- PRO Courses Guides New Tech Help Pro Expert Videos About wikiHow Pro Upgrade Sign In
- EDIT Edit this Article
- EXPLORE Tech Help Pro About Us Random Article Quizzes Request a New Article Community Dashboard This Or That Game Popular Categories Arts and Entertainment Artwork Books Movies Computers and Electronics Computers Phone Skills Technology Hacks Health Men's Health Mental Health Women's Health Relationships Dating Love Relationship Issues Hobbies and Crafts Crafts Drawing Games Education & Communication Communication Skills Personal Development Studying Personal Care and Style Fashion Hair Care Personal Hygiene Youth Personal Care School Stuff Dating All Categories Arts and Entertainment Finance and Business Home and Garden Relationship Quizzes Cars & Other Vehicles Food and Entertaining Personal Care and Style Sports and Fitness Computers and Electronics Health Pets and Animals Travel Education & Communication Hobbies and Crafts Philosophy and Religion Work World Family Life Holidays and Traditions Relationships Youth
- Browse Articles
- Learn Something New
- Quizzes Hot
- This Or That Game New
- Train Your Brain
- Explore More
- Support wikiHow
- About wikiHow
- Log in / Sign up
- Education and Communications
- Critical Reviews

How to Write an Article Review
Last Updated: September 8, 2023 Fact Checked
This article was co-authored by Jake Adams . Jake Adams is an academic tutor and the owner of Simplifi EDU, a Santa Monica, California based online tutoring business offering learning resources and online tutors for academic subjects K-College, SAT & ACT prep, and college admissions applications. With over 14 years of professional tutoring experience, Jake is dedicated to providing his clients the very best online tutoring experience and access to a network of excellent undergraduate and graduate-level tutors from top colleges all over the nation. Jake holds a BS in International Business and Marketing from Pepperdine University. There are 13 references cited in this article, which can be found at the bottom of the page. This article has been fact-checked, ensuring the accuracy of any cited facts and confirming the authority of its sources. This article has been viewed 3,084,548 times.
An article review is both a summary and an evaluation of another writer's article. Teachers often assign article reviews to introduce students to the work of experts in the field. Experts also are often asked to review the work of other professionals. Understanding the main points and arguments of the article is essential for an accurate summation. Logical evaluation of the article's main theme, supporting arguments, and implications for further research is an important element of a review . Here are a few guidelines for writing an article review.
Education specialist Alexander Peterman recommends: "In the case of a review, your objective should be to reflect on the effectiveness of what has already been written, rather than writing to inform your audience about a subject."
Things You Should Know
- Read the article very closely, and then take time to reflect on your evaluation. Consider whether the article effectively achieves what it set out to.
- Write out a full article review by completing your intro, summary, evaluation, and conclusion. Don't forget to add a title, too!
- Proofread your review for mistakes (like grammar and usage), while also cutting down on needless information. [1] X Research source
Preparing to Write Your Review

- Article reviews present more than just an opinion. You will engage with the text to create a response to the scholarly writer's ideas. You will respond to and use ideas, theories, and research from your studies. Your critique of the article will be based on proof and your own thoughtful reasoning.
- An article review only responds to the author's research. It typically does not provide any new research. However, if you are correcting misleading or otherwise incorrect points, some new data may be presented.
- An article review both summarizes and evaluates the article.

- Summarize the article. Focus on the important points, claims, and information.
- Discuss the positive aspects of the article. Think about what the author does well, good points she makes, and insightful observations.
- Identify contradictions, gaps, and inconsistencies in the text. Determine if there is enough data or research included to support the author's claims. Find any unanswered questions left in the article.

- Make note of words or issues you don't understand and questions you have.
- Look up terms or concepts you are unfamiliar with, so you can fully understand the article. Read about concepts in-depth to make sure you understand their full context.

- Pay careful attention to the meaning of the article. Make sure you fully understand the article. The only way to write a good article review is to understand the article.

- With either method, make an outline of the main points made in the article and the supporting research or arguments. It is strictly a restatement of the main points of the article and does not include your opinions.
- After putting the article in your own words, decide which parts of the article you want to discuss in your review. You can focus on the theoretical approach, the content, the presentation or interpretation of evidence, or the style. You will always discuss the main issues of the article, but you can sometimes also focus on certain aspects. This comes in handy if you want to focus the review towards the content of a course.
- Review the summary outline to eliminate unnecessary items. Erase or cross out the less important arguments or supplemental information. Your revised summary can serve as the basis for the summary you provide at the beginning of your review.

- What does the article set out to do?
- What is the theoretical framework or assumptions?
- Are the central concepts clearly defined?
- How adequate is the evidence?
- How does the article fit into the literature and field?
- Does it advance the knowledge of the subject?
- How clear is the author's writing? Don't: include superficial opinions or your personal reaction. Do: pay attention to your biases, so you can overcome them.
Writing the Article Review

- For example, in MLA , a citation may look like: Duvall, John N. "The (Super)Marketplace of Images: Television as Unmediated Mediation in DeLillo's White Noise ." Arizona Quarterly 50.3 (1994): 127-53. Print. [10] X Trustworthy Source Purdue Online Writing Lab Trusted resource for writing and citation guidelines Go to source

- For example: The article, "Condom use will increase the spread of AIDS," was written by Anthony Zimmerman, a Catholic priest.

- Your introduction should only be 10-25% of your review.
- End the introduction with your thesis. Your thesis should address the above issues. For example: Although the author has some good points, his article is biased and contains some misinterpretation of data from others’ analysis of the effectiveness of the condom.

- Use direct quotes from the author sparingly.
- Review the summary you have written. Read over your summary many times to ensure that your words are an accurate description of the author's article.

- Support your critique with evidence from the article or other texts.
- The summary portion is very important for your critique. You must make the author's argument clear in the summary section for your evaluation to make sense.
- Remember, this is not where you say if you liked the article or not. You are assessing the significance and relevance of the article.
- Use a topic sentence and supportive arguments for each opinion. For example, you might address a particular strength in the first sentence of the opinion section, followed by several sentences elaborating on the significance of the point.

- This should only be about 10% of your overall essay.
- For example: This critical review has evaluated the article "Condom use will increase the spread of AIDS" by Anthony Zimmerman. The arguments in the article show the presence of bias, prejudice, argumentative writing without supporting details, and misinformation. These points weaken the author’s arguments and reduce his credibility.

- Make sure you have identified and discussed the 3-4 key issues in the article.
Sample Article Reviews

Expert Q&A

You Might Also Like

- ↑ https://writing.wisc.edu/handbook/grammarpunct/proofreading/
- ↑ https://libguides.cmich.edu/writinghelp/articlereview
- ↑ https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC4548566/
- ↑ Jake Adams. Academic Tutor & Test Prep Specialist. Expert Interview. 24 July 2020.
- ↑ https://guides.library.queensu.ca/introduction-research/writing/critical
- ↑ https://www.iup.edu/writingcenter/writing-resources/organization-and-structure/creating-an-outline.html
- ↑ https://writing.umn.edu/sws/assets/pdf/quicktips/titles.pdf
- ↑ https://owl.purdue.edu/owl/research_and_citation/mla_style/mla_formatting_and_style_guide/mla_works_cited_periodicals.html
- ↑ https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC4548565/
- ↑ https://writingcenter.uconn.edu/wp-content/uploads/sites/593/2014/06/How_to_Summarize_a_Research_Article1.pdf
- ↑ https://www.uis.edu/learning-hub/writing-resources/handouts/learning-hub/how-to-review-a-journal-article
- ↑ https://writingcenter.unc.edu/tips-and-tools/editing-and-proofreading/
About This Article

If you have to write an article review, read through the original article closely, taking notes and highlighting important sections as you read. Next, rewrite the article in your own words, either in a long paragraph or as an outline. Open your article review by citing the article, then write an introduction which states the article’s thesis. Next, summarize the article, followed by your opinion about whether the article was clear, thorough, and useful. Finish with a paragraph that summarizes the main points of the article and your opinions. To learn more about what to include in your personal critique of the article, keep reading the article! Did this summary help you? Yes No
- Send fan mail to authors
Reader Success Stories
Prince Asiedu-Gyan
Apr 22, 2022
Did this article help you?

Sammy James
Sep 12, 2017
Juabin Matey
Aug 30, 2017
Oct 25, 2023
Vanita Meghrajani
Jul 21, 2016

Featured Articles

Trending Articles

Watch Articles

- Terms of Use
- Privacy Policy
- Do Not Sell or Share My Info
- Not Selling Info
Get all the best how-tos!
Sign up for wikiHow's weekly email newsletter
How to Write an Article Review: Template & Examples
An article review is an academic assignment that invites you to study a piece of academic research closely. Then, you should present its summary and critically evaluate it using the knowledge you’ve gained in class and during your independent study. If you get such a task at college or university, you shouldn’t confuse it with a response paper, which is a distinct assignment with other purposes (we’ll talk about it in detail below).
Our specialists will write a custom essay specially for you!
In this article, prepared by Custom-Writing experts, you’ll find:
- the intricacies of article review writing;
- the difference between an article review and similar assignments;
- a step-by-step algorithm for review composition;
- a couple of samples to guide you throughout the writing process.
So, if you wish to study our article review example and discover helpful writing tips, keep reading.
❓ What Is an Article Review?
- ✍️ Writing Steps
📑 Article Review Format
🔗 references.
An article review is an academic paper that summarizes and critically evaluates the information presented in your selected article.

The first thing you should note when approaching the task of an article review is that not every article is suitable for this assignment. Let’s have a look at the variety of articles to understand what you can choose from.
Popular Vs. Scholarly Articles
In most cases, you’ll be required to review a scholarly, peer-reviewed article – one composed in compliance with rigorous academic standards. Yet, the Web is also full of popular articles that don’t present original scientific value and shouldn’t be selected for a review.
Just in 1 hour! We will write you a plagiarism-free paper in hardly more than 1 hour
Not sure how to distinguish these two types? Here is a comparative table to help you out.
Article Review vs. Response Paper
Now, let’s consider the difference between an article review and a response paper:
- If you’re assigned to critique a scholarly article , you will need to compose an article review .
- If your subject of analysis is a popular article , you can respond to it with a well-crafted response paper .
The reason for such distinctions is the quality and structure of these two article types. Peer-reviewed, scholarly articles have clear-cut quality criteria, allowing you to conduct and present a structured assessment of the assigned material. Popular magazines have loose or non-existent quality criteria and don’t offer an opportunity for structured evaluation. So, they are only fit for a subjective response, in which you can summarize your reactions and emotions related to the reading material.
All in all, you can structure your response assignments as outlined in the tips below.
✍️ How to Write an Article Review: Step by Step
Here is a tried and tested algorithm for article review writing from our experts. We’ll consider only the critical review variety of this academic assignment. So, let’s get down to the stages you need to cover to get a stellar review.
Receive a plagiarism-free paper tailored to your instructions. Cut 20% off your first order!
Read the Article
As with any reviews, reports, and critiques, you must first familiarize yourself with the assigned material. It’s impossible to review something you haven’t read, so set some time for close, careful reading of the article to identify:
- Its topic.
- Its type.
- The author’s main points and message.
- The arguments they use to prove their points.
- The methodology they use to approach the subject.
In terms of research type , your article will usually belong to one of three types explained below.
Summarize the Article
Now that you’ve read the text and have a general impression of the content, it’s time to summarize it for your readers. Look into the article’s text closely to determine:
- The thesis statement , or general message of the author.
- Research question, purpose, and context of research.
- Supporting points for the author’s assumptions and claims.
- Major findings and supporting evidence.
As you study the article thoroughly, make notes on the margins or write these elements out on a sheet of paper. You can also apply a different technique: read the text section by section and formulate its gist in one phrase or sentence. Once you’re done, you’ll have a summary skeleton in front of you.
Evaluate the Article
The next step of review is content evaluation. Keep in mind that various research types will require a different set of review questions. Here is a complete list of evaluation points you can include.
Get an originally-written paper according to your instructions!
Write the Text
After completing the critical review stage, it’s time to compose your article review.
The format of this assignment is standard – you will have an introduction, a body, and a conclusion. The introduction should present your article and summarize its content. The body will contain a structured review according to all four dimensions covered in the previous section. The concluding part will typically recap all the main points you’ve identified during your assessment.
It is essential to note that an article review is, first of all, an academic assignment. Therefore, it should follow all rules and conventions of academic composition, such as:
- No contractions . Don’t use short forms, such as “don’t,” “can’t,” “I’ll,” etc. in academic writing. You need to spell out all those words.
- Formal language and style . Avoid conversational phrasing and words that you would naturally use in blog posts or informal communication. For example, don’t use words like “pretty,” “kind of,” and “like.”
- Third-person narrative . Academic reviews should be written from the third-person point of view, avoiding statements like “I think,” “in my opinion,” and so on.
- No conversational forms . You shouldn’t turn to your readers directly in the text by addressing them with the pronoun “you.” It’s vital to keep the narrative neutral and impersonal.
- Proper abbreviation use . Consult the list of correct abbreviations , like “e.g.” or “i.e.,” for use in your academic writing. If you use informal abbreviations like “FYA” or “f.i.,” your professor will reduce the grade.
- Complete sentences . Make sure your sentences contain the subject and the predicate; avoid shortened or sketch-form phrases suitable for a draft only.
- No conjunctions at the beginning of a sentence . Remember the FANBOYS rule – don’t start a sentence with words like “and” or “but.” They often seem the right way to build a coherent narrative, but academic writing rules disfavor such usage.
- No abbreviations or figures at the beginning of a sentence . Never start a sentence with a number — spell it out if you need to use it anyway. Besides, sentences should never begin with abbreviations like “e.g.”
Finally, a vital rule for an article review is properly formatting the citations. We’ll discuss the correct use of citation styles in the following section.
When composing an article review, keep these points in mind:
- Start with a full reference to the reviewed article so the reader can locate it quickly.
- Ensure correct formatting of in-text references.
- Provide a complete list of used external sources on the last page of the review – your bibliographical entries .
You’ll need to understand the rules of your chosen citation style to meet all these requirements. Below, we’ll discuss the two most common referencing styles – APA and MLA.
Article Review in APA
When you need to compose an article review in the APA format , here is the general bibliographical entry format you should use for journal articles on your reference page:
- Author’s last name, First initial. Middle initial. (Year of Publication). Name of the article. Name of the Journal, volume (number), pp. #-#. https://doi.org/xx.xxx/yyyy
Horigian, V. E., Schmidt, R. D., & Feaster, D. J. (2021). Loneliness, mental health, and substance use among US young adults during COVID-19. Journal of Psychoactive Drugs, 53 (1), pp. 1-9. https://doi.org/10.1080/02791072.2020.1836435
Your in-text citations should follow the author-date format like this:
- If you paraphrase the source and mention the author in the text: According to Horigian et al. (2021), young adults experienced increased levels of loneliness, depression, and anxiety during the pandemic.
- If you paraphrase the source and don’t mention the author in the text: Young adults experienced increased levels of loneliness, depression, and anxiety during the pandemic (Horigian et al., 2021).
- If you quote the source: As Horigian et al. (2021) point out, there were “elevated levels of loneliness, depression, anxiety, alcohol use, and drug use among young adults during COVID-19” (p. 6).
Note that your in-text citations should include “et al.,” as in the examples above, if your article has 3 or more authors. If you have one or two authors, your in-text citations would look like this:
- One author: “According to Smith (2020), depression is…” or “Depression is … (Smith, 2020).”
- Two authors: “According to Smith and Brown (2020), anxiety means…” or “Anxiety means (Smith & Brown, 2020).”
Finally, in case you have to review a book or a website article, here are the general formats for citing these source types on your APA reference list.
Article Review in MLA
If your assignment requires MLA-format referencing, here’s the general format you should use for citing journal articles on your Works Cited page:
- Author’s last name, First name. “Title of an Article.” Title of the Journal , vol. #, no. #, year, pp. #-#.
Horigian, Viviana E., et al. “Loneliness, Mental Health, and Substance Use Among US Young Adults During COVID-19.” Journal of Psychoactive Drugs , vol. 53, no. 1, 2021, pp. 1-9.
In-text citations in the MLA format follow the author-page citation format and look like this:
- According to Horigian et al., young adults experienced increased levels of loneliness, depression, and anxiety during the pandemic (6).
- Young adults experienced increased levels of loneliness, depression, and anxiety during the pandemic (Horigian et al. 6).
Like in APA, the abbreviation “et al.” is only needed in MLA if your article has 3 or more authors.
If you need to cite a book or a website page, here are the general MLA formats for these types of sources.
✅ Article Review Template
Here is a handy, universal article review template to help you move on with any review assignment. We’ve tried to make it as generic as possible to guide you in the academic process.
📝 Article Review Examples
The theory is good, but practice is even better. Thus, we’ve created three brief examples to show you how to write an article review. You can study the full-text samples by following the links.
📃 Men, Women, & Money
This article review examines a famous piece, “Men, Women & Money – How the Sexes Differ with Their Finances,” published by Amy Livingston in 2020. The author of this article claims that men generally spend more money than women. She makes this conclusion from a close analysis of gender-specific expenditures across five main categories: food, clothing, cars, entertainment, and general spending patterns. Livingston also looks at men’s approach to saving to argue that counter to the common perception of women’s light-hearted attitude to money, men are those who spend more on average.
📃 When and Why Nationalism Beats Globalism
This is a review of Jonathan Heidt’s 2016 article titled “When and Why Nationalism Beats Globalism,” written as an advocacy of right-wing populism rising in many Western states. The author illustrates the case with the election of Donald Trump as the US President and the rise of right-wing rhetoric in many Western countries. These examples show how nationalist sentiment represents a reaction to global immigration and a failure of globalization.
📃 Sleep Deprivation
This is a review of the American Heart Association’s article titled “The Dangers of Sleep Deprivation.” It discusses how the national organization concerned with the American population’s cardiovascular health links the lack of high-quality sleep to far-reaching health consequences. The organization’s experts reveal how a consistent lack of sleep leads to Alzheimer’s disease development, obesity, type 2 diabetes, etc.
✏️ Article Review FAQ
A high-quality article review should summarize the assigned article’s content and offer data-backed reactions and evaluations of its quality in terms of the article’s purpose, methodology, and data used to argue the main points. It should be detailed, comprehensive, objective, and evidence-based.
The purpose of writing a review is to allow students to reflect on research quality and showcase their critical thinking and evaluation skills. Students should exhibit their mastery of close reading of research publications and their unbiased assessment.
The content of your article review will be the same in any format, with the only difference in the assignment’s formatting before submission. Ensure you have a separate title page made according to APA standards and cite sources using the parenthetical author-date referencing format.
You need to take a closer look at various dimensions of an assigned article to compose a valuable review. Study the author’s object of analysis, the purpose of their research, the chosen method, data, and findings. Evaluate all these dimensions critically to see whether the author has achieved the initial goals. Finally, offer improvement recommendations to add a critique aspect to your paper.
- Scientific Article Review: Duke University
- Book and Article Reviews: William & Mary, Writing Resources Center
- Sample Format for Reviewing a Journal Article: Boonshoft School of Medicine
- Research Paper Review – Structure and Format Guidelines: New Jersey Institute of Technology
- Article Review: University of Waterloo
- Article Review: University of South Australia
- How to Write a Journal Article Review: University of Newcastle Library Guides
- Writing Help: The Article Review: Central Michigan University Libraries
- Write a Critical Review of a Scientific Journal Article: McLaughlin Library
- Share to Facebook
- Share to Twitter
- Share to LinkedIn
- Share to email

Short essays answer a specific question on the subject. They usually are anywhere between 250 words and 750 words long. A paper with less than 250 words isn’t considered a finished text, so it doesn’t fall under the category of a short essay. Essays of such format are required for...

High school and college students often face challenges when crafting a compare-and-contrast essay. A well-written paper of this kind needs to be structured appropriately to earn you good grades. Knowing how to organize your ideas allows you to present your ideas in a coherent and logical manner This article by...

If you’re a student, you’ve heard about a formal essay: a factual, research-based paper written in 3rd person. Most students have to produce dozens of them during their educational career. Writing a formal essay may not be the easiest task. But fear not: our custom-writing team is here to guide...

Narrative essays are unlike anything you wrote throughout your academic career. Instead of writing a formal paper, you need to tell a story. Familiar elements such as evidence and arguments are replaced with exposition and character development. The importance of writing an outline for an essay like this is hard...

A précis is a brief synopsis of a written piece. It is used to summarize and analyze a text’s main points. If you need to write a précis for a research paper or the AP Lang exam, you’ve come to the right place. In this comprehensive guide by Custom-Writing.org, you’ll...

A synthesis essay requires you to work with multiple sources. You combine the information gathered from them to present a well-rounded argument on a topic. Are you looking for the ultimate guide on synthesis essay writing? You’ve come to the right place! In this guide by our custom writing team,...

Do you know how to make your essay stand out? One of the easiest ways is to start your introduction with a catchy hook. A hook is a phrase or a sentence that helps to grab the reader’s attention. After reading this article by Custom-Writing.org, you will be able to...

