks of sexual behavior (STIs, pregnancy) and religious guilt; leading to them feeling under-equipped to make informed decisions about sex and sexuality later in life.
- Youth and teachers from religious schools have identified a need for comprehensive sex education curriculum that is tailored to the needs of faith communities .
Youth who live in states that limit the topics that can be covered in sex education:
- Students who live in the 34 states that require sex education programs to stress abstinence are less likely to have access to critical information on STI prevention and contraception.
- Prohibitions on addressing abortion in sex education or mandates that sex education curricula include medically inaccurate information on abortion designed to dissuade youth from terminating a pregnancy.
- Limitations on the types of contraception that can be covered in sex education curricula.
- Requirements that sex education teachers promote heterosexual, monogamous marriage in sex education.
- Lack of requirements to address healthy relationships and communication skills.
- Lack of requirements for teacher training or certification.
Comprehensive sex education has significant benefits for children and adolescents.
Youth who are exposed to comprehensive sex education programs in school demonstrate healthier sexual behaviors:
- Increased rates of contraception and condom use.
- Fewer unplanned pregnancies.
- Lower rates of STIs and HIV.
- Delayed initiation of sexual behavior.
More broadly, comprehensive sexual education impacts overall social-emotional health , including:
- Enhanced understanding of gender and sexuality.
- Lower rates of homophobia and related bullying.
- Lower rates of dating violence, intimate partner violence, sexual assault, and child sexual abuse.
- Healthier relationships and communication skills.
- Understanding of reproductive rights and responsibilities.
- Improved social-emotional learning, media literacy, and academic achievement.
Comprehensive sex education curriculum goes beyond risk reduction, to ensure that youth are supported in understanding their identity and sexuality and making informed decisions about their relationships, behaviors, and future. These benefits are critical to healthy sexual development.
Impacts of a lack of access to comprehensive sex education.
When youth are denied access to comprehensive sex education, they do not get the information and skill-building required for healthy sexual development. As such, they face unnecessary barriers to understanding their gender and sexuality, building positive interpersonal relationships, and making informed decisions about their sexual behavior and sexual health.
Impacts of a lack of comprehensive sex education for all youth can include :
- Less use of condoms, leading to higher risk of STIs, including HIV.
- Less use of contraception, leading to higher risk of unplanned pregnancy.
- Less understanding and increased stigma and shame around the spectrum of gender and sexual identity.
- Perpetuated stigma and embarrassment related to sex and sexual identity.
- Perpetuated gender stereotypes and traditional gender roles.
- Higher rates of youth turning to unreliable sources for information about sex, including the internet, the media, and informal learning from peer networks.
- Challenges in interpersonal communication.
- Challenges in building, maintaining, and recognizing safe, healthy peer and romantic relationships.
- Lower understanding of the importance of obtaining and giving enthusiastic consent prior to sexual activity.
- Less awareness of appropriate/inappropriate touch and lower reporting of child sexual abuse.
- Higher rates of dating violence and intimate partner violence, and less intervention from bystanders.
- Higher rates of homophobia and homophobic bullying.
- Unsafe school environments.
- Lower rates of media literacy.
- Lower rates of social-emotional learning.
- Lower recognition of gender equity, rights, and social justice.
In addition, the lack of access to comprehensive sex education can exacerbate existing health disparities, with disproportionate impacts on specific populations of youth.
Youth who identify as women, youth from communities of color, youth with disabilities, and youth who are LGBTQ2S+ are particularly impacted by inequitable access to comprehensive sex education, as this lack of education can impact their health, safety, and self-identity. Examples of these impacts are outlined below.
A lack of comprehensive sex education can harm young women.
- Female bodies are more prone to STI infection and more likely to experience complications of STI infection than male bodies.
- Female bodies are disproportionately impacted by long-term health consequences of STIs , including pelvic inflammatory disease, infertility, and ectopic pregnancy.
- Female bodies are less likely to have or recognize symptoms of certain STI infections .
- Human papillomavirus (HPV) is the most common STI in young women , and can cause long-term health consequences such as genital warts and cervical cancer.
- Women bear the health and economic effects of unplanned pregnancy.
- Comprehensive sex education addresses these issues by providing medically-accurate, evidence based information on effective strategies to prevent STI infections and unplanned pregnancy.
- Students who identify as female are more likely to experience sexual or physical dating violence than their peers who identify as male. Some of this may be attributed to underreporting by males due to stigma.
- Students who identify as female are bullied on school property more often than students who identify as male.
- Young women ages 16-19 are at higher risk of rape, attempted rape, or sexual assault than the general population.
- Comprehensive sex education addresses these issues by guiding the development of healthy self-identities, challenging harmful gender norms, and building the skills required for respectful, equitable relationships.
A lack of comprehensive sex education can harm youth from communities of color.
- Youth of color benefit from seeing themselves represented in sex education curriculum.
- Sex education programs that use a framing of diversity, equity, rights, and social justice , informed by an understanding of systemic racism and discrimination, have been found to increase positive attitudes around reproductive rights in all students.
- There is a critical need for sex education programs that reflect youth’s cultural values and community .
- Comprehensive sex education can address these needs by developing curriculum that is inclusive of diverse communities, relationships, and cultures, so that youth see themselves represented in their education.
- Racial and ethnic disparities in STI and HIV infection.
- Racial and ethnic disparities in unplanned pregnancy and births among adolescents.
- Nearly half of youth who are Black ages 13-21 report having been pressured into sexual activity .
- Adolescent experience with dating violence is most prevalent among youth who are American Indian/Alaska Native, Native Hawaiian/Pacific Islander, and multiracial.
- Adolescents who are Latinx are more likely than their peers who are non-Latinx to report physical dating violence .
- Youth who are Black and Latinx and who experience bullying are more likely to suffer negative impacts on academic performance than their white peers.
- Students who are Asian American and Pacific Islander report bullying and harassment due to race, ethnicity, and language.
- Comprehensive sex education addresses these issues by guiding the development of healthy self-identities, challenging harmful stereotypes, and building the skills required for respectful, equitable relationships.
- Young people of color—specifically those from Black , Asian-American , and Latinx communities– are often hyper-sexualized in popular media, leading to societal perceptions that youth are “older” or more sexually experienced than their white peers.
- Young men of color—specifically those from Black and Latinx communities—are often portrayed as aggressive or criminal in popular media, leading to societal perceptions that youth are dangerous or more sexually aggressive or experienced than white peers.
- These media portrayals can lead to disparities in public perceptions of youth behavior , which can impact school discipline, lost mentorship and leadership opportunities, less access to educational opportunities afforded to white peers, and greater involvement in the juvenile justice system.
- Comprehensive sex education addresses these issues by including positive representations of diverse youth in curriculum, challenging harmful stereotypes, and building the skills required for respectful relationships.
A lack of comprehensive sex education can harm youth with disabilities or special health care needs.
- Youth with disabilities need inclusive, developmentally-appropriate, representative sex education to support their health, identity, and development .
- Youth with special health care needs often initiate romantic relationships and sexual behavior during adolescence, similar to their peers.
- Youth with disabilities and special health care needs benefit from seeing themselves represented in sex education to access the information and skills to build healthy identities and relationships.
- Comprehensive sex education addresses this need by including positive representation of youth with disabilities and special health care needs in curriculum and providing developmentally-appropriate sex education to all youth.
- When youth with disabilities and special health care needs do not get access to the comprehensive sex education that they need, they are at increased risk of sexual abuse or being viewed as a sexual offender.
- Youth with disabilities and special health care needs are more likely than peers without disabilities to report coercive sex, exploitation, and sexual abuse.
- Youth with disabilities and special health care needs report more sexualized behavior and victimization online than their peers without disabilities.
- Youth with disabilities are at greater risk of bullying and have fewer friend relationships than their peers.
- Comprehensive sex education addresses these issues by providing education on healthy relationships, consent, communication, and bodily autonomy.
A lack of comprehensive sex education can harm youth who are LGBTQ2S+.
- Most sex education curriculum is not inclusive or representative of LGBTQ2S+ identities and experiences.
- Because school-based sex education often does not meet their needs, youth who are LGBTQ2S+ are more likely to seek sexual health information online , and thus are more likely to come across misinformation.
- The majority of parents support discussion of sexual orientation in sex education classes.
- Comprehensive sex education addresses these issues by including positive representation of LGBTQ2S+ individuals, romantic relationships, and families.
- Sex education curriculum that overlooks or stigmatizes youth who are LGBTQ2S+ contributes to hostile school environments and harms the healthy sexual and mental development .