Critical thinking is the process of evaluating and analyzing information. People who use it in everyday life are open to different opinions. They rely on reason and logic when making conclusions about certain issues. A critical thinking essay shows how your thoughts change as you research your topic. This type...

Process analysis is an explanation of how something works or happens. Want to know more? Read the following article prepared by our custom writing specialists and learn about: process analysis and its typesa process analysis outline tipsfree examples and other tips that might be helpful for your college assignment So,...

A visual analysis essay is an academic paper type that history and art students often deal with. It consists of a detailed description of an image or object. It can also include an interpretation or an argument that is supported by visual evidence. In this article, our custom writing experts...

Want to know how to write a reflection paper for college or school? To do that, you need to connect your personal experiences with theoretical knowledge. Usually, students are asked to reflect on a documentary, a text, or their experience. Sometimes one needs to write a paper about a lesson...

A character analysis is an examination of the personalities and actions of protagonists and antagonists that make up a story. It discusses their role in the story, evaluates their traits, and looks at their conflicts and experiences. You might need to write this assignment in school or college. Like any...
How to Write an Article Review: Tips and Examples

Did you know that article reviews are not just academic exercises but also a valuable skill in today's information age? In a world inundated with content, being able to dissect and evaluate articles critically can help you separate the wheat from the chaff. Whether you're a student aiming to excel in your coursework or a professional looking to stay well-informed, mastering the art of writing article reviews is an invaluable skill.
Short Description
In this article, our research paper writing service experts will start by unraveling the concept of article reviews and discussing the various types. You'll also gain insights into the art of formatting your review effectively. To ensure you're well-prepared, we'll take you through the pre-writing process, offering tips on setting the stage for your review. But it doesn't stop there. You'll find a practical example of an article review to help you grasp the concepts in action. To complete your journey, we'll guide you through the post-writing process, equipping you with essential proofreading techniques to ensure your work shines with clarity and precision!
What Is an Article Review: Grasping the Concept
A review article is a type of professional paper writing that demands a high level of in-depth analysis and a well-structured presentation of arguments. It is a critical, constructive evaluation of literature in a particular field through summary, classification, analysis, and comparison.
If you write a scientific review, you have to use database searches to portray the research. Your primary goal is to summarize everything and present a clear understanding of the topic you've been working on.
Writing Involves:
- Summarization, classification, analysis, critiques, and comparison.
- The analysis, evaluation, and comparison require the use of theories, ideas, and research relevant to the subject area of the article.
- It is also worth nothing if a review does not introduce new information, but instead presents a response to another writer's work.
- Check out other samples to gain a better understanding of how to review the article.
Types of Review
When it comes to article reviews, there's more than one way to approach the task. Understanding the various types of reviews is like having a versatile toolkit at your disposal. In this section, we'll walk you through the different dimensions of review types, each offering a unique perspective and purpose. Whether you're dissecting a scholarly article, critiquing a piece of literature, or evaluating a product, you'll discover the diverse landscape of article reviews and how to navigate it effectively.
.webp)
Journal Article Review
Just like other types of reviews, a journal article review assesses the merits and shortcomings of a published work. To illustrate, consider a review of an academic paper on climate change, where the writer meticulously analyzes and interprets the article's significance within the context of environmental science.
Research Article Review
Distinguished by its focus on research methodologies, a research article review scrutinizes the techniques used in a study and evaluates them in light of the subsequent analysis and critique. For instance, when reviewing a research article on the effects of a new drug, the reviewer would delve into the methods employed to gather data and assess their reliability.
Science Article Review
In the realm of scientific literature, a science article review encompasses a wide array of subjects. Scientific publications often provide extensive background information, which can be instrumental in conducting a comprehensive analysis. For example, when reviewing an article about the latest breakthroughs in genetics, the reviewer may draw upon the background knowledge provided to facilitate a more in-depth evaluation of the publication.
Need a Hand From Professionals?
Address to Our Writers and Get Assistance in Any Questions!
Formatting an Article Review
The format of the article should always adhere to the citation style required by your professor. If you're not sure, seek clarification on the preferred format and ask him to clarify several other pointers to complete the formatting of an article review adequately.
How Many Publications Should You Review?
- In what format should you cite your articles (MLA, APA, ASA, Chicago, etc.)?
- What length should your review be?
- Should you include a summary, critique, or personal opinion in your assignment?
- Do you need to call attention to a theme or central idea within the articles?
- Does your instructor require background information?
When you know the answers to these questions, you may start writing your assignment. Below are examples of MLA and APA formats, as those are the two most common citation styles.
Using the APA Format
Articles appear most commonly in academic journals, newspapers, and websites. If you write an article review in the APA format, you will need to write bibliographical entries for the sources you use:
- Web : Author [last name], A.A [first and middle initial]. (Year, Month, Date of Publication). Title. Retrieved from {link}
- Journal : Author [last name], A.A [first and middle initial]. (Publication Year). Publication Title. Periodical Title, Volume(Issue), pp.-pp.
- Newspaper : Author [last name], A.A [first and middle initial]. (Year, Month, Date of Publication). Publication Title. Magazine Title, pp. xx-xx.
Using MLA Format
- Web : Last, First Middle Initial. “Publication Title.” Website Title. Website Publisher, Date Month Year Published. Web. Date Month Year Accessed.
- Newspaper : Last, First M. “Publication Title.” Newspaper Title [City] Date, Month, Year Published: Page(s). Print.
- Journal : Last, First M. “Publication Title.” Journal Title Series Volume. Issue (Year Published): Page(s). Database Name. Web. Date Month Year Accessed.
Enhance your writing effortlessly with EssayPro.com , where you can order an article review or any other writing task. Our team of expert writers specializes in various fields, ensuring your work is not just summarized, but deeply analyzed and professionally presented. Ideal for students and professionals alike, EssayPro offers top-notch writing assistance tailored to your needs. Elevate your writing today with our skilled team at your article review writing service !
.jpg)
The Pre-Writing Process
Facing this task for the first time can really get confusing and can leave you unsure of where to begin. To create a top-notch article review, start with a few preparatory steps. Here are the two main stages from our dissertation services to get you started:
Step 1: Define the right organization for your review. Knowing the future setup of your paper will help you define how you should read the article. Here are the steps to follow:
- Summarize the article — seek out the main points, ideas, claims, and general information presented in the article.
- Define the positive points — identify the strong aspects, ideas, and insightful observations the author has made.
- Find the gaps —- determine whether or not the author has any contradictions, gaps, or inconsistencies in the article and evaluate whether or not he or she used a sufficient amount of arguments and information to support his or her ideas.
- Identify unanswered questions — finally, identify if there are any questions left unanswered after reading the piece.
Step 2: Move on and review the article. Here is a small and simple guide to help you do it right:
- Start off by looking at and assessing the title of the piece, its abstract, introductory part, headings and subheadings, opening sentences in its paragraphs, and its conclusion.
- First, read only the beginning and the ending of the piece (introduction and conclusion). These are the parts where authors include all of their key arguments and points. Therefore, if you start with reading these parts, it will give you a good sense of the author's main points.
- Finally, read the article fully.
These three steps make up most of the prewriting process. After you are done with them, you can move on to writing your own review—and we are going to guide you through the writing process as well.
Outline and Template
As you progress with reading your article, organize your thoughts into coherent sections in an outline. As you read, jot down important facts, contributions, or contradictions. Identify the shortcomings and strengths of your publication. Begin to map your outline accordingly.
If your professor does not want a summary section or a personal critique section, then you must alleviate those parts from your writing. Much like other assignments, an article review must contain an introduction, a body, and a conclusion. Thus, you might consider dividing your outline according to these sections as well as subheadings within the body. If you find yourself troubled with the pre-writing and the brainstorming process for this assignment, seek out a sample outline.
Your custom essay must contain these constituent parts:
- Pre-Title Page - Before diving into your review, start with essential details: article type, publication title, and author names with affiliations (position, department, institution, location, and email). Include corresponding author info if needed.
- Running Head - In APA format, use a concise title (under 40 characters) to ensure consistent formatting.
- Summary Page - Optional but useful. Summarize the article in 800 words, covering background, purpose, results, and methodology, avoiding verbatim text or references.
- Title Page - Include the full title, a 250-word abstract, and 4-6 keywords for discoverability.
- Introduction - Set the stage with an engaging overview of the article.
- Body - Organize your analysis with headings and subheadings.
- Works Cited/References - Properly cite all sources used in your review.
- Optional Suggested Reading Page - If permitted, suggest further readings for in-depth exploration.
- Tables and Figure Legends (if instructed by the professor) - Include visuals when requested by your professor for clarity.
Example of an Article Review
You might wonder why we've dedicated a section of this article to discuss an article review sample. Not everyone may realize it, but examining multiple well-constructed examples of review articles is a crucial step in the writing process. In the following section, our essay writing service experts will explain why.
Looking through relevant article review examples can be beneficial for you in the following ways:
- To get you introduced to the key works of experts in your field.
- To help you identify the key people engaged in a particular field of science.
- To help you define what significant discoveries and advances were made in your field.
- To help you unveil the major gaps within the existing knowledge of your field—which contributes to finding fresh solutions.
- To help you find solid references and arguments for your own review.
- To help you generate some ideas about any further field of research.
- To help you gain a better understanding of the area and become an expert in this specific field.
- To get a clear idea of how to write a good review.
View Our Writer’s Sample Before Crafting Your Own!
Why Have There Been No Great Female Artists?
Steps for Writing an Article Review
Here is a guide with critique paper format on how to write a review paper:
.webp)
Step 1: Write the Title
First of all, you need to write a title that reflects the main focus of your work. Respectively, the title can be either interrogative, descriptive, or declarative.
Step 2: Cite the Article
Next, create a proper citation for the reviewed article and input it following the title. At this step, the most important thing to keep in mind is the style of citation specified by your instructor in the requirements for the paper. For example, an article citation in the MLA style should look as follows:
Author's last and first name. "The title of the article." Journal's title and issue(publication date): page(s). Print
Abraham John. "The World of Dreams." Virginia Quarterly 60.2(1991): 125-67. Print.
Step 3: Article Identification
After your citation, you need to include the identification of your reviewed article:
- Title of the article
- Title of the journal
- Year of publication
All of this information should be included in the first paragraph of your paper.
The report "Poverty increases school drop-outs" was written by Brian Faith – a Health officer – in 2000.
Step 4: Introduction
Your organization in an assignment like this is of the utmost importance. Before embarking on your writing process, you should outline your assignment or use an article review template to organize your thoughts coherently.
- If you are wondering how to start an article review, begin with an introduction that mentions the article and your thesis for the review.
- Follow up with a summary of the main points of the article.
- Highlight the positive aspects and facts presented in the publication.
- Critique the publication by identifying gaps, contradictions, disparities in the text, and unanswered questions.
Step 5: Summarize the Article
Make a summary of the article by revisiting what the author has written about. Note any relevant facts and findings from the article. Include the author's conclusions in this section.
Step 6: Critique It
Present the strengths and weaknesses you have found in the publication. Highlight the knowledge that the author has contributed to the field. Also, write about any gaps and/or contradictions you have found in the article. Take a standpoint of either supporting or not supporting the author's assertions, but back up your arguments with facts and relevant theories that are pertinent to that area of knowledge. Rubrics and templates can also be used to evaluate and grade the person who wrote the article.
Step 7: Craft a Conclusion
In this section, revisit the critical points of your piece, your findings in the article, and your critique. Also, write about the accuracy, validity, and relevance of the results of the article review. Present a way forward for future research in the field of study. Before submitting your article, keep these pointers in mind:
- As you read the article, highlight the key points. This will help you pinpoint the article's main argument and the evidence that they used to support that argument.
- While you write your review, use evidence from your sources to make a point. This is best done using direct quotations.
- Select quotes and supporting evidence adequately and use direct quotations sparingly. Take time to analyze the article adequately.
- Every time you reference a publication or use a direct quotation, use a parenthetical citation to avoid accidentally plagiarizing your article.
- Re-read your piece a day after you finish writing it. This will help you to spot grammar mistakes and to notice any flaws in your organization.
- Use a spell-checker and get a second opinion on your paper.
The Post-Writing Process: Proofread Your Work
Finally, when all of the parts of your article review are set and ready, you have one last thing to take care of — proofreading. Although students often neglect this step, proofreading is a vital part of the writing process and will help you polish your paper to ensure that there are no mistakes or inconsistencies.
To proofread your paper properly, start by reading it fully and checking the following points:
- Punctuation
- Other mistakes
Afterward, take a moment to check for any unnecessary information in your paper and, if found, consider removing it to streamline your content. Finally, double-check that you've covered at least 3-4 key points in your discussion.
And remember, if you ever need help with proofreading, rewriting your essay, or even want to buy essay , our friendly team is always here to assist you.
Need an Article REVIEW WRITTEN?
Just send us the requirements to your paper and watch one of our writers crafting an original paper for you.
Related Articles
.webp)
Article Review
Article Review Writing: A Complete Step-by-Step Guide with Examples

People also read
Learn How to Write an Editorial on Any Topic
Best Tips on How to Avoid Plagiarism
How to Write a Movie Review - Guide & Examples
A Complete Guide on How to Write a Summary for Students
Write Opinion Essay Like a Pro: A Detailed Guide
Evaluation Essay - Definition, Examples, and Writing Tips
How to Write a Thematic Statement - Tips & Examples
How to Write a Bio - Quick Tips, Structure & Examples
How to Write a Synopsis – A Simple Format & Guide
How to Write a Comparative Essay – A Complete Guide
Visual Analysis Essay - A Writing Guide with Format & Sample
List of Common Social Issues Around the World
Writing Character Analysis - Outline, Steps, and Examples
11 Common Types of Plagiarism Explained Through Examples
A Detailed Guide on How to Write a Poem Step by Step
Detailed Guide on Appendix Writing: With Tips and Examples
Struggling to write a review that people actually want to read? Feeling lost in the details and wondering how to make your analysis stand out?
You're not alone!
Many writers find it tough to navigate the world of article reviews, not sure where to start or how to make their reviews really grab attention.
No worries!
In this blog, we're going to guide you through the process of writing an article review that stands out. We'll also share tips, and examples to make this process easier for you.
Let’s get started.
- 1. What is an Article Review?
- 2. Types of Article Reviews
- 3. Article Review Format
- 4. How to Write an Article Review? 10 Easy Steps
- 5. Article Review Outline
- 6. Article Review Examples
- 7. Tips for Writing an Effective Article Review
What is an Article Review?
An article review is a critical evaluation and analysis of a piece of writing, typically an academic or journalistic article.
It goes beyond summarizing the content; it involves an in-depth examination of the author's ideas, arguments, and methodologies.
The goal is to provide a well-rounded understanding of the article's strengths, weaknesses, and overall contribution to the field.

Tough Essay Due? Hire Tough Writers!
Types of Article Reviews
Article reviews come in various forms, each serving a distinct purpose in the realm of academic or professional discourse. Understanding these types is crucial for tailoring your approach.
Here are some common types of article reviews:
Journal Article Review
A journal article review involves a thorough evaluation of scholarly articles published in academic journals.
It requires summarizing the article's key points, methodology, and findings, emphasizing its contributions to the academic field.
Take a look at the following example to help you understand better.
Example of Journal Article Review
Research Article Review
A research article review focuses on scrutinizing articles with a primary emphasis on research.
This type of review involves evaluating the research design, methodology, results, and their broader implications.
Discussions on the interpretation of results, limitations, and the article's overall contributions are key.
Here is a sample for you to get an idea.
Example of Research Article Review
Science Article Review
A science article review specifically addresses articles within scientific disciplines. It includes summarizing scientific concepts, hypotheses, and experimental methods.
The type of review assesses the reliability of the experimental design, and evaluates the author's interpretation of findings.
Take a look at the following example.
Example of Science Article Review
Critical Review
A critical review involves a balanced critique of a given article. It encompasses providing a comprehensive summary, highlighting key points, and engaging in a critical analysis of strengths and weaknesses.
To get a clearer idea of a critical review, take a look at this example.
Critical Review Example
Article Review Format
When crafting an article review in either APA or MLA format, it's crucial to adhere to the specific guidelines for citing sources.
Below are the bibliographical entries for different types of sources in both APA and MLA styles:
How to Write an Article Review? 10 Easy Steps
Writing an effective article review involves a systematic approach. Follow this step-by-step process to ensure a comprehensive and well-structured analysis.
Step 1: Understand the Assignment
Before diving into the review, carefully read and understand the assignment guidelines.
Pay attention to specific requirements, such as word count, formatting style (APA, MLA), and the aspects your instructor wants you to focus on.
Step 2: Read the Article Thoroughly
Begin by thoroughly reading the article. Take notes on key points, arguments, and evidence presented by the author.
Understand the author's main thesis and the context in which the article was written.
Step 3: Create a Summary
Summarize the main points of the article. Highlight the author's key arguments and findings.
While writing the summary ensure that you capture the essential elements of the article to provide context for your analysis.
Step 4: Identify the Author's Thesis
In this step, pinpoint the author's main thesis or central argument. Understand the purpose of the article and how the author supports their position.
This will serve as a foundation for your critique.
Step 5: Evaluate the Author's Evidence and Methodology
Examine the evidence provided by the author to support their thesis. Assess the reliability and validity of the methodology used.
Consider the sources, data collection methods, and any potential biases.
Step 6: Analyze the Author's Writing Style
Evaluate the author's writing style and how effectively they communicate their ideas.
Consider the clarity of the language, the organization of the content, and the overall persuasiveness of the article.
Step 7: Consider the Article's Contribution
Reflect on the article's contribution to its field of study. Analyze how it fits into the existing literature, its significance, and any potential implications for future research or applications.
Step 8: Write the Introduction
Craft an introduction that includes the article's title, author, publication date, and a brief overview.
State the purpose of your review and your thesis—the main point you'll be analyzing in your review.
Step 9: Develop the Body of the Review
Organize your review by addressing specific aspects such as the author's thesis, methodology, writing style, and the article's contribution.
Use clear paragraphs to structure your analysis logically.
Step 10: Conclude with a Summary and Evaluation
Summarize your main points and restate your overall assessment of the article.
Offer insights into its strengths and weaknesses, and conclude with any recommendations for improvement or suggestions for further research.
Paper Due? Why Suffer? That's our Job!
Article Review Outline
Creating a well-organized outline is an essential part of writing a coherent and insightful article review.
This outline given below will guide you through the key sections of your review, ensuring that your analysis is comprehensive and logically structured.
Refer to the following template to understand outlining the article review in detail.
Article Review Format Template
Article Review Examples
Examining article review examples can provide valuable insights into the structure, tone, and depth of analysis expected.
Below are sample article reviews, each illustrating a different approach and focus.
Example of Article Review
Sample of article review assignment pdf
Tips for Writing an Effective Article Review
Crafting an effective article review involves a combination of critical analysis, clarity, and structure.
Here are some valuable tips to guide you through the process:
- Start with a Clear Introduction
Kick off your article review by introducing the article's main points and mentioning the publication date, which you can find on the re-title page. Outline the topics you'll cover in your review.
- Concise Summary with Unanswered Questions
Provide a short summary of the article, emphasizing its main ideas. Highlight any lingering questions, known as "unanswered questions," that the article may have triggered. Use a basic article review template to help structure your thoughts.
- Illustrate with Examples
Use examples from the article to illustrate your points. If there are tables or figures in the article, discuss them to make your review more concrete and easily understandable.
- Organize Clearly with a Summary Section
Keep your review straightforward and well-organized. Begin with the start of the article, express your thoughts on what you liked or didn't like, and conclude with a summary section. This follows a basic plan for clarity.
- Constructive Criticism
When providing criticism, be constructive. If there are elements you don't understand, frame them as "unanswered questions." This approach shows engagement and curiosity.
- Smoothly Connect Your Ideas
Ensure your thoughts flow naturally throughout your review. Use simple words and sentences. If you have questions about the article, let them guide your review organically.
- Revise and Check for Clarity
Before finishing, go through your review. Correct any mistakes and ensure it sounds clear. Check if you followed your plan, used simple words, and incorporated the keywords effectively. This makes your review better and more accessible for others.
In conclusion , writing an effective article review involves a thoughtful balance of summarizing key points, and addressing unanswered questions.
By following a simple and structured approach, you can create a review that not only analyzes the content but also adds value to the reader's understanding.
Remember to organize your thoughts logically, use clear language, and provide examples from the article to support your points.
Ready to elevate your article reviewing skills? Explore the valuable resources and expert assistance at MyPerfectWords.com.
Our team of experienced writers is here to help you with article reviews and other school tasks.
So why wait? Get our essay writing service today!

Write Essay Within 60 Seconds!

Dr. Barbara is a highly experienced writer and author who holds a Ph.D. degree in public health from an Ivy League school. She has worked in the medical field for many years, conducting extensive research on various health topics. Her writing has been featured in several top-tier publications.