- Youth who are LGBTQ2S+ face high levels of discrimination at school and are more likely to miss school because of bullying or victimization .
- Ongoing experiences with stigma, exclusion, and harassment negatively impact the mental health of youth who are LGBTQ2S+.
- Comprehensive sex education provides inclusive curriculum and has been shown to improve understanding of gender diversity, lower rates of homophobia, and reduce homophobic bullying in schools.
- Youth who are LGBTQ2S+ are more likely than their heterosexual peers to report not learning about HIV/STIs in school .
- Lack of education on STI prevention leaves LGBTQ2S+ youth without the information they need to make informed decisions, leading to discrepancies in condom use between LGBTQ2S+ and heterosexual youth.
- Some LGBTQ2S+ populations carry a disproportionate burden of HIV and other STIs: these disparities begin in adolescence , when youth who are LGBTQ2S+ do not receive sex education that is relevant to them.
- Comprehensive sex education provides the knowledge and skills needed to make safe decisions about sexual behavior , including condom use and other forms of STI and HIV prevention.
- Youth who are LBGTQ2S+ or are questioning their sexual identity report higher rates of dating violence than their heterosexual peers.
- Youth who are LGBTQ2S+ or are questioning their sexual identity face higher prevalence of bullying than their heterosexual peers.
- Comprehensive sex education teaches youth healthy relationship and communication skills and is associated with decreases in dating violence and increases in bystander interventions .
A lack of comprehensive sex education can harm youth who are in foster care.
- More than 70% of children in foster care have a documented history of child abuse and or neglect.
- More than 80% of children in foster care have been exposed to significant levels of violence, including domestic violence.
- Youth in foster care are racially diverse, with 23% of youth identifying as Black and 21% of identifying as Latinx, who will have similar experiences as those highlighted in earlier sections of this report.
- Removal is emotionally traumatizing for almost all children. Lack of consistent/stable placement with a responsive, nurturing caregiver can result in poor emotional regulation, impulsivity, and attachment problems.
- Comprehensive sex education addresses these issues by providing evidence-based, culturally appropriate information on healthy relationships, consent, communication, and bodily autonomy.
Sex education is often the first experience that youth have with understanding and discussing their gender and sexual health.
Youth deserve to a strong foundation of developmentally appropriate information about gender and sexuality, and how these things relate to their bodies, community, culture, society, mental health, and relationships with family, peers, and romantic partners.
Decades of data have demonstrated that comprehensive sex education programs are effective in reducing risk of STIs and unplanned pregnancy. These benefits are critical to public health. However, comprehensive sex education goes even further, by instilling youth with a broad range of knowledge and skills that are proven to support social-emotional learning, positive communication skills, and development of healthy relationships.
Last Updated
American Academy of Pediatrics

IMAGES
VIDEO
COMMENTS
The National Sex Education Standards: Core Content and Skills, K-12 (Second Edition) were developed by the Future of Sex Education (FoSE) Initiative, a partnership between Advocates for Youth, Answer, and SIECUS: Sex Ed for Social Change that seeks to create a national dialogue about the future of sex education and to promote the
Facts About Sex Education. Sex education is high quality teaching and learning about a broad variety of topics related to sex and sexuality. It explores values and beliefs about those topics and helps people gain the skills that are needed to navigate relationships with self, partners, and community, and manage one's own sexual health.
topics with their children; others feel unsure about the message that they want to provide. Others in the community also need help discuss-ing topics of sexuality with youth. Educators and other youth-serving professionals often have the responsibility of providing young people with sex education in the classroom and/or after-school programs.
The National Sex Education Standards (NSES) outline the foundational knowledge and skills students need to navigate sexual development and grow into sexually healthy adults. The updated NSES include new topics to provide increased guidance to educators on a number of issues previously unaddressed and new indicators and topic strands to better ...
At a minimum, sex education should be taught in middle school and high school. Is enough time being devoted to teaching sex education? You can gauge this by the number of grades where sex education is taught, the number of lessons, and number of minutes per lesson. Add it up. Most teens say that sex education is too little, too late.
It seeks to clarify the different domains or topics of comprehensive sexuality education (CSE) that need to be included, and for which approximate age group. The information is arranged into three sections: Plan International sees CSE as a process of transformative learning. It uses a framework of a positive approach to sexuality and healthy sexual
Developing a Scope and Sequence for Sexual Health Education [PDF - 17 pages].This resource provides an 11-step process to help schools outline the key sexual health topics and concepts (scope), and the logical progression of essential health knowledge, skills, and behaviors to be addressed at each grade level (sequence) from pre-kindergarten ...