Paper Due? Why Suffer? That’s our Job!
Keep reading
How to Write an Article Review That Stands Out

An article review is a critical assessment of another writer’s research paper or scholarly article. Such an activity aims to expand one’s knowledge by evaluating the original author’s research.
Of course, writing an article review could be tricky. But a few expert tips and tricks can get you on the right track. That’s what this interesting blog post is all about. So, ensure you read it till the end to make the most out of it.
Table of Contents
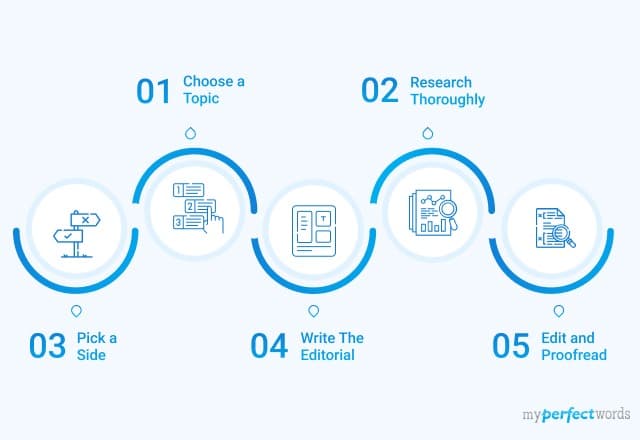
A Step-by-step Guide on How to Write an Article Review
Master the art of writing an article review with this step-by-step guide from professional paper help providers.
Step 1: Select the Right Article
The first step is to pick a suitable article for a review. Choose a scholarly source that’s connected to your area of study. You can look for pieces printed in trustworthy journals or by respected authors.
For Example:
For reviewing an article on climate change, consider selecting one from scientific journals like Nature or Science.
Step 2: Read and Understand the Article
It’s super important to read and understand the article before writing your review. Read the article a few times and jot down the notes as you go. Focus on the main arguments, major points, evidence, and how it’s structured.
Let’s say you’re looking at an article on how social media affects mental health. Ensure to take note of the following:
- The number of people involved
- How the data is analyzed
- The Results
Step 3: Structure and Introduction
To start a solid review, start with an introduction that gives readers the background info they need. Must include the article’s title, the author, and where it was published. Also, write a summary of the main point or argument in the article.
“In the article ‘The Impact of Social Media on Mental Health by John Smith, published in the Journal of Psychology:
The author examines the correlation between excessive social media usage and adolescent mental health disorders.”
Step 4: Summarize the Article
In this part, you’ll need to quickly go over the main points and arguments from the article. Make it short but must cover the most important elements and the evidence that backs them up. Leave your opinions and analysis out of it for now.
For instance, you could write:
“The author discusses various studies highlighting the negative effects of excessive social media usage on mental health.
Smith’s research reveals a significant correlation between
Increased social media consumption and higher rates of anxiety, depression, and low self-esteem among teenagers.
The article also explores the underlying mechanisms, such as social comparison and cyberbullying. All are contributing to the adverse mental health outcomes.”
Step 5: Critically Analyze and Evaluate
Now that you’ve given a rundown of the article, it’s time to take a closer look. Think about what the author did well and what could have been done better.
Check out the proof they used and if it seems solid. Give a thorough assessment, and use examples from the text to support your thoughts.
For Example
“While the article presents compelling evidence linking social media usage to mental health issues , it is important to acknowledge some limitations in Smith’s study.
The sample size of the research was relatively small. It comprises only 100 participants, which may limit the generalizability of the findings.
Additionally, the study primarily focused on one specific age group, namely adolescents. This way, there’s room for further research on other demographic groups.”
Step 6: Express Your Perspective
Here’s your chance to give your two cents and show off your smarts. Put your spin on the article by pointing out the pros, cons, and other potential improvements. Remember to back up your thoughts with facts and sound arguments.
Continuing with the Previous Example
Despite the limitations, Smith’s research offers valuable insights into the complex relationship between social media and mental health.
Future studies could expand the sample size and include a more diverse range of age groups. It is better to understand the broader impact of social media on mental well-being.
Furthermore, exploring strategies for developing digital literacy programs could be potential avenues for future research.
Step 7: Conclusion and Final Thoughts
At the end of your article review, wrap it up with a brief and powerful conclusion. Give a summary of your main points and overall thoughts about the article.
Point out its importance to the field and the impact of the study. Finish off with a thought-provoking conclusion. Give the reader a sense of finality and emphasize the need for additional research or discussion.
For instance
“In conclusion, John Smith’s article provides valuable insights into the detrimental effects of excessive social media usage on adolescent mental health.
While the research has limitations, it serves as a starting point for further investigation in this rapidly evolving field.
By addressing the research gaps and implementing targeted interventions:
We can strive to promote a healthier relationship between social media and mental well-being in our digitally connected society.”
Step 8: Editing and Proofreading
Before submission, set aside some time for editing and proofreading.
Ensure everything makes sense and everything is correct. Check out how it reads and if your points come across clearly. Get feedback from other people to get a different point of view and make it even better.
Types of Article Reviews
In college, you might be asked to write different types of review articles, including:
Narrative Review
This type of review needs you to look into the author’s background and experiences. You have to go through the specialist’s theories and practices and compare them. For the success of a narrative review, ensure that your arguments are qualitative and make sense.
Evidence Review
For a solid evidence paper, you got to put in the work and study the topic. You’ll need to research the facts, analyze the author’s ideas, their effects, and more.
Systematic Review
This task involves reviewing a bunch of research papers and summarizing the existing knowledge about a certain subject. A systematic paper type uses an organized approach and expects you to answer questions linked to the research.
Tips for Writing a Great Article Review
Here are some expert tips you could use to write an exceptional article review:
1. Figure out the main points you want to cover and why they matter.
- It will help you zero in on the key points.
2. Look for and assess pertinent sources, both from the past and present.
- It will give you a better understanding of the article you’re looking at.
3. Come Up with a Catchy Title, Summarize Your Topic in an Abstract, and Select Keywords
- It will help people read your review and get a good idea of what it’s about.
4. Write the main point of a review along with introducing the topic.
- It should help readers get a better grasp of the topic.
Outline for Writing a Good Article Review
Here’s an outline to write an excellent article review.
Introduction
– Begin with a summary of the article
– Put in background knowledge of the topic
– State why you are writing the review
– Give an overview of the article’s main points
– Figure out why the author choose to write something
– Look at the article and consider what it does well and what it could have done better.
– Highlight the shortcomings in the article
– Restate why you are writing the review
– Sum up the main points in a few sentences
– Suggest what could be achieved in the future research
Review Article Example
Title: “The Power of Vulnerability: A Review of Brené Brown’s Daring Greatly”
Introduction:
In her revolutionary book “Daring Greatly,”
Brené Brown, a renowned researcher and storyteller. Delves into vulnerability and how it can positively impact our lives, both professionally and personally.
Brown’s work has gained lots of praise. Since it resonates with people looking to build real connections in a world that often feels isolated.
This article looks to recap the main ideas and concepts from “Daring Greatly.” Also explains why it is such a captivating and insightful read.
Summary of Key Ideas:
“Daring Greatly” is all about how the vulnerability isn’t a sign of being weak. but it’s actually what it takes to be brave, strong and live a full life.
Brene Brown examines how society and culture can make it hard to be vulnerable. And, how fear of being judged or shamed stops us from being our authentic selves.
The book puts a lot of emphasis on shame and how it affects us.
Brown explains that shame thrives when it’s kept hidden away and can only be cured by being open, understanding, and compassionate.
By admitting our weaknesses, we can create meaningful connections and a sense of community.
Brown looks into the connection between being open to vulnerability and unleashing creative leadership and innovation.
She uses her own experiences and research to support her viewpoint. The book also gives useful advice on how to include vulnerability in different parts of life. Such as relationships, parenting, and the workplace.
Strengths of the Book:
Brown’s book is remarkable for her ability to mix her own experiences with comprehensive research. Combining her stories and evidence makes the material engaging and easy to understand.
Plus, her writing style is so friendly that readers feel they’re being acknowledged and accepted.
There’s advice on how to be kind to yourself. Set your limits, and accept that things won’t always be perfect. It’s like a toolkit to help you build strength and make positive changes.
Final Verdict
This book is really helpful for everyone, no matter who you are. It can help you figure out how to grow in life, have better relationships, and become a better leader. Plus, since it applies to all kinds of people, everyone can get something out of it.
If you want to write a great article review, it’s important to pick the right article, understand and analyze it critically. Finally, express your thoughts on it clearly. Ensure to stay impartial, back up your points with evidence, and write clearly and coherently.
Still if you are having troubles writing an article review, don’t hesitate to count on the expertise of our writers .
Order Original Papers & Essays
Your First Custom Paper Sample is on Us!
Timely Deliveries
No Plagiarism & AI
100% Refund
Calculate Your Order Price
Related blogs.

Connections with Writers and support
Privacy and Confidentiality Guarantee
Average Quality Score
The Tech Edvocate
- Advertisement
- Home Page Five (No Sidebar)
- Home Page Four
- Home Page Three
- Home Page Two
- Icons [No Sidebar]
- Left Sidbear Page
- Lynch Educational Consulting
- My Speaking Page
- Newsletter Sign Up Confirmation
- Newsletter Unsubscription
- Page Example
- Privacy Policy
- Protected Content
- Request a Product Review
- Shortcodes Examples
- Terms and Conditions
- The Edvocate
- The Tech Edvocate Product Guide
- Write For Us
- Dr. Lynch’s Personal Website
- The Edvocate Podcast
- Assistive Technology
- Child Development Tech
- Early Childhood & K-12 EdTech
- EdTech Futures
- EdTech News
- EdTech Policy & Reform
- EdTech Startups & Businesses
- Higher Education EdTech
- Online Learning & eLearning
- Parent & Family Tech
- Personalized Learning
- Product Reviews
- Tech Edvocate Awards
- School Ratings
Busiest Walking Trails This Summer and New Zealand’s Best Day Walksrevealed
14 best places to camp around the world, 25 best cdn providers 2024, best magsafe stands for ios 17 standby feature, the 8 best platforms to receive payment for freelancers, a tiny pub in west wales was one of the best places a travel writervisited this year, best hometowns 2024: lancaster – a hidden gem unveiled, way day is back these are the best deals to shop asap, 19 best seeds to start indoors in winter, albanese world’s best 12 flavor gummi bears, stocking stuffer, 7.5oz, how to write an article review (with sample reviews) .

An article review is a critical evaluation of a scholarly or scientific piece, which aims to summarize its main ideas, assess its contributions, and provide constructive feedback. A well-written review not only benefits the author of the article under scrutiny but also serves as a valuable resource for fellow researchers and scholars. Follow these steps to create an effective and informative article review:
1. Understand the purpose: Before diving into the article, it is important to understand the intent of writing a review. This helps in focusing your thoughts, directing your analysis, and ensuring your review adds value to the academic community.
2. Read the article thoroughly: Carefully read the article multiple times to get a complete understanding of its content, arguments, and conclusions. As you read, take notes on key points, supporting evidence, and any areas that require further exploration or clarification.
3. Summarize the main ideas: In your review’s introduction, briefly outline the primary themes and arguments presented by the author(s). Keep it concise but sufficiently informative so that readers can quickly grasp the essence of the article.
4. Evaluate the strengths and weaknesses: In subsequent paragraphs, assess the strengths and limitations of the article based on factors such as methodology, quality of evidence presented, coherence of arguments, and alignment with existing literature in the field. Be fair and objective while providing your critique.
5. Discuss any implications: Deliberate on how this particular piece contributes to or challenges existing knowledge in its discipline. You may also discuss potential improvements for future research or explore real-world applications stemming from this study.
6. Provide recommendations: Finally, offer suggestions for both the author(s) and readers regarding how they can further build on this work or apply its findings in practice.
7. Proofread and revise: Once your initial draft is complete, go through it carefully for clarity, accuracy, and coherence. Revise as necessary, ensuring your review is both informative and engaging for readers.
Sample Review:
A Critical Review of “The Effects of Social Media on Mental Health”
Introduction:
“The Effects of Social Media on Mental Health” is a timely article which investigates the relationship between social media usage and psychological well-being. The authors present compelling evidence to support their argument that excessive use of social media can result in decreased self-esteem, increased anxiety, and a negative impact on interpersonal relationships.
Strengths and weaknesses:
One of the strengths of this article lies in its well-structured methodology utilizing a variety of sources, including quantitative surveys and qualitative interviews. This approach provides a comprehensive view of the topic, allowing for a more nuanced understanding of the effects of social media on mental health. However, it would have been beneficial if the authors included a larger sample size to increase the reliability of their conclusions. Additionally, exploring how different platforms may influence mental health differently could have added depth to the analysis.
Implications:
The findings in this article contribute significantly to ongoing debates surrounding the psychological implications of social media use. It highlights the potential dangers that excessive engagement with online platforms may pose to one’s mental well-being and encourages further research into interventions that could mitigate these risks. The study also offers an opportunity for educators and policy-makers to take note and develop strategies to foster healthier online behavior.
Recommendations:
Future researchers should consider investigating how specific social media platforms impact mental health outcomes, as this could lead to more targeted interventions. For practitioners, implementing educational programs aimed at promoting healthy online habits may be beneficial in mitigating the potential negative consequences associated with excessive social media use.
Conclusion:
Overall, “The Effects of Social Media on Mental Health” is an important and informative piece that raises awareness about a pressing issue in today’s digital age. Given its minor limitations, it provides valuable
3 Ways to Make a Mini Greenhouse ...
3 ways to teach yourself to play ....
Matthew Lynch
Related articles more from author.

3 Ways to Make a Duck Costume

3 Ways to Get Beach Wavy Hair Without Heat

6 Ways to Cook Salmon Fillet

How to Dye Fabric With Tea: 9 Steps

How to Get a Cat for a Pet

3 Ways to Take Care of Your Book

How to Write an Article Review
a scholarly article, scientific paper, political article, book report, research paper, or any publication your teacher or professor assigns. It requires an in-depth understanding of the subject matter as well as the ability to critique someone else work.
What Is an Article Review
An article review asks the writer to evaluate another person’s work - understand it, analyze it, present it concisely, and question the conclusions drawn by the author. They are often used by teachers to introduce students to experts’ work in the field and to test their critical thinking skills.
This assignment isn’t like a typical essay. It answers how to review an article, but it doesn’t follow the classic 5 paragraph style of formal essay writing - there are other steps you have to follow. This makes writing one a new challenge for students, but don’t worry, this article will cover everything you need to know about how to write article review.
Article Review Types
There are several different types of article reviews, most of which you don’t have to worry about because they are either very specialized or are meant for professionals. Some examples of these are scoping review, systematic review, umbrella review, meta-analyses, and more complicated sounding names. Here, we’ll talk about the types of article reviews students usually have to deal with.
Narrative Article Review
A summation and analysis of a particular publication. It focuses on critiquing the biases of the author as well as logical inconsistencies. These can be book reports, film critiques, story critiques, etc.
Systematic Article Review
Using multiple sources to summarize information about a specific topic. This is a more complex type of article review that uses systematic methods to evaluate available research. These tend to be more technical in nature and are used often in the sciences and quantitative humanities.
Evidence Article Review
Focuses on analyzing the evidence and the findings based on that evidence. Whereas a systematic review’s primary focus isn’t the evidence, it is for this type of review.
Journal Article Review
An analysis of any type of publication focusing on the article’s opinion and subject matter. It answers how important the article is as well as analyzing the article itself.
Research Article Review
A subset of a journal article review that analyzes literary publications. It summarizes the presented research and evaluates the conclusions the original author draws.
Science Article Review
A subset of journal article reviews that analyzes scientific journals. As such, it focuses on the research methodology used and the conclusions based on the evidence.
Struggling with your Article Review Homework?
Get your assignments done by real pros. Save your precious time and boost your marks with ease.
Article Review Format
Following instructions is absolutely critical to getting a good grade. An article review has a very particular format that must be followed. Read an article review example to get a sense of what it’s like and take a look at the Template and Outline section further down for a step by step guide on how to structure your paper.
One key thing to note is the citation style. Your professor or teacher will specify which citation style to use between MLA and APA. While both styles require in-text parenthetical citations, how to write an article review APA or MLA differ slightly in style.
APA Article Review Citation
APA stands for American Psychological Association and is generally used for social studies. If you need to write an APA format article review, these are the structures.
Journal: Author’s last name, Author’s first initial. Author’s middle initial. (Year, Month Date Published). Article title. Journal Name, Volume (Issue), page number(s).
Newspaper Print: Author, A. (Year, Month Date of Publication). Article title. Newspaper Title, pp. Xx-xx.
Newspaper Online: Author, A. (Year, Month Date of Publication). Article title. Newspaper Title, Retrieved from newspaper homepage URL
Website: Author’s last name, Initial(s). (Year, Month Day of publication). Title of work. Website. https://URL
Follow this citation article review examples to write a perfect apa style article review.
MLA Article Review Citation
MLA stands for Modern Language Association and is generally used for arts and humanities subjects. For the MLA format , these are the structures.
Journal: Last, First M. “Publication Title.” Journal Title Series Volume. Issue (Year Published): Page(s). Database Name. Web. Date Month Year Accessed.
Newspaper Print: Author's Last Name, First Name. "Title of Article: Subtitle if Any." Name of Newspaper, Date of Publication, p. Page Number.
Newspaper Online: Author's Last Name, First Name. "Title of Article: Subtitle if Any." Title of Website, Date of Publication, URL. Accessed Day Month Year site was visited.
Website: Author's Last Name, First Name. Title of Website, Name of Organization Affiliated with the Website, Date of copyright or date last modified/updated, URL. Accessed Day Month Year site was visited.
The Planning Stage
What’s the structure going to be.
Knowing the different sections of a review article before reading the original article will help you process information in a useful way. Read an example of an article review to give you an idea of what to expect. There are 3 main parts to keep in mind.
- Summarize the article by identifying the most important points of information and the main claims made by the author
- Talk about what the author gets right. An analysis of the positive elements of the author’s opinions, research, and conclusions
- Discuss what the author could have done better. Think about shaky conclusions, inconsistent research, and unanswered questions.
Your first read
Do a quick read of the article. Start by reading the title, abstract, introduction, headings, the first few lines of every paragraph, and the conclusion. This should give you an idea of what the article will be about. Then read the article taking note of terms or concepts you don’t understand. After your first quick read, research the concepts that you aren’t familiar with to make sure to get a better understanding on your next read-through.
Your second read
Now read the article slowly and deliberately, highlighting important information and taking notes. Connect information with knowledge you already have on the subject. Think about what new information is being presented in the article and how it differs or supports what you already know. Read the article as many times as you need to so that you understand it perfectly. It’s impossible to write a good review if you don’t understand the article itself!
Collecting information
Write the article again in your own words. This will help you identify the main points, arguments, and conclusions of the article and deepen your understanding. Don’t worry about editing, this is just for yourself.
Creating an outline
Now that you’ve dissected the article and noted down the main points and arguments, you’re well prepared to work on your review outline. Creating an outline helps plan your essay and cuts down on a lot of writing and reviewing time.
Did you like our inspiring Article Review Writing Guide?
For more help, tap into our pool of professional writers and get expert essay editing services!
Article Review Template & Outline
Use the outline as a guide to help plan and write your review. An article review, though a unique form of writing, still follows the traditional introduction, body, and conclusion format of essays, but has several specific sections that must be included as well. Fit these into your body paragraphs.
Pre-Title Page - This section states the basics. What type of article it is, the title of the article, contributing authors, and the authors’ credentials.
Optional Corresponding Author Details - Specific details of the authors including phone numbers, email addresses, etc.
Running Head - The title of your paper shortened to 40 characters or less (only required for APA format).
Summary Page - Some teachers ask for a summary page. It’s an 800 word or less summary that gives background information, explains the purpose of the review and summarizes the results. Don’t copy pieces of text from the article or the review itself, keep the language simple, and there’s no need to use references.
Title Page - This page can be thought of as the official start of your paper. You need to include the full title, a 250 word abstract, and a few keywords.
Introduction - The beginning of your review including a thesis statement.
Body Paragraphs - Include headings and subheadings to lay out your analysis clearly.
Works Cited/References - Differs in style based on MLA or APA format. Get clarification from your teacher if it isn’t clear.
Optional Suggested Reading List - If required by the professor.
Tables and Figure Legends - If required by the type of article or professor.
Article Review Writing: Step by Step
Step 1: title selection.
Spend some time crafting an interesting and representative title. A good title is both catchy as well as informative. It often helps to start with a tentative title and modify it as you write your paper. Your title should guide you as you write your paper, but it should also be reflective of the main purpose of the review.
Step 2: Article Citation
You need to properly cite the reviewed article. The most important thing is to make sure you are citing it in either APA or MLA format, whichever one is required by your teacher.
Step 3: Brief Article Description
After citing the article, start your first paragraph by stating the title of the article, the author, the name of the journal, and the year of publication.
Step 4: Introduction
Once you’ve identified the article, give a brief description of the main points of the article. Carefully analyze the article to identify and highlight the author’s thesis. Understanding the thesis of the main article is crucial to writing a good review, so make sure you include any sub thesis. End the introduction with your own thesis, this could include accepting and expanding on the original author’s main points, or proposing reasons why the author’s conclusions were flawed.
Step 5: Article Summary
The first body paragraph should summarize the main points of the original article including the author’s arguments and takeaways. Don’t hold yourself to just 3 body paragraphs unless specifically told so by your teacher. Explore a different main point in each paragraph and explain the author’s perspective on the issues. Make sure you review the summary paragraphs so that they accurately reflect the content of the original article and the views of the author.
Step 6: Analysis
Start with a general assessment of the clarity and usefulness of the article. Analyze each point of your summary and express your opinions on what the author did well or badly. Critiquing the article is the most important element of an article review, so devote a majority of your time and effort to this section. Analyze the main points of the article and determine if the author did a good job of backing their claims with logic and fact. Finally decide if you agree with the author’s conclusions and provide supporting evidence to substantiate your claims.
Step 7: Conclusion
Summarize the main points and lessons of the original article and then state your main critiques of the article. Specify why you believe the author made specific mistakes, and how the key takeaways should be different. If possible pose a question about further research or analysis on the topic.
The Post-Writing Process: Revision
Finishing your first draft isn’t the end of the process! If you spent enough time during the prewriting stage and made a good outline you will have to spend much less time during revision.
Checklist for revision
- Do a quick read-through of the entire paper
- Make sure it flows logically from one section to another
- Make sure sentences are clear
- Make sure each paragraph only talks about one main point
- Get rid of unnecessary information
- Check your summary to make sure it represents the original paper accurately
- Check your critique to make sure it is fair and backed up by evidence
- Check the grammar
- Check the punctuation
- Check for typos
- Check your citations
Tips for Writing an Article Review
An article review is a unique form of academic writing that has a well-defined structure and specific requirements. Follow these tips to make writing one easier.
- Make sure you understand the overall structure and format
- On the first read through of the article focus on the big picture impressions
- Do research on terms and concepts you aren’t familiar with
- On the second read through, note down key points
- Spend time preparing a thorough outline
- Come up with several title ideas and choose amongst the best
- Confirm which citation style you need to use between APA and MLA
- Follow the standard introduction paragraph style but include specific requirements
- This is a formal academic paper so keep the tone and style formal as well
- The main body consists of a summary, and then a critique of the original article
- Conclude the review by summarizing your main critiques of the article
An article review tests your formal writing skills, critical thinking, ability to summarize and synthesize information, and evaluative powers. Learning how to craft a critical review of an article isn’t just helpful in academics. The skills you learn and the format will be useful when evaluating anything in your life, whether it be a movie, game review, or social media content.
This comprehensive article provides all the necessary information on how to write a review of an article, but it's clear that the process isn't straightforward. Studyfy boasts a vast team of experts who have assisted numerous students with their homework. If you need assistance, don't hesitate to reach out to them via email for services such as proofreading, essay editing, or expert advice. Whether you require a biology essay writing service , want to write essays for money online , need a custom research paper , or are looking to pay for an essay , Studyfy is here to help!
Featured Posts
How to write a scholarship essay.

How to Write a Movie Review

How to Write an Argumentative Essay

How to Write a Cause and Effect Essay
.jpg)
How to Write an Expository Essay

How to Write an Analytical Essay

Custom Essay, Term Paper & Research paper writing services
- testimonials
Toll Free: +1 (888) 354-4744
Email: [email protected]
Writing custom essays & research papers since 2008
How to write an article review.

In this short guide, we will take a step-by-step approach to teach you how to write an article review. We will explain the differences between an article review for a variety of subjects and let you know where you can find a great example of an article review on the web. We will begin by first answering the question many students have about this kind of assignment.
What is An Article Review?
An article review summarizes and evaluates another person’s article. It’s an assignment that is usually given to introduce students to written works done by experts in a specific field. A critical review of journal article can be done in just about any discipline, but we can’t go in-depth for each. So we will stay focused on the ones you are most likely to have to work in and then break down the steps you need to take for writing a review article that truly impresses.
Some of the most common types are:
- The Science Article Review
- The APA Article Review
- The Law Review Article
- The Journal Article Review
Each of these has a slightly different approach and style from one another and especially from book review writing. It’s a good idea to get your hands on an article review sample in the related field you must complete your assignment in. You can find excellent published pieces in academic journals at your school library. Or you can turn to a professional writing service to get a custom-written piece sent to you that you can use as an article review template.
What is a Peer Review Article?
Before we move on to the “how to write article review” portion of this guide, we will briefly discuss another type of review article you might come upon at some point: The peer-review article. This type of article is one that is written by a researcher or scholar and then is reviewed by experts in the field before publication. So that means the piece that you see in the journal has already been reviewed and critiqued by others. It also means that it has gone through different versions or drafts. Perhaps one of the best ways to learn how to write a critical review of a journal article is to have a look at how others review experts’ work before they reach publication.
How to Review an Article
The first thing you need to do before writing your review is fully understanding all that you have to do conduct an unbiased evaluation of the published work.
The first thing you need to know about how to review a research article is evaluating its organization. Your review will mirror the author’s structure and format. Focus on the most important elements, including main points, supporting evidence, and claims. It’s a good idea to break up the article into parts to better identify all of the essential elements that need to be addressed.
This type of assignment requires exceptional close reading. If you have gained access to an article review example you will see that the reviewer has been careful to address all of the original article’s main points and supporting evidence. Take what you get from the article and apply it to what you already know about the topic. Do this at least twice to ensure that you cover all of the most important information.
This should be done as a straightforward freewriting session. Just take the main points of the original article and attempt to rewrite in in your own words. This will let you identify the places where you are not in total agreement with what the author has presented. Your writing should be focused on all of the main arguments, main research points, and claims that the author makes.
How to Write a Review Article
The following 5 step-by-step process is all you need to know about how to start an article review. It’s a great idea to start with a couple of practice reviews so that you can become comfortable with this kind of assignment’s main elements.
The best way to adhere to the appropriate article review format is to create an outline before you start the process of writing. Review each of the summary points you made and compare them with the original article. Write down all instances of effective writing as well as any new contributions made to the field. Identify all of the article’s strengths and weaknesses and start to organize the main points with your critique in a clear and concise outline.
Take the original article, outline, and rewrite from the prior steps and start writing a rough draft covering all the main points, arguments, and findings. Since this is a draft you don’t need to worry about getting words right. Don’t stop to make corrections or grammar. Just get the draft down on the page as quickly as possible. Write the introduction, body paragraphs, and conclusion and then set the draft aside.
The main part of how to write a review of an article is writing your critique. Refer to your outline and summary to draft several paragraphs evaluating the effectiveness of the writer’s arguments. You should address whether the article was useful, thorough, and clear in explaining the subject. The critique will form the body paragraphs, so each paragraph should address a single sub-topic. In each paragraph, decide whether or not you agree with the writer backed up with sufficient support.
The introduction and conclusion should be written after you’ve written the main portion (critique body paragraphs) of the review. Your intro will identify the article, mention its central themes, and arguments made by the author. Your conclusion will summarize the main points of the article in addition to your critique of them. Each of these paragraphs should be no more than 10% to 15% of your review.
Despite everything you’ve learned about how to write an article review, you need to ensure you adhere to the fundamentals of good essay writing. This means that you should set your review aside for a few days before you start your revisions. If you have the time you should set it aside for more time before you start editing and proofreading your work. Writing a great academic review will earn you a high grade and you will be under greater scrutiny since you are critiquing someone else’s ideas, structure, and writing, so be sure to put in the extra work.
There is a lot you need to know about how to write a article review. That’s where we can step in to help. We are a group of highly-qualified academic writers that know everything there is about every kind of assignment. You may not feel you are a strong writer or you may not have the time to write the review article on your own. Whatever the reason may be, we’re available to jump in and help craft a research article review that is guaranteed to earn you a high score.

Article Review
Last updated on: Feb 9, 2023

Learn How to Write an Article Review with Examples
By: Cordon J.
Reviewed By: Chris H.
Published on: Mar 29, 2022

Students often find themselves struggling with the process of writing the article review. It seems like a very simple and straightforward task at first, but some unique features make it challenging to write an excellent one. You should know them before you start writing the article review.
Worry not! If you were assigned to write the review of an article and have no clue how to write it, you are at the right place. In this blog, you will get the most effective topics, tips, and examples that make your writing phase easy and simple.

On this Page
What is an Article Review?
An article review is a common academic assignment where you summarize and assess another person’s article. In this type of assignment, you read a specific article, evaluate it critically, and write your observations in the review.
The main purpose of writing the article review is to:
- Explore the strong and weak points
- Highlight the main methodologies
- Provide a critical evaluation
- Help clarify questions
- Explain the current state of knowledge
A review of an article should not provide new information. Instead, it explores and evaluates the work done by another writer to help you make up your mind on whether or not this piece is worth reading in its entirety.
Moreover, thinking analytically and critically is a must when working on such an assignment. This task can be more difficult than it looks, but success comes with practice.
How to Write an Article Review?
Creating a well-written article review is not easy, but you can do it with some steps. To create an informative and engaging work for your audience, you should follow the below-mentioned steps.
1. Preparation
You need to know what type of review is right for your article. This will make it easier for you to read and understand it.
Below are some main stages that help you get started.
- Read the article. Make notes or highlight the main sections.
- Summarize the main ideas, arguments, findings, and positions.
- Identify the strong claim.
- Critique the article contributes to the field.
- Examine the title, abstract, introduction, headings, and conclusion.
Remember these stages in your mind and start writing your review.
2. Create an Outline
Review each item in the article summary to determine whether it was accurate and clear. Get back to your notes and preliminary outline to see what you include in your review. Then, create an outline and organize all the information you need to add to your review.
3. Write the Title
The title of your review should reflect the main focus. You can either use an interrogative, descriptive, or declarative title to attract readers’ attention and make them want more information about what you're writing about.
4. Cite the Article
Now, place the citation in the proper format. Consider the style your professor recommends; this will help you avoid future problems.
5. Identify the Article
In this step, you should include the identification of the reviewed article. Start by referring to the title, author, and year of publication in the first paragraph.

Paper Due? Why Suffer? That's our Job!
6. Write the Captivating Introduction
An introduction of an article review should accurately summarize the content. It may also mention key themes, arguments, and authors’ claims to identify their position on this subject matter.
You must state clearly what thesis was being argued. Sometimes, the thesis statement is not clearly stated, so you have to examine it yourself.
7. Summarize the Article
An engaging summary of the article discusses its central arguments and includes a list with key findings. The author's conclusion should not be missed in any case because it provides an important perspective on what was talked about previously by summarizing all relevant facts together as well.
8. Write Your Critique
The article’s contribution and importance to the field should be discussed in the article. You can support your critique with facts, evidence, or other perspectives.
It would be great to share your opinion on what is working well and where work needs improvement.
9. Conclude the Article Review
In the concluding section, summarize the main points and your opinion about the topic. Do not add irrelevant and new information that confuses the readers.
10. Proofread
Before you submit your article review, make sure to read it thoroughly and identify any mistakes in spelling or grammar. Proofread it again and again for errors and make it error-free.
Article Review Format
To create a well-written review and get an A+ from your teacher, you must follow the proper format recommended by your professor.
Citation styles can vary depending on the instructor’s requirements. Make sure your citations are formatted correctly to avoid any plagiarism.
If your instructor does not define any format, you can choose the best one from the below-mentioned formats.
An article can be in an academic journal, a website, or a newspaper. You need to include citations for sources when writing in an APA format review.
The below table gives you a better understanding of citing different sources in APA format.
MLA citations are the format used for citing sources in an article review. For those who are not familiar with the MLA citation format, it's just like APA. It's not very difficult, and it is a common method among many academic journals.
Here is an MLA format that you can use for your help.
Article Review Examples
ARTICLE REVIEW SAMPLE
JOURNAL ARTICLE REVIEW EXAMPLE
ARTICLE REVIEW TEMPLATE
ARTICLE REVIEW EXAMPLE APA
Article Review Topics
For those who find it difficult to do research and choose the topics, don’t worry. Our experts compiled some great topics that you can use for your help.
Take a look at the below-mentioned topics and choose the one that matches your needs and interests.
Tough Essay Due? Hire Tough Writers!
- Women roles in the modern world
- What new traditions could come out of the COVID-19 situation?
- Current issues in the education of students with visual impairments
- How To stop wasting time and improve your personal effectiveness?
- The future of work is through workforce ecosystems
- The positive aspects of the use of plastic products
- Examine the strengths and weaknesses of the cloud computing
- Significance of future research of artificial intelligence
- Child abuse and its influence on character development
- Global warming
Tips for Writing the Article Review
One of the most important aspects to remember when writing an article review is keeping it interesting for both readers and authors. Here are some tips from our team on how best to approach this:
- Give insight observations about the article.
- Write relevant background information.
- The opening sentence of the introduction should be attention-grabbing.
- Cover all the key points in your review.
- Know that review can be either a literature review or a critical review.
- Keep the main points of the article in mind.
- Keep the length of the article review in mind, e.g., systematic reviews are short in length.
To write a great review, you need to make a proper plan and start writing it. Pick the article from a legal source and evaluate the information for further limitations before writing your opinion about the chosen topic.
Although, if you are overburdened and lack writing skills, you can easily consult the best ‘ write my essay ’ service 5StarEssays.com . We offer top-notch writing services to students of different academic levels at affordable rates.
Contact us and get the best writing help from professionals.

Law, Finance Essay
Cordon. is a published author and writing specialist. He has worked in the publishing industry for many years, providing writing services and digital content. His own writing career began with a focus on literature and linguistics, which he continues to pursue. Cordon is an engaging and professional individual, always looking to help others achieve their goals.
Was This Blog Helpful?
Keep reading.
- How to Write A Bio – Professional Tips and Examples

- How to Write a Poem Step-by-Step Like a Pro

- How To Write Poetry - 7 Fundamentals and Tips

- Know About Appendix Writing With the Help of Examples

- List of Social Issues Faced By the World

- How To Write A Case Study - Easy Guide

- Learn How to Avoid Plagiarism in 7 Simple Steps

- Writing Guide of Visual Analysis Essay for Beginners

- Learn How to Write a Personal Essay by Experts

- Character Analysis - A Step By Step Guide

- Obesity Essay: A Complete Guide and Topics

- Thematic Statement: Writing Tips and Examples

- Expert Guide on How to Write a Summary

- How to Write an Opinion Essay - Structure, Topics & Examples

- How to Write a Synopsis - Easy Steps and Format Guide

- Learn How To Write An Editorial By Experts

- How to Get Better at Math - Easy Tips and Tricks

- How to Write a Movie Review - Steps and Examples

- Creative Writing - Easy Tips For Beginners

- Types of Plagiarism Every Student Should Know

People Also Read
- scholarship essay examples
- writing thesis statement
- essay writing service
- evaluation essay
- cause and effect essay writing
Burdened With Assignments?

Advertisement
- Homework Services: Essay Topics Generator
© 2024 - All rights reserved
- All eBooks & Audiobooks
- Academic eBook Collection
- Home Grown eBook Collection
- Off-Campus Access
- Literature Resource Center
- Opposing Viewpoints
- ProQuest Central
- Course Guides
- Citing Sources
- Library Research
- Websites by Topic
- Book-a-Librarian
- Research Tutorials
- Use the Catalog
- Use Databases
- Use Films on Demand
- Use Home Grown eBooks
- Use NC LIVE
- Evaluating Sources
- Primary vs. Secondary
- Scholarly vs. Popular
- Make an Appointment
- Writing Tools
- Annotated Bibliographies
- Summaries, Reviews & Critiques
- Writing Center
Service Alert

Article Summaries, Reviews & Critiques
- Writing an article SUMMARY
Writing an article REVIEW
- Writing an article CRITIQUE
- Citing Sources This link opens in a new window
- About RCC Library
Text: 336-308-8801
Email: [email protected]
Call: 336-633-0204
Schedule: Book-a-Librarian
Like us on Facebook
Links on this guide may go to external web sites not connected with Randolph Community College. Their inclusion is not an endorsement by Randolph Community College and the College is not responsible for the accuracy of their content or the security of their site.
A journal article review is written for a reader who is knowledgeable in the discipline and is interested not just in the coverage and content of the article being reviewed, but also in your critical assessment of the ideas and argument that are being presented by the author.
Your review might be guided by the following questions:
Additional Resources
All links open in a new window.
How to Write an Article Review (from Essaypro.com)
How to Review a Journal Article (from University of Illinois Springfield)
Writing Critical Reviews (from Queen's University Library)
- << Previous: Writing an article SUMMARY
- Next: Writing an article CRITIQUE >>
- Last Updated: Mar 15, 2024 9:32 AM
- URL: https://libguides.randolph.edu/summaries

- Services Paper editing services Paper proofreading Business papers Philosophy papers Write my paper Term papers for sale Term paper help Academic term papers Buy research papers College writing services Paper writing help Student papers Original term papers Research paper help Nursing papers for sale Psychology papers Economics papers Medical papers Blog

How to Write an Article Review?

Writing an article review entails assessing and summarizing an article by somebody else. But, what is an article review? Well, this type of work can be defined as logical evaluation of the article’s central theme, supporting arguments, and suggestions for further research. Knowing how to review an article is very important because:
- It enables a person to spot and correct vague terms in an article.
- It enables a person to clarify questions
- It enables a person to see the perspectives and views of other people without personal biases
- It enables an individual to improve their grammar and conscious writing skills
- It encourages a person to perform better in the next article because the review provides valuable criticism or suggestions.
How to Write an Article Review in 9 Steps
Writing an article review is a process with several steps. Mastering these steps means you can review article by any writer and in any field. These skills will also come in handy if you’ll need to analyze research sources. Here are the major steps to follow when writing a review article:
Start your article review from preparation
Start by preparing to write the review. Preparation should entail organizing your workplace and making sure that you have all the resources required to review an article. This may include getting an article review sample or an article review template. Such materials can help you when it comes to organizing thoughts and getting ready for the task ahead.
Learn how to write a review of an article
Once you have materials like a sample and a template, start learning how to write an article review. This entails understanding what you are required to do when completing this task. You can find many resources online with information on how to write a review article. Take your time to learn more about the article review format and the writing process. But i f you have poor writing skills, you can hire our experts to write your paper online .
Essentially, this task requires you to summarize the main arguments, ideas, findings, and positions of the article. You also need to critique the material’s contributions and their overall effectiveness.
Your approach should depend on the kind of article you’re required to review. For instance, when learning how to review a research article, you will realize that you should not include new research. You just need to summarize and evaluate the article.
Read the article
You can’t review an article if you don’t know what it is all about. Therefore, start by reading the article carefully. This will enable you to know whether you need to write a science article review, a journal article review, or a law review article.
Once you’ve read the article, try to put it in your words. Additionally, come up with an evaluation outline. This will enable you to highlight the major points and other issues that should be featured in your review.
Research article review organization
You need to organize your review properly to make it easier for your audience to read. How you organize your review may depend on the instructions provided by the educator or professor. For instance, you may be required to write an APA article review. In that case, find out what the requirements of this writing style are.
Nevertheless, an ideal way to organize this write-up is to summarize the main claims, points, and information of an article and then discuss all positive aspects. Positive aspects can include the good insights, observations, and points of the author.
Once you have done that, identify contradictions, gaps, and inconsistencies in the work. Additionally, say whether the author has enough data or research to support their claims. Focus on finding unanswered questions in the work under review.
Start writing the review
By this time, you’ve known how to write a article review. If not, check out an article review example online to know what you’re expected to produce. Here’s how to write article review introduction:
- Write a title – This can be declarative, interrogative, or descriptive depending on your focus.
- Cite the focus article – Use the right style to cite the article after your review’s title.
- Identify the article – You can compose article identification by stating the article title, author, journal, and publication year.
This should appear in the first paragraph. As such, you need to know how to start an article review. The review introduction should include the article’s central themes, the author’s arguments, and claims. It is not an easy task to write a paper like that. The best way to get a high grade with little effort is to ask about online paper writing help from our expert writers.
Summarize the article
This is the section where you summarize the main arguments, findings, and points of the article using your words. Additionally, show your readers how the work supports the author’s claims. Here, you need to include several paragraphs and cite specific examples, background information, or statistics.
Every paragraph should include or expound on the main point. You can include direct quotes from the article author. For purposes of accuracy, read the summary a couple of time and correct mistakes.
Write a critique
You need to know how to write a critical review of a journal article to excel in this section. Here, tell your audience how well the article author has addressed their topic. Also, include your opinion about how useful or thorough the subject explanation is. Show the importance and contributions of the article under review in the field.
Discuss the central points and arguments of the article. Additionally, explain whether the points used by the author supported their argument. Show whether the author exhibited any biases. Additionally, tell your readers whether you concur with the article author. If you do, give reasons to support them and if you don’t, give reasons for disagreeing with them. What’s more, tell the readers about the audience that will benefit from the article you are reviewing.
Writing a critical review of journal article requires some research or knowledge of the industry. That’s because you need a basis for critiquing the work of another person. As such, take your time to read the article and compare it with the existing literature. You can even quote other experts in the industry to enhance the credibility of your critique.
Conclude your review
The conclusion of your review can be one or a few paragraphs depending on the size or length of the reviewed work. However, it should include a summary of the main points. Also, tell readers about the accuracy, significance, and clarity of the article that you have reviewed. If relevant, comment on the article’s implications. You can also say something about further research on the topic. It’s crucial to note that your review conclusion section should be 10% of the entire work. Therefore, be as brief as possible when writing this section.
Proofread your review
You may have written an exemplary review but few grammatical errors can ruin your grade. Therefore, reread the review carefully checking for grammatical errors and mechanics. Correct any mistake in your review and remove unnecessary information.
Writing a review should be easy if you follow these steps. However, it’s important to know what is peer review article if that’s what your instructor wants you to write. Essentially, know what exactly you’re required to write before you start. Additionally, get a good example of an article review to guide you. You can get one from your faculty or our academic writers. What’s more, use online resources to get tips and guidelines for writing a good review.
Otherwise, ask our professional writers to help you with your papers. You just need to write “Please, do my assignment for me now!” and we will write your paper soon.