It also helps young people avoid unintended pregnancies and sexually transmitted infections (STIs). Sex education works best when it's: Taught by trained professionals. Taught early and often throughout the lifespan. Includes both information and skill-building activities. Evidence-informed. Inclusive of LGBTQ+ youth.
These education standards outline seven core topics that must be addressed in sex education; one of those core topics is identity. The identity topic presents lesbian, gay, bisexual and transgender identities as possibilities for students as they progress through life and come to understand who they are.
An example of LGBTQIA+ inclusive curriculum is introduced by the National Sexuality Education Standards set forth by the Future of Sex Education Initiative. 13 These education standards outline 7 core topics that must be addressed in sex education; one of those core topics is identity. The identity topic presents lesbian, gay, bisexual, and ...
Comprehensive sexuality education (CSE) is a curriculum-based process of teaching and learning about the cognitive, emotional, physical, and social aspects of sexuality.It aims to equip children and young people with knowledge, skills, attitudes, and values that will empower them to: realize their health, well-being, and dignity; develop respectful social and sexual relationships; consider how ...
Florida's Sexual Health Education Community Outreach Toolkit. By. USF Healthy Schools Project. This Tool Kit was created to provide valuable information, innovative ideas, and strategies for community members to build awareness and support for policies and programs that improve sexual health outcomes among youth.
Specifically, the National Sexuality Education Standards were developed to address the inconsistent implementation of sexuality education nationwide and the limited time allocated to teaching the topic. The National Sexuality Education Standards: • Outline what, based on research and extensive professional expertise, are the minimum ...
The National Sex Education Standards (NSES) outline the foundational knowledge and skills students need to navigate sexual development and grow into sexually healthy adults. The updated NSES reflect advancements in research regarding sexual orientation, gender identity, social, racial, and reproductive justice, and the long-term consequences of ...
Sex education has been a new focus of attention for the Federal Centre tion for to develop a sex-education concept places a particular responsibility on it to stimulate and promote an interdisciplinary for Health Education Youths (FCHE) since 1992. The Centre's statutory remit. for Youths Sex. discourse Sex.
Comprehensive Sexuality Education (CSE) "plays a central role in the preparation of young people for a safe, productive, fulfilling life" (p. 12) [ 17] and adolescents who receive comprehensive sex education are more likely to delay their sexual debut, as well as to use contraception during sexual initiation [ 18 ].
Book an Appointment. Zip, City, or State. Service. Filter By Telehealth In-person. Or call 1-888-743-7526. Sex Ed To-Go by Planned Parenthood includes tools for ensuring an inclusive environment, supporting students who have experienced trauma, promoting healthy relationships, and answering student questions.
Comprehensive sexuality education - or the many other ways this may be referred to - is a curriculum-based process of teaching and learning about the cognitive, emotional, physical and social aspects of sexuality. It aims to equip children and young people with knowledge, skills, attitudes and values that empowers them to realize their health ...
On sexuality education, as with all other issues, WHO provides guidance for policies and programmes based on extensive research evidence and programmatic experience. The UN global guidance on sexuality education outlines a set of learning objectives beginning at the age of 5. These are intended to be adapted to a country's local context and ...
Comprehensive sex education provides children and adolescents with the information that they need to: Understand their body, gender identity, and sexuality. Build and maintain healthy and safe relationships. Engage in healthy communication and decision-making around sex. Practice healthy sexual behavior.
947 Words4 Pages. Speech outline. Topic: All schools should provide mandatory sex education. Purpose: To convince. Specific Purpose: To convince my audience to support the provision of sex education in all schools. Introduction. 1. Attention Getter: The provision of sex education in schools has been a controversial subject matter among ...
1. How parents teach their children relating to this topic 2. Students/children response on this topic D. Impact of sex education on people 1. Parents being aware and guiding their children 2. Students/children increased knowledge relating to sexual and reproductive health. Good afternoon everyone.
The guidance further outlines the importance of social aspects of SRE for young people in its definition of SRE as "the teaching of sex, sexuality, and sexual health" and includes "earning the value of respect, love and care" (p.5) along with "developing young people's confidence and "self-esteem" (p.4). ... The topics developed ...