Leave a Reply Cancel reply
Your email address will not be published. Required fields are marked *
Save my name, email, and website in this browser for the next time I comment.
Terms & Conditions Loyalty Program Privacy Policy Money-Back Policy
Copyright © 2013-2024 MyPaperDone.com
Have a language expert improve your writing
Run a free plagiarism check in 10 minutes, generate accurate citations for free.
- Knowledge Base
Methodology
- How to Write a Literature Review | Guide, Examples, & Templates
How to Write a Literature Review | Guide, Examples, & Templates
Published on January 2, 2023 by Shona McCombes . Revised on September 11, 2023.
What is a literature review? A literature review is a survey of scholarly sources on a specific topic. It provides an overview of current knowledge, allowing you to identify relevant theories, methods, and gaps in the existing research that you can later apply to your paper, thesis, or dissertation topic .
There are five key steps to writing a literature review:
- Search for relevant literature
- Evaluate sources
- Identify themes, debates, and gaps
- Outline the structure
- Write your literature review
A good literature review doesn’t just summarize sources—it analyzes, synthesizes , and critically evaluates to give a clear picture of the state of knowledge on the subject.
Instantly correct all language mistakes in your text
Upload your document to correct all your mistakes in minutes

Table of contents
What is the purpose of a literature review, examples of literature reviews, step 1 – search for relevant literature, step 2 – evaluate and select sources, step 3 – identify themes, debates, and gaps, step 4 – outline your literature review’s structure, step 5 – write your literature review, free lecture slides, other interesting articles, frequently asked questions, introduction.
- Quick Run-through
- Step 1 & 2
When you write a thesis , dissertation , or research paper , you will likely have to conduct a literature review to situate your research within existing knowledge. The literature review gives you a chance to:
- Demonstrate your familiarity with the topic and its scholarly context
- Develop a theoretical framework and methodology for your research
- Position your work in relation to other researchers and theorists
- Show how your research addresses a gap or contributes to a debate
- Evaluate the current state of research and demonstrate your knowledge of the scholarly debates around your topic.
Writing literature reviews is a particularly important skill if you want to apply for graduate school or pursue a career in research. We’ve written a step-by-step guide that you can follow below.

Here's why students love Scribbr's proofreading services
Discover proofreading & editing
Writing literature reviews can be quite challenging! A good starting point could be to look at some examples, depending on what kind of literature review you’d like to write.
- Example literature review #1: “Why Do People Migrate? A Review of the Theoretical Literature” ( Theoretical literature review about the development of economic migration theory from the 1950s to today.)
- Example literature review #2: “Literature review as a research methodology: An overview and guidelines” ( Methodological literature review about interdisciplinary knowledge acquisition and production.)
- Example literature review #3: “The Use of Technology in English Language Learning: A Literature Review” ( Thematic literature review about the effects of technology on language acquisition.)
- Example literature review #4: “Learners’ Listening Comprehension Difficulties in English Language Learning: A Literature Review” ( Chronological literature review about how the concept of listening skills has changed over time.)
You can also check out our templates with literature review examples and sample outlines at the links below.
Download Word doc Download Google doc
Before you begin searching for literature, you need a clearly defined topic .
If you are writing the literature review section of a dissertation or research paper, you will search for literature related to your research problem and questions .
Make a list of keywords
Start by creating a list of keywords related to your research question. Include each of the key concepts or variables you’re interested in, and list any synonyms and related terms. You can add to this list as you discover new keywords in the process of your literature search.
- Social media, Facebook, Instagram, Twitter, Snapchat, TikTok
- Body image, self-perception, self-esteem, mental health
- Generation Z, teenagers, adolescents, youth
Search for relevant sources
Use your keywords to begin searching for sources. Some useful databases to search for journals and articles include:
- Your university’s library catalogue
- Google Scholar
- Project Muse (humanities and social sciences)
- Medline (life sciences and biomedicine)
- EconLit (economics)
- Inspec (physics, engineering and computer science)
You can also use boolean operators to help narrow down your search.
Make sure to read the abstract to find out whether an article is relevant to your question. When you find a useful book or article, you can check the bibliography to find other relevant sources.
You likely won’t be able to read absolutely everything that has been written on your topic, so it will be necessary to evaluate which sources are most relevant to your research question.
For each publication, ask yourself:
- What question or problem is the author addressing?
- What are the key concepts and how are they defined?
- What are the key theories, models, and methods?
- Does the research use established frameworks or take an innovative approach?
- What are the results and conclusions of the study?
- How does the publication relate to other literature in the field? Does it confirm, add to, or challenge established knowledge?
- What are the strengths and weaknesses of the research?
Make sure the sources you use are credible , and make sure you read any landmark studies and major theories in your field of research.
You can use our template to summarize and evaluate sources you’re thinking about using. Click on either button below to download.
Take notes and cite your sources
As you read, you should also begin the writing process. Take notes that you can later incorporate into the text of your literature review.
It is important to keep track of your sources with citations to avoid plagiarism . It can be helpful to make an annotated bibliography , where you compile full citation information and write a paragraph of summary and analysis for each source. This helps you remember what you read and saves time later in the process.
The only proofreading tool specialized in correcting academic writing - try for free!
The academic proofreading tool has been trained on 1000s of academic texts and by native English editors. Making it the most accurate and reliable proofreading tool for students.

Try for free
To begin organizing your literature review’s argument and structure, be sure you understand the connections and relationships between the sources you’ve read. Based on your reading and notes, you can look for:
- Trends and patterns (in theory, method or results): do certain approaches become more or less popular over time?
- Themes: what questions or concepts recur across the literature?
- Debates, conflicts and contradictions: where do sources disagree?
- Pivotal publications: are there any influential theories or studies that changed the direction of the field?
- Gaps: what is missing from the literature? Are there weaknesses that need to be addressed?
This step will help you work out the structure of your literature review and (if applicable) show how your own research will contribute to existing knowledge.
- Most research has focused on young women.
- There is an increasing interest in the visual aspects of social media.
- But there is still a lack of robust research on highly visual platforms like Instagram and Snapchat—this is a gap that you could address in your own research.
There are various approaches to organizing the body of a literature review. Depending on the length of your literature review, you can combine several of these strategies (for example, your overall structure might be thematic, but each theme is discussed chronologically).
Chronological
The simplest approach is to trace the development of the topic over time. However, if you choose this strategy, be careful to avoid simply listing and summarizing sources in order.
Try to analyze patterns, turning points and key debates that have shaped the direction of the field. Give your interpretation of how and why certain developments occurred.
If you have found some recurring central themes, you can organize your literature review into subsections that address different aspects of the topic.
For example, if you are reviewing literature about inequalities in migrant health outcomes, key themes might include healthcare policy, language barriers, cultural attitudes, legal status, and economic access.
Methodological
If you draw your sources from different disciplines or fields that use a variety of research methods , you might want to compare the results and conclusions that emerge from different approaches. For example:
- Look at what results have emerged in qualitative versus quantitative research
- Discuss how the topic has been approached by empirical versus theoretical scholarship
- Divide the literature into sociological, historical, and cultural sources
Theoretical
A literature review is often the foundation for a theoretical framework . You can use it to discuss various theories, models, and definitions of key concepts.
You might argue for the relevance of a specific theoretical approach, or combine various theoretical concepts to create a framework for your research.
Like any other academic text , your literature review should have an introduction , a main body, and a conclusion . What you include in each depends on the objective of your literature review.
The introduction should clearly establish the focus and purpose of the literature review.
Depending on the length of your literature review, you might want to divide the body into subsections. You can use a subheading for each theme, time period, or methodological approach.
As you write, you can follow these tips:
- Summarize and synthesize: give an overview of the main points of each source and combine them into a coherent whole
- Analyze and interpret: don’t just paraphrase other researchers — add your own interpretations where possible, discussing the significance of findings in relation to the literature as a whole
- Critically evaluate: mention the strengths and weaknesses of your sources
- Write in well-structured paragraphs: use transition words and topic sentences to draw connections, comparisons and contrasts
In the conclusion, you should summarize the key findings you have taken from the literature and emphasize their significance.
When you’ve finished writing and revising your literature review, don’t forget to proofread thoroughly before submitting. Not a language expert? Check out Scribbr’s professional proofreading services !
This article has been adapted into lecture slides that you can use to teach your students about writing a literature review.
Scribbr slides are free to use, customize, and distribute for educational purposes.
Open Google Slides Download PowerPoint
If you want to know more about the research process , methodology , research bias , or statistics , make sure to check out some of our other articles with explanations and examples.
- Sampling methods
- Simple random sampling
- Stratified sampling
- Cluster sampling
- Likert scales
- Reproducibility
Statistics
- Null hypothesis
- Statistical power
- Probability distribution
- Effect size
- Poisson distribution
Research bias
- Optimism bias
- Cognitive bias
- Implicit bias
- Hawthorne effect
- Anchoring bias
- Explicit bias
A literature review is a survey of scholarly sources (such as books, journal articles, and theses) related to a specific topic or research question .
It is often written as part of a thesis, dissertation , or research paper , in order to situate your work in relation to existing knowledge.
There are several reasons to conduct a literature review at the beginning of a research project:
- To familiarize yourself with the current state of knowledge on your topic
- To ensure that you’re not just repeating what others have already done
- To identify gaps in knowledge and unresolved problems that your research can address
- To develop your theoretical framework and methodology
- To provide an overview of the key findings and debates on the topic
Writing the literature review shows your reader how your work relates to existing research and what new insights it will contribute.
The literature review usually comes near the beginning of your thesis or dissertation . After the introduction , it grounds your research in a scholarly field and leads directly to your theoretical framework or methodology .
A literature review is a survey of credible sources on a topic, often used in dissertations , theses, and research papers . Literature reviews give an overview of knowledge on a subject, helping you identify relevant theories and methods, as well as gaps in existing research. Literature reviews are set up similarly to other academic texts , with an introduction , a main body, and a conclusion .
An annotated bibliography is a list of source references that has a short description (called an annotation ) for each of the sources. It is often assigned as part of the research process for a paper .
Cite this Scribbr article
If you want to cite this source, you can copy and paste the citation or click the “Cite this Scribbr article” button to automatically add the citation to our free Citation Generator.
McCombes, S. (2023, September 11). How to Write a Literature Review | Guide, Examples, & Templates. Scribbr. Retrieved March 25, 2024, from https://www.scribbr.com/dissertation/literature-review/
Is this article helpful?
Shona McCombes
Other students also liked, what is a theoretical framework | guide to organizing, what is a research methodology | steps & tips, how to write a research proposal | examples & templates, "i thought ai proofreading was useless but..".
I've been using Scribbr for years now and I know it's a service that won't disappoint. It does a good job spotting mistakes”
- Search Menu
- Advance Articles
- Editor's Choice
- CME Reviews
- Best of 2021 collection
- Abbreviated Breast MRI Virtual Collection
- Contrast-enhanced Mammography Collection
- Author Guidelines
- Submission Site
- Open Access
- Self-Archiving Policy
- Accepted Papers Resource Guide
- About Journal of Breast Imaging
- About the Society of Breast Imaging
- Guidelines for Reviewers
- Resources for Reviewers and Authors
- Editorial Board
- Advertising Disclaimer
- Advertising and Corporate Services
- Journals on Oxford Academic
- Books on Oxford Academic

- < Previous
A Step-by-Step Guide to Writing a Scientific Review Article
- Article contents
- Figures & tables
- Supplementary Data
Manisha Bahl, A Step-by-Step Guide to Writing a Scientific Review Article, Journal of Breast Imaging , Volume 5, Issue 4, July/August 2023, Pages 480–485, https://doi.org/10.1093/jbi/wbad028
- Permissions Icon Permissions
Scientific review articles are comprehensive, focused reviews of the scientific literature written by subject matter experts. The task of writing a scientific review article can seem overwhelming; however, it can be managed by using an organized approach and devoting sufficient time to the process. The process involves selecting a topic about which the authors are knowledgeable and enthusiastic, conducting a literature search and critical analysis of the literature, and writing the article, which is composed of an abstract, introduction, body, and conclusion, with accompanying tables and figures. This article, which focuses on the narrative or traditional literature review, is intended to serve as a guide with practical steps for new writers. Tips for success are also discussed, including selecting a focused topic, maintaining objectivity and balance while writing, avoiding tedious data presentation in a laundry list format, moving from descriptions of the literature to critical analysis, avoiding simplistic conclusions, and budgeting time for the overall process.
- narrative discourse
Email alerts
Citing articles via.
- Recommend to your Librarian
- Journals Career Network
Affiliations
- Online ISSN 2631-6129
- Print ISSN 2631-6110
- Copyright © 2024 Society of Breast Imaging
- About Oxford Academic
- Publish journals with us
- University press partners
- What we publish
- New features
- Open access
- Institutional account management
- Rights and permissions
- Get help with access
- Accessibility
- Advertising
- Media enquiries
- Oxford University Press
- Oxford Languages
- University of Oxford
Oxford University Press is a department of the University of Oxford. It furthers the University's objective of excellence in research, scholarship, and education by publishing worldwide
- Copyright © 2024 Oxford University Press
- Cookie settings
- Cookie policy
- Privacy policy
- Legal notice
This Feature Is Available To Subscribers Only
Sign In or Create an Account
This PDF is available to Subscribers Only
For full access to this pdf, sign in to an existing account, or purchase an annual subscription.

10 Best Tips On How To Write An Article Review
Are you stressed because you don’t know How To Write An Article Review? Don’t panic! Practice helps you out in article review writing . As a student, we understand it is a challenging task. But it is a great way to improve your reading, analytical, writing, and scientific skills. So let’s start!
Before getting straight to reviewing an article, you should have some knowledge of what an article review is. So, an article review is a study of writing when you compile and access someone else’s article.
It involves a sensible evaluation of the theme of an article i.e. when you evaluate another persona’s article then there should be some point of reviewing the article.
A review can be a critical review or it can be a literature review i.e. you may or may not agree with the point the writer has made in his/her article.
A critical analysis is a comprehensive type of text dealing with a particular article or book in detail.
Sure, you can archive that dynamic content on How To Write An Article Review.
What Is An Article Review?
Table of Contents
An article review is a critical analysis of an academic article or research paper. It is written by experts in a particular field. The goal of an article review is to evaluate the quality, relevance, and significance of the article to the field and to provide a summary of its key points and arguments.
Moreover, article reviews are typically written by scholars, researchers, or students as a way to stay up-to-date with the latest developments in their field. It is used to assess the quality of published research critically. They are often published in academic journals or other educational publications.
The structure of an article review varies depending on the requirements of the assignment or the publication. However, most article reviews include an introduction that provides context for the article being reviewed, a summary of the article’s main points and arguments, a critical evaluation of the article’s strengths and weaknesses, and a conclusion that synthesizes the reviewer’s overall assessment of the article.
5 Types of article review
An article review is an evaluation and summary of someone else’s work, and it has a particular format and some guidelines to write, which you have to follow to review an article. Here, in this blog, we will provide you a complete guide on how to write an article review.
Reviewing an article is essential
- Because it helps the readers to understand the indefinite terms.
- Reviewing the article clarifies so many questions.
- As the review provides suggestion or analysis of the article to the author and that assists or helps the author to execute the work in a better way next time.
How To Write An Article Review: The pre-writing process
For reviewing an article in an excellent way, one should first prepare and then write the review.
And the formation of a review includes the following steps for How To Write A Good Article Review that you should follow: –
Step 1: – Understanding what the article review is
You should never underestimate the viewers as the viewers of the review already has information and knowledge on the topic and is not the general audience.
So first of all, you need to summarize all the main ideas of the article, the thoughts and all.
And you should also critique the participation of the matter and effectiveness of the field. The review of the article responds to the research of the authors and it does not include new analysis. The review assesses and summarizes the article.
Step 2: – Identify the organization of the review article
Before you even start to read the article you will review, you should know how your articles review will be set up and how does it work.
This will help you understand how to read the article. so that, you can get the maximum information out of it and write an effective review.
You should summarize the article and you should concentrate on the major points and information.
You should discuss the positive viewpoints of the article and think about what the author does well.
Identify all the contradictions and gaps in the text. You should also check if the author has done enough research on the topic he has written. And find if there are any questions left which are not being answered in the article.
Step 3: – Preview the article
Start by looking at the tile of the article, abstract and introduction and the headings of each paragraph of the article and the conclusion which the author has concluded.
Read the first few paragraphs just to get the idea of what the author wants to say and the article’s main point.
These steps should help you get the brief idea of the article and you will surely get the bigger picture of what is going on in the article and what the author wants to say. And by doing this you will get the look of the overall argument.

As soon as you start getting the idea of what is going on in the article, start making notes of it and start writing the questions you have in mind. Try to look for the terms and concepts you are unknown with so that you can read about those concepts and get some knowledge about it before writing the review.
Step 4: – Read the article carefully
Read the article very carefully just to make sure that you didn’t left any point the author wants to highlight.
Give it a few readings and the make notes of the essential sections. Just to highlight the main points and details.
Compare what you have read with to your actual understanding of the topic.
Pay careful attention to the meaning of the article. Make sure that you understand the article completely because half knowledge is the worst thing and by understanding the article completely you can write a good review.
Step 5: – Write the article in your own words.
After reading the article and writing the important points you should write the article again but in your own words and keep it in mind that you write the entire essential points accurately and in a logical manner. So, that it becomes easier for us to get any sort of info from the article by doing this. And then you should review the summary to discard useless items if any.
Step 6: – Write an outline of your evaluation.
After, reading and writing the article in your own words, review each and every detail in the article to discover.
Whether the author was correct and clear or not.
Write down all the instances of a productive script. And the articles that you feel, needs improvement with.
Create a record of strengths and weaknesses. The strength of the article can be a clear summation of any particular issue.
And the list of weaknesses that may any kind of weakness like it is not providing any new information on the topic or any information that you feel like that they are contradicting the facts.
And then, think about a few questions to help you critique and interconnect with the article: –
Here are some questions that you can think of to critique and engage with the article:-
- What is the point of the article?
- What is the theoretical structure and assumptions?
- Does the author define the concepts clearly?
- How satisfactory is the evidence?
- Is there transparency in the author’s writing?
- Transparency is the author’s writing?
- Does it advance the knowledge of the subject or it’s just the knowledge we can find anywhere?
Format of How To Write An Article Review: you must follow
1. Title page 2. Title ( Article name) 3. Your name 4. Date 5. Abstract: It must include around 200 to 30o words. It involves a review question summary, the study reviewed, and the study’s conclusions.
6. Introduction: It involves what the article contains. Also, it gives hints to the reader about the article and involves the background information to help the reader understand the article sections.
7. Body: It involves the main points in detail.
8. Conclusion: It sums up all the main points of your article review and states the article’s purpose.
9. Citation: You have to use a standardized reference system such as MLA, APA style , etc.
10. Format applications: Articles are commonly written in newspapers, websites, and academic journals.
Steps For How To Write An Article Review – Step-by-Step Guide
Now the answer to your question about How To Write An Article Review is here. Follow the steps while writing an article review-
step 1: – Come up with a unique title for the review.
The title you are thinking of giving to the review should consider the center of your review. You should choose between a declarative title, a descriptive title or interrogative title whichever suits the best according to your article needs.
step 2: – Cite the article.
Under the title of the article, Place a complete reference of the article in the proper form and manner. And then move to the next line to begin your article. And don’t skip a line between the citation and sentence.
step 3: – Identify the article
After the title and summoning the article you should start your review by relating to the title you have chosen for your review and author of the article and the title of the publication. And the year in the article was published should be written in the first paragraph.
steps 4: – Write the introduction of the review
The introduction of the article review should have the identifying sentence. It should also mention the fundamental theme of the article and the main aspect of the article and the thoughts and the claims by the author.
You also need to pronounce the author’s opinion.
Sometimes, there are multiple viewpoints in the thesis and the thesis may not the clearly stated than in that case, you may have to determine the thesis yourself and should write it by your own understanding and your own point of view.
step 5: – Summarizing the article
Now you have to start summarizing the main details, thoughts, and conclusions of the article in your words, pointing to your summary for assistance.
Then show how the article supports its claims and conclusions. Make sure that you don’t forget to add the conclusions of the article. Moreover, This may be done in some paragraphs, and its length will depend on the conditions established by your publisher.
step 6: – Write the critique
Now, you have to use all your article study and you have to write how thoroughly the author addressed the topic, by using your judgment.
And you should also write your opinion on how precise and useful the explanation of the subject you found in the article.
Write if you agree with the writer’s point or not.
If yes, then provide the reasons why you support the writer and if not then give the reason behind your judgment.
And then indicate the type of audience that can get benefit from reading the article.
Quick Links
- A Definitive Guide On How To Write A Literature Review Outline
- Best Of The Best Ways On How To Write A Critical Review By Experts
step 7: – Write what you have concluded from the article review.
After compiling all the main points in a paragraph. Write your own opinion about accuracy and clarity and the significance of the article in that paragraph. You can also mention if that implication is connected or not.
The conclusion should always only be at max 10% of the overall essay.
Step 8:- Proofread the work you have done: The post-writing process
To ensure that there is no mistake in the review you have written, you should always check on grammar and mechanics and check if there should not be any mistake.
Remove all sort of unnecessary information. And just for the sake of a good review you should identify and discuss 3-4 critical issues in the article.
Conclusion (How To Write An Article Review)
We all know writing a compelling and well-formatted article review is a difficult task, but now from the above discussion, we hope you get the answer to your question about How To Write An Article Review. It needs you to find the article from reliable sources, read it completely, analyze the information. So, follow the above steps carefully to write an impressive article review.
If you need any Article Review Help you can contact to Call Tutors . For more information, stay tuned with our blogs!
What are the five qualities of a good article?
The following is a brief description of five qualities of good writing: focus, development, unity, coherence, and correctness.
What makes a successful article?
An effective article is an article that achieves its goal. Now, that goal can be anything: To entertain, inform, or persuade someone to act.
What makes an article high quality?
High-quality content means writing about things your audience will find useful in a clear, understandable way.
Similar Articles

Top 19 Tips & Tricks On How To Improve Grades?
Do you want to improve your grades? If yes, then don’t worry! In this blog, I have provided 19 tips…

How To Study For Final Exam – 12 Proven Tips You Must Know
How To Study For Final Exam? Studying for the final exam is very important for academic success because they test…
Leave a Comment Cancel Reply
Your email address will not be published. Required fields are marked *
This site uses Akismet to reduce spam. Learn how your comment data is processed .
An official website of the United States government
The .gov means it’s official. Federal government websites often end in .gov or .mil. Before sharing sensitive information, make sure you’re on a federal government site.
The site is secure. The https:// ensures that you are connecting to the official website and that any information you provide is encrypted and transmitted securely.
- Publications
- Account settings
Preview improvements coming to the PMC website in October 2024. Learn More or Try it out now .
- Advanced Search
- Journal List
- PLoS Comput Biol
- v.9(7); 2013 Jul

Ten Simple Rules for Writing a Literature Review
Marco pautasso.
1 Centre for Functional and Evolutionary Ecology (CEFE), CNRS, Montpellier, France
2 Centre for Biodiversity Synthesis and Analysis (CESAB), FRB, Aix-en-Provence, France
Literature reviews are in great demand in most scientific fields. Their need stems from the ever-increasing output of scientific publications [1] . For example, compared to 1991, in 2008 three, eight, and forty times more papers were indexed in Web of Science on malaria, obesity, and biodiversity, respectively [2] . Given such mountains of papers, scientists cannot be expected to examine in detail every single new paper relevant to their interests [3] . Thus, it is both advantageous and necessary to rely on regular summaries of the recent literature. Although recognition for scientists mainly comes from primary research, timely literature reviews can lead to new synthetic insights and are often widely read [4] . For such summaries to be useful, however, they need to be compiled in a professional way [5] .
When starting from scratch, reviewing the literature can require a titanic amount of work. That is why researchers who have spent their career working on a certain research issue are in a perfect position to review that literature. Some graduate schools are now offering courses in reviewing the literature, given that most research students start their project by producing an overview of what has already been done on their research issue [6] . However, it is likely that most scientists have not thought in detail about how to approach and carry out a literature review.
Reviewing the literature requires the ability to juggle multiple tasks, from finding and evaluating relevant material to synthesising information from various sources, from critical thinking to paraphrasing, evaluating, and citation skills [7] . In this contribution, I share ten simple rules I learned working on about 25 literature reviews as a PhD and postdoctoral student. Ideas and insights also come from discussions with coauthors and colleagues, as well as feedback from reviewers and editors.
Rule 1: Define a Topic and Audience
How to choose which topic to review? There are so many issues in contemporary science that you could spend a lifetime of attending conferences and reading the literature just pondering what to review. On the one hand, if you take several years to choose, several other people may have had the same idea in the meantime. On the other hand, only a well-considered topic is likely to lead to a brilliant literature review [8] . The topic must at least be:
- interesting to you (ideally, you should have come across a series of recent papers related to your line of work that call for a critical summary),
- an important aspect of the field (so that many readers will be interested in the review and there will be enough material to write it), and
- a well-defined issue (otherwise you could potentially include thousands of publications, which would make the review unhelpful).
Ideas for potential reviews may come from papers providing lists of key research questions to be answered [9] , but also from serendipitous moments during desultory reading and discussions. In addition to choosing your topic, you should also select a target audience. In many cases, the topic (e.g., web services in computational biology) will automatically define an audience (e.g., computational biologists), but that same topic may also be of interest to neighbouring fields (e.g., computer science, biology, etc.).
Rule 2: Search and Re-search the Literature
After having chosen your topic and audience, start by checking the literature and downloading relevant papers. Five pieces of advice here:
- keep track of the search items you use (so that your search can be replicated [10] ),
- keep a list of papers whose pdfs you cannot access immediately (so as to retrieve them later with alternative strategies),
- use a paper management system (e.g., Mendeley, Papers, Qiqqa, Sente),
- define early in the process some criteria for exclusion of irrelevant papers (these criteria can then be described in the review to help define its scope), and
- do not just look for research papers in the area you wish to review, but also seek previous reviews.
The chances are high that someone will already have published a literature review ( Figure 1 ), if not exactly on the issue you are planning to tackle, at least on a related topic. If there are already a few or several reviews of the literature on your issue, my advice is not to give up, but to carry on with your own literature review,

The bottom-right situation (many literature reviews but few research papers) is not just a theoretical situation; it applies, for example, to the study of the impacts of climate change on plant diseases, where there appear to be more literature reviews than research studies [33] .
- discussing in your review the approaches, limitations, and conclusions of past reviews,
- trying to find a new angle that has not been covered adequately in the previous reviews, and
- incorporating new material that has inevitably accumulated since their appearance.
When searching the literature for pertinent papers and reviews, the usual rules apply:
- be thorough,
- use different keywords and database sources (e.g., DBLP, Google Scholar, ISI Proceedings, JSTOR Search, Medline, Scopus, Web of Science), and
- look at who has cited past relevant papers and book chapters.
Rule 3: Take Notes While Reading
If you read the papers first, and only afterwards start writing the review, you will need a very good memory to remember who wrote what, and what your impressions and associations were while reading each single paper. My advice is, while reading, to start writing down interesting pieces of information, insights about how to organize the review, and thoughts on what to write. This way, by the time you have read the literature you selected, you will already have a rough draft of the review.
Of course, this draft will still need much rewriting, restructuring, and rethinking to obtain a text with a coherent argument [11] , but you will have avoided the danger posed by staring at a blank document. Be careful when taking notes to use quotation marks if you are provisionally copying verbatim from the literature. It is advisable then to reformulate such quotes with your own words in the final draft. It is important to be careful in noting the references already at this stage, so as to avoid misattributions. Using referencing software from the very beginning of your endeavour will save you time.
Rule 4: Choose the Type of Review You Wish to Write
After having taken notes while reading the literature, you will have a rough idea of the amount of material available for the review. This is probably a good time to decide whether to go for a mini- or a full review. Some journals are now favouring the publication of rather short reviews focusing on the last few years, with a limit on the number of words and citations. A mini-review is not necessarily a minor review: it may well attract more attention from busy readers, although it will inevitably simplify some issues and leave out some relevant material due to space limitations. A full review will have the advantage of more freedom to cover in detail the complexities of a particular scientific development, but may then be left in the pile of the very important papers “to be read” by readers with little time to spare for major monographs.
There is probably a continuum between mini- and full reviews. The same point applies to the dichotomy of descriptive vs. integrative reviews. While descriptive reviews focus on the methodology, findings, and interpretation of each reviewed study, integrative reviews attempt to find common ideas and concepts from the reviewed material [12] . A similar distinction exists between narrative and systematic reviews: while narrative reviews are qualitative, systematic reviews attempt to test a hypothesis based on the published evidence, which is gathered using a predefined protocol to reduce bias [13] , [14] . When systematic reviews analyse quantitative results in a quantitative way, they become meta-analyses. The choice between different review types will have to be made on a case-by-case basis, depending not just on the nature of the material found and the preferences of the target journal(s), but also on the time available to write the review and the number of coauthors [15] .
Rule 5: Keep the Review Focused, but Make It of Broad Interest
Whether your plan is to write a mini- or a full review, it is good advice to keep it focused 16 , 17 . Including material just for the sake of it can easily lead to reviews that are trying to do too many things at once. The need to keep a review focused can be problematic for interdisciplinary reviews, where the aim is to bridge the gap between fields [18] . If you are writing a review on, for example, how epidemiological approaches are used in modelling the spread of ideas, you may be inclined to include material from both parent fields, epidemiology and the study of cultural diffusion. This may be necessary to some extent, but in this case a focused review would only deal in detail with those studies at the interface between epidemiology and the spread of ideas.
While focus is an important feature of a successful review, this requirement has to be balanced with the need to make the review relevant to a broad audience. This square may be circled by discussing the wider implications of the reviewed topic for other disciplines.
Rule 6: Be Critical and Consistent
Reviewing the literature is not stamp collecting. A good review does not just summarize the literature, but discusses it critically, identifies methodological problems, and points out research gaps [19] . After having read a review of the literature, a reader should have a rough idea of:
- the major achievements in the reviewed field,
- the main areas of debate, and
- the outstanding research questions.
It is challenging to achieve a successful review on all these fronts. A solution can be to involve a set of complementary coauthors: some people are excellent at mapping what has been achieved, some others are very good at identifying dark clouds on the horizon, and some have instead a knack at predicting where solutions are going to come from. If your journal club has exactly this sort of team, then you should definitely write a review of the literature! In addition to critical thinking, a literature review needs consistency, for example in the choice of passive vs. active voice and present vs. past tense.
Rule 7: Find a Logical Structure
Like a well-baked cake, a good review has a number of telling features: it is worth the reader's time, timely, systematic, well written, focused, and critical. It also needs a good structure. With reviews, the usual subdivision of research papers into introduction, methods, results, and discussion does not work or is rarely used. However, a general introduction of the context and, toward the end, a recapitulation of the main points covered and take-home messages make sense also in the case of reviews. For systematic reviews, there is a trend towards including information about how the literature was searched (database, keywords, time limits) [20] .
How can you organize the flow of the main body of the review so that the reader will be drawn into and guided through it? It is generally helpful to draw a conceptual scheme of the review, e.g., with mind-mapping techniques. Such diagrams can help recognize a logical way to order and link the various sections of a review [21] . This is the case not just at the writing stage, but also for readers if the diagram is included in the review as a figure. A careful selection of diagrams and figures relevant to the reviewed topic can be very helpful to structure the text too [22] .
Rule 8: Make Use of Feedback
Reviews of the literature are normally peer-reviewed in the same way as research papers, and rightly so [23] . As a rule, incorporating feedback from reviewers greatly helps improve a review draft. Having read the review with a fresh mind, reviewers may spot inaccuracies, inconsistencies, and ambiguities that had not been noticed by the writers due to rereading the typescript too many times. It is however advisable to reread the draft one more time before submission, as a last-minute correction of typos, leaps, and muddled sentences may enable the reviewers to focus on providing advice on the content rather than the form.
Feedback is vital to writing a good review, and should be sought from a variety of colleagues, so as to obtain a diversity of views on the draft. This may lead in some cases to conflicting views on the merits of the paper, and on how to improve it, but such a situation is better than the absence of feedback. A diversity of feedback perspectives on a literature review can help identify where the consensus view stands in the landscape of the current scientific understanding of an issue [24] .
Rule 9: Include Your Own Relevant Research, but Be Objective
In many cases, reviewers of the literature will have published studies relevant to the review they are writing. This could create a conflict of interest: how can reviewers report objectively on their own work [25] ? Some scientists may be overly enthusiastic about what they have published, and thus risk giving too much importance to their own findings in the review. However, bias could also occur in the other direction: some scientists may be unduly dismissive of their own achievements, so that they will tend to downplay their contribution (if any) to a field when reviewing it.
In general, a review of the literature should neither be a public relations brochure nor an exercise in competitive self-denial. If a reviewer is up to the job of producing a well-organized and methodical review, which flows well and provides a service to the readership, then it should be possible to be objective in reviewing one's own relevant findings. In reviews written by multiple authors, this may be achieved by assigning the review of the results of a coauthor to different coauthors.
Rule 10: Be Up-to-Date, but Do Not Forget Older Studies
Given the progressive acceleration in the publication of scientific papers, today's reviews of the literature need awareness not just of the overall direction and achievements of a field of inquiry, but also of the latest studies, so as not to become out-of-date before they have been published. Ideally, a literature review should not identify as a major research gap an issue that has just been addressed in a series of papers in press (the same applies, of course, to older, overlooked studies (“sleeping beauties” [26] )). This implies that literature reviewers would do well to keep an eye on electronic lists of papers in press, given that it can take months before these appear in scientific databases. Some reviews declare that they have scanned the literature up to a certain point in time, but given that peer review can be a rather lengthy process, a full search for newly appeared literature at the revision stage may be worthwhile. Assessing the contribution of papers that have just appeared is particularly challenging, because there is little perspective with which to gauge their significance and impact on further research and society.
Inevitably, new papers on the reviewed topic (including independently written literature reviews) will appear from all quarters after the review has been published, so that there may soon be the need for an updated review. But this is the nature of science [27] – [32] . I wish everybody good luck with writing a review of the literature.
Acknowledgments
Many thanks to M. Barbosa, K. Dehnen-Schmutz, T. Döring, D. Fontaneto, M. Garbelotto, O. Holdenrieder, M. Jeger, D. Lonsdale, A. MacLeod, P. Mills, M. Moslonka-Lefebvre, G. Stancanelli, P. Weisberg, and X. Xu for insights and discussions, and to P. Bourne, T. Matoni, and D. Smith for helpful comments on a previous draft.
Funding Statement
This work was funded by the French Foundation for Research on Biodiversity (FRB) through its Centre for Synthesis and Analysis of Biodiversity data (CESAB), as part of the NETSEED research project. The funders had no role in the preparation of the manuscript.

Writing a review article: what to do with my literature review

Introduction
Review articles allow the readers to get a landscape view of a topic, but readers can also use the collection of references cited in a review article to dig deeper into a topic. Thus, they are valuable resources to consult. Well written review articles are often highly cited and could increase the visibility and reputation of the authors.
Decisions to make before starting to write a review article
It might be tempting to consider adapting a literature review, that is part of an article, proposal or dissertation, into a published review article. Such a literature review can be used as a starting point to build a review article upon. However, a literature review often does not follow the quality criteria of a formal review article or specific types of reviews and therefore should be reworked based on the steps illustrated in this editorial.
Types of review articles suitable for chemistry education research and practice
Perspectives, narrative and integrative reviews, systematic reviews, meta-analyses, appropriate ways of approaching a (systematic) review – writing a review step-by-step, step 1. topic and research question.
After the topic is chosen, it may be helpful to narrow the review down to a clear aim or question that the review seeks to answer. This helps to facilitate the selection of the publications to be reviewed. In addition to the topic, the author should seek to clarify the aim of the review by identifying the likely audience for such a review and how these individuals would benefit from this particular review. Review articles should explicitly mention the nature and scope of the intended review, as well as making a case for who would benefit from the review and how they would benefit.
Step 2. Determine the search and selection criteria
Step 3. inclusion or exclusion of publications, step 4. synthesis of results, step 5. check for clarity and bias, how should review articles be cited as a reference in cerp manuscripts, reflections on the impact of a review article.
One can raise the question of whether a review article is actually supportive or harmful for the original articles included ( Ketcham and Crawford, 2007 ). Authors tend to cite a review article more often compared to original work, thus lowering the number of citations for the respective articles. However, on the other hand, if studies are included and discussed in a review, readers who would like to learn more or access the original perspectives tend to download, read and possibly cite them as well. The benefits of publishing review articles clearly outweigh any potential shortcomings, and their scarcity in the field of chemistry education opens up a venue for publication calls.
- Alfieri L., Nokes-Malach T. J. and Schunn C. D., (2013), Learning Through Case Comparisons: A Meta-Analytic Review, Educ. Psychol. , 48 , 87–113.
- Bisra K., Liu Q., Nesbit J. C., Salimi F. and Winne P. H., (2018), Inducing Self-Explanation: a Meta-Analysis, Educ. Psychol. Rev. , 30 , 703–725.
- Castro-Alonso J. C., de Koning B. B., Fiorella L. and Paas F., (2021), Five Strategies for Optimizing Instructional Materials: Instructor- and Learner-Managed Cognitive Load, Educ. Psychol. Rev. , DOI: 10.1007/s10648-021-09606-9 .
- Flaherty A. A., (2020), A review of affective chemistry education research and its implications for future research, Chem. Educ. Res. Pract. , 21 , 698–713.
- Freeman S., Eddy S. L., McDonough M., Smith M. K., Okoroafor N., Jordt H. and Wenderoth M. P., (2014), Active learning increases student performance in science, engineering, and mathematics, Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U. S. A. , 111 , 8410–8415.
- Kahveci A., (2013), in Tsaparlis G. and Sevian H. (ed.), Concepts of Matter in Science Education , Dordrecht: Springer, pp. 249–278.
- Ketcham C. M. and Crawford J. M., (2007), The impact of review articles, Lab. Invest. , 87 , 1174–1185.
- Rahman M. T. and Lewis S. E., (2020), Evaluating the evidence base for evidence-based instructional practices in chemistry through meta-analysis, J. Res. Sci. Teach. , 57 , 765–693.
- Taber K. S., (2014), The significance of implicit knowledge for learning and teaching chemistry, Chem. Educ. Res. Pract. , 15 , 447–461.
- Taylor and Francis, (2021), What is a review article?, https://authorservices.taylorandfrancis.com/publishing-your-research/writing-your-paper/how-to-write-review-article/.
- Theobald E. J., Hill M. J., Tran E., Agrawal S., Arroyo E. N., Behling S., Chambwe N., Cintrón D. L., Cooper J. D., Dunster G., Grummer J. A., Hennessey K., Hsiao J., Iranon N., Jones L., Jordt H., Keller M., Lacey M. E., Littlefield C. E., Lowe A., Newman S., Okolo V., Olroyd S., Peecook B. R., Pickett S. B., Slager D. L., Caviedes-Solis I. W., Stanchak K. E., Sundaravardan V., Valdebenito C., Williams C. R., Zinsli K. and Freeman S., (2020), Active learning narrows achievement gaps for underrepresented students in undergraduate science, technology, engineering, and math, Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U. S. A. , 117 , 6476–6483.
- 66 Ogoja Road, Abakaliki, Ebonyi State 23480 NG.
- Sun - Fri 24Hours Saturday CLOSED
- support [@] writersking.com
- +23480-6075-5653 Hot Line

- Data Collection/Analysis
- Hire Proposal Writers
- Hire Essay Writers
- Hire Paper Writers
- Proofreading Services
- Thesis/Dissertation Writers
- Virtual Supervisor
- Turnitin Checker
- Book Chapter Writer
- Hire Business Writing Services
- Hire Blog Writers
- Writers King TV
- Proposal Sample
- Chapter 1-3 Sample
- Term Paper Sample
- Report Assignment Sample
- Course work Sample
- Payment Options
- Privacy Policy
- Terms of Service/Use
- Business Guide
- Academic Writing Guide
- General Writing Guide
- Research News
- Writing Paper Samples
- March 9, 2022
- Posted by: IGBAJI UGABI
- Category: Academic Writing Guide

Writing Article Review -Meaning, Uses, types, structure and 6 Steps to writing an article review
What is an article review.
An article review is a piece of writing which summarizes one’s general understanding of a desired topic or subject matter. In other words, it is an article written for the sole aim of summarizing, examining and evaluating previously published studies regarding a particular subject matter.
Content Outline
It is written for an audience knowledgeable in the general subject matter of the reviewed article, that way, it will be easier for the audience to either agree or disagree with the writer’s views on the proposed topic.
An Article review is an academic article which summarizes the current state of understanding regarding a particular topic. It can also be regarded as a piece of writing which contains the different theories, research methods and conclusions from specific scholars regarding a particular topic.
Hence, an Article review can be regarded as a secondary source of information because it does not contain new analysis or theories concerning the subject matter of the research, it only includes past research which has been conducted on behalf of the subject matter.
What is the purpose of an article review?
The general purpose of article reviews includes the following:
- It serves as a medium for one to express his/her views regarding the written work of another scholar or writer.
- It gives prospective readers an insight into the reviewed work, hence, making them decide whether or not to read the work.
- It serves as a forum for scholars to exchange ideas or views regarding the reviewed work.
What is the use of an Article Review?
In academic writing, an Article review is used for the following:
- It is used by both lecturers and students as a tool for the proper analysis and evaluation of a particular topic.
- Since it contains different theories and views of the subject matter, it gives scholars a much better understanding of the subject matter.
- It is used to criticize and create new ideas as well as conclusions on a particular topic.
- It is used to single out the loopholes in a particular theory or ideology.
- It is used to identify the core theories and ideologies regarding a particular subject matter.
- It is used to identify the current state of understanding regarding a particular subject matter.
What are the types of Article Reviews?
An article review can be grouped into three main categories namely:
- Research Article Review.
- Journal Article Review.
- Science Article Review.
What is the structure of an Article review?
Just like other forms of academic writing, the main structure of an Article review includes:
- Introduction.
- Conclusion.
Writing the Introductory part of an Article Review:
The introductory part of an Article review can be written in the following steps:
- Write the Topic of the Article Review:
It is important to notify the readers or lecturers about the topic of the article review right at the beginning. If you were not given a specific topic for your Article review, you can start out by selecting the right topic for the article review. While selecting a topic, note the following points:
- The topic should be related to a popular subject matter in your discipline.
- The topic should be of interest to both you and your reader/lecturer. This way, it will be easy to source for past scholarly works relating to the topic and read them with an open mind. Similarly, it ought to be of interest to your reader/lecturer so that he/she will be able to go through the review with an adequate amount of gusto.
- Cite past scholarly work.
This is a very important aspect of the article review, in fact, the reliance, summarizing and criticism of past scholarly work relating to the subject matter is what makes the academic piece a review. Note that citations differ depending on your discipline.
For instance, students in Psychology and other social science-related disciplines will use the APA referencing style. Whereas, the students in Film and Theatre studies and other Arts related topics will make use of the MLA formatting style. Remember to use the updated versions of these referencing styles to cite the article review.
A clear illustration of the first two stages of the introductory part of an Article review includes:
THE ADVANTAGES OF SMALL BUSINESSES IN NIGERIA.
Articles Reviewed:
Abdulrahman.,A(2021). Intellectual Property, SMEs and Economic Recovery in Nigeria.
If you are asked to review different topics relating to a singular subject matter and you are asked to review more than five articles. Structure your introduction in the following way:
- Places the articles under different subheadings.
- Arrange the articles in Alphabetical order or according the the order required of the referencing style in your designated discipline.
ADVANTAGES OF SMALL BUSINESSES IN NIGERIA.
Abioye.,O.,Oguniyi.,A.,Olagunju.,K(2020). Estimating the Impact of COVID-19 on Small and Medium Scale Enterprise: Evidence from Nigeria.
Eze.,F.,Ikenna.,Ruhode.,E.,Iwu.,G.,Chux(2018). A Critical look at the necessity of small businesses in Nigeria. A theoretical review.
(CONCLUSION)
ADVANTAGES OF SMALL BUSINESSES IN AFRICA.
(Citations)
(Conclusion)
Writing the body of an Article Review:
The body of an Article review can be written in the following steps:
- Identify the Scholarly Work:
The article review must always commence with the proper referencing of the name of the scholarly work, the author and the date that the work was published.
For example:
The article ‘ Intellectual Property, SMEs and Economic Recovery in Nigeria’ by Abdulrahman.,A(2021)
After commencing in this manner, the writer can move on to the next step of the article review.
- State the main thesis of the reviewed scholarly work and the reason why such work was written:
After identifying the scholarly work, the next step will be to establish the main thesis of the author as well as the reason why such an article was written. Words like ‘aims’, ‘relies on’, ‘establishes’ and so on, can be used as a conjunction between the last step and this current one.
The article ‘ Intellectual Property, SMEs and Economic Recovery in Nigeria’ by Abdulrahman.,A(2021) relies on the stagnation of the Nigerian economy and provides valid solutions which can amount to its growth.
- Summarize the article:
Most scholarly articles tend to be vast in size and oftentimes, an article review can only contain a specific amount of words. Hence, it will be quite impossible for one to summarize the whole article in most cases. In order to go around the issue, the writer can identify the vital areas in the article.
For example, if the article centres on the problems and solutions revolving around the subject matter, the writer can provide a brief summary of both the problems and solutions and sieve out the unnecessary parts in the article. In order for the writer to be able to do this efficiently, he/she must:
- Pick out a familiar topic.
- Understand the topic.
- Read, understand and evaluate the articles relating to the topic thoroughly.
- Criticize the reviewed Article:
This is one of the most important aspects in the body of the article review. In order to adequately get the job done in this section, the writer must:
- Identify the strengths and weaknesses of the article.
- Ascertain whether or not the message which was passed by the author was as clear and concise as possible.
- Evaluate the main points and arguments in the article.
- Ascertain whether or not these arguments are relevant to the subject matter and its designated discipline.
- Identify any area of contradiction or bias in the research.
- Decide whether or not to agree with the author’s ideology relating to the topic.
In order to make these points more realistic, the writer can rely on the arguments or main points in the article or in other related articles. However, remember that all the articles which were relied on during the course of the criticism ought to be properly referenced, in order to avoid plagiarism.
Writing the Concluding part of the Article Review:
In order to properly conclude an article review, the writer must:
- Summarize the main points of the article.
- Summarize his/her final views of the reviewed article.
- Briefly state the level of accuracy which ought to be affiliated with the research.
- State the significance of further research relating to the article, if necessary.
Step-by-step guidelines for writing an Article Review
In order to compose a well-structured article review, the following measures must be taken accordingly, they include:
Commence with an Article Review Outline
In a nutshell, an outline can be defined as a summarized structure of what an academic piece of writing ought to look like. In other words, it is a brief piece of writing composed for the sole aim of directing the writer on what to write in his/her proposed article and how to go about it.
An outline is composed by the writer of the article review. In order to produce an outline, the writer must, first of all, have a general insight about the article that he/she ought to review.
That way, it will be easier to create, recreate and arrange subheadings for the article review in the outline. Hence, a writer is advised to conduct proper research or have proper knowledge of the article he/she ought to write a review about before commencing the writing process.
It should be noted that the use of outlines in academic writing is not restricted to the composition of article reviews only, in fact, students or scholars are advised to draft an outline before writing any academic piece.
Write the header with a citation
A header is a continuous line of text which is inputted at the top of a page. It ought to include the writer’s identification as well as the title of the work and its page number. An ideal article review ought to include a header that will contain the necessary information as regards the writer’s identity as well as a citation of the work or piece which is under review. The referencing style which will be used for the citation of the piece under review entirely depends on the discipline to which the piece belongs.
For example , if the writer ought to review an academic piece revolving around the social sciences discipline, the whole paper and the citation of the book under review ought to be composed in APA style. Hence, the necessary credentials needed for APA style includes the author’s last name, the title of the article, the name of the journal in which the article belongs, volume and issue numbers as well as the page numbers of the article.
Kick-off with a summary of the article
The summary of the article under review ought to be inculcated in the introductory part of the review. The introductory part of the review will also provide a brief overview in regard to the topics that will be discussed in detail in the body of the review.
Such topics could include the intention of the author while composing the piece, the strengths and weaknesses of the written piece, whether or not the subject matter of the article was aptly understood and agreed upon, how the article related to other works published under the same veil and so on.
It should be noted that an ideal article ought to contain five chapters, one for the introduction, three for the body of the review and one for the conclusion. Additional paragraphs can be included as a means of proper evaluation of the work, however, depending on its nature and scope.
Writing the body of the Review
As fore mentioned in the text, the body of the review ought to critically examine the opinions of the writer regarding the article under review. In other words, the main duty of the writer in this section is to criticize the article under review. The term ‘criticize under this veil is to expose the strengths, weaknesses, achievements and limitations of the article.
Similarly, the writer of the article review ought to provide a standardized percentage of the knowledge that the initial author of the work has contributed to a particular field.
After critically analyzing the work, the writer decides whether or not to support the points or views provided by the author in the original article and states the reasons behind the decision taken.
Draft a Conclusion
Before the commencement of this section, the writer is advised to go back to the article review he/she has composed and bring out its key points. The key points in this context refer to the findings and criticisms stated in the body of the work.
If the writer does this, it will be easier to provide a concise summary of the body of the review as well as the relevance of these findings in the conclusion. The writer is not permitted to introduce any new points in this section, instead, he/she should figure out the best way to wrap up the review with its past provisions.
Proofread the written work
To proofread simply means to cross-check the work in the bid to eliminate errors that were not previously identified. The errors in this context could refer to sentences, punctuation and spelling mistakes.
Although this last step is often neglected by both students and scholars alike, it plays an important role in any form of academic writing. Hence, the writer is advised to reread the works and eliminate ideas as well as unnecessary or overused words in the article. If the article emerges spotless, it is ready for submission.
Drop your comment, question or suggestion for the post improvement Cancel reply

Find Us Today
Writers King LTD, Akachukwu Plaza,
66 Ogoja Road Abakaliki, Ebonyi State,
480101 Nigeria
Phone: 0806-075-5653
- Website: https://writersking.com/
- Email: support {@} writersking.com
- +2348060755653
Quick Links
Writing guide.
A Step-by-Step Guide to Writing a Stellar Literature Review (with Help from AI)

Table of contents

Aren’t all of us mini versions of Sherlock Holmes when browsing data and archives for a research piece? As we go through the process, a comprehensive literature review is an essential toolkit to make your research shine.
A literature review consists of scholarly sources that validate the content. Its primary objective is to offer a concise summary of the research and to let you explore relevant theories and methodologies. Through this review, you can identify gaps in the existing research and bridge them with your contribution.
The real challenge is how to write an excellent literature review. Let’s learn.
What is the purpose of a literature review?
A literature review is an introduction to your research. It helps you put your perspective to the table, along with a summary of the theme.
What does my literature review communicate?
- Explanation of your research: how the information was collected, the research method, the justification of the chosen data sources, and an overview of the data analysis.
- Framework: the journey from where the concept began and how it is presented.
- Connects the previous and current research:
It presents the broader scope of your research by connecting it to the existing data and debates and underlining how your content fits the prevailing studies.
In an era of information overload, a literature review must be well-structured.
Let’s learn all about the structure and style of a literature review that’ll help you strengthen your research.
Literature review– structure and style
Begin with a question and end it with the solution– the key to structuring a literature review. It resembles an essay’s format, with the first paragraph introducing the readers to the topic and the following explaining the research in-depth.
The conclusion reiterates the question and summarizes the overall insights of your research. There’s no word count restriction. —it depends on the type of research. For example, a dissertation demands lengthy work, whereas a short paper needs a few pages.
In a literature review, maintaining high quality is vital, with a focus on academic writing style. Informal language should be avoided in favor of a more formal tone.
The content avoids contractions, clearly differentiating between previous and current research through the use of past and present tense. Wordtune assists in establishing a formal tone, enhancing your work with pertinent suggestions. This AI-powered tool ensures your writing remains genuine, lucid, and engaging.

The option of refining the tonality offers multiple possibilities for rephrasing a single sentence. Thus, pick the best and keep writing.
Get Wordtune for free > Get Wordtune for free >
Your friendly step-by-step guide to writing a literary review (with help from AI)
Do you find it challenging to begin the literature review? Don’t worry! We’re here to get you started with our step-by-step guide.
1. Narrow down the research scope
Simply begin with the question: What am I answering through my research?
Whether it’s cooking or painting, the real challenge is the prep-up for it rather than performing the task. Once you’re done, it smoothly progresses. Similarly, for your literature review, prepare the groundwork by narrowing down the research scope.
Browse and scoop out relevant data inclining well with your research. While you can’t cover every aspect of your research, pick a topic that isn’t too narrow nor too broad to keep your literature review well-balanced.
2. Hunt relevant literature
The next question: Does this data align with the issue I’m trying to address?
As you review sources of information, hunt out the best ones. Determine which findings help in offering a focused insight on your topic. The best way to pick primary sources is to opt for the ones featured in reliable publications. You can also choose secondary sources from other researchers from a reasonable time frame and a relevant background.
For example, if your research focuses on the Historical Architecture of 18th-century Europe, the first-hand accounts and surveys from the past would hold more weight than the new-age publications.
3. Observe the themes and patterns in sources
Next comes: What is the core viewpoint in most of the research? Has it stayed constant over time, or have the authors differed in their points of view?
Ensure to scoop out the essential aspects of what each source represents. Once you have collected all this information, combine it and add your interpretations at the end. This process is known as synthesis.
Synthesize ideas by combining arguments, findings and forming your new version.
4. Generate an outline
The next question: How can I organize my review effectively? When navigating multiple data sources, you must have noticed a structure throughout the research. Develop an outline to make the process easier. An outline is a skeletal format of the review, helping you connect the information more strategically.
Here are the three different ways to organize an outline– Chronologically, Thematically, or by Methodology.You can develop the outline chronologically, starting from the older sources and leading to the latest pieces. Another way of organizing is to thematically divide the sections and discuss each under the designated sub-heading.
You can even organize it per the research methods used by the respective authors. The choice of outline depends on the subject. For example, in the case of a science paper, you can divide the information into sections like introduction, types of equipment, method, procedure, findings, etc. In contrast, it’s best to present it in divisions based on timelines like Ancient, Middle Ages, Industrial revolutions, etc., for a history paper.
If you’re confused about how to structure the data, work with Wordtune.

With the Generate with AI feature, you can mention your research topic and let Wordtune curate a comprehensive outline for your study.

Having a precise prompt is the key to getting the best results.
5. Start filling!
Your next question must be: Am I ready to compose all the parts of the literature review?
Once you’re ready with the basic outline and relevant sources, start filling in the data. Go for an introductory paragraph first to ensure your readers understand the topic and how you will present it. Ensure you clearly explain the section in the first sentence.
However, if beginning from the first paragraph seems intimidating, don’t worry! Add the main body content to the sub-headings, then jump to the introduction.
Add headings wherever possible to make it more straightforward and guide your readers logically through different sources. Lastly, conclude your study by presenting a key takeaway and summarizing your findings. To make your task easier, work with Wordtune. It helps align your content with the desired tone and refine the structure.
6. Give attention to detail and edit
The last question: Am I satisfied with the language and content written in the literature review? Is it easy to understand?
Once you’re done writing the first draft of a literature review, it’s time to refine it. Take time between writing and reading the draft to ensure a fresh perspective. It makes it easier to spot errors when you disconnect from the content for some time. Start by looking at the document from a bird's eye to ensure the formatting and structure are in order.
After reviewing the content format, you must thoroughly check your work for grammar, spelling, and punctuation. One of the best approaches to editing and proofreading is to use Wordtune . It helps simplify complex sentences, enhance the content quality, and gain prowess over the tonality.
The dos and don’ts of writing a literature review
Writing a stellar literature review requires following a few dos and don'ts. Just like Sherlock Holmes would never overlook a hint, you must pay attention to every minute detail while writing a perfect narrative. To help you write, below are some dos and don'ts to remember.

Composing a literature review demands a holistic research summary, each part exhibiting your understanding and approach. As you write the content, make sure to cover the following points:
- Keep a historical background of the field of research. Highlight the relevant relation between the old studies and your new research.
- Discuss the core issue, question, and debate of your topic.
- Theories lay the foundation of research. While you’re writing a literature review, make sure to add relevant concepts and ideas to support your statements.
- Another critical thing to keep in mind is to define complex terminologies. It helps the readers understand the content with better clarity.
Examples of comprehensive literature reviews
Aren’t good examples the best way to understand a subject? Let’s look into a few examples of literature reviews and analyze what makes them well-written.
1. Critical Thinking and Transferability: A Review of the Literature (Gwendolyn Reece)
An overview of scholarly sources is included in the literature review, which explores critical thinking in American education. The introduction stating the subject’s importance makes it a winning literature review. Following the introduction is a well-defined purpose that highlights the importance of research.
As one keeps reading, there is more clarity on the pros and cons of the research. By dividing information into parts with relevant subheadings, the author breaks a lengthy literature review into manageable chunks, defining the overall structure.
Along with other studies and presented perspectives, the author also expresses her opinion. It is presented with minimal usage of ‘I,’ keeping it person-poised yet general. Toward the conclusion, the author again offers an overview of the study. A summary is further strengthened by presenting suggestions for future research as well.
2. The Use of Technology in English Language Learning: A Literature Review
This literature review is thematically organized on how technology affects language acquisition. The study begins with an introduction to the topic with well-cited sources. It presents the views of different studies to help readers get a sense of different perspectives. After giving these perspectives, the author offers a personalized opinion.
One of the critical aspects that makes this a good literature review is a dedicated paragraph for definitions. It helps readers proceed further with a clear understanding of the crucial terminologies. There’s a comparison of the modern and previous studies and approaches to give an overall picture of the research.
Once the main body is composed, the author integrates recommendations for action-based tips. Thus, the literature review isn’t just summarizing the sources but offering actions relevant to the topics. Finally, the concluding paragraph has a brief overview with key takeaways.
Wordtune: your writing buddy!
A literature review demands the right balance of language and clarity. You must refine the content to achieve a formal tone and clear structure. Do you know what will help you the most? Wordtune !.
The real-time grammar checker leaves no scope for errors and lets you retain precision in writing. This writing companion is all you need for stress-free working and comprehensive literature review development.
Let the narrative begin
A literary review isn't just about summarizing sources; it's about seamlessly bringing your perspective to the table. Always remember to set a narrative for added interest and a brilliant composition. With structure and style being the pillars of a stellar literature review, work with Wordtune to ensure zero compromises on the quality.
Share This Article:

The Official Wordtune Guide

An Expert Guide to Writing Effective Compound Sentences (+ Examples)
How I Turned Clutter into Cash: 10 Proven Instagram Copywriting Hacks
Looking for fresh content, thank you your submission has been received.
How to write a good scientific review article
Affiliation.
- 1 The FEBS Journal Editorial Office, Cambridge, UK.
- PMID: 35792782
- DOI: 10.1111/febs.16565
Literature reviews are valuable resources for the scientific community. With research accelerating at an unprecedented speed in recent years and more and more original papers being published, review articles have become increasingly important as a means to keep up to date with developments in a particular area of research. A good review article provides readers with an in-depth understanding of a field and highlights key gaps and challenges to address with future research. Writing a review article also helps to expand the writer's knowledge of their specialist area and to develop their analytical and communication skills, amongst other benefits. Thus, the importance of building review-writing into a scientific career cannot be overstated. In this instalment of The FEBS Journal's Words of Advice series, I provide detailed guidance on planning and writing an informative and engaging literature review.
© 2022 Federation of European Biochemical Societies.
Publication types
South Park: Snow Day! Review
Dull, toothless, and a big step in the wrong direction for south park games..
Like being trapped indoors without power during an actual blizzard, playing South Park: Snow Day! had me frigidly wishing I could be anywhere else. A direct follow-up to the storyline of two excellent turn-based RPGs and a decent mobile spin-off , this cooperative 3D hack-and-slash admirably tries a lot of new things – but it throws the baby out with the bathwater in the process, leaving us with a monotonous, slipshod mess. The controls are awkward and clumsy, the weapons and abilities are limp and uninteresting, and even with only five levels that can be completed in as many hours, it still feels like it drags on for far too long. Worse than that though: all the humor and shocking moments for which South Park and its recent games are known is utterly missing in action, leaving little to recommend about this hollow, repetitious dud. I don’t know what we did to deserve going from a masterful Obsidian RPG that aptly captured South Park’s attitude to this, but boy does the fall hurt.
South Park: Snow Day! is a perplexingly boring third-person multiplayer game, where you and up to three of your unluckiest friends smack and blast your way through waves of samey first graders. Aside from some mildly interesting card-based leveling mechanics and an amusing one-liner here and there (like when Jimbo takes a well-deserved jab at NFTs) there are remarkably few glimmers of potential in this misadventure. But the vast majority of your time will be spent trudging through five levels of repetitive and tedious hack-and-slash combat that feels like it’s straight out of 2008 and never gets more interesting.
South Park: Snow Day! Gameplay Screenshots

Even more disappointing is that it never once made me gasp or guffaw at an outrageous situation. South Park: The Stick of Truth saw us spelunking in Mr. Slave’s large intestine, dodging genitalia in the world’s most messed up rendition of Honey, I Shrunk the Kids, and questing in the two-dimensional and entirely accurately represented “country” of Canada. It was filled with hilarious moments that made me question how in the heck Ubisoft avoided an Adults Only rating from the ESRB. The same was largely true in the followup from Ubisoft’s internal studio, The Fractured But Whole . Snow Day returns to the Stick of Truth’s make-believe fantasy setting, but here you just occasionally fart every once in a while in lieu of actual jokes. Sure, there are some very minor moments that made me smile, like the final boss fight being a surprisingly timely reference to Dune, but those moments are so few and far between that they only ever served to get my hopes up before dashing them all over again. This is perhaps the most toothless South Park adventure ever created, which often feels like it’s directed towards actual children rather than the revolting reprobates, like me, who came here specifically to be shocked and disgusted.
The story is straightforward and one-note, as you and the South Park gang decide to continue your fantasy adventures during a snow day, and you proceed to fight against them and their hordes of minions in battle one at a time. The whole thing lasts about five hours and very little of note happens along the way – there are no big surprises, zero horrifying gross-out moments, and even the characters you know and love behave in a bizarrely tame fashion compared to how you’d expect after all these years. The wholly unhinged Randy makes a few appearances where he’s hoarding toilet paper, but never flies off the rails or delivers any memorable one-liners; even Cartman, whose entire personality is being the biggest monster imaginable, is mostly well-behaved the whole way through, despite briefly doing a stint as the bad guy himself. That appallingly flat writing makes an already bad game not even worth pushing through for a few laughs, and that’s an extremely hard pill to swallow as a decades-long South Park fan.
Should the next South Park game be turn-based or real-time combat?
After setting the bar so low it was difficult to imagine, but the untidy, soulless combat that accounts for the vast majority of playtime is Snow Day’s biggest miss. You select one of three melee weapons (twin daggers, a sword and shield, or a battle ax) and one of three ranged weapons (a bow and arrow, a wizard’s staff, or a wand) to bring into battle, allowing for precious few options for how to play. Not that it matters, really, because thanks to the floaty and imprecise controls, none of these options feel good to begin with. Each of the ranged weapons does damage from afar, requiring a cooldown or charge time that’s so long it’s almost always not worth the trouble, while all three of the melee weapons are at least more reliable for damage, but don’t lock on to enemies, have awful hit detection, and when you do connect it feels a bit like dueling someone with a helium balloon.
The only other major tools in your arsenal are the two equally underwhelming powers you get to equip, selected from eight total options, which include stuff like a healing totem that regenerates nearby allies’ HP for a short amount of time, or a deployable turret that fires snowballs at passersby. These are at least more interesting than any of the base weapon options, but since they’re recharged by doing damage and scoring kills with your other weapons, definitely don’t solve the problems with combat.
What's Your Game of The Year 2024 So Far?
Pick a winner.

One of Snow Day’s only good ideas are upgradeable cards that you collect as you fight through levels. These grant passive benefits and allow you to cultivate a build throughout each stage, then disappear once that level is over, adding a minor roguelike element to the adventure. You might find interesting cards that augment your healing totem, enabling it to do things like revive downed teammates, allow you to do more damage to enemies near it, or increase its area of effect. Or you can chase riskier cards, like one that turns your otherwise weak wand attack into a high-DPS flame-spewing hose that lights you on fire too as a tradeoff. While combat never stops being a sloppy, disappointing slog, collecting cards to augment your playstyle, then strategically leveling them up to make those abilities more powerful, injects a modicum of variety into it.
The issue is that Snow Day isn’t a roguelike in any other way. You don’t have to start the entire campaign over when you die (you just start at the beginning of that level), and even on the hardest difficulty, none of the levels are so challenging that you won’t probably beat them on the first try. So there’s not a ton of pressure to create a really solid build since there’s little to optimize for. And even if you do manage to assemble a deck of cards you like, each level ends after an hour or less, at which point you lose them all just as soon as the build starts coming together and go back to zero. I would love to see a better game try this idea, because here it’s implemented in a way that only barely improves an overwhelmingly bad time.
Another example of a poorly thought-out card mechanic is the single random Bullshit Card you get at the beginning of each level that lets you activate a more powerful ability a limited number of times. These might let you call down a rain of fiery meteors for straight DPS or recover your health and make you invisible for a short period of time to escape danger, but none of them are all that interesting and they only have a minor impact on gameplay since you can usually only cast them two or three times per level. What’s worse, though, is that enemies get Bullshit Cards too, and they do things like replace the enemy’s normal weapons with high-damage laser swords, or give the bad guys protective bubble shields that make them significantly more beefy. In most cases, these cards serve only to significantly draw out the length of combat (including pausing gameplay whenever the enemy uses one to watch the animation play out) which is already pretty unbearable to begin with.
TieGuyTravis' Funniest Games List

This is especially true in the revolting horde mode (available as free DLC) in which you’re subjected to waves of enemies in an arena. This format really dials up all the worst parts of Snow Day and cuts out any hope of stumbling upon jokes or story along the way. In these nightmare scenarios, the enemies are given a whole bunch of Bullshit Cards and use them every couple of seconds, which constantly pauses the battle for the announcer to shout “bullshit” at you. It’s super cool and didn’t at all make me want to be buried alive.
Thanks to recent successes, we know exactly what a great South Park game looks like, and South Park: Snow Day! couldn’t be farther from it. I’m a huge fan of throwing out the rulebook to try something completely fresh, especially in this age of samey sequels and forever live-service games that increasingly play it safe, but this bold attempt at a new direction misses the mark so drastically I’m aghast at just how sideways things went. Whether it’s due to the thoroughly unenjoyable combat or the uncharacteristicly toothless and unfunny story, I can’t recommend anyone waste their time on this cooperative lost cause – even my fellow die-hard South Park fans.
More Reviews by Travis Northup
Ign recommends.

Phil Spencer Has Now Been Head of Xbox for 10 Years; We Look Back at His First Decade

MIT Technology Review
- Newsletters
An AI that can play Goat Simulator is a step toward more useful machines
Google DeepMind’s new agent could tackle a variety of games it had never seen before by watching human players.
- Melissa Heikkilä archive page

Fly, goat, fly! A new AI agent from Google DeepMind can play different games, including ones it has never seen before such as Goat Simulator 3, a fun action game with exaggerated physics. Researchers were able to get it to follow text commands to play seven different games and move around in three different 3D research environments. It’s a step toward more generalized AI that can transfer skills across multiple environments.
Google DeepMind has had huge success developing game-playing AI systems. Its system AlphaGo , which beat top professional player Lee Sedol at the game Go in 2016, was a major milestone that showed the power of deep learning. But unlike earlier game-playing AI systems, which mastered only one game or could only follow single goals or commands, this new agent is able to play a variety of different games, including Valheim and No Man’s Sky. It’s called SIMA, an acronym for “scalable, instructable, multiworld agent.”
In training AI systems, games are a good proxy for real-world tasks. “A general game-playing agent could, in principle, learn a lot more about how to navigate our world than anything in a single environment ever could,” says Michael Bernstein, an associate professor of computer science at Stanford University, who was not part of the research.
“One could imagine one day rather than having superhuman agents which you play against, we could have agents like SIMA playing alongside you in games with you and with your friends,” says Tim Harley, a research engineer at Google DeepMind who was part of the team that developed the agent.
The team trained SIMA on lots of examples of humans playing video games, both individually and collaboratively, alongside keyboard and mouse input and annotations of what the players did in the game, says Frederic Besse, a research engineer at Google DeepMind.
Then they used an AI technique called imitation learning to teach the agent to play games as humans would. SIMA can follow 600 basic instructions, such as “Turn left,” “Climb the ladder,” and “Open the map,” each of which can be completed in less than approximately 10 seconds.
The team found that a SIMA agent that was trained on many games was better than an agent that learned how to play just one. This is because it was able to take advantage of concepts shared between games to learn better skills and get better at carrying out instructions, says Besse.
“This is again a really exciting key property, as we have an agent that can play games it has never seen before, essentially,” he says.
Seeing this sort of knowledge transfer between games is a significant milestone for AI research, says Paulo Rauber, a lecturer in artificial Intelligence at Queen Mary University of London.
The basic idea of learning to execute instructions on the basis of examples provided by humans could lead to more powerful systems in the future, especially with bigger data sets, Rauber says. SIMA’s relatively limited data set is what is holding back its performance, he says.
Although the number of game environments it’s been trained on is still small, SIMA is on the right track for scaling up, says Jim Fan, a senior research scientist at Nvidia who runs its AI Agents Initiative.
But the AI system is still not close to human level, says Harley. For example, in the game No Man’s Sky, the AI agent could do just 60% of the tasks humans could do. And when the researchers removed the ability for humans to give SIMA instructions, they found the agent performed much worse than before.
Next, Besse says, the team is working on improving the agent’s performance. The researchers want to get it to work in as many environments as possible and learn new skills, and they want people to be able to chat with the agent and get a response. The team also wants SIMA to have more generalized skills, allowing it to quickly pick up games it has never seen before, much like a human.
Humans “can generalize very well to unseen environments and unseen situations,” says Besse. “And we want our agents to be just the same.”
SIMA inches us closer to a “ChatGPT moment” for autonomous agents, says Roy Fox, an assistant professor at the University of California, Irvine.
Artificial intelligence
Large language models can do jaw-dropping things. but nobody knows exactly why..
And that's a problem. Figuring it out is one of the biggest scientific puzzles of our time and a crucial step towards controlling more powerful future models.
- Will Douglas Heaven archive page
OpenAI teases an amazing new generative video model called Sora
The firm is sharing Sora with a small group of safety testers but the rest of us will have to wait to learn more.
Google’s Gemini is now in everything. Here’s how you can try it out.
Gmail, Docs, and more will now come with Gemini baked in. But Europeans will have to wait before they can download the app.
Google DeepMind’s new generative model makes Super Mario–like games from scratch
Genie learns how to control games by watching hours and hours of video. It could help train next-gen robots too.
Stay connected
Get the latest updates from mit technology review.
Discover special offers, top stories, upcoming events, and more.
Thank you for submitting your email!
It looks like something went wrong.
We’re having trouble saving your preferences. Try refreshing this page and updating them one more time. If you continue to get this message, reach out to us at [email protected] with a list of newsletters you’d like to receive.

Draft NDIS bill is the first step to reform – but some details have disability advocates worried
Professor, Public Service Research, UNSW Sydney
Disclosure statement
Helen Dickinson receives funding from ARC, NHMRC and CYDA
UNSW Sydney provides funding as a member of The Conversation AU.
View all partners
Since the review of the National Disability Insurance Scheme (NDIS) released its recommendations in December, there has been a series of Town Hall events to discuss them around the country – but no actual changes. Today the government introduced a new bill to make way for NDIS reform.
Disability minister Bill Shorten said “legislation and rule changes are the key to unlocking a trustworthy and sustainable NDIS and will enable the government to drive change”.
What changes does the bill suggest? And what do people with disability need to know about what might happen next?
Read more: States agreed to share foundational support costs. So why the backlash against NDIS reforms now?
Although the NDIS Review set out a five-year timeframe for reform, many of the items within this bill are needed to modify the NDIS Act and to allow for those changes to take place. One big motivator for action is the government’s commitment to moderate cost growth of the NDIS – rather than see it grow to more than one million participants and cost up to A$100 billion a year by 2032.
Some in the disability community have expressed concern about legislation being introduced without co-design with them. Reports suggest disability advocates who did see the bill before its introduction were subject to non-disclosure agreements. The government says co-design will take place over an 18-month period to flesh out the changes.
Although states and territories asked the government to delay introducing this legislation because of concerns over foundational supports, the bill does not mention them. It is mostly focused on the scheme and the work of the National Disability Insurance Agency (NDIA) that administers it.

What changes are outlined in the legislation?
There are a large number of changes outlined in the bill and there will be a lot to unpack in coming weeks. Broadly these focus on:
- how people access the scheme and plans are created
- how participants can spend funds
- how the NDIA can step in if they have concerns funds are not being spent effectively
- the powers of the NDIS Quality and Safeguards Commission.
The first big change is in how people will be assessed for entry to the scheme.
At the moment the scheme lists impairments that are likely to give people access to the scheme, for example permanent blindness or severe intellectual disability.
The review argued this was unfair because people may have a similar level of need as a result of a condition that isn’t listed. They have had to provide more evidence, which can be difficult to obtain and expensive. It has also meant access has been driven via diagnosis rather than the impact on function and daily activities.

A new type of assessment
The changes outlined in the bill will move the NDIS towards a needs-based assessment.
This will be supported by the use of functional assessment tools, removing some need for individuals to collect evidence from medical professionals.
“Your needs assessment will look at your support needs as a whole,” Shorten said. “And we won’t distinguish between primary and secondary disabilities any longer.”
Many of the tools needed for this process do not yet exist. But some in the community are wary given the controversy over proposals to introduce Independent Assessments a few years back. Those plans were shelved after significant backlash suggested they could become dehumanising and traumatising.
Read more: 'I want to get bogged at a beach in my wheelchair and know people will help'. Micheline Lee on the way forward for the NDIS
Tightening control on budgets and supports
The bill also outlines changes to how individuals can spend their plans.
At the moment plans are made up of a number of categories of funding and line items that set out how plans should be spent. The NDIS Review noted this process is often confusing for individuals and limits how they can spend funds. The changes will allow participants to spend funding allocations in more flexible ways.
The bill defines what constitutes an NDIS support and links to the United Nations Convention on the Rights of Persons with Disabilities for the first time. Examples include “supports that facilitate personal mobility of the person in the manner and at the time of the person’s choice”.
However, holidays, groceries, payment of utility bills, online gambling, perfume, cosmetics, standard household appliances and whitegoods will not qualify as NDIS supports . Participants will only be able to spend funding on those things identified as an NDIS support and which a participant requires as a result of their impairment.
The bill would give the NDIA more power over how participants manage plans. These powers will be used if the NDIA have concerns that an individual is not able to use their plan effectively or someone else might be trying to exploit or coerce them to use their funds in a way that isn’t consistent with their best interests.
The Quality and Safeguards Commission has previously been criticised for insufficient action. The review suggested a new model of regulation that would be scaled according to the level of participant risk. A taskforce examining provider and worker registration will report back some time in the middle of this year. So there are no changes to provider registration in this bill.
There is an expansion of the commission’s compliance and enforcement powers. They will be able to scale up efforts and restrict employment of a support worker when they have been banned by an approved quality auditor.
Read more: Recommendations to reboot the NDIS have finally been released. 5 experts react
More legislative changes ahead
These won’t be the last changes we will see to the NDIS legislation in the near future.
The government has already indicated it is likely there will need to be further changes following engagement with the disability community.
Co-design requires trust and the government will be hoping that releasing this legislation without significant engagement with the disability community hasn’t damaged relationships too badly.
- Bill Shorten
- Labor NDIS review
- Disability coverage
- NDIS Review

Biocloud Project Manager - Australian Biocommons

Director, Defence and Security

Opportunities with the new CIEHF

School of Social Sciences – Public Policy and International Relations opportunities

Deputy Editor - Technology

IMAGES
VIDEO
COMMENTS
Identify the article. Start your review by referring to the title and author of the article, the title of the journal, and the year of publication in the first paragraph. For example: The article, "Condom use will increase the spread of AIDS," was written by Anthony Zimmerman, a Catholic priest. 4.
Article Review vs. Response Paper . Now, let's consider the difference between an article review and a response paper: If you're assigned to critique a scholarly article, you will need to compose an article review.; If your subject of analysis is a popular article, you can respond to it with a well-crafted response paper.; The reason for such distinctions is the quality and structure of ...
Step 1: Define the right organization for your review. Knowing the future setup of your paper will help you define how you should read the article. Here are the steps to follow: Summarize the article — seek out the main points, ideas, claims, and general information presented in the article.
How to Write an Article Review? 10 Easy Steps. Writing an effective article review involves a systematic approach. Follow this step-by-step process to ensure a comprehensive and well-structured analysis. Step 1: Understand the Assignment. Before diving into the review, carefully read and understand the assignment guidelines.
A Step-by-step Guide on How to Write an Article Review. Master the art of writing an article review with this step-by-step guide from professional paper help providers. Step 1: Select the Right Article. The first step is to pick a suitable article for a review. Choose a scholarly source that's connected to your area of study.
Follow these steps to create an effective and informative article review: 1. Understand the purpose: Before diving into the article, it is important to understand the intent of writing a review. This helps in focusing your thoughts, directing your analysis, and ensuring your review adds value to the academic community. 2.
When writing an article review, you start by summarizing the article's main points - the who, what, when, where, and why. Then comes the critical part. ... How to Write an Article Review: Essential Steps. A well-rounded critical analysis provides readers with a thorough understanding of the article's content, methodology, and scholarly ...
Step 4: Introduction. Once you've identified the article, give a brief description of the main points of the article. Carefully analyze the article to identify and highlight the author's thesis. Understanding the thesis of the main article is crucial to writing a good review, so make sure you include any sub thesis.
Just get the draft down on the page as quickly as possible. Write the introduction, body paragraphs, and conclusion and then set the draft aside. Write your critique of the article. The main part of how to write a review of an article is writing your critique. Refer to your outline and summary to draft several paragraphs evaluating the ...
For an article review, your task is to identify, summarize, and evaluate the ideas and information the author has presented. You are being asked to make judgments, positive or negative, about the content of the article. The criteria you follow to do this will vary based upon your particular academic discipline and the parameters of your ...
Critique the article contributes to the field. Examine the title, abstract, introduction, headings, and conclusion. Remember these stages in your mind and start writing your review. 2. Create an Outline. Review each item in the article summary to determine whether it was accurate and clear. Get back to your notes and preliminary outline to see ...
A journal article review is written for a reader who is knowledgeable in the discipline and is interested not just in the coverage and content of the article being reviewed, but also in your critical assessment of the ideas and argument that are being presented by the author. Your review might be guided by the following questions:
Cite the focus article - Use the right style to cite the article after your review's title. Identify the article - You can compose article identification by stating the article title, author, journal, and publication year. This should appear in the first paragraph. As such, you need to know how to start an article review.
The fundamental rationale of writing a review article is to make a readable synthesis of the best literature sources on an important research inquiry or a topic. This simple definition of a review article contains the following key elements: ... Preparation of the review article. Steps, and targets of constructing a good review article are ...
The guidelines for writing the academic article can be separated into 3 major steps: 1) preparation step with 8 sub-steps; 2) writing step with 15 sub-steps; and 3) final step with 2 sub-steps.
Examples of literature reviews. Step 1 - Search for relevant literature. Step 2 - Evaluate and select sources. Step 3 - Identify themes, debates, and gaps. Step 4 - Outline your literature review's structure. Step 5 - Write your literature review.
Abstract. Scientific review articles are comprehensive, focused reviews of the scientific literature written by subject matter experts. The task of writing a scientific review article can seem overwhelming; however, it can be managed by using an organized approach and devoting sufficient time to the process.
3. Science article review. It includes every topic in the area of science. Usually, scientific publications involve deep background information to use at the time of evaluation. 4. Critical book review. A critical review includes the analysis of the particular book or article review in depth. 5. Literature review.
Literature reviews are in great demand in most scientific fields. Their need stems from the ever-increasing output of scientific publications .For example, compared to 1991, in 2008 three, eight, and forty times more papers were indexed in Web of Science on malaria, obesity, and biodiversity, respectively .Given such mountains of papers, scientists cannot be expected to examine in detail every ...
A review article can also be called a literature review, or a review of literature. It is a survey of previously published research on a topic. It should give an overview of current thinking on the topic. And, unlike an original research article, it will not present new experimental results. Writing a review of literature is to provide a ...
The following steps should be considered to be a short guide about what to have in mind when starting to write a review article. As narrative/integrative reviews and perspectives are more fluid in their approach, these steps are mainly focusing on systematic approaches ( i.e. systematic reviews and meta-analyses).
Step by step guide to writing article review An article review is a piece of writing which summarizes one's general understanding of a desired topic or subject matter. In other words, it is an article written for the sole aim of summarizing . 66 Ogoja Road, Abakaliki,
The dos and don'ts of writing a literature review. Writing a stellar literature review requires following a few dos and don'ts. Just like Sherlock Holmes would never overlook a hint, you must pay attention to every minute detail while writing a perfect narrative. To help you write, below are some dos and don'ts to remember.
A good review article provides readers with an in-depth understanding of a field and highlights key gaps and challenges to address with future research. Writing a review article also helps to expand the writer's knowledge of their specialist area and to develop their analytical and communication skills, amongst other benefits. Thus, the ...
The story is straightforward and one-note, as you and the South Park gang decide to continue your fantasy adventures during a snow day, and you proceed to fight against them and their hordes of ...
On Writing Well: The Classic Guide to Writing Nonfiction. By William Zinsser. Leaders are readers. But they are also writers. I don't know a single leader who isn't a regular author. They may not write books or articles—though many do—but they certainly write emails, reports, updates, and more. If you lead, you need to write well.
Fly, goat, fly! A new AI agent from Google DeepMind can play different games, including ones it has never seen before such as Goat Simulator 3, a fun action game with exaggerated physics.
The review argued this was unfair because people may have a similar level of need as a result of a condition that isn't listed. They have had to provide more evidence, which can be difficult to ...
He gave CPR, the first step toward her 'Stayin' Alive.' By Lindsey Giardino, American Heart Association News. Regina Allemand (right) and her husband, Norbert. When Norbert found Regina unresponsive, he called 911 and began CPR. ... Days after writing a story about CPR, reporter used it on her dad. Rocker's wife performed CPR with the help of ...
The Department will continue to assist our external partners through webinars, resources, and updates on the Knowledge Center.We also welcome our partners to continue to submit questions related to the 2024-25 FAFSA launch using the Contact Customer Support form in FSA's Partner Connect Help Center. To submit a question, please enter your name, email address, topic, and question.